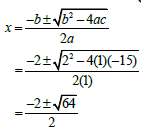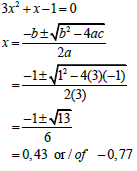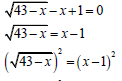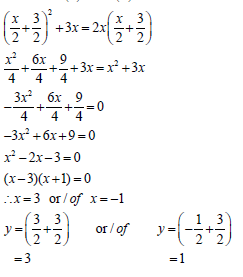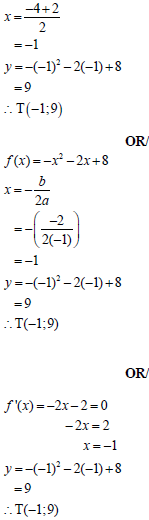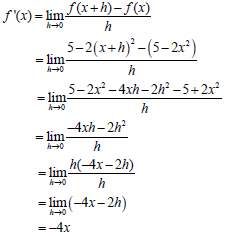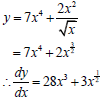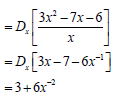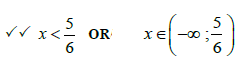Adele
Mathematics Paper 1 Memorandum - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
NOTE:
- If a candidate answers a question TWICE, mark the FIRST attempt
- Consistent accuracy applies in ALL aspects of the marking
- If a candidate crossed out an attempt of a question and did not redo the question, mark the crossed-out
- The mark for substitution is awarded for substitution into the correct
MEMORNDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1.1 | x2 + 2x -15 = 0 OR
| ? factors OR ? substitution | |||||
1.1.2 |
Penalise 1 mark for incorrect rounding | ? substitution ? x = 0, 43 ? x = -0, 77 (3) | |||||
| 1.1.3 | x(x - 3) ≥ -2
| ? standard form ? factorisation ? x ≤ 1 or/of ? x ≥ 2 (4) | |||||
| 1.1.4 |
| ? isolating the surd ? squaring both sides ? standard form ? factorisation ? selection (5) | |||||
1.2 | 2y - x = 3 (1) x = 2y - 3 (3) ∴ y = 3 or y = 1 OR | ? x = 2y - 3 ? substitution ? standard form ? factorisation ? y-values
OR ? y = x + 3 ? substitution ? standard form ? factorisation ? x-values ? y-values (5)
|
| 1.3 |
For non-real roots:
OR
| ? Δ< 0 ? standard form ? factorisation ? answer
OR
? Δ< 0 ? standard form ? factorisation ? answer (4) |
| [24] |
QUESTION 2
| 2.1.1 |
8 | ? 8 (1) |
| 2.1.2 | 2a = 4 | ? a = 2 ? b = -6 ? c = -12 ? Tn = 2n2 - 6n -12 (4) |
| 2.1.3 | T38 = 2(38)2 - 6(38) -12 | ? substitution ? answer (2) |
2.1.4 | General term for first differences: Tn(linear) = (Tn+1 - Tn )(quadratic) OR 2(n +1)2 - 6(n +1) -12 - (2n2 - 6n -12) = 400 OR Trialand error | ? Tn = 4n - 4 ? Tn = 400 ? answer OR ? 4n - 4 = 400 ? ? answer OR ?subst. for T101 and T102 ? 400 ? answer (3) |
2.2.1 | Tn = a + (n -1)d | ? substitution ? answer (2) |
| 2.2.2 | 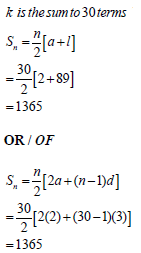 | ? Sum formula ? substitution ? answer OR ? Sum formula ? substitution ? answer (3) |
| [15] |
QUESTION 3
3.1 | T9 = ar8 = 768 | ?ar12 = 12 288 ? r =± 2 ? value of a | (3) | ||
3.2.1 | S2 = 54 - 24 | ? answer | (1) | ||
| 3.2.2 | T1 + T2 = 30 | ? a + ar = 30 19 | (1) | ||
3.2.3 | S∞ = a = 54 | ? a = 54(1- r) ? equating ?r2 = 4/9 ? answer | (4) | ||
[9] | |||||
QUESTION 4
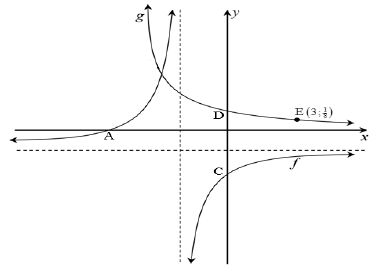 | ||||
4.1 | D(0 ; 1) | ? (0 ; 1) | (1) | |
4.2 | x = -2 ; y = -1 | ? x = -2 ? y = -1 | (2) | |
4.3 | ? ∈ R but ? # −2 | ? ? ∈ R ?? # −2 | (2) | |
4.4 | g(x) = bx | ? substitution ? answer | (2) | |
4.5 | y = -3 -1 y = -3 -1 | ? substitution y = 0 ? x = -5 ? y =- 5 | (3) | |
| 4.6 |
OR y = 2-x | ? OR ? x = 2- y ? y = -log2 x | (2)
(2) | |
| 4.7 | ||||
| 4.7.1 | -5 < x < -2 OR x ∈(-5 ; - 2) | ?? answer (A) | (2) | |
| 4.7.2 | 0 < x ≤ 1/8 OR x ∈(0 ; 1/8 ] | ?? answer (A) | (2) | |
| [16] | ||||
QUESTION 5
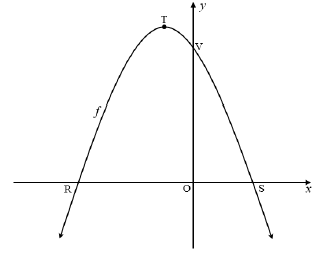 | |||||
| 5.1 | -x2 - 2x + 8 = 0 | ? f (x) = 0 | (4) | ||
5.2 |
| ? method ? x = -1 ? y = 9 OR ? - b ? x = -1 ? y = 9 OR ? -2x - 2 = 0 ? x = -1 ? y = 9 | (3) | ||
5.3.1 | f (x) = -x2 - 2x + 8 | ? f / (x) ? f / (x) = 2 ? x = -2 ? y = 8 | (4) | ||
5.3.2 | g(x) = mx + c | ? gradient ? equation | (2) | ||
| 5.4 | f (x) = -x2 - 2x + 8 OR h(x) = (x + 3)(x - 3) OR New turning point = (0 ; –9) | ? - f (x -1) OR ?? roots 3 and –3 OR ? (0 ; ??–9) | (4) | ||
| 17] | |||||
QUESTION 6
| 6.1 | 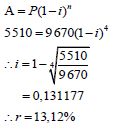 | ? subst. into correct formula |
6.2 | 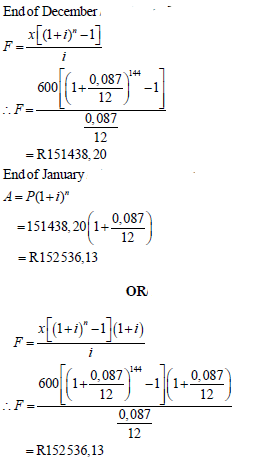 | ? n = 144 ? subst. into correct formula ? adding final month’s interest ? answer OR ? n = 144 ? subst. into correct formula ? adding final month’s interest ? answer (4) |
6.3.1 | 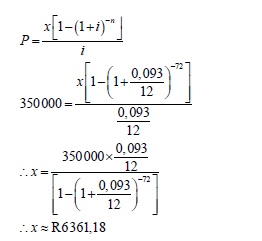 | ? i = 0, 093 and n = 72 ? substitution into correct formula ? answer (3) |
| 6.3.2 | 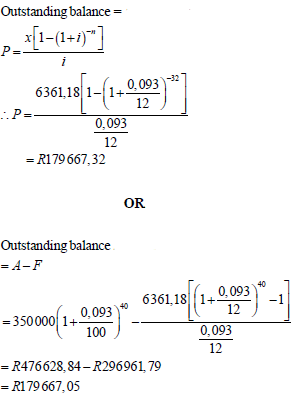 | ? i = 0,093 and/en n = 32 OR ? i = 0,093 and/en n = 40 ? P = 179 667, 32 (3) |
| 6.3.3 | 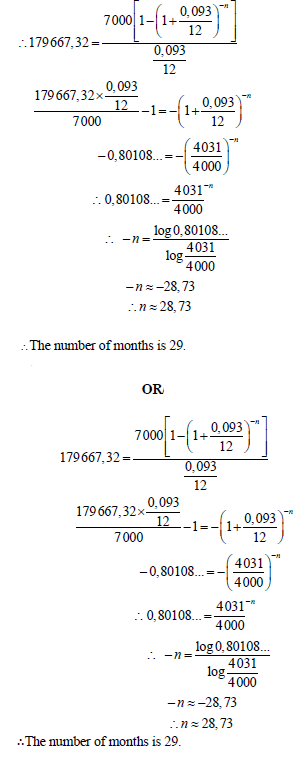 | ? subst. into correct formula ? correct use of logs ? = 28,73 ? n = 29 months OR ? subst. into correct formula ? correct use of logs ? = 28,73 ? n = 29 months (4) |
| [17] |
QUESTION 7
7.1 |
| ? substitution ? expansion ? simplification ? notation and lim (-4x - 2h) ? answer (5) |
7.2.1 |
| ? 2x½ ? 28x3 ? 3x½ (3) |
7.2.2 |
| ? 3x - 7 ? -6x-1 |
[12] |
QUESTION 8
8.1.1 | f (x) = 2(x - x1 )(x - x2 )(x - x3) | ?? f (x) = 2( x +1)( x - ½ )( x - 3) OR ?? f (x) = ( x +1)(2x -1)( x - 3) | |||
8.1.2 | f '(x) = 6x2 -10x - 4 | ? f '( x) = 6x2 -10x - 4 = 0 | (4) | ||
8.1.3 (a) | - 1/3 < x < 2 | ?? answer | (2) | ||
8.1.3 (b)
| 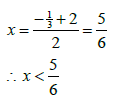 | ? f ''(x) =12x -10 OR ? x = 5/6
| (3) | ||
| 8.2 | 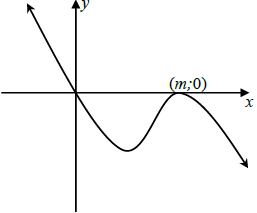 | ? f (0) = 0 | (3) | ||
[16] | |||||
QUESTION 9
9.1 | A = (½ ×15x × 8x × 2) + (15xy) + (8xy) + (17xy) | ? total surface area | (2) |
9.2 | V = (½b.h) × H | ? substitution into V ? substituing for y | (2) |
9.3 | V '(x) = 8640 - 540x2 | ? V '(x) = 8640 - 540x2 | (4) |
[8] | |||
QUESTION 10
10.1.1 | P(B) = 1- P(not) | ? 0,55 (1) |
10.1.2 | P(A and/en B) = P(A)×P(B) P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A and B) | ? P(A)×P(B) |
10.2 |
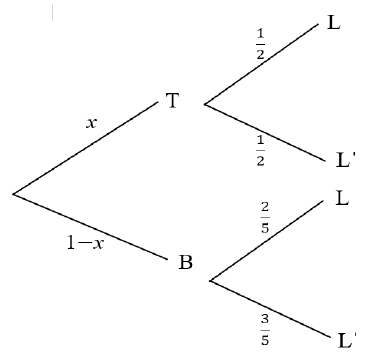
P(late) = 1/2 x + 3/5(1- x) |
? 1/2 x + 3/5(1- x) ? equating ? substitution ? answer (4) |
[8] |
QUESTION 11
| 11.1 | 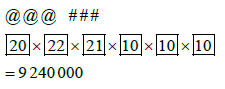 |  |
| 11.2 | 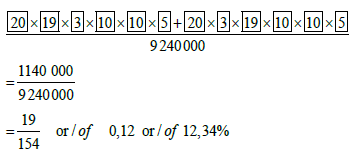 |  |
| [8] |
TOTAL: 150
Mathematics Paper 1 Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- This question paper consists of ELEVEN questions. Answer ALL the questions.
- Clearly show ALL calculations, diagrams, graphs, et cetera that you have used in determining your answer.
- You may use an approved scientific calculator (non-programmable and non- graphical), unless stated otherwise.
- Answers only will not necessarily be awarded full marks.
- If necessary, round off answers to TWO decimal places, unless stated otherwise.
- Diagrams are NOT necessarily drawn to scale.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- An information sheet with formulae is included at the end of the question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1 Solve for x:
1.1.1 x2 + 2x -15 = 0 (3)
1.1.2 3x2 + x -1 = 0 (correct to TWO decimal places) (3)
1.1.3 x(x - 3) ≥ -2 (4)
1.1.4 √43 - x - x +1 = 0 (5)
1.2 Solve simultaneously for x and y: 2 y - x = 3 and y2 + 3x = 2xy (5)
1.3 The roots of a quadratic equation are given as follows: ![]()
Determine the value(s) of p for which the equation will have non-real roots. (4)
[24]
QUESTION 2
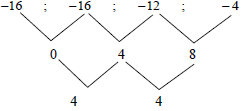
2.1 Given the quadratic number pattern: -16 ; -16 ; -12 ; -4 ; ...
2.1.1 Write down the next term of the pattern. (1)
2.1.2 Determine the general term of the pattern in the form Tn = an2 + bn + c (4)
2.1.3 Calculate the value of the 38th term of the pattern. (2)
2.1.4 Determine which two consecutive terms of the pattern will have a difference of 400. (3)
2.2 Given the arithmetic series: 2 + 5 + 8 + . . . +89 = k , calculate:
2.2.1 the number of terms in the series. (2)
2.2.2 the value of k . (3)
[15]
QUESTION 3
3.1 Given that in a geometric sequence T9 = 768 and T13 = 12288 . Determine the value(s) of the common ratio and the first term of the sequence. (3)
3.2 The sum to infinity of a convergent geometric series is 54/19 . The sum to infinity of the same series calculated from the 3rd term is 24/19 .
3.2.1 Calculate the sum of the first two terms of the series. (1)
3.2.2 Show that: ![]() (1)
(1)
3.2.3 Determine the value of r, if r > 0 (4)
[9]
QUESTION 4
The diagram below shows the graphs of ![]() and g(x) = bx , where b > 0. A and C are x and y-intercepts of f respectively, while D is the y-intercept of g.
and g(x) = bx , where b > 0. A and C are x and y-intercepts of f respectively, while D is the y-intercept of g. ![]() is a point that lies on g.
is a point that lies on g.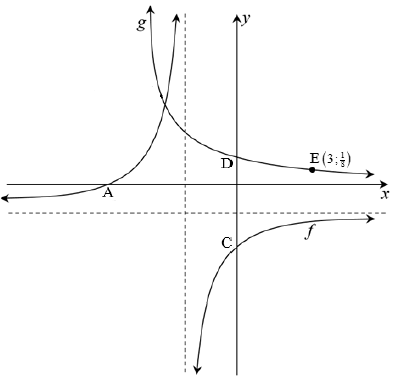
4.1 Write down the coordinates of D. (1)
4.2 Write down the equations of asymptotes of f. (2)
4.3 Write down the domain of f. (2)
4.4 Determine the value of b. (2)
4.5 Determine the coordinates of A and C. (3)
4.6 Write down the equation of g -1, in the form y = ... (2)
4.7 Determine the values of x for which:
4.7.1 f (x).g(x) > 0 (2)
4.7.2 g -1(x) ≥ 3 (2)
[16]
QUESTION 5
The diagram below shows the graph of f (x) = -x2 - 2x + 8 . R and S are x-intercepts and V the y-intercept of f . T is the turning point of f.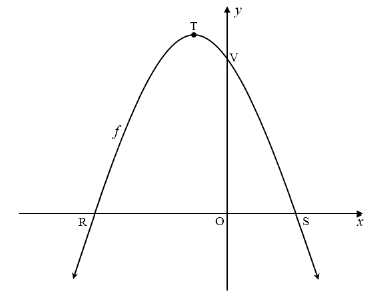
5.1 Determine the length of RS. (4)
5.2 Determine the coordinates of T. (3)
5.3 The gradient of the tangent to the graph f at a point W is equal to 2.
5.3.1 Determine the coordinates of W. (4)
5.3.2 Determine the equation of a straight line, g , which is perpendicular to the tangent and passing through V. (2)
5.4 The graph of f is shifted one unit to the right and then reflected in the x-axis to produce a new function h. Determine the equation of h in the form:
h(x) = ax2 + bx + c. (4)
[17]
QUESTION 6
6.1 Eli bought a laptop 4 years ago. The value of the laptop depreciates from R9 670,00 on a reducing-balance method to its current value of R5 509,70. Calculate the annual rate of depreciation of the laptop. (3)
6.2 Mr Duda decided to save money towards his son’s tertiary education as follows:
- He paid R600 per month into an account that paid 8,7% interest p.a. compounded monthly.
- His first payment was at the end of January in which his son started Grade 1 and the last payment at the end of December when his son completed his Grade 12. His son did not repeat any grade.
- He withdrew all his savings one month after his last payment.
Calculate the amount that was in his account by the time Mr Duda withdrew all the savings. (4)
6.3 Pilisa takes out a loan to buy a car that costs R350 000. The bank offers her an interest rate of 9,3% p.a. compounded monthly and a payment period of 6 years. Her first instalment is due at the end of the first month after taking the loan.
6.3.1 Calculate Pilisa’s monthly instalment. (3)
6.3.2 Calculate the balance of her loan after the 40th payment was made. (3)
6.3.3 Pilisa decides to increase her monthly instalment to R7 000 per month after her 40th payment. How long, after the 40th payment, will it take her to pay up the loan? (4)
[17]
QUESTION 7
7.1 Determine f '(x) from first principles if f (x) = 5 - 2x2 . (5)
7.2 Determine:
7.2.1 ![]() (3)
(3)
7.2.2 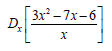 (4)
(4)
[12]
QUESTION 8
8.1 The diagram below shows the graph of f (x) = 2x3 + bx2 + cx + d. Points J(–1 ; 0), K( ½ ; 0) and L(3 ; 0) are the x-intercepts and G the y-intercept of f. M and N are the turning points and H the point of inflection of f.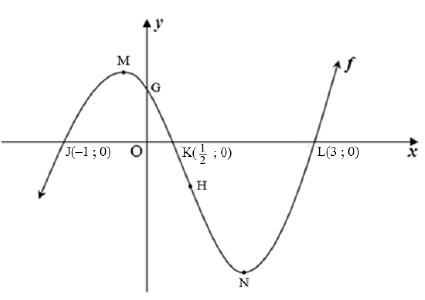
8.1.1 Determine the values of b, c and d in the equation of f. (4)
8.1.2 If it is given that f (x) = 2x3 - 5x2 - 4x + 3 , determine the coordinates of N, the minimum turning point of f. (4)
8.1.3 For which values of x , is:
- f' (x) < 0? (2)
- f concave down ? (3)
8.2 If g(x) = px3 + qx2 + rx is a cubic function that further satisfies the following conditions:
- p < 0
- g '(m) = g(m) = 0, where m > 0
Draw a sketch graph of g clearly indicating one of the turning points of g in terms of m and all intercepts. (3)
[16]
QUESTION 9
The diagram below shows a solid triangular prism. The triangle is right-angled with a height of 8x metres, a base of 15x metres, and a hypotenuse of 17x metres as indicated on the diagram. The length of the prism is y metres and the total surface area of the prism is 5 760 m2.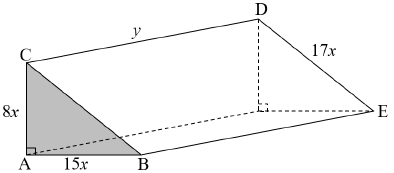
9.1 Show that ![]() (2)
(2)
9.2 Hence, show that the volume of the prism can be expressed as: V(x) = 8640x -180x3. (2)
9.3 Determine the value of x for which the volume of the prism will be a maximum. (4)
[8]
QUESTION 10
10.1 A and B are two independent events such that P(A) = 0,2 and P(not B) = 0,45. Determine:
10.1.1 P(B) (1)
10.1.2 P(A or B) (3)
10.2 Asanda travels to school on her bike or by taxi. The probability that she travels by taxi is x. If she uses her bike, the probability that she will be late for school is 2/5 and if she travels by taxi, the probability that she will be late is 1/2. Determine the value of x if the probability that Asanda is not late for school is 8/15 . (4)
[8]
QUESTION 11
In a certain province vehicle number plate codes have the following format:
@ @ @ # # # (three letters followed by 3 digits) where @ represents a letter of the alphabet and # a digit from 0 to 9. For each number plate code that is assigned to a vehicle, the following conditions must be met:
- All letters except E, G and O can be used and no letter can be repeated.
- No number plate code can start with a vowel.
- All digits can be used, and each digit can be repeated.
11.1 How many vehicles can be assigned a number plate code according to this system? (3)
11.2 Calculate the probability that a number plate code chosen from the number plates in QUESTION 11.1 at random contains only one vowel and ends with
an even digit. (5)
[8]
TOTAL: 150
INFORMATION SHEET: MATHEMATICS
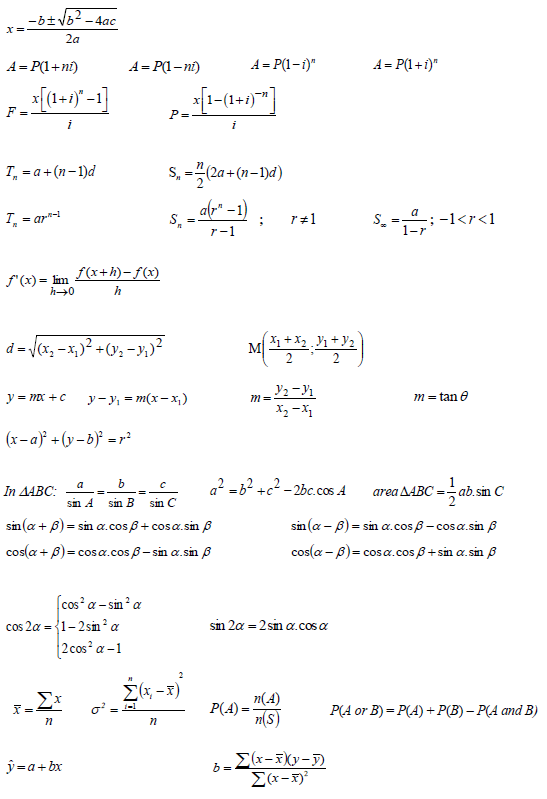
Life Sciences Paper 2 Memorandum - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
PRINCIPLES RELATED TO MARKING LIFE SCIENCES
- If more information than marks allocated is given
Stop marking when maximum marks is reached and put a wavy line and ‘max’ in the right-hand margin. - If, for example, three reasons are required and five are given
Mark the first three irrespective of whether all or some are correct/incorrect. - If whole process is given when only a part of it is required
Read all and credit the relevant part. - If comparisons are asked for but descriptions are given
Accept if the differences/similarities are clear. - If tabulation is required but paragraphs are given
Candidates will lose marks for not tabulating. - If diagrams are given with annotations when descriptions are required
Candidates will lose marks. - If flow charts are given instead of descriptions
Candidates will lose marks. - If sequence is muddled and links do not make sense
Where sequence and links are correct, credit. Where sequence and links are incorrect, do not credit. If sequence and links become correct again, resume credit. - Non-recognised abbreviations
Accept if first defined in answer. If not defined, do not credit the unrecognised abbreviation but credit the rest of the answer if correct. - Wrong numbering
If answer fits into the correct sequence of questions but the wrong number is given, it is acceptable. - If language used changes the intended meaning
Do not accept. - Spelling errors
If recognisable, accept the answer, provided it does not mean something else in Life Sciences or if it is out of context. - If common names are given in terminology
Accept, provided it was accepted at the national memo discussion meeting. - If only the letter is asked for but only the name is given (and vice versa)
Do not credit. - If units are not given in measurements
Candidates will lose marks. Marking guideline will allocate marks for units separately. - Be sensitive to the sense of an answer, which may be stated in a different way.
- Caption
All illustrations (diagrams, graphs, tables, etc.) must have a caption. - Code-switching of official languages (terms and concepts)
A single word or two that appear(s) in any official language other than the learners’ assessment language used to the greatest extent in his/her answers should be credited if it is correct. A marker that is proficient in the relevant official language should be consulted. This is applicable to all official languages.
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 C
1.1.2 D
1.1.3 A
1.1.4 B
1.1.5 D
1.1.6 A
1.1.7 C
1.1.8 B
1.1.9 B
1.1.10 B (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 Phenotype
1.2.2 Autosomes
1.2.3 Chiasmata /chiasma
1.2.4 Gene
1.2.5 Transcription
1.2.6 Cloning
1.2.7 Homologous chromosomes
1.2.8 Locus (8)
1.3
1.3.1 B only
1.3.2 Both A and B
1.3.3 B only (6)
1.4
1.4.1 Meiosis (1)
1.4.2 Metaphase 1 (1)
1.4.3
- B (1)
- F
- D and E
(Mark first TWO only) (1) (2)
1.4.4 4 / four (1)
1.4.5 Sperm / (not gamete) (1)
1.5
1.5.1 Million years ago (1)
1.5.2
- C /A (1)
- A (1)
- B (1)
1.5.3 Various hypotheses relating to evolution have been tested and verified
over time /has undergone several tests and is supported by evidence (1)
1.5.4
- Biogeography
- Genetics
- Modification by descent /homologous structures (Any 3 x 1)
(Mark first THREE only) (3)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1 A – Centromere (1)
2.1.2 DNA Replication (1)
2.1.3
- The DNA molecule unwinds
- And unzips / the weak hydrogen bonds break
- Each strand acts as a template
- Free floating nucleotides in the nucleoplasm
- Join to their complementary strand/base pair / (T-A; C-G)
- Forming two identical strands of DNA (Any 4 x 1) (4)
2.1.4
- Produce two exact copies of the cells/ DNA /chromosomes
- So that each new cell formed in mitosis has the exact genetic material/ same amount of DNA as the parent cell /chromosomes. (2)
2.2
2.2.1 Set 2 (1)
2.2.2
- All the bands of the baby that don’t match father 2 match mother 2
OR - All the DNA bars of the baby match that of father 2 and mother 2
OR - The other parents’ bands do not match all the bands of the baby (2)
2.2.3
- blood
- skin cell
- hair cell
- saliva
Mark first TWO only (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.2.4
- Biological evidence in forensic investigations /crime scenes/ identify criminals
- Tracing missing persons
- Identify dead persons /animals
- Identifying genetic disorders
- Matching tissues for organ transplants
- Establishing family relations
Mark first TWO only (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.3
2.3.1 The sickle shape red blood cells cause blockages in the blood vessels leading to damage of vital organs / transport less oxygen leading to less energy/ anaemia (1)
2.3.2 Stem cell are undifferentiated cells that have the potential to form any tissue or organ (2)
2.3.3
- CUU (1)
- Glycine (1)
- If Thymine changes to Adenine
- The mRNA/codon will be GUG instead of GAG
- The tRNA/anticodon will be CAC instead of CUC
- Therefore, the amino acid will be Valine
- instead of Glutamine (4)
2.3.4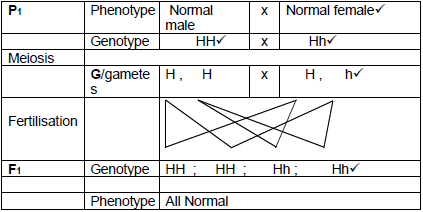
They have a 0%* chance of having a child with sickle cell disease
- P1 and F1
Meiosis and fertilisation
Any 5 + *1 Compulsory OR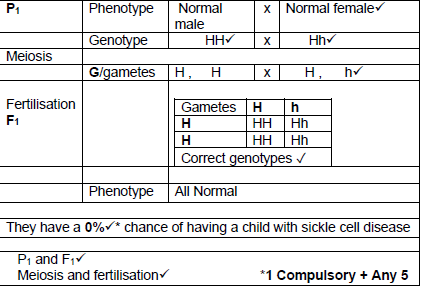 (6)
(6)
2.4
2.4.1 Karyogram / Karyotype (1)
2.4.2
- Chromosome pair 23 has
- two X chromosomes /XX/ chromosomes are the same size (2)
2.4.3
- Because there is a double set of chromosomes / 46 chromosomes/ it is diploid/ homologous pairs
- and not a single set of chromosomes / not 23 chromosomes/ not haploid (2)
2.4.4 Down’s Syndrome / trisomy 21 (1)
2.4.5
- Homologous chromosome pair 21
- does not separate /non-disjunction
- This will lead to one gamete having two copies of chromosome 21
- When this gamete fuses with a normal gamete
- the resulting zygote will have an extra copy of chromosome 21 / 3 copies of chromosome 21 (Any 3 x 1) (3)
2.5
2.5.1 Dihybrid Cross (1)
2.5.2 There are two different characteristics being crossed (1)
2.5.3
- bbtt (2)
- Both Black and no white patches
OR
Parent 1 - Black and no white patches
Parent 2 – Black and no white patches (2)
2.5.4
- Since black coat is controlled by a dominant allele
- the kitten could be homozygous/ BBtt or heterozygous /Bbtt (2)
2.5.5
- The pair of alleles on homologous chromosomes separate
- during meiosis /anaphase/ gamete formation, so that
- only one allele of each pair is present in the gamete / offspring can acquire one allele from each parent (3)
[50]
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1 Graph showing the number of monarch butterfly colonies from 1994 to 2010 (1)
3.1.2
- Use of herbicide (1)
- Number of Monarch butterfly colonies (1)
3.1.3
- The number monarch butterfly colonies decreased from 1996
- before herbicides were used in 1998. (2)
3.1.4
- An organism whose DNA/genome has been modified
- to express a desired characteristic (2)
3.1.5
- Less competition between crop and weeds / there will be more yield
- leading to an increase in the farmers’ profit (1)
3.2
3.2.1 There was not enough food for them to eat (1)
3.2.2
- Lizards were separated by water
- and therefore, there was no interbreeding (2)
3.2.3
- On the island there was variation in the size of Gymnodactylus amarali /lizards
- Some lizards had smaller heads while others had larger heads
- When there were more larger termites on the islands
- Those with smaller heads died out since they could only eat small termites
- Those with larger heads survived could eat large termites
- they reproduced and passed on their characteristic of larger heads to their offspring
- Eventually over time there was a greater proportion of lizards with larger heads (Any 5 x 1) (5)
3.2.4
- If the island species can interbreed with the mainland species
- and produce fertile offspring they are the same species /if they do not produce fertile offspring, they are not the same species (2)
3.1
3.3.1 Homo sapiens (1)
3.3.2
- to be able to tear / bite/ chew
- raw food (2)
3.3.3 Table
| Humans | Gorilla | |
| 1 | Larger cranium /brain | Smaller cranium /brain |
| 2 | Flat face / Forehead slopes less backwards | Face sloping / Forehead slopes more backwards |
| 3 | Brow ridges are less pronounced | Brow ridges are more pronounced |
| 4 | Less protruding jaws / prognathous | More protruding jaws / prognathous |
| 5 | Lower jaw has a well-developed chin | Lower jaw has a poorly developed chin |
(Mark first THREE only) Table + (Any 3 x 2) (7)
3.3.4
- Opposable thumbs
- Freely rotating arms
- Elbow joints allowing rotation of forearm
- Rotate hands at least 180°
- (Flat) nails instead of claws /bare fingertips
- Five digits/ pentadactyl
(Mark first TWO only) (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.4
3.4.1
- Australopithecus
- Ardipithecus (2)
3.4.2 4 mya (1)
3.4.3 (4.5 – 1) = 3.5 mya (2)
3.4.4
- The foramen magnum has moved to the base of the skull / is in a more forward position so that the head can be held vertically. / spinal cord can be in line with the brain/ spine to enter the skull vertically
- The position of the pelvic girdle moved to under/the bottom of the core body so it is suitable to carry the weight of the upper body
- The pelvis has become more cup shaped/wider and shorter which makes it suitable to carry the core/weight of the upper body / for better distribution of upper body weight
- The spine became S- shaped / greater lumbar curvature in spine for better balance/to support the upper body weight
Mark first TWO only (Any 2 x 2) (4)
3.4.5
- Australopithecus africanus (1)
- Sterkfontein Caves (1)
- Robert Broom / John T Robinson (1)
3.5
3.5.1 Modern humans originated in Africa and then migrated to other continents (2)
3.5.2 Fossil evidence mitochondrial DNA / mtDNA Mark first TWO only (2)
3.5.3 Americas (1)
3.5.4 (200 000 – 45 000) years = 155 000 years (2)
[49]
TOTAL SECTION B: 100
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Life Sciences Paper 2 Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Write ALL the answers in the ANSWER BOOK or PAPER provided.
- Start the answer to EACH question at the top of a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Present your answers according to the instructions of each question.
- ALL drawings MUST be done in pencil and labelled in blue or black ink.
- Draw diagrams, tables or flow charts ONLY when asked to do so.
- The diagrams in this question paper are NOT necessarily drawn to scale.
- Do NOT use graph paper.
- You must use a non-programmable calculator, protractor and a compass, where necessary.
- All calculations to be rounded off to TWO decimal spaces.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the correct answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 Which ONE of the following describes the natural shape of the DNA molecule?
- It has a sugar-phosphate frame
- It is double stranded
- It has a double helix structure
- It has complementary nucleotides
1.1.2 The diagram below represents different phases of meiosis.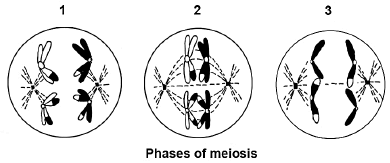
The correct order in which the phases occur is …
- 1, 2, 3.
- 3, 2, 1.
- 1, 3, 2.
- 2, 1, 3.
1.1.3 The pedigree diagram below shows the inheritance of cystic fibrosis which is controlled by a recessive allele, in a certain family.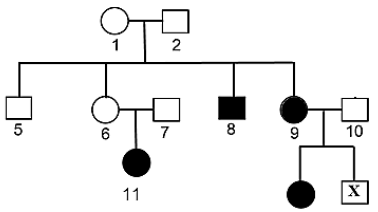
Which ONE of the following is the phenotype for individual X?
- Unaffected male
- Affected male
- Unaffected female
- ffected female
1.1.4 On the Galapagos islands there are 13 species of finches on different islands. Scientists believe that they all originated from a common ancestor that came from the mainland.
Which ONE of the following factors caused the first step in the evolution of the 13 finch species from a common ancestor?
- Breeding at different times of the year
- Geographical separation by the sea
- Producing infertile offspring
- Natural selection
1.1.5 Curly hair is dominant over straight hair. A woman who is homozygous for curly hair marries a man homozygous for straight hair.
What is the possibility of them producing a child with straight hair?
- 25%
- 50%
- 100%
- 0%
1.1.6 A man who has blood group A and a woman who has blood group O have a child together.
Which ONE of the following is the blood group genotype of the child?
- ii
- IAIB
- IAIA
- IBi
1.1.7 Which ONE of the following will occur during meiosis I?
- Chromatids separate to opposite poles
- Identical haploid cells form
- Non-disjunction
- Alleles of a gene fuse together
1.1.8 Which ONE of the following is correct about mitochondrial DNA (mt-DNA)?
- It is passed on from father to offspring
- It can be used to determine female ancestry
- It can be used to determine male ancestors of female individuals
- It traces the oldest male ancestors to Africa
1.1.9 Haemophilia is a sex-linked recessive disorder in humans. A father and his son both have haemophilia, but the mother is normal. Her genotype will be …
- XhXh
- XHXh
- XHXH
- XhY
1.1.10 What will the percentage of guanine be in a DNA molecule, if 20% of the nitrogenous bases are adenine?
- 20%
- 30%
- 40%
- 60% (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Give the correct biological term for EACH of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.2.1–1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 The physical or functional expression of a gene
1.2.2 The non-sex chromosomes
1.2.3 The point at which chromatids overlap during crossing over
1.2.4 A section of a DNA molecule that codes for a specific characteristic
1.2.5 The process during which mRNA is produced during protein synthesis
1.2.6 The production of a genetically identical copy of an organism using biotechnology
1.2.7 Chromosomes that carry the same set of genes
1.2.8 The position where a particular gene is found on a chromosome (8 x 1) (8)
1.3 Indicate whether each of the statements in COLUMN Ι, applies to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A and B, or NONE of the items in COLUMN ΙΙ. Write A only, B only, both A and B, or none next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.3) in the ANSWER BOOK.
COLUMN Ι | COLUMN ΙΙ | |
1.3.1 Type of inheritance where neither of the two alleles is dominant over the other and an intermediate phenotype is produced | A: B: | Co-dominance Incomplete dominance |
1.3.2 An example of a reproductive isolation mechanism | A: | Species-specific courtship behaviour |
| B: | Prevention of fertilisation | |
1.3.3 The number of alleles that control the human blood group | A: | Two |
B: | Three | |
(3 x 2) (6)
1.4 The diagram below represents a cell during cell division.
1.4.1 Name the type of cell division shown in the diagram above. (1)
1.4.2 Identify the phase represented by this diagram. (1)
1.4.3 Give the LETTER/S that represent/s:
- The structure that moves/pulls chromosomes/chromatids to the poles during cell division (1)
- The part that is responsible for forming the spindle fibres (1)
- TWO chromatids that are identical (2)
1.4.4 How many chromosomes will be found in each daughter cell at the end of this cell division? (1)
1.4.5 Give the name of the cells that will be formed as a result of this type of cell division in a male. (1)
1.5 The diagrams below represent three ideas proposed to explain evolution.
1.5.1 What does MYA stand for? (1)
1.5.2 Give the LETTER of the diagram (A, B or C) that would best represent:
- Punctuated equilibrium (1)
- Lamarck’s explanation of evolution if there was an environmental change 10mya (1)
- Charles Darwin’s explanation of evolution (1)
1.5.3 State a reason why the ‘theory of evolution’ is regarded as a scientific theory. (1)
1.5.4 Name THREE lines of evidence used to support the theory of evolution. (3)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1 The diagrams below show two forms of a chromosome.
2.1.1 Identify part A. (1)
2.1.2 Identify the process that led to the formation of the chromosome represented by Diagram 2. (1)
2.1.3 Describe the process mentioned in QUESTION 2.1.2. (4)
2.1.4 Give TWO reasons why the process described in QUESTION 2.1.3 is important. (2)
2.2 When a tsunami destroyed a town in Japan, several people went missing. A baby that was rescued from the ruins was claimed by three sets of parents. DNA tests were done to determine the parents of the baby.
Below are the results of the DNA test:
2.2.1 Which set of parents (set 1, 2 or 3) are the biological parents of the baby? (1)
2.2.2 Give a reason for you answer to QUESTION 2.2.1. (2)
2.2.3 Name TWO sources of DNA the police could use to produce a DNA profile. (2)
2.2.4 Mention TWO other uses of DNA profiling apart from the one mentioned above. (2)
2.3 Haemoglobin-A is a normal protein in red blood cells that transports oxygen. A mutation sometimes occurs in the gene that codes for this protein, where thymine is replaced by adenine at a single point. This mutation results in the formation of a different protein called haemoglobin-S.
Haemoglobin-S causes red blood cells to become stiff and sickle-shaped. The sickle-shaped red blood cells cause blockages in the blood vessel. A person will have sickle-cell disease. Currently the only cure for sickle cell disease is bone marrow transplants and stem cell treatment.
The diagram below shows the red blood cell shape and DNA sequence for haemoglobin-A and haemoglobin-S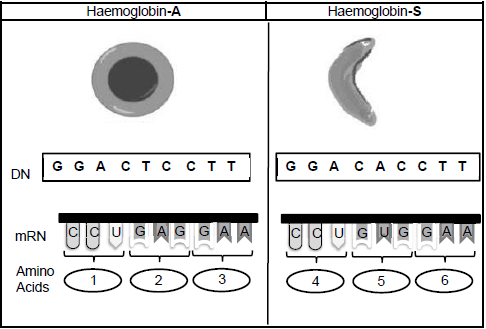
2.3.1 State a reason why sickle cell disease is dangerous. (1)
2.3.2 What are stem cells? (2)
2.3.3 Use the table below to answer the following questions.
Amino Acid | tRNA anticodon |
Leucine | GAA |
Lycine | CUU |
Glycine | GGA |
Glutamic acid | GAG |
Histidine | GUA |
Methionine | UAC |
Proline | CCU |
Valine | CAC |
Glutamine | CUC |
- Give the anticodon for amino acid 6. (1)
- Name amino acid 1. (1)
- Explain how this mutation in the haemoglobin gene affects the amino acid sequence formed. (4)
2.3.4 The allele for haemoglobin-A is dominant (H) over that for haemoglobin-S (h). A man homozygous for haemoglobin-A has a child with a heterozygous female. Use a genetic cross to show the possibility of them having a child with haemoglobin-S. (6)
[15]
2.4 The diagrams below show the chromosomes in the cells of two individuals.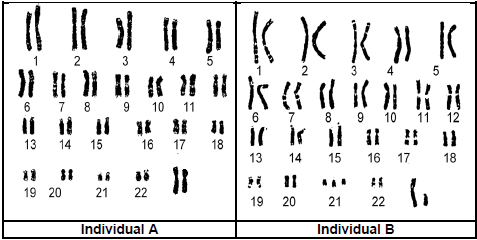
2.4.1 Name the type of diagram shown above. (1)
2.4.2 State why it can be concluded that diagram A belongs to a female. (2)
2.4.3 State why the diagrams above show the chromosomes of a somatic cell and not a gamete. (2)
2.4.4 Name the disorder that individual B has. (1)
2.4.5 Describe the cause of the disorder mentioned in QUESTION 2.4.4. (3)
2.5 In cats, two genes on different autosomes have the following alleles.
B: black coat colour b: grey coat colour | T: no white patches on coat t: white patches on coat |
Two cats were mated. Their litter of kittens had the phenotypes shown below at a ratio of 9 : 3 : 3 : 1.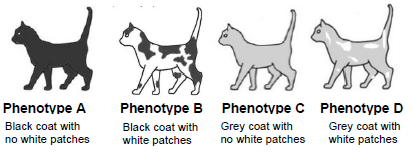
2.5.1 Name the type of cross represented here. (1)
2.5.2 Give a reason for your answer to QUESTION 2.5.1. (1)
2.5.3 Give the:
- Genotype of phenotype D (2)
- Phenotypes of the parents (2)
2.5.4 Explain why all the kittens having a black coat with white patches may not have the same genotype. (2)
2.5.5 State Mendel's principle of segregation. (3)
[50]
QUESTION 3
3.1 Some maize crops have been genetically modified to be herbicide resistant. This means that when the farmer sprays his crop field with herbicide to kill weeds, the maize will not be affected. The milkweed plant is a weed that grows between maize crops. The monarch butterfly lays its eggs on the milkweed plant. The young feed on the leaves of the milkweed plant.
Scientists investigated if the increased use of herbicides affect the number of monarch butterfly colonies in a crop field.
They planted herbicide resistant maize crops from1994 to 2010. From 1998 they started applying the herbicides to kill the weeds. Every year they counted the number of monarch butterfly colonies.
The graph below shows the data they collected from 1994 to 2010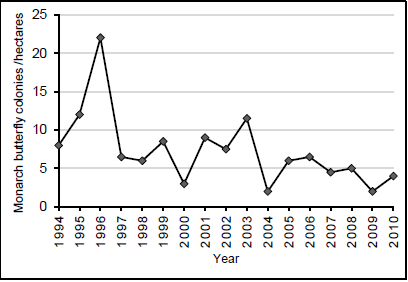
3.1.1 Provide a title for the graph above. (1)
3.1.2 Identify the:
- Independent variable (1)
- Dependent variable (1)
3.1.3 Using evidence from the graph, explain why the herbicides are the only factor that has caused the decrease in the monarch butterfly colonies. (2)
3.1.4 What is a genetically modified organism? (2)
3.1.5 Explain ONE economic advantage of the use of herbicide resistant maize crops for a farmer. (2)
3.2 Read the extract below.
In Brazil there are different lizard species that feed on termites.
|
3.2.1 State why the species of lizards with larger body size did not survive on the small islands. (1)
3.2.2 Explain why there was no gene flow between the populations of a species of lizards after the floods in 1996? (2)
3.2.3 Use Darwin’s theory of natural selection to explain why the population of the Gymnodactylus amarali lizards in the islands have larger heads. (5)
3.2.4 Describe how it can be proven that the species of lizard on the different islands are the same species as that on the mainland. (2)
3.3 The diagrams below show the skull of a human and a gorilla.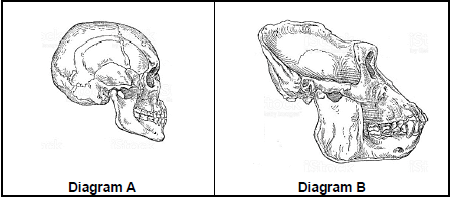
3.3.1 Give the scientific name of the organism in Diagram A. (1)
3.3.2 Explain why the teeth are larger in the skull in Diagram B. (2)
3.3.3 Apart from the size of the teeth, tabulate THREE other observable structural differences between the skull of a human and a gorilla. (7)
3.3.4 List TWO structural similarities between the forelimb of a human and gorilla. (2)
3.4 The diagram below represents the possible evolution of humans, as well as the time period for the evolution of bipedalism, use of stone tools and use of fire.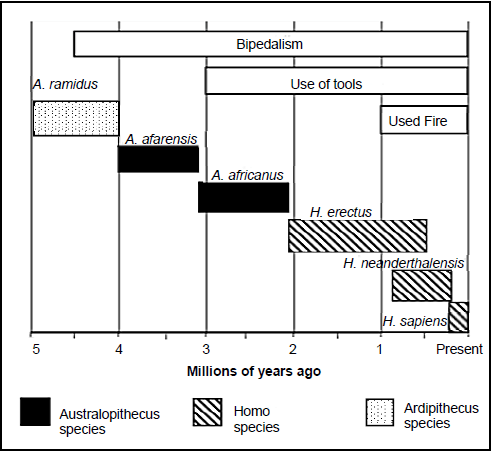
3.4.1 Name the TWO genera that were bipedal but did not use fire. (2)
3.4.2 When did the A. afarensis evolve? (1)
3.4.3 How long did it take for the hominin species to start using fire after they were bipedal? (2)
3.4.4 Explain TWO skeletal changes that took place to enable bipedalism. (4)
3.4.5 Mrs. Ples is a hominin fossil discovered in South Africa in1947.
- Give the full scientific name for Mrs Ples. (1)
- Where in South Africa was Mrs. Ples discovered? (1)
- Name ONE scientist that discovered Mrs. Ples. (1)
3.5 The map below shows the origins and movements of early humans according to the ‘Out of Africa’ hypothesis. The age of the oldest fossils found on each continent is also indicated below the name.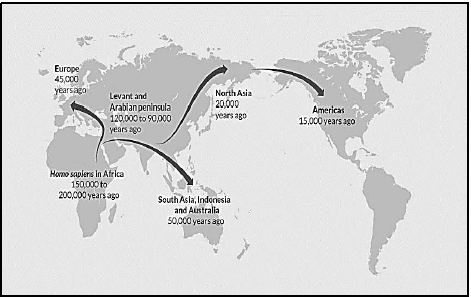
3.5.1 State the ‘Out of Africa’ hypothesis. (2)
3.5.2 Give TWO lines of evidence used to support the Out of Africa hypothesis. (2)
3.5.3 According to the map, which continent was the last to be colonised by early humans? (1)
3.5.4 Calculate the difference in the age of the oldest fossils found in Africa and those found in Europe? Show ALL your workings. (2)
[50]
TOTAL SECTION B: 100
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Life Sciences Paper 2 Errata - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
The Life Sciences P2 Grade 12 September was written on Tuesday, 07 September 2021. We were made aware of certain amendments and omissions that were discovered during the marking process.
In order to address this and to ensure that learners are not disadvantaged, the following standardised approach to marking must be adopted across the Province. The following guidelines regarding marking was prepared in conjunction with the examiner and moderator.
ERRATA
2.3.3 Due to the question being printed on the next page (i.e. page 12), learners may have ignored the diagram on the previous page (i.e. page 11) which they needed together with the table on page 12 to get the correct answer, a concession has been made to accept the following answers:
- UAC √
- Leucine √
3.1.3 (√√) Two marks will be awarded as question was not stated correctly.
Question should have read: Using evidence from the graph, explain why the herbicides are NOT the only factor that has caused the decrease in the monarch butterfly colonies.
Life Sciences Paper 1 Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Write ALL the answers in your ANSWER BOOK.
- Start the answer to EACH question at the top of a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Present your answers according to the instructions of each question.
- Do ALL drawings in pencil and label them in blue or black ink.
- Draw diagrams, tables or flow charts only when asked to do so.
- The diagrams in this question paper are NOT necessarily drawn to scale.
- Do NOT use graph paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator, protractor and a compass where necessary.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 The part of the brain that regulates the carbon dioxide concentration in the human body:
- Hypothalamus
- Cerebrum
- Cerebellum
- Medulla oblongata
1.1.2 The energy needed for the movement of a sperm is produced in the …
- mitochondria.
- nucleus.
- acrosome
- ribosome.
1.1.3 Which ONE of the following hormones stimulates puberty in females?
- LH/Luteinising hormone
- Oestrogen
- FSH/Follicle stimulating hormone
- Prolactin
1.1.4 Ovulation is the release of …
- an ovum into the fallopian tubes.
- mature graafian follicles into the uterus.
- corpus luteum into the fallopian tubes.
- an ovum into the uterus.
1.1.5 Which ONE of the following structures contains photoreceptors?
- Retina
- Choriod
- Vitreous humor
- Pupil
1.1.6 The synapse is a microscopic gap between a/an …
- cell body and the axon of one neuron.
- receptor and effector.
- axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron.
- axon of one neuron and the axon of another neuron.
1.1.7 The myelin sheath …
- prevents dehydration of the axons.
- provides energy for the transmission of impulse.
- provides electrical insulation.
- maintains a lower temperature.
1.1.8 A man lost his memory after a car accident.
Which ONE of the following parts of the brain might have been damaged in the accident?
- Cerebrum
- Cerebellum
- Medulla oblongata
- Corpus callosum
1.1.9 A list of possible visual effects is given below.
- Unable to receive a wide field of view.
- Unable to distinguish between red and green colours.
- Unable to read a book under bright light.
- Unable to register a sense of three-dimensional shape and form from visual inputs/perceive the depth of an object on 3D.
Which ONE of the following combinations will occur when a person has lost one eye in an accident?
- (i), (ii) and (iii) only
- (i), (iii) and (iv) only
- (i) and (iv) only
- (ii), (iii) and (iv) only
1.1.10 A high concentration of adrenalin in the blood leads to an increase in blood glucose levels, because …
- glycogen in the liver and muscles is converted to glucose.
- proteins are broken down to release more glucose.
- there is a decrease in metabolic rate.
- there is an increase in the digestion of carbohydrates. (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Give the correct biological term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.2.1–1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 The collective name for the membranes that protect the brain
1.2.2 The branch of the nervous system that consists of the cranial and spinal nerves
1.2.3 The branched outgrowth of a neuron that transmits nerve impulses to the cell body of the same neuron
1.2.4 The plant growth movement in response to gravity
1.2.5 The structure in the ear that absorbs excess pressure waves from the inner ear
1.2.6 The hormone that stimulates an increase in the rate of metabolism in the cells
1.2.7 The gland that secretes aldosterone
1.2.8 A structure in a female reproductive system where semen is deposited (8 x 1) (8)
1.3 Indicate whether each of the descriptions in COLUMN I apply to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A AND B or NONE of the items in COLUMN II. Write A only, B only, both A and B or none, next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.3) in the ANSWER BOOK.
| COLUMN I | COLUMN II | |||
1.3.1 | A type of gland whose secretions are transported in ducts/tubes to a target organ | A: B: | Endocrine gland Exocrine gland | |
1.3.2 | A symptom of Alzheimer’s disease | A: B: | Memory loss Confusion | |
1.3.3 | A type of lens used to correct short-sightedness (myopia) | A: B: | Biconvex lens Biconcave lens | |
(3 x 2) (6)
1.4 The diagram below represents a reflex arc.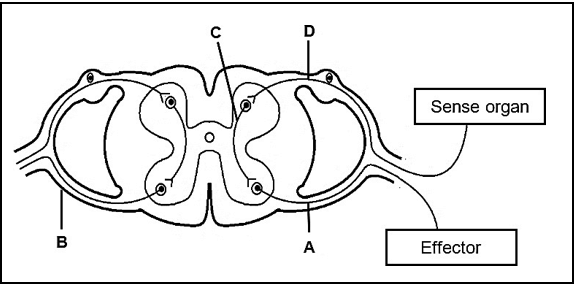
1.4.1 Write down, in the correct sequence, the LETTERS representing the neurons that transmit impulses to the effector. (2)
1.4.2 State the significance of a reflex action. (1)
1.4.3 Give ONE example of an effector in a human body. (1)
1.4.4 Write down the LETTER and the NAME of the:
- Neuron located only in the brain or spinal cord (2)
- Part that represents a root of the spinal nerve (2)
- Neuron that is damaged when a person feels pain, but is unable to react (2)
1.5 The diagram below shows some endocrine glands in a male body.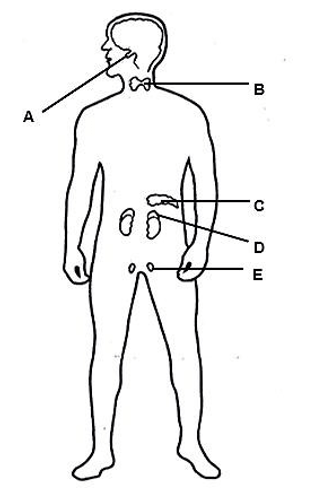
1.5.1 Identify gland:
- B (1)
- E (1)
1.5.2 Name the:
- Gland that secretes growth hormone (1)
- Hormone that stimulates gland B (1)
- Gland that secretes adrenalin (1)
1.5.3 Give the LETTER of the gland that secretes a hormone responsible for stimulating the reabsorption of water by kidney tubules. (1)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1 Read the extract below about reproduction in seahorses.
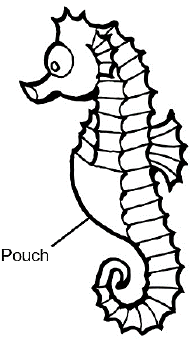
Male seahorses have a pocket-like structure on their abdomens called a pouch. During a mating ritual, the female seahorse deposits a large number of eggs into the pouch using a structure called an ovipositor. The male then releases many sperm into the pouch to fertilise the eggs. The developing embryos in the male pouch, are nourished by the yolk of the eggs. A fluid that is secreted within the pouch removes waste products and supplies the fertilised eggs with oxygen. The young are born alive when they are released from the pouch.
|
2.1.1 State the type of fertilisation that takes place in seahorses. (1)
2.1.2 Give a reason for your answer to QUESTION 2.1.1. (1)
2.1.3 Explain TWO ways by which the seahorses increase their reproductive success. (4)
2.1.4 State ONE difference between the reproductive strategy displayed by the seahorses and vivipary. (2)
2.2 In pregnant female rats, progesterone is mainly secreted by the corpus luteum. It takes about 22 days for the rat to give birth after fertilisation.
Scientists did an investigation to determine the amount of progesterone needed for the successful completion of gestation in rats.
The procedure was as follows:
- 100 female rats of the same age were selected
- They were divided into five equal groups
- All the 100 female rats were artificially inseminated at the laboratory (the sperm were inserted into the female reproductive tract using a syringe so that fertilisation can take place)
- Ovaries of each rat were removed immediately after becoming pregnant
- Group 1 was given no progesterone injection
- Group 2 was given a daily injection of 5 mg progesterone
- Group 3 was given a daily injection of 10 mg progesterone
- Group 4 was given a daily injection of 15 mg progesterone
- Group 5 was given a daily injection of 20 mg progesterone
- The number of rats who completed gestation by each group was counted and the percentage calculated
2.2.1 Define the term gestation. (2)
2.2.2 How long is the gestation period of rats? (1)
2.2.3 Identify the independent variable in this investigation. (1)
2.2.4 State TWO factors that should have been kept constant during the investigation. (2)
2.2.5 Explain why the ovaries were removed immediately after the rats were pregnant. (3)
2.2.6 Describe how the percentage of rats who completed gestation was calculated. (2)
2.2.7 Explain why Group 1 was included in the investigation. (2)
2.3 The diagram below shows the structure of the human eye.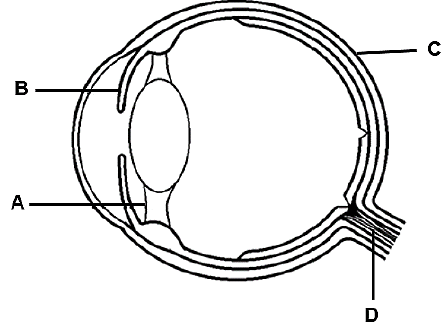
2.3.1 Identify the parts labelled:
- A (1)
- B (1)
2.3.2 State ONE function of part C. (1)
2.3.3 Describe accommodation of the eye when a person focuses on an object that is moving away. (4)
2.3.4 Explain the consequence that a damage to part D has on the vision of a person. (3)
2.4 2.4.1 Define homeostasis. (2)
2.4.2 A man jumped into icy cold sea water. His body temperature was maintained through homeostasis. Describe the role of the skin in thermoregulation during this time. (7)
2.4.3 When a person is exposed to very cold temperatures, the body loses more heat than it can produce. Explain why a prolonged exposure to very cold temperatures without protection may lead to death. (3)
2.5 The diagram below represents the male reproductive system, following a surgical procedure to prevent pregnancy.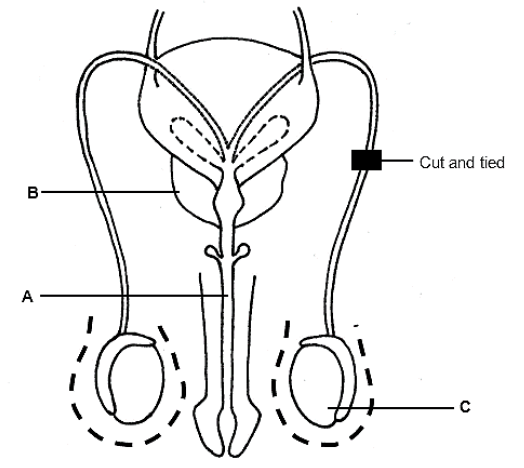
2.5.1 Identify part B. (1)
2.5.2 State ONE function of part A. (1)
2.5.3 Explain why part C moves away from the body on a very hot day. (3)
2.5.4 Explain why this procedure may fail to prevent pregnancy. (2)
[50]
QUESTION 3
3.1 A person had severe hearing loss which was caused by a damage to the ossicles and the inner ear. He underwent a cochlear implant. The cochlear implant partially restored hearing. When a person has a cochlear transplant, the sound waves are collected by the microphone and converted to a stimulus by the receiver and transmitter. The impulse is transmitted to the cochlea by an electrode.
The diagram below shows the structure of the ear with a cochlear implant.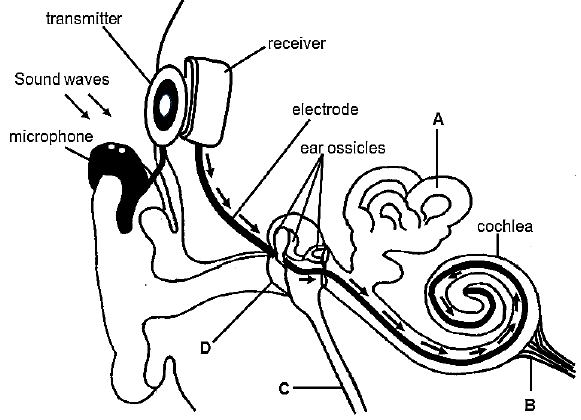
3.1.1 Identify part B. (1)
3.1.2 State ONE function of part C. (1)
3.1.3 Which part of the ear normally functions as the:
- Microphone (1)
- Receiver and transmitter (1)
3.1.4 Explain why a person may lose hearing ability if there is:
- Damage to the ossicles (3)
- A hole in part D (3)
3.1.5 Describe how part A and the brain together maintain balance. (4)
3.2 An investigation was conducted to determine the effect of auxins on direction of growth of the stem.
The procedure was done as follows:
- Two potted plants (1 and 2) of the same species and age were used
- The apical buds of both plants were removed by cutting at the same length along the stem
- The cut apical buds of both plants were placed on separate blocks of agar jelly for 2 hours
- One block of agar jelly was then placed on the right-hand top edge of the cut surface of pot plant 1 and the other block of agar jelly was then placed on the left-hand top edge of the pot plant 2, as shown in the diagram below
- Both pot plants were kept in a dark box for two weeks
- The direction of growth of the stem of both plants was observed at the end of this period
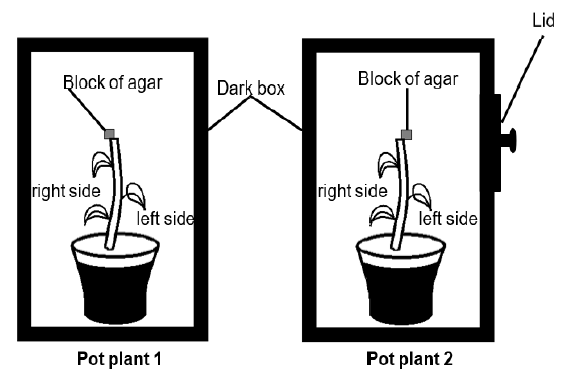
3.2.1 Give a reason why the apical buds were:
- Removed (1)
- Placed on the blocks of agar jelly for 2 hours (1)
3.2.2 Explain the results obtained for pot plant 1. (4)
3.2.3 Pot plant 2 was exposed to a unilateral light from the left-side by removing the lid on the box during this period. Explain the results that were obtained. (4)
3.2.4 Explain why fruit farmers periodically remove the apical buds from fruit trees. (2)
3.3 The graph below shows the homeostatic control of blood glucose in a healthy person.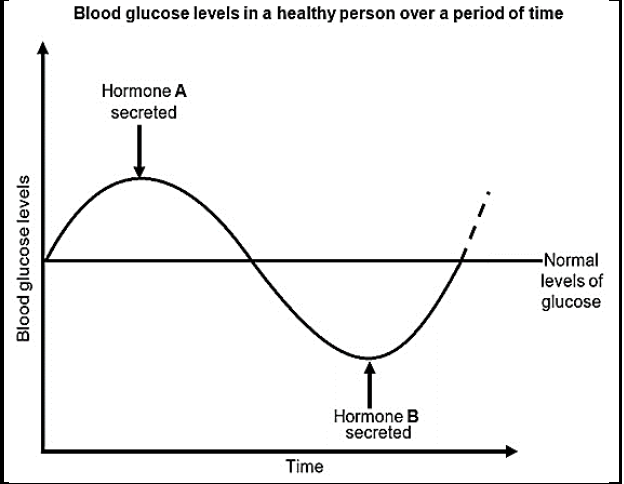
3.3.1 Identify:
- Hormone A (1)
- The gland that secretes hormone B (1)
3.3.2 Name the type of mechanism that controls the levels of hormones A and B. (1)
3.3.3 When a person is fasting whether for religious or health reasons, she/he does not eat food for a certain period. Explain the levels of hormone A in a person during fasting. (2)
3.3.4 Describe how hormone B functions to maintain normal levels of blood glucose. (4)
3.4 The diagram below represents the female reproductive system during pregnancy.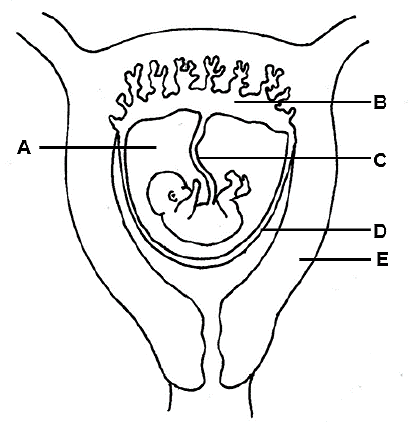
3.4.1 Identify:
- Fluid A (1)
- Extra embryonic membrane D (1)
3.4.2 Name the blood vessel in part C which transports oxygenated blood from the mother to the foetus. (1)
3.4.3 State TWO functions of part B. (2)
3.4.4 Describe the development of the zygote until part B is formed. (8)
3.4.5 Explain ONE structural suitability of part E to perform its function. (2) [50]
TOTAL SECTION B: 100
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Life Orientation Common Assessment Task - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of three sections, namely SECTION A, SECTION B and SECTION C.
- The questions in SECTION A and SECTION B are COMPULSORY.
- Answer any TWO questions in SECTION C.
- Read ALL the questions carefully.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question
numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.6 D.
1.1.1 A function of the National Benchmark Test (NBT) could be to …
- determine a potential candidate's abilities, strengths and weaknesses to follow a specific field of study.
- advise students on what type of financial aid they can access, based on the test results.
- assess whether potential students qualify for regular entry or extended programmes in a specific course.
- enable tertiary institutions to place students in any other field of study that may be available at the time.
1.1.2 Embezzlement is an illegal act of …
- obtaining money, goods or property by deceiving other people.
- getting something, especially money, by force or threats.
- giving or receiving a free reward to influence someone's actions.
- secretly taking money that belongs to the company you work for.
1.1.3 Examples of health-related components of fitness:
- Body composition, muscular endurance and reaction time
- Muscular endurance, cardiovascular fitness and flexibility
- Coordination, cardiovascular fitness and muscular strength
- Cardiovascular fitness, flexibility and body composition
1.1.4 An evaluation of an impact study is done to …
- secure all the resources needed to complete the intervention.
- identify the steps needed to conduct that specific intervention.
- decide who will be in charge of carrying out the intervention.
- determine the changes as a result of a particular intervention.
1.1.5 The Employment Equity Act (EEA), 1998 (Act 55 of 1998) intends to regulate …
- psychological testing and assessment of potential employees.
- the right of workers not to be locked out from the workplace while striking.
- employee participation in decision-making through workplace forums.
- employment of young children under the minimum school-leaving age. (5 x 1) (5)
1.2 Give ONE word/term for EACH of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.3) in the ANSWER
BOOK.
1.2.1 A condition that can be avoided by drinking water regularly during physical education activities (1)
1.2.2 The term describing a person who shows exceptional ability, knowledge and common sense about using modern technology (1)
1.2.3 The ability to maintain a controlled body position during a dance movement (1)
1.3 Answer the following questions by writing the answer next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.4) in the ANSWER BOOK. Write your answers in full
sentences.
1.3.1 Give TWO examples of possible gender inequality practices in the work place. (2 x 1) (2)
1.3.2 Explain why smoking of cigarettes may have a negative effect on your physical appearance. (1 x 2) (2)
1.3.3 Why do you think municipalities should amend by-laws regularly?(2 x 1) (2)
1.3.4 Discuss the importance of setting achievable health and fitness goals. (1 x 2) (2)
1.4 Read the source below and answer the following questions. Write your answers in full sentences.
ENTREPRENEURSHIP: PLAN A, B or C?
[Adapted from www.entrepreneur-headlines.co.za. Accessed on 16 February 2021.]
1.4.1
1.4.2 Explain why entrepreneurs should be risk-takers. (1 x 2) (2)
Recommend ONE way in which a potential entrepreneur could determine if a business opportunity will be financially viable. Motivate your answer. (1 x 2) (2)
TOTAL SECTION A: 20
SECTION B (COMPULSORY)
Answer ALL the questions in this section. Write your answers in full sentences.
QUESTION 2
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
THE IMPORTANCE OF COMMUNICATION Our personalities influence the effectiveness of our communication with others. Therefore, developing appropriate personality traits is necessary to deal with different types of personalities, emotions and conflict situations in life effectively. Being emotionally healthy does not necessarily mean that you are happy all the time or that you are satisfied with yourself and the relationships you have with others. Rather, it may mean that you are aware of your feelings and thoughts about yourself and those of others. This awareness and acknowledgement may help you to develop better coping strategies which could be used to deal with conflict or changes in relationships. [Adapted from www.familydoctor.org. Accessed on 25 January 2021.] |
2.1 Give a definition for the term personality. (1 x 2) (2)
2.2 State TWO factors that may have contributed to a young person developing positive personality traits during childhood. (2 x 1) (2)
2.3 Explain how a negative attitude towards life could affect your communication with others. (1 x 2) (2)
2.4 Discuss why avoiding conflict is not healthy for any relationship. (2 x 2) (4)
2.5 Why do you think compromising may not always be considered to be the most ideal method to resolve disagreements? (2 x 2) (4)
2.6 How would you improve your way of coping with changes in any relationship? In EACH answer, also indicate how improving these coping skills could help
you to accept the changes in your relationships. (2 x 3) (6)
[20]
QUESTION 3
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
SURVIVING EXAMINATIONS Sitting for an examination has proven to be the most difficult aspect of general student assessment. Most students fail an assessment, not because they do not know the content, but because they cannot effectively respond to the questions within the stipulated time. Knowing your content does not always mean that you are able to effectively answer examination questions since there are factors, such as managing anxiety, which play a role in determining your success in an examination. Interestingly, examination writing skills, such as time management, are typical life skills because they could be used to deal with daily life demands. [Adapted from www.study-help/understanding-question. Accessed on 15 February 2021.] |
3.1 Give a definition of the term study skills. (1 x 2) (2)
3.2 Differentiate between the following action words as used in an examination question paper:
- Illustrate
- Identify (1 x 2) (2)
3.3 Explain ONE benefit of planning your responses when sitting for an examination. (1 x 2) (2)
3.4 Discuss TWO ways in which you could deal effectively with anxiety during an examination session. (2 x 2) (4)
3.5 Assess how time management skills could assist you to perform effectively in your Grade 12 assessments. (2 x 2) (4)
3.6 How would you adapt your reading skills to respond effectively to examination questions? In EACH answer, also indicate how that could improve your ability to gain maximum marks for a question. (2 x 3) (6)
[20]
TOTAL SECTION B: 40
SECTION C
Answer any TWO questions in this section.
Your responses must consist of paragraphs. Marks will ONLY be allocated for responses written in full sentences.
QUESTION 4
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
THE DEVASTATION OF CRISES AND DISASTERS The unforeseen devastation caused by global crises and disasters, such as the Covid-19 pandemic and HIV/Aids and has taken a significant toll on people across the world. The rapid spread of such diseases causes global health crises, which impact severely on the livelihood¹ of people. Glossary:
[Adapted from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com, Accessed on 29 January 2021] |
Write paragraphs on crises and disasters. Use the following as a guideline:
- State FOUR benefits for a person who detects a disease early enough. (4 x 1) (4)
- Analyse the negative effect of people's personal views about infectious diseases on the health and safety of people. (2 x 4) (8)
- Evaluate the impact of a crisis, such as the global Covid-19 pandemic, on the current trends in the job market. (2 x 4) (8)
[20]
QUESTION 5
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
CRITICAL ANALYSIS OF THE MEDIA Limitations to freedom of expression ensure public safety, while the increasing digital divide1 between different groups in society impacts negatively on access to information for all. Glossary:
[Adapted from https://www.justice.gov.za. Accessed on 29 January 2021.] |
Write paragraphs on limitations and accessibility of information. Use the following as a guideline:
- State FOUR ways in which the media could ensure access of information to all communities. (4 x 1) (4)
- Analyse how limitations to the right to freedom of expression of the media may assist in promoting public safety. (2 x 4) (8)
- Critically discuss the impact of the increasing digital divide on different groups in society, specifically the poorer communities. (2 x 4) (8)
[20]
QUESTION 6
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
FINDING MEANING IN WORK Finding work meaningful is something that every worker should experience. However, some people may not find meaning in their work, hence they are most likely to act unethically in the workplace. [Adapted from https://sloanreview.mit.edu/article/what-makes-work-meaningful-or-meaningless. Accessed on 3 December 2020.] |
Write paragraphs on the value of work and work ethics. Use the following as a guideline:
- State FOUR ways in which work could give you a sense of purpose in life. (4 x 1) (4)
- Analyse why it is necessary for all workers to follow the required ethical behaviour in the workplace. (2 x 4) (8)
- Critically discuss the importance of understanding your core values to ensure that you find meaning in your work. (2 x 4) (8)
[20]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 100
Information Technology Paper 2 Memorandum - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 Encapsulation (1)
1.1.2 Record (1)
1.1.3 Seek time (1)
1.1.4 Green computing (1)
1.1.5 Virtual Reality/(VR) (1)
1.1.6 Internet Service Provider/(ISP) (1)
1.1.7 IT waste/E-waste/E-scrap (1)
1.1.8 Software as a Service (SaaS) (1)
1.1.9 Fuzzy logic (1)
1.1.10 Router (1)
1.2
1.2.1 B – (rapid application development) (1)
1.2.2 A – (Comma Separated Values) (1)
1.2.3 C – (multitasking) (1)
1.2.4 C – (Wireless Access Point/Protocol) (1)
1.2.5 B – (5) (1)
TOTAL SECTION A: 15
SECTION B: SYSTEM TECHNOLOGIES
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1 Cloud application is software, where most of the processing is done in the cloud by one or more servers on the internet. (1)
2.1.2
- Gmail
- Facebook (2)
2.1.3 Local front-end means that the cloud application has a part of the program that is stored and run locally on a device or it might run entirely as a page in a web browser. (1)
2.1.4 Any TWO:
- Google Docs
- Office 365
- Microsoft Office Online
- iWork
- Google G Suite
- Smart Sheet
- Feng Office
- Zoho Workplace
- Quip (2)
2.1.5 Any TWO:
- Scalability
- Ubiquity (Anywhere/anytime)
- Enables collaboration
- Outsource maintenance and upgrades of hardware
- Outsource software installation and upgrades (2)
2.1.6 Service Level Agreement (1)
2.2
2.2.1 Any ONE:
- Augmented Reality technology superimposes/covers a computer- generated image onto a user’s view of the real world.
- It provides a composite 3D view that provides full immersion.(1)
2.2.2 Any TWO:
- Product View
- Enhance content
- Training
- Productivity
- Engage the audience (2)
2.2.3 Any TWO:
- To get or enhance creativity
- Provide a new product experience
- Able to preview the product visually
- Build real-time data experience
- Enjoy experimental experiences
- Functional uses demo (2)
2.2.4 Any TWO:
- Battery life
- Bluetooth connectivity/Wi-Fi
- Field of view in 3D view
- On board OS/Web Browser
- On-board storage capacity
- Inputs/outputs (button, eye tracking, accelerometer)
- Microphone
- Sound capacity
- Display capacity
- Visual tracking (2)
2.3
- Archiving is the process of moving data that is no longer actively used to a separate storage device for long term retention.
- Back-up is the process of making copies/duplicates of data storing it on a different device in different geographical area/location. (2)
2.4
2.4.1 Virtualisation is the process of running multiple computing environments (called virtual machines) on a single set of hardware. (1)
2.4.2 Any TWO:
- Testing different operating systems and hardware
- Cloning computers
- Hosting cloud applications
- Allow multiple people to use the same computer at the same time (2)
2.4.3 Any TWO:
- Less expenditure
- Save assets
- Disaster recovery
- Green IT
- Long term benefits (2)
2.5
- Disk Check
- SMART scan (2)
TOTAL SECTION B: 25
SECTION C: COMMUNICATION AND NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1
- Switch
- Network cable
- Wireless base station (3)
3.1.2 World Wide Web (1)
3.2
3.2.1 BitTorrent is a peer-to-peer protocol used to transfer and share large files across a network such as the Internet. (1)
3.2.2 Any THREE:
- The data used to upload the file is shared between all the users downloading the file.
- The bandwidth is also shared, allowing users to download the file more quickly.
- Since the file is not uploaded to a single website or hosted by a single user, people may continue to share it for years after it was first shared.
- For websites using torrents to share pirated material, the website itself is not sharing the illegal materials nor the files linking to illegal materials.
- BitTorrent allows many users to download popular files quickly because it eliminates the bottleneck problem that you get when a file is shared from a single source/server.
- It reduces the cost to the host (no single host has to pay for millions of people downloading the file from their server).
- It forces some equality in sharing (every time you run the client software, others can download the files in your shared folder and in your downloaded files folder).
- It offers an effective use of available download bandwidth.
- BitTorrent client software is usually free. (3)
3.2.3 Any THREE:
- Many users have used torrent files to share viruses.
- Many ISPs throttle or shape torrent downloads, preventing you from downloading them at high speed.
- Torrents are often used to pirate videos and music.
- Torrenting is only legal if you have a licence to use the content which you torrent.
- BitTorrent is purely a content distribution method and does not incorporate any technology to monitor or restrict any activity. (3)
3.3
3.3.1 Remote access refers to several technologies or applications that allow you to connect to a computer over the network. (1)
3.3.2 Any THREE:
- Opening applications
- Sending e-mails
- Fixing problems
- Use the computer as if it is your computer
- See the remote computer’s display on your monitor or view the screen of the remote target computer on your local computer.
- Use the local computer’s mouse and keyboard to control the target computer remotely. (3)
3.3.3
- Local network – is a remote access that allows you to connect to a computer on your local network and use it as if it was your own computer.
- Online remote access/Virtual Private network – allows you to connect and manage a computer anywhere in the world. (4)
3.4 Any TWO:
- Software firewall installed on the user’s computer OR (Firewall installed on user’s computer).
- Software firewall that is installed on a server or router
- Hardware firewall installed between a local computer and the Internet. (2)
3.5 Network Topology refers to the layout/structure of a network. (1)
TOTAL SECTION C: 22
SECTION D: DATA AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
QUESTION 4
4.1 Any TWO:
- Accuracy
- Consistent
- Current
- Complete
- Relevant (2)
4.2
4.2.1 Data verification is a manual technique that is used to make sure that the data on a database is correct and accurate. (1)
4.2.2
- Full verification – requires that each piece of data that is entered into a database is read and checked by someone.
- Sample verification – a process in which randomly selected samples of data is checked to ensure that there are no systematic errors. (2)
4.2.3 Any TWO:
- Records who made changes to the system
- Records what the user changed from the system
- Records when they made changes (2)
4.3 Any TWO:
- Designing a database
- Security or setting up and enforcing user rights, encryption etc.
- Backup, restoration plans and policies to determine whether the database is out-growing the hardware that it runs
- General maintenance of the database
- Monitoring the database performance (2)
4.4
4.4.1 Any FOUR:
- Primary key
- Alternate key
- Synthetic OR Surrogate key
- Foreign key
- Composite key OR Concatenated key (4)
4.4.2 Field OR Column (1)
4.5
4.5.1 (True/False) OR (Yes/No) OR (Boolean) (1)
4.5.2 (a) In the diagram below (Marks allocation):
tblCustomer table
- CustNo(PK)
tblOrders table
- OrderNo(PK)
- CustNo(FK)
tblPrint table
- PrintNo(PK)
- OrderFormNo(FK) (5)
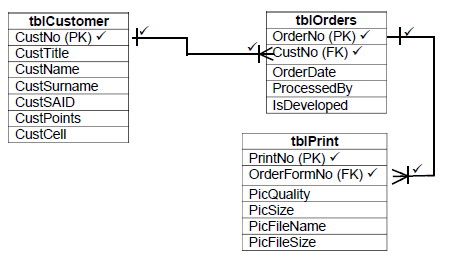
4.5.2 (b) In the diagram above (ERD mark allocation): (4)
(4)
TOTAL SECTION D: 24
SECTION E: SOLUTION DEVELOPMENT
QUESTION 5
5.1
5.1.1 Debugging refers to the process of locating and removing errors found in a program. (1)
5.1.2 Exception handling (1)
5.1.3 Try..Except block/statement (1)
5.1.4 Exception (1)
5.2
5.2.1
- Class name section
- Attributes section
- Methods section (3)
5.2.2 Any ONE:
- toString is used to format the output of a class by converting selected attributes of a class into string format.
OR - toString method is used to display the state of the class, i.e. displays the values currently held by each of the attributes. (1)
5.2.3 Unified Modelling Language (1)
5.2.4
- Getters (1)
- Setters (1)
- Helper (1)
5.3
5.3.1 11 (1)
5.3.2 25 (1)
5.3.3 Digital World (1)
5.4
5.4.1
Line No | Item | Num | Price | Cost | Total | redOut |
1 | 0 | |||||
2 | Baked beans | |||||
3 | 3 | |||||
4 | 3,29 | |||||
5 | 9,87 | |||||
6 | 9,87 | |||||
7 | Kewl Drink | |||||
8 | 5 | |||||
9 | 1,95 | |||||
10 | 9,75 | |||||
11 | 9,87 | |||||
12 | Total amount to pay: R | |||||
13 | 9 | |||||
14 ÷ 2 (7)
5.4.2 Logical error (1)
5.4.3
- Total := Total + Cost;
- redOut.Lines.Add(FloatToStr(Total)); (2)
TOTAL SECTION D: 25
SECTION F: INTEGRATED SCENARIO
QUESTION 6
6.1
6.1.1
- Fix errors or bugs in our existing programs
- Close security loopholes that hackers and malware might try to exploit
- Add new features and improvements to the existing software (3)
6.1.2 Patch is an update that can be downloaded to fix a specific bug in your software.
Service pack is a collection of fixes, updates and new features since the release of the original software or previous pack OR is a release of corrections and new features since the release of the original software. (2)
6.2
6.2.1 Computer criminal is anyone who uses ICT to commit a crime. (1)
6.2.2 Any THREE:
- Theft of physical computer equipment
- Theft of intellectual property
- Identity theft
- Financial gain/Theft of money
- Theft of data/Espionage
- Theft of resources (3)
6.2.3
- Backdoor is a hidden way to gain access to a computer, system or software.
- Piggybacking is when criminals gain access to and use someone else’s internet connection without paying for it. (2)
6.2.4 Any THREE:
- Installing and updating anti-virus software
- Using a firewall
- Keeping all your software up-to-date
- Being aware of current trends in computer crime
- Applying common sense
- Following a good password policy (3)
6.2.5
- White hat hacker (Good hacker) – helps companies to improve their security by trying to hack into their computers.
- Black hat hacker (Bad hacker) – illegally break into the computer with malicious intention. (4)
6.2.6 Distributed Denial Of Service/DDOS (1)
6.3
6.3.1 Globalisation is an increase in the rate and ease with which people, companies and governments from different countries interact. (1)
6.3.2
- Transportation
- Improvements in computers and computer networks (2)
6.3.3 Any THREE:
- Allowing families to keep in touch, even over large distances.
- Helping people to keep and maintain larger social networks.
- Increasing people’s social and romantic opportunities.
- Improving job opportunities, with citizens from other countries working in foreign countries.
- Helping people understand different points of view, with research showing how communicating with different people can increase empathy. (3)
6.4
6.4.1 Data cap is a term used to describe the data limit. (1)
6.4.2
- Bitcoin
- Bitcoin is digital money used on the Internet for various services. (2)
6.4.3 Cascading Style Sheets (1)
6.4.4 .js (1)
6.5 Knowledge-based systems (1)
6.6 Identifies and removes temporal files that are no longer needed and cleans out old files, programs and settings that cause a computer to slow down. (1)
6.7
6.7.1 Internet of Things (1)
6.7.2 IoT refers to the billions of devices around the world that are connected to the Internet through sensors or Wi-Fi. (1)
6.7.3 Any TWO:
- Increasing processing power of embedded platforms
- Development of smaller Oss and protocols
- Development of wireless communications (2)
6.8 Memes is an image, video piece or text typically/normally humorous/funny in nature that is copied and spread rapidly by the Internet users. (1)
6.9 Any TWO:
- Use disk clean-up tool
- Uninstall unused software
- Empty recycle bin
- Compress data not frequently used (2)
TOTAL SECTION F: 39
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Information Technology Paper 2 Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This paper consists of SIX sections:
SECTION A: Short questions (15)
SECTION B: System Technologies (25)
SECTION C: Communication and Network Technologies (22)
SECTION D: Data and Information Management (24)
SECTION E: Solution Development (25)
SECTION F: Integrated Scenario (39) - Read ALL the questions carefully.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- The mark allocation generally gives an indication of the number of facts/reasons required.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A: SHORT QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1 Give the correct computer term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.1.1 The grouping of attributes and behaviour of an object in one entity (1)
1.1.2 A group of related fields about an item or person that is captured in a table (1)
1.1.3 The time taken for a disk drive to locate the area on the disk where the data to read, is stored (1)
1.1.4 Initiatives to design, use and dispose of technology in an environmentally or eco-friendly way (1)
1.1.5 … is an artificial environment that is created with software (1)
1.1.6 Is a company or organisation that provides you with either a wired or wireless connection to the internet (1)
1.1.7 … is anything electronic or related to electronics that is thrown away (1)
1.1.8 Refers to applications that are hosted in the cloud and that users pay a monthly subscription to access (1)
1.1.9 A type of reasoning that works with probabilities in order to arrive at a decision (1)
1.1.10 Refers to a device that makes communication between networks over the internet possible by directing data to its correct destination (1)
1.2 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 D.
1.2.1 The process of developing an impressive software/application in a relatively short period of time is called …
- object based programming.
- rapid application development (RAD).
- extensive programming.
- object-oriented application. (1)
1.2.2 CSV means …
- Comma Separated Values.
- Comma Solution Values.
- Cine Solution Valves.
- Comma Sifting Values. (1)
1.2.3 A single processor that splits its time between different processes is called …
- multiprocessing.
- online processing.
- multitasking.
- multithreading. (1)
1.2.4 WAP means …
- Wired Access Point.
- Wireless Access Print.
- Wireless Access Point/Protocol.
- Wireless Arm Point. (1)
1.2.5 What will the value of iAnswer be when the following statement is executed?
iAnswer : = 20 DIV (10 – 20 DIV 3);
- 6
- 5
- 4
- 3 (1)
TOTAL SECTION A: 15
SECTION B: SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGIES
QUESTION 2
Since the dawn of the computing age, people have wondered if a computer would ever be capable of thought. As computer processors and software become more powerful, the question is debated more hotly. People that believe computers can think argue that, if a person had a conversation with a computer and was convinced that the computer was really a human, then the computer is intelligent.
2.1 Gone are the days where you had to e-mail yourself so that you could work at home. Gone is the hassle of copying files to and from USB flash drives.
2.1.1 Briefly explain the concept cloud application. (1)
2.1.2 List TWO well-known examples of cloud applications. (2)
2.1.3 Explain what does it mean if a cloud application has a local front end. (1)
2.1.4 Name any TWO examples of cloud office software. (2)
2.1.5 Cloud computing offers several important benefits to users. List any TWO benefits. (2)
2.1.6 Write SLA in full. (1)
2.2 There are various scientific and mass events world-wide, as well as specialised training to promote augmented reality technologies.
2.2.1 Briefly explain the purpose of augmented reality technology. (1)
2.2.2 List any TWO uses of augmented reality. (2)
2.2.3 Name TWO advantages of augmented reality. (2)
2.2.4 List any TWO hardware requirements for augmented reality. (2)
2.3 Differentiate between archiving and backup. (2)
2.4 Virtualisation is a wonderful invention in technology.
2.4.1 Briefly explain the concept virtualisation. (1)
2.4.2 List TWO uses of virtualisation. (2)
2.4.3 List TWO benefits of virtualisation. (2)
2.5 Errors and corrupted computer files are hard to detect. It can cause everything from videos not loading, applications crashing or even your operating system not opening. List any TWO utilities that can be used to identify corrupt files. (2)
TOTAL SECTION B: 25
SECTION C: COMMUNICATION AND NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES
QUESTION 3
Networks help to make life much easier, more enjoyable, makes people more productive, saves time and money, increases social opportunities and can improve knowledge.
3.1 Networks are incredibly powerful tools that most modern people and businesses depend on daily.
3.1.1 Name THREE essential equipment that you need to setup a basic network. (3)
3.1.2 Write the word WWW in full. (1)
3.2 Files can be shared on the internet simply by making them downloadable from the website. The problem with this is that all the traffic for a file shared this way has to be managed by a single webserver. The server can become slow and unresponsive if too many people are trying to access the file.
3.2.1 Briefly explain the concept BitTorrent. (1)
3.2.2 Name THREE benefits of BitTorrent. (3)
3.2.3 List THREE risks related to BitTorrent. (3)
3.3 Remote access is the buzzword used by ICT gurus/specialists nowadays.
3.3.1 Briefly explain what remote access is. (1)
3.3.2 List THREE tasks that you can perform using remote access. (3)
3.3.3 List and briefly explain TWO groups of remote access technology. (4)
3.4 On computers, firewalls prevent malicious users and viruses from sending data to and receiving data from your computer. List TWO general types of firewalls.
(2)
3.5 Briefly explain the concept network topology. (1)
TOTAL SECTION C: 22
SECTION D: DATA AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
QUESTION 4
The amount of data and information about individuals that is stored anywhere on the internet increases every day. Photos, financial records, employment history, personal relationship details and purchases are just few of the types of data and information available to others for free or a fee.
4.1 Name TWO characteristics that determine the quality of data. (2)
4.2 Databases need to be protected from several different threats, including incorrect data entry, data corruption, data loss, accidental data deletion, purposeful data deletion and unauthorised access.
4.2.1 Explain what data verification is. (1)
4.2.2 List and explain TWO main ways of data verification. (2)
4.2.3 List TWO tasks performed by an audit trail. (2)
4.3 Managing a company’s database requires a great deal of coordination. List TWO roles/responsibilities of a DBA. (2)
4.4 Keys are used to establish and identify relationships between tables.
4.4.1 List FOUR types of key fields that can be used when designing a database. (4)
4.4.2 Give another name for attribute in databases. (1)
4.5 Organised data is the key to effective database design and the normalisation process helps structure data and eliminate redundancy.
tblCustomer |
CustNo |
CustTitle |
CustName |
CustSurname |
CustSAID |
CustPoints |
CustCell |
tblOrders |
OrderNo |
CustNo |
OrderDate |
ProcessedBy |
IsDeveloped |
tblPrint |
PrintNo |
OrderFormNo |
PicQuality |
PicSize |
PicFileName |
PicFileSize |
4.5.1 In the tblOrders table, the IsDeveloped field is used to identify whether the picture is created or not. Name the data type that can be assigned to the field isDeveloped. (1)
4.5.2 Redraw the tables in your ANSWER BOOK and answer the following questions.
- Identify the primary key and foreign key in each table. Write PK for the primary key and FK for the foreign key next to the appropriate field. (5)
- Map an ERD (entity relationship diagram) by using the appropriate ERD symbol. (4)
TOTAL SECTION D: 24
SECTION E: SOLUTION DEVELOPMENT QUESTION 5
| A common problem-solving method among programmers is to break a large problem into a series of smaller problems and then to solve each of the smaller problems. |
5.1 Programming mistakes crop up quite often, we must learn how to fix them early.
5.1.1 Briefly explain the concept debugging. (1)
5.1.2 The process of writing a code to handle errors in a program is known as … (1)
5.1.3 Name the statement/clause used to handle errors in a program. (1)
5.1.4 What is another name of an error in programming except the word bug? (1)
5.2 UML is a powerful and complex modelling tool used to plan and design classes and objects. The class diagram is divided into THREE sections.
5.2.1 List the name of each section. (3)
5.2.2 Explain the purpose of ToString in classes and objects. (1)
5.2.3 Write UML in full. (1)
5.2.4 Give another name for the following keywords/names in classes and objects.
- Accessor (1)
- Mutator (1)
- Auxiliary (1)
5.3 Write down the result of each of the following functions:
sString = ‘Living in a Digital World’;
5.3.1 iPos := Pos(‘a’, sString); (1)
5.3.2 iL := Length(sString); (1)
5.3.3 sWord := Copy(sString, 13,13); (1)
5.4 Study the following code which was written to calculate the Total Amount Due after doing some grocery shopping.
Var
Num : Integer;
Price, Cost, Total : real;
Item : string begin
- Total := 0;
- Item := ‘Baked beans’;
- Num := 3;
- Price := 3.29;
- Cost := Num * Price;
- Total := Total + Cost;
- Item := ‘Kewl Drink’;
- Num := 5;
- Price := 1.95;
- Cost := Num * Price;
- Total := Cost;
- redOut.Lines.Add(‘Total amount to pay: R’);
- redOut.Lines.Add(IntToStr(Total));
end;
5.4.1 Copy the trace table provided below into your ANSWER BOOK and complete to determine output.
Line No | Item | Num | Price | Cost | Total | redOut |
1 | ||||||
2 | ||||||
3 | ||||||
(14 ÷ 2) (7)
5.4.2 The program has a programming error. Name the type of an error you have located/identified. (1)
5.4.3 Correct the TWO program segments that have errors. (2)
TOTAL SECTION E: 25
SECTION F: INTEGRATED SCENARIO
QUESTION 6
6.1 It is not only important to keep informed about the developments and trends in IT, but also keep software updated.
6.1.1 List THREE reasons of updating the software. (3)
6.1.2 Distinguish between a patch and a service pack. (2)
6.2 Computer criminals are ordinary people spending long hours doing tiresome work – often for little reward. They are very scary. Some computer criminals work in cyberspace, so for the average person, they are very hard to identify and seem like an invisible force of evil.
6.2.1 Explain the concept computer criminal. (1)
6.2.2 List any THREE common computer-related types of theft. (3)
6.2.3 Differentiate between backdoor and piggybacking. (2)
6.2.4 List any THREE measures/safeguards against computer crimes, threats and criminals. (3)
6.2.5 Name and briefly explain TWO types of hackers. (4)
6.2.6 Name the attack that makes a website unavailable by using thousands or even millions of computers to request data from the site at the same time. (1)
6.3 The speed and accuracy of computers, their ability to analyse vast quantities of data quickly and to transform, present and communicate data in a variety of formats locally and globally are their main strengths.
6.3.1 Briefly explain the concept globalisation. (1)
6.3.2 List TWO technologies which have made globalisation possible. (2)
6.3.3 List any THREE advantages of global communication. (3)
6.4 Online applications are evaluated on the way they look and feel, so website creators spend a lot of time formatting their output.
6.4.1 Explain what a data cap is. (1)
6.4.2 Name and explain the purpose of the icon below. (2)
(2)
6.4.3 Write CSS in full. (1)
6.4.4 Java script programming instructions can either be stored as separate text files with a filename extension …. (1)
6.5 Expert systems are no longer called expert systems but are known as … (1)
6.6 Explain the function of disk clean-up. (1)
6.7 To keep pace with the mass adoption of smart home devices and drive business growth without service interruptions, you need the self-improving IoT technology already used by over 500 million to secure their home networks, clouds and endpoints.
6.7.1 Write IoT in full. (1)
6.7.2 Briefly explain the concept IoT. (1)
6.7.3 List TWO technological trends that has made/enabled the IoT possible. (2)
6.8 Social networks grow more powerful with the increase in interactions among people on social platforms. Briefly explain the concept memes. (1)
6.9 Computers need sufficient unused space on the hard drive in order to function smoothly. List TWO things that you need to do to free up space on a drive. (2)
TOTAL SECTION F: 39
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Information Technology Paper 1 Memorandum - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
| NAME OF LEARNER: | ||||
| TOTAL QUESTION 1: | TOTAL QUESTION 2: | TOTAL QUESTION 3: | TOTAL QUESTION 4: | TOTAL |
| /40 | /40 | /38 | /32 | /150 |
MEMORANDUM
| QUESTION 1: GENERAL PROGRAMMING SKILLS | MAX. MARKS | MARKS ACHIEVED | |
| 1.1 | Button [1.1]
| 3 | |
| 1.2 | Button [1.2 Process]
Else
Alternative solution:
Get inputs from spinedits | 11 | |
| 1.3 | Button [1.3 Find rainfall type] Alternative solution:
Get input from edtRain
| 13 | |
| 1.4 | Button [1.4 Display Rainfall]
Calculate total quantity using LstQuantity items convertedto integer | 13 | |
| TOTAL QUESTION 1 | 40 | ||
| QUESTION 2: DATABASE PROGRAMMING | MAX. MARKS | MARKS ACHIEVED | |
| 2.1.1 | Button: [2.1.1] | 3 | |
| SQL: 'select * from Status order by Statusname DESC' | |||
Concepts:
| |||
| 2.1.2 | Button: [2.1.2] | 3 | |
| SQL: 'Select Birdname from Bird where Sightings < 200' | |||
Concepts:
| |||
| 2.1.3 | Button: [2.1.3] | 4 | |
| SQL: 'Select Birdname, Lastsighted from Bird where Birdname like ' + quotedstr('%' + sline + '%') | |||
Concepts:
| |||
| 2.1.4 | Button: [2.1.4] | 4 | |
| SQL: 'Delete from Bird where (StatusID = 6) OR (StatusID = 5)' | |||
Concepts:
| |||
| 2.1.5 | Button: [2.1.5] | 3 | |
| SQL: 'select Statusname, Birdname from Bird, Status where Bird.StatusID = Status.StatusID' | |||
Concepts:
| |||
| 2.1.6 | Button: [2.1.6] | 8 | |
| 'Select StatusID,format(avg(Sightings),"fixed",1) as AverageSightings from Bird where year(Lastsighted) = 2007 group by StatusID' | |||
| |||
| 2.1 Subtotal: SQL | 25 | ||
| 2.2.1 | Button: [2.2.1] tblbird.First; while not tblbird.eof do if pos('EAGLE',uppercase(tblbird['Birdname'])) <> 0 then reddisplay.Lines.Add(tblbird['Birdname']); tblbird.Next; | 6 | |
| 2.2.2 | Button: [2.2.2] icount := 0; tblbird.First; while not tblbird.eof do begin if tblbird['StatusID'] = 3 then begin tblbird.Edit; tblbird['StatusID'] := 2; tblbird.Post; inc(icount) end; tblbird.Next; end;reddisplay.Lines.Add('Number of changes made = ' + inttostr(icount)); | 9 | |
| 2.2 Subtotal: Code constructs | 15 | ||
| TOTAL QUESTION 2 | 40 | ||
| QUESTION 3: OBJECT-ORIENTATED PROGRAMMING | MAX. MARKS | MARKS ACHIEVED | |
| 3.1.1 | Constructor Create:
| 4 | |
| 3.1.2 | function getsightings: integer;
| 2 | |
| 3.1.3 | procedure increasequantity(iqty: integer);
| 4 | |
| 3.1.4 | function sightinggap: string;
| 7 | |
| 3.1.5 | function tostring: string;
| 5 | |
| 3.1 Subtotal: Object class | 22 | ||
| 3.2.1 | Button [Q3.2.2]
| 11 | |
| 3.2.2 | Button [Q3.2.1]
| 5 | |
| 3.2 Subtotal: Form class | 16 | ||
| TOTAL QUESTION 3 | 38 | ||
| QUESTION 4: PROBLEM SOLVING | MAX. MARKS | MARKS ACHIEVED | |
| 4.1 |
| 19 | |
| 4.2 |
| 13 | |
| TOTAL QUESTION 4 | 32 | ||
SAMPLE SOLUTIONS