Adele
Economics Paper 1 Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Answer FOUR questions as follows in the ANSWER BOOK:
SECTION A: COMPULSORY
SECTION B: Answer any TWO of the three questions
SECTION C: Answer ONE of the two questions - Answer only the required number of questions. Answers in excess of the required number will NOT be marked.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write the question number above each answer.
- Read the questions carefully.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Leave 2–3 lines between subsections of questions.
- Answer the questions in full sentences and ensure that the format, content and context of your responses comply with the cognitive requirements of the questions.
- Use only black or blue ink.
- You may use a non-programmable pocket calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY) 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1–1.1.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.9 D.
1.1.1 The severity of a phase of the business cycle is measured by the …
- trough.
- amplitude.
- extrapolation.
- trend.
1.1.2 Labour can be bought and sold in the … market.
- factor
- goods
- financial
- consumer
1.1.3 When import taxes are imposed as a percentage of the value of the imported goods, it is known as … tariffs.
- composite
- specific
- ad valorem
- average
1.1.4 If the exchange rate changed from $1 = R6 to $1 = R8, due to market forces, then …
- the $ depreciated against the R.
- the R depreciated against the $.
- the R devalued against the $.
- the $ devalued against the R.
1.1.5 Social grants to the citizens of South Africa forms part of the … policy.
- monetary
- trade
- growth
- fiscal
1.1.6 The process of transforming a mineral to a higher value product, which can be consumed locally or exported, is known as…
- gateways.
- driveways.
- export processing zones.
- beneficiation
1.1.7 The inflation target set by the South African government, is …
- 1 – 6%.
- 6 – 12%.
- 3 – 6%.
- 0 – 3%.
1.1.8 An international organisation that requires its members to standardise their indicators, is called the …
- World Bank.
- Government Financial Statistics.
- World Economic Forum.
- Human Development Index. (8 x 2) (16)
1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
1.2.1 | Trade balance | A | embedded in demand and supply side policies |
1.2.2 | Free trade | B | increase potential for large scale production |
1.2.3 | Real flow | C | producers and consumers can buy goods and services from anywhere in the world without the interference of government |
1.2.4 | New economic paradigm | D | shows relationship between tax rates and tax revenue |
1.2.5 | Laffer curve | E | the return of land to those who lost it because of discriminatory laws |
1.2.6 | National Industrial Policy Framework (NIPF) | F | the difference between what a country exports, including gold, and what it imports |
1.2.7 | Land restitution | G | measured by dividing the real GDP by the number of workers employed |
1.2.8 | Labour productivity | H | the movement of goods, services and factors of production among the participants in the economy |
I | reflects all transactions between one country and another | ||
(8 x 1) (8)
1.3 Give ONE term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK. Abbreviations, acronyms and examples will NOT be accepted.
1.3.1 Continuous flow of spending, production and income between different sectors
1.3.2 A negative economic growth for at least two successive quarters
1.3.3 Transfer of functions and ownership of entities from the private sector to the public sector
1.3.4 The worldwide interaction of economies with trade as an important element
1.3.5 Initiated to attract infrastructure and business investments to neglected and underdeveloped areas
1.3.6 All persons of either gender between the ages of 15 and 65 who supply labour for productive activities (6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: MACROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
2.1 Answer the following questions.
2.1.1 Name any TWO problems of public sector provisioning (2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 Why is borrowing not a long-term solution for a fundamental BOP disequilibrium? (1 x 2) (2)
2.2 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.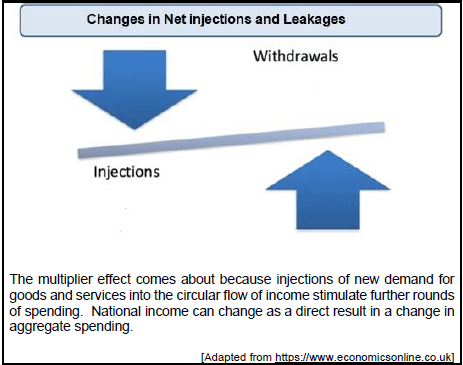
2.2.1 Name ONE example of an injection. (1)
2.2.2 Give the formula to calculate aggregate expenditure in an open economy. (1)
2.2.3 Briefly describe the term injection. (2)
2.2.4 What is the effect on national income if injections are less than withdrawals? (2)
2.2.5 Suppose the expenditure function ( E ) = 10 + 0.5Y. Draw a clearly labelled 45° diagram to show the expenditure function. (4)
2.3 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.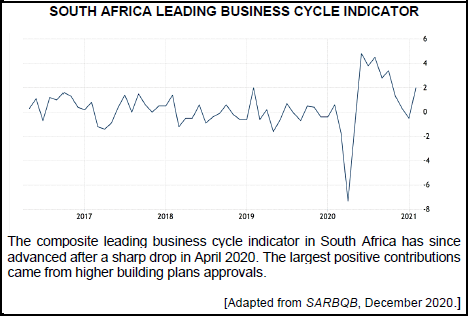
2.3.1 Give an example of a leading indicator. (1)
2.3.2 Indicate the phase of a business cycle that has the highest unemployment rate. (1)
2.3.3 Briefly describe the term business cycle. (2)
2.3.4 Explain the Keynesian approach of business cycles. (2)
2.3.5 How can the South African Reserve Bank prevent the economy from reaching a trough? (4)
2.4 Draw a fully labelled graph to show the relationship between inflation and unemployment. (8)
2.5 Assess the limitations of comparative advantage theory for countries involved in international trade. (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: ECONOMIC PURSUITS 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
3.1 Answer the following questions.
3.1.1 Name any TWO indicators relating to money supply. (2 x 1) (2)
3.1.2 How does education help in social development? (1 x 2) (2)
3.2 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.
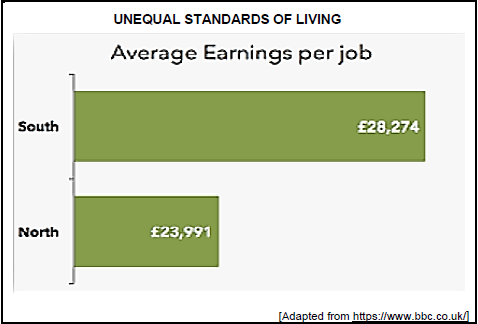
3.2.1 Give a formula to calculate per capita income. (1)
3.2.2 Identify the side where longer life expectancy is experienced. (1)
3.2.3 Briefly describe the term North-South divide. (2)
3.2.4 Compare the poverty levels of the North and South countries. (2)
3.2.5 How do countries in the ‘south’ negatively affect the environment? (4)
3.3 Study the table below and answer the questions that follow.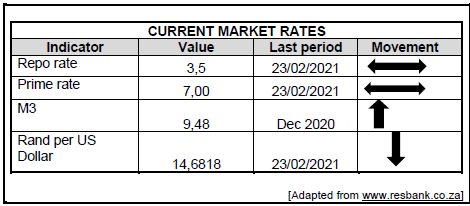
3.3.1 Identify an indicator related to interest rates. (1)
3.3.2 Name the type of exchange rate system used in South Africa. (1)
3.3.3 Briefly describe the term prime rate. (2)
3.3.4 Why is it important for the government to assess the performance of the economy? (2)
3.3.5 How can an increase in repo rate affect consumption expenditure? (4)
3.4 Discuss tariffs and quotas as methods of import substitution. (8)
3.5 How can the Expanded Public Work Programme be used to reduce the unemployment rate? (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: MACRO ECONOMICS AND ECONOMIC PURSUITS 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
4.1 Answer the following questions.
4.1.1 Name any TWO incentives used by the SA government to improve industrial development. (2 x 1) (2)
4.1.2 How can a country improve the terms of trade? (1 x 2) (2)
4.2 Study the table below and answer the questions that follow:
NATIONAL ACCOUNT AGGREGATES | |
SOUTH AFRICA’S GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCT 2019 | R millions |
Compensation of employees | 2 418 544 |
Net operating surplus | 1 296 696 |
Consumption of fixed capital | 713 078 |
Gross value added at factor cost | 4 428 317 |
Other taxes on production | 105 061 |
Other subsidies on production | 9 798 |
Gross value added at basic prices | A |
Taxes on products | 554 866 |
Subsidies on products | 10 821 |
Gross domestic product at market prices | 5 077 625 |
[Adapted from SARB Quarterly Bulletin, December 2020]
4.2.1 Give ONE example of taxes on products. (1)
4.2.2 Identify the method used to calculate Gross Domestic Product. (1)
4.2.3 Briefly describe the term consumption of fixed capital. (2)
4.2.4 Determine the value of A above. (2)
4.2.5 Why does the government provide subsidies on products? (4)
4.3 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.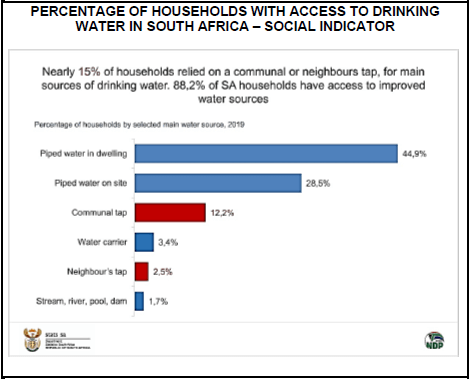
[Adapted from This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.]
4.3.1 Give any other example of a basic service. (1)
4.3.2 Indicate the percentage of South African households who do not have access to improved water sources. (1)
4.3.3 Briefly describe the term social indicator. (2)
4.3.4 What measures can be used to ensure sufficient water supplies in South Africa? (2)
4.3.5 How successful has the South African government been in rendering services as a social indicator? (4)
4.4 Briefly discuss prevention of dumping and protection of natural resources as arguments in favour of protectionism. (8)
4.5 How can the Reserve Bank effectively reduce the deficit on the balance of payments? (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer any ONE question of the TWO questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
Your answer will be assessed as follows:
STRUCTURE OF ESSAY | MARK ALLOCATION |
Introduction
| Max. 2 |
Body | Max. 26 Max. 10 |
Conclusion
| Max. 2 |
TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 5: MACROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
- Discuss in detail the reason(s) for public sector failure. (26 marks)
- How can inefficiencies contributing to public sector failure be solved? (10 marks)
[40]
QUESTION 6: ECONOMIC PURSUITS 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
- Discuss in detail the South Africa’s initiatives in regional development. (26 marks)
- Evaluate the success of South Africa's regional development policies in terms of international benchmarking. (10 marks)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Consumer Studies Memorandum - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: SHORT QUESTIONS
1.1 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1.1.1 D (1)
1.1.2 A (1)
1.1.3 C (1)
1.1.4 B (1)
1.1.5 B (1)
1.1.6 D (1)
1.1.7 C (1)
1.1.8 A (1)
1.1.9 C (1)
1.1.10 D (1)
1.1.11 B (1)
1.1.12 C (1)
1.1.13 C (1)
1.1.14 A (1)
1.1.15 D (1)
1.1.16 B (1)
1.1.17 B (1)
1.1.18 A (1)
1.1.19 D (1)
1.1.20 C (1)
1.2
1.2.1 E
1.2.2 D
1.2.3 A
1.2.4 H (4)
1.3
1.3.1 Exemption/exclusion clause
1.3.2 Warranty
1.3.3 Grey/parallel goods
1.3.4 Inflation
1.3.5 Unfair business practices (5)
1.4
- B
- C
- F
- G (Any order) (4)
1.5
1.5.1 Unpasteurised milk undercooked meat (2)
1.5.2 liver (1)
1.5.3 1–7 days (1)
1.5.4
- Calcium propionate
- Bleach (2)
1.5.5 Maximum 3 g or less (1)
[40]
QUESTION 2: THE CONSUMER
2.1 Type of interest calculated on principal amount.
- Compound (interest) (1)
2.2 TWO regenerative/renewable sources other than coal.
- Sun/solar power
- wind
- water / hydropower
- bio-energy (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.3 TWO disadvantages of fossil fuels.
- There are limited reserves
- Releases harmful gases/carbon dioxide/toxic chemicals into the atmosphere when burned
- Causes pollution and can cause respiratory diseases
- Coal gives off sulphur dioxide which creates acid rain (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.4 The agency that collects taxes.
- South African Revenue Service / SARS (1)
2.5 Comparison of PAYE and provisional tax.
ASPECT | PAYE | PROVISIONAL TAX | |
2.5.1 | When is it paid? | Monthly / at the same time as income is earned /1/12?ℎ of estimated annual tax (1) | 2 payments/twice per year (1) |
2.5.2 | Describe the category of taxpayer and give ONE example. | Those who earn a fixed/ regular income | Those who earn an irregular income Farmers, business owners, sole traders |
NOTE: Deduct ONE mark if not in table format. (6)
2.6
2.6.1 Identify the type of scam.
- Phishing (internet scam) (1)
2.6.2 Write a paragraph where you discuss the scam that is being used to put customers at risk and how consumers can protect themselves from this type of crime.
The scam
- The criminal sends an email that looks legitimate / a fake e-mail / pretending to be from the bank to get your /trick you / steal your personal information and financial information/credit card number password/username. The link will take you to a fake website so they can empty your credit account/steal your money. The information can be used for identity theft.
Protect yourself:
- Be aware that banks will not ask customers for financial information via e-mail delete suspect mail / update anti-virus software never give personal details via e-mail never open attachments from suspect mail/ spam check bank accounts regularly cancel card immediately.
NOTE: To get 5 marks both parts of the question must be answered – explaining the scam and how you can protect yourself.
Deduct ONE mark if not written in paragraph format. (5)
2.7
2.7.1 Identify a word that indicates that this is a written contract.
- Signed (1)
2.7.2 Calculate the total that she will pay at the end of the contract period.
- R250 x 12 = R3 000 + R125 = R3 125
NOTE: Mark only the final answer. Candidate does not have to show calculations. (1)
2.7.3 State THREE responsibilities that she has concerning the contract.
- Read the contract carefully
- Make sure she understands the terms and conditions before signing
- Ask questions if you need clarity on any clause
- Fulfil the contract obligations / she is obliged to pay the money on the agreed date every month
- Keep a copy of the contract (Any 3 x 1) (3)
2.7.4 Explain TWO ways how the CPA makes provision to protect Amanda should she want to cancel her gym membership.
- She must give 20 business days’ / working days’ notice
- She must give the notice in writing.
- The gym may not charge her excessively high penalty fees for the cancellation
- The cancellation fee is no more than 10% of the outstanding amount (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.8
2.8.1 Discuss FOUR actions from the way this group operates that is similar to a stokvel. (Do not rewrite the sentences)
- It is a co-operative approach which is to work together as a team / club/community
- They work towards the same goal which is to keep their farms going / to have the funds
- It has an economic function/to enable the development of their businesses
- 23 members – who belongs to a group
- Save capital for 12 months and it has clear rules on how it operates / members are protected
- Saving money/capital is pooled together to invest in a common fund
- All members benefit as they all get an advantage of buying stock for cheaper/get their share out of the scheme
- Decide together what to buy/trust each other
- Put their trust in a committee to make decisions/manage the scheme
- Social meetings whereby ideas/knowledge are exchanged
NOTE: No marks for quoting sentences. (Any 4 x 1) (4)
2.8.2 Describe how an illegal pyramid scheme would operate if this were the chosen scheme in the scenario.
- In a pyramid scheme the money would be allocated unequally / according to levels / Thabo would be at the top
The member / Thabo who starts the scheme would have the most money
Members/farmers who join later would get less commission/benefit less /not gaining any real investment
Each member/farmer would not be accumulating funds for the benefit of others but for themselves
Members could pay a fee to join (Any 3 x 1) (3)
2.9 Analyse the impact of the coronavirus on consumer’s tax contributions to the state for the two areas mentioned in the statement. (higher unemployment and lower consumption)
- The impact was severe as government lost a lot of revenue
- Personal income tax and VAT are government’s greatest revenue these two forms of revenue were impacted greatly
- A higher unemployment means less people were paying income tax
- Lower consumption meant less VAT was paid to government as less goods were bought
- Losing revenue means the government cannot meet their budget expenses
- This leads to the country borrowing money which leads to debt
- This impact leads to an increase in taxes to help with the debt
- The Coronavirus pandemic necessitated a lockdown which brought about restrictions in the different alert levels
- Level 5 would have had the severest restrictions which shut down the economy followed with a ripple effect causing the impact to worsen
- During lockdown only essential services could trade/continue
- Less VAT went to the state as spending was curbed due to shops not been allowed to trade
- People lost their jobs as some businesses had to shut down, so unemployed people were not paying income tax.
- With no salaries, people spent less money, so this VAT contribution was not paid by shops
- As alert levels changed to a lower level, restrictions were relaxed, and more shops were able to trade, depending on the level and with limited hours
- Limited hours meant less sales therefore less VAT paid to the state (Any 8 x 1) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: FOOD AND NUTRITION
3.1 Name of the ranking system that classifies foods containing carbohydrate according to how they affect blood glucose levels.
- Glycaemic Index (1)
3.2 The role of insulin.
- Maintains normal blood glucose levels
- Stimulates the enzymes in muscle and fat tissue to remove sugar from the blood
- Transports glucose from the bloodstream into the cells
- Break down/changes glucose/sugar into energy (Any 1 x 1) (1)
3.3 Give TWO different ways the pancreas which produces insulin, malfunctions in a Type 2 diabetic person.
- The pancreas does not produce enough insulin
- The insulin does not work properly/ body does not use it effectively/unable to use it (2)
3.4
3.4.1 Explain in detail the body’s response to the quick release of so much glucose into her blood.
- She will have an energy boost / rapid rise in glucose level
- The body/pancreas will respond/secrete insulin as she will now have hyperglycaemia/high blood sugar
- Insulin is secreted by the pancreas to remove the excess glucose from the bloodstream.
- Insulin allows glucose to be transported to the cells for energy
- Excess glucose is converted to glycogen for storage (used at a later stage)
- Eating high-GI foods on their own/eating wrong foods causes the body to overreact to the high sugar content and releases too much insulin. The blood sugar levels will drop too low/rapid fall in blood glucose / She will have hypoglycaemia / caused by sudden removal of glucose from the blood
- This leads to symptoms such as feeling hungry, headache, shaky, sweaty, cold, tired, weak, dizzy
NOTE: Maximum ONE symptom for the symptom mark as this is not the emphasis of the question. (Any 5 x 1) (5)
3.5 Compare the management of the diet for diabetes and osteoporosis.
RECOMMENDATION | DIABETES | OSTEOPOROSIS | |
3.5.1 | A reason why protein should be reduced | To avoid stress on kidneys/excess protein over time will weaken bones (1) | The body draws calcium from the bones to neutralise the acids released ü when protein digested (1) |
3.5.2 | The type of beverage that should be limited. | Sugar rich drinks (fruit juice, fizzy drinks)/ Alcohol/Full fat milk (1) | Tea/Coffee/alcohol (1) |
3.5.3 | A reason to include canned fish (sardines) | Fish is lower in fat/ Unsaturated fat/to reduce risk of heart disease (1) | Is a source of calcium/ Calcium in edible bones / good source of vitamin D / (1) |
(6)
3.6 The relationship between aging and bone mass with the risk of osteoporosis in females. (Interpret the graph)
- Bone mass increases up to about 25 years As you age, bone mass decreases
- An increase in a younger person is due to the body building new bone faster than old bone is removed/bones repair quickly
- Bone density increases until ± 30 years
- Peak bone mass is reached at 25 to 30 years
- After 40 years – bone mass gradually reduces/bone density is lost
- New bone is not built as fast as it is removed/calcium is withdrawn from bones faster than it is replaced
- This can lead to osteoporosis/increases the risk of osteoporosis due to the bones been lost and not fully replaced which results in porous bones
- Bone mass decreases more after 50 years as bone loss is more rapid due to menopause oestrogen levels decrease
- Oestrogen would normally protect the bones against bone loss (Any 6 x 1) (6)
3.7 Give THREE characteristics of organically produced food excluding that they are non-GMO.
- Free of (synthetic) fertilisers pesticides /insecticides/herbicides/ chemicals
- Does not use hormones
- No growth regulators/stimulates
- No livestock feed additives
- Has more flavour than other fruits and vegetables (Any 3 x 1) (3)
3.8 Explain how food irradiation can extend the shelf life of food.
- It reduces / destroys / eliminates micro-organisms/bacteria/salmonella bacteria/insects in food using short waves/short light/radio waves into the
food. (2)
3.9 Analyse why self-sufficiency may be a means to address the need of food insecurity.
- Self-sufficiency refers to growing your own crops/keeping livestock to produce some of their own food
- Food security is the individual’s ability to obtain sufficient food on a day- to-day basis / that is also safe and nutritious
- Yet not all S.A. households have access to adequate food.
- Organisations that provided food during the Covid-19 pandemic is a temporary solution
- Food inadequacy, hunger, poverty and high unemployment will remain a challenge.
- This programme teaches people to become self-sufficient by teaching them the skills /educating people to grow their own crops therefore able to feed themselves and their families which will ensure that food will be available on a continuous basis
- This enables people to have these skills for life and there will be a sense of hope for the future.
- The people can generate their own income by selling, produce that they have grown themselves.
- They will reap the benefits of being an entrepreneur as they have started their own business/ (sense of responsibility, pride, reduce crime).
- This in turn reducing poverty.
- Sustainability is achieved as people can to a certain extent meet their own needs.
- This addresses the issue of food insecurity where people would otherwise turn to cheap foods and consume a diet which is of a poor nutritional
value which is then linked to chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetics, hypertension, and heart diseases. (Any 6 x 1) (6)
3.10 Determine the different types of information that appears on food labels that relate to food safety and explain how each category guarantees consumer safety.
- The storage instructions so that the food stays safe to eat, for example, keep refrigerated or eat within 3 days of opening
- Date labelling/stamp so that the product can be consumed with the day and month time frame which could be harmful to heath if not known/ for example a use by date for perishable food
- A batch number / food recall information is essential for tracing the product so that it can be quickly recalled from the shelves in case of unsafe / unsuitable food.
- An allergen list as a consumer can have an adverse reaction to a substance, they are sensitive to. / A severe reaction like an anaphylactic shock would be fatal.
- Preparation/cooking/heating instructions so that the product is prepared at the correct temperature. Incorrect temperatures may not destroy micro-organisms / promote their growth
- Additives listed a consumer may be sensitive to an additive that is harmful to their health
- Ingredient list. A consumer may be sensitive /have adverse reaction to an ingredient that may not be in the allergen list. (Any 4 x 2) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: CLOTHING
4.1 State TWO examples where a consumer can ‘reuse’ their clothing instead of the recycling option.
- Sell or exchange unwanted garments at a second time around/charity/thrift shop
- Resew the garment into something new/upcycling
- Donate clothing to a clothes bank/church/charity shop/hospice/to the needy (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.2
4.2.1 State TWO facts why the t-shirt is considered a classic.
- It has been around for years/long time/timeless/lasted many seasons
- It has remained popular
- The design has simple lines/simplicity/basic style/tasteful
- Appeals to a larger group of people (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.2.2 Describe the term style. Refer to pictures in your answer.
- Style is the characteristics that make one item different from another product of the same type / Outline of the garment that distinguish one from another
- The T-shirts differ in the shape of the necklines
- Round neck, V-neck, button up (3)
4.3 List TWO consequences of brand piracy for businesses.
- The original manufacturers lose millions of rands/sales
- The image/reputation of the brand is harmed /less sales as customers lose faith in the brand/ quality of item poorer
- It prevents the registered trademark owners from entering the markets where pirate brands are popular/already existing
- It damages retailers selling legitimate products, resulting in missed opportunities to create jobs and results in actual job losses
- No competition in the market. /Competitors are put off by the price war they will have to wage against the low prices of counterfeit goods.
- Countries do not receive custom duties/import tax on products entering the country and this is detrimental/negative impact on the economy
(Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.4 Describe why illustration B is an example of brand piracy.
- The name is very similar to the original.
- There are very few changes to the cougar logo
- The original name and logo are protected by trademark law and it has been copied/used on purpose
- This misleads/confuses the customer (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.5 Discuss why the outfit below is suitable for a virtual meeting.
- The top half is formal as only this is seen in a virtual meeting therefore the jeans and shoes are suitable as the bottom half
- The shirt is not revealing. The jacket adds formality
- The neutral colours (tan and white) will not be too flashy
- The necklace is not too bulky and goes with the tan colour
- The features of her face will be seen/emphasis is on the face so clothes will not dominate (Any 3 x 1) (3)
4.6 Explain the term sustainable as it relates to clothing and analyse the statement to conclude whether recycled polyester is sustainable or not.
- Sustainable means that during the growing/production of crops and manufacturing of fabrics resulted in minimal impact on the environment/ environmentally friendly and resources are not depleted/damaged/made from renewable resources
Clothing made from recycled polyester/plastic bottles would otherwise land up as waste in our landfills. It means that less new fabrics must be manufactured, and some resources are saved (petroleum) and reduce our carbon footprint due to less energy and fewer chemicals to make recycled fibres less air pollution and greenhouse gases Therefore, it is a better option than buying clothing new.
Recycled polyester is not biodegradable plastic is derived from petroleum which is non-renewable therefore is not environmentally friendly and therefore it does not fulfil the meaning of the word sustainable.
To conclude: Recycled polyester is not sustainable.
NOTE:
- 2 marks for the term sustainable.
3 marks for discussion relating to statement.
1 mark for the conclusion. (6)
[20]
QUESTION 5: HOUSING
5.1
5.1.1 Name the two parties that sign a lease.
- Landlord / lessor / property owner
- Tenant / lessee / renter / Brett (2)
5.1.2 THREE disadvantages that Brett experienced when he previously rented.
- He could not have/keep a dog
- He did not change the bathroom as it required permission/consult first with landlord
- He did not like some of the rules (3)
5.1.3 List TWO requirements that Brett will have to carry out should he wish to run his own business from his rented accommodation.
- He must get permission from the landlord.
- He must obtain approval from the municipality. (2)
5.1.4 Describe how the property owner is protected when a lease is signed.
- The owner can keep the deposit if the tenant vacates the premises before the lease expires.
- He can use the deposit to pay for damages to the property.
- He has the deposit if the tenant does not pay rent for that month or two
- A signed lease should mean that the property should have been checked and a list of defects made so the landlord has proof that the damage was not there when the tenant moved in.
- The lease is a legal document in serious cases will be used in court in order to evict a tenant (Any 3 x 1) (3)
5.2 Differentiate between the responsibility for costs for security and maintenance between full-title ownership and sectional title ownership.
- Full title – one is responsible to pay for their own security and maintenance Sectional title – you are responsible for your own unit when it comes to security and maintenance but the security around the complex and maintenance of
the common property is shared / levies paid will cover these costs. (3)
5.3
5.3.1 List TWO responsibilities of the consumer when purchasing this microwave oven with regards to the warranty.
- To be informed by reading the warranty/note how long the warranty is
- Fill in the warranty card and sent to manufacturer
- Keep all the relevant documents/receipts to support the warranty
- Use the features of the microwave that are covered by the warranty during the period that is covered (Any 2 x 1) (2)
5.3.2 Promote this microwave as a salesperson to a customer on how the features of this microwave will save energy. Include both human and non-human energy in your sales talk.
- Non-human energy / electricity / monthly bill is saved / is less
Non-human refers to the ECO Mode setting which significantly reduces power usage, delivering savings to your household on monthly energy bills or / The eco mode setting will ensure that the oven draws less current when the oven is not used but is still plugged in for example the time/clock is still operative.
The power levels save electricity as you have a selection to match the power level to the cooking need The higher the power level the more current it draws, so when full power is not necessary you can save electricty.
Human energy / physical effort is saved as the interior surface is easy to clean/no more scrubbing Easy to clean and also saves time Human energy / time that is saved as the microwave cooks food quickly.
NOTE: A mark cannot be awarded just for the feature mentioned.
The feature must link to the human or non-human explanation. Marks cannot be awarded for only a discussion on human or non-human. Both forms of
energy must be covered for full marks (5)
[20]
QUESTION 6: ENTREPRENEURSHIP
6.1 Define the term target market.
- A certain group of people who will be most likely to buy your product/service
OR
The group of people you aim to sell your product to (2)
6.2 Give TWO advantages of routine/preventative maintenance of equipment when running a business.
- Ensures a continuous production flow/ does not slow down/ don’t stop production
- Reduces repairs therefore decreases costs of repairs
- Reduces unscheduled maintenance which will disrupt production
- Prevents unexpected interruptions/breakdowns during production
- Prevents a loss of income for the business (Any 2 x 1) (2)
6.3 List THREE reasons why a business should do stock control.
- Ensure the purchase of the correct, high quality raw materials and make them available for production.
- Avoids running low/shortage on raw materials which would slow down/stop production and harm reputation of the business when you miss orders
- Prevents waste of raw materials due to incorrect purchasing or overstocking /damage in storage / Overstocking needs more storage space
- Prevents spending too much money spent on stock that could be used more effectively elsewhere
- Helps to prevents theft which will slow down production
- It prevents waste – old, expired stock/use ingredients before they spoil. (Any 3 x 1) (3)
6.4
6.4.1 Identify the factor that was available to Thabo when he chose a product for his business from the sentences given below.
- Availability of human skills
- Availability of workspace (2)
6.4.2 State TWO advantages of Thabo using the truck as his point of sale.
- He can drive to where his target market is/be closer to the target market/ be in the right place
- He can distribute his products directly to the customers/ direct selling has more advantages
- He can be in contact with his target market/be very aware of their needs/make them feel important as he is personally selling his product
- Get feedback from the customers as they can speak to him and so improve his business/keep customer happy
- He can control his brand image himself as he is personally promoting the product (2)
6.4.3 Identify TWO start-up needs.
- Capital (from his uncle)
- Truck
- Ingredients
- Cooldrinks
- Sanitiser (in the truck)
NOTE: Not equipment, as he had all the equipment at home. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
6.4.4 Discuss how the products will appeal to the target market.
- The products/roosterkoek and vetkoek is homemade not mass produced
- Can be eaten anytime in the day – breakfast, lunch and snacks
- Offers a choice of filling to suit customer preference
- The fillings were tasty and tested them out on his friends
- He would have used his own tried and trusted recipes
- Well known, popular products
- The products are bread / dough based so they are filling to satisfy hunger
- The products are reasonably priced/ value for money
- The business is coming to them, which is convenient (Any 4 x 1) (4)
6.4.5 Give THREE items of information that should appear on the label if the product was pre ordered and packaged.
- Name of the product
- Description of product (Filling flavour)
- Contact details
- Ingredient list
- Date of manufacture / sell by date (Any 3 x 1) (3)
6.4.6 Describe SIX hygiene practices that need to be followed to ensure that the food is safe for the customers when selling the food from the food truck during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- He must wear a mask when assembling and selling the food
- Have hand sanitiser to sanitise his hands regularly
- Wipe the surfaces in the truck
- His hair must be covered
- Serve the food with gloves on
- Each individual portion must be separately sealed for sale
- Fillings and cooked dough must be covered when working with the food
- There must be social distancing (1 meter) between him and the customer
- The customers must socially distance whilst in the queue
- The customers must all wear masks
- Have sanitiser to spray on customers’ hands (Any 6 x 1) (6)
6.4.7 Calculate the profit that he will make per month. Show all calculations. (Work on 4 weeks per month)
- R125 x 80 = R10 000
70
R10 000 x 100 = R7 000
R7 000 x 4 = R28 000
NOTE: The ‘R’ must be indicated to the final answer to be awarded the final mark. (6)
6.4.8 Analyse why this business idea and the product choice has the potential to be a successful business.
- Thabo has always had an interest in the food industry as he enjoye cooking from a young age and worked in a bakery, so it is likely he has a passion in this field of work. (He would likely be enthusiastic when promoting his business when he sells the food).
He has the human skills as he would have learnt from the days helping his grandmother and gained experience at the bakery. Thus, he has the capability to produce these products as his products are dough-based. He may also have picked up on business skills working in the bakery. - Thabo’s product is fulfilling the need of a light meals/snacks and food is a basic need. / He established that there would always be a demand for ready to eat food/a necessity to eat in the day as he investigated this business idea. Offering cooldrink is suitable to go with the snacks and an easy way to get extra money as they will sell.
His target market would be all ages, so he has a potentially large target market. The variety of sweet and savoury fillings would appeal to specific preferences; he could also adapt the fillings to their likes/trends therefore, he shows understanding of the needs of the target market. This would increase the consumer appeal of the products so customers will want to buy his unique/ homemade products. (trendy, fresh, good price) He can even use a simple cost effective, environmentally friendly packet to serve the food items. - He could use locally available ingredients/raw materials as this would reduce transport costs and not stop production while he waits for deliver from suppliers. It assures that the ingredients are fresh. He can tailor make the fillings to what is available.
- He tested the business idea/product. He asked his friends to try out the filings so got other input.
- He is preparing the products from home and has the available workspace therefore has a production facility to plan the workflow/ production line.
- He is not trying to compete with large companies but offering something different and his enthusiasm will ensure excellent service therefore he has competitive advantage. He is planning to sell the products at a range of prices so it can meet the affordability of the customers. (This point can also be discussed under meeting the need and consumer appeal of the target market)
- The location of the truck. It will be parked at a busy area in town so he will be within reach of the target market (He does not have to spend money on delivery of goods for consumer appeal.)
- Available finance. His financial position is stable as he has the capital /low start-up costs to start the business.
He does not have to borrow money from a bank, creating debt as his uncle will invest in the business and he can rent the truck from his grandfather at a reasonable price. This reduces a high capital outlay. He does not need to buy equipment as he has this at home. / He does not have high overheads. Working from home means he does not have to pay rent on a place to produce the products.
No advertising costs will be necessary as people around there will see people eating and ask where they bought it. - He has the time and energy to put into the business as he does not have another job or another commitment.
- In the scenario with the Covid-19 restrictions, he can still have a business where sanitising, the wearing of masks and social distancing in queues can be applied.
- The business has the potential to expand as he has met the criteria of what is required in identifying a profitable business opportunity and the factors influencing his choice of suitable products as discussed above.
NOTE: This is a higher order question, and the candidates cannot just quote from the case study but need to show insight as to how the information is discussed in their analysis.
For the marking of this question, the underlined words in Italics indicate the topics relating to a potential business idea and the underlined words in bold indicate that the discussion around factors that are considered for a suitable product are covered. (Any 8 x 1) (8)
[40]
TOTAL: 200
Consumer Studies Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions:
QUESTION
CONTENT
MARKS
TIME (minutes)
1
Short questions (All topics)
40
20
2
The Consumer
40
40
3
Food and Nutrition
40
40
4
Clothing
20
20
5
Housing
20
20
6
Entrepreneurship
40
40
TOTAL:
200
180
- All the questions are COMPULSORY.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH section on a NEW page.
- You may use a calculator.
- Write in blue or black ink only.
- Pay attention to spelling and sentence construction.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: SHORT QUESTIONS
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.20) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.21 D.
1.1.1 The … governs the maximum interest rate that may be charged by credit providers.
- Repurchase Rate
- Reserve Bank
- Consumer Price Index
- National Credit Act (1)
1.1.2 An appliance given an A rating on the energy efficiency label means that …
- fewer units of electricity will be used.
- it is least efficient in electricity usage.
- it will cost you more to operate.
- the performance will be weaker. (1)
1.1.3 Municipalities charge consumers for services such as:
- Health clinic, streetlights, water and electricity
- Sanitation, public library and traffic control
- Water, electricity, sanitation and refuse removal
- Recreation, refuse removal and health clinics (1)
1.1.4 The tax threshold is the income level …
- below which income tax becomes payable.
- above which income tax becomes payable.
- which will increase the tax amount paid.
- which is tax-free on the tax tables. (1)
1.1.5 The index on a scale of 1–100 for the carbohydrates group that when eaten will result in a sudden and rapid rise of glucose in the blood.
- 1–55
- 70 or more
- 56–69
- 54 or less (1)
1.1.6 A food additive type that prevents rancidity in fats:
- Emulsifier
- Stabiliser
- Preservative
- Anti-oxidant (1)
1.1.7 The nutrient content on a product label for sodium is 120 mg per 100g. This means the salt content is …
- high.
- very low.
- low.
- virtually free. (1)
1.1.8 A ‘sell-by date’ means the …
- last date that the product is for sale.
- same thing as an expiry date.
- the date that it is unsafe to eat.
- product will be safe if stored correctly. (1)
1.1.9 Food labelling legislation benefits the consumer in that … Choose the INCORRECT answer.
- they enforce truthful descriptions.
- the consumer is given basic information.
- misleading claims can be justified.
- consumers can make informed decisions. (1)
1.1.10 Substances added to food to enhance the flavour, texture, appearance or to preserve it:
- Preservatives
- Flavourings
- Colourants
- Food additives (1)
1.1.11 A description for the curve of a fad on the fashion cycle graph:
- Slight rise that reaches a plateau
- Rise sharply and decrease rapidly
- Resembles the shape of a wave
- Shows a dip in the centre (1)
1.1.12 An example that stimulates fashion change:
- When the repo rate has increased
- The coronavirus pandemic lockdown
- Fashion information is marketed
- A country with severe flooding (1)
1.1.13 Retrospective fashions are …
- expensive exclusive successful styles.
- those that pre-empts the next fashion trend.
- looks back at the past at previous eras.
- styles that have a short life span. (1)
1.1.14 Ted bought a refrigerator for R4 999,00 cash price. On instalment sales it was advertised as R353 per month x 24 months. Purchasing this appliance (refrigerator) on credit would have cost him … more.
- R3 473,00
- R3 530,00
- R8 472,00
- R4 999,00 (1)
1.1.15 The document signed when purchasing a house:
- Lease
- Deed of Transfer
- Title Deed
- Deed of Sale (1)
1.1.16 A disadvantage of building a home:
- The previous owners’ problem is yours
- The delays when building is in progress
- You can save on construction costs
- A new home has a better resale value (1)
1.1.17 An effective advertisement for your product will …
- only have one core message for the customer.
- entice the consumer to use your product.
- focus on consumers basic needs.
- make a claim about the brand name. (1)
1.1.18 The pricing strategy refers to …
- the method used to price the products or services.
- making enough profit for the business to survive.
- analysing pricing data that determine pricing.
- factors that determine your production costs. (1)
1.1.19 The purpose of a financial feasibility study will determine:
- The profit made at the financial year end
- The employee, community, and product safety
- An effective way to reach potential clients
- Whether to go ahead with the business idea (1)
1.1.20 The factor that improves staff morale and motivation:
- Quality controls
- Storage procedures
- Staff training
- Customer relations (1)
1.2 Choose the explanation from COLUMN B that matches the term in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–H) next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.4) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.5 I.
COLUMN A TERM | COLUMN B EXPLANATION | ||
1.2.1 | Fashion cycle | A | A fashion trend which is outdated |
1.2.2 | Contemporary Fashion | B | The general direction the fashion style follows |
1.2.3 | Obsolete | C | The outline of the garment |
1.2.4 | Accessory | D | Fashion is available to many at affordable prices |
E | The path that fashion trends take | ||
F | Inexpensive clothing produced rapidly | ||
G | Appropriate for everyday wear | ||
H | A decorative item that can make the outfit look more stylish | ||
(4 x 1) (4)
1.3 Give ONE word/term for each of the descriptions below. Write only the word/ term next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 A statement in a contract that clears one party from being held responsible if he/she fails to honour the agreement or event
1.3.2 A written promise to repair/replace a part without charge if it breaks/does not work properly within a specific period
1.3.3 Goods that the supplier has managed to import but the manufacturer does not want it sold in the country
1.3.4 Reduces the buying capability of money and people have less disposable income
1.3.5 A business practice like fraud, false promises and unreasonable terms and conditions are prohibited by law (5 x 1) (5)
1.4 Identify FOUR CORRECT statements in the list below that are applicable to cash flow projection. Write the letters (A–H) next to the question number (1.4) in the ANSWER BOOK.
- A plan for the business to make a profit
- So that the business can operate on a day-to-day basis
- Essential for the business to meet its financial obligations
- Gives an indication of how much credit is available
- Indicates how much profit the business has lost
- Expected money that will come in and go out as expenses
- To evaluate expected cash inflow and outflow
- Will depend on the estimated initial investment (4 x 1) (4)
1.5 Study the illustration below and answer the questions that follow. Write only the word(s) next to the question numbers (1.5.1 to 1.5.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.

[Source: Google images]
1.5.1 Select TWO foods from the list that are typical for causing E. coli infection:
| Peanut butter; unpasteurised milk; cheese, undercooked meat; eggs; bread. |
(2)
1.5.2 Identify the organ that is affected by the Hepatitis A:
| stomach; small intestine; large intestine; lungs; liver |
(1)
1.5.3 Select ONE range of time that the symptoms for gastroenteritis may last:
| 2 weeks; 1–7 days; 12–48 hours; 2–12 hours. |
(1)
1.5.4 Select TWO additives present in bread:
| Calcium propionate; citric acid; bleach; benzoic acid |
(2)
1.5.5. The nutrient content on cheese wrapper states low fat therefore the grams of fat per 100 g would be:
| 1,5 g or less, 6 g or less, maximum 3 g or less, 300 mg |
(1) [40]
QUESTION 2: THE CONSUMER
2.1 Name the type of interest calculated on the principal amount of the loan. (1)
2.2 Give TWO examples of regenerative/renewable sources of energy that can be used to generate electricity other than using coal. (2)
2.3 List TWO disadvantages of electricity derived from fossil fuels. (2)
2.4 Give the name of the agency that collects taxes on behalf of the government. (1)
2.5 Compare the two forms of income tax, PAYE and provisional income tax with reference to the following aspects.
Tabulate your answer as follows:
ASPECT | PAYE | PROVISIONAL TAX | |
2.5.1 | When is it paid | (1) | (1) |
2.5.2 | Describe the category of the taxpayer and give ONE example | (2) | (2) |
2.6 Study the illustration below and answer the questions that follow.
[Source: Google images]
2.6.1 Identify the type of scam in the illustration above. (1)
2.6.2 Write a paragraph where you discuss the scam that is being used to put customers at risk and how consumers can protect themselves from this type of crime. (5)
2.7 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
Amanda decided to become a member at the local gym. She signed the yearly contract with a 12-month commitment. The contract required her to pay a joining fee of R125. The 12-month contract costs her R250 per month. [Examiner’s own text] |
(1)
2.7.1 Identify a word that indicates that this is a written contract. (1)
2.7.2 Calculate the total that she will pay at the end of the contract period. (1)
2.7.3 State THREE responsibilities that she has concerning the contract. (3)
2.7.4 Explain TWO ways that the CPA (Consumer Protection Act) makes provision to protect Amanda should she want to cancel her gym membership. (2)
2.8 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
Thapelo Kgopodtihate founded the Makawana Farmers’ Stokvel in the Northern Cape. It is a co-operative approach to farming which resembles characteristics of a stokvel to help young farmers develop their businesses. It was started as farmers from villages in Kuruman; all faced difficulties in keeping their farms going due to the ongoing drought. The group has 23 members. Each member saves money for a 12-month-period to accumulate capital which is invested for the benefit of all members. They decide together whether to buy livestock, feed or equipment. When there are differences in opinion the executive committee makes the decision. Buying in bulk enables them to pay lower prices to save money. Ideas are shared and young farmers can gain knowledge of farming. [Adapted from https://www.farmersweekly.co.za. Accessed on 25 November 2020.] |
2.8.1 Discuss FOUR actions from the way this group operates that are similar to a typical stokvel. (Do not rewrite the sentences.) (4)
2.8.2 Describe how an illegal pyramid scheme would operate if this was the chosen scheme in the scenario. (3)
2.9 Read the statement below that is reflecting on SA’s tax outlook and answer the question that follows.
Lockdown measures have contributed to higher unemployment and lower consumption, which has contributed to a significant reduction in tax revenue. [Source: www.fanews.co.za/article/economy. Accessed on 2 February 2021.] |
The government relies on taxes that South Africans pay for government expenditure. Analyse the impact of the coronavirus on consumers tax contributions to the state for the two areas mentioned in the statement. (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: FOOD AND NUTRITION
3.1 Give the name of the ranking system that classifies food containing carbohydrates according to how they affect blood glucose levels. (1)
3.2 State the role of insulin in the body. (1)
3.3 Give TWO different ways the pancreas which produces insulin, malfunctions in a Type 2 diabetic person. (2)
3.4 Read the case study below and answer the question that follow.
Sally is not a diabetic. She ate too many sweets and cake for her afternoon snack. This has caused her blood glucose level to rise rapidly. |
3.4.1 Explain in detail her body’s response to the quick release of so much glucose into her blood. (5)
3.5 Compare the management of the diet for diabetes and osteoporosis sufferers with reference to the following recommendations. Tabulate your answer as follows:
RECOMMENDATION | DIABETES | OSTEOPOROSIS | |
3.5.1 | A reason why protein should be reduced | (1) | (1) |
3.5.2 | The type of beverage that should be limited | (1) | (1) |
3.5.2 | A reason to include canned fish (sardines) | (1) | (1) |
(6)
3.6 Interpret the graph below to explain the relationship between aging and bone mass with the risk of osteoporosis in females.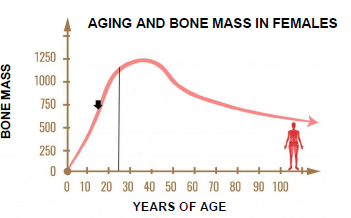
[Source: https://myfamilyphysio.com.au/osteoporosis] (6)
3.7 Give THREE characteristics of organic foods excluding that they are non-GMO. (3)
3.8 Explain how food irradiation can extend the shelf life of food. (2)
3.9 Read the following extract and answer the question that follows.
HOW TENDING A FOOD GARDEN LENDS TO GREATER FOOD SECURITY While providing food parcels during the Covid-19 pandemic addresses the short-term needs of vulnerable communities, it does not make for a sustainable food security solution during or beyond the current crisis. The Community Market Gardens programme goes beyond helping communities meet their immediate food security needs, explains Ruth Butcher, CSI consultant at MAMAS Alliance: “When it comes to food gardens, not only are they providing food relief, but there is a transfer of skills, a sense of responsibility and pride in being able to provide for one’s family. There is direct food relief, as well as the potential to generate an income from the produce. This creates a full circle of sustainability.” [Source: www.bizcommunity.com/Article/. Accessed on 6 July 2020.] |
Analyse why self-sufficiency may be a means to address the need of food insecurity. (6)
3.10 Determine the different types of information that appears on food labels that relate to food safety and explain how each category guarantees consumer safety. (4 x 2) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: CLOTHING
4.1 State TWO examples where a consumer can ‘reuse’ their clothing instead of the recycling option. (2)
4.2 Study the pictures below and answer the questions that follow.
[Source: Google Images]
4.2.1 State TWO facts why the T-shirt is considered a classic. (2)
4.2.2 Describe the term style. Refer to the pictures in your answer. (3)
4.3 List TWO consequences of brand piracy for businesses. (2)
4.4 Describe why illustration B is an example of brand piracy. (2)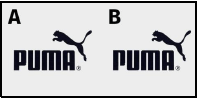
[Source: Google images]
4.5 Read the scenario below and answer the question that follows.
More businesses are operating online. A virtual meeting with clients and Appropriate clothing is good virtual etiquette – from the waist up at least. [Examiner’s own text] |
Discuss why the outfit below is suitable for a virtual meeting.
[Source: Google images] (3)
4.6 Read the statement below and answer the question that follows.
Recycled polyester is definitely a sustainable option for our wardrobe. However, we need to be aware that it is still non-biodegradable and takes years to disappear once thrown away. [Source: https://www.sustainyourstyle.org] |
Explain the term sustainable as it relates to clothing and analyse the statement to conclude whether recycled polyester is sustainable or not. (6)
[20]
QUESTION 5: HOUSING
5.1 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
Brett is looking for accommodation as he is moving cities. He cannot afford to [Examiner’s own text] |
5.1.1 Give the names of the TWO parties that sign a lease. (2)
5.1.2 State THREE disadvantages that Brett experienced when he previously rented. (3)
5.1.3 List TWO requirements that Brett will have to carry out should he wish to run his own business from his rented accommodation. (2)
5.1.4 Describe how the property owner is protected when a lease is signed. (3)
5.2 Differentiate between the responsibility for costs for security and maintenance between full-title ownership and sectional title ownership. (3)
5.3 Read the information below and answer the questions that follow.
New features of the Samsung microwave oven Power levels 10 power levels to suit your cooking needs Superior Ceramic Interior No more scrubbing or scratched surfaces. With a ceramic interior, the Samsung Mirror Grill Microwave Oven offers a smooth surface that is easy to clean. Standby Energy Savings Even at rest, similar microwave ovens use power to maintain essential functions. Selecting the ECO Mode setting on the new Samsung Mirror Grill significantly reduces power usage, delivering savings to your household on monthly energy bills. All this in addition to a 2-year warranty! |
5.3.1 List TWO responsibilities of the consumer when purchasing this microwave oven with regards to the warranty. (2)
5.3.2 Promote this microwave as a salesperson to a customer on how the features of this microwave will save energy. Include both human and non-human energy in your sales talk. (5)
[20]
QUESTION 6: ENTREPRENEURSHIP
6.1 Define the term target market. (2)
6.2 Give TWO advantages of routine/preventative maintenance of equipment when running a business. (2)
6.3 List THREE reasons why a business should do stock control. (3)
6.4 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
As a young boy Thabo discovered his enjoyment of cooking as he often helped his grandmother prepare the meals. After finishing school, he worked at a small bakery for one year, but the business closed because of the Covid- 19 pandemic. He decided to start a food truck business. The following were some of the points he made when investigating his idea.
Thabo needed a product that would be suitable for breakfast, lunch or a snack. He decided to sell roosterkoek and vetkoek with a variety of sweet or savoury fillings. He had all the equipment at home. He asked his friends to try out the fillings to ascertain which ones were tastier. Each day he would get up early to make the dough and prepare the fillings. His price would range from R8,00 to R35,00 depending on the filling chosen by the customer. Cooldrinks would also be sold. [Examiner’s own text] |
6.4.1 Identify the factor that was available to Thabo when he chose a product for his business from the sentences given below.
- Thabo showed interest in food from a young age and gained knowledge at work. (1)
- He would prepare the food before leaving home and when his truck is parked, the fillings would be placed into the products. (1)
6.4.2 State TWO advantages of Thabo using the truck as his point of sale. (2)
6.4.3 Identify TWO start-up needs. (2)
6.4.4 Discuss how the products will appeal to the target market. (4)
6.4.5 Give THREE items of information that should appear on the label if the product was pre ordered and packaged. (3)
6.4.6 Describe SIX hygiene practices that need to be followed to ensure that the food is safe for the customers when selling the food from the food truck during the COVID-19 pandemic. (6)
6.4.7 Read the information below and answer the question that follows.
| Thabo sells 80 curry mince vetkoek per week. His production cost is R125 per week. Thabo adds 70% profit to the production cost. |
Calculate the profit that he will make per month. (Work on 4 weeks per month)
Show ALL calculations. (6)
6.4.8 Analyse why this business idea and the product choice has the potential to be a successful business. (8)
[40]
TOTAL: 200
Civil Technology: Civil Services Memorandum - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE MARKERS
- Markers should:
- Familiarise themselves with the question and answer before evaluating the responses of candidates.
- Always interpret the responses of the candidates within the context of the question.
- Consider any relevant and acceptable answer during pre-marking but should strictly adhere to the answers after finalisation of the marking guideline.
- There are two approaches to answering questions, these are (1) to describe and (2) to explain.
- If a candidate is required to explain e.g., a process in 4 steps, only the first 4 responses should be considered.
- If, however a candidate is required to e.g., explain or describe how to transfer heights from one point to another using a transparent pipe level we need to consider that candidates may write a long description not necessarily well organised as an intellectual response may do. In this case the marker needs to evaluate the complete statement to judge if the candidate explained the required outcome satisfactorily and allocate marks on merit. The marker should apply his/her professional judgement with these types of questions.
- Mark what the candidate wrote and do not award marks for answers that the marker thinks the candidate meant with what was written.
- Indicate the tick or cross right at the position where the mark needs to be awarded or where the candidate made the error.
- Accept the letter corresponding with the correct answer as well as the answer written in full in multiple-choice questions.
- Accept incorrect spelling in one-word answers unless the spelling changes the meaning of the answer.
- For calculations:
- A mark is only awarded if the correct unit is written next to the answer.
- If TWO marks are awarded ONE mark is awarded for the answer and ONE mark for the correct unit.
- Where the candidate made a principle error e.g. added instead of multiplying, no marks will be awarded for the steps. If the answer is correct according to what the candidate did, the mark for the answer can be awarded for the application of skills.
- Where an incorrect answer could be carried over to the next step, the first answer will be deemed incorrect. However, should the incorrect answer be carried over correctly, the marker has to recalculate the values, using the incorrect answer from the first calculation. If correctly used, the candidate should receive the full marks for subsequent calculations.
- Markers should consider when and where a candidate has rounded off in a calculation, as well as the subsequent effect it has on the final answer obtained. The calculation should therefore be awarded marks on merit.
- Alternative methods of calculations must be considered, provided that the correct answer is obtained.
- When marking drawings:
- The member for which the mark should be awarded should be drawn correctly in the correct position to receive a mark.
- A member incorrectly drawn but wrongfully repeated in another position will be awarded the mark for the repeated incorrect member provided that the marking guideline provide for TWO or more marks for that member (positive marking).
- Marks can only be awarded for a label if the label is correctly indicating the correct member.
- Scale drawings should always be marked using an appropriate mask.
When a candidate drew the wrong drawing e.g.: - A horizontal section instead of a vertical section, no marks will be allocated to the drawing as the candidate did not respond to the expected outcome.
- An orthographic view instead of sectional view, no marks will be allocated to the drawing as the candidate did not respond to the expected outcome.
- An orthographic view instead of an isometric view, no marks will be allocated to the drawing as the candidate did not respond to the expected outcome.
- If the incorrect drawing was drawn, the candidate can be awarded for only what was asked but mark/s for the correctness of the drawing will not be awarded e.g., if a King Post roof truss was asked in the question, and candidate drew SA-Howe Truss.
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: SAFETY AND MATERIALS (GENERIC)
1.1 Answer the following question regarding scaffolding.
1.1.1
- – Guardrail (1)
- – Planks / Working platform (1)
- – Kickboard / Toe-board (1)
- – Brace (1) (4)
1.1.2 228 mm (1) x 38 mm (1) (2)
1.1.3 Provides stability to the scaffolding. (1)
1.1.4 Minimum = 900 mm (1) and maximum = 1 000 mm (1) (2)
1.2
1.2.1 Placing of building rubble:
- May not obstruct access or exits
- Safe place
- Regularly removed. (Any 1 x 1) (1)
1.2.2 When materials are transported to higher surfaces:
- Workers must maintain a safe distance
- Overhead protection (Any 1 x 1) (1)
1.3 Any THREE:
- Non-skid devices on the bottom
- Hooks at the upper ends
- Lashed, secure or fastened
- Held by someone (Any 3 x 1) (3)
1.4 Rungs (1)
1.5 The coating of a metal by electrolysis (1) with a thin layer of another metal. (1) (2)
1.6 To improve the metal’s corrosion resistance. (1)
1.7 Any TWO:
- Adds strength to the metal
- Galvanised metals are thicker
- Galvanised nails and screws prevents staining (Any 2 x 1) (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS, JOINING AND EQUIPMENT (GENERIC)
2.1 FIGURE 2.1 on ANSWER SHEET A shows a floorplan of a storeroom on scale 1 : 50. Draw the south elevation on scale 1 : 50 on ANSWER SHEET A from the given ground level, by using the following information:
- The floor level height is 200 mm above the ground level
- Wall height is 2 600 mm from the floor level to the ceiling
- Window 1 is 1 200 x 900 mm
- Door 1 is 1 100 x 2 100 mm
- Doorknob
- Roof construction pitch is 30°
- Show construction lines to determine the roof height
- Gable end at the west elevation
- Hippen end at the east elevation
Use the marks table on ANSWER SHEET A as reference. (29)
2.2
- – Nut with built-in washer like a flange (1)
- – Wing nut (1)
- – Domed top nut (1) (3)
2.3 Any TWO:
- Resist pull-out failure
- Excellent carrying capacity
- Tolerance to a variance in the hole size (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.4 Must be set-up that the telescope (1) is placed on a comfortable sightline (1) to prevent a person from bending or stretching over the telescope and tripod (1).
(3)
2.5 Any THREE:
- Wiring
- Wood
- Metal studs
- Copper pipes
- Plumbing work (Any 3 x 1) (3)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION A: 60
QUESTION 3: SAFETY, MATERIAL AND CONSTRUCTION (SPECIFIC)
3.1 FIGURE 3.1 shows workers who must work in a manhole. Answer the following questions regarding the safety measures which must be applied.
3.1.1 Similar answer:
- Prevents material or persons falling in.
- Identifies a danger zone. (Any 1 x 1) (1)
3.1.2 Similar answer:
- Pipe for extractor fan or blower.
- Provides manhole workers with fresh air. (Any 1 x 1) (1)
3.1.3 When (1) dangerous fumes / gases are (2) present in the manhole / confined spaces. (2)
3.1.4 Respirator (1)
3.2 Similar answer:
- Safety net
- Catch platform
- Rails / Barriers
- Hard hat (Any 1 x 1) (1)
3.3 Any TWO:
- Electrical tools
- Battery tools
- Fuel tools (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.4
3.4.1 True (1)
3.4.2 False (1)
3.4.3 True (1)
3.4.4 True (1)
3.5 Scale or corrosion products (1) are removed (2) by subjecting it as an electrode (3) to an electrical current (4) in an electrolytic bath. (4)
3.6 FIGURE 3.6 on ANSWER SHEET B shows layer 1 of a T-junction in a one-brick wall in stretcher bond. Draw the alternate layer of the T-junction on scale 1 : 10 on ANSWER SHEET B. (7)
3.7 English bond (1)
3.8 Give access to drain system / Cleaning of drain system (1)
3.9 Make a neat section sketch in good ratio to illustrate a manhole construction with benching. Show the following parts and indicate it with labels:
- Concrete base
- Brick walls
- Pipe channel
- Benching
- Cover frame and cover
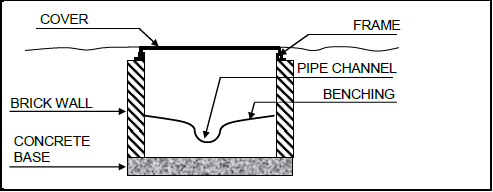
(5) [30]
QUESTION 4: COLD-WATER SUPPLY, HOT-WATER SUPPLY AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
4.1 Any THREE properties of water
- Colourless
- Free from suspended matter
- Free from harmful bacteria
- Pleasant to taste
- Moderately hard (Any 3 x 1) (3)
4.2 Prevents water from leaking from the spindle. (1)
4.3 It reduces splashing / water noise. (1)
4.4 Answer the following questions regarding the valve in FIGURE 4.4.
4.4.1 Non-return valve (1)
4.4.2 B (1)
4.4.3 Open (1)
4.4.4 Where water flows only in one direction. (1)
4.5 Answer the following questions regarding FIGURE 4.4.
4.5.1 S-trap (1)
4.5.2 (1) Keeps water back to (2) prevent odours passing to the inside. (2)
4.5.3 Inspection eye (1)
4.5.4 Cleaning of trap (1)
4.6 Wastewater – water contaminated by human waste / pollutants. Soil water – water from the sink / basin / bath / shower. (2)
4.7 Describe TWO advantages of electronic taps.
- It only allows water to flow through when the sensor is triggered / saves water.
- You do not need to touch the tap. (2 x 1) (2)
4.8 (1) Polluted water harms (2) mechanisms of valves and tap washers. (2)
4.9 4.9.1 Expansion-control vessel (1)
4.9.2 Mixer (1)
4.9.3 Non-return valve (1)
4.9.4 Float valve (1)
4.9.5 Pressure-control valve (1)
4.10 Make neat sketches of the following symbols for hot water systems.
4.10.1 Pressure-reducing valve ![]() (2)
(2)
4.10.2 Vacuum-relieve valve  (2)
(2)
4.11 (1) It occurs when a pipe bursts / faulty plumbing (2) traps air in a high point. (3) The air blocks the (4) flow of water. (4)
4.12
4.12.1 True (1)
4.12.2 True (1)
4.12.3 True (1)
4.13 Loose clothing can get caught in the moving parts. (1)
4.14 Name TWO tools which are used for cleaning blockages in drains.
- Drain-cleaning rods
- Drain-cleaning or jetting machine (2 x 1) (2)
4.15 Water pressure testing pump (1)
[40]
QUESTION 5: DRAINAGE AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
5.1 Describe the following requirements for an efficient drainage system.
5.1.1 Smooth finishing (1)
5.1.2 100 mm (1)
5.1.3
- Where 2 or more pipes meet
- At the main pipeline junction
- Every 25 metres (3)
5.2 (1) Where ground movement occur and (2) leakages must be prevented. (2)
5.3 Name TWO properties of earthenware drainpipes.
- Brittle
- Durable (2 x 1) (2)
5.4 Make a neat section sketch of a coupling socket joint for drainpipes. (3)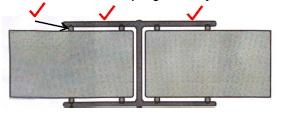
5.5 Name TWO positions in a drainage system where gullies must be installed.
- Wastewater connection at drain from the kitchen.
- Wastewater connection at drain from the bathroom. (2 x 1) (2)
5.6 Choose the correct description regarding a septic tank.
5.6.1
- Sewerage
- Water closet (2)
5.6.2 Sink to the bottom of the chamber (1)
5.6.3
- Bacteria
- Liquid (2)
5.6.4 Sludge (1)
5.7 Give the colour coding for the following drainage fittings:
5.7.1 Brown (1)
5.7.2 Blue (1)
5.7.3 Black (1)
5.8 Identify the following abbreviations for drainage fittings:
5.8.1 IR – Inspection room (1)
5.8.2 ST – Septic tank (1)
5.8.3 CE – Cleaning eye (1)
5.9 Test if drains are airtight / watertight. (1)
5.10 The side of a cubic water supply tank is 1 800 mm. Determine the following of the tank.
(Show all calculations and formulas.)
5.10.1
- Volume = S3
= 1,8 x 1,8 x 1,8
= 5,83 m3 (3)
5.10.2
- Volume water = 5,83 m3 x 1 000 ℓ/ m3
= 5 830 ℓ (2)
5.11 FIGURE 5.11 shows the pictorial view of a part of the layout for a drainage system. Answer the following questions regarding the system.
5.11.1
- – Stop end
- – 90° Single T-junction
- – Waste pipe
- – Waste bent (4)
5.11.2 Ø 110 mm (1)
5.11.3 Ø 50 mm (1)
5.11.4 PVC (1)
5.11.5 620 mm (10 mm tolerance) (1)
[40]
QUESTION 6: GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION, ROOF WORK, STORMWATER AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
6.1 FIGURE 6.1 on ANSWER SHEET C shows the top and front view of a cylindrical pipe. Draw the development of the cylindrical pipe on ANSWER SHEET C. Show all construction lines. (12)
6.2 Indicate if the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Write only ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the question number in the ANSWER BOOK.
6.2.1 True (1)
6.2.2 True (1)
6.2.3 False (1)
6.2.4 True (1)
6.3 Join gutters (1)
6.4 Bottom of a downpipe (1)
6.5 Discuss the following regulations which are applicable to stormwater disposal.
6.5.1 (1) It must be drained away from the building (2) to prevent damage to property. (2)
6.5.2 (1) At least 5 m away from any building (2) to prevent any accumulation of dampness. (2)
6.6 Name THREE negative consequences of storm water constructions which do not comply to the requirements.
Any THREE:
- Discomfort of occupants
- Loss of life
- Damage to property
- Pollution of the environment
- Negative environmental impact (Any 3 x 1) (3)
6.7 (1) Assists in cleaning the material / prevents oxidation (2) and promotes the flow of solder. (2)
6.8 Resin (1)
6.9
- – Pop rivet
- – Lap joint with cover strip (2)
[30]
TOTAL: 200
ANSWER SHEET A
2.1 FIGURE 2.1 shows the floor plan of a storeroom on scale 1 : 50.
Draw the south elevation on scale 1 : 50 on ANSWER SHEET A from the given ground level. (29)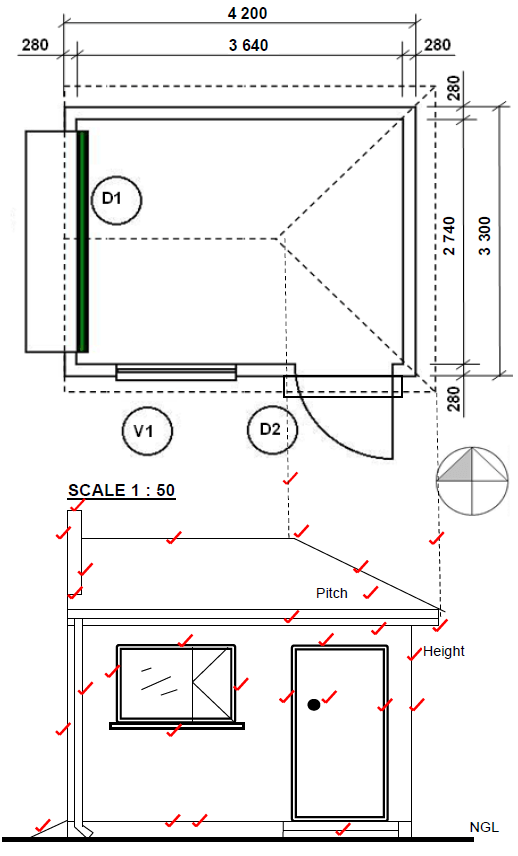
Floor level | 2 | |
Wall | 3 | |
Window | 3 | |
Windowsill | 1 | |
Door | 4 | |
Stairs | 1 | |
Ramp | 1 | |
Fascia board | 2 | |
Gutter | 1 | |
Down pipe | 1 | |
Gable ent | 4 | |
Hipped ent | 3 | |
Roof height | 3 | |
TOTAL: | 29 |
ANSWER SHEET B
3.6 FIGURE 3.6 on ANSWER SHEET B shows layer 1 of a T-junction in a one- brick wall in stretcher bond. Draw the alternate layer of the T-junction on scale
1 : 10 on ANSWER SHEET B. (7)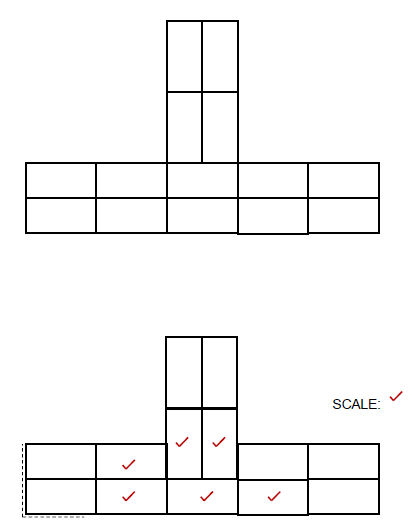
Brickwork | 6 | |
Application of scale | 1 | |
TOTAL: | 7 |
ANSWER SHEET C
6.1 FIGURE 6.1 on ANSWER SHEET C shows the top and front view of a cylindrical pipe.
Draw the development of the cylindrical pipe on ANSWER SHEET C. Show all construction lines. (12)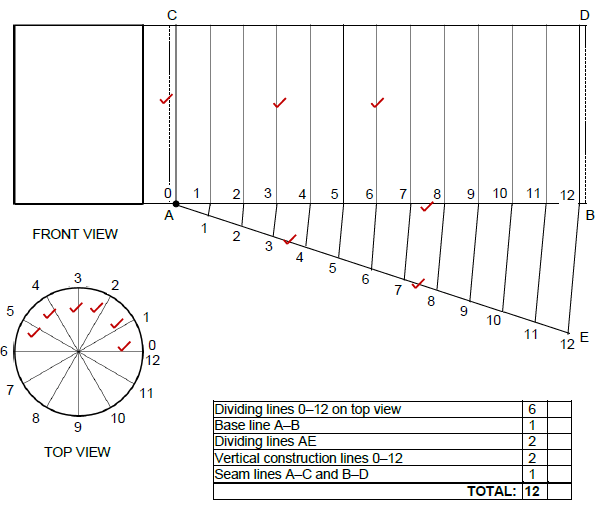
Civil Technology: Civil Services Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
REQUIREMENTS:
- ANSWER BOOK
- Drawing instruments
- A non-programmable pocket calculator
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions: TWO questions are generic and FOUR questions are subject specific.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Answer each question as a whole. Do NOT separate subsections of questions.
- Start the answer to EACH question on a NEW page.
- Do NOT write in the margins of the ANSWER BOOK.
- You may use sketches to illustrate your answers.
- Write ALL calculations and answers in the ANSWER BOOK or on the attached ANSWER SHEETS.
- Use the mark allocation as a guide to the length of your answers.
- Make drawings and sketches in pencil, fully dimensioned and neatly finished off with descriptive titles and notes to conform to the SANS/SABS Code of Practice for Building Drawings.
- For the purpose of this question paper, the size of a brick should be taken as 220 mm x 110 mm x 75 mm.
- Use your own discretion where dimensions and/or details have been omitted.
- Answer QUESTIONS 2.1, 3.6 and 6.1 on the attached ANSWER SHEETS using drawing instruments where necessary.
- Write your NAME on every ANSWER SHEET and hand them in with your ANSWER BOOK, whether you have answered the question or not.
- Owing to electronic transfer, drawings in the question paper are NOT to scale.
- Google images was used as the source of all photographs and pictures.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: SAFETY AND MATERIALS (GENERIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
1.1 Answer the following questions regarding the scaffolding in FIGURE 1.1.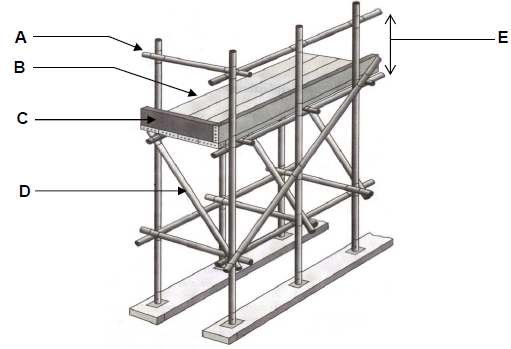
FIGURE 1.1
1.1.1 Name parts A to D. (4 x 1) (4)
1.1.2 What is the minimum width and thickness of part B? (2 x 1) (2)
1.1.3 What is the purpose of part D? (1)
1.1.4 What is the minimum and maximum measurements of E? (2 x 1) (2)
1.2 Describe the regulation that is applicable to the following facets when material is handled on a construction site:
1.2.1 Placing of building rubble (1)
1.2.2 When material is transported to higher surfaces (1)
1.3 Name THREE methods to ensure that a ladder is stable when it is used. (3 x 1) (3)
1.4 What are the horizontal parts of a ladder called? (1)
1.5 Explain the process of electroplating of a metal. (2)
1.6 Explain the purpose of electroplating of a metal. (1)
1.7 Name TWO advantages of galvanising. (2 x 1) (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS, JOINING AND EQUIPMENT (GENERIC)
2.1 FIGURE 2.1 on ANSWER SHEET A shows a floorplan of a storeroom on scale 1 : 50. Draw the south elevation on scale 1 : 50 on ANSWER SHEET A from the given ground level, by using the following information:
- The floor level height is 200 mm above the ground level
- Wall height is 2 600 mm from the floor level to the ceiling
- Window 1 is 1 200 x 900 mm
- Door 1 is 1 100 x 2 100 mm
- Doorknob
- Roof construction pitch is 30°
- Show construction lines to determine the roof height
- Gable end at the west elevation
- Hippen end at the east elevation
Use the marks table on ANSWER SHEET A as reference. (29)
2.2 Identify the type of nuts in FIGURES A to C.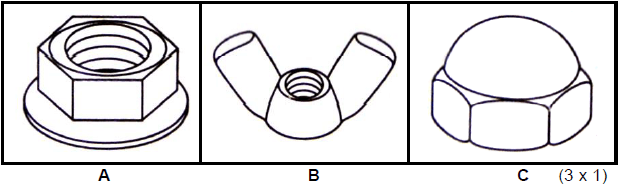
(3 x 1) (3)
2.3 Name TWO properties of rawl bolts. (2 x 1) (2)
2.4 Discuss how the height of the tripod should be set when a dumpy level is set up. (3)
2.5 Name THREE materials that can be detected in walls by a multi-detector. (3 x 1) (3)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION A: 60
QUESTION 3: SAFETY, MATERIAL AND CONSTRUCTION (SPECIFIC)
Start the question on a NEW page.
3.1 FIGURE 3.1 show workers who must work in a manhole. Answer the following questions with related to the safety measures which must be applied.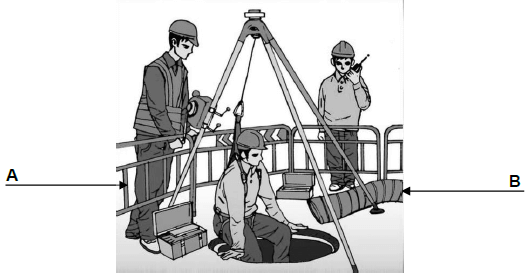
FIGURE 3.1
3.1.1 What is the purpose of structure A? (1)
3.1.2 What is the purpose of equipment B? (1)
3.1.3 Briefly describe in which circumstances equipment B will be used. (2)
3.1.4 Which personal protective equipment is lacking from the manhole worker, should there be dangerous fumes in the manhole? (1)
3.2 Which safety measure must be applied where falling objects can injure workers? (1)
3.3 Safety measures during construction work are very important. Identify TWO types of power tools which must be safeguarded. (2 x 1) (2)
3.4 Indicate if the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Write only ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the question numbers (3.4.1–3.4.4) in the ANSWER BOOK.
3.4.1 Dezincification is a form of corrosion. (1)
3.4.2 Copper-zinc alloys containing more than 5% zinc, are susceptible to dezincification. (1)
3.4.3 Dezincification is an electrochemical reaction between zinc and water. (1)
3.4.4 Dezincification can cause leaks in pipe work. (1)
3.5 Fully explain what is meant by the electrolytic cleaning of a metal surface. (4)
3.6 FIGURE 3.6 on ANSWER SHEET B shows layer 1 of a T-junction in a one- brick wall in stretcher bond. Draw the alternate layer of the T-junction on scale 1 : 10 on ANSWER SHEET B. (7)
3.7 Which type of brick bond is illustrated in FIGURE 3.7?
FIGURE 3.7 (1)
3.8 What is the purpose of a manhole in a drain system? (1)
3.9 Make a neat section sketch in good ratio to illustrate a manhole construction with benching. Show the following parts and indicate them with labels:
- Concrete base
- Brick walls
- Pipe channel
- Benching
- Cover frame and cover (5 x 1) (5)
[30]
QUESTION 4: COLD-WATER SUPPLY, HOT-WATER SUPPLY AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
4.1 Name THREE properties with which water for human use must comply. (3 x 1) (3)
4.2 What is the purpose of the packing gland inside the housing of a stopcock? (1)
4.3 Briefly motivate why the flow in the pipe of the ball valve releases the water at the bottom of the cistern. (1)
4.4 Answer the following questions with related to the valve in FIGURE 4.4.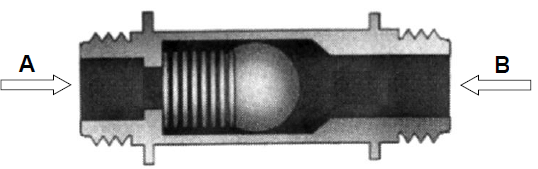
FIGURE 4.4
4.4.1 What is this valve called? (1)
4.4.2 Is A or B the correct flow direction for the valve? (1)
4.4.3 Is the valve open or closed? (1)
4.4.4 In which circumstances is this valve used? (1)
4.5 Answer the following questions regarding FIGURE 4.4. 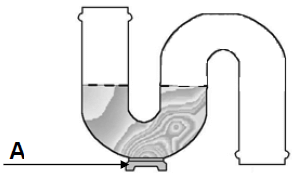
FIGURE 4.4
4.5.1 What is this structure called? (1)
4.5.2 Briefly describe the purpose of this structure. (2)
4.5.3 What is part A called? (1)
4.5.4 What is the purpose of part A? (1)
4.6 Briefly explain the difference between wastewater and soil water. (2)
4.7 Describe TWO advantages of electronic taps. (2 x 1) (2)
4.8 Motivate why muddy water must be pumped out of busted water supply pipes before they are repaired. (2)
4.9 Identify the following symbols and abbreviations for hot water systems.
4.9.1  (1)
(1)
4.9.2  (1)
(1)
4.9.3 ![]() (1)
(1)
4.9.4 FV (1)
4.9.5 PVC (1)
4.10 Make neat sketches of the following symbols for hot-water systems:
4.10.1 Pressure-reducing valve (2)
4.10.2 Vacuum-relieve valve (2)
4.11 Explain how an airlock occurs and influences a water supply system. (4)
4.12 Indicate if the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Write only ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the question numbers (4.12.1–4.12.3) in the ANSWER BOOK.
4.12.1 A heat pump is energy efficient. (1)
4.12.2 A solar geyser reduces greenhouse gases. (1)
4.12.3 Poor hot-water pressure is caused by faulty valves. (1)
4.13 Why must loose clothing be avoided when working with the pipe-thread cutting machine? (1)
4.14 Name TWO tools which are used for cleaning blockages in drains. (2 x 1) (2)
4.15 Which machine is used for the pressure testing of water systems? (1)
[40]
QUESTION 5: DRAINAGE AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
5.1 Describe the following requirements for an efficient drainage system:
5.1.1 The finishing of the inside of the pipes (1)
5.1.2 Minimum diameter of the pipes (1)
5.1.3 Placing of manholes (3)
5.2 Explain the circumstances where cast iron must be used. (2)
5.3 Name TWO properties of earthenware drainpipes. (2 x 1) (2)
5.4 Make a neat section sketch of a coupling socket joint for drainpipes. (3)
5.5 Name TWO positions in a drainage system where gullies must be installed. (2 x 1) (2)
5.6 Choose the correct description regarding the septic tank.
5.6.1 Sewerage / Soil water flows from the tap / water closet into the first chamber. (2)
5.6.2 Heavier particles are retained in the benching. / sink to the bottom of the chamber. (1)
5.6.3 Viruses / Bacteria digest the solid waste and turn it into a gas / liquid. (2)
5.6.4 The sludge / liquid must be cleaned regularly. (1)
5.7 Give the colour coding for the following drainage fittings:
5.7.1 Soil pipes (1)
5.7.2 Waste vents (1)
5.7.3 Existing drains (1)
5.8 Identify the following abbreviations for drainage fittings:
5.8.1 IR (1)
5.8.2 ST (1)
5.8.3 CE (1)
5.9 What is the purpose of the compressed air test for drains? (1)
5.10 The side of a cubic water supply tank is 1 800 mm. Determine the following volumes of the tank: (Show all calculations and formulas.)
5.10.1 The volume of the tank (3)
5.10.2 The volume of the water in the tank (2)
5.11 FIGURE 5.11 shows the pictorial view of a part of the layout for a drainage system. Answer the following questions regarding the system.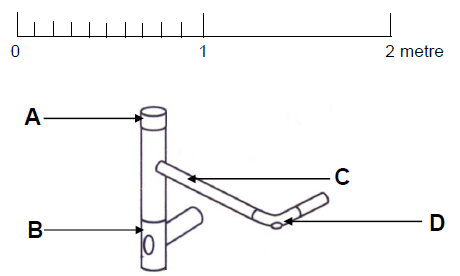
FIGURE 5.11
5.11.1 Name the sanitary fittings A to D. (4)
5.11.2 What is die section size of part B? (1)
5.11.3 What is the section size of part D? (1)
5.11.4 Of which type of material is the fitting manufactured? (1)
5.11.5 Use the graphic scale in FIGURE 5.11 and calculate the length of part C. (1)
[40]
QUESTION 6:
GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION, ROOF WORK, STORMWATER AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
6.1 FIGURE 6.1 on ANSWER SHEET C shows the top and front view of a cylindrical pipe.
Draw the development of the cylindrical pipe on ANSWER SHEET C. Show all construction lines. (12)
6.2 Indicate if the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Write only ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the question number in the ANSWER BOOK.
6.2.1 GMS-gutters have a pitch of 25 mm for each 4,8 m. (1)
6.2.2 The gutter brackets are fixed onto the facia board. (1)
6.2.3 A ripsaw is used to cut GMS-gutters to measurement. (1)
6.2.4 The seams of GMS-gutters are soldered with 50/50 solder. (1)
6.3 What is the purpose of a union clip when PVC-gutters are installed? (1)
6.4 Where, in a gutter system, is a downpipe shoe installed? (1)
6.5 Discuss the following regulations which are applicable to stormwater disposal.
6.5.1 Rainwater accumulates around buildings (2)
6.5.2 Soakaways (2)
6.6 Name THREE negative consequences of stormwater constructions that do not comply to the requirements. (3 x 1) (3)
6.7 Discuss the purpose of the flux when soldering work is done. (2)
6.8 Which type of soldering flux is manufactured from pine-tree bark? (1)
6.9 Identify the type of joining methods in FIGURES 6.9.1 and 6.9.2. (2)
(2)
[30]
TOTAL: 200
ANSWER SHEET A
2.1 FIGURE 2.1 on ANSWER SHEET A shows the floorplan of a storeroom on scale 1 : 50. Draw the south elevation on scale 1 : 50 on ANSWER SHEET A from the given ground level. (29)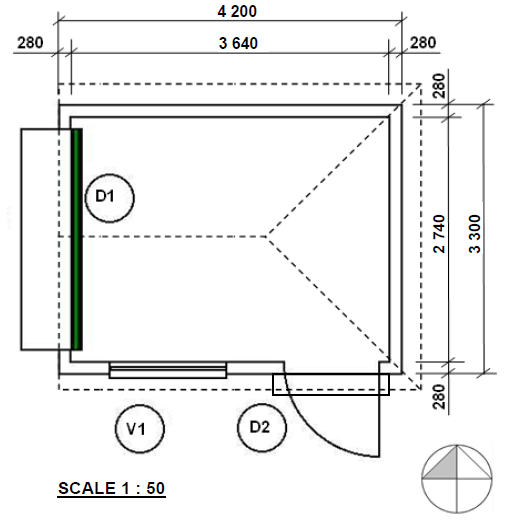
Floor level | 2 | |
Wall | 3 | |
Window | 3 | |
Windowsill | 1 | |
Door | 4 | |
Stair | 1 | |
Ramp | 1 | |
Fascia board | 2 | |
Gutter | 1 | |
Down pipe | 1 | |
Gable end | 4 | |
Hipped end | 3 | |
Roof height | 3 | |
TOTAL: | 29 |
![]()
ANSWER SHEET B
3.6 FIGURE 3.6 on ANSWER SHEET B shows layer 1 of a T-junction in a one- brick wall in stretcher bond. Draw the alternate layer of the T-junction on
scale 1 : 10 on ANSWER SHEET B. (7)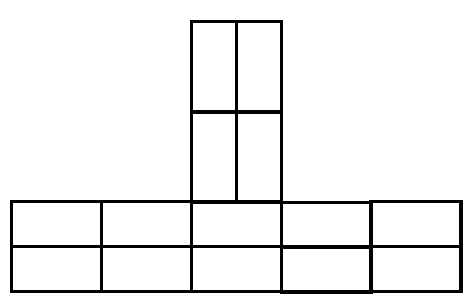
Brickwork | 6 | |
Application of scale | 1 | |
TOTAL: | 7 |
ANSWER SHEET C
6.1 FIGURE 6.1 on ANSWER SHEET C shows the top and front view of a cylindrical pipe. Draw the development of the cylindrical pipe on ANSWER SHEET C. Show all construction lines. (12)
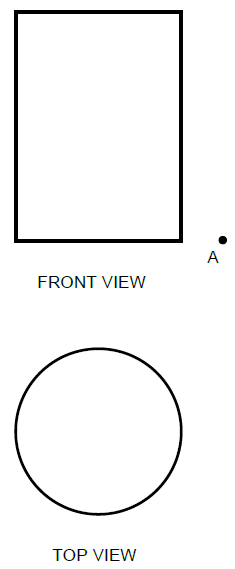
Dividing lines 0–12 on top view | 6 | |
Base line A–B | 1 | |
Dividing lines AE | 2 | |
Vertical construction lines 0–12 | 2 | |
Seam lines A–C and B–D | 1 | |
TOTAL: | 12 |
Civil Technology: Construction Memorandum - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE MARKERS
- Markers should:
- Familiarise themselves with the question and answer before evaluating the responses of candidates.
- Always interpret the responses of the candidates within the context of the question.
- Consider any relevant and acceptable answer during pre-marking but should strictly adhere to the answers after finalisation of the marking guideline.
- There are two approaches to answering questions, these are (1) to describe and (2) to explain.
- If a candidate is required to explain e.g., a process in 4 steps, only the first 4 responses should be considered.
- If, however a candidate is required to e.g., explain or describe how to transfer heights from one point to another using a transparent pipe level we need to consider that candidates may write a long description not necessarily well organised as an intellectual response may do. In this case the marker needs to evaluate the complete statement to judge if the candidate explained the required outcome satisfactorily and allocate marks on merit. The marker should apply his/her professional judgement with these types of questions.
- Mark what the candidate wrote and do not award marks for answers that the marker thinks the candidate meant with what was written.
- Indicate the tick or cross right at the position where the mark needs to be awarded or where the candidate made the error.
- Accept the letter corresponding with the correct answer as well as the answer written in full in multiple-choice questions.
- Accept incorrect spelling in one-word answers unless the spelling changes the meaning of the answer.
- For calculations:
- A mark is only awarded if the correct unit is written next to the answer.
- If TWO marks are awarded ONE mark is awarded for the answer and ONE mark for the correct unit.
- Where the candidate made a principle error e.g. added instead of multiplying, no marks will be awarded for the steps. If the answer is correct according to what the candidate did, the mark for the answer can be awarded for the application of skills.
- Where an incorrect answer could be carried over to the next step, the first answer will be deemed incorrect. However, should the incorrect answer be carried over correctly, the marker has to recalculate the values, using the incorrect answer from the first calculation. If correctly used, the candidate should receive the full marks for subsequent calculations.
- Markers should consider when and where a candidate has rounded off in a calculation, as well as the subsequent effect it has on the final answer obtained. The calculation should therefore be awarded marks on merit.
- Alternative methods of calculations must be considered, provided that the correct answer is obtained.
- When marking drawings:
- The member for which the mark should be awarded should be drawn correctly in the correct position to receive a mark.
- A member incorrectly drawn but wrongfully repeated in another position will be awarded the mark for the repeated incorrect member provided that the marking guideline provide for TWO or more marks for that member (positive marking).
- Marks can only be awarded for a label if the label is correctly indicating the correct member.
- Scale drawings should always be marked using an appropriate mask.
When a candidate drew the wrong drawing e.g.: - A horizontal section instead of a vertical section, no marks will be allocated to the drawing as the candidate did not respond to the expected outcome.
- An orthographic view instead of sectional view, no marks will be allocated to the drawing as the candidate did not respond to the expected outcome.
- An orthographic view instead of an isometric view, no marks will be allocated to the drawing as the candidate did not respond to the expected outcome.
- If the incorrect drawing was drawn, the candidate can be awarded for only what was asked but mark/s for the correctness of the drawing will not be awarded e.g., if a King Post roof truss was asked in the question, and candidate drew SA-Howe Truss.
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: SAFETY AND MATERIALS (GENERIC)
1.1 Answer the following question regarding scaffolding.
1.1.1
- – Guardrail (1)
- – Planks / Working platform (1)
- – Kickboard / Toe-board (1)
- – Brace (1) (4)
1.1.2 228 mm (1) x 38 mm (1) (2)
1.1.3 Provides stability to scaffolding. (1)
1.1.4 Minimum = 900 mm (1) and maximum = 1 000 mm (1). (2)
1.2
1.2.1 Placing of building rubble:
- May not obstruct access or exits
- Safe place
- Regularly removed (Any 1 x 1) (1)
1.2.2 When materials are transported to higher surfaces:
- Workers must maintain a safe distance
- Overhead protection (1)
1.3 Any THREE:
- Non-skid devices on the bottom
- Hooks at the upper ends
- Lashed, secure or fastened
- Held by someone (Any 3 x 1) (3)
1.4 Rungs (1)
1.5 The coating of a metal by electrolysis (1) with a thin layer of another metal. (1) (2)
1.6 To improve a metal’s corrosion resistance. (1) (1)
1.7 Any TWO:
- Adds strength to the metal
- Galvanised metals are thicker
- Galvanised nails and screws prevents staining (Any 2 x 1) (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS, JOINING AND EQUIPMENT (GENERIC)
2.1 FIGURE 2.1 on ANSWER SHEET A shows a floorplan of a storeroom on scale 1 : 50. Draw the south elevation on scale 1 : 50 on ANSWER SHEET A from the given ground level, by using the following information:
- The floor level height is 200 mm above the ground level.
- Wall height is 2 600 mm from the floor level to the ceiling.
- Window 1 is 1 200 x 900 mm.
- Door 1 is 1 100 x 2 100 mm.
- Doorknob
- Roof construction pitch is 30°
- Show construction lines to determine the roof height.
- Gable end at the west elevation.
- Hippen end at the east elevation.
Use the marks table on ANSWER SHEET A as reference. (29)
2.2
- – Nut with built-in washer like a flange (1)
- – Wing nut (1)
- – Domed top nut (1) (3)
2.3 Any TWO:
- Resist pull-out failure
- Excellent carrying capacity
- Tolerance to a variance in the hole size (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.4 Must be set-up that the telescope (1) is placed on a comfortable sightline (1) to prevent a person from bending or stretching over the telescope and tripod. (1)
(3)
2.5 Any THREE:
- Wiring
- Wood
- Metal studs
- Copper pipes
- Plumbing work (3 x 1) (3)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION A: 60
QUESTION 3: ROOFS, STAIRCASES AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
3.1
3.1.1
- – Rafter (1)
- – Strut (1)
- – Tie beam (1)
- – King post (1)
- – Queen post (1)
3.1.2 South African / Howe roof (1)
3.1.3 114 mm (1) x 38 mm (1) (2)
3.2 Any TWO requirements that roof trusses should meet:
- Sturdy enough to carry the roof covering safely
- Able to withstand wind and other forces that act on them
- Provide adequate height in rooms below the roof and ceiling assembly
- Should not allow the accumulation of rainwater upon the roof surface
- Neat and solid to enhance the appearance of the buildings (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.3
3.3.1 100 mm (1)
3.3.2 150 mm (1)
3.3.3 Reduce the fire hazard to neighbouring properties/structures. (1)
3.4 Any TWO advantages of the use of roof underlays:
- Acts as a secondary roof
- A weather shield during construction
- Waterproof and weatherproof
- Condensation barrier
- Dustproof
- Protects the building / structure
- Protects thermal insulation material
- Protects ceiling boards
- Superior wind uplifting strength prevents the lifting of tiles
- Vapour resistant
- High tensile resistance
- Cost effective
- High heat resistance (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.5
3.5.1 2 100 mm (1)
3.5.2 100 mm (1)
3.5.3 750 mm (1)
3.6
3.6.1 Landing (1)
3.6.2 Riser (1)
3.6.3 Balustrade (1)
3.7
3.7.1
- – Baluster (1)
- – Handrail (1)
3.7.2 Any ONE material that can be used for a handrail:
- Stainless steel
- Timber
- Plastic
- Concrete
- Similar answer (1)
3.8
3.8.1 True (1)
3.8.2 False (1)
3.8.3 True (1)
3.8.4 False (1)
3.9 Any TWO types of cast-in anchors:
- Hex-head bolt with washer
- L-bolt
- J-bolt
- Welded headed stud (Any 2 x 1) (2)
[30]
QUESTION 4: MATERIAL, EQUIPMENT AND TOOLS, EXCAVATIONS (SPECIFIC)
4.1
4.1.1 H (alternative for glass) (1)
4.1.2 C (tested in a laboratory) (1)
4.1.3 D (non-ferrous metal) (1)
4.1.4 G (packaging material) (1)
4.1.5 F (tested on the site) (1)
4.1.6 A (ferrous metal) (1)
4.2
4.2.1 Slump test (1)
4.2.2 Any TWO reasons for the purposes of the slump test:
- To test the density of concrete (percentage water)
- To determine the workability and consistency of batches
- To determine the slump of the mixture (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.2.3 Any ONE type of equipment that is used with the slump test:
- Metal base plate
- Cone
- Tamping rod
- Spirit level
- Ruler
- Measuring tape (Any 1 x 1) (1)
4.3 Any TWO purposes (reasons) for the curing of concrete:
- To help with the hydration of the cement
- Protect the concrete against quick drying
- To achieve optimal strength
- To achieve optimal hardness (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.4 Any TWO purposes (reasons) for the cladding of buildings:
- Aesthetic purposes
- Functional purposes
- Help to control weather elements (rain / wind)
- Prevent runoff (water) from penetrating the building (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.5 Any TWO types of cladding for buildings:
- Tile cladding
- Brick slip cladding
- Stone cladding
- Timber cladding
- Metal sheet cladding (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.6
4.6.1 Portable concrete vibrator(1)
4.6.2 Any ONE purpose of the portable concrete vibrator:
- To distract air out of the concrete
- To get the concrete into the corners of the formwork
- To get the concrete around the reinforcing
- To compact the concrete
- Similar answer (Any 1 x 1) (1)
4.6.3 Any TWO ways of maintaining the concrete vibrator:
- Maintain – lubricate and adjust to manufacturer’s instruction
- Clean after use and store in a safe, dry place
- Repair / replace damaged electrical cords
- Service regularly (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.7
4.7.1 True (1)
4.7.2 True (1)
4.7.3 True (1)
4.7.4 False (1)
4.8 Any THREE causes for the collapse of an excavation:
- Heavy rains
- Poor soil strata, structure or composition
- Sides not dug at the correct angle
- Improper use of formwork or shoring to support walls
- Vibration by machinery or heavy vehicles nearby
- Water seeping into the excavated area
- Contact with underground service
- Access to and exit from the excavation
- Soil slides due to cracks or loose soil (Any 3 x 1) (3)
4.9 Any TWO ways of making excavations safe during the night:
- Fencing
- Warning signs
- Warning lights (red or orange)
- Covering (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.10
4.10.1 1,5 m (1)
4.10.2 1,3 m (1)
4.10.3 600 mm (1)
4.11
4.11.1 Pile foundation(1)
4.11.2 Stepped foundation (1)
4.11.3 Strip foundation (1)
4.11.4 Raft foundation (1)
4.12 Any FOUR advantages for the use of pile foundations:
- Can be used in poor soil
- Can be used anywhere, even in water
- Larger base ensure stability
- Relatively quick and easy installation – if equipment is available
- Much time can be saved if prefabricated piles are used
- Can be quick and less expensive to produce
- Resist tensile stress well
- Can be manufactured elsewhere and transported to site
- Installation can continue in poor weather
- Length of piles can be adjusted
- Offers good resistance against moving soil (Any 4 x 1) (4)
[40]
QUESTION 5: BRICKWORK, GRAPHICS, PLASTER AND SCREED (SPECIFIC)
5.1
5.1.1 Cavity wall (1)
5.1.2 Stretcher bond (1)
5.1.3 50 mm (1)
5.2 THREE disadvantages of cavity walls:
- Require expert design
- Require highly skilled workmanship
- Constant supervision is needed
- Cavities are fitted with vertical damp proof coursing
- More expensive
- 50 mm tot 100 mm of the internal space is lost (Any 3 x 1) (3)
5.3
5.3.1 Wall ties (1)
5.3.2 Minimum 150 mm above ground level (1)
5.3.3 To remove wasted mortar (1)
5.3.4 Water / Moisture can escape / Warm air dries walls out (1)
5.4 Any TWO types of wall ties:
- Butterfly pattern
- Nylon wall tie
- Twisted pattern
- Double triangular pattern (Any 2 x 1) (2)
5.5
5.5.1 C (prepared layer beneath paving and bedding sand) (1)
5.5.2 D (final layer upon which paving is laid) (1)
5.5.3 A (natural soil on which the paving will be laid) (1)
5.6 Name THREE advantages of dry-laid paving:
- Very economical / Cheap
- Low initial installation cost
- Designed to accommodate the lifting of individual pavers
- Can be easily repaired
- User-friendly installation materials
- Easy to repair underground utilities
- Can also be designed as a permeable pavement
- No off-gassing (harmful gasses) installation products are used (Any 3 x 1) (3)
5.7 Any TWO reasons for construction failure of paving:
- Concrete haunch is too thin to support itself and crumble under pressure
- Too little weight to retain the structure and keep paving in place
- Bond between the haunch and edge units is weak and crumble easily
- Sub-base is not contained and will be washed out by groundwater (Any 2 x 1) (2)
5.8 Draw a neat sketch with FOUR (4) bricks in the herringbone pattern in the ANSWER BOOK. (Use own appropriate scale.) (5)
(5)
5.9
5.9.1
- – Roof tiles / Concrete roof tiles / Tiles (1)
- – Rafter (1)
- – Damp proof course (DPC) (1)
- – Tie beam (1)
5.9.2 Any TWO advantages of a closed eave:
- Provides an attractive appearance
- Prevent birds, vermin and insects from nesting in the roof
- Beam filling is not compulsory (Any 2 x 1) (2)
5.10 Discuss the difference between the rough and gauged arches: Any TWO – Rough arch:
- Inexpensive / economical
- Standard plaster bricks
- Wedge-shape joints
- Normally plastered (Any 2 x 1) (2)
Any TWO – Gauged arch:
- Looks neat and aesthetic
- Wedge-shape special bricks
- Uniform normal joints
- Normally unplaster (Any 2 x 1) (2)
5.11 Sand (1) and cement (1) (2)
5.12 Any ONE purpose of builder’s lime:
- Enhance the workability of the mixture
- Enhance the plasticity of the mixture
- Reduce cracking and crazing of plaster (Any 1 x 1) (1)
5.13 Any TWO types of screed:
- Dry screed
- Monolithic screed
- Bonded screed (Any 2 x 1) (2)
[40]
QUESTION 6: FORMWORK, REINFORCING, CONCRETE FLOORS AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
6.1 Any TWO materials to obtain a smoother finish on concrete:
- Plastic
- Metal sheeting
- Hardboard
- Fibreglass
- Similar answer (Any 2 x 1) (2)
6.2 Any TWO types of timber boards for formwork:
- Block board
- Laminated board
- Shutter board
- Plywood (Any 2 x 1) (2)
6.3 Any THREE properties of good formwork:
- Made accurately according to the dimensions indicated
- Sturdy enough to bear the mass of wet concrete without collapsing
- Able to bear the mass of workers and equipment
- Must be strong enough to provide enough support, without too much deflection, until the concrete has set
- Must withstand the pressure of the compacting and the vibrating of the concrete
- Formwork should be easy to repair on site
- Secured with wire nails, where some should protrude for easy extracting
- Secured with bolts from 13 mm to 19 mm in diameter
- Should be sealed properly so that the concrete does not leak and form honeycombs or fins
- Should be free of dirt (sawdust or releasing agents)
- Quick and simple to erect, mechanically or by hand
- Ensure the correct cover depth for reinforcing, to prevent structural failure
- Fit plywood onto laggings if a smooth finish is required
- Remove when the concrete has cured and is able to the support load
- Should be easy to remove without damaging the formwork or concrete
- Close-fitting along seams and joints
- Made from recyclable components (Any 3 x 1) (3)
6.4
6.4.1
- – Hollow-core concrete blocks / Hollow concrete block / Block (1)
- – Pre-stressed concrete rib / Precast ribs / Rib (1)
6.4.2 Rib-and-block floor (1)
6.4.3 Any ONE disadvantage of the rib-and-block floor:
- Requires mechanical handling on the site
- Requires manual labour to place blocks between the ribs (Any 1 x 1) (1)
6.5
6.5.1 High tensile steel (High yield steel) (1)
6.5.2 10 Rods (1)
6.5.3 250 mm (1)
6.6
6.6.1 Shear force / Shearing (1)
6.6.2 Compression force / Compression stress (1)
6.7 Any THREE properties (requirements) for reinforced steel bars:
- Free of salt spray, mud, splinters and any oiliness
- Completely covered in concrete to protect it against rust and fire hazards
- Resistant to tensile stress
- Easy to bend into shape
- Able to bind firmly with concrete
- Of limited expansion prevent tension when the temperature fluctuates
- Readily available and affordable
- Must be rustproof, otherwise it will impair binding (Any 3 x 1) (3)
6.8 Any TWO purposes of the cover depth:
- To protect steel against corrosion
- To ensure adequate bonding between the steel and concrete
- To ensure adequate protection of steel in the event of a fire (Any 2 x 1) (2)
6.9 Foundation strips of a garage is 6 250 x 2 750 (inside measurements). The foundation is 600 mm wide and 200 mm thick.
6.9.1 Calculate the centreline of the foundation:
- 2 / 6 250 = 12 500
2 / 2 750 = 5 500
18 000
Plus corners: 4 / 600 = 2 400
20 400 of 20,4 m (5)
6.9.2 Calculate the volume of concrete needed.
- Volume = length x width x thickness
= 20,4 m x 0,6 m x 0,2 m
= 2,448 m³ of 2,45 m³ (4)
[30]
TOTAL: 200
ANSWER SHEET A
2.1 FIGURE 2.1 shows the floorplan of a storeroom on scale 1 : 50.
Draw the south elevation on scale 1 : 50 on ANSWER SHEET A from the given ground level. (29)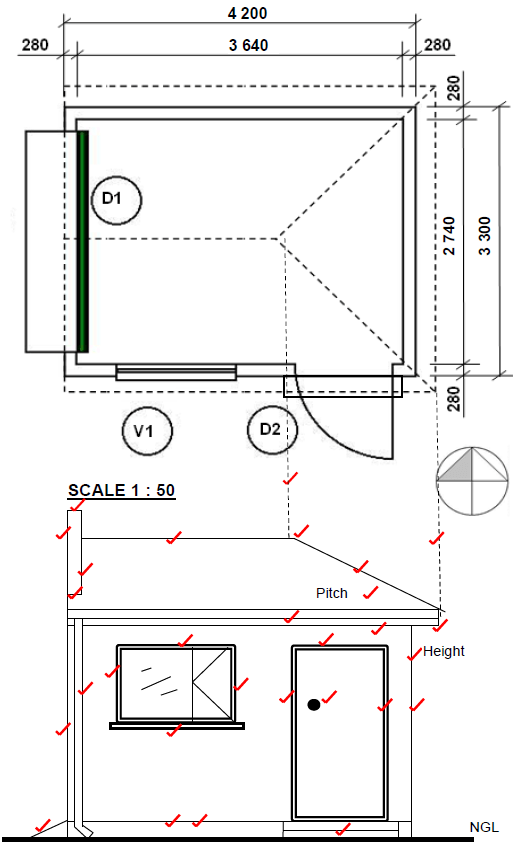
Floor level | 2 | |
Wall | 3 | |
Window | 3 | |
Window sill | 1 | |
Door | 4 | |
Stairs | 1 | |
Ramp | 1 | |
Fascial board | 2 | |
Gutter | 1 | |
Down pipe | 1 | |
Gable end | 4 | |
Hipped end | 3 | |
Roof height | 3 | |
TOTAL: | 29 |
Civil Technology: Construction Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
REQUIREMENTS:
- ANSWER BOOK
- Drawing instruments
- A non-programmable pocket calculator
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions: TWO questions are generic and FOUR questions are subject specific.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Answer each question as a whole. Do NOT separate subsections of questions.
- Start the answer to EACH question on a NEW page.
- Do NOT write in the margins of the ANSWER BOOK.
- You may use sketches to illustrate your answers.
- Write ALL calculations and answers in the ANSWER BOOK or on the attached ANSWER SHEETS.
- Use the mark allocation as a guide to the length of your answers.
- Make drawings and sketches in pencil, fully dimensioned and neatly finished off with descriptive titles and notes to conform to the SANS/SABS Code of Practice for Building Drawings.
- For the purpose of this question paper, the size of a brick should be taken as 220 mm x 110 mm x 75 mm.
- Use your own discretion where dimensions and/or details have been omitted.
- Answer QUESTION 2.1 on the attached ANSWER SHEET by using drawing instruments where necessary.
- Write your NAME on every ANSWER SHEET and hand them in with your ANSWER BOOK, whether you have answered the question or not.
- Drawings in the question paper are NOT to scale due to electronic transfer.
- Google images was used as the source of all photographs and pictures.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: SAFETY AND MATERIALS (GENERIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
1.1 Answer the following questions regarding the scaffolding in FIGURE 1.1.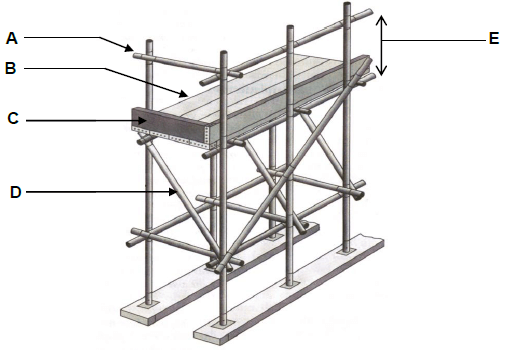
FIGURE 1.1
1.1.1 Name parts A to D. (4 x 1) (4)
1.1.2 What is the minimum width and thickness of part B? (2 x 1) (2)
1.1.3 What is the purpose of part D? (1)
1.1.4 What is the minimum and maximum measurements of E? (2 x 1) (2)
1.2 Describe the regulation that is applicable to the following facets when material is handled on a construction site:
1.2.1 Placing of building rubble (1)
1.2.2 When material is transported to higher surfaces (1)
1.3 Name THREE methods to ensure that a ladder is stable when it is used. (3 x 1) (3)
1.4 What are the horizontal parts of a ladder called? (1)
1.5 Explain the process of electroplating of a metal. (2)
1.6 Explain the purpose of electroplating of a metal. (1)
1.7 Name TWO advantages of galvanising. (2 x 1) (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS, JOINING AND EQUIPMENT (GENERIC)
2.1 FIGURE 2.1 on ANSWER SHEET A shows a floorplan of a storeroom on scale 1 : 50. Draw the south elevation on scale 1 : 50 on ANSWER SHEET A from the given ground level, by using the following information:
- The floor level height is 200 mm above the ground level
- Wall height is 2 600 mm from the floor level to the ceiling
- Window 1 is 1 200 x 900 mm
- Door 1 is 1 100 x 2 100 mm
- Doorknob
- Roof construction pitch is 30°
- Show construction lines to determine the roof height
- Gable end at the west elevation
- Hippen end at the east elevation
Use the marks table on ANSWER SHEET A as reference. (29)
2.2 Identify the type of nuts in FIGURES A to C.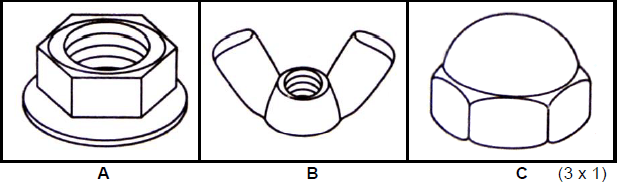
(3 x 1) (3)
2.3 Name TWO properties of rawl bolts. (2 x 1) (2)
2.4 Discuss how the height of the tripod should be set when a dumpy level is set up. (3)
2.5 Name THREE materials that can be detected in walls by a multi-detector. (3 x 1) (3)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION A: 60
QUESTION 3: ROOFS, STAIRCASES AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 Answer the following questions with regard to the roof truss in FIGURE 3.1.
FIGURE 3.1
3.1.1 Name parts A to E. (5 x 1) (5)
3.1.2 Identify the type of roof truss. (1)
3.1.3 What are the measurements of the timber used in FIGURE 3.1? (2 x 1) (2)
3.2 Name TWO requirements that roof trusses should meet. (2 x 1) (2)
3.3 Answer the following questions regarding thatched roofs.
3.3.1 What is the minimum diameter of roof poles? (1)
3.3.2 What is the thickness of the bundles, dry thatch that is fixed to the roof? (1)
3.3.3 Why should the thatched roof overhangs be constructed at least 4,5 m from any neighbouring property/structures? (1)
3.4 Name TWO advantages of the use of roof underlay. (2 x 1) (2)
3.5 Provide the MEASUREMENT for the following descriptions of staircases:
3.5.1 The minimum measurement from the pitch line to the ceiling (1)
3.5.2 The maximum measurement of the gaps between the vertical posts (1)
3.5.3 The minimum allowed width of a stair (1)
3.6 Provide ONE term for the following descriptions of staircases:
3.6.1 A level area between two flights of stairs (1)
3.6.2 The vertical part of a stair (1)
3.6.3 A combination of balusters (1)
3.7 Answer the following questions regarding the staircase in FIGURE 3.7.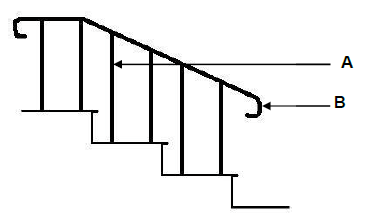
FIGURE 3.7
3.7.1 Name parts A and B. (2 x 1) (2)
3.7.2 Name ONE material that can be used at part B. (1)
3.8 Identify whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE.
3.8.1 Galvanised steel straps cannot rust. (1)
3.8.2 Galvanised steel straps must be at an anchor depth of 300 mm for heavy roofs, if the wall is built with hollow concrete blocks. (1)
3.8.3 A nail plate joins the roof truss to the wall plate. (1)
3.8.4 A cornice joins the wall plate to the wall. (1)
3.9 Name TWO types of cast-in anchors. (2 x 1) (2)
[30]
QUESTION 4: MATERIAL, EQUIPMENT AND TOOLS, EXCAVATIONS AND FOUNDATIONS (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 Choose a description from COLUMN B that best matches with an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question numbers
(4.1.1 to 4.1.6) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example: 4.1.7 J.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
4.1.1 | Perspex | A | ferrous metal |
4.1.2 | Cube test | B | dipped in molten zinc |
4.1.3 | Aluminium | C | tested in a laboratory |
4.1.4 | Polystyrene | D | non-ferrous metal |
4.1.5 | Slump test | E | basic sealant |
4.1.6 | Ductile cast iron | F | tested on the site |
G | packaging material | ||
H | alternative for glass | ||
I | highly toxic | ||
(6 x 1) (6)
4.2 Answer the following questions regarding the test in FIGURE 4.2.
FIGURE 4.2
4.2.1 Is this the slump test or the cube test? (1)
4.2.2 Name TWO purposes of this test. (2 x 1) (2)
4.2.3 Identify ONE type of tool or equipment used in FIGURE 4.2. (1)
4.3 Explain the purpose of the curing of concrete. (2)
4.4 Explain the purpose of cladding at buildings. (2)
4.5 Name TWO types of materials that can be used for the cladding of a building. (2 x 1) (2)
4.6 Answer the following questions regarding the construction machine in FIGURE 4.6.
FIGURE 4.6
4.6.1 Identify the type of machine. (1)
4.6.2 Name ONE purpose of this machine. (1)
4.6.3 Name TWO ways of maintaining the machine. (2 x 1) (2)
4.7 Identify the following statements as TRUE or FALSE.
4.7.1 At excavations all workers must wear a hard hat. (1)
4.7.2 No person is allowed to work on their own at an excavation site. (1)
4.7.3 Ladders or scaffolding must be used for accessing deep trenches. (1)
4.7.4 Weekly inspections are necessary at excavations. (1)
4.8 Name THREE causes for the collapse of an excavation. (3 x 1) (3)
4.9 Name TWO ways of making excavations safe at night. (2 x 1) (2)
4.10 Provide the MEASUREMENT in the following statements of excavations.
4.10.1 From what depth should bracing be used? (1)
4.10.2 From what depth should testing be done for atmospheric gasses? (1)
4.10.3 How far should excavated soil be away from the excavation? (1)
4.11 Choose the correct answer from the block below for the following foundation descriptions.
| strip foundation; stepped foundation; block foundation; raft foundation; pile foundation |
4.11.1 The depth of the foundation is more than three times its breadth (1)
4.11.2 Used where sites are not level (1)
4.11.3 Continuous concrete strip that is casted in a trench (1)
4.11.4 The strip foundations and the floor slab are combined (1)
4.12 Name FOUR advantages of using pile foundations. (4 x 1) (4)
[40]
QUESTION 5: BRICKWORK, GRAPHICS, PLASTER AND SCREED (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
5.1 Answer the following questions regarding the wall construction in FIGURE 5.1.
FIGURE 5.1
5.1.1 Identify the type of wall construction. (1)
5.1.2 In what type of bond has this wall been built? (1)
5.1.3 What is the minimum width of the space between the skins? (1)
5.2 Name THREE disadvantages of cavity walls. (3 x 1) (3)
5.3 Answer the following questions regarding cavity walls.
5.3.1 What joins the two walls together? (1)
5.3.2 At what height should the damp proof course be placed in a wall? (1)
5.3.3 What is the purpose of inspection holes? (1)
5.3.4 What is the purpose of weep holes? (1)
5.4 Name TWO types of wall ties. (2 x 1) (2)
5.5 Choose a description from COLUMN B that best matches with an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers
(5.5.1 to 5.5.3) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 5.5.4 E.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
| 5.5.1 Sub-grade |
|
| 5.5.2 Bedding sand | |
| 5.5.3 Sub-base | |
(3 x 1) (3)
5.6 Name THREE advantages of dry-laid paving. (3 x 1) (3)
5.7 Name TWO reasons for construction failure of paving. (2 x 1) (2)
5.8 Draw a neat sketch with FOUR (4) bricks of the herringbone paving pattern in the ANSWER BOOK. (Use own suitable scale.) (5)
5.9 Answer the following questions regarding the roof construction in FIGURE 5.9.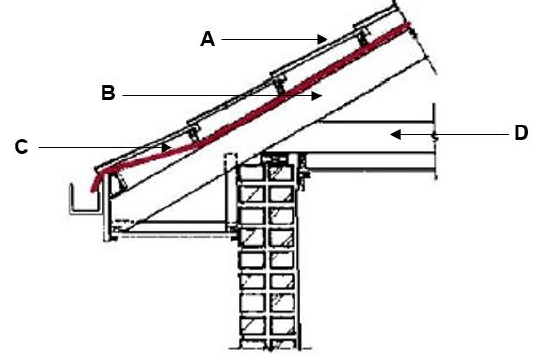
FIGURE 5.9
5.9.1 Name parts A to D. (4 x 1) (4)
5.9.2 Name TWO advantages of closed eaves. (2 x 1) (2)
5.10 Discuss the difference between gauged arches and rough arches. (4)
5.11 Name the ingredients of screed (water and lime excluded). (2)
5.12 What is the purpose of builder’s lime in a plaster mixture? (1)
5.13 Name TWO types of screed layers. (2 x 1) (2)
[40]
QUESTION 6: FORMWORK, REINFORCEMENT, CONCRETE FLOORS AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
6.1 Name TWO materials that can be used to line the formwork, in order to obtain a smoother finish of concrete. (2 x 1) (2)
6.2 Name TWO types of timber boards that can be used for formwork. (2 x 1) (2)
6.3 Name THREE properties of good formwork. (3 x 1) (3)
6.4 Answer the following questions regarding the floor construction in FIGURE 6.4.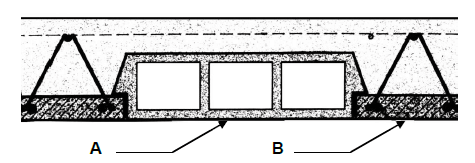
FIGURE 6.4
6.4.1 Name parts A and B. (2 x 1) (2)
6.4.2 Identify the type of concrete floor. (1)
6.4.3 Name ONE disadvantage of this floor type. (1)
6.5 Answer the following questions regarding the rod / bar code in FIGURE 6.5.
| Rod / bar code: 10Y12-02-250 |
FIGURE 6.5
6.5.1 What type of steel is used? (1)
6.5.2 How many rods are required? (1)
6.5.3 What is spacing of the rods? (1)
6.6 What forces are counteracted by the following parts in a concrete beam?
6.6.1 Shear bars (1)
6.6.2 Anchor bars (1)
6.7 Name THREE properties (requirements) of reinforcing steel bars. (3 x 1) (3)
6.8 Name TWO purposes of the cover depth for reinforcing in concrete work. (2 x 1) (2)
6.9 FIGURE 6.9 shows the inside measurements of the foundation strips for a garage. The foundation is 600 mm wide and 200 mm thick.
Answer the following questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
Table format is NOT compulsory. (Show ALL formulas and steps.)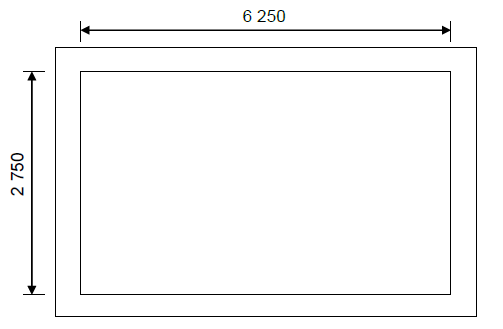
FIGURE 6.9
6.9.1 Calculate the centreline of the foundation. (5)
6.9.2 Calculate the volume of concrete needed. (4)
[30]
TOTAL: 200
ANSWER SHEET A
2.1 FIGURE 2.1 on ANSWER SHEET A shows the floorplan of a storeroom on scale 1 : 50. Draw the south elevation on scale 1 : 50 on ANSWER SHEET A
from the given ground level. (29)
![]()
Floor level | 2 | |
Wall | 3 | |
Window | 3 | |
Window sill | 1 | |
Door | 4 | |
Stair | 1 | |
Ramp | 1 | |
Fascia board | 2 | |
Gutter | 1 | |
Down pipe | 1 | |
Gable end | 4 | |
Hipped end | 3 | |
Roof height | 3 | |
TOTAL: | 29 |
Civil Technology: Woodworking Memorandum - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE MARKERS
- Markers should:
- Familiarise themselves with the question and answer before evaluating the responses of candidates.
- Always interpret the responses of the candidates within the context of the question.
- Consider any relevant and acceptable answer during pre-marking but should strictly adhere to the answers after finalisation of the marking guideline.
- There are two approaches to answering questions, these are (1) to describe and (2) to explain.
- If a candidate is required to explain e.g., a process in 4 steps, only the first 4 responses should be considered.
- If, however a candidate is required to e.g., explain or describe how to transfer heights from one point to another using a transparent pipe level we need to consider that candidates may write a long description not necessarily well organised as an intellectual response may do. In this case the marker needs to evaluate the complete statement to judge if the candidate explained the required outcome satisfactorily and allocate marks on merit. The marker should apply his/her professional judgement with these types of questions.
- Mark what the candidate wrote and do not award marks for answers that the marker thinks the candidate meant with what was written.
- Indicate the tick or cross right at the position where the mark needs to be awarded or where the candidate made the error.
- Accept the letter corresponding with the correct answer as well as the answer written in full in multiple-choice questions.
- Accept incorrect spelling in one-word answers unless the spelling changes the meaning of the answer.
- For calculations:
- A mark is only awarded if the correct unit is written next to the answer.
- If TWO marks are awarded ONE mark is awarded for the answer and ONE mark for the correct unit.
- Where the candidate made a principle error e.g. added instead of multiplying, no marks will be awarded for the steps. If the answer is correct according to what the candidate did, the mark for the answer can be awarded for the application of skills.
- Where an incorrect answer could be carried over to the next step, the first answer will be deemed incorrect. However, should the incorrect answer be carried over correctly, the marker has to recalculate the values, using the incorrect answer from the first calculation. If correctly used, the candidate should receive the full marks for subsequent calculations.
- Markers should consider when and where a candidate has rounded off in a calculation, as well as the subsequent effect it has on the final answer obtained. The calculation should therefore be awarded marks on merit.
- Alternative methods of calculations must be considered, provided that the correct answer is obtained.
- When marking drawings:
- The member for which the mark should be awarded should be drawn correctly in the correct position to receive a mark.
- A member incorrectly drawn but wrongfully repeated in another position will be awarded the mark for the repeated incorrect member provided that the marking guideline provide for TWO or more marks for that member (positive marking).
- Marks can only be awarded for a label if the label is correctly indicating the correct member.
- Scale drawings should always be marked using an appropriate mask.
When a candidate drew the wrong drawing e.g.:
- A horizontal section instead of a vertical section, no marks will be allocated to the drawing as the candidate did not respond to the expected outcome.
- An orthographic view instead of sectional view, no marks will be allocated to the drawing as the candidate did not respond to the expected outcome.
- An orthographic view instead of an isometric view, no marks will be allocated to the drawing as the candidate did not respond to the expected outcome.
- If the incorrect drawing was drawn, the candidate can be awarded for only what was asked but mark/s for the correctness of the drawing will not be awarded e.g., if a King Post roof truss was asked in the question, and candidate drew
SA-Howe Truss.
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: SAFETY AND MATERIALS (GENERIC)
1.1 Answer the following question regarding scaffolding.
1.1.1
- – Guardrail (1)
- – Planks / Working platform (1)
- – Kickboard / Toe-board (1)
- – Brace (1) (4)
1.1.2 228 mm (1) x 38 mm (1) (2)
1.1.3 Provides stability to the scaffolding. (1)
1.1.4 Minimum = 900 mm (1) and maximum = 1 000 mm (1). (2)
1.2
1.2.1 Placing of building rubble:
- May not obstruct access or exits
- Safe place
- Regularly removed. (Any 1 x 1) (1)
1.2.2 When materials are transported to higher surfaces:
- Workers must maintain a safe distance /
- Overhead protection. (Any 1 x 1) (1)
1.3 Any THREE:
- Non-skid devices on the bottoms
- Hooks at the upper ends
- Lashed, secure or fastened
- Held by someone (Any 3 x 1) (3)
1.4 Rungs (1)
1.5 The coating of a metal by electrolysis (1) with a thin layer of another metal.(1) (2)
1.6 To improve the metal’s corrosion resistance. (1)
1.7 Any TWO:
- Adds strength to the metal
- Galvanised metals are thicker
- Galvanised nails and screws prevents staining (Any 2 x 1) (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS, JOINING AND EQUIPMENT (GENERIC)
2.1 FIGURE 2.1 on ANSWER SHEET A shows a floorplan of a storeroom on scale 1 : 50. Draw the south elevation on scale 1 : 50 on ANSWER SHEET A from the given ground level, by using the following information:
- The floor level height is 200 mm above the ground level
- Wall height is 2 600 mm from the floor level to the ceiling
- Window 1 is 1 200 x 900 mm
- Door 1 is 1 100 x 2 100 mm
- Doorknob
- Roof construction pitch is 30°
- Show construction lines to determine the roof height
- Gable end at the west elevation
- Hippen end at the east elevation
Use the marks table on ANSWER SHEET A as reference. (29)
2.2
- – Nut with built-in washer like a flange (1)
- – Wing nut (1)
- – Domed top nut (1) (3)
2.3 Any TWO:
- Resist pull-out failure
- Excellent carrying capacity
- Tolerance to a variance in the hole size (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.4 Must be set-up that the telescope (1) is placed on a comfortable sightline, (1) to prevent a person from bending or stretching over the telescope and tripod. (1)
(3)
2.5 Any THREE:
- Wiring
- Wood
- Metal studs
- Copper pipes
- Plumbing work (Any 3 x 1) (3)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION A: 60
QUESTION 3: CASEMENTS, CUPBOARDS, WALL-PANELLING AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
3.1
3.1.1 520 mm – 570 mm (1)
3.1.2 Rebate (1)
3.1.3 Cornice (1)
3.2
3.2.1
- – Top rail
- – Drip groove/throat
- – Transom
- – Drip groove/throat
- – Bottom rail of fanlight
- – Putty
- – Ovolo moulding
- – Windowpane/glass (8 x 1) (8)
3.2.2 Prevents rainwater being blown into the casement and penetrating the room. (1)
3.3
- – Top shelf/storage space
- – Hanging space
- – Shelving
- – Drawer unit (4 x 1) (4)
3.4
- Melamine is waterproof
- Easy to clean
- Durable
- Smooth finish
- Improves appearance (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.5 Built-in-cupboards fastened against a wall. (1) Free standing it is moveable and can stand anywhere. (2)
3.6
3.6.1
- – 110 mm thick wall
- – Horizontal rough grounds
- – Tongue-and-groove board
- – Moulded skirting
- – Quadrant
- – Floor covering (6 x 1) (6)
3.6.2
- No wall plastering needed
- Serves to enhance the aesthetic appeal of a room (2)
3.6.3 Using nails or wall anchors or screws (1)
[30]
QUESTION 4: ROOFS, CEILINGS, TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT, AND MATERIALS (SPECIFIC)
4.1
4.1.1 C (1)
4.1.2 A (1)
4.1.3 D (1)
4.1.4 E (1)
4.1.5 F (1)
4.2
- Gypsym ceiling board
- Coverstrip
- Trapdoor panel
- Tie beam (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.3
- Sand the surface with different grade of sandpaper
- Sand until surface is free of scratches and smooth.
- Remove all the dust. (3)
4.4
- Truss hanger is a U-shaped fastener; the roof timber member rest in the ‘U’. (1)
- Gang nails is a steel plate punched to form a nail pattern and is prefabricated to be used in roof trusses. (1)
4.5
- Strength
- Density (2)
4.6
4.6.1 Hipped roofs are pitched roofs that slope downward on all sides. (1)
4.6.2 Hipped roof with valley; A valley is formed when two inclined roof surfaces meet at an internal angle. (1)
4.7 Always wear safety goggles.
- Wear a dusk mask when using the belt sander.
- Inspect the power cord regularly for damage.
- A void carrying the machine by the cord. (2)
4.8
4.8.1 Mechanical and visual grading are two methods. The head of each timber board is marked in cinnamon red letters and numbers. (2)
4.8.2 The strength (2)
4.8.3 South African Bureau of Standards (1)
4.9
4.9.1
- – Rafter joist
- – Hip/corner rafter
- – Wall plate
- – Ceiling joist
- – Jack rafter (5)
4.9.2 A roof with two slanting ends, sometimes across a short, flat gable. (2)
4.10
- Resist weather conditions such as wind and rain.
- Look durable and enhances the appearance of the building.
- Is fire resistant.
- Provides insulation against heat and cold. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.11
- Batten 38 mm x 38 mm, placed and attached at right angles to the rafters onto which concrete tiles or slates are fixed. (1)
- Purlin 50 mm x 76 mm, placed and attached perpendicular to the roof sheeting materials. (1)
4.12
- Provides a highly effective barrier against the ingress of wind-driven rain and dust.
- Allows the rain that is blown in under the tiles to flow to the gutters.
- Lowers the suction pressure under the tiles and reduces the risk of wind lifting the tiles.
- Acts as a thermal barrier by improving insulation. (6)
[40]
QUESTION 5: CENTRING, FORMWORK, SHORING AND GRAPHICS AS MEANS OF COMMUNICATION (SPECIFIC)
5.1
- Block board
- Laminated board
- Shutter board and
- Plywood (Any 1 x 1) (1)
5.2
5.2.1
- For the placing of the reinforcing bars.
- To facilitate the casting of the concrete.
- To ensure that it is thoroughly rammed into the column and the fourth side can consist of shorter lengths. (3)
5.2.2
- – Sides
- – Wedges
- – Yokes
- – Cleats
- – Bolts (5)
5.2.3 To secure the formwork. (1)
5.3 5.3.1 Nails used to secure the joint between the prop and needle. (1)
5.3.2 Made of timber to spread the weight transferred by the props over a wider area. (1)
5.4 To provide temporary support to two parallel walls that are located between 9 metres and 15 metres apart, where one or both walls show signs of failure. (2)
5.5 Temporary timber framework is used to support a stone, brick or concrete arch during construction. (3)
5.6
- – Ribs
- – Ties
- – Bearer
- – Laggings
- – Folding wedges
- – Horizontal brace (6)
5.7
5.7.1 Rib and block / Block and beam construction. (2)
5.7.2
- – In-situ concrete layer
- – Pre-cast hollow-core concrete blocks
- – Steel mat (3)
5.7.3 It is very strong and can carry heavy loads or weight. (2)
[30]
QUESTION 6: SUSPENDED FLOOR, STAIRCASES, IRON MONGERY DOORS AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
6.1 A vertical member supporting one end of a handrail at the top or bottom of a flight of stairs, the strings and the handrails are fixed to it. (2)
6.2 Flight of stairs with a landing:
- Runs in one direction and are uninterrupted flights of stairs that directly connects two floors.
- Regulations stipulate that if there are more than 16 walkways in a straight step arm, landings must be installed.
- The signs allow the user to rest during the ascent and are required where there is a steep rise between floor levels. (3)
Stairwell with a half-landing:
- Also known as U-shaped stairs.
- Landings serve as a resting place.
- Has two parallel flights of stairs that are connected by a landing that makes a 180° turn when one ascends or descends.
- Takes up less floor space than straight stairs. (3)
6.3 Overhang or edge of the tread and frequently projects over the riser below it. (2)
6.4 Night latch (1)
6.5
6.5.1 Mortised into the door stile (1)
6.5.2 Screwed onto the doorjamb (1)
6.5.3 Onto the doorjamb (1)
6.5.4 Onto the doorjamb (1)
6.6 Clearance to allow shrinkage and expansion of wood. (1)
6.7
6.7.1
- – Brace
- – V-tongue-and-groove battens
- – Stile (3)
6.7.2 To prevent the sagging of the door. (1)
6.7.3 Gives a neat appearance to the outside of the frame members. (1)
6.8 
| ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK |
| Walls | 2 |
| Frame profile of door | 1 |
| Jamb lining profile | 1 |
| Title | 1 |
| Architraves | 1 |
| TOTAL: | 6 |
6.9
6.9.1 Double stub tenon and mortise joint (1)
6.9.2
- – Bottom rail
- – Haunch
- – Double stub tenon
- – Stile
- – Groove
- – Roove (6)
6.9.3 Thickness is 1/3 of thickness of wood. (1)
6.9.4 To join the bottom rail and stile of a panel door. (1)
6.10 Fixed or hinged (2)
[40]
TOTAL: 200
ANSWER SHEET A
2.1 FIGURE 2.1 shows the floorplan of a storeroom on scale 1 : 50. Draw the south elevation on scale 1 : 50 on ANSWER SHEET A from
the given ground level. (29)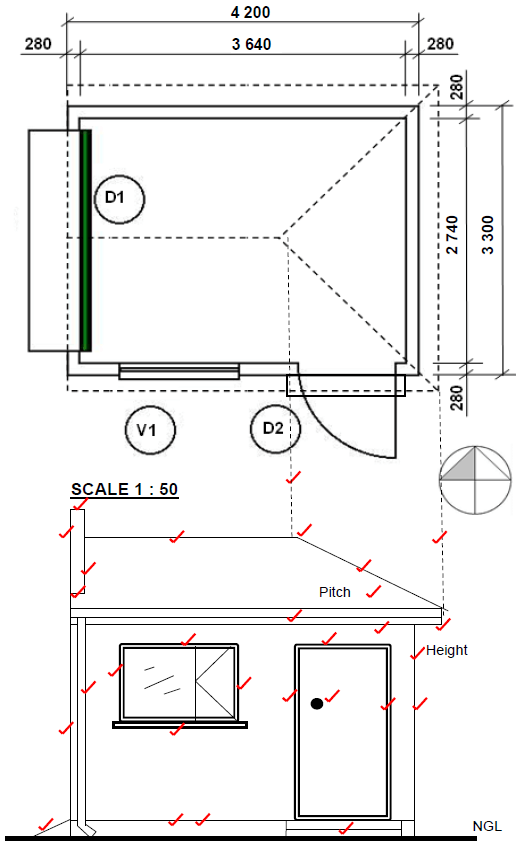
Floor level | 2 | |
Wall | 3 | |
Window | 3 | |
Windowsill | 1 | |
Door | 4 | |
Stairs | 1 | |
Ramp | 1 | |
Fascial board | 2 | |
Gutter | 1 | |
Down pipe | 1 | |
Gable end | 4 | |
Hipped end | 3 | |
Roof height | 3 | |
TOTAL: | 29 |
Computer Applications Technology Paper 2 Memorandum - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
SUGGESTIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS TO MARKERS |
|
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A | |||||
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE | QUESTION 2: MATCHING ITEMS | ||||
1.1 | A | 2.1 | S | ||
1.2 | D | 2.2 | E | ||
1.3 | B | 2.3 | L | ||
1.4 | D | 2.4 | K | ||
1.5 | A | 2.5 | A | ||
1.6 | B | 2.6 | M | ||
1.7 | A | 2.7 | B | ||
1.8 | C | 2.8 | I | ||
1.9 | A | 2.9 | D | ||
1.10 | C | 2.10 | O | ||
[10] | [10] | ||||
QUESTION 3: TRUE/FALSE ITEM | |||||
3.1 | False, Footer | (1) | |||
3.2 | False, Radio button | (1) | |||
3.3 | True | (1) | |||
3.4 | True | (1) | |||
3.5 | False, Size/type | (1) | |||
[5] | |||||
TOTAL SECTION A: | 25 | ||||
SECTION B
QUESTION 4: SYSTEM TECHNOLOGIES
4.1 | 4.1.1 | To hold data and programs being processed (i.e. temporarily / while the computer is on) | 1 | 2 |
4.1.2 | Any ONE difference (besides difference in function):
NOTE TO MARKER: Do not accept ‘RAM = volatile vs. storage = permanent’, or ‘much less RAM is required than storage’, since these relate directly to function | 1 | ||
4.2 | Any TWO input devices:
| 2 | 2 | |
4.3 | Any TWO reasons:
| 2 | 2 | |
4.4 | Any TWO trouble-shooting techniques:
| 2 | 2 | |
4.5 | Any TWO ways:
| 2 | 2 | |
4.6 | Any ONE reason:
| 1 | 1 | |
4.7 | Any TWO limitations:
| 2 | 2 | |
4.8 | Any TWO pieces of equipment:
| 2 | 2 | |
4.9 | Any ONE example:
| 1 | 1 | |
4.10 | 4.10.1 | A drone is a flying robot that can be remotely controlled or fly autonomously through software-controlled flight plans. | 1 | 3 |
4.10.2 | Any TWO benefits:
| 2 | ||
4.11 | 4.11.1 | Performs all the processing / calculations / comparisons / decisions in the computer. | 1 | |
4.11.2 | Any ONE method:
| 1 | ||
4.11.3 | Any ONE requirement (besides processor and memory):
NOTE TO MARKER: Accept specific requirements, e.g. 1 GB available hard disk space, 1024 x 768 minimum resolution, 512 MB dedicated video RAM | 1 | 3 | |
4.12 | Any THREE advantages:
| 3 | 3 | |
[25] | ||||
QUESTION 5: INTERNET AND NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES
5.1 | 5.1.1 | Any ONE reason:
| 1 | 4 |
5.1.2 | Any ONE reason:
| 1 | ||
5.1.3 | Any TWO reasons:
| 2 | ||
5.2 | 5.2.1 | Any TWO services:
| 2 | 6 |
5.2.2 | Any TWO benefits:
| 2 | ||
5.2.3 | Connects devices to one another and directs traffic between devices | 2 | ||
5.3 | 5.3.1 | Any ONE medium:
| 1 | 3 |
5.3.2 | Any TWO reasons:
| 2 |
5.4 | Any TWO disadvantages:
| 2 | 2 |
[15] |
QUESTION 6: INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
6.1 | 6.1.1 | Describe what needs to be done in your own words, taking into account what the problem is that you need to investigate and what the investigation would be about. | 1 | 2 |
6.1.2 | Any ONE:
| 1 | ||
6.2 | Any TWO reasons:
| 2 | 2 | |
6.3 | 6.3.1 | Any ONE limitation:
| 1 | 3 |
6.3.2 | Any TWO benefits:
| 2 | ||
6.4 | Any THREE reasons:
| 3 | 3 | |
[10] | ||||
QUESTION 7: SOCIAL IMPLICATIONS
7.1 | 7.1.1 | Any TWO indications:
| 2 | 5 |
7.1.2 | It might be a virus. | 1 | ||
7.1.3 | Any TWO types:
| 2 | ||
7.2 | Geotagging refers to and including the position/GPS coordinates ?of where the photo was taken in the metadata/with the file. ? | 2 | 2 | |
7.3 | Any TWO disadvantages:
NOTE TO MARKER: Do NOT accept any answers relating to costs. | 2 | 2 | |
7.4 | Any ONE indication:
| 1 | 1 | |
[10] | ||||
QUESTION 8: SOLUTION DEVELOPMENT
8.1 | Open Footnotes grouping OR Right click on footnote | 3 | 3 |
8.2 | Cell B6: | 3 | 3 |
8.3 | ExaminationDate field validation rule:
#15/04/2018# OR <=#15/04/2018# OR <#16/04/2018# | 3 | 3 |
8.4 | <hr color = "red" üwidth =50%> | 2 | 2 |
8.5 | Autofill | 1 | 1 |
8.6 | Any THREE:
| 3 | 3 |
[15] |
TOTAL SECTION B: 75
SECTION C: INTEGRATED SCENARIO QUESTION 9
9.1 | Any TWO IT/CAT related jobs:
NOTE TO MARKER: Do not accept: Programmer or any job related to database/database administrator. | 2 | 2 | |
9.2 | 9.2.1 | The use of personal characteristics ü to authenticate the identity of a person. NOTE TO MARKER: Also accept: Use parts of the body for access control | 2 | 3 |
9.2.2 | Any ONE example:
| 1 | ||
9.3 | Any TWO disadvantages:
NOTE TO MARKER: Any suitable answer. | 2 | 2 | |
9.4 | 9.4.1 | Hard drive space/storage ü reserved by the operating system to be used as RAM/memory. NOTE TO MARKER: Also accept for 2 marks: Hard drive space to be used when the RAM is full. | 1 | 3 |
9.4.2 | Operating system | 1 | ||
9.4.3 | Any ONE:
| 1 | ||
9.5 | 9.5.1 |
| 2 | 4 |
9.5.2 | Any TWO disadvantages:
| 2 | ||
9.6 | 9.6.1 | Any THREE ways:
NOTE TO MARKER: Any suitable answer. | 3 | 6 |
9.6.2 | Any TWO reasons:
| 2 | ||
9.6.3 | Piggybacking | 1 |
9.7 | 9.7.1 | Any TWO ways:
| 2 | 5 |
9.7.2 | Any TWO ways:
| 2 | ||
9.7.3 | Cryptocurrency ü (Bitcoins) | 1 | ||
[25] |
QUESTION 10
10.1 | 10.1.1 | Acceptable Use Policy | 1 | 3 |
10.1.2 | To provide the user of a network environment with the rights and responsibilities ü when using their ICT resources/ network. | 2 | ||
10.2 | Ensure that all devices ü contain the most up to date version of the same document. | 2 | 2 | |
10.3 | 10.3.1 | Any TWO skills:
| 2 | 4 |
10.3.2 | Any TWO factors:
| 2 | ||
10.4 | 10.4.1 | Additional data/information on the video that is saved with the file. | 1 | 2 |
10.4.2 | Any ONE format:
NOTE TO MARKER: Also accept any other acceptable compression format | 1 | ||
10.5 | 10.5.1 | Online seminars | 1 | 3 |
10.5.2 | Any TWO ways:
| 2 | ||
10.6 | 10.6.1 | Encryption is the process of converting information or data into a code ü to prevent unauthorized access. NOTE TO MARKER: Also accept any other acceptable answer. | 2 | 5 |
10.6.2 | The URL contains https:// | 1 | ||
10.6.3 | Any TWO:
| 2 | ||
10.7 | 10.7.1 | Social engineering refers to ‘conning’ or tricking a person into willingly giving out personal information. | 2 | 4 |
10.7.2 | Any TWO:
| 2 | ||
10.8 | Any TWO:
| 2 | 2 | |
[25] | ||||
TOTAL SECTION C: 50
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Computer Applications Technology Paper 2 Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of:
SECTION A (25 marks)
SECTION B (75 marks)
SECTION C (50 marks) - Answer ALL the questions.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Do NOT write in the right-hand margin of the ANSWER BOOK.
- Leave a line after EACH subquestion.
- Generally, one mark is allocated per fact; therefore, a 2-mark question would require TWO facts, etcetera.
- Read the questions carefully. DO NOT give more than the question requires as this will NOT be marked.
- All answers MUST be related to Computer Applications Technology.
- Answers such as ‘cheaper’, ‘slower’/’faster’ and ‘easier’ will ONLY be accepted, if they are motivated.
- Do NOT use brand names in your answers, unless specifically required.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Various options are given as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1 to 1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.11 D.
1.1 A physically disabled person who cannot use the keyboard with ease, will benefit from using this specific program/software when he/she wants to type a letter on the computer.
- Dragon Naturally Speaking
- MathPad
- Mouse skills
- CorelDraw (1)
1.2 What is the difference between upgrading of software and updating of the software?
- There is no difference, in both cases you have to go online.
- For updating software like Word, you need a license number but for upgrading it is unnecessary.
- When you update software, you probably buy a newer version and when you upgrade, you download fixes.
- When you upgrade software, you probably buy a newer version and when you update, you download fixes. (1)
1.3 Which ONE of the data types in MS Access ensures that the field serves as a primary key?
- Hyperlink
- AutoNumber
- OLE Object
- Memo/Long Text (1)
1.4 You want to use a function to search for a value that appears the most in a data range. The best function to use is:
- VALUE
- IF
- MEDIAN
- MODE (1)
1.5 Sales or holiday bookings over the Internet are known as …
- e-commerce.
- Tweets.
- VoIP.
- Ergonomics. (1)
1.6 Once data has been collected, it must be processed. A spreadsheet is an ideal tool for analysing data. Which ONE of the features mentioned below does NOT contribute to the analysis of data?
- Graphs/Charts
- Track changes
- Conditional formatting
- Functions and Formulas (1)
1.7 Which method/source would be the most suitable to use to gather information about residents’ opinions on service delivery?
- Survey
- Community (local) newspapers
- National newspapers
- Interviews (1)
1.8 The catch phrase “It’s criminal if it’s not original!” describes …
- the theft of intellectual property.
- hacking into a computer.
- software piracy.
- text encryption. (1)
1.9 Which ONE of the following is NOT a formula that is av in a Word table? ailable for calculations
- LEN
- SUM
- AVERAGE
- COUNT (1)
1.10 The overall design of an entire document including colours, fonts and effects, is known as …
- style.
- template.
- theme.
- autotext. (1)
[10]
QUESTION 2: MATCHING ITEMS
Choose a term/concept from COLUMN B that matches the description in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–T) next to the question numbers (2.1 to 2.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 2.11 Q.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | |
2.1 | The trend where separate technologies and functions that required different devices in the past are combined into a single device |
|
2.2 | It includes utility programs/software pre-installed onto your computer to help maintain the system | |
2.3 | The total amount of data transferred from one point to another within a specific time span | |
2.4 | Data identified on a website can be stored temporarily on the hard drive in a sub-directory of the browser and at the next session it is retrieved instead of opening the website via the Internet | |
2.5 | A collection of independent networked computers that act together to perform very large tasks | |
2.6 | A horizontal line, which is a little longer than a hyphen, used to express ranges and parenthetical expressions | |
2.7 | The different parts of the files can become scattered across the disk, causing the computer to become slower in retrieving the files in order to open or save them | |
2.8 | The ratio between the width and height of a screen | |
2.9 | The specification in which the speed of a printer is measured | |
2.10 | The setting on the camera for measuring the sensitivity to light | |
(10 x 1) [10]
QUESTION 3: TRUE/FALSE ITEMS
Indicate whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Choose the answer and write ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the question numbers (3.1 to 3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK. Correct the statement if it is FALSE. Change the underlined word(s) to make the statement TRUE. (Do NOT simply use the word ‘NOT’ to change the statement.)
NO mark will be awarded if only FALSE is written.
EXAMPLES:
QUESTION | ANSWER | ||
Facebook is an example of a social networking website. | True | ||
A NIC has slots for hardware components such as the CPU. | False – motherboard | ||
3.1 A header is text that appears within the bottom margin of all pages in a document or file. (1)
3.2 A check box allows the user to choose only one from a given set of options. (1)
3.3 The wild card character can be used in the Find and Replace feature of a word processor. (1)
3.4 A hyperlink is a built-in connection to another related webpage or website, usually indicated as underlined text or graphics. (1)
3.5 An e-mail program may reject an attachment based on the date of the file. (1)
[5]
TOTAL SECTION A: 25
SECTION B
QUESTION 4: SYSTEM TECHNOLOGIES
4.1 Every general-purpose computing device needs both RAM (memory) and storage.
4.1.1 Briefly explain the function of RAM. (1)
4.1.2 Give ONE difference between RAM and storage, besides their difference in function. (1)
4.2 Give TWO input devices that are found in a smartphone, but not in a typical desktop computer. (2)
4.3 Give TWO reasons why portable computers are increasingly being designed NOT to include optical drives. (2)
4.4 You are working with a wired mouse that suddenly ‘freezes’ (fails to respond). Assume that the mouse itself is clean and not damaged. Give TWO trouble-shooting techniques you could try to get the mouse working again. (2)
4.5 Discuss TWO ways in which a user could ensure that data is not deleted or altered by mistake. (2)
4.6 Explain why business invoices, statements etcetera. are generally converted to PDF files before they are sent to customers. (1)
4.7 Give TWO limitations of data projectors for showing computer output, compared to normal monitors. (2)
4.8 Name TWO pieces of equipment one would need for VR (Virtual Reality). (2)
4.9 State ONE example of how VR (Virtual Reality) can be used, except for gaming. (1)
4.10 The IT learners are considering constructing a drone as part of an awareness drive for new technology. A 3D printer will be used to print the parts of the drone.
4.10.1 What is a drone? (1)
4.10.2 State TWO possible benefits of using a 3D printer for printing parts of the drone. (2)
4.11 A computer game has the following hardware system requirements:
Intel i3 (or higher) |
4.11.1 Give the general function (in any computer) of the item specified as ‘Intel i3’. (1)
4.11.2 Assuming that the DVD drive will only be used to install the game, briefly explain how one could install the game on a computer that does NOT have a DVD drive. (1)
4.11.3 Give ONE other common hardware requirement, besides those listed above. (1)
4.12 State THREE advantages of SSDs. (3)
[25]
QUESTION 5: INTERNET AND NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES
The diagram below illustrates the network of a small business.
5.1 The computers in the cabled network are used by all staff members and the WLAN is used by clients.
5.1.1 Give ONE reason why a wireless network is more suitable for the clients. (1)
5.1.2 Give ONE reason why all devices must have a unique IP address. (1)
5.1.3 Give TWO possible reasons why clients using the WLAN could experience slow connection speed sometimes. (2)
5.2 The LAN in the administration office uses a client-server model and provides internet access.
5.2.1 Name TWO services that can be provided by an ISP besides the connection to the internet. (2)
5.2.2 State TWO benefits of using an ADSL connection. (2)
5.2.3 Explain the function of the switch as part of the LAN. (2)
5.3 The LAN to be used by the administration staff uses fibre-optic cables.
5.3.1 What medium is used by fibre-optic cables to transmit signals? (1)
5.3.2 Give TWO reasons why fibre-optic cables will be more suitable for use in a LAN than UTP cables. (2)
5.4 Give TWO disadvantages of FTP technology for the transfer of larger files over the internet. (2)
[15]
QUESTION 6: INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
6.1 Refer to a formal written report, such as your PAT, and explain the purpose of a:
6.1.1 Task definition (1)
6.1.2 References (1)
6.2 When you did research for your PAT, you found some of the information on the topic appeared to be unsuitable.
State TWO indications that some of the information found may not be accurate and cannot be used in your report. (2)
6.3 Closed questions have a set of answers to choose from.
6.3.1 Discuss ONE limitation of using closed questions in a questionnaire. (1)
6.3.2 Give TWO benefits for a researcher when closed questions are answered electronically. (2)
6.4 State THREE ways in which a chart/graph can be made easier to interpret when it is included in a report. (3)
[10]
QUESTION 7: SOCIAL IMPLICATIONS
7.1 Communicating via e-mail has become the norm for society at large.
7.1.1 Give TWO indications that a received e-mail may be a possible phishing attempt. (2)
7.1.2 Give ONE possible reason as to why your e-mail program is set to block .exe files. (1)
7.1.3 Give TWO types of theft that can be committed with the aid of computers, apart from the theft of hardware and data/intellectual property. (2)
7.2 The geotagging function of modern cameras is useful for holiday-makers and tourists. Explain what this statement means by explaining what geotagging is. (2)
7.3 Give TWO potential disadvantages of e-learning when compared to the traditional classroom approach, excluding any cost factors. (2)
7.4 Give ONE indication that a message you have received is a hoax. (1)
[10]
QUESTION 8: SOLUTION DEVELOPMENT
8.1 How do you convert an endnote to a footnote? (3)
8.2 Refer to the diagram below and answer the following question.
Each student needs a unique code to receive their overall final results.
Write down the function you would use in cell B6 to create a code in capital letters by using the first 2 letters of students’ names (column C). (3)
8.3 An examination session took place from 4 April 2018 to 15 April 2018. Change the properties of the ExaminationDate field in a database to ensure that only valid dates can be entered. (3)
8.4 Write down the tags used to insert a red colour horizontal line (hr/) in an HTML web page with a width of 50%. (2)
8.5 Which spreadsheet feature will systematically insert automatic numbers from 1 to 50 in consecutive rows? (1)
8.6 Name THREE possible data sources to create mailing labels in a mail merge. (3)
[15]
TOTAL SECTION B: 75
SECTION C: INTEGRATED SCENARIO
QUESTION 9
| Your school is launching a major drive to embrace the digital era. The expansion of their network, linked with increased Internet availability, has made it possible for them to better utilise new technologies and ICT. Apart from all the benefits, the increased use of computers and online services pose challenges in terms of providing improved hardware and educating users. |
9.1 Name TWO IT/CAT-related jobs that will be created when setting up and expanding the network. (2)
9.2 Access to the server room must be controlled. The administrative staff members use biometrics to gain access to the server room.
9.2.1 Explain the term biometrics. (2)
9.2.2 Give a suitable example of biometrics to be used in this scenario. (1)
9.3 It has been suggested that the other staff members use RFID tags to gain access to the server room.
State TWO disadvantages of using RFID tags for this application. (2)
9.4 Learners complain that their computers become very slow quickly when they open more applications. It has been suggested that they may be using too much virtual memory.
9.4.1 What is virtual memory? (1)
9.4.2 Which software implements and manages virtual memory in a computer system? (1)
9.4.3 How can the use of virtual memory be limited? (1)
9.5 A logical effect of the improvements at the school has been an increase in the use of cloud computing.
9.5.1 Cloud computing includes cloud software services, such as Office365. Explain how cloud applications work in general. (2)
9.5.2 State TWO disadvantages of using online software services. (2)
9.6 Parents/Custodians are concerned about learners’ exposure to social networking sites and cybercrime.
9.6.1 Suggest THREE ways of using social networking sites responsibly. (3)
9.6.2 Give TWO reasons why cybercrime is prevalent. (2)
9.6.3 A general crime people commit is using unsecured Wi-Fi internet connections without permission. What term is used to describe this crime? (1)
9.7 Ransomware is a type of malicious software from crypto virology that threatens to publish the victim's data or perpetually block access to it unless a ransom is paid.
9.7.1 How can you prevent ransomware attacks? (2)
9.7.2 How would you remove ransomware from your computer? (2)
9.7.3 Anonymous payment services are used for ransomware payment. Name ONE method of payment that can be used. (1)
[25]
QUESTION 10
| The local university is upgrading their library and the ICT infrastructure. The university's website can be used to check timetables and make reservations for access to the research section of the library. |
10.1 An AUP document has been compiled for the library. One of the points listed in the document states that, where possible, electronic documents should be used instead of printed documents.
10.1.1 What does the acronym AUP stand for? (1)
10.1.2 Briefly explain the purpose of having an AUP. (2)
10.2 Some of the electronic documents are stored in an online storage facility to facilitate file syncing. Explain the concept of file syncing. (2)
10.3 The university employed a web designer to redesign the website.
10.3.1 Name TWO skills that a web designer would need when creating a website. (2)
10.3.2 Students can access the website from their mobile devices. State TWO factors that a web designer must take into consideration when designing websites to be accessible from mobile devices. (2)
10.4 Some students watch videos on their electronic devices as part of research projects. The videos are saved with metadata on an SSD.
10.4.1 What is metadata? (1)
10.4.2 Suggest a suitable format for the compression of videos. (1)
10.5 Schedules for short-course lectures and webinars are displayed on the website.
10.5.1 What is a webinar? (1)
10.5.2 How can the students remain informed of changes in the schedules without visiting the website? (2)
10.6 University staff want to be sure that information sent over the network will be safe and secure. Encryption will be used to secure the data.
10.6.1 Explain what the term encryption means. (2)
10.6.2 A yellow lock is displayed on the URL bar when the user opens the university’s website.
What other visual indication is displayed that indicates that the website is secure, besides the yellow lock? (1)
10.6.3 When a user clicks on the yellow lock, the following dialogue box is displayed:
Which TWO pieces of information on the certificate can be used to verify that the website is legitimate? (2)
10.7 Staff members are often warned against social engineering.
10.7.1 Explain what social engineering is. (2)
10.7.2 What is a consequence of falling victim to social engineering? (2)
10.8 Green computing has become a focal point in the ICT field.
Suggest any TWO initiatives for the library to implement green computing. (2)
[25]
TOTAL SECTION C: 50
GRAND TOTAL: 150