Adele
HOSPITALITY STUDIES GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
HOSPITALITY STUDIES
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 MULTIPLE-CHOICE ITEMS
1.1.1 B √
1.1.2 A √
1.1.3 A √
1.1.4 C √
1.1.5 B √
1.1.6 A √
1.1.7 D √
1.1.8 B √
1.1.9 D √
1.1.10 B √ (10 x 1) (10)
1.2 MATCHING ITEMS
1.2.1 C √
1.2.2 A √
1.2.3 F √
1.2.4 E √
1.2.5 D √ (5 x 1) (5)
1.3 MATCHING ITEMS
1.3.1 D √
1.3.2 E √
1.3.3 F √
1.3.4 B √
1.3.5 A √ (5 x 1) (5)
1.4 ONE-WORD ITEMS
1.4.1 Sorbet √
1.4.2 Branding √
1.4.3 Product √
1.4.4 Gastroenteritis √
1.4.5 Professionalism √
1.4.6 Allergy √
1.4.7 Crudités √
1.4.8 Hors d’oeuvres √
1.4.9 Marbling √
1.4.10 Champagne √ (10 x 1) (10)
1.5 CHOICE ITEMS
A √
B √
D √
G √ (Any order) (4 x 1) (4)
1.6 CHOOSE FROM THE LIST
1.6.1
D √
F √
1.6.2
A √
G √
1.6.3
B √
E √ (Any order) (6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 40
SECTION B: KITCHEN AND RESTAURANT OPERATIONS;
HYGIENE, SAFETY AND SECURITY
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1 Alertness
- Staff members should be alert at all times.
- They should be aware of customers’ needs and react quickly to such needs.
- Staff members should immediately report unusual behaviour or incidents, or any suspicious person or object to the supervisor or security staff.
Co-operation
Staff members of the Ingwe Hotel should:
- Be willing and prepared to work with others.
- Work towards achieving the same objectives.
- Ensure that everyone pull their weight.
- Ask for help when needed.
- Share successes and failures.
- Enjoy working with each other.
(Any THREE acceptable answers) (3)
2.1.2
- Good service delivery will lead to satisfied customers who are willing to pay.
- Satisfied clients become loyal customers that return to the business.
- When the service is good customers will have positive word of mouth that will attract more customers.
- Once there are more customers to the establishment, there will be an increase in the income and profit. (Any 3 x 1) (3)
2.1.3 Computers will help the chefs at the Ingwe Hotel to:
- Recording dish sales and to do dish analysis.
- Project the ingredient costs as well as the production costs and calculate the selling prices.
- Use an online dictionary to translate the names of ingredients from other languages to English.
- Developing and changing recipes is simplified.
- Storing and retrieving recipes and ingredients easily.
- Compiling order lists easily and accurately.
- Do metric conversions for the ingredients automatically.
- Printing serving sizes on a recipe, which makes planning for buffet functions easier.
- Determining the nutritional value of food. (Any 3 x 1) (3)
2.2
- Online reservations will help guests to compare the prices and facilities offered by different hotels.
- Pictures of the hotels and rooms can be found online.
- Information on prices and special deals, as well as information on the establishment and environment can be found online.
- Online reservations are helpful in making last-minute travel arrangements. (Any 3 x 1) (3)
2.3
2.3.1 Cholera is transmitted through:
- Drinking water contaminated with the cholera bacteria (faeces in water).
- Eating food which has been in contact with contaminated water, flies or soiled hands.
- Eating vegetables fertilised with sewage.
- Fish and shellfish obtained from contaminated water. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.3.2
- Watering diarrhoea √
- Nausea √
- Vomiting √
- Rapid dehydration √
- Muscle cramps √
- Low blood pressure √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.3.3
- All liquids need to be treated, boiled or milk must be pasteurised. √
- Food should be cleaned and cooked properly especially in areas where cholera is present. √
- Wash hands thoroughly with antiseptic soap. √
- Cover food to protect it from flies. √
- Do not use uncooked fish or shellfish. √
- Only use treated water to wash fruits and vegetables. √
(Any 3 x 1) (3)
[20]
TOTAL SECTION B: 20
SECTION C: NUTRITION AND MENU PLANNING;
FOOD COMMODITIES
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1 Cocktail function √ (1)
3.1.2
- Cocktail functions can be cheaper if well planned. √
- No cutlery is needed to eat because a menu consists of finger food / little cutlery and crockery is required. √
- Less space is needed for cocktail parties. √
- Guests are allowed to mingle around and can interact in a more relaxed, informal way. √
- A wide variety of styles and flavours can be served. √
- Finger foods allow more creativity than a formal meal. √
- Fewer serving staff is needed. √
- A table plan is not necessary. √
- The duration of the function is usually quite short, as they only last for about two hours. √ (Any 4 x 1) (4)
3.1.3 Not suitable, √ because the menu consists of cupcakes with butter icing and chocolate cake slices √ which are too sweet √ and rich for a diabetic person. √
(Any TWO motivations) (Any 3 x 1) (3)
3.1.4
- Total price = food cost + labour costs + overhead costs + profit
= R5,750 + R1,800 + R1,200 + R3,500 √
= R12,500 √√ (3) - Gross profit = selling price – food cost
= R12, 500 √ – R5,750 √
= R6,500 √ (3) - Cost per person = selling price ÷ number of guests
= R12,500 ÷ 150 √
= R81,67 √ (2)
3.1.5 (6)
DISHES IN THE MENU | TYPES OF PASTRY |
(3) |
(3) |
3.2
- Measure ingredients accurately. √
- Use minimum flour when rolling out the dough. √
- Incorporate as much air as possible by folding the dough correctly. √
- Roll out lightly and always in the same direction. √
- Do not stretch the pastry. √
- Rest and chill the pastry after each stage of making and assembling. √
- Bake at the correct temperatures and position in the oven. √
(Any 4 x 1) (4)
3.3
3.3.1 Kebabs/Sosaties √ (1)
3.3.2
- Thick rib √
- Leg √
- Shank √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.3.3 Grilling √ (1)
3.3.4 Mint sauce √ (1)
3.4
- Meat should never be immersed in water or washed, because most of the nutrients and flavoursome components are easily dissolved in water. √
- Meat must not be salted beforehand because salt extract the meat juices from the meat. √
- Thaw meat correctly to limit losses caused by dripping during the thawing process. √
- Do not cook meat at very high or low temperatures for too long. √ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
3.5
3.5.1 Trimming – is the process of neatening √ the meat, by removing excess fat and sinew. √ (2)
3.5.2 Barding – is covering a piece of meat √ with thin slices of fat or bacon √ to prevent it from drying. √ (2)
3.5.3 Sealing – is to begin cooking meat by sautéing it over low heat √ until firm but not brown. √ (2)
[40]
QUESTION 4
4.1
4.1.1 Lacto-ovo vegetarian √ (1)
4.1.2
- Proteins √
- Fibre √ (2
4.1.3
- People can become vegetarians on moral grounds based on the objection to the killing of animals. √
- Health reasons. √
- Religious beliefs may prohibit the eating of meat. √
- The meat industry is said to have a negative effect on the environment. √
- Some people do not like the taste of meat. √
- Meat is more expensive than plant products. √ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
4.1.4
- To remove debris. √ (1)
- To allow them to expand with two thirds of their original size. √ (1)
- To reduce flatulence. √ (1)
4.2 Textured vegetable protein is beneficial to health, because it does not contain saturated fat or cholesterol. √ It is low in kilojoules and may help to decrease the risk of cardiovascular problems. √ (2)
4.3
4.3.1 Choux pastry √ (1)
4.3.2 Churros are piped long strips of choux pastry, that are deep fried √ and sprinkled with cinnamon and sugar. √ (2)
4.3.3
- They should be crisp. √
- Should be hollow inside. √
- They should be light in weight. √
- Light brown in colour. √ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
4.3.4
- To develop steam and to enhance the formation of cavities. √ (1)
- To complete the baking process and to dry out the cavities. √ (1)
- Trapped steam can cause the softening of the puffs. √ (1)
4.4
4.4.1 Smoking √ (1)
4.4.2 Smoking is the method of preservation where food is treated with salt or brine, √ and then exposed to wood smoke. √ (2)
4.4.3
- Wood smoke contains phenols and phenolic compounds that inhibit the growth of microbes. √
- It slows down the rancidity of animal fat. √
- Smoking preserve partly by drying and when moisture is removed, the growth of micro-organisms is retarded. √
- Food is treated with salt during smoking, which slows down the growth of micro-organisms. √
- Sulphur dioxide used for smoking fruit slows down the growth of micro-organisms. √
- Smoking accelerates the drying process. √
- It prevents enzymatic browning and lengthens the shelf life of food. √ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
4.4.4
- Name of the product. √
- Net weight in grams. √
- Name of the manufacturer. √
- Bar code √ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
4.5
- Haddock √
- Sausage √
- Cheese √
- Pork chops √
- Chicken √
- Ham √
- Snoek √
- Trout √ and salmon √ (Any TWO acceptable answers) (2)
4.6
4.6.1 Mousse is a light, fluffy mixture which may be sweet or savoury, hot or cold where a little or no gelatine is used and is served in a glass or coupe. √√ (2)
4.6.2
- Hydration √ – gelatine is firstly soaked in cold water in order to absorb liquid. √
- Dispersion √ – soaked gelatine is melted over steam, hot water or microwave for few seconds. √
- Gelation √ – gelatine mixture is refrigerated to set or form a solid gel. √ (6)
4.6.3 Strawberry pieces, √ mint, whipped cream √ or edible flowers. (Any 1 x 1) (1)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 80
SECTION D: SECTORS AND CAREERS, FOOD AND BEVERAGE SERVICE
QUESTION 5
5.1
5.1.1 Target market will be the learners, √ teachers √ and post office employees. √ (3)
5.1.2
- The café is near the post office and Mica secondary school which will help her with the business description. √
- Angela intends to employ three people and that will help her with the staffing / personnel plan. √
- Already applied for a bank loan, which means that she knows where she will get the money to run the café – financial plan. √
- She has planned how the money will be utilised – financial plan. √
- She is very good at budgeting to ensure that the expenditure does not exceed the income – financial plan. √
- Has created posters which she will use to market her business – marketing plan. √ (Any 5 x 1) (5)
5.1.3
- She could use competitions. √
- Give aways √
- Specials on special days √
- Buy one get one free. √
- Lucky draws. √ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
5.1.4 Visual marketing tool √ (1)
5.1.5
- Baking √
- Function catering √
- Children’s birthday parties √
- Meals on wheels √
- Vendors √
- Home industry √ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
5.1.6
- Use of bright colours to catch the eye of the potential customers. √
- Message should be kept short, direct and centred to one product. √
- Do not clutter the tool with too much information. √
- Font size and letter type should be easily readable. √
- Pictures and illustrations should be used to give visual image of the product. √
- Lay-out should be kept simple so that the message can be seen and understood easily. √
- Words like SAVE, FREE, BARGAIN, EXCLUSIVE should be used to catch the attention of potential customers. √
- Good use of art elements and principles so that the product is appealing to the eye. √
(Any FIVE acceptable answers) (5)
5.1.7
- Angela’s business will increase the local income and economic growth will be stimulated. √
- The income generated will contribute to the development and improvement of infrastructure within the community. √
- Tourists will bring valuable currency into the community. √
- The esteem and living standards of the community will improve. √
- The business will enhance job creation. √ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
5.2
- Food and beverages/restaurants √
- Bar √
- Guest rooms √
- Function rooms√
- Laundry √ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
5.3
- An accountant pays staff salaries. √
- Controls banking procedures. √
- Oversees the auditing of hotel funds. √
- Ensures payment of tax and VAT. √
- Taking care of collections which means making sure that money owed to the business, is paid. √
- Drawing up budgets. √
- Preparing financial reports. √ (Any FOUR acceptable answers) (4)
[30]
QUESTION 6
6.1
6.1.1
- Glass A – Cocktail √
- Glass B – Wine √ (2)
6.1.2 Presenting wine. √ (1)
6.1.3
- Stand on the right-hand side of the guest. √
- Hold the wine selected on a service cloth in your hand with the label facing towards the host. √
- Present the wine to the host while saying the name and vintage of the wine to confirm that it is the correct one. √
- Allow the host to feel the temperature of the wine should he wish to. √
- Open the bottle once the host is satisfied. √ (4)
6.1.4
- Name of the wine √ – Reisling √
- Producer √ – Barnard vineyards √
- Vintage √ – 2011 √ (3 x 2) (6)
6.1.5 Not suitable, √ because Reisling is a white wine √ and beef is a red meat that goes well with red wine. √ (3)
6.2
- The ingredients are mixed in the glass in which it will be served. √
- The ingredients are floated on top of each other and should form layers in the glass. √
- Swizzle sticks can be placed in the glass to allow the ingredients to mix. √ (3)
6.3
6.3.1
- Clean and care for equipment before placing them on the table. √
- Clean the crockery and polish cutlery and glasses before placing them on the table. √
- Clean and refill condiment containers. √
- Fold and place serviettes and table numbers on the table. √
- Arrange table decorations. √
(Any THREE acceptable answers) (3)
6.3.2
- When clearing the bar one should first conduct a stock take of consumables. √
- Clear the bar top and pack away all equipment. √
- Wash and polish used glasses. √
- Remove all empty bottles. √
- Empty the liqueur trolley and return stock to the bar cupboard. √
- Restock the bar from the cellar. √
(Any FOUR acceptable answers) (4)
6.3.3
- Do not serve him/her any more alcoholic beverages. √
- Keep calm. √
- Be friendly, but firm at all times and avoid showing emotions. √
- Ask the customer politely but firmly to leave, rather than allowing him/her to disturb other guests. √
- The staff can remove him/her if necessary. √
- Keep the incident as quiet as possible. √ (Any 4 x 1) (4)
[30]
TOTAL SECTION D: 60
GRAND TOTAL: 200
TOURISM GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
TOURISM
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- This question paper consists of FIVE sections.
- ALL questions in SECTIONS A, B, C, D and E are COMPULSORY.
- Start EACH QUESTION on a NEW page.
- You may use a non-programmable pocket calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
- The following table is a guide to help you allocate your time according to each section.
SECTION | QUESTION | TOPIC | MARKS | TIME |
A | 1 | Short Questions | 40 marks | 20 minutes |
B | 2 | Map Work and Tour Planning | 50 marks | 50 minutes |
3 | Foreign Exchange | |||
C | 4 | Tourism Attractions | 50 marks | 50 minutes |
5 | Heritage Tourism | |||
6 | Marketing | |||
D | 7 | Tourism Sectors | 30 marks | 30 minutes |
8 | Sustainable and Responsible Tourism | |||
E | 9 | Domestic, Regional and International Tourism | 30 marks | 30 minutes |
10 | Communication and Customer Care |
QUESTIONS
SECTION A: SHORT QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1 Four options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.20) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.21 A.
1.1.1 When planning an itinerary a tour planner should take into account that travellers on international flights must check in for their flight … prior to departure.
- 30 minutes
- 90 minutes
- 2 to 3 hours
- 1 to 2 hours
1.1.2 An example of a World Heritage Site in the Northern Cape:
- Cradle of Humankind
- Robben Island
- Vredefort Dome
- Richtersveld
1.1.3 International tourists should keep copies of … separate from their luggage.
- banking details
- passports
- customs regulations
- travel allowances
1.1.4 A customer feedback tool that does not contain many questions:
- Survey
- Feedback card
- Follow-up call
- Questionnaire
1.1.5 Upon arrival in South Africa a 100 ml bottle of perfume is regarded as … by customs.
- goods to declare
- duty-free goods
- prohibited goods
- restricted goods
1.1.6 The Black Forest is located in …
- Switzerland.
- Germany.
- Russia.
- Turkey.
1.1.7 An African country that is a yellow fever endemic area:
- Egypt
- Swaziland
- Morocco
- Democratic Republic of Congo
1.1.8 The proportion of an inbound tourism market that a country holds in relation to its main competitors:
- Foreign arrivals
- Average length of stay
- Foreign market share
- Arrival surplus
1.1.9 A disease contracted in the same way as HIV Aids:
- Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis B
- Malaria
- Cholera
1.1.10 This city will host the International Olympic Committee’s Summer Games in 2020.
- Tokyo
- Beijing
- Paris
- Los Angeles
1.1.11 South African bank notes to the value of R10 000 is regarded as … by SARS.
- goods to declare
- duty-free goods
- prohibited goods
- restricted goods
1.1.12 The abduction of 276 schoolgirls by Boko Haram in Nigeria in 2014 is an example of …
- a civil war.
- general unrest.
- an unforeseen occurrence.
- terrorism.
1.1.13 Which of the following is NOT regarded as a good environmental practice?
- Environmentally friendly buildings
- Reduce, reuse and recycle
- Local procurement
- Waste management
1.1.14 A crime prevention measure to ensure the success of an attraction:
- Providing high-quality pathways
- Availability of lockers
- Regular signage checks
- Providing emergency medical assistance
1.1.15 Tsogo Sun Hotel staff that are looking professional in their uniforms are contributing to the hotel group’s …
- corporate image.
- triple bottom line.
- BBBEE charter.
- customer service policy.
1.1.16 This world icon is one of the seven new wonders of the world:
- Machu Picchu
- Eiffel Tower
- The Sphinx
- Big Ben
1.1.17 The International Date Line (IDL) is an artificial line that lies approximately … from the Universal Time Coordinate.
- 360°
- 180°
- 90°
- 270°
1.1.18 … is the ruined remains of a large, ancient Mayan city.
- Taj Mahal
- Cuzco
- Vatican City
- Chichen Itza
1.1.19 Daylight saving time (DST) is the practice whereby clocks in a country are set one hour ahead of standard time during …
- winter.
- spring.
- autumn.
- summer.
1.1.20 An example of universal accessibility at an attraction:
- The restaurant offers kosher dishes.
- Toilet facilities are provided for people in wheelchairs.
- Staff members are able to communicate with visitors in a variety of international languages.
- All of the above (20 × 1) (20)
1.2 Choose a concept provided in the list that best completes the sentences below. You may only use each of the concepts given ONCE. Write only the concept next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
| Passport, TB, IDP, bilharzia, malaria, IDL, visa, Hepatitis A, HIV, cholera |
1.2.1 Use of insect repellent on exposed skin, staying indoors, spraying an aerosol insecticide in the sleeping area or burning of mosquito coils and mosquito mats are precautionary measures against contracting …
1.2.2 A legal document, available at AA offices, that allows the bearer to drive in a foreign country is called a ...
1.2.3 Prolonged coughing, difficulty in breathing and chest and joint pain are symptoms of …
1.2.4 Personal particulars of the applicant, details of the visit to the destination country, information regarding the applicant’s financial status and criminal record are requirements for a ...
1.2.5 Avoiding of potentially contaminated rivers and not drinking or washing in contaminated water are precautionary measures against contracting … (5 × 1) (5)
1.3 Choose the correct word(s) from those given in brackets. Write only the word(s) next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 (The Dome of the Rock/Ayers Rock) is a unique natural landmark, composed of hard, red sandstone that lies in the Uluru-Kata Tjuta National Park.
1.3.2 The (Alcázar of Segovia/Parthenon) is considered to be the most beautiful castle in Spain.
1.3.3 Tourists interested in ancient civilisations must travel to Jordan to explore (the Kremlin/Petra).
1.3.4 (The Blue Mosque/Mecca) is regarded as the spiritual centre of the Muslim faith.
1.3.5 (Mount Everest/Mount Fuji) is a nearly perfectly shaped volcano that is worshiped as a sacred mountain by Buddhists. (5 × 1) (5)
1.4 Choose the Stormsriver Adventures commitment statement regarding sustainability from COLUMN B that best matches the concept in
COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–E) next to the question number (1.4.1–1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.4.6 F.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
1.4.1 1.4.2 1.4.3 1.4.4 1.4.5 | Social pillar CSI Environmental pillar FTT (previously known as FTTSA) Economic pillar | A B C D E | School feeding scheme whereby 220 primary school children are provided with a meal four times a week. Actively assist with community fundraising projects. Sustained commitment to conservation of natural resources used in adventure products. Upliftment of the community through job creation and creation of mini‐enterprises through the training of “Adventure Contractors”. Wages, working conditions, purchasing and actions that are just. Equal distribution of benefits, respect for human rights, culture and the environment. |
(5 × 1) (5)
1.5 Select the image that best fits the description below. Write only the letter (A–F) next to the question number (1.5.1–1.5.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.5.6 G.
A | D |
B | E |
C | F |
1.5.1 A leading South African outdoor lifestyle and adventure event.
1.5.2 The banks charge users far more in interest for withdrawing money from an ATM than for making purchases.
1.5.3 An annual German event that provides a unique opportunity for the global travel trade to meet, network and conduct business.
1.5.4 A tourism marketing event that showcases the widest variety of Southern Africa’s best tourism products attracting international buyers and media from across the world.
1.5.5 Dedicated to the foreign currency of the country (or countries) you are travelling to. (5 × 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 40
SECTION B: MAP WORK AND TOUR PLANNING; FOREIGN EXCHANGE
QUESTION 2
2.1 Study the World Time Zone Map below, read the information given and answer the questions that follow.
| The 2016 Summer Olympics was a major global multi-sport event that took place in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, from 5 to 21 August 2016. The 2016 Olympics had the highest number of countries that took part in a record number of sports. More than 10,500 athletes from 206 countries participated. The opening ceremony started at the Maracanã Stadium in Rio de Janeiro on 5 August at 20:00. |
2.1.1 Calculate the time and date that fans in Paris, France had to switch on their television sets if they wanted to watch a live broadcast of the opening ceremony. Remember that France was practicing daylight saving time at the time of the opening ceremony. (5)
2.1.2 List ONE possible advantage for the tourism industry in a country practicing daylight saving time. (1)
2.1.3 Calculate the time and date that Australian fans in Sydney had to switch on their television sets if they wanted to watch a live broadcast the opening ceremony. (4)
2.1.4 Chad le Clos, one of South Africa’s top Olympic swimmers, was part of the South African contingent that took part in the Olympic Games. His father flew to Rio de Janeiro to watch his son compete.
- Mr le Clos arrived in Rio de Janeiro on flight O66152 at 19:55 on 31 July after a 13h 45m flight via Sao Paulo, Brazil. Determine the date and departure time of his flight from Johannesburg, South Africa. (6)
- Mr le Clos could have suffered from jet lag after his flight. List TWO symptoms of jet lag. (2)
2.1.5 Each member of the South African Olympic team had to have a passport to enter Brazil, but were not required to obtain a visa for the duration of their stay.
- Differentiate between a passport and a visa. (2 × 2) (4)
- Name ONE vaccination that the team was required to obtain before their departure to Brazil. (1)
2.1.6 Upon his return to South Africa, Mr le Clos bought a 750 ml bottle of wine for his wife at the duty free shops at Guarulhos International Airport in Sao Paulo.
- Explain the term duty-free shop. (2)
- Should Mr le Clos have gone through the red or the green channel upon his arrival at OR Tambo? (1)
2.2 Read the extract and answer the questions that follow.
12 day South Africa Safari Explore Southern Africa’s abundant wildlife, Zulu culture and dramatic scenery while travelling through South Africa and Swaziland, combining cultural and wildlife experiences. The tour starts with a visit to the sprawling township of Soweto and thereafter you will stop at various destinations and experience activities such as hiking, kayaking and rafting before travelling to Kruger National Park for unbelievable wildlife viewing. Highlights include camping under the African night sky in the Kruger National Park, an introduction to Zulu culture where you can learn about spear-making, dancing and basket weaving, game viewing opportunities and a guided hike at Blyde River Canyon where Bourke’s Luck Potholes offer amazing photographic opportunities. Theme: Family (this trip is for adults and children travelling together, min. age 11) Summary of tour: Inclusions: All meals, transport (4 × 4, minibuses), accommodation (camping, permanent tents, hotel and lodge), activities (game drives at Hluhluwe-iMfolozi Park, Hlane National Park and Kruger National Park, visits to a Zulu village and Bourke’s Luck Potholes). [Source: www.intrepidtravel.com] |
2.2.1 The above-mentioned tour is an example of a package tour. Do you agree with this statement? Motivate your answer. (2)
2.2.2 Taking the activities into account, identify ONE type of tourist that would consider going on this tour. (1)
2.2.3 Explain the term inclusions used in the extract. (1)
2.2.4 Advise a tourist making a booking on this tour regarding TWO items that he/she should pack before departure. (2 × 1) (2)
[32]
QUESTION 3
3.1 Study the exchange rate table below and answer the questions that follow.
Country | Currency code | BBR | BSR |
Great Britain | GBP | 18,63 | 19,34 |
European countries | EUR | 15,53 | 16,11 |
USA | USD | 14,14 | 14,46 |
3.1.1 A South African business tourist is visiting the USA. He has ZAR15 000 spending money. Calculate the amount of USD he will receive. (3)
3.1.2 A retired South African couple are planning to visit their family in London. They have ZAR25 000 to exchange for spending money.
- Calculate the amount of local currency they will receive. (3)
- Upon their return they have some of their spending money left over. Calculate the amount of ZAR they will receive if they exchange £20. (3)
- Identify the currency that they would have to exchange their ZAR for, if their family lived in France. (1)
3.2 In a paragraph, discuss the effect that a weak rand has on both inbound and outbound tourism. (2 × 2) (4)
3.3 In a paragraph explain the term multiplier effect and how it can benefit the tourism industry of a country. (2 × 2) (4)
[18]
TOTAL SECTION B: 50
SECTION C: TOURISM ATTRACTIONS; CULTURAL AND HERITAGE TOURISM; MARKETING
QUESTION 4
4.1 Study the picture clues and the map of Europe and answer the questions that follow. 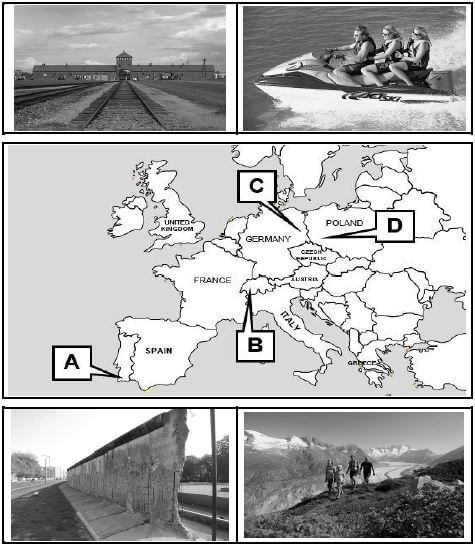
4.1.1 Identify the icons labelled A, B, C and D. (4 × 2) (8)
4.1.2 Explain why the icon labelled A is one of Europe’s most popular tourism regions. (2)
4.1.3 Give ONE reason why tourists interested in history will visit the icons labelled …
- C. (2)
- D. (2)
4.2 Study the information on uShaka Marine World and answer the questions that follow. 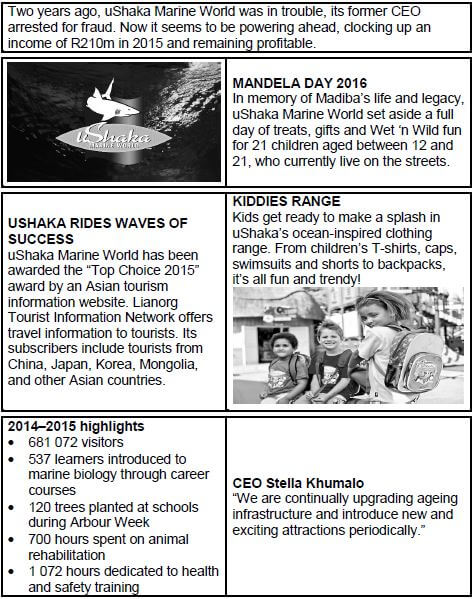
4.2.1
- Identify ONE example of unethical behaviour that has taken place at uShaka Marine World. (1)
- Suggest ONE action that could have been taken by uShaka Marine World to deal with the unethical behaviour identified in QUESTION 4.2.1(a) in order to minimise its impact on the attraction. (2)
4.2.2 Give ONE example from the extract to support uShaka Marine World’s:
- environmental management strategy (2)
- marketing strategy (2)
4.2.3 Explain how the “Top Choice 2015” award will assist the management of uShaka Marine World to exceed their expected income target. (2)
4.2.4 Suggest THREE ways in which CEO Stella Khumalo’s statement will create long term benefits for uShaka Marine World. (3 × 2) (6)
[29]
QUESTION 5
Study the map below and answer the questions. 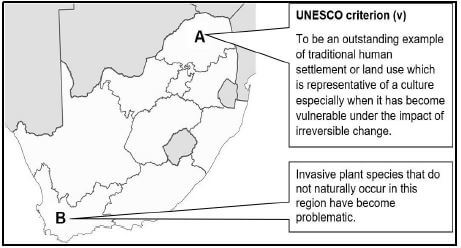
5.1 Identify the UNESCO World Heritage Sites labelled A and B. (2 × 1) (2)
5.2
5.2.1 State the type of World Heritage Site represented by the site labelled A. (1)
5.2.2 Discuss ONE example of how the World Heritage Site labelled A meets UNESCO’s criterion (v). (2)
5.3
5.3.1 Name the major type of vegetation that covers the mountains, lowland valleys and coastal plains of the World Heritage Site labelled B. (2)
5.3.2 Explain ONE way in which invasive plant species present a threat to the existence of the World Heritage Site labelled B. (2)
5.4 Discuss TWO ways in which the South African tourism industry benefits from having the World Heritage Sites labelled A and B. (2 × 2) (4)
[13]
QUESTION 6
6.1 Read the extract below.
SATourism Germany launches food and wine campaign South African Tourism has launched a food and wine campaign with Germany’s cooking community, www.chefkoch.de, a recipe network. Over the course of six weeks, a South African-themed special within the recipe network will make South Africa’s diverse cuisine and braai (barbecue) culture more accessible to Germans. [Adapted from: http://www.tourismupdate.co.za] |
Explain TWO ways how this marketing initiative will add value to South Africa as a travel destination. (2 × 2) (4)
6.2 Explain the following statement: TOMSA plays a valuable role in contributing to SA Tourism’s ability to market South Africa as a preferred tourist destination. (2 × 2) (4)
[8]
TOTAL SECTION C: 50
SECTION D: TOURISM SECTORS; SUSTAINABLE AND RESPONSIBLE TOURISM
QUESTION 7
Study the collage below and answer the questions. 
7.1 Discuss how the dress code of the SAA staff in the collage contributes to the professional image of the business. (2)
7.2 List TWO other factors, other than the company logo and appearance of staff, that can contribute to the professional image of SAA. (2 × 1) (2)
7.3 All SAA staff members must sign a contract of employment.
7.3.1 Explain why it is essential for an employee to sign a contract of employment. (2)
7.3.2 List TWO items that can be included in a contract of employment that must be signed by employees. (2 × 1) (2)
7.4 SAA employees undertake to uphold the company’s code of conduct when they are employed. Discuss the value of a code of conduct for employees in the airline industry. (2)
[10]
QUESTION 8
Read the extract and answer the questions that follow. 
8.1 Lion Sands Private Game Reserve can be regarded as a tourism business that has incorporated the triple bottom line in their business practices.
8.1.1 Discuss this statement by referring to their commitment to the environmental and social pillars of the triple bottom line. (2 × 2) (4)
8.1.2 Suggest ONE manner in which Lion Sands Private Game Reserve could show their commitment to upholding the economic pillar of the triple bottom line. (2)
8.2 List TWO examples of responsible tourism practices that could be included in a code of conduct for responsible tourists visiting the Lion Sands Private Game Reserve. (2 × 2) (4)
8.3 Suggest TWO strategies that Lion Sands Private Game Reserve could implement in order to attract environmentally conscious tourists. (2 × 2) (4)
8.4 Lion Sands Private Game Reserve has a corporate social investment programme.
8.4.1 Explain the term corporate social investment. (2)
8.4.2 Describe TWO initiatives by which Lion Sands Private Game Reserve has realised their corporate social investment programme in their local community. (2 × 2) (4)
[20]
TOTAL SECTION D: 30
SECTION E: DOMESTIC, REGIONAL AND INTERNATIONAL TOURISM; COMMUNICATION AND CUSTOMER CARE
QUESTION 9
9.1 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.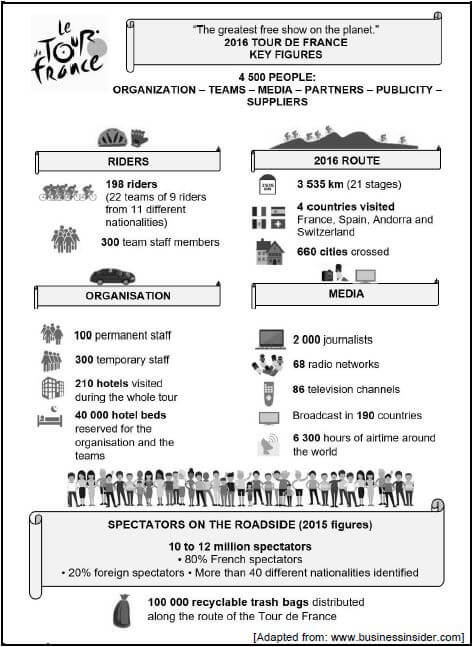
9.1.1 Give ONE reason why the Tour de France is classified as a global event. (2)
9.1.2 Explain why the Tour de France is portrayed as the “greatest free show on the planet”. (2 × 2) (4)
9.1.3 Identify ONE strategy the Tour de France organisers use to reduce the three week event’s impact on the environment. (2)
9.1.4 Discuss the benefits for the local economies of the 660 cities crossed during the Tour de France in a paragraph.
Include the following aspects in your paragraph:
- Income generation (2)
- Job creation (2)
9.2 Study the statistics below on travel patterns of foreign tourists to South Africa in 2015 and answer the questions that follow. 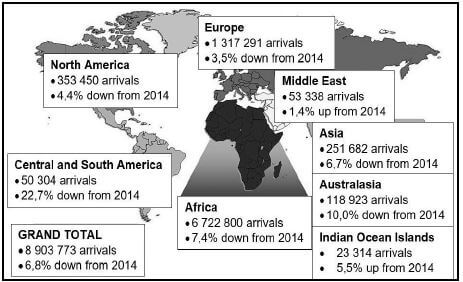
9.2.1 Identify the tourism region that recorded the sharpest decline in foreign tourist arrivals into South Africa in 2015 compared to 2014. (1)
9.2.2 Overall foreign tourist arrivals into South Africa declined by 6,8% in 2015 compared to 2014. This decline was cause for major concern as this sector was one of the best performing until recent times.
Give TWO factors that could have contributed to the decline in international inbound tourists to South Africa. (2 × 2) (4)
9.3 Study the graph below and answer the question that follows. 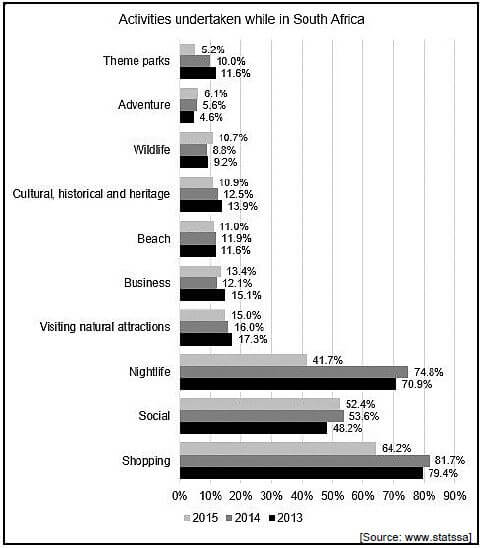
Compare the activities that foreign tourists participated in while visiting South Africa in 2014 and 2015.
State the trend between the two years. (2)
[19]
QUESTION 10
Study the extract on customer satisfaction and answer the questions that follow. 
10.1 Identify the customer feedback method used in the extract that enables customers to post reviews on products or services they have experienced. (1)
10.2 Explain how the feedback method identified in QUESTION 10.1 can be useful to potential customers. (2)
10.3 Give your opinion on the status of the Ocean Fresh Restaurant’s customer service based on the 290 customer reviews. (2 × 2) (4)
10.4 Recommend TWO intervention plans to the restaurant manager to address the complaints of AnnieH. (2 × 2) (4)
[11]
TOTAL SECTION E: 30
GRAND TOTAL: 200
TOURISM GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
TOURISM
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A: SHORT QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 C ✔
1.1.2 D ✔
1.1.3 B ✔
1.1.4 B ✔
1.1.5 A ✔
1.1.6 B ✔
1.1.7 D ✔
1.1.8 C ✔
1.1.9 B ✔
1.1.10 A ✔
1.1.11 D ✔
1.1.12 D ✔
1.1.13 C ✔
1.1.14 B ✔
1.1.15 A ✔
1.1.16 A ✔
1.1.17 B ✔
1.1.18 D ✔
1.1.19 D ✔
1.1.20 D ✔ (20 × 1) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 malaria ✔
1.2.2 IDP ✔
1.2.3 TB ✔
1.2.4 visa ✔
1.2.5 bilharzia ✔ (5 × 1) (5)
1.3
1.3.1 Ayers Rock ✔
1.3.2 Alcázar of Segovia ✔
1.3.3 Petra ✔
1.3.4 Mecca ✔
1.3.5 Mount Fuji ✔ (5 × 1) (5)
1.4
1.4.1 D ✔
1.4.2 A ✔
1.4.3 C ✔
1.4.4 E ✔
1.4.5 B ✔ (5 × 1) (5)
1.5
1.5.1 E ✔
1.5.2 D ✔
1.5.3 F ✔
1.5.4 C ✔
1.5.5 B ✔ (5 × 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 40
SECTION B: MAP WORK AND TOUR PLANNING; FOREIGN EXCHANGE
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1
- Rio de Janeiro -3
- Paris, France +1 (+ 1 hour DST ✔ = +2)
- Time difference: 5 hours ✔
- Time in Rio de Janeiro 20:00 + ✔ 5 hours = 01:00 ✔ on 6 August
- 2016 ✔
OR - 01:00 ✔✔✔✔ on 6 August 2016✔
Note: Award marks if candidate adds DST correctly at the end of the calculation. Same answer will be reached (5)
2.1.2
- Increased daytime hours can lead to increased productivity. ✔
- Businesses have more daytime hours in which to accomplish their tasks.
- DST leads to an increase in leisure hours. Tourists can therefore enjoy more daytime activities. (1)
2.1.3
- Rio de Janeiro -3
- Sydney, Australia +10
- Time difference: 13 hours ✔
- Time in Rio de Janeiro 20:00 + ✔13 hours = 33:00
- 33:00 – 24hours = 09:00 ✔ on 6 August 2016 ✔
OR - 09:00 ✔✔✔ on 6 August 2016 ✔ (4)
2.1.4
-
- Johannesburg +2
- Rio de Janeiro -3
- Time difference: 5 hours ✔
- Time in Rio de Janeiro on arrival of flight O66152:
- 19:55 + ✔5 hours = 00:55 ✔ (01/08)
- 00:55 – ✔ 13h 45m = 11:15 ✔ on 31 July ✔
OR - 11:15 ✔✔✔✔✔on 31 July ✔ (6)
-
- Tiredness ✔
- Dehydration ✔
- Leg and feet discomfort
- Swollen legs and feet
- Irritability
- Interrupted sleep
- Sense of laziness
- Headaches
- Dry skin
- Irritated nasal passages
- Nausea
- Insomnia
- Constipation
- Diarrhoea (2 × 1) (2)
2.1.5
- Passport: a document issued by a national government that certifies the identity (name, date of birth, gender and place of birth) and nationality of its holder. ✔✔
Note: Award marks in candidate adds DST correctly at the end of the calculation. Same answer will be reached.
Visa: a stamp endorsed in the applicant’s passport giving the holder permission to travel to, enter, transit or remain in a foreign country. ✔✔ (4) - Yellow fever vaccination ✔ (1)
2.1.6
- Duty free shop: Retail outlets located at points of exit from a country (e.g. international airports) that are exempt from the payment of certain taxes and duties, on the requirement that the goods sold will be sold to travellers who will take them out of the country. ✔✔ (2)
- He should have gone through the green channel. ✔ (1)
2.2
2.2.1 Yes.
- The tour includes transport, accommodation and meals in the quoted price. ✔✔
Note: Do not award marks for ‘yes’, only for motivation. (2)
2.2.2
- Adventure tourist ✔
- Tourist interested in photography
- Cultural tourist
- Nature lover (1)
2.2.3 Items that are included in the quoted price and are not charged extra for. ✔ (1)
2.2.4
- Camping clothes ✔
- Warm jacket ✔
- Hat
- Sunscreen
- Camera
- Camping equipment
Note: Accept any suitable answer (2 × 1) (2)
[32]
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1
- ZAR 15 000 ÷✔ 14,46✔ = USD/ US$ 1037,34 ✔
OR - USD/US$ 1037,34 ✔✔✔ (3)
3.1.2
- ZAR 25 000 ÷ ✔19,34 ✔= GBP 1292,66 ✔
OR
GBP 1292,66 ✔✔✔ (3) - GBP 20 × ✔18,63 ✔ = ZAR 372,60 ✔
OR
ZAR 372,60 ✔✔✔ (3) - Euro ✔/€ (1)
3.2 A weak rand means that inbound tourists get more rand for their foreign currency and therefore have more money to spend while in South Africa. From an inbound tourism perspective it is thus advantageous if the rand is weak. ✔✔ A weak rand means that South Africans get less foreign currency for their rand should they exchange their rand and therefore will have less foreign currency when they leave the country. Fewer South Africans will be able to travel and they will have less foreign currency. ✔✔ (2 × 2) (4)
3.3 The multiplier effect is when money, spent by tourists, filters down through the economy benefitting other organisations. ✔✔
This money will benefit tourism related businesses as they are the receivers of the revenue that is spent by tourists. They will, in turn have more money/ income/profit. ✔✔ (2 × 2) (4)
[18]
TOTAL SECTION B: 50
SECTION C: TOURISM ATTRACTIONS; CULTURAL AND HERITAGE TOURISM; MARKETING
QUESTION 4
4.1
4.1.1
- – The Algarve ✔✔
- – Swiss Alps ✔✔ / Jungfrau-Aletsch
- – Berlin Wall ✔✔
- – Auschwitz ✔✔ (4 × 2) (8)
4.1.2 The Algarve is known for its pleasant climate, dramatic coastline, beautiful beaches, and offers visitors a variety of opportunities for outdoor activities and sightseeing. ✔✔ (2)
4.1.3
- ∙
- To gain a greater understanding of the impact that the Berlin Wall had on the residents of a divided Berlin. ✔✔
- To witness the remaining sections of the Berlin Wall which symbolized the division between democracy and communism during the Cold War.
Note: Accept any appropriate examples. (2)
-
- To gain a greater understanding of the cruel acts against human beings that were committed at Auschwitz during the Second World War. ✔✔
- To learn about the Holocaust and the Nazi German genocide programme.
Note: Accept any appropriate examples. (2)
4.2
4.2.1
- Fraud ✔ (1)
-
- uShaka Marine World could have suspended the CEO. ✔✔
- uShaka Marine World could have appointed an acting CEO. (2)
4.2.2
-
- 120 trees planted at schools during Arbour Week ✔✔
- 700 hours spent on animal rehabilitation (2)
-
- Selling uShaka Marine World kiddies clothing range. ✔✔
- Hosting homeless children to celebrate Mandela Day. (2)
4.2.3
- The award will influence tourists from China, Japan, Korea, Mongolia, and other Asian countries to visit uShaka Marine World which will improve the attraction’s financial performance. ✔✔ (2)
4.2.4
- It will encourage repeat visits. ✔✔
- Visitors will receive value for their money. ✔✔
- It will lead to positive word-of-mouth advertising. ✔✔
- It will lead to visitor satisfaction.
- It will address seasonality.
- The actual visitor numbers will exceed the target numbers.(3 × 2) (6)
[29]
QUESTION 5
5.1
- – Mapungubwe Cultural Landscape ✔
- – Cape Floral Region ✔/Cape Floral Region Protected Areas (2 × 1) (2)
5.2
5.2.1 Cultural site ✔ (1)
5.2.2
- The people living in Mapungubwe were affected by climate change and moved away from the area. ✔✔
- The area shows evidence of the growth and decline of the Kingdom of Mapungubwe. (2)
5.3
5.3.1
- Fynbos ✔✔
- Proteas (2)
5.3.2
- Invasive species reproduce rapidly and invade large areas of the site which will threaten the continued existence of the fynbos. ✔✔
- Invasive species compete with indigenous plants for water and light.
- Invasive species will disturb the natural balance of the Cape Floral Region.
- If the Cape Floral Region is overrun by invasive species, millions of rand in tourism revenue will be lost which will also have a direct negative impact on job creation. (2)
5.4
- The sites receive national and international recognition which will result in an increase in visitor numbers. ✔✔
- An increase in tourist numbers will lead to the creation of job opportunities due to increased demand for services.
- Tourism will generate income due to a demand for products and services e.g. accommodation, transport, entry fees, food, drink, etc.
- Increased visitor numbers will set the multiplier effect into motion. ∙ Standards of living will be improved through money directly or indirectly earned by tourism.
- There will be a boost in the economic activity lending itself to increased GDP and benefiting all establishments in the area. (2 × 2) (4)
[13]
QUESTION 6
6.1
- It can create an interest amongst Germans about South African cuisine that will lead to a greater awareness of South Africa as a travel destination. ✔✔
- It can lead to an increase in the volume of foreign arrivals from Germany. ✔✔
- It could lead to positive word of mouth about South Africa as a travel destination.
- Creates a positive image of South Africa.
- Increases the possibility of considering South Africa as an attractive destination of choice. (2 × 2) (4)
6.2
- TOMSA is a private sector initiative created to raise additional funds for marketing South Africa internationally. ✔✔
- TOMSA collects a 1% Tourism Levy, voluntarily paid by customers, from participating tourism businesses e.g. tour operators, car rental companies and accommodation establishments. ✔✔
- The Tourism Business Council of South Africa (TBCSA) administers TOMSA and transfers the collected funds to S.A. Tourism for international marketing, including Germany. (2 × 2) (4)
[8]
TOTAL SECTION C: 50
SECTION D: TOURISM SECTORS; SUSTAINABLE AND RESPONSIBLE TOURISM
QUESTION 7
7.1
- Professional appearance and uniforms all contribute to a professional image of a tourism business as they project the company’s image. ✔✔
- These can help make a good first impression and make it easy to identify staff.
- Professional image can instil confidence in the company.
- Personal hygiene and grooming are just as important as dress/uniform and reflect the image of the company. (2)
7.2
- Slogan of the company ✔
- Website ✔
- Company stationery
- Marketing material
- Physical appearance of the offices/airplanes
- Environmental policies
- Customer service policies (2 × 1) (2)
7.3
7.3.1
- A contract of employment protects the employee in the workplace ✔✔
- An employment contract outlines all the main terms and conditions of employment
- It stipulates exactly what is expected of the employee in the workplace
- A contract explains the core duties of the employee together with the working hours, uniform allowances, benefits, remuneration, leave benefits, etc.
- A contract ensures that there is no misunderstanding between the employee and employer regarding employment issues. (Any ONE) (2)
7.3.2 A contract of employment describes basic conditions of employment, such as:
- working hours ✔
- uniform allowances ✔
- travel benefits
- leave
- core duties
- fringe benefits
- remuneration and deductions
- termination of service
- professional accountability and responsibility
- service ethics (2 × 1) (2)
7.4 A code of conduct sets out what is important to a business (its ethics and principles) and prescribes how staff should behave while at work. ✔✔ It helps to identify and state clearly which behaviour is welcome and which is not.
It provides the staff with guidelines regarding creation of a co-operative, collaborative atmosphere and promotion of integrity in the workplace. (2)
[10]
QUESTION 8
8.1
8.1.1 Environmental pillar:
- Lion Sands is committed to the conservation of African wildlife and the environment. ✔✔
- They attempt to maintain a balance between nature and its use for commercial purposes.
- Their ecosystems are carefully monitored and managed. (2)
Social pillar:
- Lion Sands is committed to the development of local communities. ✔✔
- They partake in social upliftment programs to assist the community. (2)
(Note: Candidates can give an example)
8.1.2
- Lion Sands could assist members of the local population to share ownership of the game reserve. ✔✔
- They could employ people from the local population.
- They could ensure that procurement of local goods and services takes place.
- They could ensure that they pay fair wages. (2)
8.2 An attraction wanting to practice responsible tourism can provide tourists with information on how to be socially and culturally responsible which may include:
- Information on the cultural, ethnic, religious, and heritage practices ✔✔
- An overview of the history of the area and the business itself ✔✔
- Guidance on appropriate dress, behaviour, food and drink
- Information on behaviour during ceremonies
- Information on crime and how to stay safe as well as crime hotlines
Information on how to benefit the local economy may include:
- Products that are made locally and where to buy these products
- Appropriate tipping practices
- Prices that should be paid at markets and whether to bargain with local traders
- Fair trade or other ethical certification schemes operating in the area
- Any local economic initiative the business supports
Tourism businesses should give visitors information regarding conservation of the environment, such as:
- Limiting water and energy use at the property
- Recycling
- Indigenous species found in the area
- Interesting features of the local ecosystem
- Guidance on protecting nature, such as staying on marked paths
- Any environmental initiatives the business supports in the area (2 × 2) (4)
8.3
- Market the destination according to its sustainability ethos using environmentally conscious marketing platforms. ✔✔
- Introduce strategies to ensure businesses are sustainable and that they act responsibly towards people, the planet and the economy. ✔✔
- Ensure that natural assets are well protected and marketed.
- Accept socio-economic strategies for residents.
- Implement sustainable tourism certification among destination businesses.
- Ensure that public sites and facilities set good examples in terms of environmental, social and economic practices.
- Encourage joint socio-economic and environmental programmes at the destination to which tourists can contribute.
- Do research about the target market in order to understand their needs, wants and expectations.
- Ensure that products the local community produce are exposed to the tourists.
- Businesses should ensure that government policies supporting sustainable and responsible tourism are followed. (2 × 2) (4)
8.4
8.4.1
- Corporate social investment refers to the support businesses give to the communities they operate in. ✔✔
- Support can be financial or can take the form of infrastructure or socio-economic support programmes. (2)
8.4.2 Henna Pre-School:
- One of the initiatives funded by Lion Sands is the Henna Pre-School that was founded in 1991 with 20 pupils and has now grown to 250 pupils. This met with the need for education and healthy meals for the local children. ✔✔
- Some of the major projects thus far have been the construction of classrooms, renovation of the kitchen and setting up borehole water for the school.
- Lion Sands also hosts the annual graduation ceremony for the children, which encourages them to understand the importance of knowledge and education. (1 × 2) (2)
HIV initiatives:
- The reserve provides support to its employees as well as to a local home based care initiative for HIV sufferers. ✔✔
- Guests at Lion Sands are given an option to tour the local community and are encouraged to make a donation to this worthy cause.
- Lion Sands is also involved in the annual activities held on World Aids Day in which HIV orphans and other vulnerable children from the community are given food parcels and school necessities. (1 × 2) (2)
Note: Candidate must mention TWO initiatives, 2 marks allocated for each.
[20]
TOTAL SECTION D: 30
SECTION E: DOMESTIC, REGIONAL AND INTERNATIONAL TOURISM; COMMUNICATION AND CUSTOMER CARE
QUESTION 9
9.1
9.1.1
- The Tour de France is a cycling event involving people from different countries around the world e.g. cyclists, spectators, media and sponsors. ✔✔
- It attracts the interest of people all over the world. (2)
9.1.2
- Millions of spectators are able to view the event from the roadside without paying. ✔✔
- The event is broadcast internationally on radio and television providing listeners and viewers with a detailed review of the event. ✔✔ (2 × 2) (4)
9.1.3 The event organisers distribute 100 000 recyclable trash bags along the route of the Tour de France to reduce pollution. ✔✔ (2)
9.1.4
-
- During the event revenue is generated in the cities through tourism-related activities e.g. accommodation, transport, food and drink, shopping, souvenirs, entertainment and other tourism-related products and services. ✔✔ (2)
-
- Employment related to the Tour de France will include jobs in the accommodation sector and catering services. ✔✔
- Employment opportunities will be created in the supply of goods and services necessary to run the Tour de France e.g. refuse collection and security along the route.
- Employment opportunities will be created in preparation for the event e.g. upgrading of facilities and infrastructural development in the host cities.
- The Tour de France provides opportunities for individuals who want to start their own event-related businesses. (2)
9.2
9.2.1 Central and South America ✔ (1)
9.2.2
- Health concerns regarding communicable diseases e.g. Ebola. ✔✔
- The introduction of stricter South African visa requirements. ✔✔
- Introduction of additional travel requirements for minors.
- Concerns about safety and xenophobic attacks.
- Economic recession in certain countries e.g. Brazil and Russia.
- Global security concerns that were linked to terrorism such as aircraft hijackings. (2 × 2) (4)
9.3
- All the activities, except wildlife, business-related activities and adventure activities showed a decline in 2015 compared to 2014. ✔✔
- The three most popular activities, shopping, social activities and nightlife showed a decline in 2015 compared to 2014. (2)
[19]
QUESTION 10
10.1
- Web-based response ✔
- On-line feedback
- Electronic communication (1)
10.2 Potential customers will be able to see other customers’ comments and make a decision based on the positive and negative comments. ✔✔ (2)
10.3
- The average sentiment based on 290 customer reviews scored 2.7 out of 10 ✔✔ and this suggests that the Ocean Fresh Restaurant provides poor customer service. ✔✔
- The majority of customers have experienced poor service at the Ocean Fresh Restaurant and this suggests that the Ocean Fresh Restaurant delivers poor service. (2 × 2) (4)
10.4
- Staff should be sent for regular training courses to improve service delivery skills. ✔✔
- Training methods should be adopted to improve the speed of service, accuracy of orders and the quality of food. ✔✔
- Staff should be trained on ways to improve time management skills
- The business should respond to feedback from customers
- Implement continuous training and supervision from managers
- Employ more staff
- Follow disciplinary procedures on staff not delivering good service
- Offer incentives to employees to maintain good work ethics. (2 × 2) (4)
[11]
TOTAL SECTION E: 30
GRAND TOTAL: 200
LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 12 PAPER 2 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
LIFE SCIENCES
GRADE 12
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Write ALL the answers in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start the answer to EACH question at the top of a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Present your answers according to the instructions of each question.
- ALL drawings MUST be done in pencil and labelled in blue or black ink.
- Draw diagrams, flow charts or tables ONLY when asked to do so.
- The diagrams in this question paper are NOT necessarily drawn to scale.
- Do NOT use graph paper.
- You must use non-programmable calculator, protractor and a compass, where necessary.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the correct answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 During which phase of meiosis do homologous chromosome pairs separate?
- Metaphase I
- Anaphase I
- Anaphase II
- Telophase II
1.1.2 A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides on a molecule of …
- rRNA.
- mRNA.
- tRNA.
- DNA.
1.1.3 Which of the following distinguishes prophase 1 of meiosis from prophase of mitosis?
- Homologous chromosomes pair up
- Spindle forms
- Nuclear membrane breaks down
- Chromosomes become visible
1.1.4 Scientists recovered the body of a woolly mammoth from the frozen soil of Siberia. The DNA sequence of the woolly mammoth was very similar to the DNA sequence of the African elephant. Which of the following is a conclusion for this data?
- The woolly mammoth and African elephant have a common ancestor
- The woolly mammoth is not related to the African elephant
- The woolly mammoth has the same number of chromosomes as the African elephant
- The woolly mammoth and the African elephant should be classified as the same species
1.1.5 DNA was analysed and found to contain 14% T (thymine). What percentage of the molecule is cytosine?
- 14%
- 28%
- 36%
- 72%
1.1.6 Which one of the following statements is a correct description of a hypothesis and a theory?
- An accepted theory becomes a hypothesis
- An accepted hypothesis becomes a theory
- Hypotheses and theories are different names for the same concept
- Theories can be tested experimentally, whereas hypotheses cannot
1.1.7 An extra finger in humans is rare, but is due to a dominant gene. When one parent is normal and the other parent has an extra finger but is homozygous for the trait, what is the chance that their children will be normal?
- 0%
- 25%
- 50%
- 75%
1.1.8 Which ONE of the following correctly describes the ploidy and number of cells produced at the end of meiosis?
PLOIDY | NUMBER OF CELLS | |
A | haploid | two |
B | haploid | four |
C | diploid | two |
D | diploid | four |
1.1.9 Scientists visiting a group of four islands P, Q, R and S found similar spiders on each island. They carried out investigations to see if the spiders from the different islands belonged to the same species.
The results are in the table below (✔ indicates successful interbreeding. X indicates unsuccessful interbreeding)
| Spiders from | ||||
| P | Q | R | S | |
P | ✔ | ✔ | X | X |
Q | ✔ | ✔ | X | X |
R | X | X | ✔ | X |
S | X | X | X | ✔ |
Which two populations belong to the same species?
- Q and R
- R and S
- Q and S
- P and Q
1.1.10 A gene in a bacterium codes for a protein that has 120 amino acids. How many mRNA nucleotides code for this protein?
- 30
- 40
- 360
- 480 (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Give the correct BIOLOGICAL TERM for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.10) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 The analysis of DNA samples to identify individuals or relationships between individuals
1.2.2 The nitrogenous base found in RNA but not in DNA
1.2.3 The division of the cytoplasm after a cell nucleus has divided
1.2.4 The organelle where protein synthesis occurs
1.2.5 A sugar that is a component of DNA
1.2.6 The preserved remains of ancient organisms
1.2.7 The different forms of a gene
1.2.8 The death of the last individual of a species
1.2.9 Having a face with protruding jaws
1.2.10 Position of a gene on a chromosome (10 x 1) (10)
1.3 Indicate whether each of the descriptions in COLUMN I applies to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A AND B or NONE of the items in COLUMN II. Write A only, B only, both A and B or none next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.3) in the ANSWER BOOK.
COLUMN I | COLUMN II |
1.3.1 Evidence of evolution |
|
1.3.2 Identical alleles for a trait |
|
1.3.3 Discovery of DNA |
|
(3 x 2) (6)
1.4 The table below shows some events which take place during protein synthesis.
A | tRNA molecules bring specific amino acids to the mRNA molecule |
B | mRNA nucleotides join with exposed DNA bases and form a molecule of mRNA |
C | The two strands of a DNA molecule separate |
D | Peptide bonds form between the amino acids |
E | The mRNA molecule leaves the nucleus |
F | A ribosome attaches to the mRNA molecule |
1.4.1 Write the letters to show the correct sequence of these events. (2)
1.4.2 In which structure of the cell does process C take place? (1)
1.4.3 Give the letters (A–F) only of those events that are associated with translation. (3)
1.4.4 The table below shows some mRNA codons and the amino acids for which they code.
mRNA codon | Amino acid |
GUU | Valine |
CUU | Leucine |
GCC | Alanine |
AUC | Isoleucine |
GAA | Glutamic acid |
ACC | Threonine |
Give the DNA base sequence that codes for threonine. (1)
1.4.5 A tRNA molecule has the anticodon GAA. Which amino acid does the tRNA molecule carry? (1)
1.5 Mice may have white fur or black fur. The diagram shows the inheritance of fur colour in mice. 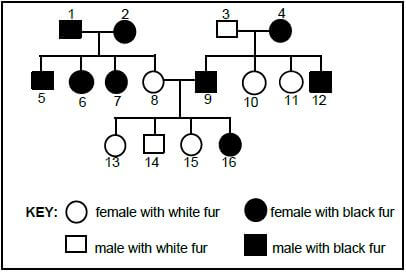
1.5.1 What is this diagram called? (1)
1.5.2 How many sets of parents are represented in this diagram? (1)
1.5.3 Give the phenotype:
- Which is dominant (1)
- Of individual 9 (1)
1.5.4 Use the letter A for the dominant allele and a for the recessive allele to give the genotype of:
- 8 (1)
- 16 (1)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1 The diagram below is a representation of the chromosomes in a human cell.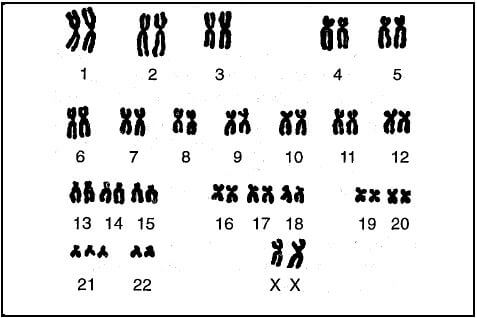
2.1.1 How many autosomes are in this cell? (1)
2.1.2 This individual is a female. Explain why this conclusion is made. (1)
2.1.3 What evidence is there to show that this individual has a genetic disorder? (1)
2.1.4 Identify the genetic disorder mentioned in QUESTION 2.1.3. (1)
2.1.5 Name the process that resulted in this genetic disorder. (1)
2.2 Describe the process whereby a copy of a DNA molecule is made. (7)
2.3 Humans have different blood groups which are coded for by a number of alleles.
Mary has the genotype IAi and her son Joseph has blood type AB.
2.3.1 How many alleles code for blood groups? (1)
2.3.2 Give:
- Mary’s blood group (1)
- Joseph’s genotype (1)
- All the possible genotypes of Joseph’s father (3)
2.4 In cats the allele for short hair is dominant (H) to the allele for long hair (h).
A short-haired cat that is heterozygous is crossed with a long-haired cat. Use a genetic cross to determine the percentage chance of the offspring being heterozygous for hair length. (6)
2.5 The European Corn Borer (ECB) worm is a pest which reduces crop yield of corn on farms. The soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) contains a gene which causes the production of a poison which kills the ECB worm.
In an effort to control the ECB worm, scientists incorporated the Bt poison gene into a corn plant resulting in corn plants that produce the same poison.
They wanted to investigate if using the Bt corn would increase crop yields.
The scientists conducted the investigation as follows:
- They planted Bt corn in one field and non Bt corn in another field (the environmental conditions for the two fields were exactly the same)
- The European Corn Borer was introduced into the fields
- The plants were grown and harvested after a period of five months
- The average yield of plants was recorded
- The experiment was repeated four times and an average was calculated. The results are shown in the table below.
TABLE SHOWING THE AVERAGE YIELD OF DIFFERENT VARIETIES OF CORN PLANTS
Average crop yield (bushels per acre) | |
Corn variety | With ECB |
non Bt | 146 |
Bt corn | 158 |
2.5.1 Name the process by which the Bt gene is inserted into corn to make Bt corn. (1)
2.5.2 State the hypothesis of this investigation. (2)
2.5.3 State the:
- Independent variable (1)
- Dependent variable (1)
2.5.4 Describe ONE way in which the reliability was ensured in this investigation. (1)
2.5.5 State the conclusion for this investigation. (2)
2.5.6 Explain ONE benefit to a farmer of using Bt corn. (2)
2.5.7 On the same set of axes, draw a bar graph to show the average crop yield of the two varieties of corn plants. (6)
[40]
QUESTION 3
3.1 Use the diagrams below of a cell process to answer the following questions.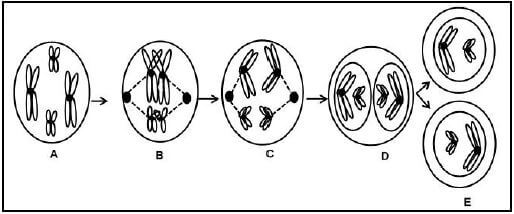
3.1.1 Name the process represented by the diagrams above. (1)
3.1.2 Give TWO reasons for your answer in QUESTION 3.1.1. (2)
3.1.3 Identify the phases labelled C and D. (2)
3.2 A population of insects was treated with an insecticide from the year 1995 to 1998. The percentage that were resistant to the insecticide was calculated.
The table below shows data from an insect population in 1995 and 1998.
| CHANGE IN AN INSECT POPULATION'S RESISTANCE TO INSECTICIDE | ||
Characteristic | Percent of population in 1995 | Percent of population in 1998 |
resistant | 0,15 | 99,1 |
not resistant | 99,85 | 0,9 |
3.2.1 Describe the changes in the insect population between 1995 and 1998. (3)
3.2.2 Describe how natural selection caused insecticide resistance in this population. (6)
3.3 The diagram below shows an evolutionary process taking place in a population of salamanders in California. The process took place gradually, millions of years ago. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow. 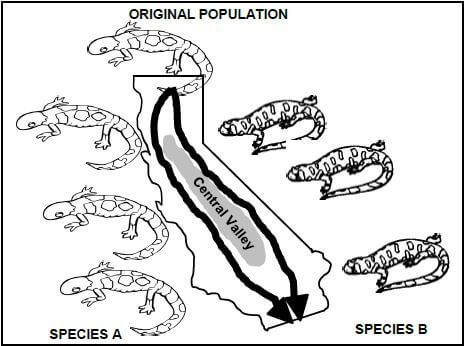
3.3.1 What evolutionary process is illustrated in the diagram above? (1)
3.3.2 Use the diagram to explain how the Species B evolved from the original population. (6)
3.3.3 Explain why this is not an example of punctuated equilibrium. (3)
3.4 The following diagrams show the pelvis and skulls of three organisms, Australopithecus, a gorilla and a modern human in no particular order. 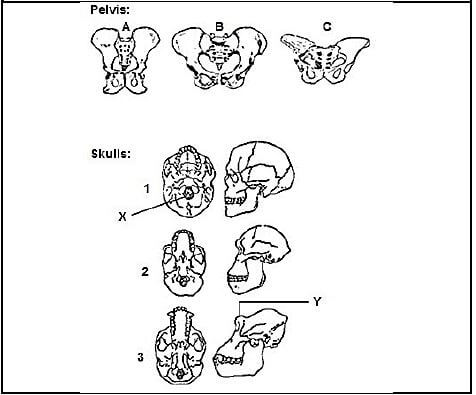
3.4.1 Give the number only of the skull belonging to the pelvis:
- A (1)
- B (1)
- C (1)
3.4.2 Give the LETTER of the pelvis and the NUMBER of the skull of the organism which is bipedal most of its adult life. (2)
3.4.3 Tabulate TWO anatomical differences between skulls 1 and 3 with respect to labels X and Y. (5)
3.4.4 List ONE feature of the teeth of skull 3. (1)
3.4.5 Explain how mitochondrial DNA is used to support the “Out of Africa” hypothesis. (5)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
Describe the mechanisms that cause variation within a species. (17)
Synthesis (3)
NOTE: NO marks will be awarded for answers in the form of flow charts, tables or diagrams.
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150
LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 12 PAPER 1 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
LIFE SCIENCES
GRADE 12
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Write ALL the answers in your ANSWER BOOK.
- Start the answers to EACH question at the top of a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Present your answers according to the instructions of each question.
- ALL drawings must be done in pencil and labelled in blue or black ink.
- Draw diagrams, flow charts or tables ONLY when asked to do so.
- The diagrams in this question paper are NOT necessarily drawn to scale.
- Do NOT use graph paper.
- You must use a non-programmable calculator, protractor and a compass where necessary.
- Write neatly and legibly.
- Round off all calculations to two decimals after the comma.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Write down the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) and choose the answer by writing the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 Before copulation the male sperm is stored temporarily in the …
- seminal vesicles.
- scrotum.
- prostate gland.
- epididymis.
1.1.2 An increased growth of algae due to too many nutrients in the water is known as …
- bleaching.
- eutrophication.
- ionisation.
- leaching.
1.1.3 The photoreceptors stimulated by dim light:
- Lens and rods
- Rods and cones
- Cones only
- Rods only
1.1.4 The average length of human gestation (from fertilisation to birth) is …
- 280 days.
- 310 days.
- 20 days.
- 210 days.
QUESTION 1.1.5 AND QUESTION 1.1.6 REFERS TO THE DIAGRAM BELOW. THE DIAGRAM REPRESENTS THE HUMAN BRAIN AND PART OF THE SPINAL CORD.
1.1.5 Which part of the brain is associated with balance and co-ordinating muscle movement?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
1.1.6 Which part controls rate of breathing and heartbeat?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
1.1.7 During the development of the embryo the function of the amnion is to …
- serve as reserve food.
- give rise to the placenta.
- prevent the developing foetus from moving about.
- hold the fluid which protects the embryo against injury.
1.1.8 Which ONE of the following features of genetically modified crops has the potential of improving food security?
GM crops …
- increase the number of alien plant species.
- increase yield.
- increase the reliance on pesticides.
- decrease genetic diversity.
1.1.9 Parents will often tell children NOT, for even a few minutes, to stare at the sun because …
- bright light causes damage to the retina.
- the bright light will damage the lens.
- it dries out the aqueous humour.
- the light energy changes to heat energy in the eye.
1.1.10 One of the functions of hormone, progesterone, is to …
- prepare the uterine wall for implantation of the embryo.
- speed up the development of the follicles.
- bring about the formation of the corpus luteum.
- stimulate the secretion of sweat. (10 × 2) (20)
1.2 Give the correct biological term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.10) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 A process by which a molecule of DNA forms a copy of itself
1.2.2 The structure in the head of a sperm cell that contains enzymes which break down the membrane surrounding the ovum
1.2.3 The division of cytoplasm during the process of meiosis
1.2.4 A change in the internal or external environment that will be detected by a receptor and converted into an impulse
1.2.5 The replanting of trees and shrubs in a forest
1.2.6 The hormone which is responsible for development of secondary sexual characteristics in males
1.2.7 A layer of earth or rock that holds water
1.2.8 Structures found only in animal cells and lower plant cells that form the spindle during cell division
1.2.9 Process by which a region becomes progressively drier and drier
1.2.10 That part of the nervous system which consists of cranial and spinal nerves (10 × 1) (10)
1.3 Indicate whether each of the statements in COLUMN І applies to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A and B or NONE of the items in COLUMN ІІ. Write A only, B only, Both A and B or None next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.3) in the ANSWER BOOK.
COLUMN І | COLUMN ІІ | |
1.3.1 | A method of reproduction in which young develop inside the mother’s body attached by an umbilical cord |
|
1.3.2 | Young are helpless at birth or hatching and require parental care for a period of time |
|
1.3.3 | Fertilisation where the presence of water is essential to take place |
|
(3 × 2) (6)
1.4 Study the diagram below of a cell division process and answer the questions: 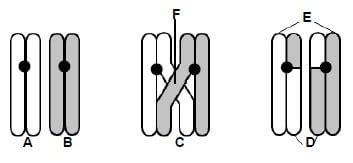
1.4.1 Name:
- The type of cell division (mitosis or meiosis) in which this process takes place (1)
- The process taking place at C (1)
- The phase in which the process mentioned in QUESTION 1.4.1(b) takes place (1)
- The structure that holds the two chromatids together (1)
- The region marked F (1)
- The phase that follows the phase represented in the diagrams above (1)
1.4.2 Identify ONE observable feature which indicates that chromosome pair A and B above are regarded as homologous. (1)
1.5 The photo below is one of a dump site. Answer the questions that follow:
1.5.1 What type of dump site is shown by the photo? (1)
1.5.2 Name a useful gas that may be obtained from this type of dump site. (1)
1.5.3 Give ONE use of the gas mentioned in QUESTION 1.5.2. (1)
1.5.4 State the name of the process where products from this dump site are collected to be re-used again. (1)
1.5.5 Name ONE of the waste components that cannot be decomposed by natural methods. (1)
1.5.6 Give the collective name given to gases causing global warming. (1)
1.5.7 Identify a health risk that poor management of this dump site can have on the community living close by. (1)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1 The diagram shows two eyes (X and Y) focused on objects (represented by arrows) at different distances from the eye. Objects A and C were 3 metres away from the eye. Objects B and D were 8 metres away from the eye.
NB: The diagrams are not drawn to scale
2.1.1 Write down the LETTER ONLY of the object that:
- Eye Y is focused on (1)
- Eye X is focused on (1)
2.1.2
- Name the eye defect which results from the inability of the Eye Y to focus on Object D. (1)
- Name the type of lens used to rectify the defect mentioned in QUESTION 2.1.2(a). (1)
2.1.3 Name and describe the process that allows Eye Y to form a clear image on the retina. (5)
2.2 The diagram below shows a certain section of the human alimentary canal.
The blood glucose level is regulated to a range of 70–110 mg per 100 mℓ blood in a normal person. If it rises above this level for an extended period the person may have diabetes mellitus.
2.2.1 Name the chemical substance secreted by the pancreas that will ensure that the glucose level in a healthy person is not higher than 110 mg per 100 mℓ blood. (1)
2.2.2 Explain how the malfunctioning of the pancreas will affect the maintenance of the correct level of glucose in the blood. (3)
2.2.3 Explain the possible negative influence on the body cells if the glucose level is above 110 mg per 100 mℓ blood for a long time. (2)
2.3 A Grade 12 learner performed an investigation to determine the effect of light on the growth of plant shoots. The learner divided the plants that were used into three groups as follows:
- Group A The tip of the shoot was intact.
- Group B The tip of the shoot was removed.
- Group C The tip of the shoot was covered by a cap that does not allow light to pass through.
The diagram in each group (A, B and C) below shows each shoot at the start of the investigation and next to each, the same shoot at the end of the investigation.
The arrows indicate the direction to which each of the shoots A, B and C were exposed. 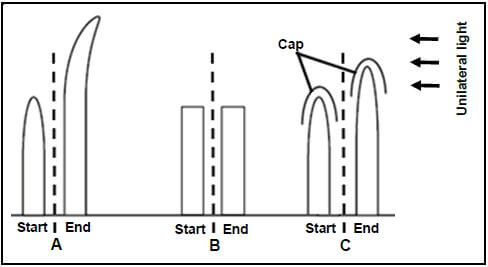
2.3.1 Name the dependent variable in this investigation. (1)
2.3.2 Which plant hormone is being investigated in this experiment? (1)
2.3.3 State TWO factors that must be kept constant during this investigation. (2)
2.3.4 Explain the results observed in:
- investigation A (3)
- investigation C (3)
2.3.5 State TWO ways in which the learner could improve the reliability of this investigation. (2)
2.4 The diagram below shows a reflex action.
2.4.1 Identify parts:
- A (1)
- E (1)
2.4.2 State ONE the function of each part:
- B (1)
- C (1)
2.4.3 Explain why the brain is not initially involved in a reflex action shown above. (3)
2.4.4 Explain what the effect will be, in the action shown in the diagram above, if a person is suffering from multiple sclerosis. (2)
2.4.5 Explain the effect on the body if the part labelled D is cut/severed. (4)
[40]
QUESTION 3
3.1 The diagram below shows the development of an ovum in an ovary of a female. 2n and n refer to the chromosome number (2n is diploid and n is haploid).
| |
3.1.1 Name the processes taking place at:
- A (1)
- B (1)
3.1.2 Explain the effect on the ovarian cycle shown above if a contraceptive containing progesterone is injected before the cycle starts. (3)
3.1.3 Describe the changes that occurs from 1 to 2 in the diagram under the influence of hormones. (6)
3.2 Records of human fertility for the period 1941 to 1990 have shown changes in the sperm count of normal men. The table below summarises the changing percentages of men with high or low sperm count over a period of 50 years.
TIME PERIOD | MEN WITH HIGH SPERM COUNT (%) | MEN WITH LOW SPERM COUNT (%) |
1941–1950 | 50 | 4 |
1951–1960 | 45 | 5 |
1961–1970 | 28 | 11 |
1971–1980 | 21 | 14 |
1981–1990 | 15 | 18 |
3.2.1 During which time period was there:
- The highest percentage of men with low sperm count (1)
- The lowest percentage of men with high sperm count (1)
3.2.2 Calculate the percentage increase of men with low sperm counts from 1971 to 1990. (2)
3.2.3 Draw a bar graph to show the percentages of men with a high sperm count for the period indicated in the table. (6)
3.3 The diagram below shows the longitudinal section of a human ear. 
3.3.1 Give the letter of the part that absorbs extra pressure/vibration set up in the cochlea. (1)
3.3.2 A surgeon place a tube called a “grommet” into the structure marked A. Once in place the child should not go swimming. Explain this instruction. (2)
3.3.3 Explain the significance of the positions of the structures labelled B. (3)
3.3.4 Name the tube connecting the middle ear to the throat and explain what role it plays regarding pressure in the ear. (2)
3.4 Study the extract below and answer the questions:
Environmental impact of Acid mine drainage Pyrite is a mineral composed of iron and sulphur that occurs in large quantities in mine dumps. When pyrite is exposed to oxygen and water, it gradually breaks down to form sulphuric acid. The sulphuric acid drains in to ground water to make ground water acidic. |
3.4.1 From the passage, name the mineral found in mine dumps causing ground water to be acidic. (1)
3.4.2 From the passage, describe the formation of acidic water in mines. (2)
3.4.3 Explain how acid mine drainage could affect:
- The infrastructure in a nearby town (2)
- Agricultural production on a nearby farm (2)
3.4.4 Explain why abandoned gold and coal mines could affect food chains in ponds/rivers/dams. (4)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
A marathon runner took only 1 liter of water with him when he set off on a race on a hot day. Describe the changes in his body to try to maintain normal body temperature. Describe the role of the hypothalamus in regulating the water balance of his body.
Content: (17)
Synthesis: (3)
NOTE: No marks will be awarded for answers in the form of a charts or diagrams.
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150
LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 12 PAPER 1 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
LIFE SCIENCES
GRADE 12
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 D ✓✓
1.1.2 B ✓✓
1.1.3 D ✓✓
1.1.4 A ✓✓
1.1.5 B ✓✓
1.1.6 C ✓✓
1.1.7 D ✓✓
1.1.8 B ✓✓
1.1.9 A ✓✓
1.1.10 A ✓✓ (10 × 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 Replication ✓
1.2.2 Acrosome ✓
1.2.3 Cytokinesis ✓
1.2.4 Stimulus ✓
1.2.5 Reforestation ✓
1.2.6 Testosterone ✓
1.2.7 Aquifer ✓
1.2.8 Centrioles ✓
1.2.9 Desertification ✓
1.2.10 Peripheral nervous system ✓ (10 × 1) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 B only ✓✓
1.3.2 B only ✓✓
1.3.3 B only ✓✓ (3 × 2) (6)
1.4
1.4.1
- Meiosis ✓ (1)
- Crossing over ✓ (1)
- Prophase I ✓ (1)
- Centromere ✓ (1)
- Chiasma ✓ (1)
- Metaphase I ✓ (1)
1.4.2 They are the same size and shape ✓ (1)
1.5
1.5.1 Open dump site ✓/landfill site (1)
1.5.2 Methane ✓ (mark first 1 only) (1)
1.5.3 As a source of energy for cooking ✓/heating/lighting/fuel (1)
1.5.4 Recycling ✓ (1) 1.5.5 Glass ✓/plastic (mark first 1 only) (1)
1.5.6 Greenhouse gases (1)
1.5.7 Breeding spot for micro-organisms ✓/insects/rodents that causes diseases (1)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1
- C ✓ (1)
- B ✓ (1)
2.1.2
- Short sightedness ✓/Myopia (1)
- Concave ✓ lens (1)
2.1.3 *Accommodation ✓
- Ciliary muscles contract ✓
- Suspensory ligaments slacken ✓
- Tension on lens decreases ✓
- Lens becomes more convex ✓
- Refractive power of lens increases ✓
- A clear image now forms on the retina ✓
(*Compulsory 1 + any 4) (5)
2.2
2.2.1 Insulin ✓ (1)
2.2.2
- Insufficient amounts or no insulin will be secreted by the pancreas ✓
- and therefore less amounts of glucose will be absorbed by liver and muscle cells ✓
- hence less amount of glucose will be converted to glycogen ✓
- causing an increase in glucose in the blood ✓ (any 3) (3)
2.2.3 Water ✓ will move out/exosmosis of the cells to the blood ✓ results in dehydration✓ of cells leading to underperformance/death of cells. ✓ (any 2) (2)
2.3
2.3.1 Growth of plant shoots ✓ growth response/bending of the tip (1)
2.3.2 Auxins ✓ (1)
2.3.3
- Same environment in which the shoots are placed ✓/same intensity of the light
- Same type of shoot used ✓
- Same age of the shoot ✓ (mark first 2) (any 2) (2)
2.3.4
- In investigation A:
- Light from the right ✓/from one side/unilateral light
- caused auxins to move to shaded side of the shoot ✓
- leading to increased cell elongation and division ✓ on the shaded side/There was therefore greater growth on the shaded side ✓
- thus bending the shoot in the direction of the source of light ✓ (3)
- In investigation C:
- Since there is no light stimulus ✓ from the side (because of the cap) there is no influence on the distribution of auxins ✓/auxins evenly distributed below the cap
- therefore the shoot grew upright ✓ (3)
2.3.5
- Repeat the investigation ✓
- Use more than one plant for each treatment ✓/increase sample size (2)
2.4
2.4.1
- A Ganglion ✓ (1)
- E Effector ✓/muscle (1)
2.4.2
- B Ensures one directional flow of impulses ✓(mark first 1 only) (1)
- C Transmits impulses from sensory neuron to motor neuron ✓ (mark first 1 only) (1)
2.4.3
- Spinal cord shortens reaction time by sending impulses directly to the effector ✓
- If the brain is involved, it delays the reaction ✓
- causing injury or even death ✓ (3)
2.4.4
- The myelin sheath is damaged by multiple sclerosis ✓
- This will cause a slow transmission of impulses ✓
- resulting in slower reaction time✓ which might leads to injury or death ✓ (any 2) (2)
2.4.5
- The person will be able to feel the pain ✓ because the sensory neuron is able to transmit the impulses to the brain ✓ since it is not damaged
- However no reaction will take place ✓
- because of the fact that no impulse will reach the effector ✓ due to the damage to the motor neuron (4) [40]
3.1
3.1.1
- A meiosis✓/oogenesis (1)
- B ovulation✓ (1)
3.1.2
- High level of progesterone in the blood causes the pituitary gland ✓/hypophysis ✓
- to secrete less FSH ✓
- therefore no new Graafian follicles will be formed ✓
- and no ovulation and menstruation will take place ✓ (any 3) (3)
3.1.3
- Under the influence of LH, ✓
- the Graafian follicle ruptures ✓
- and causes ovulation ✓/release of the ovum
- The LH converts the empty Graafian follicle ✓
- into the corpus luteum ✓
- The corpus luteum will secrete progesterone ✓ and
- a little oestrogen. ✓ (any 6) (6)
3.2
3.2.1
- 1981 – 1990 ✔ (1)
- 1981 – 1990 ✓ (1)
3.2.2
- % increase = 4 × 100 = 28,5% ✓ (2)
14✓
3.2.3 
Criteria | Mark Allocation |
Bar graph drawn (T) | 1 |
Title of graph (C) | 1 |
Correct scale for X-axis (equal width and spacing of the bars) and Y-axis (S) | 1 |
Correct label and unit for X-axis and Y-axis (L) | 1 |
Plotting of the bars (P) | 0: No bars plotted correctly |
NOTE:
- If a line graph is drawn – marks will be awarded for the ‘title and label for X and Y axes' only
- If a histogram is drawn – marks will be lost for the ‘type of graph and correct scale’ only (6)
3.3
3.3.1 C ✓ (1)
3.3.2
- If the patient swims after the grommet was put in, water will enter the middle ear rather to drain out ✓
- This will result in water building up in the middle ear ✓/middle ear can’t dry out
- which can result in middle ear infection✓/temporary loss of hearing/middle ear infection can’t be cleared up. (any 2) (2)
3.3.3
- Three semi-circular canals are positioned in different planes ✓
- so that the head movement in any direction ✓
- can be detected ✓/cause liquid in at least one canal to move ✓ and stimulates cristae ✓ (any 3) (3)
3.3.4
- Eustachian tube ✓
- Equalises air pressure on either side of the tympanic membrane so that air pressure does not cause bursting of the tympanic membrane ✓ (2)
3.4
3.4.1 Pyrite ✓ (1)
3.4.2
- Pyrite mineral deposits are exposed to water and oxygen ✓
- which breaks down (weathers), changes to sulphuric acid ✓ and flows out (2)
3.4.3
- Impact on the infrastructure
- The acid content causing the rusting of iron in structure ✓
- causing the weakening of bridges and buildings in that area ✓ (2)
- Impact on the agricultural production
- The pH of the water and soil drops ✓
- which may lead to crop failure ✓
OR - The acid water causing the leaching of essential nutrients out of the soil ✓
- reducing the fertility of the soil ✓ (any 1 × 2) (2)
3.4.4
- The acid water could kill the aquatic organisms ✓
- causing the death of other species depending on them as food source. ✓
- Decomposition of dead organisms causes an increase in CO2 level and decrease in O2. ✓
- The lack of oxygen and food kill remaining organisms in the food chain ✓ (4)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
*Thermoregulation ✓
- When environmental temperature is high ✓
- Receptors ✓ in the skin detects this
- Impulses are send to the Hypothalamus ✓
- Which sent impulses to the blood vessels ✓ in the skin ✓
- These blood vessels become wider✓/dilate/increase in diameter/vasodilation
- More blood flows through the skin ✓
- More heat is therefore lost ✓ from the body
- Through radiation ✓
- The sweat glands ✓
- Produce more sweat ✓
- That evaporates ✓ from the skin’s surface
- Leading to more heat is lost ✓
- Cooling down the body ✓ (*Compulsory 1 + 9) (10)
- Hypothalamus will respond to information received from osmoreceptors ✓
- To release more ADH into the blood ✓
- Higher concentration of ADH increases the permeability ✓
- of the renal tubules✓/distal convoluted and collecting tubules
- Allowing more water to be reabsorbed from the filtrate ✓
- Passing into the surrounding blood capillaries ✓
- Increasing the quantity of water in the blood ✓
- Less urine will be excreted✓/more concentrated (any 7) (7)
ASSESSING THE PRESENTATION OF THE ESSAY
CRITERION | RELEVANCE (R) | LOGICAL SEQUENCE (L) | COMPREHENSIVE (C) |
GENERALLY |
|
|
|
IN THIS ESSAY |
|
|
|
MARK | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Content: (17)
Synthesis: (3)
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150
LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 12 PAPER 2 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
LIFE SCIENCES
GRADE 12
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
PRINCIPLES RELATED TO MARKING LIFE SCIENCES 2017
- If more information than marks allocated is given.
Stop marking when maximum marks are reached and put a wavy line and ‘max’ in the right-hand margin. - If, for example, three reasons are required and five are given. Mark the first three irrespective of whether all or some are correct/ incorrect.
- If whole process is given when only part of it is required.
Read all and credit relevant part. - If comparisons are asked for and descriptions are given.
Accept if differences/similarities are clear. - If tabulation is required but paragraphs are given.
Candidates will lose marks for not tabulating. - If diagrams are given with annotations when descriptions are required.
Candidates will lose marks. - If flow charts are given instead of descriptions.
Candidates will lose marks. - If sequence is muddled and links do not make sense.
Where sequence and links are correct, credit. Where sequence and links are incorrect, do not credit. If sequence and links becomes correct again, resume credit. - Non-recognised abbreviations.
Accept if first defined in answer. If not defined, do not credit the unrecognised abbreviation but credit the rest of answer if correct. - Wrong numbering.
If answer fits into the correct sequence of questions but the wrong number is given, it is acceptable. - If language used changes the intended meaning.
Do not accept. - Spelling errors.
If recognisable accept provided it does not mean something else in Life Sciences or if it is out of context. - If common names given in terminology.
Accept provided it was accepted at the memorandum discussion meeting. - If only letter is asked for and only name is given (and vice versa). Do not credit.
- If units are not given in measurements.
Candidates will lose marks. Memorandum will allocate marks for units separately. - Be sensitive to the sense of an answer, which may be stated in a different way.
- Caption.
All illustrations (diagrams, graphs, tables, etc.) must have a caption. - Code-switching of official languages (terms and concepts). A single word or two that appears in any official language other than the learners' assessment language used to the greatest extent in his/her answers should be credited, if it is correct. A marker that is proficient in the relevant official language should be consulted. This is applicable to all official languages.
- Changes to the memorandum
No changes must be made to the marking memoranda without consulting the provincial internal moderator.
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 B ✔✔
1.1.2 B ✔✔
1.1.3 A ✔✔
1.1.4 A ✔✔
1.1.5 C ✔✔
1.1.6 B ✔✔
1.1.7 A ✔✔
1.1.8 B ✔✔
1.1.9 D ✔✔
1.1.10 C ✔✔ (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 DNA profiling ✔ (DNA fingerprinting)
1.2.2 Uracil✔
1.2.3 Cytokinesis ✔
1.2.4 Ribosome ✔
1.2.5 Deoxyribose ✔
1.2.6 Fossils ✔
1.2.7 Alleles ✔
1.2.8 Extinction✔
1.2.9 Prognathous✔
1.2.10 Locus✔ (10 x 1) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 Both A and B ✔✔ (2)
1.3.2 A only ✔✔(2)
1.3.3 None ✔✔ (2)
1.4
1.4.1 C B E ✔F A D ✔ (2)
1.4.2 In the nucleus ✔(1)
1.4.3 A ✔ D ✔ F ✔ (3)
1.4.4 TGG ✔(1)
1.4.5 Leucine ✔ (1)
1.5
1.5.1 Pedigree ✔ /Genetic lineage diagram (1)
1.5.2 3 ✔ (1)
1.5.3
- Black ✔ fur (1)
- Black ✔ fur (1)
1.5.4
- aa ✔ (1)
- Aa✔ (1)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1 45 ✔ (1)
2.1.2 The are two X chromosomes ✔/ XX / The gonomes are the same. (1)
2.1.3 3 chromosomes present at position 21 ✔ (2)
2.1.4 Downs’ Syndrome ✔/ Trisomy 21 (1)
2.1.5 Nondisjunction ✔ (1)
2.2
- Double stranded DNA unwinds ✔
- and unzips ✔/separate when
- the hydrogen bonds break ✔
- each DNA strand is used as a template ✔
- to form a complementary DNA strand ✔/ A-T and G-C
- using free DNA nucleotides from the nucleoplasm ✔
- Two genetically identical DNA molecules are formed ✔
- This process is called DNA replication / replication* ✔
(Any 6 +*1 compulsory mark) (7)
2.3
2.3.1 3 ✔(1)
2.3.2
- Blood group A ✔ (1)
- IAIB ✔ (1)
- IAIB ✔ IBIB ✔ IBi ✔ (3)
2.4 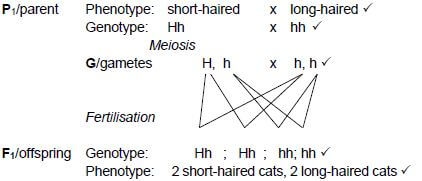
- *50% chance of heterozygous offspring ✔
- Parents and offspring ✔/P1 and F1
- Meiosis and fertilisation ✔
(Any 5 + *1 compulsory mark)
OR
P1/parent Phenotype: short hair x long hair ✔
Genotype: Hh x hh ✔
Meiosis
G/gametes H, h x h, h✔
| Gamete | H | h |
h | Hh | hh | |
h | Hh | hh | |
1 mark for correct gametes 1 mark for correct genotypes | |||
F1/offspring Genotype: Hh ; Hh ; hh ; hh ✔
Phenotype: 2 short-haired cats, 2 long-haired cats ✔
- *50% chance of heterozygous offspring
- Parents and offspring ✔/P1 and F1
- Meiosis and fertilisation ✔
(Any 5 + *1 compulsory mark) (6)
2.5
2.5.1 Genetic modification ✔/ genetic engineering (1)
2.5.2
- The Bt corn will have a higher yield than the non-Bt corn ✔✔
OR - The Bt corn will have a lower yield than the non-Bt corn ✔✔
OR - The Bt corn will have similar yield as the non-Bt corn ✔✔ (2)
2.5.3
- Corn variety ✔/ Type of corn (1)
- Average crop yield✔ (1)
2.5.4 The experiment was repeated four times. ✔
(MARK FIRST ONLY) (1)
2.5.5 Bt corn effectively increased crop yield ✔ as it produced poison which killed the ECB worm. ✔ (2)
2.5.6
- Less use of pesticides/herbicides ✔ therefore save money ✔
- Better yields ✔ to create more efficient use of land ✔
- Foods with better texture ✔ therefore reduces wastage ✔
- Food with longer shelf life ✔ can be easily exported ✔
(MARK FIRST ONLY) (Any 1 x 2) (2)
2.5.7 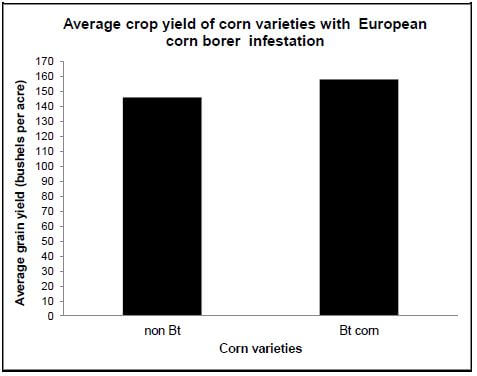
Mark allocation of the graph
Criterion | Elaboration | Mark |
Type of graph (T) | Bar graph drawn | 1 |
Caption (C) | Includes both variables: average crop yield of two corn varieties with European corn borer infestation | 1 |
X-axis | Equal width of bars AND correct label | 1 |
Y-axis | Appropriate scale, correct label and unit | 1 |
Plotting (P) | 1 bar plotted correctly 2 bars plotted correctly | 1 2 |
NOTE:
- If a line graph is drawn – marks will be awarded for the ‘title and label for X-axis. and Y-axis only.
- If axes are transposed – marks will be lost for the label for the X-axis. and Y-axis. (6)
[40]
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1 Meiosis I ✔ (1)
3.1.2
- Haploid cells produced ✔/ Cells produced have half of the original number of chromosomes
- Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles at C ✔ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.1.3
- C – Anaphase 1 ✔
- D – Telophase1 ✔ (2)
3.2
3.2.1
- After application of the insecticide in 1995 to 1998 there was an increase in the percentage of resistant insects, ✔ from 0,15% in 1995 to 99,10% in 1998. ✔
- The percentage of the non-resistant insects decreased ✔ from 99,85% to 0,90% ✔ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
3.2.2
- There is variation in the insect population ✔
- Some were resistant and some were not. ✔
- When the insecticide was first used, it killed off a large number of non-resistant insects ✔
- Some insects were resistant to the insecticide ✔ and survived ✔
- Those that survived were able to reproduce ✔
- thereby passing on the allele (gene) for resistance to offspring ✔
- Continued use of the insecticide had little effect on the resistant insects ✔
- Hence the resistant insects increased ✔and non-resistant insects decreased. ✔ (Any 6 x 1) (6)
3.3
3.3.1 Speciation ✔ (through geographic isolation) (1)
3.3.2
- The original population ✔ of salamanders
- became separated ✔ into two sub- populations
- *by the central valley ✔
- No gene flow ✔occurred between the two sub-populations
- Each population was exposed to different environmental conditions ✔/selection pressures
- Natural selection occurred independently in each sub-population ✔
- The individuals of each sub-population became different ✔
- genotypically and phenotypically ✔ from each other.
- Even if the two sub-populations were to mix ✔
- they would be unable to interbreed ✔/ reproduce
- resulting in the formation of species B. (Any 5 + 1* compulsory) (6)
3.3.3 In punctuated equilibrium:
- Evolution involves long periods of time where species do not change ✔/ very little change occurs
- This alternates with short periods of time when rapid changes occur ✔
- New species are formed in a short period of time ✔/ relative to the long periods of no/little change.
- Supported by the absence of transitional fossils ✔ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
3.4
3.4.1
- 3 ✔ (1)
- 1 ✔ (1)
- 2 ✔ (1)
3.4.2 Pelvis B ✔ and skull 1 ✔ (2)
3.4.3
Feature | Skull 1 | Skull 3 |
X-foramen magnum | Located in a backward position ✔ | Located in a more forward position ✔ |
Y-brow ridge | Less pronounced ✔ | More pronounced ✔ |
(MARK FIRST TWO ONLY) (2 x 2 + 1 mark for table) (5)
3.4.4 It has the most developed canines. ✔ (1)
3.4.5
- The mitochondrial DNA in the zygote is inherited from the mother. ✔
- Any mutation ✔
- in the mitochondrial DNA ✔can be traced back
- to a female from Africa ✔ (mitochondrial Eve)
- This proves that all women originated from Africa ✔
- and from there her offspring covered the earth. ✔ (Any 5 x 1) (5)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
Sources of genetic variation: meiosis ✔
- Gametes produced by meiosis are different because of:
- crossing over ✔during first prophase ✔
- random arrangement of chromosomes ✔during first metaphase ✔ and
- second metaphase
Random mating as a source of variation ✔
- In humans and some other mammals, mating takes place between individuals who select mating partners of a particular kind. ✔
- In most other species, mating takes place randomly amongst all individuals within the population ✔ / more than one mating partner
Chance fertilisation of egg cells by sperm cells ✔
- Usually more than one egg cell and sperm cells are produced ✔ and these are all different. ✔
- Fusion of many types of sperm cells and egg cells ✔ can produce many different types of offspring. ✔
Mutations ✔
- Mutations are sudden, random changes in the genetic code of an organism ✔
- A gene ✔ mutation occurs
- as a result of a change in the sequence of nitrogen bases ✔in the DNA molecule
- can result in the formation of a different protein ✔
- leading to new/different characteristics ✔
- A chromosome ✔ mutation occurs
- as a result of a change in the structure / number of chromosomes ✔
- Mutations occurring in sex cells ✔
- are passed on to offspring and new generations ✔
- resulting in new characteristics being formed ✔
Content: (17)
Synthesis: (3)
ASSESSING THE PRESENTATION OF THE ESSAY
Criterion | Relevance (R) | Logical sequence (L) | Comprehensive (C) |
Generally |
|
|
|
In this essay |
|
|
|
Mark | 1 | 1 | 1 |
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150
RELIGION STUDIES GRADE 12 PAPER 1 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
RELIGION STUDIES
GRADE 12
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections:
SECTION A and SECTION B. - SECTION A is COMPULSORY.
- SECTION B consists of four questions of which TWO must be answered.
- Read ALL the questions carefully before making a choice.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- The length of your answers must be in accordance with the marks allocated to each question.
- Answer each question on a NEW page.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 Briefly define the following concepts in the context of religion:
1.1.1 Ideology (2)
1.1.2 Teaching (2)
1.1.3 Parable (2)
1.1.4 Myth (2)
1.1.5 Belief (2)
1.2 Complete the following sentences by filling in the missing word(s). Write only the word next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK. Choose the answer from the following list:
| Calabash; Hebrew; Torah; Halaal; Karma |
1.2.1 Food permissible to Muslim consumption is referred to as … (2)
1.2.2 In the African culture the … may be used to drink water or traditionally brewed beer. (2)
1.2.3 The study and practice of the … are seen as the antidote of evil. (2)
1.2.4 Hindu ethics is referred as … (2)
1.2.5 The Old Testament texts were written in … (2)
1.3 From each group of words below, choose the word that does NOT fit. Write only the word next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 Bible, Vedas, Dictionary, Qur’an (2)
1.3.2 Moria, Mecca, Pretoria, Jerusalem (2)
1.3.3 Jeremiah, Jesus, Nelson Mandela, Prophet Muhammad (2)
1.3.4 Baha’u’llah, Baha’i, Rome, Kitab-iAqdas (2)
1.3.5 Unkulunkulu, Isangoma, Moses, Ancestors (2)
1.4 Indicate whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Write only “true or “false” next to the question number (1.4.1–1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 Muhammad is the founder / prophet of the Baha’i faith. (2)
1.4.2 The Vedas are regarded as holy scriptures within the Christian faith. (2)
1.4.3 According to the Jewish history, Moses was the first man to acknowledge that God is one god. (2)
1.4.4 The founder of Buddhism is the Dalai Lama. (2)
1.4.5 The sacred scripture of Judaism is the Tanach. (2)
1.5 Choose an item from COLUMN A that matches the word/description in COLUMN B. Write only the letter (A–E) to the question number (1.5.1– 1.5.5) in your ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.5.6 F.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.5.1 Baha’i |
|
(5 x 2) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
Answer any TWO of the questions in this section.
QUESTION 2
2.1 Define each of the following concepts in the context of religion:
2.1.1 Identity (4)
2.1.2 Unity (4)
2.1.3 Uniqueness (4)
2.1.4 Comparability (4)
2.1.5 Similarity (4)
2.2 Briefly discuss the role of ancestors in African Traditional Religion. (10)
2.3 Discuss the internal differences that exist within any ONE religion under the following headings:
2.3.1 Religious teachings (10)
2.3.2 Religious practices (10)
[50]
QUESTION 3
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
Similarly, each religion, no matter how closely linked to others, has unique features. Many religions are monotheistic and some are polytheistic. Many believe in life after death, some believe in reincarnation. But each one has a feature or features that distinguish it from each other. [Adapted from Shuters Religion Grade 12, Hofmeyr et al, page 5] |
3.1 Write down the features that are fulfilled by the uniqueness of a religion. (5 x 2) (10)
3.2 Briefly discuss the unique features on any ONE of the religions. (5 x 2) (10)
3.3 List FIVE common beliefs shared by the three Abrahamic faiths. (5 x 2) (10)
3.4
“Religions sometimes make use of stories or parables to communicate a moral or philosophical idea.” [Source: Unknown] |
Discuss the roles that are played by parables in philosophical or religious teachings. (10)
3.5 Briefly discuss the concept doctrine in a religious context. (10)
[50]
QUESTION 4
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
In several recent studies of religious coverage in the media, it was found that coverage had increased significantly over the last decade. However, the coverage was very negative and focused mainly on the following:
[Source: Adapted from Religion Studies Grade 12 by Steyn et al, pages 220−221] |
4.1 Do you think the media gives fair coverage to religious issues? (2)
4.2 Give reasons for your answer to QUESTION 4.1. Include ONE example to support your answer. (10)
4.3 Why, do you think, media coverage of religious issues increased sharply? (10)
4.4 Discuss ONE example from the media that refers to the political elements of religion. (10)
4.5 Discuss ONE example from the media that refers to issues involving sexual morality and religion. (10)
4.6 Discuss ONE example from media that refers to issues involving women (or minorities) and religion. (8)
[50]
QUESTION 5
5.1 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
Religions are supposed to represent our highest ideals and hopes. You would think, therefore, that religions would inspire us to seek peace and to live in harmony with others. But the record of religions, like everything that involves humans, is mixed. [Source: Adapted from Shuters Religion Grade 12, Hofmeyr et al, page 60] |
5.1.1 Identify ONE region or country of conflict in the world and give a brief history of the conflict. (10)
5.1.2 Describe the current situation of the conflict you have identified. (10)
5.1.3 Explain the role of religion in the conflict. (10)
5.1.4 Distinguish between religious freedom and religious tolerance. (4)
5.2 For each of the following religions, briefly discuss the teachings that promote human rights:
5.2.1 Buddhism (4)
5.2.2 Christianity (4)
5.2.3 Islam (4)
5.2.4 African Traditional Religion (4)
[50]
TOTAL SECTION B: 100
GRAND TOTAL: 150
RELIGION STUDIES GRADE 12 PAPER 2 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
RELIGION STUDIES
GRADE 12
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- This question paper consists of FIVE questions.
- Answer any THREE of the five questions.
- Read ALL the questions carefully before answering it.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write legibly and present your work neatly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
Read the statement below and answer the questions that follow.
| HIV and Aids is one of the major challenges facing SA. |
1.1 Give a brief relevant introduction of HIV/Aids. (8)
1.2 Explain the impact of HIV/Aids on South African society. (16)
1.3 Discuss practical strategies or steps that religious organisation can use to combat HIV/Aids. (14)
1.4 Do you think that religious organisations are currently succeeding in the struggle against HIV/Aids? Give reasons for your answer. (12)
[50]
QUESTION 2
2.1 Discuss the central teachings of any ONE religion under the following headings:
2.1.1 Nature of the world (10)
2.1.2 Nature of divinity (10)
2.1.3 Place and responsibility of the world (10)
2.2 With reference to ONE selected religion, explain the following concepts:
2.2.1 Inspiration (10)
2.2.2 Sacred book (10)
[50]
QUESTION 3
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
Darwin’s theory of evolution gave an alternative explanation for the origin of man. While evolution does not refute religious ideas about creation directly, it is clear that it offers no explanation as part of divine plan. [Source: Shutters Top Class Religion Studies, Page 163] |
3.1 Explain the theory of evolution. (12)
3.2 Discuss the response of any ONE religion to Darwin’s theory. (18)
3.3
Religions have always offered explanations regarding creation and the status of humankind. In the last four centuries, however, science has begun to offer different answers to these questions. [Source: Religion Studies, Steyn et al p. 241] |
Give a brief explanation of the Big Bang Theory. (20)
[50]
QUESTION 4
Read the following quotation and answer the questions that follow.
| Organisations such as the World Conference of Religious for Peace (WCRP), African Women of Faith Network (WCC), African Council of religious leaders (WPR), aim to create harmony among the religions of the world. |
4.1 Give a brief account of their history and discuss what work these organisations have done outside of the African continent. (14)
4.2 All religious display a number of internal differences. Discuss the internal differences within any one religion under the following headings:
4.2.1 Governance (12)
4.2.2 Practices (14)
4.3 Do you think secularism is gaining popularity in the world? Give reasons for your answer. (10)
[50]
QUESTION 5
5.1 State FIVE hermeneutical principles that can be used in the interpretation of sacred text. (10)
5.2 Read the statement below and answer the questions that follow.
| Christian settlers arrived in SA in 1652, Muslims in 1796 and Hindus in 1860 whilst ATR had always been practised in the country. |
Write an essay of environmental destruction under the following subheadings.
5.2.1 Causes of environmental destruction (14)
5.2.2 Impact of environmental destruction in the society (12)
5.3 Analyse the role of the present legislation in encouraging healthy inter religious relations in SA. (14)
[50]
TOTAL: 150
RELIGION STUDIES GRADE 12 PAPER 2 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
RELIGION STUDIES
GRADE 12
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1 Relevant introduction
- One of the pressing issues in South Africa today is HIV and Aids pandemic which is claiming the lives of many South Africans.
- In May 2003, religious communities and organisations met to discuss ways in which it could address the problem of HIV and Aids at the first conference of the religion.
- It must be treated with all the sensitivity it deserves.
- It calls for love and compassion. (8)
1.2 Explain the impact of HIV/Aids on South African society.
- There is a high rate of death of young people in the country.
- It causes family breakdown if one member is infected, because every member of the family becomes affected.
- It affects the morals of the society (values and attitudes change).
- School dropout rate increases.
- Family structures are weakened (child-headed family).
- It causes financial strain on the economy, the government spend more money which causes unequal distribution of funds.
- It causes people to be trapped in a cycle of poverty.
- It causes unemployment (sometimes people are hired on their health status).
- It causes more suffering and make people feel guilty, low self-esteem, lack of confidence and trust. (16)
1.3 Practical strategies or steps for religious organisations to combat HIV/Aids:
- Organised workshops to teach and make people aware of the epidemic.
- Educate members and communities on religious teachings about contraception.
- Provide counselling for people infected and affected.
- Awareness campaigns should be planned.
- We must all learn from successful anti-aids campaigns, e.g. in Uganda, religious organisations and government worked together to bring about moral regeneration.
- Sex outside a stable relationship was made taboo.
- Faith-based organisations, all work together to convey the message of abstinence.
- Sex within marriage only.
(Any relevant facts should be credited.) (14)
1.4 Do you think that religious organisations are currently succeeding in the struggle against HIV/Aids?
YES
- The increased rate of attendance in different religious organisation through their different healing strategies and life style contributes to the struggle against HIV and Aids.
- Awareness campaigns organised by different religious groups.
- Home-based organisations run by different religious organisations are seen operating.
- Religious groups are working with the government as joint force for effective implementation of strategies.
- Most established safe house are organised by religious organisations in order to take care of orphans.
- Seminars to raise awareness are organised by different religious groups.
- Counselling and help desks are operating effectively to bring help to communities.
- Religious groups are seen doing outreach and giving hand outs to families for them to eat and wear.
NO
- People go to religious organisations only when things are bad, and experiencing difficulties.
- Religious organisations cannot do it alone without funding.
- It becomes difficult for the organisation to attend to large numbers.
- Statistics show that the infection rate is still very high compared to other African countries.
- Religious organisations are too fragmented to be effective in the struggle.
- Religious organisations should make more input onto government policy via the National Religious Leaders Forum (NRLF).
(This is an open-ended question. The learners should be credited for the responses that are relevant even when the strategies are drawn from more than one religion.) (12)
[50]
QUESTION 2
2.1 Central teachings of any one religion: Buddhism is used as an example.
2.1.1 Nature of the world:
- The wold is just one of millions of worlds.
- In each of these worlds, a Buddha will rediscover the true nature of beings.
- Buddhism flourishes for thousands of years and then it slowly dies out.
- Another man will try to understand why people suffer and he becomes the next Buddha.
- Each cycle has a Buddha. (10)
2.1.2 Nature of divinity:
- Most forms of Buddhism accept that powerful beings exist, whom we call god.
- Buddhists teach that everything is impermanent, even the gods.
- Each Buddhist must find enlightenment alone.
- They follow the Buddha’s instruction.
- They may pray to the local deity. (10)
2.1.3 Place and responsibility of humanity in the world:
- Being born as human is very rare and precious.
- Humanity is the only condition in which enlightenment is possible.
- The primary responsibility of every humans is to become enlightened.
- One should share this way of enlightenment with others.
- They are actively engaged in the field of nuclear disarmament, anti-war efforts and ecological action. (10)
2.2 Normative sources:
2.2.1 Inspiration:
- Refers to the breath (power, knowledge) of an extra-ordinary being or power, e.g. a deity taking over a person and inspiring him or her with divine knowledge.
- Most religions have founding figures who were inspired by a higher power or wisdom, examples are Abraham, Moses, Confucius, the Buddha, Jesus Christ, Prophet Muhammad and Baha’u’llah.
- The inspiration of those figures is accepted by their followers as having been direct and immediate.
- They are believed to have stood face to face with God.
- Such immediate contact with a dimension beyond everyday life lies at the root of African religion.
(The candidate should be credited for any relevant responses other than above answers.) (10)
2.2.2 Sacred book:
- Writing entered the religious scene about 4000 years ago.
- Since then it has played an ever increasing role.
- The difference between oral and written is not merely one of medium – tradition became more fixed as a result of writings.
- Oral traditions which can run parallel to written tradition are very fluid, but once it is written down, it becomes established.
- In religions of the book (Judaism, Christianity, and Islam) sacred scriptures play a key role in teachings.
(The above answers are a guide, the candidates could include more points, and therefore should be credited for relevant responses.) (10)
[50]
QUESTION 3
3.1 Theory of evolution:
Darwin’s theory consist mainly of the following ideas:
- Species contain a great variety of minor differences.
- Both the world and species change over time.
- In the fight for survival, better adapted variations will be favoured, while those that are not will struggle to survive.
- In this way a species may gradually change its form and become more complex-by developing along a path of successful variations.
- All forms of life are connected and go back to a common origin.
- The different types of life are absolutely different but occur on one single continuum.
(Any relevant answers should be credited.) (12)
3.2 Response of any ONE religion to Darwin’s theory
(Buddhism is used as an example)
- Many Buddhists argue that the theory of evolution and Buddhism are in agreement.
- There is no account of creation in Buddhism.
- Buddhists do not mind what scientists say about the universe and people came into being.
- They believe that all life involves constant transformation and evolution.
- Buddhists believe in evaluation long times ago before Western scientists did.
- Buddhism also believe in the continuity of all living beings.
- They have no problem with the idea of human beings having evolved from more primitive primate forms.
- Their belief is Nirvana is a good example of life transformation and evolution.
- Buddhism has no intelligent designer who is responsible for creation, that is why they have no problem with evolution.
- Buddhism believes in insubstantiality (no part of a human is immortal), so they do not have a problem with evolution. (18)
3.3 Big Bang Theory
- The big bang theory is currently the most popular scientific theory about the creation of the universe.
- The scientific theory maintains that before the big bang it was not known what existed before.
- After the big bang, the universe appeared.
- It is also filled out to enormous size.
- The big bang occurred 15 billion years ago.
- Small temperatures differences in the first explosion led to varying densities throughout the universe.
- The clusters continued to condense in a lumpy way and eventually formed that vast collection of stars we call galaxies.
- Our earth is part of the solar system. (20)
[50]
QUESTION 4
4.1 History and work of organisations that have been done outside of the African continent.
World Parliament of Religions (W.P.R.)
- The initiative started in 1983.
- The Unitarian and Universalistic churches were the main drivers of the initiative.
- Western and Eastern religions were represented.
- Swami Vivekananda introduced Hindu thought processes to the West.
- This was a crucial stage in inter-religious dialogue, as previously Eastern religion was not understood\accepted as a religion by the Western world.
The World Conference of Religious for Peace (W.C.R.P.)
- It was formed in 1970.
- It was made up of leaders from all religions.
- Its common goal is peace.
- The body believes that its inter-religious relationships are the best way to bring people of deference races and classes and cultures together, for a common goal.
- This is because religions organise people into cohesive bodies that are committed to helping others in need.
World Council of Churches (W.C.C.)
- Founded in Amsterdam in 1948.
- It is purely Christian.
- It re-affirms the trinity of God. (14)
4.2 Internal Differences of One Religion [For the purpose of this memorandum Hinduism is discussed]
4.2.1 Governance
- Traditional Hinduism has no central control.
- Reformers work with the existing system.
- There was no breakaway movement.
- Traditional governance was centred on home and local temple.
- In India, each temple is independent in terms of governance.
- Local priests determines rituals to be practised within that community.
- Today in countries with major Hindu presence outside of India, there are structured Hindu movement.
(Any relevant answer should be credited.) (12)
4.2.2 Practices
- In traditional Hinduism performance of domestic and temple ritual is obligatory for all.
- Much time is taken up by these rituals.
- Hindu believes engage themselves in the lightening of lamps and the correct preparation of food.
- In Neo-Hindu movements, less emphasis is placed on rituals.
- In Neo-Hindu movement emphasis is place more on individual and group devotion (bhakti).
- Devotion is also directed to a specific form of God.
- In many cases such as devotional sessions involve a formal ritual element.
- Worships takes place at home and in the temple.
(Any relevant factors should be credited.) (14)
4.3 Do you think secularism is gaining popularity in the world? Give reasons for your answer.
YES
- Secularism is the belief that the government and morality should not be based on religion.
- Most Morden Western democracies are secular state.
- Misconduct by religious leaders causes people to be disillusioned with religion.
- The split between the Roman Catholic and Protestants was one of the causes for the rise of speculation in the West.
- Most people thought that society would only be peaceful if there is separation between religion and the state.
- The department of contributed to the spread of secularism as more people became literate.
(Any relevant answer should be credited.) (10)
[50]
QUESTION 5
5.1 Hermeneutical principles
- Grammar and historical context
- Clearest meanings
- Plan, purpose and context
- Meaning of words
- Figurative language
- Other sacred text (10)
5.2 5.2.1 Causes of environmental destruction:
Environmental destruction is caused by irresponsible use of chemicals (pesticides and plant fertilisers).
- It is also caused by the excess burning of fossil fuels.
- This increases the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- Excessive increases in carbon emissions from factories and transport result in the ‘greenhouse’ effect/global warming.
- This raises the temperature of the earth’s atmosphere, resulting in climate change.
- It is also caused by some human activities such as dumping of waste products in open areas (land pollution).
- Improper methods of farming also harm the environment, by causing soil erosion.
(Any other relevant response must be credited.) (14)
5.2.2 Impacts of environmental destruction:
- The weather and climate have changed (global warming).
- There are more frequent storms, droughts and floods across our planet.
- Desertification is increasing, especially in Africa.
- This is resulting in food shortages.
- The ozone layer has developed a hole which causes the temperature to increase.
- More people are dying yearly because of diseases caused by air pollution.
- The seriousness of diseases have increased because our bodies fail to adapt to the ever-changing environment.
- Some species are becoming extinct, as a result of climate change. (Any other relevant response must be credited.) (12)
5.3 Roles of the present legislation in encouraging healthy inter-religious relations in SA:
- In 1997, President Nelson Mandela called on religious communities to work together to build a free and just SA.
- The coalition was called the National Religious Leaders Forum (NRLF) ∙ A moral summit was held in October 1999.
- Concerns were poverty, children and women abuse, prevention of HIV and Aids, etc.
- The South African constitution was adopted in 1996.
- It establishes SA as a secular state, with no state religion.
- It forbids discrimination on the basis of religion or beliefs.
- Religious observance may be conducted at state institutions provided that:
- There are conducted on an equitable basis.
- Attendance at them is free and voluntary.
(Any relevant factors should be credited.) (14)
[50]
TOTAL: 150