Adele
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICAL LITERACY PAPER 2 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICAL LITERACY
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
MARKS: 150
Codes | Explanation |
M | Method |
MA | Method with Accuracy |
CA | Consistent Accuracy |
A | Accuracy |
C | Conversion |
D | Define |
J | Justification/Reason/Explain |
S | Simplification |
RD | Reading from a table OR a graph OR a diagram OR a map OR a plan |
F | Choosing the correct formula |
SF | Substitution in a formula |
O | Opinion |
P | Penalty, e.g. for no units, incorrect rounding off, etc. |
R | Rounding Off |
NPR | No penalty for rounding OR omitting units |
AO | Answer only |
QUESTION 1 [31]
Ques. | Solution | Explanation | Level |
1.1.1 | Emerald – R 19 089 +✔ | 1A Emerald | F L2 |
1.1.2 | Emerald = member + adult + child Onyx = member + adult + child Difference = 7 098 – 5 152 ✔ | 1RT Correct values | F L2 |
1.1.3 | Government subsidy = R5 152 – R2 530 ✔ Government % = 2 622 × 100 ✔ | 1MA Difference | F L2 |
1.1.4 | It is important for people to be healthy. ✔✔ OR Accept any other relevant reason. | 2O Importance (2) | D L4 |
1.2.1 | Volume = π × r2 × h ✔ Volume of traditional beer = 70 × 0,1336 OR Height of container = 0,7 × 0,84 Volume = π × r2 × h | 1M Calculating radius | M L3 |
1.2.2 | Length of store room = 2 m = 200 cm ✔ Width of store room = 1,5 m = 150 cm Number of containers in total | 1M Conversion | M L4 |
Ques. | Solution | Explanation | Level |
1.3.1 | Amount before increase = 336000/ 106,5%✔✔ | 1M Dividing | F L2 |
1.3.2 | Bonus = 336 000 / 12 Year 1 = 105,8 × 28 000 ✔ Year 2 = 106,5 × 29 624✔ | 1M Monthly salary | F L3 |
QUESTION 2 [42]
Ques. | Solution | Explanation | Level |
2.1.1 | 10 hours = 10 × 60 | 1MA minutes in 10 hours | M L2 |
2.1.2 | % increase = 2015 rate - 2013 rate × 100 ✔ | 1M Difference | D L3 |
2.1.3 | Amount of developing material: For 10 employees = 11 811,50 × 10 Km travelled = 35×2×2×7+2×25×3×7+12×2×5×7✓ Transport = rate for transport × number of km Total amount = 118 114,9667 + 8093,40 Balance = R130 000 - R 126 208,37 Statement invalid; Balance less than R4 000 ✓ | 1SF Substituting correct values | M&F L4 |
Ques. | Solution | Explanation | Level |
2.2.1 | USA: | 1 correct tax bracket | F L3 |
2.2.2 | Income in South Africa Income Tax Statement is valid ✓ | 1 conversion | L4 |
2.2.3 | People in the higher tax brackets are feeding the government bills. ✓✓ OR It is discouraging for people occupying higher positions and earning higher salaries. ✓✓ OR People need to be treated equally✓✓ | 2R Reason (2) | D L4 |
2.3 | Speed = distance Less time spent in Nanaga Speed = 311 They travelled above the speed limit ✔ | 1M Travelling time | M L3 |
2.4 | School B ✔ has performed better. | 1M Choosing school | D L4 |
QUESTION 3 [30]
Ques. | Solution | Explanation | Level |
3.1.1 | ✓ ✓ ✓ 58 + 279 + 45 + 455 + 232 + 303 + 280 + 49 + 498 ✓ = 2 199 km ✓ | 3RT (1mark for every three correct values) 1CA Answer (5) | M&P L2 |
3.1.2 | N1 – South Africa ✓ | 4 (1 mark for route and country). | M&P L2 |
3.1.3 | OPTION 1: OPTION 2: | 1MA Cost of breakfast | F L4 |
3.1.4 | Probability of getting a self-catering unit at no extra cost | 1A Numerator | P L2 |
3.1.5 | Distance travelled Difference = 2199 – 1736 ✔ | 1M Adding distances | M&P L4 |
3.2.1 | Percentage achievement in Mathematical Literacy is decreasing from 2013 to 2016✔✔ | 2 O Describing the trend (2) | D L4 |
3.2.2 | Maths decreased from 2013 to 2015✔ Maths increased from 2015 to 2016✔ | 1O Description for Mathematics for 2013 to 2015 | D L4 |
3.2.3 | Mathematics = 265 810 – 263 903 | 1A Increase in Mathematics | D L3 |
QUESTION 4 [47]
Ques. | Solution | Explanation | Level |
4.1.1 | C = 2 × π × r | 1SF Substituting correct formula | M L3 |
4.1.2 | D = 0,25 × 2 | 1CA finding diameter 1CA total height | M L3 |
4.1.3 | Area for red paint = area of rectangle + area of triangle = ℓ × w + ½ b × h ✔ | 1M Using correct formulae | M&F L4 |
Ques. | Solution | Explanation | Level |
4.2.1 | North East | 2A Direction (2) | M&P L2 |
4.2.2 | Mean = sum of values | 1SF Substitution | D L3 |
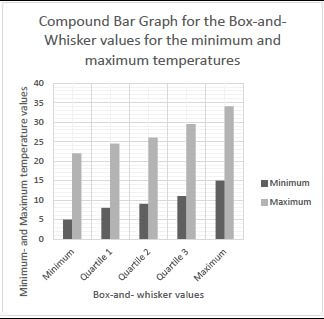
4.2.3 | Minimum temperatures: Maximum temperatures: | CA from 4.2.2 | D L3 |
Ques. | Solution | Explanation | Level |
4.2.4 | | CA from 4.2.2 and 4.2.3 | D L2 |
4.2.5 | Probability that a temperature is ≥ 28 °C | 1A Numerator | P L2 |
4.2.6 | Measured distance = 6,6 cm✓ | 1MA Measure on map (accept 6,4 - 6,8) | M&P L3 |
TOTAL: 150
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICAL LITERACY PAPER 1 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICAL LITERACY
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
MARKS: 150
Symbol | Explanation |
M | Method |
A | Accuracy |
CA | Consistent accuracy |
RT/RG/RM | Reading from a table/Reading from a graph/Read from map |
SF | Substitution in a formula |
P | Penalty, e.g. for no units, incorrect rounding off etc. |
S | Simplification |
R | Rounding/Reason |
NPR | No penalty for rounding |
QUESTION 1 [30 MARKS] | |||
QUES | Solution | Explanation/m | T/L |
1.1.1 | 750 × 100% ✔ | 1M Multiply by 100 | F LI |
1.1.2 | Balance = 3 200 – 750 ✔ | 1M subtraction | F L1 |
1.1.3 | Total amount paid = 750 + 5 × 300 ✔ | 1M Adding and Multiplying | F L1 |
1.2.1 | Rate in cents = 0,8865 × 100 ✔ | 1M Multiplying | F L1 |
1.2.2 | Amount charged = 50 × 88,65 ✔ | 1M Multiplying | F L1 |
1.2.3 | Value Added Tax ✔✔ | 2 R (2) | F L1 |
1.3.1 | Time to clock off = 7:30 + 7 hr. = 14: 30 ✔ | 1M adding 7hr | M L1 |
1.3.2 | Income = 26 × 7 × 20 ✔ =R3 640 ✔ | 1M multiplication | F L1 |
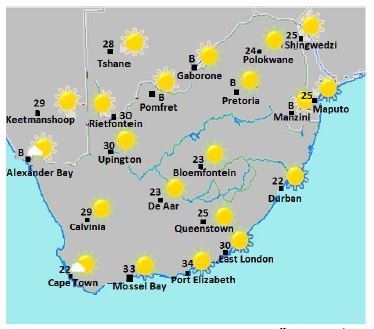
1.4.1 | Distance = 1 141 km ✔✔ | 2RT (2) | M L1 |
1.4.2 | East London ✔ and Polokwane ✔ | 2RT (2) | M L1 |
1.4.3 | Durban ✔and Cape Town ✔ | 2RT (2) | M L1 |
1.5.1 | Parents in the survey = 24 + 32 + 16 + 13 + 5 ✔ = 90 ✔ | 1M Adding | D L1 |
1.5.2 | Less than 20% = 24 + 32 ✔ | 1M Adding | D L1 |
1.5.3 | Modal range = 10–19 ✔✔ | 2RG (2) | D L1 |
1.5.4 | Bar graph ✔✔ | 2RG (2) | D L1 |
[30] | |||
QUESTION 2 [42 MARKS] | |||
QUES. | Solution | Explanation/m | T/L |
2.1.1 | Child support ✔✔ | 2RT (2) | L1 |
2.1.2 | R1 525 + 2 x R350 ✔= R1 525 + R700 ✔ = R2 225 ✔ | 1MA amount | L1 |
2.1.3 | R1 435 x 6,27% = 89,97 ✔ OR 1435 x 1,0627 ✔= R1 524,97 ✔ | 1MA multiply by 6,27% | L1 |
2.2.1 | 4 x R1 155,26 ✔ OR R5 620 – (115,80 + 192,98 + 690,18) OR R4 929,82 – R115,80 – R192,98 | 1M | L1 |
2.2.2 | R0,00 ✔✔ | 2RT (2) | |
2.2.3 | R4 621,04 x 5,6% OR 100% – 5,6% | 1MA Value of 5,6% | L3 |
2.3.1 | R8,3 billion ✔✔ OR 8 300 000 000 ✔✔ | 2RT | L1 |
2.3.2 | R19,84 + R2,71 + R0,45 + R1,8 + R2,71 + R17,59 ✔ OR R45 100 000 000 ✔✔ | 1M addition | L1 |
2.3.3 | 1 Euro = R15,3728 | 1M division | L2 |
2.3.4 | 96,0 – 36,8 ✔✔ | 1M correct values | L1 |
2.3.5 | 17,59 x 100% ✔ | 1M Division | L2 |
2.3.6 | 1,8 : 36,8 ✔✔ | 1 Ratio | L2 |
2.4.1 | R10,00 x 25 ✔ | 1M identifying R10 | L1 |
2.4.2 | 260 x R1,50 ✔ | 1M | L1 |
2.4.3 | R11,00 ✔✔ | 2RT (2) | L1 |
2.5.1 | Inflation is the increase in prices of goods and services over time. ✔✔ | 2R (2) | F L1 |
2.5.2 | Inflation rate = new prices - old prices × 100% | 1M Substitution | F L2 |
[42] |
QUESTION 3 [23 MARKS] | |||
QUES. | Solution | Explanation/m | T/L |
3.1.1 | 28 + 2 × 10,6 + 41,2 + 28 ✔✔ | 1M Addition | L2 |
3.1.2 | Number of spoons = 2 7 , 5 ✔ | 1M Division | L1 |
3.1.3 | 50 × 500 = 25 000 | 1M | L1 |
3.2.1 | Volume = length x width x height | 1SF | L2 |
3.2.2 | Volume of chocolate =3 360 | CA from 3.2.1 | L3 |
3.3.1 | Diameter | 1M x 2 and addition | L2 |
3.3.2 | Area = 2,3 m x 2,3 m ✔ | 1SF | L2 |
3.3.3 | Area = 3,142 x (0,918 m)2 ✔✔ | 1M SF | L2 |
3.3.4 | Wasted material = Area of material – Area of tablecloth to cut | CA from 3.3.2 and 3.3.3 | L2 |
[23] | |||
QUESTION 4 [20 MARKS] | ||||
QUES | Solution | Explanation/m | T/L | |
4.1.1 | Two ✔✔ | 2RM (2) | L1 | |
4.1.2 | Sample point E ✔✔ | 2 RM (2) | L1 | |
4.1.3 | Taaibuschspruit ✔ | 1RM 1st side stream 1RM 2nd side stream (2) | L1 | |
4.1.4 | Scaled length = 3 x 100 000 | 1M x 100 000 | L2 | |
4.2.1 | (a) | 16 ✔✔ | 2RD (2) | L2 |
(b) | Fixed side ✔ and Drop side ✔ | 1RD 1ste wood part | L2 | |
(c ) | B ✔✔ | 2RD (2) | L2 | |
4.2.2 | 16 ✔✔ | 2RM (2) | L1 | |
4.2.3 | 4 ✔ | 1M value of numerator | L2 | |
[20] | ||||
QUESTION 5 [35 MARKS] | |||
QUES. | Solution | Explanation/m | T/L |
5.1.1 | Northern Cape ✔ | 2RT (2) | L1 |
5.1.2 | A =11 705 + 5 105+4 568+10 070 + 13 022 + 5 091 + 1 963 + 3 543+3 589 ✔ | 1A adding | L1 |
5.1.3 | 613; 1 404; 2 122; 2 149; 2 290; 2 600; 2625; 3 492; 4 765 ✔✔ | 2M Ascending order (2) | L1 |
5.1.4 | 2 290 ✔✔ | 2CA from 5.1.3 (2) | L2 |
5.1.5 | 2 625 – 1 404 ✔✔ | 1M correct values | L1 |
5.1.6 | 58 656 | CA from 5.1.2 | L2 |
5.1.7 | Limpopo ✔✔ | 2RT (2) | L1 |
5.2. | A – Minimum value ✔ | 1M Minimum | L2 |
5.3.1 | Sample points 2 , 3 and 9 ✔✔ | 1M 1st sample point 1M 2nd and 3rd sample points (2) | L1 |
5.3.2 | Significant risk of gastrointestinal disorders ✔✔ | 2RT (2) | L1 |
5.3.3 | |||
| |||
1 Mark per two points correctly plotted (5 x 1) | (6) | ||
5.4.1 | A ---- (H;H) ✔ | 3A 1 mark for each outcome | P L2 |
5.4.2 | P(HH) =14✔✔ | 1M numerator | P L2 |
[35] | |||
TOTAL: | 150 | ||
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICAL LITERACY PAPER 1 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICAL LITERACY
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of FIVE questions. Answer ALL the questions.
-
- 2.1 Use the ANNEXURES in the ADDENDUM to answer the following questions:
ANNEXURE A for QUESTION 1.4
ANNEXURE B for QUESTION 4.1
ANNEXURE C for QUESTION 4.2
ANNEXURE D for QUESTION 5.3 - 2.2 ANSWER SHEET for QUESTION 5.3.3.
Write your GRADE and NAMES in the spaces provided on the ANSWER SHEET. Hand in the ANSWER SHEET with your ANSWER BOOK.
- 2.1 Use the ANNEXURES in the ADDENDUM to answer the following questions:
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- You may use an approved calculator (non-programmable and non-graphical), unless stated otherwise.
- Show ALL calculations clearly.
- Round off ALL final answers appropriately according to the given context, unless stated otherwise.
- Indicate units of measurement, where applicable.
- Maps and diagrams are NOT necessarily drawn to scale, unless stated otherwise. 10. Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1
Ben buys a bicycle on lay-bye for R3 200. |
1.1.1 Express the deposit as a percentage of the purchase price. (2)
1.1.2 Determine the balance, after the deposit has been paid. (2)
1.1.3 Determine the total amount paid after the deposit and five instalments has been paid. (2)
1.2
| Karen bought 50 Kwh of electricity from her municipality in June 2017 when the tariff was 0,8865 R/Kwh (Rand per kilo-watt hour), including VAT. |
1.2.1 Calculate the rate (in cents) for the tariffs charged for the 50 Kwh of electricity. (2)
1.2.2 Calculate the total amount charged for the 50 Kwh of electricity. (2)
1.2.3 Write the abbreviation VAT out in full. (2)
1.3
| A care-taker at a school is paid at the rate of R26 per hour worked. He works from 7:30 am for 7 hours, excluding a 15-minute tea break and 45-minute lunch break. He does not work during weekends. |
1.3.1 Determine the time when he goes off duty. (2)
1.3.2 Calculate his income if he worked for four weeks. (2)
1.4
| The distances between the cities in South Africa are shown in ANNEXURE A. Use it to answer the following questions. |
1.4.1 Write down the distance between Mafikeng and Port Elizabeth. (2)
1.4.2 Name TWO cities that are equal distance from Kimberley. (2)
1.4.3 Which two cities are furthest apart? (2)
1.5 A research was carried out among some parents of Zozo High School to indicate the percentage of their income they saved in June 2017. The results are shown on the graph below.
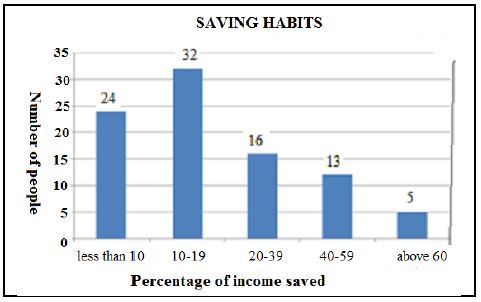 |
1.5.1 Determine the number of people that took part in the survey. (2)
1.5.2 Calculate the number of people who saved less than 20% of their income. (2)
1.5.3 What was the modal range? (2)
1.5.4 Write down the type of graph used to display the information. (2)
[30]
QUESTION 2
2.1 In South Africa many families solely depend on social grants to sustain their livelihood. Nobuzwe, a 78-year-old grandmother lives with her four grandchildren and takes care of them. Study the information in TABLE 1 below on social grants and answer the questions that follow.
| TABLE 1: MONTHLY SOCIAL GRANTS FOR FINANCIAL YEARS 2015/2016 AND 2016/2017 PER INDIVIDUAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
[Adapted from People’s guide to the budget] |
2.1.1 Identify the social grant that increased the least over the two financial years. (2)
2.1.2 Two of her four grandchildren received a child support grant.
Calculate the total amount of social grant Nobuzwe and the two grandchildren receive monthly for the 2016/2017 financial year. (3)
2.1.3 The War Veterans’ social grant was increased by 6,27% at the end of the 2015/2016 financial year. Calculate the monthly amount after the increase to the nearest rand. (3)
2.2 Ludwe, Nobuzwe’s son bought tyres for his expensive car from Lee Tyre and Exhaust centre in Cape Town. Study the information on the invoice below and answer the questions that follow.
Lee Tyre and Exhaust Centre: Tax Invoice R – Rands VAT – Value Added Tax | |||
Item detail | Price excluding VAT: (R) | Quantity | Net Value (R) |
813750 FS TZ Firehawk tyres | 1 155,26 | 4.000 | A |
BBO Wheel balance (Standard) | 28,95 | 4.000 | 115,80 |
WWA 1 Wheel alignment | 192,98 | 1.000 | 192,98 |
Sub-total | 4 929,82 | ||
VAT | 690,18 | ||
Grand total | 5 620,00 | ||
Change | 0,00 | ||
2.2.1 Calculate the value of A, the Net value of Firehawk tyres. (2)
2.2.2 Write down the amount Ludwe received as change. (2)
2.2.3 In August ONLY the tyres were discounted by 5,6%. Calculate how much Ludwe would have paid for the tyres, including VAT. (4)
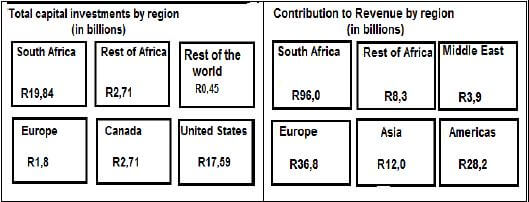
2.3 Sasol has exploration, development, production, marketing and sales operations in 36 countries around the world. Study the revenue contributions and the total capital investments by region shown in TABLE 2 below and answer the questions that follow.
| TABLE 2: |
[www.sasoltechnox.co.za] |
2.3.1 Write down the amount contributed to Revenue by the Rest of Africa. (2)
2.3.2 Calculate the total capital investments by Sasol in all regions. (2)
2.3.3 Convert the total capital investment in Europe into Euros. Given that 1 Euro = R15,3728 (2)
2.3.4 Calculate the difference in contribution to revenue between South Africa and Europe. (3)
2.3.5 Express the capital investment in the United States as a percentage of the total capital investments. (3)
2.3.6 Write down Europe’s capital investments, to that of Europe’s revenue contribution in the simplest ratio. Give your answer in the form: 1 : … (3)
2.4 Lerato High School had a memorial service for Anako, one of Nobuzwe grandchildren that was in Grade 10. Study the quotation from TABLE 3 below and answer the questions that follow.
TABLE 3: QUOTATION FOR PRINTING COSTS FROM THE STATIONERY SHOP PER COPY
A3 | A4 | |||||||
Copies | Black and White | Colour | Black and White | Colour | ||||
Quantity | S/S | D/S | S/S | D/S | S/S | D/S | S/S | D/S |
1–250 | R3,50 | R4,00 | R10,00 R12,00 | R1,50 | R2,00 | R5,00 | R6,00 | |
251–500 | R3,00 | R3,50 | R9,50 | R11,50 | R1,00 | R1,50 | R4,50 | R5,50 |
501–1 000 | R2,80 | R3,00 | R9,00 | R11,00 | R0,85 | R1,05 | R4,00 | R5,00 |
1 000+ | R2,50 | R2,70 | R8,50 | R10,50 | R0,75 | R0,95 | R3,00 | R4,50 |
S/S – Single sided D/S – Double sided
2.4.1 The school will display TWENTY FOUR A3 single sided colour advertisements in the community and ONE A3 single sided colour advertisement outside the hall. Calculate the total amount the school will pay for these copies. (2)
2.4.2 The school will print 260 double sided black and white A4 programmes for the service. Calculate the total cost for the programs. (2)
2.4.3 Write down the amount charged per copy if you copy 520 A3 double sided colour copies. (2)
2.5
| The prices of 1 kg of corn flakes was R52,95 in June 2016 and R55,95 in June 2017. |
2.5.1 The price changes shown above are as a result of inflation. Explain the term inflation from the above context. (2)
2.5.2 Calculate the inflation rate used for the price changes on the cornflakes. Give your answer to the nearest percentage.
You may use the formula:
Inflation rate =New price – Old price x 100 (3)
Old price
[42]
QUESTION 3
3.1 Excessive sugar intake is a health hazard. Study the information about the amount of sugar in the chosen items mentioned in the TABLE 4 below and answer the questions that follow.
TABLE 4: AMOUNT OF SUGAR IN DIFFERENT CHOSEN ITEMS
Item | Amount of sugar (in grams) (g) | Capacity of an item |
Sports drink | 28 | 500 mℓ |
Flavoured water | 20 | 500 mℓ |
Medium muffin | 10,6 | 65 g |
Sweetened fizzy drink | 55 | 500 mℓ |
Vitamin water | 27,5 | 500 mℓ |
Chocolate bar | 41,2 | 80 g |
1 tablespoon tomato sauce | 7,4 | … |
Ice tea | 28 | 330 mℓ |
[Source: Discovery Vitality Kids report 2014 illustrations, Sock]
NOTE: 1 teaspoon = 4,18 g 1 cup = 250 mℓ
3.1.1 Rose drinks a can of ice tea and eats two medium muffins for breakfast, one chocolate bar at break and one sports drink after running in the afternoon. Calculate Rose’s total amount of sugar intake. (3)
3.1.2 Determine the number of teaspoons of sugar in the vitamin water drink. Give your answer to the nearest teaspoon. (3)
3.1.3 Calculate the number of cups you will get when you buy 50 bottles of sports drink for your school teams. (2)
3.2 The box shown below is used to pack 80 rectangular chocolate bars. The measurements of the box are: length = 28 cm, width =15 cm and height = 8 cm.
3.2.1 Calculate the volume of the box.
You may use the formula.
Volume = length ×width× height. (2)
3.2.2 Determine the thickness of a chocolate if the area of its base is 35 cm2.
You may use the formula:
Volume = area of base × thickness (4)
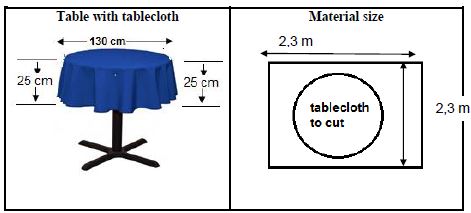
3.3 The table Lindi uses for functions in a tent has a diameter of 130 cm. The circular tablecloth used on the table overhangs 25 cm, all round. To make the tablecloth she has to add 1,8 cm right around for the hem. The tablecloth material measures 2,3 m wide and 2,3 m in length.
3.3.1 Calculate the diameter of the tablecloth to be cut from the material, including the additional centimetres for the hem. (2)
3.3.2 Calculate the area (in m2) of the tablecloth material.
You may use the formula:
Area = Length x Breadth (2)
3.3.3 Calculate the area (in m2) of a tablecloth to be cut by Lindi.
You may use the formula:
Area = π (radius)2, where π = 3,142 (3)
3.3.4 Calculate the amount of material wasted when cutting the table cloth.
You may use the formula:
Wasted material = Area of a material – Area of tablecloth to be cut (2)
[23]
QUESTION 4
4.1
Study the map on ANNEXURE B that shows the sample points for testing Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Blue Green Algae counts per 100 mℓ. |
4.1.1 Write down the total number of bridges found upstream (north east) of the R59 bridge. (2)
4.1.2 Name the SIXTH sample point on the map starting from the west side. (2)
4.1.3 Lindi travelled by boat from Ascot Bridge to Vaalview Aquatic Club. Name the side streams (tributaries) to the Vaal River that she will pass. (2)
4.1.4 The distance between the R59 Bridge and Railway Bridge is 3 km. Calculate the distance on another map if the scale is 1: 25 000. (3)
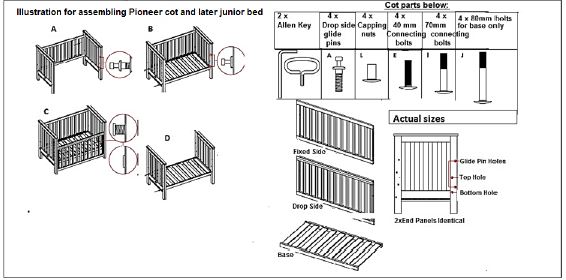
4.2 Study ANNEXURE C showing the diagrams and corresponding letters, A; B; C and D provided in order to assemble the cot and finally form a junior bed.
4.2.1
- Write down the number of holes in the end panels. (2)
- Name the wooden parts that must be removed, to form the junior bed. (2)
- Which assembly illustration shows that the base is now added? (2)
4.2.2 Calculate the number of pins and bolts needed to assemble the cot. (2)
4.2.3 Determine the probability of randomly selecting an 80 mm bolt from a bag containing only the bolts. Give your answer as a simplified common fraction. (3)
[20]
QUESTION 5
5.1 TABLE 5 below shows the number of learners who were condoned to Grade 12 (made to progress to Grade 12). Study the table and answer the questions that follow.
TABLE 5: PROGRESSED LEARNERS
Province | Total number of progressed learners who | ||
wrote matric in 2015 | passed matric in 2015 | currently is in matric in 2016 | |
Eastern Cape | 11 705 | 2 625 | 18 255 |
Free State | 5 105 | 2 600 | 7 362 |
Gauteng | 4 568 | 2 149 | N/A |
KwaZulu-Natal | 10 070 | 4 765 | 24 549 |
Limpopo | 13 022 | 3 492 | 27 523 |
Mpumalanga | 5 091 | 2 290 | 11 160 |
Northern Cape | 1 963 | 613 | 2 280 |
North West | 3 543 | 2 122 | 6 654 |
Western Cape | 3 589 | 1 404 | 3 058 |
TOTAL | A | 22 060 | … |
5.1.1 List the provinces with the number of progressed learners less than 5 000 in 2016. (2)
5.1.2 Calculate the value of A in the table. (2)
5.1.3 Arrange the number of progressed learners who passed matric in 2015 in ascending order. (2)
5.1.4 Determine the median of progressed learners who passed matric in 2015. (2)
5.1.5 Calculate the difference between the progressed learners who passed Grade 12 in 2015 from the Eastern Cape and Western Cape. (3)
5.1.6 Calculate the mean number of the progressed learners who wrote matric in 2015. Give your answer to the nearest whole number. (3)
5.1.7 Identify the province with the highest number of progressed learners in 2016. (2)
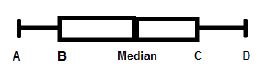
5.2 Label the box and whisker diagram by matching the terms below with the letter indicated on the diagram.
| Mean; Median; Mode; Minimum; Lower Quartile; Upper Quartile; Maximum; Range |
ONLY write down the letter and the correct term. (4)
5.3 Study TABLE 6 in ANNEXURE D that shows the sample points for testing Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Blue Green Algae counts per 100 mℓ to answer the questions that follow.
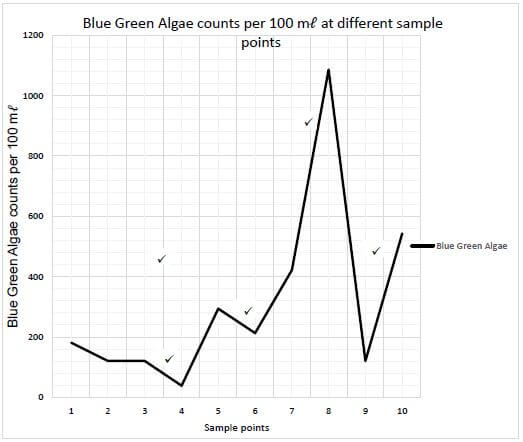
5.3.1 Identify the number(s) of sample points with the same values readings for the Blue Green Algae. (2)
5.3.2 At sample point 8, the readings were 291 for E. coli counts per 100 mℓ. Write down the guideline on such readings. (2)
5.3.3 Sketch the line graph showing the readings for Blue Green Algae counts per 100 mℓ at all sample points. Use the ANSWER SHEET to draw the graph. (6)
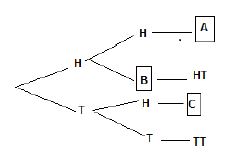
5.4 Ludwe tossed a coin twice and recorded all the possible outcomes as displayed in the tree diagram below:
5.4.1 Write down the possible outcomes represented by the letters A, B and C. (3)
5.4.2 Determine the probability of getting two heads when the coin is tossed two times. (2)
[35]
TOTAL: 150
ANSWER SHEET
GRADE 12
NAME OF LEARNER:
QUESTION 5.3.3 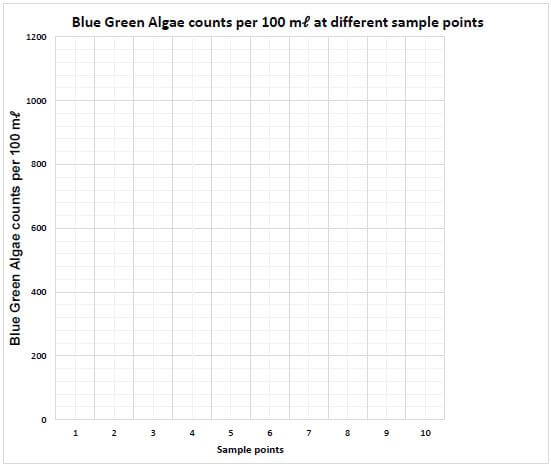
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICAL LITERACY PAPER 2 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICAL LITERACY
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- This question paper consists of FOUR questions. Answer ALL the questions.
- Use the ADDENDUM with ANNEXURES for the following questions:
ANNEXURE A for QUESTION 1.1
ANNEXURE B for QUESTION 2.1
ANNEXURE C for QUESTION 2.2
ANNEXURE D for QUESTION 3.1
ANNEXURE E for QUESTION 3.2
ANNEXURE F for QUESTION 4.2
ANSWER SHEET 1 for QUESTION 4.2.4 which is attached to the addendum.
Write your NAME in the spaces provided on the ANSWER SHEET and hand in the ANSWER SHEET with your ANSWER BOOK. - Number the questions correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- An approved calculator (non-programmable and non-graphical) may be used, unless stated otherwise.
- Show ALL calculations clearly.
- Round off ALL final answers appropriately accordingly to the given context, unless stated otherwise.
- Indicate units of measurement, where applicable.
- Maps and diagrams are NOT drawn to scale, unless stated otherwise. 10. Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1
Mrs May is a single mother who is an educator earning R336 000 per annum. She has two children, a 19-year-old boy who is at university and a 24-year-old girl who is not studying nor working. Mrs May is a member of a medical aid scheme. |
1.1.1 Identify the salary row to which Mrs May belongs for both medical aid options. (2)
1.1.2 Calculate the difference in contribution for the whole family between the two medical aid options for a month. (6)
1.1.3 If she chooses Emerald and R2 530 is deducted from her salary, calculate the percentage that the government subsidises her for medical aid. Round your answer to one decimal place.
Note: Government subsidy is the difference between medical aid amount and the amount deducted from salary. (3)
1.1.4 The medical aid scheme has a fitness exercise programme. What is the importance of such a fitness programme? (2)
1.2
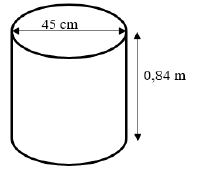
Mrs May had an initiation ceremony for her son in December 2015. Containers need to be 70% full of beer to allow space for fermentation. You may use the formulae: |
1.2.1 Calculate the volume of the traditional beer in 1 container in cubic meters (m3). (4)
1.2.2 Mrs May has a store room which has a length of 2 m and a width of 1,5 m. She claims that she is able to pack 13 big beer containers on the floor of her store room. Verify, showing all the necessary calculations, whether her claim is valid. (6)
1.3
Mrs May is planning for her son’s graduation and decides to invest her bonus money for two years. She invests the money in an institution offering interest that is compounded annually at an interest rate of 5,8% for the first year and 6,5% for the second year. |
1.3.1 Calculate her annual income before she received the increase. (3)
1.3.2 Calculate how much money will be paid out to her after the two-year period. (5)
[31]
QUESTION 2
2.1
In 2015 people were employed to develop reading material for schools. They were paid according to the number of pages they developed. Rates and information on remuneration are given in ANNEXURE B. |
2.1.1 One of the employees developed 20 pages in 10 hours. Show, using calculations, whether the employee was within the norm time, or not. (4)
2.1.2 Calculate the percentage increase in rate of developing material from 2013 to 2015. (3)
2.1.3 The manager is convinced that the R130 000 that he has budgeted for 10 employees to each develop 161 pages in seven days will be R4 000 more than the amount needed.
Note: Two employees live a distance of 35 km from the centre; three live 25 km from the centre; and the rest live 12 km from the centre.
Verify, showing all necessary calculations, whether the manager’s statement is valid. (10)
2.2
| Mr Reeva, a 58-year old USA citizen earning $350 500 taxable income per year. The USA Tax Table is shown on ANNEXURE C. |
2.2.1 Calculate how much tax Mr Reeva is paying per month. (5)
2.2.2 Mr Reeva is claiming that if his earnings were taxed in South Africa, he would be paying more tax per month. Use the South African Tax Table shown in ANNEXURE C to verify whether his statement is valid.
Given that $1 = R14,11 (7)
2.2.3 From the Tax Tables, it is evident that the more you earn, the more tax you pay. Mr Reeva claims that this is unfair. Support his claim by giving ONE reason. (2)
2.3
| Two friends are travelling from East London to Uitenhage which is a distance of 311 km. They leave East London at 06:00. They stop at Nanaga for 30 minutes for refreshments. |
If the two friends reach Uitenhage at 08:55, show with calculations whether they did not exceed the average speed limit of 120 kilometres per hour.
You may use the formula: Speed = Distance (6)
Time
2.4
| Marks are recorded and analysed after marking has been completed and marks for 2 schools are compared. In School A, the maximum mark is 87 and the minimum mark is 28 while the mean mark is 43. In School B the maximum mark is 76, the minimum mark is 53 with a mean mark of 56. |
Which school has performed better? Give TWO reasons for your choice. (5)
[42]
QUESTION 3
3.1
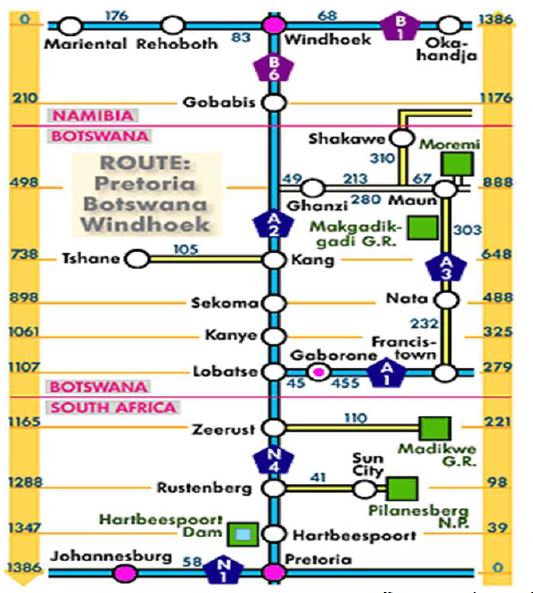
ANNEXURE D shows a strip chart from Pretoria to Windhoek. |
3.1.1 How many kilometres do they travel to Windhoek? (5)
3.1.2 Apart from route A1, which other routes do they travel on from Johannesburg? Also, give the names of the countries where these routes are found. (4)
3.1.3
At Moremi Wildlife Reserve there are two accommodation options: |
The couple stated that if they choose Option 1 and decide to have breakfast at a restaurant at R95 per person, they will be able to save R300. Show, with the necessary calculations, whether their statement is true, or not. (5)
3.1.4
| At Moremi Wildlife Reserve there are 5 self-catering units accommodating 4 people and 3 self-catering units accommodating 6 people at extra cost if there are only 4 people. |
If all self-catering units are still available when they are making their booking, determine the probability of getting a self-catering unit at no extra cost. Give your answer to the nearest percentage. (4)
3.1.5
| Mr and Mrs Smith, who are friends to the couple, are also on their way from Johannesburg to Windhoek. They take a different route and spend a night at Sun City. From Sun City they proceed to Tshane to visit some friends. After their visit, they travelled on the A2 route to Windhoek. |
The two families are claiming that the difference between the distance travelled by the couple with the two adults and the distance travelled by Mr and Mrs Smith, is 463 km. Verify, with the necessary calculations, whether the statement is valid. (5)
3.2
| The table in ANNEXURE E has information on the performance of Grade 12 learners in some of the most popular subjects from 2013 to 2016. |
3.2.1 Describe the trend of the percentage achieved in Mathematical Literacy from 2013 to 2016. (2)
3.2.2 Explain how the percentage achieved for Mathematics differ from the percentage achieved for Mathematical Literacy for the period 2013 to 2016. (2)
3.2.3 In January 2017 when the Minister of Education, Angie Motshekga, announced the 2016 matric results, she mentioned that in 2016 the enrolment for Mathematics increased from 263 903 to 265 810 and that of Mathematical Literacy decreased from 388 845 to 361 865. Write the difference in the Mathematics enrolment to the difference in the Mathematical Literacy enrolment as a ratio. (3)
[30]
QUESTION 4
4.1
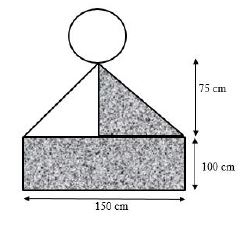
People in Mrs. Sibeko’s home village like colourful decorations. Notes:
You may use the following formulae:
|
4.1.1 Calculate the diameter of the circular part of the decoration in metres. (4)
4.1.2 If the wall is 4 m high and the decorations are at equal distances from the top and the bottom, calculate the distance that the decoration is from the top and the bottom of the hall in metres. (4)
4.1.3
| The decoration is painted using red paint for the shaded part and white paint for the unshaded parts. Paint is sold in 5 litre tins at R499 for the white paint and R505 for the red paint. Spreading rate for paint is 8 m2per litre. Two coats of each colour will be needed and 15 decorations will be painted. |
Mr. Sibeko stated that the amount of money that they will spend for red paint will be twice the amount of money that they will spend for white paint.
Verify, with the necessary calculations, whether this statement is valid or not. (12)
4.2
| The map in ANNEXURE F is showing maximum temperatures for some towns and cities in South Africa and neighbouring countries. |
4.2.1 What is the general direction of Polokwane from Calvinia? (2)
4.2.2 If the mean for the maximum temperature of all the towns and cities shown on the map is 26,762 °C, calculate the modal value B for the 5 towns and cities represented by B on the map. (4) 4.2.3
The box and whisker diagram represents the minimum temperatures: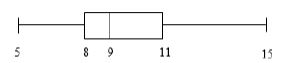 |
Calculate the difference between the interquartile ranges of the minimum temperatures and maximum temperatures. (7)
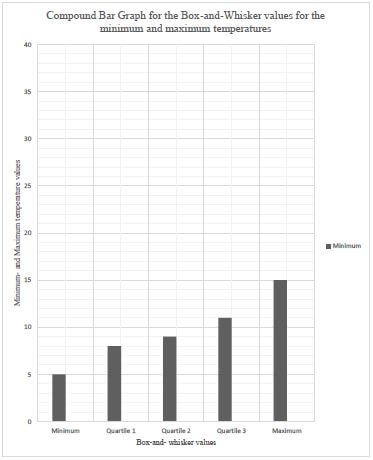
4.2.4 The box-and-whisker values for the minimum temperatures have already been plotted in ANSWER SHEET 1. Plot the box-and-whisker values for the maximum temperatures to complete a compound bar graph on the same ANSWER SHEET. (6)
4.2.5 Refer to the maximum temperatures as shown on the map and calculate the probability of having a temperature equal to or more than 28 °C. Give your answer as a decimal fraction to three decimal places. (3)
4.2.6 The actual distance between East London and Cape Town is 1 045 km. Calculate the scale used on the map and write it in the form 1 : ... Give your answer to the nearest million. (5)
[47]
TOTAL: 150
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICAL LITERACY PAPER 2 ADDENDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICAL LITERACY
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
ADDENDUM
ANNEXURE A – QUESTION 1.1
Table showing how much to pay for two different medical aid options in 2016:
EMERALD:
Salary row | R 0 – R 11 053 | R 11 053 – R 19 089 | R 19 089+ |
Member row | R 1 996 | R 2 210 | R 2 477 |
Adult row | R 1 416 | R 1 583 | R 1 761 |
Child row | R 731 | R 820 | R 914 |
ONYX:
Salary row | R 0 – R 11 053 | R 11 053 – R 23 551 | R 23 551+ |
Member row | R 3 193 | R 3 322 | R 3 587 |
Adult row | R 2 271 | R 2 351 | R 2 362 |
Child row | R 949 | R 1 030 | R 1 149 |
[Source: www.gems.gov.za]
Notes:
- Salary row reflects monthly salary before tax and other deductions.
- Member row shows how much the main member (person paying for the medical aid) has to pay.
- Adult row shows how much you pay for adult dependent.
- Child row shows how much the main member pay for child dependents (persons under the age of 21). Persons that are mentally or physically disabled, younger than 28 and still students at a recognised educational institution.
ANNEXURE B – QUESTION 2.1
Remuneration for developing reading material:
Rates for 3 consecutive years | |||
Year | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 |
Norm time (in minutes) | 26 | 26 | 26 |
Rate for developing in Rand | 147,36 | 138,25 | 169,30 |
Rate for transport in Rand | 2,45 per km | 2,64 per km | 2,82 per km |
Notes:
- Norm time = number of minutes taken to develop 1 page
- Total remuneration = amount of developing material + transport
- Amount for developing material =
norm time/60 × rate for developing × number of pages developed - Transport fee = rate for transport × number of kilometres travelled
ANNEXURE C – QUESTION 2.2
Tax Tables for Individuals:
American Tax Table 2015/2016 (1 March 2015 to 29 February 2016)
IF TAXABLE INCOME IS BETWEEN: | THE TAX DUE IS: |
0 – $9 225 | 10% of taxable income |
$9 226 – $37 450 | $922,50 + 15% of the amount over $9 225 |
$37 451 – $90 750 | $5 156,25 + 25% of the amount over $37 450 |
$90 751 – $189 300 | $18 481,25 + 28% of the amount over $90 750 |
$189 301 – $411 500 | $46 075,25 + 33% of the amount over $189 300 |
$411 501 – $413 200 | $119 401,25 + 35% of the amount over $411 500 |
$413 201 + | $119 996,25 + 39,6% of the amount over $413 200 |
[Source: www.incometax/p/america]
South African Tax Table 2015/2016 Tax Year (1 March 2015 to 29 February 2016)
TAXABLE INCOME (R) | RATES OF TAX (R) |
0 – 181 900 | 18% of each R1 |
181 901 – 284 100 | 32 742 + 26% of the amount above 181 900 |
284 101 – 393 200 | 59 314 + 31% of the amount above 284 100 |
393 201 – 550 100 | 93 135 + 36% of the amount above 393 200 |
550 101 – 701 300 | 149 619 + 39% of the amount above 550 100 |
701 301 and above | 208 587 + 41% of the amount above 701 300 |
Tax Rebates in South Africa
TAX REBATE | 2016 | 2015 |
Primary (younger than 65 years) | R13 257 | R12 726 |
Secondary (65 years and older) | R7 407 | R7 110 |
Tertiary (75 years and older) | R2 466 | R2 367 |
[Source: www.sars.gov.za]
ANNEXURE D – QUESTION 3.1
Strip chart map showing route from Pretoria to Windhoek:
 |
[Source: www.googlemaps.co.za]
ANNEXURE E – QUESTION 3.2
Grade 12 performance of some subjects from 2013 to 2016:
2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | |||||||||
SUBJECTS | Wrote | Achieved at | % achieved | Wrote | Achieved at 30% | % achieved | Wrote | Achieved | % achieved | Wrote | Achieved | % achieved |
Geography | 239 657 | 191 834 | 80,0 | 236 051 | 191 966 | 81,3 | 303 985 | 234 209 | 77,0 | 302 600 | 231 588 | 76,5 |
History | 109 046 | 94 982 | 87,1 | 115 686 | 99 823 | 86,3 | 154 398 | 129 643 | 84,0 | 157 594 | 132 457 | 84,0 |
Life Sciences | 301 718 | 222 374 | 73,7 | 284 298 | 209 783 | 73,8 | 348 076 | 245 164 | 70,4 | 347 662 | 245 070 | 70,5 |
Mathematical Literacy | 324 097 | 282 270 | 87,1 | 312 054 | 262 495 | 84,1 | 388 845 | 277 594 | 71,4 | 361 865 | 257 881 | 71,3 |
Mathematics | 241 509 | 142 666 | 59,1 | 225 458 | 120 523 | 53,5 | 263 903 | 129 481 | 49,1 | 265 810 | 135 958 | 51,1 |
Physical sciences | 184 383 | 124 206 | 67,4 | 167 997 | 103 348 | 61,5 | 193 189 | 113 121 | 58,6 | 192 618 | 119 427 | 62,0 |
[Source: www.eduation.gov.za]
ANNEXURE F – QUESTION 4.2
Map with the maximum temperatures on 11 August 2016:
ANSWER SHEET 1 FOR QUESTION 4.2.4 [Source: www.weathersa.co.za]
NAME:............................................................................... GRADE 12: ..........................................................
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICAL LITERACY PAPER 1 ADDENDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICAL LITERACY
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
ADDENDUM
ANNEXURE A: QUESTION 1.4
DISTANCES IN KM BETWEEN THE CITIES IN SOUTH AFRICA
Bloemfontein | Cape Town | Durban | East London | Johannesburg | Kimberley | Mafikeng | Port Elizabeth | Pretoria | Umtata | |
Bloemfontein | – | 1004 | 584 | 398 | 177 | 464 | 681 | 455 | 570 | |
Cape Town | 1 004 | – | 1 753 | 1 079 | 1 402 | 969 | 1 343 | 769 | 1 460 | 1 314 |
Durban | 634 | 1 753 | – | 674 | 557 | 811 | 821 | 984 | 636 | 439 |
East London | 584 | 1 079 | 674 | – | 982 | 780 | 1 048 | 310 | 1 040 | 235 |
Johannesburg | 398 | 1 402 | 557 | 982 | – | 476 | 287 | 1 075 | 58 | 869 |
Kimberley | 177 | 969 | 811 | 780 | 476 | – | 380 | 743 | 530 | 747 |
Mafikeng | 464 | 1 343 | 821 | 1 048 | 287 | 380 | – | 1 141 | 294 | 1 034 |
Polokwane | 706 | 1 710 | 886 | 1 290 | 297 | 780 | 569 | 1 383 | 250 | 1 181 |
Port Elizabeth | 681 | 769 | 984 | 310 | 1 075 | 743 | 1 141 | – | 1 133 | 545 |
Pretoria | 455 | 1 460 | 636 | 1 040 | 58 | 530 | 294 | 1 133 | – | 928 |
Umtata | 570 | 1 314 | 439 | 235 | 869 | 747 | 1 034 | 545 | 928 | – |
QUESTION 4.1 ANNEXURE B
 |
QUESTION 4.2: ANNEXURE C
Escherichia coli (E. coli) | E. coli counts per 100 mℓ at sample points | |||||||||||||
Possible symptoms include:
| Sample points | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |||
Results | 236 | 8 | 649 | 488 | 140 | 108 | 16 | 291 | 1 236 | 28 | ||||
Guideline | Low risk of gastrointestinal disorders E. coli < 130 counts/100 mℓ | Slight risk of gastrointestinal disorders E. coli 130–200 counts/ 100 mℓ | Significant risk of gastrointestinal disorders E. coli 200–400 counts/ 100 mℓ | High risk of gastrointestinal disorders E. coli >400 counts/100 mℓ | ||||||||||
Blue Green Algae | Blue Green Algae counts per 100 mℓ at sample points | |||||||||||||
Possible symptoms include:
| Sample points | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |||
Results | 181 | 121 | 121 | 39 | 294 | 213 | 422 | 1 086 | 121 | 543 | ||||
Guideline | Low risk Blue Green Algae < 20,000 cells/mℓ | Moderate risk Blue Green Algae 20,000–100,000 cells/mℓ | High risk Blue Green Algae >100,000 cells/mℓ | |||||||||||
QUESTION 5.3: ANNEXURE D
TABLE 6: RESULTS OF THE TEST FOR ESCHERICHIA AND BLUE GREEN ALGAE AT DIFFERENT SAMPLE POINTS AND A GUIDELINE TO THE RISK REGARDING READINGS
[Adapted from Barrage Weekly, 03 June, www.reservoir.co.za]
*If ingested. X sample not received / no information available. Reports generated every Friday of the year.
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICS PAPER 1 ERRATA - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICS
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
The Mathematics P1 Grade 12 September was written on Friday, 15 September 2017. We were made aware of certain amendments and omissions that were discovered during the marking process.
In order to address this and to ensure that learners are not disadvantaged, the following standardised approach to marking must be adopted across the Province. The following guidelines with regard to marking was prepared in conjunction with the examiner and moderator.
ERRATA
| 5.5 | P (−3 / 2; −9 / 4) f(x - 2) = (x - 2)(x - 2 + 3 ) | ✔✔ answer ✔f(x - 2) = x2 - x - 2 ✔x = 1 / 2 (2) |
6.2 | q(x) = -2-x | ✔ answer(1) |
6.4 | y> 0 ; y ∈ R | (1) |
6.5 | See 6.1 | ✔✓ shape and x-intercept(2) |
10.2 | V = 2x × x × (81 − 2x ) V = 81x −4/3xa | ✔✓ sub. into volume formula (2) |
10.3 | dV = 81 - 4x2 4 x = 9/2 = 4.5 | ✔81 - 4x2 ✔x2 = 81 ✔answer(3) |
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICS PAPER 1 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICS
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
NOTE:
- If a candidate answered a question TWICE, mark the FIRST attempt ONLY.
- Consistent accuracy applies in ALL aspects of the memorandum.
- If a candidate crossed out an attempt of a question and did not redo the question, mark the crossed-out attempt.
- The mark for substitution is awarded for substitution into the correct formula.
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
?
| 1.1 | 2?(? + 1) − 7(? + 1) = 0 (? + 1)(2? − 7) = 0 ? = −1 or ? = 72 | ? factors ? ?-value ? ?-value | (3) |
| 1.2 | ?2 − 5? − 1 = 0 ? = −? ± √?2 − 4?? 2? ? = −(−5) ± √(−5)2 − 4(1)(−1) 2(1) ? = 5,19 or ? = −0,19 | ? substitution into correct formula ?? x- values | (3) |
| 1.3 | 4?2 + 1 ≥ 5? 4?2 − 5? + 1 ≥ 0 (4? − 1)(? − 1) ≥ 0 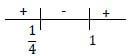 x ≤ 1/4 or ? ≤ 1 | ? standard form ? factors ?? ≤ ¼ ?? ≥ 1 | (4) |
| 1.4 | 54?+3. 100−2?+1 = 50 000 54?+3. (52. 22)−2?+1 = 50 000 54?+3. 5−4?+2. 2−4?+2 = 50 000 55. 2−4?. 22 = 50 000 2−4? = 22 −4? = 2 ? = − 1/2 | ?5−4?+2 ?2−4?+2 ?−4? = 2 ? answer | (4) |
| 1.5 | ? = 2? …………………..(1) ?2 + 2? − ? − ?2 = 36……….(2) ? = 2? sub into (2) (2?)2 + 2(2?) − ? − ?2 = 36 4?2 + 4? − ? − ?2 = 36 3?2 + 3? − 36 = 0 ?2 + ? − 12 = 0 (? − 3)(? + 4) = 0 ? = 3 or ? = −4 ? = 6 or ? = −8 | ?substitution ?standard form ? factors ? y − values ? x − values(5) | (5) |
| 1.6 | ?2 − ?? + ? − 1 = 0 ∆ = ?2 − 4?? ∆ = (−?)2 − 4(1)(? − 1) ∆ = ?2 − 4? + 4 ∆ = (? − 2)2 ∆ ≥ 0 roots are real and rational(perfect square) | ?substitution ? simplification ? (? − 2)2 ? conclusion(4) | (4) |
| [23] | |||
| QUESTION 2 | |||
| 2.1.1 | ?? = 4? − 1 483 = 4? − 1 484 = 4? ? = 121 121 terms in series | ? ?? = 4? − 1 ? equating 483 ? answer(3) | (3) |
| 2.1.2 | 121 ∑ (4? − 1) ?=1 | ? answer | (2) |
| 2.2.1 | (? − 3) − (2? − 4) = (8 − 2?) − (? − 3) −? + 1 = −3? + 11 2? = 10 ? = 5 | ? setting up equation ? simplification ? answer | (3) |
| 2.2.2 | … ; … ; … 6 ; 2 ; −2 ; … ; … ; … ?10 = 6 or ?? = −4? + 46 ? + 9? = 6 ?1 = −4(1) + 46 ? + 9(−4) = 6 ?1 = 42? = 42 | ? numerical values of?10; ?11; ?12 ? difference −4 ? a-value | (3) |
| 2.3 | ??2 + ??3 = −4 ? + ?(2) = −1 | ? setting of equations ? common factor ? ? = 2 ? value of a ? first three terms | (6) |
| [17 | |||
| QUESTION 3 | |||
| 3.1 | 41 ; 43 ; 47 ; 53 ; 61 ; 71 ; 83 ; 97 ; 113 ; 131 | ? 2nd difference ? ? = 1 ? ? = −1 ? ? = 41 ? ?? = ?2 − ? + 41 | (5) |
| 3.2 | ?41 = 412 − 41 + 41 Factors of 1681: 1 ; 41 and 1681 | ? ?41 = 1681 ? factors ? conclusion | (3) |
| 3.3 | Consider the unit digits only 1 ; 3 ; 7 ; 3 ; 1 ; 1 ; 3 ; 7 ; 3 ; 1 ; groups of 5 49999998 = 9999999,6 5 0,6 × 5 = 3 ?49999998 will end in 7 | ? unit digits ? groups of 5 ? conclusion | (3) |
| [11] | |||
| QUESTION 4 | |||
| 4.1.1 | ? = ?(1 + ?)? ? = 500 000 (1 + 7,2 )12? 1200 ? = 500 000(1.006)12? | ?sub into formula ? 12? | (2) |
| 4.1.2 | ? = 500 000(1.006)12? ? = 500 000(1.006)12×5 ? = ? 715894.21 | ? ? = 60 ? answer | (2) |
| 4.1.3 | ? = ?(1 + ?)? Will exceed R1 000 000 in 10 years. | ? setting up equation ? using logs ? conclusion | (3) |
| 4.2.1 | ?V = 10 000 [1 − (1 + 15/1200 ) −36] 15/1200 ?? = ?288 472,67 ???????/? = ?350 000 − ?288 472,67 ???????/? = ?61 527,33 | ? ? and ? ?sub into ?? formula ? ?? formuleü ?? = ?288 472,67 ? subtracting ? answer | (5) |
| 4.2.2 | 350 000 = ? [1 − (1 + 18,5/1200 ) −60] 18,5/1200 ? = ? 8 983,17 | ? ? = 18,51200 ?? = −60 ? substitution ? answer | (4) |
| [16] | |||
| QUESTION 5 | |||
| 5.1 | ?(−3; 0) | ? answer | (1) |
| 5.2 | ?(?) = ?2 + 3? ? = − ? 2? ? = − 3 2 ? (− 3) = (− 3)2 + 3 (− 3) 2 2 2 = − 9/4 ? (− 3 ; − 9) 2 4 | ?? = − 32 ?substitution ?answer | (3) |
| 5.3 | ?(−5) = 10 and ?(−3) = 0 ? = 10 − 0 −5 − (−3)? = −5 | ? calculating ?(−5) and ?(−3) ? substitution ? ?-value | (3) |
| 5.4 | ? < −3 or / of ? > 0 | ?answer | (2) |
| 5.5 | ? (− 3 ; − 9) or
| ? answer ? ?(? − 2) = ?2 − ? − 2 ? ? = − 12 | (2) |
| 5.6 | ?? = − 1/2 ? + 2 − (?2 + 3?) OR ?? = − 1/2 ? + 2 − (?2 + 3?) ? = − (− 7/4 ) 2 − 7/2 (− 7/4 ) + 2 OR ? = − ? | ? ?(?) − ?(?)
? ?(?) − ?(?)
??(?) − ?(?) | (4) |
| [15] | |||
| QUESTION 6 | |||
| 6.1 | 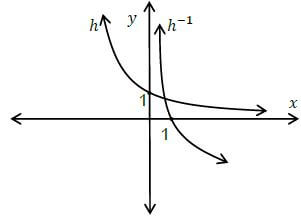 | ? shape ? y − intercept ? point on graph | (3) |
| 6.2 | ?(?) = 2? | ? answer | (1) |
| 6.3 | ℎ−1? = 2−? −? = log ? log 2 ? = − log ? / ? = − log2 ? /? = log½ ? log 2 | ? interchange ? and ? ? equation | (2) |
| 6.4 | ? ≥ 0 ; ? ∈ ? | (1) | |
| 6.5 | See 7.2.1 | ??shape and x-intercept | (2) |
| 6.6 | log1 ? = −321 −3( ) = ? 2? = 8∴ 0 < ? ≤ 8 | ?? = 8 ?0 < ? ≤ 8 | (2) |
| [11] | |||
| QUESTION 7 | |||
| 7.1 | ? = 5? = 2 | ?? = 5?? = 2 | (2) |
| 7.2 | ? = 5 − ? ? − 2 ? = −(? − 2) + 3 (? − 2) ? = 3 − 1 ? − 2 | ?? = 5−? ?−2 ?? = −(?−2)+3 (?−2) | (2) |
| 7.3 | ?(5; 0) ? = ? − 3 ? = ? + 3 ?′(0 + 3; 5 − 3) ?′(3; 2) | ?? = 3 ?? = 2 | (2) |
| [6] | |||
| QUESTION 8 | |||
| 8.1 | ?(?) = −2?2 + ?
| ? formula ? substitution of (? + ℎ) ? simplification to (−4?ℎ − 2ℎ2) ? common factor ? answer | (5) |
| 8.2 | 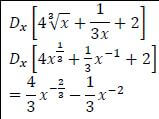 | (4) | |
| [9] | |||
| QUESTION 9 | |||
| 9.1 | ?(?) = (? − 1)2(? + 3) ?(?) = ?3 + ?2 − 5? + 3 ?′(?) = 3?2 + 2? − 5 3?2 + 2? − 5 = 0 (3? + 5)(? − 1) = 0 ? = − 5/3 or ? = 1 ?(1) = 0 ? (− 5/3 ) = 256 27 | ? ?(?) = ?3 + ?2 − 5? + 3 ? ?′(?) = 0 ? factors ? ?-values ? ?-values | (5) |
| 9.2 | 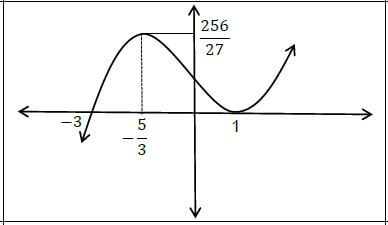 | ? shape ? ? − intercepts ? ? − intercept ? stationary points | (4) |
| 9.3 | ?′′(?) = 6? + 2 6? + 2 = 0 ? = − 1/3 ? = 128 / 27 / 4,74 / 4 20/27 | ? f′′(?) = 6? + 2 ?? = − 1/3 ? ? = 128 / 27 / 4,74 / 4 20/27 | (3) |
| 9.4 | 0 < ? < 25627 | ??answer | (2) |
| 9.5 | ?′(?) = 3?2 + 2? − 5 3?2 + 2? − 5 = −5 3?2 + 2? = 0 ?(3? + 2) = 0 ? = 0 or ? = − 2/3 ? (− 2) = 175 3 27 y = −5? + ? 175 = −5 (− 2/3 ) + ? 27 3? = 85 27 ? = −5? + 85 27 | ? f′(?) = −5 ? factors ? ? = − 2/3 ? f (− 2/3) = 175 27 ? substitution ? answer | (6) |
| [20] | |||
| QUESTION 10 | |||
| 10.1 | 243 = 2(? × 2?) + 2(2? × ℎ) + 2(? × ℎ) 243 = 4?2 + 4?ℎ + 2?ℎ 243 = 4?2 + 6?ℎ ℎ = 243 − 4?2 6? ℎ = 81 − 2? 2? 3 | ? TSA equation and sub ? simplification | (2) |
| 10.2 | ? = 2? × ? × (81 − 2?) (2? 3) ? = 81? − 4 ?3 3 | ?sub into volume formula | (1) |
| 10.3 | ?? = 81 − 4?2 ?? 81 − 4?2 = 0 ?2 = 81 4 ? = 9 = 4.5 2 | ? 81 − 4?2 ? 81 − 4?2 = 0 ? ?2 = 81 4 ? answer | (4) |
| [7] | |||
| QUESTION 11 | |||
| 11.1 | 9 × 9 × 9 × 5 × 4 = 14580 | ?9 × 9 × 9 ?5 × 4 ? 14580 | (3) |
| 11.2.1 | 12! = 119750400 2! .2! | ? 12! ?2!.2! ? 119750400 | (3) |
| 11.2.2 | 10! 2! = 1 = 0,015 119750400 66 | ?10!2! ? 119750400 ? answer | (3) |
| [9] | |||
| 11.3.1 | 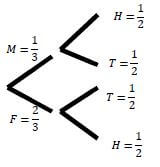 | ? first branch with values ? top part of second branch with values ? bottom part of second branch with values | (3) |
| 11.3.2 | ?(?) = 2 3 | ? ?(?) = 2/3 | (1) |
| 11.3.3 | ?(?/?) = 1 × 1 3 2 ?(?/?) = 1 6 | ? ?(?/?) = 1/6 | (2) |
| [15] | |||
| TOTAL: 150 | |||
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICS PAPER 2 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICS
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
| QUESTIONS 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1.1 | 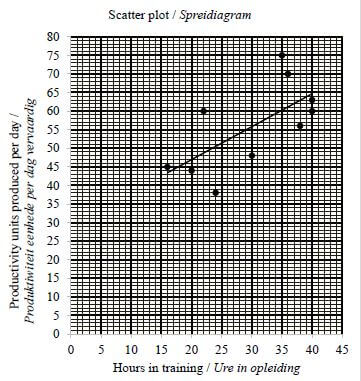 | ✔2-4 correct points ✔5-7 correct points ✔plotting all points | (3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1.2 | a = 29,22 b = 0,89 y = 29,22 + 0,89x | ✔ A ✔ B ✔ equation | (3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1.3 | (30,9 ;55,50) y-int 29, 22 | ✔ mean point (30,90;55,50 ) and y-int 29, 22 ✔ regression line | (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1.4 | y = 29,22 + 0,89(25) | ✔ answer | (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1.5 | r = 0,66 | ✔ answer | (1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1.6 | Moderately strong positive correlation | ✔ answer | (1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [12] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QUESTION 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2.1 | 140 learners | ✔ answer | (1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2.2 | 60 < x £ 70 | ✔ answer | (1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2.3 | 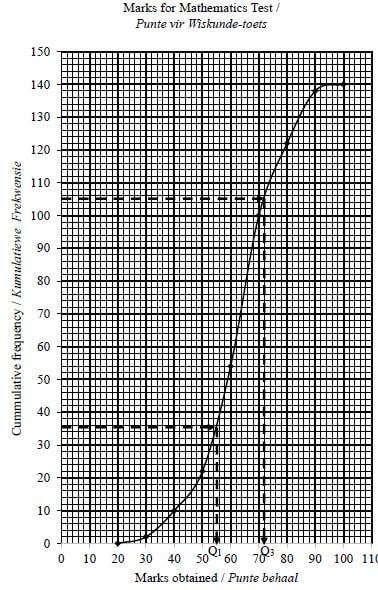 | ✔ grounding ✔ cummulative frequency ✔ plotting against the upper limit ✔ shape | (4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2.3 | Q3 - Q1 = 72 - 55 = 17 | ✔ Q3 & Q1 ✔IQR | (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [8] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QUESTION 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.1 | BC : x + 2 y = 14 y = - 1 x + 7 | ✔ = mAD = - 1/2 ✔ subst. m and A into correct formula ✔ y = - 1 x + 9 2 2 | (3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.2 | - 1 x + 9 = 0 OR mAD = mBC | ✔ y = 0 ✔ x = 9 ✔ y = 0 ✔x = 9 | (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.3 | mFD = 2 - 0 | ✔ correct subst. ✔ mFD = 2 ✔ mBC × mFD = -1 | (3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.4 | AD =√(-1 - 9)2 + (5 - 0)2 | ✔ subt. into correct formula | (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.5 | FD = √(9 -10)2 + (0 - 2)2 | ✔ subst. into correct formula | (4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.6 | mAB = mDC | ✔ subst. into correct formula | (6) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [20] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QUESTION 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4.1 | xS = 0 + 4 yS = 0 - 6 | ✔ subst. into correct formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4.2 | SP = √(2 - 4)2 + (- 3 + 6)2 | ✔ subst. into correct formula | (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4.3 | (x - 2)2 + (y + 3)2 = 13 | ✔ correct subt. centre | (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4.4 | Tangent ⊥ radius | ✔ answer | (1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4.5 | mrad = - 3 + 6 | ✔ subst. into correct form. | (4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4.6 | (0 - 2)2 + (y + 3)2 = 13 OR (0 - 2)2 + (y + 3)2 = 13 OR Draw horizontal line y = -3 with M on OT OM = 3 | ✔ x = 0 | (4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4.7 | At U , y = - 26 | ✔ U [ 0 ; -26/3] ✔ lenght of TU ✔ lenght of OT ✔ correct subst. ✔ answer | (5) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [20] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QUESTION 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5.1.1 | sin 2x = √15 cos2x = 2 cos2 x -1 | ✔ diagram | (5) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5.2 | sin(180º - θ ).sin(540º - θ ).cos(θ - 90º) | ✔ sin θ | (7) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5.3.1 | LHS = sin 5x. cos3x - cos5x.sin 3x -1 | ✔ sin (5x - 3x) ✔ simplification | (4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5.3.2 | tan 2x = 0 OR tan 2x is undefined | ✔ tan 2x = 0 / undefined ✔ 0º or 180º ✔ 90º or 270º ✔ answer | (4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [20] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QUESTION 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6.1 | 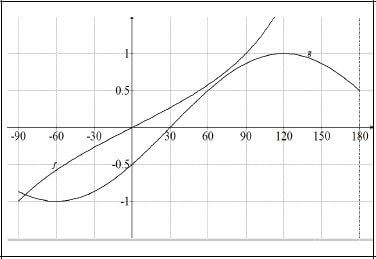 | f g | (6) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6.2 | period(e) of f(½x) = 180º ½ = 360º Answer only full marks | ? = 180º ½ ? 360º | (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6.3 | 0º < x < 30º | ?critical values | (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6.4 | x = 170º | ? answer | (1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [11] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QUESTION 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7.1 | Area ΔABC = 1 .AB.BC.sinB 2 = 1 × 17 × 17 × sin105º 2 = 139,58 | ? Area rule formula | (3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7.2 | AC 2 = AB2 + BC2 - 2.AB.BC.cosB = 727,5974081 | ? cosine rule formula | (3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7.3 | sinACD = sinD | ? sine rule formula | (3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7.4 | Converse opp ∠ s of a cyclic quad OR int.opp.∠ s of a quad suppl | ? reason OR ? reason | (1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [10] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QUESTION 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
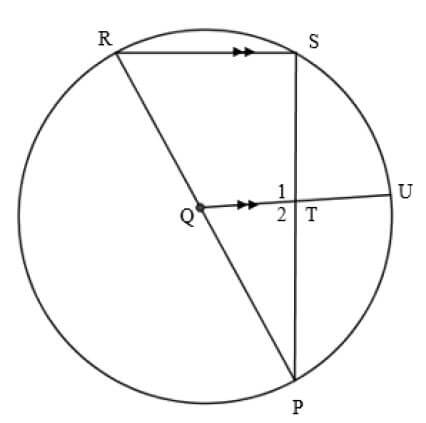 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8.1.1 | S = 90º [∠ in semi - circle] | ? S ? R | (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8.1.2 | T2 = S = 90º [corresp.∠ s RS ΙΙ Q] | ? S/R | (6) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
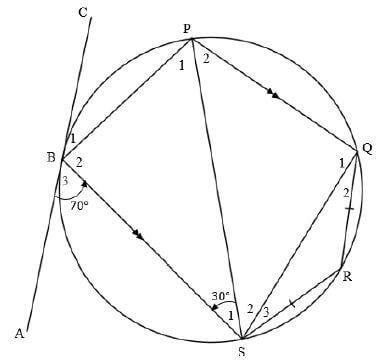 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8.2.1 | B1 = 30º [tan chord theorem] | ?S ? R | (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8.2.2 | P2 = 30º [alt ∠ s, BS ΙΙ PQ] | ?S ? R | (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8.2.3 | R = 150º [opp ∠ s of a cyclic quad] | ?S ? R | (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8.2.4 | Q2 = S3 [∠ s opp =sides] | ? S/R | (3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [17] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QUESTION 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
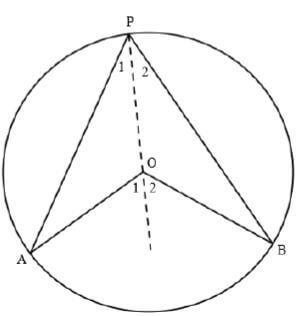 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9.1 | O1 = P1 + A and O2 = P2 + B [ext ∠ of a Δ] | ?S/R ?S/R ?S/R ?S | (4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
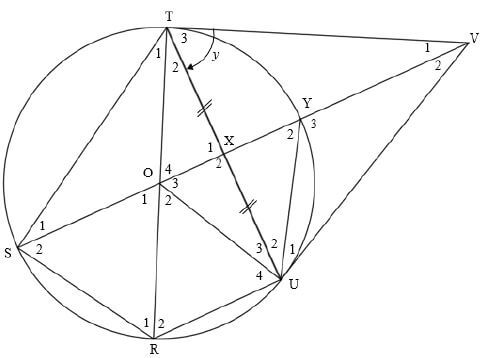 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9.2.1 | RUT = 90º [∠ in a semi - circle] OR RUT = 90º [∠ in a semi - circle] | ?S ? R | (5) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9.2.2 | R2 = y [tan chord theorem] | ?S ? R ?S ? R ? R | (5) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9.2.3 | O4 = y = O1 [vert opp.∠ s] OR VTO = 90º [tan ⊥ radius] VUO = 90º [tan ⊥ radius] ∴VTO + VUˆ O = 180º ∴TOUVisa cyclicquad [converseoppÐsof cyclicquad.supp] | ?S ? R | (5) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [19] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| QUESTION 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
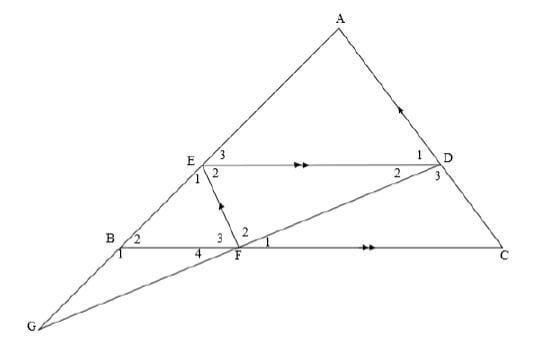 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.1 | BA = BC [prop theorem; EF ΙΙ AC] | ?S ?R ?S ?R | (4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.2 | B2 = E3 [corresp ∠s : EDΙΙBC] E1 = A [corresp ∠s : EFΙΙAC] ∴F3 = D1 [sum of ∠s of Δ ] ∴ΔBFE ΙΙΙ ΔEDA [∠∠∠] | ?S/R ?S/R ?R | (3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.3.1 | AD = ED [ΔBFE ΙΙΙ ΔEDA] FE BF AD = 10 2 3,5 AD = 40 = 5,71 7 | ?S ?R ? subst. ? AD | (4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.3.2 | DC = EF = 2 [opp.sidesof a parm] | ?S ?R | (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [13] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TOTAL : 150 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICS PAPER 2 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICS
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of 10 questions.
- Answer ALL the questions in the SPECIAL ANSWER BOOK provided.
- Clearly show ALL calculations, diagrams graphs, et cetera which you have used in determining the answers.
- Answers only will NOT necessarily be awarded full marks.
- If necessary, round off your answers to TWO decimal places, unless stated otherwise
- Diagrams are not necessarily drawn to scale.
- You may use an approved scientific calculator (non-programmable and non-graphical) unless stated otherwise.
- An information sheet with formulae is included at the end of the question paper. 9. Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
A training company wants to know if there is a link between the hours spent in training by a particular category of employee and their productivity (units produced per day). The following data was extracted from files of 10 employees.
Employee | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
Hours in training | 16 | 36 | 20 | 38 | 40 | 30 | 35 | 22 | 40 | 24 |
Productivity (units produced per day) | 45 | 70 | 44 | 56 | 60 | 48 | 75 | 60 | 63 | 38 |
1.1 Draw a scatter plot of the data on the grid provided in the ANSWER BOOK. (3)
1.2 Determine the equation of the least squares regression line. (3)
1.3 Draw the least squares regression line on the scatter plot drawn in QUESTION 1.1. (2)
1.4 Use the least squares regression line to predict the productivity (units produced per day), if a particular category of employee spent 25 hours in training. (2)
1.5 Determine the correlation coefficient of the data. (1)
1.6 Comment on the strength of relationship between the hours spent in training and the number of units produced per day. (1)
[12]
QUESTION 2
The marks obtained by learners of a certain school in a Mathematics test is represented in the histogram below: 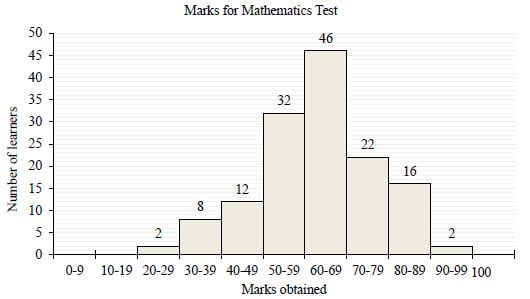
2.1 How many learners wrote the test? (1)
2.2 Write down the modal class. (1)
2.3 Draw the ogive for the given information. (4)
2.4 Use the ogive to estimate the interquartile range. (2)
[8]
QUESTION 3
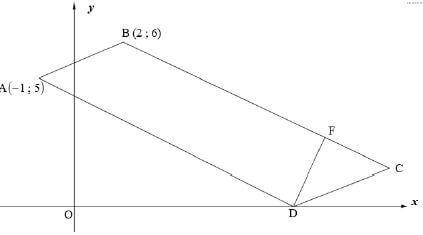
In the diagram below, A (-1 ; 5), B (2 ; 6), C and D are the vertices of parallelogram ABCD. Vertex D lies on the x-axis. The equation of BC is x + 2y = 14. 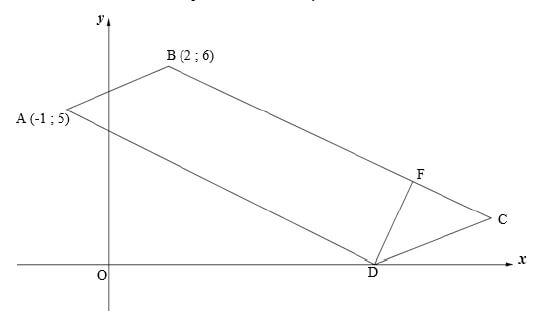
3.1 Determine the equation of line AD in the formy = mx + c. (3)
3.2 Determine the coordinates of D. (2)
3.3 If the coordinates of F are (10 ; 2), show that DF is perpendicular to BC. (3)
3.4 Calculate the length of AD. (Leave your answer in surd form.) (2)
3.5 Hence, or otherwise, calculate the area of parallelogram ABCD. (4)
3.6 Calculate the size of AB̂C. (6)
[20]
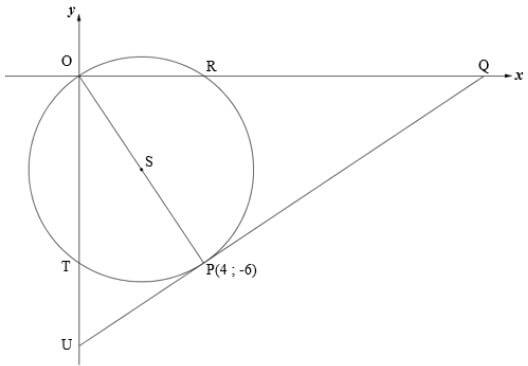
QUESTION 4
In the diagram below, the circle with centre S, passes through the origin, O, and intersects the x-axis at R and y-axis at T. The tangent to the circle at P(4 ; -6) intersects the x-axis at Q and the y-axis at U. 
4.1 Calculate the coordinates of S, the centre of the circle. (2)
4.2 Calculate the length of the radius of the circle. (Leave your answer in surd form.) (2)
4.3 Determine the equation of the circle in the form of (x − a)2 + (y − b)2 = r2. (2)
4.4 Why is QP̂U = 90°? (1)
4.5 Show that the equation of the tangent UQ is: y =2/3x −26/3. (4)
4.6 Determine the coordinates of T. (4)
4.7 Determine the ratio of Area △OTP in its simplest form. (5)
Area △PTU
[20]
QUESTION 5
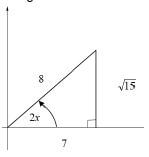
5.1 Given: sin 2x =√15 and 0° ≤ 2x ≤ 90°.
x
Determine with the aid of a diagram and without using a calculator the value of cos x. (5)
5.2 Simplify the following expression to one trigonometric ratio of θ:
sin(180° − θ) . sin(540° − θ). cos(θ − 90°)
tan(−θ). sin2(360° − θ) (7)
5.3 Given the identity: sin 5x.cos 3x.−cos 5x .sin3x − 1 = −2 sin2x.
tan 2x
5.3.1 Prove the above identity. (4)
5.3.2 For which value(s) of x will the above identity be undefined for 0° ≤ x ≤ 180°. (4)
[20]
QUESTION 6
Given f(x) = tan 1/2x and g(x) = sin(x − 30°) for x ∈ [−90°; 180°]
6.1 On the same set of axes draw the graphs of f and g. Show clearly on your graphs the turning points and asymptotes, if any. (6)
6.2 Write down the period of f. (2)
6.3 For what values of x is f(x). g(x) < 0 for x ∈ [−90°; 120°]? (2)
6.4 Write down the equation(s) of the asymptotes of h if ℎ(x) = f(x + 10°) for x ∈ [−90°; 180°] (1)
[11]
QUESTION 7
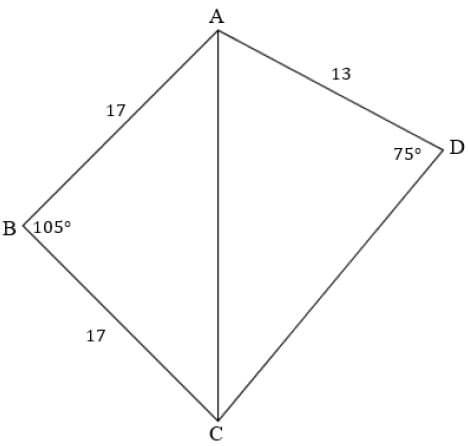
In the diagram below, ABCD is a quadrilateral with diagonal AC drawn.
AB = BC = 17 m
AD = 13 m
D̂ = 75°
B̂ = 105° 
Calculate:
7.1 The area of △ ABC. (3)
7.2 The length of AC. (3)
7.3 The size of AĈD. (3)
7.4 Give a reason why ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. (1)
[10]
Give reasons for ALL statements in QUESTION 8, 9, 10 AND 11.
QUESTION 8
8.1 PR is a diameter of the circle PRSU. QU is drawn parallel to RS and meets SP in T.
8.1.1 Write down, with a reason, the size of Ŝ. (2)
8.1.2 If the diameter is 20 cm and SP = 16 cm, calculate the length of TU. (6)
8.2 ABC is a tangent to circle BPQRS at B. PQ ∥ BS. QR = RS. Ŝ1 = 30° and B̂3 = 70°. 
Calculate, with reasons, the size of the following angles:
8.2.1 B̂1(2)
8.2.2 P̂2(2)
8.2.3 R̂ (2)
8.2.4 Q̂2(3)
[17]
QUESTION 9
9.1 A, B and P are the points on the circle with centre O. AO, BO, AP and BP are drawn. 
Prove the theorem which states that AÔB = 2AP̂B. (4)
9.2 TV and VU are tangents to the circle with centre O at T and U respectively. TSRUY are points on the circle such that RT is the diameter. X is the midpoint of chord TU. T̂3 = y. 
Prove that:
9.2.1 RU ∥ SY (5)
9.2.2 T̂1=½y (5)
9.2.3 TOUV is a cyclic quadrilateral (5)
[19]
QUESTION 10
In the diagram below, D and E are points on sides AC and AB respectively of △ ABC such that DE ∥ BC. F is a point on BC such that EF ∥ AC. AB produced and DF produced meet in G. 
10.1 Prove that: BC = AC
FC DA(4)
10.2 Prove that: Δ BFE ||| Δ EDA(3)
10.3 It is further given that EF = 2, BF = 3,5 and ED = 10, determine the length of:
10.3.1 AD (4)
10.3.2 DC (2)
[13]
TOTAL: 150