Adele
Religion Studies Paper 2 Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- This question paper consists of FOUR questions.
- Answer any THREE of the FOUR questions.
- Start each question on a NEW page.
- Read ALL the questions carefully before answering them.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- The length of your answers must correspond with the marks allocated for each question.
- Write legibly and present your work neatly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
Read the extracts below and answer the questions that follow.
All religions have a set of teachings about the nature of humanity, the world, the divine, the creation and parts of our lives. [Source: Shuters Top Class Religion Studies Grade 12] |
1.1 In the context of any ONE religion, answer the following questions with reference to the central teachings under the following headings:
1.1.1 The nature of humanity, with reference to community and individual (10)
1.1.2 The nature of life after death (10)
1.1.3 The nature of divinity (10)
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
Within most religions, interpretation of beliefs may differ from one school of thought to another. A school of thought is a strand or branch. [Source: Shuters Top Class Religion Studies Grade 12] |
1.2 With reference to ONE religion, answer the following questions.
1.2.1 State the difference in teachings (10)
1.2.2 State the difference in governance (10)
[50]
QUESTION 2
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
Religions for Peace has joined a group of organisations in an initiative that will provide help to millions of African children orphaned by gender-based violence (GBV). The Hope for African Children initiative confronts challenges such as the risk of malnutrition, illnesses, abuse, and sexual exploitation faced by orphans. [Source: Shuters Top Class Religion Studies Grade 12] |
2.1
2.1.1 Name THREE causes of gender-based violence. (6)
2.1.2 Briefly discuss the impact of gender-based violence in society. (10)
2.1.3 With reference to ONE religion you have studied, discuss its teachings to solve this problem. (10)
2.2 Discuss the role of the following organisations in solving religious conflicts:
2.2.1 World Council of Churches (8)
2.2.2 Interfaith Action for Peace in Africa (IFAPA) (6)
2.3 Name and explain FIVE hermeneutical principles. (10)
[50]
QUESTION 3
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
Secularism in personal life is similar to secularism in the state. It involves a good commitment to an ethic based on reason about human nature without reference to god(s). [Source: Shuters Top Class Religion Studies Grade 12, page 138] |
3.1
3.1.1 Discus any TWO secular worldviews. (10 x 2) (20)
3.1.2 Explain the concept secularism. (10)
3.2 In the context of religion, discuss and evaluate the role of the following:
3.2.1 Oral tradition (10)
3.2.2 Inspiration (10)
[50]
QUESTION 4
4.1 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
Whether personal or political, Western secularism has to do with adopting a foundation for life and law which excludes conventional religion. In the West, it tends to go with democratic forms of government, freedom of religion within the bounds of secular law of the land, support for human rights and no discrimination on the grounds of religious convictions. [Source: Shuters Top Class Religion Studies Grade 12, page 138] |
4.1.1 Briefly explain Darwin’s theory of evolution. (14)
4.1.2 Analyse and explain the response of the TWO religions’ version of the theory of evolution:
- Christianity (12)
- Hinduism (12)
4.1.3 Discuss the Big Bang Theory. (12)
[50]
TOTAL: 150
Religion Studies Paper 1 Memorandum - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 B – rituals (1)
1.1.2 B – the Path of the Universe (1)
1.1.3 C – Sufism (1)
1.1.4 D – Lao-Tzu (1)
1.1.5 D – Shaivism (1)
1.1.6 A – The Eucharist (1)
1.1.7 C – Secularism (1)
1.1.8 D – from Mahayana Buddhism (1)
1.1.9 B – Mass (1)
1.1.10 C – Belief in ancestors (1)
1.2
1.2.1 E – the central teachings are contained in the Tripitaka (1)
1.2.2 G – a famous spiritual text in Hinduism (1)
1.2.3 B – Zikr is one of the important rituals whereby the believer encounters God through meditation (1)
1.2.4 A – the belief that every action has an effect on the state of the soul and the chance of gaining moksha (1)
1.2.5 C – attained through a lifetime of wisdom and practice; not through inherent belief or faith (1)
1.2.6 D – provides some details of Jesus’ life and teachings (1)
1.3
1.3.1 Ahimsa – In the Hindu, Buddhist and Jainistic traditions it means respect for all living things and avoidance of violence towards others (2)
1.3.2 Abu Bakr – was the father-in-law of Prophet Muhammad. He was the successor to Muhammad / the first caliph (2)
1.3.3 Nirvana – a state of perfect happiness and peace in Buddhism (2)
1.3.4 Lutheran – is a division of Christianity (2)
1.3.5 Jesus – the founder of Christianity (2)
1.4
1.4.1 Tanach (2)
1.4.2 Pali Canon (2)
1.4.3 Worship (2)
1.4.4 Arabic (2)
1.4.5 Upanishads (2)
1.5
1.5.1 TRUE (2)
1.5.2 FALSE. The divine name of God is YAHWEH/Elohim/Adonai/Shem. (2)
1.5.3 FALSE. It was written in Arabic. (2)
1.5.4 FALSE. The worlds processed originate from two forces; yang and yin. (2)
1.5.5 FALSE. The longest epic of Hinduism is Mahabharata. (2)
1.6
1.6.1 The importance of meditation in Buddhism
- Meditation establishes control over the mind.
- This is necessary to reach a level of ‘non-attachment’.
- Buddhists engage in the meditation process in order to overcome evil.
- Knowledge according to Buddhism can be attained through meditation.(2)
1.6.2 Baha’u’llah
- The founder of the Baha’i’ faith.
- He was a Persian nobleman and a prophet. (2)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1 IDENTITY
- Identity means individuality.
- It means the religion has individuality or a certain personality that distinguishes it from other religions.
- It means the affirmation of dignity and value of a religion.
- Acknowledging who I am, we are and who others are.
- It means an exclusive religious identity in which one identifies strongly with the beliefs and doctrines of the religion and sees these as defining one’s life.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited (4)
2.1.2 “South Africa is called the Rainbow Nation.” Explain the quotation in the context of religion.
- South Africa is a country with many different religions.
- Every religion’s clothing, rituals and traditions differ.
- In South Africa all the religions are equal.
- South Africans call themselves the rainbow nation, because here are Whites, Blacks, Coloureds and Indians with different skin colours, but they live and work together as one united nation, just like the colours of a rainbow.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited (4)
2.2 UNIQUE FEATURES OF ONE RELIGION African Traditional Religion
- ATR does not have a sacred text.
- Teachings and rituals have been passed down from one generation to another through the spoken word.
- There is no special day of worship.
- Instead, rituals themselves are recorded as holy.
- Communication with the ancestors through the ritual of animal sacrifices is a unique feature of African Traditional Religion.
- Ancestors have the power to bring about illness or misfortune, good luck and health.
- When people die, it is believed they join the spirit world.
- The sharing of a communal meaI so that the living can communicate with the ancestors, is very important.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited.
Judaism
- Jews believe that they have a covenant with God.
- God is perceived as a father-like figure who is both their Creator and Protector.
- God is so holy that it is forbidden to even call His name.
- They believe that God revealed Himself through His Law.
- They lay more emphasis on the correct way of life, rather than faith or belief.
Islam
- The Muslims believe that there is one God, called Allah.
- They believe that Allah sent various prophets, but the final messenger is Prophet Muhammad.
- Their primary source are the Qur’an and the Hadith.
- They believe in the final judgement when all mankind will be judged.
- They believe that Qur’an was revealed in the Arabic language and it must be read in Arabic.
Christianity
- Christians believe in the Lord Jesus Christ as the Son of the living God.
- They believe that God sent his son to die for their sins.
- They believe that God took the human form of Jesus Christ.
- They believe that Jesus was crucified and rose from the dead.
- They believe in the Trinity – the Father, the Son and the Holy Spirit.
- They believe that forgiveness is in the name of Jesus.
- They believe that Jesus Christ is the only way to God.
- They celebrate the Holy Communion (Eucharist) as remembrance of the death of Jesus Christ.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (6)
2.3 UNDERSTANDING OF AFRICAN TRADITIONAL RELIGION TOWARDS ANCESTORS AND THEIR ROLES
- When the first generation died, their spirits joined the spirit world where the Creator lives.
- In other words, the death of the first generation was the beginning of the ancestors.
- The ancestors are regarded as messengers of the creator.
- They are the supervisors of the physical world.
- The ancestors look after the welfare of the living.
- They reveal themselves through dreams and sometimes through visions to communicate with the living.
- To communicate with God, the living uses the ancestors – they are intermediaries.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited.(6)
2.4 WRITE DOWN THE COMMON FEATURES THAT EXIST BETWEEN HINDUISM AND BUDDHISM
- They believe in reincarnation.
- They both have sacred texts.
- They both perform rituals.
- They both observe special holy days.
- They both originated in India.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited.(6)
2.5
2.5.1 DEFINE THE TERM CORRUPTION
- Corruption is defined as dishonest or fraudulent conduct by those in authority, typically involving bribery.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (2)
2.5.2 ACCORDING TO THE PRESIDENT, WHO WAS THE MOST AT RISK?
- The hungry
- The needy
- Social grant recipients
- Employees who lost their income because of the pandemic.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (2)
2.6
2.6.1 WHAT DO YOU UNDERSTAND BY MORALITY?
- Morality is the ability to differentiate between right and wrong.
- Morality means conformity to rules of right conduct.
- It can be seen as separate from religion, by secularists.
- Morality is based on ones’ social values.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (4)
2.6.2 TWO EXAMPLES TO DEMONSTRATE THAT MORALITY COMES FROM RELIGION
- All religions distinguish between right and wrong.
- Christians and Jews, to a great extent, live by the Ten Commandments for example; You must not commit adultery. (In Judaism and the Christian religion.)
- Muslims follow the Qu’ran as the path that they walk.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (4)
2.7 EXPLAIN THE CONCEPT TEACHING
- Teaching means to give information or to impart the knowledge in order to reinforce belief in a specific religion.
- In religion specifically, to teach means to give systematic information about a subject or aspects of a religion.
- Teaching is a normative explanation of something.
- A teaching plays different roles in different religions.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (4)
2.8 DEFINE TERM BELIEF IN THE CONTEXT OF RELIGION
- Belief is sometimes referred to as a religion, e.g. the Islamic faith.
- Belief describes the acceptance of a statement or religious teaching; these are held to be the truth by the adherents/followers of the faiths.
- Belief can also be described as trust and confidence.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (4)
2.9 DEFINE THE TERM GOLDEN RULE
- Universally held ethical prescription.
- The most important teachings of a religion.
- Found in nearly all religious and other ethical systems.
- Example: Do unto others as you would like others to do to you.
NOTE: Other relevant examples must be credited.(4)
[50]
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1 EXPLAIN WHAT YOU UNDERSTAND WITH HUMAN TRAFFICKING
- Human trafficking involves the use of force, fraud, or coercion to obtain some type of labour or commercial sex act.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (2)
3.1.2 ANY TWO HUMAN RIGHTS OF THE 40-YEAR-OLD THAT WERE VIOLATED
- The right to freedom of movement.
- The right to safety.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (4)
3.1.3 FROM THE EXTRACT GIVE EVIDENCE ON HOW HUMAN TRAFFICKERS FIND THEIR VICTIMS
- The promise of a better life. The woman was homeless when she was taken to Johannesburg.
- Lies about the situation the victims are getting into.
- Kidnapping and illegal detention.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (4)
3.1.4 WHAT DO YOU THINK SHOULD BE THE ROLE OF FAITH LEADERS IN ENDING HUMAN TRAFFICKING?
- Faith leaders must raise awareness of the problem and speak up about it and speak out against it.
- Faith leaders must report instances of human trafficking to the proper authorities and not participate in it.
- Faith leaders must work with other religions and NGO’s to establish safe havens for people who came out of human trafficking
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited.(4)
3.2
3.2.1 CHRISTIANITY’S TEACHINGS THAT PROMOTE HUMAN RIGHTS
- You must love your neighbour as yourself.
- This teaching encourages people to treat everybody equally.
- You shall not commit murder.
- This refers to the sanctity of human life.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (4)
3.2.2 ISLAM’S TEACHINGS THAT PROMOTE HUMAN RIGHTS
- There is no compulsion to convert to Islam.
- That is, proclaiming one’s faith should be voluntary and sincere.
- This allows for freedom of religion.
- The institution of zakat (charity) ensures that basic needs of food, shelter and clothing are met.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (4)
3.2.3 AFRICAN TRADITIONAL RELIGIONS TEACHINGS THAT PROMOTE HUMAN RIGHTS
- The principle of Ubuntu encourages help for your community.
- The ilima practice is one where the community offers assistance to all members who have need.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (4)
3.3. EXPLAIN WHAT IS MEANT WITH THE QUOTATION: “HUMAN TRAFFICKING IS A BOOMING BUSINESS”.
- Human trafficking is a fast growing or expanding business.
- Around the world, human traffickers are making billions through their illegal practices.
- They kidnap especially woman, girls and boys in order to use them as sex slaves in their prostitution rings and brothels.
- These kidnapped victims have even been used in the making of pornographic movies.
- Sometimes men get trafficked to work as cheap labour in some countries.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (4)
3.4
3.4.1 EXPLAIN COMPARABILITY
- It refers to the comparison that can be drawn between faith groups or religious institutions (e.g. denominations).
- This does not mean that things are the same.
- Means that two or more things are able to be compared.
- The act of comparing more than one thing.
- Means that two or more things are likely to show similarities and differences.
- Comparisons can be explicit or implicit.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (4)
3.4.2 EXPLAIN SIMILARITY
- Being alike.
- Having resemblance with a specific religion.
- Of the same kind, with the same nature, with the same form.
- Two or more things can be similar.
- Means characteristics that religions or people have in common.
- One must be specific about how things are similar, e.g. the similarity between two religions: that Buddhism and Hinduism have in common the belief in reincarnation.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (4)
3.5 DESCRIBE THE CONCEPT MYTH IN THE CONTEXT OF RELIGION
- The word ‘myth’ comes from the Greek word ‘mythos’ which means ‘word’ or ‘fable’.
- It refers to those stories that reveal deep truths about creation, life and death.
- Myths are made-up stories, but religion is the truth.
- A myth is a story created to explain the invisible through the visible, and to give life to our faith through symbols.
- For example, in African Traditional Religion, humans originated from reeds (‘umhlanga’).
- Myths are not factual but are used to teach values and lessons.
- Myths form the basis of teachings and even dogma in some religions.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited.(4)
3.6 EXPLAIN THE ROLE THAT PARABLES PLAY IN RELIGIOUS TEACHINGS
- The word ‘parable’ refers to a story that is told to illustrate a religious principle or answer a religious question.
- A parable is a short story that contains a definite moral.
- An example is the parable of the ‘sower and the seed’ in Christianity.
- A parable is a story that is presented in an art form.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited.(4)
3.7 DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DOCTRINE AND DOGMA
- Doctrine is a set of beliefs or principles.
- Doctrines are often contested.
- There is a sense of argument and negotiation, as doctrines are constructed in relation with philosophical worldviews.
- A dogma has to do with the claim to absolute authority of certain teachings.
- A dogma is a belief that believers must accept without any doubt.
- A dogma is more formal, fixed and authoritative and therefore not contested.
- Dogmas are binding on members if they want to claim membership of a religion.
- Dogma is an arrogant statement or opinion.
- This means that in order to be regarded as a member of a religion, a person needs to accept the dogmas of the religion.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited.(4)
[50]
QUESTION 4
4.1
4.1.1 GIVE ONE WORD WHICH TELLS DR MUSTAFA WAS EXCITED ABOUT RELIGIOUS INVOLVEMENT
- Passionate (2)
4.1.2 DO YOU AGREE THAT CLOSER TIES AMONG RELIGIONS ARE NECESSARY FOR SECURING A MORE JUST AND PEACEFUL WORLD? GIVE REASONS FOR YOUR ANSWER.
YES
- This will promote freedom of choice.
- It will encourage tolerance and respect among religions.
- Religious organisations will have an opportunity to stand together.
- Religious organisations will be able to fight together against the challenges that exist in society.
NO
- Religious differences are often the contributing factors for religious conflict.
- Some religions might take advantage due to resources to dictate, influence and overpower other religions.
- The fear of losing membership due to conforming to the teaching of other religions.
- Adapting to the teachings of other religions can lead to conflict.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (8)
4.1.3 WHAT WAS THE IMPACT OF RABBI SILVERSTEIN AND MOHAMMAD YAHYA’S MUSICAL GROUP?
- They built community bonds through their collaboration.
- They built trust within their societies through dialogue and music.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (4)
4.1.4 REFER TO THE CHRISTIAN VIEW: “RELIGION IS STILL THE FOUNDATIONAL FACT IN THE LIVES OF MOST PEOPLE.” WHAT DOES THIS QUOTATION MEAN?
- All religions are a foundation for morals and beliefs.
- It helps shape us and determine what we see as right and wrong.
- Religion is what not only gives meaning to peoples’ lives but is the founding principle of life itself.
- Religion becomes part of peoples’ lives from birth through to death.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (4)
4.2
4.2.1 DEFINE THE CONCEPT RELIGIOUS TOLERANCE
- Religious tolerance means understanding and respecting religious beliefs / beliefs and practices other than your own.
- Religious tolerance is where people allow other people to think or practice other religions and beliefs.
- Religious tolerance is mainly dependent on interaction between religious groups and individuals in a community.
- It is based on respect, tolerance and understanding for religions other than your own.
- The willingness to tolerate the opinions or behaviours that one dislikes or disagrees with.
- To accept an idea, or action differing from or conflicting with one’s own.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited.(2)
4.2.2 DO YOU THINK RELIGIOUS FREEDOM WAS PROTECTED IN SA BEFORE 1994? GIVE REASONS FOR YOUR ANSWER.
NO
- Religious freedom was not protected during the apartheid era
- During the apartheid era only Christianity was recognised as a state religion.
- Christianity was the dominant religion.
- Christian-National Education was the state’s education policy.
- Biblical Studies and Biblical Teaching were offered in schools.
- State funds were used to pay the salaries of some Christian ministers only.
- Other religions received little recognition.
- There was no religious freedom in the law books.
- In a democratic South Africa all religions are given equal status.
- Religion Studies is a NSC subject that studies different religions.
- It replaced Biblical Studies and other subjects that focused only on one religion.
- Freedom of religion is enshrined in our constitution.
- In all state and official meetings, prayers are either universal in nature, or multi-faith.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (8)
4.2.3 ONE INTERRELIGIOUS ORGANISATION THAT WORKS FOR PEACE IN CONFLICT AREAS IN AFRICA. DESCRIBE THE WORK DONE AND GIVE REASONS FOR ITS SUCCESSES OR FAILURES
- THE PROGRAMME FOR CHRISTIAN-MUSLIM RELATIONS IN AFRICA (PROCMURA)
- It is the oldest and pioneer interfaith organisation in Africa.
- The focus is on Christian relations with Muslims.
- To witness the gospel within an interfaith environment.
- To promote constructive engagement within Muslims for peace.
- To hold interfaith consultations.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited.
- THE AFRICAN COUNCIL OF RELIGIOUS LEADERS (ACRL)
- Also known as Religions for Peace.
- To ensure respect for all religious differences.
- Preserving the identity of each religious community.
- Ensuring that religions for peace participate in honouring different ways religious communities are organised.
- Upholding the principles of representation.
- To support locally led multi-religious structures.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited.
- INTERFAITH ACTION FOR PEACE IN AFRICA
- This is a Pan-African non-profit organisation.
- It was founded in 2002.
- Dedicated to working together for peace, democracy and unity on the continent.
- This organisation was established to bring peace and cooperation between religious communities across Africa.
- To ensure a decent / humane life for all.
- This organisation was also established to promote co-operation among religions.
- It also includes the authority of meetings of religious leaders, who make the ‘IFAPA’ decisions.
- It was also initiated to combine the efforts of different religions to work for peace in the African continent.
- To send interfaith delegations to conflict areas.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (8)
4.2.4 WHAT DOES THE CURRENT SA CONSTITUTION SAY ABOUT RELIGIOUS FREEDOM?
- Religious freedom refers to the state whereby different religions are at liberty to practice their religions.
- The Charter of Human Rights in the South African constitution mentions religious freedom included in the rights.
- Everyone has a right to freedom of conscience, religion, thought, belief and opinion.
- However, the religious rights of others must be respected at all times.
- Religious observation can be conducted at state-aided institutions under three conditions:
- The observations follow the rules set by the appropriate public authority.
- Religious observances may be conducted at any state institution on an equal basis.
- Attendance must be free and voluntary.
- Persons belonging to a religious community have a right to enjoy practicing their religion.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (8)
4.3 BRIEFLY DISCUSS THE DISADVANTAGES OF A SOCIETY HAVING NO RELIGIOUS FREEDOM OR TOLERANCE
- No religious harmony.
- Religious groups would not work together to fight common social ills.
- Social cohesion will be difficult if religious tolerance is not encouraged.
- Some religious practices would be suppressed as they would be construed as not acceptable by other religious groups.
- There would be religious discriminations and prejudice if there is no religious tolerance.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (6)
[50]
QUESTION 5
5.1
5.1.1 BRIEFLY EXPLAIN WHAT THE HEADING OF THE ARTICLE MEANS
- The news of these pastors’ bad actions has shaken South Africa’s faith community to the core.
- The news of what these so-called men of God did shocked the nation.
- South Africans were left astounded by the revelation of the allegations.
- The nation was dismayed by what these men were accused of.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited.(2)
5.1.2 WHY DO YOU THINK, HAS MEDIA COVERAGE INCREASED?
- It is the peripheral and negative issues that gets religions the most coverage.
- Complaints about the unethical behaviour of religious leaders from community members have increased.
- Dangerous/Suspicious church activities have come to the fore greatly.
- Controversial issues get more airtime (or space) than spiritual matters.
- If religious leaders are accused of any wrongdoing, they make headline news.
- On the contrary, if religious leaders go about their duties, clothing and feeding the poor, it is not seen as newsworthy.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (4)
5.1.3 NAME TWO EXAMPLES OF CRIMES THESE PASTORS/ PROPHETS ARE INVOLVED IN
- Sexual abuse
- Human trafficking
- Fraud(4)
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited.
5.2 HOW CAN WE WORK TOGETHER TO ENSURE THAT WE GET RID OF BOGUS PASTORS/ PROPHETS?
- The state should regulate religion.
- The state should regulate who can open a church.
- Our justice system needs to implement proper punishment.
- There is need for a call from especially the community against abusive churches and leaders.
- Arrange marches and rallies against these false pastors.
- Expose all fake and dubious pastors.
NOTE: Any relevant answers must be credited. (6)
5.3 WHAT IS QUACKERY?
- Dishonest practices and claims to have special knowledge and skills in some field.
NOTE: Any relevant answers must be credited. (2)
5.4 ANSWER THE QUESTIONS ABOUT THE CONFLICT ARTICLE
5.4.1 IS THE CONFLICT INTER OR INTRA-RELIGIOUS? GIVE REASONS FOR YOUR ANSWER
- Inter-religious.
- The conflict is between groups from different religions.
- The conflict is between Muslims and Christians.
NOTE: Any relevant answers must be credited. (4)
5.4.2 WHAT ROLE CAN RELIGIOUS ORGANISATIONS PLAY TO PREVENT SUCH CONFLICT?
- They can have multi-faith gatherings to create religious tolerance.
- All religions should work with the government so that all religions are treated equally by the state.
- All religions should advocate freedom in religion.
- People can then choose religions or worldviews based on free will.
- Both Christians and Muslim leaders should support peace initiatives.
- They must show that they support the peacekeepers of the African Union.
- Religious organisations should show support for peace initiatives.
- They should jointly participate in humanitarian efforts, so as to develop a working relationship. (8)
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited.
5.4.3 THE CONFLICT IS “COMPLICATED AND MULTI-LAYERED”. WHAT DOES THIS QUOTATION MEAN?
- It means that the conflict is not easy to understand.
- It is multi-layered as there are many issues involved.
- These issues include religion, ethnicity, land usage, etc.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (4)
5.4.4 FROM THE ARTICLE GIVE THE CONSEQUENCES OF THE CONFLICT BETWEEN THE GROUPS.
- Hundreds have been killed.
- Many were injured and taken to hospital.
- A gasoline station was destroyed.
- Trust among the people from different religions was eroded.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited. (4)
5.5 UNTIL RECENTLY IT WAS ARGUED THAT THE CONFLICT IN SUDAN IS OF A RELIGIOUS NATURE. DO YOU AGREE? GIVE REASONS FOR YOUR ANSWER.
I AGREE
- In the South of Sudan, there is a considerable Christian presence, as well as ATR adherents, while the North is completely Muslim.
- There is gross neglect of the mainly non-Muslim South by the Khartoum government.
- This is evidenced by the complete lack of infrastructure.
- The economy of the South has been destroyed because of negligence by Khartoum.
- This resulted in widespread poverty in the South.
- Attacks by militia (janjeweed) on non-Arabic villages in the South are common.
- The Khartoum government has done nothing to stop these raids.
- While there is tribal conflict, it is also along religious lines, as entire tribes follow one single religion.
- The 1983 imposition of Sharia laws was an attempt by the North to completely dominate the South.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited.
I DO NOT AGREE
- The Darfur conflict in Southern Sudan started more than a century ago.
- The main divisions were ethical/tribal and cultural.
- Religion is not a radical source of division.
- Most people of Darfur are Sunni Muslims, as is the government of Khartoum.
- In 1983 there was a civil war when the Muslim government tried to impose Islamic law in the south.
- In 2005 South Africa brokered a peace between the North and South.
- However, conflict continued.
- A UN backed referendum in 2011 decided on partition of the South.
- The harmonious relationship between Khartoum and Juba was short-lived.
- The conflict continues, with the main issue being the Heglig oil fields.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited.(8)
5.6 WHAT IS YOUR VIEW ON THE RESPONSES OF IMAM KASAM AND THE PREACHER FROM OMEGA FIRE MINISTRIES?
- Imam Kasam’s unfounded accusations could have led to more violence between Muslims and Christians.
- The preacher was wrong to incite his followers to kill the Fulani herdsmen.
- What he called for was not self-defence, but murder.
- Hatred was stoked on both sides.
- Trust and tolerance were eroded.
NOTE: Any relevant answer must be credited.(4)
[50]
TOTAL SECTION B: 100
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Religion Studies Paper 1 Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- The question paper consists of SECTION A and SECTION B.
- SECTION A: COMPULSORY
SECTION B: Answer ANY TWO questions in this section. - Read ALL the questions carefully.
- Start EACH answer on a NEW page.
- The length of your answers must be in accordance with the marks allocated to each question.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 To establish communication with their ancestors, worshippers of the African Traditional Religion must engage in …
- stories.
- rituals.
- miracles.
- ubuntu. (1)
1.1.2 The Tao is ….
- the universe.
- the path of the universe.
- oscillation.
- All the above-mentioned. (1)
1.1.3 The mystical dimension of Islam is often called …
- a trance.
- Shi’ism.
- Sufism.
- Zakaat/Zakat. (1)
1.1.4 The founder of Taoism was …
- Tao-te Ching.
- Buddha.
- Chuang-Tzu.
- Lao-tzu. (1)
1.1.5 The oldest of all the Hindu schools is …
- Shaktism.
- Vaishnavism.
- Smartas.
- Shaivism. (1)
1.1.6 A ritual based on Jesus’ last meal is …
- the Eucharist.
- Christmas.
- Easter.
- the Passover. (1)
1.1.7 … is a worldview based solely on human reasoning.
- Socialism
- Natural Sciences
- Secularism
- Enlightenment (1)
1.1.8 Zen Buddhism originated ….
- in Iran.
- from Therevada Buddhism.
- from Hinduism.
- from Mahayana Buddhism. (1)
1.1.9 Catholics attend church services called the …
- A hajj.
- Mass.
- Holy Communion.
- Mitzvot. (1)
1.1.10 A teaching not common to Judaism:
- Giving charity
- Belief in the afterlife
- Belief in the ancestors
- The Sabbath (1)
1.2 Choose an item from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–H) next to the question numbers (1.12.1–1.2.6) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.7 I. Do NOT use any letter more than ONCE.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
1.2.1 | Hinduism | A | the belief that every action has an effect on the state of the soul and the chance of gaining moksha |
1.2.2 | Bhagavad Gita | B | Zikr is one of the important rituals whereby the believer encounters God through meditation |
1.2.3 | Sufism | C | attained through a lifetime of wisdom and practice; not through inherent belief or faith |
1.2.4 | Law of Karma | D | provides some details of Jesus’ life and teachings |
1.2.5 | Enlightenment | E | the central teachings are contained in the Tripitaka |
1.2.6 | Islam | F | a number of gods in a particular religion |
G | a famous spiritual text in Hinduism | ||
H | the Ten Commandments | ||
(6 x 1) (6)
1.3 Choose the word in EACH list below that does NOT match the rest. Write down the word next to the question numbers (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK and give a reason why it does NOT fit.
EXAMPLE: Red; Yellow; Circle; Blue ANSWER: Circle
REASON: The other three are colours.
1.3.1 Ancestors; Clan; Ilimo; Ahimsa (2)
1.3.2 Baha’u’llah; Haifa; Kitáb-i-Aqdas; Abu Bakr (2)
1.3.3 Brahma; Vishnu; Nirvana; Shiva (2)
1.3.4 Talmud; Pentateuch; Lutheran; Torah (2)
1.3.5 Matthew; Mark; Jesus; John (2)
1.4 Complete the following sentences by filling in the missing word(s). Write only the word next to the question numbers (1.4.1–1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK. Choose your answer from the supplied list.
| Worship; Arabic; Pali Canon; Tanach; Upanishads; Septuagint |
1.4.1 In Judaism the primary scriptures are collectively known as the … (2)
1.4.2 The … is a sacred text of Buddhism. (2)
1.4.3 African Traditional Religion does not have a special day of … (2)
1.4.4 The Qur’an was written in the … language. (2)
1.4.5 The … are sacred texts of Hinduism. (2)
1.5 Indicate whether the statements are TRUE or FALSE. Write only ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the question numbers (1.5.1–1.5.5) in the ANSWER BOOK. Give a reason if the answer is FALSE.
1.5.1 The Shi’a holy shrine of Karbala is in Iraq. (2)
1.5.2 In Judaism, the divine name of God is David. (2)
1.5.3 The sacred text of the Bahá’i faith was originally written in Greek. (2)
1.5.4 In the Taoist view, all of the world’s processes originate from ten thousand things. (2)
1.5.5 The longest epic in Hinduism is the Vedas. (2)
1.6 Write ONE fact about EACH of the following:
1.6.1 The importance of meditation in Buddhism (2)
1.6.2 Baha’u’llah (2)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
Answer any TWO questions in this section.
QUESTION 2
2.1 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
RELIGIOUS UNIQUENESS Religion can be a central part of one’s identity. South Africa is called the Rainbow Nation. In South Africa the constitution protects freedom of religion. People are also encouraged to learn to respect different spiritual practices. However, each religion is unique, being the only one of its kind, unlike anything / any religion. The quality means it is unlike anything else of its kind or of being solitary in type or characteristics. The major faiths practiced in South Africa are Christianity, Islam, Hinduism, Traditional African Religion and Judaism. [Adapted from www.dictionary.com] |
2.1.1 Briefly define the term identity as it is used in Religion Studies. (4)
2.1.2 “South Africa is called the Rainbow Nation.” Explain the quotation in the context of religion. (4)
2.2 Choose ANY ONE religion and discuss THREE of its unique features. (3 x 2) (6)
2.3 Explain the understanding of African Traditional Religion towards the ancestors and their roles. (6)
2.4 Write down the common features that exist between Hinduism and Buddhism. (6)
2.5 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
CORRUPTION REPORTERS As a nation settled into a strict lockdown in March 2020, put in place to curb the spread of the novel coronavirus, President Cyril Ramaphosa made a promise to the public, that government would help those severely affected by the lockdown. It would protect the funds put in place to achieve this. These funds were allocated to bolster the medical response and assist the hungry and needy, social grantees and employees who lost their income, because of the pandemic and the regulations limiting economic activity. It comes as no surprise that, during the pandemic, these funds were evidently misappropriated by some who could not resist the temptation. Most of the allegations reported to Corruption Watch referred to employers either registering employees for TERS (Temporary Employer/Employee Relief Scheme), but not paying the employees when the pay-outs arrived, or companies claiming on behalf of employees but giving them only a fraction of the money due to them. Some unscrupulous businesses gave it as loans that their staff would have to pay back. [Source: corruptionwatch.org.za] |
2.5.1 Define the term corruption. (2)
2.5.2 According to President Cyril Ramaphosa, who was the most at risk during the pandemic? (2)
2.6 ‘Religion is often described as the source of morality.’
2.6.1 What do you understand by morality? (4)
2.6.2 Use at least TWO examples to demonstrate that morality comes from religion. (4)
2.7 Explain the concept teaching as it is used in Religion Studies. (4)
2.8 “Belief in a religion is not always based on what a sacred book teaches.” Define the term belief as it is used in the context of religion. (4)
2.9 Briefly explain the meaning of the following term: Golden Rule (4)
[50]
QUESTION 3
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
HOW THIS LOCAL HUMAN TRAFFICKING SURVIVOR TURNED HER LIFE AROUND The 40-year-old woman from Cape Town lived with her father after her mother abandoned her at birth. [Extract taken from www.news24.com] |
3.1
3.1.1 Explain what you understand with the term human trafficking. (2)
3.1.2 Write down any TWO human rights of the 40-year-old woman that were violated. (4)
3.1.3 From the extract give evidence how human traffickers find their victims. (4)
3.1.4 “The pastor asked me to deliver drugs.” What do you think should be the role of faith leaders in ending human trafficking? (4)
3.2 ‘Human rights have always been an important part of religion.’ For each of the following religions, briefly discuss the teachings that promote human rights.
3.2.1 Christianity (4)
3.2.2 Islam (4)
3.2.3 African Traditional Religion (4)
3.3 “Human trafficking is a booming business …” Explain what is meant with this quotation. (4)
3.4 In the context of religion, explain the following concepts:
3.4.1 Comparability (4)
3.4.2 Similarities (4)
3.5 Describe the concept myth in the context of religion. (4)
3.6 Explain the role that parables play in religious teachings. (4)
3.7 Differentiate between a doctrine and dogma. (4)
[50]
QUESTION 4
4.1 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
VIEWS FROM A RABBI, A PRIEST AND AN IMAM Religious history was made in Abu Dhabi last year. A Document on Human Fraternity was signed by Pope Francis and Dr Ahmed Al Tayeb, the Grand Imam of Al-Azhar. Christian view: A Muslim view: A Jewish view: [From africanews.com] |
4.1.1 Quote ONE word from the extract which tells us that Sheik Dr Mustafa is excited about religious involvement. (2)
4.1.2 Do you agree that closer ties among religions are necessary for securing a more just and peaceful world? Give reasons for your answer. (8)
4.1.3 What was the impact of Rabbi Daniel Silverstein and Mohammad Yahya’s musical group? (4)
4.1.4 Refer to the Christian view “Religion is still the foundational fact in the lives of most people.” What does this quotation mean? (4)
4.2 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
RELIGIOUS FREEDOM IN APARTHEID SOUTH AFRICA When the National Party triumphed in the 1948 elections, Christianity existed with political power. The Preamble of the Constitution of South Africa declared that Christian values were to be upheld. For this reason, Lubbe (1986:116–117) argues the condition which existed in apartheid South Africa can be described as religious tolerance, rather that religious freedom. The feeling among adherents of other religions that they are tolerated rather than fully free, says Lubbe (1986:117), stems from the general South African assumption that Christianity is superior to other religions. [From uir.unisa.ac.za kilian.J] |
4.2.1 Define the concept of religious tolerance. (2)
4.2.2 Do you think religious freedom was protected in South Africa before 1994? Give reasons for your answer. (8)
4.2.3 The following three organisations have been established to promote interreligious relationships. Choose ONE and discuss its functions in Africa.
- The Programme for Christian-Muslim Relations in Africa (PROCMURA)
- The African Council of Religious Leaders (ACRL)
- The Interfaith Action for Peace in Africa (IFAPA) (8)
4.2.4 “... that they are tolerated rather than fully free.” What does the current South African constitution say about religious freedom? (8)
4.3 Briefly discuss the disadvantages of a society having no religious freedom or tolerance. (6)
[50]
QUESTION 5
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
FAKE PASTORS AND FALSE PROPHETS ROCK SOUTH AFRICAN FAITH by Thuso Khumalo Rape and fraud scandals involving fake pastors have prompted calls for the regulation of churches in South Africa. There have been a number of high-profile cases in recent months involving disgraced pastors. [From www.bbc.com.] |
5.1
5.1.1 Briefly explain what the heading of this article means. (2)
5.1.2 Why, do you think, has media coverage of religious issues increased sharply in recent years? (4)
5.1.3 From the article give TWO examples of the types of crimes these pastors/prophets are involved in. (4)
5.2 President Cyril Ramaphosa asked, “How can we work together to ensure that we rid our country of bogus religious leaders?” Give meaningful solutions to the question highlighted in the article. (6)
5.3 In your own words, what is meant by quackery? (2)
5.4 Read the following extract and answer the questions that follow.
NIGERIAN LAND CONFLICT SHARPENED BY RELIGIOUS DIVISIONS 13.02.2017
- Hundreds have been killed in Kaduna State, Nigeria in recent months in a long running conflict between farmers and semi-nomadic herdsmen. There is now a large police presence and curfews have been imposed in some districts. The pastor of the Bishara Baptist Church remembers the day when the crisis struck. “There were men who arrived on motorbikes. They opened fire on several local youth and killed three of them. Others were injured and had to be taken to hospital.”
- Nobody can say exactly how many people have died in this communal violence. Mohammed Bello Tukur, a lawyer, has been observing the conflict for many years. “He described it as complicated and multi- layered. There are concrete disputes about land usage, but there are also questions of ethnic identity as well.”
- A gasoline station in Southern Kaduna was destroyed in the communal violence. “The conflict also has religious dimensions”, said Tukur. “Muslim groups are fighting Christian groups. They spread of lies and it is clear that they have a deep-seated hatred of us Muslims” Imam Kabir Kasam added.
- He accuses the Christians of profiting from the conflict because it has brought them funding from international aid organisations but was unable to give DW any examples in support of this assertion. Imam Kasam says the killings in the region should be investigated. The hatred is being stoked on both sides. A preacher from the Omega Fire Ministries recently called on his followers to kill Fulani herdsmen.
[Adapted from DW.com]
5.4.1 State whether the above-mentioned conflict between the groups is intra-religious or interreligious conflict. Give reasons for your answer. (4)
5.4.2 “Muslim groups are fighting Christian groups.” What role can religious organisations play to prevent such conflict? (8)
5.4.3 Tukur described the conflict as “complicated and multi-layered”. What does this quotation mean? (4)
5.4.4 From the article, give the consequences of the conflict between the groups. (4)
5.5 Until recently it was argued that the conflict in Sudan is of a religious nature. Do you agree? Give reasons for your answer. (8)
5.6 Refer to paragraph 4. What is your view on the responses of Imam Kasam and the preacher from Omega Fire Ministries? (4)
[50]
TOTAL SECTION B: 100
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Physical Sciences Paper 2 Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your centre number and examination number in the appropriate spaces on the ANSWER BOOK.
- This question paper consists of TEN questions. Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Leave ONE line between two subquestions, e.g. between QUESTION 2.1 and QUESTION 2.2.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- You may use appropriate mathematical instruments.
- Show ALL formulae and substitutions in ALL calculations.
- Round off your FINAL numerical answers to a minimum of TWO decimal places.
- Give brief motivations, discussions, etc. where required.
- You are advised to use the attached DATA SHEETS.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Four options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1 to 1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.11 E.
1.1 Which ONE of the following is an ALKANE?
- C6H8
- C6H10
- C6H12
- C6H14 (2)
1.2 Esters are formed by a reaction between two organic compounds, X and Y, each with a different functional group. The functional groups of these compounds are: (2)
Compound X | Compound Y | |
A | Hydroxyl group | Carboxyl group |
B | Hydroxyl group | Carbonyl group |
C | Hydroxide ion | Carboxyl group |
D | Hydroxide ion | Carbonyl group |
1.3 When butane is subjected to high temperatures and pressures, the following reaction takes place:
Butane → methane + Y
Which ONE of the following represents Y?
- CHCCH3
- CH2CHCH3
- CH3CH2CH3
- CH3CHCHCH3 (2)
1.4 A hydrochloric acid solution, HCℓ(aq), of concentration 1 mol∙dm-3 is added to EXCESS POWDERED magnesium at 25 °C. Curve I below represents the volume of hydrogen gas produced during the reaction. Curve II was obtained at different conditions using the SAME VOLUME of hydrochloric acid solution.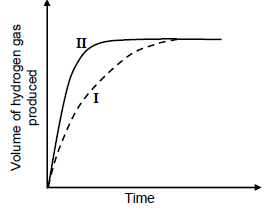
Which ONE of the following represents the conditions used to obtain curve II?
STATE OF DIVISION OF Mg | CONCENTRATION OF ACID | TEMPERATURE (°C) | |
A | Ribbon | 0,5 | 25 |
B | Ribbon | 2 | 25 |
C | Powder | 1 | 20 |
D | Powder | 1 | 30 |
(2)
1.5 In which ONE of the following reactions at equilibrium will the YIELD of the product increase when the VOLUME of the container is increased at constant temperature?
- N2O4(g) ⇌ 2NO2(g)
- H2(g) + I2(g) ⇌ 2HI(g)
- N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g)
- 2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g) (2)
1.6 Which ONE of the following statements is TRUE for an EXOTHERMIC reaction?
- More energy is absorbed than released.
- More energy is released than absorbed.
- Heat of reaction (ΔH) is positive.
- Energy of the products is greater than the energy of the reactants. (2)
1.7 Consider the equation below.
H3PO4(aq) + H2O(ℓ) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + H2PO-4 (aq)
Which ONE of the following is a conjugate acid-base pair?
- H3O+(aq) and H2O(ℓ)
- H3PO4(aq) and H2O(ℓ)
- H3PO4(aq) and H3O+(aq)
- H3O+(aq) and H2PO-4 (aq) (2)
1.8 Consider the balanced equation for the reaction below:
2Cr2+(aq) + Sn4+(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) + Sn2+(aq)
The OXIDISING AGENT is:
- Cr2+(aq)
- Cr3+(aq)
- Sn2+(aq)
- Sn4+(aq) (2)
1.9 An electrochemical cell is set up at standard conditions. The cell notation for the cell is given below.
Mg(s) | Mg2+(aq) || Pb2+(aq) | Pb(s)
The cell is now connected in a circuit. Which ONE of the graphs below BEST represents the concentrations of the electrolytes after a long time?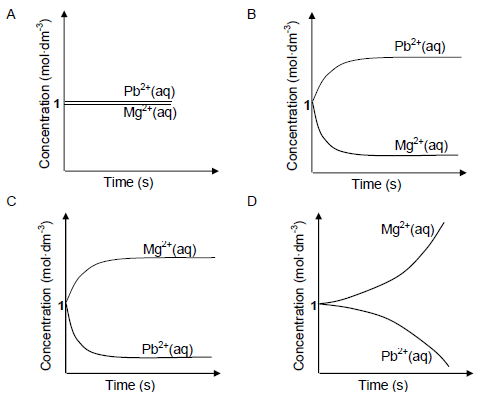 (2)
(2)
1.10 Two 50 kg bags, containing fertilisers R and S respectively, are labelled as follows:
Fertiliser R: 3 : 1 : 5 (20)
Fertiliser S: 1 : 2 : 6 (20)
Identify the fertiliser(s) most suitable for healthy leaf growth and healthy root growth.
LEAF GROWTH | ROOT GROWTH | |
A | R | R |
B | S | R |
C | R | S |
D | S | S |
(2) [20]
QUESTION 2 (Start on a new page.)
The letters A to E in the table below represent five organic compounds.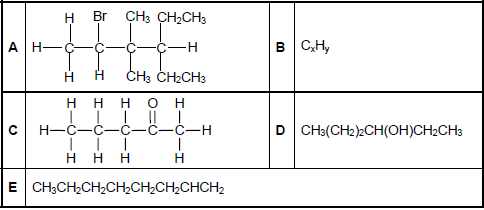
2.1 Write down the LETTER that represents EACH of the following:
2.1.1 A ketone (1)
2.1.2 A hydrocarbon (1)
2.1.3 An alkene (1)
2.2 Write down the:
2.2.1 IUPAC name of compound A (3)
2.2.2 STRUCTURAL FORMULA of compound D (2)
2.2.3 IUPAC name of the STRAIGHT CHAIN FUNCTIONAL ISOMER of compound C (2)
2.3 Compound B is a straight chain compound that undergoes the following exothermic reaction:
2CxHy + 25O2(g) → 16CO2(g) + 18H2O(g)
2.3.1 Besides being exothermic, what type of reaction is represented above? (1)
2.3.2 Determine the MOLECULAR FORMULA of compound B. (2)
The reaction above takes place in a closed container at a constant temperature higher than 100 °C and at constant pressure.
2.3.3 Calculate the TOTAL VOLUME of gas formed in the container when 50 cm3 of CxHy reacts completely with oxygen. (3)
[16]
QUESTION 3 (Start on a new page.)
Compounds A, B and C are used to investigate a factor which influences the boiling points of organic compounds. The results of the investigation are given in the table below.
COMPOUND | BOILING POINT (°C) | |
A | Butan-1-ol | 117 |
B | Butan-2-ol | 100 |
C | 2-methylpropan-2-ol | 82 |
3.1 Is this a fair investigation? Choose from YES or NO. (1)
3.2 Give a reason for the answer to QUESTION 3.1. (1)
3.3 Fully explain the difference in the boiling points of compounds B and C. (3)
3.4 Define the term positional isomer. (2)
3.5 From compounds A, B and C, choose the letter(s) that represent(s) EACH of the following:
3.5.1 Positional isomers (1)
3.5.2 A tertiary alcohol. Give a reason for the answer. (2)
3.6 The graph below represents the relationship between vapour pressure and temperature for compound A (butan-1-ol).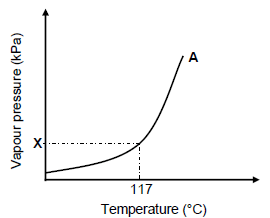
3.6.1 Write down the value of X. (1)
3.6.2 Redraw the graph above in the ANSWER BOOK. On the same set of axes, sketch the curve that will be obtained for compound C. Clearly label the curves A and C. Indicate the relevant boiling point for compound C on the graph. (2)
[13]
QUESTION 4 (Start on a new page.)
4.1 The flow diagram below shows various organic reactions using propane as starting reactant. R, T and U represent different organic compounds.
Compound T is a CARBOXYLIC ACID and compound U is a FUNCTIONAL ISOMER of pentanoic acid.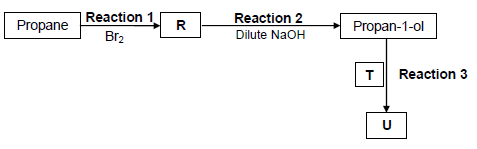
Write down the NAME of the type of reaction represented by:
4.1.1 Reaction 1 (1)
4.1.2 Reaction 2 (1)
Consider reaction 1 and reaction 2.
4.1.3 Write down the IUPAC name of compound R. (2)
Reaction 3 takes place in the presence of a catalyst and heat. Write down the:
4.1.4 NAME or FORMULA of the catalyst (1)
4.1.5 IUPAC name of compound T (2)
4.1.6 STRUCTURAL FORMULA of compound U (2)
4.2 A laboratory technician wants to prepare but-2-ene using but-1-ene as starting reagent, as shown below.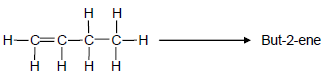
The following chemicals are available in the laboratory:
concentrated H2SO4 | H2O | concentrated NaOH |
Select the chemicals required to design this preparation from the list above.
For EACH step of the preparation, write down the balanced equation, using STRUCTURAL FORMULAE for all organic compounds. Indicate the chemicals needed in each step. (6)
[15]
QUESTION 5 (Start on a new page.)
5.1 Study the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution curve for a certain reaction below.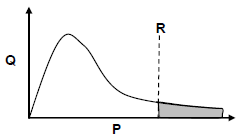
P and Q are the labels of the axes. What quantity is represented by:
5.1.1 P (1)
5.1.2 Q (1)
5.2 Line R represents the minimum energy required for the reaction to take place.
5.2.1 Write down the term for the underlined phrase. (1)
5.2.2 How will the shaded area on the graph be affected when a catalyst is added? Choose from INCREASE, DECREASE or REMAINS THE SAME. (1)
5.3 Use the collision theory to explain how a catalyst influences the rate of reaction. (4)
5.4 The reaction between POWDERED calcium carbonate, CaCO3(s), and EXCESS hydrochloric acid, HCℓ(aq), is used to investigate reaction rate at 25 °C. The balanced equation for the reaction is:
CaCO3(s) + 2HCℓ(aq) → CaCℓ2(aq) + H2O(ℓ) + CO2(g)
Several experiments are conducted using the same mass of IMPURE calcium carbonate and different initial concentrations of dilute hydrochloric acid. The graph below represents the results obtained. Assume that the impurities do not react.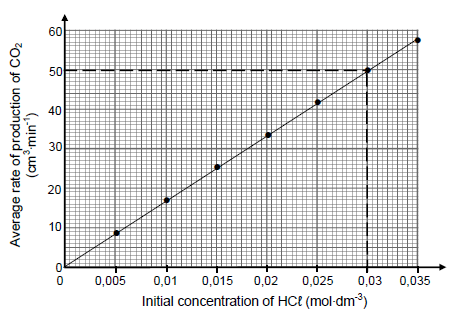
For this investigation, write down a:
5.4.1 Controlled variable (1)
5.4.2 Conclusion (2)
The CaCO3(s) in 6 g of the impure sample reacts completely with 0,03 mol∙dm-3 HCℓ(aq) in 26 minutes.
5.4.3 Use the information in the graph to calculate the percentage purity of the calcium carbonate. Assume that the molar gas volume at 25 °C is 24 000 cm3. (6)
[17]
QUESTION 6 (Start on a new page.)
Steam, H2O(g), reacts with hot carbon, C(s), at 1 000 °C according to the following balanced equation:
2H2O(g) + C(s) ⇌ 2H2(g) + CO2(g)
Initially, 36 g of steam and a certain amount of carbon were placed in a 2 dm3 sealed container and allowed to react. At equilibrium it was found that the amount of carbon changed by 0,225 mol.
6.1 Define the term dynamic equilibrium. (2)
6.2 Calculate the equilibrium constant, Kc, for the reaction at 1 000 °C. (8)
6.3 The graph shows how the rates of the forward and reverse reactions change with time.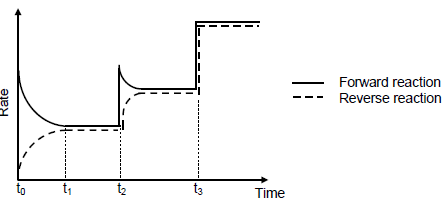
6.3.1 Give a reason why the rate of the forward reaction decreases between t0 and t1. (1)
6.3.2 What change was made to the equilibrium mixture at t3? (1) At time t2, the temperature of the system is increased.
6.3.3 Is the forward reaction EXOTHERMIC or ENDOTHERMIC? (1)
6.3.4 Refer to Le Chatelier’s principle to explain the answer to QUESTION 6.3.3. (2)
[15]
QUESTION 7 (Start on a new page.)
Two beakers, A and B, contain strong bases.
Beaker A: 500 cm3 of barium hydroxide, Ba(OH)2(aq) of unknown concentration X
Beaker B: 400 cm3 of potassium hydroxide, KOH(aq) of concentration 0,1 mol·dm-3
7.1 Define a base according to the Arrhenius theory. (2)
7.2 Calculate the number of moles of hydroxide ions ( OH-) in beaker B. (2)
7.3 The contents of beakers A and B are added together in beaker C. The solution in beaker C has a pH of 13. Assume that the volumes are additive and that the temperature of the solutions is 25 °C.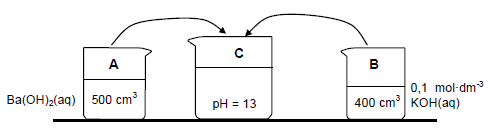
7.3.1 Calculate the concentration, X, of the Ba(OH)2 in beaker A. (8) The solution in beaker C is titrated with ethanoic acid. It was found that 15 cm3 of the solution neutralises 30 cm3 of the acid. The balanced equation for the reaction is:
CH3COOH(aq) + OH- (aq) → CH3COO- (aq) + H2O(ℓ)
7.3.2 Is ethanoic acid, CH3COOH(aq), a WEAK acid or a STRONG acid? Give a reason for the answer. (2)
7.3.3 Calculate the concentration of the ethanoic acid. (4)
[18]
QUESTION 8 (Start on a new page.)
A galvanic cell at standard conditions is represented by the cell notation below. X and Y are unknown electrodes.
X | Zn2+(aq) || Fe3+(aq) , Fe2+(aq) | Y
8.1 Write down the NAME or FORMULA of:
8.1.1 Electrode X (1)
8.1.2 Electrode Y (1)
8.1.3 The oxidising agent (1)
8.2 Write down:
8.2.1 ONE function of electrode Y (1)
8.2.2 The half-reaction that takes place at electrode Y (2)
8.2.3 The net (overall) equation for the cell reaction that takes place in this cell (3)
8.3 Calculate the initial emf of this cell. (4)
8.4 How will the initial emf of the cell be affected when the concentration of the iron(III) ions is changed to 0,6 mol∙dm-3? Choose from INCREASES, DECREASES or REMAINS THE SAME. (1)
[14]
QUESTION 9 (Start on a new page.)
The simplified diagram below represents an electrochemical cell used for the purification of copper. The impure copper contains small amounts of silver (Ag) and zinc (Zn) as the only impurities.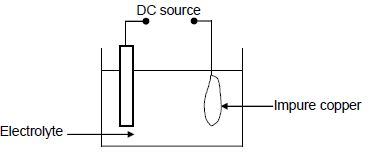
9.1 Define the term electrolysis. (2)
9.2 Write down the NAME or FORMULA of TWO positive ions present in the electrolyte. (2)
9.3 Write down the half-reaction that takes place at the cathode. (2)
9.4 Refer to the Table of Standard Reduction Potentials and explain why the purified copper will NOT contain any zinc. (3)
9.5 Calculate the maximum mass of Cu formed if 0,6 moles of electrons are transferred. (3)
[12]
QUESTION 10 (Start on a new page.)
10.1 The flow diagram below shows processes involved in the production of fertiliser C.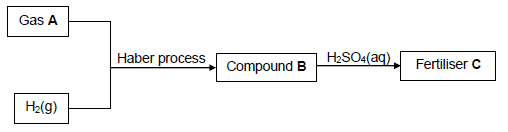
Write down the NAME or FORMULA of:
10.1.1 Gas A (1)
10.1.2 The catalyst used in the Haber process (1)
10.1.3 Compound B (1)
Write down the:
10.1.4 Name of the process used to produce gas A (1)
10.1.5 Balanced equation for the formation of fertiliser C (3)
10.2 A 40 kg bag of fertiliser contains 65% filler. The mass of the nutrients in the bag is shown in the table below.
NUTRIENTS | MASS (kg) |
Nitrogen | x |
Phosphorous | 2x |
Potassium | 5 |
Calculate the NPK ratio of the fertiliser. (3)
[10]
TOTAL: 150
DATA FOR PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 12
PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY)
TABLE 1: PHYSICAL CONSTANTS
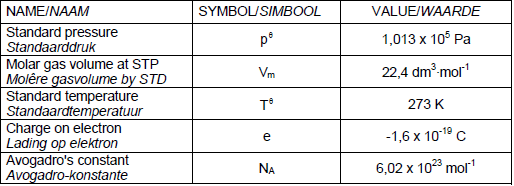
TABLE 2: FORMULAE 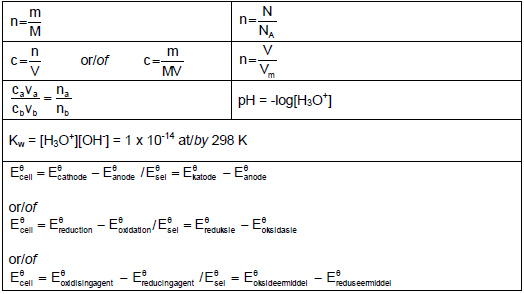
PERIODIC TABLE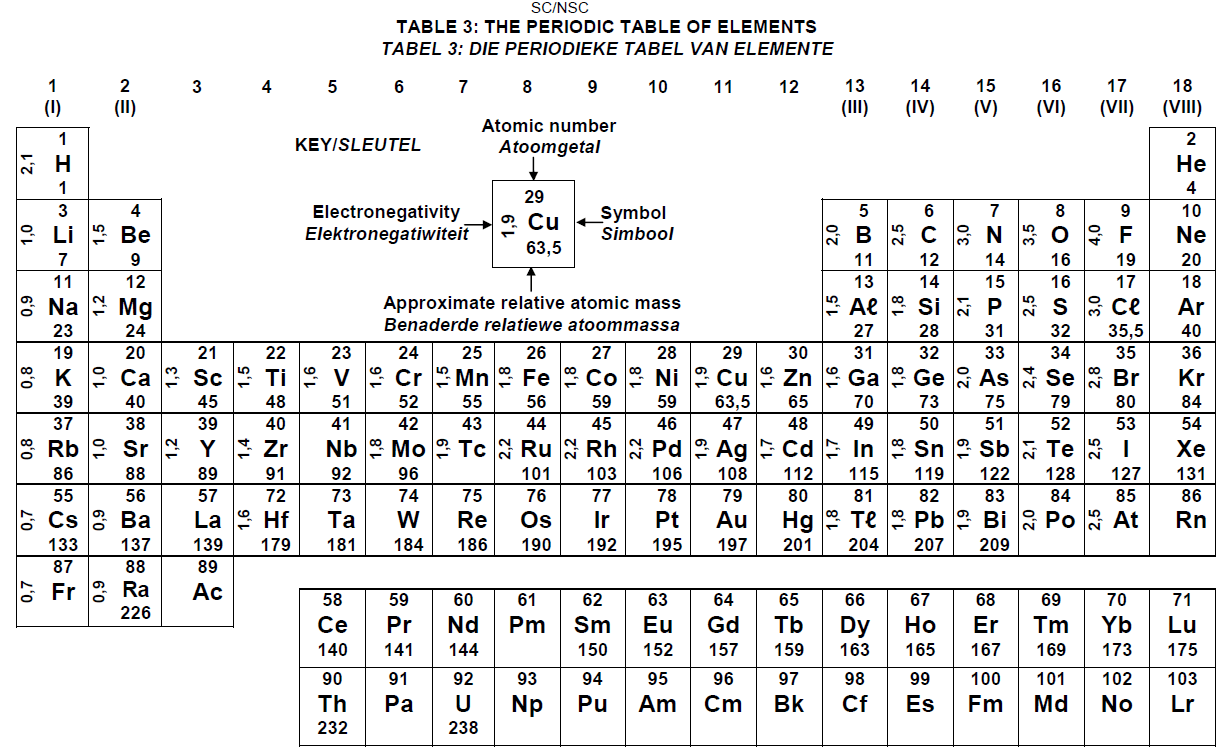
TABLE 4A: STANDARD REDUCTION POTENTIALS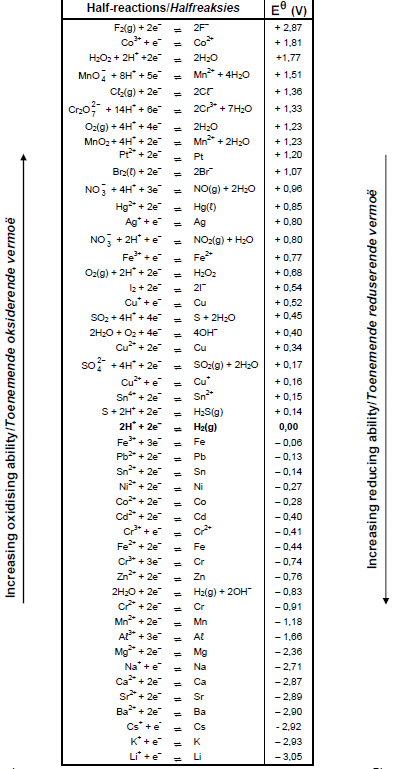
TABLE 4B: STANDARD REDUCTION POTENTIALS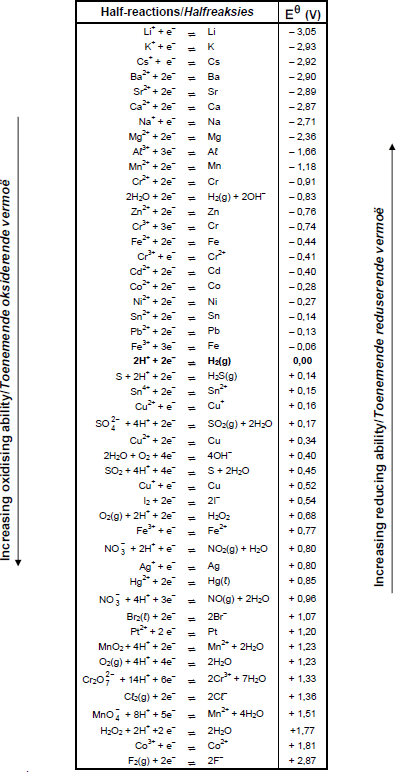
Physical Sciences Paper 1 Memorandum - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
GENERAL GUIDELINES
- CALCULATIONS
1.1 Marks will be awarded for: correct formula, correct substitution, correct answer with unit.
1.2 No marks will be awarded if an incorrect or inappropriate formula is used, even though there are many relevant symbols and applicable substitutions.
1.3 When an error is made during substitution into a correct formula, a mark will be awarded for the correct formula and for the correct substitutions, but
no further marks will be given.
1.4 If no formula is given, but all substitutions are correct, a candidate will forfeit one mark.
1.5 No penalisation if zero substitutions are omitted in calculations where correct formula/principle is correctly given.
1.6 Mathematical manipulations and change of subject of appropriate formulae carry no marks, but if a candidate starts off with the correct formula and then changes the subject of the formula incorrectly, marks will be awarded for the formula and correct substitutions. The mark for the incorrect numerical answer is forfeited.
1.7 Marks are only awarded for a formula if a calculation has been attempted, i.e. substitutions have been made or a numerical answer given.
1.8 Marks can only be allocated for substitutions when values are substituted into formulae and not when listed before a calculation starts.
1.9 All calculations, when not specified in the question, must be done to a minimum of two decimal places.
1.10 If a final answer to a calculation is correct, full marks will not automatically be awarded. Markers will always ensure that the correct/appropriate formula is used and that workings, including substitutions, are correct.
1.11 Questions where a series of calculations have to be made (e.g. a circuit diagram question) do not necessarily always have to follow the same order. FULL MARKS will be awarded provided it is a valid solution to the problem. However, any calculation that will not bring the candidate closer to the answer than the original data, will not count any marks. - UNITS
2.1 Candidates will only be penalised once for the repeated use of an incorrect unit within a question.
2.2 Units are only required in the final answer to a calculation.
2.3 Marks are only awarded for an answer, and not for a unit per se. Candidates will therefore forfeit the mark allocated for the answer in each of the following situations:
• Correct answer + wrong unit
• Wrong answer + correct unit
• Correct answer + no unit
2.4 SI units must be used except in certain cases, e.g. V.m-1 instead of N.C-1, and cm•s-1 or km•h-1 instead of m•s-1 where the question warrants this. - GENERAL
3.1 If one answer or calculation is required, but two are given by the candidate, only the first one will be marked, irrespective of which one is correct. If two answers are required, only the first two will be marked, etc.
3.2 For marking purposes, alternative symbols (s, u, t, etc.) will also be accepted.
3.3 Separate compound units with a multiplication dot, not a full stop, for example, m•s-1.
For marking purposes, m•s-1 and m/s will also be accepted. - POSITIVE MARKING
Positive marking regarding calculations will be followed in the following cases:
4.1 Sub-question to sub-question: When a certain variable is calculated in one sub-question (e.g. 3.1) and needs to be substituted in another (3.2 of 3.3),
e.g. if the answer for 3.1 is incorrect and is substituted correctly in 3.2 or 3.3, full marks are to be awarded for the subsequent sub-questions.
4.2 A multistep question of a sub-question: If the candidate has to calculate, for example, current in die first step and gets it wrong due to a substitution error, the mark for the substitution and the final answer will be forfeited. - NEGATIVE MARKING
Normally an incorrect answer cannot be correctly motivated if based on a conceptual mistake. If the candidate is therefore required to motivate in QUESTION 3.2 the answer given in QUESTION 3.1, and QUESTION 3.1 is incorrect, no marks can be awarded for QUESTION 3.2. However, if the answer for e.g. QUESTION 3.1 is based on a calculation, the motivation for the incorrect answer could be considered.
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1:
MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1.1 C ?? (2)
1.2 A ?? (2)
1.3 B ?? (2)
1.4 D ?? (2)
1.5 D ?? (2)
1.6 C ?? (2)
1.7 A ?? (2)
1.8 C ?? (2)
1.9 D ?? (2)
1.10 B ?? (2) [20]
QUESTION 2
2.1.1 When a (non-zero) resultant/net force acts on an object, it accelerates in the direction of the force. The acceleration is directly proportional to the force and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. ?? (2)
2.1.2
| OPTION 1 | OPTION 2 |
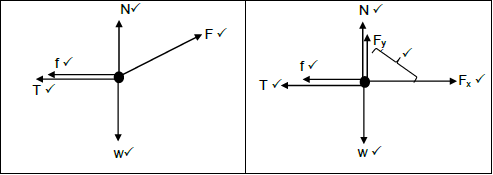 | |
(5)
Accept the following symbols: | |
N | FN/Normal/Normal force |
f | Ff / fk / fr / frictional force/kinetic frictional force / |
w | Fg,/mg/weight/FEarth on block/49 N/gravitational force/ |
T | Tension / FT / Fs |
Fapplied | F / FA / Applied force |
- Marks awarded for arrow and label
- Do not penalise for length of arrows since drawing is not drawn to scale.
- Any other additional force(s) 3/4
- If force(s) do not make contact with body. Max.3/4.
2.1.3
OPTION 1 | OPTION 2 |
Fnet = ma Any one ? | Fnet = ma Any one ? |
2.2 F = Gm1m2 ?
d2
1 842,50 ? = (6,67 × 10-11 )( 5,98 ×1024 )(200) ?
d2
d = 6 579 982,80 m
distance above earth surface
= 6 579 982,80 – 6,38 x 106 ?
= 199 982,80 m (1,9998280 x 105 m / 2,00 x 105 m) ? (5)
[17]
QUESTION 3
3.1.1 OPTION 1
UPWARDS POSITIVE | UPWARDS NEGATIVE |
vf2 = vi2 + 2aΔy ? | vf2 = vi2 + 2aΔy ? |
OPTION 2
UPWARDS POSITIVE | UPWARDS NEGATIVE |
vf = vi + aΔt | vf = vi + aΔt |
OPTION 3
UPWARDS POSITIVE | UPWARDS NEGATIVE |
vf = vi + aΔt | vf = vi + aΔt |
OPTION 4 (ACCEPT) | |
UPWARDS POSITIVE | UPWARDS NEGATIVE |
vf = vi + aΔt | vf = vi + aΔt |
(3)
3.1.2
UPWARDS POSITIVE | UPWARDS NEGATIVE |
vf = vi + aΔt ? | vf = vi + aΔt ? |
(5)
3.1.3
OPTION 1 | |
Positive marking from 3.1.1 | |
UPWARDS POSITIVE | UPWARDS NEGATIVE |
vf2 = vi2 + 2aΔy ? | vf2 = vi2 + 2a∆? ? |
OPTION 2 | |
Positive marking from 3.1.1 | |
UPWARDS POSITIVE | UPWARDS NEGATIVE |
vf = vi + aΔt | vf = vi + aΔt |
OPTION 3 | |
Positive marking from 3.1.1 | |
UPWARDS POSITIVE | UPWARDS NEGATIVE |
vf = vi + aΔt | vf = vi + aΔt |
OPTION 4 | |
Positive marking from 3.1.1 | |
UPWARDS POSITIVE | UPWARDS NEGATIVE |
vf = vi + aΔt | vf = vi + aΔt |
(4)
3.2 Positive marking from 3.1.1 and 3.1.2 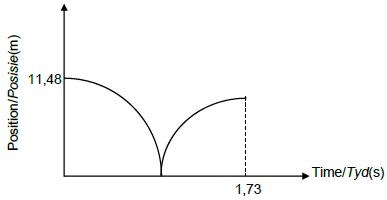
CRITERIA FOR MARKING | |
Correct shape | ? |
Height indicated(11,48 m) | ? |
Time t indicated (1,73 s) | ? |
(3) [15]
QUESTION 4
4.1 In an isolated system total linear momentum is conserved. ?? (2)
4.2.1
- ∑pi = ∑pf
mAviA + mBviB = (mA + mB)vf Any one ?
(2 x viA) + (4 x -5) ?= (2+4)(-1,67) ?
viA = 4,99 m.s-1 (East) ? (4)
4.2.2
POSITIVE MARKING FROM 4.2.1 | POSITIVE MARKING FROM 4.2.1 | ||
OPTION 1 | OPTION 2 | ||
Fnet.∆t = ∆p | Any one? | Fnet.∆t = ∆p | Any one ? |
Fnet x 0,01? = 2 (-1,67- 4,99) ? Fnet = - 1 332 N Fnet = 1 332 N west/left ? | Fnet x 0,01? = 2 [1,67- (-4,99)] ? Fnet = - 1 332 N Fnet = 1 332 N west/left ? | ||
OPTION/OPSIE 3 | OPTION/OPSIE 4 | ||
Fnet = ma | Any one? | Fnet = ma | Any one ? |
Fnet = 2 x ( - 1,67 - 4,99?) | Fnet = 2 x ( 1,67 - (- 4,99)?) | ||
OPTION 5 | OPTION 6 | ||
Fnet.∆t = ∆p Fnet.∆t = m(vf – vi) | Any one ? | Fnet.∆t = ∆p Fnet.∆t = m(vf – vi) | Any one ? |
Fnet(0,01) ? = 4(-1,67 – -5) ? Fnet = 1 332 FAB = - FBA Fnet(BA) = 1 332 N west/left ? | Fnet(0,01) ? = 4(1,67 – 5) ? Fnet = -1 332 FAB = - FBA Fnet(BA) = 1 332 N west/left ? | ||
(4) [10]
QUESTION 5
5.1 Gravitational force ? (1)
5.2
- ∆x = 12 ? = 24 m
sin30º
Wf = f.∆x cos θ ?
Wf = 35,5 x 24 cos 180º ?
Wf = - 852 J ? (4)
5.3 Zero/0 J ? (1)
5.4 Positive marking from 5.2
OPTION 1
- Wnet = ∆Ek Any one?
Wf + WF + WFg = ∆Ek
f x ∆x cos θ + F∆xcos θ + mg(h2 – h1) = ∆Ek
-852 ? + (62,5 x 24 cos180o) ? + m(9,8)(12-0) ? = 0
m = 20 kg ?
OPTION 2
- Wnc = ∆Ep + ∆Ek
Wf + WF = ∆Ep + ∆Ek Any one ?
f∆xcosθ + F∆xcos = mg(h2 – h1) + ∆Ek
-852 ?+ (62,5)(24)cos180o ?= m(9,8)(0 – 12) ?+ 0
m = 20 kg ?
OPTION 3
- Wnet = ∆Ek
Wf + WF + Ww = ∆Ek Any one?
f∆xcosθ + F∆xcos θ + mgΔxcosθ = ∆Ek
-852 ? + (62,5)(24)cos180o ? + m(9,8)(24)cos60o ? = 0 m = 20 kg ?
(5) [11]
QUESTION 6
6.1.1 520 Hz / 520 waves per second (waves.s-1)? (1)
6.1.2
- The change in frequency ?(or pitch) observed/detected by a listener because the listener and the sound source have different velocities relative to the medium of sound propagation. ?
OR - The (apparent) changed in observed/detected frequency (pitch) as a result of relative motion between the sound source and the listener. ? ? (2)
6.1.3 TOWARDS ? Detected frequency is higher than the source frequency ? (2)
6.1.4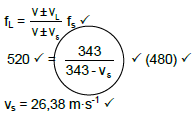 (5)
(5)
6.1.5 Decreases ?
- For a constant velocity/speed of sound, if the frequency increases, λ decreases. ?
OR - λ α 1/f at constant velocity/speed/by konstante snelheid/spoed ?
OR - f α 1/λ at constant velocity/speed/by konstante snelheid/spoed ? (2)
6.2 Light from the star is shifted towards longer wavelength (towards the red end of the spectrum) ?which indicated that the star is moving away from the earth. ? (2)
6.3
- Used to measure the direction and speed of blood flow in arteries and veins. ?
OR - Used to measure the heartbeat of a foetus in the womb. (1)
[15]
QUESTION 7
7.1.1 GAIN ? (1)
7.1.2
- n = Q ?
qe
n = 5 x 10-6 ?
1,6 x 10-19
n = 3,125 x 1013 (electrons) ? (3)
7.1.3
- E = kQ ?
r2
E = 9 x 109 x 5 x 10-5 ? ?
0,12
E = 4,5 x 106 N.C-1 ? left ? (5)
7.2.1 Negative ?
- Like charges repel each other ?
OR - The charges repel each other. If sphere A is negative, then sphere B must also be negative. ? (2)
7.2.2
- FE = Tsin30º
FE = 25sin30º ?
FE = 12,5 N
FE = kQ1Q2 ?
r2
12,5 ?= (9 × 109 )( 5 × 10-6 ) Q ?
0,052 ?
Q = 6,94 x 10-7 C ? (6)
[17]
QUESTION 8
8.1.1
- Temperature?
- Length of the conductors? (Any two)
- Thickness of the conductors
ACCEPT: Type of material (2)
8.1.2
- Gradient is the inverse of the resistance. ?/
OR - Gradient = 1 ? (1)
R
8.1.3 Conductor C. ?
- It has the highest resistance. The higher the resistance of a conductor, the more heat is produced in the conductor if the current is constant. ? (2)
8.2.1
- R = ? ?
?
R = 12 ?
1,5
R = 8 Ω ? (3)
8.2.2
- OPTION 1 OPTION 2
Rtotal = R + r ? ε = I(R+ r) ?
[8 = (4 + 3) ?+ r ]? 12 = 1,5 [(4 + 3) ?+ r] ?
r = 1 Ω ? r = 1 Ω ?
(4)
8.2.3
- W = I2R∆t ?
W = (1,5)2(3)(180) ?
W = 1 215 J ? (3)
8.3.1 Decrease? (1)
8.3.2 Increase ? (1)
8.4 Increase ?
Rext decreases. Current through battery increases. ?
W = I2r∆t / Energy transfer to the battery/work done by battery increases. ? (3)
[20]
QUESTION 9
9.1 Mechanical energy to electrical energy. ?? (2)
9.2 AC generator has slip rings and DC generator has a split ring / commutator ? (1)
9.3
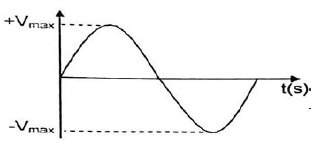
CRITERIA FOR MARKING | |
Correct shape | ? |
Axes labelled correct | ? |
Vmax indicated on graph | ? |
(2)
9.4
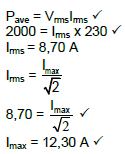 (4)
(4)
9.5 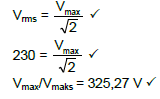 (3)
(3)
[12]
QUESTION 10
10.1 Work function (of the metal) ?
- Ek(max) = hc – W0 ?
λ
The intercept on the vertical axis = Wº ?
OR - hc = W0 + Ek(max) ?
λ
The intercept on the vertical axis is equal to the Wº ? (3)
10.2
- E = W0 + Ek(max)
hf = W0 + Ek(max) Any one ?
hf = hf0 + Ek(max)
6,63 x 10-34 x 6,16 x 1014? = 6,63 x 10-34 f0 ? + 5,6 x 10-20 ?
f0 = 5,32 x 1014 Hz ? (5)
10.3.1
- Remain the same/Bly dieselfde ?
The gradient is equal to the product of Planck’s constant and the speed of light in vacuum which are constants. ?
OR
Gradient = hc, which are constants (2)
10.3.2 Remains the same ?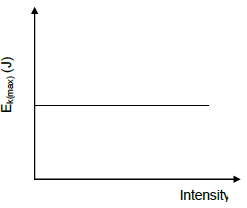
| CRITERIA FOR MARKING | |
| Axes labelled | ? |
| Correct shape | ? |
(3) [13]
TOTAL: 150
Physical Sciences Paper 1 Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your full NAME and SURNAME in the appropriate space on the ANSWER BOOK.
- The question paper consists of TEN questions. Answer ALL the questions.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Leave ONE line between two sub-questions, for example between QUESTION 2.1 and QUESTION 2.2.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- You may use appropriate mathematical instruments.
- Show ALL formulae and substitutions in ALL calculations.
- Round off your FINAL numerical answers to a minimum of TWO decimal places.
- Give brief motivations, discussions, etc. where required.
- You are advised to use the attached DATA SHEETS.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1 to 1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.11 E.
1.1 The impulse delivered by a net force acting on an object is equal to the …
- initial momentum of the object.
- final momentum of the object.
- change in momentum of the object.
- rate of change in momentum of the object. (2)
1.2 The graph below represents the relationship between the net force exerted on an object and the displacement it undergoes. The force and displacement are in the same direction.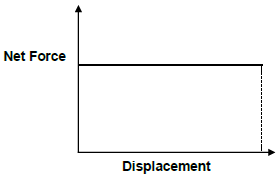
Which ONE of the following statements can be deduced from the graph?
- The area between the graph and the represents the net work done by the force. displacement axis
- The area between the graph and the represents the power dissipated by the force. displacement axis
- The gradient of the graph represents the change in kinetic energy of the object.
- The gradient of the graph represents the work done by the force. (2)
1.3 The diagram below shows all the forces acting on an object being pulled to the right by a force F acting at an angle θ to the horizontal.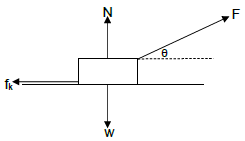
Which ONE of the following expressions can be used to determine the magnitude of the kinetic frictional force (fk) acting on the object?
- µ(w + Fsinθ)
- µ(w – Fsinθ)
- µ(N – w)
- µw (2)
1.4 The position-time graph below represents the motion of a ball from the instant it is released from rest from a certain height above the floor and bounces off the floor a number of times. Ignore the effects of air resistance.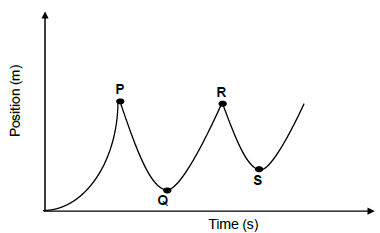
Which point (P, Q, R or S) on the graph represents the position-time coordinates of the maximum height reached by the ball after the SECOND bounce?
- P
- Q
- R
- S (2)
1.5 The kinetic energy of a car moving at velocity v is K. The velocity of the car changes to 2v. What is the new kinetic energy of the car?
- ¼K
- ½K
- 2K
- 4K (2)
1.6 A sound source approaches a stationary observer at constant velocity.
Which ONE of the following describes how the observed frequency and wavelength differ from that of the sound source?
Observed wavelength | Observed frequency | |
A | Greater than | Greater than |
B | Less than | Less than |
C | Less than | Greater than |
D | Greater than | Less than |
(2)
1.7 The electric field pattern between two charged spheres, A and B, is shown below.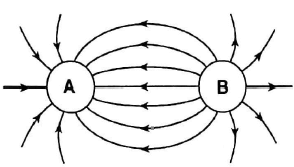
Which ONE of the following statements regarding the charge on spheres A and B is CORRECT?
- Sphere A is negatively charged, and sphere B is positively charged.
- Sphere A is positively charged, and sphere B is negatively charged.
- Spheres A and B are both positively charged.
- Spheres A and B are both negatively charged. (2)
1.8 The SI unit of measurement of the RATE OF FLOW OF CHARGE in a conductor is …
- watt.
- volt.
- ampere.
- coulomb. (2)
1.9 Which ONE of the following changes to the design of an AC generator will increase its maximum emf output?
- Change the polarity of the magnets
- Use larger slip rings
- Use larger brushes
- Increase the number of turns on the coil (2)
1.10 A line emission spectrum is formed when …
- electrons in the ground state move to a higher energy state.
- electrons in the higher energy state move to a lower energy state.
- white light passes through a cold gas.
- white light passes through a triangular prism. (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2
2.1 Two blocks of masses 2 kg and 5 kg are connected by means of a light inextensible string. The blocks are pulled along a rough horizontal surface by a force, F. The force makes an angle of 20º with the horizontal. Refer to the diagram below.
The 2 kg and 5 kg blocks experience kinetic frictional forces of 10 N and 15 N respectively.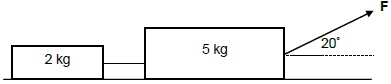
2.1.1 State Newton’s Second Law of motion in words. (2)
2.1.2 Draw a labelled free-body diagram for the 5 kg block. (5)
2.1.3 Calculate the magnitude of force F that must be applied at an angle of 20° to the horizontal to make the two blocks accelerate at 2 m.s-2 to the right. (5)
2.2 The earth exerts a force of 1 842,50 N to keep a satellite of mass 200 kg in orbit around the earth as shown in the diagram below.
Calculate the distance, above the EARTH’S SURFACE at which the satellite orbits the earth. (5)
[17]
QUESTION 3
The velocity versus time graph below shows the motion of a ball thrown vertically downwards from the top of a building and bouncing off the floor as it hits the ground.
Ignore the effects of air friction. TAKE UPWARD MOTION AS POSITIVE.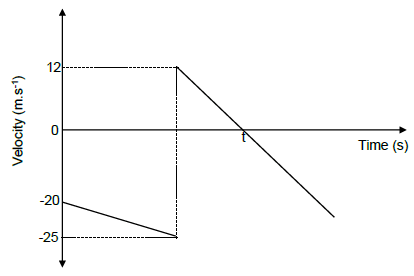
3.1 Using EQUATIONS OF MOTION ONLY, calculate the:
3.1.1 Height from which the ball is thrown (3)
3.1.2 Time t on the graph (5)
3.1.3 Magnitude of the displacement of the ball from the moment it is thrown until time t (4)
3.2 Sketch a position versus time graph for the motion of the ball from the moment it is thrown until it reaches its maximum height after the bounce. USE THE GROUND AS THE ZERO POSITION.
Indicate the following on the graph:
- The height from which the ball is thrown
- Time t (3)
[15]
QUESTION 4
The diagram below shows trolley A of mass 2 kg travelling at a velocity of v m∙s−1 east on a straight horizontal surface colliding head-on with trolley B of mass 4 kg travelling at a velocity of 5 m∙s−1 west.
After the collision, the two trolleys stick together and move at a velocity of 1,67 m·s-1 west. The collision lasted for 0,01 s. Ignore the effects of friction.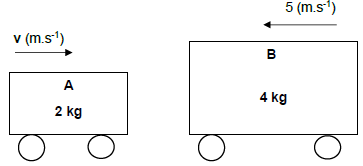
4.1 State the principle of conservation of linear momentum in words. (2)
4.2 Calculate the:
4.2.1 Magnitude of the velocity v of the trolley A before it collided with trolley B (4)
4.2.2 Force that trolley B exerts on trolley A (4)
[10]
QUESTION 5
A force of 62,5 N is applied to a trolley of mass m kg parallel to the inclined surface as shown to keep it moving down an inclined surface at a CONSTANT VELOCITY. The vertical height of the inclined surface is 12 m. Refer to the diagram below.
A kinetic frictional force of 35,5 N acts on the trolley as it moves down the inclined surface.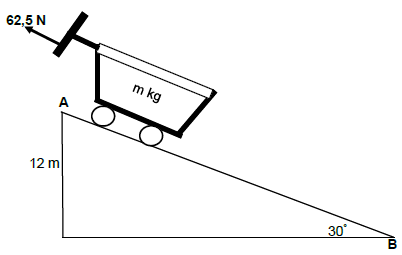
5.1 Write down the name of the conservative force acting on the trolley. (1)
5.2 Calculate the work done by the frictional force on the trolley. (4)
5.3 Write down the change in kinetic energy when the trolley reaches the bottom of the inclined surface. (1)
5.4 Use the work-energy theorem to calculate the mass, m, of the trolley. (5)
[11]
QUESTION 6
6.1 A stationary sound detector placed at a certain point records 520 sound waves per second from a moving sound source which emits sound waves of frequency 480 Hz.
6.1.1 Write down the frequency of the sound waves that the detector records in Hz. (1)
6.1.2 Define the phenomenon which explains the change in frequency observed. (2)
6.1.3 Is the sound source moving TOWARDS or AWAY from the observer? Give a reason for your answer. (2)
6.1.4 Calculate the velocity at which the sound source is moving. Take velocity of sound as 343 m·s-1. (5)
6.1.5 How would the wavelength of the sound wave produced by the sound source change if the frequency of the sound waves become higher than 480 Hz? Write down only INCREASES, DECREASES or STAYS THE SAME. Explain your answer using the wave equation. (2)
6.2 The spectral lines from a distant star are observed to be red shifted. Explain the underlined term. (2)
6.3 Write down ONE application of the Doppler effect in the field of medicine. (1)
[15]
QUESTION 7
7.1 A small sphere A carrying a charge of -5 µC hangs vertically from a ceiling by means of an inextensible string. Point P is 100 mm to the right of sphere A as shown on the Diagram 1 below.
DIAGRAM 1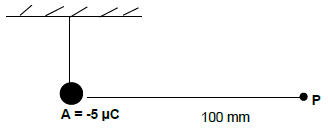
7.1.1 P Did charged sphere A LOSE or GAIN electrons to acquire a charge of -5 µC? (1)
7.1.2 Calculate the number of electrons lost or gained by charged sphere A, to acquire a charge of -5 µC. (3)
7.1.3 Calculate the electric field at point P, due to charged sphere A. (5)
7.2 An identical sphere B carrying an unknown charge placed on an insulated stand is brought closer to sphere A. Charged sphere A swings to the right and comes to rest so that the string makes an angle of 30° with the vertical and the tension in the string is 25 N. The distance between the two charged spheres is 50 mm as shown on Diagram 2 below.
DIAGRAM 2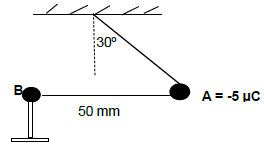
7.2.1 Is the charge on sphere B POSITIVE or NEGATIVE? Give a reason for your answer. (2)
7.2.2 Calculate the magnitude of the charge on sphere B. (6)
[17]
QUESTION 8
8.1 A group of Grade 12 learners want to determine an efficient conductor which can be used as the heating coil for a kettle that they are constructing for their Eskom Expo project.
They connected each of the three conductors (A, B and C) in a circuit and measured the current passing through the conductor and the potential difference across the conductors. Their results are as shown on the graph below.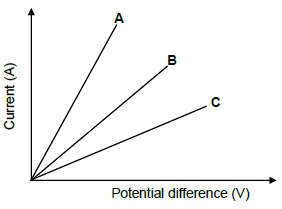
8.1.1 Name any TWO variables that must be kept constant for a fair investigation. (2)
8.1.2 Write down the physical quantity represented by the gradient of each graph. (1)
8.1.3 Which ONE of the conductors is efficient enough to be used as a heating coil in a kettle? Give a reason for your answer. (2)
8.2 The circuit diagram below represents a combination of resistors in series and parallel. The battery has an emf of 12 V and an unknown internal resistance r.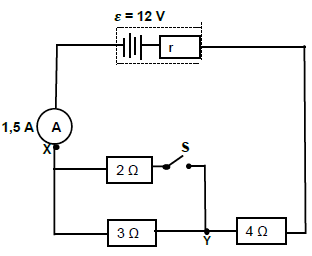
With switch S OPEN, the reading on ammeter A is 1,5 A. Calculate the:
8.2.1 Total resistance of the circuit (3)
8.2.2 Internal resistance of the battery (4)
8.2.3 Energy dissipated by the 3 Ω resistor in 3 minutes (3)
8.3 Switch S is now CLOSED. How will EACH of the following be affected? Write down only INCREASES, DECREASES or REMAINS THE SAME.
8.3.1 The total resistance of the circuit. (1)
8.3.2 The reading on ammeter A. (1)
8.4 A conducting wire of negligible resistance is now connected between points X and Y as shown on the diagram above. What effect will this have on the temperature of the battery?
Write down only INCREASES, DECREASES or REMAINS THE SAME. Explain your answer. (3)
[20]
QUESTION 9
AC generators at coal-fired power stations supply most of the electrical energy needed in our country.
9.1 State the energy conversion that takes place when this generator is in operation. (2)
9.2 State ONE structural difference between an AC generator and a DC generator. (1)
9.3 Draw a sketch graph of potential difference versus time for this AC generator. Clearly label the axes and indicate Vmax on the potential difference axis. (2)
An electric appliance is rated 2 000 W, 230 V. The appliance is connected to an alternating current power source. Calculate the:
9.4 Maximum current (Imax) produced by the generator (4)
9.5 Peak voltage (Vmax) output of the generator (3)
[12]
QUESTION 10
A group of learners conducted an experiment to determine the relationship between the inverse of wavelength 1/λ of incident photons on a metal and the maximum kinetic energy (Ek(max)) of emitted photoelectrons from the metal plate surface. They presented their results as shown on the graph below.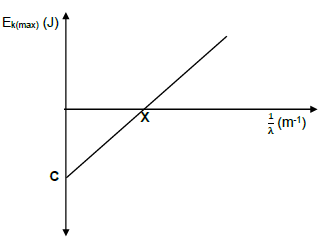
10.1 Which physical quantity is represented by the letter C (the intercept on the vertical axis) on the graph? Use a suitable equation to explain the answer. (3)
10.2 Light photons of frequency of 6,16 x 1014 Hz are incident on a metal plate and photoelectrons are released with maximum kinetic energy of 5,6 x 10-20 J.
Calculate the magnitude of the physical quantity represented by the letter X on the graph. (5)
10.3 The brightness of the incident light is now increased. What effect will this change have on the following? (Write down only INCREASES, DECREASES or REMAINS THE SAME.)
10.3.1 The gradient of the graph. Explain your answer. (2)
10.3.2 The maximum kinetic energy of the released photoelectrons.
Draw a graph of the relationship between brightness of incident photons and maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons to explain your answer. (3)
[13]
TOTAL: 150
DATA FOR PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 12
PAPER 1 (PHYSICS)
TABLE 1: PHYSICAL CONSTANTS
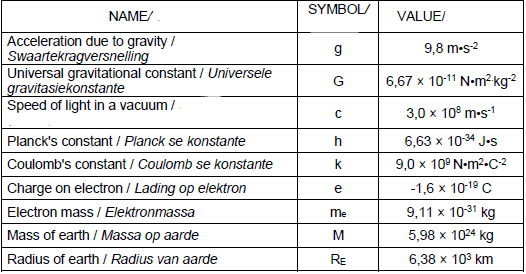
TABLE 2: FORMULAE
MOTION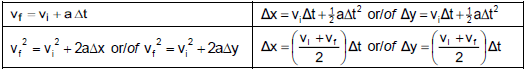
FORCE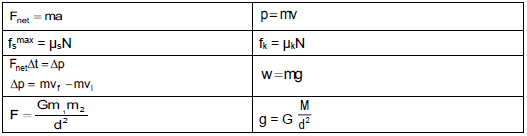
WORK, ENERGY AND POWER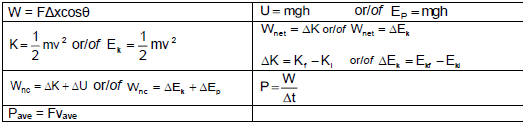
ELECTROSTATICS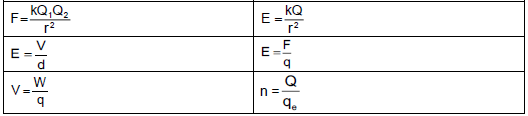
Mechanical Technology: Automotive Memorandum - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (GENERIC)
1.1 C
1.2 D
1.3 D
1.4 A
1.5 B
1.6 B (6 x 1) [6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 Safety Precautions
- Pressure gauges must be checked and tested regularly and adjusted or replaced if any malfunctioning occurs.
- Supporting pins that keep the platform at a desired height on the frame must be inspected for damage.
- Check the floor for oil and apparatus for leaks.
- The platform on which the workpiece rests must be rigid and square with the press cylinder. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.2 Product layout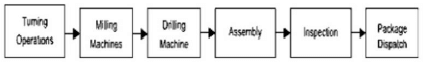 (2)
(2)
2.3 Perspex shield
- is installed to shield flying objects from harming the operator’s eye. (1)
2.4
2.4.1 Machine Identification
- Surface grinder (1)
2.4.2 Surface grinder parts label
- Workpiece
- Machine spindle
- Magnetic table
- Grinding wheel (4)
[10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1 Heat treatment refers to heating and cooling of metals under controlled conditions in their solid state so as to change their properties. (2)
3.2 Heat treatment properties
| PROCESS | PROPERTY | |
| 3.2.1 | Hardening | Very hard, high tensile strength and brittle |
| 3.2.2 | Tempering | Tough, hard |
| 3.2.3 | Annealing | Soft, ductile, low tensile strength |
| 3.2.4 | Normalising | Tough and machinable |
(4)
3.3 Purpose of case-hardening
- Harden surface
- Provides high surface wear resistance
- Tough core (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.4 Carbon effect
- Steel with low carbon content will not respond very much to the hardening process.(2)
3.5 Workshop tests on materials
- Sound test Bend test Filing test
- Machining test (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.6 Reasons for annealing
- To relieve internal stresses that may have been set up during other processes.
- To soften them in order to facilitate the machining processes.
- To make material ductile.
- Refine their grain structures.
- Reduce brittleness (Any 2 x 1) (2)
[14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (SPECIFIC)
4.1 B
4.2 C
4.3 C
4.4 A
4.5 B
4.6 C
4.7 D
4.8 D
4.9 D
4.10 A
4.11 C
4.12 B
4.13 B
4.14 A (14 x 1) [14]
QUESTION 5: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
5.1
5.1.1 Equipment
- Compression tester (1)
5.1.2 Parts of a compression tester
- – Flexible pipe
- – Adaptors’ screw
- – Gauge
- – Relief valve (Release) (4)
5.1.3 Purpose of a compression tester
- To measure the pressure that the piston will create when moving from bottom dead centre to top dead centre (2)
5.2 Function of a cylinder leakage tester
- To check whether the engine leaks gases from the cylinder during compression stroke (2)
5.3 Set-up procedure of cylinder leakage test
- Turn the engine until both valves are closed on the cylinder under test
- Unscrew the spark plug and screw the adaptor into the spark plug hole
- Use the spanner to lock the crankshaft pulley
- Couple the compressed air pipe to the tester and then to the adaptor while the relief valve on the tester is closed
- Open the relief valve on the tester slowly
- Take the readings and compare with specification (6)
5.4 Reason for analysing exhaust gases
- To determine the amount of the different types of gases emitted from a car engine and compare with standards to ensure that it does not exceed the
safety limit. (2)
5.5
5.5.1 Bubble gauge
- It is used to test the caster, camber and king pin inclination angle of a motor vehicle (2)
5.5.2 Turntable
- A turntable makes it possible to turn the front wheel 20° in and zero the bubble gauge and then turn the wheel 20° out and check the caster reading (3)
5.5.3 Periscopic optical alignment gauge
- To check the toe-in and toe-out of a vehicle (1)
[23]
QUESTION 6: ENGINES (SPECIFIC)
6.1
6.1.1 Engine component
- Crankshaft (1)
6.1.2 Crankshaft parts labeling
- – Crank nose
- – Crankpin journals/Big end journal
- – Flywheel mounting
- – Main journals
- – Counterweights
- – Main journal oil way (6)
6.1.3 Function of the crankshaft
- To convert the reciprocating motion of the piston into a rotary motion (2)
6.1.4 Number of cylinders
- 4-cylinder (1)
6.2
6.2.1 Function of a vibration damper
- A vibration damper adds mass to the crankshaft on the opposite side of a normal flywheel in order to counteract the torsion of the crankshaft (2)
6.2.2 Parts labeling
- – Crankshaft
- – Crankshaft flange
- – Secondary flywheel
- – Friction disc
- – Friction spring
- – Spring plate (6)
6.3 Engine cylinder configuration
- In-line engines
- V-type engines
- Flat engines (Horizontally opposed engines) (Any 2 x 1) (2)
6.4 Factors that determine firing order
- Position of the crank on the crankshaft
- The arrangement of cams on the camshaft (2)
6.5.1 Lag
- It is a delay felt by the driver between pressing the accelerator pedal and feeling the turbo kick in (2)
6.5.2 Boost
- It is the increase in manifold pressure generated by the turbocharger in the intake manifold which exceeds the atmospheric pressure. (2)
6.5.3 Waste gate
- A component of a turbocharger that wastes some of the exhaust gases by causing it to bypass the turbocharger turbine. (2)
[28]
QUESTION 7: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
7.1 7.1.1 Clearance volume
- The volume of the space above the crown of the piston in the combustion chamber when the piston is at the top dead centre (2)
7.1.2 Compression ratio
- The relationship between the total volume of a cylinder when the piston is at bottom dead centre to the volume of the charge in the cylinder when the piston is at top dead centre. (2)
7.2 Cylinder bore
- Stroke = 85 mm = 8,5 cm
CV = 60 cm3
CR = 10 : 1
CR = ?? + ??
??
= 10 = ?? + 60
60
SV = 540 cm3
540 = ?2 × ?
4
540 = ? × ?2 × 8,5
4
D = 8,994 cm
= 90 mm (6)
7.3 Methods of increasing compression ratio
- Remove shims from between crankcase and cylinder block
- Fit thinner gasket between cylinder block and cylinder head
- Machine metal from cylinder head
- Skim metal from cylinder block
- Fit piston with suitable higher crowns
- Fit crankshaft with longer stroke
- Increase cylinder bore (Any 3 x 1) (3)
7.4 New compression ratio
- Bore increase by 4,8 mm
90 mm + 4,8 mm = 94,8 mm = 9,48 cm
SV = ? × 9,482 × 8,5
4
= 600 cm3
CR = 600+60
60
= 11 : 1 (5)
7.5
7.5.1 Indicated power
- P = PLANn
P = 1°100 kPa = 1 100 000 Pa
L = 80 mm = 0,08 m
D = 95 mm = 0,095 m
A = ? × 0,0952
4
= 7,088218425 × 10-3 m2
N = 4 200
60×2
= 35r/s
N = 4 cylinders
Indicated power= 1 100 000 x 0,08 x 7,088218425 x 10-3 x 35 × 4
= 87 326,85 W
= 87,33 kW (6)
7.5.2 Torque
- T = f×r
But f= mg = 35 x10
= 350 N
T = 350 x 0,5
= 175 Nm (3)
7.5.3 Brake power
- BP = 2 ? NT
= 2 x ? x 70 x 175
= 76 969,02 W
= 77 kW (3)
7.5.4 Mechanical efficiency
- Mechanical efficiency = ?? × 100%
??
= 77 × 100%
87.33
= 88,12% (2)
[32]
QUESTION 8: MAINTENANCE (SPECIFIC)
8.1
8.1.1 High hydrocarbon reading (possible causes)
- Incomplete combustion
- Improper timing
- Vacuum leak
- Faulty air management system (Any 1 x 1) (1)
8.1.2 Corrective measures
- Reset fuel mixture
- Check and reset ignition system
- Check and repair vacuum leaks (Any 1 x 1) (1)
8.1.3 High carbon monoxide (possible causes)
- Too rich mixture
- Ignition misfire
- Dirty air filter
- Bad fuel delivery system
- Faulty thermostat
- Bad PVC valve system
- Catalytic converter not working (Any 1 x 1) (1)
8.1.4 Corrective measures
- Reset fuel mixture
- Check misfire and repair
- Replace air filter
- Check and correct fuel delivery system
- Check and repair coolant sensor
- Check and replace the catalytic converter (Any 1 x 1) (1)
8.2 Compression test safety requirements
- Ensure the tester can handle the pressure you want to test
- Clean the plug hole environment with compressed air before removing the spark plug
- Ensure the relief valve is working
- Ensure the use of the correct adaptor for the plug hole
- Ensure the throttle valve is opened (Any 3 x 1) (3)
8.3 Manufactural specification (cylinder leakage test)
- Listen at intake for hissing sound (inlet valve leaking)
- Listen at exhaust for hissing sound (exhaust valve leaking)
- Listen for hissing sound in dip stick (piston rings worn)
- Listen for hissing sound after opening the tapper cover fillet cap (piston ring worn)
- If you see bubbles in the radiator water, the cylinder head gasket is blown
(Any 3 x 1) (3)
8.4 Low oil pressure reading (possible causes)
- Worn oil pump
- Blocked pick-up screen in the oil sump
- Worn main big-end and camshaft bearings
- Blocked oil filter
- Dirty or contaminated oil
- Oil leaks
- Too little oil in the engine
- Incorrect oil viscosity
- Defective oil pressure relief valve
(Any 3 x 1) (3)
8.5 Components for possible leakage
- Water hoses
- Blown cylinder head gasket
- Water pump
- Radiator
- Corroded core plugs
- Interior heater radiator
- Faulty radiator cap (Any 4 x 1) (4)
8.6 Manufactural specifications (cooling system pressure test)
- Ratio combination of antifreeze and water in the system
- Pressure allowed in the radiator
- Pressure of the radiator cap
- Reading of the water coolant tester
(Any 2 x 1) (2)
8.7
8.7.1 Fuel pressure too high (possible causes)
- Faulty fuel pump
- Blocked fuel filter
- Cracked or restricted fuel line
- Clogged fuel pump inlet strainer
- Low voltage to pump
- Faulty fuel pressure regulator
- Defective fuel pump relay
- Empty fuel tank
(Any 2 x 1) (2)
8.7.2 Fuel pressure too high (possible causes)
- Restriction in return fuel line
- Faulty fuel pressure regulator (2)
[23]
QUESTION 9: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL (AUTOMATIC GEARBOX) (SPECIFIC)
9.1 Purpose of automatic gearbox
- To relieve the driver of clutch and gearshift operation thereby allowing the driver to concentrate on driving the vehicle, promoting smoother and easier
driving (2)
9.2 Differences between an automatic gearbox and manual gearbox
- There is no clutch pedal in vehicles with automatic gearbox but there is a clutch pedal in vehicles with manual gearbox
- Gear shift happens automatically in automatic gearbox but it’s the driver’s responsibility to change gears in manual gearbox
- Automatic transmission uses thin oil while manual gearbox uses thicker oil
- Automatic transmission uses torque converter while manual gearbox uses clutch assemble (Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.3 Disadvantages of automatic gearbox
- It’s more expensive to manufacture
- The propeller shaft of an automatic transmission must be removed if the car is to be towed over a long distance
- If the starter fails, there are no other alternatives to get the engine running
(Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.4 Function of a torque converter
- To multiply engine torque automatically according to road and engine speeds (2)
9.5
9.5.1 Stall speed
- At stall speed, the maximum torque multiplication is delivered as the pump reaches the highest velocity but the turbine is still at rest.
That is when the vehicle is just about to start moving. (3)
9.5.2 Increasing speed
- The vehicle starts moving as the turbine begins to turn. As the speed increases, the torque multiplication tapers off gradually. (2)
9.6 Advantages of torque converter
- Torque increases automatically
- Torque is transferred smoothly
- Minimum servicing is required (Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.7 Advantages of transmission control unit (TCU)
- Better fuel economy
- Reduces engine emissions
- Greater shift system reliability
- Improved shift feel
- Improved shift speed
- Improved vehicle handling (Any 3 x 1) (3)
[18]
QUESTION 10: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL (AXLES AND STEERING GEOMETRY AND ELECTRONICS) (SPECIFIC)
10.1 Causes of camber wear
- Suspension misalignment
- Bent strut
- Dislocated strut tower
- Weak or broken spring
- Bent spindle
- Damaged control arm (Any 2 x 1) (2)
10.2 Different between positive and negative camber
- Positive camber is the outward tilt of the front wheel away from the vehicle when viewed from the front of the vehicle. While negative camber is the inward tilt of the front wheel into the vehicle when viewed from the front of the vehicle. (4)
10.3
10.3.1 Alignment angle
- Negative caster (2)
10.3.2 Parts labeling
- – Contact point of king pin Centre line
- – King pin
- – Perpendicular line
- – Negative caster angle
- – Centre line of king pin
- – Front of vehicle
- – Point of wheel contact (7)
10.3.3 Advantages of negative caster
- Easier turning of wheels
- Better corner qualities (2)
10.4 Factors to be considered before attempting wheel alignment adjustment
- Kerb mass
- Uneven wear on tyres
- Tyre pressure
- Run-out on the wheels
- Correct pre-load on the wheel bearing
- Kingpins and bushes
- Suspension ball joints for wears
- Suspension bushes for excessive free movement
- Steering box play
- Tie-rod ends
- Sagged springs
- Shock absorber
- Spring U-bolts
- Chassis for possible cracks and loose cross members (Any 2 x 1) (2)
10.5 Static balance
- It is the equal distribution of all weight around the axis of rotation in the rotation plane (2)
10.6 Pre-checks on wheels before balancing
- Check the tyres for bruises, cracks and damaged side walls
- Check the rim for any damage
- Check for any foreign object on the rim and tyre (Any 2 x 1) (2)
10.7
10.7.1 Alignment
- Ackermann principle (1)
10.7.2 Parts Labelling
- – Rear axle
- – Longitudinal axis
- – Steering arm
- – Front wheel
- – Extended centre lines from steering arms
- – Intersection (6)
10.7.3 Purpose
- To enable the correct turning angle of the front wheels when negotiating a curve in order to prevent skidding (2)
[32]
TOTAL: 200
Mechanical Technology: Automotive Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your NAME and SURNAME on the ANSWER BOOK.
- Read ALL the questions carefully.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Show ALL calculations and units. Round off final answers to TWO decimal places.
- Candidates may use non-programmable scientific calculators and drawing instruments.
- The value of gravitational force should be taken as 10 m.s-2.
- All dimensions are in millimetres, unless stated otherwise in the question.
- A formula sheet is attached to the question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
- Use the criteria below to assist you in managing your time.
QUESTION | CONTENT | MARKS | TIME IN MINUTES |
GENERIC | |||
1 | Multiple-choice questions | 6 | 6 |
2 | Safety | 10 | 10 |
3 | Materials | 14 | 14 |
SPECIFIC | |||
4 | Multiple choice questions | 14 | 10 |
5 | Tools and Equipment | 23 | 20 |
6 | Engines | 28 | 25 |
7 | Forces | 32 | 25 |
8 | Maintenance | 23 | 20 |
9 | Systems and Control (Automatic Gearbox) | 18 | 20 |
10 | Systems and Control (Axles, Steering Geometry) | 32 | 30 |
TOTAL: | 200 | 180 | |
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (GENERIC) (COMPULSORY)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the correct answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1–1.6) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.7 A.
1.1 Which ONE of the following safety procedures is applicable to the maintenance/operation of a hydraulic press?
- Do not apply a wrench to revolving work.
- Guards could be removed when pressing soft material.
- Pressure gauges must be tested regularly and adjusted or replaced if any malfunctioning occurs.
- Use the machine table as an anvil. (1)
1.2 What is the best way of dealing with a hazard to ensure others are not put at risk?
- Remove it immediately
- Leave it for the supervisor to sort out
- Not placing a barrier tape around it
- Display a notice or warning sign (1)
1.3 Which of the following is a safety precaution related to a work bench?
- The tool rest must not be more than 3 mm from the grinding wheel.
- Make sure the chuck is correctly tightened.
- Stand on the side when switching on the machine.
- Keep rolling stock or items away from the bench end. (1)
1.4 What is the colour of an acetylene cylinder?
- Maroon
- Grey
- Green
- Black (1)
1.5 Starting devices on machinery are normally … in colour.
- red
- green
- black
- orange (1)
1.6 ONE of the following is NOT a safety device used in conjunction with guillotines.
- Self-adjusting guard
- Current scale
- Automatic sweep-away
- Electronic presence detection sensor (1)
[6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 State TWO safety precautions that should be observed before pressing a bearing from a shaft using a hydraulic press. (2)
2.2 Sketch and label a product layout. (2)
2.3 What is the reason for mounting a Perspex shield on a bench grinding machine? (1)
2.4 Study both pictures in FIGURE 2.4 and answer the questions that follow.
FIGURE 2.4
2.4.1 Name the machine shown in FIGURE 2.4. (1)
2.4.2 Identify the parts labelled A to D (4)
[10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1 Explain the term heat treatment. (2)
3.2 Tabulate the following heat treatment processes and identify ONE PROPERTY of each.
| PROCESS | PROPERTY | |
| 3.2.1 | Hardening | |
| 3.2.2 | Tempering | |
| 3.2.3 | Annealing | |
| 3.2.4 | Normalising |
3.2.1 Hardening
3.2.2 Tempering
3.2.3 Annealing
3.2.4 Normalising (4 x 1) (4)
3.3 Describe the specific purpose for case-hardening on mild steel. (2)
3.4 What effect does carbon have when hardening steel? (2)
3.5 Name TWO workshop tests which are used to make a distinction between materials. (2)
3.6 State TWO reasons for annealing as a heat-treatment process. (2)
[14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (SPECIFIC)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (4.1–4.14) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 4.15 A.
4.1 Which ONE of the following safety rules does not relate to an emission gas analyser?
- The hose connection must be straight and the valve on the condenser must be closed.
- You can only change the filter paper when it turns red.
- The vehicle under testing must not have leakage in the exhaust and vacuum system.
- Condensate must be blown out of the hoses and pickup probe regularly using compressed air. (1)
4.2 Which ONE of the following tests indicates the condition of the valves in the cylinder head of an engine?
- Fuel test
- Cooling system pressure test
- Cylinder leakage test
- Gas analyser (1)
4.3 In a four-cylinder engine, which of the firing order displayed below is NOT applicable?
- 1, 3, 4, 2
- 1, 2, 4, 3
- 1, 2, 3, 4
- 1, 3, 2, 4 (1)
4.4 What is the unit of torque?
- N.m
- N/m2
- N/m
- N/m3 (1)
4.5 When carrying out dynamic balancing, there are a number of factors that must be considered in order to achieve a correct wheel balance. Which of the following is NOT applicable?
- The plane of imbalance
- The speed of the unbalanced forces
- The extent of the unbalanced forces
- The sense of the direction of unbalanced forces (1)
4.6 The … is used to obtain different gear rations between the driving and the driven gear members of an automatic transmission system.
- brake system
- catalytic converter
- epicyclic gear system
- clutch system (1)
4.7 In an air induction system, the regulation of the idle speed by adjusting the air volume allowed to by-pass the closed throttle valve at cold start is caused by the …
- pressure regulator.
- throttle position sensor.
- mass air flow meter.
- idle speed control valve. (1)
4.8 There are different types of Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) used within the automobile trade to remove soot from the exhaust gases of a diesel engine. Which of the following is NOT applicable in this regard?
- Cordirite wall flow filter
- Silicon carbide wall flow filters
- Ceramic fibre filters
- Fuel filter (1)
4.9 Which of the following methods are commonly used to increase the output frequency of an alternator?
- Increase the turns of wire on the stationary coil
- Increase the magnetic fields
- Increase the rotational frequency at which the magnet rotates
- All of the above. (1)
4.10 If a man raises a bucket of water of mass 6 kg from a 10 m deep well in 30 seconds, what will be the power released?
- 20 W
- 15 W
- 18 W
- 30 W (1)
4.11 The … is an important factor that determines the thermal efficiency of an engine.
- Design of the intake manifold
- Type of mass air flow meter
- Combustion chamber design
- Fuel pump (1)
4.12 Which ONE of the following is an advantage of a variable geometry turbocharger to a non-variable type turbocharger?
- Throttling loss of the waste gate valve
- Higher air-fuel ratio and higher peak torque at low engine speed
- Poor boost
- Higher pressure developed at the exhaust manifold (1)
4.13 What is the gear ratio of a gear train with a driver gear rotating at 300 r/min and the driven gear rotating at 50 r/min?
- 5 : 1
- 6 : 1
- 3 : 5
- 2 : 1 (1)
4.14 Which device in the exhaust system converts the toxic gases produced in the combustion chamber of an engine into less harmful gases at the tail pipe?
- Catalytic converter
- Torque converter
- Exhaust manifold
- Exhaust valve seals (1)
[14]
QUESTION 5: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
5.1 FIGURE 5.1 below shows equipment that is commonly used during maintenance activities in an automotive workshop. Answer the questions that follow.
FIGURE 5.1
5.1.1 Identify the equipment in FIGURE 5.1. (1)
5.1.2 Label parts A–D. (4)
5.1.3 What is the purpose of the equipment in FIGURE 5.1? (2)
5.2 What is the function of a cylinder leakage tester? (2)
5.3 In point form, explain the set-up procedure to follow while performing a cylinder leakage test on a car engine. (6)
5.4 Why is it important to analyse the gas emission of an internal combustion engine during the course of maintenance in the workshop? (2)
5.5 What is the purpose of the following wheel alignment equipment?
5.5.1 Bubble gauge (2)
5.5.2 Turntable (3)
5.5.3 Periscopic optical alignment gauge (1)
[23]
QUESTION 6: ENGINES (SPECIFIC)
6.1 The diagram in FIGURE 6.1 below shows a component of an internal combustion engine. Answer the questions that follow.
FIGURE 6.1
6.1.1 Identify the diagram in FIGURE 6.1. (1)
6.1.2 Label part A–F. (6)
6.1.3 What is the function of the engine in FIGURE 6.1 above? (2)
6.1.4 What type of cylinder engine is applicable to the engine in figure 6.1? (1)
6.2 The diagram in FIGURE 6.2 below shows a friction face type vibration damper mounted to the front of the crankshaft of an internal combustion engine. Answer the questions that follow.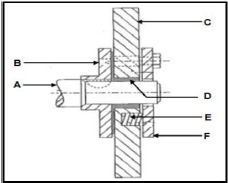
FIGURE 6.2
6.2.1 What is the function of the damper in FIGURE 6.2 above? (2)
6.2.2 Label parts A–F. (6)
6.3 List TWO types of engine cylinder configuration commonly used by automobile industries. (2)
6.4 State TWO factors that determine the firing order of an internal combustion engine. (2)
6.5 Briefly explain the following terms relating to a turbocharger component and operations:
6.5.1 Lag (2)
6.5.2 Boost (2)
6.5.3 Waste gate (2)
[28]
QUESTION 7: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
7.1 Briefly explain the following terms in the cylinder of an internal combustion engine:
7.1.1 Clearance volume (2)
7.1.2 Compression ratio (2)
7.2 Calculate the bore of an engine cylinder that has a compression ratio of 10 : 1 and a stroke of 85 mm if the clearance volume is 60 cm3. (6)
7.3 State THREE methods that can be used to increase the compression ratio of an internal combustion engine. (3)
7.4 If the bore in QUESTION 7.2 is increased by 4,8 mm, while keeping the stroke and the clearance volume constant at 85 mm and 60 cm3 respectively, what will be the new compression ratio of the engine? (5)
7.5 The following data was recorded during the course of carrying out a brake test on a four-stroke four-cylinder petrol engine:
- Brake arm length: 500 mm
- Mass registered on the scale: 35 kg
- Engine speed of rotation: 4 200 r/min
- Mean effective pressure: 1 100 kPa
- Cylinder bore: 95 mm
- Stroke length: 80 mm
Calculate the following:
7.5.1 Indicated power (6)
7.5.2 Torque (3)
7.5.3 Brake power (3)
7.5.4 Mechanical efficiency of the engine (2)
[32]
QUESTION 8: MAINTENANCE (SPECIFIC)
8.1 TABLE 8.1 below shows information regarding the result of the gas analysis of an internal combustion engine.
FAULTS | POSSIBLE CAUSES | CORRECTIVE MEASURE |
High hydrocarbon | 8.1.1 | 8.1.2 |
High carbon monoxide | 8.1.3 | 8.1.4 |
(4)
FIGURE 8.1
8.2 List THREE safety measures that must be followed during compression testing of an internal combustion engine. (3)
8.3 Give THREE manufactural specifications in determining the cause of leakage during a cylinder leakage test. (3)
8.4 Give THREE possible causes of a low oil pressure reading when conducting an oil pressure test on an internal combustion engine. (3)
8.5 Mention FOUR possible components where coolant could leak when using the cooling system pressure tester on a vehicle. (4)
8.6 Name TWO manufactural specifications that are needed when doing a cooling system pressure test. (2)
8.7 State TWO possible causes of each of the following when conducting a fuel pressure test on a vehicle fuel system:
8.7.1 Fuel pressure too low (2)
8.7.2 Fuel pressure too high (2)
[23]
QUESTION 9: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL (AUTOMATIC GEARBOX) (SPECIFIC)
9.1 What was the purpose of introducing automatic gearboxes in vehicles? (2)
9.2 State TWO main differences between an automatic gearbox and a manual gearbox. (2)
9.3 Give TWO major disadvantages of an automatic gearbox. (2)
9.4 What is the function of a torque converter? (2)
9.5 Briefly explain the following states of motion in a torque converter:
9.5.1 Stall speed (3)
9.5.2 Increasing speed (2)
9.6 Give TWO advantages of a torque converter in an automatic transmission system. (2)
9.7 A transmission control unit (TCU) is a device that controls modern electronic automatic transmissions through the use of sensors and an electronic control unit (ECU). State THREE advantages of this device. (3)
[18]
QUESTION 10: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL (AXLES AND STEERING GEOMETRY) (SPECIFIC)
10.1 State TWO main causes of camber wear in the suspension system of a motor vehicle. (2)
10.2 What is the difference between positive and negative camber? (4)
10.3 The diagram in FIGURE 10.3 below shows a wheel alignment angle of a vehicle suspension. Answer the questions that follow.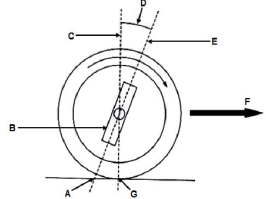
FIGURE 10.3
10.3.1 Identify the type of wheel alignment angle displayed in FIGURE 10.3 above. (2)
10.3.2 Label parts A–G in FIGURE 10.3 above. (7)
10.3.3 Give TWO advantages of the wheel alignment angle in FIGURE 10.3 above. (2)
10.4 State TWO factors to be taken into account before attempting a wheel alignment adjustment. (2)
10.5 What do you understand by the term static balance? (2)
10.6 State TWO pre-checks on wheels before they are balanced (2)
10.7 FIGURE 10.7 below shows the wheel alignment angle of a motor vehicle. Use the diagram to answer the questions that follow.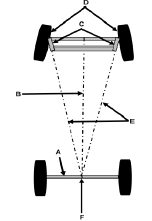
FIGURE 10.7
10.7.1 What type of wheel alignment angle is shown in FIGURE 10.7 above? (1)
10.7.2 Label parts A–F in FIGURE 10.7 above. (6)
10.7.3 What is the purpose of the diagram in FIGURE 10.7 above? (2)
[32]
TOTAL: 200
FORMULA SHEET FOR MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY (AUTOMOTIVE)

Mechanical Technology: Fitting and Machining Memorandum - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (GENERIC)
1.1 C
1.2 D
1.3 D
1.4 A
1.5 B
1.6 B (6 x 1) [6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 Safety Precautions
- Pressure gauges must be checked and tested regularly and adjusted or replaced if any malfunctioning occurs.
- Supporting pins that keep the platform at a desired height on the frame must be inspected for damage.
- Check the floor for oil and apparatus for leaks.
- The platform on which the workpiece rests must be rigid and square with the press cylinder. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.2 Product layout (2)
(2)
2.3 Perspex shield
- is installed to shield flying objects from harming the operator’s eye. (1)
2.4
2.4.1 Machine Identification
- Surface grinder (1)
2.4.2 Surface grinder parts label
- Workpiece
- Machine spindle
- Magnetic table
- Grinding wheel (4)
[10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1 Heat treatment refers to heating and cooling of metals under controlled conditions in their solid state so as to change their properties.(2)
3.2 Heat treatment properties
| PROCESS | PROPERTY | |
| 3.2.1 | Hardening | Very hard, high tensile strength and brittle |
| 3.2.2 | Tempering | Tough, hard |
| 3.2.3 | Annealing | Soft, ductile, low tensile strength |
| 3.2.4 | Normalising | Tough and machinable |
(4)
3.3 Purpose of case-hardening
- It hardens the surface.
- It provides a wear resistant surface.
- Strengthens core to withstand applied loads. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.4 Carbon effect
- Steel with low carbon content will not respond very much to the hardening process.(2)
3.5 Workshop tests on materials
- Sound test
- Bend test
- Filing test
- Machining test (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.6 Reasons for annealing
- To relieve internal stresses that may have been set up during other processes.
- To soften them in order to facilitate the machining processes.
- To make material ductile.
- Refine their grain structures.
- Reduce brittleness (Any 2 x 1) (2)
[14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (SPECIFIC)
4.1 A
4.2 D
4.3 A
4.4 A
4.5 A
4.6 B
4.7 A
4.8 C
4.9 D
4.10 B
4.11 B
4.12 A
4.13 A
4.14 B (14 x 1) [14]
QUESTION 5: TERMINOLOGY (LATHE AND MILLING MACHINE) (SPECIFIC)
5.1 Lathe Taper turning
5.1.1
- Set-over = ?−? × ?????ℎ ?? ?????????
2 ?????ℎ ?? ?????
= (75-50)/2 x 400 / 250
= 12.5 x 1.6
= 20 mm (2)
5.1.2
- tan ? = ?.
2 ?
= 12.5 / 250
= 0.05
= tan−1 0.05 ? 2
Θ = 5.724° (3)
5.2 Milling Cutters.
5.2.1
- – Helical milling cutter
- – Side and face Cutter/ also Accept Staggered tooth cutter
- – Dovetail
- – T–Slot
- – End mill (5)
5.3 Cutting Square Threads
5.3.1 Lead = Pitch x Number of Starts
- = 2 x 12 = 24 mm (1)
5.3.2 Mean Diameter = OD – 0,5 Pitch
- = 85 – 0,5 x 12
= 91 mm (2)
5.3.3 Tan θ = Lead / π x Dm
- Tan θ = 24 / 91
Θ = 14,77 ° (2)
5.4 Dividing Head components
- A – Index plate: the aim of the index plate is to enable one revolution of the crank to be further subdivided into fractions of a revolution, especially where the fraction is not a factor of 40.
- D – Worm-shaft with a Single – start worm engages with a worm gear with 40 teeth.
- E – Worm wheel/gear obtain a rotary movement of the spindle. (3)
[18]
QUESTION 6: TERMINOLOGY (INDEXING) (SPECIFIC)
6.1 GEAR CALCULATIONS:
6.1.1 Gang Milling: Simultaneously using several cutters of different diameters and forms on the arbor, workpiece can be machined to size in one movement of the milling machine table. (1)
6.1.2 Straddle Milling: consists of two side and face cutters, separated by spacing collars of required dimensions to produce parallel work in one cut. (1)
6.2 Procedure to cut external metric V-screw thread using compound slide method
- Set up the workpiece in the centre lathe and turn the part to be threaded to the required diameter of the thread.
- Set the compound slide to 30º to the left of the centre line of that cross- slide and set the cutting tool up accurately in the tool post.
- Consult the index plate of the quick-change gear box and shift the levers accordingly for the necessary pitch of the screw thread.
- Start the centre lathe and set the cutting tool at touching point on the workpiece.
- Move the cutting tool a short distance off, to clear the end of the workpiece and feed the compound slide 0.05 mm inwards.
- With the centre lathe revolving, engage the half nuts at the correct line on the threading dial, putting the first cut of the screw thread in progress.
- Stop the centre lathe and check the screw thread pitch with a screw thread pitch gauge. (Any 5 x 1) (5)
6.3 Definition of Indexing is the process of evenly dividing the circumference of a circular work piece into equally spaced divisions, such as in cutting gear teeth, cutting splines, milling grooves in the reamers and taps. (1)
6.4 Milling methods
- Up-cut milling
- Down-cut milling (2)
6.5 Differential indexing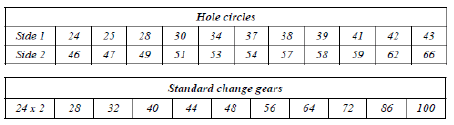
6.5.1 Indexing Required
- Indexing = 40
?
= 40/120
= 1 x 22
3 22
= 22/66
Indexing is 22 holes in a 66-hole circle (3)
6.5.2 Change of gears
- Gear ratio: ?????? = ?−? ? 40
?????? ? 1
= 120 −113 ? 40
120
= + 7 ? 8
3 8
= 56/24 - The driver gear has 56 teeth
- The driven gear has 24 teeth (5)
6.5.3
- The direction of motion is clockwise
- The crank handle will turn the same direction as index plate (2)
6.6 Dove tail Calculations
- Θ = 40°
α = 20° - x = r /(tan α)
= 10 /(tan 20)
= 27,47 mm - X = 80 + 2 R + 2 x
= 80 + 20 + (2 x 27,47)
= 154,949 mm (6)
6.7 Types of Milling machines
- Vertical milling machine
- Horizontal milling machine (2)
[28]
QUESTION 7: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
7.1 Hardness Testers
7.1.1 Brinell Hardness tester
- The Brinell Hardness Test involves indenting the test material with a piece hardened steel or carbide ball of 10 mm. The diameter of the indentation left in the test material is measured with a low-powered microscope.(3)

7.1.2 Rockwell Hardness tester
- Rockwell Hardness Test method involves indenting the test material with a diamond cone or hardened steel-ball indenter.(3)

7.2 Hardness measure of a metal.
- Resistance to penetration
- Elastic hardness
- Resistance to abrasion (Any 2 x 1) (2)
7.3 Screw thread micrometre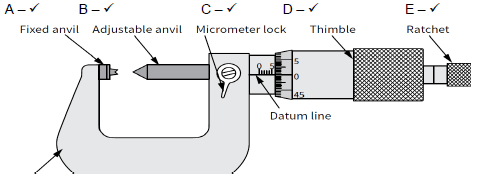 (5)
(5)
[13]
QUESTION 8: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
8.1 Resultant Force Calculations: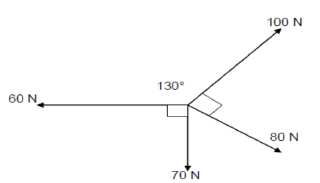
- Xcom = 100 cos 50 + 80 cos 40 - 60
= 65,56 N (2) - Ycom = 100sin 50 – 80 sin 40 - 70
= 95,18 N (2) - R = √(?2 + ?²)
R = 115.576 N
Tan θ = y/x
Tan Θ = 95.18/65.56
Θ = 55.44
= 55.44 °
Equilibrant = Resultant BUT IN THE OPPOSITE DIRECTION
Equilibrant = 115.567 N at 235.44 º (5)
8.2 Moments
- Converting the UDL to Point Load
4 x 10 = 40 kN @ 3 m from the left hand end
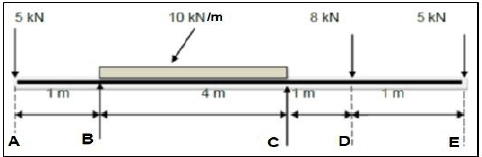
Calculation the Reactions by taking moments:
- CLOCKWISE MOMENTS = ANTICLOCK-WISE MOMENTS
(RC x 4) + (5 x 1) = (5 x 6) + (40 x 2) + (8 x 5)
Rc = 36,25 kN
(RB x 4) + (5 x 2) + (8 x 1) = (40 x 2) + (5 x 5)
RB = 21,75 kN (5)
8.3 Stress Calculations
8.3.1 Tensile Stress Calculations
F = 40 kN; D = 98, d = 67mm: L = 80 mm: E = 90 PGa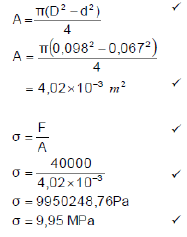 (5)
(5)
8.3.2 The Strain calculations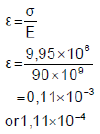 (3)
(3)
8.3.3 Change in length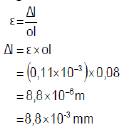 (3)
(3)
8.4 Stress/Strain diagram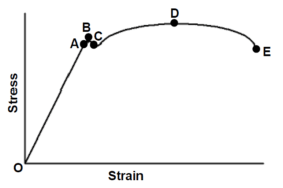
- – Limit of Proportionality
- – Elastic limit
- – Yield point
- – Maximum Force/Point
- – Point of Fracture (6)
8.5 FOS stands for Factor Of Safety or Safety Factor. (2)
[33]
QUESTION 9: MAINTENANCE
9.1 Material Classifications
9.1.1 PVC – Thermoplastic (1)
9.1.2 Glass fibre – Thermo-setting plastic (1)
9.1.3 Nylon – Thermoplastic (1)
9.2 Reasons for using cutting fluid when working on the centre lathe.
- It prolongs the life of a cutting tool.
- It prevents the shavings or metal chips from sticking and fusing to the cutting tool.
- It will carry away the heat generated by the turning process.
- It flushes away shavings/metal chips.
- It improves the quality of the finish of the turned surface. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.3 Gear Drives Maintenance.
- Checking and replenishment of lubrication levels
- Ensuring that gears are properly secured to shafts
- Cleaning and replacement of oil filters
- Reporting excessive noise and wear, vibrations and overheating for expect attention. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.4 Reasons for the use of carbon fibre
- It is light in weight.
- It is tougher and stronger.
- It can be bent to any shape when heated above 150 ºC. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.5 ONE property and ONE use of each composite
Composite | Property | Uses | |
9.5.1 | Teflon |
| Orthopaedic and prosthetic appliances, hearing aids, joints, upholstery, electric insulation and non-stick coating pans (Any 1) |
9.5.2 | Vesconite |
|
|
9.5.3 | Baskelite |
|
|
(6)
9.6
- Contact pressure
- Temperature
- Sliding velocity
- Type of a lubricant
- Surface roughness (Any 3 x 1) (3)
[18]
QUESTION 10: JOINING METHODS (SPECIFIC)
10.1 Square Thread Calculations: T = 48 mm ; m = 3
10.1.1
- PCD = T x m
= 48 x 3 = 144 mm (2)
10.1.2 Add = Module = 3 mm (1)
10.1.3
- Clearance = 0,157 x 3
= 0,471 mm (2)
10.1.4
- Ded = 1,157 x 3
= 3,471 mm (2)
10.1.5
- OD = PCD + 2 x 3
= 150 mm (2)
10.1.6
- Circular Pitch
= π x m
= π x 3 = 9,424 mm (1)
10.2 Left-hand square screw thread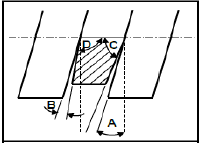
- – Leading Angle (1)
- – Following or Trailing Angle (1)
- – Clearance (1)
- – Helix angle (1)
10.3 A multi-start thread allows for a faster travel or movement and is more efficient as it loses less power through friction compared to single start thread. (2)
10.4 Screw Thread fit is a combination of allowances and tolerances and a measure of tightness or looseness between the bolt and nut. (2)
[18]
QUESTION 11: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL (DRIVE SYSTEMS) (SPECIFIC)
11.1 Rotational velocity is where a body rotates (spin) around its axis. It is the rotation rate or how fast a body revolves or turns. It is measured in radians
per second. (2)
11.2 Hydraulic system calculations
11.2.1 Calculate the Fluid pressure 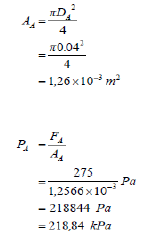 (4)
(4)
11.2.2 Load on the piston B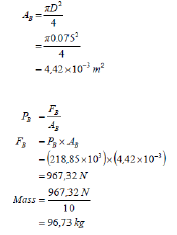 (4)
(4)
11.2.3 Hydraulic System Applications
- Machine tools, motor vehicle, hydraulic jacks (Any 2 x 1) (2)
11.3 Hydraulics refers to the transmission and control of forces and movement by means of fluid. Fluid (generally oil) is used to transmit energy. (2)
11.4 Belt Drive Calculations
- Nmotor x Dmotor = Nblade x Dblade
130 x 1205 = 385 x Dblade
Dblade = 406,883 pm (2)
11.5 Pneumatic symbols
11.5.1 | Pump |
|
11.5.2 | Air receiver | |
11.5.3 | Filter |
11.6
11.6 Gear-Drive system calculations:
Data: (6)
11.6.1 Rotation speed of Electric motor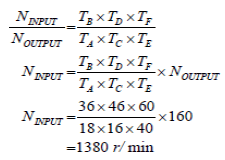 (3)
(3)
11.6.2 Velocity ratio
- VR = NINPUT
NOUTPUT
= 1380
160
= 8,625:1
- 863:1 (2)
11.6.3 Driven will rotate Clockwise (1)
[28]
TOTAL: 200
Mechanical Technology: Fitting and Machining Questions - Grade 12 September 2021 Preparatory Exams
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your NAME and SURNAME on the ANSWER BOOK.
- Read ALL the questions carefully.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Show ALL calculations and units. Round off final answers to TWO decimal places.
- Candidates may use non-programmable scientific calculators and drawing instruments.
- The value of gravitational force should be taken as 10 m/s2.
- All dimensions are in millimetres, unless stated otherwise in the question.
- A formula sheet is attached to the question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
- Use the criteria below to assist you in managing your time.
QUESTION | CONTENT | MARKS | TIME IN MINUTES |
GENERIC | |||
1 | Multiple-choice questions | 6 | 6 |
2 | Safety | 10 | 10 |
3 | Materials | 14 | 10 |
SPECIFIC | |||
4 | Multiple-choice questions | 14 | 10 |
5 | Terminology (Lathe and Milling Machine) | 18 | 20 |
6 | Terminology (Indexing) | 28 | 25 |
7 | Tools and Equipment | 13 | 10 |
8 | Forces | 33 | 33 |
9 | Maintenance | 18 | 12 |
10 | Joining Methods | 18 | 12 |
11 | Systems and Control (Drive Systems) | 28 | 28 |
TOTAL: | 200 | 180 | |
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (GENERIC) (COMPULSORY)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the correct answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1–1.6) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.7 A.
1.1 Which ONE of the following safety procedures is applicable to the maintenance/operation of a hydraulic press?
- Do not apply a wrench to revolving work.
- Guards could be removed when pressing soft material.
- Pressure gauges must be tested regularly and adjusted or replaced if any malfunctioning occurs.
- Use the machine table as an anvil. (1)
1.2 What is the best way of dealing with a hazard to ensure others are not put at risk?
- Remove it immediately
- Leave it for the supervisor to sort out
- Not placing a barrier tape around it
- Display a notice or warning sign (1)
1.3 Which of the following is a safety precaution related to a workbench?
- The tool rest must not be more than 3 mm from the grinding wheel.
- Make sure the chuck is correctly tightened.
- Stand on the side when switching on the machine.
- Keep rolling stock or items away from the bench end. (1)
1.4 What is the colour of an acetylene cylinder?
- Maroon
- Grey
- Green
- Black (1)
1.5 Starting devices on machinery are normally … in colour.
- red
- green
- black
- orange (1)
1.6 ONE of the following is NOT a safety device used in conjunction with guillotines.
- Self-adjusting guard
- Current scale
- Automatic sweep-away
- Electronic presence detection sensor (1)
[6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 State TWO safety precautions that should be observed before pressing a bearing from a shaft using a hydraulic press. (2)
2.2 Sketch and label a product layout. (2)
2.3 What is the reason for mounting a Perspex shield on a bench grinding machine? (1)
2.4 Study both pictures in FIGURE 2.4 and answer the questions that follow.
FIGURE 2.4
2.4.1 Name the machine shown in FIGURE 2.4. (1)
2.4.2 Identify the parts labelled A to D. (4)
[10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1 Explain the term heat treatment. (2)
3.2 Tabulate the following heat treatment processes and identify ONE PROPERTY of each.
| PROCESS | PROPERTY |
| 3.2.1 Hardening | |
| 3.2.2 Tempering | |
| 3.2.3 Annealing | |
| 3.2.4 Normalising |
(4 x 1) (4)
3.3 Describe the specific purpose for case-hardening mild steel. (2)
3.4 What effect does carbon have when hardening steel? (2)
3.5 Name TWO workshop tests which are used to make a distinction between materials. (2)
3.6 State TWO reasons for annealing as a heat-treatment process. (2)
[14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (SPECIFIC)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the correct answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (4.1–4.14) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 4.17 A.
4.1 Which lathe operation is shown in FIGURE 4.1?
FIGURE 4.1
- Straight turning
- Internal parallel boring
- Thread cutting
- Reaming (1)
4.2 Identify the type of milling operation shown in FIGURE 4.2.
FIGURE 4.2
- Plain straight-tooth cutter
- Straight-tooth side-milling cutter
- Slitting saw
- Up-cutting milling (1)
4.3 Which ONE of the following lathe components must be engaged when you are cutting threads?
- Lead screw
- Feed shaft
- Cross slide dial
- Spindle-speed gear levers (1)
4.4 What does the abbreviation CNC stand for?
- Computer Numerical Control
- New Control Coding
- Company Numbers Control
- None of the above (1)
4.5 What is the deformation of a bar that is 0,73 m long when the strain is 0,5 x 10‾³?
- 0,365 mm
- 0,036 mm
- 0,653 mm
- 0,498 mm (1)
4.6 The main reason for performing a hardness test on engineering materials is to determine the …
- elasticity of the material.
- resistance of the material against denting
- corrosion of the material.
- fluidity of the metal. (1)
4.7 What does the symbol “D” denote in the Brinell hardness test shown in FIGURE 4.7?
FIGURE 4.7
- Indentation diameter
- Hardness number
- Test piece
- Force applied (1)
4.8 Which ONE of the following is categorised as a mechanical drive?
- Screw drive
- Lead screw
- Gear drive
- White metal (1)
4.9 What will be the drill size for a M12 x 1,5 screw thread?
- 13,5 mm
- 1,5 mm
- 12 mm
- 10,5 mm (1)
4.10 A workpiece must have 13 gear teeth machined on its circumference. What type of indexing would you perform on this gear-blank?
- Angular indexing
- Simple indexing
- Rapid indexing
- New indexing (1)
4.11 If the module of a spur gear is 3 mm, what will be the addendum?
- 6
- 3
- 1,5
- 9 (1)
4.12 As shown in FIGURE 1.4, determine what the stress in a hollow pipe with a 50 mm outside diameter and a 30 mm inside diameter will be if a load of 80 N is applied.
FIGURE 4.12
- 63,70 kPa
- 63,70 MPa
- 63,70 Pa
- 63,70 GPa (1)
4.13 There are different types of machine processes in manufacturing. Which process would you use to cut an internal thread of a hole?
- Tapping
- Boring
- Slotting
- Spot facing (1)
4.14 Identify the symbol, shown in FIGURE 4.14 below, which relates to a pneumatic system.
FIGURE 4.14
- Valve
- Filter
- Compressor
- Motor (1)
[14]
QUESTION 5: TERMINOLOGY (LATHE AND MILLING MACHINE) (SPECIFIC)
5.1 FIGURE 5.1 shows a tapered shaft which is to be turned to the dimensions given.
FIGURE 5.1
5.1.1 Calculate the amount of tailstock set-over. (2)
5.1.2 Calculate the included angle of the tapered portion in degrees and minutes. (3)
5.2 FIGURE 5.2 shows pictures of milling cutters.
FIGURE 5.2
5.2.1 Name the milling cutters A–E. (5)
5.3 A circular shaft with an outside diameter of 85 mm must be machined with a two-start square thread of 12 mm pitch. Calculate the following:
5.3.1 The lead of the thread (1)
5.3.2 The mean diameter of the thread (2)
5.3.3 The helix angle of the thread (2)
5.4 FIGURE 5.4 below shows a drawing of a dividing head of a milling machine.
FIGURE 5.4
Explain the functions of parts A, D and E. (3)
[18]
QUESTION 6: TERMINOLOGY (INDEXING) (SPECIFIC)
6.1 Explain the following milling processes:
6.1.1 Gang milling (1)
6.1.2 Straddle milling (1)
6.2 Explain, step by step, the procedure to cut an external metric V-screw thread with a pitch of 2 mm on a centre lathe using the compound slide method. (5)
6.3 Define the term indexing as applied to milling processes. (1)
6.4 State the TWO milling methods. (2)
6.5 Calculate the differential indexing of a gear with 111 teeth. Hence determine:
6.5.1 The indexing required (Hint: Choose 120 divisions) (3)
6.5.2 The changed gears required for the dividing head (5)
6.5.3 What the meaning is of the positive (+) sign and the negative (-) sign for the change of gears (2)
6.6 The drawing in FIGURE 6.7 shows two precision rollers placed in an internal dovetail. Use the given information to answer the question that follows.
FIGURE 6.7
Calculate the measurement of the widest part (X) of the dovetail drawing. (6)
6.7 Name TWO common types of milling machines. (2)
[28]
QUESTION 7: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
7.1 Explain how the following hardness tests are performed:
7.1.1 Brinell hardness tester (3)
7.1.2 Rockwell hardness tester (3)
7.2 Name the TWO ways in which hardness is measured. (2)
7.3 Study the screw thread micrometres shown in FIGURE 7.3.
FIGURE 7.3
7.3 Label parts A–E. (5)
[13]
QUESTION 8: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
8.1 FIGURE 8.1 below shows a system of forces with four concurrent applied forces.
FIGURE 8.1
Calculate:
8.1.1 The sum of the horizontal components in magnitude and direction (2)
8.1.2 The sum of the vertical components in magnitude and direction (2)
8.1.3 The magnitude and direction of the resultant force and its equilibrant (5)
8.2 The diagram in FIGURE 8.2 below shows a beam with three vertically applied point loads of 5 kN, 8 kN and another 5 kN and also a 10 kN/m uniformly distributed load for a span of 4 m between supports B and C.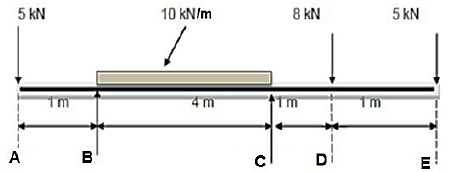
FIGURE 8.2
Calculate the magnitude of reactions RB and RC. (5)
8.3 A load of 40 kN is exerted on a brass bush used in a hydraulic press. The outer and inner diameters of the bush are 98 mm and 67 mm respectively. The original length of the bush is 80 mm and Young's modulus for brass is 90 GPa.
Calculate the:
8.3.1 Stress in the bush material (5)
8.3.2 Strain (3)
8.3.3 Change in length (3)
8.4 Draw and label the stress/strain diagram. (6)
8.5 What does the abbreviation FOS stand for in relation to stress calculations? (2)
[33]
QUESTION 9: MAINTENANCE (SPECIFIC)
9.1 Classify the following materials as either thermoplastic composites or thermo hardened (thermosetting) composites:
9.1.1 PVC (1)
9.1.2 Glass fibre (1)
9.1.3 Nylon (1)
9.2 Why is it essential to use a cutting fluid on a milling machine or centre lathe? State TWO reasons.(2)
9.3 How do you conduct preventative maintenance of gear system? State TWO. (2)
9.4 Give TWO reasons for using carbon fibre in the manufacture of bicycle frames. (2)
9.5 In tabulated form, compare ONE property and ONE use of the following plastic materials:
9.5.1 Teflon (2)
9.5.2 Vesconite (2)
9.5.3 Bakelite (2)
9.6 Name THREE factors that influence the coefficient of friction. (3)
[18]
QUESTION 10: JOINING METHODS (SPECIFIC)
10.1 A spur gear has 48 teeth and a module of 3. Determine, by means of calculations, the following:
10.1.1 The pitch-circle diameter (2)
10.1.2 The addendum (1)
10.1.3 The clearance (2)
10.1.4 The dedendum (2)
10.1.5 The outside diameter of the gear (2)
10.1.6 Circular pitch (1)
10.2 Draw a neat sketch of a metric square-screw thread. Indicate the following on the sketch:
10.2.1 Leading angle (1)
10.2.2 Following angle (1)
10.2.3 Clearence (1)
10.2.4 Helix angle (1)
10.3 Why would a multi-start thread be preferred mostly to a single-start thread? (2)
10.4 Describe what is meant by screw thread fit. (2)
[18]
QUESTION 11: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL (SPECIFIC)
11.1 Define rotational velocity of chains. (2)
11.2 A hydraulic system is used to lift a lathe. The specifications of the system are presented diagrammatically in FIGURE 11.2.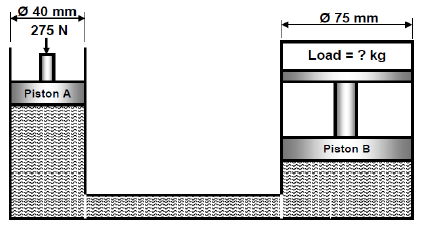
FIGURE 11.2
Calculate the following:
11.2.1 The fluid pressure in the hydraulic system when the system is in equilibrium (4)
11.2.2 Load in kilograms that can be lifted by piston B if a force of 275 N is exerted upon piston A (4)
11.2.3 State TWO applications of the system above. (2)
11.3 Define what is meant by hydraulics. (2)
11.4 A power saw’s motor has a pulley, 130 mm in diameter, that turns at 1 205 rpm. The speed at which the driven pulley drives the saw blades is 385 rpm. Calculate the diameter of the driven pulley. (2)
11.5 Make neat, freehand sketches of the ISO symbols representing the following pneumatic components:
11.5.1 Pump (2)
11.5.2 Air receiver (2)
11.5.3 Filter (2)
11.6 FIGURE 11.6 below shows a gear-drive system. Driver gear A on the shaft of the electric motor has 18 teeth that mesh with gear B with 36 teeth on a counter shaft. On the counter shaft is another driver gear, C, with 16 teeth that mesh with gear D with 46 teeth. The second counter shaft has driver gear E with 40 teeth, which drives gear F with 60 teeth on the output shaft.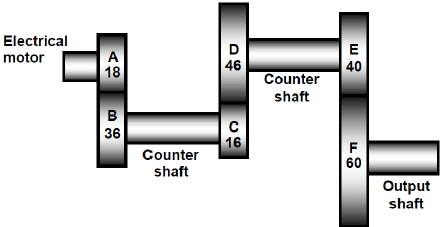
FIGURE 11.6
Calculate the:
11.6.1 Rotation frequency of the input shaft on the electric motor if the output shaft rotates at 160 r/min (3)
11.6.2 Velocity ratio between the input and output shaft (2)
11.6.3 In which direction will the driven shaft rotate if the driver gear rotates anti-clockwise? (1)
[28]
TOTAL: 200
FORMULA SHEET FOR MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY (FITTING AND MACHINING)