Adele
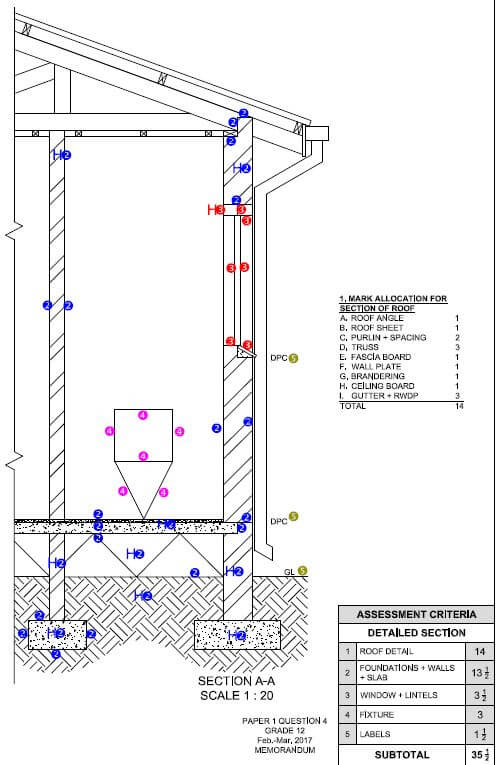
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
MEMORANDUM
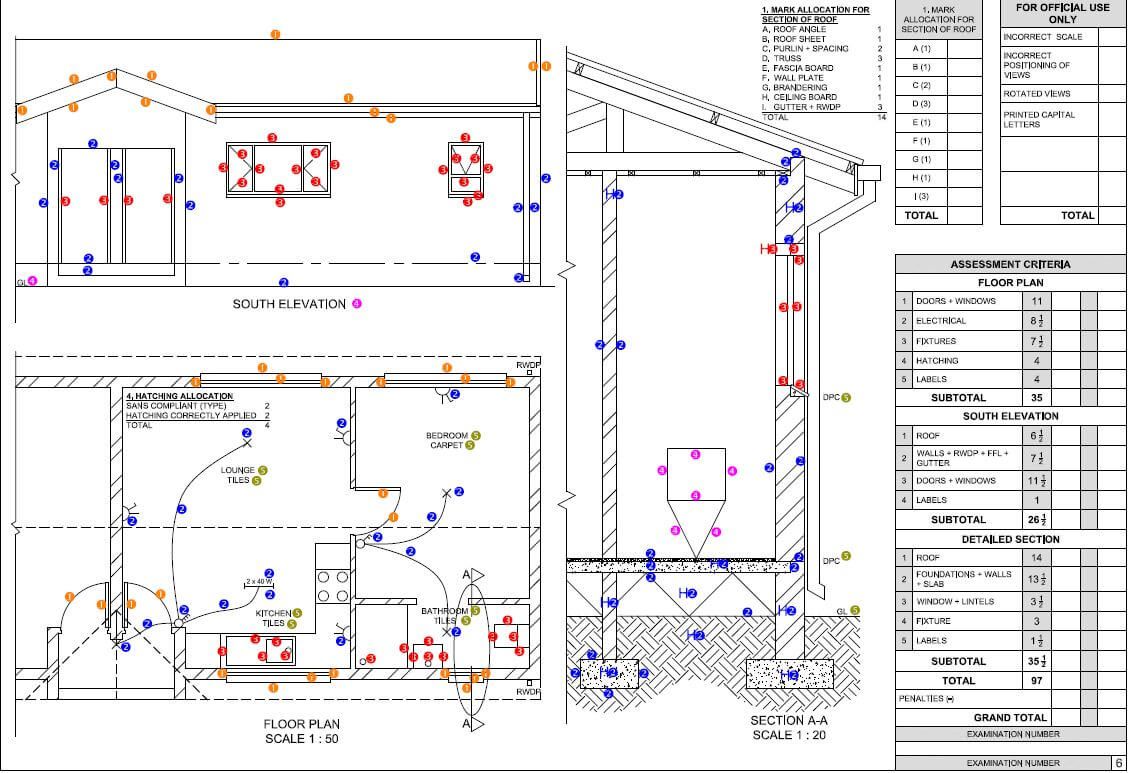
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SEVEN questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Sketches and diagrams must be large, neat and fully labelled.
- Show ALL calculations and round off answers correctly to TWO decimal places.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show the units for all answers of calculations.
- A formula sheet is provided at the end of this question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY
1.1 State TWO unsafe acts that may lead to an accident. (2)
1.2 Distinguish between an unsafe act and an unsafe condition. (2)
1.3 State FOUR points in the procedure that should be followed when a person is experiencing an electric shock. (4)
1.4 Explain why a person under the influence of alcohol may not operate machinery in the workplace. (2)
[10]
QUESTION 2: THREE-PHASE AC GENERATION
2.1 Define the following terms:
2.1.1 Active power (2)
2.1.2 Reactive power (2)
2.2 Draw a neat, labelled diagram that represents the waveforms of a three phase AC-generated system. (5)
2.3 A balanced three-phase inductive load is connected in delta across a three phase supply. The load draws a current of 30 A from the 380 V/50 Hz supply. It has a power factor of 0,75 lagging.
Given:
IL = 30 A
VL = 380 V
p.f. = 0,75 lagging
Calculate the:
2.3.1 Phase current (3)
2.3.2 Impedance of the load (3)
2.3.3 State what will happen to the current drawn by the load if the power factor of the load is improved. (1)
2.3.4 State ONE economic benefit of improving the power factor. (1)
2.4 The two-wattmeter method is used to measure the power drawn by an induction motor. The readings on the wattmeters are 100 W and 250 W respectively. Calculate the total input power.
Given:
P1 = 100 W
P2 = 250 W (3)
[20]
QUESTION 3: THREE-PHASE TRANSFORMERS
3.1 State the purpose of a transformer. (1)
3.2 Name TWO cooling methods used in a transformer. (2)
3.3 State where a delta-star transformer connection is used. (1)
3.4 FIGURE 3.1 below represents the delta-star connection of a three-phase transformer.
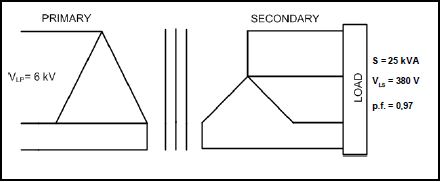 |
| FIGURE 3.1: THREE-PHASE TRANSFORMER |
Given:
S = 25 kVA
VLP = 6 kV
VLS = 380 V
p.f. = 0,97 lagging
Calculate the:
3.4.1 Secondary line current (3)
3.4.2 Primary line current (3)
3.4.3 Primary phase current (3)
3.4.4 Transformation ratio (3)
3.5 Explain why the secondary turn of a distribution transformer is connected in star. (2)
3.6 State why regular maintenance of transformers is important. (2)
[20]
QUESTION 4: THREE-PHASE MOTORS AND STARTERS
4.1 State ONE advantage of a three-phase induction motor over a single-phase induction motor. (1)
4.2 Describe why it is important that the rotor of a motor rotates freely before it is energised. (2)
4.3 State TWO electrical tests that must be done on a motor before it is energised. (2)
4.4 Describe ONE condition that may exist if there is an electrical connection between the rotor and the stator of a three-phase induction motor. (2)
4.5 State TWO losses that occur in a three-phase motor. (2)
4.6 A three-phase delta-connected motor, rated at 15 kVA, is connected to a 380 V/50 Hz supply. The motor has a power factor of 0,8 and an efficiency of 95%.
Given:
VL = 380 V
S = 15 kVA
f = 50 Hz
p.f. = 0,8
ŋ = 95%
Calculate the:
4.6.1 Output power of the motor at full load if the motor is 100% efficient (3)
4.6.2 Output power of the motor at full load at 95% efficiency (3)
4.6.3 The current drawn by the motor (3)
4.7 Answer the following questions with reference to a three-phase induction motor.
4.7.1 State what will happen to the output power of the motor if the efficiency of the motor has been improved. (1)
4.7.2 Describe what will happen to the reactive power of the motor if the power factor of the motor has been improved. Structure your answer with reference to voltage, current and power. (3)
4.8 FIGURE 4.1 below represents the control circuit of a star-delta starter.
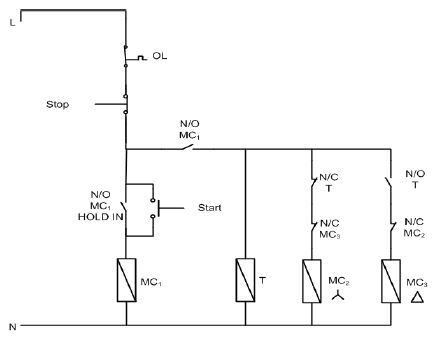 |
| FIGURE 4.1: CONTROL CIRCUIT OF A STAR-DELTA STARTER |
4.8.1 Describe how a star-delta starter reduces the starting current of the motor. (3)
4.8.2 State why it is necessary to reduce the starting current of a three phase induction motor. (3)
4.8.3 Describe the function of the overload unit in the starter. (3)
4.8.4 Describe the interlocking used in the circuit to prevent the motor from being switched into delta while still connected in star. (5)
4.9 Describe why induction motors must be supplied with a constant frequency. (3)
4.10 State how the number of pole pairs of an induction motor affects the speed of a motor. (1)
[40]
QUESTION 5: RLC
5.1 State TWO factors that influence the value of the reactance of a coil when connected across an AC supply. (2)
5.2 State how an increase in capacitance will affect the reactance of a capacitor. (1)
5.3 Explain the term resonance with reference to an RLC circuit. (3)
5.4 Refer to the diagram in FIGURE 5.1 below.
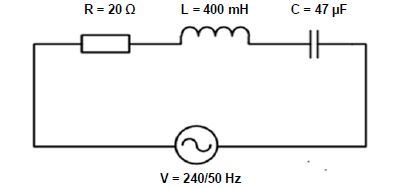 |
| FIGURE 5.1: RLC SERIES CIRCUIT |
Given:
R = 20 Ω
L = 400 mH
C = 47 µF
V = 240 V
f = 50 HZ
Calculate the:
5.4.1 Inductive reactance of the inductor (3)
5.4.2 Capacitive reactance of the capacitor (3)
5.4.3 Impedance of the circuit (3)
5.4.4 Q-factor of the circuit when the circuit is at resonance (3)
5.5 State, with a reason, whether the circuit in FIGURE 5.1 is more inductive or more capacitive. (2)
[20]
QUESTION 6: LOGIC
6.1 Answer the following questions in respect of PLCs.
6.1.1 Write the abbreviation PLC in full. (1)
6.1.2 State TWO advantages of a PLC system over relay logic. (2)
6.1.3 Name TWO input devices that may be connected to a PLC. (2)
6.1.4 Name ONE component that is still used to switch high-current devices on or off. (1)
6.1.5 Define the term program in relation to a PLC. (3)
6.1.6 Name ONE device used to control a PLC remotely. (1)
6.1.7 Draw a block diagram to illustrate the components of a PLC system. (5)
6.2 Simplify the following expression with Boolean algebra: ![]() (6)
(6)
6.3 Draw a three-variable Karnaugh map and simplify the following Boolean expression: ![]() (8)
(8)
6.4 Refer to the circuit in FIGURE 6.1 below.
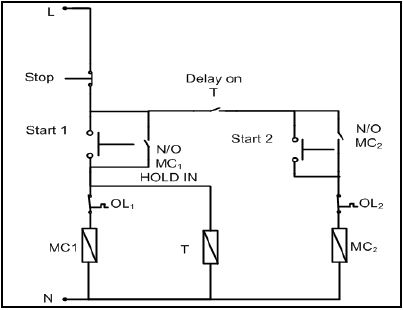 |
| FIGURE 6.1: SEQUENCE STARTER WITH A TIMER |
6.4.1 Draw the ladder logic diagram that would execute the same function in a PLC system. (10)
6.4.2 Name ONE electrical application of FIGURE 6.1. (1)
[40]
QUESTION 7: AMPLIFIERS
7.1 Draw and label the symbol of an operational amplifier (op amp). (5)
7.2 State THREE characteristics of an ideal op amp. (3)
7.3 Describe why op amp circuits are placed in an integrated circuit (IC) package. (2)
7.4 Describe what the term negative feedback means in respect of an op amp. (3)
7.5 State TWO advantages of negative feedback. (2)
7.6 Refer to FIGURE 7.1 below and draw the output of an ideal op amp in relation to the input waveforms shown. (3)
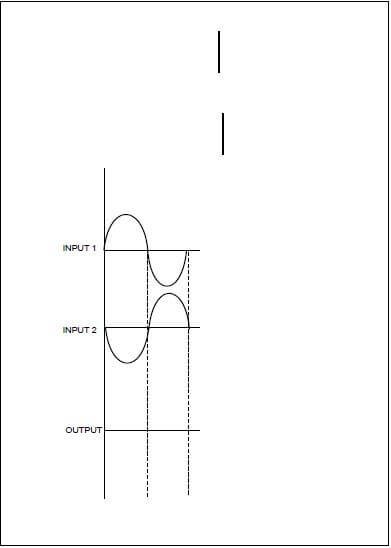 |
| FIGURE 7.1: OP AMP |
7.7 Refer to FIGURE 7.2 below and answer the questions that follow. +Vcc
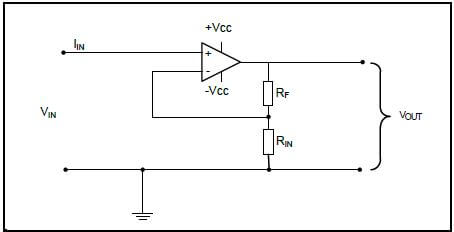 |
| FIGURE 7.2: NON-INVERTING OP AMP CIRCUIT |
7.7.1 Draw the input and output waveforms on the same Y-axis, as shown in FIGURE 7.3 below. (3)
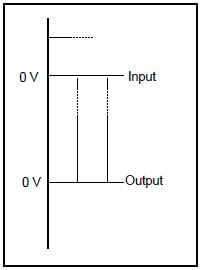 |
| FIGURE 7.3: OUTPUT WAVEFORM |
7.7.2 Calculate the voltage gain if the feedback resistance is 12 kΩ and the input resistor has a value of 3,3 kΩ.
Given:
RF = 12 kΩ
RIN = 3,3 kΩ
VIN = 6 V (3)
7.7.3 Calculate the output voltage if an input signal of 6 V is applied to the op amp. (3)
7.7.4 Describe what happens to the gain of the op amp if the value of RF is decreased. (2)
7.8 Refer to FIGURE 7.4 below and answer the questions that follow.FIGURE
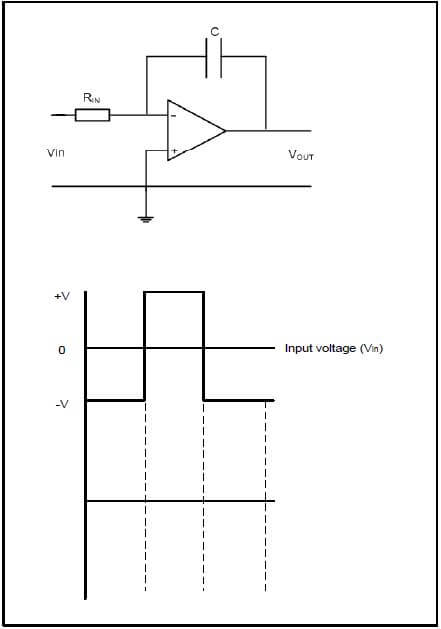 |
| 7.4: INTEGRATOR OP AMP CIRCUIT |
7.8.1 Draw and label the given input waveform and, in line directly below it, draw the output waveform. (6)
7.8.2 Describe the function of the capacitor in this op amp circuit. (3)
7.9 Refer to FIGURE 7.5 below and answer the questions that follow.
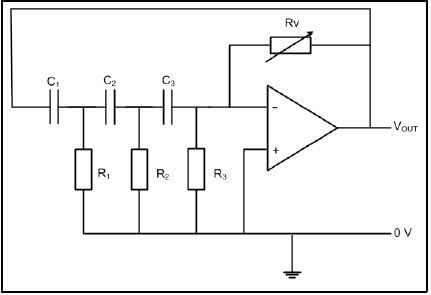 |
| FIGURE 7.5: RC PHASE-SHIFT OSCILLATOR CIRCUIT |
Given:
R1 = R2 = R3 = 12 kΩ
C1 = C2 = C3 = 260 nF
7.9.1 State TWO applications of the oscillator. (2)
7.9.2 Calculate the oscillating frequency of the oscillator. (3)
7.9.3 Identify the output waveform of the oscillator. (1)
7.9.4 State the type of feedback used in this oscillator. (1)
7.10 Describe the function of the dual DC supply to an op amp. (3)
7.11 Name the output waveform of a differentiator circuit when a triangular input wave is applied. (1)
7.12 State ONE application of a differentiator. (1)
[50]
TOTAL: 200
FORMULA SHEET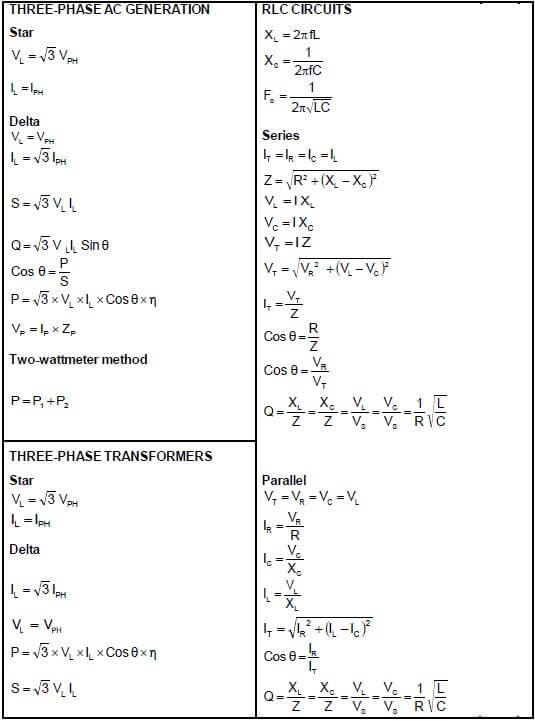
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
INSTRUCTIONS TO MARKERS
- All questions with multiple answers imply that any relevant, acceptable answer should be considered.
- Calculations:
2.1 All calculations must show the formula/e
2.2 Substitution of values must be done correctly
2.3 All answers MUST contain the correct unit to be considered
2.4 Alternative methods must be considered, provided that the same answer is obtained
2.5 Where an erroneous answer could be carried over to the next step, the first answer will be deemed incorrect. However, should the incorrect answer be carried over correctly, the marker has to re calculate the values, using the incorrect answer from the first calculation. If correctly used, the learner should receive the full marks for subsequent calculations - The memorandum is only a guide with model answers. Alternative interpretations must be considered, and marked on merit. However, this principle should be applied consistently throughout the marking session at ALL marking centres.
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY
1.1
- Working on a live system with exposed conductors. ✔
- Working with portable electric equipment that is not insulated correctly. ✔
- Using electrical machines without using the required safety equipment or clothing. (2)
1.2
- An unsafe act is the performance of a task or other activity that is conducted in a manner that may threaten the health and/or safety of workers✔
- An unsafe condition is a condition in the work place that may cause property damage and or injury✔ (2)
1.3
- Do not touch the victim with your bare hands until the supply is turned off. ✔ Switch off the mains supply. ✔
- Call a teacher or medical person for help. ✔
- If the electricity cannot be switched off and the victim is still in contact with it push the wire away with an insulated object. ✔ (4)
- 1.4 No person may enter or remain in a workplace under the influence of drugs as he may place himself and other persons in danger✔ while operating machinery. ✔ (2)
[10]
QUESTION 2: THREE-PHASE AC GENERATION
2.1
2.1.1 The actual power consumed✔ by the load✔ (2)
2.1.2
- The power lost✔ in the form of heat✔
- The power lost to overcome the reactive component of the load (2)
2.2 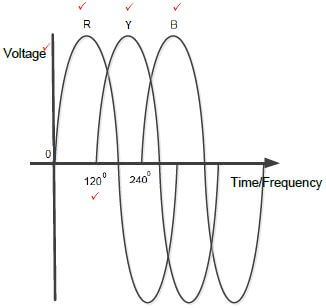 (5)
(5)
2.3
2.3.1
IP = IL ✔
√3
= 30 ✔
√3
= 17,32 A ✔ (3)
2.3.2
Z = VP ✔
IP
= 380 ✔
17,32
= 21,93Ω ✔ (3)
2.3.3 If the power factor is improved, the load will draw less current✔ (1)
2.3.4 Cost saving as consumers use less current✔ (1)
2.4
PT = P1 + P2 ✔
= 100 + 250 ✔
= 350 W ✔ (3)
QUESTION 3:THREE-PHASE TRANSFORMERS
3.1 The purpose of the transformer is to step down or step up an AC voltage✔ (1)
3.2
- Air-cooled ✔
- Water-cooled ✔
- Oil-cooled (2)
3.3 Distribution system to the end consumer✔ (1)
3.4
3.4.1
ILS = S ✔
√3VLS
= 25000 ✔
√3 × 380
= 37,98 A ✔ (3)
3.4.2
ILP = S ✔
√3VLP
= 25000 ✔
√3 × 6000
= 2,40A ✔ (3)
3.4.3
IPh = IL ✔
√3
= 2,40 ✔
√3
= 1,38 A ✔ (3)
3.4.4
NP = IPh(S) ✔
NS IPh(P)
= 37,98 ✔
1,38
= 27,5 : 1
TR ≈ 27 : 1 ✔ (3)
3.5 It can serve both single phase✔ and three-phase loads✔ because of the availability of neutral point (2)
3.6
- Regular maintenance will maintain the efficiency of the transformer✔ and increase the lifespan of the transformer✔
- To identify and detect any abnormal function of the transformer (2)
[20]
QUESTION 4: THREE-PHASE MOTORS AND STARTERS
4.1
- They require less maintenance as they do not have as many parts as a single phase motor✔
- For the same size frame as a single phase motor they deliver a higher torque. (1)
4.2 If the rotor is not rotating freely and switched on it may cause extensive damage✔ to the motor or the operator may get injured ✔ (2)
4.3
- Check that all electrical connections are secure ✔
- Check the insulation resistance between windings ✔
- Check the insulation resistance between windings and earth (2)
4.4 Electrical connection would indicate that there is a short circuit between the rotor and stator✔ which is a fault condition which could cause damage to the motor. ✔ (2)
4.5
- Mechanical loses ✔
- I2R losses ✔
- Iron losses (2)
4.6
4.6.1
POUT (100) = S × cosθ ✔
= 15000 × 0.8 ✔
12000 W
12 kW ✔ (3)
4.6.2
POUT = POUT(100) × η ✔
= 12000 × 0,95 ✔
= 11,4 KW ✔ (3)
4.6.3
IL = S ✔
VL × √3
= 15000
√3 × 380
= 22,79 A ✔ (3)
4.7
4.7.1 More power will be available to do the work required of the motor✔ (1)
4.7.2
- If the power factor of the motor was improved the voltage would still remain constant✔ and the motor would still deliver the same power ✔but it would require less current to deliver the power✔ or the reactance power will decrease (3)
4.8
4.8.1
- The starter reduces the voltage across each phase✔ by connecting the motor in star ✔ VPH = VL
√3 - This reduction in voltage across each phase will reduce the current in each phase✔ (3)
4.8.2
- At start the motor draws more current than normal full load current✔ this can cause the motor to experience unnecessary tripping ✔as the protection will be set to close to full load current. Reducing the current at start reduces the unnecessary tripping. ✔ (3)
4.8.3
- The overload unit relay offers protection to the motor and operator ✔under fault conditions.✔ It will operate removing power from the motor making conditions safe.✔ (3)
4.8.4
- When connected in the star mode MC2 (N/C) contacts ✔which are N/C contacts on the star contactor✔ will be open as the star contactor is energized.✔ These contacts are in series with the delta contactor coil✔ so will prevent the coil from been energized when the motor is running in star.✔ (5)
4.9
- The frequency of the voltage and current supplied to the motor determines the speed at which induction motors will operate NS = f/p✔ this means that if the frequency changes so may the speed of induction motors operating✔ which may be problematic depending upon the function of the motor. ✔ (3)
4.10 The speed is indirectly proportional to the number of pole pairs. ✔ (1)
[40]
QUESTION 5: RLC
5.1
- Inductance of the inductor✔
- Applied frequency✔ (2)
5.2 An increase in the capacitance of a capacitor will result in a decrease in the capacitive reactance of a capacitor. ✔ (1)
5.3
- Resonance is when the capacitive reactance of a circuit is equal to the inductive reactance of a circuit✔
- The resistance is equal to the impedance and ✔ Ɵ = 0✔ (3)
5.4
5.4.1
XL = 2πfL ✔
= 2 × π × 50 × 400mH ✔
= 125,66 Ω ✔ (3)
5.4.2
XC = 1 ✔
2πfC
= 1 ✔
2 × π × 50 × 47 × 10-6
= 67,72 Ω ✔ (3)
5.4.3
Z = √ R2 + (XL - XC)2 ✔
= √ 202 + (125,66 - 67,72)2 ✔
= 61, 29 Ω ✔ (3)
5.4.4
Q = 1/R √L/C ✔
= 1 √400 × 10-3 ✔
20 7 × 10-6
= 4,61 ✔ (3)
5.5 The circuit is more inductive✔ because the inductive reactance is larger than the capacitive reactance✔ (2)
[20]
QUESTION 6: LOGIC
6.1 6.1.1 Programmable Logic Controller✔ (1)
6.1.2
- PLC control allows for easy quick change to be made to a system without having to do major rewire. ✔
- PLC programs can be stored electronically. ✔
- PLC control reduces components therefore reducing the size of control panels.
- Reduction in the components used reduces cost.
- Less/No moving parts depending on the type of PLC
- More reliable (2)
6.1.3
- Stop button ✔
- Start button✔
- Overload contact (2)
6.1.4
- Relays✔
- Contactors
- Power transistors (1)
6.1.5 A series of instructions✔ written in ladder logic/function block or instruction list ✔ that is used to control the operation of a PLC. ✔ (3)
6.1.6
- Cell phone✔
- Computer
- Programming cable (1)
6.1.7 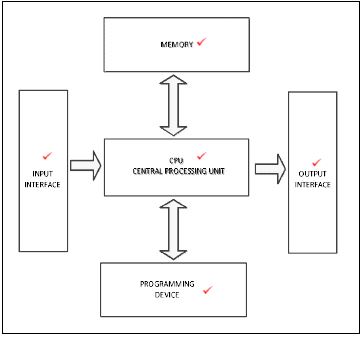
6.2 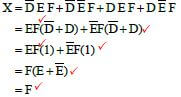 (6)
(6)
6.3 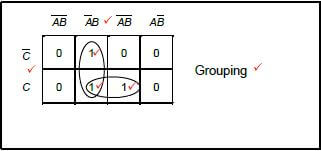
![]() (8)
(8)
6.4
6.4.1 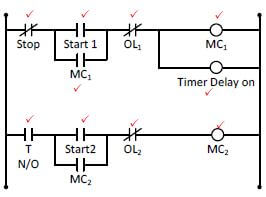
6.4.2 Motor starting application. ✔ (1)
[40]
QUESTION 7: AMPLIFIERS
7.1 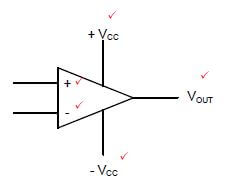 (5)
(5)
7.2
- Open loop voltage gain is infinite ✔
- Input impedance is Infinite✔
- Output impedance is zero ✔
- Infinite bandwidth (3)
7.3
- OP-amp circuits are placed in IC packages for protection ✔and for easy circuit use. ✔
- Op-amps are packaged as an integrated circuit in a hard plastic body with external pins for connections into circuits
(Accept any relevant answer (physical packaging, bubble wrap, etc.) (2)
7.4 Negative feedback occurs when a portion of the output signal in the op-amp circuit is feedback ✔to the input but 180° out of phase with the input ✔therefore subtracted from the input. ✔ (3)
7.5
- Reduces distortion and noise ✔
- Increases stability of the amplifier ✔
- Increases the bandwidth of the amplifier
- Output is predictable (2)
7.6
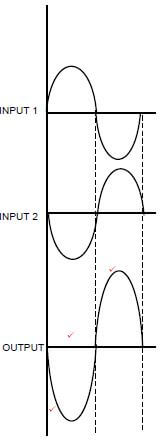
- Must show amplification✔
- Correct phase✔
- Inversion✔ (3)
7.7
7.7.1 
FIGURE: 7.2 (3)
7.7.2
AV = 1 + RF
RIN
= 1 + 12
3.3
= 4,64 ✔ (3)
7.7.3
VOUT = AV × VIN
= 4,64 × 6
= 27,84 V ✔ (3)
7.7.4 If RF is decreased, the gain of the op-amp will decrease ✔ as the gain is directly proportional to the value of the RF. ✔ (2)
7.8
7.8.1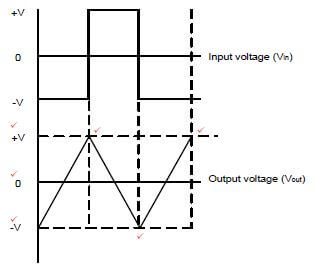
FIGURE: 7.2 (6)
7.8.2 The capacitor acts as a timing device ✔ with the resistor which determines the rate at which the output voltage increases✔ determining the time it takes to reach saturation. ✔ (3)
7.9
7.9.1 They are used as audio frequency generators in audio amplifiers. ✔ Musical instruments✔, tone generator, GPS units. (2)
7.9.2
Fr = 1
2π √6RC
= 1
2π √6 × 12 × 103 × 260 × 10-9
= 20,82 Hz ✔ (3)
7.9.3 Sine wave shape ✔ (1)
7.9.4 Positive feedback ✔ (1)
7.10 The dual DC supply supplies energy✔ to the op amp to enable the op amp to amplify an input signal.✔ The dual DC supply sets the voltage parameters both positive and negative✔. (3)
7.11 Square Wave ✔ (1)
7.12
- Monitoring the rate of change in temperature of a furnace✔
- Square wave generator (1)
[50]
TOTAL: 200
ECONOMICS PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
ECONOMICS
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Answer FOUR questions as follows in the ANSWER BOOK:
SECTION A: COMPULSORY
SECTION B: Answer TWO of the three questions.
SECTION C: Answer ONE of the two questions. - Answer only the required number of questions. Answers in excess of the required number will NOT be marked.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write the question number above each answer.
- Read the questions carefully.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Leave 2–3 lines between subsections of questions.
- Answer the questions in full sentences and ensure that the format, content and context of your responses comply with the cognitive requirements of the questions.
- Use only black or blue ink.
- You may use a non-programmable pocket calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Write down the question number (1.1.1–1.1.8), choose the answer and make a cross (X) over the letter (A–C) of your choice in the ANSWER BOOK.
EXAMPLE:
1.1.9 ![]()
1.1.1 The point where economic contraction is at its lowest is called a …
- trough.
- peak.
- trend.
1.1.2 The reduction or removal of tariffs that prevent the free flow of goods and services between countries is called …
- protectionism.
- trade embargo.
- trade liberalisation.
1.1.3 The new economic paradigm that relates to the smoothing of business cycles is rooted in …-side policies.
- demand-and-supply
- only demand
- only supply
1.1.4 A form of economic integration that removes all tariffs between member countries is called a …
- free-trade area.
- customs union.
- common market.
1.1.5 The Reserve Bank uses the … policy to influence aggregate money supply.
- fiscal
- monetary
- budgetary
1.1.6 The gap between rich and poor has widened because the demand for … workers has decreased globally.
- unskilled
- skilled
- highly skilled
1.1.7 An industrial policy that encourages industrial development in a few urban areas is called …
- decentralisation.
- privatisation.
- centralisation.
1.1.8 A regional development initiative that focuses on the socio economic development of Southern Africa is known as the …
- African Union.
- Southern African Growth Initiative.
- Southern African Development Community. (8 x 2) (16)
1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches the item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.9 J.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.2.1 Multiplier effect |
|
(8 x 1) (8)
1.3 Give ONE term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 A set of accounts that shows a systematic record of the trade and financial transactions between a country and the rest of the world
1.3.2 The curve that shows the relationship between tax rates and tax revenue
1.3.3 The market engaged in the buying and selling of foreign currencies
1.3.4 A spatial area that forms a passageway, allowing access from one area to another as part of regional development
1.3.5 It is used to measure the performance and trends of economic variables over time
1.3.6 The withdrawal of money from the circular flow (6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK. QUESTION 2: MACROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
2.1 Answer the following questions.
2.1.1 Name any TWO monetary policy instruments. (2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 Identify ONE benefit of import substitution for domestic households. (1 x 2) (2)
2.2 Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
THE CIRCULAR FLOW OF INCOME AND SPENDING 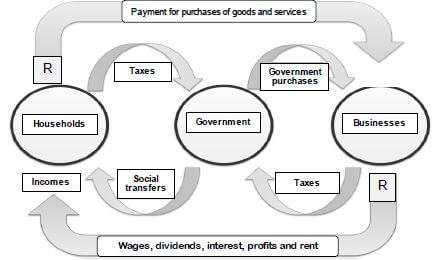
[Adapted from Google Images 2015]
2.2.1 Identify ONE injection in the diagram above. (1)
2.2.2 Name the type of economy portrayed by the above diagram. (1)
2.2.3 Briefly describe the term circular flow. (2)
2.2.4 What is the main objective of social transfers? (2)
2.2.5 Briefly explain the importance of the factor market in the circular flow. (2 x 2) (4)
2.3 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
BUY LOCAL AND BOOST THE SOUTH AFRICAN ECONOMY The Proudly South African campaign requested the support of all South African producers. South Africa currently faces the challenge of competing in an unfair global economy. All South Africans should buy home-grown products and contribute to job creation. [Adapted from Finweek, 12 October 2015] |
2.3.1 Identify the challenge faced by South Africa to succeed in international markets from the extract above. (1)
2.3.2 Name ONE brand from the extract which is imported from Korea. (1) 2.3.3 Briefly describe the term protectionism. (2)
2.3.4 What measures can government take to ensure that local industries are protected? (2)
2.3.5 In your opinion, how can local support boost the South African economy? (4)
2.4 Distinguish between the amplitude and trend line as features underpinning forecasting. (2 x 4) (8)
2.5 How can the establishment of more labour-intensive industries benefit South Africa? (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: ECONOMIC PURSUITS 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
3.1 Answer the following questions.
3.1.1 Name any TWO aspects that can be used to differentiate countries in the North-South divide. (2 x 1) (2)
3.1.2 What is the relationship between economic growth and economic development? (1 x 2) (2)
3.2 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.
GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT PLANS OF SOUTH AFRICA The National Development Plan (NDP) foresees a South Africa where everyone feels free, yet bounded to others, where everyone embraces their full potential. Realising such a society will require transformation of the economy and focused efforts to build the country's capabilities. Poverty and inequality should be reduced and the economy must grow faster in ways that benefit all South Africans. [Adapted from OECD Economics Survey 2015] |
3.2.1 Identify ONE growth and development plan for South Africa in the extract above. (1)
3.2.2 What is the main aim of the RDP? (1)
3.2.3 What message is depicted in the cartoon above, in an economic context? (2)
3.2.4 What role has the RDP played in improving the lives of people since 1994? (2)
3.2.5 In your opinion, how can the NDP bring about 'a better life for all'? (4)
3.3 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
AFRICA MUST DIVERSIFY The Minister of Trade and Industry has called for the African economies to diversify in order to attract foreign direct investment. He warned that economic integration in Africa was facing a threat if infrastructure development did not take place. Economies were inward looking and focused on the exports of raw materials to shore up its gross domestic product. [Adapted from Business Report, 5 October 2015] |
3.3.1 According to the Minister of Trade and Industry, why is it important for African economies to diversify? (1)
3.3.2 What new approach should countries follow in doing business? (1)
3.3.3 Briefly describe the term common market. (2)
3.3.4 Give ONE reason why developing countries diversify as part of their import substitution policies. (2)
3.3.5 How can South Africa benefit by focusing on value-added production? (4)
3.4 Discuss competitiveness and investment in human capital as benchmark strategies for industrial development. (2 x 4) (8)
3.5 How can the development of small businesses benefit the South African economy? (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: MACROECONOMICS AND ECONOMIC PURSUITS
40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
4.1 Answer the following questions.
4.1.1 Name any TWO forms of import substitution. (2 x 1) (2)
4.1.2 What impact will an increase in the VAT rate have on the standard of living of the poor? (1 x 2) (2)
4.2 Study the table below and answer the questions that follow.
| BALANCE OF PAYMENTS (BoP) THE CURRENT ACCOUNT (R MILLIONS)
[Adapted from SARB Quarterly Bulletin, June 2016] |
4.2.1 Which institution provides the statistics above? (1)
4.2.2 Which item records transactions relating to donations and gifts to other countries? (1)
4.2.3 Briefly describe the capital transfer account as part of the BoP. (2)
4.2.4 Give ONE reason for the decline in gold exports. (2)
4.2.5 Calculate the trade balance for 2015. Show ALL calculations. (4)
4.3 Study the cartoon below and answer the questions that follow.
 [Source: Paresh cartoons.com] |
4.3.1 Identify ONE major challenge in the cartoon above. (1)
4.3.2 State ONE negative consequence of poverty in the cartoon above. (1)
4.3.3 What does the 'Mandela Legacy' refer to? (2)
4.3.4 Suggest ONE way in which South Africa can be freed from inequality. (2)
4.3.5 How can human resources be targeted to be more effective in solving the problems in the cartoon above? (4)
4.4 Briefly discuss special economic zones as part of the industrial development plan of South Africa. (4 x 2) (8)
4.5 How can South Africa benefit from trading in global markets? (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer any ONE of the two questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK. Your answer will be assessed as follows:
STRUCTURE OF ESSAY | MARK ALLOCATION |
Introduction | Max. 2 |
Body | Max. 26 Max. 10 |
Conclusion
| Max. 2 |
TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 5: MACROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
The state plays a significant role in a mixed economic system and is therefore one of the largest sectors in the economy.
- Discuss the macroeconomic objectives of the state. (26)
- How successful is the implementation of South Africa's fiscal policy? (10) [40]
QUESTION 6: ECONOMIC PURSUITS 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
Economic and social indicators are used globally to compare and describe economic performances of countries.
- Examine the following social indicators:
- Demographics
- Education
- Nutrition and health (26)
- What can the South African government do to improve the delivery of social services to its citizens? (10)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
ECONOMICS PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
ECONOMICS
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Answer FOUR questions as follows in the ANSWER BOOK:
SECTION A: COMPULSORY
SECTION B: Answer TWO of the three questions.
SECTION C: Answer ONE of the two questions. - Answer only the required number of questions. Answers in excess of the required number will NOT be marked.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write the question number above each answer.
- Read the questions carefully.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Leave 2–3 lines between subsections of questions.
- Answer the questions in full sentences and ensure that the format, content and context of your responses comply with the cognitive requirements of the questions.
- Use only black or blue ink.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Write down the question number (1.1.1–1.1.8), choose the answer and make a cross (X) over the letter (A–C) of your choice in the ANSWER BOOK.
EXAMPLE:
1.1.9 ![]()
1.1.1 In the long run, an individual business in perfect competition will be in equilibrium when marginal …
- revenue equals total cost.
- cost equals average variable cost.
- cost equals marginal revenue.
1.1.2 An imperfect market where information is complete:
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic competition
- Oligopoly
1.1.3 The demand curve of a monopolistic competitor is …
- positively sloped.
- negatively sloped.
- horizontal.
1.1.4 An example of a fixed-cost item:
- Electricity
- Rent
- Telephone
1.1.5 Headline inflation is used by the SARB to decide on the level of …
- employment.
- the interest rate.
- production.
1.1.6 Foreigners travelling to South Africa are regarded as … tourists.
- domestic
- outbound
- inbound
1.1.7 Attending a sports event is an example of … tourism.
- cultural
- eco
- business
1.1.8 Core inflation excludes items with … prices.
- high
- stable
- volatile (8 x 2) (16)
1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches the item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.9 J.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.2.1 Marginal cost |
(8 x 1) (8) |
1.3 Give ONE term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 A market structure where only two businesses dominate the market
1.3.2 Products that are identical and standardised
1.3.3 A monopoly that exists because of high development costs
1.3.4 An inflation rate of more than 50%
1.3.5 The process of managing the environment in such a way that it remains intact
1.3.6 The provision of goods and services such as roads, telephone lines, radio and television services (6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 2: MICROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
2.1 Answer the following questions.
2.1.1 Name TWO kinds of inefficiencies that can exist in the imperfect market. (2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 What would happen if firms in an oligopolistic market compete on prices? (1 x 2) (2)
2.2 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow. 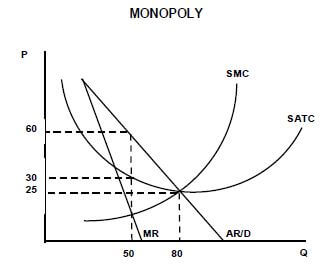
2.2.1 What is the selling price for the monopolist? (1)
2.2.2 Does the equilibrium position above represent a short run or a long run? (1)
2.2.3 Why will a monopolist always make economic profit in the long run? (2)
2.2.4 What is the requirement for this monopoly to be classified as an artificial monopoly? (2)
2.2.5 Calculate the total profit that this monopolist is making. Show ALL calculations. (4)
2.3 Study the cartoon below and answer the questions that follow.
[Adapted from Internet Cartoons]
2.3.1 Which cause of market failure is illustrated above? (2)
2.3.2 Briefly describe the term market failure. (2)
2.3.3 How can labour as a factor of production become more mobile? (2)
2.3.4 How does the South African government attempt to solve the problem of income inequality? (2 x 2) (4)
2.4 Compare monopolistic competition with perfect competition. (4 x 2) (8)
2.5 Explain why governments sometimes proceed with a project even if the private costs exceed the private benefits in a cost-benefit analysis. (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
3.1 Answer the following questions.
3.1.1 Name TWO causes of cost-push inflation. (2 x 1) (2)
3.1.2 What effect will green tax have on the production output of a business that generates a negative externality? (1 x 2) (2)
3.2 Study the table below and answer the questions that follow.
INTERNATIONAL TOURIST ARRIVALS IN SOUTH AFRICA | ||
MARKETS | 2014 | 2015 |
Africa (land) | 1 713 543 | 1 617 570 |
Africa (air) | 102 006 | 95 332 |
Americas | 107 859 | 92 710 |
Asia and Australasia | 103 903 | 81 498 |
Europe | 405 894 | 402 223 |
Total tourist arrivals | 2 435 341 | 2 292 169 |
[Source: www.southafrica.net]
3.2.1 Identify TWO markets in the table that contributed the most to tourism in South Africa during 2015. (2 x 1) (2)
3.2.2 Suggest possible reasons that have led to a general decline in international tourism in 2015. (2 x 2) (4)
3.2.3 Calculate the percentage decline in total tourist arrivals in South Africa between 2014 and 2015. Show ALL calculations. (4)
3.3 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.
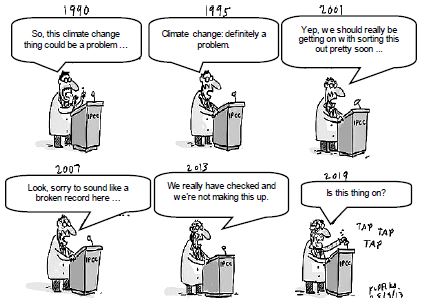
GLOBAL WARMING AND CLIMATE CHANGE The environmental problems of global warming and climate change are real threats to the survival of plants and animals. Through various conferences United Nations has been attempting to address the issues. [Adapted from www.google.co.za] |
3.3.1 What is the effect of the emission of greenhouse gases on the environment? (2)
3.3.2 What is the message conveyed by the cartoon? (2)
3.3.3 Name the international agreement that was formed to deal with global warming and climate change. (2)
3.3.4 How can the world stop the global warming trend? (2 x 2) (4)
3.4 Differentiate between producer price index and consumer price index. (2 x 4) (8)
3.5 Why is South Africa regarded as a major air polluter in the world? (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: MICROECONOMICS AND CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
4.1 Answer the following questions.
4.1.1 Name TWO methods of non-price competition. (2 x 1) (2)
4.1.2 How can a decline in savings influence the economy negatively? (1 x 2) (2)
4.2 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.
MINIMUM WAGES In South Africa there are different categories in which minimum wages are applied: civil engineering, contract cleaning services, domestic workers, farm workers, forestry, hospitality, leadership allowance, private security, wholesale and retail, taxis and bargaining council minimum wages. In the United Kingdom, however, there is a national minimum wage that includes all sectors.
|
4.2.1 Identify any TWO sectors in South Africa where minimum wages are applied in the extract above. (2 x 1) (2)
4.2.2 Briefly describe the term minimum wage. (2)
4.2.3 What is the advantage of having a national minimum wage instead of a minimum wage per sector? (2)
4.2.4 Refer to the graph above and explain the implication of the R3 500 minimum wage imposed by the government. (2 x 2) (4)
4.3 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
INFLATION AND ECONOMIC GROWTH Inflation has never been good to the economy. However, whenever there is expected inflation, governments around the world take appropriate steps to minimise inflation to a certain extent. Inflation and economic growth are parallel lines and can never meet. Inflation reduces the value of money and makes it difficult for the common people to survive. Inflation and economic growth are incompatible because the former affects all sectors. [Source: www.fin24.com] |
4.3.1 What, according to the extract, is the effect of inflation on money? (2)
4.3.2 Briefly describe the term stagflation. (2)
4.3.3 Explain the effect of an increase in interest rates on inflation. (1 x 2) (2)
4.3.4 What are the negative effects of inflation on economic growth? (2 x 2) (4)
4.4 Explain the roles played by any TWO key institutions that monitor competition in South Africa. (2 x 4) (8)
4.5 To what extent is inflation targeting beneficial to the economy? (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer any ONE of the two questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK. Your answer will be assessed as follows:
STRUCTURE OF ESSAY | MARK ALLOCATION |
Introduction | Max. 2 |
Body | Max. 26 Max. 10 |
Conclusion
| Max. 2 |
TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 5: MICROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
In a perfect market the industry influences the behaviour of an individual business to a certain extent.
- With the aid of graphs, explain the following about an individual business under conditions of perfect competition:
- The effect on price if the individual producer increases or decreases his output (supply)
- The derivation of the supply curve from cost curves for the individual producer (26)
- Without using a graph, explain why the price of a product under perfect competition will be equal to the lowest point on the long-run average cost curve. (10) [40]
QUESTION 6: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
Tourism plays an important role and can affect the economy negatively or positively.
- Examine the effects of tourism on the following:
- Poverty
- Employment
- Externalities (26)
- How can South Africa promote domestic tourism? (10) [40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
ECONOMICS PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
ECONOMICS
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1.1.1 C – cost equals marginal revenue ✓✓
1.1.2 A – monopoly ✓✓
1.1.3 B – negatively sloped ✓✓
1.1.4 B – rent ✓✓
1.1.5 B – interest rate ✓✓
1.1.6 C – inbound ✓✓
1.1.7 A – cultural ✓✓
1.1.8 C – volatile ✓✓ (8 x 2) (16)
1.2 MATCHING ITEMS
1.2.1 C ✓ the additional cost when producing an extra unit
1.2.2 E ✓ an arrangement between businesses with the aim of limiting competition amongst them
1.2.3 G ✓ intervention by government to recover external cost
1.2.4 A ✓ the minimum earnings required to prevent an entrepreneur from leaving the business
1.2.5 I ✓ an increase in the general price level in a particular year
1.2.6 B government sets regulations which enforce environmental standards
1.2.7 H ✓ shows the relative importance of an item in a basket of goods and services that are used to calculate inflation
1.2.8 D ✓ dumping waste on the earth's surface (8 x 1) (8)
1.3 IDENTIFY THE CONCEPT
1.3.1 Duopoly ✓
1.3.2 Homogeneous ✓
1.3.3 Natural ✓
1.3.4 Hyperinflation ✓
1.3.5 Preservation ✓
1.3.6 Infrastructure / public goods ✓ (6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 2: MICROECONOMICS
2.1
2.1.1 Name TWO kinds of inefficiencies that can exist in the imperfect market.
- Productive/technical inefficiencies ✓
- Allocative inefficiencies ✓ (2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 What would happen if firms in an oligopolistic market compete on prices?
- It can lead to a price war which will lower profits which might lead to certain firms leaving the market in the long run ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
2.1 Data response
2.2.1 What is the selling price for the monopolist?
- Selling price is R60 ✓ (1)
2.2.2 Does the equilibrium position above represent a short run or a long run?
- Short run ✓ (1)
2.2.3 Why will a monopolist always make economic profit in the long run?
- It is possible to manipulate prices to ensure a profit because there is no competitors ✓✓
- There is a deliberate decline in produce – less than the market demand, therefore higher prices are charged ✓✓
- Sell a unique product without any competition ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.2.4 What is the requirement for this monopoly be classified as an artificial monopoly?
- If entry is restricted by factors such as legal requirement e.g. licencing, patents and copyrights ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant answer) (2)
2.2.5 Calculate the total profit this monopolist is making. Show all calculations.
- Total Profit = Total revenue – Total Cost
= (60 x 50) – (30 x 50) ✓
= 3 000 – 1 500 ✓
= 1 500 ✓✓
OR - Total Profit = Unit profit x quantity
= (60-30) ✓ x 50 ✓
= R1 500 ✓✓- Max 2 marks if only the correct answer is given.
- If the formula is given, a mark can be awarded if the calculations are incorrect. (4)
2.3 Data Response
2.3.1 Which cause for market failure is illustrated above?
- Incomplete information/lack of information ✓✓ (2)
2.3.2 Briefly describe the concept market failure.
- The best available (optimal) production outcome has not been achieved / misallocation of resources ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.3.3 How can labour as a factor of production become more mobile?
- Training/attaining skills/increased wages/travelling facilities or infrastructure/technology ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.3.4 How does the South African government attempt to solve the problem of income inequality?
The government can attempt to solve the problem of income inequality by:
- implementing a progressive tax system which has reduced the income gap between income earners ✓✓
- levying indirect taxes on consumption (e.g. VAT), while certain basic items that the poor often consumes, were excluded ✓✓
- providing free primary health care in provincial hospitals and clinics ✓✓
- making provision for those who cannot afford to pay by offering a free basic education ✓✓
- making transfer payments and subsidies payable to the poor and previously disadvantaged ✓✓
- implementing minimum wages ✓✓
- implement job creation programmes ✓✓
- implementing BBBEE and labour laws ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Any 2 x 2) (4)
2.4 Compare monopolistic competition with perfect competition.
- Under monopolistic competition less will be produced at a higher price than the perfect competitor ✓✓
- The perfect competitor produces at the minimum point on the LAC curve, whereas this is not the case under monopolistic competition ✓✓
- Both the perfect competitor and monopolistic competitor will make a normal profit in the long run ✓✓
- It is easier for the perfect competitor to enter the market, compared to the monopolistic competition ✓✓
- (Accept any other correct relevant answer)
- (Accept tabular format)
- (Accept comparison in terms of other characteristics) (4 x 2)
- (Allocate a maximum of 4 marks for mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
2.5 Explain why governments sometimes proceed with a project even if the private costs exceed the private benefits in a Cost-Benefit Analysis?
Governments might proceed with a project when:
- the primary objective is to provide public goods and services. ✓✓
- social costs and social benefits are also taken into account when deciding on a project. ✓✓
- a service is vital to the existence of the community. ✓✓
- when a need for infrastructure is necessary but might not have any benefits in terms of profit, e.g. the building of a community centre or a bridge ✓✓
- funding of these projects are mainly financed through tax revenue and does not impoverish any individual as such. ✓✓
- this infrastructure adds to the welfare of the community at large and is non-excludable to anyone using it. ✓✓
(Allocate a maximum of 2 marks for mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
3.1
3.1.1 Name TWO causes of cost push inflation.
- Higher Wages ✓
- Increase in input costs ✓
- Increase in price of imports ✓
- Exchange rate depreciation ✓
- High profit margins ✓
- Low productivity ✓
- Limited natural resources ✓
- Increase in interest rates ✓
- Supply shock ✓
- Natural disasters ✓ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.1.2 What effect will green tax have on the production output of a business that generates a negative externality?
- The levying of taxes will reduce the output of those products ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
3.2 Data response
3.2
3.2.1 Identify TWO markets in the table that contributed the most to tourism in South Africa during 2015?
- Africa land ✓
- Europe ✓ (2 x 1) (2)
3.2.2 Suggest possible reasons that have led to a general decline in international tourism in 2015?
- Dampening of the world economy (Recession) ✓✓
- Legislation governing international traveling e.g. VISA regulation ✓✓
- Increase in crime in some areas (Safety issues) ✓✓
- Poor electricity supply / poor infrastructure ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Any 2 x 2) (4)
3.2.3 Calculate the percentage decline in total tourist arrivals in South Africa between 2014 and 2015.
Show all calculations.
- 143 172 ✓ x 100 ✓
2 435 341 1
= 5,8 / 5.9 / 6 % ✓✓
Allocate 2 marks for the correct answer. (4)
3.3 Data response
3.3.1 What is the effect of the emission of greenhouse gases on the environment?
- It can lead to increased temperatures/global warming/climate change ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.3.2 What is the message conveyed by the cartoon?
- Despite numerous summits on environmental issues, climate change is still a problem ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.3.3 Name the international agreement that was formed to deal with global warming and climate change.
- Kyoto Protocol ✓✓ (2)
3.3.4 How can the world stop the global warming trend?
- Reduce the emission of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere by using environmentally friendly technology such as solar energy ✓✓
- Planting of trees that produces oxygen which is important for cleaner air ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 2) (4)
3.4 Differentiate between Production Price Index and Consumer Price Index.
Production price index
| Consumer price index
|
(2 x 4)
(Allocate a maximum of 4 marks for mere listing of facts / examples)(8)
3.5 Why is South Africa regarded as a major air polluter in the world?
- Industries such as SASOL and ESKOM (Medupi) burn a larger quantity of coal and this produces CO2 into the atmosphere / The country has the world's largest single CO2 emitter which is at SASOL in Secunda ✓✓
- Mining activities such as extraction and refining creates a large amount of air pollution ✓✓
- South Africa is the biggest CO2 polluter in Africa (40%) and rated the world's 13th largest producer of greenhouse gases. Top 6 in the developing world for Greenhouse gasses ✓✓
- The use of non-environmentally friendly energy sources ✓✓
- (Accept reference to the candidate’s local environment)
- (Accept any other correct relevant response)
- (Allocate a maximum of 2 marks for mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: MICROECONOMICS AND CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
4.1
4.1.1 Name TWO methods of non-price competition.
- Advertising ✓
- Loyalty points ✓
- After sales services ✓
- Packaging ✓
- Branding ✓
- Door-to-door sales ✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 1) (2)
4.1.2 How can a decline in savings influence the economy negatively?
- When people save less, they often spend more ✓ which can lead to higher prices. ✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
4.2 Data response
4.2.1 Identify any TWO sectors in South Africa where minimum wages are applied in the extract above.
- Civil Engineering ✓
- Contract Cleaning services ✓
- Domestic Workers ✓
- Farm Workers ✓
- Forestry ✓
- Hospitality ✓
- Leadership Allowance ✓
- Private Security ✓
- Wholesale and Retail ✓
- Taxi ✓
- Bargaining Council Minimum Wages ✓ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.2.2 Briefly describe the term minimum wage.
- It is the minimum remuneration a worker should earn legally per hour, day or week for work done ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
4.2.3 What is the advantage of having a national minimum wage instead of a minimum wage per sector?
- Prevent discrimination among workers in the different sectors ✓✓
- That national minimum wage could be higher which will improve the standard of living ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
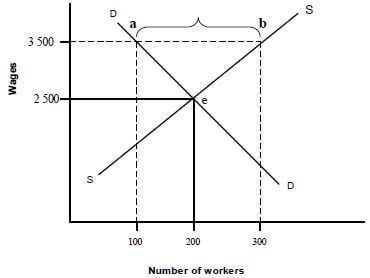
4.2.4 Refer to the above graph and explain the implication of the R3 500 minimum wage imposed by the government.
- The wage rate will be higher than the market rate of R2 500✓✓
- At this rate more people will avail themselves, therefore the supply of labour will increase from 200 to 300 ✓✓
- On the other side, the demand for labour will decrease from 200 to100 ✓✓
- This will create an oversupply of workers, supply exceeds demand / unemployment will increase ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 2) (4)
4.3 Data response
4.3.1 What, according to the extract, is the effect of inflation on money?
- It reduces the value of money ✓✓ (2)
4.3.2 Briefly describe the term stagflation.
- Stagflation can be described as low economic growth, high unemployment and high rates of inflation ✓✓ (2)
4.3.3 Explain the effect of an increase in interest rates on inflation.
- An increase in interest rates makes buying on credit more expensive. This often results in a decrease in aggregate demand which will lead to a lower inflation rate ✓✓
(Accept other correct relevant response) (2)
4.3.4 What are the negative effects of inflation on economic growth?
- High inflation creates uncertainty of the economic environment and reflects negatively on production ✓✓
- Uncertainty discourages investment which in turn leads to reduced economic growth ✓✓
- Reduced growth has a knock on effect on all sectors of the economy which can lead to a recession ✓✓
- May lead to unemployment ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Any 2 x 2) (4)
4.4 Explain the roles played by any TWO key institutions that monitor competition in South Africa.
- Competition Commission ✓
- Investigate restrictive business practices ✓✓
- Grant permission in cases of mergers and take-overs ✓✓
- Makes recommendations about penalties for businesses that it finds guilty of uncompetitive behaviour ✓✓
- Competition Tribunal ✓
- Accept or reject recommendations made by the Competition Commission ✓✓
- Has jurisdiction throughout the Republic ✓✓
- It is a tribunal of record and independent from the other competition institutions ✓✓
- Grant exemption, authorise or prohibit large mergers, adjudicate if misconduct takes place ✓✓
- Competition Appeal Court ✓
- Make final rulings on disputed matters/Considers appeals made against decisions made by the Competition Tribunal ✓✓
- Has a status similar to High Court ✓✓
- It has jurisdiction throughout the Republic and is a Court of Record ✓✓ (8)
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 4)
(Allocate a maximum of 4 marks for mere listing of facts / examples)
4.5 To what extent is inflation targeting beneficial to the economy?
- It helps to keep prices at a lower level ✓✓
- It increases people's expectation that prices will be stable in the medium term ✓✓
- It is useful in controlling demand pull inflation because the concept is simple and easy to understand ✓✓
- It enhances producers' confidence in the economy as it enable them to make investments knowing that inflation will be under control ✓✓
- It reduces uncertainty and promotes sound planning in public and private sectors ✓✓
- It provides a yardstick that serves to discipline monetary policy and improves the accountability of the central bank ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (4 x 2)
(Allocate a maximum of 2 marks for mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer any ONE of the two questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK. Your answer will be assessed as follows:
STRUCTURE OF ESSAY | MARK ALLOCATION |
Introduction | Max. 2 |
Body | Max. 26 Max. 10 |
Conclusion
| Max. 2 |
TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 5: MICROECONOMICS
In a perfect market the industry influences the behaviour of an individual business to a certain extent.
- With the aid of graphs, explain the following about an individual business under conditions of perfect competition:
- The effect on price if the individual producer increases or decreases his output (supply)
- The derivation of the supply curve from cost curves for the individual producer (26)
- Without using a graph, explain why the price of a product under perfect competition will be equal to the lowest point on the long-run average cost curve. (10) [40]
INTRODUCTION
Perfect competition is a market structure where the market price is determined by the interaction between demand and supply. ✓✓ (Max 2)
MAIN PART
The effect on price if the individual producer increases or decreases his output (supply) 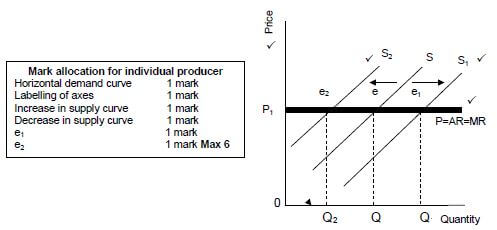
- The demand curve for the individual business is a horizontal line because he is a price taker ✓✓
- If the individual producer increases its supply, the supply curve will shift to the right from SS to S1S1 ✓✓
- At this point the equilibrium quantity has increased from Q to Q1, but the equilibrium price has remained at P1 ✓✓
- If the individual producer decreases its supply, the supply curve will shift from SS to S2S2 ✓✓
- The equilibrium quantity has decreased but the equilibrium price has remained constant at P1 ✓✓
- The individual producer is not able to influence the equilibrium or market price by manipulating its supply ✓✓
(Graphs max 6 marks and discussion max 8 marks)
(Max 14)
The derivation of the supply curve from cost curves for the individual producer 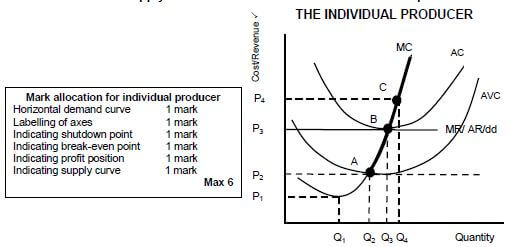
- The individual supply is derived by taking different market prices and determining how much the business should produce at each price ✓✓
- The individual firm maximizes profit where the marginal revenue (MR) is equal to marginal cost (MC) - Point B ✓✓
- Provided that the average income (AR) is enough to cover the average variable cost (AVC) ✓✓
- Average variable costs comprise costs like labour cost, material costs and fuel and electricity costs ✓✓
- Under perfect conditions, the producer will produce where P=MR=MC, if AR=P>AVC ✓✓
- Thus we derive that the supply curve of the firm is the section of the MC curve above the intersection with the AVC curve ✓✓
- The supply curve therefore is ABC on the graph ✓✓
- At P1, no production will take place ✓✓
- At P2, the AR=AVC, the firm will consider shutting down ✓✓
- At P3, the AR=AC, the breakeven point, where normal profits are made ✓✓
- At P4, where AR > AC - at this point abnormal (economic profits) are made ✓✓
(Graphs max 6 marks and discussion max 8 marks) (Max 14)
Max body (26)
ADDITIONAL PART
Without using a graph, explain why the price of a product under perfect competition will be equal to the lowest point on the long-run average cost curve. (10)
- If the firm is making economic profit, it could adapt its production capacity by building a bigger production plant ✓✓
- The industry can expand because new businesses could enter the market ✓✓
- The increased production will push the market supply curve to the right thus lowering the market price ✓✓
- Economic profits will eventually disappear due to falling average revenue ✓✓
- Long run equilibrium is achieved where the lowest point of the AC curve is tangent to the Demand/AR curve.(Which is the price) ✓✓
- If the business is making an economic loss then firms will leave the business or cut back on production ✓✓
- This will shift the market supply curve to the left thus increasing prices ✓✓
- Economic loss will eventually disappear due to increasing average revenue ✓✓
- This price will eventually be equal to the minimum point on the LAC curve i.e. Normal profit ✓✓
- Large scale production makes lower unit cost possible as a result of specialisation, and improved technology ✓✓
(Max 10)
CONCLUSION
The supply curve of the firm under perfect competition is the section of the MC curve above the intersection with the AVC curve ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant conclusion) (Max. 2)
[40]
QUESTION 6: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
Tourism plays an important role and can affect the economy negatively or positively.
- Examine the effects of tourism on the following:
- Poverty
- Employment
- Externalities (26)
- How can South Africa promote domestic tourism? (10) [40]
INTRODUCTION
Tourism is the activities of people travelling to places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year, for leisure, business and other purposes ✓✓ (Max. 2)
MAIN PART
Poverty
- Tourism is one of the fastest and most efficient redistribution mechanisms in development ✓✓
- Tourism stimulates economic growth and brings development to the poor in rural areas ✓✓
- Tourism offers opportunities to diversify sources of income for poor people ✓✓
- Allowing them a stake ✓ for example, to start and operate small-scale tourism businesses around community assets and to establish SMMEs to provide services ✓✓
- Empowerment ✓ for example, to exploit opportunities of on-the-job and other training ✓✓
- Creating partnerships ✓ linking up with mainstream tourism businesses supplying goods and services ✓✓ (Max 10)
Employment
- Tourism sector directly and indirectly employ people ✓✓
- The sector is the largest creator of jobs (employs 7% of the workforce in SA) ✓✓ for the following reasons:
- Tourism is labour intensive ✓ It has the lowest ratio of investment to employment creation ✓✓ This means that more jobs can be created with every unit of capital invested in tourism ✓✓ Many tourist activities are therefore within the reach of small tour operators ✓✓
- Tourism employ many skills ✓ Various skills are employed in the tourism sector ✓✓ for example, tour guides, hairdressers, accountant ✓ It also offers a huge potential for on-the-job training ✓✓
- Tourism provides immediate employment ✓ If it is properly organised and focused, the tourism sector can create many jobs within a short period of time ✓✓
- Tourism provides entrepreneurial opportunities ✓ The tourism industry accommodates informal sector enterprises ✓✓ from craft and fruit vendors to pavement vendors, chair rentals and others ✓ (Max 10)
Externalities
The rapidly expanding tourism industry could have both positive and negative impacts that extend well into the future:
- Attracts large amounts of revenue, but can cause undue environmental damage (uses resources and produces waste) ✓✓
- Rapid growth aimed at short-term benefits has more negative than positive effects: degeneration of traditions and cultural values, environmental damage to sites and natural settings – pollution and waste ✓✓
- Global tourism will grow due to increased population, improved living standards, increased free time and expansion of transportation systems, but put unnecessary pressure on tourist sites ✓✓
- Economic effect on individuals: new transport systems, recreation, shops and increase in property value compared to an increased inflation rate ✓✓
- Economic effect on government: more direct and indirect tax compared to conservation of infrastructure and tourist attractions ✓✓
- Social effect on individuals: improved health care and education compared to traffic congestion, crime ✓✓
- Social effect on government: an increased value put on culture, less migration compared to policing, sanitation, and health services ✓✓ (Max 10)
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Max 26)
(Allocate a maximum of 8 marks for mere listing of facts / examples)
ADDITIONAL PART
South Africa can promote domestic tourism by
- Improving its marketing and advertising ✓✓
- Domestic tourism is encouraged through increased advertising ✓✓
- TV magazine programmes like Shot'left inform people about local places of interest ✓✓
- Promoting special holiday packages ✓✓
- Special off-season rates make it possible to enjoy cheaper holidays ✓✓
- Enhancing efficiency of tourist information outlets✓
- Many towns have information outlets that supply pamphlets and information about a specific area. ✓✓
- Distributing information booklets (awareness) and offer transport to visit places of interest. This is mostly done by hotels and other accommodation resorts ✓✓
- Improving infrastructure ✓ a greater variety, using new technology to provide reliable infrastructure ✓✓
- Government effectively managing its tourist sites and other tourist attractions ✓✓ e.g. maintenance, upgrading, security etc. ✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Max.10)
CONCLUSION
Tourist expenditure is as real as any other consumer expenditure and international tourism can in addition be seen as an invisible export product ✓✓ (Max. 2)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
ECONOMICS PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
ECONOMICS
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1.1.1 A – trough ✓✓
1.1.2 C – trade liberalisation ✓✓
1.1.3 A – demand-and-supply ✓✓
1.1.4 A – free-trade areas ✓✓
1.1.5 B – monetary ✓✓
1.1.6 A – unskilled ✓✓
1.1.7 C – centralisation ✓✓
1.1.8 C – Southern African Development Community ✓✓ (8 x 2) (16)
1.2 MATCHING ITEMS
1.2.1 F – small initial change in spending produces a proportionally larger increase in national income ✓
1.2.2 H – coordinates trade and promotes locally manufactured products worldwide ✓
1.2.3 A – economic fluctuations affected by causes outside the market system ✓
1.2.4 B – does not change until after the business cycle has changed ✓
1.2.5 I – levied on high-income earners ✓
1.2.6 C – reflects the demographic and gender composition of a country ✓
1.2.7 E – ratio between inputs and outputs ✓
1.2.8 D – sets out the broad approach to industrialisation of government ✓ (8 x 1) (8)
1.3 GIVE THE CONCEPT
1.3.1 Balance of Payments ✓
1.3.2 Laffer curve ✓
1.3.3 Foreign exchange / Forex ✓
1.3.4 Corridor ✓
1.3.5 Economic indicator ✓
1.3.6 Leakage ✓ (6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 2: MACROECONOMICS
2.1 Answer the following questions.
2.1.1 Name any TWO monetary policy instruments.
- Repo rate / Interest rates ✓
- Open market transactions ✓
- Minimum cash reserve requirements ✓
- Moral suasion ✓
- Exchange rate policy ✓ (2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 Identify ONE benefit of import substitution for domestic households?
- More job opportunities / increase in income ✓✓
- Better choice of goods and services / Greater variety of products ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
2.2 DATA RESPONSE
2.2.1 Identify ONE injection in the diagram above.
- Government expenditure / government purchases ✓ (1)
2.2.2 Name the type of economy portrayed by the above diagram?
- Closed economy / three sector economy ✓ (1)
2.2.3 Briefly describe the term circular flow.
- The circular-flow model of the economy is a simplification showing how the economy works and the relationship between income, production and spending in the economy as a whole ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.2.4 What is the main objective with social transfers?
- Redistribution of income/poverty alleviation/correct imbalances of the past/promote equality/close the gap between rich and poor ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.2.5 Briefly explain the importance of the factor market in the circular flow.
- The households own the factors of production and sell the factors on the input market and receive an income (wages, rent, interest and profit) in return to use in buying goods and services ✓✓
- Businesses purchase the factors of production from the household in the factor market to be used in the production of goods and services ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) Any (2 x 2) (4)
2.3 DATA RESPONSE
2.3.1 Identify the challenge faced by South Africa to succeed in the international markets from the extract above.
- 'Competing in an unfair global economy' ✓ (1)
2.3.2 Name ONE brand from the extract which is imported from Korea.
- Samsung/Hyundai ✓ (1)
2.3.3 Briefly describe the term protectionism.
- Protectionism refers to government policies and regulations which are designed to benefit local producers of goods and services in their competition with imported goods, thus helping them to survive ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.3.4 What measures can government take to ensure that local industries are protected?
The government can:
- install import quotas ✓✓
- charge higher tariffs on imported goods ✓✓
- ban or restrict certain goods previously imported ✓✓
- subsidise local industries ✓✓
- enforce a local content requirement to protect employment ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.3.5 In your opinion, how can local support boost the South African economy?
By exporting -
- surplus production ✓✓
- foreign currency is earned for the country / BoP equilibrium✓✓
- employment opportunities are created ✓✓
- increased consumption of locally produced products takes place ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (4)
2.4 Distinguish between the amplitude and trend line as features underpinning forecasting.
Trend line
- The trend is the general direction of the economy ✓✓
- The trend line that rises gradually will be positively sloped in the long run. This rising line indicates a growing economy ✓✓
- The trend line represent the average position of a business cycle ✓✓
Amplitude
- Amplitude refers to the deviation from the trend line to the trough and from the trend line to the peak of the business cycle ✓✓
- It shows the severity of each phase of the business cycle, the shorter the amplitude – indicates a mild recession ✓✓
- The larger the amplitude, the more extreme the changes that occur ✓✓
- If the peak is far from the trend line it means the underlying causes of expansion are very strong / If the peak is close to the trend line, the underlying causes are weak ✓✓ (Any 2 x 4)
(Allocate a maximum of 4 marks for mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
2.5 How can the establishment of more labour-intensive industries benefit South Africa?
Establishment of more labour intensive industries will benefit South Africa by:
- providing more jobs ✓✓
- improving the utilisation of available resources ✓✓
- e.g. mining, agriculture and manufacturing industries ✓
- transferring a greater variety of knowledge and skills to the workers ✓✓
- using artisans, technicians and engineers that will lead to better economic growth ✓✓
- improving the standard of living of the citizens (economic development) ✓✓
- generating more revenue for the state via income tax ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(Allocate a maximum of 2 marks for mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: ECONOMIC PURSUITS
3.1 Answer the following questions.
3.1.1 Name any TWO aspects that can be used to differentiate countries in the North-South divide.
- Unequal standard of living ✓
- Globalisation inequalities (challenges in globalisation) ✓
- Environment ✓ Any (2 x 1) (2)
3.1.2 What is the relationship between economic growth and economic development?
- Economic growth should ensure more job opportunities and higher/ income to more households thus leading to improvement to the standards of living of the people ✓✓ (1 x 2) (2)
3.2 DATA RESPONSE
3.2.1 Identify ONE growth and development plan for South Africa from the extract above.
- National Development Plan (NDP) / Reconstruction and Development Programme (RDP) ✓ (1)
3.2.2 What is the main aim of the RDP?
- The improvement of the lives of the majority of South Africans / better life for all ✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1)
3.2.3 What message is depicted in the cartoon above, in an economic context?
- People living under conditions of poverty with an expectation of change ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.2.4 What role did the RDP play in the improvement in the lives of the people since 1994?
The RDP:
- met the basic needs of people.
- increased infrastructure development.
- laid the foundation for sustained economic growth and job creation.
- developed human resources.
- ensured the safety and security of South Africa’s citizens and the state.
- transformed the government to reflect development and people-centred nature of the democratic state. (2)
3.2.5 In your opinion, how can the NDP bring about a better life for all?
- The NDP can fully transform the economic activities of the country ✓✓
- It can assist in the: transformation of the overall mind set of all the South Africans in realising that everybody will be judged according to his/her potential and ability/reduction of poverty and inequality in society ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (4)
3.3 DATA RESPONSE
3.3.1 According to the Minister of Trade and Industry, why is it important for African economies to diversify?
- To be able to attract foreign direct investment ✓ (1)
3.3.2 What new approach should countries follow in doing business?
- The approach should be consumption-based ✓ (1)
3.3.3 Briefly describe the concept common market.
- Countries that are part of a common market enhances the free movement of labour capital and money between borders of member countries/people may work and live where they wish in a common market ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.3.4 Give ONE reason why developing countries diversify as part of their import substitution policies?
- The industrial base of their economies need to be strengthened and expanded ✓✓
- This will make them less dependent on foreign countries and give them more control over their economies / cut out the risk of world fluctuations in prices and demand problems ✓✓
- Inexperienced manufacturers cannot compete with others, that justifies protection measures ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.3.5 How can South Africa benefit by focusing on value-added production?
South Africa can benefit by:
- establishing export driven industries ✓✓
- creating more employment opportunities ✓✓
- improving free trade by establishing new trade partners ✓✓
- e.g. BRICS ✓
(Accept any other correct relevant answers) (4)
3.4 Discuss competitiveness and investment in human capital as benchmark strategies for industrial development.
Competition
- Companies are more focused, innovative and effective if strong competition is present. ✓✓
- This improves the overall quality of the manufactured products. ✓✓
- As with technological advancement, high quality products can more easily be exported and compete on an international level. ✓✓ (Max 4)
Human capital
- The development of human capital through skills development is of critical importance, as skilled employees are more productive than untrained ones. ✓✓
- By investing in human capital, a country is assured of having long-term economic growth. ✓✓ (Max 4) (Accept tabular format)
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(Allocate a maximum of 4 marks for mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
3.5 How can the development of small businesses benefit the South African economy?
Small businesses can benefit the South African economy by:
- Providing guidance to create employment for structurally unemployed people that might lead towards a more inclusive economy ✓✓
- Promoting entrepreneurial development among women and the youth in rural areas where unemployment is very high ✓✓
- Helping in the diversification of the economy by promoting the upliftment of a variety of skills ✓✓
- Enhancing competition most needed to benefit the consumer pricewise
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(Allocate a maximum of 2 marks for mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: MACROECONOMICS AND ECONOMIC PURSUITS
4.1 Answer the following questions.
4.1.1 Name TWO forms of import substitution.
- Voluntary ✓
- Enforced ✓ (2 x 1) (2)
4.1.2 What impact will an increase in the VAT rate have on the standard of living of the poor?
- It will reduce their consumption spending hence they would buy less than they did before the increase ✓✓ (1 x 2) (2)
4.2 DATA RESPONSE
4.2.1 Which institution provides the above statistics?
- South African Reserve Bank (SARB) ✓ (1)
4.2.2 Which item records transactions relating to donations and gifts to other countries?
- Current transfers ✓ (1)
4.2.3 Briefly describe the capital transfer account as part of the BoP.
- It is a net amount that includes transactions and grants relating to ownership of fixed assets, debt forgiveness and the value of household and personal effects and financial claims and liabilities of migrants ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
4.2.4 Give ONE reason for the decline in gold exports?
- Less reliance on gold as a value stabilising commodity ✓✓
- Worldwide recession led to a low gold price ✓✓
- Closing-down of gold shafts led to down-scaling of gold production ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant answer) (2)
4.2.5 Calculate the trade balance for 2015. Show all calculations.
- Trade Balance = Merchandise exports + Net gold exports – Merchandise imports
= R973 778 ✓ + R67 662 ✓ - R1 075 850 ✓
= - R34 410 ✓
(1 mark for correct answer without calculations) (4)
4.3 DATA RESPONSE
4.3.1 Identify ONE major challenge in the cartoon above.
- Inequality/poverty ✓ (1)
4.3.2 Give ONE negative consequence of poverty in the cartoon above.
- Hunger/malnutrition/crime ✓ (1)
4.3.3 What does the Mandela Legacy refer to?
- The Mandela Legacy tried to solve major problems of poverty, social and economic inequality and create a transparent and democratic government where universal respect for humanity exists ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
4.3.4 Suggest ONE way in which South Africa can be freed from inequality.
- Fair distribution of national income ✓✓
- Creation of employment opportunities ✓✓
- Have an investor-friendly legislation that will attract FDI ✓✓
- Provide education and training ✓✓
- Encourage entrepreneurship ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
4.3.5 How can human resources be targeted to be more effective in solving the problems in the cartoon above?
- More emphasis should be placed on education, which receives the biggest slice of budget expenditure, to benefit all involved in education ✓✓
- Major partners in the private sector should take responsibility to accommodate workers skilled on different levels and focus on manufacturing using labour intensive production methods ✓✓
(If the challenges mentioned in the cartoon are addressed, accept the candidate’s response) (4)
4.4 Briefly discuss Special Economic Zones as part of South Africa's industrial development plan.
Special Economic Zones (SEZ)
- Geographically demarcated area where specific economic activities have been identified to be developed ✓✓
- These areas may enjoy incentives such as tax relief and support systems to promote industrial development ✓✓
- It creates a basis for a broader range of industrial parks ✓✓
- It also provides economic infrastructure to enable the effective clustering of value-adding and employment-enhancing manufacturers ✓✓
The aims of SEZ's:
- Promote rapid development by acting as a magnet for investment in key growth areas ✓✓
- Enable the development of new industrial regions through the establishment of new industrial hubs in under-developed regions and the strengthening of existing one ✓✓
- SEZ's are used for the purposes such as export promotion, enterprise development, urban renewal, rural development and domestic or regional production ✓✓ (Any 4 x 2)
(Allocate a maximum of 4 marks for mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
4.5 How can South Africa benefit from trading in global markets?
South Africa can benefit from trading in global markets by:
- partaking more intensively in free trade that will fuel efficiency through elimination of extra costs and wastage ✓✓
- pursuing lower prices which will benefit the local consumer in the satisfaction of a greater variety of wants ✓✓
- accessing more goods and services produced in other countries which will increase the variety to choose from ✓✓
- assisting local producers to increase production and employ more domestic factors of production which will limit unemployment and have a positive effect on the standard of living of many South Africans ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(Allocate a maximum of 2 marks for mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer any ONE of the two questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK. Your answer will be assessed as follows:
STRUCTURE OF ESSAY | MARK ALLOCATION |
Introduction | Max. 2 |
Body | Max. 26 Max. 10 |
Conclusion
| Max. 2 |
TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 5: MACROECONOMICS
The state plays a significant role in a mixed economic system and is therefore one of the largest sectors in the economy.
- Discuss the macroeconomic objectives of the state. (26)
- How successful is the implementation of South Africa's fiscal policy? (10) [40]
INTRODUCTION
Economic growth is required for economic development and can only occur if policy planning in the country embraces those policies that which would ensure sustainability in the economy ✓✓ (Max 2)
MAIN PART
Price stability ✓
- Implies that prices in the economy do not change much over time ✓✓
- Price stability is the opposite of inflation ✓✓
- When prices are relatively stable and inflation is low, markets can function optimally and the government can promote economic growth and development more effectively ✓✓
- The SARB strives to keep the inflation rate within the target range of 3 to 6% ✓✓ (Max 6)
Exchange rate stability ✓
- If more money flows into the country than going out, we could have a surplus on the BOP ✓✓
- The state promotes domestic production of surpluses to increase exports and by monitoring changes in exchange rates ✓✓
- Fluctuations, such as the depreciation and appreciation of a currency, can create uncertainties for investors, producers and retailers ✓✓
- South Africa uses a floating exchange rate system, which allows its exchange rate to determine its own value, based on demand and supply ✓✓
- The South African currency has fluctuated considerably over the last two decades ✓✓
- Over the last decade it appreciated to reach a peak of R6,36 to the US dollar by the end of 2005 ✓✓
- Thereafter it depreciated sharply by 33% to R8,44 to the US dollar in 2010 and 2012 ✓✓
- International reserves increased from 12,9% a decade ago to 28,67% in 2011 ✓✓
- The SARB uses a free-floating exchange rate system ✓✓
- Instability of exchange rates such as during the latter part of the 2000s is a great problem for businesses ✓✓
- However, the international benchmark is whether market forces determine rates ✓✓ (Max 6)
Full employment ✓
- Full employment means that all persons who would like to work and who are looking for work should be able to find work, or create work for themselves / where all resources are utilised efficiently ✓✓
- Employment in the formal non-agricultural sectors of the economy increased at a low rate ✓✓
- However, in 2009 and 2010 it turned negative because of the effect of global recession ✓✓
- The average growth of less than one per cent over the ten years is disappointingly low ✓✓
- The result is that the unemployment rate is increased from 15% in 1994 to 25,2% in 2012 ✓✓
- Public sector employment increased during and after the global recession, reducing the total effect on employment ✓✓
- The government supports education, labour-intensive businesses and the informal sector ✓✓
- Low rates of unemployment also correlates with other socio-indicators, such as a lower crime rate and higher standard of health ✓✓ (Max 6)
Economic equity ✓
- This is the reasonable division of income among the population ✓✓
- Redistribution of income and wealth achieves the reasonable division of income ✓✓
- Measures that the government uses to achieve that are:
- Using the progressive income tax system, higher income groups pay higher tax rates ✓✓
- Government uses taxes to finance social goods and services such as housing, education and primary health care ✓✓
- Government pays cash grants such as old-age grants, disability grants, child support grants, etc. ✓✓
- Government implements policies such as BBBEE to achieve that ✓✓ (Max 6)
Economic growth ✓
- This refers to an increase in the productive capacity of the economy of the country for a specific period of time e.g. a year / an increase in the production of goods and services in the economy ✓✓
- It is usually measured in terms of growth in the national output valued at market prices referred to a the gross domestic product (GDP) ✓✓
- South Africa is a developing country and in terms of the World Bank's classification it is an upper-middle income country ✓✓
- The average economic growth rate was 3.8% per year in the ten years between 2001 and 2012 ✓✓
- The government applied structural reform as the guiding principle in the fiscal policy discipline of the country ✓✓
- Structural reform means that the budget had to reflect on transformation aims of the government, e.g. on education, health and welfare ✓✓
- Under the GEAR policy, which was phased out by 2010, the budget deficit was reduced to less than 30% of the GDP in all the years before 2009 ✓✓
- This was the acceptable international benchmark for best practice ✓✓
- The government is internationally acknowledged for its fiscal discipline and this stands the country in good stead in the international community ✓✓
- The state attempts to ensure that there is a continual improvement in the productive capacity of the economy by offering quality education and skills training ✓✓
- Economic growth makes it possible to improve the standard of living of people and also reduce poverty ✓✓ (26)
(Max 6) (Accept current statistics)
(Allocate a max of 8 marks for headings/subheadings/examples)
ADDITIONAL PART
The government have the following in place to raise revenue:
- Progressive personal income tax where those higher-income earners are taxed at a higher rate ✓✓
- Wealth tax where properties like houses, offices and factory buildings in urban areas are taxed annually ✓✓
- Other redistributions that advantage the poor and low income earners ✓✓
Expenditure:
- Cash benefits provided in the form of old-age pensions, disability grants, child support grants ✓✓
- Benefits in kind which include the provision of healthcare, education and schools meals ✓✓
- Property subsidies that help the beneficiaries to acquire ownership of fixed residential property ✓✓
- Government complies in terms of expenditure and taxation in a way that enhances its chances of achieving macroeconomic objectives ✓✓
- Government invest in more infrastructure to develop the economy, e.g. the Medupi power plant for the increase in the supply of electricity, the De Hoop dam ✓✓
- The provision of housing to the impoverished and previously disadvantaged black majority ✓✓
- Provision of meals at schools for school children ✓✓
(Max 10) (Accept any other correct relevant response)
CONCLUSION
Macroeconomic objectives are a desirable for the government to have for they serve as the roadmap in addressing the socio-economic circumstances in the country ✓✓
(Max 2) [40]
QUESTION 6: ECONOMIC PURSUITS
Economic and social indicators are used globally to compare and describe economic performances of countries.
- Examine the following social indicators:
- Demographics
- Education
- Nutrition and health (26)
- What can the South African government do to improve the delivery of social services to its citizens? (10)
[40]
INTRODUCTION
Social indicators are measures that economists use to evaluate the performance of a country in terms of the social well-being of its citizens✓✓ (Max 2)
MAIN PART
Demographics
- This deals with the characteristics of the population, such as size, race, age sex, income geographic distribution, language, education occupation religion ✓✓
- Definable issues related to human well-being over a period of time ✓✓
- Population growth ✓ The population numbered 52,98 million in 2013 ✓✓
- Growth is slowing down ✓✓
- Measuring population growth is important for delivering social services and for identifying the size of the tax base (the total number of people paying taxes) ✓✓
- Life expectancy ✓ South Africa's life expectancy rate is down from 62,8 years to 49.7 years in 2015 ✓✓
- Dependency rate ✓ the high-age dependency rate in South Africa indicates the level of dependency on those who are working ✓✓
- Human Development Index ✓ This is a socio-economic indicator of human development. Three basic aspects are considered: the standard of living, quality of health care and general standard of education ✓✓
- It combines measures of life expectancy, school enrolment, literacy and income to allow a broader view of a country’s development than does income alone ✓✓ (Max 10)
Education
- The standard of living is related to the level of education ✓✓
- Education is a key social indicator:
- Public expenditure ✓ the percentage of the national budget that is directed towards education ✓✓
- Secondary enrolment ✓ this shows the percentage of an age group attending high school ✓✓
- Primary completion ✓ the percentage of an age group that has completed primary education is an indicator of the efficiency of the education system ✓✓
- Youth literacy rate ✓ the percentage of the 15-24 age group that are literate ✓✓ (Max. 10)
Nutrition and Health
- The standard of living of the population is related to the quality of nutrition and health:
- Nutrition
Child malnutrition ✓ Malnutrition is expressed in two ways – weight for age (underweight) and height for age (dwarfism) ✓✓ Malnutrition in all its forms amounts to an intolerable burden not only national health system but on the entire cultural, social and economic fabrics of the nation ✓✓
The proportion of underweight children is the most important indicator of malnutrition ✓✓ - Overweight children ✓ there is an association between obesity of children and other diseases ✓✓
- Health
- Infant mortality: ✓ The number of children that will die before one year of age one way of measuring the health of a population ✓✓ Child mortality is substantially higher in poor households ✓✓
Under-five mortality ✓ the number of children that will die before the age of 5 years ✓✓
- Nutrition
Health expenditure
- The amount of health expenditure by the state and private sector, as a percentage of GDP ✓✓
- Health care has extensive positive externalities ✓✓
- Access to safe drinking water: ✓ the percentage of a population that has reasonable access to safe drinking water ✓✓
- Access to sanitation facilities: ✓ the percentage of a population with at least adequate sanitation facilities that can prevent human, animal and insect contact ✓✓
(Max 10) (Allocate a max of 8 marks for headings/subheadings/examples) (Max 26)
ADDITIONAL PART
The South African government can
- provide free health services of quality at the provincial hospitals and clinics, because everyone is not able to pay for these services ✓✓
- develop more major road infrastructure leading into economic hubs to accommodate more traffic ✓✓
- extend school feeding schemes to more primary schools in the country where major unemployment is experienced in communities ✓✓
- improve the provision of clean water to communities, especially when droughts are experienced ✓✓
- increase free housing services and grants to the needy ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Max. 10)
CONCLUSION
Social indicators are the best yardsticks in checking on the development and progression of communities as a result of government initiative to improve the lives of the society at large / South African government annually increases its budget expenditure on health and education to improve the lives of its citizens ✓✓ (Max. 2)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
REQUIREMENTS:
- Drawing instruments
- A non-programmable pocket calculator
- ANSWER BOOK
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Answer each question as a whole. Do NOT separate subsections of questions.
- Start the answer to EACH question on a NEW page.
- Do NOT write in the margins of the ANSWER BOOK.
- You may use sketches to illustrate your answers.
- Write ALL calculations and answers in the ANSWER BOOK or on the attached ANSWER SHEETS.
- Use the mark allocation as a guide to the length of your answers.
- Make drawings and sketches in pencil, fully dimensioned and neatly finished off with descriptive titles and notes to conform to the SANS/SABS Code of Practice for Building Drawings.
- For the purpose of this question paper, the size of a brick should be taken as 220 mm x 110 mm x 75 mm.
- Use your own discretion where dimensions and/or details have been omitted.
- Answer QUESTIONS 1.8, 2.6, 3.3, 4.4, 5.2, 5.3, 6.1 and 6.2 on the attached ANSWER SHEETS using drawing instruments, where necessary.
- Write your CENTRE NUMBER and EXAMINATION NUMBER on every ANSWER SHEET and hand them in with your ANSWER BOOK, whether you have used them or not.
- Due to electronic transfer, drawings in the question paper are NOT to scale.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: CONSTRUCTION, SAFETY AND MATERIAL
Start this question on a NEW page.
1.1 FIGURE 1.1 below shows a building site.
FIGURE 1.1
1.1.1 Name the safety equipment shown in FIGURE 1.1. (1)
1.1.2 Explain the purpose of the safety equipment shown in FIGURE 1.1. (1)
1.1.3 Explain under what circumstances it would be necessary to install this safety equipment on a building site. (2)
1.2 Name the type of reinforcing material used to strengthen brickwork. (1)
1.3 Name TWO types of brick bonds used in the building industry. (2)
1.4 Distinguish between a closer brick and a full brick in terms of size. (1)
1.5 Name TWO types of finishing that would be used on a newly plastered kitchen wall. (2)
1.6 Motivate why you used ONE of the finishings that you named in QUESTION 1.5. (1)
1.7 Distinguish, by means of line diagrams, between the profiles of corrugated iron sheeting and IBR sheeting. (2)
1.8 FIGURE 1.8 below illustrates an incomplete sectional view of the substructure of a building. 
FIGURE 1.8
Use ANSWER SHEET 1.8 to complete the sketch by drawing the following:
- Concrete floor penetrating the one-brick wall halfway
- Screed
- Backfilling on both sides
- Blinding layer
- Hardcore filling
- DPC (10)
1.9 FIGURE 1.9 shows the incomplete top view of a roof layout showing the roof trusses and the outer walls of a rectangular building. Analyse the illustration and answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 1.9
1.9.1 Identify parts A, B and C. (3)
1.9.2 Name the type of roof shown in FIGURE 1.9. (1)
1.10 State ONE type of material that DPC may be made of. (1)
1.11 Describe TWO requirements that preservatives should comply with to be used effectively on timber. (2)
[30]
QUESTION 2: ADVANCED CONSTRUCTION AND EQUIPMENT
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–M) next to the question number (2.1.1–2.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 2.1.11 N.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
2.1.1 Builder's line | A part of a pile (10 x 1) (10) |
2.2 FIGURE 2.2 below shows hand tools that are used on a site and in a workshop. Write down the correct name of each tool next to the letter (A–C) in the ANSWER BOOK.
FIGURE 2.2 (3)
2.3 FIGURE 2.3 below shows a construction of the reinforcement of a beam and a column. 
FIGURE 2.3
2.3.1 Name any THREE components used in reinforcement. (3)
2.3.2 What would you use to keep the reinforcement bars away from the formwork when the concrete is being poured? (1)
2.4 Name TWO types of pile foundations. (2)
2.5 FIGURE 2.5 below shows formwork supporting a concrete beam. Analyse the illustration and answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 2.5
2.5.1 Identify components A, B and C. (3)
2.5.2 Explain TWO functions of component D. (2)
2.5.3 Explain the effect that form oils and emulsions, applied to formwork, will have on the concrete. (1)
2.6 Use ANSWER SHEET 2.6 and make a neat sketch, in good proportion, of a vertical section through the bottom part of a steel-frame dry-wall construction.
Show the following details on your sketch:
- Steel floor track fixed to the floor with nylon anchors
- Steel rail with channel facing to the front
- Cladding on one side
- Skirting board on one side
- Label ONE part of the sketch. (6)
2.7 Predict ONE consequence/result if concrete is not adequately cured. (1)
2.8 If any ONE of the ingredients of concrete were left out, what would be the effect/result? (1)
2.9 Draw, in good proportion, a line diagram in the ANSWER BOOK to show the brickwork of a one-brick, semi-circular gauged arch.
- Show THREE bricks of the semi-circular gauged arch as well as the construction showing the method to draw the bricks on the diagram. (2)
- Label the extrados and intrados of the arch clearly on the diagram. (2)
2.10 In terms of cost and labour, explain TWO disadvantages of installing an in situ cast concrete suspended floor instead of a rib and block floor. (2)
2.11 Explain ONE reason why you would NOT use a cavity wall as a partition wall inside a building. (1)
[40]
QUESTION 3: CIVIL SERVICES
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 Name the fitting that is installed under a wash basin to prevent bad smells from the sewerage system from entering the building. (1)
3.2 Explain the function of the anaerobic bacteria in a septic tank. (1)
3.3 Use ANSWER SHEET 3.3 and draw a line diagram of a septic tank. (7)
Show any THREE labels. (3)
3.4 Define storm water. (2)
3.5 Explain TWO reasons why sewage should not be directed into a storm-water system. (2)
3.6 Explain the purpose of a safety valve, as used in a geyser. (1)
3.7 What will happen if the thermostat inside a geyser does not work properly? (1)
3.8 Distinguish between a high-pressure geyser and a gravity geyser in terms of the incoming water supply. (2)
3.9 Motivate why black paint is used to paint the inside of the tray of a solar panel. (1)
3.10 Draw the symbols for the following:
3.10.1 One-way double-pole switch (2)
3.10.2 Two-way switch (2)
3.10.3 Water meter (2)
3.11 Distinguish between the placement of an elbow and the placement of a tee-coupler/T-fitting, as used in cold-water installation. (2)
3.12 State ONE negative result if a pressure-reducing valve is not installed on the cold-water supply of a building. (1)
[30]
QUESTION 4: QUANTITIES, MATERIALS AND JOINING
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 FIGURE 4.1 below shows the front view of a single casement with two window panes. The tenons of all the joints are through and through. The horns on both sides are 25 mm long. Study the drawing and use the information to complete the cutting list. Write down the answer next to the question number (4.1.1 to 4.1.8) in the ANSWER BOOK. 
FIGURE 4.1
MEMBER | QUANTITY | 4.1.1 | LENGTH | WIDTH | THICKNESS | MATERIAL |
Frame head | 1 | mm | 4.1.2 | 114 | 75 | Meranti |
Sash top rail | 1 | mm | 580 | 60 | 4.1.3 | Meranti |
Frame stile | 4.1.4 | mm | 1 200 | 114 | 75 | Meranti |
Sash stile | 2 | mm | 1 050 | 4.1.5 | 44 | Meranti |
Glazing bar | 1 | mm | 4.1.6 | 30 | 44 | Meranti |
4.1.7 | 1 | mm | 580 | 60 | 44 | Meranti |
Window sill | 1 | mm | 780 | 4.1.8 | 75 | Meranti |
(8)
4.2 Various options are given as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (4.2.1–4.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 4.2.6 C.
4.2.1 The main difference between coach screws and other screws, such as drywall screws and round-head screws, is the …
- length.
- thickness.
- head.
- strength. (1)
4.2.2 … nails should be used to fix skirting to brickwork.
- Oval wire
- Clout-headed
- Wire
- Steel (1)
4.2.3 … is used to seal the joint when galvanised fittings are used to join pipes.
- Silicone sealer
- Contact glue
- Plumbing tape/Hemp
- PVC weld (1)
4.2.4 When making a soldered joint, the melted solder is drawn into the joint by a … action.
- pushing
- pulling
- drawing
- capillary (1)
4.2.5 To secure roof trusses to a wall you may use hoop iron or …
- nylon straps.
- 4 mm diameter galvanised wire.
- screws.
- heavy-duty expansion anchor (Rawl bolt). (1)
4.3 Name ONE place where a heavy-duty expansion anchor (Rawl bolt) may be used. (1)
4.4 FIGURE 4.4 below shows the floor plan of a storeroom. 
FIGURE 4.4
SPECIFICATIONS:
- Outside measurements of the storeroom: 7 000 mm x 3 000 mm
- Height of the walls from the finished floor level (FFL) to the wall plate: 2 950 mm
- Thickness of the plaster: 15 mm
- Size of the window: 900 mm x 600 mm
- Size of the door: 2 100 mm x 900 mm
Use ANSWER SHEET 4.4 and calculate:
4.4.1 The total outside area of the building that should be plastered from the finished floor level up to the wall plate. Ignore the reveals. (13)
4.4.2 The volume of plaster needed for the external walls. Round off your answers to TWO decimals. (3)
[30]
QUESTION 5: APPLIED MECHANICS
Start this question on a NEW page.
5.1 FIGURE 5.1 below shows a shaped lamina with an isosceles triangular hole. All dimensions are in millimetres.
Study FIGURE 5.1 and answer the questions by writing only the answer next to the question number (5.1.1–5.1.7) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 5.1.8 2 900 mm².
HINT: Use the formula on the FORMULA SHEET. 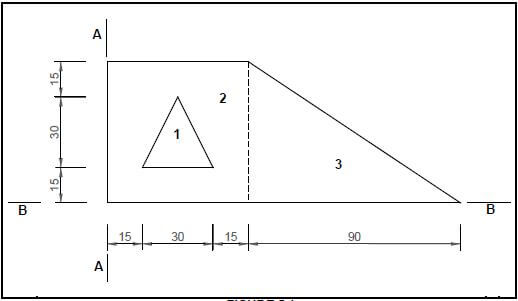
FIGURE 5.1
Determine the following:
5.1.1 Area of part 1 (1)
5.1.2 Area of part 2 without the hole (1)
5.1.3 Area of part 3 (1)
5.1.4 Total area of the lamina (1)
5.1.5 Position of the centroid of part 1 from A–A (1)
5.1.6 Position of the centroid of part 3 from A–A (2)
5.1.7 Position of the centroid of part 2 from B–B (1)
5.2 ANSWER SHEET 5.2 shows TWO diagrams of a cantilever frame. Use the answer sheet to answer the questions that follow.
5.2.1 Name DIAGRAMS A and B. Write the answer on the lines provided. (2)
5.2.2 On DIAGRAM A, indicate the nature of the forces in each member by means of arrows. (4)
5.2.3 Complete the table by indicating the nature and magnitude of the forces. (Deduce the information from the drawings given.) (6)
5.3 FIGURE 5.3 below shows the space diagram of a beam with a span of 8 metres with two point loads and a uniformly distributed load. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow. 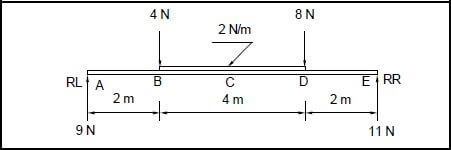
FIGURE 5.3
5.3.1 From FIGURE 5.3, deduce the value of the shear forces at A, B, D and E and draw the shear force diagram on ANSWER SHEET 5.3. Indicate the value of the shear forces on the diagram.
Use scale 5 mm = 1 N. (7)
5.3.2 Calculate the bending moment at C. (3)
[30]
QUESTION 6: GRAPHICS AND COMMUNICATION
6.1 FIGURE 6.1 below shows the SITE PLAN of a proposed dwelling. Study the drawing and complete the table on ANSWER SHEET 6.1. 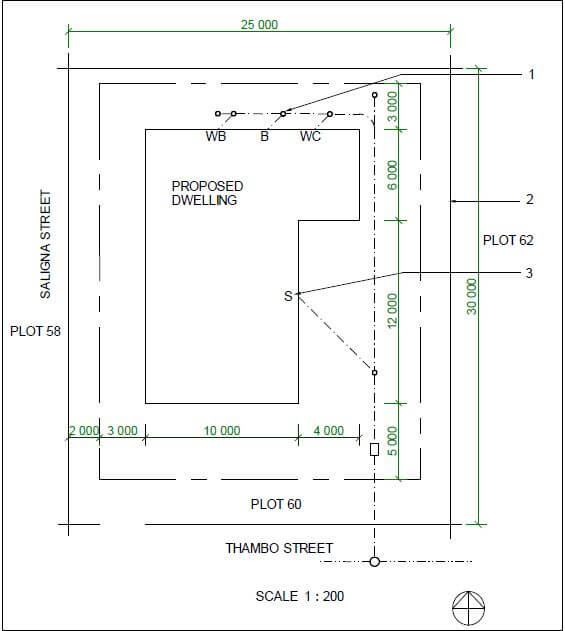
FIGURE 6.1 (15)
6.2 FIGURE 6.2 below shows a line diagram of the floor plan of a two-bedroom house. 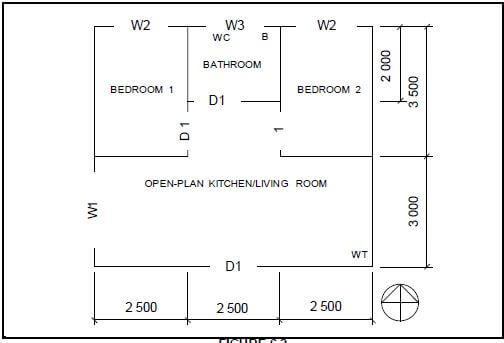
Study FIGURE 6.2 and develop and draw, on ANSWER SHEET 6.2, to scale 1 : 50, the FLOOR PLAN of the building. Use the specifications below and on the next page. (Use the assessment criteria on ANSWER SHEET 6.2 as a guideline for your drawing.)
SPECIFICATIONS:
- The measurements indicated on the drawing are the inside measurements of each room.
- Windows and doors:
WINDOWS AND DOORS | WIDTH | HEIGHT |
Window 1 (W1) | 1 600 | 1 500 |
Window 2 (W2) | 1 600 | 1 200 |
Window 3 (W3) | 1 600 | 900 |
Door openings 1 (D1) | 900 | 2 100 |
- All windows are positioned in the middle of the external wall of each room.
- The internal doors are positioned 200 mm from the corner of the wall.
- The front door is positioned in the middle of the wall of the open-plan kitchen/living room.
- All external walls of the house are 220 mm wide.
- All internal walls are 110 mm wide.
Show the following on the drawing:
- The external and internal walls, as well as the windows and doors in the spaces as indicated
- The drawing symbols for a bath and water closet in the bathroom and a wash tub in the open-plan kitchen/living room in the position as indicated on the line diagram
- The overall length of the building on the northern side of the house THREE marks will be allocated for the application of the scale.
Start the drawing from corner A, as indicated in the bottom left-hand corner of ANSWER SHEET 6.2. (25)
[40]
TOTAL: 200
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 1.8 
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Concrete floor drawn in correct place | 1 | |
Screed drawn in correct place | 1 | |
Symbol for screed | 1 | |
Back filling drawn in correct place | 2 | |
Symbol for back filling | 1 | |
Blinding layer drawn in correct place | 1 | |
Hardcore filling drawn in correct place | 1 | |
Symbol for hardcore filling | 1 | |
DPC drawn in correct place | 1 | |
TOTAL | 10 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 2.6 ![]()
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Steel floor track | 1 | |
Nylon anchor | 1 | |
Steel rail | 1 | |
Cladding | 1 | |
Skirting board | 1 | |
ONE label | 1 | |
TOTAL | 6 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 3.3
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
External walls | 1 | |
Inner wall | 1 | |
Opening in inner wall | 1 | |
Concrete base | 1 | |
Inlet and outlet | 2 | |
Cover/Manhole | 1 | |
Any THREE labels | 3 | |
TOTAL | 10 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 4.4
Write your answers in the spaces indicated with _________.
4.4.1
A | B | C | D | |
Area to be plastered: | ||||
Total outside length of short walls: | ||||
= 2/ mm | ||||
= mm | ||||
Total outside length of long walls: | ||||
= 2/ mm | ||||
= mm | ||||
Total outside length of all the walls: | ||||
= mm + mm | ||||
= mm | ||||
| (3) | ||||
1/ | _______ | Outside area of walls before deductions: | ||
_______ | ______ m2 | (2) | ||
1/ | _______ | Area of window opening: | ||
_______ | ______ m2 | (2) | ||
1/ | _______ | Area of door opening: | ||
_______ | ______ m2 | (2) | ||
Total wall area to be plastered: | ||||
__________ m2 - __________ m2 - __________ m2 | ||||
= _____________ m2 | (4) |
4.4.2
Volume of plaster needed: | ||||
1/ | _______ | |||
_______ | ______ m2 | (3) |
[16]
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 5.2  (4)
(4)
DIAGRAM A __________________________ (1) 
DIAGRAM B ________________________ (1)
SCALE 1 mm = 1 N
MEMBER | NATURE | MAGNITUDE |
AC | ||
BC | --- | |
CD | ||
DA | --- |
(6)
Tolerance of 1 N to either side
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 5.3 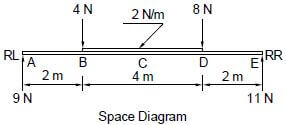
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARKS | CANDIDATE'S MARKS |
Drawing correct | 5 | |
Indicate four or more values of shear forces on drawing | 1 | |
Correct application of scale | 1 | |
TOTAL | 7 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 6.1
NO. | QUESTIONS | ANSWERS | MARKS |
1 | Name the scale used for the site plan. | 1 | |
2 | Name the colour that you would use to shade the proposed dwelling on a site plan. | 1 | |
3 | Identify number 1. | 1 | |
4 | What is the number of the plot on which the house will be built? | 1 | |
5 | Describe abbreviation 3. | 1 | |
6 | Determine the distance from the boundary line to the proposed dwelling on the western side of the building. | 1 | |
7 | Determine the distance between the building line and the building on the northern side of the building. | 1 | |
8 | In which street is the entrance to the site located? | 1 | |
9 | Draw the roof line of a gable roof for the building indicated in the column alongside. |  | 3 |
10 | Calculate the total area of the building in square metres. | 2 | |
11 | If the area of the site is 750 m², what percentage will the building occupy on the site: 29,2% OR 27,2% OR 25,2%? | 2 | |
TOTAL | 15 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 6.2
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARKS | LM | ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARKS | LM |
External walls | 4 | Bath | 1 | ||
Internal walls | 5 | Dimensions | 2 | ||
Windows | 4 | Application of scale | 3 | ||
Doors | 4 | ||||
Wash tub | 1 | ||||
Water closet | 1 | ||||
TOTAL | 25 |
FORMULA SHEET
IMPORTANT ABBREVIATIONS
SYMBOL | DESCRIPTION | SYMBOL | DESCRIPTION | SYMBOL | DESCRIPTION |
c | Centroid | b | Breadth/Width | r | Radius |
ℓ | Length | s | Side | A | Area |
FORMULAE
AREA OF | FORMULA (in words) | FORMULA (in symbols) | FORMULA FOR THE POSITION OF CENTROIDS | |
X-axis | Y-axis | |||
Square | side × side | s × s | s/2 | s/2 |
Rectangle | length × breadth | ℓ × b | ℓ /2 | b/2 |
Right-angled triangle | ½ x base × height | ½b × h | b/3 | h/3 |
Equilateral triangle/ Isosceles triangle | ½ x base × height | ½b × h | b/2 | h/3 |
Position of centroid = (A1×d) ± (A2 ×d)
Total area
OR
Y = ∑Ay
∑A
OR
X = ∑Ax
∑A
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: CONSTRUCTION, SAFETY AND MATERIAL
1.1
1.1.1 Safety net/Catch net √ (1)
1.1.2 Prevents objects and debris from falling onto workers and visitors. √ (1)
1.1.3
- Where work is done on higher levels and people move below. √ (2)
- Where falling objects pose a danger to workers below. √
ANY OTHER ACCEPTABLE ANSWER
1.2 Brick force √ (1)
1.3
- Stretcher bond √
- English bond √ (2)
1.4 A closer brick is half the width of a full brick. √ (1)
1.5
- Paint the wall √
- Tile the wall √ (2)
1.6 Paint:
- Paint is much cheaper. √
- ∙ Paint lasts long if good quality paint is used.
- ∙ Paint is cleaned easily.
- ∙ Paint is quicker to apply.
Tiles:
- Tiles are expensive at first but last longer. (1)
- Tiles are easy to clean.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE OR ANY OTHER ACCEPTABLE
1.7 Corrugated iron sheeting √ ![]()
IBR iron sheeting √ (2)![]()
1.8 ANSWER SHEET 1.8 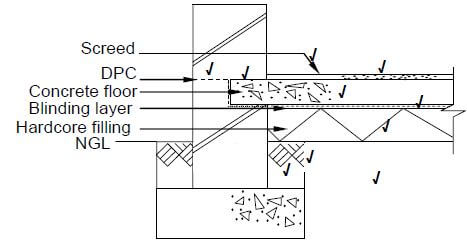
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Concrete floor drawn in correct place | 1 | |
Screed drawn in correct place | 1 | |
Symbol for screed | 1 | |
Backfilling drawn in correct place | 2 | |
Symbol for back filling | 1 | |
Binding layer drawn in correct place | 1 | |
Hardcore filling drawn in correct place | 1 | |
Symbol for hardcore filling | 1 | |
DPC drawn in correct place | 1 | |
TOTAL | 10 |
(10)
1.9
1.9.1
- A - Hipped rafter/Corner rafter √
- B - Purlin √
- C - Brick wall √ (3)
1.9.2 Hipped roof √ (1)
1.10 DPC – Thin layer of plastic sheeting/membrane, bituminous felt. √ (1)
1.11 Preservatives must:
- be poisonous enough to kill insects without being harmful to humans. √
- be affordable. √
- not smell unpleasant.
- not cause corrosion of metals in the wood.
- ∙ strengthen rather than weaken the wood.
- not spoil the appearance of the wood.
- not change the dimensions or the strength of the wood. (2)
[30]
QUESTION 2: ADVANCED CONSTRUCTION AND EQUIPMENT
2.1
2.1.1 D √ (1)
2.1.2 L √ (1)
2.1.3 J √ (1)
2.1.4 H √ (1)
2.1.5 I √ (1)
2.1.6 A √ (1)
2.1.7 M √ (1)
2.1.8 E √ (1)
2.1.9 G √ (1)
2.1.10 B √ (1)
2.2
- A - Plumb bob √
- B - Spirit level/Level √
- C - Cross cut saw/Rip saw/Panel saw/Saw √ (3)
2.3
2.3.1
- Anchor bar √
- Shear bar √
- Main bar √
- Stirrup/Binder (3)
ANY THREE OF THE ABOVE
2.3.2
- Spacers √
- Concrete block/Cover depth blocks
- Steel stands/Cover depth stands
- Plastic spacers (1)
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE OR ANY OTHER ACCEPTABLE ANSWER
2.4
- In-situ (driven) foundation piling √
- Pre-formed concrete piles √
- Driven in situ piles/Franki piles
- Steel tube caisson piles
- Short-bored piles (2)
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE OR ANY OTHER ACCEPTABLE ANSWER
2.5
2.5.1
- A - Concrete beam √
- B - Bearer √
- C - Brace √ (3)
2.5.2
- Wedges make the striking of formwork easier. √
- Assist in setting up the formwork to the correct height. √
- Wedges make the formwork more rigid. (2)
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE OR ANY OTHER ACCEPTABLE ANSWER
2.5.3
- Form oils prevent concrete from sticking to the formwork. √
- Form oil will ensure smooth finish of concrete surface.
- Form oils may cause discolouring of the concrete surface. (1)
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE OR ANY OTHER ACCEPTABLE ANSWER
2.6 ANSWER SHEET 2.6 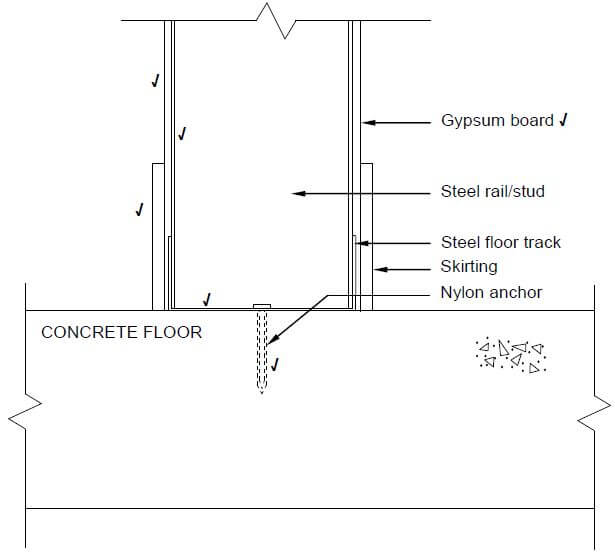
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Steel floor track | 1 | |
Nylon anchor | 1 | |
Steel stud | 1 | |
Cladding | 1 | |
Skirting board | 1 | |
ONE label | 1 | |
TOTAL | 6 |
(6)
2.7
- The concrete will dry out quickly. √
- There may not be sufficient water in the concrete for the hydration process to continue.
- The concrete will not gain adequate strength. (1)
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE
2.8
- If stone is not used there will be no bulk. √
- Compression strength will be compromised if stone is not used.
- If sand is not used there will be lots of voids in the concrete.
- If cement is not used there will be no hydration.
- The ingredients will not adhere to each other if cement is not used.
- If water is not used there is no hydration and the ingredients will not adhere to each other. (1)
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE OR ANY OTHER ACCEPTABLE ANSWER
2.9 
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Construction | 1 | |
Any three bricks | 1 | |
Label intrados | 1 | |
Label extrados | 1 | |
TOTAL | 4 |
(4)
2.10
- In situ cast concrete floors are more expensive. √
- In situ cast concrete floors take longer to install. √
- In situ cast concrete floors require skilled labour to install. (2)
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE OR ANY OTHER ACCEPTABLE ANSWER
2.11
- Too expensive √
- Cavity wall is too wide and takes up too much space.
- Inner walls are not exposed to wet weather conditions.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE OR ANY OTHER ACCEPTABLE ANSWER(1)
[40]
QUESTION 3: CIVIL SERVICES
3.1
- P-trap √
- S-trap
- Water traps (1)
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE
3.2 The function of anaerobic bacteria in a septic tank is to decompose the solids until nothing but sludge remains. √ (1)
3.3 ANSWER SHEET 3.3 
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
External walls | 1 | |
Inner wall | 1 | |
Opening in inner wall | 1 | |
Concrete base | 1 | |
Inlet and outlet | 2 | |
Cover/Manhole | 1 | |
Any THREE labels | 3 | |
TOTAL | 10 |
(10)
3.4 √ √
- Storm water is rain, hail or snow that falls on the earth in large quantities in a short spread of time. (2)
3.5
- Sewage should not be directed into a storm water system because it is illegal √, it causes pollution √ and is a health risk. (2)
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE OR ANY OTHER ACCEPTABLE ANSWER
3.6
- The safety valve releases excess pressure in the cylinder. √
- The safety valve is to open and release the inside pressure by discharging some of the hot water or steam. (1)
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE OR ANY OTHER ACCEPTABLE ANSWER
3.7
- The water will overheat if the thermostat does not switch off. √
- A person may be scalded because of the very hot water.
- There may be insufficient hot water for the household if the thermostat does not switch on at the correct temperature.
- There may not be any hot water at all if the thermostat does not switch on. (1)
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE OR ANY OTHER ACCEPTABLE ANSWER
3.8 A high-pressure geyser needs high incoming water pressure, √ whilst a gravity geyser will be used where the water pressure is low. √ (2)
3.9 Black backgrounds absorb heat the best. √ (1)
3.10  @ (2)
@ (2)
3.11 Elbow fittings are placed at the end of a pipe where there is a change in direction of flow of water. √ T-coupler/T-fitting is placed between pipes where water supply must be divided. √ (2)
3.12 If a pressure-reducing valve is not fitted:
- there will not be a constant downstream pressure to the installation. √
- water temperature in a shower may be affected if another tap is opened elsewhere in the system.
- hot water may be forced back through the geyser into cold water pipes due to the unbalanced pressure in the system.
- the high pressure of the municipality will not be lowered
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE OR ANY OTHER ACCEPTABLE ANSWER(1)
[30]
QUESTION 4: MATERIALS AND QUANTITIES
4.1 4.1.1 Unit √ (1)
4.1.2 780/780 mm √ (1)
4.1.3 44/44 mm √ (1)
4.1.4 2 √ (1)
4.1.5 60/60 mm √ (1)
4.1.6 580/580 mm √ (1)
4.1.7 Bottom rail/Sash bottom rail √ (1)
4.1.8 150/150 mm √ (1)
4.2
4.2.1 C √ (1)
4.2.2 D √ (1)
4.2.3 C √ (1)
4.2.4 D √ (1)
4.2.5 B √ (1)
4.3 Used for fixing timber/steel to brickwork, concrete and natural stone. √ It is used where medium to heavy duty fixings are required, such as steel to brick or concrete, railings, staircases, gates.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
ANSWER SHEET 4.4
4.4.1
A | B | C | D | |
Area to be plastered: | ||||
Total outside length of short walls: | ||||
= 2/3 000 mm | ||||
= 6 000 mm √ | ||||
Total outside length of long walls: | ||||
= 2/7 000 mm | ||||
= 14 000 mm √ | ||||
Total outside length of all the walls: | ||||
= 6 000 mm + 14 000 mm | ||||
= 20 000 mm √ | ||||
| (3) | ||||
1/ | 20,0 | Outside area of walls before deductions: | ||
2,95 √ | 59,0 m² √ | (2) | ||
1/ | 0,9 | Area of window opening: | ||
0,6 √ | 0,54 m² √ | (2) | ||
1/ | 2,1 | Area of door opening: | ||
0,9 √ | 1,89 m2√ | (2) | ||
Total wall area to be plastered: | ||||
√ √ √ 59,0 m² – 0,54 m² - 1,89 m² | ||||
= 56,57 m² √ need to be plastered | (4) |
4.4.2
Volume of plaster needed: | ||||
1/ | √ 56,57 m2 | |||
√ 0,015 m | 0,85 m2√ | (3) |
[30]
QUESTION 5: APPLIED MECHANICS
5.1
5.1.1 450 mm² √ (1)
5.1.2 3 600 mm² √ (1)
5.1.3 2 700 mm² √ (1)
5.1.4 5 850 mm² √ (1)
5.1.5 30 mm √ (1)
5.1.6 90 mm √√ OR 60 mm + 30 mm √ = 90 mm √ (2)
5.1.7 30 mm √ (1)
5.2 ANSWER SHEET 5.2 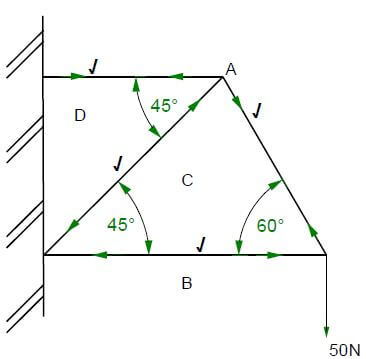
SPACE DIAGRAM 
VECTOR DIAGRAM
SCALE 1 mm = 1 N
USE A MASK TO MARK THIS QUESTION
MEMBER | NATURE | MAGNITUDE |
AC | Tie √ | 54,5 N √ |
BC | Strut √ | --- |
CD | Strut √ | 67 N √ |
DA | Tie √ | --- |
(6)
Tolerance of 1 N to either side
NOTE: Markers are to measure the members from the force diagram on ANSWER SHEET 5.2 in the question paper. Use scale 1 mm = 1 N.
ANSWER SHEET 5.3
5.3.1 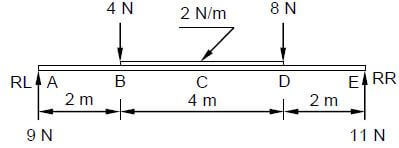
SPACE DIAGRAM 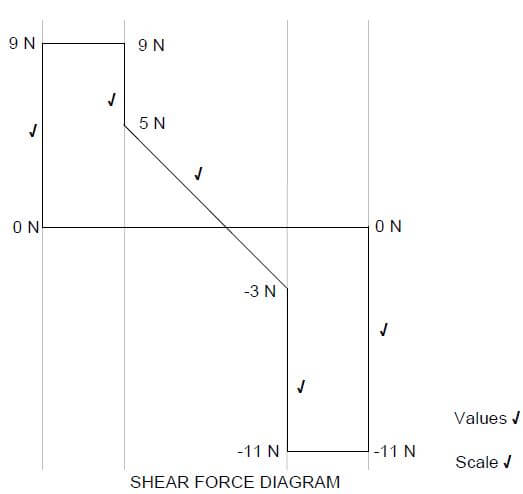
SHEAR FORCE DIAGRAM
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARKS | CANDIDATE'S MARKS |
Drawing correct | 5 | |
Indicate four or more values of shear forces on drawing | 1 | |
Correct application of scale | 1 | |
TOTAL | 7 |
(7)
NOT TO SCALE: USE A MASK TO MARK THIS QUESTION
5.3.2 Calculated from the left:
BMc = (9 x 4) - (4 x 2) - (4 x 1) √
= 36 - 8 - 4 √ = 24 Nm √
OR
Calculate from the right:
BMc = (11 x 4) - (8 x 2) - (4 x 1)
= 44 - 16 - 4
= 24 Nm (3)
[30]
QUESTION 6: GRAPHICS AND COMMUNICATION
ANSWER SHEET 6.1
NO. | QUESTIONS | ANSWERS | MARKS |
1 | Name the scale used for the site plan. | 1:200 √ | 1 |
2 | State the colour that you would use to shade new buildings on a site plan. | Red √ | 1 |
3 | Identify number 1. | Inspection eye √ | 1 |
4 | What is number of the plot on which the house will be built? | 60 √ | 1 |
5 | Identify number 3. | Sink √ | 1 |
6 | Determine the distance from the boundary line to the proposed dwelling on the western side of the building. | 5 000 mm/5 m √ | 1 |
7 | Determine the distance between the building line and the building on the northern side of the building. | 3 000 mm/3 m √ | 1 |
8 | In which street is the entrance to the site located? | Thambo Street √ | 1 |
9 | Draw the roof line of a gable roof for the building. |  | 3 |
10 | Calculate the total area of the building in square metres. | 204 m² √ | 2 |
11 | If the area of the site is 750 m², what percentage will the building occupy on the site? 29,2% OR 27,2% OR 25,2% | 27,2%√√ | 2 |
TOTAL | 15 |
ANSWER SHEET 6.2
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARKS | LM | ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARKS | LM |
External Walls | 4 | Bath | 1 | ||
Internal Walls | 5 | Dimensions | 2 | ||
Windows | 4 | Application of scale One or two incorrect = 3 Three or four incorrect = 2 More than five incorrect = 1 No measurement correct = 0 | 3 | ||
Doors | 4 | ||||
Wash tub | 1 | ||||
Water closet | 1 | ||||
TOTAL | 25 |
ACCURACY √ √ √
NOT TO SCALE: USE A MASK TO MARK THIS QUESTION
[40]
TOTAL: 200
BUSINESS STUDIES GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
BUSINESS STUDIES
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- This question paper consists of THREE sections and covers all main topics.
SECTION A: COMPULSORY
SECTION B: Consists of FIVE questions. Answer any THREE of the five questions in this section.
SECTION C: Consists of FOUR questions. Answer any TWO of the four questions in this section. - Read the instructions for each question carefully and take particular note of what is required.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper. No marks will be awarded for answers that are numbered incorrectly.
- Except where other instructions are given, answers must be in full sentences.
- Use the mark allocation and nature of each question to determine the length and depth of an answer.
- Use the table below as a guide for mark and time allocation when answering each question.
SECTION
QUESTION
MARKS
TIME (minutes)
A: Objective-type questions
COMPULSORY1
40
30
B: FIVE direct/indirect-type questions
CHOICE
(Answer any THREE.)2
60
30
3
60
30
4
60
30
5
60
30
6
60
30
C: FOUR essay-type questions
CHOICE
(Answer any TWO.)7
40
30
8
40
30
9
40
30
10
40
30
TOTAL
300
180
- Begin the answer to EACH question on a NEW page, for example QUESTION 1 – new page, QUESTION 2 – new page, et cetera.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Write down the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10), choose the answer and make a cross (X) over the letter (A–D) of your choice in the ANSWER BOOK.
EXAMPLE: |
1.1.1 Employers pay 1% as a skills development levy if their annual salary expense exceeds ...
- R50 000.
- R500 000.
- R1 000 000.
- R100 000.
1.1.2 The process whereby a business stops operating and sells all assets to pay off debts:
- Retrenchment
- Market development
- Divestiture
- Liquidation
1.1.3 Which ONE of the following businesses can be classified under the tertiary sector?
- Solly Training & Development CC
- Trust Furniture Manufacturers
- TRIX Coal Mine
- Nandi Sugar Cane Growers
1.1.4 A minimum of R1 000 must be invested in this form of investment:
- Unit trusts
- Shares
- Fixed deposit
- RSA Retail Savings Bonds
1.1.5 Unlimited liability means …
- owners' personal assets are protected in the event that the business becomes insolvent.
- owners stand to lose their personal assets in the event that the business becomes insolvent.
- owners cannot lose more than what they have invested in the business in the event that the business becomes insolvent.
- owners are not entitled to share in the profits of the business.
1.1.6 Businesses apply this management and leadership theory to change, develop and motivate employees over a short period of time:
- Situational theory
- Trait theory
- Transformational theory
- Leaders and followers
1.1.7 The right of employees to join trade unions is known as freedom of …
- association.
- expression.
- movement.
- speech.
1.1.8 Businesses protect the environment through …
- recycling programmes.
- dumping toxic waste in rivers and dams.
- air pollution.
- non-compliance with environmental legislation.
1.1.9 A human resources activity where the competency of the employee is matched with his/her position:
- Interview
- Induction
- Placement
- Screening
1.1.10 The production manager for BAC Beverages conducts regular inspections on final goods to ensure that the required standards are met. This process is known as quality …
- circles.
- planning.
- assurance.
- control. (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Complete the following statements by using the word(s) in the list below. Write only the word(s) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK. Each word should only be used ONCE.
| decision-making; National Credit Act; problem-solving; managers; retirement; piecemeal; retrenchment; Consumer Protection Act; leaders; time-related; Porter's Five |
1.2.1 … forces businesses to disclose more information about their products and processes.
1.2.2 … have authority because of their position in the company.
1.2.3 … is usually applied to reduce the number of employees due to restructuring in the business.
1.2.4 … requires creative thinking skills to generate and evaluate alternative solutions.
1.2.5 … salary determination is used to pay employees when agreed upon parts of a project are completed. (5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches a term in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–J) next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.3.6 K.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
| 1.3.1 Belbin role theory 1.3.2 Private company 1.3.3 Strategy evaluation 1.3.4 Financial function 1.3.5 Storming stage |
|
(5 x 2) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 40
SECTION B
Answer ANY THREE questions in this section.
NOTE: Clearly indicate the QUESTION NUMBER of each question that you choose. The answer to EACH question must start on a NEW page, for example QUESTION 2 on a NEW page, QUESTION 3 on a NEW page, et cetera.
QUESTION 2: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS
2.1 Name the SIX components of the PESTLE analysis. (6)
2.2 List THREE business environments and state the extent of control that businesses have over each environment. (9)
2.3 Explain the meaning of learnerships. (4)
2.4 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
GLEN SHUTTLE SERVICE (GSS) Glen Shuttle Service transports clients to and from the airport. Some clients have requested GSS to sell soft drinks while travelling. GSS has decided to merge with Clear Beverages to be able to satisfy the needs of their clients. |
2.4.1 Identify the type of integration strategy that GSS applied in the scenario above. Motivate your answer. (3)
2.4.2 State TWO other integration strategies. (2)
2.4.3 Give THREE reasons why businesses may use integration strategies. (6)
2.5 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
QUICK CASH FUNDING (QCF) Quick Cash Funding makes loans available to anyone who needs cash at short notice. QCF encourages people to apply for loans regardless of their financial status. They also use misleading and deceptive methods to attract potential clients. |
2.5.1 Quote TWO ways from the scenario above in which QCF is not complying with the National Credit Act (NCA), 2005 (Act 34 of 2005). (2)
2.5.2 Recommend ways in which QCF can comply with this Act. (8)
2.6 Discuss the impact of the Broad-Based Black Economic Empowerment (BBBEE) Act, 2003 (Act 53 of 2003) (amended in 2013) on businesses. (10)
2.7 Justify the effectiveness of the Employment Equity Act (EEA), 1998 (Act 55 of 1998) on businesses. (10)
[60]
QUESTION 3: BUSINESS VENTURES
3.1 State FOUR factors to be considered when responding to questions at the end of a presentation. (8)
3.2 Identify the type of shares represented by EACH statement below.
3.2.1 Shares are issued to existing shareholders as compensation for loss of dividends.
3.2.2 Shareholders receive their dividends before others can be paid out.
3.2.3 These shares are issued to shareholders who started the company.
3.2.4 These shareholders may receive higher dividends when the company has made large profits. (8)
3.3 Outline the functions of the Johannesburg Securities Exchange Ltd (JSE). (8)
3.4 Elaborate on the importance of investing in fixed deposits. (3)
3.5 Tabulate the differences between compound and simple interest. (8)
3.6 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
BALOYI TRADERS (BT) Ms Green, a manager at Baloyi Traders, regularly requests employees to contribute ideas on how to increase business profits. |
3.6.1 Name the leadership style that Ms Green is applying in the scenario above. Motivate your answer. (3)
3.6.2 Discuss the impact of Ms Green's leadership style identified in QUESTION 3.6.1 on Baloyi Traders. (8)
3.6.3 Advise Ms Green on the benefits of using the situational leadership theory in the workplace. (6)
3.7 Explain how the following factors can contribute to the success and/or failure of a non-profit company:
3.7.1 Capital (4)
3.7.2 Management (4)
[60]
QUESTION 4: BUSINESS ROLES
4.1 List FIVE economic rights of employees in the workplace. (5)
4.2 Explain how businesses should handle conflict in the workplace. (8)
4.3 Identify the unethical or unprofessional business practice illustrated in each of the following scenarios:
4.3.1 Masakhane Stores charges more for the same goods in the village than in the city.
4.3.2 The director of KNZ Consulting uses the business credit card to pay for personal expenses.
4.3.3 Employees of Zamu Attorneys spend more time on social networks during office hours than on their duties. (6)
4.4 Describe how businesses can apply the brainstorming technique to solve their business problems. (8)
4.5 Discuss the following criteria for assessing successful team performance:
4.5.1 Interpersonal attitude and behaviour (2)
4.5.2 Communication (2)
4.6 Elaborate on the importance of team dynamic theories in improving team performance. (4)
4.7 Discuss the benefits of diversity in the workplace. (8)
4.8 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
NATASHA DÉCOR (ND) The financial manager of Natasha Décor ensures that value-added tax (VAT) is paid over to SARS on time. Employees are paid according to the amount of effort and time spent at work. ND do not use identical ideas from their competitors to benefit their own business. |
List the THREE ways in which ND conduct business professionally, responsibly and ethically. Quote from the scenario to support your answer. Use the table below to present your answer.
| BUSINESS PRACTICE | QUOTE FROM SCENARIO |
(9)
4.9 Recommend ways in which businesses may create an environment that promotes creative thinking in the workplace. (8)
[60]
QUESTION 5: BUSINESS OPERATIONS
5.1 Name FIVE methods of external recruitment. (5)
5.2 State THREE aspects that should be included in the induction programme. (6)
5.3 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
TOM FLOORING (TF) Mr Du Preez is the newly appointed financial manager at Tom Flooring. His employment contract only bears his signature. The contract states that he may be required to work 12 hours overtime per week. He is expected to perform other duties which are not listed in his contract. |
5.3.1 Identify the challenges with regard to Mr Du Preez's employment contract. Make recommendations for improvement. (9)
5.3.2 Outline any TWO other legal requirements of the employment contract. (4)
5.4 Discuss the selection procedure as one of the activities of the human resources function. (8)
5.5 Identify the total quality management (TQM) element illustrated in EACH statement below.
5.5.1 The management of JKM Fresh Fruits ensures that customer complaints are handled within 24 hours.
5.5.2 The employees of Tumi's Consulting regularly attend training courses on service delivery.
5.5.3 Home Appliances Manufacturers uses modern production technology to ensure their products are in line with the latest innovations.
5.5.4 The managing director of Themba's Holiday Lodge allows the staff to make inputs during strategic planning sessions.
5.5.5 Duncan Computers can afford to employ two additional experts in their Information Technology department. (10)
5.6 Explain how total quality management (TQM) can reduce the cost of quality. (6)
5.7 Distinguish between quality performance and quality management. (4)
5.8 Suggest TWO quality indicators for EACH of the following business functions:
5.8.1 Marketing function (4)
5.8.2 Administration function (4)
[60]
QUESTION 6: MISCELLANEOUS TOPICS
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS
6.1 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
DAVE DIGITAL SOUND (DDS) DDS specialise in selling radios and car sound systems. They employ qualified sound engineers. The business does not have sufficient capital to buy and sell sound systems that cater for large events. Businesses in the same industry are closing down due to ineffective marketing campaigns. DDS is located in a high crime area. |
6.1.1 Compile a SWOT analysis for DDS. (4)
6.1.2 Suggest ONE strategy to handle each weakness and threat identified in QUESTION 6.1.1. (4)
6.2 Discuss the advantages of the Compensation for Occupational Injuries and Diseases Act (COIDA), 1993 (Act 130 of 1993) (amended in 1997). (6)
BUSINESS VENTURES
6.3 Give TWO examples of non-verbal presentation methods. (2)
6.4 Explain how return on investment and risk may influence the decision to invest in shares. (4)
6.5 Compare a partnership and a personal-liability company as forms of ownership in terms of the following criteria:
6.5.1 Continuity (4)
6.5.2 Taxation (4) BUSINESS ROLES
6.6 Outline any FOUR problem-solving steps. (4)
6.7 Identify the King Code principle illustrated in EACH statement below.
6.7.1 Rocky Traders publishes the value of their shares in their financial reports. (2)
6.7.2 The directors of John Shoes Ltd take responsibility for their decisions and actions. (2)
6.8 Mr Nel is employed as a sales representative. He is subjected to unfair treatment in the workplace. Explain the correct procedure that he should follow to deal with his grievance. (8)
BUSINESS OPERATIONS
6.9 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
CLEANCUT BUTCHERY (CB) Cleancut Butchery employs ten dedicated workers who always meet deadlines. CB has decided to offer them free accommodation and medical aid as a token of appreciation for good service. |
6.9.1 Name TWO types of fringe benefits offered by CB. (2)
6.9.2 Discuss the advantages of fringe benefits for CB. (6)
6.10 Analyse the negative impact on businesses if TQM is poorly implemented. (8)
[60]
TOTAL SECTION B: 180
SECTION C
Answer ANY TWO questions in this section.
NOTE: Clearly indicate the QUESTION NUMBER of the chosen question. The answer to EACH question must start on a NEW page, for example QUESTION 7 on a NEW page, QUESTION 8 on a NEW page, et cetera.
QUESTION 7: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS (LEGISLATION)
| The relationship between employers and employees is guided by the Labour Relations Act (LRA), 1995 (Act 66 of 1995). Businesses who do not comply with this Act may face penalties. |
As a labour relations expert, provide a detailed report on the following aspects of the Labour Relations Act:
- Outline the rights of employers and employees according to the LRA.
- Discuss the purpose of the Labour Relations Act.
- Evaluate the impact of this Act on businesses.
- Recommend ways in which businesses can comply with the LRA. [40]
QUESTION 8: BUSINESS VENTURES (INSURANCE AND PRESENTATION)
SMARTSURANCE (SS) Mr Funa is an insurance broker at Smartsurance. He has to do a presentation on different types of insurance products at a meeting of local business owners. He is also expected to convince potential clients on the importance of insurance. |
Mr Funa needs details on the following aspects to be included in his presentation. He requires you to:
- Distinguish between compulsory and non-compulsory insurance. Give TWO practical examples of each.
- Explain the importance of insurance for businesses.
- Discuss THREE principles of insurance.
- Advise him on how he can improve his next presentation. [40]
QUESTION 9: BUSINESS ROLES (SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY AND CORPORATE CITIZENSHIP)
| Businesses are compelled to initiate corporate social responsibility (CSR) programmes that are aimed at enhancing the quality of life of communities. Some businesses believe that they should not be expected to invest in corporate social investment (CSI) projects as these are not the primary objectives of their business. |
Support the above argument by referring to the following aspects:
- Describe differences between CSR and CSI.
- Evaluate the impact of CSI on businesses.
- Explain the relationship between social responsibility and triple bottom line.
- Recommend FIVE ways in which businesses can contribute time and effort to advance the well-being of their employees. [40]
QUESTION 10: BUSINESS OPERATIONS (HUMAN RESOURCES AND QUALITY OF PERFORMANCE)
SHAKES MANUFACTURING LTD (SML) Shakes Manufacturing Ltd is a large business specialising in the manufacturing of school uniforms. Schools are not happy with the quality of SML's products. The management of SML wants to recruit and appoint a production manager to monitor and evaluate their quality processes. |
Provide a detailed report on the following aspects:
- Explain the recruitment procedure that SML should follow to fill the vacancy.
- Advise SML on the benefits of inducting the production manager.
- Elaborate on the advantages of monitoring and evaluating SML's quality processes as a TQM element.
- Recommend ways in which the general manager of SML can contribute to the quality of performance of the business. [40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 80
GRAND TOTAL: 300