Adele
Economics Paper 1 Grade 12 Questions - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Answer FOUR questions as follows in the ANSWER BOOK.
SECTION A: COMPULSORY
SECTION B: Answer TWO of the three questions.
SECTION C: Answer ONE of the two questions. - Answer only the required number of questions. Answers in excess of the required number will NOT be marked.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write the question number above each answer.
- Read the questions carefully.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Leave 2–3 lines between subsections of questions.
- Answer the questions in full sentences and ensure that the format, content and context of your responses comply with the cognitive requirements of the questions.
- Use only black or blue ink.
- You may use a non-programmable pocket calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY) 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1–1.1.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.9 D.
1.1.1 The method used to derive total remuneration on factors of production is called the … method.
- production
- income
- circular
- expenditure
1.1.2 An indication of long-term growth in the economy is referred to as the …
- trend line.
- amplitude.
- length.
- trough.
1.1.3 South African Defence Force services are provided by ... government.
- district
- local
- provincial
- central
1.1.4 The current balance of payment has … account(s).
- two
- one
- three
- four
1.1.5 The number of employed persons as a percentage of the economically active population (EAP) is called the …
- economic growth.
- productivity rate.
- employment rate.
- labour productivity.
1.1.6 Economic integration where member countries agree on a common economic policy is called a/an ...
- economic union.
- free trade area.
- custom union.
- common market.
1.1.7 Which strategy failed in its objective to halve poverty and unemployment by 2014?
- New Growth Path (NGP)
- Accelerated and Shared Growth Initiative for South Africa (AsgiSA)
- Reconstruction and Development Plan (RDP)
- National Development Plan (NDP)
1.1.8 An indicator generally used to measure the cost of production is known as the … index.
- consumer price
- headcount
- price
- production price (8 x 2) (16)
1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches the item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question numbers (1.2.1–1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
1.2.1 | Portfolio investments | A | SARB consultation with commercial banks to act in a desirable manner according to prevailing economic conditions |
1.2.2 | System of National Accounts | B | the lower turning point of a business cycle |
1.2.3 | Moral suasion | C | a trade agreement between a group of emerging markets |
1.2.4 | BRICS | D | probable number of years a person will live after birth |
1.2.5 | Peak | E | government estimates of income and expenditure for a three-year period |
1.2.6 | MTEF | F | buying of financial assets such as shares in companies on the stock exchange of another country |
1.2.7 | Life expectancy | G | controlled by SARB |
1.2.8 | Money supply | H | the upper turning point of the business cycle |
I | prescribed by the United Nations to compile the gross domestic product figures | ||
(8 x 1) (8)
1.3 Give ONE term/word for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term/word next to the question numbers (1.3.1–1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK. NO ABBREVIATIONS will be accepted as answers.
1.3.1 A summary of the value of different leading indicators into a single value
1.3.2 Return of land to those who have lost it due to discriminatory laws of the past
1.3.3 When a product is sold on a foreign market at a price that is lower than the cost of production in the country of origin
1.3.4 The policy that aims to stabilise prices by combating inflation
1.3.5 An economy that excludes the foreign sector
1.3.6 The worldwide interaction of economies, with trade as a key element (6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 2: MACROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
2.1 Answer the following questions.
2.1.1 Name any TWO methods of import substitution. (2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 How can world trade improve through specialisation? (1 x 2) (2)
2.2 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow.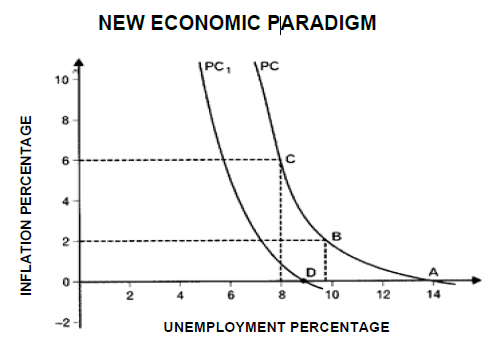
[Source: Enjoy Economics]
2.2.1 Provide a name for the graph given above. (1)
2.2.2 What is the original natural rate of unemployment in the graph above? (1)
2.2.3 Briefly describe the term new economic paradigm. (2)
2.2.4 Explain how the government can use its fiscal policy to speed up the recovery of an economy. (2)
2.2.5 With the aid of a graph, illustrate the effect of demand-side and supply-side policies in smoothing out business cycles. (4)
2.3 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow.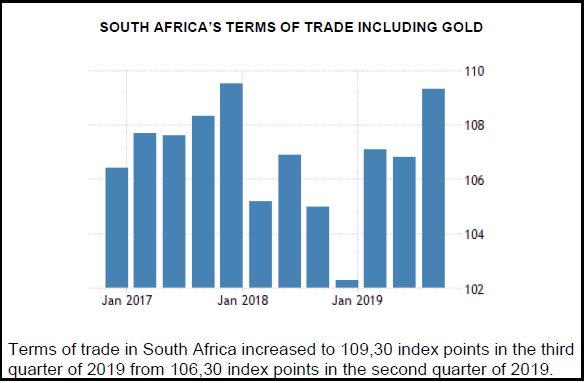
[Source: tradingeconomics.com]
2.3.1 How much has the terms of trade increased in the last two quarters of 2019? (1)
2.3.2 What caused an increase in South Africa’s terms of trade in the third quarter of 2019? (1)
2.3.3 Briefly describe the term terms of trade. (2)
2.3.4 Explain the effect of an improvement in terms of trade on the economy. (2)
2.3.5 How does the current account deficit (negative balance of trade) affect terms of trade? (2 x 2) (4)
2.4 Discuss the reasons for export promotion. (4 x 2) (8)
2.5 Analyse the benefits of deregulation for households. (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: ECONOMIC PURSUITS 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
3.1 Answer the following questions.
3.1.1 Name any TWO international organisations that require members to standardise their indicators. (2 x 1) (2)
3.1.2 How do countries in the North-divide contribute to the destruction of the environment? (1 x 2) (2)
3.2 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
SOUTH AFRICA’S ECONOMIC OUTLOOK FOR 2020 SA's economic growth rate often found itself in negative territory during the year 2019. The renewed Eskom load-shedding in December 2019 led to forecasts on growth in 2020 likely to be less than the 1,4–1,6 percent range expected earlier by the SA Reserve Bank (SARB) and other economists.Economic growth in SA has virtually flat-lined. South African policy makers need to take a pro-active approach to build better economic prospects in 2020. [Source: Adapted from www.iol.co.za] |
3.2.1 Name an economic indicator used to measure economic growth. (1)
3.2.2 What is the term used to describe countries with low economic growth? (1)
3.2.3 Briefly describe the term economic growth. (2)
3.2.4 How does economic growth lead to economic development? (2)
3.2.5 What can South African policy makers do to improve the country’s economic standing? (4)
3.3 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.
The consolidated budget spending is projected to exceed R2 trillion for the first time ever. Gross tax revenue collected during the first two months of 2020/21 is already R35,3 billion behind target. The country expects to miss the tax target for this year by over R300 billion.The consolidated budget spending is projected to exceed R2 trillion for the first time ever. Gross tax revenue collected during the first two months of 2020/21 is already R35,3 billion behind target. The country expects to miss the tax target for this year by over R300 billion. EXPECTATIONS FROM THE REVISED BUDGET: The Minister may adjust the progressive personal income tax tables, thus seeking to advance the redistributive effect given how the COVID-19 pandemic has worsened income and wealth inequality. National Treasury confirmed that Finance Minister Tito Mboweni, will announce new taxes in his February budget next year and this would include the wealth tax. The new taxes would help to stabilise debt and raise up to R40 billion in the next few years. |
[Source: adapted from the internet]
3.3.1 Identify the demand-side policy in promoting growth and development from the extract above. (1)
3.3.2 Give an example of wealth tax. (1)
3.3.3 Briefly describe the term progressive tax system. (2)
3.3.4 Explain the contribution of taxes to social development. (2)
3.3.5 How can the government through its budgetary processes redistribute income and wealth? (2 x 2) (4)
3.4 Briefly discuss capital formation and free advisory services as a supply side approach in promoting growth and development in South Africa. (4 x 2) (8)
3.5 Critically discuss how the Broad-based Black Economic Empowerment has benefitted the South African economy. (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: MACROECONOMICS AND ECONOMIC PURSUITS
40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
4.1 Answer the following questions.
4.1.1 Name TWO problems of public sector provisioning. (2 x 1) (2)
4.1.2 Why is it important to assess the performance of an economy? (1 x 2) (2)
4.2 Study the cartoon below and answer the questions that follow.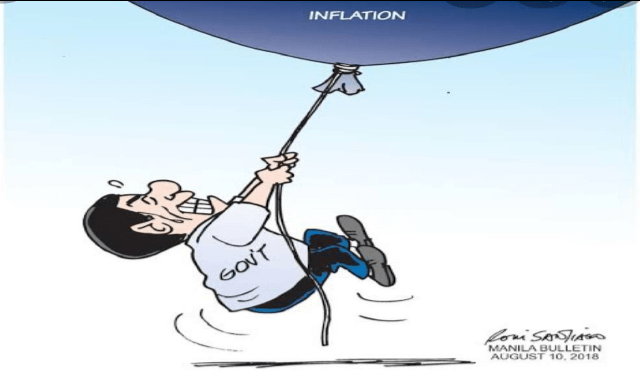
[Adapted from google images]
4.2.1 Name a monetary instrument used to achieve price stability. (1)
4.2.2 What is the inflation target range set by the South African Reserve Bank? (1)
4.2.3 Briefly describe the term repurchase rate (Repo rate). (2)
4.2.4 Explain the reason why government pursues price stability as a macroeconomic objective. (2)
4.2.5 How does the South African Reserve Bank maintain price stability? (4)
4.3 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
LET’S GO BACK TO THE NDP: encouraging active citizens with their own development The sight of people in orange uniforms carrying brooms and garbage bags, sweeping and weeding roadside verges, often alone, has been a common one across the country since 2003 when the Department of Public Works launched its Expanded Public Works Programme (EPWP).The government adopted the NDP at the beginning of the past decade to eliminate poverty and reduce inequality.By 2030 the NDP envisages a reduction in the number of people who live in households with a monthly income below R419 per person from 39% to 0%. [Source: Adapted from National] |
4.3.1 What type of workers are often employed through the Expanded Public Works Programme? (1)
4.3.2 How is the NDP funded? (1)
4.3.3 Briefly describe the term economic development (2)
4.3.4 Explain how the development of human resources can be used as an approach to alleviate poverty. (2)
4.3.5 How can the NDP increase the employment rate in South Africa? (2 x 2) (4)
4.4 Briefly discuss poverty and trade as challenges of globalisation. (8)
4.5 Why should developing countries ensure survival of labour-intensive industries in a global economy? (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer any ONE of the two questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK. Your answer will be assessed as follows:
STRUCTURE OF ESSAY | MARK ALLOCATION |
Introduction
| Max. 2 |
Body: Additional part: Give own opinion / Critically discuss / Evaluate / Critically evaluate / Draw a graph and explain / Use the graph given and explain / Complete the given graph / Calculate / Deduce / Compare / Explain / Distinguish / Interpret / Briefly debate | Max. 26 Max. 10 |
Conclusion
| Max. 2 |
TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 5: MACROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
- Discuss in detail the markets within the four-sector model. (26)
- Evaluate the contribution/role of firms in growing the economy. (10)
QUESTION 6: ECONOMIC PURSUITS 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
- Discuss social indicators in detail. (26)
- How successful has the South African government been in promoting economic development through the use of these social indicators?(10)
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Consumer Studies Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: SHORT QUESTIONS
1.1 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1.1.1 D (1)
1.1.2 C (1)
1.1.3 C (1)
1.1.4 B (1)
1.1.5 A (1)
1.1.6 B (1)
1.1.7 C (1)
1.1.8 D (1)
1.1.9 A (1)
1.1.10 C (1)
1.1.11 B (1)
1.1.12 A (1)
1.1.13 B (1)
1.1.14 A (1)
1.1.15 A (1)
1.1.16 B (1)
1.1.17 B (1)
1.1.18 A (1)
1.1.19 B (1)
1.1.20 C (1)
1.2
1.2.1 E
1.2.2 A
1.2.3 F
1.2.4 C (4)
1.3
1.3.1 C
1.3.2 F
1.3.3 E
1.3.4 D
1.3.5 G (5)
1.4
1.4.1 dress code
1.4.2 target market
1.4.3 trade name
1.4.4 sustainable production
1.4.5 indirect
1.4.6 corporate (6)
1.5 B, C, E, G, H (Any order) (5)
[40]
QUESTION 2: THE CONSUMER
2.1
2.1.1 Acronym for CPI.
- Consumer Price Index (1)
2.1.2 Explain how the monitoring of the basket is compiled.
- It is done over a set period monthly / quarterly / annually (a year) (1)
2.1.3 Discuss what is meant by the phrase basket of goods and services.
- It is a sample of typical goods and services purchased by households.
- It consists of about 400 different products from different categories /12 categories / different groups
- Examples: food, alcohol, non-alcoholic beverages, appliances and furniture, communication services, health services, education and restaurants.
NOTE: Two marks can be awarded for examples. (Any 2) (2)
2.1.4 Explain how the CPI is used as an indicator to measure inflation.
- The CPI measures price changes / the increase in prices / calculates the price increases
- The rise of prices/increase in prices is referred to as inflation
- When inflation goes up the value of the rand is less / you can buy less for your money / buying power decreases
- The inflation rate is calculated from the CPI / the percentage increase in the CPI is referred to as the inflation rate
- When the CPI % goes up, the inflation rate goes up. (Any 3) (3)
2.2
2.2.1 Name the institution that adjusts the repo rate.
- The South African Reserve Bank / Reserve bank(1)
2.2.2 State how the lowering of the repo rate would affect a consumer owing money on a credit card.
- The interest rate (charged by the bank) on the outstanding amount would be lower. (2)
2.3
2.3.1 The tax type that provides the greatest revenue
- Personal income tax (1)
2.3.2 Identify the name of the tax type that the government did not receive any revenue from during the initial lockdown period and discuss why.
- Excise tax as no sales allowed for alcohol/ liquor and cigarettes (4)
2.4 Justify why it is every citizen’s moral obligation to pay taxes.
- Paying your taxes is a requirement by law, therefore it is the right thing to do.
- If you do not pay your taxes, you will face penalties, such as fines or even going to jail.
- To finance/fund government expenses such as provincial, municipal and local authorities
- To improve / provide good services e.g. roads
- For public services i.e. schools, universities, hospitals and clinics
- For defence and security
- Taxes are used to fund social and economic programmes
- Improve living conditions/quality of life so that we all benefit
- Supports government grants / pensions (Any 5) (5)
[20]
QUESTION 3: FOOD AND NUTRITION
3.1
3.1.1 List TWO groups of food sensitive consumers who should avoid eating the Jungle energy bar.
- Gluten intolerant
- Those with allergies to cow’s milk, peanuts, tree nuts and soya
- Lactose intolerant
NOTE: NO marks for listing the allergens ONLY as they are stated in the question.
(Gluten (oats), peanuts, cow’s milk, tree nuts and soya) (Any 2) (2)
3.1.2 Identify from the nutritional content given, ONE regulation that has been followed by the prescribed format for labelling a food product.
- The nutrient amounts are given per 100 g
- The correct types of nutrients have been listed (values have been given for protein, carbohydrates, fat, fibre and sodium) (Any 1) (1)
3.1.3 Name the health-related condition that a person may suffer from when they do not follow the advice to avoid a high sodium intake.
- Hypertension / high blood pressure (1)
3.1.4 Name the bar with the highest sodium content.
- Trek bar / Trek peanut power bar (1)
3.2 Write a paragraph describing the health condition and causes of Type 1 diabetes.
- A condition where the blood-glucose level is abnormally high because the body cannot control it.
- The pancreas is unable to produce insulin / pancreas cells and damaged.
- Blood-glucose cannot be moved to the cells and be changed into energy
- Blood-glucose levels rise/high blood glucose level / hyperglycaemia
- Blood then spills over into the urine
- Insulin has to be replaced through insulin injections. The onset is usually sudden in people younger than 30 years old /children / young adults
- Can be caused by genes / pre-existing genetic condition can be triggered by infection, stress or trauma
- This can cause symptoms such as weight loss / excessive hunger, thirst / need to urinate more / tiredness and digestive problems.
NOTE: A maximum of 2 marks for the symptoms
Deduct ONE mark if not written in paragraph format. (Any 5) (5)
3.3 Differentiate between systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure to explain blood pressure readings.
- Systolic blood pressure: The first number (top number) – the amount of pressure in your arteries when the heart beats / contracts.
- Diastolic blood pressure: The second number / bottom number – blood is exerting against your artery walls while the heart is resting / between beats (4)
3.4 Discuss THREE reasons why a petite 55-year-old woman would be more prone to developing osteoporosis.
- She is female / females are more susceptible to developing osteoporosis as they have a lower bone mass
- At 55 years most likely post-menopausal and there is a decrease in the oestrogen levels / oestrogen normally prevents bone loss.
- Body shape is small which puts her more at risk as they she bone to lose. (3 x 2) (6)
3.5 Name TWO foodborne diseases that are associated with a lack of personal hygiene.
- Hepatitis A (infective jaundice)
- E-coli infection
- Dysentery
- Gastro-enteritis (Any 2) (2)
3.6
3.6.1 Name the term which relates to the underlined words in the quote below.
- ‘The greatest impact of a disrupted climate will be on human food production and food availability’.
Food security / local food production ?(1)
3.6.2 Analyse how a person suffering from a heart condition and high cholesterol levels would reap the benefits of a predominantly plant based diet in the dietary management of their disease.
- Pulses would provide their protein needs. This would decrease their red meat intake which would decrease their fat intake / animal fats / unhealthy.
- Fewer animal proteins would mean their saturated fat decreases. Less saturated fat implies that their cholesterol intake is also reduced and the trans fats which otherwise increase the risk of another heart attack / raise blood cholesterol levels.
- Plant foods contain no cholesterol.
This helps to meet the requirement and not to exceed the 300 mg of cholesterol intake per day. - Their source of plant fats increases which is the healthier fats This means their mono-unsaturated fats increase e.g. avocado, nuts and seeds.
- The polyunsaturated fats increase as they replace animal-based sources with nuts and seeds. The presence of plant oils also increases
- They could still enjoy fish in limited amounts which has mainly unsaturated fat
- Fish has omega-3 fatty acids that protect the heart and blood vessels
- Pulses are high in fibre. They would increase their fibre intake as pulses are high in soluble fibre. Soluble fibres have a cholesterol lowering effect
- Pulses have starch which would assist feeling full/satiety value
- A predominantly plant-based diet would also help to increase their fruit and vegetable intake. (meets the minimum five servings per day An increase in fruit and vegetables would also increase the minerals, vitamins and antioxidants Fruit and vegetables also add fibre to the diet
- Pulses are rich in iron, potassium and folate which have a protective role to play
NOTE: Do NOT mark facts twice, for example with fibre. They cannot give the word fibre twice unless it is attached to the point of fruit and vegetable. It provides fibre and then also pulses provide fibre. The same with fats. Plant oils increase would be the same fact as healthier fats increase in the diet.
(5 points + elaboration for each point) (5 x 2) (10)
3.6.3 Discuss the implications that drought would have on food production.
- A lack of rain/water means that food production declines.
- This leads to scarcity of stock / unavailability ? will raise prices/more expensive to buy ?
- Workers get retrenched / unemployment increases/ job losses. This leads to increase poverty / financial constraints ? / businesses may have to close
- The country may have to import leads to pressure on the government’s budget / cause food insecurity / lowers food
security Any 7) (7)
[40]
QUESTION 4: CLOTHING
4.1
4.1.1 Describe the term contemporary fashion in picture A.
- It is the fashion / trend / style that many people wear / accepted by many people. ?
- The fashion that is presently worn/what is currently popular/reached its height of popularity / presently sold in stores.
- The fashion is manufactured in large quantities/ mass produced.
- Fashion is sold at moderate to low prices. (Any 2) (2)
4.1.2 Draw a sketch of the fashion cycle. Indicate on your drawing by means of an arrow, which phase the garment in picture A would be
situated on the fashion cycle. Name the stage next to the arrow. (2)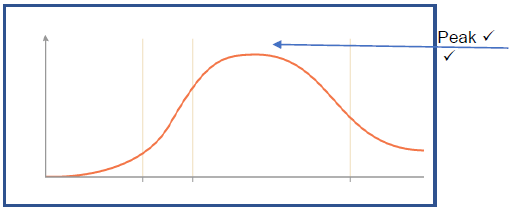
- One mark for the arrow labelled in the correct place
- One mark for the name of the stage (2)
4.1.3 Explain how the fashion styles represented in pictures B, C and D could influence a designer when designing a contemporary garment.
PICTURE B
- Famous designers’ showcase/market their fashions on the catwalk / set new trends at fashion shows / on the runway.
- The haute couture design reflects an artistic/exaggerated expression
- Designers then get inspiration/ideas from the fashion shows
- The contemporary puffer jacket is not as puffy / a more streamlined design but the idea of an insulated jacket is used (Max. 2)
PICTURE C
- Designers look to the past/a previous era for inspiration/new ideas
- They bring back the look with a modern twist. / Reinvent it
- In this case the fashion will be retrospective
- This 1938 puffer jacket has inspired a bulky look / has adaption such a a hood/more toned-down version for a warm jacket (Max. 2)
PICTURE D
- A designer could be influenced by what celebrities wear as they are fashion leaders who set new trends
- Billy Eilish as an18-year-old singer, the youth identified with her/wanted to be like her/would want to wear what she wears/wear an oversized puffer jacket
(Max. 2) (3 x 2) (6)
4.2 Discuss how this lady has worn her puffer jacket as part of her outfit so that it is suitable for professional work wear.
- She has chosen a black jacket and black is a formal colour
- Wears it with all black skirt and accessories
- Wears it with a belt so not baggy / slim fitting
- Jacket is a high neck style, so not revealing
- Wearing gloves adds formal feel
- Although a high heel, the closed shoe adds a formal look
- The use of the colour gold would add a formal look (Any 3) (3)
4.3
4.3.1 Identify from the text TWO different key areas that describe the word sustainability.
- Protects the environment /reduces the impact on the environment/ addresses environmental issues/addresses issues of soil health and pesticide use to water stewardship
- Protectss the people/improve working conditions/for people to work productively in conditions of freedom, equity, security and human dignity/focusing in particular on promoting women’s empowerment and preventing child labour (2)
4.3.2 Name the term that is given to companies whose products are manufactured by following ethical practices such as protecting people and the environment.
- Fair trade (1)
4.3.3 Explain how non-organic textiles are also considered to be sustainable pertaining to how crops is grown/produced.
Give ONE example of a non-organic sustainable crop.
- Grown in an environmentally friendly way/ low-carbon footprint
- There is little soil damage / consider soil health /can be planted and regrown without damage to the soil
- Limited chemicals used during growth / pesticides / herbicides
- Use less / toxic materials used / crop is pest-tolerant
- Crop requires less water/water stewardship/using water effectively
- May be biodegradable
- Examples: hemp, cotton, bamboo, soya
NOTE: Question is based on when the crop is grown/produced and NOT the manufacturing of the fibre. (Any 3 + 1 example) (4)
[20]
QUESTION 5: HOUSING
5.1
5.1.1 State TWO reasons why Billy would choose property to buy as an option for investment.
- The rent he charges the tenant can pay off the bond he owes
- Property increases in value over time so when he sells it, he will make a profit
- His family can inherit it / bequeath the property to them (Any 2) (2)
NOTE: Question is based on an investment. Do NOT award mark for general reasons. Example – He has extra income to live on.
5.1.2 Give the name of the contract whereby Billy has purchased the property.
- Deed of Sale (1)
5.1.3 Discuss sectional title as a form of ownership.
- A person is the owner of a unit / section of a building / complex
- They also have a share in / jointly own the common property, for?example lifts, garden, pool
- All owners of units are members of the body corporate
- A monthly levy is paid by all the owners to run/maintain the common property, example mowing the lawn
- The levy money goes to the body corporate
- The body corporate is responsible for running the complex (Any 6) (6)
5.1.4 Explain the term transfer duty.
- It is a government tax paid when property changes ownership / transferred into the new owner’s name and is paid to SARS
- The amount is based on home loan amount / value of the property based on purchase price (Any 3) (3)
5.1.5 Give ONE reason why no transfer duty is paid for PROPERTY A.
- No transfer duty is paid on properties that cost R750 000 or less (1)
5.1.6 List the financial responsibilities of a tenant.
- To pay the deposit before occupying the property
- To pay one month’s rent upfront before occupying the property
- Pay the monthly instalments at the time agreed
- May have to pay electricity and / or water depending on lease agreement (Any 2) (2)
5.1.7 Using the information given in the scenario and the table, select which property Billy should buy and justify your answer with FIVE reasons.
- PROPERTY A
- REASONS:
- Save on transfer fees
- Purchase price cheaper
- Levy and rates costs per month cheaper
- Net rental returns higher
(1 mark for property choice + 4 reasons) (5)
5.2 Explain how the bond repayments are affected when interest is calculated according to the variable rate.
- The amount of interest you pay back fluctuates meaning you will pay more or less interest on your bond. If the interest goes down, the monthly repayment amount goes down.
- If the interest goes up, the monthly repayments will also go up. (4)
5.3 Describe the role of the deeds office when purchasing a house.
- The deeds office is where the property will be registered in your name as the new owner
- The transfer of ownership/transfer documents takes place here and the registration of the mortgage bond /bond documents in the name of the buyer
- The buyer pays a conveyancer a fee to draft the paperwork / documentation required by the Deed’s office
- At the Deeds office a conveyancer oversees the transfer of the property into the buyer’s name
- The conveyancer will draft a document called the Deed of transfer
- Once the Registrar of Deeds signs the Deed of transfer, the document is now called the title deed and you become the legal owner of the property (Any 6) (6)
5.4
5.4.1 Describe THREE issues that the Khumalo family must consider before purchasing a dishwasher.
- Size of the family/ five / they have 3 children / dishwashers’ size
- They entertain on weekends so will need more capacity
- Lifestyle – both of them work so must consider their time saved
- The space available / they can take a standard size dishwasher
(Any 3) (3)
5.4.2 Discuss THREE of the aspects they should consider concerning the environmental impact when choosing a dishwasher.
- The water usage / litres of water used per cycle / a half load cycle option will use less water
- The electricity usage / energy rating / energy efficiency / A++ rating uses less electricity
- Noise level / noise pollution / less decibels is quieter
- Capacity ‒ a bigger capacity means less loads saving water and electricity
- Economy cycle works quicker so saves electricity and will use less water (3)
5.4.3 Identify FOUR consumer responsibilities that Mrs. Khumalo did before making purchase.
- She has done research to compared different brands
- She compared prices
- She will ask about the warranty ? and delivery costs
- She checked her budget (Any 4) (4)
[40]
QUESTION 6: ENTRPRENEURSHIP
6.1 Explain the terms best sale scenario and worst sale scenario.
- Best sale scenario: When your product sells very well When your sales meet your sales target / you sell all your products You make a profit
- Worst sale scenario: What could happen if your product does not sell very well / sells poorly You sell less than break-even point You make run loss / do not make a profit (6)
6.2 List FIVE ways how a business can use their time efficiently on the production line.
- Make a daily priority list of tasks
- Assigning a time limit for each task
- Following a routine
- Completing the tasks as quickly as possible and not procrastinating
- Keeping the workplace well-organized, tidy and clean
- Plan the use of equipment
- Plan what each worker does so that maximum number of products is produced
- Set a performance target (Any 5) (5)
6.3
6.3.1 Name THREE important requirements of packaging applicable to her bread.
- Sufficiently attractive for the target market / eye catching
- Suitable material for the bread i.e. paper bag
- The right size for a mini loaf
- The right shape for a mini loaf
- Protect from the environment – dehydration
- Strong enough while being transported
- Safe and hygienic for its shelf life (Any 3) (3)
6.3.2 Calculate the selling price of one mini loaf of bread. Show ALL calculations. Round off to the nearest rand.
- R35 + R40 = R75 x 60% = R45
R45 + R75 = R120 ÷ 6 = R20
NOTE: The “R” must be indicated as part of the final answer (6)
6.4
6.4.1 Select a sentence from the interview that indicates that Mapholo’s naming of her brand was important to her for this business.
- I named my brand ‘Ledikana’ because the village where I grew up called my mother Ledikana
OR - She loved beautiful things, including fashion and hats. (1)
6.4.2 Identify FOUR factors from the first two paragraphs that ensured that Mapholo’s business had the potential to become profitable.
- She had passion / interest
- She had a target market / she sold to customers at the funeral/ weekend stall / weekend market
- She had a product to sell / sold hats / traditional clothing
- She had a location / marketplace / at work
- She had tested the idea / sold 10 hats in the first week and also at a little stall
- She made the time / used her spare time even though she was working full time
- She was capable / she could design and sew
- She had the equipment
- Her financial position / capital / start-up costs / savings (Any 4) (4)
6.4.3 Identify the factor one has to consider in the choice of a suitable product for a business when Mapholo’s customers loved her merchandise at her first shop.
- Consumer appeal (1)
6.4.4 Give TWO advantages of Mapholo doing direct selling at the weekend market.
- She is in touch with her customers / good for customer relations
- She can promote her fashions as she will be wearing the garments
- She controls the image of her brand
- She controls the price she wants to sell her clothing for (Any 2) (2)
6.4.5 Mapholo has employed staff. List FOUR reasons why it is beneficial to train staff.
- Better quality work
- Increased motivation / morale
- Increased work/job satisfaction
- Ability to work independently
- Increased productivity
- Reduction of waste
- Reduce maintenance and repair costs of equipment
- Acquisition of new skills (Any 4) (4)
6.4.6 Analyse the steps Mapholo took as she progressed from the start of her business until she employed full time workers that impacted positively on her business which resulted in a successful business.
- She started small / started from home, so she had a low capital outlay. This meant that she did not need to borrow money and start her business in debt.
- She continued working her full-time job which enabled her to continue earning a salary while she explored the small business option in her spare time.
- She discovered her passion – a key human resource for a successful business.
- She made hats to order, ensuring sales/ no unsold stock and did not just make hats in the hope of selling This meant that she was producing / a product what the target market wanted and with them wearing the hats gave her free advertising/ word of mouth.
- She identified a gap in the market and went with it (initially with the hats and progressed onto clothing).
- She had an outlet, the stall at the weekend market which was a non-expensive option and gave her items exposure / broadened her target markets.
- She broadened her target market further by getting sales at work which would lead to more free advertising.
- She used her creativity by designing the hats herself and she continued to develop her skills / creativity by designing clothing which would give her a unique brand.
- She made the items herself so had the ability to sew a valuable human resource.
- She saved her money to finance her growing business so would therefore, save on interest if she had borrowed money.
- She selected a suitable brand name that her target market would identify with her story. The brand image would likely grow with her values of beautiful fashion.
- She moved with the target markets needs / could read the target market trends when she made traditional clothing / colourful, ethnic designs.
- By opening the shop at the airport, she would get the tourist market / further expand her target market / grow the business more and can charge higher prices making more profit.
- She takes her profits and ploughs it back into the business as she further expands by opening another store.
- She employs more people to manage the increased demand and seizes the opportunity for growth / risk taker. (Any 8) (8)
[40]
TOTAL: 200
Consumer Studies Grade 12 Questions - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions.
SECTION
MARKS
TIME(minutes)
QUESTION 1:
Short questions (All topics)
40
20
QUESTION 2:
The Consumer
20
20
QUESTION 3:
Food and Nutrition
40
40
QUESTION 4:
Clothing
20
20
QUESTION 5:
Housing
40
40
QUESTION 6:
Entrepreneurship
40
40
TOTAL:
200
180
- All questions are COMPULSORY.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH section on a NEW page.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Write in blue or black ink only.
- Pay attention to spelling and sentence construction.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: SHORT QUESTIONS
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A‒D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1‒1.1.20) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.21 D.
1.1.1 The calculation of this type of interest does not consider interest accrued from investment growth:
- Compound interest
- Fixed interest
- Variable interest
- Simple interest (1)
1.1.2 The Act that governs the interest rate charged by credit providers:
- Financial Intelligence Act
- Consumer Protection Act
- National Credit Act
- National Consumer Tribunal (1)
1.1.3 Food items that are zero-rated VAT in the system includes …
- lentils, mealie rice, milk and cheese.
- dried beans, fruit, cheese and eggs.
- rice, samp, eggs and brown bread.
- brown bread, milk, tuna and oil. (1)
1.1.4 Provisional tax will be paid:
- On a monthly basis at the same time that income is earned
- In two payments spread over the tax year
- In a single large sum at the end of the tax year
- Monthly by individuals earning above the tax threshold (1)
1.1.5 Which of the following will contribute to malnutrition in people suffering from HIV/Aids?
- Consuming too much insoluble fibre
- Drinking lots of clean and safe water
- Eating six small meals per day
- Consuming plenty of fruits and vegetables (1)
1.1.6 Thando has gastro-enteritis. The main complication will be …
- kidney failure.
- dehydration.
- coughing.
- liver damage. (1)
1.1.7 An advantage of eating low GI foods:
- Blood vessels are constricted
- Cholesterol levels are well maintained
- Blood sugar levels are better maintained
- The pancreas is over stimulated (1)
1.1.8 An advantage of genetically modified food:
- No chemicals or pesticides are used
- Waste materials ploughed back into the soil
- The use of growth hormones and antibiotics
- The crop yield is greater, so more people can be fed (1)
1.1.9 The following type of additives have a negative influence on the behaviour of some children:
- Colourants
- Emulsifiers
- Gelling agents
- Stabilisers (1)
1.1.10 This disease is not transferred by contaminated water:
- Hepatitis A
- Escherichia coli
- Tuberculosis
- Dysentery (1)
1.1.11 The standard fashion stays in for …
- a season.
- 2 to 3 years.
- many seasons.
- 5 to 6 years. (1)
1.1.12 The change in skirt length is an example of:
- A trend
- A silhouette
- Mass fashion
- Couture (1)
1.1.13 The factor that determines the loan amount a person qualifies for when applying for a home loan:
- Location
- Income level
- Family size
- Occupation (1)
1.1.14 If you decide to build a house, you need to make sure the builder you choose is registered with the ...
- NHBRC.
- SABC.
- NCR.
- SARS. (1)
1.1.15 … is a form of security for the repayment of a loan.
- Collateral
- Mortgage
- Bond
- Subsidy (1)
1.1.16 The criterion that must be considered when buying household appliances for consumers with diverse disabilities:
- Available space
- Universal design
- Energy consumption
- Environmental impact (1)
1.1.17 For a business to be sustainable the ...
- total amount of money received is saved.
- profit is maintained without exhausting available cash.
- product must be fresh and available.
- staff must be well trained and competent. (1)
1.1.18 A possible risk of overstocking:
- Stock may become obsolete or damaged
- The business’s reputation may be harmed
- Production slows down
- Large orders go missing (1)
1.1.19 An example of good customer relations:
- Attend to customer complaints later rather than sooner
- Use the feedback to improve your service
- Return customer calls when you are not busy
- Ask the shop assistant to be friendly (1)
1.1.20 This aspect of a business ensures that products meet the prescribed standards:
- Financial management
- Stock control
- Product specification
- SWOT analysis (1)
[20]
1.2 Choose the nutritionally related foodborne disease from COLUMN B that matches the management in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A‒F) next to the question numbers (1.2.1‒1.2.4) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.5 G.
COLUMN A MANAGEMENT | COLUMN B NUTRITIONAL RELATED DISEASE | ||
1.2.1 | Avoid excessive amounts of protein which draws calcium from the bones | A | Anaemia |
1.2.2 | Increasing Vitamin C will help with the absorption of iron | B | High blood cholesterol |
1.2.3 | Nutritional counselling to ensure a balanced food intake | C | Obesity |
1.2.4 | Reduce the kilojoule intake by eating smaller amounts of food | D | High blood pressure |
E | Osteoporosis | ||
F | Anorexia nervosa | ||
(4 x 1) (4)
1.3 Choose the explanation in COLUMN B that matches a term from COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A‒G) next to the question numbers (1.3.1‒1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.3.6 H.
COLUMN A TERM | COLUMN B EXPLANATION | ||
1.3.1 | Overheads | A | The flow of money in and out of a business |
1.3.2 | Capital | B | The cost of the product is covered by the sales |
1.3.3 | Selling price | C | Additional costs such as salaries, electricity, water and cleaning materials |
1.3.4 | Profit | D | The amount left when expenses are subtracted from the income |
1.3.5 | Production costs | E | The price calculated as display on the product and includes all other costs |
F | Money or assets used to start a business | ||
G | The total amount paid for raw materials and overheads | ||
(5 x 1) (5)
1.4 Choose the correct word/term in brackets. Write only the word/term next to the question numbers (1.4.1‒1.4.6) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 A set of rules about the type of clothes a company expects employers to wear is referred to as the (dress code/code of conduct).
1.4.2 The (market group/target market) is a specific group of potential buyers that will purchase a product.
1.4.3 The (trade name/trademark’s act) can make the product easy to recognise and distinguish from competitor products.
1.4.4 The production of goods to satisfy the basic needs of consumers and to improve the quality of life without harming the environment is an adequate definition for (sustainable production/sustainable profitability).
1.4.5 Licences such as a driver’s and car licence are forms of (direct/indirect) tax.
1.4.6 (Corporate/Casual) clothing are garments designed to represent a company and are worn while at work. (6 x 1) (6)
1.5 Identify FIVE CORRECT statements from the list below which depict the types of insurance that are applicable to homeowners and their possessions in the home. Write only the letters (A–H) next to the question number (1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
- This cover protects employees if they get injured while on a business property.
- This policy protects one’s loved ones from suffering the burden of paying off a bond if the owner dies.
- This cover can include structures such as a garage and a swimming pool.
- This cover relieves loved ones from the emotional burden of looking for money for a burial.
- This policy covers a building structure against damage caused by natural disasters.
- This covers against any medical emergency such as an unexpected illness.
- This covers loss of household goods like furniture and appliances against theft.
- This policy can include permanent fixtures like baths and toilets from damage during a fire. (5 x 1) (5)
[40]
QUESTION 2: THE CONSUMER
2.1 Read the information below and answer the questions that follow.
The government imposed a five-week lockdown from 27 March to [Adapted from Stats SA] |
2.1.1 Write the acronym CPI in full. (1)
2.1.2 The lockdown has necessitated the monitoring of prices to be done on a weekly basis as a temporary measure. Explain how the monitoring of the basket is compiled. (1)
2.1.3 Discuss what is meant by the phrase, a basket of goods and services. (2)
2.1.4 Explain how the CPI is used as an indicator to measure inflation. (3)
2.2 Read the statement below and answer the questions that follow.
In May 2020, the repo rate was lowered to support the economy that has been weakened by the Covid-19 lockdown. [Adapted from Cape Business News] |
2.2.1 Name the institution that adjusts the repo rate. (1)
2.2.2 State how the lowering of the repo rate would have affected a consumer owing money on a credit card. (2)
2.3 Study the information on tax revenues in South Africa represented in the pie chart below and answer the questions that follow.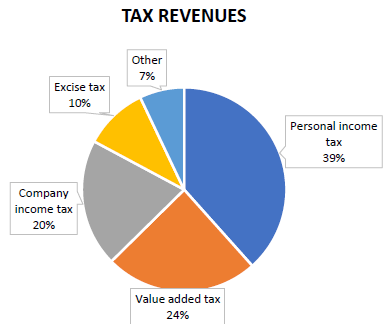
2.3.1 Identify the tax type that provides the greatest revenue. (1)
2.3.2 Name the tax type that the government did not receive any revenue from during the initial lockdown period. Discuss why this resulted in no revenue. (4)
2.4 Justify why it is each citizen’s moral obligation to pay taxes. (5)
[20]
QUESTION 3: FOOD AND NUTRITION
3.1 Study the table below of two health bars and answer the questions that follow.
JUNGLE PEANUT BUTTER ENERGY BAR | TREK PEANUT POWER ENERGY BAR | |
INFORMATION RELATING TO ALLERGENS AND INTOLERANCES | ALLERGENS: GLUTEN (OATS), PEANUTS, COW’S MILK, TREE NUTS AND SOYA | GLUTEN, WHEAT AND DAIRY FREE |
NUTRITIONAL VALUE | Per 100 g | Per 100 g |
Energy | 2 170 kJ | 1 548 kJ |
Protein | 13 g | 18,5 g |
Carbohydrate of which total sugar | 38 g 25,0 g | 46,7 g 38,4 g |
Total fat of which is saturated fat | 34,3 g 13,4 g | 10,9 g 1,8 g |
Dietary fibre | 8,3 g | 5,5 g |
Total sodium | 166 mg | 0,8 g |
3.1.1 List TWO groups of food-sensitive consumers who should avoid eating the Jungle energy bar. (DO NOT rewrite the allergens.) (2)
3.1.2 Identify from the nutritional content given, ONE regulation that has been followed by the prescribed format for labelling a food product. (1)
3.1.3 Name the health-related condition that a person may suffer from when they do not follow the advice to avoid a high sodium intake. (1)
3.1.4 Name the bar with the highest sodium content. (1)
3.2 Write a paragraph describing the health condition and causes of Type 1 diabetes. (5)
3.3 Differentiate between systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure to explain blood pressure readings. (4)
3.4 Discuss THREE reasons why a petite 55-year-old woman would be more prone to developing osteoporosis. (3 x 2) (6)
3.5 Name TWO food borne diseases that are associated with a lack of personal hygiene. (2)
3.6 Read the information below and answer the questions that follow.
PLANT-BASED ON THE RISE [Adapted from www.womenshealth.co.za: January 2020] |
3.6.1 Name the term which relates to the underlined words in the quote below.
“The greatest impact of a disrupted climate will be on human food production and food availability.” (1)
3.6.2 Refer to the paragraphs under the subheading: Plant-based on the rise.
Analyse how a person suffering from a heart condition and high cholesterol levels would reap the benefits of a predominantly plant- based diet in the dietary management of this disease. (5 x 2) (10)
3.6.3 Discuss the implications that drought would have on food production. (7)
[40]
QUESTION 4: CLOTHING
4.1 Study the pictures of the puffer jacket in different forms below and answer the questions that follow.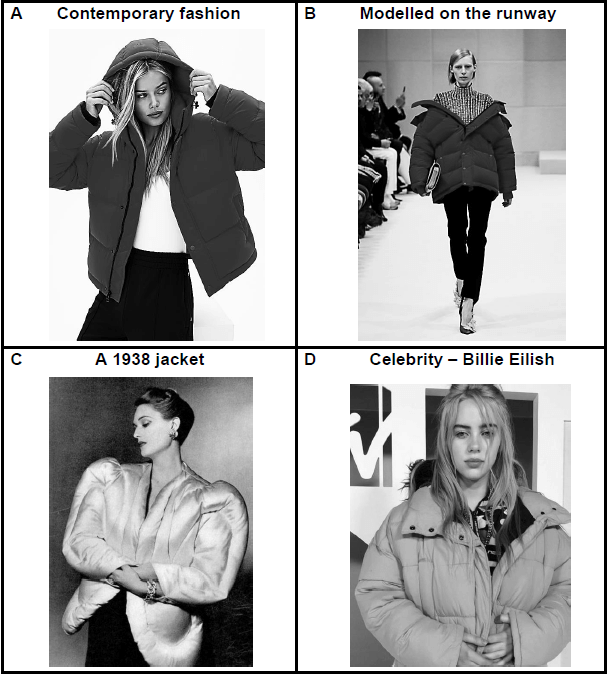
[Source: www. google images]
4.1.1 Describe the term contemporary fashion in picture A. (2)
4.1.2 Draw a sketch of the fashion cycle. Indicate on your drawing by means of an arrow, which phase the garment in picture A would be situated on the fashion cycle. Name the stage next to the arrow. (2)
4.1.3 Explain how the fashion styles represented in pictures B, C and D could influence a designer when designing a contemporary garment. (3 x 2) (6)
4.2 Study the picture below and answer the question that follow.
 |
All items are black. The jacket centre zip and buckle on the belt and shoe heels is gold. White beaded flowers on each shoe. |
[Source: Google images]
Discuss how this lady has worn her puffer jacket as part of her outfit, so that it is suitable for professional work wear. (3)
4.3 Read the information below and answer the questions that follow.
The Better Cotton Initiative (BCI) is the largest cotton sustainability programme in the world. Less than 20% of cotton is grown in a way that actively protects people and the environment. Our comprehensive programme of training, practical demonstrations and knowledge-sharing helps farmers to reduce their impacts on the environment and improve working conditions. We address multiple environmental issues – from soil health and pesticide use to water stewardship – and raise awareness of work that provides opportunities for people to work productively in conditions of freedom, equity, security and human dignity, focusing particularly on promoting women’s empowerment and preventing child labour. [Source: https://bettercotton.org/] |
4.3.1 Identify from the text TWO different key areas that describe the word sustainability. (2)
4.3.2 Name the term that is given to companies whose products are manufactured by following ethical practices such as protecting people and the environment.
(1)
4.3.3 Explain how non-organic textiles are also considered to be sustainable pertaining to how crops are grown/produced. Give ONE example of a non-organic sustainable crop. (4)
[20]
QUESTION 5: HOUSING
5.1 Read the scenario below, study the table provided and answer the questions that follow.
| Billy would like to buy a sectional title apartment as an investment. He came across two possibilities ‒ both on the ground floor. The one apartment had one bedroom and the other had two bedrooms. He did some research and concluded that the market that can afford to rent for R7 000,00 per month is much bigger than those that can afford to rent above R8 250,00 per month. He must keep in mind the rental return on the investment. |
PROPERTY A: ONE- BEDROOM GROUND FLOOR APARTMENT | PROPERTY B: TWO- BEDROOM GROUND FLOOR APARTMENT | |
Price | R740 000 | R980 000 |
Rental pm. | R7 000 | R8 250 |
Levy pm. | R977 | R1 650 |
Rates pm. | R320 | R420 |
Net rental return | 9,25% per annum | 7,25% per annum |
pm – per month [Source: https://businesstech.co.za]
NOTE: Net rental return is the rental income less direct costs, such as levies, rates and taxes, insurance and the potential cost of maintenance.
5.1.1 State TWO reasons why Billy would choose property to buy as an option for investment. (2)
5.1.2 Give the name of the contract with which Billy has purchased the property. (1)
5.1.3 Discuss sectional title as a form of ownership. (6)
5.1.4 Explain the term transfer duty. (3)
5.1.5 Give ONE reason why no transfer duty is paid for PROPERTY A. (1)
5.1.6 List the financial responsibilities of a tenant. (2)
5.1.7 Using the information given in the scenario and table, select which property Billy should buy. Justify your answer with FOUR reasons. (5)
5.2 Explain how the bond repayments are affected when interest is calculated according to the variable rate. (4)
5.3 Describe the role of the Deeds Office when purchasing a house. (6)
5.4 Study the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
Mr and Mrs Khumalo want to purchase a dishwasher. They both work and having a dishwasher will save them time washing dishes during the week. They have three children all under the age of ten. They enjoy entertaining and often have social braais on weekends, so the dishwasher will help on weekends too. Their kitchen has a built-in space for a standard size dishwasher. Their living, dining and kitchen area is open plan. They did research on the internet and have looked at two options. They are not prepared to spend more than R4 400 on this appliance. Mrs Khumalo intends to find out about the warranty and delivery costs before she buys a dishwasher. [Own text] |
5.4.1 Describe THREE issues that the Khumalo family must consider before purchasing a dishwasher. (3)
5.4.2 Discuss THREE of the aspects they should consider concerning the environmental impact when choosing a dishwasher. (3)
5.4.3 Identify FOUR consumer responsibilities that Mrs Khumalo did before making the purchase. (4)
[40]
QUESTION 6: ENTREPRENEURSHIP
6.1 Explain the terms best sale scenario and worst sale scenario. (6)
6.2 List FIVE ways how a business can use its time efficiently on the production line. (5)
6.3 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
Yolanda bakes and sells small individually sized bread loaves which are ideal to eat with soup. She bakes them in a baking tray which has SIX mini loaf shapes. Her costs are as follows: Cost of ingredients for one tray: R35,00 Overheads: R40,00 Profit: 60% |
6.3.1 Name THREE important requirements of packaging applicable to her bread. (3)
6.3.2 Calculate the selling price of one mini loaf of bread. Show ALL calculations. Round the answer off to the nearest rand. (6)
6.4 Read the interview below and answer the questions that follow.
An interview with Mapholo Ratau, an entrepreneur who manufacturers contemporary African clothing and accessories. [Source: lionessesofafrica.com/blog/2019/11/15] |
6.4.1 Select a sentence from the interview that indicates that Mapholo’s naming of her brand was important to her for this business. (1)
6.4.2 Identify FOUR factors from the first two paragraphs that ensured that Mapholo’s business had the potential to become profitable. (4)
6.4.3 Identify the factor one has to consider in the choice of a suitable product for a business when Mapholo’s customers loved her merchandise at her first shop.
(1)
6.4.4 Give TWO advantages of Mapholo doing direct selling at the weekend market. (2)
6.4.5 Mapholo has employed staff. List FOUR reasons why it is beneficial to train staff. (4)
6.4.6 Mapholo is a successful entrepreneur.
Analyse the steps Mapholo took as she progressed from the start of her business until she employed full-time workers, that impacted positively on her business which resulted in a successful business. (8)
[40]
TOTAL: 200
Civil Technology: Construction Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: SAFETY AND MATERIALS (GENERIC)
1.1
1.1.1 2 (1)
1.1.2 228 mm (1)
1.1.3 900 mm (1)
1.1.4 150 mm (1)
1.1.5 Non-slippery layer (1)
1.2 Similar answer:
- Prevents horizontal movement between the platform and structure(1)
1.3 Identify THREE of the following requirements that are applicable to the supplier of hazardous chemical substances:
1.3.1 First-aid measures must be shown
1.3.4 Fire-fighting measures must be shown
1.3.6 Storage instructions must be shown (3 x 1) (3)
1.4 Minimum = 30⁰ (1) and maximum = 50⁰ (1) (2)
1.5 Similar answer:
- Aluminium conducts electricity (1) and workers who use a ladder could be shocked (1) (2)
1.6 Describe the difference between the surface finish of a water-based paint and an oil-based paint:
- Water-based – provides an elastic, flexible finish (1) Oil-based – provides a hard, durable finish (1) (2)
1.7 Any THREE advantages of the curing of concrete:
- Increases strength
- Decreases permeability
- Improves durability
- Reduces cracks
- Makes concrete more watertight
- Provides volume stability
- Concrete can carry more weight (3 x 1) (3)
1.8 Briefly describe the powder-coating process:
- Plastic finish in powder form (1) is applied by means of a compressed air spray- gun (1) (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS, JOINING AND EQUIPMENT (GENERIC)
2.1 Answer the following questions with regard to the site plan on ANSWER SHEET A.
2.1.1 See ANSWER SHEET A (10)
2.1.2 See ANSWER SHEET A (6)
2.2
2.2.1 ![]() (2)
(2)
2.2.2 ![]() (2)
(2)
2.2.3  (2)
(2)
2.2.4 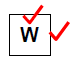 (2)
(2)
2.2.5 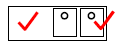 (2)
(2)
2.3
2.3.1 Unfinished wood (1)
2.3.2 Two-way switch (1)
2.4 When driven into place (1) it cannot be turned (1) (2)
2.5 Prevents backing off OR it acts as a lock nut (1) (1)
2.6 18 mm (1)
2.7
2.7.1 1,35 m (1)
2.7.2 1,412 – 1,285 = 0,127 x 100 = 12,7 m (0,1 m leeway allowed) (3)
2.7.3 Minimum = 30 m (1) and maximum = 200 m (1) (2)
2.8 It can affect the measuring function of the tool. (1)
2.9 Batteries must be removed. (1)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION A: 60
QUESTION 3: ROOFS, STAIRS AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
3.1 Any FOUR types of roofs or roof trusses:
- South African roof truss
- Single Howe truss
- Lean-to-roof
- Couple roof
- Closed couple roof
- Collar-tie roof
- King post roof truss
- W-truss or Fink truss
- Fan truss
- Scissors truss
- Mono-pitched roof (4 x 1) (4)
3.2 Any FOUR advantages of the use of roof underlays:
- Acts as a secondary roof
- A weather shield during construction
- Waterproof and weatherproof
- Condensation barrier
- Dustproof
- Protects the building/structure
- Protects thermal insulation material
- Protects ceiling boards
- Superior wind uplifting strength prevents lifting of tiles
- Vapour resistant
- High tensile resistance
- Cost effective
- High heat resistance (4 x 1) (4)
3.3
3.3.1
- A – Purlin / Batten (1)
- B – Rafter (1)
- C – Ridge tile / ridge plate (1)
- D – Nail plate (1)
- E – King post (1)
3.3.2 38 mm (1) x 114 mm (1) (2)
3.3.3 Holds/fixes the different timber pieces together (1)
3.4
3.4.1 Concrete tiles, clay or slate /heavy roofs (1)
3.4.2 Thatched roofs (1)
3.4.3 Iron sheeting/steel roof sheets/corrugated/IBR (1)
3.5
3.5.1 True (1)
3.5.2 False (1)
3.5.3 True (1)
3.5.4 True
3.6
3.6.1 Joining roof truss to brickwork (1)
3.6.2
- A – Galvanized steel strap / hoop-iron strap (1)
- B – Wall plate (1)
3.6.3 600 mm (1)
3.6.4 Nailed / Bolted (1)
3.7 Any TWO types of cast-in anchors:
- Hex-head bolt with washer
- L-bolt
- J-bolt
- Welded headed stud (2 x 1) (2)
[30]
QUESTION 4:
MATERIAL, EQUIPMENT AND TOOLS, EXCAVATIONS (SPECIFIC)
4.1
4.1.1 D hard, but brittle and breaks easily (1)
4.1.2 H pumps high volumes of concrete (1)
4.1.3 G alloy of copper and zinc (1)
4.1.4 C pumps smaller volumes of concrete (1)
4.1.5 A highly toxic (1)
4.1.6 E packaging material (1)
4.2
4.2.1 Slump test (1)
4.2.2 100 mm (1)
4.2.3 600 mm (1)
4.2.4 Any TWO reasons for the purposes of the slump test:
- To test the density of concrete (percentage water)
- To determine the workability and consistency of batches
- To determine the slump of the mixture (2 x 1) (2)
4.3 Any TWO ways of curing concrete:
- Water by means of hosepipe or sprinkling
- Cover with water-retaining substances such as damp sand, sacking, straw, hessian and canvas
- Plastic membrane and plastic sheets
- Commercial sealant
- Pool forming
- Similar answer (2 x 1) (2)
4.4 Ferrous (1) and non-ferrous metals (1) (2)
4.5 Any THREE types of cladding for buildings:
- Tile cladding
- Brick slip cladding
- Stone cladding
- Timber cladding
- Metal sheet cladding (3 x 1) (3)
4.6
4.6.1 Tamping rammer(1)
4.6.2 Any THREE ways of maintaining the tamping rammer:
- Lubricate and adjust according to manufacturer’s instructions
- Clean after use and store in a safe, dry place
- Repair / replace damaged electrical cords
- Service regularly
- Remove loose dirt and soil after use (3 x 1) (3)
4.6.3 To keep control of the powerful machine (1)
4.7 Any FOUR causes for the collapse of an excavation:
- Heavy rains
- Poor soil strata, structure or composition
- Sides not dug at the correct angle
- Improper use of formwork or shoring to support walls
- Vibration by machinery or heavy vechiles nearby
- Water seeping into the excavated area
- Contact with underground service
- Access to and exit from the excavation
- Soil slides due to cracks or loose soil (4 x 1) (4)
4.8 Any THREE ways of making excavations safe during the night:
- Fencing
- Warning signs
- Warning lights (red or orange)
- Covering (3 x 1) (3)
4.9
4.9.1 With a ladder/scaffolding (1)
4.9.2 Avoid trench sides from collapsing (one metre away) (1)
4.9.3 Test for low oxygen, hazardous fumes and toxic gases (1)
4.10
4.10.1 False (1)
4.10.2 False (1)
4.10.3 False (1)
4.11
4.11.1 Firm soil/Hard soil/Stable soil (1)
4.11.2
- A – Strut (1)
- B – Walling board (1)
- C – Wedge (1)
[40]
QUESTION 5: BRICKWORK AND GRAPHICS (SPECIFIC)
5.1
5.1.1 One brick wall / Outside wall (1)
5.1.2 220 mm (1)
5.1.3 Stretcher bond (1)
5.2 Any THREE advantages of cavity walls:
- Prevent rainwater from penetrating the interior wall surface
- Provide good thermal and sound insulation
- Cheaper materials can be used for internal walls
- Reduces / prevent expensive exterior finishes (3 x 1) (3)
5.3 See ANSWER SHEET B. (5)
5.4 5.4.1 50 mm (1)
5.4.2 8 m (1)
5.4.3 To remove wasted mortar (1)
5.4.4 Wall ties (1)
5.4.5 Allows water that penetrates the outside wall to drain (1)
5.5 Double triangular pattern (1)
5.6
5.6.1
- A – Beam filling (1)
- B – Fascia board (1)
- C – Tie beam (1)
- D – Plaster (1)
5.6.2 Open eave construction (1)
5.7
5.7.1 F (prepared layer beneath paving and bedding sand) (1)
5.7.2 C (best edge restraint for paving) (1)
5.7.3 A (natural soil on which the paving will be laid) (1)
5.7.4 D (final layer upon which paving is laid) (1)
5.8 Any TWO advantages of mortar-set paving:
- Little maintenance is required
- Low life-cycle cost
- Resistant to point loads
- Resistant to fatigue and reflecting traffic patterns
- Resistant to edge movement
- User-friendly installation material is used
- No weeds will be able to grow in between the joints
- No off-gassing installation products used
- Insects will not be able to ruin the appearance of the paved structure (2 x 1) (2)
5.9 Any TWO reasons for construction failure of paving:
- Concrete haunch too thin to support itself and cracks or crumbles under pressure
- Too little weight to retain the structure and keep paving in place
- Bond between haunch and edge units is weak and will easily crumble
- Sub base is not contained and will be washed out by groundwater (2 x 1) (2)
5.10 Draw a neat sketch with EIGHT (8) bricks of the basket-weave paving: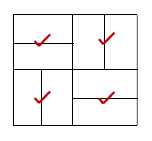
Bricks drawn in good proportion = (5)
5.11
5.11.1 Segmental gauged arch (1)
5.11.2
- A – Key brick (1)
- B – Skewback (1)
- C – Intrados (1)
- D – Extrados (1)
[40]
QUESTION 6: FORMWORK, REINFORCEMENT, FOUNDATIONS, CONCRETE FLOORS AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
6.1 Concrete is mixed / poured on site (1)
6.2 Any THREE properties of good formwork:
- Made accurately according to the dimensions indicated
- Sturdy enough to bear the mass of wet concrete without collapsing
- Able to bear the mass of workers and equipment
- Must be strong enough to provide sufficient support, without too much deflection, until the concrete has set
- Formwork should be easy to repair on site
- Secured with wire nails, where some should protrude for easy extracting
- Secured with bolts from 13 mm to 19 mm in diameter
- Should be sealed properly so that the concrete does not leak and form honeycombs or fins
- Should be free of dirt (sawdust or releasing agents)
- Quick and simple to erect, mechanically or by hand
- Ensure the correct cover depth for reinforcing, to prevent structural failure
- Fit plywood onto laggings if a smooth finish is required
- Remove when the concrete has cured and is able to support load on its own
- Should be easy to remove withou damaging the formwork or concrete
- Close-fitting along seams and joints
- Made from recyclable components (3 x 1) (3)
6.3
6.3.1
- A – Soffit / Shutter board (1)
- B – Strut / Prop (1)
- C – Bearer / Head tree (1)
- D – Brace / Strut (1)
- E – Folding wedges (1)
6.3.2 Beam (1)
6.4
6.4.1 High-tensile steel (1)
6.4.2 250 mm (1)
6.4.3 16 mm (1)
6.5
6.5.1 Tensile stress / force (1)
6.5.2 Shear stress / force (1)
6.6 Any THREE properties (requirements) for reinforced steel bars:
- Free of salt spray, mud, splinters and any oiliness
- Completely covered in concrete to protect it against rust and fire hazards
- Resistant to tensile stress
- Easy to bend into shape
- Able to bind firmly with concrete
- Of limited expansion prevent tension when temperature fluctuates
- Readily available and affordable
- Must be rustproof, otherwise it will impair binding (3 x 1) (3)
6.7 Any TWO types of pile foundations:
- Precast concrete piles / prefabricated piles
- Steel tube caisson piles
- In-situ (driven) foundation piles
- Short-bored (auger) piles (2 x 1) (2)
6.8 Any TWO reasons for using pile foundations:
- Ground conditions not stable / solid enough
- Distribute the load to more stable ground (underground / water supports)
- Provides stability when raft / floating foundation is used
- When structures are subjected to horizontal forces, resist pile foundations bending stress while still lending vertical support
- Soils prone to swelling and shrinking (clay soil)
- Superstructure is exposed to uplifting forces (offshore platforms)
- Where soil erosion is possible (bridges) (2 x 1) (2)
6.9 Foundation strips for a store-room is 5 650 x 3 375 (inside measurements) The foundation is 750 mm wide and 250 mm deep (thick)
6.9.1 Calculate the centre line of the foundation: (5)
- 2 / 5 650 = 11 300
2 / 3 375 = 6 750
18 050
Plus corners: 4 / 750 = 3 000
21 050
6.9.2 Calculate the volume of concrete needed (3)
- Volume = length x width x depth
= 21,05 m x 0,75 m x 0,25 m
= 3,947 m³ (3)
[30]
TOTAL: 200
ANSWER SHEET A
2.1 Answer the following questions in regard to the site plan on ANSWER SHEET A:
2.1.1 Any TEN particulars that are not shown according to the checklist:
- Plot no. 31 is not shown
- Plots depth measurement is not shown
- Street name is not shown
- Branch sewage at S is not shown
- Connecting manhole (1,5m inside plot boundary) is not shown
- Measurements of southern building boundary is not shown
- Structure measurements are not shown
- RE (rodding eye) symbol is not shown
- IE symbols are not shown
- VP and symbol are not shown at WC
- Entrance to plot is not shown
- No datum level is shown (10)
2.1.2 Identify SIX particulars that are shown incorrectly on the site plan:
- Construction is over the building boundary on the west side
- North arrow must be on the right-hand side, at the bottom of the page
- Scale is wrongly shown
- Corner of branch sewage at WB is wrong
- RE and symbol missing at the change of direction in sewage line
- House depth measurements are not shown (6)
ANSWER SHEET B
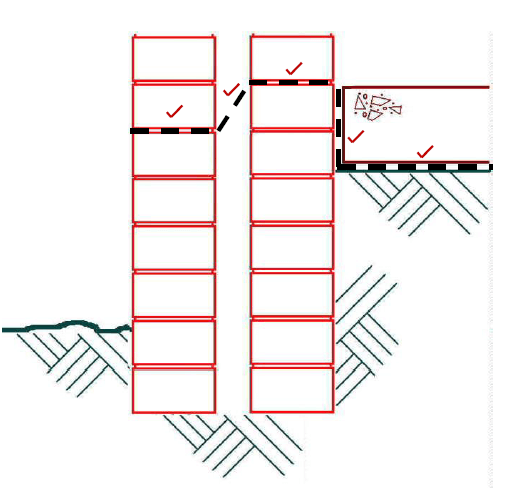
5.3 Draw in the damp-proof course (DPC). (5)
Civil Technology: Civil Services Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: SAFETY AND MATERIALS (GENERIC)
1.1
1.1.1 2 (1)
1.1.2 228 mm (1)
1.1.3 900 mm (1)
1.1.4 150 mm (1)
1.1.5 Non-slippery layer (1)
1.2 Similar answer:
- Prevents horizontal movement between the platform and structure (1)
1.3 Identify THREE of the following requirements that are applicable to the supplier of hazardous chemical substances:
1.3.1 First-aid measures must be indicated
1.3.4 Fire-fighting measures must be indicated
1.3.6 Storage instructions must be indicated (3 x 1) (3)
1.4 Minimum = 30⁰ (1) and maximum = 50⁰ (1) (2)
1.5 Similar answer:
- Aluminium conducts electricity (1) and workers who use a ladder could be shocked (1) (2)
1.6 Describe the difference between the surface finish of a water-based paint and an oil-based paint:
- Water-based – provides an elastic, flexible finish (1) Oil-based – provides a hard, durable finish (1) (2)
1.7 Any THREE advantages of the curing of concrete:
- Increases strength
- Decreases permeability
- Improves durability
- Reduces cracks
- Makes concrete more watertight
- Provides volume stability
- Concrete can carry more weight (3 x 1) (3)
1.8 Briefly describe the powder coating process:
- Plastic finish in powder form (1) is applied through a compressed air spray-gun (1) (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS, JOINING AND EQUIPMENT (GENERIC)
2.1 Answer the following questions with regard to the site plan on ANSWER SHEET A:
2.1.1 See ANSWER SHEET A (10)
2.1.2 See ANSWER SHEET A (6)
2.2
2.2.1 Undisturbed earth ![]() (2)
(2)
2.2.2 Plaster ![]() (2)
(2)
2.2.3 Ramp with a slope of 1 : 5 1 : 5  (2)
(2)
2.2.4 Electrical meter W  (2)
(2)
2.2.5 Sink unit – double  (2)
(2)
2.3
2.3.1 ![]() Unfinished wood (1)
Unfinished wood (1)
2.3.2 ![]() Two-way switch (1)
Two-way switch (1)
2.4 When driven into place (1) it cannot be turned (1) (2)
2.5 Prevents backing off OR it acts as a lock nut (1)
2.6 18 mm (1)
2.7
2.7.1 1,35 m (1)
2.7.2 1,412 – 1,285 = 0,127 x 100 = 12,7 m (0,1 m leeway allowed) (3)
2.7.3 Minimum = 30 m (1) and maximum = 200 m (1) (2)
2.8 It can affect the measuring function of the tool. (1)
2.9 Batteries must be removed. (1)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION A: 60
QUESTION 3: SAFETY, MATERIAL AND CONSTRUCTION (SPECIFIC)
3.1 Respirator / Extractor / Blower (1)
3.2
3.2.1 Safety signage must be displayed. (1)
3.2.2 Safety rope and belt must be used. (1)
3.3 (1) Above openings where persons work (1) to prevent falling objects from injuring workers (2)
3.4 Contractor (1)
3.5 White powder / Brass turns red (1)
3.6 Corrosion (1)
3.7 (1) When an electrochemical process takes place between (1) two dissimilar metals or alloys (2)
3.8 Any THREE:
- Electrically insulating the two metals
- No contact with an electrolyte
- Applying an antioxidant paste to copper and aluminium surfaces
- Choosing metals with similar electrode potential
- Connecting a DC supply to oppose the corrosive galvanic current (3 x 1) (3)
3.9 FIGURE 3.9 on ANSWER SHEET B shows layer 1 of a combination corner of a half brick wall in stretcher bond. Draw the alternative layer of the half brick wall on scale 1 : 10 on ANSWER SHEET B. (10)
3.10 (1) Benching is built with a slope / an incline (1) to ensure that sewage spills slide back into the channel pipe and (1) rats / vermin cannot settle there (3)
3.11 Bottom of the benching can be reached safely (1)
3.12 1 : 40 (1)
3.13 (1) When water runs down trenches, (1) it causes erosion / weak sides / water in trenches (2)
[30]
QUESTION 4: COLD-WATER SUPPLY, HOT-WATER SUPPLY AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
4.1
4.1.1 Stopcock (1)
4.1.2 Full-way valve (1)
4.1.3 Ball valve (1)
4.1.4 Non-return valve (1)
4.2 FIGURE 4.2 on ANSWER SHEET B shows a bibcock with three missing parts. Use the sketch on ANSWER SHEET B and draw the three missing parts. Supply labels to identify the three parts. (6)
4.3 (1) The cool water that runs out before (1) the hot water when (1) a hot water tap is opened (3)
4.4 (1) The red water is diverted to a storage tank / garden / rainwater tank etc. (1) so that the water does not get wasted / thus no ongoing waste of costs (2)
4.5 Any TWO requirements:
- Smooth cut
- Straight cut (2)
4.6
4.6.1 A Johnson coupling (1)
4.6.2 Galvanised mild steel pipe work (1)
4.7 It protects the geyser against corrosion. (1)
4.8 4.8.1 False (1)
4.8.2 True (1)
4.8.3 True (1)
4.8.4 True (1)
4.8.5 False (1)
4.9 4.9.1 4.9.A – Vacuum tube
4.9.B – Pressurised inner tank
4.9.C – Reflector (3)
4.9.2 It operates (1) according to an open-vented or gravity-fed system under a pressure of (1) under 0,5 bar. (1) The higher the system is installed above the tap, (1) the higher the pressure will be. (4)
4.10 55 °C (1)
4.11 Any THREE advantages of a heat pump:
- Moves heat instead of generating it
- More energy efficient
- Powered by electricity
- Saves electricity
- Best for moderate climates (3 x 1) (3)
4.12 Compressed-air test apparatus (1)
4.13 Any THREE maintenance measures for drain-cleaning rods.
- Clean the drain rods after use.
- Hose down the rods and then wash them in a solution of warm water, washing-up liquid and Jeys Fluid.
- Coil spring rods can be cleaned using a jet wash.
- Allow the rods and tools to dry before storing them. (3 x 1) (3)
[40]
QUESTION 5: DRAINAGE AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
5.1
5.1.1 Ø 40 mm; Ø 50 mm (2)
5.1.2 90° (1)
5.1.3 135° (1)
5.1.4 Inspection eye (1)
5.1.5 (1) Access opening to (1) allow the cleaning of pipes (2)
5.2 Make a neat sketch to illustrate the shape of a P-trap. Also indicate the water level of the water lock in the trap.(3)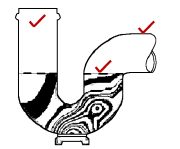
5.3 (1) Vent pipe / ventilation pipe / vent valve / anti-siphon pipe (1) are connected vertically to the (1) lowest point of the main sewer system (1) and extends above the roof (Vent valve extends ± 1 m above the ground level) (4)
5.4 5.4.1 False (1)
5.4.2 True (1)
5.4.3 True (1)
5.4.4 False (1)
5.5 Any TWO disadvantages:
- Heavy
- Difficult to work with (2 x 1) (2)
5.6
5.6.1 C (1)
5.6.2 F (1)
5.6.3 A (1)
5.6.4 B (1)
5.7 (1) The system will be saturated (1) resulting in pollution / contaminated (2)
5.8
5.8.1  Gully (2)
Gully (2)
5.8.2  Urinal (2)
Urinal (2)
5.8.3  Invert level (2)
Invert level (2)
5.9
5.9.1 22 mm cold water pipe: 6 m + 1,5 m + 5 m = 12,5 m (1)
5.9.2 15 mm cold water pipe: 2 x 1 m + 1,2 m = 3,2 m (1)
5.9.3 22 mm elbow 90°: 2 (1)
5.9.4 22 x 15 mm reducing elbow 90°: 1 (1)
5.9.5 15 mm elbow 90°: 2 (1)
5.9.6 22 x 22 x 15 mm Reducing tee: 1 (1)
5.10 πr²h = 22 x 0,9 x 0,9 x 2,8 = 7,128 m³ (2)
7
[40]
QUESTION 6: GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION, ROOF WORK, STORM WATER AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
6.1
6.1.1 Soil pipes – brown (1)
6.1.2 Stormwater drains – not coloured (1)
6.1.3 All existing drains – black (1)
6.2
6.2.1 VP – Vent pipe (1)
6.2.2 IO / IE – Inspection eye (1)
6.2.3 IL – Invert level (1)
6.2.4 NGV / NGL – Natural ground level (1)
6.3 FIGURE 6.3 on ANSWER SHEET C shows the top and front elevation of a pyramid with a square base. Draw the development of the pyramid according to the radial-line method on ANSWER SHEET C. Show all construction lines. (10)
6.4
6.4.1
- A – Gutter and bracket
- B – Offset
- C – Holderbat
- D – Downpipe
- E – Rain-water shoe (5)
6.4.2 25 mm for each 4,8 m / 1 : 600 (1)
6.5 (1) To withstand the force (1) of the flowing water (2)
6.6 To keep solids out of the stormwater pipe (1)
6.7 5 m (1)
6.8
6.8.1 Spring toggle fixing (1)
6.8.2 Any TWO uses:
- Hanging of brackets against plasterboard
- Fixing in hollow-core brick fittings
- Fixing lights to the ceiling (2 x 1) (2)
[30]
TOTAL: 200
ANSWER SHEET A
2.1 Answer the following questions with regard to the site plan on ANSWER SHEET A:
2.1.1 Any TEN particulars that are not shown according to the checklist:
- Plot no. 31 is not shown
- Depth measurement of plot is not shown
- Street name is not shown
- Branch sewage at S is not shown
- Connecting manhole (1,5 m inside plot boundary) is not shown
- Measurements of southern building boundary is not shown
- Structure measurements are not shown
- RE (rodding eye) symbol is not shown
- IE symbols are not shown
- VP and symbol are not shown at WC
- Entrance to plot is not shown
- No datum level is shown (10)
2.1.2 Identify SIX particulars that are incorrectly indicated on the site plan:
- Construction is over the building boundary on the west side
- North arrow must be right-hand side, at the bottom of the page
- Scale is wrongly shown
- Corner of branch sewage at WB is wrong
- RE and symbol missing at the change of direction in sewage line
- House depth measurements are not shown (6)
ANSWER SHEET B
3.9 FIGURE 3.9 on ANSWER SHEET B shows layer 1 of a combination corner of a half brick wall in stretcher bond. Draw the alternative layer of the half
brick wall on scale 1 : 10 on ANSWER SHEET B.
(10)
| Brickwork | 8 |
| Application of scale | 2 |
| TOTAL: | 10 |
4.2 FIGURE 4.2 on ANSWER SHEET B shows a bibcock with three missing parts. Use the sketch on sheet B and draw the three missing parts. Supply labels to identify the three parts. (6)
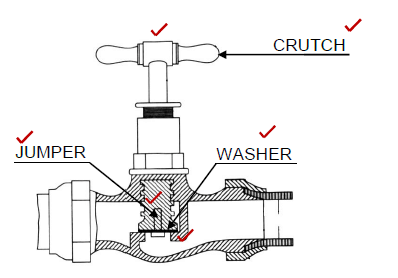
| Parts | 3 |
| Labels | 3 |
| TOTAL: | 6 |
ANSWER SHEET C
6.3 FIGURE 6.3 on ANSWER SHEET C shows the top and front elevation of a pyramid with a square base. Draw the development of the pyramid according
to the radial-line method on ANSWER SHEET C. Show all construction lines. (10)
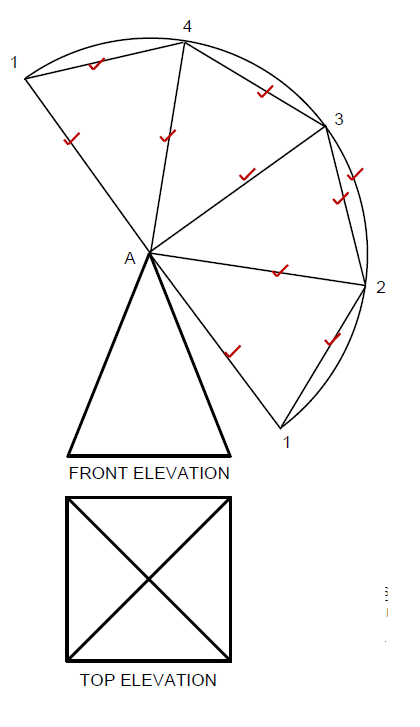
Arcs 1, 2, 3 and 4 | 1 |
Seam lines A1 to A4 | 5 |
Base lines 1–4 | 4 |
TOTAL: | 10 |
Civil Technology: Woodworking Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: SAFETY AND MATERIALS (GENERIC)
1.1
1.1.1 2 (1)
1.1.2 228 mm (1)
1.1.3 900 mm (1)
1.1.4 150 mm (1)
1.1.5 Non-slippery layer (1)
1.2 Similar answer:
- Prevents horizontal movement between the platform and structure (1)
1.3 Identify THREE of the following requirements that are applicable to the supplier of hazardous chemical substances:
1.3.1 First-aid measures must be indicated
1.3.4 Fire-fighting measures must be indicated
1.3.6 Storage instructions must be indicated (3 x 1) (3)
1.4 Minimum = 30⁰ (1) and maximum = 50⁰ (1) (2)
1.5 Similar answer:
- Aluminium conducts electricity (1) and workers who use a ladder could be shocked (1) (2)
1.6 Describe the difference between the surface finish of a water-based paint and an oil-based paint:
- Water-based – provide an elastic, flexible finish (1) Oil-based – provide a hard, durable finish (1) (2)
1.7 Any THREE advantages of the curing of concrete:
- Increases strength
- Decreases permeability
- Improves durability
- Reduces cracks
- Makes concrete more watertight
- Provides volume stability
- Concrete can carry more weight (3 x 1) (3)
1.8 Briefly describe the powder coating process:
- Plastic finish in powder form (1) is applied through a compressed air spray-gun (1) (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS, JOINING AND EQUIPMENT (GENERIC)
2.1 Answer the following questions with regard to the site plan on ANSWER SHEET A:
2.1.1 See ANSWER SHEET A (10)
2.1.2 See ANSWER SHEET A (6)
2.2
2.2.1 Undisturbed earth ![]() (2)
(2)
2.2.2 Plaster ![]() (2)
(2)
2.2.3 Ramp with a slope of 1 : 5 1:5  (2)
(2)
2.2.4 Electrical meter W  (2)
(2)
2.2.5 Sink unit – double  (2)
(2)
2.3
2.3.1 ![]() Unfinished wood (1)
Unfinished wood (1)
2.3.2 ![]() Two-way switch (1)
Two-way switch (1)
2.4 When driven into place (1) it cannot be turned (1) (2)
2.5 Prevents backing off OR it acts as a lock nut (1)
2.6 18 mm (1)
2.7
2.7.1 1,35 m (1)
2.7.2 1,412 – 1,285 = 0,127 x 100 = 12,7m (0,1m leeway allowed) (3)
2.7.3 Minimum = 30 m (1) and maximum = 200 m (1) (2)
2.8 It can affect the measuring function of the tool. (1)
2.9 Batteries must be removed. (1)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION A: 60
QUESTION 3: CASEMENTS, CUPBOARDS, WALL-PANELLING AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
3.1 3.1.1 16 mm (1)
3.1.2 Stuck mould (1)
3.1.3 Rebate (1)
3.2
3.2.1 Drip groove (1)
3.2.2 Transom
- Bottom rail of fanlight 60 mm x 44 mm Putty
- Ovol moulding
- Windowpane/glass (3 x 1) (3)
3.2.3 Enhances the appearance and can open separately to allow ventilation (1)
3.3 ANSWER SHEET B (5)
3.4
3.4.1
- Top shelf/storage space
- Hanging space
- Shelving
- Drawer unit (4)
3.4.2
- Melamine is waterproof
- Easy to clean
- Durable
- Smooth finish
- Improves appearance (Any 1) (1)
3.4.3
- E = Front rail G = Side of cabinet
- F = Handrail H = Kick plate (4)
3.5 Fanlight (1)
3.6
3.6.1
- A = Cornice
- B = Horizontal rough grounds
- C = Quadrant mould (3)
3.6.2
- Provide storage space
- Improves/enhances the aesthetic appeal of the room
- Looks expensive (2)
3.7 A casement window can be defined as a window assembly that has at least one casement or vertically hinged sash (frame that holds the glass) (2)
[30]
QUESTION 4: ROOFS, CEILINGS, TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT, AND MATERIALS (SPECIFIC)
4.1
4.1.1 A = Router B = Radial arm saw (2)
4.1.2
- Lubricate and adjust according to the manufacturer’s instructions
- Clean the saw after use
- Repair or replace damaged electrical cords
- Use machinery only for the intended purpose
- Keep ventilation holes open and clean (2)
4.1.3
- Always wear safety goggles
- Use both hands to operate the machine
- Stand firmly and comfortably
- Wear a dusk mask when using the router
- The workpiece must be gripped firmly before starting the moulding (2)
4.2
- Gypsum ceiling board
- Cover strips
- Trapdoor panel
- Tie beam (2)
4.3
- Sand the wood with different grades of sandpaper
- Sand until it is smooth and free from scratches
- Remove all dust (3)
4.4 Hurricane clips:
- Securing purlins to rafter (roof truss)
- Securing trusses to wall plates
- Ideally used at eaves overhangs
- Where trusses cross each other or where truss members cross each other or meet at 90°
- To fix opposite faces of roof members
Storm clips: Securing roof tiles to the battens (2)
4.5
- Strength
- Density (2)
4.6
- King post positioned in the middle of the roof truss
- Brandering is nailed to the tie beam and to existing brandering
- Roof sheeting to cover the roof (3)
4.7
- Always wear safety goggles
- Wear a dusk mask when using the belt sander
- Inspect the power cord regularly for damage
- Avoid carrying the machine by the cord (2)
4.8
4.8.1
- A. Tie beam
- B. Brandering
- C. Brandering
- D. Trapdoor
- E. Ceiling board (5)
4.8.2 Cover strips keep the panels in place (2)
4.8.3
Sectional view showing a metal T-strip (3)
4.9
4.9.1
- A. Hipped end
- B. Purlin
- C. Ridge
- D. Valley rafter
- E. Overhang
- F. Gable end (6)
4.9.2 75 mm x 50 mm (2)
4.10
- Must be able to withstand natural elements like rain, wind and corrosion
- Must look expensive and must be able to improve the appearance of the building
- Must be able to withstand fire
- To insulate against heat and cold (2)
[40]
QUESTION 5: CENTRING, FORMWORK,SHORING AND GRAPHICS AS MEANS OF COMMUNICATION (SPECIFIC)
5.1
- Plastic
- Metal sheeting
- Hardboard
- Fibreglass (1)
5.2 ANSWER SHEET C (6)
5.3
5.3.1 Double flying shore: used to provide temporary support to two parallel walls that are located between 9 metres and 15 metres apart where one or both walls show signs of failure (1)
5.3.2 Dead shore:
- Support structures
- Carry the dead weight of the structure above them, for example walls and floors
- New openings for existing walls and doors underpinning, is needed during restoration of the wall (1)
5.4
5.4.1 Steel dogs: nails used to secure the joint between prop and needle (1)
5.4.1 Sole plate: made of timber to spread the weight transferred by the props over a wider area (1)
5.4.3 Props or struts: placed vertically on top of each other on the different floors to strengthen or brace the floors and ceilings (1)
5.5
5.5.1
- A – Concrete/floor slab
- B – Brace/strut
- C – Prop
- D – Sole plate (4)
5.5.2
- To support the formwork
- Keep the different formwork components sturdy and fixed
- Facilitate the raising or lowering of the formwork to the required height
- For levelling the formwork
- Ease the striking of formwork after the concrete has cured (4)
5.6
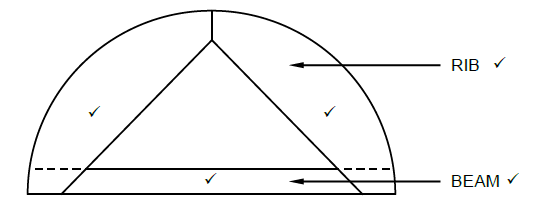
| ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK |
| Beam | 1 |
| Ribs | 2 |
| Two labels | 2 |
| Correctness of drawing | 1 |
| TOTAL: | 6 |
(6)
5.7
5.7.1
- To lower
- To raise the centre (2)
5.7.2
- Table saw
- Bandsaw
- Jigsaw
- Portable circular saw
- Circular saw (Any 2) (2)
[30]
QUESTION 6: SUSPENDED FLOORS, STAIRCASES, IRONMONGERY, DOORS AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
6.1
- A. Place to rest
- B. For safety reasons in case of an accident
- C. Change of direction (2)
6.2
(5)
6.3
- On a cupboard door
- On a drawer (2)
6.4 Night latch (1)
6.5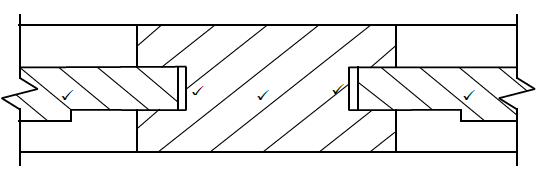
Correctness
| ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK |
| Muntin | 1 |
| Raised panels | 2 |
| Space for expansion and shrinkage | 1 |
| Hatching | 1 |
| Correctness of drawing | 1 |
| TOTAL | 6 |
(6)
6.6 The opening allows for shrinkage and expansion of wood (1)
6.7
6.7.1 A: Brace B: Tongue and groove panels C: Stile (3)
6.7.2 To prevent sagging (1)
6.7.3 Gives a neater appearance at the outside of the frame members (1)
6.8
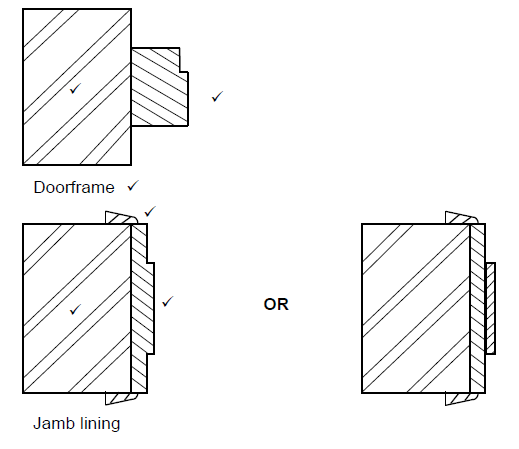
| ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK |
| Walls | 2 |
| Frame profile of door | 1 |
| Jamb lining profile | 1 |
| Title | 1 |
| Architraves | 1 |
| TOTAL: | 6 |
6.9
6.9.1
- A = 220mm wall
- E = Floor joist
- B = 12 mm plaster F = Wall plate/bearers
- C = Skirting G = Damp-proof course (DPC)
- D = Floorboard H = Foundation (8)
6.9.2 To cover the gaps between the flooring and the wall (1)
6.9.3
- Span of the floor
- The centre-to-spacing between the floor joist; and
- The grade of timber of the floor (3)
[40]
TOTAL: 200
ANSWER SHEET A
2.1 Answer the following questions with regard to the site plan on ANSWER SHEET A:
2.1.1 Any TEN particulars that are not shown according to the checklist:
- Plot no. 31 is not shown
- Plot depth measurement is not shown
- Street name is not shown
- Branch sewage at S is not shown
- Connecting manhole (1,5 m inside plot boundary) is not shown
- Measurements of southern building boundary are not shown
- Structure measurements are not shown
- RE (rodding eye) symbol is not shown
- IE symbols are not shown
- VP and symbol are not shown at WC
- Entrance to plot is not shown
- No datum level is shown (10)
2.1.2 Identify SIX particulars that are shown incorrectly on the site plan:
- Construction is over the building boundary on the west side
- North arrow must be right-hand side, at the bottom of the page
- Scale is shown incorrectly
- Corner of branch sewage at WB incorrect
- RE and symbol missing at the change of direction in sewage line
- House depth measurements are not shown (6)
ANSWER SHEET B
QUESTION 3.3
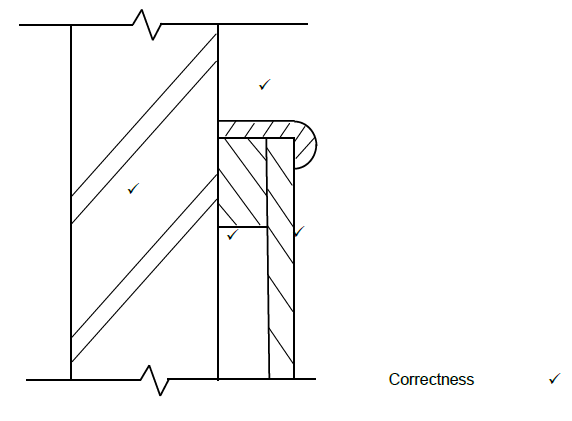
| ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK |
| Wall | 1 |
| Capping | 1 |
| Rough ground | 1 |
| Tongue and groove board | 1 |
| Correctness of drawing | 1 |
| TOTAL: | 6 |
ANSWER SHEET C
QUESTION 5.2
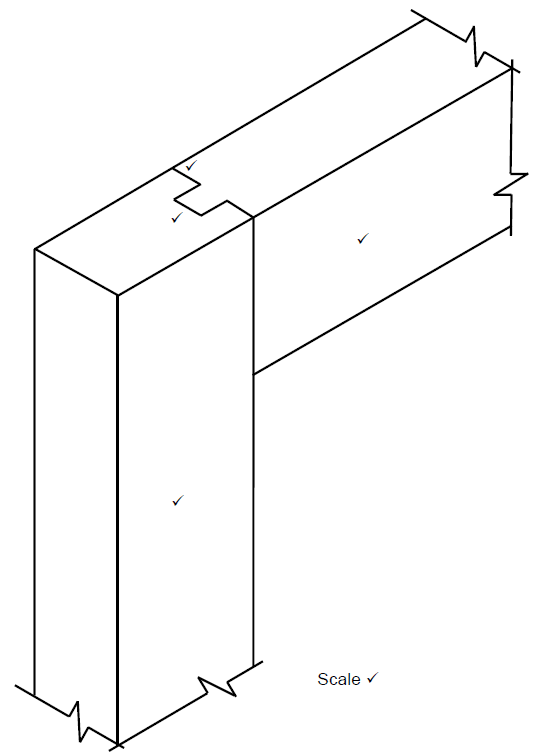
| ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK |
| Stile | 1 |
| Top rail | 1 |
| Mortise | 1 |
| Haunch | 2 |
| Application of scale | 1 |
| TOTAL: | 6 |
Civil Technology: Woodworking Grade 12 Questions - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
REQUIREMENTS:
- ANSWER BOOK
- Drawing instruments
- A non-programmable pocket calculator
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION:
- This question paper consists of SIX questions: TWO questions are generic and FOUR questions are subject specific.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Answer each question as a whole. Do NOT separate subsections of questions.
- Start the answer to EACH question on a NEW page.
- Do NOT write in the margins of the ANSWER BOOK.
- You may use sketches to illustrate your answers.
- Write ALL calculations and answers in the ANSWER BOOK or on the attached ANSWER SHEETS.
- Use the mark allocation as a guide to the length of your answers.
- Make drawings and sketches in pencil, fully dimensioned and neatly finished off with descriptive titles and notes to conform to the SANS/SABS Code of Practice for Building Drawings.
- For the purpose of this question paper, the size of a brick should be taken as 220 mm x 110 mm x 75 mm.
- Use your own discretion where dimensions and/or details have been omitted.
- Answer QUESTIONS 2.1, 3.3 and 5.2 on the attached ANSWER SHEETS using drawing instruments where necessary.
- Write your NAME and SURNAME on every ANSWER SHEET and hand them in with your ANSWER BOOK, whether you have used them or not.
- Drawings in the question paper are NOT to scale due to electronic transfer.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: SAFETY AND MATERIALS (GENERIC)
Start this question on a new PAGE.
1.1 Choose the correct requirements regarding scaffolding.
1.1.1 It must have a safety factor of at least 2 / 4. (1)
1.1.2 The width of the wooden solid scaffold platforms is at least 114 mm / 228 mm.(1)
1.1.3 Guard rails must be at least 750 mm / 900 mm in height. (1)
1.1.4 Toe-boards must be at least 150 mm / 1500 mm high. (1)
1.1.5 Platforms must be covered with a non-slip layer / rust free layer. (1)
1.2 Briefly motivate why suspended scaffolding should be as near as possible to the structure were work is being done.(1)
1.3 Identify below THREE regulations for handling hazardous chemical substances as they apply to the supplier providing these chemicals to somebody else.
1.3.1 First aid measures must be indicated.
1.3.2 Origin of the containers must be indicated.
1.3.3 Emergency contact numbers must be indicated.
1.3.4 Fire-fighting measures must be indicated.
1.3.5 Transport routes must be indicated.
1.3.6 Storage instructions must be indicated. (3 x 1) (3)
1.4 What is the minimum and maximum slope of stairs during the construction process?(2)
1.5 Briefly motivate why aluminium ladders must never be used close to electrical wires.(2)
1.6 Describe the difference between a water-based paint and an oil-based paint on a finished surface.(2)
1.7 Name THREE advantages of the curing process of concrete. (3 x 1) (3)
1.8 Describe the process of powder coating. (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS, JOINING AND EQUIPMENT (GENERIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 Answer the following questions with regard to the site plan on ANSWER SHEET A.
2.1.1 Identify TEN details according to the checklist that are not indicated on the plan. (10 x 1) (10)
2.1.2 Identify SIX details that are incorrectly indicated on the elevation. (6 x 1) (6)
2.2 Make neat sketches to illustrate the following drawing symbols:
2.2.1 Undisturbed earth (2)
2.2.2 Plaster (2)
2.2.3 Ramp with slope of 1 : 5 (2)
2.2.4 Electricity meter (2)
2.2.5 Sink unit – double (2)
2.3 Identify the material illustrated by the following drawing symbols:
2.3.1 ![]() (1)
(1)
2.3.2 ![]() (1)
(1)
2.4 Briefly explain the advantages of the square shoulder screw. (2)
2.5 What is the purpose of the nylon inserts in some nuts? (1)
2.6 What is the screw gauge for an M6/18 Rawl bolt that needs to be drilled? (1)
2.7 FIGURE 2.7 shows the reading of a dumpy level on a telescopic staff. Answer the following questions with regard to the reading.
FIGURE 2.7
2.7.1 What is the height reading in FIGURE 2.7? (1)
2.7.2 Determine the distance from the dumpy level to the staff according to the reading in FIGURE 2.7. Show all the calculations. (3)
2.7.3 What is the minimum and maximum distance that could be determined accurately by the dumpy level? (2)
2.8 Briefly motivate why labels and metal plates should be removed from the multi-detector before using the instrument. (1)
2.9 Which precaution must be taken when a multi-detector has not been used for a long period? (1)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION A: 60
QUESTION 3:
CASEMENTS, CUPBOARDS, WALL-PANELLING AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions by choosing a word/term from the list below. Write only the word/term next to the question numbers (3.1.1–3.1.3) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example. 3.1.4 fanlight.
| stuck mould; rebate; 16 mm; skirting; 15 mm |
3.1.1 The thickness of melamine used for cupboard doors (1)
3.1.2 A mould that is moulded onto a piece of timber (1)
3.1.3 A groove or recess in wood to accommodate a panel, pane, etc. (1)
3.2 FIGURE 3.2 below shows a vertical section through a certain part of a double casement window with a fanlight. Study the picture and answer the questions that follow.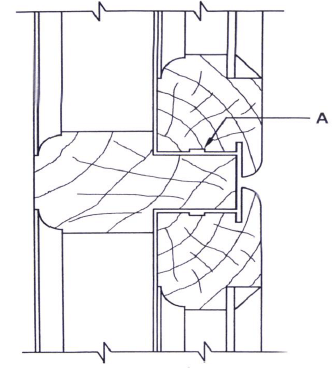
FIGURE 3.2
3.2.1 Identify A. (1)
3.2.2 Name THREE timber parts of the casement and frame. (3)
3.2.3 What is the purpose/function of a fanlight in a double casement? (1)
3.3 Use ANSWER SHEET B and draw, in good proportion, a neat sketch of a vertical section through the top part of a wall panel that ends halfway between the ceiling and the floor.
Use the assessment criteria on the ANSWER SHEET as a guide. (5)
3.4 FIGURE 3.4 below shows the inside of a built-in cupboard without doors. Study the drawing and answer the questions that will follow.
FIGURE 3.3
3.4.1 A well-designed cupboard should consist of four main parts/units. Name the parts/units A to D in the drawing above. (4)
3.4.2 Give a reason for using melamine rather than plain chipboard for the inside of a built-in cupboard. (1)
3.4.3 Identify parts E to H. (4)
3.5 What is the window above the opening of a door or window of a building called? (1)
3.6 FIGURE 3.6 below shows the sectional view of a tongue and groove wall panel from the floor to the ceiling, joined to a 110 mm brick wall. Study the drawing and answer the questions that follow.
FIGURE 3.6
3.6.1 Identify parts A to C. (3)
3.6.2 Identify TWO reasons for panelling a wall. (2)
3.7 Define a casement window. (2)
[30]
QUESTION 4: ROOFS, CEILINGS, TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT AND MATERIALS (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 FIGURE 4.1 below shows two woodworking machines. Study the pictures and answer the questions that follow.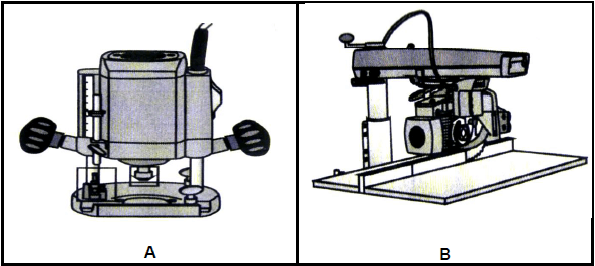
FIGURE 4.1
4.1.1 Identify A and B. (2)
4.1.2 Describe TWO aspects that must be considered when taking care of machine B. (2)
4.1.3 Describe TWO safety aspects that one would check before switching on machine A. (2)
4.2 Name TWO parts of a conventional trap door. (2)
4.3 Describe the first THREE steps that need to be considered when preparing timber before applying preservatives. (3)
4.4 Differentiate between hurricane clips and storm clips regarding the specific roof members that they will secure. (2)
4.5 State TWO properties that are tested in both mechanical and visual grading. (2)
4.6 Name the differences between the following members of a roof:
- King post
- Brandering
- Roof sheeting (3)
4.7 Describe TWO safety aspects of a belt sander. (2)
4.8 FIGURE 4.8 below shows a sectional view through the construction of a trap door. Study the picture below and answer the questions that follow.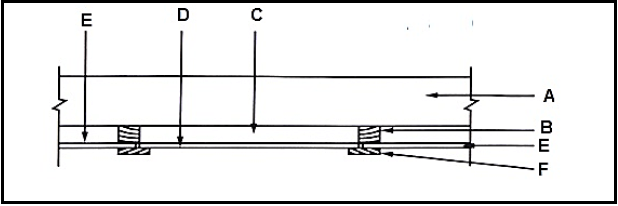
FIGURE 4.8
4.8.1 Identify parts A to E. (5)
4.8.2 Explain the function of part F. (2)
4.8.3 Illustrate by using a hand drawing ONE alternative way of making a trap door. (3)
4.9 FIGURE 4.9 below shows a pictorial view of a roof with a hipped end and a gable end with valley. The roof will be covered with corrugated iron sheeting. Study FIGURE 4.9 and answer the questions that follow.
FIGURE 4.9
4.9.1 Identify members A to F. (6)
4.9.2 What are the breadth and thickness of part B in mm? (2)
4.10 Explain TWO characteristics of a good roof covering. (2)
[40]
QUESTION 5: CENTRING, FORMWORK, SHORING AND GRAPHICS AS MEANS OF COMMUNICATION (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
5.1 Name the material that can be used for the sides of the formwork for a square column. (1)
5.2 Use ANSWER SHEET B and draw to scale 1 : 2 an assembled isometric view of a through haunched mortise/tap and tenon joint to join a stile and a top rail. The timber used is 60 mm wide and 20 mm thick.
Start the drawing from the given corner on ANSWER SHEET C.
Do NOT show hidden details.
Use the assessment criteria on the ANSWER SHEET as a guide. (6)
5.3 Explain the function of the following:
5.3.1 Double-flying shore (1)
5.3.2 Dead shore (1)
5.4 Describe the function of the following components of a dead shore:
5.4.1 Steel dog (1)
5.4.2 Sole plate (1)
5.4.3 Prop/Strut (1)
5.5 FIGURE 5.5 below shows a vertical sectional view through formwork for two concrete beams. Study FIGURE 5.5 and answer the questions that follow.
FIGURE 5.5
5.5.1 Identify parts A to D. (4)
5.5.2 Explain the purpose of folding wedges during the construction of formwork. (4)
5.6 Draw in your ANSWER BOOK, in good proportion, a centre for a semicircular arch that will be built over a door opening. Label any TWO parts on the drawing. (6)
5.7 Briefly explain TWO purposes of wedges during the construction of centering. (2)
5.8 Name TWO electrical tools that you could use to cut folding wedges to size. (2)
[30]
QUESTION 6: SUSPENDED FLOORS, STAIRCASES, IRONMONGERY, DOORS AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
6.1 Explain the purpose of the landing in a staircase. (2)
6.2 Draw in your ANSWER BOOK, in good proportion, a neat line diagram of a staircase. (5)
6.3 Name TWO places where a straight cupboard lock can be used. (2)
6.4 Name a lock that is mounted onto the internal surface of doors to provide extra security. (1)
6.5 Draw in your ANSWER BOOK, in good proportion, a horizontal section through a muntin and raised panels of a three-panel door. (6)
6.6 Explain the purpose of opening A in FIGURE 6.6 below. (1)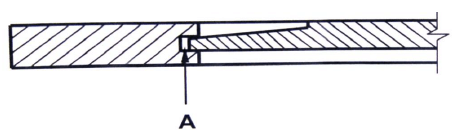
FIGURE 6.6
6.7 Study FIGURE 6.7 below which shows the inside bottom corner of a framed ledge and braced door.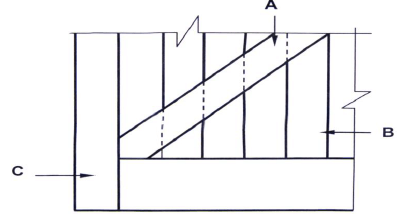
FIGURE 6.7
6.7.1 Identify members A to C. (3)
6.7.2 What is the purpose of the two braces on the door? (1)
6.7.3 Give a reason why stub mortise and tenon joints are preferred on the frame members of the door. (1)
6.8 Draw in your ANSWER BOOK, in good proportion, two horizontal sectional views to show the difference between a door frame and a jamb lining fixed to a wall. Print the title below ONE of these drawings. (6)
6.9 FIGURE 6.9 shows the construction detail of a suspended floor.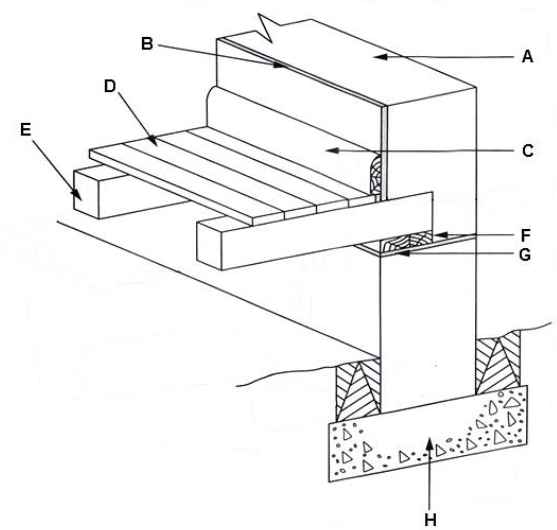
FIGURE 6.9
6.9.1 Name parts A to H. (8)
6.9.2 Briefly motivate the use of part C. (1)
6.9.3 Briefly explain how to determine the size of the floor joistS in suspended floors. (3)
[40]
TOTAL: 200
ANSWER SHEET A
2.1 Answer the following questions with regard to the site plan on ANSWER SHEET A:
2.1.1 Identify TEN details according to the checklist that are not indicated on the plan. (10)
2.1.2 Identify SIX details that are incorrectly indicated on the elevation. (6)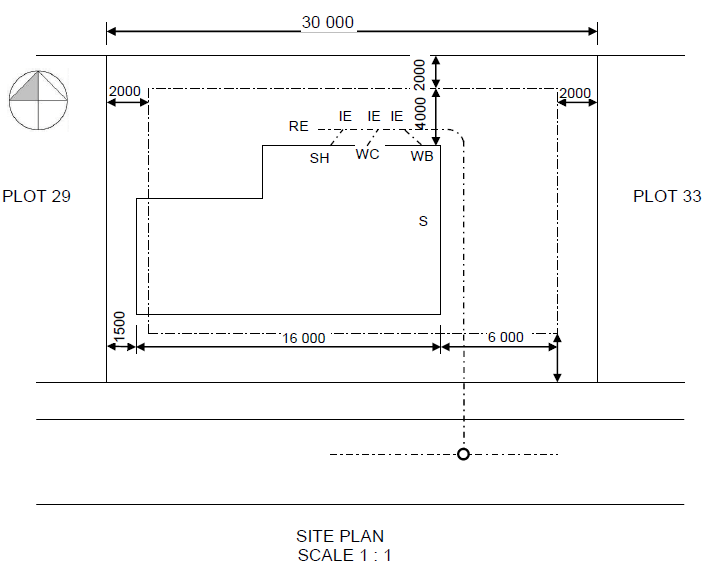
ANSWER SHEET B
ANSWER SHEET 3.3
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE’S MARK |
Wall | 1 | |
Capping | 1 | |
Rough ground | 1 | |
Tongue and groove board | 1 | |
Correctness of drawing | 1 | |
TOTAL: | 5 |
ANSWER SHEET C
ANSWER SHEET 5.2
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE’S MARK |
Stile | 1 | |
Top rail | 1 | |
Mortise | 1 | |
Haunch | 2 | |
Application of scale | 1 | |
TOTAL: | 6 |
Civil Technology: Civil Services Grade 12 Questions - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
REQUIREMENTS:
- ANSWER BOOK
- Drawing instruments
- A non-programmable pocket calculator
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions: TWO questions are generic and FOUR questions are subject specific.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Answer each question as a whole. Do NOT separate subsections of questions.
- Start the answer to EACH question on a NEW page.
- Do NOT write in the margins of the ANSWER BOOK.
- You may use sketches to illustrate your answers.
- Write ALL calculations and answers in the ANSWER BOOK or on the attached ANSWER SHEETS.
- Use the mark allocation as a guide to the length of your answers.
- Make drawings and sketches in pencil, fully dimensioned and neatly finished off with descriptive titles and notes to conform to the SANS/SABS Code of Practice for Building Drawings.
- For the purpose of this question paper, the size of a brick should be taken as 220 mm x 110 mm x 75 mm.
- Use your own discretion where dimensions and/or details have been omitted.
- Answer QUESTIONS 2.1, 3.9, 4.2 and 6.3 on the attached ANSWER SHEETS using drawing instruments where necessary.
- Write your NAME and SURNAME on every ANSWER SHEET and hand them in with your ANSWER BOOK, whether you have used them or not.
- Drawings in the question paper are NOT to scale due to electronic transfer.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: SAFETY AND MATERIALS (GENERIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
1.1 Choose the correct requirements regarding scaffolding.
1.1.1 It must have a safety factor of at least 2 / 4. (1)
1.1.2 The width of the wooden solid scaffold platforms is at least 114 mm / 228 mm. (1)
1.1.3 Guard rails must be at least 750 mm / 900 mm in height. (1)
1.1.4 Toe-boards must be at least 150 mm / 1 500 mm high. (1)
1.1.5 Platforms must be covered with a non-slip layer / rust-free layer. (1)
1.2 Briefly motivate why suspended scaffolding should be as near as possible to the structure where work is being done. (1)
1.3 Identify below THREE regulations for handling hazardous chemical substances as they apply to the supplier providing these chemicals to somebody else.
1.3.1 First-aid measures must be indicated.
1.3.2 Origin of the containers must be indicated.
1.3.3 Emergency contact numbers must be indicated.
1.3.4 Fire-fighting measures must be indicated.
1.3.5 Transport routes must be indicated.
1.3.6 Storage instructions must be indicated. (3 x 1) (3)
1.4 What is the minimum and maximum slope of stairs during the construction process? (2)
1.5 Briefly motivate why aluminium ladders must never be used close to electrical wires. (2)
1.6 Describe the difference between a water-based paint and an oil-based paint on a finished surface. (2)
1.7 Name THREE advantages of the curing process of concrete. (3 x 1) (3)
1.8 Briefly describe the process of powder coating. (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS, JOINING AND EQUIPMENT (GENERIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 Answer the following questions with regard to the site plan on ANSWER SHEET A.
2.1.1 Identify TEN details according to the checklist that are not indicated on the plan. (10 x 1) (10)
2.1.2 Identify SIX details that are incorrectly indicated on the elevation. (6 x 1) (6)
2.2 Make neat sketches of the following drawing symbols:
2.2.1 Undisturbed earth (2)
2.2.2 Plaster (2)
2.2.3 Ramp with slope of 1 : 5 (2)
2.2.4 Electricity meter (2)
2.2.5 Sink unit – double (2)
2.3 Identify the material illustrated by the following drawing symbols:
2.3.1 ![]() (1)
(1)
2.3.2 ![]() (1)
(1)
2.4 Briefly explain the advantage of the square shoulder screw. (2)
2.5 What is the purpose of the nylon inserts in some nuts? (1)
2.6 What is the screw gauge for an M6/18 Rawl bolt that needs to be drilled? (1)
2.7 FIGURE 2.7 shows the reading of a dumpy level on a telescopic staff. Answer the following questions with regard to the reading.
FIGURE 2.7
2.7.1 What is the height reading in FIGURE 2.7? (1)
2.7.2 Determine the distance from the dumpy level to the staff according to the reading in FIGURE 2.7. Show all the calculations. (3)
2.7.3 What are the minimum and maximum distances that could be determined accurately by the dumpy level? (2)
2.8 Briefly motivate why labels and metal plates should be removed from the multi-detector before using the instrument. (1)
2.9 Which precaution must be taken when a multi-detector has not been used for a long period? (1)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION A: 60
QUESTION 3: SAFETY, MATERIAL AND CONSTRUCTION (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 What personal protective equipment must be worn when workers enter manholes where dangerous gases may be encountered? (1)
3.2 Describe the following safety requirements which must be applied to the safeguarding of openings in construction work:
3.2.1 Stairs and floors without railings (1)
3.2.2 When working in windy conditions on upper levels (1)
3.3 Explain the use of a safety net when construction work must be done. (2)
3.4 Who is responsible for implementing the safety plan on a construction site? (1)
3.5 How is dezincification in brass objects identified? (1)
3.6 Through what process does dezincification takes place? (1)
3.7 Briefly describe what galvanic corrosion is. (2)
3.8 Name THREE methods to prevent corrosion in metals. (3 x 1) (3)
3.9 FIGURE 3.9 on ANSWER SHEET B shows layer 1 of a combination corner of a half-brick wall in stretcher bond. Draw the alternative layer of the half- brick wall on scale 1 : 10 on ANSWER SHEET B. (10)
3.10 Explain the construction and purpose of the benching in a manhole. (3)
3.11 What is the purpose of step iron units in a manhole? (1)
3.12 At what gradient are Ø 100 mm drain pipes laid? (1)
3.13 Briefly motivate why surface water must be diverted away from drain trench excavations. (2)
[30]
QUESTION 4: COLD-WATER SUPPLY, HOT-WATER SUPPLY AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 Identify the type of valve that meets each of the following requirements.
4.1.1 It is installed at water meters and allows water to flow in one direction only. (1)
4.1.2 It has no washer; it is opened and closed by a wheel. (1)
4.1.3 It regulates the water level in cisterns. (1)
4.1.4 It is fitted with a hinged lock valve. (1)
4.2 FIGURE 4.2 on ANSWER SHEET B shows a bibcock with three missing parts. Use the sketch on ANSWER SHEET B and draw the three missing parts. Supply labels to identify the three parts. (6)
4.3 Fully describe what red water in a water supply system is. (3)
4.4 Briefly describe the purpose of a red water diverter in a water supply system. (2)
4.5 Name TWO requirements which the cut on copper pipes must comply with when it is cut with a pipe cutter. (2 x 1) (2)
4.6 Answer the following questions with regard to the pipe coupling in FIGURE 4.6.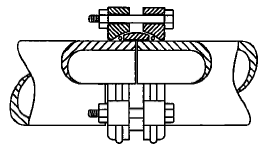
FIGURE 4.6
4.6.1 What is the coupling in FIGURE 4.6 called? (1)
4.6.2 Which type of pipe is joined by means of this type of coupling? (1)
4.7 What is the purpose of the anode in a high-pressure geyser? (1)
4.8 Indicate if the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Write only ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the question numbers in the ANSWER BOOK.
4.8.1 A shut-off valve is installed to the hot-water outlet of the high-pressure geyser. (1)
4.8.2 The hot-water pipes leading out of the geyser must be suitable to withstand water temperatures of up to 70°. (1)
4.8.3 A 200-litre geyser should not be wall-mounted. (1)
4.8.4 An electric isolator switch should be installed at least 1 metre from the geyser. (1)
4.8.5 The heating element of any water heater must be positioned close to the top of the container. (1)
4.9 Answer the following questions with regard to the solar geyser in FIGURE 4.9.
FIGURE 4.9
4.9.1 Name parts A to C. (3)
4.9.2 Explain how the water pressure in the system is determined by referring to water supply principles. (4)
4.10 What is the maximum water temperature which should be supplied by geysers? (1)
4.11 Name THREE advantages of a heat pump. (3 x 1) (3)
4.12 Which tool is used to identify leakages in drainage pipes? (1)
4.13 Name any THREE maintenance measures for drain-cleaning rods. (3 x 1) (3)
[40]
QUESTION 5: DRAINAGE AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
5.1 Answer the following questions with regard to the wastewater fittings in FIGURES 5.1.A and 5.1.B.
 | |
| FIGURE 5.1. A | FIGURE 5.1. B |
5.1.1 In which section sizes are these types of pipes available? (2)
5.1.2 At which angle is part 5.1.A manufactured? (1)
5.1.3 At which angle is part 5.1.B manufactured? (1)
5.1.4 What is part 5.1.C called? (1)
5.1.5 Briefly explain the purpose of part 5.1.C. (2)
5.2 Make a neat sketch to illustrate the shape of a P-trap. Also indicate the water level of the water lock in the trap. (3)
5.3 Name and describe the system which has the purpose of preventing the siphonic action from breaking the water seal in the traps of the drainage system. (4)
5.4 Indicate if the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Write only ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the question numbers in the ANSWER BOOK.
5.4.1 A water closet must be connected to a gully. (1)
5.4.2 The purpose of a gully is to prevent blockages. (1)
5.4.3 A gully is equipped with a trap. (1)
5.4.4 Sewer pipes should be at least 80 mm in diameter. (1)
5.5 Name TWO disadvantages of cast iron pipes. (2 x 1) (2)
5.6 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–F) next to the question numbers (5.6.1–5.6.4) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 5.6.5 G.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
5.6.1 | Inspection chamber | A | installed where the drainage excavation has a steep gradient |
5.6.2 | Manhole | B | its purpose is to treat sewage |
5.6.3 | Ramp | C | not deeper than 750 mm |
5.6.4 | Septic tank | D | serves as a water lock |
E | used to clean water-supply pipes | ||
F | deeper than 750 mm | ||
(4 x 1) (4)
5.7 Briefly explain why stormwater should not be channelled into a French drain. (2)
5.8 Make neat sketches to illustrate the following symbols:
5.8.1 Gully (2)
5.8.2 Urinal (2)
5.8.3 Invert level (2)
5.9 FIGURE 5.9 shows an isometric line diagram of the cold-water supply on scale 1 : 100 from the water meter to a building. The main cold-water pipe has a diameter of 22 mm and the branch pipes a diameter of 15 mm. Study the drawing and determine the following quantities that are needed to complete the installation.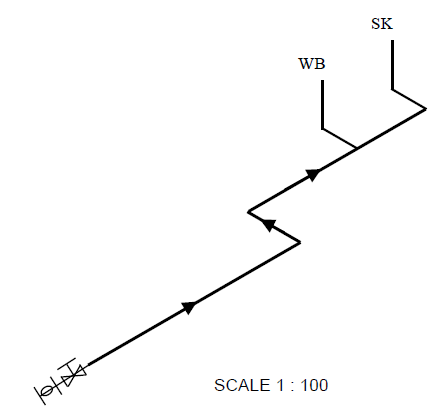
FIGURE 5.9
5.9.1 The length of a 22 mm cold-water pipe (1)
5.9.2 The length of a 15 mm cold-water pipe (1)
5.9.3 22 mm 90° elbow (1)
5.9.4 22 x 15 mm 90° reducing elbow (1)
5.9.5 15 mm 90° elbow (1)
5.9.6 22 x 22 x 15 mm reducing tee (1)
5.10 A cylindrical water supply tank is 2 200 mm high and has a diameter of 1 800 mm. Determine the volume of the tank in m³.
(Show all calculations and formulae.) (2)
[40]
QUESTION 6: GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION, ROOF WORK, STORM WATER AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
6.1 Which colour codes are used to indicate the following drainage installations on a plan?
6.1.1 Soil pipes (1)
6.1.2 Storm-water drains (1)
6.1.3 All existing drains (1)
6.2 Identify the following abbreviations of drainage systems:
6.2.1 VP (1)
6.2.2 IO / IE (1)
6.2.3 IL (1)
6.2.4 NGV / NGL (1)
6.3 FIGURE 6.3 on ANSWER SHEET C shows the top and front elevation of a pyramid with a square base. Draw the development of the pyramid according to the radial-line method on ANSWER SHEET C. Show all construction lines. (10)
6.4 Answer the following questions with regard to the gutter system in FIGURE 6.4.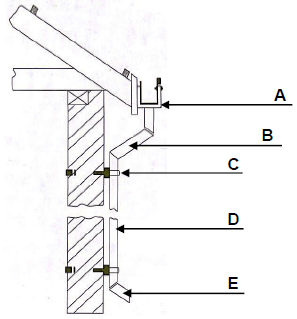
FIGURE 6.4
6.4.1 Name parts A to E. (5)
6.4.2 At what angle is the gutter installed? (1)
6.5 Briefly motivate why surface channels for storm water are manufactured of reinforced concrete. (2)
6.6 Why must storm-water openings be covered with a grill? (1)
6.7 What is the minimum distance from a building that storm-water soakaways must be constructed? (1)
6.8 Answer the following questions with regard to the fixer in FIGURE 6.8.
FIGURE 6.8
6.8.1 What is this type of fixer called? (1)
6.8.2 Name TWO uses of the fixer. (2 x 1) (2)
[30]
TOTAL: 200
ANSWER SHEET A
2.1 Answer the following questions with regard to the site plan on ANSWER SHEET A.
2.1.1 Identify TEN details according to the checklist that are not indicated on the plan.(10)
2.1.2 Identify SIX details that are incorrectly indicated on the elevation. (6)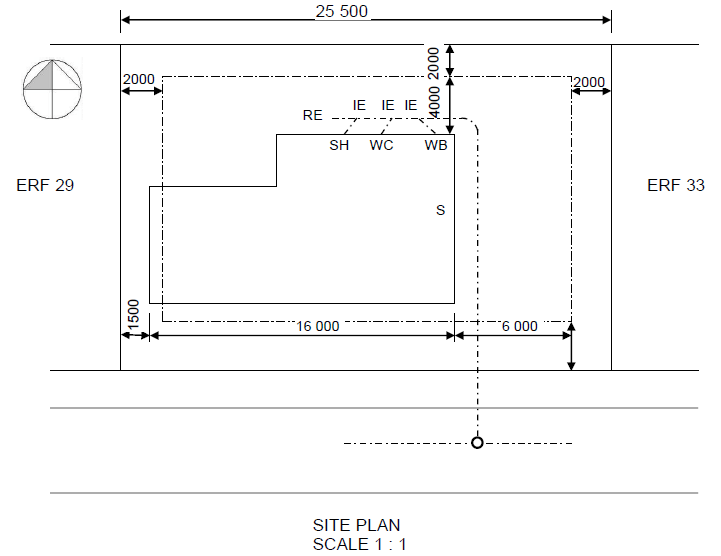
ANSWER SHEET B
3.9 FIGURE 3.9 on ANSWER SHEET B shows layer 1 of a combination corner of a half-brick wall in stretcher bond. Draw the alternative layer of the half-
brick wall on scale 1 : 10 on ANSWER SHEET B. (10)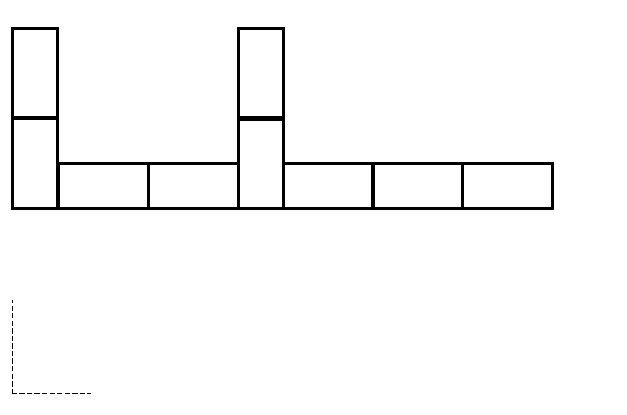
Brickwork | 8 | |
Application of scale | 2 | |
TOTAL: | 10 |
4.2 FIGURE 4.2 on ANSWER SHEET B shows a bibcock with three missing parts.
Use the sketch on ANSWER SHEET B and draw the three missing parts. Supply labels to identify the three parts. (6)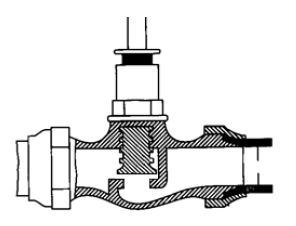
Parts | 3 | |
Labels | 3 | |
TOTAL: | 6 |
ANSWER SHEET C
6.3 FIGURE 6.3 on ANSWER SHEET C shows the top and front elevation of a pyramid with a square base. Draw the development of the pyramid according
to the radial-line method on ANSWER SHEET C. Show all construction lines. (10)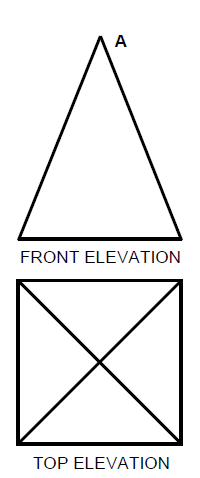
Arcs 1, 2, 3 and 4 | 1 | |
Seam lines A1 to A4 | 5 | |
Base lines 1–4 | 4 | |
TOTAL: | 10 |
Civil Technology: Construction Grade 12 Questions - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
REQUIREMENTS:
- ANSWER BOOK
- Drawing instruments
- A non-programmable pocket calculator
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions: TWO questions are generic and FOUR questions are subject specific.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Answer each question as a whole. Do NOT separate subsections of questions.
- Start the answer to EACH question on a NEW page.
- Do NOT write in the margins of the ANSWER BOOK.
- You may use sketches to illustrate your answers.
- Write ALL calculations and answers in the ANSWER BOOK or on the attached ANSWER SHEETS.
- Use the mark allocation as a guide to the length of your answers.
- Make drawings and sketches in pencil, fully dimensioned and neatly finished off with descriptive titles and notes to conform to the SANS/SABS Code of Practice for Building Drawings.
- For the purpose of this question paper, the size of a brick should be taken as 220 mm x 110 mm x 75 mm.
- Use your own discretion where dimensions and/or details have been omitted.
- Answer QUESTIONS 2.1 and 5.3 on the attached ANSWER SHEETS using drawing instruments where necessary.
- Write your NAME and SURNAME on every ANSWER SHEET and hand them in with your ANSWER BOOK, whether you have used them or not.
- Drawings in the question paper are NOT to scale due to electronic transfer.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: SAFETY AND MATERIALS (GENERIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
1.1 Choose the correct requirements regarding scaffolding.
1.1.1 It must have a safety factor of at least 2 / 4. (1)
1.1.2 The width of the wooden solid scaffold platforms is at least 114 mm / 228 mm. (1)
1.1.3 Guard rails must be at least 750 mm / 900 mm in height. (1)
1.1.4 Toe-boards must be at least 150 mm / 1 500 mm high. (1)
1.1.5 Platforms must be covered with a non-slip layer / rust-free layer. (1)
1.2 Briefly motivate why suspended scaffolding should be as near as possible to the structure where work is being done.(1)
1.3 Identify below THREE regulations for handling hazardous chemical substances as they apply to the supplier providing these chemicals to somebody else.
1.3.1 First-aid measures must be indicated.
1.3.2 Origin of the containers must be indicated.
1.3.3 Emergency contact numbers must be indicated.
1.3.4 Fire-fighting measures must be indicated.
1.3.5 Transport routes must be indicated.
1.3.6 Storage instructions must be indicated. (3 x 1) (3)
1.4 What is the minimum and maximum slope of stairs during the construction process?(2)
1.5 Briefly motivate why aluminium ladders must never be used close to electrical wires. (2)
1.6 Describe the difference between a water-based paint and an oil-based paint on a finished surface.(2)
1.7 Name THREE advantages of the curing process of concrete. (3 x 1) (3)
1.8 Briefly describe the process of powder coating. (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS, JOINING AND EQUIPMENT (GENERIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 Answer the following questions with regard to the site plan on ANSWER SHEET A.
2.1.1 Identify TEN details according to the checklist that are not indicated on the plan. (10 x 1) (10)
2.1.2 Identify SIX details that are incorrectly indicated on the elevation. (6 x 1) (6)
2.2 Make neat sketches of the following drawing symbols:
2.2.1 Undisturbed earth (2)
2.2.2 Plaster (2)
2.2.3 Ramp with slope of 1 : 5 (2)
2.2.4 Electricity meter (2)
2.2.5 Sink unit – double (2)
2.3 Identify the material illustrated by the following drawing symbols:
2.3.1 ![]() (1)
(1)
2.3.2 ![]() (1)
(1)
2.4 Briefly explain the advantage of the square shoulder screw. (2)
2.5 What is the purpose of the nylon inserts in some nuts? (1)
2.6 What is the screw gauge for an M6/18 Rawl bolt that needs to be drilled? (1)
2.7 FIGURE 2.7 shows the reading of a dumpy level on a telescopic staff. Answer the following questions with regard to the reading.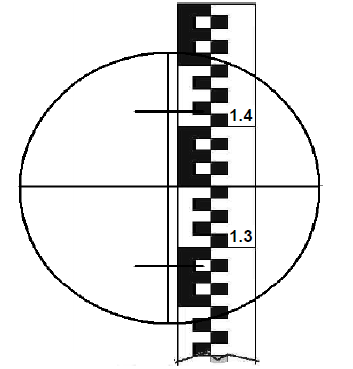
FIGURE 2.7
2.7.1 What is the height reading in FIGURE 2.7? (1)
2.7.2 Determine the distance from the dumpy level to the staff according to the reading in FIGURE 2.7. Show all the calculations. (3)
2.7.3 What are the minimum and maximum distances that could be determined accurately by the dumpy level? (2)
2.8 Briefly motivate why labels and metal plates should be removed from the multi- detector before using the instrument. (1)
2.9 What precaution must be taken when a multi-detector has not been used for a long period? (1)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION A: 60
QUESTION 3: ROOFS AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 Name FOUR different types of roofs or roof trusses. (4 x 1) (4)
3.2 Name FOUR advantages of using roof underlays. (4 x 1) (4)
3.3 Answer the following questions on the roof truss construction in FIGURE 3.3.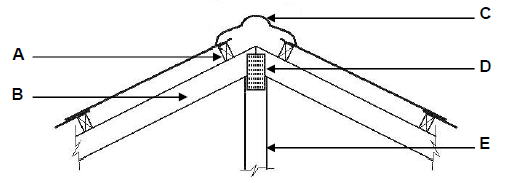
FIGURE 3.3
3.3.1 Name parts A to E. (5 x 1) (5)
3.3.2 What are the measurements (sizes) of parts B and E? (2 x 1) (2)
3.3.3 What is the purpose (function) of part D? (1)
3.4 Answer the following questions with regard to roofs.
3.4.1 On what type of roofing must the steel wire be embedded in the wall for at least 300 mm to anchor the roof truss? (1)
3.4.2 What type of roof must be constructed at least 4,5 m away from any boundary or neighbouring structures? (1)
3.4.3 What type of roof is the most economical? (1)
3.5 Identify the following statements as TRUE or FALSE.
3.5.1 Workers may not work on a roof in rainy conditions. (1)
3.5.2 Mono-pitched roofs slope in two directions. (1)
3.5.3 All joining materials must be resistant to rust. (1)
3.5.4 Steel sheet roofing requires a pitch of 30⁰. (1)
3.6 Answer the following questions with regard to the construction in FIGURE 3.6.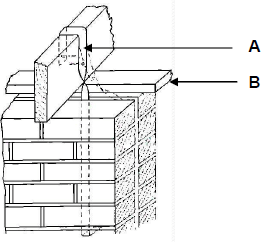
FIGURE 3.6
3.6.1 What is joined together in FIGURE 3.6? (1)
3.6.2 Name parts A and B. (2 x 1) (2)
3.6.3 If roof sheeting is used, what is the minimum depth that part A should be built into the wall? (1)
3.6.4 How should part A be fixed to the beam? (1)
3.7 Name TWO types of cast-in anchors. (2 x 1) (2)
[30]
QUESTION 4: MATERIAL, EQUIPMENT AND TOOLS, EXCAVATIONS (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–H) next to the question numbers (4.1.1–4.1.6) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 4.1.7 K.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
4.1.1 | Cast iron | A | highly toxic |
4.1.2 | Boom pump | B | alloy of steel and tin |
4.1.3 | Brass | C | pumps small volume of concrete |
4.1.4 | Line pipe concrete pump | D | hard, but brittle and breaks easily |
4.1.5 | Lead | E | packaging material |
4.1.6 | Polystyrene | F | dipped in molten zinc |
G | alloy of copper and zinc | ||
H | pumps high volume of concrete | ||
4.2 Answer the following questions with regards to the test in Figure 4.2
FIGURE 4.2
4.3 Name TWO ways of curing concrete. (2 x 1) (2)
4.4 Name the TWO main groups into which metals can be classified. (2 x 1) (2)
4.5 Name THREE types of material that can be used for the cladding of buildings. (3 x 1) (3)
4.6 Answer the following questions on the construction machine in FIGURE 4.6.
FIGURE 4.6
4.6.1 Identify the type of machine. (1)
4.6.2 Name THREE ways of maintaining the machine. (3 x 1) (3)
4.6.3 Why should the operator use both hands on this machine when using it? (1)
4.7 Name FOUR causes for the collapse of an excavation. (4 x 1) (4)
4.8 Name THREE ways of making excavations safe during the night. (3 x 1) (3)
4.9 Explain the safety regulations for the following during excavations:
4.9.1 Access to a deep excavation (1)
4.9.2 The distance of machinery away from trenches (1)
4.9.3 Testing for atmospheric hazards for trenches deeper than 1,3 m (1)
4.10 Identify the following statements as TRUE or FALSE.
4.10.1 Bracing is necessary for trenches deeper than one metre. (1)
4.10.2 Shoring is not compulsory where the banks are sloped. (1)
4.10.3 Excavated material must be two metres from trench edges. (1)
4.11 Answer the following questions with regard to the shuttering in FIGURE 4.11.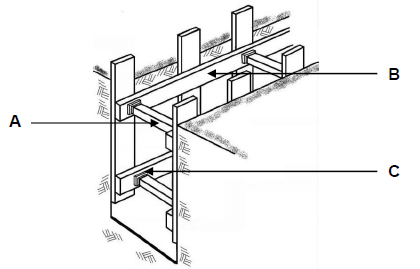
FIGURE 4.11
4.11.1 Identify the type of soil in FIGURE 4.11. (1)
4.11.2 Name parts A to C. (3 x 1) (3)
[40]
QUESTION 5: BRICKWORK AND GRAPHICS (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
5.1 Answer the following questions on the wall construction in FIGURE 5.1.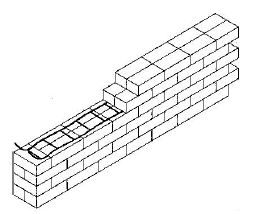
FIGURE 5.1
5.1.1 Identify the type of wall construction. (1)
5.1.2 What is the width of the wall? (1)
5.1.3 In what type of bond has this wall been built? (1)
5.2 Name THREE advantages of cavity walls. (3 x 1) (3)
5.3 Draw in the damp-proof course (DPC) on ANSWER SHEET B. (5 x 1) (5)
5.4 Answer the following questions with regard to cavity walls.
5.4.1 What is the minimum space between the two skins (walls)? (1)
5.4.2 What is the maximum length of a cavity wall? (1)
5.4.3 What is the purpose of inspection holes? (1)
5.4.4 What connects the two skins? (1)
5.4.5 What is the purpose of the weep holes? (1)
5.5 Identify the type of wall tie in FIGURE 5.5. (1)
FIGURE 5.5
5.6 Answer the questions with regard to the construction in FIGURE 5.6.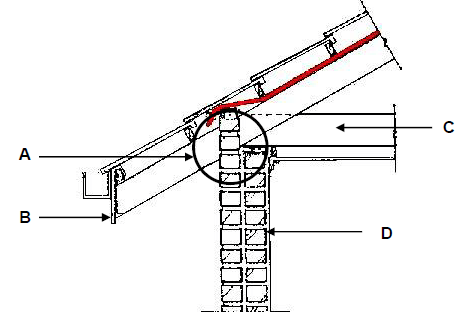
FIGURE 5.6
5.6.1 Name parts A to D. (4 x 1) (4)
5.6.2 Is this an open or closed eave construction? (1)
5.7 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–F) next to the question numbers (5.7.1–5.7.4) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 5.7.5 G.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | |
Subbase | A | natural soil on which the paving will be laid |
Kerb | B | sand used as grouting between paving blocks |
Subgrade | C | best edge restraint for paving |
Bedding sand | D | final layer upon which paving is laid |
E | preparation of the subbase | |
F | prepared layer beneath paving and bedding | |
sand |
(4 x 1) (4)
5.8 Name TWO advantages of mortar-set paving. (2 x 1) (2)
5.9 Name TWO reasons for construction failure of paving. (2 x 1) (2)
5.10 Draw a neat sketch with EIGHT (8) bricks of the basket-weave paving pattern in the ANSWER BOOK. (5)
5.11 Answer the following questions on the arch structure in FIGURE 5.11.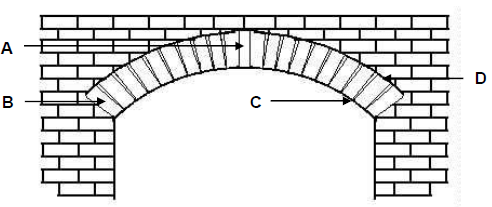
FIGURE 5.11
5.11.1 Identify the type of arch. (1)
5.11.2 Name parts A to D. (4 x 1) (4)
[40]
QUESTION 6: FORMWORK, REINFORCEMENT, FOUNDATIONS, CONCRETE FLOORS AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
6.1 What is the meaning of the term in-situ concrete? (1)
6.2 Name THREE properties of good formwork. (3 x 1) (3)
6.3 Answer the following questions with regard to the formwork in FIGURE 6.3.
FIGURE 6.3
6.3.1 Name parts A to E. (5 x 1) (5)
6.3.2 Is this formwork used for a column or a beam? (1)
6.4 Answer the following questions with regard to the bar code in FIGURE 6.4.
FIGURE 6.4
6.4.1 What type of steel is used? (1)
6.4.2 What is the spacing of the bars? (1)
6.4.3 What is the diameter of the bars? (1)
6.5 Which forces withstand the following parts of a concrete beam?
6.5.1 Main bar (1)
6.5.2 Stirrups (1)
6.6 Name THREE properties (requirements) of reinforced steel bars. (3 x 1) (3)
6.7 Name TWO types of pile foundations. (2 x 1) (2)
6.8 Name TWO reasons for using pile foundations. (2 x 1) (2)
6.9 FIGURE 6.9 shows the inside measurements of the foundation strips for a storeroom.
The foundation is 750 mm wide and 250 mm deep (thick).
Answer the following questions in the ANSWER BOOK. (Table form NOT necessary.)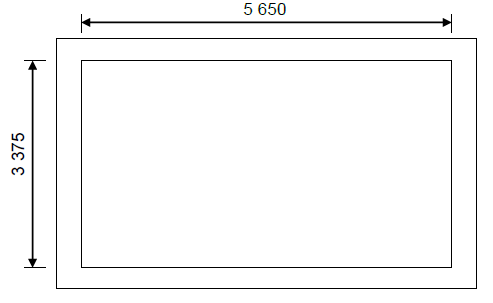
FIGURE 6.9
6.9.1 Calculate the centre line of the foundation. (5)
6.9.2 Calculate the volume of concrete needed. (3)
[30]
TOTAL: 200
ANSWER SHEET A
2.1 Answer the following questions with regard to the site plan on ANSWER SHEET A.
2.1.1 Identify TEN details according to the checklist that are not indicated on the plan. (10)
2.1.2 Identify SIX details that are incorrectly indicated on the elevation. (6)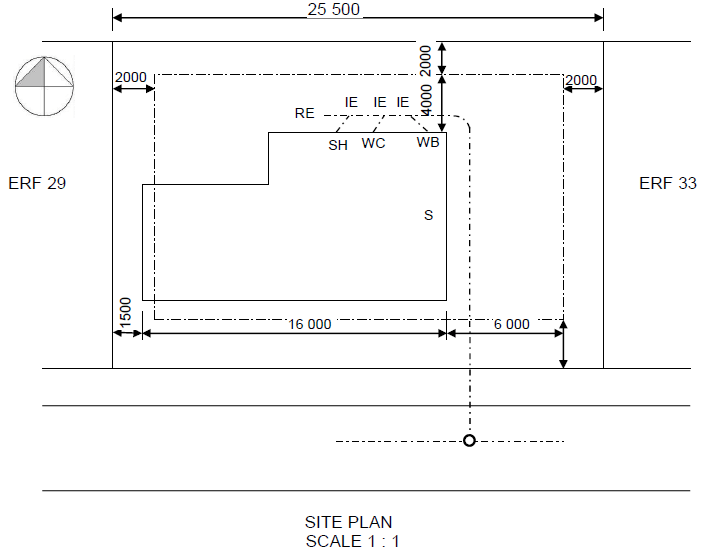
ANSWER SHEET B
5.3 Draw in the damp-proof course (DPC) on ANSWER SHEET B. (5)
Computer Application Technology Paper 2 Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
SUGGESTIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS TO MARKERS
- Revisit the questions and the marking guideline frequently during the marking session.
- It is advisable to read the question frequently (and re-read) together with the candidate's response to check that it correlates, so that you are not misled by the candidate's statements/answers.
- Be careful not to focus on keywords or general statements, but rather read the entire answer. If in doubt, read the entire answer and then the question paper and the marking guideline.
- Ask yourself or your senior marker if the response could 'fit' into the marking guideline before allocating the correct marks to the candidate.
- Accept correct answers that are expressed differently, e.g. the marking guideline states 'slow' and the candidate responds with 'not fast'.
- Beware of overlapping answers to a specific question. In general, ONE mark is awarded per fact.
- Do not choose answers on the candidate's behalf. Where a question requires a candidate to LIST or NAME/STATE: mark the first number of instances required,e.g. the first TWO facts if the candidate presents a list of FIVE facts and only TWO facts were required, even if presented in paragraph format.
- Questions requiring longer answers must be regarded as a single unit. Marks can be awarded if correct statements are found anywhere in the paragraph.
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE | QUESTION 2: MATCHING COLUMNS | ||||||
1.1 | A | (1) | 2.1 | K | (1) | ||
1.2 | D | (1) | 2.2 | P | (1) | ||
1.3 | A | (1) | 2.3 | O | (1) | ||
1.4 | D | (1) | 2.4 | L | (1) | ||
1.5 | B | (1) | 2.5 | A | (1) | ||
1.6 | B | (1) | 2.6 | E | (1) | ||
1.7 | C | (1) | 2.7 | G | (1) | ||
1.8 | D | (1) | 2.8 | M | (1) | ||
1.9 | C | (1) | 2.9 | B | (1) | ||
1.10 | C | (1) | 2.10 | D | (1) | ||
[10] | [10] | ||||||
QUESTION 3: TRUE/FALSE ITEM | |||||||
3.1 |
False System software |
(1) | |||||
3.2 | True | (1) | |||||
3.3 | True | (1) | |||||
3.4 | False Pharming | (1) | |||||
3.5 | False Plug-in | (1) | |||||
[5] | |||||||
TOTAL SECTION A: | 25 | ||||||
SECTION B
QUESTION 4: SYSTEM TECHNOLOGIES
4.1 | 4.1.1 | Key function of operating system to manage memory The operating system needs memory (RAM) to control the programs loaded in order not to use the same area of memory at the same time and corrupt each other’s data/instructions. | 2 |
4.1.2 | TWO examples of how an operating system provides a basic level of security.
| 2 | |
4.1.3 | Function of utilities and relationship with operating system
| 2 | |
4.2 | 4.2.1 | Need special software to create a ‘zipped’ file. Motivate.
OR
| 2 |
4.2.2 | Common reason to zip a file when sending e-mail attachment
| 2 | |
4.3 | ‘Cache memory’ and why it can improve the overall performance | 2 | |
4.4 | 4.4.1 | Display specification in the first line of the advert
| 3 |
4.4.2 | Size of the memory and storage – clear distinction | 2 | 9 | |
| ||||
(Note to marker: GB measurement should be present for marks. Size without indication of component = no marks) | ||||
4.4.3 | Is Windows 10 a proprietary or an open source? | 1 | ||
Proprietary | ||||
4.4.4 | Specific port that the laptop user to connect to: | 1 | ||
Data projector | ||||
(a) HDMI or SVGA (VGA) | ||||
External hard drive | 1 | |||
(b) USB port | ||||
4.4.5 | ONE reason for choosing an SSD instead of a HDD | 1 | ||
| ||||
4.5 | TWO advantages of using HDMI technology instead of VGA
| 2 | 2 | |
4.6 | State TWO ways user could install software – not an optical drive
( Any two) | 2 | 2 | |
[25] | ||||
QUESTION 5: INTERNET AND NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES
5.1 | TWO factors that should be carefully considered when choosing an ISP
| 2 | 2 | |
5.2 | TWO limitations of using an ADSL connection
| 2 | 2 | |
5.3 | 5.3.1 | Describe the above package as ‘capped’ or ‘uncapped. Motivate.
| 2 | 5 |
5.3.2 | Common term used when an ISP slows Internet speed
| 1 | ||
5.3.3 | Give TWO factors that can influence internet speed.
| 2 | ||
5.4 | Explain the term click-jacking.
| 2 | 2 | |
5.5 | Type of internet connection that uses light for data transmission.
| 1 | 1 | |
5.6 | 5.6.1 | TWO long-term solutions to poor picture quality in video conferencing
| 2 | 2 |
5.6.2 | Explain what the term bandwidth means.
| 1 | 1 | |
[15] | ||||
QUESTION 6: INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
6.1 | Explain why using an online questionnaire is an effective option Data capture
AND
| 2 | 2 |
6.2 | Survey – A set of written/typed questions handed to a group or many people. | 2 | 2 |
6.3 | What does the term 'information overload' refer to?
| 1 | 1 |
6.4 | How will you know that a web page is authentic and reliable?
| 2 | 2 |
6.5 | TWO potential advantages of using queries instead of filters
| 2 | 2 |
6.6 | Why a bibliography should be added to a research report
| 1 | 1 |
[10] |
QUESTION 7: SOCIAL IMPLICATIONS
7.1 | Explain how a blog differs from a vlog.
| 2 | 2 |
7.2 | Discuss TWO skills required by people who wish to follow a career in Big Data.
| 2 | 2 |
7.3 | What is the purpose of an EULA agreement?
| 2 | 2 |
7.4 | Give TWO potential disadvantages of e-learning
(Note to marker: Do NOT accept any answers relating to costs.) | 2 | 2 |
7.5 | Describe the function of virtual assistant software.
| 2 | 2 |
[10] |
QUESTION 8: SOLUTION DEVELOPMENT
8.1 | How do you convert an endnote to a footnote?
| 3 | 3 | |
8.2 | The function you would use in cell B6:
| 4 | 4 | |
8.3 | 8.3.1 | The name of the function that was used in Column C to determine the position of the space
| 1 | 1 |
8.3.2 | Spreadsheet feature that was used to display the words in cell C1
| 1 | 1 | |
8.3.3 | Spreadsheet feature that was used in Column A to systematically insert automatic numbers
| 1 | 1 | |
8.4 | 8.4.1 | Criterion would you enter in a query to extract suburbs starting with ‘A’
| 2 | 4 |
8.4.2 | State which data type was used for the field DwellingNumber.
| 1 | ||
8.4.3 | Which criterion would you enter in a query to find those records that do not have a value entered in the DwellingNumber field?
| 1 | ||
8.5 | Briefly explain what the Widow/Orphan control in a word processor is used for.
(Note to marker: Accept equivalent wordings, e.g. to prevent a single line of a paragraph from appearing on a page other than that on which the rest of the paragraph is located.) | 1 | 1 |
[15] |
SECTION C
QUESTION 9: INTEGRATED SCENARIO
9.1 | Identify AND describe the type of device (VRX5) above.
| 2 | 2 |
9.2 | Name ONE use and ONE disadvantage of the VRX5.
AND
| 2 | 2 |
9.3 | TWO reasons why you would rather prefer to have a laptop
| 2 | 2 |
9.4 | Identify TWO software-related problems that could reduce the speed of a computer and potential solution for EACH.
(Any two problems?? with appropriate solutions??) | 4 | 4 | |
9.5 | TWO devices that could assist him to interact with the content on the monitor
| 2 | 2 | |
9.6 | Give TWO disadvantages of using VoIP software
(Note to marker: TWO disadvantages (excluding Internet requirement) | 2 | 2 | |
9.7 | TWO possible uses for voice recognition software
| 2 | 2 | |
9.8 | 9.8.1 | How do you prevent ransomware?
| 2 | |
9.8.2 | Why do many people pay the ransom?
| 2 | 5 | |
9.8.3 | Name ONE method of payment that can be used.
| 1 | ||
9.9 | 9.9.1 | Give TWO reasons for a software developer to release updates.
| 2 | 4 |
9.9.2 | State TWO potential disadvantages of not being able to disable automatic updates.
| 2 | ||
[25] | ||||
QUESTION 10
10.1 | What does the “G” in 4G or 5G stand for?
| 1 | 1 |
10.2 | Name TWO ways (protocols) in which on-line devices would wirelessly connect to each other.
(Note to marker: Accept any other correct answer) | 2 | 2 |
10.3 | Name ONE wearable computer mentioned in the article
Give ONE task that a user can perform with this device
(Note to marker: Accept any other correct answer) | 2 | 2 |
10.4 | What is the computer called that would centrally store all information received from connected devices?
| 1 | 1 |
10.5 | Explain why HD-streaming will demand a lot of bandwidth.
| 2 | 2 |
10.6 | Name the unit in which transfer speed to or from the internet is measured
| 1 | 1 |
10.7 | Give ONE reason why upload speeds are normally slower than download speeds
| 1 | 1 |
10.8 | 10.8.1 | C | 1 | 3 |
10.8.2 | B | 1 | ||
10.8.3 | A | 1 | ||
10.9 | 10.9.1 | Name TWO advantages for education when mobile communication becomes faster and more reliable
(Note to marker: Accept any other correct answer) | 2 | 4 |
10.9.2 | Give TWO examples of instant messaging applications.
| 2 | ||
10.10 | 10.10.1 | Give the most appropriate data type for the Value field.
| 1 | 2 |
10.10.2 | Give the most appropriate data type for the TabletID field.
| 1 | ||
10.11 | List TWO general advantages of using computer-based training software.
| 2 | 2 | |
10.12 | Name TWO ways in which AR and/or VR technology can advantage the health sector.
(Note to marker: Accept any other correct answer) | 2 | 2 |
10.13 | Name TWO disadvantages of 3D printers.
| 2 | 2 |
[25] | |||