Adele
Computer Applications Technology Paper 1 Memorandum - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
MEMORANDUM
| QUESTION 1 | File Name: 1_World Literacy Day | Total Q1: 27 | |||
No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | Candidate Mark | ||
1.1.1 | Cover Page
| 1 | 1 | ||
1.1.2 | Cover Page
| 1 |
2 | ||
1 | |||||
1.2. | Table of Contents
|
1 |
2 | ||
1 | |||||
1.3 | Page Numbering
| 1 | 3 | ||
1 | |||||
1 | |||||
1.4 | Shading
| 1 1 |
2 | ||
1.5 | Footnotes
| 1 | |||
1 | 3 | ||||
1 | |||||
1.6 | Picture formatting
| 1 |
3 | ||
1 | |||||
1 | |||||
1.7 | References
| 1 | |||
1 | 3 | ||||
1 | |||||
1.8 | Find and Replace
(Only 5 changes) | ||||
1 1 | 2 | ||||
1.9 | Page Orientation
| |||||
1 1 | 2 | |||||
1.10 | Table Styles
| 1 |
3 | |||
1 | ||||||
1 | ||||||
1.11 | Word Count
| 1 | 1 | |||
Total for QUESTION 1 | [27] |
QUESTION 2 File Name: 2_Registration Form Total Q2: 17
No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | Candidate Mark | ||
2.1 | Margins
| 1 | 1 | ||
2.2 | Page
| 1 | 1 | ||
2.3 | Picture
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
2.4 | Legacy Form tools
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
2.5 | Dropdown field
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
2.6 | Smart Art
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
2.7 | Linked Documents
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
2.8 | Footer
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
Total for QUESTION 2 | [17] | ||||
QUESTION 3 File Name: Attendees Total Q3: 46
No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | Candidate Mark | ||
Attendee_Info worksheet | |||||
3.1.1 | Cell formatting
| 1 | 1 | ||
3.1.2 | Text Alignment
| 1 | 1 | ||
3.1.3 | Freeze Panes
| 1 | 1 | ||
3.2 | Date
| 1 1 |
2 | ||
3.3 | B9
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
3.4 | S10
| 1 1 1 |
3 | ||
3.5 | U11 Calculation
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
3.6 | V13 Calculation
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
3.7 | Conditional formatting Formula =$T9="No" Range =$D$9:$D$108
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | Candidate Mark | |||
3.8 | W9
| |||||
1 1 | 4 | |||||
1 | ||||||
1 | ||||||
3.9 | X9
| |||||
1 | ||||||
1 | 4 | |||||
1 | ||||||
1 | ||||||
3.10 | G111 Date
| |||||
1 1 | 3 | |||||
1 | ||||||
3.11 | G113
(Ignore if Absolute cell reference was not used) | |||||
1 | ||||||
1 1 | 5 | |||||
1 | ||||||
1 | ||||||
3.12 | G115
| |||||
1 | ||||||
1 | 4 | |||||
1 | ||||||
1 | ||||||
3.13 | Graph
| |||||
1 | ||||||
1 | ||||||
1 1 | 7 | |||||
1 | ||||||
1 | ||||||
1 | ||||||
Total for QUESTION 3 | [46] |
QUESTION 4 File Name: 4_Digital literacy Total Q4: 35
No | Criteria | Maximum Mark | Candidate Mark | ||
Table: Personal Information | |||||
4.1.1 | Field: Date of Birth
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
4.1.2 | Course Code: Input Mask
| 1 1 1 1 | 4 | ||
4.1.3 | Field: Courses
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
4.2 | Form: Attendee Information
| 1 1 1 1 1 1 | 6 | ||
QUERIES | |||||
4.3.1 | Qry4_3_1
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
4.3.2 | Qry4_3_2
| 1 1 1 1 1 1 | 6 | ||
REPORT | |||||
4.4 | Report4_4
| 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 | 10 | ||
Total for QUESTION 4 | [35] | ||||
QUESTION 5 File Name: 5_Digital Literacy Total Q5: 17
- This question should be marked from the HTML code.
- Numerical attribute values do not need to be in inverted
No | Criteria | Maximum Mark | Candidate Mark | ||
5.1 | Background Colour
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
5.2 | Image
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
5.3 | Unordered Lists
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
5.4 | Table
| 1 1 1 1 1 1 | 6 | ||
5.5 | Links
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
Closing tag(s) or triangular brackets and correct nesting correctly used. | 1 | 1 | |||
Total for QUESTION 5 | [17] |
QUESTION 6 File Name: 6_Digital Technology in SA Total Q6: 8 6_Compare and 6_Compare 1
No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | Candidate Mark | ||
6.1.1 | Non-Breaking Space
| 1 | 1 | ||
6.2 | Cut and Paste
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
6.3 | Track Changes
| 1 | 1 | ||
6.4 | Compare documents
6_Compare 1)
| 1 1 1 1 | 4 | ||
Total for QUESTION 6 | [8] | ||||
TOTAL: | 150 | ||||
Computer Applications Technology Paper 1 Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Owing to the nature of this practical examination, it is important to note that, even if you complete the examination early, you will NOT be permitted to leave the examination room until all the administrative functions associated with the examination have been finalised. During the examination, the normal rules regarding leaving the examination room apply.
- If you are working on the network, or the data files have been preloaded, you must follow the instructions provided by the invigilator/teacher. Alternatively, the invigilator will give you a CD/DVD/flash drive containing all the files needed for the examination. If a CD/DVD/flash drive has been issued to you, you must write your examination number and centre number on the CD/DVD/flash drive.
- At the end of the examination, you must hand in the CD/DVD/flash drive given to you by the invigilator with ALL your answer files saved onto the CD/DVD/flash drive, OR you should make sure that ALL the answer files are saved on the network/computer as explained to you by the invigilator/teacher.
- Make absolutely sure that ALL files can be read. Do NOT save unnecessary files/folders and do NOT hand in duplicate answer files/folders. Do NOT delete any original files that you did not work on.
- The information sheet that has been provided with the question paper MUST BE COMPLETED AFTER THE THREE-HOUR EXAMINATION SESSION.
Hand it to the invigilator at the end of the examination. - A copy of the master files will be available from the invigilator. Should there be any problems with a file, you may request another copy from the invigilator.
- This question paper consists of SIX questions. Answer ALL the questions.
- Read through each question before answering or solving the problem. Do NOT do more than is required by the question.
- Ensure that you save each document using the file name given in the question paper. Save your work at regular intervals as a precaution against possible power failures.
- You may NOT use any resource material.
- Accuracy will be taken into account, e.g. if a question requires the answer to be in cell F3 in a spreadsheet, and you enter the answer in cell G4, it will NOT be marked.
- Ensure that the regional settings are set to South Africa and date and time settings, number settings and currency settings are correctly set.
- In all questions involving word processing, you should set the language to English (South Africa). The paper size is assumed to be A4 Portrait, unless instructed otherwise. Use centimetres as the unit of measurement.
- Formulae and/or functions must be used for ALL calculations in questions involving spreadsheets. Use absolute cell references only where necessary to ensure that formulae are correct when you copy them to other cells in a spreadsheet.
NOTE: All formulae and/or functions should be inserted in such a manner that the correct results will still be obtained even if changes are made to the existing data. - You may NOT use a word processing program such as Word to answer the HTML question.
- The examination folder/CD/DVD/flash drive that you receive with this question paper contains the files listed below. Ensure that you have all the files before you begin this examination.

QUESTIONS
SCENARIO Each year on the 8th of September the world celebrates World Literacy Day. The purpose of this day is to make people aware of the high illiteracy rate in the world and use measures to decrease it. |
QUESTION 1: WORD PROCESSING
A document was created to give more information about the World Literacy Day. Open and edit the 1_World Literacy Day word processing document.
1.1 Insert a cover page in the document. The cover page must display the following:
1.1.1 Select the Filigree Cover page. (1)
1.1.2 Type the document name and date in the required field. Delete all other fields. (2)
1.2 The table of content has been inserted. Please do the following:
- Modify the table of contents so that the headings of Heading 2 appear. (2)
1.3 Edit the page numbering so that number 1 appears on the page after the table of contents. (3)
1.4 Locate the paragraph under the heading ‘What is World Literacy Day?’ and apply a Green Accent 6 shading to the whole paragraph. (2)
1.5 Find the text Miriam Webster Dictionary marked in yellow under the heading History of International Literacy Day.
- Insert a footnote with the following explanation: America's most trusted online dictionary for English word definitions, meanings and pronunciation.
- Ensure that the footnote is below the text. (3)
1.6 Find the picture Figure 1 and move it to the right of the paragraph as shown below. Set the size of the picture to height 3.5 cm and width 7.5 cm.(3)
1.7 Locate the Placeholder 1 marked in blue. Edit the placeholder by inserting the following source:
- Book title: Practical guide to functional literacy: a method of training for development.
- Published in 1973. m (3)
1.8 Emphasise all the occurrences of the word ‘literacy’ by making the words bold. Only ‘literacy’ in lowercase must be changed. (2)
1.9 Set the orientation of ONLY the second last page to landscape. (2)
1.10 Locate the table under the heading International Literacy Day Dates and modify as follows:
- Apply a Grid Table 4 Accent 6 style.
- Edit the style to align text horizontally and vertically. (3)
1.11 Use a word processing feature to count the number of words in the document starting from the heading, ‘What is World Literacy Day?’ up to the end of paragraph 4.5. (1)
[27]
QUESTION 2: WORD PROCESSING
A registration form has been created for the attendees to fill in and e-mail to the registration office.
Open the 2_Registration Form word processing document and modify the document as follows.
2.1 Set the top and the bottom page margins to 1 cm. (1)
2.2 Insert a double line page border for the page. (1)
2.3 Centre the picture and apply a soft edge oval picture style. (2)
2.4 Set the text form field for the title to:
- Maximum length to 4
- Text format to uppercase (2)
2.5 Modify the dropdown form field for Gender field to include:
- Male and Female as choice options.
- Add a help message ‘For accommodation purposes’ on help text. (3)
2.6 Modify the horizontal hierarchy for the courses to resemble the image below.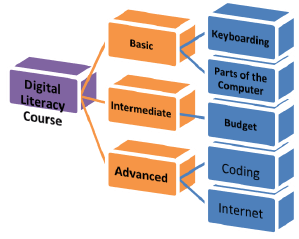 (3)
(3)
2.7 Locate the text, ‘Insert here’ and insert the pdf file ‘Benefits-digital- literacy.pdf’ as an embedded file. The file must show as an icon. (3)
2.8 Add the text, ‘Registration Form’ in the footer of the document. Right align the text. (2)
[17]
QUESTION 3: SPREADSHEET
Various courses will be offered to the community members and they have to register for them. A spreadsheet 3_Attendees has been created to record all the attendees.
Open the 3_Attendees spreadsheet and work in the Attendee_Info worksheet.
3.1 Improve the readability of the spreadsheet by applying the following formatting features to the worksheet.
3.1.1 Merge and centre rows A1 to X2. (1)
3.1.2 Align the headings in A8 to G8 horizontally and vertically. (1)
3.1.3 Use the word processing feature to ensure that the contents in rows 1 to 8 remain on the screen when the user scrolls down. (1)
3.2 Use a function in cell G7 to add today’s date in the format yyyy-mmmm-dd. (2)
3.3 Use a suitable function in cell B9 to add a suitable title for the attendee. The male attendees must have ‘Mr’ as their title and female attendees must have
‘Ms’. (3)
3.4 Add a function in cell S10 to calculate the number of courses Ewie Langhon will attend. (3)
3.5 The amount for each course is in cell V7. In cell U11 calculate the total amount Bambie Mulles will pay for his courses. Make sure that the formula will work correctly when copied down. (3)
3.6 Barnabas decided to do all 11 courses and has paid 75% of the total amount. In cell V13 calculate the amount paid by Barnabas. (2)
3.7 Use a word processing feature in column D (Last Name) to automatically highlight with the colour of your choice any person who does not have a laptop. (3)
3.8 The attendees are grouped into four teams depending on how many courses they do.
- 5 courses and less are Greens.
- 8 courses and less are Blues.
- 10 courses and less are Reds.
- More than 10 courses are Yellows.
Insert a function in cell W9 to determine in which team Ogdon Polly is. Copy the formula to the other cells. (4)
3.9 The organisers decided to give a discount to attendees who own a laptop and have already paid R50,00 deposit.
Insert a function in cell X9 to display the text ‘Discount’ for those people who do qualify for a discount and leave the cell blank for those who do not qualify. (4)
3.10 Insert a function or a formula in cell G111 to determine and display the current age of the last person, Nichole. This function or formula must give the correct age even if the current date changes. (3)
3.11 Insert a LOOKUP function in cell G113 to determine how many attendees attended the Budget Intermediate Course. Use the information in the Statistics worksheet. (5)
3.12 Insert a function in cell G115 to calculate the total amount that will be paid by attendees who own a laptop. (4)
3.13 A graph has been created in the Statistics worksheet. Modify the graph as follows:
- Format the chart area of the graph by adding the picture, 3Digital Literacy, found in your data folder, as a background picture.
- Set the transparency of the picture to 50%.
- Use a filter option to remove the two courses, Typing a letter and Budget.
- Add a data callout label to the most popular course.
- Use a spreadsheet feature to move the graph to a new worksheet called Graph. (7)
[46]
QUESTION 4: DATABASE
The information of the attendees needs to be stored in a database. Modify the database provided and work in the design view, except when requested otherwise.
Open 4_Digital Literacy database and do the following:
4.1 Table: Personal Information
4.1.1 Add a validation rule to the Date of Birth field to prevent the user from entering a date later than the current date. (3)
4.1.2 Each course is assigned with a code. Add an input mask to the Course Code field to only accept a code in the following format:
- Three optional digits,
- followed by a hyphen,
- followed by three compulsory uppercase letters, eg. 22-DLC, 1-SBE or 398-KPP. (4)
4.1.3 Insert a combo box for the Course field so that the list of courses can be selected. The courses are stored in the table Course Information. (3)
4.2 Open the form Attendee Information.
Add a function to the details tab to:
- Calculate the age of the attendee in years.
- Format the function to display the age as a whole number.
- Display a suitable label for the calculated age. (6)
4.3 Queries
4.3.1 Modify Qry4_3_1 to:
- Display all attendees who are 18 years and younger.
- Sort the attendees according to the Level of Literacy in descending order. (3)
4.3.2 The organisers want to give the attendees Internet data. Only Vodacom vouchers are available. They decided to give money to other attendees.
Modify Qry4_3_2 as follows:
- Show all users who do not use Vodacom.
- Create a calculated field called Data to calculate the money that each person will receive. Each person will be given an allowance of R30 per day.
- Calculate in datasheet view the total amount that will be spend on the attendees. (6)
4.4 Report
Create a report called rpt4_4 based on the Attendee Information table.
- Show only the following fields: Last Name, Date of Birth, Gender, No of Courses, Level of Literacy and No of days to attend.
- Group the records according to the Gender.
- Then sort according to Level of Literacy.
- Display the report in landscape format.
- Insert a function in the group footer to calculate the number of female and male attendees.
- Add a descriptive label to the calculation.
- Ensure that all the data displays fully.
Save and close the rpt4_4. (10)
[35]
QUESTION 5: WEB DESIGN (HTML)
Open the incomplete 5_Digital Literacy.html web page in a web browser and also in a text editor. You may NOT use a word processing program such as Word to answer the HTML question.
NOTE:
- Question numbers are inserted as comments in the coding as guidelines to show approximately where the answer(s) should be inserted. Do NOT delete the comments.
- A HTML tag sheet has been attached for reference.
Your final web page should look like the example below.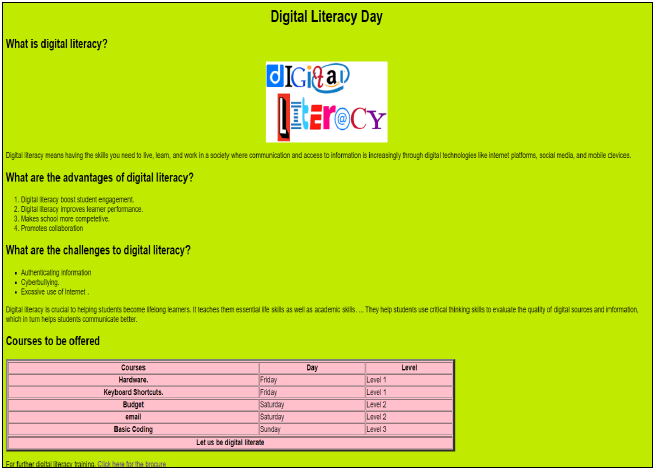
5.1 Set the website page colour to Cream. (2)
5.2 Rectify the error that occurred when the webmaster was inserting a picture. Centre the picture. (3)
5.3 Fix the error under the heading ‘What are the challenges to digital literacy?’ to be bulleted, using square bullets. (2)
5.4 Modify the table as follows:
- Change the colour of the table to pink.
- The border must be 5 pt and width 70%.
- Row 7 must be merged across the three columns; the text must be centred and in bold.(6)
5.5 Create a link on the text below the table to open the Brochure file in your data folder.(3)
[17]
QUESTION 6: GENERAL
Open 6_Digital Technology in SA and modify the document as follows:
6.1 Locate the two words, ‘South Africa’ in the first paragraph. Use a word processing feature to ensure that the two words remain together even if they are pushed to the next line. (1)
6.2 Find the paragraph that is bordered and filled with an orange fill on the first page. Move it and paste it at the end of the document without keeping the current formatting. (2)
6.3 The author of the document has made two changes in the document. Find the two changes and accept them. (1)
Open 6_Compare
6.4 Use a word processing feature to compare the two documents: 6_Compare and 6_Compare 1. Make a screenshot of the results and paste it at the end
of the 6_Compare document. (4)
[8]
TOTAL: 150
ANNEXURE A – HTML TAG SHEET
Basic Tags | Formatting Tags continued | |||
Tag | Description | Tag | Description | |
<body></body> | Defines the body of the web Page | <li></li> | Inserted before each list item, and adds a number or symbol depending upon the type of list selected | |
<body bg color="pink"> | Sets the background colour of the web page | |||
<body text="black"> | Sets the colour of the body text | <img src="/name"> | Adds an image | |
<head></head> | Contains information about the document | <img src="/name" align="left"> | Aligns an image: can also be "right", "center"; "bottom", "top", "middle" | |
<html></html> | Creates an HTML document – starts and ends a web page | <img src="/name" border="1"> | Sets size of border around an image | |
<title></title> | Defines a title for the document | <img src="/name" width="200" height ="200"> | Sets the height and width of an image | |
<!-- --> | Comment | |||
Text Tags | <img src="/name" alt="alternative text"> | Displays alternative text when the mouse hovers over the image or when the image is not found | ||
Tag | Description | |||
<hl></hl> | Creates the largest heading | |||
<h6></h6> | Creates the smallest heading | <hr/> | Inserts a horizontal line | |
<b></b> | Creates bold text | <hr size="3"/> | Sets size (height) of line | |
<i></i> | Creates italic text | <hr width="80%"/> | Sets width of line, in percentage or absolute value | |
<font size="3"></font> | Sets size of font, from "1" to "7" | <hr color="ff0000"/> | Sets the colour of the line | |
<font color="green"></font> | Sets font colour | Table Tags | ||
<font face="Times New Roman"></font> | Sets font type | Tag | Description | |
Link Tags | <table></table> | Creates a table | ||
Tag | Description | <tr></tr> | Creates a row in a table | |
<a href="/URL"></a> | Creates a hyperlink | <td></td> | Creates a cell in a table | |
<a href="/URL"><img src="/URL"></a> | Creates an image link | <th></th> | Creates a table header (a cell with bold, centered text) | |
<a name="NAME"></a> | Creates a target location | <table width="50"> | Sets the width of the table | |
<a href="#NAME"></a> | Links to a target location created somewhere else in the document | <table border="1"> | Sets the width of the border around the table cells | |
Formatting Tags | <table cellspacing="1"> | Sets the space between the table cells | ||
Tag | Description | <table cellpadding="1"> | Sets the space between a cell border and its contents | |
<p></p> | Creates a new paragraph | <tr align="left"> | Sets the alignment for cell(s) (can also be "center" or "right") | |
<p align="left"> | Aligns a paragraph to the "left" (default), can also be "right", or "center" | <tr valign="top"> | Sets the vertical alignment for cell(s) (can also be "middle" or "bottom") | |
<br/> | Inserts a line break | <td colspan="2"> | Sets the number of columns a cell should span | |
<ol></ol> | Creates a numbered list | <td rowspan="4"> | Sets the number of rows a cell should span | |
<ol type="A","a", "I","i","1"></ol> | Defines the type of numbering used | |||
<ul></ul> | Creates a bulleted list | |||
<ul type="disc", "square","circle"></ ul> | Defines the type of bullets used | |||
INPUT MASK CHARACTER SHEET
CHARACTER | DESCRIPTION |
0 | Digit (0 to 9, entry required, plus [+] and minus [–] signs not allowed) |
9 | Digit or space (entry not required, plus [+] and minus [–] signs not allowed) |
# | Digit or space (entry not required; spaces are displayed as blanks while in Edit mode, but blanks are removed when data is saved; plus [+] and minus [–] signs allowed) |
L | Letter (A to Z, entry required) |
? | Letter (A to Z, entry optional) |
A | Letter or digit (entry required) |
a | Letter or digit (entry optional) |
& | Any character or a space (entry required) |
C | Any character or a space (entry optional) |
. , : ; - / | Decimal placeholder and thousand, date and time separators (The actual character used depends on the settings in the Regional Settings Properties dialog box in the Windows Control Panel.) |
< | Causes all characters to be converted to lower case |
> | Causes all characters to be converted to upper case to right. You can include the exclamation point anywhere in the input mask. |
! | Causes the input mask to display from right to left, rather than from left to right. Characters typed into the mask always fill it from left to right. You can include the exclamation point anywhere in the input mask. |
\ | Causes the character that follows to be displayed as the literal character (for example, \A is displayed as just A) |
COMPUTER APPLICATIONS TECHNOLOGY P1 – SEPTEMBER 2021
INFORMATION SHEET (to be completed by the candidate AFTER the 3-hour session)
SUITE USED | Microsoft Office 2010 | Microsoft Office 2013 | Microsoft Office 2016 | Office 365 |
WEB BROWSER USED (QUESTION 6) | Mozilla Firefox | Google Chrome | Internet Explorer | Other (Specify) |
FOLDER NAME:
Tick if saved and/or attempted.
Question Number | File name | Saved (√) | Attempted (√) | Maximum mark | Maximum achieved | Marker | HOD | Cluster | EM |
1 | 1_World Literacy Day | 27 | |||||||
2 | 2_Registration Form | 17 | |||||||
3 | 3_Attendees | 46 | |||||||
4 | 4_Digital Literacy | 35 | |||||||
5 | 5_Digital Literacy | 17 | |||||||
6 | 6_Digital Technology in SA | 8 | |||||||
6_Compare | |||||||||
6_Compare 1 | |||||||||
TOTAL: | 150 |
Comment (for marker use only)
.............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
Business Studies Paper 2 Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- This question paper consists of THREE sections and covers TWO main topics.
SECTION A: COMPULSORY
SECTION B: Consists of THREE questions.
Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section.
SECTION C: Consists of TWO questions.
Answer any ONE of the two questions in this section. - Read the instructions for each question carefully and take note of what is required.
Note that ONLY the first TWO questions in SECTION B and the FIRST question in SECTION C will be marked. - Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper. No marks will be awarded for answers that are numbered incorrectly.
- Except where other instructions are given, answers must be written in full sentences.
- Use the mark allocation and nature of each question to determine the length and depth of an answer.
- Use the table below as a guide for mark and time allocation when answering each question.
SECTION
QUESTION
MARKS
TIME
(minutes)
A: Objective-type questions COMPULSORY
1
30
30
B: THREE direct/indirect-type questions
CHOICE:
Answer any TWO.2
40
30
3
40
30
4
40
30
C: TWO essay-type questions CHOICE:
Answer any ONE.5
40
30
6
40
30
TOTAL
150
120 minutes
- Begin the answer to EACH question on a NEW page, e.g. QUESTION 1 – new page, QUESTION 2 – new page.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.6 D.
1.1.1 The directors of Bob Ltd issued … shares to their shareholders as compensation for unpaid dividends.
- founders
- redeemable
- ordinary
- bonus
1.1.2 Emma's personal assets may be claimed as payment for the debts of her business. This is an example of … liability.
- public
- unlimited
- personal
- limited
1.1.3 This aspect should be considered when designing a multimedia presentation:
- Choose a dark background to increase visibility
- Use a very small font to include detailed information on each slide
- Ensure that a picture is included in each slide
- Structure information in a logical sequence
1.1.4 Reporting unsafe working responsibility of the … conditions to management is the
- employee.
- trade union.
- production manager.
- employer.
1.1.5 Johnny's Paint Warehouse applied the … technique when they requested a panel of experts to complete a set of questionnaires to find solutions.
- empty chair
- force field analysis
- Delphi
- nominal group (5 x 2) (10)
1.2 Complete the following statements by using the word(s) provided in the list below. Write only the word(s) next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
| public; non-insurable; corporate social investment; leader; information; members; insurable; corporate social responsibility; manager; privacy |
1.2.1 SB Textiles is affected by changes in fashion. This is an example of … risk.
1.2.2 Zulu Ltd can raise capital by issuing shares to the …
1.2.3 Estelle is a good … because she administers plans and enforces rules to reach set targets.
1.2.4 The internal policy of Kopano (Pty) Ltd includes stakeholders' interests and environmental issues as part of their … programmes.
1.2.5 Corbett Manufacturers respect the employees' right to … by keeping their personal information confidential. (5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches a term in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–J) next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.3.6 K.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | |
1.3.1 | Capital gain |
|
1.3.2 | Average clause | |
1.3.3 | Inclusivity | |
1.3.4 | Decision-making | |
1.3.5 | Triple bottom line | |
(5 x 2) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer ANY TWO questions in this section.
NOTE: Clearly indicate the QUESTION NUMBER of each question that you choose. The answer to EACH question must start on a NEW page, e.g. QUESTION 2 on a NEW page, QUESTION 3 on a NEW page.
QUESTION 2: BUSINESS VENTURES
2.1 Name FOUR factors that should be considered when making an investment decision. (4)
2.2 Outline the factors that should be considered when preparing a presentation. (6)
2.3 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
TOMELO TRADERS (TT) Tomelo Traders is well known for selling quality products. Tomelo, the owner, insured his business property against fire and theft. He disclosed all relevant information which may affect the extent of the risk, to the insurance company. |
2.3.1 Identify TWO principles of insurance applicable to TT. Motivate your answer by quoting from the scenario above. Use the table below as a GUIDE to answer QUESTION 2.3.1.
PRINCIPLES OF INSURANCE | MOTIVATIONS |
1. | |
2. |
(6)
2.3.2 Advise the management of TT on the advantages of insurance for businesses. (6)
2.4 Explain how management could contribute to the success and/or failure of a partnership. (4)
2.5 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
CONSULTING SERVICES (CS) Ayanda, the owner of Consulting Services, invested R8 000 at Wonder Bank for three years. The bank offered her an interest rate of 10% per annum. The interest is calculated on the original amount plus interest. |
2.5.1 Identify the type of interest on which Ayanda's investment will be calculated. Motivate your answer by quoting from the scenario above. (3)
2.5.2 Calculate the amount of interest that Ayanda will receive after three years using the type of interest identified in QUESTION 2.5.1. Show ALL workings. (5)
2.6 Evaluate the impact of government/RSA retail savings bonds as a form of investment. (6)
[40]
QUESTION 3: BUSINESS ROLES
3.1 Name any THREE stages of team development. (3)
3.2 Outline the roles of the health and safety representatives in protecting the workplace environment. (6)
3.3 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
MANDY TRADERS (MT) Mandy Traders is located in an area where many people are struggling to find work due to a lack of skills. The majority are not able to satisfy their basic needs and therefore they receive food parcels from non-governmental organisations. |
3.3.1 Identify TWO socio-economic issues that pose a challenge to MT. Motivate your answer by quoting from the scenario above. Use the table below as a GUIDE to answer QUESTION 3.3.1.
SOCIO-ECONOMIC ISSUES | MOTIVATIONS |
1. | |
2. |
(6)
3.3.2 Explain how the management of MT could deal with HIV/Aids as a socio-economic issue. (4)
3.4 Discuss the causes of conflict in the workplace. (6)
3.5 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
SEBASTIAN AUDITORS (SA) Sebastian Auditors employ workers from diverse backgrounds. A translator was appointed to ensure that all employees understand what is discussed during meetings. |
3.5.1 Identify the diversity issue that SA has addressed. Motivate your answer by quoting from the scenario above. (3)
3.5.2 Discuss the benefits of diversity in the workplace. (6)
3.6 Analyse the impact of brainstorming as a problem-solving technique. (6)
[40]
QUESTION 4: MISCELLANEOUS TOPICS
BUSINESS VENTURES
4.1 Give TWO examples of non-verbal presentations. (2)
4.2 Outline the characteristics of a private company. (6)
4.3 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
SUPERIOR CONSTRUCTION (SC) Superior Construction employs a large number of workers at their construction sites. SC contributes to the Unemployment Insurance Fund and the Compensation for Occupational Injuries and Diseases Fund. They also take out life insurance for key personnel. |
4.3.1 Quote TWO types of compulsory insurance in the scenario above. (2)
4.3.2 Explain ONE type of compulsory insurance quoted in QUESTION 4.3.1. (4)
4.4 Advise presenters on how they could handle feedback in a non-aggressive and professional manner after a presentation. (6)
BUSINESS ROLES
4.5 Outline the correct procedure to deal with grievances in the workplace. (6)
4.6 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
MOHAMMED ADVERTISERS (MA) Mohammed Advertisers struggled to design a new advertising campaign to attract more clients. MA decided to train their employees on how to use innovative techniques. The employees were also requested to put any new |
4.6.1 Quote TWO ways in which MA created an environment that promoted creative thinking in the scenario above. (2)
4.6.2 Explain the advantages of creative thinking in the workplace. (6)
4.7 Evaluate the impact of corporate social responsibility (CSR) on communities. (6)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer ANY ONE question in this section.
NOTE: Clearly indicate the QUESTION NUMBER of each question chosen. The answer to EACH question must start on a NEW page e.g. QUESTION 5 on a NEW page OR QUESTION 6 on a NEW page.
QUESTION 5: BUSINESS VENTURES (MANAGEMENT AND LEADERSHIP)
| Successful leaders know that a positive attitude enables them to achieve business goals. The situational leadership theory guides businesses on managing people. Some leaders believe in the effectiveness of the charismatic and transactional leadership styles, while others prefer the autocratic leadership style. |
Write an essay on leadership in which you address the following aspects:
- Outline the role of personal attitude in successful leadership.
- Explain the situational leadership theory.
- Discuss the impact of the following leadership styles on businesses:
- Charismatic
- Transactional
- Suggest situations in which the autocratic leadership style could be applied in the workplace.
[40]
QUESTION 6: BUSINESS ROLES (ETHICS AND PROFESSIONALISM)
| The King Code principles provide guidelines on the application of ethical and professional business practices. Businesses need to identify unprofessional behaviour that poses challenges in their operations and develop strategies to deal with them. |
Write an essay on ethical and professional behaviour in which you address the following aspects:
- Outline the differences between ethical and professional behaviour.
- Explain how businesses could apply the King Code principles of accountability and transparency for good corporate governance.
- Describe how the following unprofessional business practices pose a challenge to businesses:
- Abuse of work time
- Unauthorised use of workplace funds and resources
- Recommend ways in which businesses could deal with EACH of the above unprofessional business practices.
[40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Business Studies Paper 1 Memorandum - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
NOTES TO MARKERS
- PREAMBLE
The notes to markers are provided for quality assurance purposes to ensure the following:- Fairness, consistency and reliability in the standard of marking
- Facilitate the moderation of candidates' scripts at the different levels
- Streamline the marking process considering the broad spectrum of markers across the country
- Implement appropriate measures in the teaching, learning and assessment of the subject at schools/institutions of learning
- Candidates’ responses must be in full sentences for SECTIONS B and C. However, this would depend on the nature of the question.
- A comprehensive marking guideline has been provided but this is by no means exhaustive. Due consideration should be given to an answer that is correct but:
- Uses a different expression from that which appears in the marking guideline
- Comes from another credible source
- Original
- A different approach is used
NOTE: There is only ONE correct answer in SECTION A.
- Take note of other relevant answers provided by candidates and allocate marks accordingly. (In cases where the answer is unclear or indicates some understanding, part-marks should be awarded, for example, one mark instead of the maximum of two marks.)
- The word ‘Sub-max’ is used to facilitate the allocation of marks within a question or sub-question.
- The purpose of circling marks (guided by ‘max’ in the breakdown of marks) on the right-hand side is to ensure consistency and accuracy in the marking of scripts as well as for calculation and moderation purposes.
- Subtotals to questions must be written in the right-hand margin. Circle the subtotals as indicated by the allocation of marks. This must be guided by ‘max’ in the marking guidelines. Only the total for each question should appear in the left-hand margin next to the appropriate question number.
- In an indirect question, the theory as well as the response must be relevant and related to the question.
- Correct numbering of answers to questions or sub questions is recommended in SECTIONS A and B. However, if the numbering is incorrect, follow the sequence of the candidate’s responses. Candidates will be penalised if the
latter is not clear. - No additional credit must be given for repetition of facts. Indicate with an ‘R’.
- The differentiation between ‘evaluate’ and ‘critically evaluate’ can be explained as follows:
11.1 When ‘evaluate’ is used, candidates are expected to respond in either a positive/negative manner or take a neutral (positive and negative) stance, e.g. Positive: ‘COIDA eliminates time and costs spent √ on lengthy civil court proceedings.’ √
11.2 When ‘critically evaluate’ is used, candidates are expected to respond in either a positive/negative manner or take a neutral (positive and negative) stance. In this instance candidates are also expected to support their responses with more depth, e.g. ‘COIDA eliminates time and costs spent √ on lengthy civil court proceedings, √ because the employer will not be liable for compensation to the employee for injuries sustained during working hours as long as it can be proved that the business was not negligent.’ √
NOTE:- The above could apply to ‘analyse’ as well.
- Note the placing of the tick (√) in the allocation of marks.
- The allocation of marks must be informed by the nature of the question, cognitive verb used, mark allocation in the marking guideline and the context of each question.
Cognitive verbs, such as:
12.1 Advise, name, state, outline, motivate, recommend, suggest, (list not exhaustive) do not usually require much depth in candidates’ responses. Therefore, the mark allocation for each statement/answer appears at the end.
12.2 Define, describe, explain, discuss, elaborate, distinguish, differentiate, compare, tabulate, analyse, evaluate, critically evaluate (list not exhaustive) require a greater depth of understanding, application and reasoning. Therefore, the marks must be allocated more objectively to ensure that assessing is conducted according to established norms so that uniformity, consistency and fairness are achieved. - Mark only the FIRST answer where candidates offer more than one answer for SECTION B and C questions that require one answer.
- SECTION B
14.1 If for example, FIVE facts are required, mark the candidate's FIRST FIVE responses and ignore the rest of the responses. Indicate by drawing a line across the unmarked portion or use the word ‘Cancel’.
NOTE: This applies only to questions where the number of facts is specified.
14.2 If two facts are written in one sentence, award the candidate FULL credit. Point 14.1 above still applies.
14.3 If candidates are required to provide their own examples/views, brainstorm this at the marking centre to finalise alternative answers.
14.4 Use of the cognitive verbs and allocation of marks:
14.4.1 If the number of facts are specified, questions that require candidates to 'describe/discuss/explain' may be marked as follows:- Fact 2 marks (or as indicated in the marking guidelines)
- Explanation 1 mark (two marks will be allocated in SECTION C)
The ‘fact’ and ‘explanation’ are given separately in the marking guideline to facilitate mark allocation.
14.4.2 If the number of facts required is not specified, the allocation of marks must be informed by the nature of the question and the maximum mark allocated in the marking guideline.
14.5 ONE mark may be awarded for answers that are easy to recall, requires one-word answers or is quoted directly from a scenario/case study. This applies to SECTIONS B and C in particular (where applicable).
- SECTION C
15.1 The breakdown of the mark allocation for the essays is as follows:
Introduction | Maximum: 32 |
Content | |
Conclusion | |
Insight | 8 |
TOTAL | 40 |
15.2 Insight consists of the following components:
Layout/Structure | Is there an introduction, a body, and a conclusion? | 2 | ||
Analysis and interpretation | Is the candidate able to break down the question into headings/subheadings/interpret it correctly to show understanding of what is being asked? | 2 | ||
Marks to be allocated using this guide: All headings addressed: 1 (One 'A') Interpretation (16 to 32 marks): 1 (One 'A') | ||||
Synthesis | Are there relevant decisions/facts/responses made based on the questions? | 2 | ||
Marks to be allocated using this guide: | ||||
Option 1: | Only relevant facts: 2 marks (No '-S') Where a candidate answers 50% or more (two to four sub-questions) of the question with only relevant facts; no '-S' appears in the left margin. Award the maximum of TWO (2) marks for synthesis. | |||
Option 2: | Some relevant facts: 1 mark (One '-S') Where a candidate answers less than 50% (only one sub-question) of the question with only OR some relevant facts; one '-S' appears in the left margin. Award a maximum of ONE (1) mark for synthesis. | |||
Option 3: | Some relevant facts: 1 mark (One '-S') Where a candidate writes FOUR questions, but one sub-question of the question with no relevant facts; one ‘-S’ appears in the left margin. Award a maximum of ONE (1) mark for synthesis. | |||
Option 4: | No relevant facts: 0 marks (Two '-S') Where a candidate answers less than 50% (only one sub-question) of the question with no relevant facts; two '-S' appear in the left margin. Award a ZERO mark for synthesis. | |||
Originality | Is there evidence of examples based on recent information, current trends and developments? | 2 | ||
TOTAL FOR INSIGHT: TOTAL MARKS FOR FACTS: TOTAL MARKS FOR ESSAY (8 + 32): | 8 32 40 | |||
NOTE: | 1. | No marks will be awarded for contents repeated from the introduction and conclusion. | ||
2. | The candidate forfeits marks for layout if the words INTRODUCTION and CONCLUSION are not stated. | |||
3. | No marks will be awarded for layout, if the headings INTRODUCTION and CONCLUSION are not supported by an explanation. | |||
NOTE:
- No marks will be awarded for contents repeated from the introduction and conclusion.
- The candidate forfeits marks for layout if the words INTRODUCTION and CONCLUSION are not stated.
- No marks will be awarded for layout, if the headings INTRODUCTION and CONCLUSION are not supported by an explanation.
15.3 Indicate insight in the left-hand margin with a symbol e.g. (‘L, A, -S and/or O’).
15.4 The breakdown of marks is indicated at the end of the suggested answer/ marking guideline to each question.
15.5 Mark all relevant facts until the SUB-MAX/MAX mark in a subsection has been attained. Write SUB-MAX/MAX after maximum marks have been obtained but continue reading for originality “O”.
15.6 At the end of each essay indicate the allocation of marks for facts and marks for insight as follows: (L – Layout, A – Analysis, S – Synthesis, O – Originality) as in the table below.CONTENT
MARKS
Facts
32 (max.)
L
2
A
2
S
2
O
2
TOTAL
40
15.7 When awarding marks for facts, take note of the sub-maxima indicated, especially if candidates do not make use of the same subheadings. Remember, headings and subheadings are encouraged and contribute to insight (structuring/logical flow/sequencing) and indicate clarity of thought. (See MARK BREAKDOWN at the end of each question.)
15.8 If the candidate identifies/interprets the question INCORRECTLY, then he/she may still obtain marks for layout.
15.9 If a different approach is used by candidates, ensure that the answers are assessed according to the mark allocation/subheadings as indicated in the marking guideline.
15.10 15.10.1 Award TWO marks for complete sentences. Award ONE mark for phrases, incomplete sentences and vague answers.
15.10.2 With effect from November 2015, the TWO marks will not necessarily appear at the end of each completed sentence. The ticks (√) will be separated and indicated next to each fact, e.g. ‘Product development is a growth strategy, √ where businesses aim to introduce new products into existing markets.’ √
This will be informed by the nature and context of the question, as well as the cognitive verb used.
15.11 With effect from November 2017, the maximum of TWO (2) marks for facts shown as headings in the marking guidelines, will not necessarily apply to each question. This would also depend on the nature of the question.
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 B √√
1.1.2 D √√
1.1.3 A √√
1.1.4 C √√
1.1.5 A √√ (5 x 2) (10)
1.2
1.2.1 National Credit Regulator √√
1.2.2 forty-five √√
1.2.3 horizontal √√
1.2.4 applicant √√
1.2.5 management √√ (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 J √√
1.3.2 F √√
1.3.3 H √√
1.3.4 A √√
1.3.5 G √√ (5 x 2) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Mark the FIRST TWO answers only.
QUESTION 2: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS
2.1 Types of diversification strategies
- Concentric diversification √
- Horizontal diversification √
- Conglomerate diversification √
NOTE: Mark the first THREE (3) only. (3 x 1) (3)
2.2 Purpose of the Employment Equity Act
- The EEA allows employees who do the same work to be paid equally. √√
- Eliminates discrimination on grounds of gender/race/disability in the workplace. √√
- Promotes equal opportunity and fair treatment in the workplace. √√
- Protects employees from victimisation if they exercise the rights given to them by the EEA. √√
- Promotes diversity in the workplace by ensuring that people of diverse backgrounds are appointed. √√
- Ensures equal representation in the workplace through the implementation of affirmative action. √√
- Ensures equal representation of all population groups in the workplace. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to the purpose of the Employment Equity Act.
Max. (6)
2.3 PESTLE factors
2.3.1 PESTLE factors from the scenario
PESTLE FACTORS | MOTIVATIONS | ||
1. Technological √√ | Paul Furnitures is losing some of their customers as the business does not have online transaction facilities. √ | ||
2. Social √√ | They are experiencing a decline in sales due to the high unemployment rate. √ | ||
3. Environmental √√ | The packaging material that PF uses is not recyclable. √ | ||
| Sub-max. (6) | Sub-max. (3) | ||
NOTE:
- Mark the first THREE (3) factors only.
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format.
- Award marks for the PESTLE factors even if the quotes were incomplete.
- Do not award marks for the motivations if the PESTLE factors were incorrectly identified. Max. (9)
2.4 Funding of SETA’s
- Skills Development levies paid by employers √ e.g. 80% is distributed to the different SETA and 20% is paid into the National Skills Fund. √
- Donations and grants √ from the public. √
- Surplus funds √ from government institutions. √
- Funds received √ from rendering their services. √
- Any other relevant answer related to how SETA’s are funded.
Max. (4)
2.5 Legislation
2.5.1 Consumer Protection Act/CPA √√ (2)
2.5.2 Advantages of CPA on businesses
- Enable MT / businesses to resolve disputes fairly √ through the National Consumer Commission/Consumer Court/Industrial ombudsmen. √
- Businesses may build a good image √ when they ensure that consumer rights are not violated. √
- May gain consumer loyalty, √ if they comply with CPA. √
- Businesses are less likely to have court cases against them√ for consumer rights violations. √
- Businesses may be protected √ if they are regarded as consumers. √
- Businesses may be safeguarded √ from dishonest competitors.√
- Prevents larger businesses √ from undermining smaller ones. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the advantages of CPA on MT/ businesses.
Max. (4)
2.6 Types of intensive strategies
Market penetration √√
- New products penetrate an existing market at a low price, until it is well known to the customers and then the prices increase. √
- It is a growth strategy where businesses focus on selling existing products to existing markets. √
- Focuses on gaining a larger share of the market by reducing prices to increase sales/increasing advertising and promotion. √
- Any other relevant answer related to market penetration as a type of intensive strategy.
Type (2)
Discussion (1)
Sub-max. (3)
Market development √√
- A process of exploring/finding/searching new markets for existing products. √
- Businesses sell their existing products to new markets √/Involves targeting consumers in a potential market that is outside its normal target market. √
- Business must research the market it wants to enter. √
- They change the way the products are distributed to reach a different market. √
- Any other relevant answer related to market development as a type of intensive strategy.
Type (2)
Discussion (1)
Sub-max. (3)
Product development √√
- Businesses generate new ideas and develop a new product or service. √
- The introduction of a new product or service into existing markets. √
- A business may need to acquire new technology to develop new products. √
- They improve/change the packaging of current products so that they look and seem different and appeal to the market. √
- Any other relevant answer related to product development as a type of intensive strategy.
Type (2)
Discussion (1)
Sub-max. (3)
NOTE: Mark the first TWO (2) only.
Max. (6)
2.7 Steps in evaluating a strategy
- Examine the underlying basis of a business strategy. √√
- Look forward and backwards into the implementation process. √√
- Compare the expected performance with the actual performance. √√
- Measure the business performance in order to determine the reasons for deviations and analyse these reasons. √√
- Take corrective action so that deviations may be corrected. √√
- Set specific dates for control and follow up. √√
- Draw up a table of the advantages and disadvantages of a strategy. √√
- Decide on the desired outcome. √√
- Consider the impact of the strategic implementation in the internal and external environments of the business. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to the steps in evaluating a strategy.
NOTE: Accept steps in any order.
Max. (6)
[40]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS | |
QUESTION 2 | MARKS |
2.1 | 3 |
2.2 | 6 |
2.3.1 | 9 |
2.4 | 4 |
2.5.1 | 2 |
2.5.2 | 4 |
2.6 | 6 |
2.7 | 6 |
TOTAL | 40 |
TOTAL 40
QUESTION 3: BUSINESS OPERATIONS
3.1 Sources of external recruitment
- Recruitment agencies √
- Billboards √
- Printed media, e.g. newspapers/flyers/magazine/posters √
- Electronic media, e.g. radio/TV√
- Social media/Social networks/Internet/Business websites √
- Walk-ins √
- Head hunting √
- Professional associations √
- Networking √
- Educational/Training institutions √
- Word-of-mouth √
- Any other relevant answer related to the sources of external recruitment.
NOTE: Mark the first TWO (2) only.
(2 x 1) (2)
3.2 Placement procedure as a human resource activity
- Businesses should outline the specific responsibilities of the new position, including the expectations/skills required for this position. √√
- Determine the successful candidate's strengths/weaknesses/ interests/skills by subjecting him/her to a range of psychometric tests. √√
- Determine the relationship between the position and the competencies of the new candidate. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to the placement procedure as a human resource activity.
Max. (4)
3.3 Employment contract
3.3.1 Aspects included in the employment contract from the scenario
- hours of work √
- probation period √
- termination of contract √
NOTE: Mark the first TWO (2) only.
(2 x 1) (2)
3.3.2 Legal requirements of the employment contract
- The employer and employee √ must both sign the contract. √
- Employer and employee must agree √ to any changes to the contract. √
- No party may unilaterally √ change aspects of the employment contract. √
- The remuneration package/including benefits √ must be clearly indicated. √
- It may not contain any requirements √ that conflict with the BCEA. √
- The employment contract should include √ a code of conduct and code of ethics.
- Aspects of the employment contract √ can be renegotiated during the course of employment. √
- The employer must explain √ the terms and conditions of the employment contract to the employee. √
- Conditions of employment/duties/responsibilities of the employees √ must be stipulated clearly. √
- All business policies, procedures and disciplinary codes/rules √ can form part of the employment contract. √
- The employer must allow the employee to thoroughly read through the contract √ before it is signed. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the legal requirements of the employment contract.
Max. (6)
3.4 Impact of fringe benefits on businesses
Positives/Advantages
- Attractive fringe benefit packages √ may result in higher employee retention/reduces employee turnover. √
- Attracts qualified/skilled/experienced employees √ who may positively contribute towards the business goals/objectives. √
- Improves productivity √ resulting in higher profitability. √
- It increases employee satisfaction/loyalty √ as they may be willing to go the extra mile. √
- Businesses save money √ as benefits are tax deductible. √
- Fringe benefits can be used as leverage √ for salary negotiations. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the positive impact/advantages of fringe benefits on businesses.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- A business which cannot offer fringe benefits √ fails to attract skilled workers. √
- A business which offers employees different benefit plans may create resentment √ to those who receive less benefit resulting in lower productivity. √
- It can create conflict/lead to corruption √ if allocated unfairly. √
- Fringe benefits are additional costs √ that may result in cash flow problems. √
- Decreases business profits, √ as incentive/package/remuneration costs are higher. √
- Administrative costs increase √ as benefits need to be correctly recorded for tax purposes. √
- Workers only stay with the business for fringe benefits, √ and may not be committed/loyal to the tasks/business. √
- Businesses has to pay advisors/attorneys √ to help them create benefit plans that comply with legislation. √
- Errors in benefit plans√ may lead to costly lawsuits/regulatory fines. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact/disadvantages of fringe benefits on businesses.
Max. (6)
3.5 Quality of performance
3.5.1 Quality indicators of the purchasing function from the scenario
- Jane place orders timeously and follow-up to ensure goods are delivered on time. √
- She also monitors and reports on minimum stock levels to avoid running out of stock. √
NOTE: Mark the first TWO (2) only.
(2 x 1) (2)
3.5.2 Other quality indicators of the purchasing function
- Businesses should buy raw materials/products in bulk√ at lower prices. √
- Select reliable suppliers √ that render the best quality raw materials/capital goods at reasonable prices. √
- Effective co-ordination between purchasing and production departments√ so that purchasing staff understand the requirements of the production process. √
- Required quantities should be delivered √ at the right time and place. √
- Implement and maintain stock control systems √ to ensure the security of stock. √
- Maintain optimum stock levels √ to avoid overstocking/reduce out-dated stock. √
- Effective use of storage space √ and maintain product quality while in storage. √
- Involve suppliers √ in strategic planning/product design/material selection/quality control process. √
- Ensure that there is no break in production √ due to stock shortages. √
- Establish relationships with suppliers √ so that they are in alignment with the business’s vision/mission/values. √
- Have a thorough understanding√ of supply chain management.√
- Any other relevant answer related to other quality indicators of the purchasing function.
NOTE: Do not award marks for responses quoted in QUESTION 3.5.1.
Max. (4)
3.6 Benefits of a good quality management system
- Effective customer services are rendered, √ resulting in increased customer satisfaction. √
- Time and resources √ are used efficiently. √
- Productivity increases through proper time management√/using high quality resources. √
- Products/Services are constantly improved √ resulting in increased levels of customer satisfaction. √
- Vision/Mission/Business goals √ may be achieved. √
- The business may achieve a competitive advantage√ over its competitors. √
- Regular training will continuously improve√ the quality of employees' skills/knowledge. √
- Employers and employees will have a healthy working relationship√ resulting in happy/productive workers. √
- Increased market share and profitability may result √ in business growth/ expansion. √
- Improved business image, √ as there are less defects/faulty products/ returns. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the benefits of a good quality management system.
Max. (4)
3.7 Impact of TQM if it is poorly implemented by businesses
- Setting unrealistic deadlines √ that may not be achieved. √
- Employees may not be adequately trained √ resulting in poor quality products. √
- Decline in productivity, √ because of stoppages. √
- Businesses may not be able to make necessary changes of products/services √ to satisfy the needs of customers. √
- Business reputation/image may suffer√ because of poor quality/ defective goods. √
- Customers will have many alternatives to choose from √ and the impact could be devastating to businesses. √
- Investors might withdraw investment, √ if there is a decline in profits. √
- Decline in sales√ as more goods are returned by unhappy customers. √
- High staff turnover√, because of poor skills development. √
- Undocumented/Uncontrolled quality control systems/processes √ could result in errors/deviations from pre-set quality standards. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the impact of TQM if it is poorly implemented by businesses.
Max. (4)
3.8 Advantages of monitoring and evaluation of quality processes on large businesses as a TQM element
- Prevents product defects and minimises wastage/customer complaints. √√
- Good quality checks/procedures minimise the replacement/ breakdown of equipment/machinery on a regular basis. √√
- May be equipped to get things done right the first time. √√
- Improve performance and maintain high quality standards. √√
- Improve current and future management of quality outputs/outcomes/ impact. √√
- Provide clear indication about quality aspects that are contributing to the achievement of goals/targets. √√
- Modify interventions that may improve the efficient use of resources. √√
- Support management to acquire information needed to make informed decision about processes. √√
- Cost of production is reduced as deviations from set standards can be corrected. √√
- Strategies are revised in order to improve the quality of the product and services/business image. √√
- Allows for quality control checks and procedures at key points. √√
- Key performance indicators are carefully selected to monitor and evaluate the outcome. √√
- Benchmarking is used to find best practices in order to determine the competitive position of the business. √√
- Quality circles meet on regular basis to evaluate the progress in terms of quality. √√
- Continuous research is conducted on latest developments to ensure that TQM planning is up to date. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to the advantages of monitoring and evaluation of quality processes as a TQM element on large businesses
Max. (6)
[40]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS | |
QUESTION 3 | MARKS |
3.1 | 2 |
3.2 | 4 |
3.3.1 | 2 |
3.3.2 | 6 |
3.4 | 6 |
3.5.1 | 2 |
3.5.2 | 4 |
3.6 | 4 |
3.7 | 4 |
3.8 | 6 |
TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 4: MISCELLANEOUS TOPICS
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS
4.1 Provisions of the BCEA
- Hours of work/Work hours √
- Overtime √
- Leave √
- Meal breaks and rest periods √
- Public holidays √
- Termination of employment √
- Child and forced labour √
NOTE: Mark the first TWO (2) only.
(2 x 1) (2)
4.2 Challenges of business environments and extent of control
CHALLENGES 4.2.1 | BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS 4.2.2 | EXTENT OF CONTROL 4.2.3 | |
ZC is operating in a high crime area which has a negative impact on their profitability. √ | Macro environment √ | No control √ | |
ZC is also losing their clients to Monja Computers who offer their services at reasonable prices. √ | Market environment √ | Partial/Some/ Limited/Less/Little control √ | |
| Sub-max. (2) | Sub-max. (2) | Sub-max. (2) | |
NOTE:
- Mark the first TWO (2) challenges only.
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format.
- If the business environment is not linked to the challenge, mark the challenge only.
- Award full marks for the business environment even if the challenge is not quoted in full.
- The extent of control must be linked to the business environment.
- Do not award marks for the business environment if the challenges were incorrectly identified.
- Award marks for the challenges even if the business environment is incomplete/incorrect.
- Do not award marks for the extent of control if the business environment is not mentioned.
- Accept responses in any order.
Max. (6)
4.3Application of Porter’s Five Forces model
4.3.1 Threat/Barriers of new entrants to the market
- If the barriers to enter the market are low, √ then it is easy for new businesses to enter the market/industry. √
- If the business is highly profitable, it will attract potential competitors√ that want to benefit from high profits. √
- New competitors can quickly/easily enter the market, √ if it takes little time/ money to enter the market. √
- If there are a few suppliers of a product/service but many buyers, √ it may be easy to enter the market. √
- Any other relevant answer related to how businesses could apply the threat/barriers of new entrants to the market to analyse the market environment.
Max. (4)
4.3.2 Bargaining power of buyer/Power of buyers
- Assess how easy it is for buyers/customers √ to drive prices down. √
- Determine the number of buyers/the importance of each buyer to the business √ and the cost of switching to other products. √
- A few powerful buyers√ are often able to dictate their terms to the business. √
- Buyers buying in bulk can bargain for prices √ in their favour. √
- If buyers can do without the business's products √ then they have more power to determine the prices and terms of sale. √
- Conduct market research √ to gather more information about its buyers. √
- Any other relevant answer related to how businesses could apply the bargaining power of buyers/power of buyers to analyse the market environment.
Max. (4)
4.4 Ways in which businesses can comply with COIDA
- Businesses should provide a healthy/safe working environment. √√
- Register with the Compensation Commissioner and provide the particulars of the business. √√
- Keep records of employees’ income and details of work for four years. √√
- Obliged to report all incidents causing death/injury/illness of employees. √√
- Submits returns of earnings not later than 1 March annually. √√
- Levies must be paid to the Compensation Fund. √√
- Ensure that the premises/equipment/machinery is in good working condition. √√
- Allow regular assessment of the workplace by inspectors in order to determine the level of risk their employees are exposed to. √√
- Employers may not make deductions for COIDA from employees' remuneration packages. √√
- Businesses must ensure that claims are lodged within twelve months of the date of the accident. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to ways in which businesses can comply with COIDA.
Max. (4)
BUSINESS OPERATIONS
4.5 Aspects that should be included in an induction programme
- Safety regulations and rules. √
- Overview of the business. √
- Information about the business products/services. √
- Meeting with senior management who will explain the company’s vision/ values/job descriptions/daily tasks. √
- Tour of the premises. √
- Introduction to key people and close colleagues. √
- Conditions of employment, e.g. working hours/leave application process/ disciplinary procedures, √ etc.
- Administration details on systems/processes/logistics. √
- Discussion of the employment contract and conditions of service. √
- Discussion on personnel policies, e.g. making private phone calls/using the internet, √ etc.
- Discussion on employee benefits. √
- Corporate social responsibility programmes. √
- Any other relevant answer related to aspects that should be included in an induction programme.
NOTE: Mark the first TWO (2) only.
(2 x 1) (2)
4.6 Salary determination methods from given statements
4.6.1 Time-related √√
4.6.2 Piecemeal √√ (4)
4.7 Benefits of induction for businesses
- Allows new employees to settle in quickly √ and work effectively. √
- Ensures that new employees understand rules and restrictions in the business. √
- New employees may establish relationships √ with fellow employees at different levels. √
- Make new employees feel at ease in the workplace, √ which reduces anxiety/ insecurity/fear. √
- The results obtained during the induction process provide √ a base for focussed training. √
- Increases quality √ of performance/productivity. √
- Minimises the need √ for on-going training and development. √
- Employees will be familiar with organisational structures, √ e.g. who are their supervisors/low level managers. √
- Opportunities are created for new employees √ to experience/explore different departments. √
- New employees will understand their role/responsibilities √ concerning safety regulations and rules. √
- New employees will know the layout of the building/factory/offices/ where everything is, √ which saves production time. √
- Learn more about the business so that new employees understand their roles/responsibilities √ in order to be more efficient. √
- Company policies are communicated, √ regarding conduct and procedures/safety and security/employment contract/conditions of employment/working hours/leave. √
- Realistic expectations for new employees √ as well as the business are created. √
- New employees may feel part of the team √ resulting in positive morale and motivation. √
- Employees may have a better understanding of business policies √ regarding ethical/professional conduct/procedures/CSR, √ etc.
- Reduces the staff turnover √ as new employees have been inducted properly. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the benefits of induction for businesses.
Max. (4)
4.8 Total quality management
4.8.1 Total quality management elements from the scenario
TQM ELEMENTS | MOTIVATIONS | ||||
1. | Continuous improvement to processes and systems √√ | FFL makes use of the services of quality circles to stay ahead of their competitors. √ | |||
2. | Adequate financing and capacity√√ | They can also afford market researchers to gather information about their target market. √ | |||
| Sub-max. (4) | Sub-max. (2) | ||||
NOTE:
- Mark the first TWO (2) only.
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format.
- Award marks for the TQM elements even if the quotes were incomplete.
- Do not award marks for the motivations if the TQM elements were incorrectly identified.
Max. (6)
4.9 Ways in which TQM can reduce the cost of quality
- Introduce quality circles to discuss ways of improving the quality of work/ workmanship. √√
- Schedule activities to eliminate duplication of tasks. √√
- Share responsibility for quality output amongst management and workers. √√
- Train employees at all levels, so that everyone understands their role in quality management. √√
- Develop work systems that empower employees to find new ways of improving quality. √√
- Work closely with suppliers to improve the quality of raw materials/inputs. √√
- Improve communication about quality challenges/deviations, so that everyone can learn from experience. √√
- Reduce investment on expensive, but ineffective inspection procedures in the production process. √√
- Implement pro-active maintenance programmes for equipment/machinery to reduce/eliminate breakdowns. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to ways in which TQM can reduce the cost of quality.
NOTE: Mark the first TWO (2) only (2 x 2) (4)
[40]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS | |
QUESTION 4 | MARKS |
4.1 | 2 |
4.2.1 | 2 |
4.2.2 | 2 |
4.2.3 | 2 |
4.3.1 | 4 |
4.3.2 | 4 |
4.4 | 4 |
4.5 | 2 |
4.6 | 4 |
4.7 | 4 |
4.8.1 | 6 |
4.9 | 4 |
TOTAL | 40 |
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Mark the FIRST question only.
QUESTION 5: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS (LEGISLATION)
5.1 Introduction
- Black Economic Empowerment is an integrated and connected socio- economic development process which contributes directly to SA’s economic transformation. √
- BBBEE achieves substantial change in the racial composition of ownership and increases the access to economic activities and skills training of previously disadvantaged individuals. √
- Enterprise and supplier development enable large businesses to empower black owned businesses and suppliers. √
- Businesses enjoy the benefits of the BBBEE Act even though this Act may disadvantage other businesses. √
- Penalties/Consequences for non-compliance encourage businesses to comply with this Act. √
- Any other relevant introduction related to the differences between BEE and BBBEE Act/implications of BBBEE pillars/impact of BBBEE on businesses/penalties for non-compliance. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
5.2 Differences between BEE and the BBBEE Act
BLACK ECONOMIC EMPOWERMENT (BEE) | BROAD BASED BLACK ECONOMIC EMPOWERMENT (BBBEE) |
It is a government policy √ which may not be enforced. √ | It is an Act √ that is enforced/must be complied with by businesses. √ |
Benefits only a few previously disadvantaged people √ in the economy. √ | Encourages a wider group of previously disadvantaged people/ black women/people who are physically challenged/youth/people in rural areas √ to participate in the economy. √ |
Few previously disadvantaged individuals share in the wealth √ of the economy. √ | Aims at distributing the country's wealth √ across a broader spectrum of society. √ |
Focuses only on three pillars √ that did not include all previously disadvantaged people. √ | Focuses on seven/five pillars √ which includes all sectors of the society, especially the previously disadvantaged. √ |
Any other relevant answer related to BEE. | Any other relevant answer related to BBBEE. |
Sub-max. (4) | Sub-max. (4) |
NOTE:
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format.
- The difference does not have to link but must be clear.
- Award a maximum of FOUR (4) marks if the difference is not clear/Mark either BEE or BBBEE only.
Max. (8)
5.3 Implications of BBBEE pillars for businesses Ownership
- Business should include black people √ in shareholding/partnerships/ franchises. √
- Encourage small black investors to invest √ in big companies and share ownership. √
- Exempted Micro Enterprises (EMEs) with an ownership of 50% or more of black people √ are promoted to level 3 of the BEE scorecard. √
- More opportunities are created for black people √ to become owners/ entrepreneurs. √
- Large businesses should form joint ventures √ with small black owned businesses and share business risks. √
- Businesses sometimes find it difficult to locate √ suitable black business partners/shareholders. √
- Many black people cannot afford shares √ in companies/contributions to partnerships. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the implications of ownership as a BBBEE pillar for businesses.
Sub-max. (8)
Skills development
- Businesses must engage black employees √ in skills development initiatives. √
- Provide learnerships/Learning programmes √ to black employees. √
- Business must contribute 1% of their payroll √ to fund the skills development programmes. √
- Businesses could benefit from the increased √ pool of skilled/trained workers. √
- Businesses must go the extra mile to train staff √ where learnerships are not offered. √
- Productivity is compromised as mentors/coaches have to find the time√ to participate in learnerships/training. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the implications of skills development as a BBBEE pillar for businesses.
Sub-max. (8)
Max. (16)
5.4 Impact of BBBEE on businesses
Positives/Advantages
- Businesses that comply with BBBEE regarding the pillars √ will be rated high on the BEE scorecard/may get government tenders/may attract other BBBEE business partners/-suppliers. √
- Encourages businesses to address the demands√ for redress/ equity directly. √
- Provides a variety of business codes√ to improve employment equity. √
- Provides for human resources development√ through training and development. √
- Promotes enterprise development, √ by developing entrepreneurial skills of designated people to start their own businesses. √
- Businesses will have a good overview on how it is performing √ in comparison to other businesses in the rest of the country. √
- A good BBBEE rating√ will improve the image of the business. √
- By focusing on BBBEE, the business will show commitment √ towards the social/education/economic developments in the community/ country. √
- Once rated, the business will understand how to develop BBBEE strategies √ that will increase its BBBEE ratings on an annual basis. √
- Fronting is discouraged, √ as it may lead to the disqualification of a business's entire scorecard/BBBEE status. √
- Share prices of BBBEE compliant businesses are likely to increase √ as they attract more business. √
- Businesses that support Small, Micro, Medium Enterprises (SMMEs), √ may increase their own BBBEE ratings. √
- Complying with BBBEE requirements gives businesses experience/exposure √ to be able to provide better employment opportunities/staff development. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the positive impact of BBBEE on businesses.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- Businesses have to go through the process of having their BBBEE compliance/verified √ by an independent BEE verification agency. √
- Businesses that wish to do business with the government, √ must have their BEE status assessed annually. √
- Provides for preferential procurement, √ so certain businesses may be excluded from supplying goods/services. √
- Processes may lead to corruption/nepotism, √ if not monitored properly. √
- Many businesses have been disadvantaged due to BBBEE ratings √ as they may not be able to meet all the scoring. √
- Processes and procedures may be costly for a business √ as there are many legal requirements for scoring enough points to be compliant. √
- Businesses could experience large financial implications/penalties √ if they do not comply with BBBEE. √
- Businesses will have to spend money in areas covered by the seven/five BBBEE pillars √ to obtain a good BBBEE rating. √
- Investment/Ownership issues √ can cause unhappiness between existing shareholders. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact of BBBEE on businesses.
Max. (14)
5.5 Penalties for non-compliance with the BBBEE Act
- Businesses may face imprisonment for non-compliance and fronting practices. √√
- The penalty could be a fine of up to 10% of the company’s annual turnover. √√
- Government will cancel any contract awarded that was based on false information regarding BBBEE status. √√
- A business can be banned from participating in government contracts for a period of 10 years. √√
- Business licenses may not be renewed, and authorisations may not be issued. √√
- Businesses that fail to achieve at least a minimum 40% of compliance with ownership, skills development and new enterprise and supplier development will be automatically downgraded by one level. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to penalties that businesses could face for non-compliance with BBBEE Act.
Max. (8)
5.6 Conclusion
- BBBEE Act increased the number of previously disadvantages people that manage and control the country’s economy. √√
- More previously disadvantaged individuals have been receiving access to ownership and training therefore empowering rural and local communities. √√
- The BBBEE Act is an enabling framework that allows for the development of Codes of Good Practice. √√
- Businesses should strive to comply with the BBBEE Act to avoid unnecessary fines and negative publicity. √√
- Any other relevant conclusion related to the differences between BEE and BBBEE Act/implications of BBBEE pillars/impact of BBBEE on businesses/penalties for non-compliance.
(Any 1 x 2) (2)
[40]
QUESTION 5: BREAKDOWN OF MARKS
DETAILS | MAXIMUM | TOTAL |
Introduction | 2 |
Max 32 |
Differences between BEE and BBBEE Act | 8 | |
Implication of BBBEE pillars
|
16 | |
Impact of BBBEE on businesses | 14 | |
Penalties/consequences for non- compliance with the BBBEE Act | 8 | |
Conclusion | 2 | |
INSIGHT | ||
Layout | 2 |
8 |
Analysis, interpretation | 2 | |
Synthesis | 2 | |
Originality/Examples | 2 | |
TOTAL MARKS | 40 |
*LASO – For each component:
Allocate 2 marks if all requirements are met.
Allocate 1 mark if only some of the requirements are met. Allocate 0 marks where requirements are not met at all.
QUESTION 6: BUSINESS OPERATIONS (HUMAN RESOURCES FUNCTION)
6.1 Introduction
- A job analysis assists businesses in identifying the details of the vacancy and of the candidate. √
- Internal recruitment allows for businesses to first look for a suitable candidate within the organisation. √
- The interviewer is responsible for planning and administering of the interview process. √
- The human resource function should implement the Skills Development Act/SDA to keep abreast with the latest development in the industry in which the business operates. √
- Any other relevant introduction related to the differences between job description and job specification/impact of internal recruitment/role of the interviewer /implication of the SDA on human resources function.
(Any 2 x 1) (2)
6.2 Differences between job description and job specifications
JOB DESCRIPTION | JOB SPECIFICATION |
Describes duties/responsibilities of a specific job/Summary of the nature/type of the job. √√ | Specifies the minimum acceptable personal qualities/skills/qualifications needed for the job. √√ |
Written description of the job and its requirements. √√ | Written description of specific qualifications/skills/experience needed for the job. √√ |
Describes key performance areas/tasks for a specific job, e.g. job title/working conditions/ relationship of the job with other jobs in the business, √√ etc. | Describes key requirements of the person who will fill the position, e.g. formal qualifications/willingness to travel/work unusual hours, √√ etc. |
Any other relevant answer related to job description. | Any other relevant answer related to job specification. |
Sub-max. (4) | Sub-max. (4) |
NOTE:
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format.
- The differences do not have to link but must be clear.
- Award a maximum of FOUR (4) marks if the differences are not clear/Mark either job description or job specification only.
Max. (8)
6.3 Impact of internal recruitment on businesses Positives/Advantages
- Cheaper/Quicker to fill √ the post. √
- Placement is easy, √ as management knows the employees’ skills/ personality/experience/strengths. √
- Provides opportunities for career paths √ within the business. √
- The employee already has an understanding of how the business operates, √ induction/training is not always necessary. √
- Reduces the chances of losing employees, √ as future career prospects are available. √
- Detailed, reliable information can be obtained √ from the supervisors/ employee records. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the positive impact/advantages of internal recruitment on businesses.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- Current employees may not bring new ideas √ into the business. √
- Promoting a current employee may cause resentment √ amongst other employees. √
- Promotion may disrupt business operations √ as it creates open vacancies that need to be filled. √
- The number of applicants is limited √ to current staff only. √
- Employees who do not really have the required skills for the new job √ may be promoted. √
- Current employees may need to be trained/developed √ before they can be promoted, which can be expensive. √
- Staff that is not promoted may feel demotivated √ which may hamper productivity. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact/disadvantages of internal recruitment on businesses.
Max. (16)
6.4 Role of the interviewer while preparing for an interview
- The interviewer should develop a core set of questions √ based on the skills/knowledge/ability required. √
- Check/read the application/verify the CV √ of every candidate for anything that may need to be explained. √
- Book and prepare √ the venue for the interview. √
- Set the interview date √ and ensure that all interviews take place on the same date, if possible. √
- Inform all shortlisted candidates √ about the date and place of the interview. √
- Plan the programme for the interview √ and determine the time that should be allocated to each candidate. √
- Notify all panel members conducting the interview √ about the date and place of the interview. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the role of the interviewer while preparing for an interview.
Max. (12)
6.5 Implications of SDA on the human resources function
- The human resource function must contribute 1% of their salary bill to the Skills Development Levy/SDL. √√
- Ensure training in the workplace is formalised/structured. √√
- Appoint a full/part time consultant as a skills development facilitator. √√
- Assist managers in identifying skills/training needs to help them to introduce learnerships. √√
- The human resources manager should interpret the aims and requirements of the SDA and adapt workplace skills training programmes accordingly. √√
- Identify the training needs of the employees and provide them with training opportunities so that they will perform their tasks efficiently. √√
- Use the National Qualification Framework/NQF to assess the skills levels of employees. √√
- Interpret/Implement the aims/requirements of the framework for the National Skills Development Strategy. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to the implications of the Skills Development Act on the human resources function.
Max. (10)
6.6 Conclusion
- A clear job analysis enables the human resources manager to select the best candidate from those who apply for the job. √√
- Internal recruitment enables businesses to reward hardworking employees the opportunity to promotion positions. √√
- Employees are the most important resource in any business and its success is strongly influenced by a good interview process. √√
- The SDA not only ensure that employees are well qualified, but also that their skills are continuously improved to ensure the business stays competitive in the future. √√
- Any other relevant conclusion related to the differences between job description and job specification/impact of internal recruitment/role of the interviewer/implication of the SDA on human resources function.
(Any 1 x 2) (2)
[40]
QUESTION 6: BREAKDOWN OF MARK ALLOCATION
DETAILS | MAXIMUM | TOTAL |
Introduction | 2 |
Max. 32 |
Differences between job description and job specifications | 8 | |
Impact of internal recruitment | 16 | |
Role of the interviewer before the interview | 12 | |
Implications of SDA on the human resources function | 10 | |
Conclusion | 2 | |
INSIGHT | ||
Layout | 2 |
8 |
Analysis, interpretation | 2 | |
Synthesis | 2 | |
Originality/Examples | 2 | |
TOTAL MARKS | 40 |
*LASO – For each component:
Allocate 2 marks if all requirements are met.
Allocate 1 mark if only some of the requirements are met. Allocate 0 marks where requirements are not met at all.
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Business Studies Paper 1 Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- This question paper consists of THREE sections and covers TWO main topics.
SECTION A: COMPULSORY
SECTION B: Consists of THREE questions.
Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section.
SECTION C: Consists of TWO questions.
Answer any ONE of the two questions in this section. - Read the instructions for each question carefully and take particular note of what is required.
Note that ONLY the first TWO questions in SECTION B and the FIRST question in SECTION C will be marked. - Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper. NO marks will be awarded for answers that are numbered incorrectly.
- Except where other instructions are given, answers must be written in full sentences.
- Use the mark allocation and nature of each question to determine the length and depth of an answer.
- Use the table below as guide for mark and time allocation when answering each question.
SECTION
QUESTION
MARKS
TIME
(minutes)
A:
Objective-type questions COMPULSORY
1
30
30
B:
THREE direct/indirect type questions CHOICE:
Answer any TWO.2
40
30
3
40
30
4
40
30
C:
TWO essay-type questions CHOICE:
Answer any ONE.5
40
30
6
40
30
TOTAL
150
120 minutes
- Begin the answer to EACH question on a NEW page, e.g. QUESTION 1 – new page, QUESTION 2 – new page.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY) QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example
1.1.6 D.
1.1.1 This Act makes provision for the establishment of the Commission for Conciliation, Mediation and Arbitration (CCMA):
- Consumer Protection Act (CPA), 2008 (Act 68 of 2008)
- Labour Relations Act (LRA), 1995 (Act 66 of 1995)
- Employment Equity Act (EEA), 1998 (Act 55 of 1998)
- National Credit Act (NCA), 2005 (Act 34 of 2005)
1.1.2 Deep Mines operates in the … sector as they specialise in the extraction of gold.
- secondary
- tertiary
- economic
- primary
1.1.3 Ntando Braai offers a unique service and have a greater power in the market. This refers to … as an element of Porter’s Five Forces model.
- competitive rivalry
- power of suppliers
- threat of substitute
- market strategy
1.1.4 Okuhle followed the … procedure when they invited five shortlisted candidates to attend an interview.
- recruitment
- employment
- selection
- placement
1.1.5 The … function ensures that relevant information is available to management for decision-making.
- administration
- public relations
- general management
- production
(5 x 2) (10)
1.2 Complete the following statements by using the word(s) provided in the list below. Write only the word(s) next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
| forward; management; National Credit Regulator; horizontal; fortyfive;applicant; performance; debt counsellor;forty; interviewer |
1.2.1 The … oversees compliance with the National Credit Act, 2005 (Act 34 of 2005).
1.2.2 Workers may not work more than … hours in a week.
1.2.3 Buhle Butchery applied … integration when they took over Thomas Butchery to reduce the threat of competition.
1.2.4 During the interview it is the role of the … to ask clarity seeking questions.
1.2.5 Businesses make use of quality … to ensure that the quality of goods and services is consistent.
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches a term in COLUMN
A. Write only the letter (A–J) next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.3.6 K.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.3.1 SWOT analysis |
|
1.3.2 Liquidation | |
1.3.3 Dismissal | |
1.3.4 PDCA cycle | |
1.3.5 Quality assurance |
(5 x 2) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer ANY TWO questions in this section.
NOTE: Clearly indicate the QUESTION NUMBER of each question that you choose. The answer to EACH question must start on a NEW page, e.g. QUESTION 2 on a new page, QUESTION 3 on a NEW page.
QUESTION 2: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS
2.1 Name THREE types of diversification strategies. (3)
2.2 Outline the purpose of the Employment Equity Act (EEA), 1998 (Act 55 of 1998). (6)
2.3 Read the scenario below and answer the question that follows.
PAUL FURNITURES (PF) Paul Furnitures is losing some of their customers as the business does not have online transaction facilities. They are experiencing a decline in sales due to the high unemployment rate. The packaging material that PF uses is not recyclable. |
2.3.1 Identify THREE factors of the PESTLE analysis that pose challenges to PF. Motivate your answer by quoting from the scenario above.
Use the table below as a GUIDE to answer QUESTION 2.3.1.
PESTLE FACTORS | MOTIVATIONS |
1. | |
2. | |
3. |
(9)
2.4 Explain how SETA’s are funded. (4)
2.5 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
MANGO TRADERS (MT) Mango Traders specialises in the manufacturing of a variety of summer clothes. MT discloses the price of their products on sale. |
2.5.1 Identify the Act that MT is complying with in the scenario above. (2)
2.5.2 Explain the advantages of the Act identified in QUESTION 2.5.1 for MT as a business. (4)
2.6 Discuss any TWO types of intensive strategies. (6)
2.7 Advise businesses on steps they should consider when evaluating a strategy. (6)
[40]
QUESTION 3: BUSINESS OPERATIONS
3.1 Name any TWO sources of external recruitment. (2)
3.2 Outline the placement procedure as a human resource activity. (4)
3.3 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
NKOSI TRANSPORTING (NT) Sonika recently started working at NT as a driver. She was requested to carefully read her employment contract, which included her hours of work, probation period and termination of contract. |
3.3.1 Quote any TWO aspects of the employment contract from the scenario above. (2)
3.3.2 Explain the legal requirements of the employment contract. (6)
3.4 Evaluate the impact of fringe benefits on businesses. (6)
3.5 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
NEDLO COLDRINKS LIMITED (NSL) Nedlo Coldrinks Limited specialises in the manufacturing of a variety of soft drinks. Jane, the purchasing manager, places orders timeously and follow-up to ensure goods are delivered on time. She also monitors and reports on minimum stock levels to avoid running out of stock. |
3.5.1 Quote TWO quality indicators of the purchasing function from the scenario above. (2)
3.5.2 Describe other quality indicators of the purchasing function. (4)
3.6 Explain the benefits of a good quality management system. (4)
3.7 Discuss the impact of total quality management (TQM) if it is poorly implemented by businesses. (4)
3.8 Advise businesses on the advantages of monitoring and evaluation of quality processes on large businesses as a total quality management (TQM) element. (6) [40]
QUESTION 4: MISCELLANEOUS TOPICS BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS
4.1 State any TWO provisions as stipulated in the Basic Conditions of Employment (BCEA), 1997 (Act 75 of 1997). (2)
4.2 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
ZANELE COMPUTERS (ZC) Zanele Computers offers a variety of computer software services. ZC is operating in a high crime area which has a negative impact on their profitability. ZC is also losing their clients to Monja Computers who offer their services at reasonable prices. |
Use the table below as a GUIDE to answer QUESTION 4.2.1 to 4.2.3.
CHALLENGES 4.2.1 | BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS 4.2.2 | EXTENT OF CONTROL 4.2.3 |
1. | ||
2. |
4.2.1 Quote TWO challenges for ZC from the scenario above. (2)
4.2.2 Classify ZC’s challenges according to any TWO of the THREE business environments. (2)
4.2.3 State the extent of control ZC has over EACH business environment named in QUESTION 4.2.2. (2)
4.3 Explain how businesses could apply the following forces of Porter’s Five Forces model to analyse their position in the market:
4.3.1 Threat/Barriers of new entrants to the market (4)
4.3.2 Bargaining power of buyer/Power of buyers (4)
4.4 Suggest ways in which businesses can comply with the Compensation for Occupational Injuries and Diseases Amendment Act (COIDA), 1997 (Act 61 of 1997). (4)
BUSINESS OPERATIONS
4.5 Name any TWO aspects that should be included in an induction programme. (2)
4.6 Identify the salary determination methods used by Roshan Bags in EACH statement below:
4.6.1 John, the cleaner, gets paid a thousand rand for the number of hours he spends on a task.
4.6.2 Amla gets paid sixteen rands for each bag she makes. (4)
4.7 Explain the benefits of induction for businesses. (4)
4.8 Read the scenario below and answer the question that follows.
FUMA FOOTWEAR LIMITED (FFL) Fuma Footwear Limited is a large business that specialises in the manufacturing of quality sneakers. FFL makes use of the services of quality circles to stay ahead of their competitors. They can also afford market researchers to gather information about their target market. |
4.8.1 Identify TWO total quality management (TQM) elements applied by FFL. Motivate your answer by quoting from the scenario above.
Use the table below as a GUIDE to answer QUESTION 4.8.1.
TQM ELEMENTS | MOTIVATIONS |
1. | |
2. |
(6)
4.9 Suggest TWO ways in which total quality management (TQM) can reduce the cost of quality. (4)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer ONE question in this section.
NOTE: Clearly indicate the QUESTION NUMBER of each question chosen. The answer to the question must start on a NEW page, e.g. QUESTION 5 on a NEW page or QUESTION 6 on a NEW page.
QUESTION 5: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS (LEGISLATION)
The government initiated the Broad-Based Black Economic Empowerment Act (BBBEE), 2003 (Act 53 of 2003) (amended in 2013) to overcome the shortcomings of Black Economic Empowerment (BEE). The BBBEE pillars have various implications for businesses as they need to apply these pillars in the workplace. Businesses may face penalties for non-compliance with the BBBEE Act. |
Write an essay on the BBBEE Act in which you include the following aspects:
- Differentiate between BEE and the BBBEE Act.
- Explain the implications of the following BBBEE pillars for businesses:
- Ownership
- Skills development
- Discuss the impact of BBBEE on businesses.
- Advise businesses on penalties that they may face for non-compliance with this Act. [40]
QUESTION 6: BUSINESS OPERATIONS (HUMAN RESOURCES FUNCTION)
Businesses compile a job analysis of vacant positions before they consider using the internal and external recruitment methods. Businesses must prepare interview questions for shortlisted candidates. They must also ensure that the human resources manager knows the implications of the Skills Development Act in his/her department. |
Write an essay on the human resource function in which you include the following aspects:
- Outline the differences between job description and job specifications as components of a job analysis.
- Explain the impact of internal recruitment on businesses.
- Discuss the role of the interviewer while preparing for an interview.
- Advise the human resources manager on the implications of the Skills Development Act to his/her department. [40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Agricultural Sciences Paper 2 Memorandum - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 C
1.1.2 A
1.1.3 B
1.1.4 D
1.1.5 A
1.1.6 C
1.1.7 D
1.1.8 C
1.1.9 C
1.1.10 B (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 D
1.2.2 E
1.2.3 A
1.2.4 C
1.2.5 F (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 Codominance
1.3.2 Atavism
1.3.3 Cash flow
1.3.4 Price fixing
1.3.5 Budget (5 x 2) (10)
1.4
1.4.1 Variation
1.4.2 Selling
1.4.3 Seasonal
1.4.4 Balance sheet
1.4.5 Capital (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
2.1
2.1.1 Condition that exists on the market at R5
- Market equilibrium (1)
2.1.2 Law of supply from the table
- The higher the price the higher the quantity supplied (2)
2.1.3 TWO factors that could have affected the demand of peaches
- Changes in consumer preferences
- Number of consumers on the market
- Festive seasons
- Complementary products
- Availability of substitutes (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.1.4 Line graph showing the demand of peaches
(6)
2.2
2.2.1 Caption for the diagram
- Marketing chain / Agri-business chain (1)
2.2.2 Labels for A and B
- A – Supply chain
- B – Demand chain (2)
2.2.3 THREE marketing functions in the diagram
- Transport
- Storage
- Processing (3)
2.2.4 TWO ways of streamlining the agri-business chain
- Improving road infrastructure
- Improving access to market information
- Marketing collectively
- Processing products close to where they are produced
- Using cold storage and refrigerated trucks
- Grading and standardisation of products (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.3
2.3.1 Exporters and importers (1)
2.3.2 Brokers (1)
2.3.3 Consumers (1)
2.3.4 Food processing companies (1)
2.3.5 Retailers (1)
2.4
2.4.1 The marketing channel illustrated
- Stock sales (1)
2.4.2 Marketing system associated with the marketing channel
- Free marketing (1)
2.4.3 Motivation for use of the channel above by the farmers
- Payment is guaranteed
- Seller has access to a wider market than the local one (2)
2.4.4 TWO other marketing channels available to the farmers
- Internet marketing
- Direct marketing
- Farm gate marketing
- Fresh produce marketing (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.5
2.5.1 Definition of a business plan
- It is a document that describes a business you want to start and states what its goals and objectives are. (2)
2.5.2 TWO important aspects of a business plan
- Secure funding
- To guide daily operations
- To determine financial needs
- To test the feasibility of a business idea
- To allow the entrepreneur to foresee problems
- To reposition/analyse the business
- To gain knowledge about marketing opportunities and competitors
- To ensure effective business management
- Mapping out the objectives/goals of the enterprise
- Provides information on the internal/external business environment
- Provision of time frames (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.5.3 ONE example of an entrepreneurial success factor
- Leadership
- Risk-taking
- Perseverance
- Motivation
- Market driven (Any 1 x 1) (1)
[35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
3.1
3.1.1 Definition of land
- An area of ground used for farming and agricultural production. (2)
3.1.2 Identification of economic functions of land shown in diagrams A and B.
- A – Land provides physical space needed for production processes.
- B – Land provides physical space where the farmer produces products. (2)
3.1.3 TWO economic characteristics of land as a production factor
- Land is limited.
- Urban development affects land availability.
- The value of land appreciates over time.
- Land is indestructible.
- The production capacity of land varies widely.
- Land is subject to the law of diminishing returns.
(Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.1.4 TWO measures a farmer can take to improve the productivity of land B
- Consolidation of uneconomic farming units
- Use of scientific farming methods
- Water management
- Use of farming methods that are suited to the area
(Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.2
3.2.1 Problem associated with labour described in the passage
- HIV/AIDS (1)
3.2.2 TWO measures farmers can take to address the problem identified in QUESTION 3.2.1.
- Awareness campaigns
- Providing access to condoms
- Ensuring access to treatment (STI’s) and anti-retroviral drugs through government programmes.
- Nutritional schemes
- Avoid multiple partners
- Support groups (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.2.3 TWO other problems associated with labour
- High cost of labour
- Limited education
- Availability of labour
- Strikes
- Abuse of alcohol and drugs
(Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.2.4 TWO strategies that can be used by farmers to improve labour productivity
- Motivating labourers
- Having the right type and number of labourers
- Upskilling/training the workforce
- Provision of adequate living conditions (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.3
3.3.1 Identification of budget
- Enterprise budget (1)
3.3.2 An example of a variable cost
- Seed
- Fertiliser and lime
- Machinery fuel
- Labour costs
- Harvesting (Any 1 x 1) (1)
3.3.3 Justification of answer to QUESTION 3.3.2
- The cost above increases with the level of production. (2)
3.3.4 Calculation of profit/loss
- Profit = Income – Expenses
OR
= R2 100 – (R100+R700+R100+ R600+R450+R100+ R300+R200+R100)
= R2 100 – R2 650
= - R550 OR Loss of R550 (3)
3.3.5 Deduction of enterprise viability
- The enterprise is not viable due to the loss (2)
3.4
3.4.1 Identification of farm record
- Farm inventory (1)
3.4.2 Importance of an inventory list
- Allows the farm to track available assets for insurance purposes or to determine if equipment may need to be repaired
- To track equipment loss to natural disasters or theft (Any 1 x 1) (1)
3.4.3 Type of capital in the document
- Movable capital (1)
3.4.4 Problem associated with capital that is unique to movable capital
- Depreciation (1)
3.4.5 TWO methods used to create capital
- Savings
- Production
- Credit/grants (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.5
3.5.1 Internal and external forces affecting the company in the passage above.
- Internal force – skilled workforce / aging equipment
- External force – increased competition (2)
3.5.2 Type of risk faced by the company
- Market and price risk (1)
3.5.3 Explanation of how the internal and external forces lead to the risk mentioned in QUESTION 3.5.2.
- Increased competition and aging equipment will result in the company’s products being more expensive than that of the competitors resulting in low sales. (2)
[35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
4.1
4.1.1 Punnet square

Rubric
Punnet square with gametes and offspring genotypes
Correct male gametes
Correct female gametes
Correct offspring genotype (4)
4.1.2 Genotypic ratio
- 3 Rr : 1 rr (1)
4.1.3 Probability of spherical seeds being produced
- ¾ x 100
75 % (3)
4.1.4 Type of dominance and reason
- Complete dominance Only one characteristic was expressed in heterozygote offspring (2)
4.1.5 Deduction whether seed shape is qualitative or quantitative
- Qualitative (1)
4.1.6 Motivation for answer to QUESTION 4.1.5.
- The characteristic is controlled by a gene pair. (1)
4.2
4.2.1 Identification of mutation type
- Chromosomal mutation (1)
4.2.2 Identification of mutation types
- B – Duplication
- C – Inversion
- D – Translocation (3)
4.2.3 Importance of variation
- It is the basis for selection
- It is used to improve crop varieties and livestock breeds (2)
4.2.4 An example of a physical mutation agent
- Radiation/Gamma rays/X-rays/alpha particles (1)
4.3
4.3.1 Identification of animal C
- Mule (1)
4.3.2 Identification of breeding system
- Species crossing (1)
4.3.3 Motivation of answer to QUESTION 4.3.1 above
- Involves mating of animals of different species (2)
4.3.4 TWO benefits of animal C over animal A
- Animal C is more disease and pest resistant than animal A Animal C is more hardy/resistant to extreme environmental conditions than animal A (2)
4.3.5 TWO disadvantages of breeding method depicted above
- It is of little practical importance since only few animal species can interbreed
- Products of species crossing are infertile (2)
4.4
4.4.1 Identification of plant improvement method
- Genetic engineering/Genetic modification (1)
4.4.2 ONE advantage of this technology that is mentioned in the passage
- Improve crop productivity/food security (1)
4.4.3 TWO advantages of genetic engineering over traditional plant improvement methods
- They are faster
- They are more precise
- They are not limited to individuals of the same species
(Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.4.4 TWO current applications of GM technology in plants
- Development of disease resistant plants
- Development of herbicide resistant plants
- Longer shelf life
- Improved nutritional content (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.4.5 TWO potential human health risks of GMO
- Allergies
- Unknown effects on human life
- Food safety concerns (Any 2 x 1) (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Agricultural Sciences Paper 2 Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start each question on a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show ALL calculations, including formulae, where applicable.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the correct answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 An Act of parliament that regulates employment contracts.
- Labour Relations Act
- Employment Equity Act
- Basic Conditions of Employment Act
- Occupational Health and Safety Act
1.1.2 The principle of management in which the manager checks whether results are achieved, and goals are reached.
- Control
- Planning
- Organising
- Directing
1.1.3 A risk management strategy ideal for an industry that is changing rapidly.
- Insurance
- Flexibility
- Specialisation
- Hedging
1.1.4 Products that are price inelastic in terms of demand:
- Are luxury items
- Have no substitutes
- Take a large portion of the consumer’s budget
- Are necessary goods
Choose the CORRECT combination:
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
1.1.5 Which ONE of the following is not part of the marketing mix?
- Processing
- Product
- Price
- Place
1.1.6 The following statements apply to eco-labelling:
- Allows the consumers to see that the producer is using good agricultural practices
- It is used by organic farmers
- It is concerned with maximising profits
- It is a form of sustainable marketing
Choose the CORRECT combination:
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
1.1.7 … is not an example of an agricultural co-operative.
- Purchasing co-operative
- Production co-operative
- Marketing co-operative
- Supply co-operative
1.1.8 The idea that for any particular trait, a pair of alleles of each parent separates and only one allele from each parent passes to an offspring is Mendel's principle of:
- Hybridisation
- Independent assortment
- Segregation
- Dominance
1.1.9 Sex-linked traits are more common in males than in females, because …
- all alleles on the X chromosome are dominant.
- all alleles on the Y chromosome are recessive.
- a recessive allele on the X chromosome will always produce the trait in a male.
- any allele on the Y chromosome will be co-dominant with the matching allele on the X chromosome.
1.1.10 A selection method that requires the most robust record-keeping regime for its successful implementation.
- Progeny
- Pedigree
- Mass
- Family (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Choose a term/phrase from COLUMN B that matches a description in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–H) next to question numbers
(1.2.1 to 1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 I.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
1.2.1 | Responsible for quantitative characteristics | A | Multi segment marketing |
1.2.2 | Exist in a population when there are many variations of a gene present | B | Market segmentation |
1.2.3 | A marketing strategy where a company tries to gain customers from more than one type of market from the same product and uses | C | Cooperative marketing |
1.2.4 | Marketing of produce is based on a pool system | D | Poly genes |
1.2.5 | Effective combination and co- ordination of all resources to maximise profit | E | Multiple alleles |
F | Management | ||
G | Organising | ||
H | Prepotency | ||
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question numbers (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 A mechanism of inheritance in which two dominant alleles are both expressed fully in the phenotype
1.3.2 The reappearance of an ancestral characteristic in an organism after the characteristic has been absent for many generations
1.3.3 The net amount of cash and cash equivalents being transferred into and out of the business
1.3.4 An agreement between participants on the same side in a market to collectively raise, lower or stabilise prices
1.3.5 A document that provides an estimate of expected income and expenditure for a given period of time (5 x 2) (10)
1.4 Change the UNDERLINED WORD(S) in each of the following statements to make them TRUE. Write only the answer next to the question numbers (1.4.1–1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 Mutation refers to differences that exist between individuals of the same species.
1.4.2 Marketing is the exchange of goods for cash.
1.4.3 Casual workers are employed to perform repetitive tasks on the farm.
1.4.4 A cash flow statement is a summary of the assets and liabilities of a business.
1.4.5 Net worth refers to money or equipment saved or accumulated by the farmer to use in the production process. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 The table below shows the demand and supply of peaches.
Price (R) | Quantity supplied (kg) | Quantity Demanded (kg) |
7 | 80 | 30 |
6 | 70 | 45 |
5 | 60 | 60 |
4 | 50 | 75 |
3 | 40 | 90 |
2 | 30 | 105 |
1 | 20 | 120 |
2.1.1 Name the condition that exists in the market at R5. (1)
2.1.2 Deduce the law of supply from the table above. (2)
2.1.3 Give TWO factors that could have affected the demand of peaches in the table above. (2)
2.1.4 Draw a line graph to show the quantity of peaches demanded in the table above. (6)
2.2
2.2.1 Provide a caption for the diagram above (1)
2.2.2 Divide the diagram above into two sections by providing the labels A and B. (2)
2.2.3 Identify THREE marketing functions in the diagram above. (3)
2.2.4 Suggest TWO ways of making the process above more efficient. (2)
2.3 Below are the different types of buyers on agricultural markets in South Africa.
| Retailers; Consumers, Food processing companies;Exporters and importers; Brokers |
Identify the type of buyers for each of the following:
2.3.1 Companies that buy and sell agricultural products in foreign markets. (1)
2.3.2 These agents work for commission on behalf of other participants. (1)
2.3.3 Individuals or companies that buy fresh and processed foods for final use. (1)
2.3.4 Enterprises that use agricultural commodities as raw materials. (1)
2.3.5 Intermediaries, which include supermarkets, who divide up large shipments of produce and sell them to end users. (1)
2.4 The image below shows a marketing channel that is popular with farmers.
2.4.1 Name the marketing channel illustrated above. (1)
2.4.2 Name the marketing system associated with the marketing channel. (1)
2.4.3 Justify the use of the marketing channel above by farmers by giving TWO reasons. (2)
2.4.4 List TWO other channels, except the one stated in QUESTION 2.4.1, that farmers can use to market produce. (2)
2.5
| Entrepreneurs are individuals who are willing and able to convert a new idea into a successful business. To start new businesses, entrepreneurs need to develop a business plan. |
2.5.1 Define the underlined phrase in the passage. (2)
2.5.2 Give TWO reasons why the document mentioned above is important. (2)
2.5.3 Give ONE entrepreneurial success factor. (1)
[35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1
3.1.1 Define the term land. (2)
3.1.2 Identify TWO economic functions of land shown above. (2)
3.1.3 Give TWO economic characteristics of land as a production factor. (2)
3.1.4 Suggest TWO measures a farmer can take to improve the productivity of the land shown in B. (2)
3.2
| From 1985 until 2009, 11 million labourers in agriculture died of HIV/Aids related diseases. Most of the victims were in their prime, that is 20-years of age. People in this age bracket should be economically active and producing at full capacity. |
3.2.1 Identify the problem associated with labour described in the passage above. (1)
3.2.2 Recommend TWO measures farmers can take to reduce the threat of the problem mentioned above. (2)
3.2.3 State TWO other problems associated with labour in agriculture, that are not mentioned in the passage above. (2)
3.2.4 Give TWO strategies that can be employed by farmers to improve labour productivity. (2)
3.3 A farmer wants to go into tomato production. The farmer decided to draft the budget below to determine the viability of tomato production.
Income | Amount (R) |
300 kg at R7,00/kg | 2 100,00 |
Expenses | |
Seed | 100 |
Fertiliser and lime | 700 |
Machinery fuel | 600 |
Irrigation | 450 |
Harvesting | 100 |
Labour | 300 |
Miscellaneous | 200 |
Insurance | 100 |
Profit/Loss | ………. |
3.3.1 Identify the budget shown above. (1)
3.3.2 Identify ONE variable cost from the budget shown above. (1)
3.3.3 Justify your answer to QUESTION 3.3.2 above. (2)
3.3.4 Calculate the profit/loss. (3)
3.3.5 Deduce with a reason whether this enterprise is viable. (2)
3.4 The table below shows a piece of a farm record.
Asset | Number | Make | Model | Year |
Apple sorters and graders | ||||
Brooder stoves | ||||
Combines and threshers | ||||
Corn pickers | ||||
Cultivators | ||||
Fertiliser and lime spreader | ||||
Harrows – Disc | ||||
Harrows – Spike tooth | ||||
Harrows – Spring tooth | ||||
Irrigation pump | ||||
Incubators | ||||
Tractors |
3.4.1 Identify the farm record shown above. (1)
3.4.2 Motivate the importance of such records on farms. (1)
3.4.3 State the type of capital in the farm record above. (1)
3.4.4 Identify the problem associated with capital that is unique to the type of capital above. (1)
3.4.5 Mention TWO methods that can be used to create capital. (2)
3.5
| An orange juice manufacturing company has been in business for 30 years, as a result it has a highly skilled workforce. The challenge, however, is the aging equipment and increased competition from recently established companies. |
3.5.1 Identify ONE internal and ONE external force affecting the company in the passage above. (2)
3.5.2 Identify the type of risk that is faced by this company due to the challenges mentioned above. (1)
3.5.3 Explain how the company’s internal and external forces lead to the risk mentioned in QUESTION 3.5.2. (2)
[35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1
| In pea plants, spherical seeds (R) are dominant over dented seeds (r). In a genetic cross a plant that is heterozygous for the seed shape trait is self- pollinated. |
4.1.1 Use a punnet square to show the cross described above. (4)
4.1.2 Determine the genotypic ratio. (1)
4.1.3 Calculate the probability of spherical seeds being produced from the cross above. (3)
4.1.4 Deduce with a reason the type of dominance in the cross. (2)
4.1.5 Deduce whether the seed shape is a quantitative or qualitative characteristic. (1)
4.1.6 Motivate your answer to QUESTION 4.1.5 above. (1)
4.2 
4.2.1 Classify the mutations above as chromosomal or gene mutations. (1)
4.2.2 Identify the mutations B, C and D. (3)
4.2.3 The process shown above results in variation. Give TWO reasons why variation is important in agriculture. (2)
4.2.4 Give ONE example of a physical agent that can cause the changes depicted above. (1)
4.3
4.3.1 Identify animal C in the diagram above. (1)
4.3.2 Identify the breeding system depicted above. (1)
4.3.3 Motivate your answer to QUESTION 4.3.2 above. (2)
4.3.4 Describe TWO benefits of animal C, over animal A. (2)
4.3.5 Give TWO disadvantages of this breeding system. (2)
4.4
| In the last 15 years, GM crop producing countries, have benefited from adoption of this new technology in the form of improved crop productivity, food security. The increased income to resource-poor farmers is a key benefit at the individual level, especially as most countries using this technology are in the developing world, including three African countries (South Africa, Burkina Faso and Egypt). Despite clear benefits to countries and farmers who grow GMOs, many people are concerned about suspected potential risks associated with GMOs. |
4.4.1 Identify the plant improvement method described in the passage above. (1)
4.4.2 Give ONE advantage of this technology that is mentioned in the passage above. (1)
4.4.3 Give TWO advantages of the plant improvement method in QUESTION 4.4.1 over traditional methods. (2)
4.4.4 Describe TWO current applications of this technology in plants. (2)
4.4.5 Mention TWO human health risks of GMOs. (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Agricultural Sciences Paper 1 Memorandum - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 C
1.1.2 B
1.1.3 C
1.1.4 D
1.1.5 A
1.1.6 D
1.1.7 B
1.1.8 C
1.1.9 D
1.1.10 C (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 B only
1.2.2 A only
1.2.3 None
1.2.4 B only
1.2.5 Both A and B (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 Biological value/BV
1.3.2 Quarantine
1.3.3 Cryptorchidism
1.3.4 Impotence
1.3.5 Freemartin (5 x 2) (10)
1.4
1.4.1 Lipase
1.4.2 Weaning
1.4.3 Colostrum/beestings
1.4.4 Ovum/egg cell
1.4.5 Repeat breeder (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: ANIMAL NUTRITION
2.1 Digestion in farm animals
2.1.1 Indication whether the teeth represent the lower or upper jaws
- Lower jaw (1)
2.1.2 Naming the type of digestion done by the teeth
- Physical (1)
2.1.3 Explaining the importance of teeth together with saliva in FARM ANIMAL 1
- Teeth break down large food particles into smaller particles Saliva moistens, softens and bind the particles together to form a bolus (2)
2.1.4 Part of a fowl that performs the same function done by teeth
- Ventriculus/gizzard (1)
2.1.5 Explanation of the path of milk in FARM ANIMAL 2
- Milk flows from the mouth to the oesophogal groove and land directly into the abomasum (2)
2.2 Villi
2.2.1 Part in the alimentary canal where villi is found
- Small intestines (1)
2.2.2 Indication of the nutrient absorbed in part A and B Part A – Digested protein and carbohydrates
- Part B – Digested fats (2)
2.2.3 Process that follows after the absorption of nutrients
- Assimilation (1)
2.2.4 ONE adaptation feature of the villi
- Presence of blood and lymph capillaries
- Microvilli to increase the surface area for absorption
- Thin layer of epithelial cells with carrier molecules (Any 1 x 1) (1)
2.3 Feed components
2.3.1 Identification of the feed suitable for:
- Young growing animals – Feed C
- Fattening old ewes – Feed A
- Insulation against temperature changes – Feed B (3)
2.3.2 Calculation of the nutritive ratio of feed B
- NR = 1 : %TDN -– % DP
% DP
1 : 85% – 20%
20%
1 : 3,25
OR
NR = 1 : % digestible non-nitrogen substances
% digestible protein
1 : 65
20
1 : 3,25 (3)
2.3.3 Determining the ratio of feed A and feed C to be mixed to get a feed with 18% DP
Ratio of feed A : Feed C is 22 : 8 (4)
2.4 Growth stimulants
Naming the most applicable substance:
- Tranquilisers
- Thyroid regulator (2)
2.5Fodder flow
2.5.1 Bar graph
Criteria/rubric/marking guideline
- Correct heading
- x-axis: Correctly calibrated and labelled (Time)
- y-axis: Correctly calibrated and labelled (Quantity of lucerne)
- Correct units (kg/ha and months)
- Bar graph
- Accuracy (6)
2.5.2 Calculation of the total amount of lucerne the cows will need in June
- Number of animal x requirement/kg/day x 30
= 35 x 5 kg x 30
= 5 250 kg (2)
2.5.3 Determination of whether there will be enough lucerne for these lactating cows in June
- Supply in June = 50 kg/Ha x 42 hectares
= 2 100 kg
2 100kg – 5 250 kg – 3 150 kg
There will be a shortage of 3 150 kg. (3)
[35]
QUESTION 3: ANIMAL PRODUCTION, PROTECTION AND CONTROL
3.1 Production system
3.1.1 Identification of the animal production system
- Extensive production system (1)
3.1.2 TWO reasons
- Lot of space and few animals/low-density
- Animal production adapted to existing environment/environment not modified
- Low input costs
- Use of thorny shrubs as fencing (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.1.3 Linking the production system with a relevant farming system
- Subsistence (1)
3.1.4 Identification of the measures to increase animal production under the following:
- Nutrition – Planting of the kikuyu
- Reproduction – Breeding animals adapted to the environment
- General enterprise management – Dividing grazing area into camps/practising rotational grazing (3)
3.2 Facilities/equipment
3.2.1 Identification of the facilities/equipment
- PICTURE B – Furrowing crate
- PICTURE D – Drinker (2)
3.2.2 Purpose of using the facility
- Labelled A in PICTURE C – to restrain an animal (1)
3.2.3 TWO design features of the facility labelled B in PICTURE C
- Should have high solid sides to prevent animals from seeing out
- Narrow curved/not curved too sharply (2)
3.2.4 Indication of the information to be included in the permit
- Details of the owner
- Number of animals
- Type of animals
- Description of animals
- Registration number of the vehicle
- Destination to which animals are being taken
- Name and ID number of the driver (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.3 Animal handling and behaviour
3.3.1 TWO signs of pigs in distress
- Tail biting
- Ear biting
- Cannibalism
- Belly nibbling
- Snout rubbing (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.3.2 TWO effects of incorrect handling of animals during transportation
- Animals will be injured
- Delayed rigor mortis
- Poor quality of meat (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.4 Diseases
3.4.1 TWO signs showing that the animal is sick
- Dull glossy eyes
- pink membrane around the eyes
- Rapid pulse rate
- Laboured breathing
- Animal walks slowly or limps when forced to walk
- Discoloured urine and faeces may be too hard or too soft
- Dull rough coat (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.4.2 TWO methods a farmer can use to test animal health
- Taking an animal’s temperature
- Determining pulse rate
- Determining respiratory rate (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.5 Life cycle of an anthrax
3.5.1 Indication of the pathogen
- Bacteria (1)
3.5.2 TWO ways in which the disease can be transmitted
- Ingestion of the animal product
- Inhalation
- Cutaneous/through the skin (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.5.3 Justification that the disease is zoonotic
- It is transferred from the animals to human beings (2)
3.5.4 TWO steps the farmer can take to prevent further spread of the disease
- Burn or bury the carcasses of infected animals
- Dispose all manure, bedding and other contaminated materials
- Clean and disinfect stables, pens, milking parlours and all equipment (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.6Ticks
3.6.1 Classification of the parasite
- External parasite (1)
3.6.2 Reason
- They create an opening on the skin of an animal (1)
3.6.3 Name of the tick belonging to the following class:
- Three-host tick – Bont tick
- One-host tick – Blue tick (2)
3.6.4 TWO economic impacts of ticks for the farmer
- Decreased production
- Decreased income/profit
- High cost of treatment (Any 2 x 1) (2)
[35]
QUESTION 4: ANIMAL REPRODUCTION
4.1 Reproductive systems
4.1.1 Identify the letter
- B (1)
- I (1)
- G (1)
- Diagram A – C
Diagram B – J (2)
4.1.2 Naming the inner and the middle membranes surrounding the foetus
- Inner membrane – Amnion
- Middle membrane – Allantois (2)
4.1.3 Explanation of the role of the parts
- Part A – Regulates the temperature of the testis for optimum sperm production
- Part F – Collects the ovum released during ovulation (2)
4.2 Reproductive processes
4.2.1 Identification of the processes
- B – Fertilisation
- C – Pregnancy/gestation (2)
4.2.2 Indication of the first and the last stage of pregnancy
- First stage– Ovum phase
- Last stage- Foetal stage (2)
4.2.3 Name of the process labelled A
- Artificial Insemination/AI (1)
4.2.4 TWO economic benefits of artificial insemination for the farmer
- Less expensive because there is no need to buy a bull
- Large number of offspring can be produced from the superior bulls
- Semen of superior bulls can be used even after death
- Semen of multiple sires can be used without maintaining many expensive bulls
- Higher conception rate is achieved (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.2.5 TWO factors causing retention of placenta
- Deficiency of vitamin A
- Sexually transmitted diseases
- Infections/abortion
- Exhaustion following difficult calving
- Mineral deficiency
- Hereditary defects
- Over-conditioning of dry cows (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.3 Cloning
4.3.1 Identification of the reproductive process
- Cloning/nuclear transfer (1)
4.3.2 Explanation of a reason
- Somatic cell from the donor is fused with a nucleated egg cell giving rise to an offspring that is genetically identical to the donor sheep (2)
4.3.3 Naming of the process
- Enucleation (1)
4.3.4 Indication of the letter of the sheep
- D
- A
- B (3)
4.3.5 TWO aims of the cloning
- Produce large number of genetically identical animals
- Produce offspring from high quality animals
- Preserve and extend proven superior genetics
- Achieve high quality meat and dairy products
- Increase number of endangered species (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.4 Udder and lactation
4.4.1 Identification of parts
- A – Alveoli
- B – Lobe
- C – Teat (3)
4.4.2 Indication of the role of alveoli
- It is where milk is formed (1)
4.4.3 Naming the stage in the lactation cycle between month 10 and the next calving period
- Dry/rest period (1)
4.4.4 Importance of dry period for lactating cow
- To give time for glandular tissue of the udder to recover and prepare for optimum milk production in the next lactation cycle (2)
4.4.5 Identification of the number of months’ lactation period last
- 10 months (1)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Agricultural Sciences Paper 1 Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show ALL calculations, including units and formulae, where applicable.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 B.
1.1.1 The process whereby food is pushed through the alimentary canal by the contraction and relaxation of the muscles is known as … .
- rumination.
- digestion.
- peristalsis.
- absorption.
1.1.2 The nutrient that provides immunity to protect an animal’s body against germs and antigens.
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Lipids
- Fats
1.1.3 The palatability and digestibility of a low-grade roughage for a ruminant can be improved by …
- mixing roughage with molasses.
- supplementing the ration with non-protein nitrogen substances.
- supplementing it with teff hay.
- adding small quantities of urea and biuret.
Choose the CORRECT combination:
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
1.1.4 A shortage of phosphorus in the bodies of farm animals leads to a condition known as …
- goiter.
- anaemia.
- parakeratosis.
- pica.
1.1.5 The method of handling farm animals applicable to sheep:
- Catching the animal as high as possible on a hind leg
- Using a neck clamp to bring animal to a standstill.
- Moving the animal from behind.
- Throwing stones to direct animals.
1.1.6 The following is NOT a characteristic of an intensive production enterprise:
- A relatively small piece of land is used.
- Large sum of capital is invested.
- Lots of labour is utilised.
- Enterprise covers a vast area of land.
Choose the correct combination:
- (i), (iii), and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
1.1.7 The following statement is TRUE about enzootic diseases.
- Transmitted from humans to animals.
- Affects specific animals in a particular region.
- Not regarded as contagious diseases.
- Result from disorders that disturb metabolic processes.
1.1.8 The statements below apply to the life cycle of a single-host tick.
- Eggs hatch into larvae.
- Nymph develops into an adult.
- Larvae and nymph live on an intermediate host.
- Larvae develops into a nymph
Choose the CORRECT combination:
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
1.1.9 A characteristic observed during the microscopic evaluation of semen:
- Volume
- Colour
- Density
- Abnormalities
1.1.10 … refers to the attachment of the embryo to the endometrium of a sow.
- Copulation
- Synchronisation
- Implantation
- Retention (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Indicate whether each of the descriptions in COLUMN B applies to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A AND B or NONE of the items in COLUMN A. Write A only, B only, both A and B or none, next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 B only.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
1.2.1 | A: | Cafeteria style | Method of supplementing calcium borogluconate in dairy cows with milk fever |
B: | Injection | ||
1.2.2 | A: | Lupins | A protein-rich concentrates from plant origin which are used to balance roughage |
B: | Oilcake meals | ||
1.2.3 | A: | Advanced technology | A factor to increase animal production under extensive farming |
B: | Provision of ventilators | ||
1.2.4 | A: | Drenching | The method of administering medication to animals on the skin |
B: | Topical | ||
1.2.5 | A | Inexperience | The factor that causes infertility in young bulls |
B: | Nutrition | ||
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 The measure of the quality of a protein in a feed
1.3.2 The service rendered by the state where animals are kept in isolation for a particular period while being tested for diseases
1.3.3 The phenomenon where the testis remain in the abdominal cavity
1.3.4 The term used to describe bulls that is interested in cows but lack the ability to serve it
1.3.5 A sterile female calf born when the twins of the opposite sex develop in the uterus of a cow (5 x 2) (10)
1.4 Change the UNDERLINED WORD(S) in each of the following statements to make it TRUE. Write only the answer next to the question numbers (1.4.1 to 1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 The enzyme in the small intestine of an animal that splits the fat molecule is called amylase.
1.4.2 Castration is the process of removing young suckling animals permanently from their mothers.
1.4.3 A dilutant is a yellowish, salty creamy liquid secreted from the mammary glands at parturition and provide antibodies.
1.4.4 Spermatozoon is the end product of the process of oogenesis.
1.4.5 Hermaphrodite is a cow that needs to mate three or more times before it conceives. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: ANIMAL NUTRITION
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 The diagram below indicates the teeth of farm animals.
2.1.1 Indicate whether the teeth in the diagram above represent the lower or upper jaws. (1)
2.1.2 Name the type of digestion done by the teeth in the diagram above. (1)
2.1.3 Explain the importance of teeth together with saliva in FARM ANIMAL 1. (2)
2.1.4 Name the part of a fowl that performs the same function done by teeth in the diagram above. (1)
2.1.5 Explain the path of milk in FARM ANIMAL 2. (2)
2.2 The structure below shows a part of the alimentary canal in farm animals.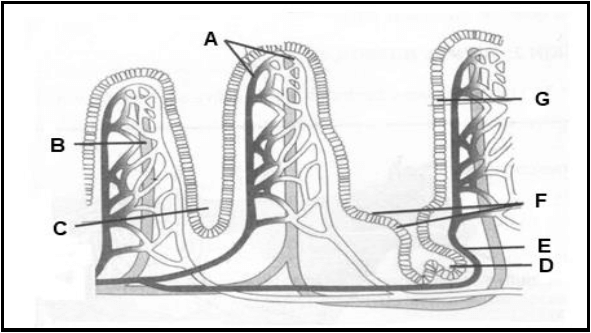
2.2.1 Name the part of the alimentary canal where the structure illustrated above is found. (1)
2.2.2 Indicate the nutrients absorbed in parts labelled A and B. (2)
2.2.3 Mention the process that follows after absorption of nutrients stated in QUESTION 2.2.2. (1)
2.2.4 Name ONE adaptation feature of the structure above that helps it to perform its function. (1)
2.3 The graph below shows different feeds with different feed components. (Digestible carbohydrates, fats and protein)
2.3.1 Identify the feed from the graph above that would be most suitable for each of the following situations:
- Young growing animals
- Fattening of old ewes
- Provision of insulation against temperature changes (3)
2.3.2 Suppose feed B has 85% TDN; then calculate the nutritive ratio of this feed. (3)
2.3.3 Determine the ratio of feed A and feed C that can be mixed to get a feed with 18% DP. (4)
2.4 Chemical substances are used in feedlots for beef production to increase the growth rate. Name the most applicable substance that can be administered to animals in each of the following cases:
- A substance administered to cattle in a feedlot to calm them down
- A substance administered to increase the metabolic rate of farm animals (2)
2.5 The table below shows the production of lucerne in kg DM/Ha for a period of one year on a 42-hectare farm.
MONTHS OF THE YEAR | QUANTITY OF LUCERNE PRODUCED (KG DM/HA) |
January | 1 200 |
February | 800 |
March | 200 |
April | 200 |
May | 100 |
June | 50 |
July | 50 |
August | 200 |
September | 300 |
October | 400 |
November | 600 |
December | 1 200 |
2.5.1 Use the information in the table above to draw a bar graph. (6)
2.5.2 If the farmer has 35 lactating cows and each need 5 kg of lucerne a day for optimum production. Calculate the total amount of lucerne the cows will need in June. (Show ALL calculations.) (2)
2.5.3 Determine whether there will be enough lucerne for these lactating cows in June. (Show ALL calculations.) (3)
[35]
QUESTION 3: ANIMAL PRODUCTION, PROTECTION AND CONTROL
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1
| A farmer owning 40 hectares of land in a sourveld area planted kikuyu to finish off steers on a pasture. About 20 hectares allocated for grazing was divided into four camps using thorny shrubs to fence off each camp. Five animals were allowed in one camp on a rotational basis. The farmer believed in breeding animals adapted to the environment so that they utilise grazing as much as possible instead of artificially changing the environment to suit animals. |
3.1.1 Identify the animal production system used by the farmer in the scenario above. (1)
3.1.2 Give TWO reasons for the answer in QUESTION 3.1.1. (2)
3.1.3 Name the farming system that can be linked with the production system in QUESTION 3.1.1. (1)
3.1.4 Identify the measures in the scenario above, to increase animal production under the following:
- Nutrition
- Reproduction
- General enterprise management (3)
3.2 The pictures below show facilities/equipment used in an animal producton system.
3.2.1 Identify the facility/equipment in PICTURE B and PICTURE D. (2)
3.2.2 State the purpose of using the facility labelled A in PICTURE C. (1)
3.2.3 Indicate TWO design features of the facility labelled B in PICTURE C. (2)
3.2.4 A permit is one of the requirements needed when moving animals using the facility in PICTURE A. Indicate the information that must be included in the permit. (2)
3.3 Pigs are sensitive animals that are frightened easily and can display certain behavioural patterns when in distress.
3.3.1 Name TWO signs of distress in pigs. (2)
3.3.2 Incorrect handling of animals during transportation can have an effect on animals and their products. Justify this statement with TWO effects. (2)
3.4 It is important that animals must be tested on a regular basis to detect diseases in its early stages.
3.4.1 Give TWO signs that show that an animal is sick. (2)
3.4.2 Indicate TWO methods a farmer can use to test animal health. (2)
3.5 The illustration below shows the life cycle of the anthrax.
3.5.1 Indicate the pathogen that causes the disease illustrated above. (1)
3.5.2 Identify from the illustration TWO ways in which the disease can be transmitted. (2)
3.5.3 The disease above is zoonotic. Justify this statement by referring to the illustration. (2)
3.5.4 Name TWO steps the farmer can take to prevent a further spread of the disease in the above illustration when the outbreak has occurred. (2)
3.6 Ticks are the most transmitters of diseases in farm animals. They create an opening on the skin of an animal and allow pathogens to penetrate and cause diseases.
3.6.1 Classify the parasite in the scenario above. (1)
3.6.2 Give a reason for the answer in QUESTION 3.6.1. (1)
3.6.3 Ticks are classified according to their life cycle. Name the tick that belongs to the following classes:
- Three-host tick
- One-host tick (2)
3.6.4 Indicate TWO economic impacts of ticks for the farmer. (2)
[35]
QUESTION 4: ANIMAL REPRODUCTION
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 The diagrams below show the organs in the reproductive system of a bull and a cow.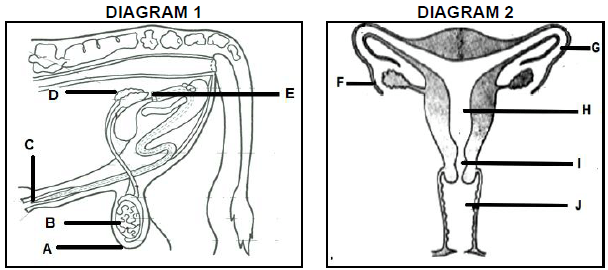
4.1.1 Identify the letter from the diagrams above where each of the following occurs.
- Spermatogenesis (2)
- Deposition of semen during artificial insemination (1)
- Sperm cell fuses with the egg cell (1)
- Copulating organ Diagram A and Diagram B (1)
4.1.2 Name the inner and the middle membranes surrounding the fetus at the part labelled H. (2)
4.1.3 Parts labelled A and F play an important role in the reproductive systems above. Justify this statement by explaining the role of these parts. (2)
4.2 The flow chart below shows the reproductive processes in cows.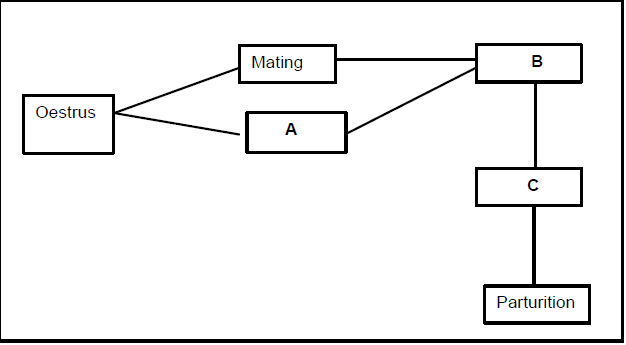
4.2.1 Identify the processes labelled B and C. (2)
4.2.2 The process labelled C is characterised by three stages. Indicate the first and the last stage. (2)
4.2.3 The process labelled A can be induced to a cow. Name that process. (1)
4.2.4 State TWO economic benefits of the process mentioned in QUESTION 4.2.3 for the farmer. (2)
4.2.5 Indicate TWO factors that may cause the retention of the placenta during parturition. (2)
4.3 The diagram below illustrates the reproductive process in farm animals.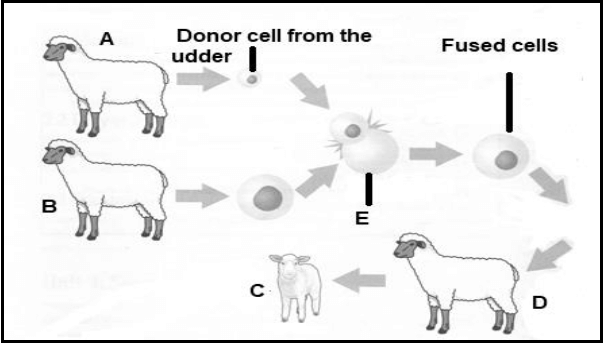
4.3.1 Identify the reproductive process illustrated above. (1)
4.3.2 Refer to the illustration above to explain a reason for your answer in QUESTION 4.3.1. (2)
4.3.3 Name the process that has occurred in the cell labelled E. (1)
4.3.4 Indicate the letter of the sheep that corresponds with the information below:
- Acts as a surrogate
- Genetically identical to sheep C
- Donated an egg cell (3)
4.3.5 State TWO aims of the reproductive process illustrated in the diagram above. (2)
4.4 Below is the diagram showing the structure of an udder and the pie chart.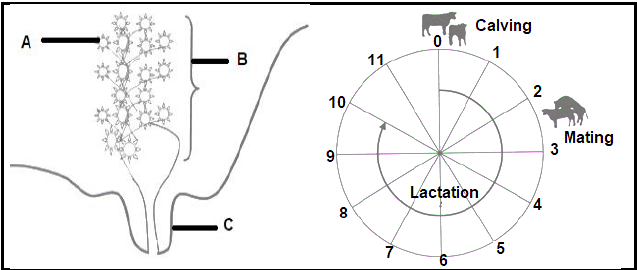
4.4.1 Identify parts labelled A, B and C. (3)
4.4.2 Indicate the role of part A during lactation. (1)
4.4.3 Name the stage in the lactation cycle between month 10 and the next calving. (1)
4.4.4 Explain the importance of the stage mentioned in QUESTION 4.4.3 for the lactating cow. (2)
4.4.5 Identify from the lactation cycle the number of months lactation period last. (1)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Accounting Paper 2 Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully and follow them precisely.
- Answer ALL questions.
- A special ANSWER BOOK is provided in which to answer ALL questions.
- Show ALL workings to earn part-marks.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- You may use a dark pencil or blue/black ink to answer questions.
- Where applicable, show ALL calculations to ONE decimal point.
- If you choose to do so, you may use the Financial Indicator Formula Sheet attached at the end of this question paper. The use of this formula sheet is NOT compulsory.
- Write neatly and legibly.
- Use the information in the table below as a guide when answering the question paper. Try NOT to deviate from it.
QUESTION | TOPIC | MARKS | MINUTES |
1 | Manufacturing | 45 | 35 |
2 | Debtors' Reconciliation and VAT | 40 | 30 |
3 | Stock Valuation | 30 | 25 |
4 | Budgeting | 35 | 30 |
TOTAL | 150 | 120 | |
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MANUFACTURING (45 marks; 35 minutes)
1.1 Choose the cost item in the list provided that matches the example below. Write only the cost item next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.3) in the
ANSWER BOOK.
| indirect labour; direct labour; direct materials; indirect materials |
1.1.1 Cleaning materials used in the factory
1.1.2 Salary of the factory foreman
1.1.3 Cost of the raw materials used in the production process (3 x 1) (3)
1.2 AFRESH CREATIONS
Afresh Creations manufacture one type of bath towels. The financial year ended on 29 February 2020.
REQUIRED:
1.2.1 Calculate the direct material cost. (4)
1.2.2 Prepare the Production Cost Statement for the year ended 29 February 2020. (18)
1.2.3 Refer to Information C.
Normal time for all workers is 40 hours per week. The information provided in James' job card for the last week is a reflection of his attendance over the financial year.
Identify TWO concerns regarding the above situation. Also provide ONE suggestion to address the concerns identified. (6)
INFORMATION:
A. Stock balances:
29 FEBRUARY 2020 | 1 MARCH 2019 | |
Raw material stock | R 314 500 | R 115 200 |
Work-in-progress stock | ? | 53 500 |
B. Extract from the records on 29 February 2020: (See Information C for adjustments.)
Raw materials purchased on credit | R 738 900 |
Damaged raw material returned to suppliers | 15 300 |
Factory overhead cost | 322 100 |
Production wages (direct labour) | 598 750 |
C. Additional information:
- One worker, James, was omitted from the Production Wages Register. Details from his job card for the last week in February 2020 are as follows:
Hours worked
Normal rate
Overtime hours
Overtime rate
30
R120
5
R180
Total employer's contribution amounts to 10% of gross wage.
- Insurance of R15 880 was incorrectly omitted from factory overhead costs. This includes a premium of R2 220 paid for the period 1 January 2020 to 30 June 2020. This expense must be allocated between the factory and the sales department in the ratio 3 : 1.
- The bookkeeper included R39 600 (75%) of the wages to cleaners in the factory overhead cost. Only 2/3 of this expense should be allocated to the factory.
D. The business produced 22 500 towels during the financial year, at R60 per unit.
1.3 FRAGRANCE MANUFACTURERS
This business manufactures perfumes and shampoo. The owner, Marie Klasen, has compared the profit she earned over the past two years (2019 and 2020).
REQUIRED:
1.3.1 Identify ONE variable cost of each product that was not well controlled. Note that the inflation rate is 6%. Quote figures. In each case, give a solution for the problem identified. (6)
1.3.2 Provide a calculation to prove that the break-even point of 26 250 units for perfumes in 2020 is correct. (4)
1.3.3 Comment on the break-even point and level of production of perfumes. State TWO points with figures. (4)
INFORMATION:
A. UNIT COSTS AND SELLING PRICES
PERFUMES (Unit costs) | SHAMPOO (Unit costs) | |||
2020 R | 2019 R | 2020 R | 2019 R | |
FIXED COSTS | 36,75 | 30,00 | 18,48 | 22,00 |
Factory overhead cost | ||||
Administration cost | ||||
VARIABLE COSTS | 108,00 | 88,00 | 50,00 | 38,50 |
Direct material cost | 50,00 | 48,00 | 25,00 | 15,00 |
Direct labour cost | 40,00 | 30,00 | 18,00 | 17,00 |
Selling and distribution cost | 18,00 | 10,00 | 7,00 | 6,50 |
SELLING PRICE | 150,00 | 140,00 | 90,00 | 80,00 |
B. UNITS AND BREAK-EVEN POINT
Total units produced and sold | 30 000 | 35 000 | 12 500 | 10 000 |
Break-even point (units) | 26 250 | 20 200 | 5 775 | 5 300 |
QUESTION 2: DEBTORS' RECONCILIATION AND VAT (40 marks; 30 minutes)
2.1 DEBTORS' RECONCILIATION
The information relates to Mamela Traders for September 2020.
REQUIRED:
2.1.1 Calculate the correct Debtors' Control balance on 30 September 2020. Show figures and indicate '+', '–' or 'no change' at each adjustment. (8)
2.1.2 Calculate the correct 30 September 2020. total of the Debtors' List on 30 September 2020 (11)
2.1.3 Despite sending monthly statements timeously, the accountant noticed that this was not effective in improving collections.
- Refer to Information C. Calculate the % of debtors who do not comply with the credit terms.(4)
- Refer to Information A. Identify ONE other problem with regard to the control over debtors (2)
- Provide TWO suggestions to address the problems identified. (2)
INFORMATION:
A. Balances on 30 September 2020 before taking into account the errors and omissions:
- Debtors' control balance in the General Ledger, R100 310.
- List of debtors' balances:
D Dlamini G Swardt N Nomandla L Vos X Meyer | Credit Limit R20 000 30 000 15 000 40 000 10 000 | Balance R27 000 22 470 17 600 34 440 (2 000) |
B. Errors and omissions:
- The total of the Debtors' Journal was overcast by R3 600.
- No entry was made for a sales invoice issued to Vos for R2 760.
- Interest of R230 must be charged on the overdue account of Swardt.
- Goods returned by Nomandla, R1 400, were posted to the wrong side of his account in the Debtors' Ledger. The entry in the General Ledger was correct.
- The amount of R6 300 received from Dlamini was incorrectly recorded as R3 600 in the Cash Receipts Journal and posted as such to the Ledger Accounts.
- The balance of Meyer must be transferred to his account in the Creditors' Ledger.
C. On 30 September 2020, the Debtors' Age Analysis revealed the following:
Balance | Current Month | 30 days | 60 days | 90 days |
R99 000 | R15 420 | R22 200 | R44 500 | R16 880 |
Credit terms: Debtors are granted 30 days to settle their accounts.
2.2 VAT
FOREVER TRADERS
Tom Smith is the sole owner. The information relates to the VAT period ended 31 August 2020.
The standard VAT rate of 15% is applicable to all goods purchased and sold.
REQUIRED:
2.2.1 Calculate the VAT amount that is payable to SARS on 31 August 2020. (9)
2.2.2 During September, the accountant came across a document for furniture bought by Tom Smith for his personal home, for R46 000 cash. Tom said that R6 000 VAT included in this amount must be regarded as input VAT. Further investigation revealed that similar documents were regularly entered in the books over the past year. Advise the accountant on dealing with this matter. State TWO points. (4)
INFORMATION:
A. Amount due to SARS on 1 August 2020 is R31 470.
B. The following transactions appeared in the records for August 2020:
DETAILS | EXCLUDING VAT | VAT AMOUNT | INCLUDING VAT |
Total sales | R535 000 | R80 250 | R615 250 |
Purchases of stock | 385 000 | 57 750 | 442 750 |
Discount received from suppliers | 11 500 | ? | |
Goods returned by debtors | 22 500 | ? | 25 875 |
Stock taken by owner at cost | 9 600 | ? | |
Debtors' accounts written off | ? | 36 800 |
QUESTION 3: INVENTORY VALUATION (30 marks; 25 minutes)
On-Time Watches (Pty) Ltd has two shareholders, Lizzy and Patsy Ndou. The business sells watches. The periodic inventory system and the first-in-first-out (FIFO) method is used to value the watches. The financial year-end was 30 June 2020.
The business sold only one type of watch, the XS Sports, in the past. Even though these watches were selling well, Lizzy felt that the business was not earning enough profit. She convinced Patsy that importing exclusive watches (the Euroclox) would be a good solution for this problem.
REQUIRED:
3.1 Calculate the following for the imported Euroclox watches on 30 June 2020, using the FIFO method:
- The value of the closing stock (5)
- Stock-holding period (in days) using the closing stock amount (3)
- % mark-up on cost (3)
3.2 Patsy was still not convinced about the decision to import the Euroclox watches, but it appears that Lizzy's decision was beneficial to the business. In each case below, quote figures or indicators.
3.2.1 Compare the mark-up % achieved on each model and comment on how this has affected the sales and profitability of the two models. (4)
3.2.2 Compare the stock-holding period for each model and the demand for each model and comment on how these affected the management of the stock items of the two models. (4)
3.3 Lizzy is interested in finding out if the weighted-average method of valuing the Euroclox watches will result in a significantly different stock value.
- Calculate the value of the 270 watches using the weighted-average method. (5)
- Explain the effect this would have on the gross profit. Quote figures. (2)
- Explain why it would not be appropriate for her to use the weighted- average method for the new watches in the future. State TWO points. (4)
INFORMATION:
A. Stock records for imported Euroclox watches:
DATE | NUMBER OF UNITS | UNIT PRICE | TOTAL AMOUNT |
Purchases: | |||
1 July 2019 | 200 | R 1 615,50 | R 323 100 |
30 September 2019 | 500 | 1 700,00 | 850 000 |
20 December 2019 | 1 200 | 1 900,00 | 2 280 000 |
25 March 2020 | 400 | 2 000,00 | 800 000 |
15 May 2020 | 250 | 2 400,00 | 600 000 |
Total purchases | 2 550 | R4 853 100 | |
Returns: 15 May 2020 | 90 | ? | |
Available for sale | 2 460 | ? | |
| |||
Stock on 30 June 2020 | 270 | ? | |
Sales | 2 190 | R2 700 | R5 913 000 |
Cost of sales | R4 033 100 | ||
B. Information obtained from the financial records on 30 June 2020:
EUROCLOX MODEL | XS SPORTS MODEL | |
Mark-up % | ? | 75% |
Stock-holding period | ? | 120 days |
Selling price per watch | R2 700 | R560 |
Average cost price per watch | R1 842 | R320 |
Average gross profit per watch | R858 | R240 |
Gross profit | R1 879 900 | R840 000 |
Sales of watches | R5 913 000 | R1 960 000 |
Units sold | 2 190 watches | 3 500 watches |
Closing units on hand | 270 watches | 1 381 watches |
QUESTION 4: BUDGETS (35 marks; 30 minutes)
You are provided with information of Fantasy Laptops, a business owned by Ray Rennie, for the budget period December 2020 to February 2021.
The business sells various types of laptop computers and does not sell on credit. They also repair these items for customers at a fee.
REQUIRED:
4.1 Refer to Information A and B.
- Complete the Creditors' Payment Schedule for February 2021. (7)
4.2 Refer to Information C and D.
- Calculate:
- % increase expected in security costs from 1 February 2021
- % commission paid to salespersons during February 2021
- Water and electricity budgeted for December 2020
- The loan repayment to be made on 31 December 2020 (12)
4.3 Refer to Information E.
The internal auditor has noticed that packing material was R800 overspent and consumable stores were R1 500 overspent.
Comment on the control of packing materials and consumable stores. Quote figures or calculations. (6)
4.4 Refer to Information D.
During the Coronavirus lock-down in April and May 2020, the business lost money because there were no sales and fee income. However, Ray had to continue making payments to keep the business afloat (as a going concern).
- Give ONE reason why he did not want to stop paying salaries and wages. (2)
- Identify ONE other payment in the list in Information D that he would not have been able to stop and give a reason. (2)
- Identify ONE payment in the list in Information D that he would have stopped and give a reason. (2)
4.5 Refer to Information F.
Ray Rennie, the owner, requires help in making a financial decision.
He is undecided as to whether he should lease or buy a delivery vehicle. His two options are reflected as Option X and Option Y.
Apart from generating more sales or having the use of the vehicle, state TWO advantages of EACH option. (4)
INFORMATION:
A. Mark-up % and sales:
A mark-up of 75% on cost is used to set the sales prices of the laptops.
ACTUAL SALES | PROJECTED SALES | |||
October 2020 | November 2020 | December 2020 | January 2021 | February 2021 |
R490 000 | R490 000 | R770 000 | R560 000 | R525 000 |
B. Purchases and payment to suppliers (creditors):
- All stock is bought on credit.
- Stock sold is replaced in the month of sales.
- Some creditors offer a discount for payment in the month of purchase.
- 50% is paid in the month of purchase to earn a 10% discount.
- 30% is settled in the month after the purchase transaction month.
- 20% is settled in the second month after the purchase transaction month.
C. Information on specific items from the Cash Budget:
- Security: The guards are outsourced from Keepsafe Guarding.
- Commission: Salespersons are paid commission in the same month on sales only. They do not receive a fixed salary.
- Water and electricity: The expected increase from 1 January 2021 is 24%.
- Loan and interest: The loan from Delta Bank bears interest at 12,5% per year. Interest is not capitalised and a fixed loan repayment is made on 31 December each year.
- Consumable stores: These are used to repair laptops for customers.
D. Extract from the Cash Budget:
December 2020 | January 2021 | February 2021 | |
R | R | R | |
Fee income: repair services | 100 000 | 150 000 | 150 000 |
Interest on loan (12,5% p.a.) | 9 375 | 8 125 | |
Repayment of loan | ? | ||
Commission to salespersons | 123 200 | 89 600 | 84 000 |
Consumable stores for repairs | 42 000 | 63 000 | 63 000 |
Security | 18 000 | 18 000 | 28 500 |
Water and electricity | ? | 18 600 | 18 600 |
Salaries and wages | |||
Packing materials | |||
Insurance |
E. The internal auditor identified the following figures for October 2020:
Budgeted R | Actual R | Variance % | |
Sales | 490 000 | 400 000 | -18,4% |
Fee income | 85 000 | 126 000 | +48,2% |
Packing materials | 22 000 | 22 800 | +3,6% |
Consumable stores | 24 500 | 26 000 | +6,1% |
F. Options for securing a delivery vehicle:
Ray feels that he should buy a delivery vehicle for R520 000 or lease (hire) the vehicle on a monthly basis to enable his business to generate more sales after the Coronavirus lockdown. He has only R100 000 in his investments that he can use. These investments are currently earning interest at 6,5% p.a.
He has two options to consider:
Option X (buy the vehicle):
Purchase the vehicle by using the money in his investments and take out a new 5-year loan for R420 000 at a high interest rate. He will have to repay the loan over five years. Interest over the five years will be R176 000.
Option Y (hire/lease the vehicle):
Hire (lease) the vehicle from Sentinel Ltd for R15 000 per month over 60 months.
TOTAL: 150
GRADE 12 ACCOUNTING FINANCIAL INDICATOR FORMULA SHEET | |
Gross profit x 100 | Gross profit x 100 |
Net profit before tax x 100 | Net profit after tax x 100 |
Operating expenses x 100 | Operating profit x 100 |
Total assets : Total liabilities | Current assets : Current liabilities |
(Current assets – Inventories) : Current liabilities | Non-current liabilities : Shareholders' equity |
(Trade and other receivables + Cash and cash equivalents) : Current liabilities | |
Average trading stock x 365 | Cost of sales |
Average debtors x 365 | Average creditors x 365 |
Net income after tax x 100 | Net income after tax x 100 (*See note below) |
Net income before tax + Interest on loans x 100 | |
Shareholders’ equity x 100 | Dividends for the year x 100 |
Interim dividends x 100 | Final dividends x 100 |
Dividends per share x 100 | Dividends for the year x 100 |
Total fixed costs | |
NOTE: | |