Adele
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
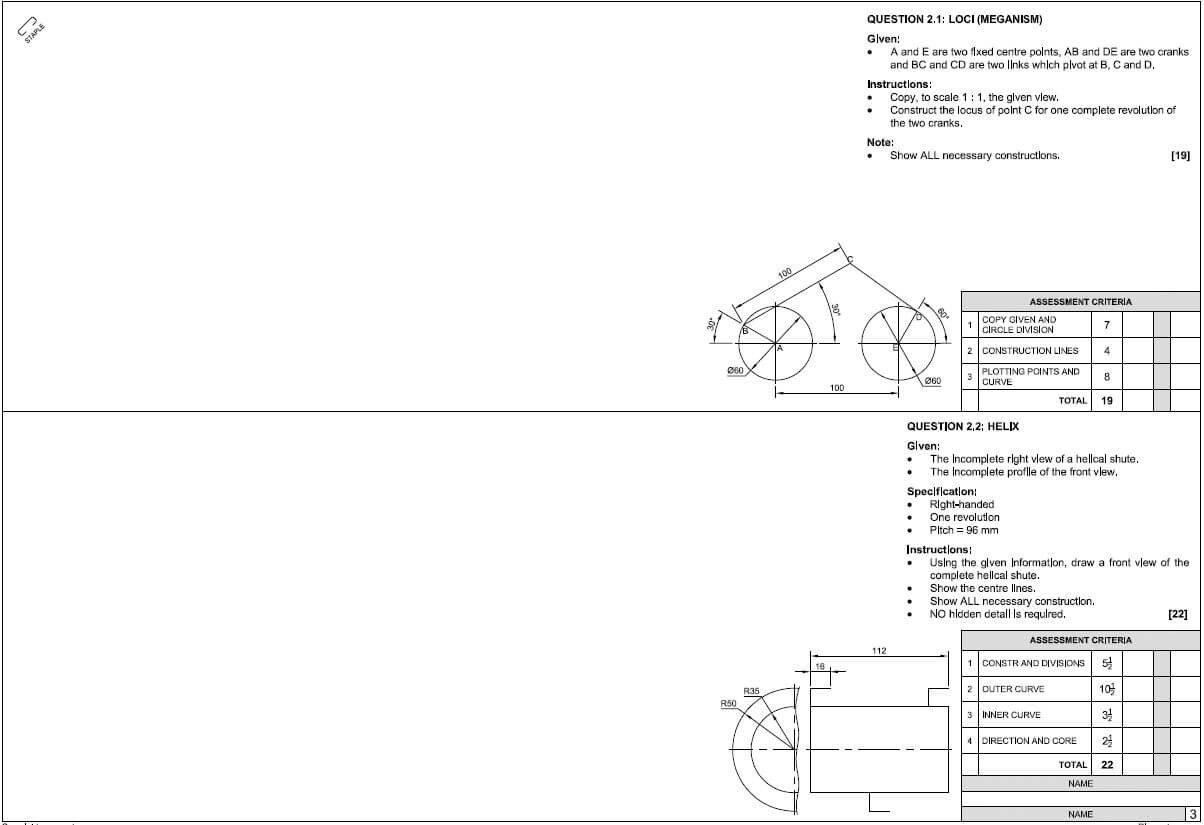
QUESTION 1: CONSTRUCTION PROCESSES
1.1 FIGURE 1.1 shows the substructure of a structure.
1.1.1 150 mm / 200 mm (1)
1.1.2 150 mm (1)
1.1.3 220 mm (1)
1.1.4 Concrete (1)
1.1.5 Hard core filling (1)
1.1.6 Any TWO purposes of part 1.1.D.
- Solid base for concrete floor
- Give level surface. (2 x 1) (2)
1.2 Any similar answer:
- (1) Water weakens (2) sub-soil / foundations can sink.
- (1) Water can dam up against foundations (2) and spread to walls. (2)
1.3 (1) Makes burning process easy because (2) it burns right through to the centre of the brick. (2)
1.4 Any THREE properties of face bricks.
- Hard
- Strong
- Does not absorb water
- Inner and outer walls (3 x 1) (3)
1.5 Describe in point form the manufacturing process of clay bricks.
- (1) Clay / scale / brick soil are dug out, (2) ground and (3) mixed with water.
- (4) Cast in moulds. (5) Dried. (6) Baked in kilns. (6)
1.6 FIGURE 1.6 shows a wood door frame.
1.6.1 (1) Anchors / Frame ties (2) are built into brick joints. (2)
1.6.2
- 1.1.A – Head
- 1.1.B – Strut
- 1.1.C – Frame stile (3)
1.6.3 813 (1)
1.6.4 Anchor frame to floor. (1)
1.7 Name the tools in FIGURES 1.7.1 to 1.7.3.
1.7.1 Plaster trowel (1) 1.7.2 Belt sander (1)
1.7.3 Line and pins (1)
[30]
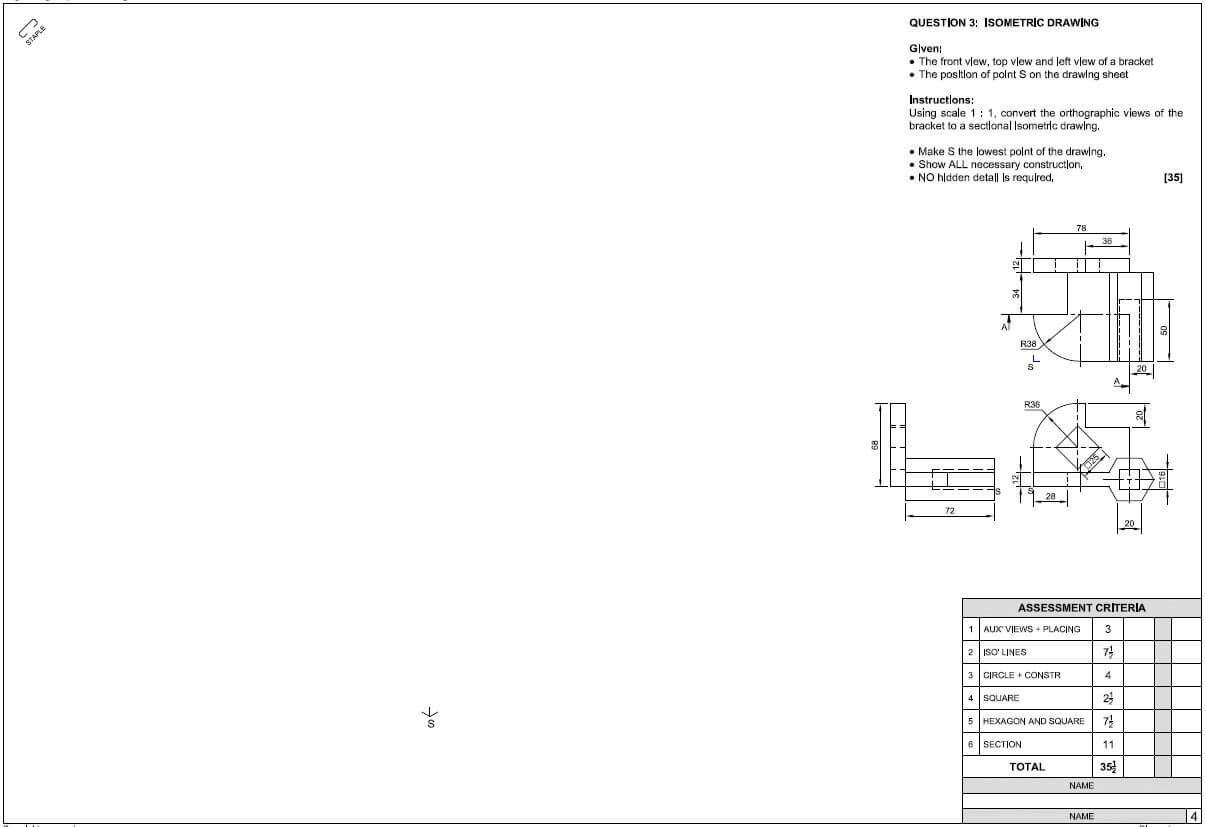
QUESTION 2: ADVANCED CONSTRUCTION PROCESSES
2.1
2.1.1 Main bar (1)
2.1.2 Withstand tensile stress / Shear stress over shear line (1)
2.1.3 High tensile steel (1)
2.1.4 16 mm (1)2.1.5 Sturrups (1)
2.1.6 Any TWO purposes of the bars at 2.1.B.
- Withstand shear stress
- Bind main bars (2 x 1) (2)
2.2 Any TWO requirements of the steel for steel reinforcement
- (1) Capable of resisting tensile stress (2) without significant strain
- (1) Easily bent (2) into required shape
- (1) Surface must bond adequately (2) with concrete (Any 2 x 2) (4)
2.3 Similar answer:
- (1) Prevent damp from (2) penetrating to reinforcement / causing rust. (2)
2.4
- Rough arch – Standard bricks
- Gauged arch – Wedge shape bricks (2)
2.5 Similar answer:
- (1) Allow for / glass not break (2) expansion and shrinking of glass. (2)
2.6 Any THREE safety rules when working on floors and stairs with open sides.
- Sufficiently lighting
- Free from material, waste and obstacles
- Sufficiently covered
- Sufficient trap platforms or nets
- Safety equipment must be used (3 x 1) (3)
2.7
2.7.1 – clamp
2.7.2 – bearer
2.7.3 – strut
2.7.4 – prop
2.7.5 – soleplate (5 x 1) (5)
2.8 Open eave construction: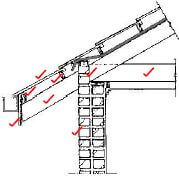
- Outer wall
- Rafter
- Tie beam
- Facia board (gutter board)
- 2 purlins
- Tile roof covering
- Beam filling (8)
2.9 (1) Wall or soil (2) which must be supported. (2)
2.10 Indicate whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE.
2.10.1 False (1)
2.10.2 False (1)
2.10.3 True (1)
2.10.4 True (1)
2.10.5 False (1)
[40]
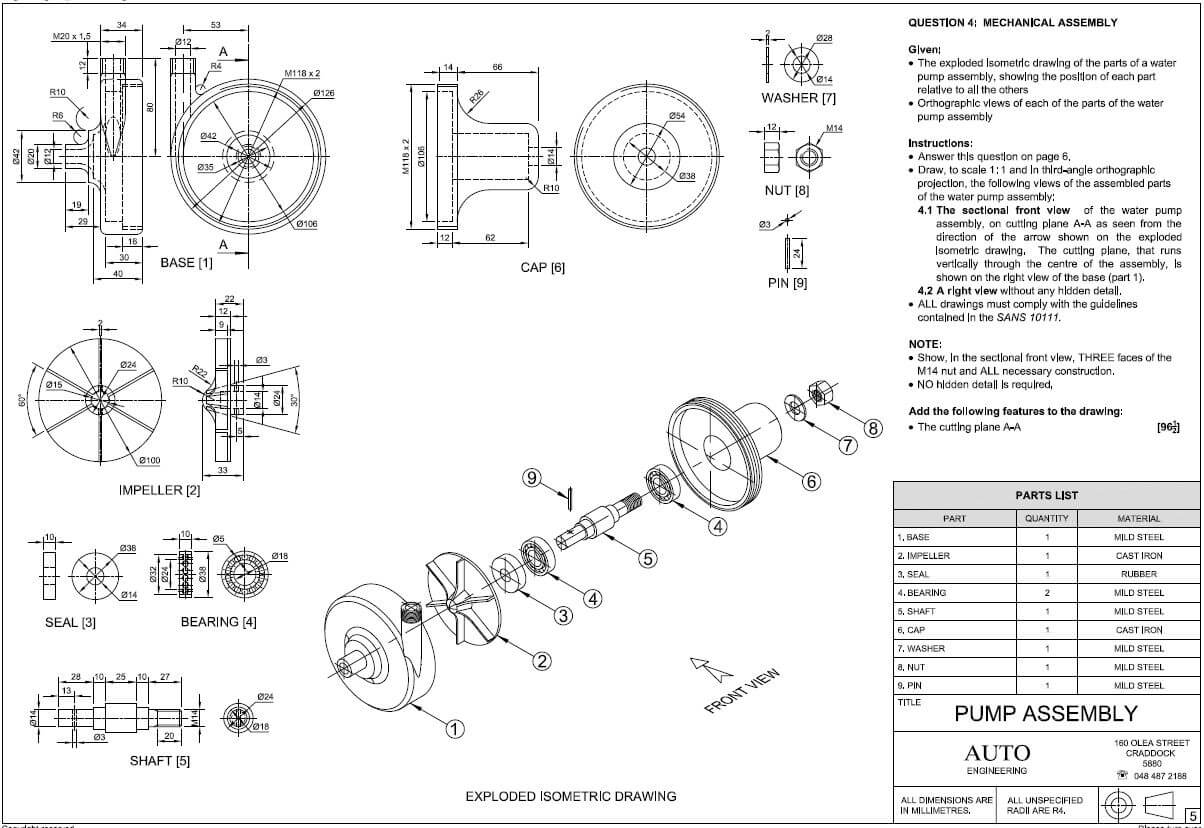
QUESTION 3: CIVIL SERVICES
3.1 3.1.1 Septic tank (1)
3.1.2 (1) Digests and liquefy by (2) anaerobic bacteria and other biological life such as maggots / worms / micro-organisms. (2)
3.1.3 Gas escape (1)
3.1.4 (1) Not disturbing (2) surface water layer. (2)
3.1.5 French drain (1)
3.2 (1) Sucking / pressure as result of outlet of drain (2) can push or suck water lock out. (2)
3.3 S-trap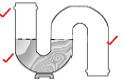 (3)
(3)
3.4
3.4.1 STRAIGHT (1)
3.4.2 SLIGHTLY SMALLER (1)
3.4.3 6 mm (1)
3.5 Any THREE methods to generate electricity.
- Hydro
- Wind
- Sun
- Steam – Coal / Nuclear (Any 3 x 1) (3)
3.6 Protect electrical cables (1)
3.7 (1) Lead water to water tank (2) in roof to raise pressure. (3) Water then lead to draw-off points. (3)
3.8 User pipe (1)
3.9
3.9.1 False (1)
3.9.2 True (1)
3.9.3 False (1)
3.9.4 False (1)
3.9.5 False (1)
3.10
3.10.1 Stop cock (1)
3.10.2 Any ONE example where this type of tap must be installed.
- Before geysers
- Cistern
- Storage tanks
- Water service point (Any 1 x 1) (1)
[30]
QUESTION 4: MATERIALS AND QUANTITIES
4.1 (1) Chemical (2) Physical / bind / harden (2 x 1) (2)
4.2 (1) Damp in air (2) react with cement particles (2)
4.3 Any ONE purpose of lime in a mortar mix.
- Better workability
- Better plasticity property for mortar
- When sand has insufficient round particles
- When not sufficient fine sand particles
- Better water retaining capacity (Any 1 x 1) (1)
4.4 Stone (1)
4.5 Any THREE methods of curing of concrete.
- Retaining formwork
- Covers
- Ponding
- Spraying
- Curing compounds (Any 3 x 1) (3)
4.6 Similar answer:
- (1) To test compressive stress to (2) ensure that concrete comply to requirements. (2)
4.7 Name TWO uses of each of the following materials:
4.7.1 Copper:
- Electrical wires
- Electrical equipment
- Water pipes
- Heads of soldering irons (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.7.2 Zink:
- Alloy material
- Covering of iron and roof sheets (2 x 1) (2)
4.8 Channel iron. ![]() (2)
(2)
4.9 Any THREE properties of a good preservative for wood.
- Easily absorbed
- Cheap
- Readily available
- Not poisonous / harmful to humans and animals
- Not easily macerate
- Not corrode metal
- Not reduce strength of wood
- Not unpleasant smell
- Not spoil natural beauty of wood
- Not resist paint, varnish, glue, etc.
- Not flammable (Any 3 x 1) (3)
4.10 (1) Odd number layers (2) veneer glued upon the other. (2)
4.11 Use the quantity list on ANSWER SHEET A and determine the volume concrete which will be needed for a floor with a length of 6 m, width of 3 m and thickness of 75 mm. (3)
4.12 Use the quantity list on ANSWER SHEET A and determine the number of bricks which will be needed for a cavity wall with a length of 4 m and a height of 2,4 m. (5)
[30]
QUESTION 5: APPLIED MECHANICS
5.1 FIGURE 5.1 on ANSWER SHEET B show the space diagram of a lean to roof. Determine graphically scale 1 mm = 1 N on ANSWER SHEET B the size and nature of the forces in the parts of the truss by drawing the force diagram and completing the table. 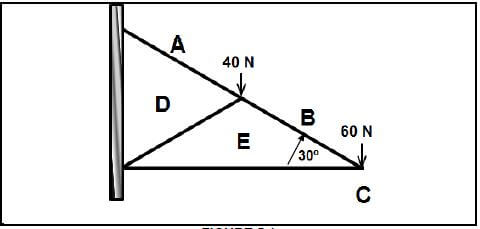 (14)
(14)
5.2 FIGURE 5.2 on ANSWER SHEET C show a beam with point loads. Calculate on ANSWER SHEET C the following: 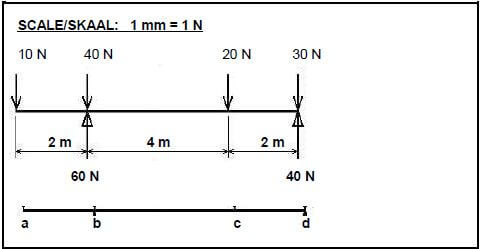
FIGURE 5.2
5.2.1 The bending moment values (6)
5.2.2 Complete the bending moment diagram on scale 1 mm = 1 N according to the bending moment values (4)
5.3 Determine the sentroid of the body in FIGURE 5.3 from point P. (The table on ANSWER SHEET C can be used for the calculations.) 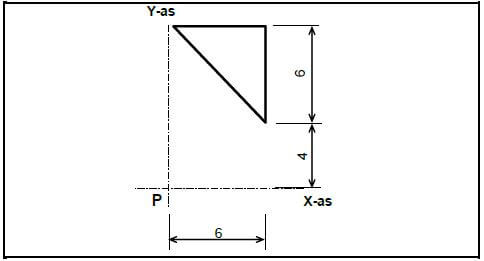
FIGURE 5.3 (6)
[30]
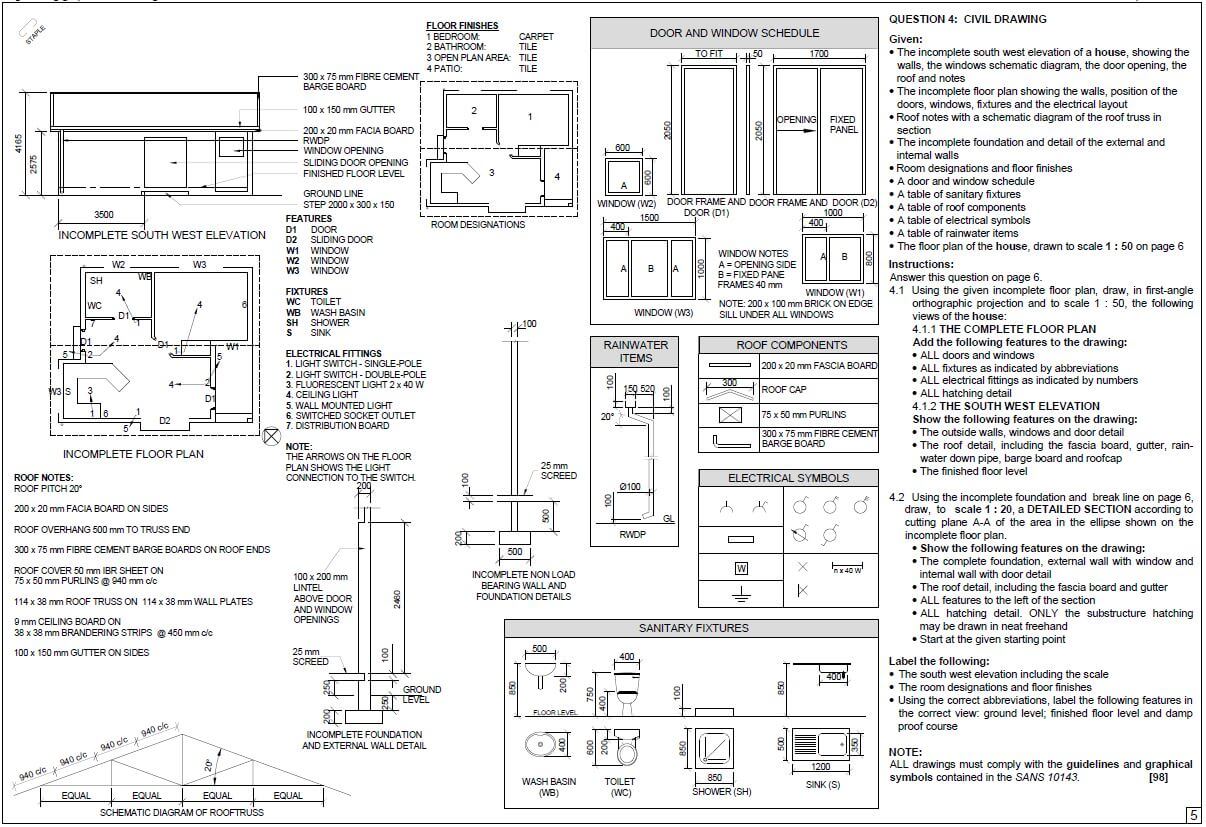
QUESTION 6: GRAPHICS AND COMMUNICATION
6.1 Any FOUR responsibilities of the architect in the design of a structure.
- Determine the needs of the owners
- Determine the arrangement of rooms
- Determine arrangement of windows and doors
- Show dimensions
- Show outside views
- Show roof appearance (4 x 1) (4)
6.2
6.2.1 Water closet (2)
6.2.2 Sink ![]() (2)
(2)
6.2.3 Water meter ![]() (2)
(2)
6.3 Site plan (1)
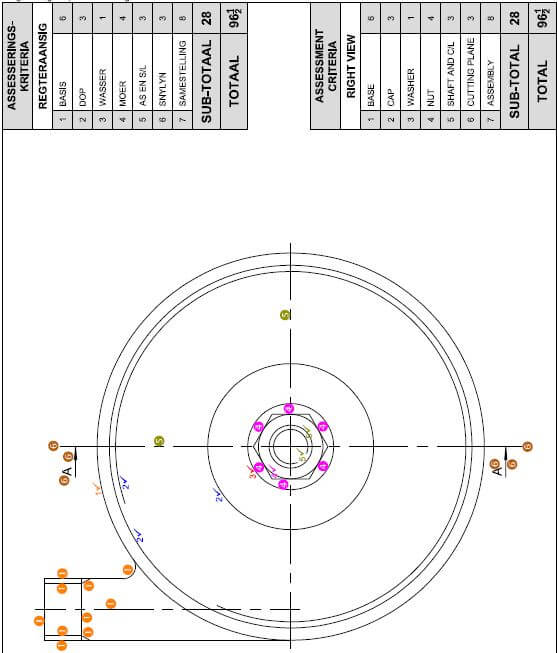
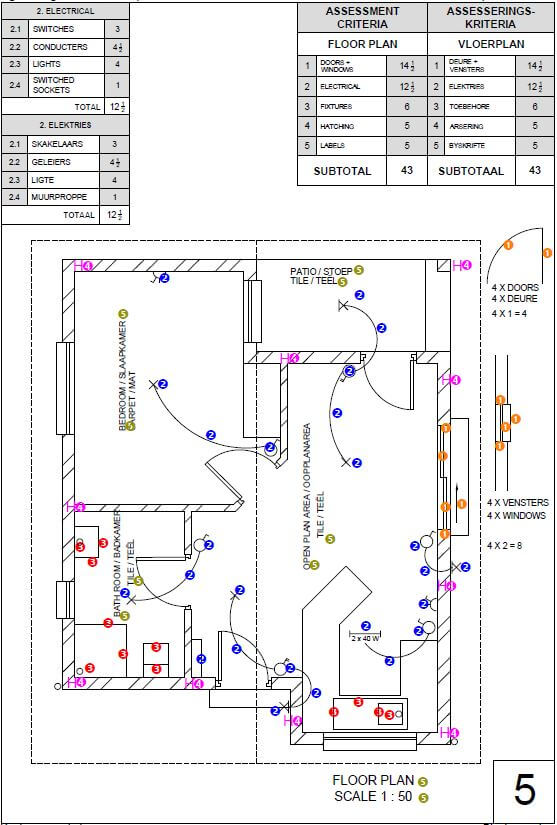
6.4 FIGURE 6.4 on ANSWER SHEET D shows the floor plan of a store room on scale 1 : 50. Draw the south elevation on scale 1 : 50 on ANSWER SHEET D from the given ground level line by using the following information:
- The floor level above the ground level: 200 mm
- Wall height from the floor level to the ceiling: 2 600 mm
- Window 1 : 600 x 2 100 mm
- Door 1 : 1 400 x 2 100 mm
- Door knob
- Roof construction pitch: 30º
- Indicate construction line to determine the roof height
- Gabel end at west elevation
- Hipped roof at east elevation
Use the mark table on ANSWER SHEET D as reference.
(29)
[40]
TOTAL: 200
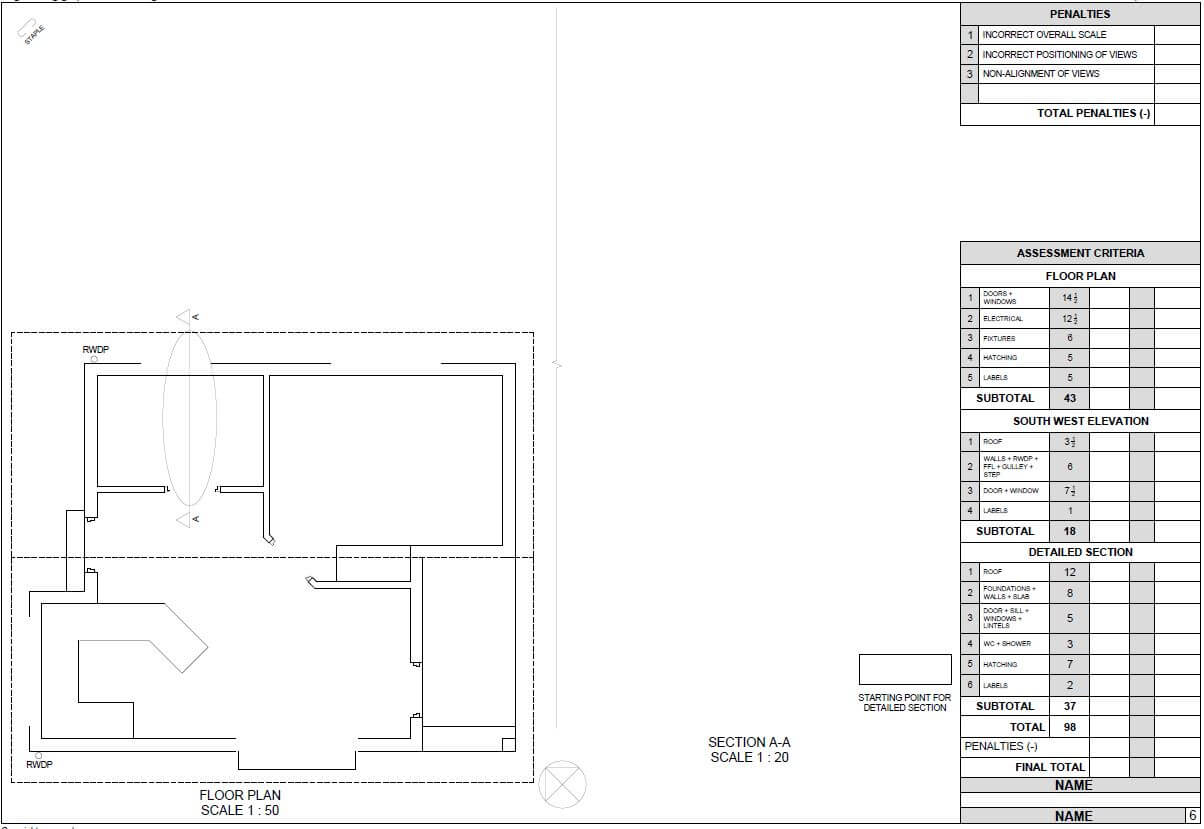
ANSWER SHEET | CIVIL TECHNOLOGY | NAME: |
4.11 Use the quantity list on ANSWER SHEET A and determine the volume concrete which will be needed for a floor with a length of 6 m, width of 3 m and thickness of 75 mm. (3)
4.12 Use the quantity list on ANSWER SHEET A and determine the number of bricks which will be needed for a cavity wall with a length of 4 m and a height of 2,4 m. (5)
A | B | C | D |
4.11 | |||
1/ | 6 | ||
3 | |||
0,75 | 13,5 | Thus: 13,5 m2 concrete needed for the floor | |
4.11 | |||
1/ | 4 | ||
2,4 | 9,6 | Wall area = 9,6 m2 | |
9,6 | |||
100 | 960 | Thus: 960 bricks needed for the wall | |
ANSWER SHEET | CIVIL TECHNOLOGY | NAME: |
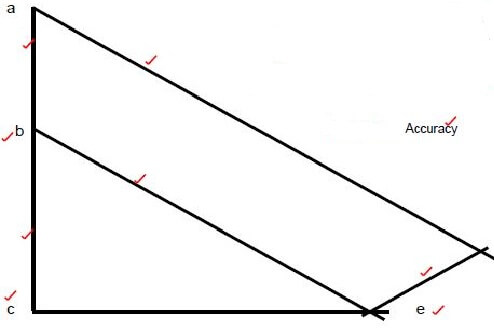
QUESTION 5.1 (14)
SPACE DIAGRAM: 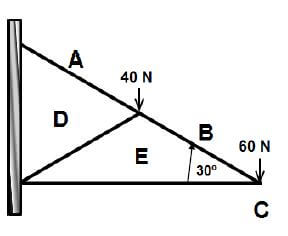
FORCE DIAGRAM
SCALE: 1 mm = 1 N
|
| Nature | |
PART | Size | | |
AD | 160 N | ||
BE | 120 N | | |
CE | 104 N | ||
DE | 40 N | ||
ANSWER SHEET | CIVIL TECHNOLOGY | NAME: |
QUESTION. 5.2
5.2.1 The bending moment values (4)
- a = 0 N.
b = (-10 N x 2) = -20 N
c = (-10 N x 6) + (-40 N x 4) + (60 N x 4) = 20 N
d = (-10 N x 8)+(-40 N x 6) + (60 N x 60) + (-20 x 2) = 0 N
5.2.2 The bending moment diagram (4)
SCALE: 1 mm = 1 N 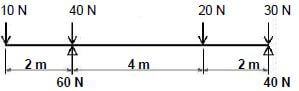
FIGURE 5.2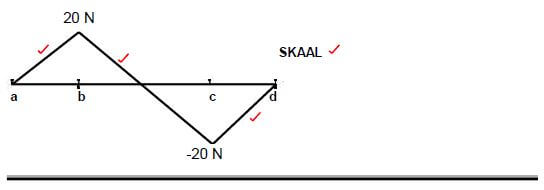
QUESTION 5.3 (6)
Shape | X | Y |
 | h 6 | h 6 |
ANSWER SHEET | CIVIL TECHNOLOGY | NAME: |
QUESTION 6.4 (26) 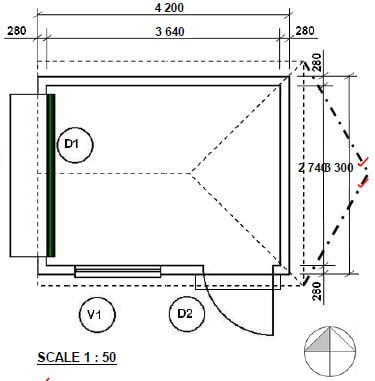
SCALE 1 : 50 
Floor level | 2 | |
Wall | 3 | |
Window | 3 | |
Window sill | 1 | |
Door | 4 | |
Step | 1 | |
Ramp | 1 | |
Facia board | 2 | |
Gutter | 1 | |
Down pipe | 1 | |
Gable end | 4 | |
Hipped roof | 3 | |
Roof height | 3 | |
TOTAL | 29 |
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
REQUIREMENTS:
- ANSWER BOOK
- Drawing instruments
- A non-programmable calculator
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions.
- ALL questions are COMPULSORY.
- Answer each question as a whole. Do NOT separate subsections of questions.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- You may use sketches to illustrate your answers.
- ALL calculations and written answers must be done in the ANSWER BOOK or on the attached ANSWER SHEETS.
- Use the mark allocation as a guide for the length of your answer.
- Make drawing and sketches in pencil, fully dimensioned and neatly finished off with descriptive titles and notes, to conform to the SANS (SABS) Recommended Practice for Building Drawings.
- For the purpose of this examination, the size of a brick should be taken as 220 mm x 110 mm x 75 mm.
- Use your discretion where dimensions and/or details have been omitted.
- Answer QUESTION 4.11, 4.12, 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, and 6.4 on the attached ANSWER SHEETS using drawing instruments where necessary.
- Due to electronic transfer, drawings in the question paper are NOT to scale.
QUESTIONS
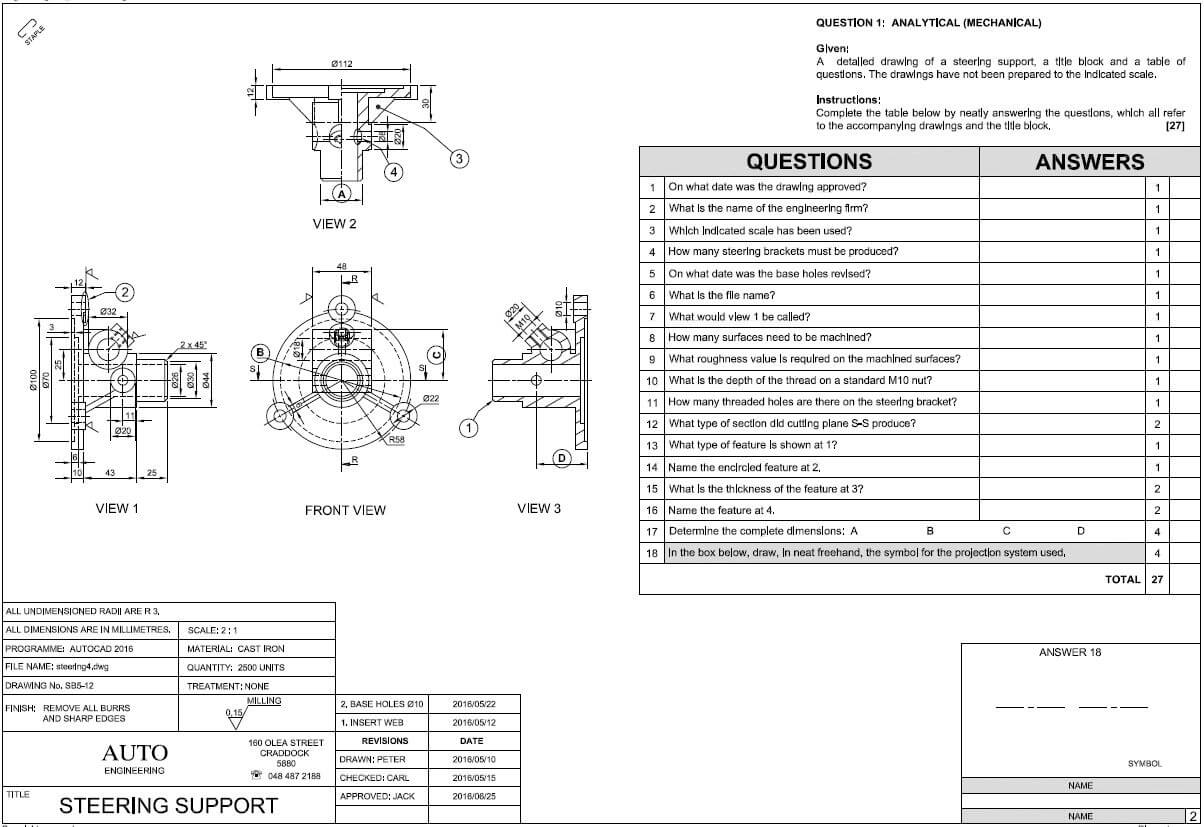
QUESTION 1: CONSTRUCTION PROCESSES
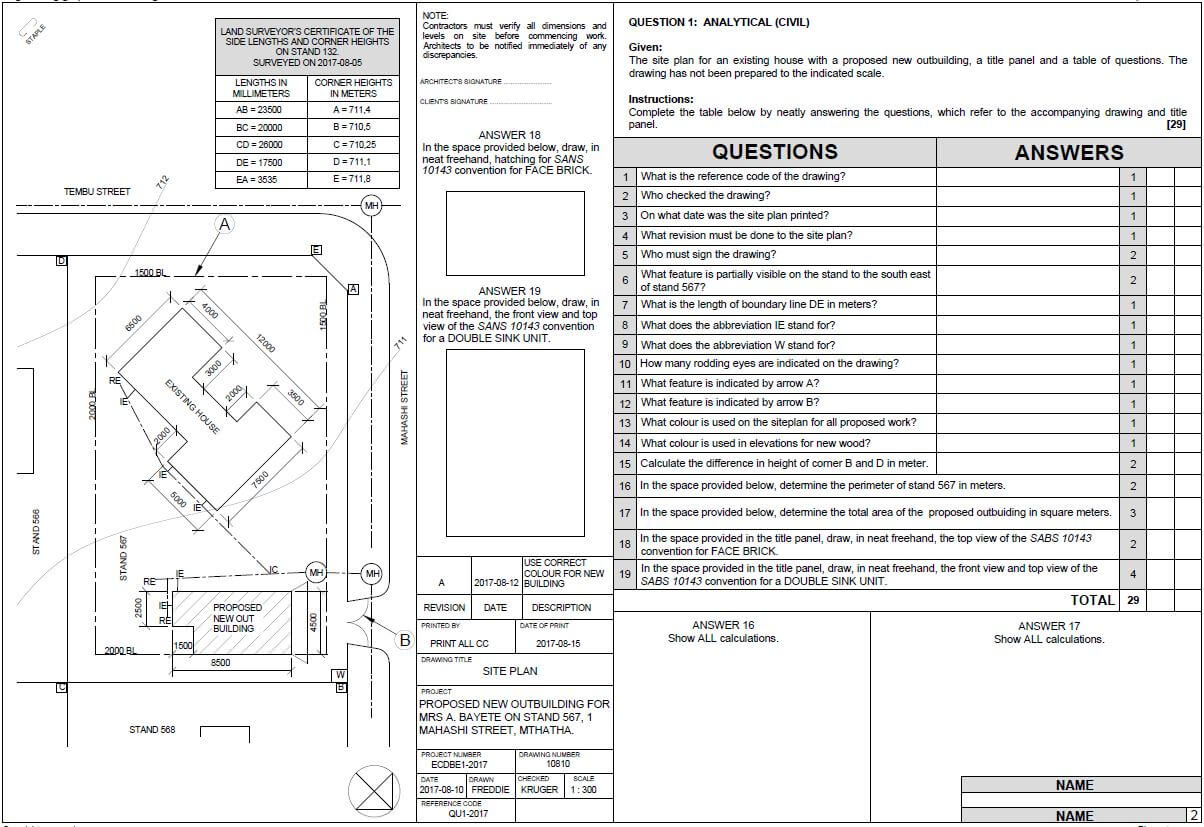
1.1 FIGURE 1.1 shows the substructure of a structure. Answer the following questions with regard to the construction in FIGURE 1.1. 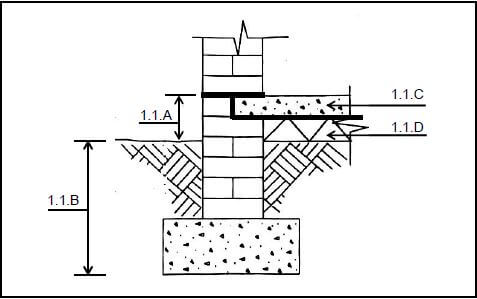
FIGURE 1.1
1.1.1 What is the minimum measurement of the damp-proofing above the ground level at 1.1.A? (1)
1.1.2 What is the minimum measurement of the foundation bottom below ground at 1.1.B? (1)
1.1.3 What is the thickness of the wall construction in FIGURE 1.1? (1)
1.1.4 What type of material is the floor at 1.1.C manufactured from? (1)
1.1.5 What is part 1.1.D called? (1)
1.1.6 Name TWO purposes of part 1.1.D. (2 x 1) (2)
1.2 Briefly motivate why the water table level must be determined when an effective foundation for a structure is planned. (2)
1.3 Describe the advantage of holes in clay bricks during the baking process. (2)
1.4 Name THREE properties of face bricks. (3 x 1) (3)
1.5 Describe in point form the manufacturing process of clay bricks. (6)
1.6 FIGURE 1.6 shows a wooden door frame. Answer the following questions with regard to the door frame in FIGURE 1.6. 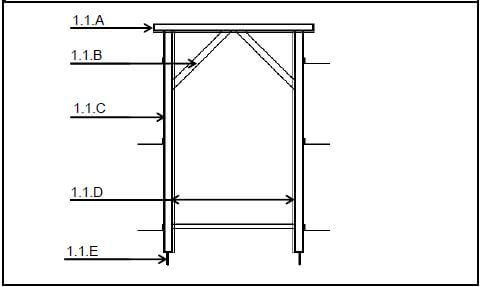
FIGURE 1.6
1.6.1 Briefly describe the method of building door frames into walls. (2)
1.6.2 Name parts 1.1.A to 1.1.C. (3)
1.6.3 What is the measurement of the door opening at 1.1.D? (1)
1.6.4 What is the purpose of the pegs at 1.1.E? (1)
1.7 Name the tools in FIGURES 1.7.1 to 1.7.3.
| 1.7.1 | 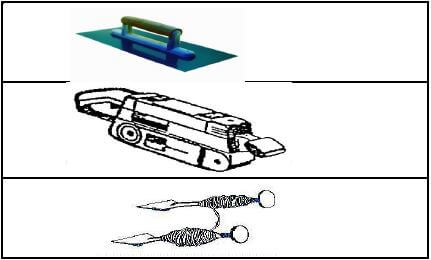 | (1) |
| 1.7.2 | (1) | |
| 1.7.3 | (1) |
[30]
QUESTION 2: ADVANCED CONSTRUCTION PROCESSES
2.1 Answer the following questions with regard to the reinforced concrete beam in FIGURE 2.1. 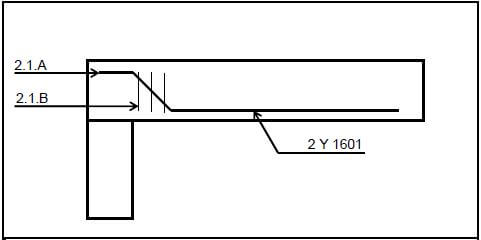
FIGURE 2.1
2.1.1 What is bar 2.1.A called? (1)
2.1.2 What is the purpose of bar 2.1.A? (1)
2.1.3 From which type of steel is bar 2.1.A manufactured? (1)
2.1.4 What is the sectional size of bar 2.1.A? (1)
2.1.5 What are the bars at 2.1.B called? (1)
2.1.6 Name TWO purposes of the bars at 2.1.B. (2 x 1) (2)
2.2 Describe TWO requirements with which the steel for steel reinforcement must comply. (2 x 2) (4)
2.3 Briefly describe the purpose of efficient concrete covering for reinforced concrete. (2)
2.4 Briefly describe the difference between the type of bricks which are used for a rough arch and bricks that are used for a gauged arch. (2)
2.5 Briefly motivate why a clearance of 2 mm must be around the glass when it is fixed to a frame. (2)
2.6 Name THREE safety rules to be observed when working on floors and stairs with open sides. (3 x 1) (3)
2.7 Name the parts of beam the shuttering in FIGURE 2.7. (5) 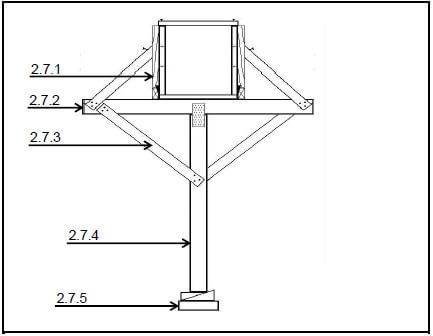
FIGURE 2.7
2.8 Make a neat sectional sketch to illustrate the construction of an open eave construction. The following parts must be indicated in the sketch: outer wall, rafter, tie beam, facia board (gutter board), 2 purlines, tile roof covering and beam filling. (8)
2.9 Briefly describe the purpose of a raking shore. (2)
2.10 Indicate whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Write only the word ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the number in the ANSWER BOOK.
2.10.1 Trestles are used to support walls. (1) 2.10.2 Scaffolds for high buildings must be assembled at an angle of 5°. (1) 2.10.3 High scaffolds must be attached to a building. (1) 2.10.4 Scaffolds should not be moved while workers are still on it. (1)
2.10.5 The depth of kitchen units is 900 mm. (1)
[40]
QUESTION 3: CIVIL SERVICES
3.1 Answer the following questions with regard to the drainage structure in FIGURE 3.1. 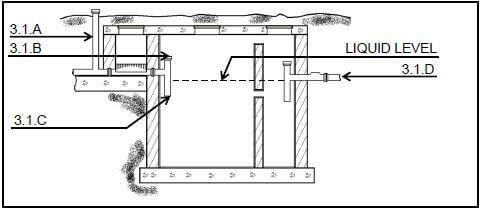
FIGURE 3.1
3.1.1 What is the structure called? (1)
3.1.2 Briefly describe how the organic matter decomposes in the structure. (2)
3.1.3 What is the purpose if the inlet pipe opening at 3.1.B? (1)
3.1.4 Briefly motivate why the inflow at 3.1.B must be lower than the liquid level. (2)
3.1.5 To which structure is the effluent at 3.1.D discharged? (1)
3.2 Briefly describe the disadvantageous effects in a drain system when it is not equipped with a ventilation pipe. (2)
3.3 Make a neat sketch to illustrate the construction of an S-trap. (3)
3.4 Identify the correct answer in each of the following descriptions of the drain test methods. Write only the correct word next to the number in the ANSWER BOOK.
3.4.1 The mirror and torch test check that the drain pipe is STRAIGHT / SEALED. (1)
3.4.2 The ball of the ball test must be 10 mm / SLIGHTLY SMALLER than the diameter of the pipe. (1)
3.4.3 If the drop in the water level is greater than 16 mm / 6 mm, the pipe probably has a leak. (1)
3.5 Name THREE methods of generating electricity. (3 x 1) (3)
3.6 What is the purpose of the conduit pipes in an electrical system? (1)
3.7 Briefly describe what an indirect water supply system is. (3)
3.8 What is the water supply pipe from the water service point to the dwelling called? (1)
3.9 Indicate whether the following statements with regard to solar heating systems are TRUE or FALSE. Write only the word ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the number in the ANSWER BOOK.
3.9.1 The hot water of the independent solar heating system is stored in the geyser. (1)
3.9.2 The tray of the solar heating system is coated with an isolation material. (1)
3.9.3 The inside of the tray of the solar heating system is coated with white paint to reflect the sun’s rays. (1)
3.9.4 The best position for the sun collector is due east. (1)
3.9.5 Photovoltaic cells can also be used to heat the water. (1)
3.10 Answer the following questions with regard to the tap in FIGURE 3.10. 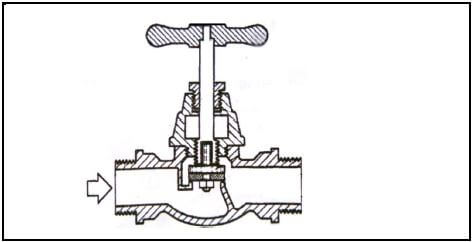
FIGURE 3.10
3.10.1 What is this type of tap called? (1)
3.10.2 Give ONE example where this type of tap must be installed. (1 x 1) (1)
[30]
QUESTION 4: MATERIALS AND QUANTITIES
4.1 Name TWO reactions which take place during the hydration process of cement. (2 x 1) (2)
4.2 Briefly motivate why cement must not be stored longer than three months. (2)
4.3 Name ONE purpose of lime in a mortar mix. (1 x 1) (1)
4.4 Which ingredient is first put into the concrete mixer when concrete must be mixed? (1)
4.5 Name THREE methods that can be used for curing concrete. (3 x 1) (3)
4.6 Briefly motivate why the cube test must be performed on concrete. (2)
4.7 Name TWO uses of each of the following materials in the construction trade:
4.7.1 Copper (2 x 1) (2)
4.7.2 Zink (2 x 1) (2)
4.8 Make a neat sketch to illustrate the profile of channel iron. (2)
4.9 Name THREE properties of a good preservative for wood. (3 x 1) (3)
4.10 Briefly describe the composition of plywood. (2)
4.11 Use the quantity list on ANSWER SHEET A and determine the volume of concrete which will be needed for a floor with a length of 6 m, width of 3 m and thickness of 75 mm. (3)
4.12 Use the quantity list on ANSWER SHEET A and determine the number of bricks which will be needed for a cavity wall with a length of 4 m and a height of 2,4 m. (5)
[30]
QUESTION 5: APPLIED MECHANICS
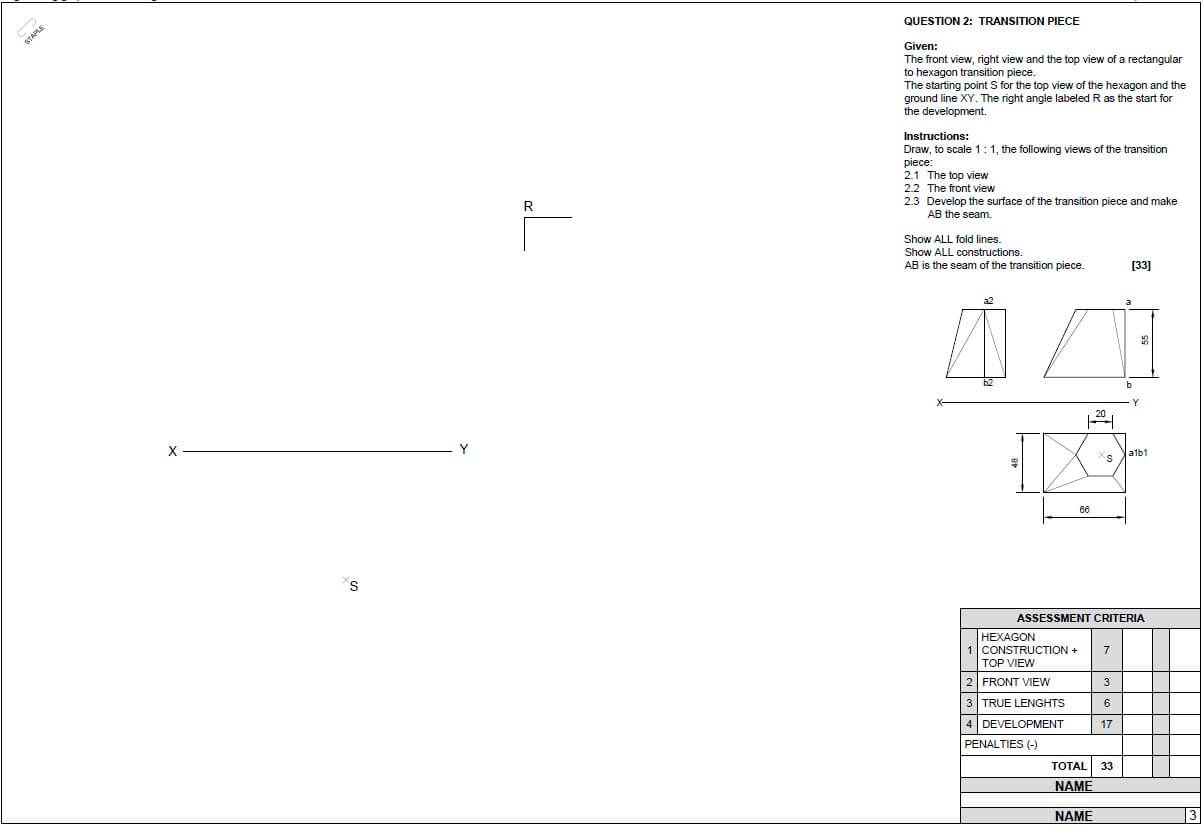
5.1 FIGURE 5.1 on ANSWER SHEET B shows the space diagram of a lean-to roof. Determine graphically on scale 1 mm = 1 N on ANSWER SHEET B the size and nature of the forces in the parts of the truss by drawing the force diagram and completing the table.  (14)
(14)
FIGURE 5.1
5.2 FIGURE 5.2 on ANSWER SHEET C shows a beam with point loads. Calculate, on ANSWER SHEET C, the following: 
FIGURE 5.2
5.2.1 The bending moment values (6)
5.2.2 Complete the bending moment diagram on scale 1 mm = 1 N according to the bending moment values (4)
5.3 Determine, from point P, the sentroid of the body in FIGURE 5.3. (The table on ANSWER SHEET C can be used for the calculations.) 
FIGURE 5.3 (6)
[30]
QUESTION 6: GRAPHICS AND COMMUNICATION
6.1 Name FOUR responsibilities of the architect which must be reflected in the sketch drawings of the design of a structure. (4 x 1) (4)
6.2 Make neat sketches to illustrate the following symbols:
6.2.1 Water closet (2)
6.2.2 Sink (2)
6.2.3 Water meter (2)
6.3 In which working drawing is the entrance to a site indicated? (1)
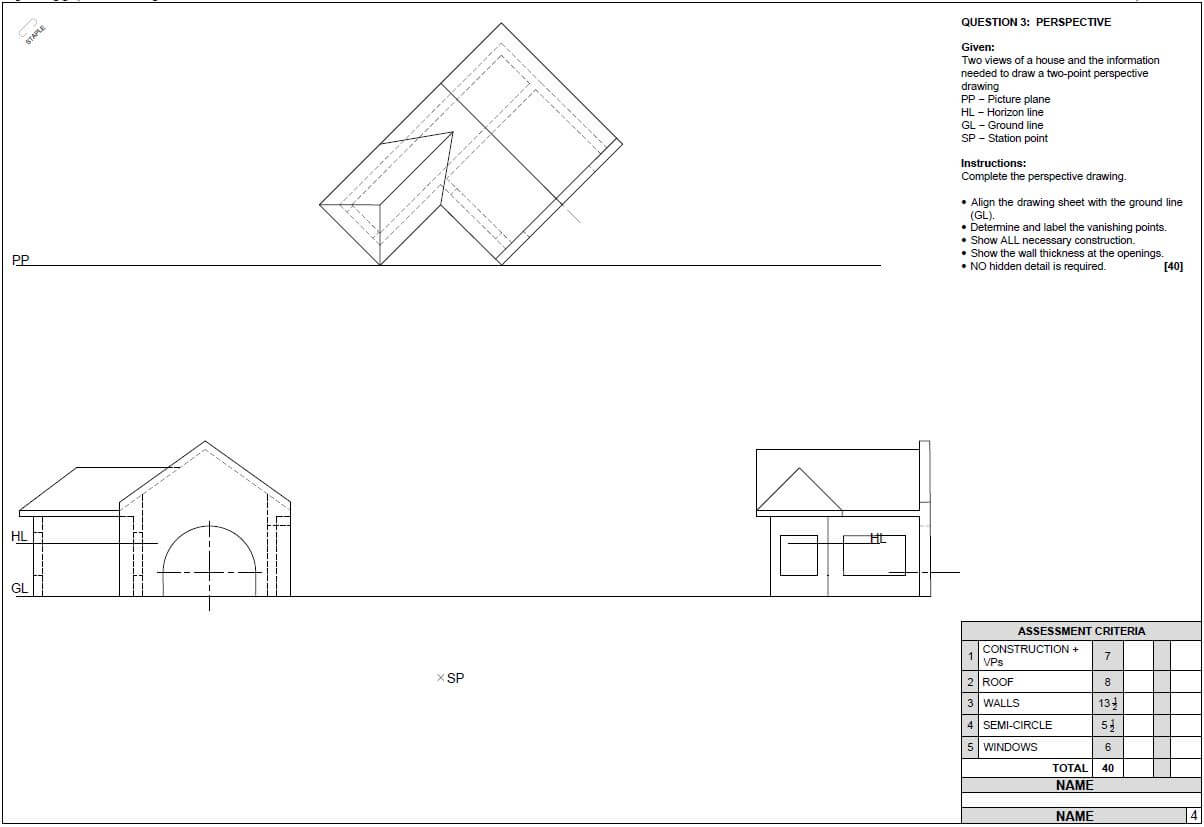
6.4 FIGURE 6.4 on SHEET D shows the floor plan of a store room on scale 1 : 50. Draw, on SHEET D, the south elevation on scale 1 : 50 from the given ground level line by using the following information:
- The floor level above the ground level: 200 mm
- Wall height from the floor level to the ceiling: 2 600 mm
- Window 1 : 600 x 2 100 mm
- Door 1 : 1 400 x 2 100 mm
- Door knob
- Roof construction pitch: 30º
- Indicate construction lines to determine the roof height
- Gabel end at west elevation
- Hipped roof at east elevation
Use the marks table on ANSWER SHEET D as reference. (29)
[40]
TOTAL: 200
ANSWER SHEET A | CIVIL TECHNOLOGY | NAME: |
4.11 Use the quantity list on ANSWER SHEET A and determine the volume of concrete which will be needed for a floor with a length of 6 m, width of 3 m and thickness of 75 mm. (3)
4.12 Use the quantity list on ANSWER SHEET A and determine the number of bricks which will be needed for a cavity wall with a length of 4 m and a height of 2,4 m. (5)
A | B | C | D |
ANSWER SHEETB | CIVIL TECHNOLOGY | NAME: |
QUESTION 5.1
SPACE DIAGRAM:
FORCE DIAGRAM
SCALE: 1 mm = 1 N
|
| Aard/Nature | |
PART | Size | | |
AD | |||
BE | |||
CE | |||
DE | |||
ANSWER SHEET C | CIVIL TECHNOLOGY | NAME: |
QUESTION 5.2
5.2.1 The bending moment values (4)
- = ...........................................................
- = ...........................................................
- = ...........................................................
- = ...........................................................
5.2.2 FIGUUR 5.2: The bending moment diagram (4)
SCALE: 1 mm = 1 N 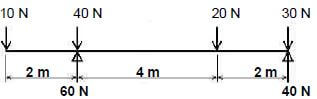
FIGURE 5.2
QUESTION 5.3 (6)
Shape | X | Y |
 |
ANSWER SHEET D | CIVIL TECHNOLOGY | NAME: |
QUESTION 6.4 (26) 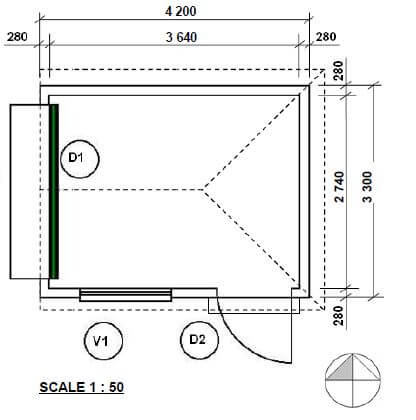
Floor level | 2 | |
Wall | 3 | |
Window | 3 | |
Window sill | 1 | |
Door | 4 | |
Step | 1 | |
Ramp | 1 | |
Facia board | 2 | |
Gutter | 1 | |
Down pipe | 1 | |
Gable end | 4 | |
Hipped roof | 3 | |
Roof height | 3 | |
TOTAL | 29 |
FORMULA SHEET
IMPORTANT ABBREVIATIONS
SYMBOL | DESCRIPTION | SYMBOL | DESCRIPTION | SYMBOL | DESCRIPTION |
| G | Centre of gravity | h | Height | d | Diameter |
c | Centroid | b | Breadth/Width | r | Radius |
ℓ | Length | s | Side | A | Area |
| π | pi = 22/7 = 3,142 | ø | Diameter | V | Volume |
FORMULAE
AREA OF | FORMULA (in words) | FORMULA (in symbols) | FORMULA FOR THE POSITION OF CENTROIDS | |
X-axis | Y-axis | |||
Square | side × side | s × s | s/2 | s/2 |
Rectangle | length × breadth | ℓ × b | ℓ /2 | b/2 |
Right-angled triangle | ½ x base × height | ½b × h | b/3 | h/3 |
Equilateral triangle/ Isosceles triangle | ½ x base × height | ½b × h | b/2 | h/3 |
| Circle | π × radius × radius | πr2 | Centroid is in the centre | |
| CircleSemi-circle | π × diameter × diameter divided by 4 | πd2 4 | ||
| π × radius r × radius divided by 2 | πr2 2 | Centroid is 0,424r on the centre line | ||
Position of centroid = (A1×d) ± (A2 ×d)
Total area
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN GRADE 12 PAPER 1 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN
GRADE 12
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
QUESTIONS
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN GRADE 12 PAPER 2 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN
GRADE 12
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
QUESTIONS

ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN GRADE 12 PAPER 2 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN
GRADE 12
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
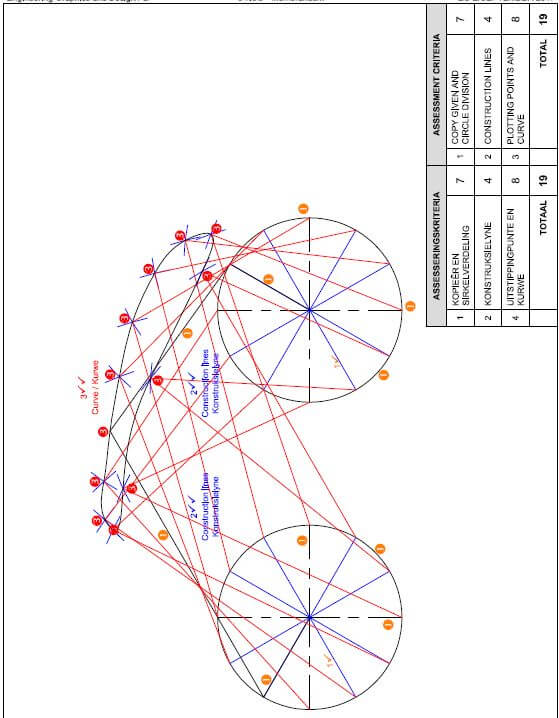
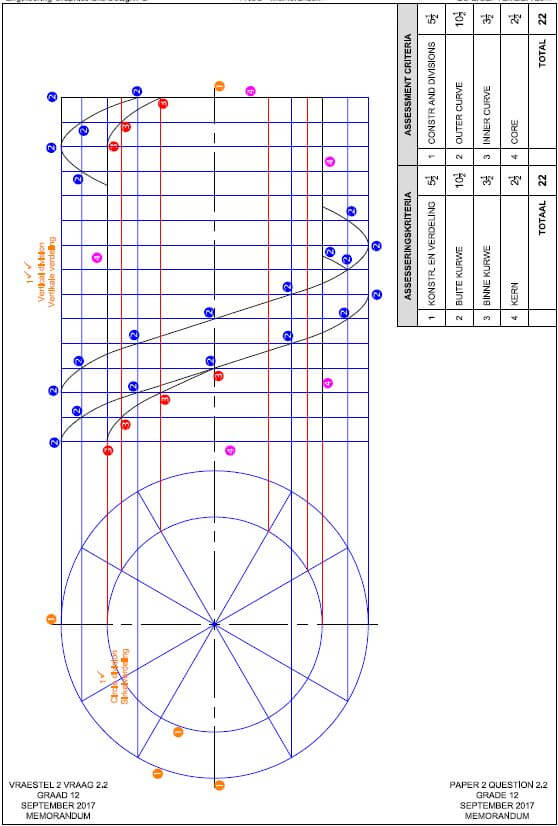

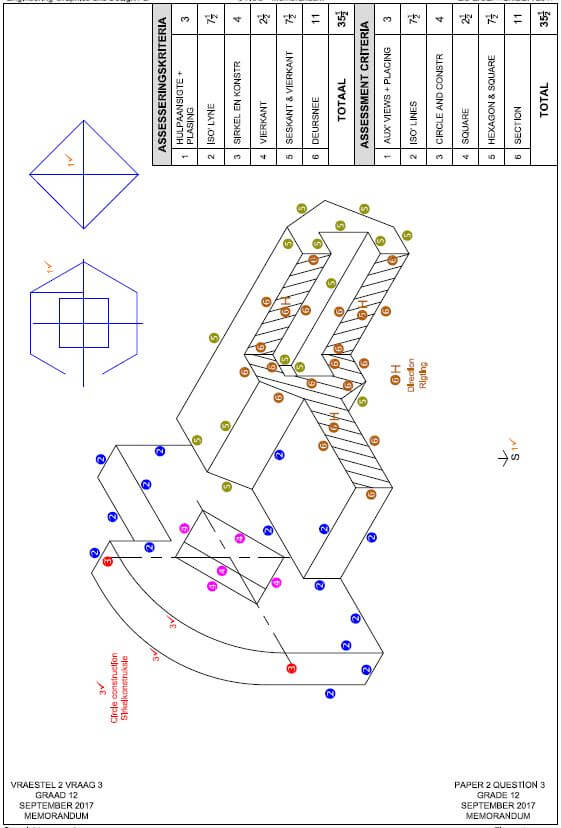
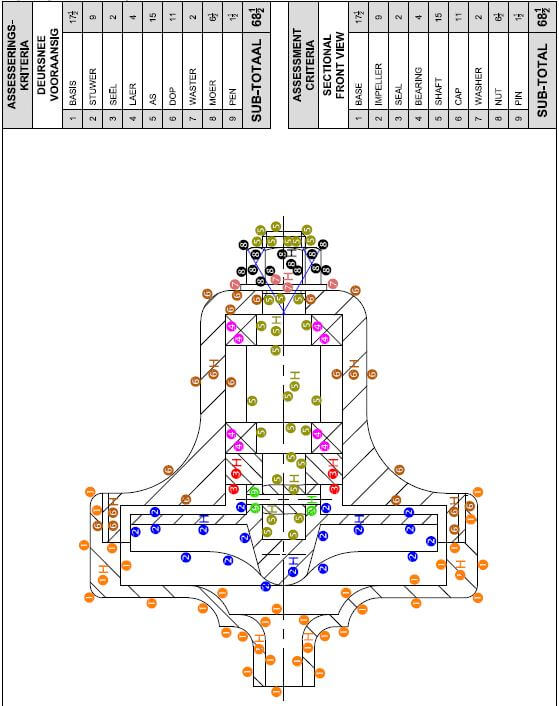
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN GRADE 12 PAPER 1 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN
GRADE 12
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Sketches and diagrams must be large, neat and fully labelled.
- ALL calculations must be shown, and correctly rounded off to TWO decimal places.
- Answers must be numbered correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Non-programmable calculators may be used.
- Show the units for all answers of calculations.
- A formula sheet is provided at the end of the question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY
1.1 Explain why no person under the influence of drugs may enter or remain in a workplace where machinery is used. (2)
1.2 Name TWO electrical devices that protect equipment under fault conditions. (2)
1.3 Explain the negative impact HIV/Aids has on productivity in the electrical workshop. (2)
1.4 Whose responsibility is it to maintain safety in an electrical technology workshop? Motivate your answer. (3)
1.5 State ONE unsafe condition that may lead to an accident in an electrical technology workshop. (1)
[10]
QUESTION 2: THREE-PHASE AC GENERATION
2.1 In a balanced three-phase delta-connected circuit, the phase voltage is 380 V and the phase current is 12 A. If the phase angle is 25°, calculate the following:
2.1.1 The true power (3)
2.1.2 The apparent power (3)
2.2 A small alternator supplies power to a balanced inductive load. The current in each phase of the alternator is 20 A and it lags the voltage by 30°. The phase voltage is 220 V. Calculate the line voltage if the coils of the alternator are connected in star. (3)
2.3 Give ONE reason why electricity is generated in three-phase and not in single phase. (1)
2.4 Name the type of power factor that a three-phase generator has, and explain why it has such a type of power factor. (3)
2.5 State the function of a kilowatt-hour meter. (1)
2.6 How many electrical degrees apart are the three coils placed in three-phase generation? (1)
2.7 Draw a voltage phasor diagram that represents a three-phase supply. (4)
2.8 Indicate whether the reading on a voltmeter when measuring an AC voltage is a maximum value, average value or effective/rms value. (1)
[20]
QUESTION 3: THREE-PHASE TRANSFORMERS
3.1 Name and explain TWO types of losses that occur in transformers. (4)
3.2 The delta-connected primary winding of a three-phase transformer is supplied with 11 kV. The secondary winding is star-connected and supplies 400 V to a balanced star-connected load of 10 kW with a power factor of 0,8. Calculate the following at full load:
Given: Vp = 11 kV
VS = 400 V
P = 10 kW
Cos θ = 0,8
3.2.1 The total kVA of the load (3)
3.2.2 The secondary line current (3)
3.2.3 The secondary phase current (2)
3.3 Describe why the secondary winding of a transformer must be connected in star if the transformer is to supply both a domestic and an industrial load. (3)
3.4 Name THREE causes of heat build-up in transformers. (3)
3.5 Explain what will happen to the primary current of an ideal transformer if the load is doubled. (2)
[20]
QUESTION 4: THREE-PHASE MOTORS AND STARTERS
4.1 After a motor has been started and is running, what other functions does the starter perform? (2)
4.2 Name THREE parts of a three-phase induction motor. (3)
4.3 Explain why a star-delta starter is used to start three-phase induction motors. (3)
4.4 A three-phase 15 kW induction motor is connected in delta to a 380 V/50 Hz supply. The motor is 100% efficient with a power factor of 0,9 at full load.
Give: P = 15 kW
V = 380 V
f = 50 Hz
η = 100%
Cos θ = 0,9
Calculate:
4.4.1 The current drawn from the supply (3)
4.4.2 The apparent power of the motor (3)
4.4.3 The phase current of the motor (3)
4.5 With reference to insulation resistance tests on the stator of a three-phase induction motor:
4.5.1 Describe why it is important to test the insulation resistance between the windings and the frame of the motor. (2)
4.5.2 Describe the insulation resistance reading you would expect when measuring between the windings of the motor. (3)
4.6 Describe how the direction of rotation of a three-phase motor may be changed. (1)
4.7 Describe why it is necessary to have protective devices as part of motor control. (2)
4.8 Explain what occurs to the three-phase induction motor if one phase fails. (3)
4.9 With reference to a star-delta starter, answer the following questions:
4.9.1 State the function of the starter. (1)
4.9.2 Describe how it achieves this function. (3)
4.10 Describe the principle of operation of an overload unit in a direct-on-line starter. (4)
4.11 Draw and label the control circuit of a direct-on-line starter. (4)
[40]
QUESTION 5: RCL CIRCUITS
5.1 A capacitor with a capacitive reactance of 250 Ω, an inductor with an inductive reactance of 300 Ω and a resistor with a resistance of 500 Ω are all connected in series to a 220 V/50 Hz supply.
Given:
XC = 250 Ω
XL = 300 Ω
R = 500 Ω
VS = 220 V
f = 50 Hz
5.1.1 Calculate the total impedance of the circuit. (3)
5.1.2 Calculate the power factor of the circuit and state whether it is leading or lagging. (4)
5.2
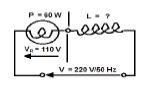
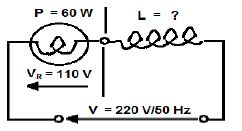 |
FIGURE 5.2
Calculate:
5.2.1 The resistance of the 60 watt 110 V lamp (3)
5.2.2 The total current flowing through the circuit (3)
5.2.3 The impedance of the circuit (3)
5.2.4 The inductance of the inductor (4)
[20]
QUESTION 6: LOGIC
6.1 Explain the term program when referring to a PLC. (3)
6.2 What do the letters PLC represent? (1)
6.3 Name THREE basic devices used in programming a PLC. (3)
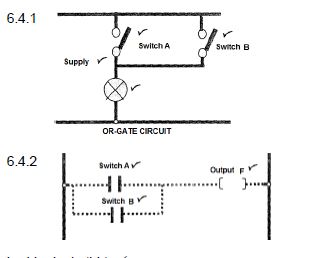
6.4 With reference to an OR-gate, draw the following:
6.4.1 The circuit diagram, using two switches and a lamp to simulate the gate operation (4)
6.4.2 The ladder logic diagram (3)
6.5 Name THREE programming languages used in programming PLCs. (3)
6.6 Simplify the expression below by using Boolean algebra: ![]() (5)
(5)
6.7 Explain why the maintenance of a PLC system (soft-wired system) should be less than that of a relay system (hard-wired system). (2)
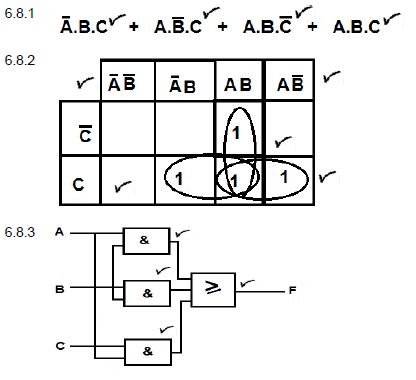
6.8 A digital control system uses three positional sensing devices on a conveyor belt in a bottling plant. Each sensing device produces an output of 1 when the position is confirmed. These devices are to be used in conjunction with a logic network of AND / OR gates.
The output of the network (F) is to be 1 when two or more of the sensing devices [Sensor 1(A), 2(B) and 3(C)] are producing signals of 1.
 |
| FIGURE 6.8: CONVEYOR-BELT SYSTEM |
6.8.1 Write down the Boolean equation of the control system. (4)
6.8.2 Simplify the equation using a Karnaugh map. (8)
6.8.3 Draw the gate network of the simplified system. (4)
[40]
QUESTION 7: AMPLIFIERS
7.1 Name THREE applications of an operational amplifier (op amp). (3)
7.2 List THREE characteristics of an ideal operational amplifier (op amp). (3)
7.3 Describe the term open loop with reference to an operational amplifier (op amp). (3)
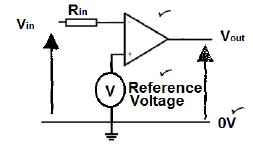
7.4 Draw the diagram of an operational amplifier (op amp) as an inverting voltage comparator. (3)
7.5 Explain the term positive feedback. (2)
7.6 Explain what effect the very high input impedance (close to infinity) of an op amp will have on the preceding circuit (circuit connected to the input of the op amp). (4)
7.7 Give THREE application of RC phase shift. (3)
7.8
 |
| FIGURE 7.8 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT |
7.8.1 With the given input signal at the non-inverting input, draw both the input and output signals on the same axis. (2)
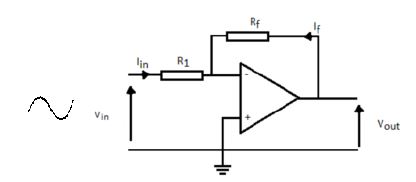
7.8.2 Explain the function of Rf in the circuit. (3)
7.8.3 Explain what will occur to the gain of the operational amplifier (op-amp) if the value of Rf is decreased. (3)
7.8.4 What is the function of Rin in the circuit? (3)
7.9 Draw the circuit diagram of a Hartley oscillator. (5)
7.10 A comparator circuit compares two electrical signals. State, with a reason, the nature of the output if both signals have exactly the same value. (2)
7.11 In the amplification process the amplitude of the wave form changes, what happens to the frequency of the wave form? (1)
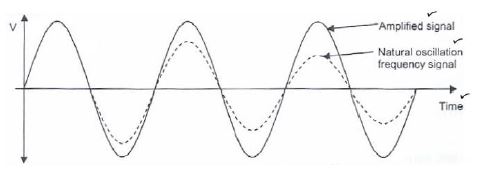
7.12 Explain the term natural oscillation frequency and draw THREE complete cycles to demonstrate natural oscillation frequency. (6)
7.13 Operational amplifiers are commonly used in complex circuits (between stages) to link the stages. State, with a reason, the application (function) of the operational amplifier when utilised between stages. (2)
7.14 Where would you use a non-inverting amplifier? Give ONE example to illustrate your answer. (2)
[50]
TOTAL: 200
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY
FORMULA SHEET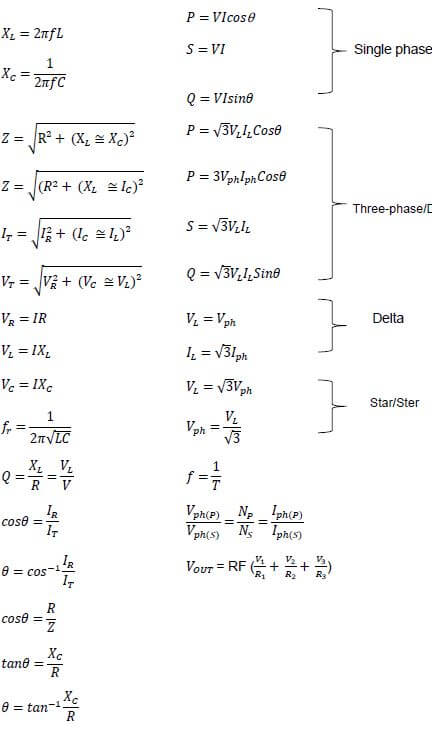
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY
1.1 No person may enter or remain in a workplace under the influence of drugs as he may place himself ✔ and other persons in danger while operating machinery. ✔ (2)
1.2
- Earth-leakage system ✔
- Overload circuit breakers ✔
- No-volt coil prevents automatic restarting after power interruption.
- Fuses
- Emergency stop switch
(ANY TWO) (2)
1.3 If Aids is not brought under control:
- it can affect productivity in that employees with skills may become ill or die ✔
- person may not function well, may take time off work, ✔
- Colleagues may be unwilling to work with a person having HIV due to the stigma associated with HIV.
(ANY TWO RELEVANT ANSWERS) (2)
1.4
- Safety is the responsibility of any person who enters or works in an electrical technology workshop. ✔
- Each person has a responsibility to himself and others around him. ✔
- It only takes one person to ignore safety procedures to cause serious problems for all in the electrical technology workshop. ✔
(ANY SOUND MOTIVATED RESPONSE MUST BE CONSIDERED) (3)
1.5
- Wet floors ✔
- Wet work areas
- Bare conductors
(ANY OTHER RELEVANT ANSWERS) (1)
[10]
QUESTION 2: THREE-PHASE AC GENERATION
2.1
2.1.1
| P = √3VLILcosθ ✔ = √3 × 380 × 20,78cos25º ✔ =12,40 kW ✔ | ButIL = √3IPH = √3 × 12 = 20,78 A |
OR | P = 3VPHIPHcosθ ✔ = 3.380.12.cos25º ✔ =12,40 kW ✔ |
(3)
2.1.2
| S = √3VLIL ✔ = √3 × 380 × 20,78 ✔ = 13,68 kVA ✔ | OR | S = P ✔ cos θ = 12,40 ✔ cos 25 =13,68kVA ✔ |
(3)
2.2
| VL = √3PH ✔ = √3 × 220 ✔ = 381,05 V ✔ |
(3)
2.3
- For high power generation the three-phase system is functional and efficient. ✔
- The voltages between all phases (i.e. line voltages) are the same
- The direction of rotation of three-phase machines can be easily changed
- Transmission and distribution are fairly simple
(ANY ONE) (1)
2.4 A generator has a lagging power factor ✔ as it consists of coils which are inductive. ✔ Current through an inductor connected to an AC supply lags the applied voltage. ✔ (3)
2.5 The function of a kWh meter is to measure the amount of power consumed by a consumer over a period of time (energy). ✔ (1)
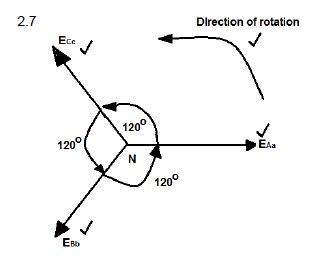
2.6 120 degrees (1)
2.7 (4)
 |
2.8 Effective value or rms value ✔ (1)
[20]
QUESTION 3: THREE-PHASE TRANSFORMERS
3.1
- Copper losses ✔ losses due to the resistance of the copper wires used ✔
- Stray losses ✔ occurs when some of the magnetic field does not cut the secondary winding ✔
- Iron losses ✔ heat losses due to hysteresis of the core ✔
- Dielectric losses ✔ occurs when insulation of windings is damaged, causing leakage currents ✔ (4)
3.2
3.2.1
- S = P ✔
cos θ
= 10000
0,8
= 12, 5kW ✔ (3)
3.2.2
- IL(S) = P ✔
√3L(S) cosθ
= 10000 ✔
√3 × 400 × 0,8
= 18,04A ✔ (3)
3.2.3
- IPh(S) = IL(S) ✔
= 18,04 A ✔ (2)
3.3 To create a three-phase four-wire system ✔ so that a transformer can supply both single-phase ✔ and three-phase. (To distribute power to both domestic and industrial installations.) ✔ (3)
3.4
- Losses and current flow in transformers causes heat build-up ✔
- Overloading ✔
- Poor Cooling ✔
- Lack of Ventilation
- Poor Connections / Hot connections
- Excessive vibration due to poor mechanical construction
(ANY RELEVANT ANSWERS) (3)
3.5 The primary phase current will also be doubled ✔ as it is directly proportional to the load. ✔ (2)
[20]
QUESTION 4: THREE-PHASE MOTORS AND STARTERS
4.1 The purpose of using a starter to start a three-phase motor is to safely control the motor, ✔ protect electrical equipment and the user of the motor. ✔ (2)
4.2
- Stator ✔
- Rotor ✔
- End plates ✔
- Fan
- Terminal box
- Bearings
(ANY THREE) (3)
4.3 To reduce the voltage at start-up. ✔ This in turn reduces the starting current.▪✔ Reduced starting current leads to fewer nuisance tripping problems at start or to less heat build-up and decreases the chance of burn-out of the motor. ✔ (3)
4.4
4.4.1
- IL = P
√3 × VLcosθ✔
= 15000
√3 × 380 × 0,9 ✔
= 25,32 A ✔ (3)
4.4.2
- Papp = P ✔
cosθ
= 15000
0,9 ✔
= 25
√3
= 16,67 kVA ✔ (3)
4.4.3
- IL = √3 × IPH✔
IPH = IL
√3
= 25
√3 ✔
= 14,43A ✔ (3)
4.5
4.5.1
- S = P
cos θ
=90 000
0,85
= 105,88 kVA (2)
4.5.2
- IL= P
√3VL cos θ
= 90 000
√3 x 400 x 0,85
= 152,83 A (3)
4.6 By reversing the connections of any two of the three supply lines to the stator. ✔ (1)
4.7 To protect electrical equipment from damage ✔ during faulty operating conditions and protecting the operator of the equipment. ✔ (2)
4.8 The motor will keep on operating, but to maintain the same output power ✔ the current on the other two phases will increase. ✔ If the protection is set correctly, it will engage, protecting the motor from permanent damage. ✔ (CONSIDER RELEVANT MOTIVATED ANSWERS) (3)
4.9
4.9.1 The function of a star-delta starter is to reduce the starting current of a motor at start as a motor draws 3 to 4 times full-load current at start.✔ (1)
4.9.2 The motor is connected in star at start. ✔ This reduces the voltage across the motor windings which in turn reduces the current in the windings.✔ Once the starting current has reduced, the motor windings are changed over to delta, restoring full-line voltage across the windings, therefore full current. ✔ (3)
4.10 The overload relay is designed to protect the motor ✔ and motor wiring against current fault conditions. ✔ It will open and cut power to the motor. ✔ (4)
4.11
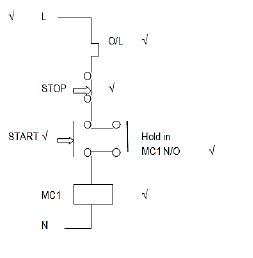 |
(4)
[40]
QUESTION 5: RCL CIRCUITS
5.1
5.1.1
- Z = √R2 + (XL - KC)2
= √5002 + (300 - 250)2
= 502, 49Ω (3)
5.1.2
- cosθ = R ✔
Z
= 500
502, 49 ✔
= 0,995✔ Lagging ✔ (4)
5.2
5.2.1
- R = V2 ✔
P
= 1102
60✔
= 201, 67 Ω ✔ (3)
5.2.2
- I = P
VR ✔
= 60
110 ✔
= 0,55 A ✔ (3)
5.2.3
- Z = V
I ✔
= 220
0,55 ✔
= 400 A ✔ (3)
5.2.4
- XL = √Z2 - R2
2πfL = √Z2 - R2
L = √Z2 - R2
2πf ✔
= √4002 - 201, 672
2.π.50 ✔
= 1,1 H ✔ (4)
[20]
QUESTION 6: LOGIC
6.1 A series of instructions ✔ written in a language ✔ that a PLC can recognise and interpret into an output. ✔ (3)
6.2 Programmable Logic Controller ✔ (1)
6.3
- User interface (On the PLC Unit – Screen & Buttons).✔
- Computer or laptop with interface cable.✔
- Handheld programming device.✔ (3)
6.4
6.5
- Ladder logic (LL). ✔
- Logic block diagram (LBD). ✔
- Function Block Diagram (FBD)
- Structured Text Sequential Flow / Function Chart
(ANY THREE) (3)
6.6 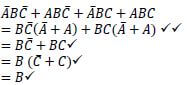 (5)
(5)
6.7 Fewer components such as contactors are subject to wear because less of these items are used. ✔Additionally units have built-in diagnostic functions. ✔ (2)
6.8
[40]
QUESTION 7: AMPLIFIERS
7.1
- Linear amplifiers √
- Pulse amplifiers √
- Buffer circuits Integrating √
- Differentiating
- Summing amplifiers
(ANY THREE) (3)
7.2
- Input draws no current √
- The voltage drop between the input terminals is zero √
- The open-loop voltage gain is infinite √
- Output impedance is zero. Input impedance is infinite
- Frequency Response is infinite
(ANY THREE) (3)
7.3 Means that there is no feedback (neither negative nor positive) √ from the output back to the input. √ The gain of the circuit is at a maximum. √ (3)
7.4
7.5 A portion of the output signal is fed back to the input signal ✔ and is in phase with the input signal (2)
7.6 This will reduce the loading effect on the previous circuit. ✔ In so doing, no current will be drawn ✔ from that circuit. Therefore, the voltage appearing √ at its output terminals ✔ will be passed on to the op amp with little or no loss. (4)
7.7
- Audio oscillators ✔
- Electronic organ ✔
- GPS units ✔ (3)
7.8
7.8.1

7.8.2 Output signal ✔ is fed back to the inverting input ✔ through feedback resistor Rf .✔ (3)
7.8.3 If the resistance of Rf is decreased Vrf will decrease ✔ this is feedback on the inverting input of the op-amp ✔ increasing the overall gain of the circuit. ✔ (3)
7.8.4 Rin allows further control ✔ of the op-amp circuit gain. ✔ Setting Rin at a high value compared to Rf creates a voltage-follower circuit. ✔ (3)
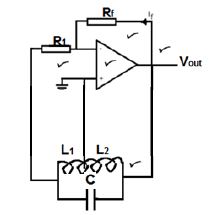
7.9
7.10 The output of the comparator will be zero. ✔ This is due to a comparator only amplifying the difference between the input signals. ✔ (2)
7.11 The frequency of the wave form remains unchanged. ✔ (1)
7.12
The electrical signal that the oscillator produces is called the natural oscillation frequency. ✔ Natural oscillation diminishes in amplitude and disappears due to a lack of positive feedback. ✔ (6)
7.13 When an op-amp is utilised between stages it is used as a buffer amplifier to adapt/match the impedance between the stages. ✔✔ (2)
7.14 Any application where a phase shift is not required, ✔ such as: audio amplifiers. ✔ (2)
[50]
TOTAL: 200
ENGLISH FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE GRADE 12 PAPER 1 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
ENGLISH FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE
GRADE 12
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS TO MARKERS
- Candidates are expected to answer ALL the questions.
- This memorandum serves as a guide to markers. Some responses may require a marker’s discretion.
- Candidates’ responses should be assessed as objectively as possible.
MARKING THE COMPREHENSION
- Because the focus is on understanding, incorrect spelling and language errors in responses should not be penalised unless such errors change the meaning/understanding. (Errors must still be indicated.)
- If a candidate uses words from a language other than the one being examined, disregard those words, and if the answer still makes sense, do not penalise. However, if a word from another language is used in a text and required in an answer, this will be acceptable.
- For open-ended questions, no marks should be awarded for YES/NO or I AGREE/I DISAGREE. The reason/substantiation/motivation is what should be considered.
- When one word answers are required and the candidate gives a whole sentence, mark correct provided that the correct word is underlined/highlighted.
- When two/three facts/points are required and a range is given, mark only the first two/three.
- Accept dialectal variations.
- For multiple-choice questions, accept BOTH the letter corresponding with the correct answer AND/OR the answer written out in full.
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A: COMPREHENSION
NOTE: Incorrect spelling and language errors should not be penalised, because the focus is on understanding.
QUESTION 1
1.1.1 ‘peculiar’ √ (Spelling must be correct) (1)
1.1.2 The coffee shop is still busy/alive with activity, √ while things in the rest of the Central Business District are calming down/becoming more quiet. √ (2)
1.2 There will be many people/workers√ who will visit the coffee shop (during their lunch time/lunch break).√ (2)
1.3
- The writer wants to emphasise that even if you are young √ you can still assist people with mental disabilities. √
OR - The writer wants to encourage young people √ to commit themselves to helping those with mental disabilities. √
NOTE: Accept any ONE of the above answers. (2)
1.4 The stereotypes surrounding people with disabilities that Wendy Vermeulen is trying to break down is that they are not employable/they cannot work √ and that they are stupid. √ (2)
1.5 A chef would be able to teach cooking skills√ and a special-needs teacher would have been trained to work with mentally challenged young people.√ (2)
1.6 Down’s Syndromes √
Autistic young people √ (2)
1.7 Brownies & Downies want to train young people who are intellectually/mentally challenged to work in hospitality. √ They also want to allow these young people to interact with the public. √ (2)
1.8 The term ‘household name’ means Brownies & Downies has become very popular/well known. √ (1)
1.9 The statement is false because everyone √ has access to the coffee shop. (1)
1.10 C/are associated with them. √ (1)
1.11 The title is suitable because people are able to enjoy a cup of coffee √ and all proceeds go towards training √ the young people who are intellectually challenged. (2)
1.12 Wendy Vermeulen is trying to encourage South Africans to make a success of the concept of ‘Brownies & Downies’. She also hints at the fact that it will be difficult and require perseverance but it is important that people with disabilities should not be excluded from society. √√
NOTE The above answers are merely examples of possible responses. Allow for the candidate’s own but relevant interpretation.
A candidate can score 1 mark for an answer that is not well substantiated. (2)
1.13 Open-ended. Accept a suitable response, e.g.
- Yes, it is offensive because the name’s rhyming nature creates the impression of ridiculing it. The diminutive form ‘Downies’ can also be considered as being belittling or degrading.
OR - No, it is not offensive because it explains the concept of eating brownies and being served by people with Down’s syndrome. The name also makes people aware of those with intellectual disabilities.
NOTE- The above answers are merely examples of possible responses.
- Do not award a mark for YES/NO.
- Allow for the candidate’s own but relevant interpretation.
- A candidate can score 1 mark for an answer that is not well substantiated. Combination answers are acceptable. (2)
1.14
- Twelve-year-olds/12 year olds. √ (1)
- At the age of twelve there is still strict parental guidance so the children’s time on their phones will be monitored by their parents. √
OR
Many twelve-year-olds do not own cell phones yet, so they cannot engage in texting.√
OR
Many twelve-year-olds spend most of their time doing their homework or they are involved in extramural activities at school so there is no time for texting.√
NOTE: Accept any ONE of the above answers. (1)
1.15
- Fifteen-year-olds are becoming more independent√ and are allowed more freedom by their parents so they will communicate with friends more often. √
- Many fifteen-year-olds may have just been allowed to own a cell phone√ so texting is a novelty to them. √
NOTE: Accept any relevant answer. (2)
1.16 The information has been presented in the form of a bar graph so that the readers can see the different columns showing the different age groups and their percentages who text their friends daily. √ You do not have to read through complicated facts and figures to understand which teens text their friends daily. / Visually more appealing/effective.√ (2)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B: SUMMARY
QUESTION 2
The following points form the answer to the question.
QUOTATIONS | FACTS | ||
1 | ‘But you should show a positive attitude towards your classes and give your best effort to everything.’ | 1 | Always try your best./Be positive. |
2 | ‘You may not agree 100% with your teachers and parents at all times, but you should always maintain a respectful, pleasant attitude towards them.’ | 2 | Be respectful to adults. |
3 | ‘If you know how to do something in class that others do not, offer to help them’. | 3 | Always be willing to help others. |
4 | ‘Being a trustworthy person is a quality of a good leader’. | 4 | Always be honest/reliable/ dependable. |
5 | ‘Being consistent in how you treat everyone is an important way to build and maintain trust’. | 5 | Be fair to everyone./Treat everyone the same. |
6 | ‘A good leader is always positive’. | 6 | Stay positive. |
7 | ‘A leader does not participate in bullying or gossip but makes all students feel welcome and respected. | 7 | Do not take part in bullying or gossip. /Show respect. |
Marking the summary
The summary should be marked as follows:
- Mark allocation:
- 7 marks for 7 points (1 mark per main point)
- 3 marks for language
- Total marks: 10
- Distribution of language marks when a candidate has not quoted verbatim:
- 1–3 points correct: award 1 mark
- 4–5 points correct: award 2 marks
- 6–7 points correct: award 3 marks
- Distribution of language marks when a candidate has quoted verbatim:
- 6–7 quotes: award no language mark
- 1–5 quotes: award 1 language mark
NOTE:
- Word Count:
- Markers are required to verify the number of words used.
- Do not deduct any marks if the candidate fails to indicate the number of words used, or if the number of words used is indicated incorrectly.
- If the word limit is exceeded, read up to the last sentence above the stipulated upper limit and ignore the rest of the summary.
TOTAL SECTION B: 10
SECTION C: LANGUAGE
- Spelling
- One-word answers must be marked correct even if the spelling is incorrect, unless the error changes the meaning of the word.
- In full-sentence answers, incorrect spelling should be penalised if the error is in the language structure being tested.
- Where an abbreviation is tested, the answer must be punctuated correctly.
Sentence structures must be grammatically correct and given in full sentences/as per instruction.
For multiple-choice questions, accept BOTH the letter corresponding with the correct answer AND/OR the answer written out in full as correct.
QUESTION 3: ANALYSING AN ADVERTISEMENT
3.1 Carnation √ (1)
3.2 Sportsmen/sportswomen/people who participate in sport.√ The picture of the running shoes/takkies/sport shoes are worn by people who play sport./
The words ‘game on’/ ‘on and off the field’/ ‘winning game’ all refer to sport. √ (2)
3.3 A/get rid of blisters. √ (1)
3.4 If you use this product you will always be able to showcase your talent and succeed✔ because you will be able to prevent ✔ and treat blisters effectively.✔ (3)
3.5 The function of the exclamation marks is to strengthen the tone of the advertisement./Draw attention to the benefits of using Carnation Blister Care. √ (1)
3.6 Open-ended. The advertisement supports the slogan by showing pictures of the products that you can use to treat your blisters. The picture of the raised sports shoe shows someone is walking/running. This suggests that your feet have been healed of the blisters; that is why you are able to put on your sports shoes and walk/run.
NOTE: These are merely examples. Accept any relevant answer.
A candidate can score 1 mark if the answer is not well-substantiated. (2)
[10]
QUESTION 4: ANALYSING A CARTOON
4.1
4.1.1 Visual clues: Her mouth is wide open/her arms are stretched out/her eyes are wide open. √
Verbal clue: There is a double question mark. √
NOTE: Accept TWO of the above answers that discuss both verbal and visual clues. (2)
4.1.2 Until √ (1)
4.1.3 B/a serious problem. √ (1)
4.2 The music notes./The music notes indicate the sound of the cell phone’s keypad. √ (1)
4.3
- The words are written in bold /large font which implies that she is angry and will decline the invitation. √
OR - The three question marks suggest that she is angry so she will not accept the invitation. √
OR - Sara’s wide open mouth shows that she is screaming (angry) so she will decline the invitation. √
(Accept any TWO of the above.) (2)
4.4 The smoke shows that Sara is still fuming/angry. (1)
4.5 Open-ended. Accept a suitable response, e.g.
- Yes. I would have accepted the invitation because he desperately needed someone to accompany him to the dance. You cannot go to a dance alone because you would have no one to dance with so you would not enjoy yourself. I may need to ask him for a favour in the future then he would also help me out.
OR - No. I would not have accepted the invitation at the last minute. Girls have to prepare in advance for such an event and by him asking at the last minute it would make it very difficult to prepare yourself properly.
NOTE: These are merely examples. Accept any relevant answer. A candidate can score 1 mark if the answer is not well substantiated✔✔ (2)
[10]
QUESTION 5: LANGUAGE AND EDITING SKILLS
TEXT F
5.1 Brackets √ and commas. √ (2)
5.1.2
- accommodates √ (1)
- its √ (1)
- of √ (1)
- is √ (1)
5.1.3 Lottie de Vries said that the school’s doors were √ open because of the many volunteers who had √ supported the school.
NOTE: Award ONE mark for each of the underlined changes and ONE mark for removing the comma, removing the quotation marks and inserting the final full stop as well as the correct use of capital and small letters throughout. (3)
5.1.4 A speech therapist is employed √ by the therapy department. √ (2)
5.1.5
- Although the school receives a subsidy from the Department of Education √ it is still heavily reliant on charitable donations. √
OR - The school is still heavily reliant on charitable donations √ although it receives a subsidy from the Department of Education. √ (2)
5.1.6 who (1)
5.2
5.2.1 lionesses √ (Must be plural) (1)
5.2.2 departure √ (1)
5.2.3 pride √ (1)
5.2.4 can’t they/can they not √ (1)
5.2.5 Did the two feline brothers make a home in Mountain Zebra Park?
NOTE: No marks must be allocated if the candidate has omitted the question mark. (1)
5.2.6 B/an indefinite article (1)
[20]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 80
ENGLISH FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE GRADE 12 PAPER 2 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
ENGLISH FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE
GRADE 12
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Candidates are required to answer questions from TWO sections.
- Candidates’ responses should be assessed as objectively as possible
- MARKING GUIDELINES
3.1 A candidate may not answer more than ONE question on the same genre.
3.2 If a candidate gives two answers where the first one is wrong and the next one is correct, mark the first answer and ignore the rest.
3.3 If the candidate does not use inverted commas when asked to quote, do not penalise.
3.4 For open-ended questions, no marks should be awarded for YES/NO or I AGREE/I DISAGREE. The reason/substantiation/motivation is what should be considered.
3.5 No marks should be awarded for TRUE/FALSE or FALSE/OPINION. The reason/substantiation is what should be considered.
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A: NOVELS
QUESTION 1: THE STRANGE CASE OF DR JEKYLL AND MR HYDE
1.1
1.1.1
- B / Known for his decency and charitable works. √
- E / A lawyer, and trusted friend of Henry Jekyll √
- D / He goes for walks on Sundays with Utterson √
- C / A member of parliament √ (4)
1.1.2 The butler does not ask any questions. He certainly knows him; he takes him straight to Dr Lanyon. √√ (2)
1.1.3 Utterson wanted to know if Dr Lanyon has any information regarding Dr Jekyll.
The three men are good friends therefore he felt comfortable in sharing his concerns with Dr Lanyon. √√ (2)
1.1.4 ‘shock of hair prematurely white’ √ (1)
1.1.5
- A / elated to see Utterson √ (1)
- Utterson leaped from his chair and welcomed Utterson with both hands. √ (1)
1.1.6 ‘After a little rambling talk, the lawyer led up to the subject which so disagreeably pre-occupied his mind.’ √ (1)
1.1.7 Dr Lanyon was a man of science and a firm believer in logic. He does not agree with the supernatural deed of Dr Jekyll. √√ (2)
1.1.8 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows and understanding of the following aspects among others:
- Yes.
As Dr Jekyll’s lawyer, Utterson has the right to be concerned as he (Jekyll) has written a will that leaves all his money to his new partner, Mr Hyde. Utterson has heard bad things of Hyde and disliked him at first sight. The lawyer (Utterson) thinks his friend is being blackmailed. √√√
OR - No.
Utterson is merely Dr Jekyll’s lawyer. His concern is not who will inherit the money of Dr Jekyll. His sole responsibility is the lawfulness of the will. Utterson cannot allow his judgement of Hyde to influence the decision of his client. √√√
NOTE: For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1 or 2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The interpretation must be grounded in the text of the novel. (3)
AND
1.2
1.2.1 Poole is Dr Jekyll’s butler. √ (1)
1.2.2
- It is a clear night with a full moon and transparent clouds.
- It was cold and windy.
- The strong wind contributes to the emptiness of the street. √√√ (3)
1.2.3
- Utterson was carrying a heavy burden/he had a feeling that something terrible was going to happen. √√ (2)
- Utterson has been afraid that the evil Mr Hyde has influenced Dr Jekyll. Mr Poole’s terrible state of mind contributes to the feeling of Utterson. √√ (2)
1.2.4 Intelligent / split personality / mysterious / gentlemen / coward (3)
NOTE: Accept any THREE.
1.2.5
- The theme of mystery/supernatural.
- The quiet, cold windy evening.
- Poole is scared and he is sweating.
- The mention of blood and the movement of the trees. √√√ (3)
1.2.6 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows and understanding of the following aspects among others:
- He creates an atmosphere of horror by referring to:
- The weather conditions
- The deserted streets
- The mention of the word ‘blood’
- The scary movement of the trees
- It was cold and Poole was sweating. √√√√
NOTE: For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1 or 2 or 3 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated.
The interpretation must be grounded in the text of the novel. (4)
[35]
OR
QUESTION 2: CRY, THE BELOVED COUNTRY
2.1
2.1.1
- D / representing good moral values and Christian ethics √
- A / killed Arthur Jarvis √
- B / ignorant of the injustices in South Africa √
- E / a politician who enjoys the spotlight √ (4)
2.1.2
- Stephen Khumalo √ (1)
- He received a letter which informed him that his sister, Gertrude was sick. He went to Johannesburg to fetch his sister. √ (1)
2.1.3 She is a good and generous/Christian who believes in helping others / she not a racist / she takes in priests of all races in her house. √√ (2)
2.1.4
- The modern lavatory was new to him.
- He was nervous of the many plates, knives and forks on the dinner table.
- He did not know how to use the cutlery, he copied the other priests. √
Accept any ONE of the above. (1)
2.1.5 The church did not adhere to apartheid laws/separation/grouping/ racism. √ (1)
2.1.6 ‘priest from England’ √ (1)
2.1.7 The land is over-grazed/dry/it not suitable for farming/barren/leads to poverty, therefore people leave for Johannesburg in search of work. √√√ (3)
2.1.8 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows and understanding of the following aspects among others:
- Yes.
Stephen Khumalo is an upright and honest man. He makes sacrifices. He is brave because he ventured the unknown Johannesburg. He is forgiving/he forgives his son. He marries his son and the woman in order for the child not to be born illegitimately. - No.
He leaves his wife alone in Ndotsheni. He spends money which was saved for a new stove. He occasionally gives into temptation to hurt people by using harsh words. He brings home a pregnant woman. He tried to plead for his son’s life by going to Jarvis/a coward act. √√√√ (4)
NOTE: For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1 or 2 or 3 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated.
The interpretation must be grounded in the text of the novel.
2.2
2.2.1 C / squatter camp √ (1)
2.2.2
- They felt pity for the homeless people/too many people living in one house therefore they started building houses for them. √ (1)
- People from other townships (Alexandra/Pimville / Sophiatown) came in during the night and built houses using grass, sacks and poles on illegal grounds. √√ (2)
- There was a huge shortages of houses.
The houses were not properly built.
They houses did not protect them against the fierce weather. √√√ (3)
2.2.3
| Stephen Khumalo | John Khumlo |
Quiet gentleman
| Womaniser (4) |
2.2.4 ‘Men come, and machines come, and they start building rough houses for us.’ √ (1)
2.2.5 Injustice/racial tension.
- Black South Africans are allowed to own limited quantities of land. The soil in Ndotsheni is exhausted by over-planting and over-grazing, the land becomes sharp and hostile. For this reason, most young people leave the villages to seek work in the cities. Overcrowding in Johannesburg in the townships lead to crime and diseases. Houses of bad quality are built for these people. √√√ (3)
2.2.6 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows and understanding of the following aspects among others:
- Yes.
The population grew and there was not enough land for everyone to make a living. People were looking for jobs elsewhere to use their skills. They wanted to earn enough money to send home to the rural areas. Poverty drove them to Johannesburg. √√√
OR - No.
People should not leave the rural areas. They should educate themselves and learn not to over-graze their lands. People need to develop their resources to the best of their ability. It is difficult to adapt to city life. √√√
NOTE: For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1 or 2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The interpretation must be grounded in the text of the novel. (3)
[35]
SECTION B: DRAMA
QUESTION 3: THE TRAGEDY OF MACBETH
3.1
3.1.1
- E / challenges the witches to speak but is startled by their predictions. √
- A / Thane of Fife √
- D / brave, noble and honest √
- C / has better judgement than his father √ (4)
3.1.2 They have choppy fingers √ and skinny lips. √ (2)
3.1.3 Banquo will never become King. He is murdered by Macbeth. His sons/descendants will become King of Scotland. √√ (2)
3.1.4 Macbeth is no longer noble. He kills the King. After their encounter with the witches, Macbeth saw Banquo as a threat/obstacle to be King of Scotland. In the end Banquo is also killed. √√ (2)
3.1.5 Banquo was stunned/shocked because he realises that the witches’ first prediction comes true. √√ (2)
3.1.6 The witches appear to be women, yet they have male features as well. Macbeth is reflecting on the weird meeting with the witches and their prophecies, which seem to have been fanatical, yet true. The ‘borrowed clothes’ in which Ross dresses Macbeth when he tells him he is the new Thane of Cawdor hide a person’s true personality – there is a difference between the outer appearance and the inner truth. √√√ (3)
3.1.7 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows and understanding of the following aspects among others:
- No.
The witches' knowledge of future events clearly indicates that they have supernatural powers, and they also clearly enjoy using those powers to cause chaos and confusion among mankind. But it is important to realise that the witches never force anyone to do anything. Instead, they tell half-truths to trap people into giving into their own dark desires. The witches do not have the power to kill or murder anyone. - Yes.
The witches can be blamed for their prophecies. Macbeth did not consult them for a reading of his future. They approached him and created greed and obsession in him. Unnecessary murders took place and Scotland was brought to its knees. √√√
NOTE: For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1 or 2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated.
The interpretation must be grounded in the text of the novel. (3)
AND
3.2
3.2.1 The three witches √ (1)
3.2.2 Lady Macbeth should have a very determined tone. √ (1)
3.2.3
- Banquo is suspicious of Macbeth. He has more reasons to as he was present when the witches predicted Macbeth’s future.
- Banquo claims to be an honourable and principled man but does not take a stand against Macbeth like Macduff does. √√ (2)
3.2.4 (c) Soliloquy √ (1)
3.2.5 Macbeth and Lady Macbeth were about to enter as King and Queen/ Macbeth and Lady Macbeth were just crowned as King and Queen. √ (1)
3.2.6
- Macbeth and Banquo are both ambitious.
- Unlike Macbeth, Banquo resist putting selfish ambition above his honour for his country (Scotland). √√ (2)
3.2.7
- The ‘bloody cousins’ are Malcolm and Donalbain, the sons of King Duncan.
- After the King was murdered they fled in fear of their lives. Macbeth blames them for murdering their father, the King. √√√ (3)
3.2.8 These visions and hallucinations are figments of his guilty imagination. /Macbeth has seen or heard strange things like the floating dagger/the blood / the voice that says he is murdering sleep and Banquo’s ghost. Macbeth is not only at war with others, but with himself as well. √√ (2)
3.2.9 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows and understanding of the following aspects among others:
- Yes.
The drama is still relevant today because there are still people like Macbeth. Macbeth did not wait for the predictions of the witches to come naturally. He became greedy when the first prediction came true. He became dishonest and killed innocent people to achieve what he wanted. Status made him disloyal to his counterparts and friends. He became an undeserving leader. - No.
The drama is not relevant today because people are more educated/ enlightened today and do not adhere to predictions of the witches. Hierarchy in royalty is followed honourably. They do not use swords anymore. √√√√
NOTE: For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1 or 2 or 3 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The interpretation must be grounded in the text of the novel. (4)
[35]
OR
QUESTION 4: MY CHILDREN, MY AFRICA
4.1
4.1.1
- B / a semi-desert plateau in South Africa √
- D / a township on the outskirts of a town √
- E / a Chinese philosopher √
- A / a religious movement √ (4)
4.1.2 Isabel regards her life at school as the happiest years. √ (1)
4.1.3 Isabel needs to walk around the desk. Pointing to the names on the desk. Frowning because she finds it difficult to pronounce the name(s). √√ (2)
4.1.4 Tense/nervous/anxious/frustration √ (1)
4.1.5
- They are both in the same grade.
- They regard each other as equal.
- They are both intelligent.
- Isabel knows what she wants to do after school because of her advantaged situation.
- Thami is uncertain of his future due to his disadvantaged situation.
- Thami comes from a poor black family. Isabel’s family is rich. √√√√
NOTE: TWO differences and TWO similarities MUST be mentioned. (4)
4.1.6 Learners/students of affluent schools are normally well-prepared for debates because they have resources. They get well-prepared for after school (career orientated). They are ignorant of the situations at the previously disadvantaged schools. √√ (2)
4.1.7 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows and understanding of the following aspects among others:
- Yes.
Thami is also one of the deprived learners is eligible for better education. The education was inferior at the time. The protest was predominantly against Afrikaans. Thami and his peers deserved equal education. - No.
It was dangerous for him to take part in the protest. It is not necessary for protests. The problem can be solved peacefully through negotiations. √√√√
NOTE: For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1 or 2 or 3 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated.
The interpretation must be grounded in the text of the novel. (4)
4.2
4.2.1
- The protestors/comrades of boycotts and stay-aways. √ (1)
- Isabel is angry/troubled/confused/sad.
She does not want to let the change interfere. √ (1)
4.2.2 All the protestors/comrades disapprove contact with white people. Thami could be killed/tortured if he is caught visiting Isabel. √√ (2)
4.2.3 B / Traitor √ (1)
4.2.4 Thami was angry/aggravated with Isabel because she did not understand what he was trying to say. √ (1)
4.2.5
- Mr M is Thami’s teacher and helps Thami and Isabel prepare for the poetry quiz/competition. √√ (2)
- Mr M is shocked at what he heard from Thami. He is angry and disappointed. √√ (2)
4.2.6 Racism / Separation
Thami is a black boy and is not allowed to visit in the white area during the apartheid era. It was unlikely for Whites and Blacks to be friends. Thami would have been seen as a traitor if he frequents the white area. Isabel was ignorant of the situation in the black schools. Her life was also in danger in the township school. √√√ (3)
4.2.7 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows and understanding of the following aspects among others:
- Yes.
The drama is still relevant today because like the students are protesting, because of inadequate education. Affluent schools, similar to the one Isabel attends, are still above township schools in terms of resources and education. Teachers, like Mr M, still encourages racial interaction, as well as twinning schools. Just like Mr M was killed, teachers today also sacrifice their lives due to violence in schools.
OR - No.
The drama is not relevant today because education in the South African schools has improved and Afrikaans is not a compulsory medium of instruction anymore. Thami was forced to stay in a separate township, not like Isabel. Today people can choose to live in any suburb or township. Previously disadvantaged school get supplied my excellent resource equipment from the Department of Education and other stakeholders. √√√√
NOTE: For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1 or 2 or 3 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated.
The interpretation must be grounded in the text of the novel. (4)
[35]
SECTION C: SHORT STORIES
QUESTION 5
THE DOLL’S HOUSE
5.1
5.1.1
- D / She gives the Burnell girls a doll house. √
- A / Her age gives her better privileges than her sisters. √
- B / She has no respect for the less fortunate. √
- C / She always holds her sister’s skirt. √ (4)
5.1.2
- ‘I’ refers to Isabel. √ (1)
- She is the eldest of the three sisters/authority √ (1)
- They might feel insecure/less important OR admiration √ (1)
5.1.3
- It portrays the consciousness of their economic status.
- Their focus is on materialistic possessions.
- They are snobs / They think they are better than the rest of the people. √√√ (3)
5.1.4
- They are both the youngest.
- They have limited say in things/decisions because of their age and social circumstances respectively.
- They are both attracted to the lamp which symbolises hope for them in different ways. √√ (2)
5.1.5 The doll house smelled horrible because it was newly painted. √ (1)
5.1.6
- The Burnell family, with the exception of Kezia, consider themselves better/above others.
- When the Burnell children receive the doll house, they were given permission to invite friends to view it, but not the Kelveys.
- Kezia does not get her mother’s permission to invite the Kelveys because of their lower class status.
- Ms Kelvey is a working class woman/cleans the homes of well-off people, and Mr Kelvey is in jail.
- The Kelveys are poor. Mrs Kelvey collects pieces old clothes from people she works for to make dresses for her children. (2)
5.1.7 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows and understanding of the following aspects among others:
- Yes.
Kezia is innocent, she ignores the instructions of her mother and invited the poor girls to see the doll house. She is gentler/kinder and more sensitive than her sister/friends. She takes risks for the benefit of the poor girls. √√√
OR - No.
Kezia tries to turn the focus of attention to herself. She wants to experience authority and popularity like her sister, even if it is from those who are not accepted in their social circles. She is disobedient. She ignores the instructions of her mother. √√√
NOTE: For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1 or 2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The interpretation must be grounded in the text of the novel. (3)
AND
A CHIP OF GLASS RUBY
5.2
5.2.1
- Three Bedrooms √ (1)
- Eleven people√ (1)
- It symbolises the economic status of the non-white people who lived under poor/disadvantage conditions.√ (1)
5.2.2
- Mrs Bamjee assisted political activists during the struggle.
- She used the duplicating machine to assist in distributing pamphlets.
- She brought in activists and helped them more and more which lead to her arrest. √√√ (3)
5.2.3 D / Girlie √ (1)
5.2.4 Mrs Bamjee is radical/kind/dutiful/caring/political activist/considerate/ woman of integrity. √√ (2)
5.2.5
- LITERAL: A chip of glass ruby refers to the jewellery that Indian women wear in their nose.
This highlights the Indian traditional way of life. - FIGURATIVE: Mrs Bamjee can be referred to as a chip of glass ruby. She is delicate and she is precious. √√ (2)
5.2.6 He changes from being apolitical to one of understanding and appreciation of what his wife is doing. His wife remembers his birthday. He becomes appreciative; he brings her flowers to prison. √√√ (3)
5.2.7 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows and understanding of the following aspects among others:
- Yes.
The reader has sympathy for Mr Bamjee who has been left with the household responsibilities of a woman. The children are left stranded without a mother. Jimmy and Girlie are left outside the prison for hours only to be informed that Mrs Bamjee had been moved to another prison. - No.
Mr Bamjee could have supported his wife instead of distancing himself from her activities. The children were irresponsible to spend time outside the prison for such a long time. They were too young to be involved in politics. (They shared the same political views as their mother.) √√√√
NOTE: For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1 or 2 or 3 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated.
The interpretation must be grounded in the text of the novel. (4)
[35]
SECTION D: POETRY
QUESTION 6
6.1 STILL I RISE by MAYA ANGELOU
6.1.1
- B / lyric √ (1)
- ‘You’ refers to the oppressors. √ (1)
- Simile √ (1)
- The poet is adamant not to be pushed into dirt/gutters any longer. They will challenge their oppressors and they will raise their heads. √√ (2)
6.1.2 She is confident/strong personality. √√ (2)
6.1.3
- Confidence/determination √ (1)
- She compares herself to the sun and the moon. She raises herself emotionally to stay strong, just as the sun and the moon rise everyday no matter what. √√ (2)
6.1.4 The repetition signifies how victorious and triumphant she is. √√ (2)
6.1.5 The message that the poet wants to bring home to the readers is her strength to strike back against the discrimination of races and gender. This offers hope and courage for others who suffer from the same ordeal. √√√ (3)
6.1.6 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows and understanding of the following aspects among others:
- She wanted her voice to be heard for the unheard/voiceless/ degraded/oppressed.
- She is fighting and resenting racism. √√√
NOTE: For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1 or 2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The interpretation must be grounded in the text of the novel. (3)
AND
SONNET 18 by WILLIAM SHAKESPEARE
6.2
6.2.1
- Shakespearian/English/Elizabethan/Miltonic Sonnet OR Italian/Petrarchan/Miltonic Sonnet √ (1)
- It is divided into three groups of four line/quatrains.
The rhyme scheme abab cdcd efef and end with rhyming couplet gg.
OR
The first eight (8) lines/octave make a statement.
The word ‘but’ introduces the sestet.
It suggests a shift in the argument. √√ (2)
6.2.2
- Personification. √ (1)
- The wind is portrayed as having human qualities.
It is violent toward the delicate buds. √√ (2)
6.2.3
- Sometimes the sun is too hot and other times it is hidden, perhaps by the clouds.
- He calls the sun the ‘eye of heaven’ and gives it a complexion which generally refers to the skin of the face. √√ (2)
6.2.4 A / everlasting√ (1)
6.2.5
- The poet believes that his lover’s beauty is eternal/ immortal. √ (1)
- Death will not be able to brag about its power because it will be powerless.
Coming near to death is compared to someone who walks in the shadow of someone else. √√ (2)
6.2.6
- In the couplet the poet refers to the victory over death.
- He says that even if the poet and his lover must die, they will remain alive in the hearts of those who read the poem. √√ (2)
6.2.7 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows and understanding of the following aspects among others:
- The poem is unrealistic.
- Her beauty cannot literally last forever because she is not immortal. The poet is exaggerating, no one is eternal. The lasting beauty is implied in the memory of the poet. She died a long time ago. √√√
- The poem is realistic.
- Shakespeare successfully wrote a beautiful love poem. The poet paints a beautiful picture of his lover’s outer beauty. He refers to the everlasting beauty as the inner beauty that can last forever. Even if the person is dead, her inner beauty can still be spoken about and therefore live forever in the hearts and memory of people. √√√
NOTE: For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1 or 2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The interpretation must be grounded in the text of the novel. (3)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION D: 35
GRAND TOTAL: 70