Adele
Mechanical Technology: Automotive Grade 12 Questions - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
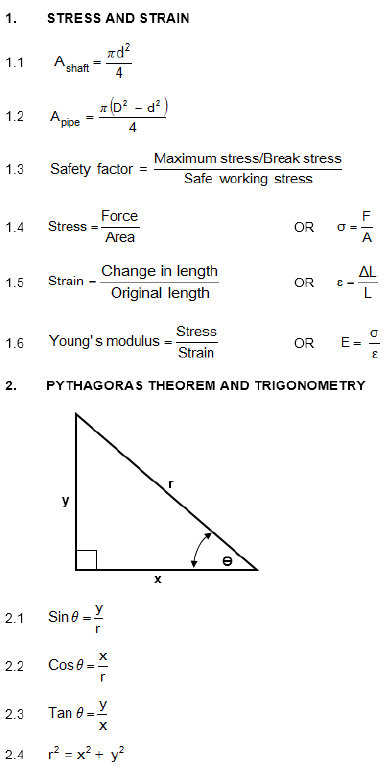
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your full names on the ANSWER BOOK.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Show ALL calculations and units. Round off final answers to TWO decimal places.
- Candidates may use non-programmable scientific calculators and drawing instruments.
- The value of gravitational acceleration should be taken as 10 m.s-2
- All dimensions are in millimeters, unless stated otherwise in the question.
- A formula sheet is attached to the question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
- Use the criteria below to assist you in managing your time.
QUESTION | CONTENT | MARKS | TIME in minutes |
GENERIC | |||
1 | Multiple-choice questions | 6 | 6 |
2 | Safety | 10 | 10 |
3 | Materials | 14 | 14 |
SPECIFIC | |||
4 | Multiple-choice questions | 14 | 10 |
5 | Tools and Equipment | 23 | 20 |
6 | Engines | 28 | 25 |
7 | Forces | 32 | 25 |
8 | Maintenance | 23 | 20 |
9 | Systems and Control (Automatic Gearbox) | 18 | 20 |
10 | Systems and Control (Axles, Steering Geometry and Electronics) | 32 | 30 |
TOTAL | 200 | 180 | |
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (GENERIC)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the correct answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1–1.6) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.7 D.
1.1 Which of the following safety measures is applicable to guillotines in terms of the Occupational Health and Safety Act?
- Clamp the workpiece securely to the table.
- Do not leave the chuck key on the machine.
- Machine must be fitted with fixed guards to prevent fingers from reaching through the point of operation.
- Use the table of the machine as an anvil. (1)
1.2 What is the purpose of cooling the blade of a band saw with cutting fluid?
- To cause friction
- To ensure clean cuts and remove metal waste
- To ensure straight cuts
- To move the blade forward and backwards (1)
1.3 Which ONE of the following safety procedures is applicable to the operation of a hydraulic press?
- Do not apply wrench to revolving work.
- Guards could be removed when pressing soft material.
- Pressure gauges must be tested regularly and adjusted or replaced if any malfunction occurs.
- Use the machine table as an anvil. (1)
1.4 Which ONE of the following tests is used to measure the ductility of a metal?
- Bend tests
- Sound tests
- Hardness tests
- Machining tests (1)
1.5 File tests are used as the simplest method of checking the ... of material.
- toughness
- hardness
- ductility
- softness (1)
1.6 Sound tests can be performed by tapping a material with a …
- hacksaw.
- spanner.
- hammer.
- file. (1)
[6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 Name any TWO pieces of personal safety equipment that you need to wear when using gas welding equipment.(2)
2.2 Give TWO safety rules that must be followed while the surface grinder is in operation.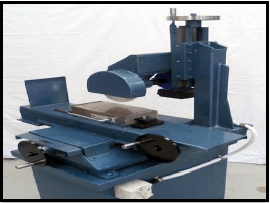 (2)
(2)
2.3 When completing a task on any machine, what safety aspect must be considered before leaving the machine? (1)
2.4 State TWO safety measures to observe before switching the angle grinder on. (2)
(2)
2.5 Why is it important to wear a welding helmet when using arc welding equipment? (1)
2.6 Name TWO types of workshop layouts. (2)
[10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1 The following table shows the different types of tests and materials.
Copy and complete the table in your ANSWER BOOK by stating how these materials will react under the different tests.
| MATERIALS | DIFFERENT TYPES OF TESTS | ||
| Sound | Filing | Bend | |
| Cast iron | |||
| Mild steel | |||
(6)
3.2 Explain the purpose of heat-treatment processes. (1)
3.3 The hardness that can be achieved from a specific treatment depends upon THREE factors. Name any TWO factors. (2)
3.4 Explain the purpose of the following heat treatment processes:
3.4.1 Tempering (2)
3.4.2 Annealing (2)
3.5 What does the hardness of steel depend upon? (1)
[14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (SPECIFIC)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (4.1–4.14) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 4.15 A.
4.1 FIGURE 4.1 shown below is an OBDII car diagnosis machine.
FIGURE 4.1
Which ONE of the following applications does NOT require the use of this tool?
- Determine the castor angle of a wheel
- Scan a car electronic control module (ECM)
- Detect faults in the form of codes
- Clear errors decoded by a car electronic control module (1)
4.2 During the process of applying the emission gas analyser on a car’s exhaust system, which ONE of the following set-up procedures is NOT applicable?
- Connect the analyser to the 12-volt vehicle battery terminals
- Do not connect the armoured hose from the condenser pick-up to the rear of the machine until the display is 0.00
- Release the pressure built up in the system with the pressure release valve
- Insert the silicon hose probe and clamp unto the exhaust tail pipe (1)
4.3 Which ONE of the following types of equipment is used to determine the percentage leakage of a cylinder in an internal combustion engine?
- Bubble gauge
- Emission gas analyser
- Compression tester
- Cylinder leakage tester (1)
4.4 Identify the equipment shown in FIGURE 4.4 below.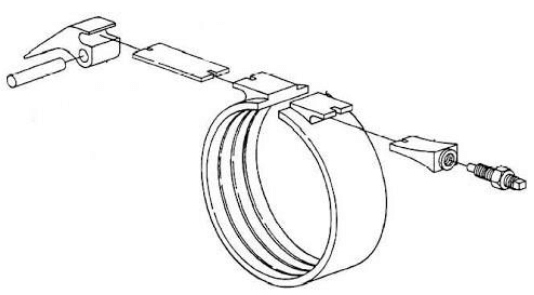
FIGURE 4.4
- Pump
- Brake band
- Stator
- Impeller (1)
4.5 What is the name of the total volume displaced when a piston moves from bottom dead centre to top dead centre in an internal combustion?
- Clearance volume
- Swept volume
- Compression volume
- Cylinder volume (1)
4.6 What is the purpose of the waste gate of a turbocharger of an internal combustion engine?
- Provides more boost to the engine
- Cool the air coming to the inlet manifold
- Waste excess oxygen coming to the combustion chamber
- Waste some exhaust gases by causing it to bypass the turbocharger turbine (1)
4.7 FIGURE 4.7 shown below is a supercharger.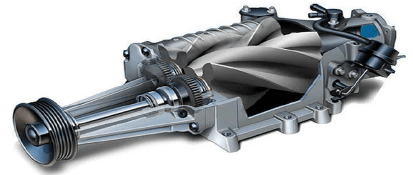
FIGURE 4.7
Identify the type of supercharger:
- Roots supercharger
- Centrifugal supercharger
- Twin-screw supercharger
- Sliding-vane supercharger (1)
4.8 What is the purpose of a catalytic converter in the exhaust system of a spark ignition (SI) engine vehicle?
- Regulates the amount of oxygen in the exhaust manifold
- Permits the flow of exhaust gases in one direction only
- Prevents flow of exhaust gases
- Converts the pollutants in the exhaust gases of the engine into a non-toxic substance (1)
4.9 Lambda oxygen sensors are installed in the exhaust outlet of the turbine of turbo chargers to sense the oxygen content of the exhaust gases. Why are they installed in turbocharged cars?
- Turbocharged cars have a high carbon exhaust content
- Turbocharged cars have a high air boost in the inlet manifold
- Turbocharged cars have a high fuel consumption
- There is no air flow metre (1)
4.10 How does the idle speed control valve influence the speed of an engine at cold start?
- Increases the speed of an engine at cold start
- Decreases the speed of an engine at cold start
- Prevents the engine from overheating by regulating the idle speed at cold start
- Causes the engine to stop running as the temperature rises (1)
4.11 Which ONE of the following is the correct function of the throttle position sensor in an air induction system?
- Controls the oxygen content in the exhaust gases
- Adjusts the throttle valve for maximum performance
- Detects the position of the throttle valve
- Detects the position of the camshaft (1)
4.12 Identify the type of gear system arrangement displayed in FIGURE 4.12 below.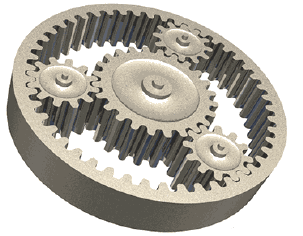
FIGURE 4.12
- Double gear arrangement
- Single gear arrangement
- Double epicyclic gear system
- Single epicyclic gear system (1)
4.13 Which ONE of the following is a possible cause of an engine over-heat?
- Faulty alternator
- Faulty water pump
- Too much oil in the sump
- Leakage in the fuel line (1)
4.14 How does camber affect tyre wears?
- One side of the tyre wears excessively
- Thin outer or inner edge wear
- Uniform tyre wear
- Prevents tyre wear (1)
[14]
QUESTION 5: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
5.1 The figure below shows the alignment equipment used in an automotive workshop. Answer the questions that follow.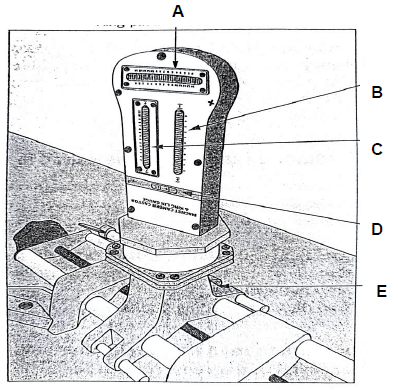
FIGURE 5.1
5.1.1 Identify the equipment in FIGURE 5.1. (1)
5.1.2 Label parts A–E. (5)
5.1.3 List THREE alignment angles that can be tested with the tool in FIGURE 5.1 above. (3)
5.2 In point form, describe the set-up procedures you must follow when reading the camber in the alignment settings of a car suspension system using a
bubble gauge. (5)
5.3 Name THREE faults that can be established when performing dynamic wheel balancing. (3)
5.4 What is the main purpose of the following tools in an automotive workshop?
5.4.1 Turn table (2)
5.4.2 Wheel balancer (2)
5.4.3 Optical alignment tool (2)
[23]
QUESTION 6: ENGINES (SPECIFIC)
6.1 A crankshaft is subject to vibrations as the engine runs. Give TWO factors responsible for this vibration. (2)
6.2 List TWO types of vibration damper used in an engine. (2)
6.3 How does the following built-in feature improve engine balance?
6.3.1 Crankshaft (2)
6.3.2 Connecting rods and pistons (2)
6.3.3 Flywheels (2)
6.4 State THREE factors that determine the configuration of an engine. (3)
6.5 List any TWO types of engine cylinder configurations. (2)
6.6 What type of engine configuration is displayed in FIGURE 6.6 below?
FIGURE 6.6 (1)
6.7 Give TWO factors that determine the firing order of an engine. (2)
6.8 What is the firing order of a five cylinder in-line engine? (1)
6.9 The figure below shows the internal components of a turbo charger. Label parts A–F. (6)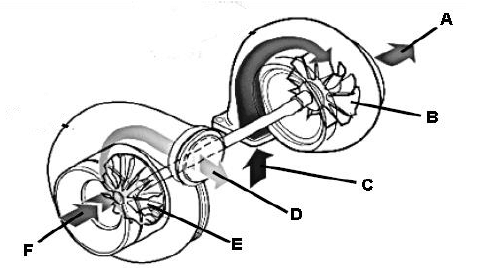
FIGURE 6.9
6.10 List any THREE disadvantages of using a turbocharger in an internal combustion engine. (3)
[28]
QUESTION 7: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
7.1 What do you understand by the term compression ratio? (2)
7.2 A compression ignition engine (CI) has a cylinder diameter of 90 mm, a stroke length of 110 mm and a clearance volume of 70 cm3.Calculate the compression ratio of the engine. (6)
7.3 What will be the new compression ratio of the engine IF the engine in QUESTION 7.2 undergoes overhauling and in the process the bore is increased to 96,1 mm in order to fit into a bigger, new piston? (4)
7.4 Give any FOUR methods that can be used to raise the compression ratio of an internal combustion engine. (4)
7.5 What do you understand by the term indicated power of an engine? (2)
7.6 The following data was recorded during a test carried out on a four-stroke, four-cylinder petrol engine:
- Mean effective pressure on the piston: 1 200 kPa
- Length of stroke: 86 mm
- Cylinder bore: 90 mm
- Revolutions per minute: 4 200 rpm
- Torque: 180 Nm @ 4200 rpm
- Number of cylinders: 4
Calculate the following:
7.6.1. Indicated power in kW (7)
7.6.2. The brake power in kW (3)
7.6.3. Mechanical efficiency (2)
7.7 What do you understand by the term mechanical efficiency of an internal combustion engine? (2)
[32]
QUESTION 8: MAINTENANCE (SPECIFIC)
8.1 A car exhaust gas was analysed and it was discovered that there was a high carbon monoxide reading.
8.1.1 State THREE possible causes that may be responsible for the high carbon monoxide reading. (3)
8.1.2 Give THREE necessary measures that can be taken to correct the faults. (3)
8.1.3 Name THREE other gases that may be analysed during the process of exhaust gas analysis. (3)
8.2 During the process of compression testing on a 6-cylinder SI engine, it was discovered that two of the cylinders had an unusually low reading. What will
be the next step to verify the condition of these two cylinders? (1)
8.3 During a cylinder leakage testing procedure, it was discovered that there are some signs of failure in the cylinders. What are the possible causes of the following failures?
8.3.1 Hissing sound from the inlet manifold (1)
8.3.2 Bubbles from radiator (1)
8.3.3 Hissing sound from the dip stick (1)
8.4 Give FOUR manufactural specifications that must be taken into account when conducting oil pressure testing. (4)
8.5 List THREE possible causes of low fuel pressure readings during fuel pressure testing. (3)
8.6 List any THREE possible components where the coolant could leak during cooling system pressure testing. (3)
[23]
QUESTION 9: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL (AUTOMATIC GEARBOX) (SPECIFIC)
9.1 What was the main purpose behind the design of an automatic gearbox in place of a manually driven gearbox? (2)
9.2 Give THREE advantages of using an automatic gear box. (3)
9.3 The diagram in FIGURE 9.3 below shows one of the components of an automatic transmission system.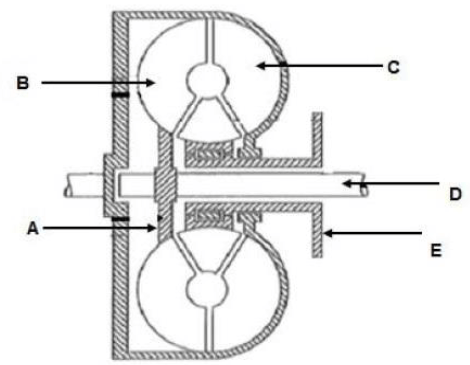
FIGURE 9.3
Use the diagram to answer the following questions.
9.3.1 Identify the equipment in FIGURE 9.3 above. (1)
9.3.2 Label parts A–E in FIGURE 9.3 above. (5)
9.3.3 State THREE functions of the equipment in FIGURE 9.3 above. (3)
9.3.4 What is the function of the part labelled C? (2)
9.4 When the speed in a torque converter increases, how will it influence the torque multiplication? (2)
[18]
QUESTION 10: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL (AXLES, STEERING GEOMETRY AND ELECTRONICS) (SPECIFIC)
10.1 State FOUR properties of a good steering mechanism. (4)
10.2 With the aid of a neat and well labelled sketch, demonstrate the toe-in of the front wheel of a motor vehicle. (4)
10.3 State the purpose of each of the following angles:
10.3.1 Caster (2)
10.3.2 Ackermann principle (2)
10.3.3 King pin inclination (2)
10.4 The diagram in FIGURE 10.4 below shows an alignment angle of a car front wheel. Answer the questions that follow.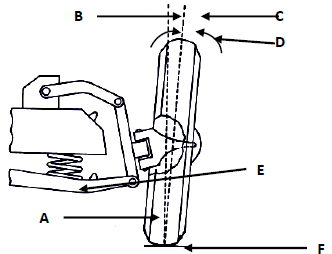
FIGURE 10.4
10.4.1 Identify the type of alignment angle in FIGURE 10.4 above. (1)
10.4.2 Label the parts A–F in FIGURE 10.4 above. (6)
10.4.3 Briefly explain the type of alignment angle displayed in FIGURE 10.4 above. (2)
10.5 List FIVE factors that must be taken into account before wheel alignment can be checked or adjusted. (5)
10.6 What is the purpose of wheel balancing? (2)
10.7 Name the TWO types of wheel balancing used in tyre fitment centers. (2)
[32]
TOTAL: 200
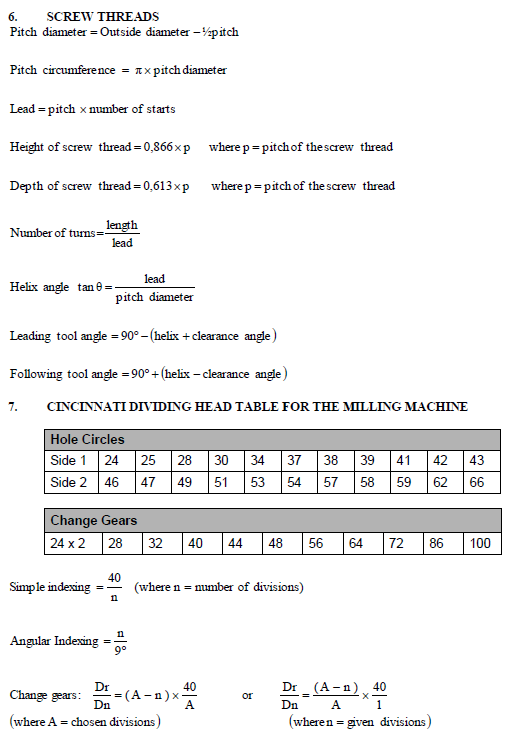
FORMULA SHEET FOR MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY (AUTOMOTIVE)

Mechanical Technology: Welding and Metalwork Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (GENERIC)
1.1 C (1)
1.2 B (1)
1.3 C (1)
1.4 A (1)
1.5 B (1)
1.6 C (1) [6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 Gas welding (PPE)
- Eye protection
- Overall / leather apron
- Safety boots
- Gloves (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.2 Safety rules that must be followed while the surface grinder is in operation:
- Make sure that the sparks pose no danger to co-workers.
- Do not force the material onto the grinding wheel.
- Do not plunge grind.
- Bring the material slowly into contact with the grinding wheel.
- Never clean or adjust the machine whilst it is in motion.
- Use cutting fluid.
- Know where the emergency stop is located.
- Stop machine before any adjustment
- Keep tools clear from moving parts. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.3 Completing a task on any machine
- Switch the machine off. (1)
2.4 TWO safety precautions before switching on the angle grinder
- Make sure that there are no cracks or chips on the disc.
- Make sure that the emery disc that is fitted is rated above the revolutions at which it is turned by the motor.
- Make sure that the space between the tool rest and the emery disc does not exceed 3 mm.
- Ensure that guards are in place
- When switching on the machine, do not stand in front of it, until it reaches its full speed.
- Do not force or bump the work piece against the emery disc.
- Grind only on the front surface of the wheel, not the sides.
- All grinding machines must have a sign indicating the revolutions at which the spindle rotates. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.5 Importance of a welding helmet
- To protect your eyes and face from ultra-violet rays and radiation (1)
2.6 Types of workshop layouts:
- Process layout
- Product layout (2)
[10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1
MATERIALS | DIFFERENT TYPES OF TESTS | ||
Sound |
Filing |
Bend | |
Cast iron | Very dull sound ? | Easy ? | Cannot bend ?/ Snaps/breaks ?/ Fractures easily ? |
Mild steel | Medium metallic sound ? | Easy ? | Bends easily ? |
(6)
3.2 Heat treatment process
- Is the heating and cooling of metals in their solid state so as to change their properties. (1)
3.3 Hardness factors:
- Workpiece size
- Quenching rate
- Carbon content (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.4 Heat treatment processes:
3.4.1 Tempering
- Is a process applied to steel and it relieves the strain induced during the hardening process.
- It decreases the degree of hardness
- It increases toughness
- It reduces brittleness
- It gives steel fine grain structure (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.4.2 Annealing
- Relieves internal stress
- Softens the metal
- Makes metal ductile
- Refines the grain structure
- Reduces brittleness (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.5 Hardness of steel depends upon
- Carbon content (1)
[14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (SPECIFIC)
4.1 A (1)
4.2 D (1)
4.3 C (1)
4.4 C (1)
4.5 D (1)
4.6 B (1)
4.7 D (1)
4.8 D (1)
4.9 A (1)
4.10 A (1)
4.11 A (1)
4.12 B (1)
4.13 B (1)
4.14 A (1) [14]
QUESTION 5: TERMINOLOGY (TEMPLATES) (SPECIFIC)
5.1 Template loft: Is the heart of the structural workshop. (2)
5.2 THREE qualities of a good template loft:
- Accuracy
- Quietness
- Better lighting
- Separate from main building
- Wooden floor with black matt finish
- Large space to accommodate required work (Any 3 x 1) (3)
5.3 Web template
- Is used to mark out the positions of holes on the webs of the channel iron and girder sections. (2)
5.4 A steel ring:
5.4.1 Dimensions of the required material:
- Mean diameter = Outside diameter – Plate thickness
= 500 – 30
= 470 mm - Mean circumference = π x Mean diameter
= π x 470
=1 476,55 mm (6)
5.4.2 Make a neat sketch of the steel ring indicating the mean diameter, outside diameter and the thickness of the material:
- 1476,55 mm of 30 x 30 mm square steel bar is required to fabricate the ring.
Material thickness (4)
(4)
5.5 Fillet weld on T-joint: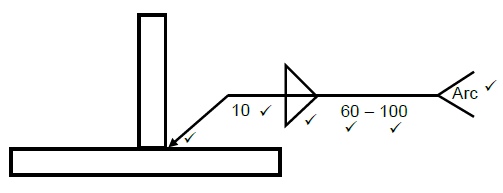 (6)
(6)
[23]
QUESTION 6: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
6.1 Uses of the machines
6.1.1 Guillotine
- To cut sheet metal
- To cut plate metal (2)
6.1.2 Bench grinder
- Hand grinding-cutting tools
- Sharpening cutting tools (2)
6.1.3 Press machine
- Is used to install or remove components such as bearings or bushes in machines or mechanical devices (2)
6.2 Joining equipment labels:
6.2.1
- A – Gauges
- B – Outlet
- C – Inlet
- D – Bonnet (4)
6.2.2 Oxygen regulator (1)
6.3 Function of stock and dies:
- They are used to cut internal and external threads of the bolt and nut. (1)
6.4 Function of regulators:
- To reduce the cylinder pressure to operating or working pressure. (2)
6.5 Operating principle of plasma cutter:
- The process involves creating an electrical channel of ionised gas; that is the plasma cutter itself, through the work piece that is being cut; this forms an electric circuit back to the plasma cutter via a grounding clamp; accomplishing this via air that is blowing towards the work piece through a focused nozzle. (4)
[18]
QUESTION 7: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
7.1 Term definition
7.1.1
- Force: is an influence which changes or tends to change the state of rest of a body or motion
OR
It is often more convenient to think about a “pull” or “push”
(Any 1 x 2) (2)
7.1.2 Hooke’s law: Strain is directly proportional to the stress it caused, provided the limit of proportionality is not Exceeded. (2)
7.2 Stress and strain
7.2.1
- Area = ???
?
= ? x (0,024)2
4
= 4,525 x 10−4?2 - Stress = ?????
????
= 60 ? 103
4,525 ? 10−4
= 132,579 x 106 Pa (2)
7.2.2
- Strain = Change in length
Original length
= 0,22 X 10−3
212 X 10−3
= 1,038 x 10−3
= 1,04 x 10−3 (2)
7.2.3
- Young’s modulus of elasticity (E) = ??????
??????
= 132,58 X 106
1,04 X 10−3
= 127,48 x 109
= 127,48 GPa (4)
7.3 Calculations of the reactions, bending moments and shear force
7.3.1
- Moments about RL: RR X 8 = (2 x 4) + (6 x 5) + (3 x 6)
= 8 + 30 + 18
= 56
RR = 7 N - Moments about RR: RL X 8 = (3 x 2) + (6 x 3) + (2 x 4)
= 6 + 18 + 8
= 32
RL = 4 N (6)
7.3.2 The bending moments at points A, B and C.
- ??? = (4 x 4) = 16 N
??? = (4 x 6) – (2 x 2) – (6 x 1) = 14 N
??? = (4 x 7) – (2 x 3) – (6 x 2) – (3 x 1) = 7 N (3)
7.3.3 Shear forces at points, A, B and C
- SFA = 4 2 = 2
SFB = 4 – 2 – 6 = -4
SFC = 4 – 2 – 6 – 3 = -7 (3)
7.3.4 and 7.3.5
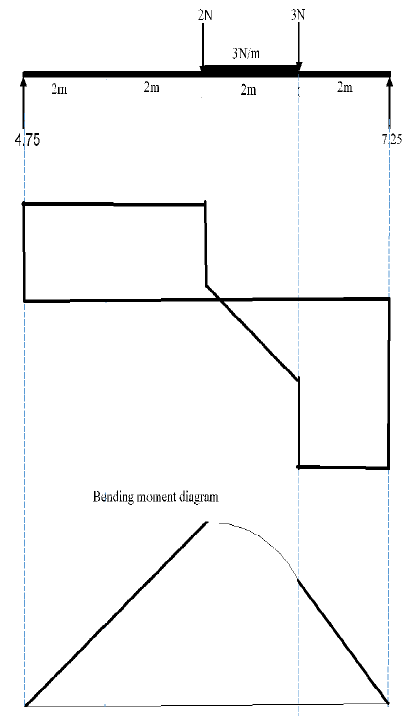
7.4
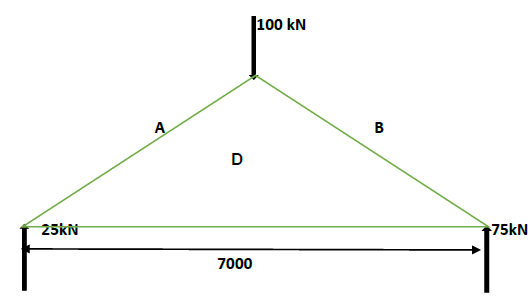
Space diagram = 1 mark
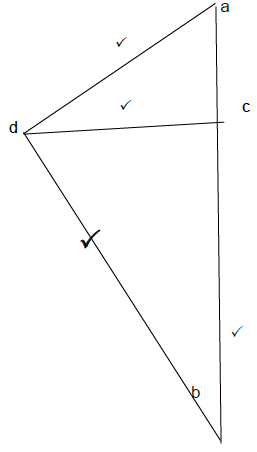
Member | Force | Nature |
AD | 29 kN ? | Strut ? |
BD | 76 kN ? | Strut ? |
CD | 14 kN ? | Tie ? |
(11) [45]
QUESTION 8: JOINING METHODS (INSPECTION WELD) (SPECIFIC)
8.1 Arc welding
- Rate of rod burning and the progress of the weld
- Amount of penetration and fusion
- The way the weld metal is flowing
- The sound of the arc, indicating correct current and voltage for the particular weld (Any 2 x 1) (2)
Oxy-acetylene
- Correct flame for the work on hand
- Correct angle of blowpipe and rod, depending on the method being used
- Depth of fusion and amount of penetration
- The rate of progress along the joint (Any 2 x 1) (2)
8.2
- HAZ (Heat-affected zone)
- Centreline cracks
- Crater cracks
- Transverse cracks (Any 2 x 2) (4)
8.3
- A – Penetration
- B – Width
- C – Height
- D – Weld bead
- E – Base metal (5)
8.4
- Shape of profile
- Uniformity
- Overlap
- Undercutting
- Penetration bead
- Root groove (Any 2 x 1) (2)
8.5
8.5.1 Spatter
- Caused by voltage being too low or amperage being too high. (2)
8.5.2 Incomplete penetration
- The weld bead does not penetrate the full depth of the weld or into the root of the weld.
- Two opposing weld beads do not inter-penetrate.
- The weld does not penetrate to the toe of a fillet weld but only bridges across it. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
8.6 Arc welding
- Rate of rod burning and the progress of the weld
- Amount of penetration and fusion
- The way the weld metal is flowing
- The sound of the arc, indicating correct current and voltage for the particular weld (Any 2 x 1) (2)
8.7 Testers
8.7.1 Nick-break test is done to:
- Determine the internal quality of the weld metal and can reveal the internal defects(2)
8.7.2 Machinability test is done to:
- Determine the hardness and strength of the welded joint.(2)
[25]
QUESTION 9: JOINING METHODS (STRESSES) (SPECIFIC)
9.1 Term definition
9.1.1 Weld distortion: Takes place in a welded joints due to uneven expansion and contractions as a result of intense heat of the arc or oxy-acetylene flame.(2)
9.1.2 Residual Stress: Is the internal stress distribution locked into the material; these stresses are present even after all external loads or forces have been removed. (2)
9.2 Factors affecting grain size
- The prior amount of cold work
- The temperature and time of the annealing process
- Composition and constitution
- Its melting point (Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.3
- Low carbon steel 0,15 – 0,30%
- Medium carbon steel 0,31 – 0,70%
- High carbon steel 0,71 – 1,5%
(Any 2 x 2) (4)
9.4 Quenching mediums
- Brine
- Water
- Oil
- Metal salt
- Air (Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.5 Factors affecting shrinkage in welding
- Size of work piece
- Weld thickness
- Thermal conductive properties of parent metal (Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.6
9.6.1 Transverse shrinkage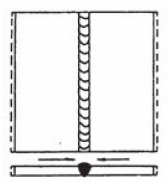 (2)
(2)
9.6.2 Longitudinal shrinkage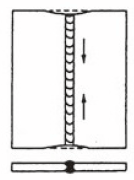 (2)
(2)
[18]
QUESTION 10: MAINTENANCE (SPECIFIC)
10.1 Keeping records assists in upholding warrantees and guarantees because service requirements inevitably form part of agreements.(1)
10.2 Due to the danger associated with a large machine, it is critical to isolate the machine completely before any maintenance is undertaken to ensure nobody can turn on the machine.(2)
10.3 Friction can be reduced by applying cutting fluid or light oil to the drill bit.(1)
10.4
10.4.1 Cutting plate of excessive thickness or hardness will overload both the blade and hydraulic system.(2)
10.4.2 The feed speed which is higher than the rate at which the power saw can cut, effectively results in the blade being forced into the materials.(2)
[8]
QUESTION 11: DEVELOPMENT (SPECIFIC)
11.1
11.1.1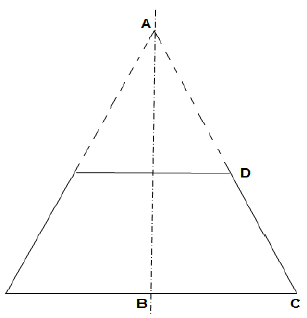
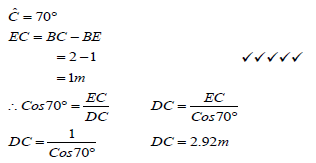 (5)
(5)
11.1.2 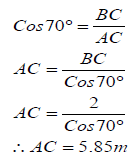 (4)
(4)
11.1.3
- Circumf . πD
π4)
= 12.57m (3)
11.2 Square-to-round transition piece:
11.2.1 The true length FG is firstly needed to draw the pattern.
- IK = 300(2units)
IH = 150(1unit)
HK =1 √3 (1unit × √3 )
The true length FG:
Plan length FG = FG - GK
= 400 - 300
=100 mm
The true FG is equalto H'F
H'F2 = H'G2 + GF2
= 8002 + 1002
H'F = √650 000
True length FG = 806 mm (5)
11.2.2 To determine the plan length CI, the sides CE and EI of triangle CEI must first be calculated.
- CE=CF-EF
= 400- 150
= 250 mm - ButEI=FH
FH = FK -HK
= 400- 259,8
=140,2mm - True length(CI)=FH2 +EI2
= 2502 +140,22
= 82156,04
= 286,63 mm (4)
[21]
TOTAL: 200
Mechanical Technology: Welding and Metalwork Grade 12 Questions - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your full name(s) on the ANSWER BOOK.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Show ALL calculations and units. Round off final answers to TWO decimal places.
- Candidates may use non-programmable scientific calculators and drawing instruments.
- The value of gravitational acceleration should be taken as 10 m/s2.
- All dimensions are in millimetres, unless stated otherwise in the question.
- A formula sheet is attached to the question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
- Use the criteria below to assist you in managing your time.
QUESTION | CONTENT | MARKS | TIME in minutes |
GENERICS | |||
1 | Multiple-choice questions | 6 | 10 |
2 | Safety | 10 | 15 |
3 | Materials | 14 | 15 |
SPECIFIC | |||
4 | Multiple-choice questions | 14 | 13 |
5 | Terminology (Templates) | 23 | 18 |
6 | Tools and Equipment | 18 | 15 |
7 | Forces | 45 | 30 |
8 | Joining Methods (Inspection of Weld) | 23 | 18 |
9 | Joining Methods (Stresses and Distortion) | 18 | 18 |
10 | Maintenance | 8 | 10 |
11 | Development | 21 | 18 |
TOTAL | 200 | 180 | |
QUESTIONS
SECTION A: GENERIC
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE (GENERIC)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the correct answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1–1.6) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.7 D.
1.1 Which of the following safety measures is applicable to guillotines in terms of the Occupational Health and Safety Act?
- Clamp the workpiece securely to the table.
- Do not leave the chuck key on the machine.
- Machine must be fitted with fixed guards to prevent fingers from reaching through the point of operation.
- Use the table of the machine as an anvil. (1)
1.2 What is the purpose of cooling the blade of a band saw with cutting fluid?
- To cause friction
- To ensure clean cuts and remove metal waste
- To ensure straight cuts
- To move the blade forward and backwards (1)
1.3 Which ONE of the following safety procedures is applicable to the operation of a hydraulic press?
- Do not apply wrench to revolving work.
- Guards could be removed when pressing soft material.
- Pressure gauges must be tested regularly and adjusted or replaced if any malfunction occurs.
- Use the machine table as an anvil. (1)
1.4 Which ONE of the following tests is used to measure the ductility of a metal?
- Bend tests
- Sound tests
- Hardness tests
- Machining tests (1)
1.5 File tests are used as the simplest method of checking the ... of material.
- toughness
- hardness
- ductility
- softness (1)
1.6 Sound tests can be performed by tapping a material with a …
- hacksaw.
- spanner.
- hammer.
- file. (1)
[6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 Name any TWO pieces of personal safety equipment that you need to wear when using gas welding equipment.(2)
2.2 Give TWO safety rules that must be followed while the surface grinder is in operation. (2)
(2)
2.3 When completing a task on any machine, what safety aspect must be considered before leaving the machine? (1)
2.4 State TWO safety measures to observe before switching the angle grinder on. (2)
(2)
2.5 Why is it important to wear a welding helmet when using arc welding equipment? (1)
2.6 Name TWO types of workshop layouts. (2)
[10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1 The following table shows the different types of tests and materials.
Copy and complete the table in your ANSWER BOOK by stating how these materials will react under the different tests.
| MATERIALS | DIFFERENT TYPES OF TESTS | ||
| Sound | Filing | Bend | |
| Cast iron | |||
| Mild steel | |||
(6)
3.2
Explain the purpose of heat-treatment processes. (1)
3.3 The hardness that can be achieved from a specific treatment depends upon THREE factors. Name any TWO factors. (2)
3.4 Explain the purpose of the following heat treatment processes:
3.4.1 Tempering (2)
3.4.2 Annealing (2)
3.5 What does the hardness of steel depend upon? (1)
[14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (SPECIFIC)
Various options are given as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (4.1–1.14) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 4.15 A.
4.1 Which of the following best describes a template loft?
- It is the heart of the structural workshop.
- It is the welding workshop for roof trusses.
- It is the drawing workshop for roof trusses.
- It is where complicated steel structures are kept. (1)
4.2 What is the purpose of a supplementary symbol?
- To show you where to weld
- To indicate where to weld
- To indicate side weld in a welding joint
- To indicate additional information about the weld (1)
4.3 What is the maximum thickness of sheet metal that can be cut with a hand guillotine?
- 3,2 mm
- 1,6 mm
- 1,2 mm
- 2,1 mm (1)
4.4 Identify the following weld symbol.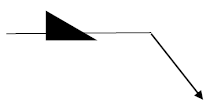
- Butt joint
- Lap joint
- Fillet weld symbol
- Square butt symbol (1)
4.5 Which property of material is tested using a Brinell tester?
- Tensile strength
- Elasticity
- Hardness
- Brittleness (1)
4.6 Which ONE of the following safety regulations applies to the MIG/MAGS welding process?
- Check the colour coding on cylinders.
- Hold the workpiece in your hand during the welding process.
- Turn the relief valve very slowly.
- Ensure that the welding area is well-ventilated. (1)
4.7 What is the purpose of cooling the blade of a power saw with cutting fluid?
- To cause friction
- To ensure small cuts with no wastage
- To ensure a straight cut
- To prevent the blade from overheating and binding or breaking (1)
4.8 Calculate Young’s modulus of elasticity for a metal with a strain value of 2 x 10-3 caused by stress of 6 MPa.
- 12 MPa
- 3 MPa
- 12 GPa
- 3 GPa (1)
4.9 Stress can be defined as an internal force in a material resisting a/an …
- internal load.
- spin load.
- moving load.
- external load. (1)
4.10 When does overloading occur in a pedestal drill ?
- When the drill bit is forced into the material
- When the chuck is forced into the material
- When excessive force is applied on the ma chine
- When the machine is moving fast (1)
4.11 Which ONE of the following is an inspection during arc welding?
- Rate of rod burning and the progress of th e weld
- Correct flame for the work on hand
- Correct angle of the blow pipe
- Depth of fusion (1)
4.12 Which ONE of the following is a cause for undercutting during arc welding?
- Clean bead
- Travel speed too high
- Slag inclusion
- Distortion (1)
4.13 A destructive test is a method of testing a weld …
- without destroying the finished product.
- by destroying the finished product.
- by weld defects.
- without weld defects. (1)
4.14 Which ONE of the following factors influences the rate of cooling of the weld metal during the welding process?
- Weld metal thickness
- Amount of oxygen used in process
- Current setting of the welding machine
- Electrode thickness (1)
[14]
QUESTION 5: TERMINOLOGY (TEMPLATES) (SPECIFIC)
5.1 Define a template loft. (2)
5.2 Describe THREE qualities of a good template loft. (3)
5.3 State the function of a web template. (2)
5.4 A steel ring with an outside diameter of 500 mm must be manufactured from a 30 x 30 mm square bar.
5.4.1 Calculate the dimensions of the required materials. (6)
5.4.2 Make a neat sketch of the steel ring indicating all the dimensions of the material. (4)
5.5 Make a neat sketch of a weld symbol indicating the following information of a site weld on a T-joint done with arc welding.
- The intermitted square butt weld on both sides is 10 mm in size
- The lengths of the weld beads are 60 mm each
- The pitch of the weld is 100 mm (6)
[23]
QUESTION 6: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
6.1 State TWO uses of each of the following machines:
6.1.1 Guillotine (2)
6.1.2 Bench grinder (2)
6.1.3 Press machine (2)
6.2 FIGURE 6.2 below shows a joining equipment.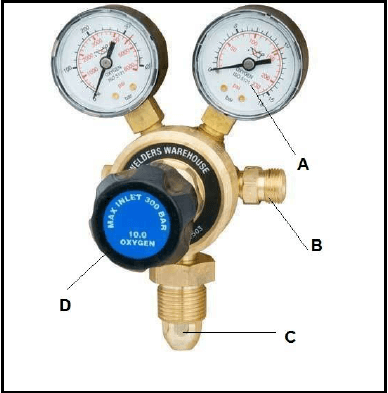
FIGURE 6.2 (4)
6.2.1 Label A–D.
6.2.2 Identify the joining equipment shown in FIGURE 6.2 above. (1)
6.3 What is the function of stock and dies? (1)
(1)
6.4 What is the primary function of the regulator fitted to the gas cylinder of the oxy-acetylene equipment? (2)
6.5 Explain the operating principle of plasma cutting machine that is used in a welding workshop. (4)
[18]
QUESTION 7: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
7.1 Define the following terms:
7.1.1 Force (2)
7.1.2 Hooke’s Law (2)
7.2 A machinist is performing a tensile test using a mild steel bar with a diameter of 24 mm. An applied load of 60 kN cause an extension of 0,22 mm and the original length was 212 mm.
Calculate the following:
7.2.1 Stress in the mild steel bar (2)
7.2.2 Strain in the mild steel bar (2)
7.2.3 Young’s modulus of elasticity (4)
7.3 FIGURE 7.3 below is diagram of a beam with a UDL resting on the beam. The beam is supported at two ends.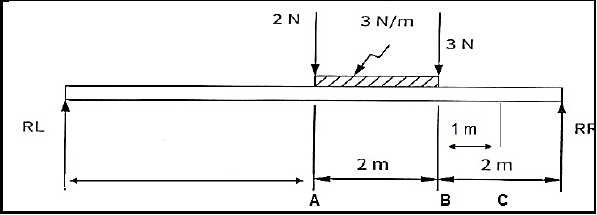
FIGURE 7.3
Calculate the following for FIGURE 7.3:
7.3.1 The magnitudes of RL and RR (6)
7.3.2 The bending moments at points A, B and C (3)
7.3.3 Shear forces at points, A, B and C (3)
7.3.4 Draw a shear force diagram (5)
7.3.5 The bending moment diagram
NOTE:
- Space diagram scale 1 : 100
- Shear force diagram scale 2 mm =1 N
- Bending moment diagram scale 2 mm = 1 N.m. (5)
7.4 Construct the space and force diagram of the following steel frame structure in order to determine the magnitude and nature of the forces in each member of the framework.
- Space diagram 1 : 100
- Force diagram 1 mm = 1 kN
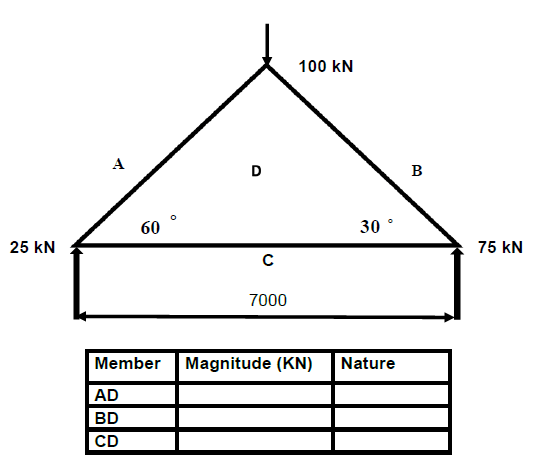
(11)
[45]
QUESTION 8: JOINING METHODS (INSPECTION WELD) (SPECIFIC)
8.1 Name TWO things to be observed during oxy-acetylene or arc welding to ensure that weld defects are not formed. (2)
8.2 Describe TWO types of cracks in welded joints. (4)
8.3 Label the diagram in FIGURE 8.3. (5)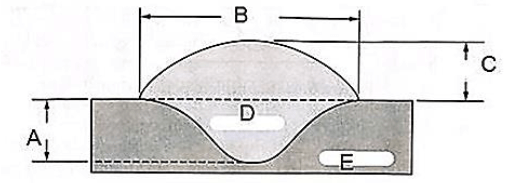
FIGURE 8.3
8.4 State TWO elements that should be inspected during the visual inspection process. (2)
8.5 State TWO causes of each of the following arc-welding defects:
8.5.1 Spatter / welding spatter (2)
8.5.2 Incomplete penetration (2)
8.6 Name TWO factors that should be observed to ensure a good welded joint during the arc-welding process. (2)
8.7 Give ONE reason for performing the following destructive tests:
8.7.1 Nick-break test (2)
(2)
8.7.2 Machinability test (2)
(2)
[23]
QUESTION 9: JOINING METHODS (STRESSES) (SPECIFIC)
9.1 Define the following terms:
9.1.1 Weld distortion (2)
9.1.2 Residual stress (2)
9.2 Give any TWO main factors affecting grain size of steel when being cold worked. (2)
9.3 State any TWO types of steel groups and name the percentage carbon content in each. (4)
9.4 Name TWO types of quenching mediums. (2)
9.5 Discuss any TWO factors that affect shrinkage in welding. (2)
9.6 Describe with the aid of a sketch/diagram the following terms:
9.6.1 Transverse shrinkage (2)
9.6.2 Longitudinal shrinkage (2)
[18]
QUESTION 10: MAINTENANCE (SPECIFIC)
10.1 What is the purpose of keeping service records of maintenance of machines in the workshop? (1)
10.2 Give TWO reasons of locking out large machines before maintenance. (2)
10.3 How can friction be reduced when drilling holes? (1)
10.4 Explain how the following machines can be overloaded:
10.4.1 Guillotine (2)
10.4.2 Horizontal band saw (2)
[8]
QUESTION 11: TERMINOLOGY (DEVELOPMENT) (SPECIFIC)
11.1 FIGURE 11.1 below shows a conical hopper.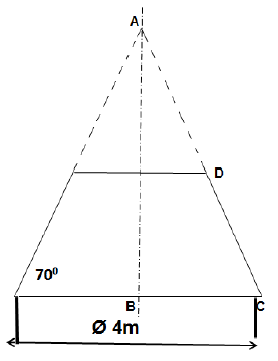
FIGURE 11.1
Calculate the following:
11.1.1 The true length DC (5)
11.1.2 The true length AD (4)
11.1.3 The base circumference of the hopper (3)
11.2 FIGURE 11.2 below shows a square-to-round transition piece. In order to develop the transition, the true lengths must be calculated: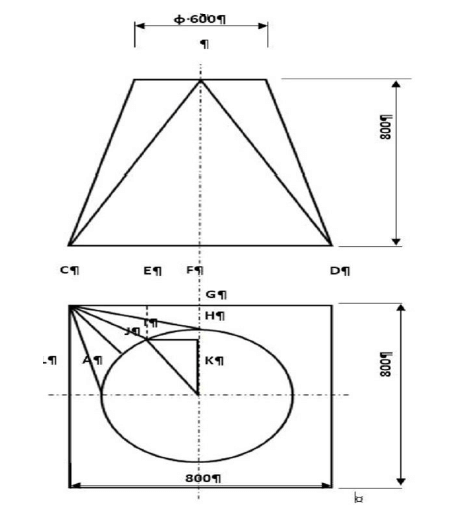
FIGURE 11.2
Determine the following true lengths with the help of calculations:
11.2.1 True length FG (5)
11.2.2 True length CI (4)
[21]
TOTAL: 200
FORMULA SHEET FOR MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY: WELDING AND METALWORK
Mechanical Technology: Fitting and Machining Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (GENERIC)
1.1 C (1)
1.2 B (1)
1.3 C (1)
1.4 A (1)
1.5 B (1)
1.6 C (1) [6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 Gas welding (PPE)
- Eye protection
- Overall / leather apron
- Safety boots
- Gloves (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.2 Safety rules that must be followed whilst the surface grinder is in operation:
- Make sure that the sparks are of no danger to co-workers.
- Do not force the material onto the grinding wheel.
- Do not plunge grind.
- Bring the material slowly into contact with the grinding wheel.
- Never clean or adjust the machine whilst it is in motion.
- Use cutting fluid.
- Know where the emergency stop is located.
- Stop machine before any adjustment
- Keep tools clear from moving parts. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.3 Completing a task on any machine
- Switch the machine off. (1)
2.4 TWO safety precautions before switching the angle grinder on
- Make sure that there are no cracks or chips on the disc.
- Make sure that the emery disc that is fitted is rated above the revolutions at which it is turned by the motor.
- Make sure that the space between the tool rest and the emery disc does not exceed 3 mm.
- Ensure that guards are in place.
- When switching on the machine, do not stand in front of it, until it reaches its full speed.
- Do not force or bump the work piece against the emery disc.
- Grind only on the front surface of the wheel, not the sides.
- All grinding machines must have a sign indicating the revolutions at which the spindle rotates. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.5 Importance of a welding helmet
- To protect your eyes and face from ultra-violet rays and radiation (1)
2.6 Types of workshop layouts:
- Process layout
- Product layout (2)
[10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1
MATERIALS | DIFFERENT TYPES OF TESTS | ||
Sound | Filing | Bend | |
Cast iron | Very dull sound ? | Easy ? | Cannot bend ?/ Snaps/breaks ?/ Fractures easily ? |
Mild steel | Medium metallic sound ? | Easy ? | Bends easily ? |
(6)
3.2 Heat treatment process
- Is the heating and cooling of metals in their solid state so as to change their properties (1)
3.3 Hardness factors:
- Workpiece size
- Quenching rate
- Carbon content (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.4 Heat treatment processes:
3.4.1 Tempering
- Is a process applied to steel and it relieves the strains induced during the hardening process
- Decreases the degree of hardness
- Increases toughness
- Reduces brittleness
- Gives steel fine grain structure (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.4.2 Annealing
- Relieves internal stress
- Softens the metal
- Makes metal ductile
- Refines the grain structure
- Reduces brittleness (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.5 Hardness of steel depends upon
- Carbon content (1)
[14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (SPECIFIC)
4.1 B (1)
4.2 D (1)
4.3 D (1)
4.4 A (1)
4.5 A (1)
4.6 B (1)
4.7 A (1)
4.8 B (1)
4.9 B (1)
4.10 A (1)
4.11 B (1)
4.12 B (1)
4.13 C (1)
4.14 B (1) [14]
QUESTION 5: TERMINOLOGY (LATHE AND MILLING MACHINE) (SPECIFIC)
5.1 Lathe components
5.1.1 Chuck is a lathe component used to mount and hold the workpiece at one end. (1)
5.1.2 Tool post is securely clamped to the compound slide and is used to support and fasten the cutting tool in the proper position for cutting action. (1)
5.1.3 Compound slide is situated on top of the cross slide and is used for turning operations such as taper turning and thread cutting. (1)
5.2 Milling Cutters Classes
5.2.1 Arbor cutters
- Examples: plain cutter , side cutter, staggered-tooth cutter, slitting-saw cutter, angular cutter, profile/form cutters, side-and- face cutter, helical cutter (2)
5.2.2 Shank cutters
- Examples: end mill; shell end mill; T-slot cutter and Woodruff keyseat cutter (2)
5.3 Taper-turning calculations
- Θ = 8,5° θ/2 = 4,25°
Tan θ/2 = (D – d )/ 2L
Tan 4,25 x 2 x 250 = (55-d)
d = 17,84 mm
d = 18 mm (4)
5.4 Dividing head components
- – Index plate
- – Index crank
- – Sector arms
- – Single-start worm
- ‒ Worm wheel/gear (5)
5.5 Lead calculations
- Lead = No. of starts x pitch
= 3 x 1,75 mm
= 5,25 mm (2)
[18]
QUESTION 6: TERMINOLOGY (INDEXING) (SPECIFIC)
6.1 Gear calculations:
6.1.1 Dividing head: it breaks up the circumference of a circular workpiece into a number of equal parts. It is mounted between centers in cunjunction with the tailstock; or it can be fitted with a chuck for direct mounting of work. (1)
6.1.2 Index plate: to enable one revolution of the crank to be further subdivided into fractions of a revolution, especially where the fraction is the factor of 40. (1)
6.1.3 Sector arm: to enable indexing where fractions of turns are required, so that it can be adjusted to any angle that would contain a specific number of holes.(1)
6.2 Procedure to cut external metric V-screw thread using compound slide method.
- Set up the workpiece in the centre lathe and turn the part to be threaded to the required diameter of the thread.
- Set the compound slide to 30º to the left of the centre line of that cross-slide and accurately set up the cutting tool in the tool post.
- Consult the index plate of the quick-change gear box and shift the levers accordingly for the necessary pitch of the screw thread.
- Start the centre lathe and set the cutting tool at touching point on the workpiece.
- Move the cutting tool a short distance off, to clear the end of the workpiece and feed the compound slide 0,05 mm inwards.
- With the centre lathe revolving, engage the half nuts at the correct line on the threading dial, putting the first cut of the screw thread in progress.
- Stop the centre lathe and check the screw thread pitch with a screw thread pitch gauge. (Any 5 x 1) (5)
6.3 Definition of Indexing: It is the process of evenly dividing the circumference of a circular work piece into equally spaced divisions, such as in cutting gear teeth, cutting splines, milling grooves in the reamers and taps. (1)
6.4 Milling methods
- Up-cut milling
- Down-cut milling (2)
6.5 Differential indexing
6.5.1 Indexing required
- Indexing = 40
?
= 40/120
= 1 x 22
3 22
= 22/66
Indexing is 22 holes in a 66-hole circle. (3)
6.5.2 Change of gears
- Gear ratio : ?????? = ?−? x 40
?????? ? 1
= 120 −113 x 40
120
= + 7 x 8
3 8
= 56/24 - The driver gear has 56 teeth.
- The driven gear has 24 teeth. (5)
6.5.3
- The direction of motion is clockwise.
- The crank handle will turn the same direction as the index plate (1)
6.6 Dove tail calculations:
- Find the difference of distance over the rollers (L):
L = (M ‒ R) – (m ‒ r)
= (127,64 ‒ 25) – (100,32 ‒ 15)
= 102,64 – 85,32
L = 17,32 mm
For the angle θ
Tan θ/2 = (R ‒ r) / L
= 10/17,32
Θ = 30 x 2
Θ = 60° (6)
6.7 Constraints to balancing
- Requires specialised machinery
- Difficult to ascertain the exact point of unbalance
- Requires accurate removal or addition of material’s weight to the object.
- Can lead to interference with parts of the machine when weights are added to parts (Any 2 x 1) (2)
[28]
QUESTION 7: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
7.1 Hardness testers:
7.1.1 Brinell hardness tester (3)
(3)
7.1.2 Rockwell hardness tester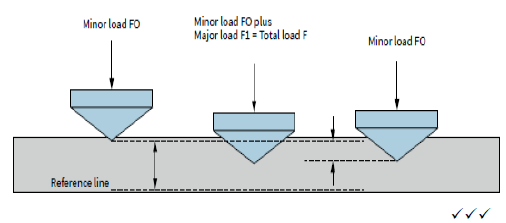 (3)
(3)
7.2 Hardness measure of a metal
- Resistance to penetration
- Elastic hardness
- Resistance to abrasion (3)
7.3 Screw-thread micrometres
- 6 + 0,5 + 0,3 = 6,80 mm (2)
7.4 Micrometre reading
- 41,25 mm
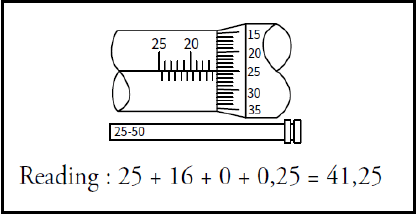 (2)
(2)
[13]
QUESTION 8: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
8.1 Resultant force calculations: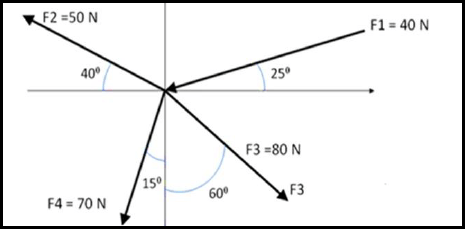
- Xcom = 80 cos 30 – 40 cos 75 – 70 cos 25 – 50 cos 40
= 80,0686 N - Ycom = 50 sin 40 – 80 sin 30 – 70sin 25 – 40 sin 75
= ‒16,91 N - R = √(?2 + ?²)
R = 81,836 N
Tan θ = y/x
Tan Θ = 16,91/80,0
Θ = 360 ‒ 11,925°
= 348,075°
Equilibrant = Resultant BUT IN THE OPPOSITE DIRECTION
Equilibrant = 81,836 N at 168,075° (12)
8.2 Moments
- Converting the UDL to point lolad
1 x 10 = 10 kN @ 5 mm from eft hand end
Calculation of the reactions.Taking moments:
- RD x 20 = (5 x 5) + (10 x 30) + (20 x 15)
= 31,25 kN
(Ra x 20) + (10 x 10) = (20 x 5) + (5 x15)
= 3,75 kN (5)
8.3 Stress calculations:
8.3.1 Tensile Stress Calculations
- F = 10 kN; d = 20 mm: L = 2 m : E = 200 PGa
? = ?
?
? = ??2
A = π x 0,01²
A = 3,141 x 10^-4 m² - δ = ?
?
= 10 000/3.141 x 10 ^-4
= 318,31 x 10⁶ Pa
= 318,31 MPa (4)
8.3.2 The change in length calculations.
- ?? = ?; E = 200 GPa; F = 10 kN; L = 2 m; Ϭ = 318,31 MPa
?? = s × L
?
= 318,31 x 10⁶ x 2) / 200 x 10⁹
= 0,318 mm (4)
8.4 Stress/Strain diagram: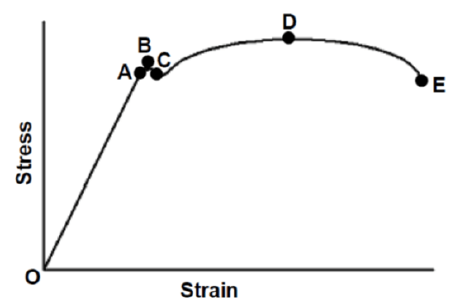
- A – Limit of proportionality
- B – Elastic limit
- C – Yield point
- D – Maximum force / point
- E – Point of fracture (6)
8.5 FOS stands for Factor OR Safety or Safety Factor. (1)
8.6 Young’s modulus states that stress in metal is directly proportional to the strain it causes, provided the limit of proportionality is not exceeded. (1)
[33]
QUESTION 9: MAINTENANCE (SPECIFIC)
9.1 Purpose of composites:
9.1.1 Bakelite can be used in disc brake cylinders, saucepan handles, distributor rotors, electrical plugs and switches, and parts for electrical irons. (2)
9.1.2 Fibre glass is used as a surface covering, woven cloth, wearing fibres, plastic covers and stuffing for pillow. (2)
9.1.3 Carbon fibre is used for sport equipment like tennis, squash and badminton racquets, racing bicycle frames, construction skis, surfboards and boat masts, compressor blades for jet engines. (2)
9.2 Reasons for using cutting fluid when working on the centre lathe:
- It prolongs the life of a cutting tool.
- It prevents the shavings or metal chips from sticking and fusing to the cutting tool.
- It will carry away the heat generated by the turning process.
- It flushes away shavings/metal chips.
- It improves the quality of the finish of the turned surface.
(Any 1 x 1) (1)
9.3 Mechanical drives:
- Gear drives
- Chain drives
- Belt drives (3)
9.4 Reasons for the use of carbon fibre:
- It is light in weight
- It is tougher and stronger
- It can be bent to any shape when heated above 150 ºC (Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.5 ONE property and ONE use of each composite
COMPOSITE | PROPERTY | USES |
9.5.1 PVC |
(Any 1 x 1) |
(Any 1 x 1) |
9.5.2 Vesconite |
(Any 1 x 1) |
(Any 1 x 1) |
9.5.3 Nylon |
(Any 1 x 1) |
(Any 1 x 1) |
(6) [18]
QUESTION 10:
JOINING METHODS (SPECIFIC)
10.1 Square thread calculations:
10.1.1
- PCD = T x m
= 60 x 4 = 240 mm
10.1.2 Add = Module = 4
10.1.3
- Clearance = 0,157 x m
= 0,628 mm
10.1.4
- Ded = 1,157 x m
= 4,628 mm
10.1.5
- OD = PCD + 2 x m
= 248 mm
10.2 Left-hand square screw-thread:
- A – Leading angle
- B – Following or Trailing Angle
- C – Clearance
- D – Helix angle (4)
10.3 A multi-start thread allows for faster travel or movement and is more efficient as it loses less power to friction compared to single-start thread. (2 )
10.4 Screw-thread fit is a combination of allowances and tolerances and a measure of tightness or looseness between the bolt and nut. (2)
[18]
QUESTION 11: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL (SPECIFIC)
11.1 Gear drives work on the principle that the turning motion of one gear be transferred to another gear if the gears are mounted close so that they mesh or
engage. (2)
11.2 Hydraulic system calculations:
11.2.1 Calculate the force applied on Piston A.
- da = 30 mm; Db = 130 mm; M = 2 000 kg
Weight Calculation (W)
W = m x g
= 2 000 x 10
= 20 Kn (2)
11.2.2
- A = π (r)²
= π x 0,065²
= 0,0133 m ²
? = ?
?
= 20 000/0,0133
= 1,507 MPa
11.2.3
- A = ?Da²/4
= ? (0,03)²/4
= 7,0686 x10−4 m²
F = P x A
= 1,507 x 10 ⁶ x 7,068 x 10−4
Force = 1065,235 N (4)
11.2.4 Hydraulic system applications:
- Machine tools, motor vehicle, hydraulic jacks (Any 1 x 1) (1)
11.3 Velocity ratio is defined as the ratio of a distance through which any part of a machine moves, to that which the driving part moves during the same time.(2)
11.4 Belt drive calculations:
- Nmotor x Dmotor = Nblade x Dblade
135 x 1 200 = 395 x Dblade
Dblade = 410,127 rpm (3)
11.5 Pneumatic drives:
- Vehicle painting
- Air brakes
- Opening and closing doors
- Dismantling vehicle tire (Any 3 x 1) (3)
11.6 Simple gear calculations:
- TA = 56 teeth; NA = 700 rpm
11.6.1 TB = ?? X ??
??
= (56 x 700)/ 980
= 40 teeth (3)
11.6.2
- Nc = ?? X ??
??
= (40 x 980)/ 64
= 612,5 rpm (3)
11.6.3 Driven gear will rotate anti-clockwise (1)
[28]
TOTAL: 200
Mechanical Technology: Fitting and Machining Grade 12 Questions - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your NAME on the ANSWER BOOK.
- Read ALL the questions carefully.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Show ALL calculations and units. Round off final answers to TWO decimal places.
- You may use a non-programmable scientific calculator and drawing instruments.
- The value of gravitational force should be taken as 10 m.s-2.
- All dimensions are in millimetres, unless stated otherwise in the question.
- A formula sheet is attached to the question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
- Use the criteria below to assist you in managing your time management.
QUESTION | CONTENT | MARKS | TIME In minutes |
GENERIC | |||
1 | Multiple-choice questions | 6 | 6 |
2 | Safety | 10 | 10 |
3 | Materials | 14 | 14 |
SPECIFIC | |||
4 | Multiple-choice questions | 14 | 10 |
5 | Terminology (Lathe and Milling) | 18 | 20 |
6 | Terminology (Indexing) | 28 | 25 |
7 | Tools and Equipment | 13 | 10 |
8 | Forces | 33 | 33 |
9 | Maintenance | 18 | 12 |
10 | Joining Methods | 18 | 12 |
11 | Systems and Control | 28 | 28 |
TOTAL | 200 | 180 | |
QUESTIONS
SECTION A: GENERIC
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE (GENERIC)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the correct answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1–1.6) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.7 D.
1.1 Which of the following safety measures is applicable to guillotines in terms of the Occupational Health and Safety Act?
- Clamp the work piece securely to the table.
- Do not leave the chuck key on the machine .
- Machine must be fitted with fixed guards to prevent fingers from reaching through the point of operation.
- Use the table of the machine as an anvil. (1)
1.2 What is the purpose of cooling the blade of a band saw with cutting fluid?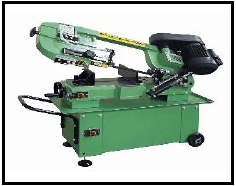
- To cause friction
- To ensure clean cuts and remove metal waste
- To ensure straight cuts
- To move the blade forward and backwards (1)
1.3 Which ONE of the following safety procedures is applicable to the operation of a hydraulic press?
- Do not apply wrench to revolving work.
- Guards could be removed when pressing soft material.
- Pressure gauges must be tested regularly and adjusted or replaced if any malfunction occurs.
- Use the machine table as an anvil. (1)
1.4 Which ONE of the following tests is used to measure the ductility of a metal?
- Bend tests
- Sound tests
- Hardness tests
- Machining tests (1)
1.5 File tests are used as the simplest method of checking the ... of material.
- toughness
- hardness
- ductility
- softness (1)
1.6 Sound tests can be performed by tapping a material with a …
- hacksaw.
- spanner.
- hammer.
- file. (1) [6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 Name any TWO pieces of personal safety equipment that you need to wear when using gas welding equipment. (2)
2.2 Give TWO safety rules that must be followed while the surface grinder is in operation. (2)
2.3 When completing a task on any machine, what safety aspect must be considered before leaving the machine? (1)
2.4 State TWO safety measures to observe before switching the angle grinder on. (2)
(2)
2.5 Why is it important to wear a welding helmet when using arc welding equipment? (1)
2.6 Name TWO types of workshop layouts. (2)
[10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1 The following table shows the different types of tests and materials.
Copy and complete the table in your ANSWER BOOK by stating how these materials will react under the different tests.
| MATERIALS | DIFFERENT TYPES OF TESTS | ||
| Cast iron | Sound | Filing | Bend |
| Mild steel | |||
(6)
3.2 Explain the purpose of heat treatment processes. (1)
3.3 The hardness that can be achieved from a specific treatment depends upon THREE factors. Name any TWO factors. (2)
3.4 Explain the purpose of the following heat treatment processes:
3.4.1 Tempering (2)
3.4.2 Annealing (2)
3.5 What does the hardness of steel depend upon? (1)
[14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE CHOICE (SPECIFIC)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (4.1–4.14) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 4.15 D.
4.1 Which lathe operation is shown in FIGURE 4.1?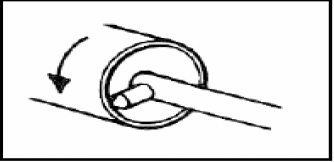
FIGURE 4.1
- Straight turning
- Internal parallel boring
- Thread cutting
- Reaming (1)
4.2 Identify the type of milling operation shown in FIGURE 4.2.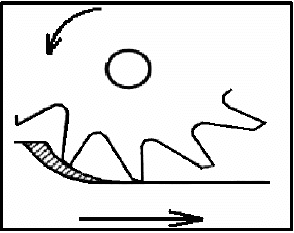
FIGURE 4.2
- Plain straight-tooth cutter
- Straight-tooth side-milling cutter
- Slitting saw
- Down-cut milling (1)
4.3 What is the purpose of cutting fluid?
- Acts as a non-lubricant
- Makes chips stick to the cutter
- Reduces the quality of the finish
- Cools a cutting tool and workpiece (1)
4.4 Compressive stress is stress that acts …
- against the length of an object.
- perpendicular to the surface.
- parallel to a surface.
- against the shortening of an object. (1)
4.5 What will the induced stress be, if a load of 50 N is applied to a square bar with a cross-sectional area of 144 × 10‾⁶ m² ?
- 347,22 kPa
- 3,47 kPa
- 0,347 kPa
- 34,7 kPA (1)
4.6 The main reason for performing a hardness test on engineering materials is to determine the …
- elasticity of the material.
- resistance of the material against denting
- corrosion of the material.
- fluidity of the material (1)
4.7 What does the symbol ‘X’ denote in the Brinell hardness test shown in FIGURE 4.7 below?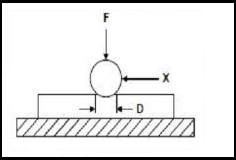
FIGURE 4.7
- Ball diameter
- Hardness number
- Test piece
- Force applied (1)
4.8 Which ONE of the following engineering materials is a thermo-hardened composite?
- Teflon
- Bakelite
- Bronze
- White metal (1)
4.9 What would the spindle speed be, if you were milling a material that has a cutting speed of 35 m/min with a cutter of 50 mm in diameter?
- 233 r/min
- 223 r/min
- 322 r/s
- 232 r/min (1)
4.10 Which ONE of the following indexing methods can be used to mill an angle of 41º 28’?
- Angular indexing
- Simple indexing
- Rapid indexing
- None of the above (1)
4.11 Which of the following is the definition of pressure?
- Pressure is the force acting on an object in a downward direction.
- Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction parallel to the surface
- Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface
- Pressure is the force per unit volume applied in a direction parallel to the surface (1)
4.12 The hydraulic system shown in FIGURE 4.12 below is used to lift a load. What is the pressure exerted on piston A? Given: the area of piston A is 1 cm².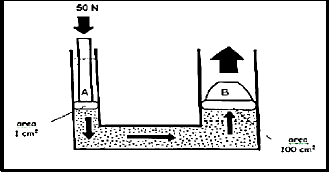
FIGURE 4.12
- 50 Pa
- 500 Pa
- 5 000 Pa
- 500 000 Pa (1)
4.13 Determine the width of a parallel key if the diameter is 36 mm.
- 8 mm
- 10 mm
- 9 mm
- 36 mm (1)
4.14 Identify the symbol, shown in FIGURE 4.14 below, which relates to a pneumatic system.
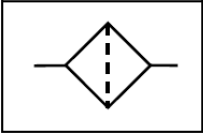
FIGURE 4.14
- Valve
- Fitter
- Compressor
- Motor (1)
[14]
QUESTION 5: TERMINOLOGY (LATHE AND MILLING MACHINE) (SPECIFIC)
5.1 Describe the function of the following centre lathe components:
5.1.1 Chuck (1)
5.1.2 Tool post (1)
5.1.3 Compound slide (1)
5.2 State the TWO classes of milling cutters and give ONE example of each. (4)
5.3 A 55 mm diameter shaft, 450 mm long, must be taper-turned with an included angle of 8.5º for a length of 250 mm. Calculate the small diameter of the taper.
(4)
5.4 FIGURE 5.4 shows a drawing of a dividing head of a milling machine.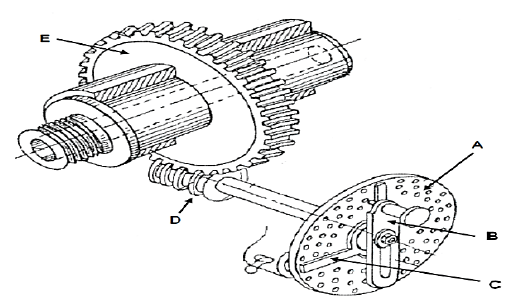
FIGURE 5.4
5.4.1 Label parts A–E. (5)
5.5 Calculate the lead of a triple start thread with a 1,75 mm pitch. (2)
[18]
QUESTION 6: TERMINOLOGY (SPECIFIC)
6.1 Explain the function of the following milling machine components:
6.1.1 Dividing head (1)
6.1.2 Index plate (1)
6.1.3 Sector arm (1)
6.2 Explain, step by step, the procedure used to cut an external metric V-screw thread with a pitch of 2 mm on a centre lathe using the compound slide method. (5)
6.3 Define the term indexing as applied to milling processes. (1)
6.4 State the TWO milling methods. (2)
6.5 Calculate the differential indexing of a gear with 113 teeth, determining:
6.5.1 The indexing required (Hint: Choose 120 divisions) (3)
6.5.2 The change gears required for the dividing head (5)
6.5.3 What is the meaning of the positive (+) sign and the negative (-) sign for the change of gears? (1)
6.6 The drawing in FIGURE 6.7 shows two precision rollers placed in an external dovetail.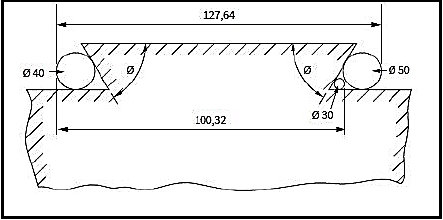
FIGURE 6.7
Calculate the angle θ using the values given in the drawing. (6)
6.7 State TWO disadvantages/constraints experienced when balancing is done practically. (2)
[28]
QUESTION 7: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
7.1 With the aid of neat sketches, highlight the difference between the following testers:
7.1.1 Brinell hardness tester (3)
7.1.2 Rockwell hardness tester (3)
7.2 State THREE ways in which materials hardness is measured. (3)
7.3 Determine the pitch from the screw thread micrometres shown in FIGURE 7.3.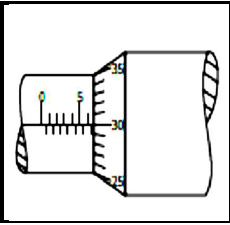
FIGURE 7.3 (2)
7.4 Draw the depth micrometre reading of 41,25 mm. (2)
[13]
QUESTION 8: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
8.1 FIGURE 8.1 below shows a system of forces with four concurrently applied forces. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the equilibrant of this system of forces.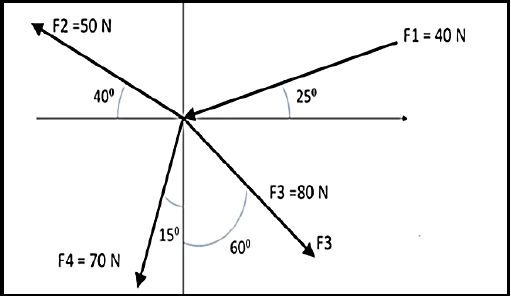
FIGURE 8.1 (12)
8.2 The diagram in FIGURE 8.2 below shows a beam with two vertically applied point loads of 10 kN and 20 kN and also a 1 kN/m uniformly distributed load on it.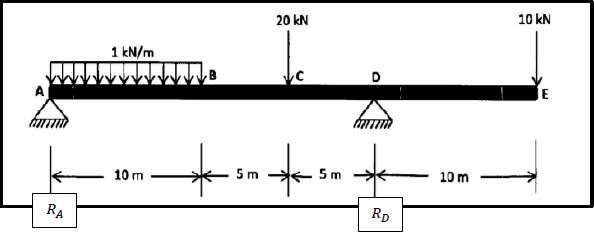
FIGURE 8.2
Calculate the magnitude of reactions RA and RD. (5)
8.3 A tensile force of 10 kN is applied to a round steel bar with a diameter of 20 mm and a length of 2 m. Young’s modulus of elasticity for this steel is 200 GPa.
Calculate:
8.3.1 The stress (4)
8.3.2 The extension due to the tensile force (4)
8.4 Draw and label the stress/strain diagram. (6)
8.5 What does the abbreviation FOS stand for in relation to stress calculations? (1)
8.6 Define the term Young’s modulus. (1)
[33]
QUESTION 9: MAINTENANCE (SPECIFIC)
9.1 What is the purpose of the following thermo-hardened composites?
9.1.1 Bakelite (2)
9.1.2 Glass fibre (2)
9.1.3 Carbon fibre (2)
9.2 Why is it essential to use a cutting fluid on a milling or centre lathe? (1)
9.3 List THREE mechanical drives generally used in engineering. (3)
9.4 Give TWO reasons for using carbon fibre in the manufacture of bicycle frames. (2)
9.5 In tabulated form compare ONE property and ONE use of the following thermoplastic materials:
9.5.1 PVC (2)
9.5.2 Vesconite (2)
9.5.3 Nylon (2)
[18]
QUESTION 10: JOINING METHODS (SPECIFIC)
10.1 A product inspector inspects gears that have been manufactured, he finds out that there is some uncertainty regarding the gear specifications. You are requested to calculate the following gear terms of a straight-tooth gear with 60 teeth and a module of 4.
Determine, by means of calculations, the following:
10.1.1 The pitch-circle diameter (2)
10.1.2 The addendum (2)
10.1.3 The clearance (2)
10.1.4 The dedendum (2)
10.1.5 The outside diameter of the gear (2)
10.2 FIGURE 10.2 below shows a cutting tool suitable for cutting left-hand square screw thread, in position.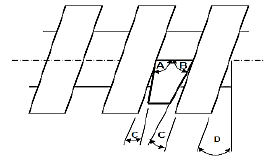
FIGURE 10.2 (4)
Label parts A–D.
10.3 Why would a multi-start thread be preferred mostly to a single start thread? (2)
10.4 Describe what is meant by screw thread fit. (2)
[18]
QUESTION 11: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL (SPECIFIC)
11.1 Describe the principle of operation of a gear drive. (2)
11.2 A hydraulic system is being used to lift goods when loading it into trucks. The specifications of the system are diagrammatically presented in FIGURE 11.2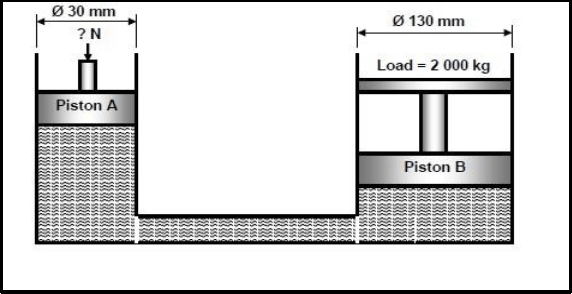
Calculate the following:
11.2.1 Convert the 2 000 kg mass into weight in Newtons (2)
11.2.2 The fluid pressure in the hydraulic system when the system is in equilibrium. (4)
11.2.3 The force that needs to be exerted onto piston A (4)
11.2.4 State ONE application of the system above. (1)
11.3 Define what is meant by velocity ratio. (2)
11.4 A power saw’s motor has a pulley, 135 mm in diameter, that turns at
1 200 rpm. The speed at which the driven pulley drives the saw blades is 395 rpm. Calculate the diameter of the driven pulley. (3)
11.5 Give THREE applications where pneumatics systems are used. (3)
11.6 The gear system in FIGURE 11.6 below is used to control a hoisting device. The driver gear has 56 teeth and rotates at 700 r/min. The idler gear used to change the direction, rotates at 980 r/min. The driven gear has 64 teeth.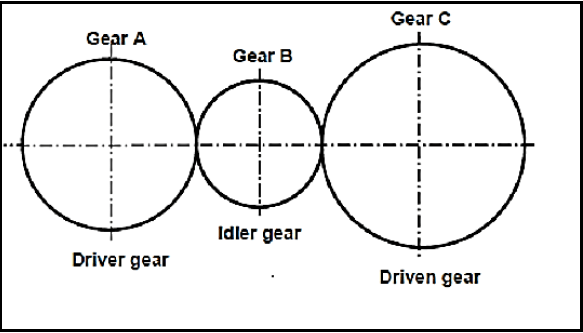
FIGURE 11.6
Calculate the:
11.6.1 Number of teeth on the idler gear (3)
11.6.2 The rotation frequency of the driven gear (3)
11.6.3 In which direction will the driven gear rotate if the driver gear rotates anti-clockwise? (1)
[28]
TOTAL: 200
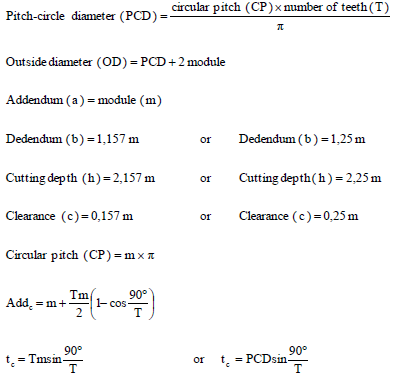
FORMULA SHEET FOR MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY (FITTING AND MACHINING)
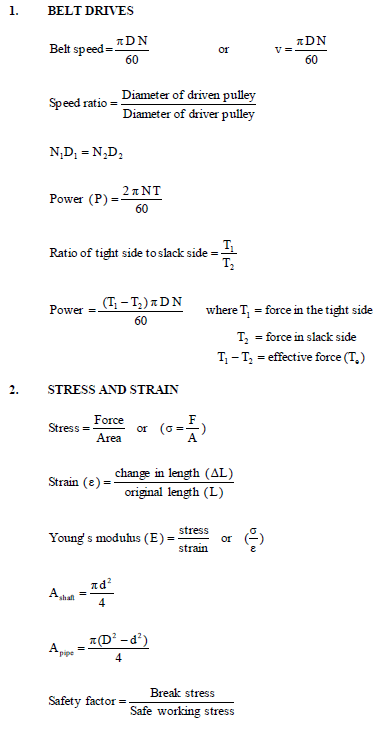

Life Sciences Paper 2 Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
PRINCIPLES RELATED TO MARKING LIFE SCIENCES
- If more information than marks allocated is given
Stop marking when maximum marks is reached and put a wavy line and ‘max’ in the right-hand margin. - If, for example, three reasons are required and five are given
Mark the first three irrespective of whether all or some are correct/incorrect. - If whole process is given when only a part of it is required
Read all and credit the relevant part. - If comparisons are asked for but descriptions are given
Accept if the differences/similarities are clear. - If tabulation is required but paragraphs are given
Candidates will lose marks for not tabulating. - If diagrams are given with annotations when descriptions are required
Candidates will lose marks. - If flow charts are given instead of descriptions
Candidates will lose marks. - If sequence is muddled and links do not make sense
Where sequence and links are correct, credit. Where sequence and links are incorrect, do not credit. If sequence and links become correct again, resume credit. - Non-recognised abbreviations
Accept if first defined in answer. If not defined, do not credit the unrecognised abbreviation but credit the rest of the answer if correct. - Wrong numbering
If answer fits into the correct sequence of questions but the wrong number is given, it is acceptable. - If language used changes the intended meaning
Do not accept. - Spelling errors
If recognisable, accept the answer, provided it does not mean something else in Life Sciences or if it is out of context. - If common names are given in terminology
Accept, provided it was accepted at the national memo discussion meeting. - If only the letter is asked for but only the name is given (and vice versa)
Do not credit. - If units are not given in measurements
Candidates will lose marks. Marking guideline will allocate marks for units separately. - Be sensitive to the sense of an answer, which may be stated in a different way.
- Caption
All illustrations (diagrams, graphs, tables, etc.) must have a caption. - Code-switching of official languages (terms and concepts)
A single word or two that appear(s) in any official language other than the learners' assessment language used to the greatest extent in his/her answers should be credited if it is correct. A marker that is proficient in the relevant official language should be consulted. This is applicable to all official languages.
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 A
1.1.2 C
1.1.3 D
1.1.4 D
1.1.5 A
1.1.6 B
1.1.7 C
1.1.8 B
1.1.9 B
1.1.10 A (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 alleles
1.2.2 double helix
1.2.3 interphase
1.2.4 population
1.2.5 Prophase I
1.2.6 phylogenetic tree / cladogram
1.2.7 biogeography
1.2.8 extinction (8)
1.3
1.3.1 A only
1.3.2 Both A and B
1.3.3 Both A and B (3 x 2) (6)
1.4
1.4.1 James Watson, Francis Crick (2)
1.4.2 Double helix (1)
1.4.3
- DNA codes for the formation of different proteins required in the body
- DNA is responsible for transmitting hereditary characteristics (2)
1.4.4
- Nucleus
- Mitochondrion (2)
1.4.5 Maurice Wilken (1)
(8)
1.5
1.5.1 Dihybrid cross (1)
1.5.2
- red (1)
- ffhh (2)
- red, tall (2)
- FH, Fh, fH, fh (1-3 correct, 4 correct ) (2)
(8)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1 Protein Synthesis (1)
2.1.2 cytoplasm /outside the nucleus (1)
2.1.3
- DNA (1)
- polypeptide chain /protein (1)
2.1.4 UGU (2)
2.1.5 ACG (1)
2.1.6 CCA (2)
2.1.7 Lysine (1)
2.1.8 If base sequence was UUU instead of AAA then:
- anticodon on tRNA would be AAA
- therefore amino acid would be Phenylanine
- instead of Lysine(3)
(13)
2.2
2.2.1 pedigree diagram (1)
2.2.2
- Blue skin female (1)
- Nn (1)
2.2.3 recessive allele (1)
2.2.4 Mabala and Maurice are both normal but their son Lunar has blue skin therefore, Mabala and Maurice are carriers of the disease
2.2.5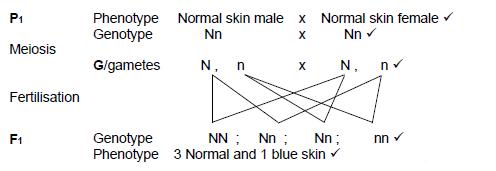
They have a 25% * chance of having a child with blue skin
P1 and F1
Meiosis and fertilisation
1 compulsory* + Any 6
OR
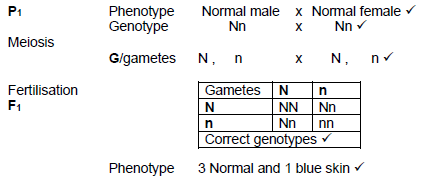
They have a 25% * chance of having a child with blue skin
P1 and F1
Meiosis and fertilisation
1 compulsory* + Any 6 (7)
2.3
2.3.1
- In the original population of Antarctic fish there was variation
- Some fish produced the antifreeze protein while others did not
- Those that did not produce antifreeze protein did not survive the icy, freezing waters
- Those that produced antifreeze survived the icy, freezing waters
- They reproduced and past on their characteristic to the next generation
- And eventually over time the number of antifreeze producing fish in the population increased (Any 5 x 1) (5)
2.3.2 Genetic Modification (1)
2.3.3
- Engineer cold resistant plants
- preserving food at very low temperatures (2)
2.3.4
- The gene coding for antifreeze protein production is isolated from a fish cell
- The gene is cut out using restriction enzymes
- A bacterial plasmid is removed and is cut open using restriction enzymes
- The antifreeze producing gene is inserted into the plasmid
- The genetically modified plasmid is returned to the bacterium
- The bacterium multiplies and all of the offspring have the gene for antifreeze protein production
- The bacteria produce anti-freeze (Any 5) (5)
2.3.5
- People who are allergic to fish proteins may not know that the plant contains it and will therefore be at risk.
- Vegans and vegetarians may not want to eat animal products and will be forced to if it is in plants
Mark first ONE only (Any 1) (1)
[40]
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1 Co-dominance (1)
3.1.2 Both alleles are expressed in the offspring’s phenotype (2)
3.1.3
Genotype | RR | RB | BB |
Number of offspring | 5 | 10 | 5 |
OR
Genotype | Number of offspring |
RR | 5 |
RB | 10 |
BB | 5 |
Guidelines for assessing the table
| Correct table format (Separation of columns) | 1 |
| Column headings | 2 |
| Data entered | 1 : 1 to 2 sets correctly enetred 2 : All 3 data sets correctly entered |
(5)
3.1.4 Both parents have a Phenotype – Red and Genotype – RR (2)
3.2
3.2.1
- Increase in Muscle Protein Synthesis (1)
- Amount of protein (1)
3.2.2
- Get permission from participants / doctor
- Determine how to measure MPR / how data will be collected
- Train data collectors on how to measure MPR
- Determine sample size
Mark first TWO only (Any 2) (2)
3.2.3
- It had a large sample size /100 participants
- It obtained similar results to two other investigations (2)
3.2.4 Percentage increase
- = 1 x 100 = 9,09% (2)
11
3.2.5
- There is very little increase in MPR from 20 g to 40 g
- therefore you will gain very little for double the amount of protein (2) (10)
3.3
3.3.1 Stem cell are undifferentiated cells that has the potential to form any tissue of organ (2)
3.3.2
- Cord blood, umbilical cord blood
- Bone marrow
- Blood, peripheral blood stem cells
- Menstrual blood OR Adult stem cells
- Skin
- Teeth
- Placental tissue
(Any 2) (2)
3.3.3 Spinal cord injuries /neurodegenerative diseases (Parkinson’s disease / Alzheimer’s disease / Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) (Any 1) (1)
3.4 3.4.1 There are 3 alleles / more than two for blood groups A, B and O (2)
3.4.2 ![]() (2)
(2)
3.4.3 If the man was IBi and the woman was IAi then they would both pass the recessive allele/I to their child. (3)
3.4
3.5.1
- All elephants had short trunks / noses
- They frequently stretched their trunk / nose to reach for leaves in the trees
- As a result, their trunks became longer
- The characteristic for long trunks acquired in this way was then passed on to the next generation
- Eventually all elephants had long trunks (5)
3.5.2
- Organisms evolved, not because they wanted to evolve but because changes took place randomly, in response to the environment
- There is very little evidence to support Lamarck’s idea that changes brought about by adaptation to the environment are inherited from parent to offspring (2)
3.5.3 Characteristics are past from parents to offspring (1)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
Composition of karyotype
- There are 23 pairs /46 chromosomes in
- human somatic cells /body cells
- which are arranged into homologous pairs
- Each somatic cell has 22 pairs/44 autosomes and
- a pair/2 gonosomes /sex chromosomes/ X and Y chromosome
- Autosomes are arranged in pairs from largest to smallest in a karyotype
- Males have XY chromosomes
- Females have XX chromosomes
- The X chromosome is larger than the Y chromosome (Any 6) (6)
Importance of meiosis
- Production of haploid gametes
- Halving effect overcomes the doubling effect of fertilization
- Thus, maintaining a constant chromosome number
- Introduces variation (Any 3) (3)
Effect of non-disjunction in humans
- Humans may be affected by aneuploidy
- Aneuploidy/Non-disjunction occurs when chromosomes do not separate
- during anaphase
- During anaphase 1 a single pair of homologous chromosomes do not separate
- Or during anaphase 2 chromatids do not separate
- One gamete will receive two copies of the same chromosome
- While the other gamete will receive none
- If fertilisation occurs between the abnormal gamete and a normal gamete the resulting cell / zygote will have one less chromosome / the zygote will be monosomic
- Or the zygote may have an extra chromosome / the zygote will be trisomic
- Down Syndrome / Trisomy 21 is an example of aneuploidy in humans
(Any 8) (8)
ASSESSING THE PRESENTATION OF THE ESSAY
Criterion | Relevance (R) | Logical sequence (L) | Comprehensive (C) |
Generally | All information provided is relevant to the question | Ideas are arranged in a logical/cause-effect sequence | All aspects required by the essay have been sufficiently addressed |
In this essay in Q4 | Only information relevant to the description of:
There is no irrelevant information | All the information regarding the
Is given in a logical manner | At least:
|
Mark | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Content 17
Synthesis 3
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Life Sciences Paper 1 Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
PRINCIPLES RELATED TO MARKING LIFE SCIENCES
- If more information than marks allocated is given
Stop marking when maximum marks are reached and put a wavy line and ‘max’ in the right-hand margin. - If, for example, three reasons are required and five are given
Mark the first three irrespective of whether all or some are correct/incorrect. - If whole process is given when only a part of it is required
Read all and credit the relevant part. - If comparisons are asked for, but descriptions are given
Accept if the differences/similarities are clear. - If tabulation is required, but paragraphs are given
Candidates will lose marks for not tabulating. - If diagrams are given with annotations when descriptions are required
Candidates will lose marks. - If flow charts are given instead of descriptions
Candidates will lose marks. - If sequence is muddled and links do not make sense
Where sequence and links are correct, credit. Where sequence and links are incorrect, do not credit. If sequence and links become correct again, resume credit. - Non-recognised abbreviations
Accept if first defined in answer. If not defined, do not credit the unrecognised abbreviation, but credit the rest of the answer if correct. - Wrong numbering
If answer fits into the correct sequence of questions, but the wrong number is given, it is acceptable. - If language used changes the intended meaning
Do not accept. - Spelling errors
If recognisable, accept the answer, provided it does not mean something else in Life Sciences or if it is out of context. - If common names are given in terminology
Accept, provided it was accepted at the national memo discussion meeting. - If only the letter is asked for, but only the name is given (and vice versa)
Do not credit. - If units are not given in measurements
Candidates will lose marks. Marking guidelines will allocate marks for units separately. - Be sensitive to the sense of an answer, which may be stated in a different way
- Caption
All illustrations (diagrams, graphs, tables, etc.) must have a caption. - Code-switching of official languages (terms and concepts)
A single word or two that appear(s) in any official language other than the learner’s assessment language used to the greatest extent in his/her answers should be credited, if it is correct. A marker that is proficient in the relevant official language should be consulted. This is applicable to all official languages.
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 C
1.1.2 B
1.1.3 B
1.1.4 D
1.1.5 B
1.1.6 C
1.1.7 B
1.1.8 D (8 x 2) (16)
1.2
1.2.1 Vasodilation
1.2.2 Hypothalamus
1.2.3 Negative feedback
1.2.4 Parasympathetic system
1.2.5 Aldosterone
1.2.6 Synapse
1.2.7 Placenta (7 x 1) (7)
1.3
1.3.1 None
1.3.2 A only
1.3.3 A only (3 x 2) (6)
1.4
1.4.1
- A (1)
- E (1)
- B (1)
- F (1)
1.4.2 Spinal cord (1)
1.4.3 Reflex action (1)
1.4.4 Brain and the spinal cord (2)
1.4.5
- C (1)
- D (1)
1.5
1.5.1
- A – Vagina (1)
- B – Cervix (1)
- F – Uterus (1)
1.5.2
- C endometrium (2)
- D Ovary (2)
- E Fallopian tube (2)
1.5.3 Sperm will not be able to fertilise the ovum / sperm will not be able to reach ovum and cause fertilisation (1)
1.5.4 Both ovaries release ova alternately (1)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1
- Prophase I (1)
- Metaphase I (1)
2.1.2
- A – Centromere (1)
- B – Homologous chromosomes / Chromosomes (1)
- D – Centriole (1)
2.1.3
- Homologous chromosomes lie side by side
- Chromatids from the paternal and maternal chromosomes
- Establish contact points called chiasmata and
- Exchange genetic material between chromatids and
- This is known as crossing over (Any 4) (4)
2.1.4
- Homologous chromosomes randomly arrange themselves
- on either side of the equator and this
- leads to the formation of new combinations of genetically
- different chromosomes
- in the daughter cells (gametes) causing variation* in the next generation (1* compulsory point + any 2) (3)
2.2
2.2.1 Altricial development (1)
2.2.2
- Eyes closed
- no down feathers covering the body / bodies naked
- unable to feed themselves
(Mark first THREE only) (3)
2.2.3
- Complete dependence on parents until fully developed
OR - unable to defend/move
- therefore, they are an easy target for predation (Any 1) (1)
2.2.4
- The egg yolk that supplies nutrients to the developing embryo is small therefore,
- the hatchlings are unable to develop fully before hatching (2)
2.3
2.3.1 Long/far-sightedness (Hypermetropia) (1)
2.3.2
- Eye ball is too rounded
- due to the inability of the lens of the eye to become more convex
- therefore, the image of the near object that falls on the retina is blurred while
- the most clearly focussed image falls behind the retina(4)
2.3.3
- It can be corrected with a convex lens
(Mark first ONE only) (1)
2.3.4
- The radial muscles of the iris contract
- the circular muscles relax
- the pupil dilates
- the amount of light entering the eye is increased (4)
2.4
2.4.1 Luteinizing hormone (LH) (1)
2.4.2 The highest level of LH causes ovulation (1)
2.4.3 13th day of the cycle (1)
2.4.4
- High level of oestrogen / an increase in level of oestrogen causes the endometrium to become more
- vascular and spongy/thicker (2)
2.4.5 Progesterone (1)
2.4.6
- The maintenance of high levels of progesterone / hormone B after 28 days indicates pregnancy
- hormone B / progesterone is required to maintain pregnancy / maintain the endometrium (2)
2.4.7
- High levels of progesterone inhibit the secretion of FSH in order to stop the development of new follicles and
- cause ovulation / no new ova produced
- during pregnancy / disrupts pregnancy (3)
[40]
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1 Thyroid gland (1)
3.1.2 Treatment of thyroxin / substance tadpoles were treated with (1)
3.1.3
- Quantity of NaOH and thyroxin treatment
- Time of treatment/ feeding
- Time of collecting data
- Size of tadpoles
- Type of nutrients
- Quantity of nutrients
- Level of activity / area of captivity
- Environmental conditions
- Method of determining the body mass
(Mark first TWO only) (Any 2) (2)
3.1.4 The initial body mass taken before the treatment (1)
3.1.5
- High levels of thyroxin in the body
- increase the rate of metabolism
- More glucose will be oxidised / more of their fuel reserves are used up
- to release more energy / allowing them to be more active
- this leads to drop in the body mass (4)
3.1.6
- When the thyroxin level drops below normal limits
- pituitary gland / hypophysis is stimulated
- Pituitary gland secretes more TSH
- High TSH level stimulates the thyroid gland
- The thyroid gland secretes more thyroxin
- The thyroxin level thus increases
- Thyroxin level returns to normal (5)
3.2
3.2.1
- B – Medulla oblongata (1)
- C – Corpus callosum (1)
- E – Cerebellum (1)
3.2.2
-
- It conducts impulses between the brain and the receptors / effectors
- Serves as a reflex centre for actions such as blinking, sneezing, coughing etc. (Any 1) (1)
(Mark first ONE only)
-
- Cerebro-spinal fluid in the central canal supplies nutrients and oxygen for nerve cells / removes CO2 and waste products from the nerve cells / protects the brain and spinal cord against physical injury
(Mark first ONE only) (1)
- Cerebro-spinal fluid in the central canal supplies nutrients and oxygen for nerve cells / removes CO2 and waste products from the nerve cells / protects the brain and spinal cord against physical injury
3.2.3
-
- During a haemorrhage, the blood leaks out of the blood capillaries
- and this disrupts the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the nerve cells / removal of CO2 and metabolic waste causing them to die / causes excessive pressure (3)
-
- Loss of sensation / consciousness / unable to process impulses from sense organs
- loss of higher intellectual abilities such as memory, judgement, reasoning. etc.
- unable to initiate voluntary muscular actions (3)
3.3
3.3.1 Auxin (1)
3.3.2 Auxin is present / produced at the growing tip of stem or root (1)
3.3.3 To cancel the effect of unilateral light on plumule growth / to show that the light has no effect on the upward bending of plumule / to exclude a phototropic response (1)
3.3.4 When a plumule is placed horizontally:
- Auxins are attracted by gravity
- There is a high concentration of auxins on the lower side of the plumule
- which stimulates growth / cell elongation / cell division on the lower side
- There is a low concentration of auxins on the upper side of the plumule
- which inhibits growth / cell elongation / cell division on the upper sides
- The lower side of the plumule grows faster / uneven growth occurs causing the plumule to grow/ bend upwards
- The plumule grows away from gravity*/ the plumule is negatively geotropic
1* Compulsory mark + (Any 3) (4)
3.3.5 The germinating seed is attached to the disc of rotating clinostat (1)
3.4
3.4.1
- Has a protective function
- Acts as a climate control system for the testes / temperature control
(Mark first TWO only) (2)
3.4.2 Epididymis (1)
3.4.3
- Fertility is reduced
- because the temperature is always high
- This will lead to production of abnormal sperms / fewer sperm are formed / proteins in the cells that form the sperm will denature
OR - Fertility is reduced
- because the pressure is increased / reducing circulation of the blood
- This will lead to the production of abnormal sperm / Fewer sperms are formed (3)
3.4.4 Take regular breaks while driving long distances (1)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
The process that led to an increased breathing rate:
- The adrenal gland
- secretes more adrenalin into the blood
- An increased level of carbon dioxide in the surrounding area due to the heavy smoke
- causes carbon dioxide levels in the blood to increase above the normal levels
- Receptor cells in the carotid artery in the neck are stimulated
- to send impulses to the medulla oblongata in the brain
- Medulla oblongata stimulates breathing muscles (intercostal muscles and diaphragm)
- and heart
- Breathing muscles contract more actively
- Increases the rate and depth of breathing
- The heart beats faster
- More carbon dioxide is taken to and exhaled from the lungs
- causing the breathing rate to increase
Max. 10 (10)
Restoring balance
Balance is achieved in the following way:
- The maculae
- in the utriculus and sacculus and
- the cristae
- in the semi-circular canals are stimulated
- They generate impulses
- which are transmitted through the auditory nerve
- to the cerebellum
- where they are interpreted
- Impulses are transmitted via the motor neuron
- to skeletal muscles
- to restore balance
Max. 7 (7)
Content (17)
Synthesis (3)
(20)
ASSESSING THE PRESENTATION OF THE ESSAY
Relevance | Logical sequence | Comprehension |
All information provided is relevant to the question | Ideas arranged in a logical/ cause-effect sequence | Answered all aspects required by the essay in sufficient detail |
All information is relevant to the:
There is no irrelevant information | The sequence of events and facts in the:
| The following must be included:
|
1 mark | 1 mark | 1 mark |
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Life Sciences Paper 2 Grade 12 Questions - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Write ALL the answers in the ANSWER BOOK provided.
- Start the answer to EACH question at the top of a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Present your answers according to the instructions of each question.
- ALL drawings MUST be done in pencil and labelled in blue or black ink.
- Draw diagrams, tables or flow charts ONLY when asked to do so.
- The diagrams in this question paper are NOT necessarily drawn to scale.
- Do NOT use graph paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator, protractor and compass, where necessary.
- All calculations have to be rounded off to TWO decimal spaces.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the correct answer and write only the letter (A‒D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1‒1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 A trait that has a range of phenotypes is an example of ...
- continuous variation.
- codominance.
- discontinuous variation.
- complete dominance.
1.1.2 Study the diagram below.
Which of the following combinations correctly identifies the parts of the above molecule?
FIGURE B | Molecule 1 | Molecule 2 | Bond 3 | |
| A | DNA | Cytosine | nitrogenous base | Weak Hydrogen |
| B | DNA | Adenine | nucleotide | Sugar Phosphate |
| C | RNA | Adenine | nucleotide | Weak Hydrogen |
| D | RNA | Thymine | nitrogenous base | Weak Hydrogen |
QUESTIONS 1.1.3 and 1.1.4 refer to the diagram below.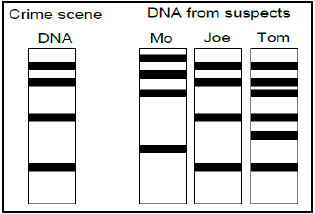
1.1.3 The result of the procedure shown above is called …
- cloning.
- DNA replication.
- fingerprinting.
- DNA profiling.
1.1.4 Study the list below:
- Paternity testing
- Matching of tissue for organ transplants
- Identification from fingerprints
- Curing genetic disorders
Which combination shows the CORRECT uses of the procedure shown in the diagram above?
- (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- Only (i), (ii) and (iv)
- Only (i), (ii) and (iii)
- Only (i) and (ii)
1.1.5 When gene flow between two populations is stopped, the following is said to have happened:
- Speciation
- Adaptation
- Resistance
- Variation
1.1.6 Which of the following is an example of artificial selection?
- DDT resistance in mosquitoes
- Breeding of cows to increase milk production
- Antibiotic resistance in bacteria
- Development of a different species of Galapagos finch
1.1.7 The diagram below represents three species (A, B and C) which each live on a different island, separated by the sea.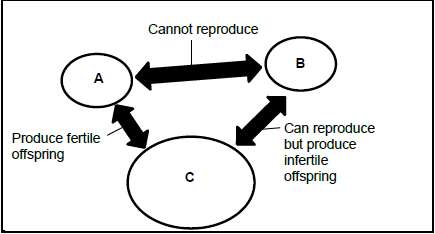
Which ONE of the following statements is correct?
- All three populations are different species
- Populations B and C are different species and A and B are the same species
- Populations A and C are the same species and B and C are different species
- All three populations are the same species
1.1.8 The forelimbs of vertebrates, as shown below, are an example of …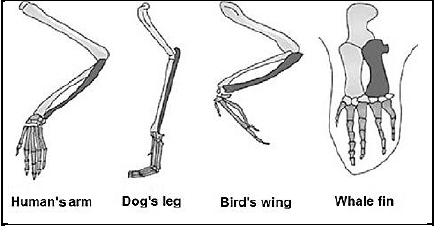
- vestigial structures.
- homologous structures.
- analogous structures.
- convergent evolution.
1.1.9 The diagram shows homologous chromosome pair number 3 from each of four fruit flies. The alleles for antenna shape (normal or abnormal) and body pattern (with stripes or without stripes) are indicated on the chromosomes.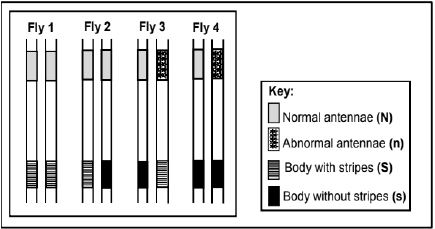
Which fly is homozygous for antennae shape and heterozygous for body pattern?
- Fly 1
- Fly 2
- Fly 3
- Fly 4
1.1.10 A hummingbird uses its long beak to feed on the nectar in flowers. According to Gould and Eldridge’s theory of punctuated equilibrium, the long beak of the hummingbird developed …
- rapidly over a short period of time.
- because the more the hummingbird used its beak, the longer it grew.
- because their beaks have been constantly changing all the time.
- gradually over a long period of time.
(10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Give the correct biological term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.2.1‒1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 Alternate forms of the same gene
1.2.2 Natural shape of the DNA molecule
1.2.3 Stage in the cell cycle when DNA replication occurs
1.2.4 Organisms with similar characteristics which live in the same habitat and interbreed freely to produce fertile offspring
1.2.5 Phase in meiosis when crossing over occurs
1.2.6 The diagrammatic representation showing possible evolutionary relationships among different species
1.2.7 The study of past and present distribution of individual species across the world
1.2.8 The process by which all individuals of a particular species die out so that not even a single one exits (8 x 1) (8)
1.3 Indicate whether each of the statements in COLUMN Ι applies to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A and B, or NONE of the items in COLUMN ΙΙ. Write A only, B only, both A and B, or none next to the question numbers (1.3.1‒1.3.3) in the ANSWER BOOK.
COLUMN Ι | COLUMN ΙΙ | ||
1.3.1 | Scientist who only studies fossils | A: | Palaeontologist |
B: | Archaeologist | ||
1.3.2 | Needed for natural selection to | A: | Variation |
occur | B: | Competition | |
1.3.3 | Reproduction isolating barrier | A: | Breeding at different times of the year |
B: | Infertile offspring |
(3 x 2) (6)
1.4 The diagram below represents the model of DNA proposed by scientists in 1953.
1.4.1 Name the scientists who first published the structure of DNA. (2)
1.4.2 What is the natural shape of DNA? (1)
1.4.3 Give TWO functions of DNA. (2)
1.4.4 Where is DNA found in the human cell? (2)
1.4.5 Name the other scientist that was awarded the Nobel Prize for the discovery of the structure of DNA. (1)
1.5 In a plant species two characteristics, flower colour and plant height, were studied. Each of these characteristics has two variations: flowers may be red or white in colour and the plants may be tall or short.
When two plants that are heterozygous for flower colour and height were crossed, 9 offspring were red and tall, 3 were white and tall, 3 were red and short and 1 was white and short.
The alleles for each characteristic are shown in the table below.
CHARACTERISTIC | DOMINANT ALLELE | RECESSIVE ALLELE |
Flower colour | F | f |
Plant height | H | h |
1.5.1 What is the term for a genetic cross involving two characteristics? (1)
1.5.2 Give the:
- Dominant phenotype for flower colour (1)
- Genotype of a white flowering, short plant (2)
- Phenotype of a plant that is heterozygous for flower colour and homozygous dominant for plant height (2)
- Possible gametes of a heterozygous red, heterozygous tall plant (2)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1 Study the diagram below.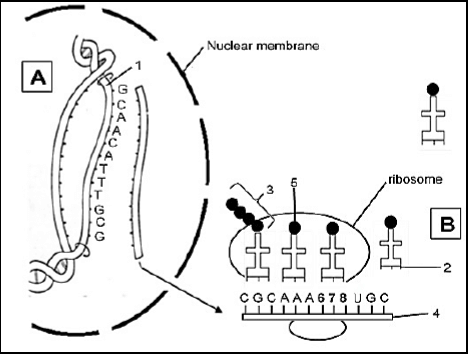
2. 1.1 Name the process represented by A and B combined. (1)
2. 1.2 Where in the cell does process B occur? (1)
2. 1.3 Identify the following:
- Molecule 1 (1)
- Polymer 3 (1)
2. 1.4 Give the correct base sequence to replace numbers 6, 7 and 8. (2)
2. 1.5 Write down the anticodon at label 2. (1)
USE THE TABLE BELOW TOGETHER WITH THE ABOVE DIAGRAM TO ASWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS
| ANTICODONS OF tRNA AND THE CORRESPONDING AMINO ACIDS THAT THEY CARRY | |
| tRNA ANTICODONS | AMINO ACIDS |
| UUU | Lysine |
| ACA | Cysteine |
| GCA | Arginine |
| GUU | Glutamine |
| CCA | Glycine |
| AAA | Phenylalanine |
2.1.6 What is the DNA base triplet for Glycine? (2)
2.1.7 Name the amino acid found at label 5. (1)
2.1.8 Explain how the composition of the protein molecule would change if the base sequence of the second codon on molecule 4 (from the left)
was UUU instead of AAA. (3)
2.2 ‘Blue people’ is a genetic disorder caused when a person does not produce the enzyme that converts methemoglobin (which is blue) into haemoglobin (which is red). This results in high levels of methemoglobin in the blood. It causes the skin to turn blue, the lips purple, and the blood chocolate brown.
The diagram below shows members in a family who have blue skin. The genotype of some members of the family are known and indicated on the diagram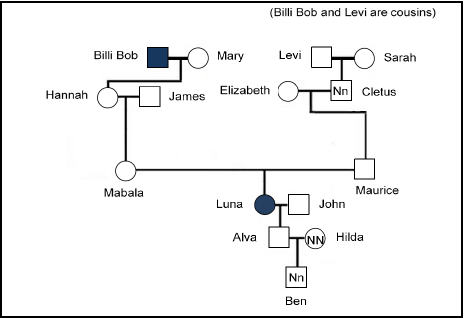
[Adapted from <htpp://ghr.nlm.nih.gov;indiana.edu/;NCBI1000Genomes Browser.]
2.2.1 Name the type of diagram shown above. (1)
2.2.2 Give the:
- Phenotype of Luna (1)
- Genotype of Hannah (1)
2.2.3 Is this disease caused by a dominant or recessive allele? (1)
2.2.4 Give a reason for your answer in QUESTION 2.2.3. (2)
2.2.5 Mabala and Maurice both have normal skin colouring. Using a genetic cross show how it is possible for their son Luna to be blue. (7)
2.3 Read the following passage.
Antarctic fish have evolved to live in the freezing waters of the Southern Ocean. They live in waters that are well below 0°C. Normally cells would freeze and burst at this temperature, killing the fish. Antarctic fish have developed proteins that act as antifreeze. These antifreeze proteins help the fish avoid freezing in their icy habitats by stopping the formation of ice crystals in the cells. These antifreeze proteins could also be commercially important. Scientists could use these antifreeze protein genes to engineer cold resistant plants or they could be used when preserving food at very low temperatures. They prevent ice crystals from forming and ruining the food. Investigators have already successfully introduced fish antifreeze proteins into yeast and bacteria through recombinant DNA technology. They can use these bacteria and yeast to produce large quantities of antifreeze proteins. |
2.3.1 Describe how Antarctic fish may have developed antifreeze proteins through natural selection. (5)
2.3.2 Name the process by which the genetic makeup of an organism is altered to include a new characteristic. (1)
2.3.3 Give TWO ways that these antifreeze proteins have been used commercially to benefit humans. (2)
2.3.4 Briefly describe how antifreeze protein is produced through recombinant DNA technology with bacteria. (5)
2.3.5 Give ONE reason why using antifreeze proteins in plants could be ethically wrong. (1)
[40]
QUESTION 3
3.1 Zebra fish come in many different colours. Emihle bought a blue male (BB) and a red female zebra (RR) fish for her fish tank. The offspring that were born were all blue and red striped.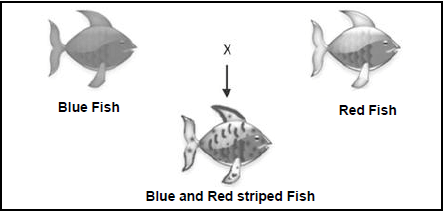
Later, Emihle decided to have a second fish tank and breed two blue and red striped fish with each other. There were 20 offspring born in total and they had three different colours: blue, red and blue and red striped.
3.1.1 Name the type of dominance shown in the above example. (1)
3.1.2 Explain the answer given in QUESTION 3.1.1. (2)
3.1.3 Draw a table showing the number of offspring of the different genotypes from Emihle’s second breeding. (5)
3.1.4 What should be the genotype(s) and phenotype(s) for the parent fish if Emihle wanted only offspring that were red? (2)
3.2 Read the following passage.
Many athletes have to train hard to build muscle. Muscle is a protein and is therefore formed by protein synthesis. Athletes need to eat and train to ensure optimal Muscle Protein Synthesis (MPS). They always want to know how much protein they must eat to build bigger muscles.
Scientists carried out an investigation to determine the optimal daily protein (in grams) needed for maximal increase in Muscle Protein Synthesis.
The investigation was carried out as follows:
- They studied 100 bodybuilders
- Each bodybuilder was given the same daily weightlifting exercise programme
- All athletes were fed the measured protein meal straight after exercising
- Their MPS was recorded 4 hours after exercising
The graph below shows the results of the investigation. These results were similar to two other investigations carried out by other scientists.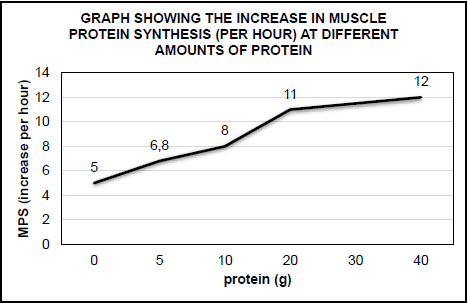
The conclusion reached by the scientists was as follows:
The optimal daily protein needed for maximal increase in Muscle Protein Synthesis is 20 g.
3.2.1 State the:
- Dependent variable (1)
- Independent variable (1)
3.2.2 Give TWO planning steps that investigators would need to follow. (2)
3.2.3 Give reasons why this investigation can be considered reliable. (2)
3.2.4 Calculate percentage increase in MPS from 20 g to 40 g. (2)
3.2.5 Using the data provided, suggest why the scientists’ conclusion stated that 20’g of protein was the optimal amount of protein needed daily for
increased Muscle Protein Synthesis. (2)
3.3 The diagram shows one way that stem cells can be produced from human embryos.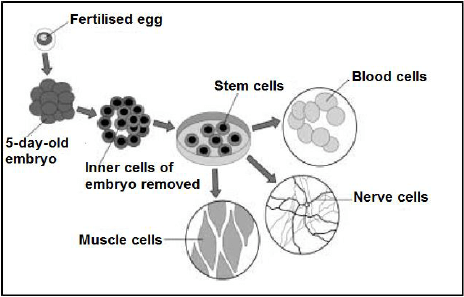
3.3.1 What are stem cells? (2)
3.3.2 Give TWO sources of stem cells other than human embryos. (2)
3.3.3 Give ONE medical condition that can be treated by using nerve cells grown from stem cells. (1)
3.4 Human blood type is an example of multiple alleles.
3.4.1 Why are blood types an example of multiple alleles? (2)
3.4.2 Give the possible genotypes for a man who is blood type B. (2)
3.4.3 If a man has blood group B and a woman has blood group A, explain how it is possible to have a child who has blood group O. (DO NOT
draw a genetic diagram.) (3)
3.5 The diagrams below show the Phiomia, an ancestor of the elephants and a modern African elephant. The Phiomia lived 35 million years ago. Both the Phiomia and modern African elephant reach up into trees to get leaves to eat.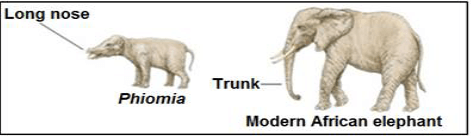
3.5.1 Explain how Jean-Baptiste Lamarck would explain how the modern African elephant developed a long trunk. (5)
3.5.2 Give TWO reasons why Lamarck’s theory is no longer accepted today. (2)
3.5.3 Give ONE similarity between Lamarck’s theories and Darwin’s theory of natural selection. (1)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
Discuss the composition of the human karyotype. Also explain why meiosis is important and how non-disjunction during meiosis can affect humans.
Content: (17)
Synthesis: (3)
NOTE: NO marks will be awarded for answers in the form of flow charts, tables or diagrams.
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Life Sciences Paper 1 Grade 12 Questions - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Write ALL the answers in your ANSWER BOOK.
- Start the answer to EACH question at the top of a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Present your answers according to the instructions of each question.
- Do ALL drawings in pencil and label them in blue or black ink.
- Draw diagrams, tables or flow charts only when asked to do so.
- The diagrams in this question paper are NOT necessarily drawn to scale.
- Do NOT use graph paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator, protractor and a compass where necessary.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1–1.1.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.9 D.
1.1.1 During Meiosis II …
- the chromosomes arrange at the equator of the cell in homologous pairs.
- the chromosome number is halved.
- chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell individually.
- whole chromosomes move to the opposite poles of the cell.
1.1.2 Which part of the male reproductive system secretes testosterone?
- Vas deferens
- Testis
- Seminal vesicle
- Prostate gland
1.1.3 The process by which ova are produced from the germinal epithelium of the ovaries is known as …
- gametogenesis.
- oogenesis.
- spermatogenesis.
- ovulation.
1.1.4 A ganglion is …
- an obstruction in a blood vessel.
- a collection of cells secreting hormones into the blood.
- a type of nerve cell involved in a reflex action.
- a collection of nerve cell bodies.
1.1.5 When the level of blood glucose rises, the body immediately reacts to lower the level by secreting …
- glycogen.
- insulin.
- glucagon.
- adrenalin.
1.1.6 The diagram below shows the direction of plumule (young stem) growth in various seedlings 1, 2, 3 and 4 placed in cardboard boxes. The arrows indicate the direction of light.
Which ONE of the above seedlings shows the correct response to light?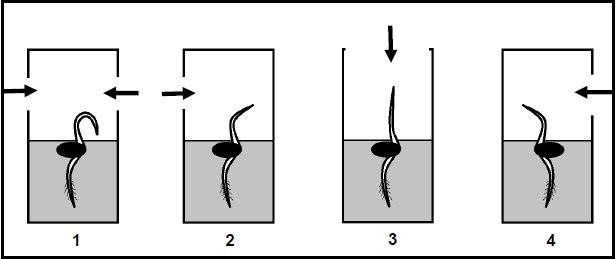
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
1.1.7 Which ONE of the following responses is expected if the growing tip of seedling 4 is cut after 4 weeks of growth?
- The plant will die
- Lateral branches will be formed
- The plant will stop growing
- The stem of the plant will grow towards gravity
1.1.8 The graph below shows the results of an investigation on the effect of blood alcohol concentration on reaction time (the time taken to react to an external stimulus).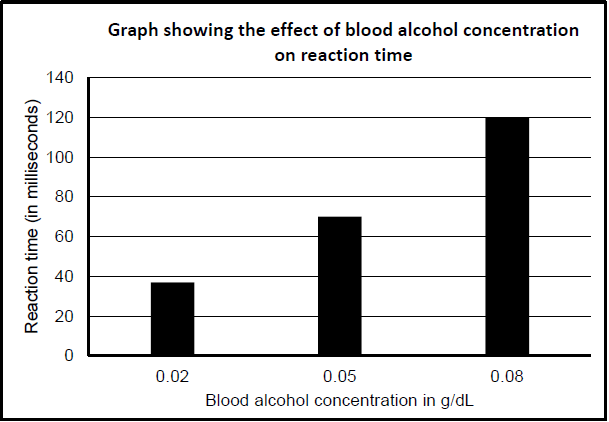
What conclusion can be drawn from the result of the investigation shown above?
The high level of blood alcohol concentration …
- has no effect on reaction time.
- decreases the reaction time.
- increases one’s ability to react faster.
- increases the reaction time. (8 x 2) (16)
1.2 Give the correct biological term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.2.1–1.2.7) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 The increase of the internal diameter of blood vessels so that more blood flows through them
1.2.2 The heat-regulating centre in the brain
1.2.3 A phenomenon where an increase in one hormone inhibits the secretion of another hormone
1.2.4 The component of the autonomic nervous system that decreases the heartbeat back to normal
1.2.5 The hormone that regulates the salt concentration in the human body
1.2.6 The site of transmission of electric nerve impulses between two nerve cells (neurons) or between a neuron and a gland or muscle cell
1.2.7 A temporary organ that connects the developing fetus through the umbilical cord to the uterine wall (7 x 1) (7)
1.3 Indicate whether each of the descriptions in COLUMN I apply to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A AND B or NONE of the items in COLUMN II. Write A only, B only, both A and B or none next to the question numbers (1.3.1–1.3.3) in the ANSWER BOOK.
COLUMN I | COLUMN II | |
1.3.1 Endocrine glands in a human | A: | Cowper’s gland |
body | B: | Gastric glands |
1.3.2 The blood vessel that transports | A: | Umbilical vein |
oxygen and nutrients from the | B: | Umbilical cord |
mother’s body to the foetus | ||
1.3.3 Brings about elongation of | A: | Gibberellins |
internodes of stems | B: | Abscisic acid |
(3 x 2) (6)
1.4 The diagram below shows the regions (A, B and E) of the nervous system that can be blocked by local anaesthetic (a drug or agent that produces a complete or partial loss of feeling) for various medical procedures.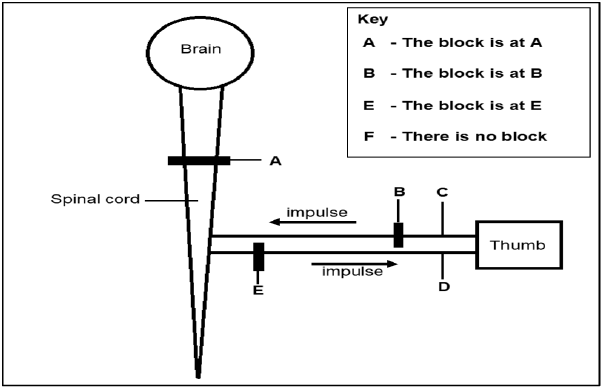
1.4.1 Write down the correct letter for each statement, using the key given in the diagram above.
- When the skin of the thumb is stimulated, the thumb and the hand move involuntarily, but the patient cannot move the hand voluntarily or feel it move. (1)
- The patient can feel the thumb being touched or pinched, but cannot move the thumb. (1)
- The patient can move the thumb, but cannot feel the movement. (1)
- When the skin of the thumb is stimulated, the thumb moves, and the patient knows it is moving. (1)
1.4.2 Which labelled part of the central nervous system will be actively involved to generate a quick response in a normal and healthy person, when the thumb accidently touches a hot surface? (1)
1.4.3 Name the type of reaction mentioned in QUESTION 1.4.2. (1)
1.4.4 Which TWO parts shown in the diagram are protected by meninges? (2)
1.4.5 Identify the letter representing the peripheral nerve that is composed of:
- Sensory neurons (1)
- Motor neurons (1)
1.5 The diagram below shows the female reproductive organs. Two tubes were cut and tied by means of a surgical procedure to prevent pregnancy.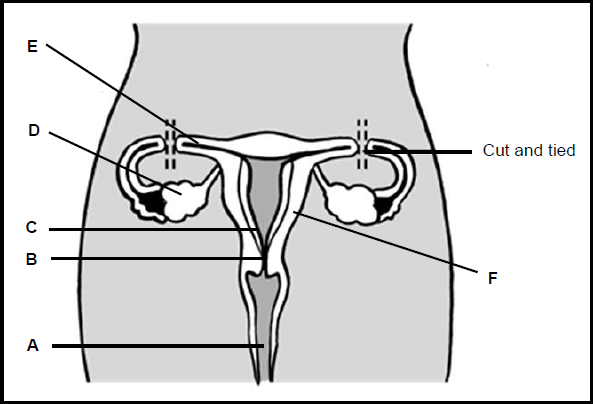
1.5.1 Identify:
- A (1)
- B (1)
- F (1)
1.5.2 Give the LETTER and NAME of the part:
- Where the embryo is implanted (2)
- That produces ova (2)
- Where fertilisation normally takes place (2)
1.5.3 How does the surgical procedure mentioned above prevent pregnancy? (1)
1.5.4 Give a reason for the surgical procedure performed on both tubes. (1)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1 The diagram below represents two stages of meiotic division.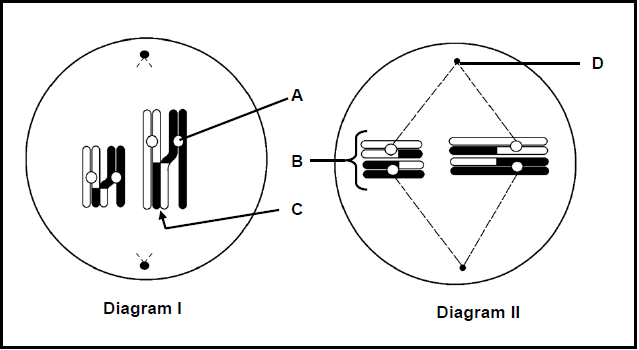
2.1.1 Identify the stage of meiosis represented by:
- Diagram I (1)
- Diagram II (1)
2.1.2 Identify:
- A (1)
- B (1)
- D (1)
2.1.3 Describe the process that takes place at C. (4)
2.1.4 Explain the significance of the event shown in Diagram II. (3)
2.2 The diagram below shows one of the developmental strategies prevalent among a certain bird species.
2.2.1 Identify the developmental strategy shown in the diagram. (1)
2.2.2 Give THREE observable reasons for the answer in QUESTION 2.2.1. (3)
2.2.3 State ONE possible disadvantage of this developmental strategy. (1)
2.2.4 Explain the physical appearance of the hatchlings by referring to their egg content. (2)
2.3 The diagram below shows a defective eye structure.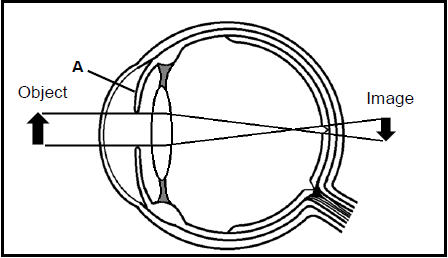
2.3.1 Identify the eye defect shown in the diagram. (1)
2.3.2 By referring to the diagram, explain how the structural defects shown in the diagram, cause the eye condition mentioned in QUESTION 2.3.1. (4)
2.3.3 State ONE way in which this condition can be corrected. (1)
2.3.4 Describe how the part labelled A is able to control the incoming light under dim conditions after sunset. (4)
2.4 The graph below shows the female hormone levels during the menstrual cycle.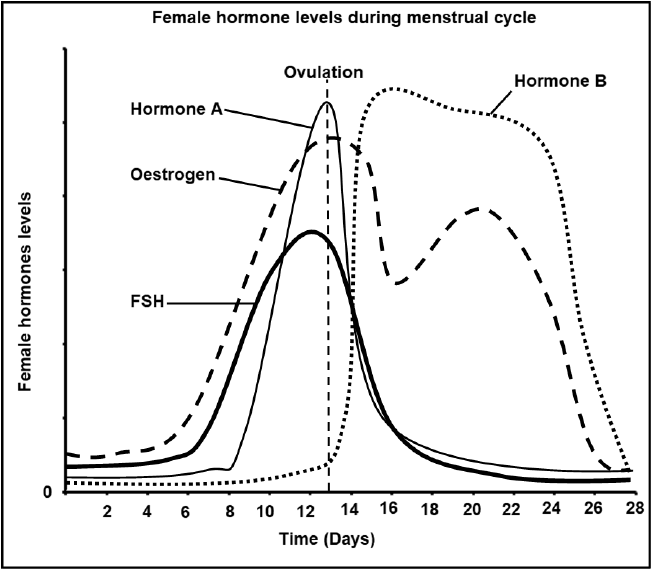
2.4.1 Identify hormone A. (1)
2.4.2 Give a reason for your answer in QUESTION 2.4.1. (1)
2.4.3 On which day of the cycle did ovulation take place? (1)
2.4.4 Describe the effect of oestrogen on the endometrium from the 7th to the 13th day of the cycle. (2)
2.4.5 The drop in the level of which hormone causes menstruation? (1)
2.4.6 Suggest a possible reason for the maintenance of a high level of hormone B beyond the 28 days of the cycle. (2)
2.4.7 Explain why the secretion of FSH is inhibited by the high levels of hormone B. (3)
[40 ]
QUESTION 3
3.1 An experiment was conducted to determine the effect of the hormone thyroxin on the body mass of Xenopus laevis frogs.
The procedure was as follows:
- Forty-four Xenopus laevis frog tadpoles were captured and divided into two equal groups.
- The average initial body mass of each of the groups was calculated before the start of the experiment.
- Twenty-two Xenopus laevis frog tadpoles were treated with a solution of thyroxin for 21 days.
- Twenty-two Xenopus laevis frog tadpoles were treated with 1% NaOH for 21 days.
- The treatment was stopped after 21 days and then the final average body mass for each group was calculated.
The results of the experiment are given below.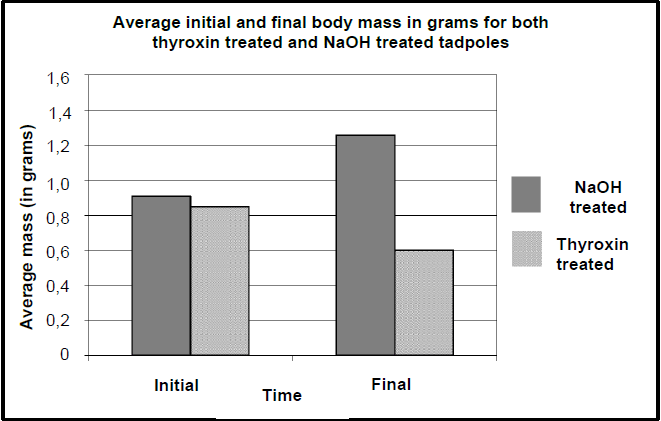
3.1.1 Name the gland that secretes thyroxin. (1)
3.1.2 Identify the independent variable in this experiment. (1)
3.1.3 State any TWO variables that should have been kept constant during the experiment. (2)
3.1.4 Which information displayed in the graph is used as baseline data to make a conclusion at the end of the experiment? (1)
3.1.5 Explain why there is a drop in the final body mass of the thyroxin treated tadpoles as compared to NaOH treated tadpoles. (4)
3.1.6 Describe how a constant level of thyroxin is maintained in the human blood when its level drops below the normal. (5)
3.2 The diagram below shows the structure of a human brain.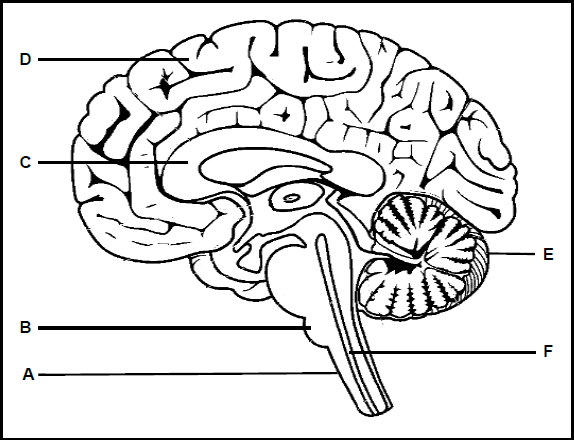
3.2.1 Identify the parts labelled:
- B (1)
- C (1)
- E (1)
3.2.2 Give ONE function of the:
- Part labelled A (1)
- Fluid found in the part labelled F (1)
3.2.3 A haemorrhage (excessive bleeding due to rupture of blood vessels) at the part labelled D may cause permanent dysfunction.
- Explain the cause of damage to the part labelled D. (3)
- State THREE possible consequences of the damage mentioned in QUESTION 3.2.3 (a) to a patient. (3)
3.3 An experiment was conducted to investigate the direction of plumule growth when the germinating seed was placed vertically on a stationary clinostat as shown in the diagram below. The growing tips of the germinating seed were exposed to light from all directions. The wet tissue paper was periodically sprayed with water to keep the seed moist. The seed was kept in this position for four days. The tip of the plumule began to bend and grew in an upward direction after four days.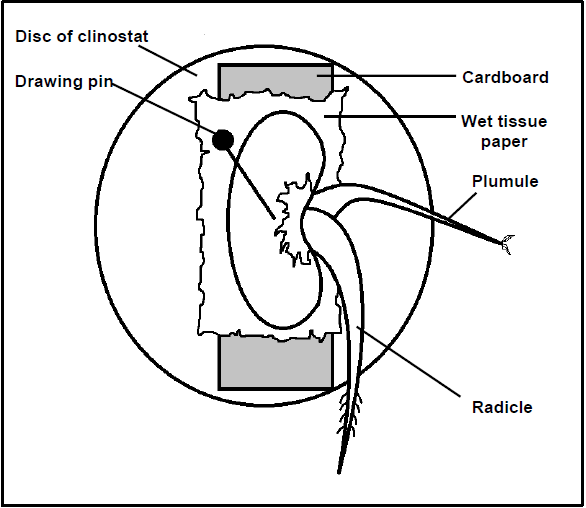
3.3.1 Name the hormone that controls the direction of plumule growth in a germinating seed. (1)
3.3.2 State where the hormone mentioned in QUESTION 3.3.1 can be located. (1)
3.3.3 Give a reason for exposing the germinating seed to light from all directions. (1)
3.3.4 Explain the direction of plumule growth as observed after four days. (4)
3.3.5 How does the control differ from the experiment? (1)
3.4 An extract detailing the scrotum is given below.
The scrotum is the loose pouch-like sac of skin that hangs behind the penis. It contains the testicles (also called testes), as well as many nerves and blood vessels. The scrotum has a protective function and acts as a climate control system for the testes. For normal sperm development, the testes must be at a temperature slightly cooler than the body temperature. Special muscles in the wall of the scrotum allow it to contract (tighten) and relax, moving the testicles closer to the body for warmth and protection or farther away from the body to cool the temperature. [Source: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/9117-male-reproductive-system] |
3.4.1 From the extract, state TWO functions of the scrotum. (2)
3.4.2 Name the structure in which the sperms develop and mature. (1)
3.4.3 Explain the consequences on human reproduction if a male wears tight- fitting underwear all the time. (3)
3.4.4 What advice would you give to long-distance male drivers to minimise the possible adverse effect on their ability to reproduce? (1)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
Mr Nkosi was trapped in a smoky room of a hotel which was on fire. His breathing rate increased as he was covered with thick smoke from the bottom floors. He was able to break the window and jumped out of his room. He landed on a street waste bin and managed to restore his balance.
Describe the process that led to an increased breathing rate while he was surrounded by thick smoke. Also describe how he was able to restore his balance when he landed on the street waste bin.
Content: (17)
Synthesis: (3)
[20]
NOTE: NO marks will be awarded for answers in the form of flow charts or diagrams.
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Information Technology Paper 2 Grade 12 Memorundum - NSC Past Papers And Memos September 2020 Preparatory Examinations
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A: SHORT QUESTION
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 Constructor (1)
1.1.2 Composite keys (1)
1.1.3 Bus (1)
1.1.4 Digital Divide (1)
1.1.5 Utility Software (1)
1.1.6 Bandwidth (1)
1.1.7 Identity theft (1)
1.1.8 Core (1)
1.1.9 Outsourcing (1)
1.1.10 RIA (Rich Internet Application) (1)
1.2
1.2.1 A – 2579 (1)
1.2.2 C – 15 (1)
1.2.3 C – Interpreter (1)
1.2.4 B – Click farms (1)
1.2.5 B – Delimiter (1)
TOTAL SECTION A: 15
SECTION B: SYSTEM TECHNOLOGIES
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1 Any ONE:
- Refers to operating systems on mobile devices that are designed to keep the device on and working at all times – even when the display is dark.
States that mobile technology is never off, it is always working in the background. (1) - Smartphone
Tablets (2) - Any ONE:
- It makes mobile devices fast and responsive.
- It makes them seem smart and intuitive. (1)
2.1.2
- Wearable refers to devices that you wear on your body instead of carrying them around in a pocket or bag. (1)
- Any TWO:
- Goggle Glass
- Apple Watch / Smart watch
- Pebble/Gear smartwatches (2)
2.2
2.2.1 We want them to perform at their best and deliver results we can rely on. (1)
2.2.2
- Security
- Saving time
- Reliability (3)
2.2.3
- Keep your software installation CD/DVD/download in a place where you can easily find and access them (NOT in a folder on your hard drive, but on some removable storage).
- Make sure you have records of all your license keys and serial numbers / Keep printouts of this information (License keys and serial numbers).
- Make sure you follow a good backup policy and know how to restore your data (3)
2.2.4 A firewall is the hardware or software that monitors which applications are using the communication link and which communication ports are being used.
Any ONE function:
- Checks and changes settings for individual applications and control access to specific ports.
- Restricts computer’s communication to the most common settings. (2)
2.3
2.3.1 Any ONE:
- The disk is fragmented when files are broken up into several pieces and stored all over the disk/storage device.
- The disk is fragmented when the files are scattered all over the disk/storage device. (1)
2.3.2 It takes the computer longer to read files from/write files to a fragmented disk. (1)
2.3.3 Disk defragmentation is the task of running a special software that re- arranges the files on the disk so that the files are stored in sequence. (1)
2.4
2.4.1 Any TWO tips:
- Install only ONE anti-virus product.
- Set the software to download new virus definitions automatically.
- Set the software to scan removable drives automatically when they are plugged in.
- Set your software to scan your entire computer automatically at least once a week. (2)
2.4.2 Any TWO tips:
- Use different passwords for different accounts
- Make your passwords long
- Avoid passwords that can be found in a dictionary
- Avoid personal information about yourself or your family (2)
TOTAL SECTION B: 23
SECTION C: COMMUNICATION AND NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1 Any THREE permissions
- Read – allows a user to only read or copy a file or folder.
- Write – allows a user to write to and modify the contents of a file or folder.
- Execute – allows a user to view and access a folder and file’s content as well as to execute/run the program file.
- List Folder Contents – allows the listing of files and subfolders in a folder.
- Modify – allows the reading, writing and deletion of files and folders.
- Full Control – allows reading, writing, changing and deleting of files and folders. Also allows you to add, change and remove access permissions for users. (3)
3.1.2 Administrators
Any ONE explanation
- They have full control over the system.
- They can install software and hardware drives.
- They create and modify new user accounts and groups and reset passwords.
- They have full access to all the files and folders.
Standard users
Any ONE explanation
- They are permitted to log on to the computer, run programs, customise their accounts.
- Work with files in their user folders or in those common folders to which they have been granted access.
- They can change their own passwords but not those of others.
- They are restricted from making system changes. (4)
3.2
3.2.1
- BitComet
- uTorrent (2)
3.2.2
- Seeders refer to people who are sharing the file in BitTorrent processing.
- The more seeders a torrent has, the faster you are likely to able to download the file. (2)
3.3
3.3.1 Remote controlling a computer – allows you to control a computer (from anywhere in the world) as if you are sitting in front of it. Virtual Private Network (VPN) – allows you to log on to a network from a remote location via the Internet. (4)
3.3.2 Third party remote access/control software:
Any TWO
- TeamViewer
- LogMeIn
- GoToMyPC (2)
3.4
3.4.1 Digital signature is an electronic signature that is used to identify the sender of a message or signatory/signer of a document.
Any ONE function:
- It provides proof to the recipient that the file or email comes from the person who claims to have sent it.
- It verifies the data has not been altered/changed in any way since the moment it was signed. (2)
3.4.2
- Thawte
- Verisign
Accept any other verifiable CA. (2)
3.5
3.5.1 Appification is the trend for information to be accessed via dedicated apps on mobile devices. (1)
3.5.2 Any THREE reasons
- An app’s interface is easier to navigate.
- An app has a dedicated purpose and does not result in distraction and loss of focus.
- With an app you do not have to remember the URLs or manage menus of bookmarks to get where you want to go.
OR
- The app knows where to find its data and does not need to be directed by you.
- All the interface data (pictures, layout etc.) is already installed on your device as part of the app and does not need to be downloaded.
- Apps can be set to fetch data on their own in the background, even when you are not using them and also notify you automatically of significant changes or events.
- Apps can work with a syncing service.
- Apps can use additional sensors in your mobile device (e.g. GPS, compass, accelerometers etc). (3)
3.6 The Internet of Things/IoT (1)
3.7
- Local storage – data is stored on the user’s computer/local hard drive.
- Online storage – data is stored on the web server. (4 ÷ 2) (2)
TOTAL SECTION C: 28
SECTION D: DATA AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
QUESTION 4
4.1 DBMS is the software that allows you to work with electronic databases. (1)
4.2 Transaction refers to any activity regarding the creation, loading, editing, saving or deleting of data managed by a DBMS. (1)
4.3
- Commit/Post – occurs when the DBMS gets the instruction to save whatever changes have been made back to storage.
- Purge/Consolidate – removes deleted records from the database to compact and streamline the file. (2)
4.4
- The unnecessary repetition of data across multiple fields in a database, which can lead to update anomalies.
- The intentional duplication or distribution of the database across multiple storage media to ensure that the data will always be available and accessible even if one storage medium fails OR Mirroring the database. (2)
4.5
4.5.1 Parallel data set is a technique whereby multiple copies of data are kept.
- It is used immediately, resulting in no downtime when there is data failure. (2)
4.5.2 Doubling the storage requirements for the system. (1)
4.5.3 For safety and security. (1)
4.6
- Overflow is an error condition that occurs when there are not enough bits available to represent an integer value accurately.
- Truncation is the misrepresentation of a string variable because there are not enough bytes available to store all the characters in the string. (2)
4.7
4.7.1 Any ONE:
- To ensure that there is no redundant data.
- To ensure that data is not being repeated in one way or another.
- To ensure that there is no duplication of data.
- To ensure that a database is in an optimal state, with no chance of anomalies. (1)
4.7.2
 (7)
(7)
4.7.3
 (4)
(4)
TOTAL SECTION D: 24
SECTION E: SOLUTION DEVELOPMENT
QUESTION 5
5.1
5.1.1 Try / Except (1)
5.1.2 Any ONE:
- Bug
- Exception (1)
5.1.3 Step-and-watch refers to a debugging facility in Delphi used to control execution of the program and view the values of variables while the programming code is executed. (2)
5.1.4 Trace table (1)
5.2
5.2.1 Data structure refers to the way data is organised.
- Arrays and Text files (3)
5.2.2 Arrays (1)
5.2.3
- 18 (1)
- 9 (1)
- I just L (1)
- VE Delphi (1)
- VEXTRA Delphi (1)
5.3
5.3.1 Constructor is a method used create an object in memory and to initialise the properties/private fields of an object. (2)
5.3.2 Free OR Destroy (2)
5.4
Line No | Value1 | Value2 | Value3 | Value4 | Value5 | Screen Output |
1 | 9 | |||||
2 | Solution | |||||
3 | 12 | |||||
4 | 6 | |||||
5 | 6 | |||||
6 | 48 | |||||
7 | 54 | |||||
8 | 0 | |||||
9 | 3 | |||||
10 | 3 | |||||
11 | 54 |
(12 ÷ 2) (6)
TOTAL SECTION D: 24
SECTION F: INTEGRATED SCENARIO
QUESTION 6
6.1
6.1.1
- Any ONE
- E-waste refers to broken, outdated and discarded hardware that we neither want nor need.
OR - E-waste is anything electronic or related to electronics that is thrown away. (1)
- E-waste refers to broken, outdated and discarded hardware that we neither want nor need.
- Any THREE
- Old computers
- Old CRT monitors
- Broken hard drives
- Dead or unwanted cellphones
- TVs
- Gaming devices
- Batteries (3)
- Any TWO
- Cancer
- Pollution
- Causes radiation
- Poison water
- Damage living things that come into contact with them
- Contamination (2)
- Poisonous parts are removed properly before the materials get put into the dump site. (1)
6.1.2 Green computing refers to initiatives to design, use and dispose of technology in an environmentally or eco-friendly way. (1)
6.2
6.2.1
- Spammer refers to someone who sends out unsolicited / unasked- for/unwanted e-mails in the form of advertisements. (1)
- Any ONE
- Spam clogs the Internet with a lot of unnecessary traffic (impacts on speed).
- It also wastes time because you have to sift through so much junk in inbox. (1)
- Any ONE
- Use a spam filter in your e-mail client program.
- Avoid entering your e-mail address into website forms. (1)
6.2.2
- There is low risk of physical danger (They are not physically present when they commit the crime).
- It is difficult to detect the crime.
- It is difficult to trace who committed the crime. (3)
6.2.3 Malware / Virus (1)
6.2.4 Zombie PC (1)
6.3
6.3.1
- Decision Support Systems (DSS)
- Expert systems / Knowledge-based systems (2)
6.3.2 Any THREE
- Genetic research
- Weather modelling and climate prediction
- Physics research (e.g. nuclear research)
- Circuit design
- Financial modelling
- Web searching / indexing (3)
6.3.3 Any ONE
6.4
6.4.1 Any TWO
- Turn off notifications on your mobile device when you are busy.
- Only enable them for a limited group of people.
- Set aside specific time for engaging with social media.
- When doing important work, switch off your phone or put it on silent and disable vibrate option.
- Try to remove yourself from FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) phobia. (2)
6.4.2 Any TWO
- The Internet never forgets.
- The Internet is a public space.
- You cannot be sure how your information/uploads are going to be shared.
- The personal information you share today/now might come back to haunt you in future.
- There is nothing stopping anyone who can access what you have shared from copying it, saving it or sharing it in other places. (2)
6.5 Transaction Processing System (1)
6.6 Software as a Service refers to the concept of renting software instead of buying a license to use it forever. (1)
6.7 Any TWO places
- DRM (Digital Rights Management)
- ATM
- Internet browsers
- Skype calls
- Online storage services (2)
6.8 Backdoor is a hidden way to gain access to a computer, system or software. (1)
6.9
- Skimmer reads the electronic details from a card.
- Video camera records your PIN/password. (2)
6.10 Any TWO effects
- Decreased discretionary spending (we spend a lot of money on things to make us safer).
- Decreased productivity (time that could be spent on productivity is wasted on preventing crime).
- Increased social stratification (it separates different social classes from each other).
- Development of a culture of fear and suspicion. (2)
TOTAL SECTION F: 36
GRANDTOTAL: 150
 (4)
(4)