Adele
Computer Application Technology Paper 1 Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1 File Name: 1_4th Industrial Revolution Total Q1: 35
No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | ||
1.1.1 | Cover Page
|
1 |
1 | |
1.1.2 | Cover Page
|
1 |
1 | |
1.2.1 | Table of Contents
|
1 1 1 |
3 | |
1.2.2 | Style
| 1
1 |
2 | |
1.3 | Find and Replace
| 1
1 |
2 | |
1.4 | Border
| 1
1
1 |
3 | |
1.5 | Picture
| 1
1
1 |
3 | |
1.6 | Endnote
|
1
1 |
2 | |
| No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | ||
1.7 | Citation | 1
1
1 |
3 | |
Journal Article (source) used | ||||
Author Klaus Schwab inserted | ||||
Year 2020 inserted | ||||
1.8 | Page setup
| 1 |
3 | |
Page 5 set to landscape | 1 | |||
All other pages set to remain in portrait |
1 | |||
1.9 | Spell Check
|
1 |
1 | |
1.10 | Paragraphs
| 1
1 |
2 | |
1.11 | Page numbering | 1
1
1
1 1 |
5 | |
Page numbering inserted | ||||
In the footer of the document | ||||
Centred | ||||
First two pages not numbered | ||||
Numbering starts on page 3 as page 1 | ||||
1.12 | Watermark | 1
1
1
1 |
4 | |
Watermark inserted | ||||
On the last page only | ||||
Text 4IR appear | ||||
Displaying horizontally | ||||
Total for QUESTION 1 | [35] | |||
QUESTION 2 File Name: 2_ 4IR Research Total Q2: 15
No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | ||
2.1 | Paper size
| 1
1 |
2 | |
2.2 | Layout
| 1 | ||
1 | ||||
4 | ||||
1 | ||||
1 | ||||
2.3 | Table
| 1 | ||
1 | ||||
1 | 5 | |||
1 | ||||
1 | ||||
2.4 | Paragraph | |||
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
2.5 | Date
| |||
1 1 | 2 | |||
Total for QUESTION 2 | [15] | |||
QUESTION 3 File Name: 3_Resourcing Total Q3: 56
- Mark the questions from the formulae and not the values/answers in the cell.
- Check against candidate's actual work (Cell references may differ, depending on the candidate's response).
- Candidate may use multiple formulae or cells as 'building blocks' to reach answers.
- Named ranges can be used instead of cell references.
- The answers must still be correct even if changes are made to the existing data.
No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | |||
WardInfo worksheet | |||||
3.1.1 | Merge and Centre
|
1 1 |
2 | ||
3.1.2 | Fill
(accept any diagonal stripes) |
1
1 |
2 | ||
3.1.3 | Wrap Text
|
1 |
1 | ||
3.1.4 | Panes
| 1
1 |
2 | ||
3.2 | Comment
| 1
1 |
2 | ||
3.3 | Text functions (Cell B5)
|
1
1
1
1 |
4 | ||
| No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | ||
3.4 | Cell K5
|
1
1 |
2 | |
3.5 | Cell L8
|
1 1 |
2 | |
3.6 | M5
| 1 | ||
1 | ||||
4 | ||||
1 | ||||
1 | ||||
3.7 | Cell N6
| 1 | ||
1 |
3 | |||
1 | ||||
3.8 | Conditional formatting
|
1 | ||
1 | 3 | |||
1 | ||||
3.9 | Cell O5
| |||
1 | ||||
1 |
4 | |||
1 | ||||
1 | ||||
3.10 | Cell E37
| |||
1 | ||||
1 |
4 | |||
1 | ||||
1 | ||||
| No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | ||
3.11 | Cell E39 |
1
1
1 1 |
4 | |
=IF(AND(C7="Rural";N7>25);"Award";"No | ||||
Award") | ||||
Functions: IF and AND | ||||
Condition (C7="Rural";N7>25); | ||||
Value if true is correct | ||||
Value if false is correct | ||||
3.12 | Cell E41 | 1 | ||
=COUNTIF(C5:C34;"Semi Rural")
| 1 |
3 | ||
Range: C5:C34; | 1 | |||
Criteria: "Semi Rural" | ||||
3.13 | Cell E43 |
5 | ||
=VLOOKUP(A7;ExtraInfo!A2:C31;3;FALSE) | 1 | |||
Function: Vlookup | 1 | |||
Lookup value : A7 | ||||
Lookup range : ExtraInfo!A2:C31 (ignore | 1 | |||
if no absolute cell reference was used)
| 1 | |||
| 1 | |||
3.14 | Cell E45 | |||
=COUNTBLANK(E5:E34)
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
3.14 | Graph Worksheet |
1
1
1
1 1 1 1 |
7 | |
Graph title Readiness for 4IR | ||||
Both series points plotted correctly. | ||||
Any Stacked Bar graph used. | ||||
Vertical axis appears as in graph | ||||
Centred | ||||
Legend series added to top of graph | ||||
Move graph to the worksheet 4IR | ||||
Total for QUESTION 3 | [56] | |||
QUESTION 4 File Name: 4_4IR Total Q4: 42
No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | ||
Table: Wards | ||||
4.1.1 | Field: WardName
| 1 | 1 | |
4.1.2 | Field: WardNumber
| |||
1 1 | 2 | |||
4.1.3 | Image
|
1 |
1 | |
4.1.4 | Validation <= 2020/06/30 OR < 2020/07/01 OR <=#2020/06/30# OR <#2020/07/01#
| |||
1 1 | 3 | |||
1 | ||||
4.1.5 | Devices Field
| |||
1 | ||||
1 1 | 3 | |||
4.2 | Form: frm4_2 |
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 |
10 | |
Form frm4_2 based on WardInfo table and | ||||
Columnar layout selected | ||||
Selected fields: WardName; WardNumber; | ||||
Location; Budget; Expenditure and Balance | ||||
The background of the form header is yellow | ||||
Font size of heading is 36 pt | ||||
Heading is centred | ||||
4_Form.jpg picture inserted | ||||
In form header aligned right | ||||
Format of Budget field changed to Currency with | ||||
zero decimal places | ||||
Button inserted in form footer | ||||
Shows the next record when button is clicked | ||||
| No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | ||
4.3.1 | Qry4_3_1
|
1
1
1 |
3 | |
4.3.2 | Qry4_3_2 |
1
1 1 1 |
4 | |
Only Rural | ||||
and Semi-Rural records show | ||||
Total calculated | ||||
Total of Budget field (SUM) | ||||
4.3.3 | Qry4_3_3 |
1 1 1 1 1 |
5 | |
Loan: 30/100*[Budget] | ||||
Criteria Balance : <0 | ||||
Loan: | ||||
30/100 | ||||
*[Budget] | ||||
Loan set to R currency | ||||
Report | ||||
4.4 | Report4_4 | 1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1 1 1 | ||
Report created | ||||
Grouped according to Location and then | ||||
according to Budget | ||||
Total budget for each Location calculated | ||||
in the Location footer = Sum([Budget]) | ||||
Rural Locations are formatted red | ||||
New field Future Projections created . | 10 | |||
Calculation of Future Projections | ||||
=10/100 | ||||
*[Budget] | ||||
+[Budget] | ||||
OR =110/100*[Budget] | ||||
Total for QUESTION 4 | [42] | |||
QUESTION 5 File Name: 5_MyWebsite Total Q5: 21
- This question should be marked from the HTML code.
- Numerical attribute values do not need to be in inverted commas.
No | Criteria | Maximum Mark | ||
5.1 | Heading 1
|
1
1 |
2 | |
5.2 | Anchor
| 1
1
1 |
3 | |
5.3 | Image
|
1 1 |
2 | |
5.4 | Bulleted list
|
1 1 1 |
3 | |
5.5 | Table
| 1 1 |
2 | |
5.6 | Table row
|
1
1
1 |
3 | |
5.7 | Table row
|
1 1 |
2 | |
5.8 | Link
|
1 1 1 |
3 | |
Closing tag(s) or triangular brackets and correct nesting correctly used | 1 | 1 | ||
Total for QUESTION 5 | [21] |
QUESTION 6 File Name: 6_Calculation, 6_Quote Total Q6: 11
No, | Criteria | Maximum Mark | ||
6.1.1 | Date | |||
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
6.1.2 | Table |
1 1 1 1 |
4 | |
Table created | ||||
3 columns and 2 rows | ||||
Spacing between columns set | ||||
to 0.3 cm | ||||
6.2 | Mail Merge | |||
Recipients list filtered to send letters | 1 | |||
to the Wards that have a negative balance <0 | 1 | |||
Insert Ward Names in the Ward Name field | 1 | 5 | ||
Mail merge completed | 1 | |||
Completed letters saved as Letters | 1 | |||
(Expect 6 Letters) | ||||
Total for QUESTION 6 | [11] | |||
TOTAL | 180 | |||
Computer Application Technology Paper 2 Grade 12 Questions - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of:
SECTION A (25 marks)
SECTION B (75 marks)
SECTION C (50 marks) - Answer ALL the questions.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Do NOT write in the right-hand margin of the ANSWER BOOK.
- Leave a line after EACH sub-question.
- Generally, one mark is allocated per fact. A 2-mark question would therefore require TWO facts, etc.
- Read the questions carefully and do NOT give more information than the question requires as this will NOT be marked.
- All answers MUST be related to Computer Applications Technology.
- Answers such as ‘cheaper’, ‘slower’/’faster’, ‘easier’, etc. will ONLY be accepted, if they are motivated.
- Do NOT use brand names in answers, unless specifically required.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1–1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.11 D.
1.1 An USB port is used to connect peripherals to a computer. If you have a limited number of USB ports you can use an USB … to extend the number of ports.
- hub
- flash disk
- extension cable
- modem (1)
1.2 Which keys should you press to open Task Manager?
- Alt + Ctrl
- Ctrl + Alt + Enter
- Alt + PrtScr
- Ctrl + Alt + Del (1)
1.3 Which ONE of the following combinations of spreadsheet functions will display a code in capital letters of the last 3 letters of a name?
- CAPITAL
- UPPER
- LEFT
- RIGHT
- (ii) and (iv)
- (ii) and (iii)
- (i) and (iv)
- (iii) and (iv) (1)
1.4 ... refers to an injury that can occur from the continuous use of an input device such as a keyboard.
- CPU
- RSS
- RFID
- RSI (1)
1.5 ... is an example of an e-commerce website.
- Spotify
- eBay
- iCloud
- YouTube (1)
1.6 A(n) … is NOT an example of malware.
- trojan
- ad-blocker
- worm
- keylogger (1)
1.7 Which ONE of the following devices would be used to provide an emergency supply of electricity in the case of a power failure?
- Surge protector
- Power Supply Unit
- UPS
- Router (1)
1.8 Which one of the following is an example of secondary memory?
- RAM
- ROM
- Printer
- Memory Card (1)
1.9 A reason why a webcam would NOT be suitable to take pictures or photographs at a prestigious event such as a prize-giving.
- Face-to-face communication
- High costs
- Low video quality
- Inadequate storage (1)
1.10 To print all comments and changes made in a document, the following must be enabled in the Print dialog box.
- Print Selection only
- Only Print even pages
- Print Mark-up
- Scale to Paper size (1) [10]
QUESTION 2: MATCHING COLUMNS
Choose a term/concept from COLUMN B that matches a description in
COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–P) next to the question number (2.1–2.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 2.11 Q.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
2.1 | A program that searches the Web for web pages relevant to the keywords or phrases entered by the person looking for information | A | Shaping |
2.2 | A process where a project is funded by multiple small donations from many contributors | B | Driver |
2.3 | An example of a popular, free, online office suite | C | VPN |
2.4 | A communication technology that requires a pairing process | D | Disk Cleanup |
2.5 | A technique used by ISPs to prioritise some services | E | FTP |
2.6 | Protocol for sending large files via Internet | F | PPM |
2.7 | A file type including both audio and video content | G | MP4 |
2.8 | A device that can be used to store data permanently | H | Podcast |
2.9 | Software that allows a computer to communicate with hardware or devices | I | LTE |
2.10 | An utility that can be used to make more storage space available by deleting unnecessary files | J | Internet |
K | Search engine | ||
L | Bluetooth | ||
M | SSD | ||
N | Pop-ups | ||
O | Google Docs | ||
P | Crowd funding | ||
(10 x 1) [10]
QUESTION 3: TRUE/FALSE ITEM
Indicate whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Write ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the question number (3.1–3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK. Correct the statement if it is FALSE. Change the underlined word(s) to make the statement TRUE. (You may not simply use the word ‘NOT’ to change the statement. NO mark will be awarded if only FALSE is written down.)
EXAMPLES:
QUESTION | ANSWER | |
Google is the world’s most popular search engine. | True | |
A NIC has slots for hardware components such as the CPU. | False – motherboard | |
3.1 Application software controls and manages resources on a computer. (1)
3.2 A hotspot is an area where you can obtain wireless access to the internet. (1)
3.3 OCR software is used to convert scanned images of text into text that can be edited in a program such as a word processor. (1)
3.4 Phishing redirects users to false web sites without them even knowing it. (1)
3.5 Add-on software, such as flash players, extend the capabilities of a browser. (1)
[5]
TOTAL SECTION A: 25
SECTION B
QUESTION 4: SYSTEM TECHNOLOGIES
4.1 An operating system is the most important software that runs on a computer. It allows you to communicate with the computer.
4.1.1 One of the key functions of an operating system is to manage memory. Why is this such a crucial function? (2)
4.1.2 Give TWO examples of how an operating system provides us with a basic level of security. (2)
4.1.3 Utilities form part of system software. What is the function of utilities and what is the ‘relationship’ between utilities and the operating system? (2)
4.2 You received a ‘zipped’ file as an e-mail attachment and you have scanned it for viruses and it seems to be ‘safe’.
4.2.1 Do you need special software to create a ‘zipped’ file? Briefly motivate your answer. (2)
4.2.2 What is the most common reason to zip a file which you are sending as an e-mail attachment? (2)
4.3 A computer advert advertises a CPU with a ‘cache memory’ size of 8192KB. Explain what ‘cache memory’ is and why it can improve the overall
performance of a computer. (2)
4.4 Study the advertisement of a laptop below:
- 13.3 inch FHD LED Display
- Intel Core i7 8565U Processor
- 16 GB RAM
- 512 GB SSD
- Intel® UHD Graphics 620
- Windows 10 Home
- 3 Year Warranty (Upon Registration)
4.4.1 Explain what each display specification in the first line of the advert refers to. (3)
4.4.2 What is the size of the memory and storage respectively? Make a clear distinction between the TWO concepts you are referring to. (2)
4.4.3 Is Windows 10 a proprietary or an open source operating system? (1)
4.4.4 Name the specific port that the laptop should have to enable the user to connect to the following:
- A data projector (1)
- An external hard drive (1)
4.4.5 State ONE reason for choosing an SSD instead of a HDD. (1)
4.5 State TWO advantages of using HDMI technology instead of VGA technology.(2)
4.6 State TWO ways in which a user could install software on a computer that does not have an optical drive.(2)
[25]
QUESTION 5: INTERNET AND NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES
5.1 State TWO factors that should be carefully considered when choosing an ISP (internet service provider), other than cost. (2)
5.2 Give TWO limitations of using an ADSL connection. (2)
5.3 Study the internet connection package advertised below and answer the questions that follow.
| 30 GB data per month Shaped |
5.3.1 Would you describe the above package as ‘capped’ or ‘uncapped’? Motivate your answer. (2)
5.3.2 Give the common term used when an Internet Service Provider slows down your internet speed when you download huge amounts of data. (1)
5.3.3 Give TWO factors (besides the one in QUESTION 5.3.2) that can influence Internet speed. (2)
5.4 Learners may be click-jacked when browsing a social media website. Explain the term click-jacking. (2)
5.5 Name the type of internet connection that uses light for data transmission. (1)
5.6 Many companies use video conferencing to communicate with each other over a network.
5.6.1 A person regularly experiences poor picture quality in video conferencing (the picture keeps ‘breaking up’). Suggest TWO long-term solutions for this problem. (2)
5.6.2 Briefly explain what the term bandwidth means. (1)
[15]
QUESTION 6: INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
6.1 Explain why using an online questionnaire is an effective option for gathering data, by referring to:
- Data capture
- Data processing (2)
6.2 What is the difference between a survey and an interview? (2)
6.3 What does the term ‘information overload’ refer to? (1)
6.4 How will you know that a web page is authentic and reliable for use in research?(2)
6.5 Give TWO potential advantages of using queries instead of filters in a database.(2)
6.6 Explain why a bibliography should be added to a research report. (1)
[10]
QUESTION 7: SOCIAL IMPLICATIONS
7.1 Explain how a blog differs from a vlog. (2)
7.2 Big Data is very large structured and unstructured data sets that are analysed using computers to reveal trends and patterns.Discuss TWO skills required by people who wish to follow a career in Big Data.(2)
7.3 When you buy and/or install new software an EULA agreement must be accepted. What is the purpose of this agreement?(2)
7.4 Give TWO potential disadvantages of e-learning, experienced during the COVID-19 pandemic, when compared to the traditional classroom approach, excluding any cost factors.(2)
7.5 Describe the function of virtual assistant software. (2)
[10]
QUESTION 8: SOLUTION DEVELOPMENT
8.1 How do you convert an endnote to a footnote? (3)
8.2 Refer to the diagram below and answer the following question.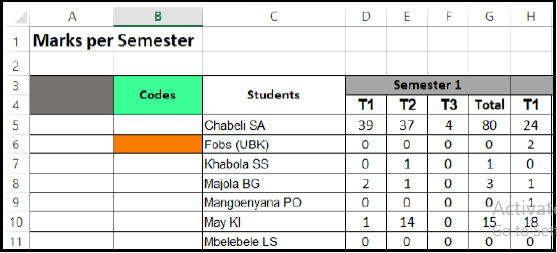
Each student needs a unique code to receive their overall final results.
Write down the function you would use in cell B6 to create this unique code by using the following instructions:
- The first 2 letters of students names (column C); followed by
- The total for the semester (column G).
EXAMPLE: AS80 (4)
8.3 Study the spreadsheet below and answer the questions that follow.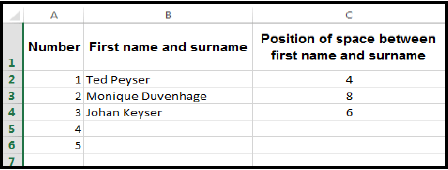
8.3.1 Give only the name of the function that was used in Column C to determine the position of the space between the first name and the surname in Column B.
(1)
8.3.2 Name the spreadsheet feature that was used to display the words in cell C1 below one another within the same cell. (1)
8.3.3 Name the spreadsheet feature that was used in Column A to systematically insert automatic numbers from 1 to 5 in consecutive rows. (1)
8.4 Study the screenshot extract of a database table below and answer the questions that follow.
8.4.1 Which criterion would you enter in a query to extract suburbs starting with ‘A’? (2)
8.4.2 State which data type was used for the field DwellingNumber. (1)
8.4.3 Which criterion would you enter in a query to find those records that do not have a value entered in the DwellingNumber field? (1)
8.5 Briefly explain what the Widow/Orphan control in a word processor is used for. (1)
[15]
TOTAL SECTION B: 75
SECTION C
QUESTION 9: INTEGRATED SCENARIO
Your parents have decided to buy a laptop. The salesman convinced them to also buy a VRX5 as it is part of modern technology. They have never heard of VRX5 before. Below is an image of the VRX5. Assist them by answering the following questions.
|
9.1 Identify AND describe the type of device (VRX5) above. (2)
9.2 Name ONE use and ONE disadvantage of the VRX5. (2)
9.3 Give TWO reasons why you would prefer to have a laptop instead of a desktop computer in this context. (2)
9.4 Identify TWO software-related problems that could reduce the speed of a computer.Write down a potential solution for EACH of the problems. (4)
9.5 You will be sharing your laptop with your partially sighted brother. Name TWO devices that could assist him to interact with the content on the monitor. (2)
9.6 Skype is a popular software package that uses VoIP technology. Give TWO disadvantages of using VoIP software, besides the fact that an internet connection is needed. (2)
9.7 Give TWO possible uses for voice recognition software other than for security purposes. (2)
9.8 Ransomware is a type of malicious software from crypto virology that threatens to publish the victim's data or perpetually block access to it unless a ransom is paid.
9.8.1 How do you prevent ransomware? (2)
9.8.2 Why do many people pay the ransom? (2)
9.8.3 Anonymous payment services are used for ransomware payment. Name ONE method of payment that can be used. (1)
9.9 Windows 10 has no option to turn off automatic system updates.
9.9.1 Give TWO reasons why software developers release updates. (2)
9.9.2 State TWO potential disadvantages of not being able to disable automatic updates. (2)
[25]
QUESTION 10: INTEGRATED SCENARIO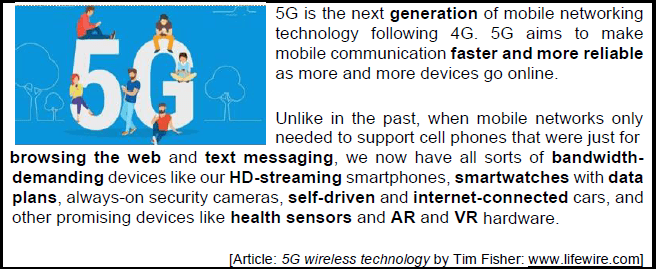
10.1 What does the ‘G’ in 4G or 5G stand for? (1)
10.2 Name TWO ways (protocols) in which on-line devices would wirelessly connect to each other. (2)
10.3 Name ONE wearable computer mentioned in the article above and give ONE task that a user can perform with this device. (2)
10.4 What is the computer called that would centrally store all information received from connected devices? (1)
10.5 Explain why HD-streaming will demand a lot of bandwidth. (2)
10.6 Name the unit in which transfer speed to or from the internet is measured. (1)
10.7 Give ONE reason why upload speeds are normally slower than download speeds. (1)
10.8 Match the data plan in COLUMN B to a user in COLUMN A. Just write the question number (10.8.1–10.8.2) and the letter (A–C) of the data plan down, for example 10.8.4 D.
COLUMN A USER | COLUMN B DATA PLAN | ||
10.8.1 | Student who uses the internet as needed for research | 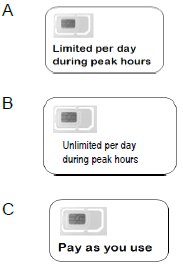 | |
10.8.2 | Business user who does meetings via Skype with clients across the globe | ||
10.8.3 | Office user who mostly uses e-mails and visit social networking sites | ||
(3 x 1) (3)
10.9 During the COVID-19 pandemic schools want to function digitally (paperless) as much as possible.
10.9.1 Name TWO advantages for education when mobile communication becomes faster and more reliable. (2)
10.9.2 Learners will use instant messaging for communicating with teachers and each other. Give TWO examples of instant messaging applications. (2)
10.10 The school provided tablets to learners during the pandemic. A database was created to keep track of the tablets.
The following fields were created:
Field Name | Data Type | Description |
Name | Short Text | The name of the recipient of the tablet, e.g. Mpho Dlamini |
Category | Short Text | The grade of a learner, e.g. Gr 12 |
Value | 10.10.1 | The value of the tablet, e.g. R4 500.00 |
TabletID | 10.10.2 | A photograph of the serial number of the tablet, e.g. SN 123654785.png |
Answer the following questions based on the design of the database table above:
10.10.1 Give the most appropriate data type for the Value field. (1)
10.10.2 Give the most appropriate data type for the TabletID field. (1)
10.11 List TWO general advantages of using computer-based training software. (2)
10.12 Name TWO ways in which AR and/or VR technology can be of benefit to the health sector. (2)
10.13 Name TWO disadvantages of 3D printers. (2)
[25]
TOTAL SECTION C: 50
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Computer Application Technology Paper 1 Grade 12 Questions - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Owing to the nature of this practical examination, it is important to note that, even if you complete the examination early, you will NOT be permitted to leave the examination room until all the administrative functions associated with the examination have been finalised. During the examination, the normal rules regarding leaving the examination room apply.
- If you are working on the network, or the data files have been preloaded, you must follow the instructions provided by the invigilator/teacher. Alternatively, the invigilator will give you a CD/DVD/flash drive containing all the files needed for the examination. If a CD/DVD/flash drive has been issued to you, you must write your name and surname and class section on the CD/DVD/flash drive.
- At the end of the examination, you must hand in the CD/DVD/flash drive given to you by the invigilator with ALL your answer files saved onto the CD/DVD/flash drive, OR you should make sure that ALL the answer files are saved on the network/computer as explained to you by the invigilator/teacher.
- Make absolutely sure that ALL files can be read. Do NOT save unnecessary files/folders and do NOT hand in duplicate answer files/folders. Do NOT delete any original files that you did not work on.
- The information sheet that has been provided with the question paper MUST BE COMPLETED AFTER THE THREE-HOUR EXAMINATION SESSION.
Hand it to the invigilator at the end of the examination. - A copy of the master files will be available from the invigilator. Should there be any problems with a file, you may request another copy from the invigilator.
- This question paper consists of SIX questions. Answer ALL the questions.
- Read through each question before answering or solving the problem. Do NOT do more than is required by the question.
- Ensure that you save each document using the file name given in the question paper. Save your work at regular intervals as a precaution against possible power failures.
- You may NOT use any resource material.
- Accuracy will be taken into account, e.g. if a question requires the answer to be in cell F3 in a spreadsheet, and you enter the answer in cell G4, it will NOT be marked.
- Ensure that the regional settings are set to South Africa and date and time settings, number settings and currency settings are correctly set.
- In all questions involving word processing, you should set the language to English (South Africa). The paper size is assumed to be A4 Portrait, unless instructed otherwise. Use centimetres as the unit of measurement.
- Formulae and/or functions must be used for ALL calculations in questions involving spreadsheets. Use absolute cell references only where necessary to ensure that formulae are correct when you copy them to other cells in a spreadsheet.
NOTE: All formulae and/or functions should be inserted in such a manner that the correct results will still be obtained even if changes are made to the existing data. - You may NOT use a word processing program such as Word to answer the HTML question.
- The examination folder/data disk that you receive with this question paper will contain the folder and files listed below. Ensure that you have the folder and all the files before you begin this examination.

QUESTIONS
SCENARIO As time goes on, technology is evolving and it affects all of us. Whether we like it or not the Fourth Industrial Revolution has arrived. It affects education, business, labour etc. |
QUESTION 1: WORD PROCESSING
A document was created to give more information about the 4th Industrial Revolution. Edit the document as requested.
Open the 1_4th Industrial Revolution word processing document.
1.1 Modify the cover page as follows:
1.1.1 Change the year of the document to the current year. (1)
1.1.2 The picture in the cover page is upside down, rotate/turn the picture so that it appears normal. (1)
1.2 A table of contents has been inserted in the document.
1.2.1 The paragraph shaded in blue below the heading, “What exactly is the fourth Industrial Revolution?” appears in the table of contents.
Modify the paragraph so that only the heading appears in the table of contents and not the paragraph. (3)
1.2.2 Modify heading style 2 as follows:
- Change the font colour to any blue colour.
- Spacing after the paragraph should be 12 pt. (2)
1.3 Find all the occurrences of “4th Industrial Revolution” and replace them with 4IR. (2)
1.4 Locate the image below the heading “Where did the term “Fourth Industrial Revolution” come from?”
- Apply a 2 pt yellow border around the image.
- Add an Offset Top shadow effect to the image. (3)
1.5 Move the Figure 2 image to the right of the highlighted paragraph, same as the Figure 1 image. Make sure that the caption Figure 2 appears below the image. (3)
1.6 Locate the words “Klaus Schwab” shaded in red. Insert an endnote with the following text, “Founder and Executive Chairman of the World Economic Forum”. (2)
1.7 Locate the text “Placeholder1” shaded in light green and do the following:
- Add a new journal article (source) with the author named “Klaus Schwab”.
- Add the year 2020 to the year field.(3)
1.8 Change the orientation of the page starting with the heading, “What are the technologies driving change?” shaded in yellow to landscape.
NOTE: Only page 5 should be landscape. (3)
1.9 Find and correct the spelling error in the document. (1)
1.10 Sort the paragraphs on page 6 starting with “Virtual Reality” and ending with “Energy Capture” in ascending order. (2)
1.11 Insert automatic page numbering in the footer of the document as follows:
- The page numbers must be centred.
- The first and the second page of the document must NOT be numbered.
- Page numbering must start on the third page with number 1, then 2, etc. (5)
1.12 Insert a text watermark only on the last page with text 4IR displayed horizontally. (4)
[35]
QUESTION 2: WORD PROCESSING
You were also requested to modify and distribute the letter to people who have an interest to be judges.
Open the 2_4IR Research word processing document and modify the document as follows:
2.1 Adjust the page setup as follows:
- Top and bottom margins should be 1,5 cm.
- Change the size of the page to 20 cm wide and 28 cm high.(2)
2.2 Locate the paragraphs starting with the words “The keynote”, “Instead” and “A vast”.
- Place this text in THREE columns.
- Change the spacing between the columns to 1,1 cm.
- Ensure that the highlighted words always appear at the top of a column.
- Justify all the text in the columns.(4)
2.3 A survey was done to test the readiness of people about the 4IR. Results are displayed below the heading “A survey ...”, starting with “Technologies” and ending with “33”.
- Convert the text to a table.
- Apply a Grid Table 4 Accent 2 style to the table.
- Use a word feature to ensure that the table headings will repeat if the table moves to the next page.
- Centre all the contents of the table, vertically and horizontally.(5)
2.4 Add a shadowed double line border to the last paragraph of the document.(2)
2.5 Add the current date in the page footer. The date should automatically update each time the document is opened.(2)
[15]
QUESTION 3: SPREADSHEET
The municipality in your locality is offering resources to the communities in order to upskill them, to prepare them for the 4IR.
Open the 3_ Resources spreadsheet and work in the WardInfo worksheet.
3.1 Format the worksheet as follows:
3.1.1 Merge and centre the contents of cells A1:O1. (2)
3.1.2 Apply a 'Thin Diagonal Stripe' pattern style fill effect to the merged cell. (2)
3.1.3 Ensure that the contents of row 3 are visible without increasing the width of the column. (1)
3.1.4 Freeze the panes so that all the headings in row 3 display when you scroll down. (2)
3.2 Insert a comment in cell E4 and enter the words “Unit Price”. (2)
3.3 A Ward Number has been supplied for each ward. Create a ward number in cell B5 for Ward 1 by using the following:
- First letter of the Ward Name.
- Last two letters of the Ward Name.
- First letter of the location in small letters. (4)
3.4 Each ward has been given a budget to resource the community. The amount is in column J. The wards have to spent the money on computers, tablets, internet access, projectors and interactive white boards.
In cell K5 insert a function to add all the expenditure for Ward 1. (2)
3.5 In cell L8, calculate the balance from the amount spent by Ward 4. (2)
3.6 Use a formula in cell M5 to determine the number of computers that Ward 1 bought. Copy the formula down to all wards. (4)
3.7 In cell N6 calculate what percentage of the expenditure was spent on computers in Ward 2. Round the answer off to zero decimal place. (3)
3.8 Use a spreadsheet feature in cells L5:L34 to automatically apply a green fill with dark green text to the numbers that show an over expenditure. (3)
3.9 All the wards that did not exceed their budget were rewarded with a bonus. Insert a function in cell O5 to show Bonus for the wards that qualified for
a bonus and leave blank for those who did not qualify. (4)
3.10 It was advised that most of the budget must be used to buy computers. In cell E37 calculate the amount spent by Urban wards on computers. (4)
3.11 Rural wards were requested to spend more than 25% of their budget on computers. Those that do, will receive an award. Insert a function in cell E39 to show whether Ward 3 will receive an award. If so, then Award must display and if not, then No Award must display. (4)
3.12 In cell E41 calculate the number of Semi-Rural wards. (3)
3.13 Use a LOOKUP function in cell E43, to determine the gender of the councillor for Ward 3. (5)
3.14 Insert a function in cell E45 to show the number of wards that did not buy computers. (2)
3.15 Graph/Chart
A survey was done to test the readiness of people regarding the 4IR. Use the information from the survey in the worksheet SurveyResults to create a graph as shown below. Move the graph to 4IR worksheet.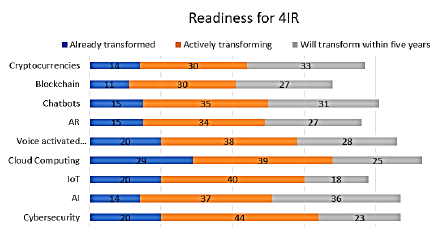
(7)
[56]
QUESTION 4: DATABASE
Assistance has been promised to respective municipalities regarding the 4IR roadshows. The assistance will be in the form of human and financial resources.
Open the 4_4IR database and do the following:
4.1 Table: Wards
4.1.1 Ensure that any data currently stored in the WardName field will appear in capital letters. (1)
4.1.2 Change the field properties of the WardNumber field so that:
- It is a required field.
- The data in this field is displayed in fixed format.(2)
4.1.3 An image of the map to the ward is needed. Change the data type of the Image field so that you can add an image to the field. (1)
4.1.4 Change the field properties of the SubmissionDate field so that:
- It does not accept a date after 30 June 2020.
- Appropriate validation text is entered.(3)
4.1.5 Create a new field called Devices.
Use the data in the Item field of the Info table to provide the values for the new field. (3)
4.2 Form
Create a form called frm4_2 based on the WardInfo table, containing the following fields:
WardName; WardNumber; Location; Budget; Expenditure and Balance. The following should be taken into consideration:
- Columnar layout was used to create it.
- The font size of the heading is 36 pt.
- The heading should be centred.
- The background colour of the form header must be yellow.
- Insert the image 4_Form.jpg from your examination folder in the form header and align the image to the right.
- Change the format of the Budget field to Currency with zero decimal places.
- Add a button from the available controls in the form footer of the form.
- The function of the button when clicked is to show the next record.
Save and close the frm4_2 form. (10)
4.3 Queries
4.3.1 Create a query to calculate the amount of money that each Location has spent. Only show the Location and calculated field. Save the query as Qry4_3_1. (3)
4.3.2 Modify the query Qry4_3_2 to show only the Rural and Semi-Rural wards. Use a database function to calculate the total budget used by these wards. (4)
4.3.3 Wards with a negative balance will be given a 30% loan calculated from the budget they received.
- Modify the Qry4_3_3 to show only those wards that qualify for this loan.
- Calculate the amount that each Ward will receive as a loan.
- The name of the calculated field must be Loan.
- Set the new field’s currency to South African Currency. (5)
4.4 Report
Create a report with the following fields, WardName; WardNumber; Location and Budget from the WardInfo table.
- First group by Location then by Budget.
- Add a formula to the Location group footer to calculate the total budget for each Location.
- Use conditional formatting to change the Rural Locations to red font.
Create a new field called Future Projections where you will add 10% to the Budget to see envisaged expenses for the following year, if prices increase by 10%. (10)
[42]
QUESTION 5: WEB DESIGN (HTML)
One of the Ward councillors created a website to enlighten the community about 4IR.
Open the incomplete 5_Website.html web page in a web browser and also in a text editor. You may NOT use a word processing program such as Word to answer the HTML question.
NOTE:
- Question numbers are inserted as comments in the coding as guidelines to show approximately where the answer(s) should be inserted. Do NOT erase the comments.
- An HTML tag sheet has been attached for reference.
Your final web page should look like the example below.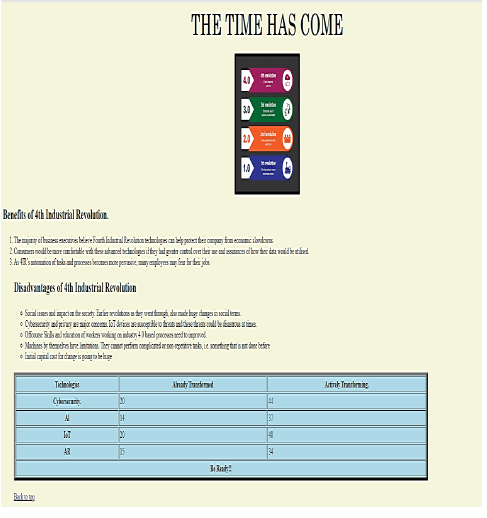
5.1 Centre the heading of the website and set the font size to 50. (2)
5.2 Create an anchor at the top of this website. (3)
5.3 The picture at the top of the website does not display correctly. Fix the error so that the picture displays the same way as the example on the previous page.
(2)
5.4 The list of disadvantages of “4th Industrial Revolution” do not display correctly. Correct the errors. (3)
5.5 Format the website so that the colour of the table is light blue and the width is 80%. (2)
5.6 Add the missing row in the table as displayed in the image on previous page. (3)
5.7 Format the last row to be spread across three columns and the text to bold. (2)
5.8 Create a hyperlink that will move the user back to the top of the website. (3)
[21]
QUESTION 6: GENERAL
Wards were requested by the municipality to get quotations to purchase technology devices.
J & C Tech Suppliers prepared a quotation for all the wards. The source of the quote is 6_Calculations.
6.1 Open the word processing document 6_Quote and modify the quote as follows:
6.1.1 Insert today’s date in the following format: (2020)(03)(10), make sure that the date updates automatically. (2)
6.1.2 Use a Word Processing feature to create the table below. The table shows devices that are sold by J & C Suppliers. The spacing between columns is 0.3 cm.
(4)
6.2 This quotation will ONLY be sent to the wards that have exhausted their budgets. Use the Customer sheet in the 6_Calculator spreadsheet as the recipients list to do the following:
- Use mail merge feature to send letters to these wards.
- Insert the Ward Names in the Ward Name field.
- Complete the mail merge.
Save the merged letters as Letters in the exam folder.(5)
[11]
TOTAL: 180
HTML TAG SHEET
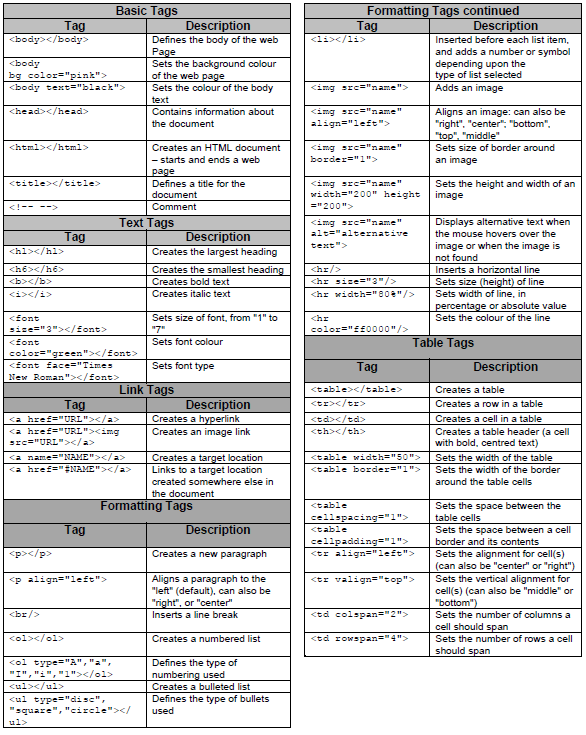
INPUT MASK CHARACTER SHEET
CHARACTER | DESCRIPTION |
0 | Digit (0 to 9, entry required, plus [+] and minus [–] signs not allowed) |
9 | Digit or space (entry not required, plus [+] and minus [–] signs not allowed) |
# | Digit or space (entry not required; spaces are displayed as blanks while in Edit mode, but blanks are removed when data is saved; plus [+] and minus [–] signs allowed) |
L | Letter (A to Z, entry required) |
? | Letter (A to Z, entry optional) |
A | Letter or digit (entry required) |
a | Letter or digit (entry optional) |
& | Any character or a space (entry required) |
C | Any character or a space (entry optional) |
. , : ; - / | Decimal placeholder and thousand, date and time separators (The actual character used depends on the settings in the Regional Settings Properties dialog box in the Windows Control Panel.) |
< | Causes all characters to be converted to lower case |
> | Causes all characters to be converted to upper case to right. You can include the exclamation point anywhere in the input mask. |
! | Causes the input mask to display from right to left, rather than from left to right. Characters typed into the mask always fill it from left to right. You can include the exclamation point anywhere in the input mask. |
\ | Causes the character that follows to be displayed as the literal character (for example, \A is displayed as just A) |
COMPUTER APPLICATIONS TECHNOLOGY P1 – SEPTEMBER 2020
INFORMATION SHEET (to be completed by the candidate AFTER the 3-hour session) SCHOOL:
NAME: ................................................................................ WORK STATION NUMBER: ................................................................................
SUITE USED | Microsoft Office 2010 | Microsoft Office 2013 | Microsoft Office 2016 | Office 365 |
WEB BROWSER USED (QUESTION 6) | Mozilla Firefox | Google Chrome | Internet Explorer | Other (Specify) |
FOLDER NAME:
Tick if saved and/or attempted.
Question Number | File name | Saved (√) | Attempted (√) | Maximum mark | Maximum achieved | Marker | HOD | Cluster | EM |
1 | 1_4th Industrial Revolution | 35 | |||||||
2 | 2_4IR Research | 15 | |||||||
3 | 3_Resources | 56 | |||||||
4 | 4_4IR | 42 | |||||||
5 | 5_Website | 21 | |||||||
6 | 6_Calculator 6_Quote | 11 | |||||||
TOTAL: | 180 | ||||||||
Comment (for marker use only)
....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
........................................................................................
Business Studies Paper 2 Grade 12 Questions - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- This question paper consists of THREE sections and covers TWO main topics.
SECTION A: COMPULSORY
SECTION B: Consists of THREE questions.
Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section.
SECTION C: Consists of TWO questions.
Answer any ONE of the two questions in this section. - Read the instructions for each question carefully and take particular note of what is required.
Note that ONLY the first TWO questions in SECTION B and the FIRST question in SECTION C will be marked. - Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper. NO marks will be awarded for answers that are numbered incorrectly.
- Except where other instructions are given, answers must be written in full sentences.
- Use the mark allocation and nature of each question to determine the length and depth of an answer.
- Use the table below as a guide for mark and time allocation when answering each question.
SECTION
QUESTION
MARKS
TIME
(minutes)
A: Objective-type questions COMPULSORY
1
30
30
B: THREE direct/indirect type questions
CHOICE:
Answer any TWO.
2
40
30
3
40
30
4
40
30
C: TWO essay-type questions CHOICE:
Answer any ONE.
5
40
30
6
40
30
TOTAL
150
120
- Begin the answer to EACH question on a NEW page, for example QUESTION 1 – new page, QUESTION 2 – new page.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.6 D.
1.1.1 Workers with low morale can be inspired by the insight and personality of … leaders.
- democratic
- autocratic
- laissez-faire
- charismatic
1.1.2 A visual presentation of a set of sales figures shown as a series of rectangles:
- Line graph
- Bar graph
- Table
- Diagram
1.1.3 Salon Mandy’s employees claimed from the … fund during the Covid-19 level 5 lockdown.
- unemployment insurance
- compensation for injuries and diseases
- road accident
- compensation
1.1.4 Collaboration means that team members ...
- do not rely on each other.
- work effectively on their own.
- are willing to co-operate in the team to achieve objectives.
- are held accountable for their actions.
1.1.5 The principle of the King Code where there must be regular communication between management and the stakeholders is referred to as …
- transparency.
- accountability.
- responsibility.
- discipline. (5 x 2) (10)
1.2 Complete the following statements by using the words provided in the list below. Write only the word(s) next to the question numbers (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
| discrimination; nominal group; dividends; conflict; subrogation; excess; capital gain; empty chair; inclusivity; grievance |
1.2.1 The portion of an insurance claim that Donald Traders must pay when the business lodges a claim, is referred to as …
1.2.2 Pablo bought shares at R10 each from Caller Mobile two years ago. The shares are now worth R20. This return on investment is called …
1.2.3 The … technique provides managers time to think about the question in silence before responding.
1.2.4 Lunga can lodge a … when he disagrees with the resolution taken by senior management.
1.2.5 Employing people from different backgrounds, is known as … (5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches a term in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–J) next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.3.6 K.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
1.3.1 | Leadership | A | employees open up to each other and confront each other's ideas |
1.3.2 | Liquidity | B | alternative solutions are generated and critically evaluated |
1.3.3 | Reinstatement | C | employees come to an agreement and reach consensus |
1.3.4 | Decision-making | D | applicable when property/goods are under-insured |
1.3.5 | Storming | E | controls systems and procedures to get the job done |
F | alternatives are considered before choosing the best one | ||
G | assets are sold to pay creditors due to a lack of capital or a cash flow problem | ||
H | applicable when property/goods are over-insured | ||
I | inspire staff to trust and support each other | ||
J | asset or security can quickly be bought or sold and can easily be converted into cash | ||
(5 x 2) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer ANY TWO questions in this section.
NOTE: Clearly indicate the QUESTION NUMBER of each question that you choose. The answer to EACH question must start on a NEW page, e.g. QUESTION 2 on a NEW page, QUESTION 3 on a NEW page.
QUESTION 2: BUSINESS VENTURES
2.1 State any TWO factors that should be considered when making investment decisions. (2)
2.2 Identify the leadership style applied by Mpilo (Pty) Ltd in EACH case below.
2.2.1 Mpilo ensures that employees are requested to give inputs during planning sessions. (2)
2.2.2 Employees are allowed to make their own decisions as long as they do not violate the company's policies. (2)
2.2.3 Employees are rewarded for meeting their targets and punished for not meeting deadlines. (2)
2.3 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
| Mzimasi bought a business property worth R500 000 and insured it forMzimasi bought a business property worth R500 000 and insured it forR200 000. Fire destroyed part of the property to the value of R50 000. |
2.3.1 Name the insurance clause that is applicable to the scenario above. (2)
2.3.2 Calculate the amount that Mzimasi will receive as a compensation from the insurer. Show ALL calculations. (4)
2.4 Explain TWO types of preference shares. (6)
2.5 Discuss the importance of insurance to businesses. (6)
2.6 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
| Lynnette inherited R50 000 from her late mother’s estate. She decided to invest the money in a fixed deposit at Safe Bank at 12% compounded interest per annum for two years. |
2.6.1 Define a fixed deposit as a type of investment. (2)
2.6.2 Calculate the amount of interest that Lynnette will receive after two years. Show ALL calculations. (4)
2.7 Suggest a situation in which an autocratic leadership style can be applied in a workplace. (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: BUSINESS ROLES
3.1 Name FOUR components of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR). (4)
3.2 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
KING SAWMILLS (KSM) King Sawmills manufacture household and industrial timber. KSM employs 50 employees and regular medical check-ups are conducted. The health of employees is attended to on a day-to day basis. KSM also provide safety training for employees to avoid accidents. |
3.2.1 Identify TWO roles of the health and safety representatives from the scenario above. (2)
3.2.2 Explain the responsibilities of employees in promoting health and safety in the workplace. (6)
3.3 Discuss the benefits of diversity in the workplace. (6)
3.4 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
MOZE & JOE EXPLORATION (MJE) Moze and Joe was awarded a tender for the exploration of natural gas along the south-east coast and the Karoo. Moze is interested in inviting a panel of experts to assess the impact of the project on the environment while Joe wants to list all the driving and restraining forces. |
3.4.1 Identify TWO problem-solving techniques applied by MJE. Motivate your answer by quoting from the scenario above.
Use the table below as a guide to answer QUESTION 3.4.1. (6)
PROBLEM-SOLVING TECHNIQUE | MOTIVATION |
1. | |
2. |
3.4.2 Discuss the advantages of ONE problem-solving technique identified in QUESTION 3.4.1. (4)
3.5 Describe how businesses can apply the brainstorming technique to solve complex business problems. (4)
3.6 Suggest ways in which businesses can deal with difficult employees in the workplace. (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: MISCELLANEOUS TOPICS
BUSINESS VENTURES
4.1 Give any TWO examples of non-verbal presentations. (2)
4.2 Identify the type of investment that were used by GG Engineers in each statement described below.
4.2.1 GG Engineers invested a minimum of R1 000 at a fixed rate to the fund with guaranteed returns, no risks attached. (2)
4.2.2 GG Engineers invested in a combination of different shares and securities managed by a fund manager. (2)
4.3 Outline the functions of the Johannesburg Securities Exchange (JSE). (4)
4.4 Discuss the following principles of insurance:
4.4.1 Indemnification (4)
4.4.2 Security (4)
BUSINESS ROLES
4.5 Classify EACH case below whether it represents an unethical or unprofessional business practice.
4.5.1 The sales representative of Queen Holdings plays computer games during working hours. (2)
4.5.2 Power Wheels advertised second-hand tyres as new. (2)
4.6 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
EKHAYA BUSH SAFARIS (EBS) Vusi is the human resource manager of Ekhaya Bush Safaris. EBS employed Kate, Judy and Simon as waiters. Vusi dislikes Simon and treats him differently from the two female employees. He seldom meets with his employees to give feedback. Simon is unhappy and intends to quit the job. |
4.6.1 Quote TWO causes of conflict from the scenario above. (2)
4.6.2 Advise EBS on how they should handle conflict in the workplace. (8)
4.7 Explain the implication of equality, respect and dignity on businesses. (4)
4.8 Discuss the advantages of creative thinking in the workplace. (4)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer ONE question in this section.
NOTE: Clearly indicate the QUESTION NUMBER of the question chosen. The answer to the question must start on a NEW page, e.g.
QUESTION 5 on a NEW page or QUESTION 6 on a NEW page.
QUESTION 5: BUSINESS VENTURES (PRESENTATION)
| Lindy, CEO of African Minerals Ltd, is planning to make a presentation at a business conference. She prepares PowerPoint slides and handouts to support her presentation. She is not a public speaker and lacks confidence in answering questions from the audience. |
With reference to the scenario above, write an essay on the following aspects:
- Outline the aspects that Lindy should consider when designing a multimedia presentation.
- Explain the factors that Lindy should keep in mind while presenting.
- Discuss the advantages of PowerPoint slides and handouts as types of visual aids.
- Advise Lindy on how to respond to questions after the presentation.
[40]
QUESTION 6: BUSINESS ROLES (SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY, CSR AND CSI)
| South Africa is facing many socio-economic issues that affect all its citizens. Many businesses are trying to solve these challenges by investing their time, money and skills in social programmes through corporate social investment (CSI). Corporate social responsibility encourages businesses to meet the requirements of the triple bottom line. |
Keeping the above statement in mind, write an essay on the following aspects:
- Outline the purpose of CSI.
- Explain the link between social responsibility and triple bottom line.
- Evaluate the impact of CSI on businesses.
- Suggest ways in which businesses can contribute time and effort in improving the well-being of employees.
[40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Business Studies Paper 1 Grade 12 Questions - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- This question paper consists of THREE sections and covers TWO of the main topics.
SECTION A: COMPULSORY
SECTION B: Consists of THREE questions
Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section.
SECTION C: Consists of TWO questions
Answer any ONE of the two questions in this section. - Read the instructions for each question carefully and take particular note of what is required.
Note that ONLY the first TWO questions in SECTION B and the FIRST question in SECTION C will be marked. - Number the answers carefully according to the numbering system used in this question paper. No marks will be awarded for answers that are numbered incorrectly.
- Except where other instructions are given, answers must be written in full sentences.
- Use the mark allocation and nature of each question to determine the length and depth of an answer.
- Use the table below as a guide for mark and time allocation when answering each question.
SECTION
QUESTION
MARKS
TIME
(minutes)
A: Objective-type questions COMPULSORY
1
30
20
B: THREE direct/indirect type questions
CHOICE:
Answer any TWO.
2
40
35
3
40
35
4
40
35
C: TWO essay-type questions CHOICE:
Answer any ONE.
5
40
30
6
40
30
TOTAL
150
120
- Begin the answer to EACH question on a NEW page, e.g. QUESTION 1 – new page, QUESTION 2 – new page, etc.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1–1.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.6 D.
1.1.1 This Act allows consumers access to debt counselling:
- Basic Conditions of Employment Act (BCEA), 1997 (Act 75 of 1997)
- Consumer Protection Act (CPA), 2008 (Act 68 of 2008)
- Labour Relations Act (LRA), 1995 (Act 66 of 1995)
- National Credit Act (NCA), 2005 (Act 34 of 2005)
1.1.2 Andile Leather Bags gives a written warranty for durable products. This consumer right is referred to as the right to …
- fair/honest dealings.
- fair value/good quality and safety.
- fair/just reasonable terms and conditions.
- accountability from suppliers.
1.1.3 This vertical integration strategy is used when a business combines with their supplier:
- Forward
- Backward
- Horizontal
- Concentric
1.1.4 The process of matching a new employee’s skills and abilities with the requirements of a job is known as …
- placement.
- recruitment.
- training.
- selection.
1.1.5 The … function ensures that all departments meet their deadlines.
- marketing
- purchasing
- general management
- production (5 x 2) (10)
1.2 Complete the following statements by using the word(s) provided in the list below. Write only the word(s) next to the question numbers (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
| quality assurance; Consumer Protection; management control; tertiary; Compensation for Occupational Injuries and Diseases; job analysis; secondary; quality control; ownership; human resources function |
1.2.1 Mandy’s Courier Services operates in the … sector as they specialise in rendering transport services to other businesses and individuals.
1.2.2 The … Act compels businesses to contribute monthly towards the Compensation Fund.
1.2.3 Epic Traders has appointed black people in senior executive positions Hereby they apply the … pillar of the BBBEE Act.
1.2.4 The … refers to the components of the job description and the job specification of a position.
1.2.5 Walter Clothing Manufacturer uses … when inspection is carried out during and after the production process to ensure that the required standards have been met at every stage of the process. (5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches a term in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–J) next to the question numbers (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.3.6 K.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
1.3.1 | BBBEE | A | an agreement between the employer and employee that is legally binding |
1.3.2 | National Skills Development Strategy | B | the process whereby a business compares the application documents against the requirements of the position |
1.3.3 | Recruitment | C | a policy that benefits only a few previously disadvantaged people in the economy |
1.3.4 | Employment contract | D | the ability to measure the specified standards of each department |
1.3.5 | Quality | E | provides access to training programmes |
F | an Act that is enforced and encourages a wider group of previously disadvantaged people to participate in the economy | ||
G | provides training material for facilitators | ||
H | an agreement between the employer, employee and trade union that is legally binding | ||
I | the ability of goods/services to meet the specific needs of customers | ||
J | the process whereby a business identifies a vacancy and attracts suitable candidates for the position | ||
(5 x 2) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer ANY TWO questions in this section.
NOTE: Clearly indicate the QUESTION NUMBER of each question that you choose. The answer to EACH question must start on a NEW page, e.g. QUESTION 2 on a new page, QUESTION 3 on a NEW page.
QUESTION 2: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS
2.1 Name any TWO types of defensive strategies. (2)
2.2 Outline the role of SETAs in supporting the Skills Development Act (SDA), 1998 (Act 97 of 1998). (8)
2.3 Read the scenario below and answer the question that follows.
SUPER SHOE MANUFACTURERS (SSM) Super Shoe Manufacturers is struggling to sell their shoes due to them being situated in a high crime area. The management of SSM devised a strategy that will assist them to respond to this challenge. Thereafter they put the strategy into action by using action plans. |
Identify the TWO steps in developing a strategy used by SSM. Motivate your answer by quoting from the scenario above.
Use the table below as a GUIDE to answer QUESTION 2.3.
STEPS IN DEVELOPING A STRATEGY | MOTIVATION |
| 1. | |
| 2. |
(6)
2.4 Explain the positive impact of the Broad-Based Black Economic Empowerment Act, 2003 (Act 53 of 2003) (BBBEE) on businesses. (6)
2.5 Discuss the following provisions of the Basic Conditions of Employment Act (BCEA), 1997 (Act 75 of 1997):
2.5.1 Hours of work/Working hours (4)
2.5.2 Overtime (4)
2.6 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
BLUE BERRY FARM (BBF) The management of Blue Berry Farm does not employ young women to work on the farm. They also do not appoint people with disabilities. |
2.6.1 Quote TWO ways in which Blue Berry Farm does not comply with the Employment Equity Act, (EEA) 1998 (Act 55 of 1998). (2)
2.6.2 Recommend practical ways in which BBF may comply with the EEA. (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: BUSINESS OPERATIONS
3.1 Give any FOUR examples of employee benefits. (4)
3.2 Read the scenario below and answer the question that follows.
KHAN DOORS (KD) Khan Doors specialises in the manufacturing of wooden doors. Mandisa gets paid R600 for each door she completes. Suki, the cleaner, gets paid R40/hour for performing her duties. |
Identify TWO types of salary determination methods used by Khan Traders that are applicable to Mandisa and Suki. Motivate your answer by quoting from the scenario above.
Use the table below as a GUIDE to answer QUESTION 3.2.
EMPLOYEE | TYPE OF SALARY DETERMINATION METHOD | MOTIVATION |
1. Mandisa | ||
2. Suki |
(6)
3.3 Explain the link between salary determination and the Basic Conditions of Employment Act (BCEA), 1997 (Act 75 of 1997). (4)
3.4 Discuss the advantages of external recruitment as a method of recruitment. (4)
3.5 Identify the total quality management (TQM) elements applied by Johan Traders in EACH case below.
3.5.1 The employees regularly attend training courses on service delivery. (2)
3.5.2 The management of Johan Traders always request their buyers to complete a questionnaire on the quality of their products and services. (2)
3.6 Elaborate on the meaning of total quality management (TQM). (4)
3.7 Discuss the advantages of a good quality management system. (6)
3.8 Suggest ways in which TQM can reduce the cost of quality. (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: MISCELLANEOUS TOPICS
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS
4.1 Name THREE types of business environments and state the extent of control businesses have over EACH of these environments.
Use the table below as a GUIDE to answer QUESTION 4.1.
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS | EXTENT OF CONTROL | |
1. | ||
2. | ||
3. | ||
(6)
4.2 Outline the rights of employees according to the Labour Relations Act (LRA), 1995 (Act 66 of 1995). (6)
4.3 Explain how businesses could apply the following forces from the Porter’s Five Forces model to analyse their position in the market:
4.3.1 Bargaining power of suppliers/Power of suppliers (4)
4.3.2 Power of competitors/Competitive rivalry (4)
BUSINESS OPERATIONS
4.4 List any FOUR sources of internal recruitment. (4)
4.5 Discuss reasons for the termination of an employment contract. (6)
4.6 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
WILLIAMS MOTOR MANUFACTURERS (WMM) The employees of Williams Motor Manufacturers meet regularly to investigate problems and suggest solutions to the management. They also monitor strategies to improve the smooth running of business operations. |
4.6.1 Quote TWO roles of quality circles as part of continuous improvement of processes and systems to improve the quality of products at WMM. (2)
4.6.2 Advise WMM on how to apply the PDCA model to improve the quality of products. (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer ONE question in this section.
NOTE: Clearly indicate the QUESTION NUMBER of each question chosen. The answer to the question must start on a NEW page, e.g. QUESTION 5 on a NEW page or QUESTION 6 on a NEW page.
QUESTION 5: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS (STRATEGIES)
| The business environments pose many challenges to business operations; therefore, it is important for businesses to use strategies to overcome these challenges. Businesses can also use the PESTLE analysis to understand these challenges better and to find ways in which businesses can deal with them. The evaluation of these strategies forms a vital part of the strategic management process. |
Write an essay on business strategies in which you include the following aspects:
- Describe the THREE types of intensive strategies that businesses may use to address challenges in the macro environment.
- Discuss the advantages of diversification strategies.
- Explain how the following PESTLE elements/factors may pose challenges to businesses:
- Social
- Technological
- Legal
- Advise businesses on the steps they should consider when evaluating strategies.
[40]
QUESTION 6: BUSINESS OPERATIONS (HUMAN RESOURCES)
| Mega Consultants (MC) ensures that their selection process is well structured. The human resources manager has an important role to play in preparing for the interviewing of candidates. MC offers a comprehensive induction programme and also fringe benefits to new employees which impacts the business. |
Write an essay on human resources in which you address the following aspects:
- Outline the selection procedure as a human resource activity.
- Explain the role of the interviewer before the interview.
- Discuss the advantages of induction for businesses.
- Evaluate the impact of fringe benefits on businesses.
[40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Business Studies Paper 2 Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
NOTES TO MARKERS
- PREAMBLE
The notes to markers are provided for quality assurance purposes to ensure the following:- Fairness, consistency and reliability in the standard of marking
- Facilitate the moderation of candidates' scripts at different levels
- Streamline the marking process considering the broad spectrum of markers across the country
- Implement appropriate measures in the teaching, learning and assessment of the subject at schools/institutions of learning
- Candidates’ responses must be in full sentences for SECTIONS B and C. However, this would depend on the nature of the question.
- A comprehensive marking guideline has been provided but this is by no means exhaustive. Due consideration should be given to an answer that is correct, but:
- Uses a different expression from that which appears in the marking guidelines
- Comes from another credible source
- Original
- A different approach is used
NOTE: There is only ONE correct answer in SECTION A.
- Take note of other relevant answers provided by candidates and allocate marks accordingly. (In cases where the answer is unclear or indicates some understanding, part-marks should be awarded, for example, one mark instead of the maximum of two marks.)
- The word ‘Sub max’ is used to facilitate the allocation of marks within a question or sub-question.
- The purpose of circling marks (guided by ‘max’ in the breakdown of marks) on the right-hand side is to ensure consistency and accuracy in the marking of scripts as well as for calculation and moderation purposes.
- Subtotals to questions must be written in the right-hand margin. Circle the subtotals as indicated by the allocation of marks. This must be guided by ‘max’ in the marking guideline. Only the total for each question should appear in the left-hand margin next to the appropriate question number.
- In an indirect question, the theory as well as the response must be relevant and related to the question.
- Correct numbering of responses to questions is recommended in SECTION A and B. However, if the numbering is incorrect, follow the sequence of the candidate’s responses. Candidates will be penalised if the latter is not clear.
- No additional credit must be given for repetition of facts. Indicate with an R.
- The differentiation between 'evaluate' and 'critically evaluate' can be explained as follows:
11.1 When 'evaluate' is used, candidates are expected to respond in either a positive/negative manner or take a neutral (positive and negative) stance, e.g. Positive: 'COIDA eliminates time and costs spent on lengthy civil court proceedings.'
11.2 When 'critically evaluate' is used, candidates are expected to respond in either a positive/negative manner or take a neutral (positive and negative) stance. In this instance, candidates are also expected to support their responses with more depth, e.g. 'COIDA eliminates time and costs spent on lengthy civil court proceedings, because the employer will not be liable for compensation to the employee for injuries sustained during working hours as long as it can be proved that the business was not negligent.'
NOTE:- The above could apply to 'analyse' as well.
- Note the placing of the tick () in the allocation of marks.
- The allocation of marks must be informed by the nature of the question, cognitive verb used, mark allocation in the marking guidelines and the context of each question.
Cognitive verbs, such as:
12.1 Advise, name, state, mention, outline, motivate, recommend, suggest, (list not exhaustive) do not usually require much depth in candidates' responses. Therefore, the mark allocation for each statement/answer appears at the end.
12.2 Define, describe, explain, discuss, elaborate, compare, distinguish, compare, tabulate, differentiate, justify, analyse, evaluate, critically evaluate (list not exhaustive) require a greater depth of understanding, application and reasoning. Therefore, the marks must be allocated more objectively to ensure that assessing is conducted according to established norms so that uniformity, consistency and fairness are achieved. - Mark only the FIRST answer where candidates offer more than one answer for SECTION B and C questions that require one answer.
- SECTION B
14.1 If for example, FIVE facts are required, mark the candidate’s FIRST FIVE responses and ignore the rest of the responses. Indicate by drawing a line across the unmarked portion or use the word ‘Cancel’.
NOTE: This only applies to questions where the number of facts is specified.
14.2 If two facts are written in one sentence, award the candidate FULL credit. Point 14.1 above still applies.
14.3 If candidates are required to provide their own examples/views, brainstorm this to come up with alternative answers.
14.4 Use of the cognitive verbs and allocation of marks:
14.4.1 If the number of facts is specified, questions that require candidates to 'describe/discuss/explain' may be marked as follows:- Fact 2 marks (or as indicated in the marking guideline)
- Explanation 1 mark (two marks will be allocated in Section C)
The 'fact' and 'explanation' are given separately in the marking guidelines to facilitate mark allocation.
14.4.2 If the number of facts required is not specified, the allocation of marks must be informed by the nature of the question and the maximum mark allocated in the marking guidelines.
14.5 ONE mark may be awarded for answers that are easy to recall, requires one-word answers or is quoted directly from a scenario/case study.
This applies to SECTIONS B and C in particular (where applicable).
- SECTION C
15.1 The breakdown of the mark allocation for the essays is as follows:
15.2 Insight consists of the following components:Introduction
Maximum: 32
Content
Conclusion
Insight
8
TOTAL
40
NOTE:Layout/Structure
Is there an introduction, a body, and a conclusion?
2
Analysis and interpretation
Is the candidate able to break down the question into headings/subheadings/interpret it correctly to show understanding of what is being asked?
2
Marks to be allocated using this guide:
All headings addressed: 1 (One 'A')
Interpretation (16 to 32 marks): 1 (One 'A')Synthesis
Are there relevant decisions/facts/responses made based on the questions?
2
Marks to be allocated using this guide:
No relevant facts: 0 (Two '-S')
Some relevant facts: 1 (One '-S')
Only relevant facts: 2 (No '-S')Option 1:
Where a candidate answers 50% or more of the question with only relevant facts; no '-S' appears in the left margin. Award the maximum of TWO (2) marks for synthesis.
Option 2:
Where a candidate answers less than 50% of the question with only OR some relevant facts; one '-S' appears in the left margin. Award a maximum of ONE (1) mark for synthesis.
Option 3:
Where a candidate answers less than 50% of the question with no relevant facts; two
'-S' appear in the left margin. Award a ZERO mark for synthesis.
Originality
Is there evidence of examples based on recent information, current trends and developments?
2
TOTAL FOR INSIGHT:
TOTAL MARKS FOR FACTS:
TOTAL MARKS FOR ESSAY (8 + 32):
8
32
40
- No marks will be awarded for contents repeated from the introduction and conclusion
- The candidate forfeits marks for layout if the words INTRODUCTION and CONCLUSION are not stated.
- No marks will be allocated for layout, if the headings ‘INTRODUCTION and CONCLUSION are not supported by an explanation.
15.3 Indicate insight in the left-hand margin with a symbol e.g. (‘L, A, -S and/or O’).
15.4 The breakdown of marks is indicated at the end of the suggested answer/ marking guidelines to each question.
15.5 Mark all relevant facts until the SUBMAX/MAX mark in a subsection has been attained. Write SUBMAX/MAX after maximum marks have been obtained but continue reading for originality “O”.
15.6 At the end of each essay, indicate the allocation of marks for facts and marks for insight as follows: (L – Layout, A – Analysis, S – Synthesis, O – Originality) as in the table below.
15.7 When awarding marks for facts, take note of the sub-maxima indicated, especially if candidates do not make use of the same subheadings. Remember headings and sub-headings are encouraged and contribute to insight (structuring/logical flow/sequencing) and indicate clarity of thought.CONTENT
MARKS
Facts
32 (max.)
L
2
A
2
S
2
O
2
TOTAL
40
(See MARKS BREAKDOWN at the end of each question.)
15.8 If the candidate identifies/interprets the question INCORRECTLY, then he/she may still obtain marks for layout.
15.9 If a different approach is used by candidates, ensure that the answers are assessed according to the mark allocation/subheadings as indicated in the memorandum.
15.10
15.10.1 Award TWO marks for complete sentences. Award ONE mark for phrases, incomplete sentences and vague answers.
15.10.2 With effect from November 2015, the TWO marks will not necessarily appear at the end of each completed sentence. The ticks () will be separated and indicated next to each fact, e.g. ‘Product development is a growth strategy/where business aim to introduce new products into existing markets.’
This will be informed by the nature and context of the question, as well as the cognitive verb used.
15.11 With effect from November 2017, the maximum of TWO (2) marks for facts shown as headings in the memo, will not necessarily apply to each question. This would also depend on the nature of the question.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 D
1.1.2 B
1.1.3 A
1.1.4 C
1.1.5 B (5 x 2) (10)
1.2
1.2.1 excess
1.2.2 capital gain
1.2.3 nominal group
1.2.4 grievance
1.2.5 inclusivity (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 I
1.3.2 J
1.3.3 H
1.3.4 F
1.3.5 A (5 x 2) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS
QUESTION 1 | MARKS |
1.1 | 10 |
1.2 | 10 |
1.3 | 10 |
TOTAL | 30 |
SECTION B
Mark the FIRST TWO answers only.
QUESTION 2: BUSINESS VENTURES
2.1 Factors to be considered when making investment decisions
- Return on investment (ROI)
- Risk
- Investment term/period
- Inflation rate
- Taxation
- Liquidity
- Personal budget
- Investment planning factors
- Volatility/Fluctuation on investment markets.
- Any other relevant answer related to the factors that must be considered when making investment decision.
NOTE: Mark the first TWO (2) only. (2 x 1) (2)
2.2 Leadership styles
2.2.1 Democratic
2.2.2 Liassez-fair/free reign
2.2.3 Transactional (6)
2.3 Insurance
2.3.1 Average clause (2)
2.3.2
- Amount insured x Amount of damages/loss
Value of insured item
R200 000 × R50 000
R500 000
= R20 000 (4)
NOTE:
- Allocate full marks (4) if the answer is correct and no workings are shown.
- If workings were shown correctly, but the final answer is wrong, award a maximum of TWO(2) marks.
- If the answer is incorrect, award a maximum of ONE mark for the understanding of concept and method.
2.4 Types of preference shares
Participating preference shares
Shareholders:
- are guaranteed minimum fixed dividends.
- are entitled to share in any surplus company profits.
- receive higher dividends when the company performs well.
- have preferential rights over ordinary shares on repayment when the company closes down.
- Any other relevant answer related to participating preference shares.
Identification (2)
Explanation (1)
Sub-max. (3)
Non-participating preference shares
Shareholders:
- receive an amount equal to the initial investment plus accrued and unpaid dividends upon liquidation.
- do not have a right to participate in profits after equity shareholders have been paid a dividend.
- will not get extra dividend in case of surplus profits.
- are entitled to receive only a fixed rate of dividend every year.
- Any other relevant answer related to non-participating preference shares.
Identification (2)
Explanation (1)
Sub-max. (3)
Cumulative preference shares
- Shareholders are compensated for past dividends that were not paid out when profits were too low to declare dividends/Receive dividends not previously paid out.
- Any other relevant answer related to cumulative preference shares.
Identification (2)
Explanation (1)
Sub-max. (3)
Non-cumulative preference shares
- Shareholders are not compensated for past dividends that were not paid out when profits were low.
- Any other relevant answer related to non-cumulative preference shares.
Identification (2)
Explanation (1)
Sub-max. (3)
Redeemable preference shares
- Shares can be redeemed/bought back at the option of the issuing company, either at a fixed price on a specified date/over a certain period of time.
- Any other relevant answer related to redeemable preference shares.
Identification (2)
Explanation (1)
Sub-max. (3)
Non-redeemable preference shares
- Shares are only bought back when the company closes down for reasons other than bankruptcy.
- Any other relevant answer related to non-redeemable preference shares.
Identification (2)
Explanation (1)
Sub-max. (3)
Convertible preference shares
- Shares can be converted into a predetermined number of ordinary shares on the date specified when the preference shares were issued.
- Any other relevant answer related to convertible preference shares.
Identification (2)
Explanation (1)
Sub-max. (3)
Non-convertible preference shares
- Shares cannot be converted into ordinary shares.
- Any other relevant answer related to non-convertible preference shares.
Identification (2)
Explanation (1)
Sub-max. (3)
NOTE: Mark the first TWO (2) only.
Types (4)
Explanation (2)
Max. (6)
2.5 Importance of insurance for businesses
- Transfers the risk from the business/insured to an insurance company/insurer.
- Transfer of risk is subject to the terms and conditions of the insurance contract.
- Protects the business against theft/loss of stock and/or damages caused by natural disasters such as floods, storm damage, etc.
- The business will be compensated for insurable losses, e.g. destruction of property through fire.
- Business assets, e.g. vehicles/equipment/buildings need to be insured against damage and/or theft.
- Business is protected against the loss of earnings, e.g. strikes by employees which result in losses worth millions.
- Protects the business against dishonest employees.
- Life insurance can be taken on the life of partners in a partnership to prevent unexpected loss of capital.
- Should the services of key personnel be lost due to accidents/death, the proceeds of an insurance policy can be paid out to the business/beneficiaries.
- Replacement costs for damaged machinery/equipment are very high therefore insurance can reduce/cover such costs.
- Protects a business from claims made by a member of the public for damages that the business is responsible for.
- Protects the business against losses due to death of a debtor.
- Any other relevant answer related to the importance of insurance to businesses.
Max. (6)
2.6 Investment securities
2.6.1 Fixed deposit
- A conservative method of investment at a fixed rate for a fixed period /at a financial institution/bank.
- Interest is earned at a fixed rate regardless of changes in the economic climate.
- Any other relevant answer related to defining a fixed deposit as a type of investment. (2)
2.6.2 Compound interest
Option 1
- FORMULA: P x (1 + r)n
R50 000 x (1+12/100)2
R50 000 x (1,12)2 = R37 632
Total interest = R62 720 - R50 000
= R12 720
Option 2
- Year 1: R50 000 x 12% = R6 000
Year 2: R56 000 x 12% = R6 720
Total interest = R12 720
NOTE:
- Allocate full marks (4) if the answer is correct and no workings are shown.
- If workings were shown correctly, but the final answer is wrong, award a maximum of THREE marks.
- If the answer is incorrect, award a maximum of ONE mark for the understanding of concept and method. (4)
2.7 Situations in which the autocratic leadership style can be applied
- In crisis situations, e.g. in the case of unforeseen challenges/accidents.
- When all the information is available to solve the problem.
- In emergencies, where there is a shortage of time.
- When employees are motivated and the leader has already earned the trust of the followers.
- When dealing with employees who are not cooperative.
- When employees are new/not fully trained.
- Any other relevant answer related to situations in which the autocratic leadership style can be applied.
Max. (8)
[40]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS
QUESTION 2 | MARKS |
2.1 | 2 |
2.2 | 6 |
2.3.1 | 2 |
2.3.2 | 4 |
2.4 | 6 |
2.5 | 6 |
2.6.1 | 2 |
2.6.2 | 4 |
2.7 | 8 |
TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 3: BUSINESS ROLES
3.1 Components of CSR
- Environment/Environmental awareness
- Ethical corporate social investment
- Health and safety
- Corporate governance
- Business ethics
- Employment equity
- Supply chain
- Customers
- Community
- Any other relevant answer related to the components of CSR.
NOTE: Mark the first FOUR (4) only. (4 x 1) (4)
3.2 Health and safety representatives
- Roles of health and safety representatives from the scenario
3.2.1
- Regular medical check-ups are conducted.
- The health of employees is attended to on a day-to-day basis.
- KSW also provides safety training for employees to avoid accidents.
NOTE: Mark the first TWO (2) only. (2 x 1) (2)
3.2.2 Responsibilities of employees in promoting health and safety in the workplace
- Must take care of their own health and safety in the workplace.
- Co-operate and comply with the rules and procedures e.g. wear prescribed safety clothing.
- Report unsafe or unhealthy conditions.
- Report accidents to the employer by the end of the shift.
- Use prescribed safety equipment.
- Take reasonable care of their own safety.
- Inform the employer of any illness that may affect the ability to work.
- Any other relevant answer related to the responsibilities of employees in promoting health and safety in the workplace.
Max. (6)
3.3 Benefits of diversity in the workplace
- Workforce diversity improves the ability of a business to solve problems/innovate/cultivate diverse markets.
- Employees value each other's diversity and learn to connect/communicate across lines of difference.
- Diversity in the workforce improves morale/motivation.
- Employees demonstrate greater loyalty to the business because they feel respected/accepted/understood.
- Diversified workforce can give businesses a competitive advantage as they can render better services.
- Being respectful of differences/demonstrating diversity makes good business sense/improves profitability.
- Diverse businesses ensure that its policies/practices empower every employee to perform at his/her full potential.
- Stakeholders increasingly evaluate businesses on how they manage diversity in the workplace.
- Employees from different backgrounds can bring different perspectives to the business.
- A diversified workforce stimulates debate on new/improved ways of getting things done.
- Employees represent various groups and are therefore better able to recognise customer needs and satisfy consumers.
- Businesses with a diverse workforce are more likely to have a good public image and attract more customers.
- Any other relevant answer related to the benefits of diversity in the workplace.
Max. (6)
3.4 Problem-solving
3.4.1 Problem-solving techniques from the scenario
PROBLEM-SOLVING TECHNIQUE | MOTIVATION | |
Delphi | Moze is interested in inviting a panel of experts to assess the impact of the project on the environment. | |
Force-field analysis | Joe wants to list all the driving and restraining forces. | |
| Sub-max. (4) | Sub-max. (2) | |
NOTE:
- Do not award marks for motivation if the problem- solving technique is incorrectly identified.
- Award marks for problem-solving even if the quote is incomplete.
Max. (6)
3.4.2 Advantages of Delphi technique or Force-field analysis
Advantages of the Delphi technique
- Businesses save time/costs when using a group of experts without bringing them together.
- Experts will give clear ideas/solutions on how to improve on low productivity/ profitability.
- Panel members/Experts can give new information on problems.
- Information received from experts can be kept confidential.
- It reduces noise levels in an office environment since there is no group discussion.
- Panel members/Experts need to reach consensus, so that the best solution is found.
- All experts are given an equal opportunity to give their opinions, so no-one dominates the process.
- Any other relevant answer related to the advantages of the Delphi technique in solving business problems.
Max. (4)
OR
Force-field analysis
- It provides a visual summary of all the various factors supporting and opposing a particular idea.
- Employees feel included and understood.
- Employees develop and grow with the business.
- Informed decisions can be made as forces for and against are critically evaluated.
- Enables businesses to strengthen the driving forces and weaken the restraining forces.
- Businesses are able to have an idea of the timeline required and the requirements of additional resources.
- Any other relevant answer related to the advantages of force- field analysis.
Max. (4)
3.5 Application of the brainstorming technique
- State/Define the business problem clearly, so that all participants/stakeholders understand the problem.
- Members state possible causes of the business problems.
- Set a time limit for each brainstorming session.
- Record/Write ideas down where all participants can see it. /Ideas may also be shared online during an e-brainstorming session.
- Use each suggestion to inspire new thoughts/ideas.
- Do not judge/criticise/discuss the ideas, so that many ideas could be generated as quickly as possible.
- All members of the group randomly make suggestions.
- The group rates ideas according to its usefulness/success/ difficulty/cost to implement.
- The group evaluates all ideas and combines similar ones/draw up a refined list.
- Discuss a plan of action on how to implement the best ideas.
- Any other relevant answer related to the application of the brainstorming technique to solve business problems.
NOTE:
- Do not allocate marks for advantages and disadvantages.
- Steps could be in any order.
Max. (4)
3.6 Ways in which businesses can deal with difficult employees in the workplace
OPTION 1
- Get perspective from others who have experienced the same kind of situation to be able to understand difficult employees.
- Act pro-actively if possible, as a staff/personnel problem is part of a manager's responsibilities.
- Regular meetings with supervisors/departmental heads should help to identify difficult/problem behaviour.
- Ask someone in authority for their input into the situation.
- Identify the type of personality which is creating the problem.
- Meet privately with difficult employees, so that there are no distractions from other employees/issues.
- Make intentions and reasons for action known, so that the difficult person/people feel at ease.
- Employees should be told what specific behaviours are acceptable by giving details about what is wrong/unacceptable and also an opportunity to explain their behaviour.
- A deadline should be set for improving bad/difficult behaviour.
- The deadline date should be discussed with the difficult employee and his/her progress should be monitored/assessed prior to the deadline.
- Guidelines for improvement should be given.
- Do not judge the person, but try to understand him/her and understand his/her intentions and why he/she reacts in a certain way.
- Keep communication channels open/Encourage employees to communicate their grievances to management.
- Build rapport/sound relations by re-establishing personal connection with colleagues, instead of relying on e-mails/messaging/social media.
- Help difficult employees to be realistic about the task at hand.
- Remain calm and in control of the situation to get the person(s) to collaborate.
- Treat people with respect, irrespective of whether they are capable/competent or not.
- Sometimes it may be necessary to ignore and only monitor a difficult person.
- Identify and provide an appropriate support program to address areas of weakness.
- Any other relevant answer related to how businesses can deal with difficult people/personalities in the workplace.
AND/OR
OPTION 2 (Personalities)
Type of personality Strategy to deal with a personality
Type of personality | Strategy to deal with a personality |
Complainer |
|
Indecisiveness |
|
Over agree |
|
Negativity |
|
Experts |
|
Quiet |
|
Aggressive |
|
NOTE:
OPTION 2
- Allocate a maximum of THREE (3) marks for only identifying the type of personality without a strategy.
- Allocate TWO (2) marks for indicating the strategy without identifying the type of the personality/Take particular note of overlap of strategies.
Max. (8)
[40]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS
QUESTION 3 | MARKS |
3.1 | 4 |
3.2.1 | 2 |
3.2.2 | 6 |
3.3 | 6 |
3.4.1 | 6 |
3.4.2 | 4 |
3.5 | 4 |
3.6 | 8 |
TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 4: MISCELLANEOUS TOPICS
BUSINESS VENTURES
4.1 Examples of non-verbal presentations
- Tables
- Graphs/bar graph/line graph/histogram/pie graph
- Diagrams
- Illustrations/Pictures/Photographs/Scenarios
- Written/Business reports
- Flip charts
- Handouts
- Slide shows
- Any other relevant answer related to example of non-verbal presentations.
NOTE: Mark the first TWO (2) only. (2 x 1) (2)
4.2 Types of investments
4.2.1 RSA retail savings bond
4.2.2 Unit trusts (4)
4.3 Functions of the Johannesburg Securities Exchange
- Gives opportunities to financial institutions such as insurance companies to invest their funds in shares.
- Serves as a barometer/indicator of economic conditions in South Africa.
- Keeps investors informed on share prices by publishing the share prices daily.
- Acts as a link between investors and public companies.
- Shares are valued and assessed by experts.
- Small investors are invited to take part in the economy of the country through the buying/selling of shares.
- Venture capital market is made available on the open market.
- Orderly market for securities serves as a disciplined market for securities.
- Encourages new investments in South African companies.
- Mobilises the funds of insurance companies and other institutions.
- Raises primary capital.
- Regulates the market for dealing with shares.
- Plans, researches and advises on investment possibilities.
- Ensures that the market operates in a transparent manner.
- Provides protection for investors.
- Encourages short-term investment.
- Facilitates electronic trading of shares/STRATE.
- Any other relevant answer related to the functions of the Johannesburg Securities Exchange (JSE).
Max. (4)
4.4 Principles of insurance
4.4.1 Indemnification/Indemnity
- Usually applies to short term insurance, as the insured is compensated for specified/proven harm/loss.
- Insurer agrees to compensate the insured for damages/losses specified in the insurance contract , in return for premiums paid by the insured to the insurer.
- Protects the insured against the specified event that may occur.
- Pay-outs from insurance companies/insurer will only be made if there is proof that the specified event took place/if the insured can prove the amount of the loss/damage.
- The amount of indemnification/compensation is limited to the amount of provable loss/damage even if the amount in the policy/insurance contract is higher.
- The insured must be placed in the same position as before the occurrence of the loss/damage. /The insured may not profit from insurance.
- Any other relevant answer related to indemnification/indemnity as a principle of insurance.
Max. (4)
4.4.2 Security/Certainty
- Applies to long-term insurance where the insurer undertakes to pay out an agreed upon amount in the event of a loss of life.
- A predetermined amount will be paid out when the insured reaches a pre-determined age /or gets injured due to a predetermined event.
- Aims to provide financial security to the insured at retirement/the dependents of the deceased.
- Any other relevant answer related to security/certainty as a principle of insurance.
Max. (4)
BUSINESS ROLES
4.5 Unethical and unprofessional business practices
4.5.1 Unprofessional (2)
4.5.2 Unethical (2)
4.6 Conflict
4.6.1 Causes of conflict from the scenario
- Vusi dislikes Simon and treats him differently from the two female employees.
- He seldom meets with his employees to give feedback.
- Simon is unhappy and intends to quit his job.
NOTE: Mark the first TWO (2) only. (2 x 1) (2)
4.6.2 Handling of conflict in the workplace
- Acknowledge that there is conflict in the workplace.
- Identify the cause(s) of the conflict.
- Pre-negotiations may be arranged where workers/complainants will be allowed to state their case/views separately.
- A time and place are arranged for negotiations where all employees involved are present.
- Arrange a meeting between conflicting employers/employees.
- Make intentions for intervention clear so that parties involved may feel at ease.
- Each party has the opportunity to express his/her own opinions/feelings/Conflicting parties may recognise that their views are different.
- Analyse the cause(s) of conflict by breaking it down into different parts/Evaluate the situation objectively.
- Blame shifting should be avoided and a joint effort should be made.
- Direct conflicting parties towards finding/focusing on solutions.
- Devise/Brainstorm possible ways of resolving the conflict.
- Conflicting parties agree on criteria to evaluate the alternatives.
- The best possible solution(s) is/are selected and implemented.
- Parties must agree to on the best solution.
- Evaluate/Follow up on the implementation of the solution(s).
- Monitor progress to ensure that the conflict has been resolved.
- Expertise on handling conflict maybe sourced from outside the business.
- Any other relevant answer related to how businesses should handle conflict in the workplace.
NOTE: If problem solving steps do not demonstrate the handling of conflict (explanation), award a maximum of TWO (2) marks only.
Max. (8)
4.7 Implication of equality, respect and on businesses
- Businesses should treat all their employees equally regardless of their race/colour/age/gender/disability , etc.
- All workers should have access to equal opportunities/positions/ resources.
- Employers and employees need to comply with legislation with regard to equal opportunities/human rights in the workplace.
- Businesses should develop equity programmes/promote strategies to ensure that all employees are treated equally regardless of status/rank/power.
- Mission statement should include values of equality/respect.
- Training/Information/Business policies should include issues such as diversity/ discrimination/harassment.
- Employers should respond swiftly and fairly to reported incidents of discrimination in the workplace.
- Ensure that employees work in an environment that is conducive to safety/ fairness/free from embarrassment.
- Orders/Tasks should be given respectfully and allow the recipient/employee to have a say in the manner in which the task should be performed.
- Treat workers with respect/dignity by recognising work well done/the value of human capital.
- Any other relevant answer related to the implications of equality, respect and dignity for businesses.
Max. (4)
4.8 Advantages of creative thinking in the workplace
- Better/Unique/Unconventional ideas/solutions are generated.
- May give the business a competitive advantage if unusual/unique solutions/ ideas/strategies are implemented.
- Complex business problems may be solved.
- Productivity increases as management/employees may quickly generate multiple ideas which utilises time and money more effectively.
- Managers/Employees have more confidence as they can live up to their full potential.
- Managers will be better leaders as they will be able to handle/manage change(s) positively and creatively.
- Managers/Employees can develop a completely new outlook which may be applied to any task(s) they may do.
- Leads to more positive attitudes as managers/employees feel that they have contributed towards problem solving.
- Improves motivation amongst staff members.
- Managers/Employees have a feeling of great accomplishment and they will not resist/obstruct the process once they solved a problem/contributed towards the success of the business.
- Management/employees may keep up with fast changing technology.
- Stimulates initiative from employees/managers , as they are continuously pushed out of their comfort zone.
- Creativity may lead to new inventions which improves the general standard of living.
- Any other relevant answer related to the advantages of creative thinking in the workplace.
Max. (4)
[40]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS
QUESTION 4 | MARKS |
4.1 | 2 |
4.2 | 4 |
4.3 | 4 |
4.4 | 8 |
4.5 | 4 |
4.6.1 | 2 |
4.6.2 | 8 |
4.7 | 4 |
4.8 | 4 |
TOTAL | 40 |
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Mark only the FIRST answer in this section.
QUESTION 5: BUSINESS VENTURES (PRESENTATION)
5.1 Introduction
- The purpose of a presentation is to exchange information as it involves speaking and listening for both the presenter and the audience.
- An effective presentation is one in which the desired outcome is achieved.
- Various factors need to be considered when designing a multimedia presentation to make it effective/eye-catching/memorable.
- PowerPoint enables the presenter to elaborate on important facts.
- Handouts are presented in a booklet/sheet of paper on which information is shown.
- When responding to audience questions/remarks, the presenter should not be aggressive/defensive.
- Any other relevant introduction related to the aspects that should be considered when designing a multimedia presentation / factors kept in mind while presenting/ advantages of PowerPoint and handouts as types of visual aids/ how to respond to questions after the presentation.
(Any 2 x 1) (2)
5.2 Aspects of designing a multimedia presentation
- Use legible font and font size.
- Start with the text.
- Keep the text/images/language simple.
- Structure information in logical order.
- Limit information on a slide.
- Make sure there are no spelling mistakes.
- Use bright colours to increase visibility.
- Use pictures to make it interesting for the audience.
- Select a relevant/appropriate background.
- Choose images that help communicate your message.
- Create clear/relevant graphics.
- Add special effects, e.g. sound/animation.
- Create hyperlinks to allow access to files/other slides/video clips.
- Any other relevant answer related to the aspects that must be considered when designing a multimedia presentation.
Max. (10)
5.3 Factors to be considered while/during presentation
- Lindy should establish credibility by introducing herself at the beginning of the presentation.
- Do not ramble on at the start to avoid losing the audience/their interest.
- Stand in a good position/upright where the audience can clearly see the presenter/presentation.
- Make the purpose/main points of the presentation clear at the start of the presentation.
- Use suitable section titles/headings/subheadings/bullets to simplify the presentation.
- Mention/Show most important information first.
- Add some appropriate humour in the presentation.
- Avoid hiding behind equipment as it may give an impression of uncertainty.
- Capture listeners' attention/Involve the audience with a variety of methods, e.g. short video clips/sound effects/humour, etc.
- She should make eye contact with the audience and look in all directions.
- Be audible to all listeners/audience to keep them focused.
- Vary the tone of voice/tempo within certain sections to prevent monotony.
- Make the presentation interesting with visual aids/anecdotes/examples/ Use visual aids effectively.
- Use appropriate gestures, e.g. use hands to emphasize points.
- Speak with energy and enthusiasm.
- Pace yourself and do not rush/talk too slowly.
- Keep the presentation short/simple to avoid repetition of facts.
- Manage time effectively to allow time for questions.
- Ensure that the audience will leave with/take away specific information/ benefits.
- Summarise the main points of the presentation to conclude the presentation.
- Conclude/End with a strong/striking ending that will be remembered.
- Any other relevant answer related to the factors to be considered while presenting.
Max. (12)
5.4 Visual aids
5.4.1 Advantages of PowerPoint slides
- Graphic programmes have the capacity to convey ideas and support what the presenter says.
- Easy to combine with sound/video clips.
- Simple/Less cluttered slides may capture the interest of the audience.
- Video clips can provide variety and capture the attention of the audience.
- Variations of colour/background/sound immediately capture the attention of the audience and retain their interest throughout the presentation.
- Slides should only be used where they can enhance the facts or summarise information.
- PowerPoint slides can help to convey a large amount of facts in a short time.
- Any other relevant answer related to the advantages of PowerPoint slides as a type of visual aid.
Sub-max. (8)
Advantages of hand-outs
- Meaningful hand-outs may be handed out at the start of the presentation to attract attention/encourage participation.
- Notes/Hard copies of the slide presentation can be distributed at the end of the presentation as a reminder of the key facts of the presentation.
- Extra information, e.g. contact details/price lists may be handed out to promote the services of the business.
- Useful information for improving the next presentation may be obtained when the audience completes feedback questionnaires after the presentation.
- It is easy to update handouts with recent information or developments.
- Notes may be compared with electronic slides to validate the accuracy.
- Any other relevant answer related to the advantages of handouts as a visual aid.
Sub-max. (8)
Max. (16)
5.5 Responding to questions after the presentation
- The presenter should stand throughout the feedback session.
- Be polite/confident/courteous when responding to questions.
- Ensure that each question/comment is clearly understood before responding/re-phrase questions if uncertain.
- She should first listen and then respond.
- Provide feedback as soon as possible after the question was asked or after the session.
- Be direct/honest/sincere when responding to questions.
- Use simple language to support the examples used in the presentation.
- Keep answers short and to the point.
- Apologise/acknowledge her errors/mistakes if pointed out by the audience.
- Encourage questions from the audience/investors.
- Always address the questions and not the person.
- Acknowledge good questions to motivate audience to ask more questions.
- The presenter should not involve himself in a debate when responding to questions.
- The presenter should not avoid the questions if he/she does not know the answer, but rather promise feedback on it.
- Address the full audience/investors and not only the person who posed the question.
- Any other relevant answer related on how to respond to questions after the presentation.
Max. (8)
5.6 Conclusion
- Good designed multimedia presentation enables the presenter to achieve his/her goals.
- A well-presented presentation creates a good impression and will attract potential investors.
- All methods of presentation must be effectively used to retain the attention of the audience.
- Being professional during a presentation/feedback/questions session should contribute to the success of the presentation.
- Any other conclusion related to the aspects that should be considered when designing a multimedia presentation/factors kept in mind while presenting/ advantages of PowerPoint and handouts as types of visual aids/ how to respond to questions after the presentation.
(Any 2 x 1) (2)
[40]
BREAKDOWN OF MARK ALLOCATION
DETAILS | MAXIMUM | TOTAL |
Introduction | 2 |
Max. 32 |
Aspect for designing a multimedia presentation | 10 | |
Factors to be considered while/during presenting/presentation |
12 | |
Advantages of PowerPoint and handouts | 16 | |
Responding to questions after the presentation | 8 | |
Conclusion | 2 | |
INSIGHT | ||
Layout | 2 |
8 |
Analysis, interpretation | 2 | |
Synthesis | 2 | |
Originality/Examples | 2 | |
TOTAL MARKS | 40 |
LASO - For each component:
Allocate 2 marks if all requirements are met.
Allocate 1 mark if only some of the requirements are met.
Allocate 0 marks where requirements are not met at all.
QUESTION 6: BUSINESS ROLES (SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY, CSR & CSI)
6.1 Introduction
- Businesses are corporate citizens and therefore have a responsibility towards society.
- Corporate Social Responsibility/CSR is the way a business conducts its operations ethically and morally, regarding the use of human, physical and financial resources.
- CSR improves the lifestyle and quality of life of their human resources and caring for the environment by ensuring that they have the most efficient and sustainable resources.
- CSR programmes and CSI projects should be relevant to the needs of communities.
- They should address socio-economic issues that affect business operations.
- CSI is a component of CSR, where social responsibility is the intention and social investment is the action.
- Businesses should consider the importance of the well-being of the community in relation to profitability and productivity.
- Any other relevant introduction related to the purpose of CSI/link between social responsibility and triple bottom line/impact of CSI on businesses/ways in which businesses can contribute time and effort in improving the well-being of employees.
(Any 2 x 1) (2)
6.2 Purpose of CSI
- CSI aims at contributing towards sustainable development of its immediate communities.
- CSI is enforceable by law and government requires business to make CSI contributions.
- CSI projects play a positive role in the development of communities.
- CSI reveals a business’s attitude towards the community in which it operates.
- CSI projects are long-term investments.
- It is relevant to the South African context where socio-economic upliftment is such a priority.
- Any other relevant answer related to the purpose of CSI.
Max. (10)
6.3 Link between triple bottom line and social responsibility
Profit/Economic
- Triple Bottom line means that businesses should not only focus on profit, but should also invest in CSI projects.
- Businesses should not make a profit at the expense of its community.
- Any other relevant answer related to the link between profit and social responsibility.
Aspect (2)
Explanation (2)
Sub-max. (4)
People/Social
- Business operations should not have a negative impact on/exploit people/employees/customers.
- Businesses should engage/invest in sustainable community programmes/projects that will benefit/uplift communities.
- Improve the life style/quality of life of their human resources/employees.
- Any other relevant answer related to the link between people and social responsibility.
Aspect (2)
Explanation (2)
Sub-max. (4)
Planet/Environment
- Businesses should not exhaust resources/harm the environment for production purposes.
- They may support energy-efficient/eco-friendly products/programmes.
- Recycle/Re-use waste , e.g. packaging from recycled material.
- Any other relevant answer related to the link between the planet/environment and social responsibility.
Aspect (2)
Explanation (2)
Sub-max. (4)
Max. (12)
6.4 Impact of CSI on businesses
Positives/Advantages
- May attract experienced employees/increase the pool of skilled labour which could increase productivity.
- Positive/Improved image as the business looks after employees/conducts itself in a responsible way.
- A business may have a competitive advantage , resulting in good publicity/an improved reputation.
- Promotes customer loyalty resulting in more sales.
- CSI projects may be used as a marketing strategy to promote their products.
- The business enjoys the goodwill/support of communities.
- CSI projects promote teamwork within businesses.
- CSI helps to attract investors because of increased profits/income.
- Gives businesses tax advantages such as tax reduction/-rebates.
- Assists in solving socio-economic issues like poverty/unemployment, etc.
- The government is less likely to enforce issues through legislation to businesses that voluntarily participate in CSI projects.
- Employees feel as if they are making a difference in working for the business.
- It helps to retain staff/lower staff turnover as employees' health and safety are considered.
- Improves the health of its employees through focused CSI projects.
- Businesses become more community-based by working closely with the community to roll out skills development projects.
- Any other relevant answer related to the positive impact of CSI on businesses.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- Business may not be supported/Customers may not buy their products/services resulting in a decrease in sales.
- Small and medium enterprises find it difficult to implement CSI programmes.
- Detailed reports must be drawn up which can be time consuming.
- Social spending reduces business/economic efficiency which makes it less competitive.
- Social involvement is funded from business profits which could have been used to the benefit of customers/reduce prices.
- CSI activities distract business focus from its core business functions.
- Businesses find it difficult to adhere to legislation governing CSI.
- It can increase financial risk, as programmes cost money and may impact negatively on profits.
- It is difficult to accurately measure the effectiveness of social investment.
- It is not easy to determine the exact needs of the communities , which may result in fruitless expenditure on CSI.
- Most managers are not trained /lack experience to handle social programmes.
- Employees may spend more time working on CSI projects instead of focusing on their core duties.
- Providing goods/services that meet the needs of consumers is, according to some stakeholders, already socially responsible.
- Shareholders may receive less dividends, as some profits are spent on CSI.
- Some shareholders/stakeholders might withdraw their support from the business as they feel that social issues should be the government's responsibility.
- Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact of CSI on businesses.
Max. (16)
6.5 Ways of contributing to the well-being of the employees
- Businesses should improve the general quality of life of employees, e.g. pay fair wages/skills development etc.
- Start a nutritional programme so that employees may enjoy at least one healthy meal per day.
- Provide subsidised housing/accommodation for their employees.
- Allow staff to use some working time to get involved/participate in projects of their choice.
- Provide overtime schedules for fair workload distribution.
- Provide transport to employees who work unusually long hours.
- Establish coaching/mentoring programmes for junior employees.
- Conduct team-building sessions to improve employees' morale.
- Encourage employees to attend capacity-building workshops/training/staff development/team-development programmes.
- Offer counselling sessions to employees with personal/emotional challenges.
- Encourage employees to stay fit/healthy by getting them involved in health activities to minimise stress/substance abuse/obesity.
- Any other relevant recommendations related to ways in which businesses may contribute to the well-being of employees.
Max. (8)
6.6 Conclusion
- Corporate social responsibility is an obligation required by law and benefits both business and society.
- CSI projects allow businesses to influence people's lives in many ways.
- Businesses use CSR programmes to comply with laws and ethical business practices.
- Any other relevant conclusion to the purpose of CSI/link between social responsibility and triple bottom line/impact of CSI on businesses/ways in which businesses can contribute time and effort in improving the well-being of employees.
(Any 1 x 2) (2)
[40]
BREAKDOWN OF MARK ALLOCATION
DETAILS | MAXIMUM | MARKS |
Introduction | 2 | Max. 32 |
Purpose of CSI | 10 | |
Link between social responsibility and triple bottom line | 12 | |
Impact of CSI on businesses | 16 | |
Ways of contributing to the well-being of the employees | 8 | |
Conclusion | 2 | |
INSIGHT | ||
Layout | 2 |
8 |
Analysis, interpretation | 2 | |
Synthesis | 2 | |
Originality/Examples | 2 | |
TOTAL MARKS | 40 |
LASO - For each component:
Allocate 2 marks if all requirements are met.
Allocate 1 mark if only some of the requirements are met. Allocate 0 marks where requirements are not met at all.
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Business Studies Paper 1 Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 D √√
1.1.2 B √√
1.1.3 B √√
1.1.4 A √√
1.1.5 C √√ (5 x 2) (10)
1.2
1.2.1 tertiary √√
1.2.2 Compensation for Occupational Injuries and Diseases √√
1.2.3 management control √√
1.2.4 job analysis √√
1.2.5 quality assurance √√ (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 F √√
1.3.2 E √√
1.3.3 J √√
1.3.4 A √√
1.3.5 I √√ (5 x 2) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Mark the FIRST TWO answers only.
QUESTION 2: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS
2.1 Types of defensive strategies
- Retrenchment √
- Divestiture/Divestment √
- Liquidation √
NOTE: Mark the first TWO (2) only. (2 x 1) (2)
2.2 Role of SETAs
- Develop sector skills plans in line with the National Skills Development Strategy. √√
- Draw up skills development plans for their specific economic sectors. √√
- Approve workplace skills plans and annual training reports. √√
- Allocate grants to employers, education and training providers. √√
- Pay out grants to companies that comply with the requirements of the Skills Development Act. √√
- Monitor/Evaluate the actual training by service providers. √√
- Promote and establish learnerships. √√
- Register learnership agreements/learning programmes. √√
- Provide training material/programmes for skills development facilitators. √√
- Provide accreditation for skills development facilitators. √√
- Oversee training in different sectors of the South African economy. √√
- Promote learnerships and learning programmes by identifying suitable workplaces for practical work experience. √√
- Collect levies and pay out grants as required. √√
- Report to the Director General. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to the role of SETAs in supporting the SDA.
Max. (8)
2.3 Developing a strategy
STEPS IN DEVELOPING A STRATEGY | MOTIVATION | ||
1. Formulate strategies √√ | The management of SSM devised a strategy that will assist them to respond to this challenge. √ | ||
2. Implementing strategies √√ | Thereafter they put the strategy into action by using action plans. √ | ||
| Sub-max. (4) | Sub-max. (2) | ||
NOTE:
- Award marks for the steps in developing a strategy even if the quote is incomplete.
- Do not award marks for the motivation, if the steps in developing a strategy was incorrectly identified.
Max. (6)
2.4 Positive impact of BBBEE on businesses
- Businesses that comply with BBBEE regarding the pillars √ will be rated high on the BEE scorecard/may get government tenders/may attract other BBBEE business partners/-suppliers. √
- Encourages businesses to address the demands √ for redress/ equity directly. √
- Provides a variety of business codes √ to improve employment equity. √
- Provides for human resources development √ through training and development. √
- Promotes enterprise development, √ by developing entrepreneurial skills of previously disadvantaged/designated people to start their own businesses. √
- Businesses will have a good overview on how it is performing √ in comparison to other businesses in the rest of the country. √
- A good BBBEE rating √ will improve the image of the business. √
- By focusing on BBBEE, the business will show commitment √ towards the social/education/economic developments in the community/ country. √
- Once rated, the business will understand how to develop BBBEE strategies √ that will increase its BBBEE ratings on an annual basis. √
- Fronting is discouraged, √ as it may lead to the disqualification of a business's entire scorecard/BBBEE status. √
- Share prices of BBBEE compliant businesses are likely to increase √ as they attract more business. √
- Businesses that support Small, Micro, Medium Enterprises (SMMEs), √ may increase their own BBBEE ratings. √
- Complying with BBBEE requirements gives businesses experience/exposure √ to be able to provide better employment opportunities/staff development. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the positive impact of BBBEE on businesses.
Max. (6)
2.5 Provisions of BCEA
2.5.1 Hours of work/Working hours
- Workers may not work for more than 45 hours √ in any week. √
- Workers may work nine hours a day √ if they work five days or less per week √/eight hours a day √ if they work more than five days a week. √
- Night work performed after 18:00 and before 6:00 the next day by agreement, √ must be compensated by allowance/reduction of work hours. √
- Ordinary work hours may be extended by agreement √ by a maximum of 15 minutes per day √/maximum of sixty minutes per week √ to complete duties when serving the public. √
- Ordinary work hours may be reduced √ to a maximum of 40 hours per week/8 hours per day. √
- Any other relevant answer related to hours of work as a provision of the BCEA.
Max. (4)
2.5.2 Overtime
- Workers must agree √ to work overtime. √
- Workers cannot work more than three hours overtime √ per day √/10 hours √ per week. √
- Overtime must be compensated as follows:
- One and half times the normal rate of pay √ for overtime worked on weekdays and Saturdays. √
- Double the normal rate of pay √ for overtime worked on Sundays and public holidays. √
- Overtime must be paid either at the specified rate for overtime √ or an employee may agree to receive paid time off. √
- Minister of Labour may prescribe the maximum permitted √ working hours, including overtime, for health and safety reasons for a certain category of work. √
- Any other relevant answer related to overtime as a provision of the BCEA.
Max. (4)
2.6 Employment Equity Act
2.6.1 Ways of non-compliance with the EEA
- The management of Blue Berry Farm does not employ young women to work on the farm. √
- They also do not appoint people with disabilities. √
NOTE: Mark the first TWO (2) only. (2 x 1) (2)
2.6.2 Ways in which businesses can comply with the EEA
- BBF/A business should guard against discriminatory appointments. √√
- Assess the racial composition of all employees, including senior management. √√
- Ensure that there is equal representation of all racial groups in every level of employment. √√
- Promote equal opportunities and fair treatment. √√
- Clearly define the appointment process, so that all parties are well informed. √√
- Use certified psychometric tests to assess applicants/employees to ensure that suitable candidates are appointed. √√
- Ensure that diversity/inclusivity in the workplace is achieved. √√
- Implement affirmative action measures to redress disadvantages experienced by designated groups. √√
- Prepare an employment equity plan in consultation with employees. √√
- Implement an employment equity plan. √√
- Submit the employment equity plan to the Department of Labour. √√
- Assign one or more senior managers to ensure implementation and monitoring of the employment equity plan. √√
- Eliminate barriers that have an adverse impact on designated groups. √√
- BBF/A business should accommodate people from different designated groups. √√
- Retain/Develop/Train designated groups, including skills development.√√
- Regularly report to the Department of Labour on progress in implementing the plan. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to ways in which businesses may comply with the EEA.
Max. (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: BUSINESS OPERATIONS
3.1 Examples of employee benefits
- Medical Aid Fund/Health Insurance Fund √
- Pension Fund √
- Provident Fund √
- Funeral benefits √
- Car/Travel/Housing/Cellphone/Clothing allowance √
- Performance based incentives √
- Issuing of bonus shares √
- Staff discount/Free or low-cost meal/Canteen facilities √
- Any other relevant answer related to examples of employee benefits.
NOTE: Mark the first FOUR (4) only.
(4 x 1) (4)
3.2 Types of salary determination methods
EMPLOYEE | TYPE OF SALARY DETERMINATION METHOD | MOTIVATION | |
1. Mandisa | Piece meal √√ | Mandisa gets paid R600 for each door she completes. √ | |
2. Suki | Time-related √√ | Suki, the cleaner, gets paid R40/hour for performing her duties. √ | |
Sub-max. (4) | Sub-max. (4) | ||
NOTE:
- Award marks for the type of salary determination method even if the quote is incomplete.
- Do not award marks for the motivation, if the type of salary determination method was incorrectly identified. Max. (6)
3.3 Link between salary determination and the BCEA
- BCEA outlines legalities, such as the employment contract, √ which may affect salary determination. √
- Payment of salaries should be based on whether the employee √ is permanent or employed on a fixed contract. √
- The BCEA sets out conditions that ensure √ fair labour and human resources practices. √
- According to the BCEA, businesses may use different remuneration methods √ to pay their employees. √
- Businesses are supposed to deduct income tax (PAYE) √ from the employees' taxable salaries. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the link between salary determination and the BCEA.
Max. (4)
3.4 Advantages of external recruitment as a method of recruitment
- New candidates bring new talents/ideas/experiences/skills √ into the business. √
- It may help the business to meet affirmative action √ and BBBEE targets. √
- There is a larger pool of candidates √ to choose from. √
- There is a better chance of getting a suitable candidate √ with the required skills/qualifications/competencies who does not need much training/development which reduce costs. √
- Minimises unhappiness/conflict √ amongst current employees who may have applied for the post. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the advantages of external recruitment as a method of recruitment.
Max. (4)
3.5 TQM elements
3.5.1 Continuous skills development/Education and training √√ (2)
3.5.2 Total client/customer satisfaction √√ (2)
3.6 Meaning of total quality management
- TQM is an integrated system/methodology applied throughout the organisation, √ which helps to design/produce/provide quality products/ services to customers. √
- It is a thought revolution in management, √ where the entire business is operated with customer orientation in all business activities. √
- TQM enables businesses to continuously improve on the delivery of products/ services √ in order to satisfy the needs of customers. √
- Management ensures that each employee is responsible √ for the quality of his/her work/actions. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the meaning of total quality management.
Max. (4)
3.7 Advantages of a good quality management system
- Effective customer services are rendered, √ resulting in increased customer satisfaction. √
- Time and resources √ are used efficiently. √
- Productivity increases √ through proper time management/using high quality resources. √
- Products/Services are constantly improved √ resulting in increased levels of customer satisfaction. √
- Vision/Mission/Business goals √ may be achieved. √
- Business has a competitive advantage √ over its competitors. √
- Regular training will continuously improve √ the quality of employees’ skills/ knowledge. √
- Employers and employees will have a healthy working relationship √ resulting in happy/productive workers. √
- Increased market share/more customers √ improve profitability. √
- Improves business image √ as there are less defects/returns. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the advantages of a good quality management system.
Max. (6)
3.8 Ways in which TQM can reduce the cost of quality
- Introduce quality circles to discuss ways of improving the quality of work/ workmanship. √√
- Schedule activities to eliminate duplication of tasks. √√
- Share responsibility for quality output amongst management and workers.√√
- Train employees at all levels, so that everyone understands their role in quality management. √√
- Develop work systems that empower employees to find new ways of improving quality. √√
- Work closely with suppliers to improve the quality of raw materials/inputs. √√
- Improve communication about quality challenges/deviations, so that everyone can learn from experience. √√
- Reduce investment on expensive, but ineffective inspection procedures in the production process. √√
- Implement pro-active maintenance programmes for equipment/ machinery to reduce/eliminate breakdowns. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to ways in which TQM can reduce the cost of quality.
Max. (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: MISCELLANEOUS TOPICS
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS
4.1 Business environments and extent of control
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS | EXTENT OF CONTROL |
1. Micro environment √ | Full control √ |
2. Market environment √ | Partial/Some/Limited/Less/Little control √ |
3. Macro environment √ | No control √ |
Sub-max. (3) | Sub-max. (3) |
NOTE:
- Mark the first THREE (3) only.
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format.
- Award marks for the business environment even if the extent of control is not indicated/incorrect.
- The extent of control must be linked to the business environment.
Max. (6)
4.2 Rights of employees according to the LRA
- Employees may join a trade union of their choice. √√
- Request trade union representatives to assist/represent employees in grievance/disciplinary hearings. √√
- Trade union representatives may take reasonable time off work with pay, to attend to trade union duties. √√
- Embark on legal strikes as a remedy for grievances. √√
- Refer unresolved workplace disputes to the CCMA. √√
- Refer unresolved CCMA disputes to the Labour Court on appeal. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to rights of employees according to the LRA.
Max. (6)
4.3 Porter’s Five Forces model
4.3.1 Bargaining power of suppliers/Power of suppliers
- Suppliers that deliver high quality product √ may have power over the business. √
- Assess the power of the suppliers √ in influencing prices. √
- The more powerful the suppliers, √ the less control the business has over them. √
- The smaller the number of suppliers, √ the more powerful they may be as the choice of suppliers may be limited. √
- Identify the kind of power suppliers' have √ in terms of the quality of products/services/reliability/ability to make prompt deliveries. √
- Any other relevant answer related to how businesses could apply the bargaining power of suppliers/power of suppliers to analyse the market environment.
Max. (4)
4.3.2 Power of competitors/Competitive rivalry
- Competitors selling the same/similar products/services √ may have a greater impact on the market of the business. √
- If competitors have a unique product/service, √ then they will have greater power. √
- A business with many competitors in the same market √ has very little power in their market. √
- Businesses should draw up a competitor's profile of all competitors √ so that they can determine their own strengths as well as those of competitors. √
- Some businesses have necessary resources to start price wars √ and continue selling at a loss until some/all competitors leave the market. √
- Any other relevant answer related to how businesses could apply the power of competitors/competitive rivalry to analyse the market environment. Max.(4)
BUSINESS OPERATIONS
4.4 Sources of internal recruitment
- Internal e-mails/Intranet/web sites to staff √
- Word of mouth √
- Business newsletter/circulars √
- Internal/management referrals √
- Notice board of the business √
- Internal bulletins √
- Recommendation of current employees √
- Head hunting within the business/organisational database √
- Any other relevant answer related to the sources of internal recruitment.
NOTE: Mark the first FOUR (4) only. (4 x 1) (4)
4.5 Reasons for the termination of an employment contract
- The employer may dismiss an employee for valid reasons, √ e.g. unsatisfactory job performance, misconduct, etc. √
- Employer may no longer have work for redundant employees √/cannot fulfil the contract/is restructuring. √
- The employer may retrench √ some employees due to insolvency/may not be able to pay the employees. √
- Employees decided to leave √ and resign voluntarily. √
- An employee may have reached the pre-determined age √ of retirement. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the reasons for the termination of an employment contract. Max.(6)
4.6.1 Roles of quality circles as part of continuous improvement of processes and systems
- The employees of Williams Motor Manufacturers meet regularly to investigate problems and suggest solutions to the management. √
- They also monitor strategies to improve the smooth running of business operations. √
NOTE: Mark the first TWO (2) only. (2 x 1) (2)
4.6.2 Application of PDCA model/cycle in improving the quality of products
- Plan
- Williams Motor Manufacturers/WMM should identify the problem and develop a plan for improvement to processes and systems. √√
- Answer questions such as 'What to do'/ 'How to do it'. √√
- Plan the new method and approach in order to improve the quality of their products. √√
Sub-max. (2)
- Do
- WMM should implement the change on a small scale. √√
- Implement the processes and systems as planned. √√
Sub-max. (2)
- Check/Analyse
- Use data to analyse the results of change. √√
- Determine whether it made a difference and what needs to be improved. √√
- Check whether the processes are working effectively. √√
- WMM should assess/test and establish if it is working/if things are going according to plan. √√
Sub-max. (2)
- Act as needed
- Implement the improvement to meet the needs of the business. √√
- Devise strategies on how to continually improve. √√
- If the change was successful, implement it on a wider scale. √√
- WMM should continuously revise the process until they get it right the first time. √√
Sub-max. (2)
- Any other relevant answer related to how WMM can apply the PDCA model/cycle to improve the quality of their products.
NOTE:
- The steps could be integrated in the application.
- Award a maximum of FOUR (4) marks for only mentioning the steps of the PDCA model.
Max. (8)
[40]
SECTION C
Mark the FIRST question ONLY.
QUESTION 5: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS
5.1 Introduction
- Businesses should always conduct the strategic management process as they operate in a dynamic environment that pose many challenges. √
- The implementation of business strategies enables businesses to respond to challenges presented by business environments. √
- Diversification and intensive strategies enable businesses to remain sustainable in the market environment. √
- PESTLE analysis is used to identify and evaluate the factors in the external environment that can influence the business. √
- PESTLE analysis enables businesses to have a better understanding of the external environment and the industry in which it operates. √
- The effectiveness of business strategies must be evaluated so that best strategies are used to overcome challenges. √
- Any other relevant introduction related to intensive strategies/ diversification strategies/PESTLE/strategy evaluation.
Any (2 x 1) (2)
5.2 Types of intensive strategies
Market penetration √√
- New products penetrate an existing market at a low price √, until it is well known to the customers and then the prices increase. √
- It is a growth strategy where businesses focus on selling existing products √ to existing markets. √
- Focuses on gaining a larger share of the market √ by reducing prices to increase sales/increasing advertising and promotion. √
- Any other relevant answer related to market penetration as a type of intensive strategy.
Type (2)
Description (2)
Sub-max. (4)
Market development √√
- A process of exploring/finding/searching new markets √ for existing products. √
- Businesses sell their existing products √ to new markets √/Involves targeting consumers in a potential market √ that is outside its normal target market. √
- Business must research √ the market it wants to enter. √
- They change the way the products are distributed √ to reach a different market. √
- Any other relevant answer related to market development as a type of intensive strategy.
Type (2)
Description (2)
Sub-max. (4)
Product development √√
- Businesses generate new ideas √ and develop a new product or service. √
- The introduction of a new product or service √ into existing markets. √
- A business may need to acquire new technology √ to develop new products. √
- They improve/change the packaging of current products √ so that they look and seem different and appeal to the market. √
- Any other relevant answer related to product development as a type of intensive strategy.
Type (2)
Description (2)
Sub-max. (4)
NOTE: Mark the first THREE (3) only. (3 x 4) (12)
5.3 Advantages of diversification strategies
- Increase sales √ and business growth. √
- Improves the business brand √ and image of the business. √
- Reduces the risk √ of relying only on one product. √
- More products can be sold to existing customers √ and additional more new markets can be established. √
- Businesses gain more technological capabilities √ through product modification. √
- Diversification into a number of industries or product line √ can help create a balance during economic fluctuations. √
- Business produces more output using less inputs √ as one factory may be used to manufacture more products. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the advantages of diversification strategies.
Max. (8)
5.4 PESTLE elements/factors posing challenges to businesses
Social
- Customers may not be able to afford products √ due to low income levels/ high unemployment. √
- Businesses may not be conversant √ with the language of their customers. √
- Some customers may prefer to spend their money on medical bills √ for the treatment of chronic illnesses. √
- High crime rate may affect the trading hours of businesses √ resulting in decreased profit. √
- Any other relevant answer related to how the social factor as a PESTLE element may pose a challenge to businesses.
Sub-max. (6)
Technological
- Businesses may not keep up with/be aware √ of the latest technology. √
- Employees may not be skilled √ to operate/maintain new technology/ equipment. √
- Businesses may not be able to afford √ new technology. √
- May not be able to cater for/afford √ online transactions/e-commerce. √
- Any other relevant answer related to how the technological factor as a PESTLE element may pose a challenge to businesses.
Sub-max. (6)
Legal
- Certain Acts may have a direct impact √ on a business, e.g. the CPA/ BCEA. √
- Legal requirements for operating certain types of businesses √ are time- consuming. √
- High legal costs involved in obtaining a license/trade mark/patent √ may prevent some establishments. √
- Legalities of business contracts √ may limit business operations. √
- Any other relevant answer related to how the legal factor as a PESTLE element may pose a challenge to businesses.
Sub-max. (6)
Max. (16)
5.4 Steps in evaluating a strategy
- Examine the underlying basis of a business strategy. √√
- Look forward and backwards into the implementation process. √√
- Compare the expected performance with the actual performance. √√
- Measure the business performance in order to determine the reasons for deviations and analyse these reasons. √√
- Take corrective action so that deviations may be corrected. √√
- Set specific dates for control and follow up. √√
- Draw up a table of the advantages and disadvantages of a strategy. √√
- Decide on the desired outcome. √√
- Consider the impact of the strategic implementation in the internal and external environments of the business. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to steps that businesses should consider when evaluating strategies.
NOTE: Accept steps in any order.
Max. (10)
5.6 Conclusion
- The strategic management process enables businesses to stay ahead of competitors and increase their market share. √√
- Businesses must develop/formulate or change their current strategies in order to remain competitive. √√
- Businesses that apply the PESTLE analysis are able to respond quickly to the external pressures and adapt to them. √√
- The implementation of diversification and intensive strategies may allow businesses to recover from unstable economic conditions. √√
- Strategy evaluation enable businesses to keep abreast with changes in the business environments. √√
- Any other relevant conclusion related to intensive strategies/diversification strategies/PESTLE/strategy evaluation.
(Any 1 x 2) (2)
[40]
QUESTION 6: BUSINESS OPERATIONS
6.1 Introduction
- The human resources manager (HRM) is responsible for selecting and appointing competent and skilled employees. √
- The HRM can appoint the best candidate if the selection and interviewing procedures are properly applied. √
- The aim of induction is to introduce the new employee to the job/the new environment. √
- Some businesses offer fringe benefits in addition to the salaries to employees. √
- Any other relevant introduction related to selection procedure/roles of the interviewer when preparing for an interview/advantages of induction/impact of fringe benefits. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
6.2 Selection procedure
OPTION 1
- Businesses should determine fair assessment criteria on which selection will be based. √√
- Use the assessment criteria to assess all CVs/application forms received during recruitment/preliminary screening is done by sorting the applications received according to the criteria for the job. √√
- Check that applicants have not submitted false documents such as forged certificates/degrees. √√
- Make a preliminary list of all applicants who qualify for the post. √√
- Screen and check references, e.g. check applicants' criminal records/credit history/social media √√, etc.
- Conduct preliminary interviews to identify suitable applicants. √√
- Inform all applicants about the outcome of the application. √√
- Compile a shortlist of approximately five people. √√
- Invite the shortlisted applicants/candidates for an interview. √√
- Shortlisted candidates may be subjected to various types of selection tests, e.g. skills test. √√
- A written offer is made to the chosen candidate. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to the selection procedure/steps as an activity of the human resources function.
OR
OPTION 2
- Receive documentation, e.g. application forms and sort it according to the criteria of the job. √√
- Evaluate CVs and create a shortlist/Screen the applicants. √√
- Check information in the CVs and contact references. √√
- Conduct preliminary sifting interviews to identify applicants who are not suitable for the job, although they meet all requirements. √√
- Assess/Test candidates who have applied for senior positions/to ensure the best candidate is chosen. √√
- Conduct interviews with shortlisted candidates. √√
- Offer employment in writing to the selected candidate(s). √√
- Any other relevant answer related to the selection procedure/steps as an activity of the human resources function.
NOTE: Accept the procedure/steps in any order. Max. (10)
6.3 Roles of the interviewer when preparing for an interview
- The interviewer should develop a core set of questions √ based on the skills/knowledge/ability required. √
- Check the application/verify the CV of every candidate √ for anything that may need to be explained. √
- Book and prepare the venue √ for the interview. √
- Set the interview date √/Ensure that all interviews take place on the same date, if possible. √
- Inform all shortlisted candidates about the date √ and place of the interview. √
- Notify all panel members conducting the interview about the date √ and place of the interview. √
- Allocate the same amount of time √ to interview each candidate on the program. √
- Any other relevant answer related to roles of the interviewer when preparing for an interview.
Max. (12)
6.4 Advantages of an induction programme for businesses
- Increases quality √ of performance/productivity. √
- Allows new employees to settle in quickly √ and work effectively. √
- Ensures that new employees understand rules √ and restrictions in the business. √
- New employees may establish relationships √ with fellow employees at different levels. √
- Employees will be familiar with organisational structures √, e.g. who are their supervisors/low level manager. √
- Make new employees feel at ease in the workplace √, which reduces anxiety/ insecurity/fear. √
- New employees will understand their role/responsibilities √ concerning safety regulations and rules. √
- Minimises/Decreases the need √ for on-going training and development. √
- The results obtained during the induction process √ provide a base for focussed training. √
- Opportunities are created for new employees to experience/explore √ different departments. √
- New employees will know the layout of the building/factory/offices/ where everything is √, which saves production time. √
- Learn more about the business so that new employees understand their roles/responsibilities √ in order to be more efficient. √
- Company policies are communicated √, regarding conduct and procedures/safety and security/employment contract/conditions of employment/working hours/leave. √
- Realistic expectations for new employees √ as well as the business are created. √
- New employees may feel part of the team √ resulting in positive morale and motivation. √
- Employees may have a better understanding of business policies √ regarding ethical/professional conduct/procedures/CSR, etc. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the advantages of an induction programme for businesses.
Max. (14)
6.5 Impact of fringe benefits on businesses
Positives/Advantages
- Attractive fringe benefit packages √ may result in higher employee retention/reduces employee turnover. √
- Attracts qualified/skilled/experienced employees √ who may positively contribute towards the business goals/objectives. √
- It increases employee satisfaction/loyalty √ as they may be willing to go the extra mile. √
- Improves productivity √ resulting in higher profitability. √
- Businesses save money √ as benefits are tax deductible. √
- Fringe benefits can be used as leverage √ for salary negotiations. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the positive impact/advantages of fringe benefits on businesses.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- Fringe benefits are additional costs √ that may result in cash flow problems. √
- Administrative costs increase √ as benefits need to be correctly recorded for tax purposes. √
- Decreases business profits, √ as incentive/package/remuneration costs are higher. √
- It can create conflict/lead to corruption √ if allocated unfairly. √
- Workers only stay with the business for fringe benefits, √ and may not be committed/loyal to the tasks/business. √
- Businesses who offer employees different benefit plans may create resentment √ among those who receive fewer benefits resulting in lower productivity. √
- Businesses who cannot offer fringe benefits √ fail to attract skilled workers. √
- Businesses have to pay advisors/attorneys √ to help them create benefit plans that comply with legislation. √
- Errors in benefit plans √ may lead to costly lawsuits/regulatory fines. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact/ disadvantages of fringe benefits on businesses.
Max. (10)
6.6 Conclusion
- The goals and objectives of businesses cannot be achieved without qualified and skilled employees. √√
- Businesses should have suitable/effective selection procedure in place. √√
- Employees are the most important resource in any business and its success is strongly influenced by a good selection process which includes a fair and well-planned interview. √√
- A well prepared and organised interview process will result in identifying and appointing the most suitable and deserving candidate. √√
- A good induction programme enables new employees to have a basic understanding of what is expected in the new job/position. √√
- Businesses should plan carefully for fringe benefits so that potential candidates can consider the advantages and disadvantages of joining the business. √√
- Any other relevant conclusion related to selection procedure/roles of the interviewer when preparing for an interview/advantages of induction/impact of fringe benefits.
(Any 1 x 2) (2)
[40]
Agricultural Sciences Paper 2 Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 C
1.1.2 A
1.1.3 C
1.1.4 B
1.1.5 D
1.1.6 A
1.1.7 B
1.1.8 C
1.1.9 B
1.1.10 D (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 E
1.2.2 F
1.2.3 C
1.2.4 A
1.2.5 H (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 Equilibrium point / Market equilibrium
1.3.2 Entrepreneurs
1.3.3 Strategic risk management
1.3.4 Labour productivity
1.3.5 Sex-linked trait (5 x 2) (10)
1.4
1.4.1 Demand
1.4.2 Cash flow
1.4.3 Allele
1.4.4 Inbreeding depression
1.4.5 Mutagen (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
2.1
2.1.1 Identification of price determining factor
- Supply (1)
2.1.2 Explanation of how factors will cause a shift in the supply curve
- Technology – Better technology can result in reduced production costs resulting in improved supply
- Environmental conditions – Conducive environmental conditions will result in higher yields leading to increase in supply (4)
2.1.3 Factors influencing supply
- Price
- Production costs
- Subsidies
- Seasonality
- Competitive products
- Legislation (Any 2) (2)
2.2
2.2.1 Name of process
- Agri-business chain / Marketing chain (1)
2.2.2 Marketing channel shown by the arrow
- A – Farm gate marketing
- B - Fresh produce markets (2)
2.2.3 Advantage of marketing channel A to the consumer
- Prices are lower than retail prices (1)
2.2.4 Methods of dealing with factors hampering the marketing chain
- Processing products close to where they are produced (1)
- Using cold storage / refrigerated transport / processing (1)
2.2.5 Description of how the following affect the agri-business chain
- Increases transportation costs (1)
- Seasonality of produce interrupts the market’s demand for consistent supply and increases storage costs (2)
2.3
2.3.1 Identification of marketing approaches
- A – Niche marketing
- B – Mass marketing
- C – Multi-segment marketing (3)
2.3.2 Identification of a marketing approach with high prices
- A (1)
2.3.3 TWO reasons to support your answer
- Consumers are prepared to pay high prices for unique products
There is less competition (2)
2.4.2 Methods of promoting products that are suitable for marketing approach B
- Newspapers
- Television
- Radio
- Billboards
- Magazines
- Electronic media (Any 2) (2)
2.4
2.4.1 Name of marketing system
- Cooperative marketing (1)
2.4.2 Principles cooperative marketing
- Voluntary and open membership
- Democratic member control
- Autonomy and independence
- Concern for community
- Risk is shared by all members (Any 2) (2)
2.4.3 Benefits of cooperative marketing
- Economies of scale
- Increased bargaining power
- Reduced risk due to risk-sharing
- Ability to meet market requirements for volume and consistent supply
- Access to funding
- Access to better infrastructure (Any 2) (2)
2.4.4 Name of document
- Business plan (1)
2.4.5 Components of a business plan
- Title page
- Contents page / Summary of enterprise details
- Executive summary
- Overview of the industry
- Overview of the business
- Organisational structure and ownership
- Human resources plan
- Marketing plan
- Financial plan
- SWOT analysis (Any 2) (2)
(NB: All components of business plan accommodated) Not sure I understand what is meant here??
2.5 Aspects of a SWOT analysis
- A. Opportunity
- B. Strength
- C. Threat (3)
[35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
3.1
3.1.1 Meaning of the following economic characteristics of land
- Industrial and residential areas reduce the amount of land available for agriculture (1)
- The amount of land available for agriculture in a country does not increase (1)
- The decrease in the marginal output of a production process as the amount of a single factor of production is incrementally increased, while the amount of all other factors of production remain constant (2)
3.1.2 Methods of increasing the productivity of land
- Consolidation of uneconomic farming units
- Use of scientific farming methods
- Water management
- Use of farming methods that are suited to the area (Any 3) (3)
3.2
3.2.1 Deduction of type of farm workers
- A – Seasonal workers
- B – Permanent worker (2)
3.2.2 Motivation for answers to QUESTION 3.2.1
- A – Harvesting is a seasonal activity
- B – Office / paper work is done by a farm manager who is a permanent employee (2)
3.2.3
- Farm worker that is most likely to be exploited
Farm worker A (1) - Justification of answer to QUESTION 3.2.3 (a)
Because they are the least educated / they have less bargaining power due lack of formal training (1)
3.2.4 Piece of legislation that protects Farm worker A from exploitation.
- Basic Conditions of Employment Act (1)
3.3.
3.3.1 Benefits of record keeping
- A – variable costs
- B – Overhead costs
- C – Gross margin
- D – Net profit (4)
3.3.2 Importance of an enterprise budget
- Enables a farmer to determine the viability of an enterprise
- Enterprise budgets can be used to help make decisions such as pricing products / comparing production practices
- Enterprise budgets can be used to develop a product mix that matches business goals (2)
3.4 3.4.1 Deduction of capital type
- A – movable
- B – floating / running / working
- C – fixed (3)
3.4.2 Capital item funded through medium term credit
- A (1)
3.4.3 Problems associated with capital
- Scarcity of capital
- High interest rates / expensive capital
- Overcapitalisation
- Undercapitalisation
- Depreciation (Any 2) (2)
3.4.4 Methods of creating capital
- Savings
- Credit
- Production (2)
3.5
3.5.1 Management principles expressed in the passage
- Planning
- Implementation
- Control (3)
3.5.2 Management skills possessed by the manager
- Financial management skills
- Labour management skills
- Planning skills
- Organisation skills (2)
3.5.3 Motivation for answers to QUESTION 3.5.2
- Financial management skills – The farmer drafted budgets
- Labour management skills - Decide which activities are going to be done by who
- Planning skills – Prepares production plans / drafts budgets
- Organisation skills – Decided which activities are going to be done by who, when and how (2)
[35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
4.1
4.1.1 Mechanism of inheritance described in the passage
- Epistasis (1)
4.1.2 Motivation of the answer in QUESTION 4.1.1
- A separate gene controls the expression of the pigment production gene (1)
4.1.3 Phenotypes of animals with the following phenotypes
- A – Albino
- B – Brown (2)
4.1.4 Genotypes of the ram’s gametes
-
- AC
- Ac
- aC
- ac (Any 2) (2)
- Phenotypic ratio
- 9:3:3:1 (1)
4.2
4.2.1 Punnet square
Rubric
- Punnet square with gametes and offspring genotypes
- Correct male gametes
- Correct female gametes
- Correct offspring genotype (4)
4.2.2 Phenotypic ratio
- 2 ? 100 black : 2 ? 100 white = 50% black : 50% white (2)
4 4
4.3
4.3.1 Advantage of indigenous over exotic breeds
- More resistant to ticks and diseases such as heartwater (1)
4.3.2 Identification of breeding method
- Cross breeding (1)
4.3.3 Name given to products of breeding method used in the passage
- Hybrids (1)
4.3.4 Disadvantages of breeding system described in the passage
- Hybrids vary greatly and can be disappointing
- Can lead to calving problems
- Requires knowledge and experience (Any 2) (2)
4.4
4.4.1 Meaning of the acronym EBV
- Estimated Breeding Value (1)
4.4.2 Implication of EBV figure for weaning weight
- The animal in question will produce offspring with a weaning weight of 10 kg above the flock average (2)
4.4.3 Conclusion that can be drawn from a heritability of 85%
- The characteristic is influenced more by genes than the environment(2)
4.4.4 Type of variation shown by the traits in the table
- Continuous (1)
4.4.5 Bar graph showing the relationship between EBV and heritability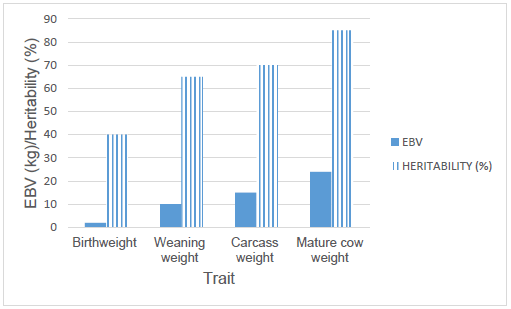
Checklist
- Correct heading
- X axis correctly calibrated with label (Trait)
- Y axis correctly calibrated with label (EBV/Heritability)
- Graph type (Bar graph)
- Correct units (kg and %)
- Accuracy (6)
4.5
4.5.1 Deduction of an environmental benefit from the passage
- Reduces the risk associated with overuse of fertilisers and pesticides (1)
4.5.2 Explanation of how genetic engineering reduces pollution from fertilisers and pesticides
- With genetic modification crops can be made to be pest resistance reducing the need for pesticides
OR - With genetic modification nutrient use efficiency in crops can be improved resulting in less need for fertilisers, therefore less pollution from fertilisers (2)
4.5.3 Social risks associated with the use of genetically modified seeds
- Poor developing countries will become dependent on developed countries for seed
- Farmers cannot retain seeds resulting in high seed costs
- Some people think it’s ethically unacceptable to produce GM crops (Any 2) (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Agricultural Sciences Paper 1 Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 B
1.1.2 D
1.1.3 A
1.1.4 C
1.1.5 C
1.1.6 B
1.1.7 A
1.1.8 D
1.1.9 A
1.1.10 B (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 None
1.2.2 Both A and B
1.2.3 B only
1.2.4 A only
1.2.5 A only (10)
1.3
1.3.1 Maintenance ration
1.3.2 Vaccination/immunisation
1.3.3 Corpus luteum/yellow body
1.3.4 Ejaculation
1.3.5 Prolactin (10)
1.4
1.4.1 Essential amino acids
1.4.2 Contagious/infectious
1.4.3 Di-oestrus
1.4.4 Vas deferens
1.4.5 Prolapse (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: ANIMAL NUTRITION
2.1 Alimentary canal of a farm animal
2.1.1 Indication of the age of animals
- Diagram A – Young animal/calf
- Diagram B – Adult animal (2)
2.1.2 Reason visible in diagram A and diagram B to justify the answer
Diagram A
- Presence of oesophageal groove
- Under-developed rumen/reticulum/omasum
- Fully developed abomasum (Any 1) (1)
Diagram B
- Rumination process/regurgitation
- Developed rumen/reticulum/omasum (Any 1) (1)
2.1.3 Identification of the processes
- Arrow A – Swallowing
- Arrow B – Regurgitation (2)
2.1.4 Explanation of the importance of regurgitation in digestion
- Regurgitation breaks down food into smaller particles to increase the surface area for digestion (2)
2.1.5 Difference of part F/caeca with that of a pig
- A pig has one caecum (1)
2.1.6 Identification of the letter
- D (1)
2.2 Mineral deficiency symptoms/supplementation and type of animal
Writing the missing information
- A – Calcium B – Iron
- C – Soil sods/injection
- D – Mineral lick (4)
2.3 Nutritional composition of feeds
2.3.1 Classification of feeds
- Concentrates (1)
2.3.2 TWO importance of feeding animals with concentrates
- Provides energy and protein requirements of an animal
- Necessary for fattening/finishing animals
- For the production of protein rich products
- To balance roughage
- Essential for growth (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.3.3 Identification of the feed
- Wide nutritive ratio: Oat meal
- Narrow nutritive ratio: Peanut oilcake meal (2)
2.3.4 Calculation of the ratio of each feed to get the 16% DP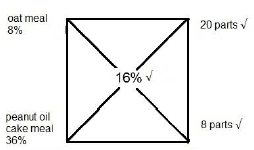
Ratio of oatmeal to peanut oilcake meal is 20 : 8 (4)
2.4
2.4.1 Line graph
Criteria/rubric/marking guideline
- Correct heading
- X-axis: Correctly calibrated and labelled (Live weight)
- Y-axis: Correctly calibrated and labelled (Metabolic energy requirement)
- Line graph
- Accuracy
- Correct units (Mj/g) (6 x 1) (6)
2.4.2 Deduction of the trend of metabolic requirement per live weight of a cow
- Metabolic energy requirement increases with the increase in live weight (2)
2.4.3 Calculation of the metabolic energy requirement of a cow with a live weight of 400 kg in 5 days
- Metabolic energy requirement x number of days
= 23 mJ/day x 5 days
= 115 mJ (2)
2.4.4 TWO importance of calculating energy value of a feed
- To determine animal’s diet
- To determine feeding standards
- To determine ration formulation (Any 2 x 1) (2)
QUESTION 3: ANIMAL PRODUCTION, PROTECTION AND CONTROL
3.1 Animal handling
3.1.1 Identification of the picture
- Picture C
- Picture D
- Picture B/C
- Picture A (4)
3.1.2 Indication of how the techniques are used
- Hobbling – Tying an animal with a device such as rope to hamper its ability to walk
- Immobilising – Put an electric current through their body to prohibit movement (2)
3.2 Factors to increase production
3.2.1 Indication of the production system
- Intensive production system (1)
3.2.2 Identification of the factors to increase production
- A – General enterprise management
- B – Breeding/reproduction
- C – Nutrition/feeding (3)
3.2.3 ONE factor to increase production which is not illustrated
- Environment (1)
3.2.4 Indication of the way farmers can address the environment
- Provision of housing/shelter (1)
3.3 Animal behaviour
3.3.1 Type of animal showing the behaviour
- A – Pigs B – Cattle
- C – Poultry
- D – Sheep (4)
3.3.2 THREE signs of pigs under stress
- Tail biting
- Ear biting
- Cannibalism
- Belly nibbling
- Snout rubbing (Any 3 x 1) (3)
3.4 Life cycle of a parasite
3.4.1 Classification of the parasite – External parasite
- Name – Blowfly (2)
3.4.2 Type of an animal susceptible to the parasite
- Wool sheep (1)
3.4.3 THREE stages of the life cycle of a parasite visible in the picture
- Larvae
- Pupae
- Adult (3 x 1) (3)
3.4.4 ONE precautionary measure to prevent the infestation by the parasite.
- Timing of shearing and crutching
- Clipping and cleaning of coat around the affected area
- Tail docking (Any 1 x 1) (1)
3.5 Animal diseases
3.5.1 Disease that can be transmitted by each of the following methods
- Transmitted by a bont tick – Heart water
- Transmitted by contaminated shearing equipment ─ Lumpy wool
- Ingesting eggs from feed contaminated with manure ─ Coccidiosis
- Transmitted through inhalation – Bovine tuberculosis (4)
3.5.2 Indication of a non-infectious disease
- Anaemia (1)
3.6 Indication of where the practice to control disease is the role of state or the farmer
3.6.1 Application of prescribed medication
- Farmer (1)
3.6.2 Importation of vaccines
- State (1)
3.6.3 Ensuring proper sanitation in a milking parlour
- Farmer (1)
3.6.4 Export and import bans
- State (1)
[35]
QUESTION 4: ANIMAL REPRODUCTION
4.1 Reproductive system
4.1.1 Identification of the animal with the reproductive system
- Cow (1)
4.1.2 TWO reasons visible to support the answer
- Presence of ovary
- Presence of fallopian tubes
- Presence of cervix
- Presence of the vagina (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.1.3 Identification of the letter
- D
- C
- B (3)
4.1.4 TWO hormones produced in part labelled D/ovary
- Oestrogen
- Progesterone (2)
4.2 Infertility and sterility in bulls
4.2.1 Differentiation between sterility and infertility
- Sterility is the total loss of fertility and infertility is the temporal loss of fertility (2)
4.2.2 TWO congenital defects leading to sterility in bulls
- Hypoplasia
- Cryptorchidism
- Hermaphroditism
- Sperm defects (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.2.3 TWO conditions that may cause inability of a bull to copulate
- Injuries to the penis
- Defective penis/corkscrew/too short
- Poorly developed hind legs
- Diseases causing inflammation of the joints (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.3 Semen collection, dilution and storage
4.3.1 TWO requirements for semen collection
- Equipment must be sterile and readily available
- Bull must be clean during semen collection
- Collecting vial must be warmed to prevent damage to sperm cells caused by cold shock
- Area where semen is collected must be close to a laboratory
- Presence of a teaser bull (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.3.2 Indication of the main purpose for diluting the semen
- To increase the volume of the semen (1)
4.3.3 TWO advantages of storing semen for the farmer
- Extending the productive life of superior bulls
- No need to keep and maintain expensive bulls (2)
4.4 Embryo Transplant/transfer
4.4.1 Re-arranging the steps to ensure successful embryo transfer
- Treatment of the cow with the gonadotropin hormone
- Semen is placed into the reproductive tract of a cow
- Foley catheter is used to recover the embryo
- Isolation and classification of the embryo
- Transfer of embryo to the uterus of a cow (5)
4.4.2 TWO types of cows involved in embryo transplant
- Donor
- Surrogate/recipient (2)
4.4.3 TWO disadvantages of the embryo transplant
- It is expensive
- Requires skill and experience
- Synchronisation of the recipient and donor is difficult
- Donor may not become pregnant
- Recipient cow could abort
- Labour intensive
- Time consuming
- Decreases genetic variability
- Greater management demand (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.5 Normal lactation
4.5.1 Identification of the week when the cow reached her maximum production
- Week 8 (1)
4.5.2 TWO benefits of the milk produced within the first 3 days of parturition for the calf
- It provides antibodies to increase the calf’s resistance to diseases
- Supplies nutrients to the calf
- Necessary for the normal growth, functioning and maturation of the alimentary canal (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.5.3 Explanation of the relationship between the percentage of butter fat content and quantity of milk produced
- When milk production reached its maximum during week 8 and decreased until week 42 butterfat content decreased at week 8 and
increased until week 42. (2)
4.5.4 Period in lactating cow after 42 weeks
- Dry period (1)
4.5.5 Importance of dry period
- It gives the glandular tissue of the udder time to recover. (1)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Agricultural Sciences Paper 2 Grade 12 Questions - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show ALL calculations, including formulae, where applicable.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 This Act aims to increase market access for all participants:
- Meat Safety Act
- Consumer Protection Act
- Marketing of Agricultural Products Act
- oodstuffs, Cosmetics and Disinfectants Act
1.1.2 ... is found on the demand side of an agribusiness value chain.
- Service
- Manufacturing
- Processing
- Research of new cultivars
1.1.3 The following are reasons why agricultural products are price inelastic in terms of supply:
- Long production period
- Most agricultural products are perishable
- Availability of substitutes
- Harvesting and marketing of agricultural produce is seasonal
Choose the CORRECT combination:
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
1.1.4 Price fixing occurs in a …
- monopoly.
- free market.
- monopsony.
- controlled market.
Choose the CORRECT combination:
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
1.1.5 A farmer’s total income after selling tomatoes is R20 000. The farmer incurred R34 500 in production and marketing costs. The
farmer therefore has made … .
- a profit of R14 500.
- a profit of R54 500.
- a loss of -R14 500.
- a loss of R14 500.
1.1.6 Which ONE of the following is NOT an example of a production risk?
- Availability of capital
- Technology
- Pests and diseases
- Machinery efficiency
1.1.7 The following are economic functions of land except that …
- land can be used as collateral.
- land can be bought or sold.
- land is a source of minerals.
- land provides space for agricultural activities.
1.1.8 … is a method of crop improvement in which individual plants are selected on the basis of phenotype from a mixed population, their seeds are bulked and used to grow the next generation.
- Family selection
- Pedigree selection
- Mass selection
- Progeny selection
1.1.9 Which ONE of the following applies ONLY to a dihybrid cross?
- Law of segregation
- Law of independent assortment
- Dominance
- Fertilisation
1.1.10 ONE of the following is NOT an advantage of genetic engineering over traditional methods:
- Precision
- Not limited to individuals of the same species
- Results are obtained within a relatively short space of time
- Requires fewer skills and experience (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Choose a term/phrase from COLUMN B that matches a description in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–J) next to question numbers (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 K.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
1.2.1 | Marking products with a distinctive label so that consumers know their manufacturer conforms to recognised environmental standards | A | heredity |
1.2.2 | A management strategy in which the cost of the consequences of a risk is distributed among several stakeholders | B | budget |
1.2.3 | A complete list of assets on a farm | C | inventory |
1.2.4 | The passing on of characteristics from one generation to the next | D | green marketing |
1.2.5 | The study of heredity and the variation of inherited characteristics | E | eco-labelling |
F | risk sharing | ||
G | diversification | ||
H | genetics | ||
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions. Write ONLY the word/term next to the question numbers (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 When the demand for a product at a specific price is equal to the supply of that product at the same specific price
1.3.2 People who recognise business opportunities and are willing to take the risk of starting their own business
1.3.3 The process of identifying, assessing and managing uncertainties or scenarios that could affect an organisation’s ability to achieve its long- term objectives
1.3.4 Output per unit labour input
1.3.5 A trait associated with a gene that is carried only by the male or female parent (5 x 2) (10)
1.4 Change the UNDERLINED WORD(S) in each of the following statements to make them TRUE. Write only the answer next to the question numbers in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 Supply is the quantity of goods consumers are prepared to buy at a given price.
1.4.2 A whole farm budget provides an overview of cash inflow and outflow during a specified period of time.
1.4.3 A locus refers to one of the alternative forms of a gene.
1.4.4 Heterosis is the reduced biological fitness in a given population as a result of inbreeding.
1.4.5 A vector is an agent, such as radiation or a chemical substance, which causes genetic mutation. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 The graph below shows one of the price-determining factors.
2.1.1 Identify the price-determining factor represented by the curve above. (1)
2.1.2 Briefly explain how each of the following factors below will make the curve to shift in the direction shown by the arrow:
- Technology (2)
- Environmental conditions (2)
2.1.3 Give TWO factors, in addition to those given in QUESTION 2.1.2, that would influence the shape of the curve above.(2)
2.2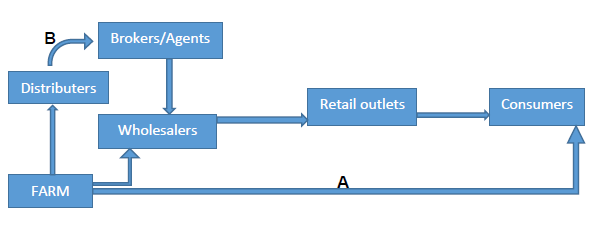
2.2.1 Name the process shown by the flow diagram above. (1)
2.2.2 Identify the marketing channels shown by the arrows A and B. (2)
2.2.3 Give ONE advantage of marketing channel A to the consumer. (1)
2.2.4 Suggest methods which can be used to deal with each of the challenges below that could hamper the process mentioned in QUESTION 2.2.1:
- Distance to markets (1)
- Perishability of produce (1)
2.2.5 Describe how each of the following factors affects the process above:
- Low volume in relation to size (1)
- Seasonality of production (2)
2.3 The statements below describe various approaches which can be used by farmers to market their produce.
- The business of promoting and selling a product or service to a specialised segment of a market.
- A market strategy in which a farmer decides to ignore market segment differences and appeal to the whole market with one offer or one strategy.
- A marketing strategy where a company tries to gain customers from more than one type of market for the same product and uses.
2.3.1 Identify the marketing approaches A–C. (3)
2.3.2 Identify a marketing approach in which prices are likely to be high. (1)
2.3.3 Give TWO reasons to support your answer. (2)
2.3.4 Suggest TWO methods of promoting products that are suitable for marketing approach B. (2)
2.4 The photograph below shows two of a group of farmers who are marketing their produce collectively.
[Extracted from google.com]
2.4.1 Name the marketing system depicted above. (1)
2.4.2 Suggest TWO principles that govern the association of the farmers above. (2)
2.4.3 Give TWO benefits derived by the farmers from the marketing system they chose. (2)
2.4.4 State the name of a key document the farmers above will have to prepare so as to acquire funding to grow their business. (1)
2.4.5 List TWO components of such a document. (2)
2.5 An organisation has the following attributes.
- A neighbouring farmer producing similar produce has gone bankrupt.
- The farm has a highly qualified and experienced farm manager.
- The farm has negative net worth.
Deduce whether each of the attributes A–C given above represents a strength, weakness, opportunity or threat to the business. (3)
[35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1
| Land is an area of ground, especially one that is used for a particular purpose such as farming or building. |
3.1.1 Explain the meaning of each of the following economic characteristics of land:
- Urban development (1)
- Land is limited (1)
- Land is subject to the law of diminishing returns (2)
3.1.2 A farmer observed that farm yields on his farm have been declining for the past three years. Suggest THREE methods this farmer can use to improve
the productivity of his land. (3)
3.2 The illustrations below shows two types of labour found on farms.
3.2.1 Deduce the type of farm workers represented by images A and B above. (2)
3.2.2 Motivate your answers to QUESTION 3.2.1 above. (2)
3.2.3
- Identify the farm worker that is most likely to be exploited by the employer. (1)
- Justify your answer to QUESTION 3.2.3 (a) above. (1)
3.2.4 Name a piece of legislation that protects farm worker A from exploitation. (1)
3.3 Below are aspects of either an enterprise or a whole farm budget.
| overhead costs; variable costs; net profit; gross margin |
3.3.1 Use the terms in the table above to differentiate an enterprise budget from the whole farm budget. Write only the correct term next to the letters A–D. (4)
ENTERPRISE BUDGET | WHOLE FARM BUDGET | |
Type of costs | A | B |
Type of returns | C | D |
3.3.2 Justify the use of enterprise budgets in farm business management. (2)
3.4 The diagrams below show various types of capital.
3.4.1 Deduce the types of capital represented by the images A–C above. (3)
3.4.2 Give the letter of the capital item which is funded using medium term credit. (1)
3.4.3 Describe TWO problems that are associated with capital. (2)
3.4.4 Suggest TWO methods farmers use to create capital. (2)
3.5 Read the scenario below and answer the questions which follow.
| A farm manager drafts budgets and prepares production plans. The manager then decides which activities are going to be done by who, when and how. During various production activities the manager monitors progress and ensures that everything is done as planned. The manager finally takes time to evaluate his/her decision-making. |
3.5.1 Deduce THREE main management principles described in the passage above. (3)
3.5.2 Identify TWO management skills that the manager above possesses. (2)
3.5.3 Motivate your answer to QUESTION 3.5.2. (2)
[35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1
| In goats, brown coat colour (AA), is dominant over black coat colour (aa). However, a separate gene (C) is necessary for pigment production. A goat with a recessive c allele at this locus is unable to produce pigment and is albino regardless of the allele present at locus A. |
4.1.1 Identify the mechanism of inheritance described in the passage above. (1)
4.1.2 Motivate your answer to QUESTION 4.1.2. (1)
4.1.3 Determine the phenotypes of animals with the following phenotypes:
- Aacc
- AaCc (2)
4.1.4 Determine the following if a ram with genotype AaCc is crossed with an ewe with genotype AaCc:
- Deduce TWO genotypes of the ram’s gametes (2)
- Determine the phenotypic ratio of the cross above (1)
4.2 A farmer crossed a black bull (Rr) with a white cow (rr).
4.2.1 Use a Punnet square to illustrate the cross above. (4)
4.2.2 Determine the phenotypic ratio of the offspring as a percentage. (2)
4.3
| Some years ago, cattle breeders observed that the Hereford was a better beef producer than the indigenous Afrikaner cattle. However, the Hereford was not adapted to South African conditions as it was less resistant to ticks and more susceptible to diseases such as heartwater. The breeders crossed Afrikaner cattle with Hereford to produce a new breed. |
4.3.1 Deduce an advantage of indigenous breeds over exotic breeds from the passage above. (1)
4.3.2 Identify the breeding method used by the breeders in the passage above. (1)
4.3.3 Give the name given to the products of the breeding system utilised above. (1)
4.3.4 Give TWO disadvantages of the breeding system described in the passage above. (2)
4.4
TRAIT | EBV (kg) | HERITABILITY (%) |
Birthweight | 2 | 40 |
Weaning weight | 10 | 65 |
Carcass weight | 15 | 70 |
Mature cow weight | 24 | 85 |
4.4.1 What does the acronym EBV stand for? (1)
4.4.2 Explain the meaning of the EBV figure for weaning weight. (2)
4.4.3 What conclusion can be drawn from a trait with a heritability of 85%? (2)
4.4.4 Name the type of variation shown by the traits in the table above. (1)
4.4.5 On the same axis, draw a bar graph to show the relationship between EBV and heritability. (6)
4.5
| Genetic engineering is not essential for all crop improvement. However, in some cases it helps to improve yields and nutritional value, and reduces the risks and costs associated with the overuse of fertilisers and pesticides. |
4.5.1 Deduce an environmental benefit of genetic engineering in the passage above. (1)
4.5.2 Explain how genetic engineering results in the benefit mentioned in QUESTION 4.5.1. (2)
4.5.3 Mention TWO social risks associated with the use of genetically modified seeds. (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150