Adele
RELIGION STUDIES GRADE 12 PAPER 1 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
RELIGION STUDIES
GRADE 12
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 Ideology refers to a substitute for the term religion. It is a system of beliefs supporting a social or political system and secular system or that which is not an authority. (2)
1.1.2 Teaching means to give information or to impart the knowledge in order to enforce belief. It also means to give systematic information about a subject. (2)
1.1.3 Parable refers to a story that is told to illustrate a religious principle or answer a religious question. It is usually very short and contains a definite moral. (2)
1.1.4 Myth means fable. It also means reference to religious stories in which deep truths about life are revealed. (2)
1.1.5 Belief means a firm opinion. It also means faith or religion. (2)
NOTE: Each fact carries 2 marks. Any correct fact/points must be credited.
1.2
1.2.1 Halaal (2)
1.2.2 Calabash (2)
1.2.3 Torah (2)
1.2.4 Karma (2)
1.2.5 Hebrew (2)
1.3
1.3.1 Dictionary (2)
1.3.2 Pretoria (2)
1.3.3 Nelson Mandela (2)
1.3.4 Rome (2)
1.3.5 Moses (2)
1.4
1.4.1 FALSE (2)
1.4.2 FALSE (2)
1.4.3 FALSE (2)
1.4.4 FALSE (2)
1.4.5 TRUE (2)
1.5
1.5.1 D / Kitab-iAqdas (2)
1.5.2 E / China (2)
1.5.3 B / Divine law of Islam (2)
1.5.4 A / Constitution (2)
1.5.5 C / African Traditional Religion (2)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1 Identity
- Identity means individuality.
- It means the religion has a certain individuality or a certain
- ersonality that distinguishes it from other religion.
- It means the affirmation of the dignity and value of a religion.
- It means an exclusive religious identity in which one identifies strongly with the beliefs and doctrines of the religion and sees these as defining one’s life. (4)
2.1.2 Unity
- Unity refers to those factors that lead to the sharing of a common identity.
- It refers to harmony and concord that exist between religions.
- It may also refer to the acknowledgement of common ground among different faith groups. (4)
2.1.3 Uniqueness
- It is those features that make the religion different from other religions.
- It is those features that make it identifiable as a different religion.
- There is uniqueness in beliefs, practices and normative texts. (4)
2.1.4 Comparability
- This means that two or more things are able to be compared.
- This does not mean that they are similar.
- Things can be compared and it is found that they are different.
- The other meaning may be that things can be compared because they are fit to be compared. (4)
2.1.5 Similarity
- It refers to “being alike”.
- It is important to specify similarities.
(Any correct points carries 2 marks (2 x 2 = 4)) (4)
2.2 Role of ancestors in African Traditional Religion.
- They are the messengers of the Creator.
- They are seen by followers as the supervisors of the physical world.
- They look after the welfare of the living.
- They reveal themselves through dreams and sometimes through visions to communicate with the living.
- To communicate with God, the living uses the ancestors – they are their intermediaries. (5 x 2) (10)
2.3 Internal differences that exist within one religion (Islam as an example)
2.3.1 Religious teachings
Shi'a
- They believe that the caliphate (successor) should be from the descendants of the Prophet Muhammad.
- They claim that these caliphs are divinely-appointed imams with supernatural knowledge and authority who must lead the faithful.
- They follow some Hadith (e.g. recordings of Ali and Fatima) of Prophet Muhammad and reject others.
- They commemorate the death of Hussain, whom they believe was martyred at Karbala.
- They share a collective guilt for not coming to his aid when he was killed.
- The Shi'a have two schools of law.
- The Shi’a follow the teachings of a modern day imam.
Sunni
- Sunni's believe that the faithful, rather than the descendants, should elect their leaders, (e.g. Abu Bakr).
- Sunni refers to 'following' the Sunnah (example) of the Prophet Muhammad.
- All the companions of the Prophet are given equal respect in Islamic jurisprudence. (Islamic law)
- The Sunni have four schools of law.
- The Sunni follow the teachings of the 7th and 8th century scholars. (10)
2.3.2 Religious practices in Islam
Sunni
- Religious practices are strictly in accordance with the Sunnah of the Prophet, as laid down in the Hadith.
- An 'imam' is simply the leader of the congregational prayer.
- 'Imam' does not denote formal training in Sunni Islam.
- There are four recognised scholars with regard to legal matters in Islam.
- They pray five times daily.
- The concept of Muttah (temporary marriage) is not recognised, as they contend it was discontinued by the Prophet.
- In the event of a dispute, the issue is decided by means of a consensus.
Shi'a
- Those Hadith from Ali and Fatima, daughter of prophet, are given more prominence.
- The shrine of Hussain in Karbala is an important pilgrimage for Shi'as.
- Muttah is allowed.
- Shi’a Muslims are allowed to combine some of their five daily prayers into three.
- They can pray three times a day.
- They practise self-mutilation (striking themselves).
- There are two advisory schools of law, Akbari and Usuli.
- In the event of a dispute, the issue is decided upon by a central authority (ayatollah). (10)
[50]
QUESTION 3
3.1 Features that are fulfilled by the uniqueness of a religion.
- It strengthens the believer’s faith.
- It identifies the religion from amongst other religions.
- It guides the believer’s way of life.
- It helps the believer to unite in the spiritual life as a communion with other believers.
- It assist believers to explain why they chose a particular religion.
- It helps members to identify who belongs to the faith and who does not. (10)
3.2 Uniqueness of any ONE religion.
African Traditional Religion as an example.
- They believe in the existence of a Supreme Being.
- They communicate with their God through the ancestors.
- Their communication with the ancestors is through the ritual of animal sacrifice.
- Harmony between the living and the ancestors is of great importance.
- Ancestors can bring illness, misfortune, and also blessings.
- During the ritual of sacrifice the living call the ancestors to be present.
- Community solidarity is a pronounced feature in ATR.
- The community orientation of African society is clearly reflected in its rituals.
- Rituals are rich in symbols, e.g. the goat-hide bracelet (Isipandla)
- They do not have a special day of worship.
- There is no founder.
- There is no written text.
- There are no sacred buildings, but there are sacred places.
- There is a great variance of belief among African Traditional Religions.
(Any relevant response will be credited.) (10)
3.3 Five beliefs shared by Abrahamic religions
- Believe in one God.
- Believe in the existence and the role of the Devil or Satan.
- Believe in the existence and the role of angels.
- Believe in life after death.
- Believe in the authority of the sacred texts as the Word of God.
- They believe in Judgement Day. (10)
3.4 The Role of parables in religious teachings
- They provide us with a rich source of religious teaching (wisdom).
- They contain religious beliefs, ideas, morals, and warnings.
- They speak about God, the world, human relationships and the nature of things.
- It conveys moral or philosophical truths.
- It is a simple story that conveys a deep, spiritual truth. (10)
NOTE: Other relevant points must be credited.
3.5 Concept of doctrine
- Doctrine is a belief held by a religious group.
- It is a synonym for teaching.
- It is sometimes used to refer to the entire set of beliefs in a religion.
- Doctrine is a statement of essential beliefs.
- It functions to safeguard what is essential to the religion.
- They are the essential pillars of the religion.
- Teaching and doctrine are closely connected to the notion of religious teachings.
(Any relevant response will be credited.) (10)
[50]
QUESTION 4
4.1 Yes/No.
NOTE: This is an open-ended question, and credit must be given to relevant examples given by learners. (2)
4.2 YES.
- In South Africa, (or other countries) there is equal coverage given to each religion e.g. TV programme, “Issues of faith”.
- If religious coverage is not fair, complaints can be made to the BCCSA or the Human Rights Commission.
These are made by individuals or religious bodies such as the Jewish Board of Deputies, Hindu Maha Sabha, etc. - Representatives of various faiths are interviewed.
- This allows for different viewpoints to be represented.
NO.
- Research shows this is not the case, as in the extract above.
- The Catholic Church gets mainly negative coverage regarding alleged child abuse by its priests.
- The media never engages in the promotion of religion or general religious issues.
- Only sensationalist reporting is done.
- In world media, religion is often depicted as being the cause of wars, suffering and abuse (e.g. abuse of women). (10)
4.3
- The wars in Iraq and Afghanistan have thrust Islam into the limelight.
- In the West little was/is known about it in the past,
- There is increased competition among media houses.
- Wars and conflict often divide people along religious lines.
- The coverage is only on issues that sell newspapers, such as scandals, conflict with secular law, etc.
- Religion is seen as big business, in many cases.
- Examples of this are the Hajj, the ZCC Easter gathering, etc.
(Any relevant responses must be credited.) (10)
4.4
- The civil conflict in Nigeria is often shown as conflict between the Muslim North and Christian South.
- There is an effort by Muslims to enforce Shariah law, even on non Muslims.
- Muslims fear that they will be ruled by a Christian government.
- Christians fear that Nigeria would become an Islamic state.
- There is concern as to who will exert political control over the oil resources.
- The oil interests also encourage foreign powers to take sides in the conflict.
- Some Muslim sects have lost faith in the government and have taken the law into their own hands, e.g. Boko Haram.
- Boko Haram provides basic services to its supporters, in the absence of government services. [Mail and Guardian, 2 April 2012, p.24) (10)
4.5 E.g. Homosexuality and the Catholic church
- The Catholic Church is strongly against homosexuality.
- The Catholic Church refers to the Biblical story of Sodom and Gomorra.
- Numerous protests condemning the church's stand get a lot of media coverage.
- The church’s view do not get the same coverage in the media as anti-religious sentiments.
- They ignore the unconditional love of God.
(Any relevant fact will be credited.) (10)
4.6 E.g. Polygamy in ATR or Islam
- Women in polygamous marriages are shown as being abused by their husbands
- Women involved in extra-marital relationships are presented as more acceptable.
- This is evident in the many extra-marital relationships shown on TV.
- Religious texts are often misquoted by the media to justify the ill treatment of women.
(Any relevant response will be credited.) (8)
[50]
QUESTION 5
5.1
5.1.1 Conflict in Darfur
- The Darfur conflict in Southern Sudan started more than 100 years ago.
- The main divisions were ethnic/tribal and cultural.
- Religion is not a radical source of division.
- Most people of Darfur are Sunni Muslims, as is the government of Khartoum.
- There are some Christians and ATR adherents in the south.
- Drought has increased competition for limited resources and brought nomads and farmers into conflict.
- In 1983 there was a civil war when the Muslim government tried to impose Islamic law in the South.
(Credit any relevant example.) (10)
5.1.2 Current situation of the conflict in Darfur
- In 2005 South Africa brokered a peace deal between the North and the South.
- However, conflict continued.
- In 2006, the President resisted United Nations involvement to resolve the dispute.
- A UN backed referendum in 2011 decided on partition of the South.
- The situation is accepted and it is peaceful and calm.
(Any relevant response will be credited.) (10)
5.1.3 Role of religion in the conflict
- Religion is not a radical source of division.
- Most people on both sides of the conflict are Sunni Muslim.
- Religion played an indirect role in the 1983 civil war.
- Religion have played a major role in trying to help.
- Two religious organisations involved were the Catholic
Agency for Oversees Development and Islamic Relief Agency. - This help include building of clinics and schools and repairing infrastructure. (10)
5.1.4 Relationship between religious tolerance and religious freedom
- The two terms are closely related.
- Religious freedom is determined by the government of the day.
- Religious tolerance is mainly depended on attitudes of religious groups or individuals with a given community.
- It is the acceptance and respect of the religious beliefs and practices of other people without any preconditions.
- Religious freedom prepares a good ground for religious tolerance.
NOTE: other relevant points must be credited. (4)
5.2 5.2.1 For each of the following religions, briefly discuss the teachings that promote human rights.
Buddhism
- They promote shared humanness.
- There is a shared aspiration of gaining happiness and avoiding suffering. (4)
5.2.2 Christianity
- ʽLove thy neighbour as you love yourself’: This teaching encourage treating everyone equally.
- Thou shall not kill’: This refers to the sanctity of human life. (4)
5.2.3 Islam
- There is no compulsion to convert to Islam − that is, proclaiming one’s faith should be voluntary and sincere. This allows for freedom of religion.
- The institution of zakaat (charity) ensures that basic needs of food, shelter and clothing are satisfied. (4)
5.2.4 African Traditional Religion
- The principle of ubuntu encourages helping one’s community.
- The practice of Ilima is one in which the community provides help to those of its members who are indigent.
(Any other relevant fact must be credited. Teachings may be expressed in the learner's own words.) (4)
TOTAL MARKS SECTION B: 100
GRAND TOTAL: 150
CONSUMER STUDIES GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
CONSUMER STUDIES
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions.
SECTION
MARKS
TIME (MINS)
QUESTION 1: Short questions – (All topics)
40
20
QUESTION 2: The consumer
20
20
QUESTION 3: Food and Nutrition
40
40
QUESTION 4: Clothing
20
20
QUESTION 5: Housing
40
40
QUESTION 6: Entrepreneurship
40
40
TOTAL
200
180
- ALL the questions are compulsory and must be answered in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start each question on a NEW page.
- You may use a calculator.
- Write in black or blue ink only.
- Pay attention to spelling and sentence construction.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1 SHORT QUESTIONS
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.20) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.1.1 The measure used to determine the increase in price as well as to calculate the inflation rate:
- Inflation rate
- Interest rate
- Consumer Price Index
- Repo rate (1)
1.1.2 A false and fraudulent business practice is called:
- Stokvel
- Scam
- Pyramid scheme
- Grey goods (1)
1.1.3 Tax paid from selling a house is known as …
- estate tax.
- capital gains tax.
- property tax.
- property evaluation tax. (1)
1.1.4 The condition in which the blood glucose level drops abnormally low:
- Hypertension
- Hypoglycaemia
- Diabetes
- Hyperglycaemia (1)
1.1.5 Lactose intolerance develops when the body cannot digest the … in the milk.
- calcium
- fat
- carbohydrates
- protein (1)
1.1.6 … would be the best boost for the immune system for a person who is HIV positive.
- Guava juice
- Tea
- Coffee
- Water (1)
1.1.7 The combination of food that will contribute to high cholesterol levels:
- Butter and lamb chops
- Low fat milk and ‘lite’ margarine
- Skimmed milk and low fat yoghurt
- Sunflower oil and soya beans (1)
1.1.8 The food borne disease that affects the liver:
- Dysentery
- E-coli
- Gastroenteritis
- Hepatitis A (1)
1.1.9 Brand piracy is …
- unauthorised use of protected trade names.
- use of poor quality products that are not sustainable.
- copying of counterfeit trade names.
- importing goods into a country. (1)
1.1.10 ‘Sportswear has become street wear’. This statement refers to a …
- decline in fashion.
- fashion trend.
- fashion cycle.
- classic fashion. (1)
1.1.11 A signed sales agreement is a contract between a …
- buyer and home owner.
- buyer and an estate agent.
- home owner and an attorney.
- home owner and a tenant. (1)
1.1.12 The money you borrow from a bank to buy a home is …
- loan.
- collateral security.
- bond registration.
- mortgage bond. (1)
1.1.13 The monthly bond repayment should be between ... of the homeowner’s monthly income.
- 20% - 30%
- 25% - 30%
- 25% - 35%
- 20% - 25% (1)
1.1.14 Mr Hermanus was in an accident and is now permanently wheel chaired bound. The following insurance will cover his home loan outstanding balance:
- Bond insurance
- Long-term insurance
- Household insurance
- Homeowner’s insurance (1)
1.1.15 The … is the document that proves legal ownership of a property.
- Title Deed
- Deed of Sale
- Full title property
- Sectional Title (1)
1.1.16 The following endorsement shows that a household appliance meets specific criteria:
- SANF
- SABC
- SABS
- SANCU (1)
1.1.17 The amount added to the cost price to cover all expenses and still make a profit is called the …
- selling price.
- start-up.
- production cost.
- operational cost. (1)
1.1.18 Identify the business that has the most sustainable profitability.
- Suzanne does not always have enough money to buy raw materials.
- Ringani sells more products each month and she opened another branch.
- Thandi had to dismiss two employees as she no longer had work for them.
- Dorothy spends too much of her business income on clothes. (1)
1.1.19 Quality control is …
- the demand for a specialised service.
- the process of inspecting products.
- the evaluation of the proposed project.
- a method used to price products. (1)
1.1.20 The selling price for 5 products is R750.00 and the production cost is R530,00. Indicate how much profit is made per product.
- R44,00
- R56,00
- R163,00
- R220,00 (1) (20 × 1) (20)
1.2 Choose the description from COLUMN B that matches a term in COLUMN A. Write the letter (A–I) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
1.2.1 1.2.2 1.2.3 1.2.4 1.2.5 | Contract Cooling-off period Exemption clauses Stokvel Insurance contract | A B C D E F G H I | A one-sided business practice Forms the automatic renewal of contracts Goods sold by a business without the authorisation of the manufacturer Liability for personal injuries is excluded Allows a direct marketing contract to be cancelled within five working days An agreement with legal implications between two people Saving club where people pledge regular contributions A party is cleared from its liabilities if he/she fails to deliver goods honoured by agreement The agreement between the party and the insurance |
(5 × 1) (5)
1.3 Choose the term in COLUMN B that matches the description in COLUMN A. Write the letter (A–H) next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
1.3.1 1.3.2 1.3.3 1.3.4 1.3.5 | A new fashion worn by fashion leaders An illegal copy of a product The direction in which the fashion moves The specific characteristics that make one product or item different from another Fashion that is always considered tasteful | A B C D E F G H | Fads Trade mark Style Classic fashion Trend Brand piracy Counterfeit High fashion |
(5 × 1) (5)
1.4 Give the correct word/term for each of the description. Write only the words/terms next to the question number (1.4.1–1.4.5) in your ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 When all people have access at all times to sufficient safe and nutritious food
1.4.2 Natural or chemical substances added to food during processing to perform a specific function
1.4.3 Food grown without artificial fertilisers, growth regulators or pesticides
1.4.4 Food technology that reduces or eliminates micro-organisms to improve the shelf life of food
1.4.5 Food which a gene of another food is implanted to introduce characteristics of the other food (5 × 1) (5)
1.5 From the list below, identify FIVE examples of the application of universal design in household appliances. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question number (1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
- A child safety lock is attached
- Dialogue display is easy to read with large text
- Twin-tubs can take two loads at the same time
- Some washing machines use less water
- The door can open with an 180o angle
- The racks are adjustable and can be removed
- An alarm indicates the end of the programme
- Front loaders need attention during the washing process
- The HEPA filters are hypoallergenic (5 × 1) (5)
[40]
QUESTION 2 THE CONSUMER
2.1 Define the following terms:
2.1.1 Guarantee (2)
2.1.2 Inflation (2)
2.2
2.2.1 Explain the meaning of phishing. (2)
2.2.2 Give THREE ways to protect yourself against phishing. (3)
2.3 Read the following scenario and answer the questions that follow:
| Shaun buys imported cigarettes from a foreigner’s shop. The cigarettes are very cheap compared to other well-known cigarette brands. |
2.3.1 Describe the type of goods referred to in the scenario. (3)
2.3.2 Identify the type of tax Shaun pays when he purchases cigarettes. (1)
2.3.3 Explain the reasons why this type of tax is paid by consumers such as Shaun. (2)
2.4 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow:
|
2.4.1 Name TWO items from the scenario that is exempted from value added tax (VAT). (2)
2.4.2 Discuss how the information in the scenario will affect consumers’ household budget. (3)
[20]
QUESTION 3 FOOD AND NUTRITION
3.1 Name TWO foods that cause allergies. (2)
3.2 State THREE benefits that organically grown food may have for the natural environment. (3)
3.3 “Food irradiation is a technology used to improve the safety of food products such as herbs”. Discuss FOUR reasons why this statement is true. (4)
3.4 Compare milk allergy with lactose intolerance. Tabulate your answer as follows:
| Milk allergy | Lactose intolerance |
| (2) | (2) |
(4)
3.5 Explain why coronary heart disease is referred to as lifestyle disease. (3)
3.6 Answer the following questions on cholesterol.
3.6.1 Describe high cholesterol. (3)
3.6.2 Describe how regular checking of blood cholesterol levels can benefit a person suffering from high cholesterol. (3)
3.6.3 State FOUR dietary guidelines to manage high cholesterol. (4)
3.7 Differentiate between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Tabulate your answer as follows:
| Type 1 | Type 2 |
| (2) | (2) |
(4)
3.8 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow:
Tammy is living with her grandparents in a one-bedroom house. The grandparents receive a small pension that is too little to provide them with daily balanced meals. |
3.8.1 Explain how the disease could have been transmitted. (2)
3.8.2 Analyse the impact of the vegetable and fruit on Tammy’s health. (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4 CLOTHING
4.1 Define the following terms:
4.1.1 Retrospective fashion (2)
4.1.2 Organic textiles (2)
4.2 Explain how fashion is influenced by technological developments. (3)
4.3 Describe what a basic working wardrobe is. (2)
4.4 Discuss why fashion cycles overlap. (3)
4.5 Explain why it is important to buy quality clothes when you choose clothes for work. (2)
4.6 Read the following information and give your opinion that the role appearances play in the world of work.
| Corporate clothing should be simple, but classic. Dressing in a corporate uniform ensures a basic standard of appearance. In this way, clients will listen to what you have to say. |
(6)
[20]
QUESTION 5 HOUSING
5.1 Explain the following terms:
5.1.1 Transfer duty (2)
5.1.2 Transfer fees (2)
5.2 Name THREE cost items that must be included in a mortgage bond repayment. (3)
5.3 Give the information that must appear on a contract for a builder and owner to sign. (4)
5.4 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow:
The Buys family has a son age eight and a daughter fifteen. They bought a flat in a secured complex. They often used the swimming pool. They spent a lot of their money on transport to work and school. Mr Buys was transferred to another town and the family decided to relocate. |
Identify and explain the type of ownership of the Buys family:
5.4.1 When they bought the house in the new town (3)
5.4.2 When they bought the flat (3)
5.5 Discuss FOUR advantages of renting the apartment. (4)
5.6 Name FOUR advantages of owning a flat in a secured complex. (4)
5.7 Explain why this house is ideal for this family. (3)
5.8 The Buys family intend buying a vacuum cleaner.
|
5.8.1 Explain why this vacuum cleaner is considered to be environmentally friendly. (4)
5.8.2 Evaluate the suitability of this vacuum cleaner to clean a three bedroom house with tile floors as well as carpeted floors. (8)
[40]
QUESTION 6 ENTREPRENEURSHIP
6.1 Name FOUR reasons for packaging products. (4)
6.2 Explain mark-up with regard to small business practices. (2)
6.3 State THREE benefits of training unskilled workers. (3)
6.4 Read the case study below and answer the questions that follow:
| Wendy Smith who has a passion for baking, began a small business from home. She decided on making healthy breakfast biscuits. She adapted her aunt’s choc-chip biscuit recipe using raisins instead chocolate and instead of butter use margarine. She started with basic equipment and an electric beater. Soon with many orders the business outgrew her home and she had to move to bigger premises. Today she supplies many shops and her business is advertised on a commerce website. “I am passionate about the design for each biscuit, the way we packed our product and the way our production process is executed. My number one priority with leading team’s vision is listening and carrying out ideas and suggestions from our customers. They have shaped the growth of the company.” |
Her business in figures:
|
6.4.1 Wendy came up with an idea and recognised the need for a product in a given target market. Describe the target market that her product would appeal to. (2)
6.4.2 What is the importance of keeping to the product specification? (2)
6.4.3 Wendy drew up a business plan before launching her business. People is one of the 5P’s to be combined for successful marketing. Name the other 4P’s of a marketing plan and explain how Wendy fulfilled each of these. (8)
6.4.4 “They have shaped the growth of the company”. Elaborate on the importance of good customer relations. (3)
6.4.5 Name the information that should be on the label of the breakfast biscuits. (4)
6.5 Use the following information with regard to calculating costs in order to answer the question that follow:
Jamé’s Florists Cost per bouquet
|
6.5.1 Calculate the selling price of a bouquet. Show ALL calculations. (3)
6.5.2 Calculate the profit on this specific product for this month if she sold 40 bouquets during this period. (2)
6.5.3 Analyse how a financial feasibility study will assist Jamé to determine the sustainable profitability of her business. (7)
[40]
TOTAL: 200
CONSUMER STUDIES GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
0CONSUMER STUDIES
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1 SHORT QUESTIONS
1.1 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
1.1.1 C ✔ (1) Remembering Easy
1.1.2 B ✔(1) Remembering Easy
1.1.3 B ✔(1) Remembering Easy
1.1.4 B ✔ (1) Remembering Moderate
1.1.5 D ✔ (1) Remembering Easy
1.1.6 A ✔ (1) Remembering Easy
1.1.7 A ✔ (1) Remembering Easy
1.1.8 D ✔ (1) Remembering Easy
1.1.9 A ✔ (1) Remembering Moderate
1.1.10 B ✔ (1) Remembering Easy
1.1.11 A ✔ (1) Remembering Easy
1.1.12 A ✔ (1) Remembering Easy
1.1.13 B ✔ (1) Remembering Easy
1.1.14 C ✔ (1) Remembering Easy
1.1.15 A ✔ (1) Remembering Easy
1.1.16 C ✔ (1) Remembering Easy
1.1.17 C ✔ (1) Remembering Easy
1.1.18 B ✔ (1) Remembering Easy
1.1.19 B ✔ (1) Remembering Easy
1.1.20 A ✔ (1) Applying Moderate (20 × 1) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 F ✔ (1)
1.2.2 E ✔ (1)
1.2.3 H ✔ (1)
1.2.4 G ✔ (1)
1.2.5 I ✔ (1)
Remembering, Easy (5 × 1) (5)
1.3
1.3.1 B ✔ (1)
1.3.2 G ✔ (1)
1.3.3 H ✔ (1)
1.3.4 C ✔ (1)
1.3.5 D ✔ (1)
Remembering, Moderate (5 × 1) (5)
1.4
1.4.1 Food security ✔(1)
1.4.2 Food additives ✔(1)
1.4.3 Organic foods ✔ (1)
1.4.4 Radiation ✔ (1)
1.4.5 Genetic modified foods ✔(1)
Remembering, Moderate (5 × 1) (5)
1.5
A ✔ (1)
B ✔ (1)
E ✔ (1)
F ✔ (1)
G ✔ (1)
(In any sequence) Understanding, Moderate (5 × 1) (5)
[40]
QUESTION 2 THE CONSUMER
2.1 2.1.1 Guarantee
- A guarantee is a promise in writing that the quality and durability of a product or service will meet certain standards and that if the product or service does not satisfy the terms of the guarantee, you will be refunded.
OR - A guarantee is an assurance that a product will remain in working order for a particular length of time. A guarantee is a promise from the manufacturer that they will sort out any problems with a product or service within a specific fixed period of time.
Remembering, Easy (2)
2.1.2 Inflation
- Is the rise in prices of goods and services, measured over a specific period, and subsequently a drop in purchasing power of money.
OR - It is the average increase in prices of goods and services in a year.
Remembering, Easy (2)
2.2 2.2.1 Explain the meaning of phishing
- Any fake e-mails/websites, phone calls pretending to be the bank or a financial institution. Designed to steal your money by getting your personal information or sending a link to retrieve personal information.
Remembering, Easy (2)
2.2.2 Give THREE ways to protect yourself against phishing.
- If you suspect an e-mail is fake or spam, delete it without opening it.
- Keep anti-spam and antivirus software up to date on your computer.
- Never give your personal details by e-mail.
- Never open attachments on e-mails that claim to come from your bank – they could contain spay word that could track your keystrokes and gather your personal information.
- Check your bank and credit card account statements regularly.
- If you think that you may have provided financial information such as credit card number to a phisher, contact your financial institution or credit card company immediately.
- Make sure that you use legitimate websites/e-mails/phone calls.
- Antivirus programmes secure insecure websites/spam/codes/pin/passwords used.
Remembering, Easy (Any 3) (3)
2.3 2.3.1 Describe the type of goods referred to in the scenario.
- Grey good/parallel goods ✔ are goods that have been imported ✔ into the country through unofficial or unauthorised ✔ distribution channels. These goods are not illegal goods ✔
Application, Moderate (3)
2.3.2 Identify the type of tax Shaun pays when he purchases cigarettes.
- Excise tax/Sin tax ✔
Remembering, Easy (1)
2.3.3 Explain the reasons why this type of tax is paid by consumers such as Shaun.
- To decrease the amount of people that smoke because it is a health risk ✔
Remembering, Moderate (2)
2.4 2.4.1 Name TWO items from the scenario that is exempted from value added tax (VAT).
- Maize meal
- Maize rice
- Samp
Remembering, Easy (Any 2) (2)
2.4.2 Discuss how the information in the scenario will affect consumers’ household budget.
- Drought may lead to the maize meal, maize rice and samp (grains) shortages which will lead to increased prices✔
- Manufacturing factories may close down due to shortage of grains to process✔which will lead to job losses
- This can result in consumers having less disposable income to purchase grains/other items/luxuries
- The weak rand may also result in increased imported grain prices that will put further strain on household budgets
Analysing, Difficult (Any 3) (3)
[20]
QUESTION 3 FOOD AND NUTRITION
3.1 Name TWO foods that cause allergies.
- Peanuts, milk, eggs, shellfish, soya beans, wheat
Remembering, Easy (Any 2) (2)
3.2 State THREE benefits that organically grown food may have for the natural environment.
Organic farmers use natural pesticides to protect the environment.
- They concentrate on the sustainable use of resources.
- It improves the soil quality/prevents soil pollution.
- It reduces air pollution as very little or no fuel is used to manufacture organic fertilisers.
- Protects the water supply. Water remains cleaner because there are no run-off poisonous chemicals into the water.
Understanding, Easy (Any 3) (3)
3.3 “Food irradiation is a technology used to improve the safety of food products such as herbs”. Discuss FOUR reasons why this statement is true.
- Food is treated with short light or radio waves to improve the safety, acceptability and shelf life.
- The rays penetrate deep into the food/killing/eliminating/reducing/destroying unwanted bacteria/harmful organisms/insects in food therefore reduced food spoilage.
- The waves pasteurised and lengthen/extend the shelf life of food. Unwanted bacteria/organisms are destroyed.
- It protects people from food-borne diseases.
- Herbs are safe to use. Herbs can have a high level of bacteria/insect contamination during production, but after irradiation they are safe to use.
Applying, Difficult (Any 4) (4)
3.4 Compare milk allergy with lactose intolerance.
| Milk allergy | Lactose intolerance |
|
|
Deduct one mark if not answered in table format.
Understanding, moderate
3.5 Explain why coronary heart disease is referred to as lifestyle disease.
- It is a disease related to a high intake of saturated fats, especially trans fat in junk foods.
- People consume food that contains many hidden fats, that they do not realise they are eating.
- There are many lifestyle factors that contribute to the disease such as poor diet that leads to obesity/overweight, lack of physical activity, excessive alcohol intake, smoking, stress.
Understanding, moderate (Any 3) (3)
3.6 Answer the following questions on cholesterol.
3.6.1 Describe high cholesterol.
- High cholesterol develops when excessive amounts of cholesterol ✔ high density lipoproteins are deposited in the arteries. ✔ This will narrow/block the arteries increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. ✔
Remembering, Easy (3)
3.6.2 Describe how regular checking of blood cholesterol levels can benefit a person suffering from high cholesterol.
- Cholesterol accumulates slowly/largely unnoticed/no symptoms, therefore regular checks are necessary to create awareness, and only then the condition can be managed. ✔
- High cholesterol may be genetic/hereditary and regular check-ups may reveal the condition. ✔
Understanding, moderate (Any 3) (3)
3.6.3 State FOUR dietary guidelines to manage high cholesterol.
- Control the amount of fat/saturated fat/egg yolks/organ meats/some seafood consumed on daily basis. ✔
- Eat lots of fibre/soluble fibre/oat bran/legumes.✔
- Eat lots of fruit and vegetables as they contain very little fat, but a great deal of vitamins, mineral, fibre, anti-oxidants. ✔
- Reduce high-fat dairy products/use low-fat dairy products.✔
- Avoid hidden fat in your diet, e.g. processed foods containing fat. ✔
Understanding, moderate (Any 4) (4)
3.7 Differentiate between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
| Type 1 | Type 2 |
| The pancreas is unable to produce insulin, ✔ and has to be replaced with an insulin injection. ✔ (2) | The pancreas✔ produces insulin, but it is not enough/does not work effectively. ✔ (2) |
Understanding, Easy (4)
3.8 Scenario
3.8.1 Explain how the disease could have been transmitted.
- The bacteria are spread through the air, when an infected person coughs, sneezes, speaks or sings. People breathing the same air for prolonged periods. (2)
Applying, Difficult
3.8.2 Analyse the impact of the vegetable and fruit on Tammy’s health.
- Tammy should consume five to six portions of fruit and vegetables daily. ✔
- The vegetables from their garden will help Tammy in her recovery period. ✔
- Spinach/oranges/carrots/cabbage provides vitamin A and is an anti-oxidant which keep Tammy’s lining of her lungs and intestine intact. ✔ This makes it difficult for the germs to enter the body ✔ and causes infection.
- Oranges/tomatoes/carrots provide vitamin C which helps Tammy to recover from infections.
- Cabbage provide zinc ✔ which protects the immune system ✔ and iron is important as it helps with the formation of red blood cells ✔ and prevent anaemia/keep the blood healthy ✔ and plays a role in a healthy immune system. ✔ (Any 7)
Conclusion: The vegetables and fruit will be beneficial/impact positively on Tammy’s health ✔ (1) (8)
Analyse, Difficult
[40]
QUESTION 4 CLOTHING
4.1 Define the following terms:
4.1.1 Retrospective fashion
- Retrospective fashion refers to clothes that imitate the style of a previous era. ✔✔
Remembering, Easy (2)
4.1.2 Organic textiles
- It is natural fibres that have been grown without any pesticides and toxic materials, preserving the health of humans and the environment. ✔✔
Remembering, Easy (2)
4.2 Explain how fashion is influenced by technological developments.
- Technological developments in the textile industry accelerate fashion change, e.g. improved elasticity or minimal care requirements. ✔
- Developments in the manufacturing industry, e.g. improved knitting and sewing machines have speeded up the manufacturing process, saving time and money. ✔
- Easier communication allows latest fashion trends to be viewed all over the world. ✔
- Improved distribution methods bring new fashion garments to stores within days. ✔
Understanding, moderate (Any 3) (3)
4.3 Describe what a basic working wardrobe is.
- A basic working wardrobe is the outfits/garments you wear to work that is suitable for the work environment. ✔
- All the clothing items ✔ you choose to wear to work ✔ specific clothes suited for the daily tasks/work.
Remembering, Easy (2)
4.4 Discuss why fashion cycles overlap.
- Fashion cycles overlap because consumers are bored with the old trend. ✔
- Fewer consumers wear the old trend as the interest is decreasing.✔
- A new trend is introduced/begins/launched/celebrities are photographed wear the trend. ✔
- Fewer consumers wear the old trend, until no one wears it any more. ✔
- While the old trend declines, interest in the new trend increases. ✔
- By the time a new fashion trend has established itself and is well on its way to its peak. ✔
Understanding, Easy (Any 3) (3)
4.5 Explain why it is important to buy quality clothes when you choose clothes for work.
- If you buy quality items from the start, they will last longer. ✔
- It is a much better investment plan than buying cheap clothes. ✔
Remembering, Moderate (2)
4.6 Read the following information and give your opinion that the role appearances play in the world of work.
| Corporate clothing should be simple, but classic. Dressing in a corporate uniform ensures a basic standard of appearance. In this way, clients will listen to what you have to say. |
- Clothes will send a message to customers about the type of work and the company one work for. The corporate dress code will also include personal hygiene and posture to give a better impression when working with customers. ✔
- If one wears appropriate clothes the employer and customers will have confidence in one and ones work because one shows that one is professional at work. ✔
- If one dress according to the corporate rules it will show the employer that one is serious about and respects ones work. ✔
- Less is more – simple, but classy thus more clothes are not always better than less classy clothes. ✔
- A sophisticated corporate look commands respect. ✔
- One is judged on physical appearance – a corporate uniform ensures a standardised company image. ✔
Analysing, moderate (6)
[20]
QUESTION 5 HOUSING
5.1 Explain the following terms:
5.1.1 Transfer duty
- It is a government tax on the property to transfer it into your name and is based on the amount to the Receiver of Revenue. ✔ It is based on the value of the property. ✔
Remembering, Easy (2)
5.1.2 Transfer fees
- It is paid to the attorney who oversees the transfer process of the property. ✔✔
Remembering, Easy (2)
5.2 Name THREE cost items that must be included in a mortgage bond repayment.
- Payment of capital (amount borrowed) ✔
- Interest ✔
- Homeowner’s comprehensive insurance/monthly instalments ✔
- Homeowner’s premium ✔
- Administration cost ✔
Remembering, Easy (Any 3) (3)
5.3 Give the information that must appear on a contract for a builder and owner to sign.
- A detailed breakdown of all costs, including building and legal cost. ✔
- The exact dimensions or size of the house, according to house plan. ✔
- The date by which the building should be completed. ✔
- The statement of the guarantees provided to ensure that any structural defects, roof leaks will be fixed. ✔
- The dates and way in which payments are to be made. ✔
- A cancellation clause laying down the conditions under which the contract can be cancelled or suspended. ✔
- The consequences if either the builder or owner does not fulfil their part of the agreement. ✔
- The specification list attached to the plan, which describes all the materials, finishes and fittings to be used in the construction of the house. ✔ (Any 4) (4)
5.4 Scenario
Identify and explain the type of ownership of the Buys family:
5.4.1 When they bought the house in a new town
- Full-title ownership ✔
Remembering, Easy - The Buys family – the legal owner ✔ of the entire property – the land and all the structures on it ✔
Application, Easy (3)
5.4.2 When they bought the flat
- Sectional title ownership ✔
Remembering, Easy - Section title – lawful ✔ owner of a unit or section of a building.
The sectional title holder also owns a share of all common properties, including lifts, passages, stairways, garden areas and pool. ✔
Application, Easy (3)
5.5 Discuss FOUR advantages of renting the apartment.
- A tenant pays a fixed amount over a specific period. ✔
- A tenant does not pay land and property tax. ✔
- A tenant is not responsible for the maintenance of the property
- A tenant can run a business from the unit if he or she obtains permission from the property owner and the municipality. ✔
- From the start, both parties know exactly what is expected it is the conditions of the lease agreement. ✔
- It is easy to move after giving due notice. ✔
- A tenant can have fewer monthly expenses than a house owner, for example, tenants do not have to pay homeowners insurance. ✔
- Renting is more affordable for people who cannot afford to buy a home. ✔
Remembering, Easy (Any 4) (4)
5.6 Name FOUR advantages of owning a flat in a secured complex.
- They are the legal owners of the property – can leave in the will for their children. ✔
- The owner has a sense of security and independence. ✔
- Living in a complex could be safer. ✔
- They can use all common areas in the complex. ✔
- The owner has less administration to do. ✔
- They can sell the flat at a profit to buy another house.✔
- The homeowners association administers the property of the sectional tile block, which means less responsibility for the family. ✔
- They can make changes to the property. ✔
Applying, Easy (Any 4) (4)
5.7 Explain why this house is ideal for this family.
- The house has three bedrooms/big enough/suitable for the family’s needs/privacy for the members. ✔
- It is safe – alarm and safety gates. ✔
- It is close to the school – save on transport cost; it is also convenient if the children participates on extramural activities. ✔
- The shopping centre is nearby, it is convenient for shopping and they will also save on transport cost. ✔
- The shopping centres also has entertainment for the family. ✔
Application, Moderate (Any 3) (3)
5.8 The Buys family intend buying a vacuum cleaner.
|
5.8.1 Explain why this vacuum cleaner is considered to be environmentally friendly.
- The dust retention prevent the dust in the air ✔ therefore reduces air pollution.
- It uses less energy, therefore has a low impact on the carbon footprint. ✔
- Due to the low energy usage it reduces the need for fossil fuels to burn ✔ in order to create electricity.
- Anti-bacterial protection prevent release of dust mites into the air ✔ leaving the air cleaner, makes it a healthier option.
Applying, Moderate (Any 4) (4)
5.8.2 Evaluate the suitability of this vacuum cleaner to clean a three bedroom house with tile floors as well as carpeted floors.
- The 1,5 litre dust capacity makes it large enough✔
- It can extend to reach awkward corners✔ therefore the need to move furniture around is reduced ✔ this reduced the human energy consumption. ✔
- The smooth running wheels make it possible to move it around with the least amount of resistance ✔ and it causes the least amount of damage to surfaces✔
- Suitable to clean carpets and tiles, it is not necessary to have two different machines. ✔
- The washable filters reduces the need to replace the filter therefore saving money in the long-term.✔
- Use less electricity and results in reduced electricity bill ✔ (Any 7)
Conclusion:
- The vacuum cleaner is suitable for a three-bed roomed house (1) (8)
Evaluate, Difficult
[40]
QUESTION 6 ENTREPRENEURSHIP
6.1 Name FOUR reasons for packaging products.
- To protect the product ✔
- Keep the product safe and hygienic ✔
- It could act as a silent/attract the attention of the consumers ✔
- Well-designed packaging can reflect well on a business image ✔
Remembering, Easy (4)
6.2 Explain mark-up with regard to small business practices.
- The amount/percentage added to the cost price✔ of goods to cover overhead expenses✔/still leave money for profit. (2)
6.3 State THREE benefits of training unskilled workers.
- Better quality work is delivered ✔
- Increased motivation ✔
- Increased work satisfaction ✔
- Ability to work independently ✔
- Increased productivity ✔
- Reduction of waste ✔
- Acquisition of new skills/knowledge ✔
Remembering, Easy (Any 3) (3)
6.4 6.4.1 Target market
- People who need a quick breakfast ✔
- People who skipped breakfast ✔
- Those who want a low kilojoule option ✔
Application, Moderate (Any 2) (2)
6.4.2 What is the importance of keeping to the product specification?
- Ensures that the customer will always get a good quality product ✔
- Ensures standardisation/a certain standard is maintained/product ✔
- Will always have the same appearance taste ✔
Remember, Easy (Any 2) (2)
6.4.3 Marketing Plan
- Promotion ✔ – Website ✔
- Price ✔ – R23,80 per unit ✔
- Product ✔ – Breakfast biscuit (mini breakfast biscuit) ✔
- Place ✔ – from home ✔ (not rental premises)
Applying, Moderate (8)
6.4.4 Customer relations
- Wendy has valued the input from her clients ✔
- She will be able to maintain a quality product ✔
- By listening to their needs and responding to their needs she has ensured loyal customers to her brand ✔
- Word of mouth ✔
Applying, Easy (Any 3) (3)
6.4.5 Information on label
- Brand name ✔
- Trade name ✔
- Ingredient list ✔
- Contact details ✔
- Portion size ✔
- Allergens ✔
- Serving suggestion ✔
- Storage instruction ✔
- Price of the product ✔
- Net quality of contents ✔
- Date stamp
Applying, Easy (Any 4) (4)
6.5 Calculation
6.5.1 Calculate the selling price of a bouquet. Show ALL calculations.
- Selling price = production cost + mark-up
= (R120,00 + R80,00) ✔ + 75% of R200
= R200,00 + R150,00 ✔
= R350,00
Applying, Moderate (3)
6.5.2 Calculate the profit on this specific product for this month if she sold 40 bouquets during this period.
- R150,00 × 40 ✔ = R600,00 ✔
Applying, Moderate (2)
6.5.3 Analyse how a financial feasibility study will assist Jamé to determine the sustainable profitability of her business.
- Main purpose of a feasibility study is to discover the strengths and weakness of an existing or new business. Janey’s strength is that she took over an existing business or new business ✔ She has a passion✔ for flower arrangements and good human skills. ✔ She has a vision for the shop. ✔
- Know all the cost ✔ involved, because she is a financial manager and realise all the expenditure
- Estimate potential sales, she looked at opening another section ✔ and supplying undertakers with bouquets.
- She will know how much profit they will make every month. ✔
- She will not need any start-up capital as she took over an existing business. ✔
- She will know the type of return on investment (profit) can be expected. ✔ (Any 6)
Conclusion:
- A financial feasibility study will help her to determine the cost and the selling price of a product accurately. ✔ (1)
Evaluating, moderate (7)
[40]
TOTAL: 200
ACCOUNTING GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
ACCOUNTING
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully and follow them precisely.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- A special ANSWER BOOK is provided in which to answer ALL the questions.
- Show ALL workings to earn part-marks.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- You may use a dark pencil or black/blue ink to answer the questions.
- Where applicable, show all calculations to ONE decimal place.
- A breakdown of the questions is provided. You must attempt to comply with the suggested time allocation for each question.
QUESTION 1: 40 marks; 25 minutes | |
Main topic: | This question integrates: |
Reconciliations | Financial Accounting
|
| QUESTION 2: 40 marks; 25 minutes | |
Main topic: | This question integrates: |
Inventory valuation | Managing Resources
|
| QUESTION 3: 50 marks; 30 minutes | |
Main topic: | This question integrates: |
Company Financial Statements | Financial Accounting
Managing Resources
|
| QUESTION 4: 70 marks; 45 minutes | |
Main topic: | This question integrates: |
Financial Statements, Cash flow and Interpretation | Managerial Accounting
|
| QUESTION 5: 60 marks; 30 minutes | |
Main topic: | This question integrates: |
Cost Accounting and Fixed Assets | Managerial Accounting
Managing resources
|
| QUESTION 6: 40 marks; 25 minutes | |
Main topic: | This question integrates: |
Budgeting | Managerial accounting
|
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: RECONCILIATIONS (40 marks; 25 minutes)
1.1 Choose the correct answer from the words provided within brackets. Write only the answer, next to each number (1.1.1–1.1.4) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.1.1 A stale cheque, one that is more than 6 months old, must be cancelled in the (Cash Receipts Journal/Cash Payments Journal).
1.1.2 A (debit/credit) balance on the bank statement indicates an overdraft.
1.1.3 A (debit note/credit note) is the source document for goods returned by a debtor.
1.1.4 A (cash discount/trade discount) is offered when accounts are settled within a certain time. (4)
1.2 DEBTORS RECONCILIATION AND AGE ANALYSIS
The information below, relates to JT Traders for June 2017.
REQUIRED:
1.2.1 Calculate the correct Debtors Control balance on 30 June 2017. (4)
1.2.2 Calculate the correct balances for the debtors listed in the ANSWER BOOK. (12)
1.2.3 Refer to the Age Analysis (Information C):
- Calculate the percentage of debtors that are not complying with the 30 days credit terms. (3)
- Explain TWO internal control measures that JT Traders can use to ensure that only reliable clients are granted credit. (4)
INFORMATION:
A. Balances on 30 June 2017 (before errors and omissions):
Debtors Control balance | R74 600 |
Debtors list | 70 000 |
| N. Pillai | 21 600 |
| Y. Bosman | 12 400 |
| C. Tele | 24 900 |
| A. Botha | ? |
B. Errors and omissions discovered:
- The Debtors Journal was overcast by R3 500.
- An allowance of R800 granted to Pillai for damaged goods dispatched was entered in the wrong side of her account.
- Goods sold on credit to Botha for R6 300 was posted incorrectly to his account as R3 600. Posting to the General Ledger was correct.
- A cheque for R2 500 received from Tele was recorded in the account of Bosman in error.
- A cheque for R4 230 received from Pillai was returned by the bank marked “R/D – insufficient funds”. A discount of R270 was granted when this cheque was received. This has not yet been recorded.
C. DEBTORS AGE ANALYSIS
| AMOUNT OWING | CURRENT MONTH | 30 DAYS | 60 DAYS | More than 60 DAYS |
| R70 000 | 12 600 | 21 000 | 28 000 | 8 400 |
Debtors are allowed 30 days to settle their accounts.
1.3 CREDITORS RECONCILIATION
Marge Traders buys goods on credit from Simpson Suppliers. The information presented is for July 2017.
REQUIRED:
- Reconcile the Creditors Ledger account of Simpson Suppliers in the books of Marge Traders with the statement received.
- Commence with the opening balances as provided in the ANSWER BOOK. (13)
INFORMATION:
A. Creditors Ledger of Marge Traders
Simpson Suppliers (CL6)
DATE | DETAILS | FOL | DEBIT | CREDIT | BALANCE | |
July | 1 | Balance | b/d | 34 200 | ||
5 | Invoice No. 443 | CJ | 4 770 | 38 970 | ||
10 | Cheque No. 2810 | CPJ | 15 000 | 23 970 | ||
Discount | CPJ | 750 | 23 220 | |||
12 | Invoice No. 568 | CJ | 5 640 | 28 860 | ||
18 | Debit Note No. 114 | CAJ | 980 | 27 880 | ||
28 | Invoice No. 667 | CJ | 7 120 | 35 000 | ||
B. Statement received from Simpson Suppliers
| |||||
DATE | DETAILS | DEBIT | CREDIT | BALANCE | |
June | 28 | Account rendered | 38 830 | ||
30 | Invoice No. 376 | 3 370 | 42 200 | ||
July | 1 | Receipt No. 1144 | 8 000 | 34 200 | |
5 | Invoice No. 443 | 7 740 | 41 940 | ||
10 | Receipt No. 1328 | 15 000 | 26 940 | ||
12 | Invoice No. 568 | 6 640 | 33 580 | ||
18 | Credit Note No. 743 | 980 | 34 560 | ||
22 | Invoice No. 772 | 3 860 | 38 420 | ||
Includes transactions up to 25th of each month | |||||
C. Differences noted:
- Invoice No. 443 was recorded incorrectly in the creditors ledger.
- The statement did not reflect the discount for early payment on the 10th. This will be rectified on the next statement.
- It was discovered that Invoice No. 568 on the statement included goods valued at R1 000 ordered by the warehouse manager. The manager is facing disciplinary action.
- Goods valued at R980 were returned on the 18th. It is shown as a debit entry in both the creditor’s ledger account as well as the statement of account.
- Invoice No. 772 on the statement was for goods sold to a different business. This will be corrected on the next statement.
- The statement was received on 25 July 2017.
40
QUESTION 2: INVENTORY VALUATION (40 marks; 25 minutes)
2.1 Choose the stock system/method from the list provided, that is best described by each of the statements below. Write only the stock system/method next to each number (2.1.1–2.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
| First-in-first-out (FIFO); weighted average; perpetual; specific identification; periodic |
2.1.1 Similar value, low cost stock items are valued by taking into account the total cost of the items divided by the number of items available for sale.
2.1.2 The closing stock value of goods is determined by assuming that the goods bought first, are sold first.
2.1.3 Cost of sales is recorded at the point of sale and stock records are adjusted accordingly.
2.1.4 The closing stock figure to be used to calculate the cost of sales, is determined by a physical stock count at the end of an accounting period.
2.1.5 Sales and cost of sales records are maintained for the individual items sold due to these being high value goods. (5)
2.2 COMRADES LTD
Comrades Ltd sells sporting equipment. The information relates to the tracksuits and vests departments for the financial year ended 30 April 2017.
REQUIRED:
2.2.1 Calculate the selling price per unit for tracksuits. (2)
2.2.2 Calculate the cost of sales of tracksuits using the FIFO method. (7)
2.2.3 Calculate the stock turnover rate of tracksuits (use the average stock). (5)
2.2.4 It was discovered that vests were missing from the June 2016 delivery. Calculate the number and value of the missing vests. (7)
2.2.5 Calculate the Gross Profit made by the vests department. Note that this department uses the weighted average method to value stock. (8)
2.2.6 The owner is not satisfied with the performance of the vests department. Identify TWO problems, other than the missing vests, in this department. Quote figures. In each case, provide a solution to the problem. (6)
INFORMATION:
TRACKSUITS | VESTS | |||||
Working days per year | 264 days | 264 days | ||||
Days worked by department | 250 days | 172 days | ||||
Stock turnover rate | 2.2.3 | 2 times | ||||
Sales | UNITS | AMOUNT | UNITS | AMOUNT | ||
515 | R296 125 | 298 | ? | |||
Selling price per unit | 2.2.1 | R140 | ||||
Stock | UNITS | UNIT PRICE | AMOUNT (R) | UNITS | UNIT PRICE | AMOUNT (R) |
Opening stock | 125 | 40 000 | 160 | 13 760 | ||
Purchases: | 500 | 170 450 | 340 | 33 740 | ||
June 2016 | 120 | R330 | 39 600 | 75 | R92 | 6 900 |
August 2016 | 150 | R340 | 51 000 | 160 | R95 | 15 200 |
November 2016 | 130 | R345 | 44 850 | 60 | R110 | 6 600 |
January 2017 | 100 | R350 | 35 000 | 45 | R112 | 5 040 |
Returns | 10 units of the January 2017 purchases | |||||
Closing stock | 96 | ? | ? | 186 | ? | 17 670 |
40
QUESTION 3: AUDIT REPORTS AND COMPANY FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (50 marks; 30 minutes)
3.1 AUDIT REPORTS
Choose the audit opinion from COLUMN B that best describes the audit report in COLUMN A. Write the letter only (A–C) next to the numbers (3.1.1–3.1.3) in the ANSWER BOOK. (3)
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
3.1.1 Qualified audit report |
|
3.2 RUHI LTD
Ruhi Ltd is a listed company with an authorised share capital of 800 000 ordinary shares. The information provided is for the financial year ended 28 February 2017.
REQUIRED:
3.2.1 Prepare the Retained Income note to the Balance Sheet. (10)
3.2.2 Complete the Balance Sheet on 28 February 2017. Show all workings in brackets. Some amounts are provided in your ANSWER BOOK. (26)
3.2.3 The CEO, Bakkies Spencer, owns 42% of the issued shares on 28 February 2017. The Board of Directors wants to issue the unissued shares in the next financial year.
- Do a calculation to show the number of shares that Bakkies must buy to gain control of the company. (5)
- Bakkies wants to buy the shares at the current net asset value without advertising them to the public. As an existing shareholder, why would you not be satisfied with this arrangement? Explain. Provide TWO points. (4)
3.2.4 Ruhi Ltd is planning to spend R300 000 on staff development and training over the next two years. How will this expense be explained (disclosed) in the published annual report? Give ONE point. (2)
INFORMATION:
A. The following balances/totals were extracted from the company records on 28 February 2017:
R | |
Ordinary share capital | ? |
Retained income (20 January 2017) | 7 480 |
Fixed assets at carrying value | 4 060 545 |
Fixed Deposit: Londa Bank | 415 000 |
Loan: Dube Bank | 766 400 |
Inventory (all Trading Stock) | 222 600 |
Trade and other payables | 231 920 |
SARS: Income tax (provisional tax payments) | 280 000 |
Cash in bank | 212 400 |
B. Share Capital and Dividends:
- On 1 March 2016, 80% of the authorised share capital was in issue.
- On 20 January 2017, the company repurchased 40 000 shares at R1,25 above the average share price of R6,00. This transaction was recorded.
- An interim dividend of R179 200 was paid on 30 August 2016.
- A final dividend of R210 000 was declared on 28 February 2017.
C. Fixed Deposit:
- R165 000 of the fixed deposit matures on 30 June 2017. The balance matures in 2020.
D. Loan: Dube Bank
The loan statement received reflected the following:
Balance on 1 March 2016 | R920 000 |
Total of monthly repayments (including interest) | 153 600 |
Interest capitalised | 65 400 |
Balance on 28 February 2017 | ? |
A portion of the loan will be settled during the next financial period.
E. Profit and tax:
- The net profit after tax amounted to R681 720.
- Income tax is calculated at 31% of the net profit.
F. Financial indicators on 28 February 2017:
Solvency ratio | 4 : 1 |
Current ratio | 1,5 : 1 |
Net asset value (NAV) | 650 cents |
Market price (Securities Exchange) | 710 cents |
50
QUESTION 4: FINANCIAL STATEMENTS, CASH FLOW AND INTERPRETATION (70 marks; 45 minutes)
4.1 CONCEPTS: MATCHING
Choose an accounting concept from COLUMN B that best matches the questions in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–D) next to the number (4.1.1–4.1.3) in the ANSWER BOOK.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
4.1.1 To what extent does the business rely on borrowed funds? |
(3) |
4.2 MANI LTD
Information for the financial year ended 30 June 2017 is provided. REQUIRED:
4.2.1 Prepare the Share Capital note to the Balance Sheet on 30 June 2017. (10)
4.2.2 Calculate the following amounts to be used in the Cash Flow Statement:
Use brackets to indicate amounts that represent an outflow of cash.
- Dividends paid (4)
- Income tax paid (4)
- Change in investment (2)
- Change in loan (2)
4.2.3 Calculate the cost of the additional equipment purchased. (6)
4.2.4 Complete the net change in cash and cash equivalents section of the Cash Flow Statement. (5)
4.2.5 Calculate the following financial indicators on 30 June 2017:
- Gross profit percentage (mark-up percentage) (4)
- Net asset value per share (NAV) (3)
- Return on average shareholders’ equity (6)
4.2.6 Were the directors justified in increasing the loan? Explain. Quote TWO financial indicators (with figures) in your answer. (7)
4.2.7 Explain why the shareholders are not satisfied with:
- Dividend pay-out policy
- Their return earned
Quote financial indicators (with figures) in your explanation. (8)
4.2.8 Comment on the price paid to re-purchase the shares on 31 March 2017.
Quote TWO financial indicators (with figures) in your comments. (6)
INFORMATION:
A. Extracts from the Income Statement on 30 June 2017:
R | |
Sales | 11 440 000 |
Gross Profit | 4 290 000 |
Depreciation | 510 000 |
Interest expense | 132 000 |
Net profit before income tax | 1 048 000 |
Income tax | 314 400 |
B. Extracts from the Balance Sheet on 30 June:
30 JUNE 2017 | 30 JUNE 2016 | |
Fixed assets (carrying value) | 9 806 000 | 8 410 800 |
Investments | 80 000 | 120 000 |
Shareholders’ equity | 8 801 400 | 7 821 800 |
| Ordinary share capital | 8 412 800 | ? |
| Retained income | 388 600 | ? |
| Loan: Viva Bank | 1 250 000 | 950 000 |
| Cash and cash equivalents | 2 500 | 98 500 |
| Bank overdraft | 65 300 | - |
| SARS: Income tax | 22 300 (Cr) | 31 000 (Dr) |
| Shareholders for dividends | 264 000 | 320 000 |
C. Share Capital:
The authorised share capital comprises 1 200 000 shares.
1 July 2016 | Issued share capital comprised 800 000 ordinary shares |
1 October 2016 | Additional shares issued at R9,80 per share |
31 March 2017 | 120 000 shares repurchased at R10,00 per share |
30 June 2017 | Closing balance comprised 880 000 ordinary shares |
D. Dividends:
- Total dividends for the year amounted to R514 000.
- An interim dividend was paid on 1 December 2016 and a final dividend was declared on 30 June 2017. Only shareholders on the share register were entitled to dividends.
E. Fixed assets:
- Extensions to the warehouse were completed at a cost of R1 800 000.
- Equipment at carrying value of R440 400 was disposed and new equipment was purchased, to upgrade the present administration section.
F. The following financial indicators were calculated on 30 June:
2017 | 2016 | |
Debt/equity ratio | 0,1 : 1 | 0,1 : 1 |
Current ratio | 1,2 : 1 | 1,3 : 1 |
Acid test ratio | 0,6 : 1 | 0,6 : 1 |
Earnings per share | 80 cents | 78 cents |
Dividends per share | 55 cents | 75 cents |
Net asset value per share | ? | 978 cents |
Return on average capital employed | 12,5% | 11,3% |
Return on average equity | ? | 7,9% |
Market price of shares (JSE) | 1120 cents | 1100 cents |
Interest rate on loans | 13% | 13% |
Interest rate on fixed deposits | 9% | 9% |
70
QUESTION 5: COST ACCOUNTING AND FIXED ASSETS (60 marks; 30 minutes)
5.1 Indicate whether the following statements are True or False. Write only the answer next to the question numbers (5.1.1–5.1.3) in the ANSWER BOOK. (3)
5.1.1 The salary of the factory cleaner is regarded as an indirect labour cost.
5.1.2 Depreciation on factory plant and equipment is a variable cost.
5.1.3 Prime cost is calculated by adding direct material cost and indirect material cost.
5.2 TS FINE-WEAR
Thandi and Sindy own TS Fine-wear, a clothing manufacturing business that makes a single style winter jacket for schools.
REQUIRED:
5.2.1 Calculate the direct labour cost. (7)
5.2.2 Refer to Information C:
Calculate the amounts for (a) and (b) on the note for Factory Plant and Equipment. (13)
5.2.3 Prepare the Factory Overhead Cost note. (12)
5.2.4 Calculate the cost of sales for the year ended 31 December 2017. (5) INFORMATION:
A. Stock balances:
31 DECEMBER 2017 | 1 JANUARY 2017 | |
Raw material | R56 800 | R87 400 |
Work-in-process | 50 000 | 20 000 |
Finished goods | 41 000 | 46 000 |
Factory consumable stores | 8 760 | 9 420 |
B. Details of factory personnel:
Factory foreman and Maintenance staff | R300 000 Salary package is inclusive of benefits. |
Workers in production: | |
Number of workers | 5 |
Normal time | 1 800 hours per annum per worker. |
Normal time rate | R70 per hour |
Overtime hours worked | A total of 660 hours recorded as per register |
Overtime rate | 1,6 times the normal rate |
The employer’s contribution amounts to 9% of basic wage | |
C. Factory Plant and Equipment
| Cost (1 January 2017) | R420 000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation (1 January 2017) | (198 000) |
| Carrying value (1 January 2017) | 222 000 |
| Movements: | |
| Additions | 76 000 |
| Disposals | (a) |
| Depreciation | (b) |
| Carrying value (31 December 2017) | |
| Cost (31 December 2017) | 436 000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation (31 December 2017) |
- Old equipment were sold on 1 September 2017 for R6 500 cash, resulting in a loss on sale of asset of R2 500.
- New equipment were purchased on 1 October 2017 to replace the equipment sold.
- Equipment is depreciated at 15% p.a. on cost.
D. Factory consumables used amounted to R52 750.
E. The following expenses (amongst others) appeared in the pre-adjustment trial balance on 31 December 2017:
Insurance | R 32 300 |
Water and electricity | 98 700 |
Rent expense | 102 000 |
Depreciation | 116 000 |
Factory sundry expenses | 19 150 |
- 2/3 of the water and electricity expense relates to the factory.
- The insurance total includes an annual premium of R4 200 entered into and paid in full on 1 September 2017.
- 60% of the insurance must be allocated to the factory.
- Rent expense is shared by the factory, sales and office departments in the ratio 5 : 2 : 1.
F. The business produced 29 500 jackets at a cost of R60 each.
5.3 PASS MANUFACTURERS
PASS Manufacturers makes a single brand sports jacket and caps.
The owner requested a cost analysis for the last two financial years and was presented with the information below.
REQUIRED:
5.3.1 Do a calculation to prove that the break-even point for jackets in 2017 is correct. (4)
5.3.2 Comment on the break-even points and the level of production for both products. (4)
5.3.3 The owner decided to increase the selling price of caps in 2017.
- Calculate the percentage increase in the selling price. (4)
- Provide ONE reason why the owner felt it necessary to increase the selling price. (2)
5.3.4 Identify ONE variable cost for jackets and ONE variable cost for caps that were not well controlled. Provide figures. In each case, provide a solution/advice to address the problem. (6)
INFORMATION:
JACKETS | CAPS | |||
2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | |
Variable cost | 73,00 | 63,90 | 39,80 | 33,70 |
Direct material cost | 40,00 | 32,00 | 15,00 | 14,00 |
Direct labour cost | 22,50 | 21,40 | 15,50 | 12,50 |
Selling and distribution cost | 10,50 | 10,50 | 9,30 | 7,20 |
| Fixed cost | 41,20 | 35,30 | 20,80 | 20,30 |
| Factory overhead cost | 26,00 | 21,80 | 11,00 | 10,80 |
Administration cost | 15,20 | 13,50 | 9,80 | 9,50 |
| Units produced and sold | 15 000 | 15 000 | 9 500 | 9 500 |
Break-even units | 14 715 | 10 362 | 7 134 | 9 500 |
Selling price per unit | R115,00 | R115,00 | R67,50 | R54,00 |
60
QUESTION 6: BUDGETING (40 marks; 25 minutes)
6.1 Explain why:
6.1.1 Depreciation and bad debts will not appear in a Cash Budget. (2)
6.1.2 A cash budget is different from a Projected Income Statement. (2)
6.2 KWT DISTRIBUTORS LTD
You are provided with information for the budget period November and December 2017.
REQUIRED:
6.2.1 Complete the Debtors Collection Schedule. (12)
6.2.2 Calculate the missing amounts denoted by (i) to (v) on the Cash Budget. (20)
6.2.3 Comment on the internal controls regarding the collection from debtors and the payment to creditors. Provide TWO points. (4)
INFORMATION:
- Cash sales amount to 40% of total sales.
Goods are marked-up by 25% on cost. - Debtors are granted credit terms of 30 days. The actual collection trend revealed that:
- 50% of debtors pay in the month of sale to receive 5% discount.
- 30% is received in the month following the month of sales;
- 18% is collected in the second month after the sale;
- 2% of debtors is written off thereafter.
- Stock is replaced in the month sold (a base stock is maintained)
- Rent income will increase by 8% in December 2017.
- 80% of stock is bought on credit. Creditors are paid in full in the month following the month of purchases.
- Salaries and wages are expected to remain the same for the budget period. Staff members on leave in December will receive their pay, totalling R35 600, during November.
- A loan will be received from a director, Thabo, on 1 November 2017 at 13%p.a. interest. Interest is not capitalised. A fixed monthly instalment and interest will be paid at the end of each month.
- The company will pay interim dividends during December.
- Incomplete Debtors Collection Schedule:
MONTH
CREDIT SALES
NOVEMBER
DECEMBER
September
180 000
?
October
186 000
55 800
?
November
?
92 625
?
December
210 000
?
TOTAL ? ? - Information from the Projected Income Statement:
NOVEMBER 2017
Sales
325 000
Cost of sales
260 000
Commission income
24 800
Depreciation
12 600
Interest expense
1 625
- Incomplete Cash Budget for 2017:
RECEIPTS | NOVEMBER | DECEMBER |
Cash sales | 130 000 | (i) |
Cash from debtors | ||
Commission income | 24 800 | 26 000 |
Rent income | (ii) | 19 710 |
Loan from director Thabo | 150 000 | 0 |
TOTAL RECEIPTS | ||
PAYMENTS | ||
Cash purchases of stock | 52 000 | 56 000 |
Payments to creditors | (iii) | 208 000 |
Directors fees | 20 000 | 20 000 |
Salaries and wages | 180 600 | (iv) |
Loan instalment (including interest) | 13 625 | (v) |
Interim dividends | 0 | 86 500 |
Sundry expenses | 15 875 | 16 510 |
| TOTAL PAYMENTS | ||
40
TOTAL: 300
ACCOUNTING GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
ACCOUNTING
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MARKING PRINCIPLES:
- Penalties for foreign items are applied only if the candidate is not losing marks elsewhere in the question for that item (no foreign item penalty for misplaced items). No double penalty applied.
- Penalties for placement or poor presentation (e.g. details) are applied only if the candidate is earning marks on the figures for that item.
- Full marks for correct answer. If the answer is incorrect, mark the workings provided.
- If a pre-adjustment figure is shown as a final figure, allocate the part-mark for the working for that figure (not the method mark for the answer).
- Unless otherwise indicated, the positive or negative effect of any figure must be considered to award the mark. If no + or – sign or bracket is provided, assume that the figure is positive.
- Where indicated, part-marks may be awarded to differentiate between differing qualities of answers from candidates.
- This memorandum is not for public distribution, as certain items might imply incorrect treatment. The adjustments made are due to nuances in certain questions
- Where penalties are applied, the marks for that section of the question cannot be a final negative.
- Where method marks are awarded for operation, the marker must inspect the reasonableness of the answer before awarding the mark.
- 'Operation' means 'Check operation'. 'One part correct' means 'Operation and one part correct'.
- In awarding method marks, ensure that candidates do not get full marks for any item that is incorrect at least in part. In such cases, do not award the method mark. Indicate by way of ⌧
- Be aware that some candidates provide valid alternatives beyond the memorandum.
- Codes: f = foreign item; p = placement/presentation.
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: RECONCILIATIONS
1.1 Choose the correct answer from the words provided within brackets. Write only the answer, next to each number.
1.1.1 | Cash Receipts Journal (CRJ) ✔ |
1.1.2 | Debit ✔ |
1.1.3 | Credit note ✔ |
1.1.4 | Cash discount ✔ (4) |
1.2 DEBTORS RECONCILIATION
1.2.1
Calculate the correct Debtors Control balance on 30 June 2017.
(4) |
1.2.2 Calculate the balances for the following debtors:
Pillai 21 600 ✔ – 1 600 ✔✔ + 4 500 ? 1.2.1 | 24 500 ?* |
Tele 24 900 ✔ – 2 500 ✔ | 22 400 ?* |
Botha 11 100 ✔✔ + 2 700 ✔ | 13 800 ?* |
| * One part correct (12) | |
1.2.3
Calculate the percentage of debtors that are not complying with the 30 days credit terms. (3) |
Explain TWO internal control measures that JT Traders can use to ensure that only reliable clients are granted credit.
(4) |
1.3 CREDITORS RECONCILIATION
NO. | CREDITOR’S LEDGER | STATEMENT BALANCE |
Balance | 35 000 | 38 420 |
(i) | 2 970 | |
(ii) | (750) ✔✔ | |
(iii) | 1 000 ✔✔ | |
(iv) | (1 960) | |
(v) | (3 860) ✔✔ | |
(vi) | 7 120 ✔✔ | |
TOTAL | 38 970 ? for both totals | 38 970 (13) |
Allocate 1 mark for the amount and 1 mark for the sign (accept brackets, negative sign)
Q1: | 40 |
QUESTION 2: INVENTORY VALUATION
2.1.
2.1.1 | Weighted average ✔ |
2.1.2 | FIFO ✔ |
2.1.3 | Perpetual ✔ |
2.1.4 | Periodic ✔ |
2.1.5 | Specific identification ✔ (5) |
2.2 COMRADES LTD
2.2.1
Calculate the selling price per unit for tracksuits. 296 125 = R575 ✔✔ (2 marks or 0) (2) |
2.2.2
Calculate the cost of sales of tracksuits using the FIFO method. 33 570 (2 marks) one part correct (7) |
2.2.3
Calculate the stock turnover rate of tracksuits (use the average stock). 2.2.2 (5) |
2.2.4
It was discovered that vests were missing from the June 2016 delivery. Calculate the number and value of the vests missing. VALUE: (7) |
2.2.5
Calculate the Gross Profit made by the vests department.
*one part correct (8) |
2.2.6 Identify TWO problems other than the missing vests in the VESTS department. Quote figures. In each case, provide a solution to the problem.
PROBLEM | SOLUTION ✔ / ADVICE ✔ |
Problem 1: |
|
Problem 2: |
(6) |
Q2: | 40 |
QUESTION 3: COMPANY FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
3.1
3.1.1 | B ✔ |
3.1.2 | C ✔ |
3.1.3 | A ✔ (3) |
3.2 RUHI LTD
3.2.1 RETAINED INCOME
Balance on 1 March 2016 (7 480 ✔ + 50 000 ?#) | 57 480?one part correct |
Funds used to repurchase shares (40 000 x 1,25) | (50 000) #✔✔ |
Net profit after income tax | 681 720 ✔ |
Ordinary share dividends | (389 200) ✔ |
| Interim dividend | 179 200 ✔ |
| Final dividend | 210 000 ✔ |
| Balance on 28 February 2017 | 300 000 ? |
| operation (10) |
3.2.2 BALANCE SHEET AS AT 28 FEBRUARY 2017
ASSETS | ||
Non-current assets operation | 4 310 545 ✔ | |
| Fixed assets | 4 060 545 | |
| Fixed Deposit (415 000 – 165 000) | 250 000 ✔✔ | |
| Current assets CL x 1,5 | 889 455 ✔✔ | |
| ✔ Inventories (Trading Stock) | 222 600 ✔ | |
| ✔ Trade and other receivables balancing figure | 289 455 ? | |
| Cash and cash equivalents (212 400 ✔ + 165 000 ✔) | 377 400 ✔ | |
| 13 | TOTAL ASSETS Total Equity + Liabilities | 13 5 200 000 ? |
| EQUITY AND LIABILITIES | ||
| Shareholders’ equity operation | 3 900 000 ?* | |
| Ordinary share capital balancing figure | 3 600 000 ? | |
| Retained income refer 3.2.1 | 300 000 ? | |
| Non-current liabilities | 707 030 | |
Loan: Dube Bank (831 800 ✔?* – 124 770 ?) | 707 030 ?* | |
| Current liabilities | 592 970 | |
| Trade and other payables | 231 920 | |
| Shareholders for dividends see 3.2.1 | 210 000 ? | |
| SARS: Income tax (306 280 ✔✔ – 280 000 ✔) | 26 280 ?* | |
| Current portion of loan balancing figure | 124 770 ? | |
| 13 | TOTAL EQUITY AND LIABILITIES | 5 200 000 (26) |
-1 foreign items (-2 max.) Misplaced items must be marked wrong. Current liability items may be combined *one part correct
3.2.3
Do a calculation to show the number of shares that Bakkies must buy to gain control of the company. 800 000 x 50% + 1 = 400 001 or (50% + 100 = 400 100) ✔✔
(5) |
Bakkies wants to buy the shares at the current net asset value without advertising them to the public. As an existing shareholder, why would you not be satisfied with this arrangement? Explain. Provide TWO points.
(4) |
3.2.4
Ruhi Ltd is planning to spend R300 000 on staff development and training over the next two years. How will this expense be explained (disclosed) in the published annual report? Give TWO points.
(2) |
Q3: | 50 |
QUESTION 4: FINANCIAL STATEMENTS, CASH FLOW AND INTERPRETATION 4.1 CONCEPTS: MATCHING
4.1.1 | D ✔ |
4.1.2 | B ✔ |
4.1.3 | A ✔ (3) |
4.2 MANI LTD
4.2.1 SHARE CAPITAL
Authorised share capital
| 1 200 000 ordinary shares |
Issued share capital
800 000 | Ordinary shares on 1 July 2016 | 7 600 000 ?* |
200 000 ?* | Shares issued at R9,80 each | 1 960 000 ✔✔ |
(120 000) ✔ | Shares repurchased (ASP: R9,56 ✔✔) | (1 147 200) ? |
880 000 ✔ | Ordinary shares on 30 June 2017 | 8 412 800 ✔ |
| *balancing figures (10) |
4.2.2 Amounts for the Cash Flow Statement.
(Final answer must show INFLOW or OUTFLOW of cash)
WORKINGS | ANSWER | |
Dividends paid Or 320 000 (one mark) + 250 000 (two marks) | (570 000) ? | (4) |
Income tax paid | (261 100) ? | (4) |
Change in investment | 40 000 ✔? | (2) |
Change in loans | 300 000 ✔? | (2) |
Accept alternative presentation of information such as signs reversed, ledger accounts etc.
4.2.3
Calculate the cost of the additional equipment purchased. (6) |
4.2.4
| NET CHANGE IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS | (161 300) ✔ |
| Cash balance on 1 July 2016 | 98 500 ✔ |
| Cash balance on 30 June 2017 2 500 ✔– 65 300 ✔ | (62 800) ?* (5) |
-1 for poor presentation (No or incorrect details) *one part correct
4.2.5
Calculate the gross profit percentage (mark-up percentage). (4) |
Calculate the net asset value per share (NAV). (3) |
Calculate the return on average shareholders’ equity. (6) |
4.2.6
Were the directors justified in increasing the loan? Explain. Quote TWO relevant financial indicators (with figures) in your answer. Financial Indicators: ✔✔ ✔✔
Explanation: ✔✔
(7) |
4.2.7
Explain why the shareholders are not satisfied with the dividend pay out policy and their return earned. Quote financial indicators (with figures) in your explanation.
Return earned:
Explanation: ✔✔
(8) |
4.2.8
Comment on the price paid to repurchase the shares on 31 March 2017. Quote TWO financial indicators (with figures) in your comments. (6) |
Q4: | 70 |
QUESTION 5: COST ACCOUNTING AND FIXED ASSETS
5.1
5.1.1 | True ✔ |
5.1.2 | False ✔ |
5.1.3 | False ✔ (3) |
5.2. TS FINE-WEAR
5.2.1
Direct labour cost (7) |
5.2.2
WORKINGS | ANSWER | ||
(a) | 6 500 ✔ + 2 500 ✔✔ | 9 000 ? | (4) |
(b) | 420 000 + 76 000 – 436 000 |
62 850 ? | (9) |
5.2.3 Factory overhead cost
Indirect labour | 300 000 ✔ |
Indirect material | 52 750 ✔ |
Water and electricity 98 700 x 2/3 | 65 800 ✔?* |
Insurance (32 300 ✔ – 2 800 ✔✔) x 60% | 17 700 ?* |
Rent expense 102 000 x 5/8 | 63 750 ✔?* |
Depreciation See 5.2.2 (b) | 62 850 ? |
Factory sundry expenses | 19 150 |
| |
| 582 000 ?* | |
| *one part correct (12) |
5.2.4
Calculate: Cost of sales (5) |
5.3 PASS MANUFACTURERS
5.3.1
Do a calculation to prove that the break-even point for jackets in 2017 is correct. (4) |
5.3.2 Comment on the break-even points and the level of production for both products. Quote figures.
Jackets: | Comment: ✔ figures ✔
|
Caps: | Comment: ✔ figures ✔
(4) |
5.3.3
Calculate the percentage increase in the selling price. 13,50 ✔✔ (4) |
Provide ONE reason why the owner felt it necessary to increase the selling price.
(2) |
5.3.4
COST IDENTIFIED | ADVICE OR SOLUTION | |
Jackets | Cost:
| Look for cheaper suppliers.
|
Caps | Cost:
| Control overtime.
|
Q5: | 60 |
QUESTION 6: BUDGETING
6.1 Explain why:
6.1.1
Depreciation and bad debts will not appear in a Cash Budget.
(2) |
6.1.2
A cash budget is different from a Projected Income Statement.
(2) |
6.2 KWT DISTRIBUTORS LTD
6.2.1
MONTHS | CREDIT SALES | NOVEMBER | DECEMBER |
September | 180 000 | 32 400 ✔✔ | |
October | 186 000 | 55 800 | 33 480 ✔✔ |
November | 195 000 ✔✔ | 92 625 | 58 500 ?? |
December | 210 000 | 99 750 ✔✔ | |
Total collection from debtors | 180 825 ✔ | 191 730 ? | |
| (12) | |||
6.2.2 Calculate:
WORKINGS | ANSWER | |
(i) | Cash sales for December: | 140 000 ✔✔ |
(ii) | Rent income amount for November: | 18 250 ? |
(iii) | Payments to creditors for November: | 198 400 ? |
(iv) | Salaries and wages for December: | 109 400 ? one part correct |
(v) | Loan instalment (including interest) for December: | 13 495 ? |
| (5) |
6.2.3
Comment on the internal controls regarding the collection from debtors and the payment to creditors. Provide TWO points.
(4) |
Q6: | 40 |
TOTAL: 300
BUSINESS STUDIES GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
BUSINESS STUDIES
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- This question paper consists of THREE sections and covers all main topics.
SECTION A: COMPULSORY
SECTION B: Consists of FIVE questions.
Answer any THREE of the five questions in this section.
SECTION C: Consists of FOUR questions.
Answer any TWO of the four questions in this section. - Read the instructions for each question carefully and take particular note of what is required.
- Number the answers carefully according to the numbering system used in this question paper. No marks will be awarded for answers that are numbered incorrectly.
- Except where other instructions are given, answers must be written in full sentences.
- Use the mark allocation and nature of each question to determine the length and depth of an answer.
- Use the table below as guide for mark and time allocation when answering each question.
SECTION | QUESTION | MARKS | TIME |
A: Objective-type questions | 1 | 40 | 30 minutes |
B: FIVE direct/indirect type questions CHOICE (Answer any THREE.) | 2 | 60 | 30 minutes |
3 | 60 | 30 minutes | |
4 | 60 | 30 minutes | |
5 | 60 | 30 minutes | |
6 | 60 | 30 minutes | |
C: FOUR essay-type questions CHOICE (Answer any TWO.) | 7 | 40 | 30 minutes |
8 | 40 | 30 minutes | |
9 | 40 | 30 minutes | |
10 | 40 | 30 minutes | |
TOTAL | 300 | 180 minutes |
- Begin the answer to EACH question on a NEW page, for example QUESTION 1 – new page, QUESTION 2 – new page, et cetera.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 E.
1.1.1 Workers are entitled to ... consecutive days’ annual leave per year.
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
1.1.2 This strategy does not form part of the intensive strategies.
- Product penetration
- Product development
- Market development
- Market penetration
1.1.3 The main purpose of the Labour Relations Act (LRA) (No. 66 of 1995) is to …
- ensure that employees work in a more suitable and less dangerous environment.
- promote equal opportunity and fair treatment in the workplace.
- promote economic development, social justice, labour peace and democracy in the workplace.
- ensure that qualified people from designated groups have equal opportunities in the workplace.
1.1.4 A partnership has ...
- limited liability and limited continuity.
- unlimited liability and unlimited continuity.
- limited liability and unlimited continuity.
- unlimited liability and limited continuity.
1.1.5 The return on an investment in shares is called ...
- dividends.
- interest.
- capital gain.
- profit.
1.1.6 The … clause is applied to determine the amount that the insurer will pay out, when goods are underinsured.
- excess
- reinstatement
- subrogation
- average
1.1.7 ... means valuing each other regardless of status, culture or disability.
- Discrimination
- Leadership
- Diversity
- Inclusivity
1.1.8 Team dynamic theories help businesses to …
- allocate tasks to team members with similar personalities.
- allocate tasks according to the roles of team members.
- promote total satisfaction.
- establish good relationships with teams.
1.1.9 This function creates a favourable image of the business.
- General management
- Human resources
- Public relations
- Purchasing
1.1.10 Quality circles usually form part of the … TQM element.
- continuous improvements of processes and systems.
- top management involvement.
- teamwork.
- monitoring and evaluation of quality processes.
(10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Complete the following statements by using the word(s) in the list below. Write only the word(s) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
| JSE; empty chair; tertiary; screening; compulsory; secondary; CSR; brainstorming; shortlisting; fringe |
1.2.1 The ... sector includes all industries that offer services to other businesses and consumers.
1.2.2 The ... gives opportunities to financial institutions to invest their funds in shares.
1.2.3 ... is a creative thinking problem-solving technique in which several people think about a single problem and suggest ideas that could lead to a solution.
1.2.4 ... is to eliminate the unsuitable candidates for the position. 1.2.5 Medical aid is an example of ... benefits. (5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches a term in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–J) next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.3.6 K.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.3.1 Employment Equity Act |
|
(5 x 2) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 40
SECTION B
Answer any THREE questions from the five questions in SECTION B. Start EACH question on a NEW page.
QUESTION 2: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT
2.1 Identify the element of Porter’s Five Forces model that applies to each of the following statements:
2.1.1 Royal Clothing attracts more customers than Pro Clothing because they offer lower prices.
2.1.2 Local Plastics is the only place where retailers can buy plastic shopping bags.
2.1.3 Handsome Stores want to start an exclusive fashion boutique that requires huge capital investment to cover the high establishment costs and expensive stock.
2.1.4 Medi-Care has a few regular customers who always place large orders.
2.1.5 Customers prefer warmer coats to more expensive, formal jackets. (5 x 2) (10)
2.2 Name THREE business sectors. (3)
2.3 Describe the strategic management process. (6)
2.4 Read the article below and answer the questions that follow.
THE ROLE OF SETAS There are 25 Sector Education and Training Authorities (SETAs) in South Africa and each is classified according to economic sectors. The functions and responsibilities of SETAs are set out in the Skills Development Act (SDA), 1998 (Act 97 of 1998). The Act states that the role of a SETA is to develop a sector skills plan, implement the plan, develop and administer learnerships. SETA’s also support the implementation of the National Qualifications Framework and undertake quality assurance. [Adapted from Mail & Guardian, 23 October 2003] |
2.4.1 Quote THREE roles of SETAs mentioned in the article above. (3)
2.4.2 Explain the purpose of the Skills Development Act (SDA), 1998 (Act 97 of 1998). (6)
2.5 Explain THREE defensive strategies that businesses can use to overcome their challenges. (9)
2.6 Discuss any THREE consumer rights as stipulated in the Consumer Protection Act (CPA), 2008 (Act 68 of 2008). (9)
2.7 Read the following statement and answer the questions that follow.
| The primary purpose of the Broad-Based Black Economic Empowerment Act (BBBEE), 2003 (Act 53 of 2003) (amended in 2013) is to address and enhance the economic participation of Black people in the South African economy. This is achieved by implementing the following pillars: ownership, management and control, skills development, enterprise and supplier development and socio-economic development. |
2.7.1 Quote the primary purpose of the BBBEE Act from the statement above. (1)
2.7.2 Identify any THREE pillars of BBBEE mentioned in the statement above. (3)
2.7.3 Justify the introduction of the BBBEE Act. (4)
2.7.4 Evaluate the impact of the BBBEE Act on businesses. (6)
[60]
QUESTION 3: BUSINESS VENTURES
3.1 Identify the form of ownership which is applicable to each of the following statements below.
3.1.1. The name ends in (Pty) Ltd.
3.1.2 This company raises capital by selling shares to the public.
3.1.3 Relies on grants and donations from fundraising as source of capital.
3.1.4 The Government owns 50% of the shares in this company. (4 x 2) (8)
3.2 Define the following insurance concepts:
3.2.1 Excess (2)
3.2.2 Premium (2)
3.3 Explain the importance of insurance to businesses. (5)
3.4 Distinguish between insurance and assurance. Support your answer by providing ONE example of each. (6)
3.5 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
| Frank wants to invest R25 000 in a fixed deposit for three years. The bank offers him 15% simple interest or 10% compound interest after the end of three years. |
3.5.1 Name the type of investment mentioned in the scenario above. (1)
3.5.2 Analyse the risk factor of the type of investment identified in QUESTION 3.5.1. (3)
3.5.3 Calculate the amount that Frank’s investment would be worth at the end of three years if he chooses the compound interest option. (6)
3.5.4 Differentiate between simple and compound interest. (4)
3.6 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
MEDI-AWAY LTD Medi-away LTD specialises in removing medical waste from hospitals and private surgeries. Gavin Moore, the owner of the business, follows all the organisational rules and policies systematically. He also makes sure that employees adhere strictly to the rules. |
3.6.1 Identify the type of leadership style that is applicable to the scenario above. Motivate your answer by quoting from the scenario. (3)
3.6.2 Evaluate the impact of the leadership style identified in QUESTION 3.6.1 on leadership and management. (6)
3.7 Discuss the advantages of the transactional leadership style. (6)
3.8 Describe how the following factors may lead to the success and/or failure of a personal-liability company:
3.8.1 Capital (4)
3.8.2 Management (4)
[60]
QUESTION 4: BUSINESS ROLES
4.1 Name any THREE stages of team development. (3)
4.2 Explain the advantages of creative thinking in the workplace. (6)
4.3 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
TRUE BLUE SPORTS (TBS) Roy, the owner of True Blue Sports, does not record all the transactions of his business as required by South African Revenue Services. He was criticised for not conducting his business in a professional, responsible and ethical manner. |
4.3.1 Identify the unethical business practice in the scenario above. Motivate your answer by quoting from the scenario. (3)
4.3.2 Name any FOUR other unethical business practices. (4)
4.3.3 Recommend THREE ways in which TBS should conduct business professionally, responsibly and ethically. (6)
4.4 Describe THREE criteria for successful teams. (9) 4.5 Explain the differences between ethics and professionalism. (6)
4.6 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
GO TRAVELS Go Travels is a travel agency that offers transport and accommodation bookings for international sporting teams. They are finding that more teams are arranging their own bookings and are concerned that they will be out of business one of these days. The management of Go Travels decided to request a group of business experts to complete questionnaires to help solve their problem. |
4.6.1 Identify the problem-solving technique used by Go Travels to solve their problem. Motivate your answer. (3)
4.6.2 Explain to Go Travels the advantages of the problem-solving technique identified in QUESTION 4.6.1. (6)
4.7 Discuss the benefits of diversity in the workplace. (6)
4.8 Suggest ways in which the businesses can deal with the following diversity issues in the workplace:
4.8.1 Age (4)
4.8.2 Disability (4)
[60]
QUESTION 5: BUSINESS OPERATIONS
5.1 Name THREE methods of external recruitment. (3)
5.2 Outline the placement procedure that should be considered when placing an employee in his/her new position. (6)
5.3 Explain the benefits of an induction programme on businesses. (6)
5.4 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
REAL CLEAN LTD Real Clean LTD has employed Jane as a cleaner. Real Clean LTD signed an employment contract with Jane which regulates their employment relationship. Real Clean LTD gave Jane the details of the termination of the employment contract. |
5.4.1 Identify the employer and employee in the employment contract. Support your answer by quoting from the scenario. (4)
5.4.2 Mention FOUR aspects that must be included in an employment contract. (4)
5.4.3 Advise Jane on the reasons of the termination of the employment contract. (6)
5.5 Explain the benefits of a good quality management system. (6)
5.6 Distinguish between quality performance and quality management. (8)
5.7 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
JP CLOTHING LTD JP Clothing LTD manufactures designer clothing for mothers and toddlers. Jabu, the owner and manager, knows that the quality of her clothing determines her sales. Customers always speak very highly of the quality of the clothing. |
5.7.1 Identify the Total Quality Management (TQM) element applicable to the scenario above. Motivate your answer by quoting from the scenario. (3)
5.7.2 Discuss the impact of the TQM element identified in QUESTION 5.7.1, has on JP Clothing LTD as a large business. (6)
5.8 Advise businesses on how to apply the PDCA cycle to improve the quality of products and services. (8)
[60]
QUESTION 6: MISCELLANEOUS TOPICS
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT
6.1 Name THREE provisions of the Basic Conditions of Employment Act, 1997 (Act 75 of 1997). (3)
6.2 Outline any THREE steps in evaluating a strategy. (6)
6.3 Evaluate the impact of the Compensation for Occupational Injuries and Diseases Amendment Act (COIDA), 1997 (Act 61 of 1997) on businesses. (6)
BUSINESS VENTURES
6.4 Name any THREE factors that should be considered when making investment decisions. (3)
6.5 Identify the types of shares represented by EACH statement below.
6.5.1 These shareholders may receive higher dividends when the company has made larger profits.
6.5.2 Shares are issued to existing shareholders as compensation for loss of dividends.
6.5.3 These shares are issued to shareholders who started the company. (3 x 2) (6)
6.6 Explain the advantages of co-operatives. (6)
BUSINESS ROLES
6.7 Read the scenario below and answer the question that follows.
DEEP EARTH (DE) The vision of Deep Earth, one of the world’s largest mining groups, is inspired by a statement made by the company’s founder. He said, “The aim of this group have always been to make a profit and a permanent contribution to the well-being of our employees”. |
Advise Deep Earth on how to contribute towards the well-being of their employees. (8)
6.8 State any THREE possible causes of conflict in the workplace. (3)
6.9 Suggest TWO ways in which businesses can deal with difficult people. (4)
BUSINESS OPERATIONS
6.10 Differentiate between piecemeal and time-related remuneration. (4)
6.11 Discuss the negative impact of Total Quality Management if it is poorly implemented by business. (5)
6.12 Suggest THREE quality indicators of the administration function. (6)
[60]
TOTAL SECTION B: 180
SECTION C
Answer ANY TWO questions in this section.
NOTE: Clearly indicate the QUESTION NUMBER of each question that you choose. The answer to EACH question must start on a NEW page, for example QUESTION 7 on a new page, QUESTION 8 on a NEW page, et cetera.
QUESTION 7: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT
| The National Credit Act, 2005 (Act 34 of 2005) (NCA) protects the consumer in the credit market and make credit and banking services more accessible. The Act helps to enhance control for a better and more responsible credit practices and industry. |
With reference to the statement above:
- Discuss the purpose of the National Credit Act
- Explain the rights of consumer as outlined in this Act
- Analyse the impact of this Act on businesses
- Suggest ways in which businesses can comply with this Act [40]
QUESTION 8: BUSINESS VENTURES
| Ann Watson, the new Chief Executive Officer (CEO) for Main Tech has to prepare and present the annual financial results to the Management Board. |
Advise Ann on her presentation of the financial results. You must include the following aspects in your answer:
- Outline FOUR aspects that must be considered when designing a multimedia presentation
- Evaluate the use of a PowerPoint presentation and posters as suitable visual aids that may support her presentation
- Propose ways in which Ann may respond to feedback in a professional manner ∙ Advise Ann on how she can improve her next presentation [40]
QUESTION 9: BUSINESS ROLES
READ MORE BOOKS (RMB) Read More Books (RMB) is a well-established book shop. RMB wants to improve their image, and contribute towards the well-being of the community and the environment by focussing on social responsibility. |
RMB contacted you as a business advisor to assist them with their corporate social responsibility (CSR) and corporate social investment (CSI) challenges. Your advice must include the following:
- Elaborate on the meaning of CSR and CSI
- Explain the relationship between social responsibility and triple bottom line
- Evaluate the impact of CSR on businesses
- Suggest FIVE practical ways in which RMB’s Corporate Social Investment (CSI) projects can contribute to the community [40]
QUESTION 10: BUSINESS OPERATIONS
| The financial manager of Wow (Pty) Ltd recently announced his retirement. Peter, the human resources manager, needs to find a new financial manager. Peter had to compile a job description and job specification of the position before advertising the position. He has advertised the position on the business’s notice board. He is also responsible for the arrangements during the selection process. |
Refer to the scenario above and write an essay in which you include the following aspects:
- Explain the differences between job description and job specification
- Discuss the impact of internal recruitment on businesses
- Explain the selection procedure that Peter should follow to identify the most suitable candidate
- Advise Peter on the purpose of the interview and his role as an interviewer [40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 80
GRAND TOTAL: 300
BUSINESS STUDIES GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
BUSINESS STUDIES
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
NOTES TO MARKERS
- Candidates’ responses for SECTIONS B and C must be in full sentences; however this would depend on the nature of the question.
- A comprehensive memorandum has been provided but this is by no means exhaustive. Due consideration should be given to an answer that is correct but:
- Uses a different expression from that which appears in the memorandum
- Comes from another source
- Original
- A different approach is used
NOTE: SECTION A:- There are no alternative answers.
- Each question has only one correct answer.
- Take note of other relevant answers provided by candidates and allocate marks accordingly. (In cases where the answer is unclear or indicates some understanding, part-marks should be awarded, for example, one mark instead of the maximum of two marks.)
- The word ‘sub-max’ is used to facilitate the allocation of marks within a question or sub-question.
- The purpose of circling marks (guided by ‘max.’ in the breakdown of marks) on the right-hand side is to ensure consistency and accuracy in the marking of scripts.
- In an indirect question, the theory as well as the response must be relevant and related to the question.
- Incorrect numbering of questions or sub-questions in SECTIONS A and B will be severely penalised. Therefore, correct numbering is strongly recommended in all sections.
- No additional credit must be given for repetition of facts. Indicate with an R.
- Subtotals to questions must be written in the right-hand margin. Circle the subtotals as indicated by the allocation of marks. This must be guided by ‘max’ in the marking guideline. Only the total for each question should appear in the left-hand margin next to the appropriate question number.
- SECTION B
10.1 If, for example, FIVE facts are required, mark the candidate’s FIRST FIVE responses and ignore the rest of the responses. Indicate by drawing a line across the unmarked portion or use the word ‘Cancel’.
NOTE: This only applies to questions where the number of facts is specified.
10.2 If two facts are written in one sentence, award the candidate FULL credit. Point 10.1 above still applies.
10.3 If candidates are required to provide their own examples/views, brainstorm this to come up with alternative answers.
10.4 USE OF THE COGNITIVE VERB AND ALLOCATION OF MARKS
10.4.1 Where the number of facts are specified questions that require candidates to ‘explain/discuss/describe’ will be marked as follows:- Heading 2 marks
- Explanation 1 mark (or as indicated in the marking guideline).
The ‘heading’ and ‘explanation’ are given separately to facilitate mark allocation.
10.4.2 If the number of facts is not specified, the candidate must be informed by the nature of the question and the maximum marks allocated.
10.5 ONE mark will be awarded for answers that are easy to recall, requires one-word answers, or is quoted directly from scenario/case study. This applies to SECTIONS B and C in particular.
- SECTION C
11.1 The breakdown of the mark allocation for the essays is as follows:
Introduction | Maximum: 32 |
Content | |
Conclusion | |
Insight | 8 |
TOTAL | 40 |
11.2 Insight consists of the following components:
Layout/Structure | Is there an introduction, body, proper paragraphs and a conclusion? | 2 |
Analysis and interpretation | Is the candidate able to breakdown the question into headings/sub-headings/interpret it correctly to show understanding of what is being asked? | 2 |
Synthesis | Are there relevant decisions/facts/responses made based on the questions?
NB:
| |
2 | ||
Originality | Is there evidence of examples, recency of information, current trends and developments? | 2 |
TOTAL FOR INSIGHT: | 8 | |
NOTE:
- No marks will be awarded for contents repeated from the introduction and conclusion.
- The candidate forfeits marks for layout if the words INTRODUCTION and CONCLUSION are not stated.
- No marks will be allocated for layout, if the headings ‘Introduction, Conclusion,’ etc. in ‘Insight’ is not supported by an explanation.
- With effect from November 2017 a candidate will be awarded a maximum of ONE (1) mark for headings/sub-headings and ONE (1) mark for interpretation (16 or more out of 32 marks). This applies specifically to the analysis and interpretation part of insight.
11.3 Indicate insight in the left-hand margin with a symbol e.g. (‘L, A, S and/or O’).
11.4 The components of insight are indicated at the end of the suggested answer for each question.
11.5 Mark all the relevant facts until the MAXIMUM mark in a subsection has been attained. Write MAX. after maximum marks have been obtained.
11.6 At the end of each essay indicate the allocation of marks for facts and marks for insight as follow: (L – Layout, A – Analysis, S – Synthesis, O – Originality) as in the table below.
CONTENT | MARKS |
Facts | 32 (max.) |
L | 2 |
A | 2 |
S | 2 |
O | 2 |
TOTAL | 40 |
11.7 When awarding marks for facts, take note of the sub-maxima indicated, especially if candidates do not make use of the same subheadings. Remember headings and sub-headings are encouraged and contribute to insight (structuring/logical flow/sequencing) and indicate clarity of thought. (See MARKS BREAKDOWN at the end of each question.)
11.8 If the candidate identifies/interprets the question INCORRECTLY, then he/she may still obtain marks for layout.
11.9 If a different approach is used by candidates, ensure that the answers are assessed according to the mark allocation/subheadings as indicated in the marking guideline.
11.10
11.10.1 Award TWO marks for complete sentences. Award ONE mark for phrases, incomplete sentences and vague answers.
11.10.2 With effect of from November 2015, the TWO marks will not necessarily appear at the end of each completed sentence. The ticks (√) will be separated and indicated next to each fact, e.g. “Product development is a growth strategy/where businesses aim to introduce new products √ into existing markets.”√ This will be informed by the nature and context of the question, as well as the cognitive verb used.
11.11 With effect from November 2017, the maximum of TWO (2) marks for facts shown as headings in the memo, will not necessarily apply to each question. This would also depend on the nature of the question.
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 C √√ 21
1.1.2 A √√ Product penetration
1.1.3 C √√ Promotes economic development, social justice, labour peace and democracy in the workplace.
1.1.4 D √√ unlimited liability and limited continuity
1.1.5 A √√ dividends
1.1.6 D √√ average
1.1.7 D √√ Inclusivity
1.1.8 B √√ allocate tasks according to the roles of team members
1.1.9 C √√ Public relations
1.1.10 C √√ teamwork (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 Tertiary √√
1.2.2 JSE √√
1.2.3 brainstorming √√
1.2.4 screening √√
1.2.5 fringe √√ (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 H √√
1.3.2 F √√
1.3.3 E √√
1.3.4 A √√
1.3.5 C √√ (5 x 2) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 40
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS | |
1.1 | 20 |
1.2 | 10 |
1.3 | 10 |
TOTAL | 40 |
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT
2.1 Porter’s Five Forces
2.1.1 Competitive rivalry √√
2.1.2 Power of suppliers √√
2.1.3 Threat/Barrier to new entry √√
2.1.4 Power of buyers √√
2.1.5 Threat of substitution √√ (5 x 2) (10)
2.2 Business sectors
- Primary √ sector
- Secondary √ sector
- Tertiary √ sector
NOTE: Mark the first THREE (3) only.
(3 x 1) (3)
2.3 Strategic management process
OPTION 1
- Have a clear vision, a mission statement √ and measurable/realistic objectives in place. √
- Identify opportunities/weaknesses/strengths/threats √ by conducting environmental scanning/situational analysis. √
- Tools available for environmental scanning √ may include a SWOT-/ PESTLE-/Porters Five Forces-analysis. √
- Formulate alternative strategies √ to respond to the challenges/scanning results. √
- Develop (an) action plan(s), √ including the tasks to be done/deadlines to be met/resources to be procured, etc. √
- Implement selected strategies √ by communicating it to all stakeholders/organising the business's resources/motivating staff. √
- Continuously evaluate, √ monitor, √ measure strategies√ in order to take corrective action. √
Any other relevant answer related to a description of the strategic management process.
OR
OPTION 2
- Review √ vision statement. √
- Analyse/Re-examine √ mission statement. √
- Conduct an analysis √ using models such as PESTLE/PORTERS. √
- Formulate strategy, √ referring to strategies such as defensive/retrenchment. √
- Implement strategy, √ using templates such as action plans. √
- Control of strategy √ to identify gaps in planning. √
- Evaluate strategy √ to identify deviations in implementation. √
- Take corrective action √ to ensure goals/objectives are met. √
Any other relevant answer related to a description of the strategic management process.
NOTE: The steps may be in any order.
Max: (6)
2.4.1 Roles of SETAs from the scenario
- Develop a sector skills plan.√
- Implement the plan.√
- Develop and administer learnerships.√
- Support the implementation of the National Qualifications Framework.√
- Undertake quality assurance.√
NOTE: Mark the first THREE (3) only. (3 x 1) (3)
2.4.2 Purpose of SDA
- Develops the skills of people in South Africa√ in order to improve productivity.√
- Invests√ in education and training of workers.√
- Encourages businesses√ to improve the skills of their workers.√
- Improves the chances of getting a job√ for previously disadvantaged people.√
- Redresses imbalances of the past√ through education and training.√
- Provides for the implementation of strategies√ on a national, sector and workplace basis.√
- Provides funds for skills development√ through the levy-grant scheme and a National Skills Fund.√
- Encourages workers to participate√ in learning programmes.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the purpose of the SDA.
Max: (6)
2.5 Defensive strategies
Retrenchment:√√
- Business is restructured, √ therefore staff numbers are reduced. √
- Decreasing the number of product lines, √ may lead to the closing of a department. √
Strategy (2)
Explanation (1)
Submax. (3)
Divestiture/Disinvestment: √√
- Unprofitable divisions √ of the business are sold/outsourced to improve operational efficiency. √
- Unproductive assets are sold, √ to improve cash flow. √
Strategy (2)
Explanation (1)
Submax. (3)
Liquidation:√√
- Sells all assets/stops operating √ to pay off debts. √
- Forced liquidation √ may be used as an option by creditors. √
Strategy (2)
Explanation (1)
Submax. (3)
Any other relevant answer related to the defensive strategies.
NOTE: Mark the first THREE (3) only.
(3 x 3) (9)
2.6 Consumer rights
Right to choose √√
Consumers have the right to:
- Choose suppliers √ and goods. √
- Shop around √ for the best prices. √
- Return goods √ that are unsafe/defective √ for a full refund. √
- Reject goods √ that are not the same as the sample marketed. √
- Cancel/renew √ fixed term agreements. √
- Request written quotations √ and cost estimates. √
Any other relevant answer related to the consumers' right to choose.
Heading (2)
Explanation (1)
Submax. (3)
Right to privacy and confidentiality √√
- Consumers have the right to stop/restrict √ unwanted direct marketing. √
- They can object √ to unwanted promotional e-mails and telesales. √
- They have the right to stop/lodge complaints √ about the sharing of their personal details. √
Any other relevant answer related to the consumers' right to privacy and confidentiality.
Heading (2)
Explanation (1)
Submax. (3)
Right to fair and honest dealings √√
- Suppliers may not use physical force √ or harass customers. √
- Suppliers may not give misleading √ or false information. √
- Businesses may not promote √ pyramid schemes and chain-letter schemes. √
- Businesses may not overbook/oversell goods/services √ and then not honour the agreement. √
Any other relevant answer related to the consumers' right to fair and honest dealings.
Heading (2)
Explanation (1)
Submax. (3)
Right to information about products and agreements/Right to disclosure and information √√
- Contracts and agreements should be in plain language √ and easy to understand. √
- Businesses should display prices √ which are fully inclusive disclosing all costs. √
- Consumers may request the unit and bulk price √ of the same product. √
- If two prices for the same product are displayed, √ consumers should pay the lower price. √
- Businesses should label products √ and trade descriptions correctly. √
Any other relevant answer related to the consumers' right to information.
Heading (2)
Explanation (1)
Submax. (3)
Right to fair/responsible marketing/promotion √√
- Businesses should not mislead consumers on pricing, √ benefits/uses of goods. √
- Consumers may cancel purchases made through direct marketing √ within five working days/cooling off-period. √
- All information related to the country of origin/expiry dates/ingredients of the products √ should be disclosed. √
Any other relevant answer related to the consumers' right to fair marketing/ promotion.
Heading (2)
Explanation (1)
Submax. (3)
Right to fair value/good quality and safety √√
- Consumers have the right to demand √ quality service or goods. √
- They have the right to return faulty items √ if the fault occurs within six months after purchasing the item. √
- Consumers may receive √ an implied warranty or a written warranty. √
Any other relevant answer related to the consumers' right to fair value, good quality and safety.
Heading (2)
Explanation (1)
Submax. (3)
Right to accountability from suppliers √√
- Consumers have the right to be protected √ in lay-bye agreements. √
- Businesses should honour √ credit vouchers and prepaid services. √
Any other relevant answer related to the consumers' right to accountability from suppliers.
Heading (2)
Explanation (1)
Submax. (3)
Right to fair, just and reasonable terms and conditions √√
- Businesses should provide consumers √ with written notices of clauses that may limit consumer rights. √
- Businesses may not market or sell goods √ at unfair prices. √
Any other relevant answer related to the consumers' right to fair, just and reasonable terms and conditions.
Heading (2)
Explanation (1)
Submax. (3)
Right to equality in the consumer market place√√
- Businesses should not limit access√ to goods and services.√
- Businesses may not vary the quality of their goods√ to different consumers.√
- Businesses may not charge different prices√ for the same goods/services.√
- Businesses should not discriminate√ when marketing their products and services in different areas/places.√
Any other relevant answer related to the consumers' right to equality in the consumer market place.
Heading (2)
Explanation (1)
Submax. (3) (3 x 3) (9)
2.7.1 Primary purpose of the BBBEE Act quoted from the scenario
- To address and enhance the economic participation of Black people in the South African economy. √ (1)
2.7.2 Pillars of BBBEE quoted from the scenario
- Ownership √
- Management and control √
- Skills development √
- Enterprise and supplier development √
- Socio-economic development √
NOTE: Mark the first THREE (3) only. (3 x 1) (3)
2.7.3 Introduction of the BBBEE Act
- The purpose of BBBEE is to enable wealth √ to be spread more broadly. √
- Through BBBEE the government strives √ to involve all businesses (profit and non-profit organisations). √
- BBBEE Act includes a wider group of previously disadvantaged people, √ such as black women, people with disabilities, youth and people living in rural areas through social-economic strategies such as management, ownership, employment equity, social responsibility, preferential procurement and enterprise development. √
- BBBEE Broad-based Black Economic Empowerment is a growth strategy that targets inequality within the South African economy √ by encouraging more black management, promoting employment equality, encouraging skills training in businesses, nurturing black entrepreneurship and building black SMMEs by means of affirmative action. √
Any other relevant answer related to the introduction of Broad-Based Black Economic Empowerment (BBBEE).
Max. (4)
2.7.4 Impact of the BBBEE Act on businesses
Positives/Advantages
- Workers will be skilled √ because businesses are compelled to send them for skills training. √
- Businesses that comply with BBBEE regarding the pillars √ will be rated high on the BEE score card/may get government tenders. √
- Encourages businesses to address the demands for redress √ and equity directly. √
- Provides a variety of business codes √ to improve employment equity. √
- Provides opportunities for/Empowers previously disadvantaged employees √ through uplifting socio-economic processes. √
- Provides for human resources development √ through training and development. √
- Promotes enterprise development, √ by developing entrepreneurial skills of designated people to start their own businesses. √
- Businesses will have a good overview on how it is performing √ with regard to the national requirements of the country. √
- A good BBBEE rating√ will improve the image of the business. √
- By focusing on BBBEE the business will show commitment √ towards the social/educational/economic developments in the community/country. √
- Once rated, the business will understand how to develop BBBEE strategies √ that will increase its BBBEE ratings on an annual basis. √
- Fronting is discouraged, √ as it may lead to the disqualification of a business's entire score card/BBBEE status. √
- Share prices of BBBEE compliant businesses are likely to increase √ as they attract more business. √
- Businesses that support Small, Micro, Medium Enterprises (SMMEs), √ may increase their own BEE ratings. √
- Complying with BBBEE requirements gives businesses experience/exposure √ to be able to provide better employment opportunities/staff development. √
Any other relevant answer related to the positive impact of BBBEE on businesses.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- Businesses have to go through the process of having their BBBEE compliance measured/verified √ by an independent BBBEE verification agency. √
- Businesses that wish to do business with the government, √ must have their BBBEE status assessed annually. √
- Provides for preferential procurement, √ so certain businesses may be excluded from supplying goods/services. √
- Processes may lead to corruption/nepotism, √ if not monitored properly. √
- Many businesses have been disadvantaged due to BEE ratings √ as they may not be able to meet all the criteria for scoring. √
- Processes and procedures may be costly for a business √ as there are many legal requirements for scoring enough points to be compliant. √
- Businesses could experience large financial implications/penalties √ if they do not comply with BBBEE. √
- Businesses will have to spend money in areas covered by the seven/five pillars of BBBEE √ to obtain a good BBBEE rating. √
- Investment and ownership issues √ can cause unhappiness between existing shareholders. √
Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact of BBBEE on businesses.
Max. (6)
[60]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS | |
2.1 | 10 |
2.2 | 3 |
2.3 | 6 |
2.4.1 | 3 |
2.4.2 | 6 |
2.5 | 9 |
2.6 | 9 |
2.7.1 | 1 |
2.7.2 | 3 |
2.7.3 | 4 |
2.7.4 | 6 |
TOTAL | 60 |
QUESTION 3: BUSINESS VENTURES
3.1 Forms of ownership
3.1.1 Private company √√
3.1.2 Public company √√
3.1.3 Non-profit company √√
3.1.4 State-owned company √√ (4 x 2) (8)
3.2.1 Excess
- The payment that needs to be made by the insured √ towards the claim. √
- The amount that is not paid by the insurance company, √ but the responsibility of the insured. √
- The insured makes this payment √ to prevent the insured from claiming unnecessary. √
Any other relevant answer related to excess.
Max. (2)
3.2.2 Premium
- A payment to the insurer √ for cover usually based on the insured value of the goods and the risk involved. √
- The amount of money to be paid monthly/annually √ by the insured to the insurer for indemnification. √
Any other relevant answer related to a premium.
Max. (2)
3.3 Importance of insurance to businesses
- Transfers the risk from the business/insured √ to an insurance company/insurer. √
- The transfer of the risk is subject to the terms and conditions √ of the insurance contract. √
- Protects the business against theft and loss of stock and/or damages√ caused by natural disasters such as floods, storm damage, etc. √
- The business will be compensated √ for insurable losses. √
- Valuable business assets √ e.g. vehicles/equipment/buildings need to be insured against damage and/or theft. √
- Business is protected against the loss of earnings √ e.g. strikes by employees result in losses worth millions of rands.√
- Protects the business against deeds of dishonesty √ by employees. √
- Insurance can be taken against the life of partners’ √ in a partnership.√
- Should the services of key personnel be lost due to accidents or death, √ the proceeds of an insurance policy can be paid out to the business/beneficiaries. √
- Replacement costs for damaged machinery/equipment are very high, √ therefore, insurance can reduce/cover these costs. √
- Protects the business against losses √ due to the death of a debtor. √ - Any other relevant answer related to the importance of insurance to businesses.
Max. (5)
3.4 Distinction between insurance and assurance
INSURANCE | ASSURANCE |
Based on the principle of indemnity. √√ | Based on the principle of security/certainty. √√ |
Is a form of risk management in which the insured transfers the cost of potential loss to another entity for monetary compensation known as a premium. √√ | It is a contract where the insurer undertakes to pay an agreed sum of money after a certain period has expired/on the death of the person, whichever occurs first. √√ |
It covers a specified event that may occur. √√ | Specified event is certain, although the time of event is uncertain. √√ |
Applicable to short term insurance. √√ | Usually applicable to long term insurance. √√ |
Any other relevant answer related to the definition of insurance. | Any other relevant answer related to the definition of assurance. |
Submax. (2) | Submax. (2) |
Example: property insurance/money in transit/theft/burglary/fire. √ | Example: life insurance/endowment policies/retirement annuities. √ |
Submax. (1) | Submax. (1) |
NOTE: Mark the first example only.
Distinction (4)
Example (2)
Max. (6)
NOTE:
- The answer does not have to be in a tabular format but the distinction must be clear.
- Award a maximum of TWO (2) marks if the distinction is not clear./Mark either insurance or assurance only.
3.5.1 Fixed deposit √ (1)
3.5.2 A fixed deposit is a low risk investment, √ as investors are guaranteed√ of the final payment from the financial institutions.√ (3)
3.5.3 Investment
- R25 000 √ + R2 500 (R25 000 x 10%) = R27 500 √
R27 500 + R2 750 (R27 500 x 10%) √ = R30 250 √
R30 250 + R3 025 (R30 250 x 10%) √ = R33 275 √
OR - P (1+i)ᶰ √√
25 000(1+0,1)³ OR 25 000(1,1)³ OR 25 000(1,331) √√
= R33 275 √√
NOTE:
- Allocate full marks (6) if the answer is correct and no workings are shown.
- If calculations were shown correctly, but the final answer is wrong, award a maximum of FOUR (4) marks.
- If the answer is incorrect, award a maximum of TWO (2) marks for the understanding of concept and method.
- If there are no workings shown and the answer is incorrect, allocate a ZERO mark.
Max. (6)
3.5.4 Differences between simple and compound interest
SIMPLE INTEREST | COMPOUND INTEREST |
Calculated on the original/principal amount √ invested. √ | Calculated each period on the original/principal amount √ including all interest accumulated during past periods. √ |
Accumulated interest from prior periods √ is not used in calculations for the following period. √ | Accumulated interest from prior periods √ is used in calculations for the following period. √ |
Interest charged remain fixed √ for the full period of investment. √ Money charged by the borrower √ on the fixed amount for a certain period. √ | Based on the concept of adding accumulated interest to the original/principal amount √ and interest is earned on interest. √ |
Any other relevant answer related to simple interest. | Any other relevant answer related to compound interest. |
Submax. (2) | Submax. (2) |
Max. (4)
NOTE:
- The differences must be clear.
- Answer does not have to be in tabular format.
- Award a maximum of TWO (2) marks if the difference is not clear/Mark either simple or compound interest only.
- Accept paragraph style answer.
3.6.1 Type of leadership style
- Bureaucratic √√ (2)
Motivation
- The owner of the business follows all the organisational rules and policies systematically./He makes sure that employees adhere strictly to the rules.√ (1) Max. (3)
3.6.2 Impact of the bureaucratic style in the workplace
Positives/Advantages
- Managers ensure that government policies/business rules/procedures √ are always followed accurately. √
- Tight control measures implemented/followed √ ensure high quality service delivery. √
- Ensures accountability √ to the general public/community. √
- Improves health and safety in dangerous workplaces, √ e.g. mines, construction sites. √
- Followers know what is expected of them √ because of complete instructions. √
- Strict control over systems/procedures, √ ensure high quality output. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the positive impact of a bureaucratic leadership style.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- Complicated/Official rules √ may seem unnecessary/time consuming. √
- Leaders/Directors may acquire power √ and can disregard/ignore inputs from others. √
- Very little room for error, √ so workers feel they are not treated as humans. √
- Lack of creativity/innovation/self-fulfilment √ may lead to stagnation/decrease in productivity. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact of a bureaucratic leadership style.
Max. (6)
3.7 Advantages of the transactional leadership style
- Encourages employees to work hard √ as they will receive rewards. √
- Improves employees' productivity/morale √ as they feel motivated/good about themselves. √
- Business goals/objectives √ may be achieved. √
- Employees know exactly √ what is expected of them. √
- Disciplinary procedures √ are well communicated. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the advantages of the transactional leadership style.
Max. (6)
3.8 Personal-liability company (PLC)
3.8.1 3.8.2
Capital | |
Success | Failure |
|
Max. (4) |
Management | |
Success | Failure |
|
Max. (4) |
[60]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS | |
3.1 | 8 |
3.2 | 4 |
3.3 | 5 |
3.4 | 6 |
3.5.1 | 1 |
3.5.2 | 3 |
3.5.3 | 6 |
3.5.4 | 4 |
3.6.1 | 3 |
3.6.2 | 6 |
3.7 | 6 |
3.8.1 | 4 |
3.8.2 | 4 |
TOTAL | 60 |
QUESTION 4: BUSINESS ROLES
4.1 Stages of team development
- Forming √
- Storming √
- Norming √
- Performing √
- Adjourning/Mourning √
- Any other relevant answer related to the stages of team development. NOTE: Mark the first THREE (3) only.
(3 x 1) (3)
4.2 Advantages of creative thinking in the workplace
- Starts/Ignites business's process of problem solving, √ as there are usually more problems and not enough solutions. √
- Better/Unique/Unconventional ideas/solutions √ is generated. √
- May give a business a competitive advantage √ if unusual/unique solutions/ideas/strategies are implemented. √
- Complex business problems √ may be solved. √
- Productivity increases √ as business's management/employees may quickly generate multiple ideas to utilise time and money more effectively. √
- Managers/Employees have more confidence √ as they can live up to their full potential. √
- Managers will be better leaders √ as they will be able to handle/manage change(s) positively and creatively. √
- Managers/Employees can develop a completely new outlook, √ which may be applied to any task(s) they may do. √
- Leads to more positive attitudes √ as managers/employees feel that they have contributed towards problem solving. √
- Improves motivation √ amongst staff members. √
- Managers/Employees have a feeling of great accomplishment √ and they will not resist/obstruct once they solved a problem/contributed towards the success of the business. √
- Business's management/employees may keep up √ with fast changing technology. √
- Stimulates brain function of employees/managers, √ as they are continuously pushed out of their comfort zone. √
- Creativity may lead to new inventions √ which improves the general standard of living. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the advantages of creative thinking in the workplace.
Max. (6)
4.3.1 Unethical business practice
- Tax evasion√√ (2)
Motivation
- Roy, the owner of True Blue Sports, does not record all the transactions of his business as required by South African Revenue Services. √ (1) Max. (3)
4.3.2 Unethical business practices
- Sexual harassment √
- Unauthorised use of workplace funds and resources √
- Unfair advertising √
- Pricing of goods in rural areas √
- Abuse of work time √
- Any other relevant answer related to unethical business practices.
NOTE: Mark the first FOUR (4) only.
(4 x 1) (4)
4.3.3 Professional, responsible, ethical and effective business practice
- True Blue Sports should not start other business ventures at the expense of others. √√
- They should pay fair wages. √√
- All employees should be treated equally. √√
- Appoint honest/trustworthy accountants with a good reputation. √√
- Staffing and other processes should be open and transparent. √√
- Draw up a code of ethics. √√
- Managers must set the tone for professional/responsible/ethical behaviour. √√
- There must be adequate internal control systems in place. √√
- There should be honesty in all relationships/transactions in the business. √√
- Employees should understand ethical business practices through effective communication/training. √√
- Seminars on business ethics should be held for managers and the employees to help them understand the importance of the ethical work culture of the business. √√
- Management must consider the impact of their decisions/actions on all stakeholders. √√
- Regulations applicable to environmental protection should be taken seriously. √√
- They should charge fair prices in rural areas. √√
Any other relevant recommendation related to ways in which TBS should conduct business professionally, responsibly and ethically.
NOTE: Mark the first THREE (3) only.
(3 x 2) (6)
4.4 Criteria for successful teams
Interpersonal attitudes and behaviour √√
- Members have a positive attitude of support and motivation √ towards each other. √
- Good/Sound interpersonal relationships √ will ensure job satisfaction/ increase productivity of the team. √
- Members are committed/passionate√ towards achieving a common goal/objectives. √
- Team leader acknowledges/gives credit to members √ for positive contributions. √
- Any other relevant answer related to interpersonal attitudes and behaviour of successful teams.
Criteria (2)
Explanation (1)
Submax. (3)
Shared values/Mutual trust and support √√
- Shows loyalty/respect/trust towards team members √ despite differences. √
- Shows respect √ to the knowledge/skills of other members. √
- Perform team tasks with integrity/pursuing responsibility/meeting team deadlines √ with necessary commitment to team goals. √
- Any other relevant answer related to shared values/mutual trust and support of members in successful teams.
Criteria (2)
Explanation (1)
Submax. (3)
Communication √√
- A clear set of processes/procedures for teamwork √ ensures that every team member understands his/her role. √
- Ability to communicate well √ and make quick decisions. √
- Communicates with team members √ and allows for feedback. √
- Encourages discussion about the problem √ so that solutions can be found. √
- Continuous review of team progress √ ensures that team members can rectify mistakes/act pro-actively to ensure that goals/targets are reached. √
- Any other relevant answer related to communication in successful teams.
Criteria (2)
Explanation (1)
Submax. (3)
Co-operation/Collaboration √√
- Clearly defined realistic goals are set, √ so that all members know exactly what is to be accomplished. √
- Willingness to co-operate as a unit √ to achieve team objectives. √
- Co-operate with management √ to achieve team/business objectives. √
- Agree on methods/ways to get the job done effectively √ without wasting time on conflict resolution. √
- All members √ take part in decision-making. √
- A balanced composition of skills/knowledge/experience/expertise √ ensures that teams achieve their objectives. √
- Any other relevant answer related to co-operation/collaboration in successful teams.
Criteria (2)
Explanation (1)
Submax. (3)
NOTE:
- Mark the first THREE (3) only.
- Consider any other relevant criteria for a successful team.
(3 x 3) (9)
4.5 Difference between ethics and professionalism
ETHICS | PROFESSIONALISM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Submax. (3) | Submax. (3) |
NOTE:
- The differences must be clear.
- Answer does not have to be in tabular format.
- Award a maximum of THREE (3) marks if the differences is not clear./Mark either ethics or professionalism only.
- Accept paragraph style answer.
Max. (6)
4.6.1 Problem-solving technique
- Delphi technique √√ (2)
Motivation
- To request a group of business experts to complete questionnaires. √ (1) Max. (3)
4.6.2 Advantages of the Delphi technique
- A group of experts will be used √ without bringing them together. √
- Experts will give clear ideas/solutions √ on how to improve on low productivity/ profitability. √
- Panel members/Experts can give new information √ on problems. √
- Information received from experts √ can be kept confidential. √
- It reduces noise levels in an office environment √ since there is no group discussion. √
- Panel members/Experts need to reach consensus, √ so that the best solution is found. √
- All experts are given an equal opportunity to give their opinions, √ so no one dominates the process. √
- Any other relevant advantages related to the use of the Delphi technique in solving business problems.
Max. (6)
4.7 Benefits of diversity in the workplace
- Workforce diversity improves the ability of a business √ to solve problems/innovate/ cultivate diverse markets. √
- Employees value each other's diversity √ and learn to connect/communicate across lines of difference.√
- Diversity in the workforce improves √ morale/motivation. √
- Employees demonstrate greater loyalty to the business √ because they feel respected/accepted/understood. √
- A diversified workforce can give businesses a competitive advantage √ as they can render better services. √
- Being respectful of differences/demonstrating diversity √ makes good business sense/improves profitability. √
- Diverse businesses ensure that its policies/practices √ empower every employee to perform at his/her full potential. √
- Customers increasingly evaluate businesses √ on how they manage diversity in the workplace. √
- Employees from different backgrounds √ can bring different perspectives to the business. √
- A diversified workforce stimulates debate √ on new and improved ways of getting things done. √
- Employees represent various groups √ and are therefore better able to recognise customer needs and satisfy consumers. √
- Businesses with a diverse workforce are more likely to have a good public image √ and attract more customers. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the benefits of diversity in the workplace.
Max. (6)
4.8 Ways in which the businesses can deal with diversity issues in the workplace
4.8.1 Age
- Promotions should not be linked to age, but rather to specific skills set. √√
- A business must not employ children aged 15 or younger. √√
- The ages of permanent workers should vary from 18 to 65 to include all age groups. √√
- A business may employ a person who is older than the normal retirement age provided that person is the most suitable candidate. √√
- Businesses must encourage older employees to help young employees to develop their potential. √√
- Young employees must be advised to respect and learn from older employees. √√
- The business should encourage employees to be sensitive to different perspectives of various age groups. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to the way in which businesses can deal with age as a diversity issue in the workplace.
Max. (4)
4.8.2 Disability
- Provide employment opportunities for people with disabilities. √√
- Accommodate people with disabilities by providing facilities/ramps for wheelchairs, √√ etc.
- Ensure that workers with special needs are not marginalised/feel excluded from workplace activities. √√
- Business should be well informed with how to deal with disabled employees. √√
- Policies and programs should accommodate the needs of people with disabilities. √√
- Create an organisational culture and climate that is conducive for people with disabilities. √√
- Employees should be trained to deal with colleagues with disabilities. √√
- Bringing in external experts to help with disability and accommodation issues. √√
- Ensure that employees with disabilities are treated fairly. √√
- Focus on job skills/work performance of the disabled, rather than their disability/possible problems they may pose in the future.√√
- Any other relevant answer related to the way in which businesses can deal with disability as a diversity issue in the workplace.
Max. (4)
[60]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS | |
4.1 | 3 |
4.2 | 6 |
4.3.1 | 3 |
4.3.2 | 4 |
4.3.3 | 6 |
4.4 | 9 |
4.5 | 6 |
4.6.1 | 3 |
4.6.2 | 6 |
4.7 | 6 |
4.8.1 | 4 |
4.8.2 | 4 |
TOTAL | 60 |
QUESTION 5: BUSINESS OPERATIONS
5.1 Methods of external recruitment
- Printed media, e.g. newspapers/flyers √
- Electronic media, e.g. radio/TV √
- Social media/Social networks/Internet/Business websites √
- Recruitment agencies √
- Walk-ins √
- Head-hunting √
- Professional associations √
- Networking √
- Educational/Training institutions √
- Posters/Bill boards just outside the business√
- Any other relevant answer related to the methods of external recruitment.
NOTE:
- Mark the first THREE (3) only.
- . Allocate a maximum of ONE (1) mark for examples on each method.
(3 x 1) (3)
5.2 Placement procedure
- The business must outline the specific responsibilities of the new position, √ including the expectations and skills required for this position. √
- The business should determine the employee’s strengths, weaknesses, interest, and skills √ by subjecting the employee to a range of psychometric tests. √
- The business must determine the relationship between the position √ and the competencies of the employee. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the placement procedure.
Max. (6)
5.3 Benefits of induction programme
- New employees who are familiar with the business's policies/procedures √ may easily adapt to his/her new work environment. √
- New employees learn more about the business √ and understand their role in the business/what is expected in the job. √
- Increased productivity √ and quality of service/performance. √
- Minimises the need √ for on-going training and development. √
- Better/More focused training may be provided √ based on the results obtained from the induction process. √
- New employees will understand √ rules/restrictions in the business. √
- New employees will know where everything is √ and who the supervisors/low level managers are for better communication purposes. √
- New employees may feel part of the team resulting √ in positive morale/motivation. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the benefits of an induction programme on businesses.
Max. (6)
5.4.1 Employment contract
- Employer – Real Clean LTD √
- Employee – Jane √ (2 x 1) (2)
Motivation
- Real Clean LTD is the employer because “Real Clean LTD has employed Jane as a cleaner.”√
- Jane is the employee because “Real Clean LTD signed an employment contract with Jane.” √ (2 x 1) (2)
Max. (4)
5.4.2 Aspects of an employment contract
- Key performance areas/Duties and responsibilities √
- Code of conduct √
- Job description √
- Name and address of the business/employer √
- Name and address and other personal information of the employee √
- Job title √
- Probation period √
- Bonus and salary/employee wages/salary and method of calculating the wage/salary √
- Remuneration package/other payments the employee is entitled to √
- The date of commencement of employment √
- Details of termination of a contract/notice period √
- Rate of overtime payment √
- All deductions that will be made from the employee salary/wage must be clearly indicated √
- Leave √
- Working hours √
- Any other relevant answer related to the aspects included in an employment contract.
NOTE: Mark the first FOUR (4) only. (4 x 1) (4)
5.4.3 Reasons for terminating an employment contract
- Real Deal LTD may dismiss employees for valid reason(s), e.g. unsatisfactory job performance, misconduct √√, etc.
- Real Clean LTD (employer) may no longer have work for redundant employees/ cannot fulfil the contract/is restructuring. √√
- Real Clean LTD may retrench some employees due to insolvency/may not be able to pay the employees. √√
- Employees decided to leave and resign voluntarily. √√
- An employee may have reached the pre-determined age for retirement. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to the reasons for termination of an employment contract.
Max. (6)
5.5 Benefits of a good quality management system
- Effective customer service will be rendered, √ resulting in increased customer satisfaction. √
- Time and resources √ are used efficiently. √
- Productivity increase √ through proper time management √ and using high quality resources. √
- Products and services are constantly improved, √ resulting in greater customer satisfaction. √
- Vision and mission √ may be achieved. √
- The business may achieve a competitive advantage √ over its competitors. √
- Continuous training √ will continuously improve the quality of employees’ skills and knowledge. √
- Employers and employees will have a healthy working relationship, √ which results in happy workers. √
- Increased market share √ and profitability. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the benefits of a good quality control system.
Max. (6)
5.6 Distinction between quality performance and quality management
QUALITY PERFORMANCE | QUALITY MANAGEMENT |
Total performance of each department measured √ against specified standards. √ | It is techniques/tools√ used to design/improve the quality of a product.√ |
Can be obtained if all departments work together√ towards the same quality standards. √ | Can be used for accountability√ within each of the business function.√ |
Quality is measured√ through physical product/statistical output of processes/surveys of the users and/or buyers of goods/services.√ | Aims to ensure that the quality of goods/services√ is consistent√/ Focuses on the means√ to achieve consistency. √ |
Any other relevant answer related to quality performance. | Any other relevant answer related to quality management. |
Submax. (4) | Submax. (4) |
NOTE:
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format.
- The distinction must be clear.
- Award a maximum of FOUR (4) marks if the distinction is not clear./Mark either quality performance or quality management only.
Max. (8)
5.7.1 TQM element
- Total Client/customer satisfaction √ (2)
Motivation
- Customers always speak very highly of the quality of the clothing/Jabu knows that the quality of her clothing determines her sales.√ (1) Max. (3)
5.7.2 Total client/customer satisfaction
Positives/Advantages
- Large businesses use market research/customer surveys √ to measure/monitor customer satisfaction/analyse customers' needs. √
- Continuously promote √ a positive company image. √
- May achieve a state of total customer satisfaction, if businesses follow sound business practices √ that incorporate all stakeholders. √
- Strive to understand and fulfil customer expectations √ by aligning cross functional teams across critical processes. √
- Ensures that cross-functional teams understand its core competencies √ and develop/strengthen it. √
- May lead to higher customer retention/loyalty √ and businesses may be able to charge higher prices. √
- Businesses may be able to gain access √ to the global market. √
- May lead to increased √ competitiveness/profitability. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the positives impact of total client/customer satisfaction.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- Employees who seldom come into contact with customers √ often do not have a clear idea of what will satisfy their needs. √
- Monopolistic companies have an increased bargaining power, √ so they do not necessarily have to please customers. √
- Not all employees √ may be involved/committed to total client satisfaction. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the negatives impact of total client/customer satisfaction.
Max. (6)
5.8 PDCA model/cycle in the continuous improvement to processes and systems
- Plan √
- Businesses should identify the problem. √
- Develop a plan for improvement to processes and systems. √
- Answer questions such as 'what to do' and 'how to do it'. √
- Plan the method and approach. √
Submax. (2)
- Do √
- Businesses should implement the change on a small scale.√
- Implement the processes and systems.√
Submax. (2)
- Check/Analyse √
- Use data to analyse the results of change. √
- Determine whether it made a difference. √
- Check whether the processes are working effectively. √
- Businesses should assess, plan and establish if it is working/if things are going according to plan. √
Submax. (2)
- Act as needed √
- Institutionalise the improvement. √
- Devise strategies on how to continually improve. √
- If the change was successful, implement it on a wider scale. √
- Continuously revise the process. √
Submax. (2)
- Any other relevant answer related to how businesses can use the PDCA model/cycle to continuously improve their processes and systems.
NOTE:
- Do not award marks for the impact of continuous improvement to processes and systems.
- The step could be integrated in the explanation.
Step (1)
Explanation (1)
Max. (8)
[60]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS | |
5.1 | 3 |
5.2 | 6 |
5.3 | 6 |
5.4.1 | 4 |
5.4.2 | 4 |
5.4.3 | 6 |
5.5 | 6 |
5.6. | 8 |
5.7.1 | 3 |
5.7.2 | 6 |
5.8 | 8 |
TOTAL | 60 |
QUESTION 6: MISCELLANEOUS TOPICS
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT
6.1 Provisions of the Basic Conditions of Employment Act (BCEA)
- Overtime √
- Working hours √
- Meal breaks and rest periods √
- Leave conditions √
- Working on public holidays √
- Legal requirements of the employment contract √
- Termination conditions of the employment contract √
- Remuneration √
- Provision for compliance √
- Any other relevant answer related to the provisions of the BCEA.
NOTE:
- Mark the first THREE (3) only.
- . Allocate a maximum of ONE (1) mark for an example of a specific provision. (3 x 1) (3)
6.2 Steps of strategy evaluation
- Examine the underlying basis of a business strategy. √√
- Formulate strategies to meet objectives, favourably. √√
- Implement strategies using action plans, √√ etc.
- Look forward and backwards into the implementation process. √√
- Compare the expected performance with the actual performance. √√
- Measure business performance in order to determine the reasons for deviations and analyse these reasons. √√
- Take corrective action so that deviations may be corrected. √√
- Set specific dates for control and follow up. √√
- Draw up a table of the advantages and disadvantages of a strategy. √√
- Decide on the desired outcome. √√
- Consider the impact of the strategic implementation in the internal and external environments of the business. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to the steps in evaluating a strategy.
NOTE: Mark the first THREE (3) only.
(3 x 2) (6)
6.3 Impact of COIDA on businesses
Positives/Advantages
- Promotes safety √ in the workplace. √
- Creates a framework √ for acceptable employment practices/safety regulations. √
- Supply administrative guidelines/mechanisms √ for dealing with/processing claims. √
- Eliminates time and costs spent √ on lengthy civil court proceedings. √
- Covers all employees at the workplace √ if both parties meet all the necessary safety provisions in the Act. √
- Employees are compensated financially for any injury/disability √ resulting from performing their duties at their workplace. √
- In the event of the death of an employee as a result of a work-related accident/ disease, √ his/her dependant(s) will receive financial support. √
- Employers are protected from financial burden should an accident occur in the workplace √ provided that the employer was not negligent. √
- Employees do not have to contribute √ towards this fund.√
- Employees receive medical assistance √ provided there is no other party involved. √
- Any compensation to an employee/the family √ is exempt from income tax. √
- The processes √ are relatively simple. √
- Makes businesses more socially responsible √ as they cannot just employ workers at random in dangerous working conditions. √
- Workers are treated with dignity/respect √ as businesses view them as valuable assets and not just as workers. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the positive impact of COIDA on businesses.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- Claiming processes/procedures √ can be time consuming. √
- Processes/ Procedures required by this Act may be costly √ as paperwork places an extra administrative burden on businesses. √
- Employers have to register all their workers/make annual contributions to COIDA, √ which may result in cash flow problems. √
- Employers may be forced to pay heavy penalties √ if they are found guilty of negligence/not enforcing safety measures. √
- Workers who are temporarily/permanently employed in foreign countries √ are not covered. √
- Domestic/Military workers √ are not covered. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact of COIDA on businesses.
Max. (6)
BUSINESS VENTURES
6.4 Factors to consider when making investment decisions
- Return on investment (ROI) √
- Risk √
- Investment term/period √
- Tax implications/Taxation √
- Inflation rate √
- Fluctuations/Volatility of investment markets √
- Liquidity √
- Personal budget √
- Track record/History/Performance of the business √
- Any other relevant answer related to factors that must be considered when making investment decisions
NOTE: Mark the first THREE (3) only. (3 x 1) (3)
6.5 Types of shares
6.5.1 Ordinary shares √√
6.5.2 Bonus shares √√
6.5.3 Founder shares √√ (3 x 2) (6)
6.6 Advantages of co-operatives
- Formed by persons having a common interest √ to allow more members to work as a team. √
- Members may cast their votes to elect committee representatives √ that will deal with day-to-day administration and can elect the most trustworthy members. √
- Liability to members is limited √ to an amount equal to the nominal value of the share for which the member has not paid and what he/she holds in the co-operative. √
- Personal properties of members are free from risk √ because of limited liability. √
- There is no middleman between the co-operative and its suppliers/ customers/clients √ which may lead to profit maximisation. √
- Easy and less complicated to form this business √ as there is very little/simple legal requirements. √
- Registered co-operatives formed by previously disadvantaged people may obtain support from the government √ in the form of government tenders. √
- It is a legal person apart from its members √ and can enter into contracts in its own name. √
- Auditing financial statements is legally required, √ so trustworthy reports are prepared in accordance with co-operative principles. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the advantages of co-operatives. Max. (6)
BUSINESS ROLES
6.7.1 Well-being of employees
- DE must ensure fair wages/salaries for workers based on the nature of work and prevailing economic conditions in the markets. √√
- Working conditions must not only consider safety, medical and canteen facilities, but also benefit like housing leave, retirement etc. √√
- Fair bonuses, based on business earnings, should be paid as acknowledgement for hard work and commitment. √√
- Provision for employees’ participation in decision-making that affects them. √√
- Recreation facilities for employees should be provided. √√
- Physical, medical assessments should be offered annually to workers. √√
- Trauma debriefing, counselling or assistance to any employee who requires these services should be readily available. √√
- Financial assistance may be offered in the case of any hardship caused unexpected medical costs. √√
- Flexible working hours may be allowed to enhance productivity. √√
- DE must support the programmes for employees infected and affected by HIV/Aids may be offered. √√
- Childcare facilities should be available on the premises for working mothers in the business √√
- Any relevant answer related to ways in which DE can contribute towards the well-being of their employees.
Max. (8)
6.8 Causes of conflict in the workplace
- Lack of proper communication between leaders and members √
- Differences in backgrounds/cultures/values/beliefs/language √
- Limited business resources √
- Different goals/objectives for group/individuals √
- Personality differences between group/individuals √
- Different opinions √
- Unfair workload √
- Ill-managed stress √ unrealistic expectations √
- Poor organisation/leadership/administrative procedures and systems √
- Confusion about scheduling/deadlines √
- Ignoring rules/procedures √
- Misconduct/Unacceptable behaviour √
- High/Intense competition/Competitiveness √
- Poor communication √
- Unclear responsibilities √
- Distracted by personal objectives √
- Constant changes in the workplace √
- Unfair treatment of workers/Favouritism by management/Discrimination √
- Lack of trust amongst workers √
- Any other relevant answer related to the possible causes of conflict in the workplace.
NOTE: Mark the first THREE (3) only. (3 x 1) (3)
6.9 Dealing with difficult people
OPTION 1
- Get perspective from others who have experienced the same kind of situation to be able to understand the difficult employee. √√
- Act pro-actively if possible, as a staff/personnel problem is part of a manager's responsibilities. √√
- Regular meetings with supervisors/departmental heads should help to identify difficult/problem behaviour. √√
- Ask someone in authority for their input into the situation. √√
- Identify the type of personality which is creating the problem. √√
- Meet privately with difficult employees, so that there are no distractions from other employees/issues. √√
- Make your intentions and reasons for your actions known so that they will feel at ease. √√
- Employees should be told what specific behaviours are acceptable by giving details about what is wrong/unacceptable and also an opportunity to explain their behaviour. √√
- A deadline should be set for improving bad/difficult behaviour. √√
- The deadline date should be discussed with the employee and his/her progress should be monitored/assessed prior to the deadline. √√
- Guidelines for improvement should be given. √√
- Do not judge the employee, but try to understand him/her/Understand the person's intentions and why they react in a certain way. √√
- Keep communication channels open and encourage employees to communicate their grievances to management. √√
- Build rapport/sound relations by re-establishing personal connection with colleagues, instead of relying on e-mails/messaging/social media.√√
- Help difficult employees to be realistic about the task at hand. √√
- Remain calm and in control of the situation to get the person(s) to collaborate. √√
- Treat people with respect, irrespective of whether they are capable/ competent or not. √√
- Sometimes it may be necessary to ignore but monitor a difficult person. √√
- Identify and provide an appropriate support program to address areas of weakness. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to managing difficult employees.
NOTE: Mark the first TWO (2) only. (2 x 2) (4)
AND/OR
OPTION 2 (Personalities)
Type of personality | Strategy to deal with a personality |
Complainer √ |
|
Indecisive √ |
|
Over agree √ |
|
Negativity √ |
|
Expert √ |
|
Quiet √ |
|
Aggressive √ |
|
NOTES (applicable to OPTION 2):
- Allocate a maximum of TWO (2) marks for only identifying the type of personality without a strategy.
- Allocate TWO (2) marks for indicating the strategy without identifying the type of the personality/Take particular note of overlap of strategies.
- Mark the first TWO (2) only. (2 x 2) (4)
BUSINESS OPERATIONS
6.10 Remuneration
PIECEMEAL/PIECE RATE/PIECEWORK | TIME-RELATED |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Submax. (2) | Submax. (2) |
NOTE:
- The distinction must be clear.
- Allocate a maximum of TWO (2) marks if distinction is not clear./Mark either piecemeal or time-related remuneration only.
Max. (4)
6.11 Impact of TQM if poorly implemented
- Setting unrealistic deadlines √ that may not be achieved. √
- Employees may not be adequately trained √ resulting in poor quality products. √
- Decline in productivity, √ because of stoppages. √
- Businesses may not be able to make necessary changes √ to satisfy the needs of customers. √
- The reputation of the business √ may suffer because of faulty goods. √
- Customers will have many alternatives to choose from √ and the impact could be devastating to the business. √
- Investors might withdraw investment, √ if there is a decline in profits. √
- Bad publicity √ due to poor quality products supplied. √
- Decline in sales, √ as returns from unhappy customers' increase. √
- High staff turnover, √ because of poor skills development. √
- Undocumented quality control systems/processes √ could result in error or deviations from pre-set quality standards. √
Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact of TQM if poorly implemented.
Max. (5)
6.12 Quality indicators of the administration function
- Fast and reliable data capturing and processing systems. √√
- Supply reliable information to management on time. √√
- Make relevant information available for quick decision-making. √√
- Handle complaints quickly and effectively. √√
- Use modern technology efficiently. √√
- Implement effective risk management policies to minimise business losses. √√
- Quality assurance and control evaluations are recorded accurately. √√
- All documentation is kept neatly and orderly in a safe place. √√
- Easy to recall/find information/documentation. √√
- Financial documents are kept up to date and recorded accurately. √√
- All systems and processes are documented. √√
Any other relevant answer related to quality indicators for the Administration function.
NOTE: Mark the first THREE (3) only. (3 x 2) (6)
[60]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS | |
6.1 | 3 |
6.2 | 6 |
6.3 | 6 |
6.4 | 3 |
6.5 | 6 |
6.6 | 6 |
6.7 | 8 |
6.8 | 3 |
6.9 | 4 |
6.10 | 4 |
6.11 | 5 |
6.12 | 6 |
TOTAL | 60 |
TOTAL SECTION B: 180
SECTION C
QUESTION 7: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT
7.1 Introduction
- Many consumers overspend when buying on credit. √
- The National Credit Act was put in place to improve the debt of both businesses and consumers. √
- The Act ensures that credit is used in a way that adds value to customers' lives. √
- If consumers/customers are not using credit carefully, they may become over-indebted. √
Any other relevant introduction relating the National Credit Act.
Max. (2)
7.2 Purpose of the National Credit Act
- Protects the consumer against unfair credit agreements, √ e.g. charging interest rates well above the maximum stipulated by law. √
- Introduces a single functional system of regulations √ that will apply to all credit activities. √
- Ensures that all credit providers and credit consumers √ are treated equally. √
- Encourages responsible √ borrowing. √
- Justifies rights and responsibilities √ for consumers and credit providers. √
- Discourages careless granting of credit by service providers √ to unsuspecting consumers. √
- Regulates the interest rate to be charged by service providers √ to consumers. √
- Makes provision for the establishment √ of the National Credit Regulator (NCR). √
- Makes provision for the establishment √ of a credit register (database). √
Any other relevant answer related to the purpose of the National Credit Act. Max. (12)
7.3 Rights of consumer in the National Credit Act
The right to:
- Apply for credit √ and to be free from discrimination. √
- Obtain reasons √ for credit being refused.√
- Receive pre-agreement documentation √ before concluding any credit transaction. √
- Fair √ and responsible marketing. √
- Choose which goods they will buy √ and return such goods if they are not satisfied. √
- Receive Information √ in plain and understandable language. √
- Receive documents √ as required by the Act. √
- Access and challenge √ credit records and information. √
Any other relevant answer related to consumer rights as stipulated in the NCA.
Max. (10)
7.4 Impact of NCA on business
Positives/Advantages
- Encourages √ more prudent buying from suppliers. √
- The whole credit process √ is transparent. √
- Lower bad debts, √ as credit is granted after proper credit checking. √
- Better cash flow, √ because there is control over debtors. √
- Increases cash sales √ as more customers tend to buy for cash. √
- Gains √ goodwill and loyalty from the consumers. √
- Business/Credit provider has the right to assess the creditworthiness √ of clients/consumers. √
- Leads to more consumers through credit sales √ as they are now protected from abuse. √
Any other relevant answer related to the positive impact of the National Credit Act to business.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- Decrease in credit sales √ due to customer loss/economic decline (downturn). √
- May not easily √ be granted overdraft/credit facilities. √
- Creditors may not pester customers √ to agree to a credit agreement telephonically or through visits at home. √
- More working capital is needed √ due to higher administrative costs. √
- Businesses profit could decline, √ because they can no longer depend on customers who had easy access to credit. √
- Misinterpretation of the Act √ may lead to huge losses, e.g. increased bad debts. √
- Failure to abide by all the provisions of the Act √ might result in a lawsuit, e.g. granting credit to a customer whose name is under review. √
- Paperwork and administrative processes √ are costly and time consuming. √
Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact of the NCA to businesses.
Max. (14)
7.5 Compliance with NCA
- Credit providers must submit an annual compliance report to the National Credit Regulator. √√
- Credit providers also need to have procedures in place to comply with the provisions of the Financial Intelligence Centre Act. √√
- To practice due diligence and inform borrowers of the laws and consequences that could result from the borrowing money and over extending their credit. √√
- Credit providers must conduct a proper assessment of each consumer’s ability to meet their obligations. √√
- Credit providers must provide successful applicants with a pre-agreement statement. √√
- The pre-agreement statement should provide the consumer with enough information to ensure they understand the obligations under the agreement. √√
Any other relevant answer related to ways businesses can comply with the NCA.
Max. (10)
7.6 Conclusion
- Customers have the responsibility to take ownership of credit by honouring the payments. √√
- This Act allows and enables responsible lending and eliminates reckless borrowing. √√
Any other relevant conclusion relating the National Credit Act.
Max. (2)
[40]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS
Details | Maximum | Total |
Introduction | 2 | Max. 32 |
Purpose of the National Credit Act | 12 | |
Rights of consumer in the NCA | 10 | |
Impact of NCA on businesses | 14 | |
Compliance | 10 | |
Conclusion | 2 | |
INSIGHT | ||
Layout | 2 | |
Analysis, interpretation | 2 | |
Synthesis | 2 | |
Originality/Examples | 2 | |
TOTAL MARKS | 40 |
*LASO – For each component:
- Allocate 2 marks if all requirements are met.
- Allocate 1 mark if only some of the requirements are met.
- Allocate 0 marks where requirements are not met at all.
QUESTION 8: BUSINESS VENTURES
8.1 Introduction
- Business managers need to present information about their business to stakeholders. √
- A verbal presentation will focus on an oral/spoken presentation to the directors. √
- The purpose of a verbal presentation is to exchange information as it involves speaking and listening for both the presenter and the audience/ directors. √
- Visual aids combine pictures and sound that will enhance the quality of the presentation. √
- Visual aids can help to convey a large amount of facts in a short time. √
- Choosing the most effective visual aids should capture the attention of the directors and support the logical flow of the presentation. √
- When responding to questions/remarks, the presenter should not be aggressive/defensive. √
Any other relevant introduction related to presentations, visual aids, responding to feedback and improving presentations.
Max. (2)
8.2 Aspects to be considered when designing a multimedia presentation
- Choose a text/font that is clearly legible. √√
- Select a background that is not distracting/support easy reading. √√
- Choose images that support the facts. √√
- Create graphics to illustrate/analyse information. √√
- Add special effects to highlight the important facts/capture the attention of the audience. √√
- Create hyperlinks to allow for Web browsing/for easy access to other files. √√
- Avoid using unnecessary/meaningless visual aids. √√
Any other relevant answer related to aspects to be considered when designing a multimedia presentation.
NOTE: Mark the first FOUR (4) only. (4 x 2) (8)
8.3 Evaluate visual aids
PowerPoint presentation / Data projection
Positives/Advantages
- Graphic programmes have the capacity to convey ideas √ and support what the presenter says. √
- Easy to combine √ with sound/video clips. √
- Simple/Less cluttered slides √ may capture the interest of the audience. √
- Video clips can provide variety √ and capture the attention of the audience. √
- Variation of colour/background/sound immediately captures the attention of the audience √ and retains their interest throughout the presentation. √
- Slides should only be used √ where they can enhance the facts or summarise information. √
Any other relevant answer related to the positive evaluation of a data projector/PowerPoint presentation.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- Unprofessional handling of the data projector/PowerPoint presentation material √ may lead to irritation/may result in the audience losing interest. √
- Less effective √ to people with visual impairments. √
- Simply reading off the slides √ makes a presentation boring/meaningless. √
- Unable to show slides √ without electricity/data projector. √
Any other relevant answer related to the negative evaluation of a data projector/Power-point presentation.
Submax. (8)
Posters
Positives/Advantages
- Useful in promoting √ the logo/vision of the business. √
- It should be colourful/eye-catching/creative √ to support the core message of the presentation. √
- May contain large illustrations/pictures/features of the products/key concepts √ to emphasise detail, e.g. creative jewellery/unique features of the jewellery. √
- Can make impact √ when placed strategically in/outside the venue. √ - Any other relevant answer related to the positive evaluation of posters.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- May overpower/draw attention away from the presentation √ if it is too big/not placed correctly. √
- May not always be useful in a small venue/audience√ as it can create a 'crowded' atmosphere. √
- Only focuses on visual aspects √ as it cannot always be combined with sound/audio. √
Any other relevant answer related to the negative evaluation of posters.
Submax. (8)
Max. (16)
8.4 Ways to respond to feedback in a professional manner
- Ann must stand throughout the feedback session. √√
- Be polite, confident and courteous/humorous. √√
- Listen and then respond. √√
- Make sure that you understand the question/s before responding. √√
- Acknowledge good questions. √√
- Rephrase questions if uncertain. √√
- Do not get involved in a debate. √√
- Do not avoid the question, if you do not know the answer, refer the question to the audience or the employees √√ /Rectify if incorrect answers are given. √√
- Address the whole audience and not only the person asking the question. √√
- Provide feedback as soon as possible after the observed event. √√
- Be direct, honest, sincere. √√
- She must use simple language and support what you say with an example/ keep the answer short and to the point. √√
- Presenter must encourage questions from the audience. √√
- Do not allow any one member of the audience to dominate the discussion.√√
- Note/write down the questions asked to be able to respond correctly. √√
- Ann should address questions in an orderly manner. √√
Any other relevant answer related to how Ann may respond to feedback in a professional manner.
Max. (12)
8.5 Recommendations for improvement
- Ann should revise objectives that were not achieved. √√
- Use humour appropriately. √√
- She should always be prepared to update/keep her information relevant. √√
- Reflect on any problem/criticism and avoid it in future presentations. √√
- Any information that Ann receives as feedback from a presentation should be analysed and where relevant, incorporated/used to update/amend her presentation. √√
- Reflect on the time/length of the presentation to add/remove content. √√
- Increase/Decrease the use of visual aids or replace/remove aids that did not work well. √√
- Reflect on the logical flow of the format/slides/application of visual aids. √√
Any other recommendation related to how Ann can improve on her next presentation.
Max. (10)
8.6 Conclusion
- A well-prepared presentation creates a good impression and will attract potential investors.√√
- A good presentation promotes the image of the business/owner/ management.√√
- Being professional during a verbal presentation and feedback/questions session should contribute to the success of the presentation.√√
Any other relevant conclusion related to presentations, visual aids, responding to feedback and improving presentations.
Max. (2)
[40]
BREAKDOWN OF MARK ALLOCATION
Details | Maximum | Total |
Introduction | 2 | Max. 32 |
Aspects of designing a multimedia | 8 | |
Use of visual aids | 16 | |
Ways to respond to feedback in a professional manner | 12 | |
Recommendations for improvement | 10 | |
Conclusion | 2 | |
INSIGHT | ||
Layout | 2 | |
Analysis, interpretation | 2 | |
Synthesis | 2 | |
Originality/Examples | 2 | |
TOTAL MARKS | 40 |
*LASO – For each component:
- Allocate 2 marks if all requirements are met.
- Allocate 1 mark if only some of the requirements are met.
- Allocate 0 marks where requirements are not met at all.
QUESTION 9: BUSINESS ROLES
9.1 Introduction
- Businesses and their communities are interdependent and the one cannot do without the other. √
- The interdependence can be improved if businesses and communities recognise their social responsibility. √
- A responsible business should contribute towards the upliftment of the community. √
- CSR improves the lifestyle and quality of life of their human resources and caring for the environment by ensuring that they have the most efficient and sustainable resources. √
- Businesses are corporate citizens and therefore have a responsibility towards society. √
- CSI is a component of CSR, where social responsibility is the intension and social investment is the action. √
- Through their CSR programmes businesses can focus on the triple bottom line, which is making profits, uplifting/supporting the people and their communities, and caring for the environment/planet. √
Any other relevant introduction related to social responsibility, CSR, CSI and triple bottom line.
Max. (2)
9.2 CSR and CSI
Corporate social responsibility/CSR
- The way a business conducts itself ethically and morally, √ regarding the use of human resources, physical resources and their funds. √
- An business’s obligation √ to protect/promote the welfare of all shareholders, who have an interest on or that will be affected by a business. √
- An obligation by a business to pursue √ sound long term goals for society. √
- Refers to any strategy used by a business to take responsibility √ for their impact on society and the environment. √
- It is not a single action but rather an approach √ to doing business that guides all decision making in the firm. √
- It is the way in which companies manage their business operations √ so that it does not negatively affect all stakeholders. √
Any other relevant answer related to Corporate Social Responsibility. Submax. (4)
Corporate social investment/CSI
- Refers to the contribution that the company makes √ to uplift, develop and solve problems in the community. √
- Refer to any project undertaken by an organisation √ which is over and above the normal business activities of the company and not directly aimed at increasing profitability. √
- Programmes √ that will benefit the community and/or the environment, into which time, skills, expertise and money are invested. √
Any other relevant answer related to Corporate Social Investment. Submax. (4)
Max. (8)
9.3 Relationship between social responsibility and triple bottom line Profit/Economic √√
- Triple Bottom line means that businesses should not only focus on profit/ charge high prices, √ but should also invest in CSI projects. √
- Businesses should not make a profit √ at the expense of its community. √
Any other relevant answer related to the link between profit and social responsibility.
Heading (2)
Explanation (2)
Submax. (4)
People/Social √√
- Business operations should not have a negative impact on/exploit √ people/ employees/customers. √
- Businesses should engage/invest in sustainable community programmes/ projects √ that will benefit/uplift communities. √
- Improve the life style/quality of life √ of their human resources/employees. √
Any other relevant answer related to the link between people and social responsibility.
Heading (2)
Explanation (2)
Submax. (4)
Planet/Environment √√
- Businesses should not exhaust resources/harm the environment √ for production purposes. √
- They may support energy-efficient/eco-friendly √ products/programmes. √
- Recycle/Re-use waste, √ e.g. packaging from recycled material. √
Any other relevant answer related to the link between the planet/environment and social responsibility.
Any other relevant answer related to the key aspect between the relationship, between social responsibility and the triple bottom line.
Heading (2)
Explanation (2)
Sub-max. (4)
Max. (12)
NOTE: The link should be clear in each of the three 'P's (people, planet and profit).
9.4 Impact of CSR on businesses
Positives/Advantages
- Can serve as a marketing strategy √ and promote the image of the business.√
- A company may have a competitive advantage, √ as it leads to good publicity and an improved reputation. √
- May attract √ experienced employees √ /increase the pool of skilled labour √ that would increase productivity. √
- It helps to attract and retain√ staff √ /Lower √ staff turnover √ as employees’ health and safety √ are considered √ /Improves √ the health of its employees.√
- The business enjoys the goodwill √ and support of communities. √
- CSR helps to attract √ investors. √
- If the CSR is aligned with company policies/vision/mission statement, √ it shows accountability towards all stakeholders. √
- Businesses that support CSR through various programmes, √ encourages and rewards employees √ if they get involved in CSI programmes.
- CSI programmes have better success rate if it is fully supported √ by top management. √
- Sustained environmental consideration programmes may lead to reducing costs, √ which can make funds available for other business operations. √
- If the corporate sector gets involved voluntarily in CSR, √ it is less likely that Government will enforce the issue through legislation.√
- Businesses may enjoy √ tax rebates from SARS. √
Any other relevant answer related to positive impact of CSR on businesses.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- The community may not support √ the enterprise √/ i.e. may not buy √ the products of the enterprise. √
- Difficulty √ in adherence to legislation √ governing CSR.
- Small and medium enterprises find it difficult √ to implement CSI programmes. √
- CSI activities can distract √ businesses from their core business functions. √
- Social involvement is paid from a company’s profit √ that could have been used to lower prices to the benefit of customers. √
- Detailed reports must be drawn up, √ which can be time consuming. √
- Social spending reduces √ a company’s economic efficiency and makes it less competitive. √
- It can increase financial risk, √ as programmes cost money and may impact negatively on profits. √
- Company directors are accountable to shareholders, √ not to the communities. √
- It is difficult to accurately measure √ the effectiveness of social investment. √
- It is difficult to determine √ the exact needs of the community. √
- Most managers are not trained and lack experience √ to handle social programmes. √
- Some shareholders/stakeholders might withdraw their support from the company √ as they feel that social issues should be the government’s responsibility. √
- Providing goods and services that meet the needs of the consumers is, √ according to some stakeholders, already socially responsible. √
- Some CSI programmes will be regarded as a public relations stunt, as these programmes improve the business’s image √ without having a sustainable/long term effect. √
- Shareholders, as the only real stakeholders, may suffer √ as their profits are spent on CSR. √
- Employees may spend more time working √ on CSI programmes instead of focusing on their core duties. √
Any other relevant answer related to negative impact of CSR on businesses.
Max. (16)
9.5 Ways in which CSR projects can contribute to the community
- Charitable contribution towards NGOs/Businesses can donate blankets to old age homes/orphanages/running soup kitchens. √√
- Involvement in community education/Build schools in communities/Offer bursaries to needy students/Donate old computers to less privileged schools/Provide/Support adult education and training in the local community. √√
- Teach entrepreneurial skills/Offer support to individuals starting new business ventures. √√
- Conduct skills development/job creation projects/Offering bricklaying courses. √√
- Sponsor art and cultural programmes, such as school choirs. √√
- Support youth programmes, such as sport/recreational activities. √√
Any other relevant answer related to the contribution of corporate social investment (CSI) projects to the community.
NOTE:
- Mark the first FIVE (5) only.
- Award a maximum of TWO (2) marks if the example demonstrates the same practical way and contribution of CSI projects to the community.
- Award only ONE (1) mark for short/one word responses.
Max. (10)
9.6 Conclusion
- Despite challenges, most businesses do take their social responsibility very seriously and contribute positively to communities/society. √√
- Successful CSI programmes will improve the general standard of living of the community. √√
- CSI programmes will contribute positively if they are strategically planned and not just be given hand-outs/contributions randomly. √√
- CSR is an obligation required by law and benefits both business and society. √√
- CSR programmes and CSI projects allow businesses to influence people’s lives in many ways. √√
- Businesses use CSR programmes and CSI projects to comply with the laws and ethics. √√
- Triple bottom line allows businesses to consider the impact of their operations on people, profit and the planet. √√
Any other relevant conclusion related to social responsibility, CSR, CSI and triple bottom line.
Max. (2)
[40]
BREAKDOWN OF MARK ALLOCATION
DETAILS | MAXIMUM | TOTAL |
Introduction | 2 | Max. 32 |
CSR and CSI | 8 | |
Relationship between social responsibility and triple bottom line | 12 | |
Impact of CSR on businesses | 16 | |
Ways in which CSR project contribute | 10 | |
Conclusion | 2 | |
INSIGHT | ||
Layout | 2 | |
Analysis, interpretation | 2 | |
Synthesis | 2 | |
Originality/Examples | 2 | |
TOTAL MARKS | 40 |
*LASO – For each component:
- Allocate 2 marks if all requirements are met.
- Allocate 1 mark if only some of the requirements are met.
- Allocate 0 marks where requirements are not met at all.
QUESTION 10: BUSINESS OPERATIONS
10.1 Introduction
- The human resources manager (HRM) is responsible for selecting and appointing competent and skilled employees. √
- It is important that the HRM follows correct/fair procedures in selecting and interviewing. √
- The HRM can appoint the best candidate if the selection and interviewing procedures are properly applied. √
- The shortlisted applicants should be interviewed in order to evaluate their suitability for the job. √
Any other relevant introduction related to the recruitment, selection, job description and specification and interviewing.
Max. (2)
10.2 Differences between job description and job specification
JOB DESCRIPTION | JOB SPECIFICATION |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Submax. (4) | Submax. (4) |
Max. (8)
NOTE:
- Answer does not have to be in tabular format.
- The differences must be clear.
- Award a maximum of FOUR (4) marks if the differences are not clear./Mark either job description or job specification only.
10.3 Internal recruitment
Positives/Advantages
- The business recruits from existing employees √ through promotions/transfer from inside the business. √
- Opportunities for promotion reward good work √ and motivate current employees. √
- Staff morale and productivity increases √ if suitable staff members are promoted regularly. √
- Current employees understand √ how the business operates. √
- The business knows the candidate, √ his/her personality, strengths and weaknesses. √
- Reliable/Key staff members are retained √ if they are promoted/ transferred within the business. √
- Detailed, reliable information on candidates √ can be obtained from super visors/employee records. √
- Recruitment process is faster and less expensive √ if the candidates are known. √
Any other relevant answer related to positive impact of internal recruitment on businesses.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- Current employees may not bring √ new ideas into the business. √
- Promoting a current employee may cause resentment amongst √ other employees. √
- The number of applicants is limited √ to current staff only. √
- Employees who do not really have the required skills for the new job √ may be promoted. √
- Current employees may need to be trained/developed before they can be promoted, √ which can be expensive. √
- Staff that is not promoted may feel demotivated √ which may hamper productivity. √
Any other relevant answer related to negative impact of internal recruitment on businesses.
Max. (12)
10.4 Selection procedure
- Determine fair assessment criteria √ on which selection will be based. √
- Use the assessment criteria to assess all CVs/application forms √ received during recruitment√/Preliminary screening√ is done by sorting the applications received according to the criteria for the job. √
- Check that applicants are not submitting false documents √ such as forged certificates/degrees. √
- Make a list of all applicants √ who qualify for the post. √
- Screen and check reference, √ e.g. check applicants’ criminal records/ credit history/social media, √ etc.
- Conduct preliminary interviews √ to sift out applicants who qualify for the job. √
- Inform all applicants√ about the outcome of the application. √
- Compile a shortlist√ of approximately five people. √
- Invite the shortlisted applicants/candidates √ for an interview. √
- Shortlisted candidates may be subjected to various types of selection tests, √ e.g. skills test. √
- A written offer is made √ to the chosen candidate. √
Any other relevant answer related to the selection procedure.
NOTE: Procedure can be in any order.
Max. (14)
10.5 Purpose of the interview and role as interviewer
Purpose of the interview
- To determine a candidate's suitability for the job. √√
- Match the information given by the applicant with the requirements of the job. √√
- To get more information from the applicant. √√
- Evaluate the skills and personal characteristics of the applicant. √√
- Provides the applicant with the opportunity to find out more about the job and the company/ask questions about the job/salary/working conditions. √√
Any other relevant explanation of the purpose of an interview.
Submax. (6)
Role of the interviewer
- Peter must develop a core set of questions based on the required skills, knowledge and ability required. √√
- Check the application and verify the CV for anything that may need to be explained. √√
- Book and prepare the venue for the interview. √√
- Set the interview date and ensure that all interviews take place on the same date, if possible. √√
- Inform all shortlisted candidates about the date/place of the interview. √√
- Notify all panel members conducting the interview about the date/place of the interview. √√
- Allocate the same amount of time to each candidate. √√
- Introduce members of the interviewing panel to each candidate/interviewee. √√
- He should make the interviewee feel at ease. √√
- Explain the purpose of the interview to the panel and the interviewee. √√
- Do not misinform/mislead the interviewee. √√
- Avoid discriminatory/controversial types of questions, e.g. asking a female candidate about family planning/having children. √√
- Provide an opportunity for the interviewee to ask questions. √√
- Peter must close the interview by thanking the interviewee for attending the interview. √√
Any other relevant answer related to the role of the interviewer.
Submax. (6)
Max. (12)
10.6 Conclusion
- The goals and objectives of the businesses cannot be achieved without qualified and skilled employees. √√
- Employees are the most important resource in any business and its success is strongly influenced by recruiting and appointing quality employees. √√
- A well prepared and organised interview process will results in identifying and appointing the most suitable and deserving candidate. √√
Any other relevant conclusion related to the recruitment, selection, job description and specification and interviewing.
Max. (2)
[40]
BREAKDOWN OF MARK ALLOCATION
Details | Maximum | Total |
Introduction | 2 | Max. 32 |
Job description and job specification | 8 | |
Internal recruitment | 12 | |
Selection procedure | 14 | |
Purpose of interview and role of the interviewer | 12 | |
Conclusion | 2 | |
INSIGHT | ||
Layout | 2 | |
Analysis, interpretation | 2 | |
Synthesis | 2 | |
Originality/Examples | 2 | |
TOTAL MARKS | 40 |
*LASO – For each component:
- Allocate 2 marks if all requirements are met.
- Allocate 1 mark if only some of the requirements are met.
- Allocate 0 marks where requirements are not met at all.
TOTAL SECTION C: 80
GRAND TOTAL: 300
GEOGRAPHY GRADE 12 PAPER 1 ANNEXURE - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
GEOGRAPHY
GRADE 12
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
ANNEXURE
FIGURE 1.1: FEATURES ASSOCIATED WITH A COASTAL LOW
[Source: Adapted from www.1stweather.com]
FIGURE 1.2: DRAINAGE BASIN FEATURES 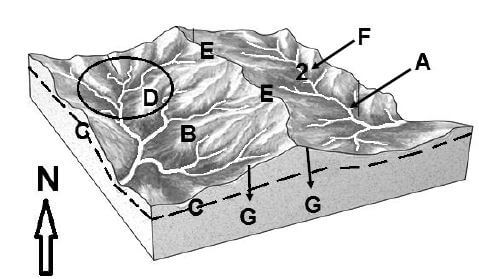
[Source: Adapted from http://www.google.co.za]
FIGURE 1.3: A TROPICAL CYCLONE IN ITS MATURE STAGE 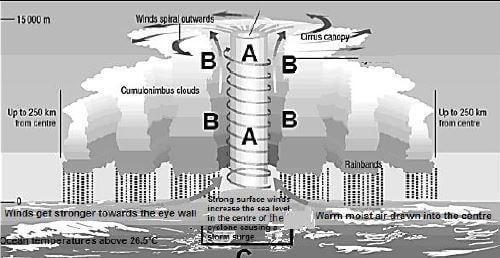
[Source: Adapted from http://www.google.co.za/images]
FIGURE 1.4: VALLEY IN THE NORTHERN HEMISPHERE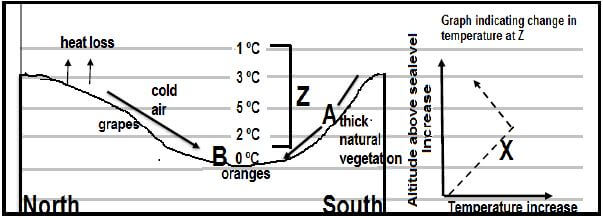
[Source: Adapted from Windows of the world]
FIGURE 1.5: DRAINAGE PATTERNS 
[Source: http://www.google.co.za/images]
FIGURE 1.6: RIVER IN A HIGHLYING AREA 
[Source: http://www.google.co.za/images]
FIGURE 2.1: AIR PRESSURE SYSTEMS IN SOUTH AFRICA 
[Source: http://www.google.co.za/images]
FIGURE 2.2: FLOW PATTERNS OF RIVERS 
[Source: http://www.google.co.za/images]
FIGURE 2.3: SYNOPTIC WEATHER MAP AND WEATHER FORECAST FOR CAPE TOWN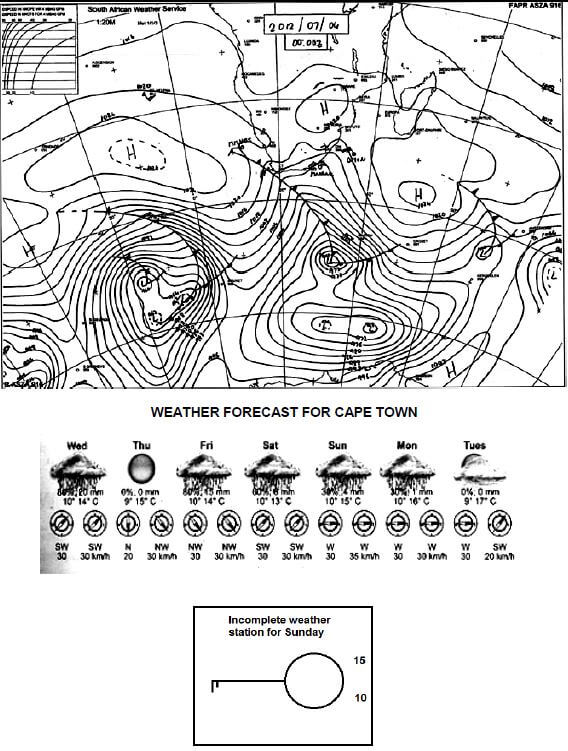
[Source: Adapted from Study Master Geography]
FIGURE 2.4: CLIMATIC CONTRASTS BETWEEN URBAN AND RURAL AREAS
| Climatic element | Differences between urban and rural areas |
| Insolation | 13-17% less than the surrounding rural areas |
| Air temperature | |
| (a) Annual mean | 0,5 – 1,0 °C higher than in the surrounding rural areas |
| (b) Winter minimum | 1,0 – 2,0 °C higher than in the surrounding rural areas |
| Relative humidity | 2–3% less than in surrounding rural areas |
| Precipitation | |
| (a) Annual mean | 5–10% more than in surrounding rural areas |
| (b) Thunderstorms | More than over surrounding rural areas |
| Cloudiness | 5–10% more than in surrounding rural areas |
[Source: New Windows on the World]
FIGURE 2.5: A MEANDERING RIVER 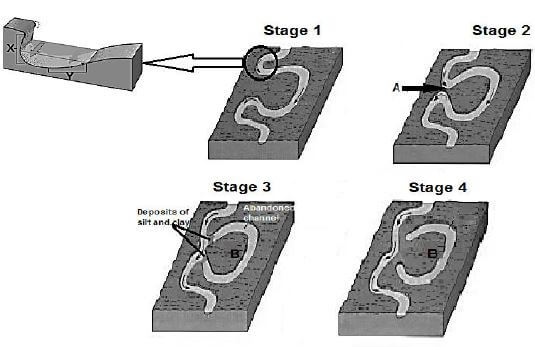
[Source: Physical Geology – Earth Revealed/google images]
FIGURE 2.6: RIVER CAPTURE 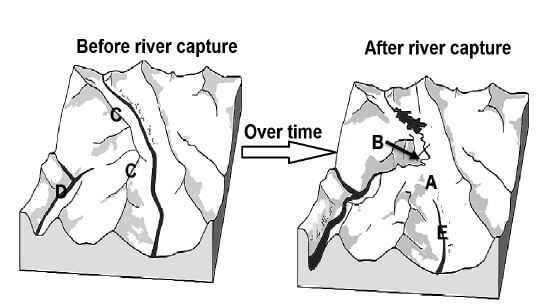
[Source: Adapted from www.orangesenqurak/org/river aspx]
FIGURE 3.1: BUSINESS DISTRICTS 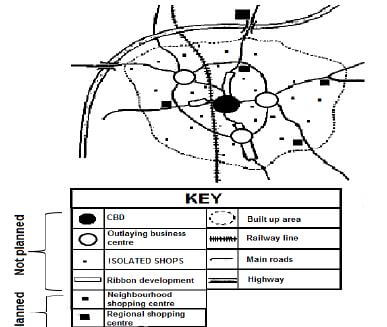
[Source: Adapted from X-kit Grade 12]
FIGURE 3.3: SETTLEMENT PATTERN 
[Source: http://www.google.co.za/images]
FIGURE 3.4: TRAFFIC CONGESTION 
[Source: http://www.google.co.za/images]
FIGURE 3.5: KEY SECTORS OF SOUTH AFRICA’S ECONOMY 
[Source: Statssa.co.za]
FIGURE 3.6: SOUTH WESTERN CAPE INDUSTRIAL REGION 
[Source: Focus on Geography/Grade 12 – Earl, et al]
FIGURE 4.2: TYPES OF SECTORS OF EMPLOYMENT IN SOUTH AFRICA A B 
[Source: http://www.google.co.za/images]
FIGURE 4.3: LAND RESTITUTION
The Macleantown case study on land restitution The benefits of land restitution appear to be more symbolic than material. [Source: Mzingaye Brilliant Xaba and Monty J. Roodt / 9 December 2016 00:05] |
FIGURE 4.4: LAND USE ZONE IN AN URBAN AREA 
[Source: http://www.google.co.za/images/urban landuse]
FIGURE 4.5: MANUFACTURING IN SOUTH AFRICA
Manufacturing in South Africa South Africa has developed an established, diversified manufacturing base that has shown its resilience (staying power) and potential to compete in the global economy.The manufacturing sector provides a locus for stimulating the growth of other activities, such as services, and achieving specific outcomes, such as employment creation and economic empowerment. This platform of manufacturing presents an opportunity to significantly accelerate the country’s growth and development [Source: www.brandsouthafrica.com] |
FIGURE 4.6: THE MAPUTO DEVELOPMENT CORRIDOR
The Maputo Development Corridor is one of the most ambitious and exciting initiatives undertaken within the Southern African region, stretching from Gauteng in South Africa, to Maputo in Mozambique. The corridor includes the Mpumalanga province with its rich minerals and aesthetic beauty.
[Source: Extract adapted from News 24] |
GEOGRAPHY GRADE 12 PAPER 2 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
GEOGRAPHY
GRADE 12
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1.1 C ✔
1.2 C ✔
1.3 B✔
1.4 D✔
1.5 C✔
1.6 B✔
1.7 B ✔
1.8 A ✔
1.9 B ✔
1.10 D ✔
1.11 B✔
1.12 B✔
1.13 A✔
1.14 C✔
1.15 C ✔ (15 x 1) (15)
[15]
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: MAPWORK CALCULATIONS AND TECHNIQUES
2.1 FIGURE 2.1 represents an incomplete cross section between points 4 and 5 on the orthophoto map.
2.1.1 Complete the cross section.
2.1.2 Label the position of spot height 203. 
Marks allocated to:
- Outline of slope finished. ✔
- Spot height 203 (203 m) within the dotted lines. ✔
(2 x 1) (2)
2.1.3 Why is there no intervisibility between points 4 and 5 on the cross section?
- There is an obstruction between 4 and 5. ✔
- There is higher land (spot height 203) which blocks 4 from 5 from being seen. ✔
[Any ONE] (1 x 1) (1)
2.1.4 Calculate the vertical exaggeration of the cross section. Show ALL calculations. Marks will be awarded for calculations.
Formula: VE = Vertical scale (VS)
Horizontal scale (HS)
- VS = 5 mm = 5 (x 1 000) [1 : 1 000]
VS = 1: 1 000 ✔
HS = 1 ∶10 000 ✔
VE = 1 ÷ 1
1 000 10 000
= (1/1×10/1) ✔ OR (1 /1 000 × 10 000 / 1) ✔
= 10 /1
= 10 times ✔
(Learner must indicate unit.)
(4 x 1) (4)
2.1.5 Provide ONE reason why the vertical scale in a cross section is exaggerated (made bigger).
- It allows for the relief features to be seen more clearly. ✔
- If the vertical scale is not exaggerated, the relief feature will be flat. ✔
[Any ONE] (1 x 1) (1)
2.2
2.2.1 Calculate the average gradient between the trigonometric station (block G5) to trigonometric station (block H2) on the topographic map. Show ALL calculations. Marks will be awarded for calculations.
Formula: Gradient = Vertical interval (VI)
Horizontal equivalent (HE)
- VI = 726,5 m – 200,3 m VI = 726,5 m – 200,3 m
= 526,2 m ✔ = 526,2 m ✔
HE = 7,5 cm x 500 OR HE = 7,5 cm x 50 000
[Range 7,4 – 7,6] 500
= 3 750 m ✔ = 3 750 m ✔
[Range 3 700 – 3 800]
G = (526,2 /3 750 )✔ G = (526,2 /3 750 )✔
[Mark allocated for substitution]
= 1/ 7,1 = 1 / 7,1
= 1 : 7,1 / 1 in 7,1✔ = 1 : 7,1 / 1 in 7,1 ✔
[Range 1 : 7,0 – 1 : 7,3]
(4 x 1) (4)
2.2.2 With reference to the answer in QUESTION 2.2.1, is the gradient a true reflection of the actual landscape?
Give a reason for your answer.
No. ✔
Reason:
- We are calculating the average gradient and not the actual gradient. ✔
- From trigonometric station 94 to trigonometric station 138 there is a sharp change in gradient from mountainous area to a flat plain. ✔
[Any ONE] (2 x 1) (2)
2.3
2.3.1 Refer to the demarcated area in RED on the topographical map, which represents the orthophoto map. Use the demarcated area to calculate the surface area of the orthophoto map in km². Show ALL calculations. Marks will be awarded for calculations.
Formula: Area = length (L) x breadth (B)
- Length = 9,3 cm ✔ x 0,5 = 4,65 km (Range 4,6 – 4,7)
(9,2 cm – 9,4 cm)
[Accept other formulas to calculate length.]
Breadth = 7,4 cm ✔ x 0,5 = 3,7 km (Range 3,65 – 3,75)
(7,3 cm – 7,5 cm)
[Accept other formulas to calculate breadth.]
= 4,65 km ✔ x 3,7 km ✔
= 17,2 km² ✔
Range: 16,7 km² – 17,7 km²
[Accept other calculation methods.]
(5 x 1) (5)
2.3.2 Explain why the area covered by the orthophoto on the topographic map looks smaller than the orthophoto itself.
- The orthophoto map has a larger scale ✔
- Scale of orthophoto map is 5 times larger than the topographic map✔
- Scale of orthophoto map is 1 : 10 000 and the scale of the topographic map is 1 : 50 000 ✔
[Concept] (1 x 1) (1)
[20]
SECTION C
QUESTION 3: APPLICATION AND INTERPRETATION
3.1 Refer to the graph below, the information on page 3 and the topographical map to answer the questions that follow.
[Source: https://en.climate-data.org/location/23402]
3.1.1 Calculate the average monthly rainfall (mm) for Citrusdal.
- 315 ÷ 12 = 26,25 mm ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
3.1.2 State the type of climate that this type of rainfall is associated with.
- Mediterranean climate ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
3.1.3 Given the above rainfall data (graph) and Citrusdal’s location, suggest ONE reason why there are many non-perennial streams in the area.
- Long dry summer – below average rainfall ✔
- Location on the SW coast dominated by cold Benguela current ✔
- Area experiences seasonal rain ✔
[Any ONE] (1 x 1) (1)
3.2 Grade 12 learners on a field trip to Citrusdal, discovered that the temperature at 12:00 (midday) at the caravan park labelled A, is a few degrees lower than the temperature near the industrial area labelled G, on the topographic map. Give reasons for the difference in temperature between the caravan park and the industrial area.
Caravan park is colder because:
- It is situated on the outskirts/far from the build-up area ✔✔
- It is close to water/Oliphant’s River. ✔✔
- There is a lot of vegetation nearby therefore more transpiration and lower temperatures. ✔✔
- There is less pollution or less activities that cause pollution. ✔✔
Industrial area is warmer because:
- It is situated in a built-up area – generating own heat. ✔✔
- There is less vegetation nearby. ✔✔
- There is more pollution (dome) such as dust and soot that absorb and retain heat for longer. ✔✔
[Any TWO] (2 x 2) (4)
3.3 Provide TWO pieces of evidence to justify that the site of the Oliphant’s River valley, situated on the west of the topographic map, is ideal for agriculture.
- Flat land / gentle slope / contour lines far apart ✔✔
- Close to water source / irrigation possible ✔✔
- Fertile soil / arable land ✔✔
[Any TWO] (2 x 2) (4)
3.4 There are numerous dams in the agricultural region of the area covered by the topographic map. Of what importance are these dams to the farmers during the dry seasons?
- Irrigation of cultivated lands / orchards and vineyards ✔✔
- Availability of water to live-stock ✔✔
- Water for domestic use ✔✔
[Any ONE] (1 x 2) (2)
3.5 Refer to the Oliphant’s River in block I2 on the topographic map.
3.5.1 Identify the stream channel pattern.
- Braided stream ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
3.5.2 Provide evidence from the topographic map to support your answer to QUESTION 3.5.1.
- Gentle gradient slows river velocity resulting in deposition. ✔✔
- The orchards on the sandbanks indicate that the sandbanks are above the level of water. ✔✔
- Shallow river splits into smaller rivulets (streams) around sandbanks. ✔✔
[Any TWO] (2 x 2) (4)
3.6 Refer to the town of Citrusdal.
3.6.1 Is Citrusdal a recreation, mining or gap town?
- Gap town ✔(1 x 1) (1)
3.6.2 Give evidence from the topographic map to support your answer.
- Situated between mountain ranges. ✔✔
- Situated between the Cederberg and Oliphant mountains. ✔✔
[Any ONE] (1 x 2) (2)
3.6.3 Explain the economic advantage of Citrusdal’s’ location.
- Tourism - Western Cape Fold mountains / Natural hot springs found there. ✔✔
- Agriculture – Citrus farming and vineyards contribute to the economy. ✔✔
- Employment in primary, secondary and tertiary sectors ✔✔
- Close to Cape Town and market. ✔✔
- Provides services for people travelling through the area. ✔✔
[Any TWO] (2 x 2) (4)
[25]
QUESTION 4: GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS (GIS)
4.1 During the 2008 floods, accessibility to the Oliphant’s River Valley was limited to determine the extent of the damage. A GIS specialist used remote sensing to access flooded areas along the Oliphant’s River Valley.
4.1.1 Define the term remote sensing.
- Refers to the observation of the earth from a distance using satellites to gather information without having direct contact with an area. ✔
[Concept] (1 x 1) (1)
4.1.2 State TWO reasons as to why the GIS specialist chose remote sensing.
- Data can be collected from inaccessible areas. ✔
- Large areas can be captured as images. ✔
- Can be made available at short notice especially in times of floods (disaster management). ✔
- It can be used to track changes and development in an area over time. ✔
[Any TWO] (2 x 1) (2)
4.1.3 The GIS specialist also found that farming had a negative impact on the Oliphant’s River. He/she suggested that buffering should take place around the Oliphant’s River. Evaluate how this would prevent the mismanagement of the river.
- Limits pollution from pesticides wastes been deposited. ✔✔
- Leave areas around the river clear from farming expansion. ✔✔
- Prevents riverbank erosion. ✔✔
- Limits the negative effect on aquatic life of the river. ✔✔
[Any TWO] (2 x 2) (4)
4.2 Define the term spatial data.
- Refers to the location and shape of geographical features. ✔
[Concept] (1 x 1) (1)
4.3 Classify each of the following spatial objects in block E5, as a point, line or polygon (area).
- Non-perennial river / hiking trail: (line) ✔
- Spot height: (point) ✔
- Dam / cultivated lands: (polygon) ✔
(3 x 1) (3)
4.4 The diagram below illustrates the concept of data integration found in block A10 on the topographic map. Study the diagram and answer the questions below:
[Source: Examiner]
4.4.1 Define the term data integration.
- Combining different types of data for decision-making. ✔
- Linking information from a variety of sources. ✔
[Concept] (1 x 1) (1)
4.4.2 Mention ONE problem that was experienced with data integration as shown in the diagram / figure prior to the introduction of GIS.
- Maps have different scales ✔
- First map 1 : 30 000, second map 1 : 80 000, third map 1 : 60 000, fourth map 1 : 50 000 [learner only needs to compare scales of two maps] ✔
[Any ONE] (1 x 1) (1)
4.4.3 State TWO ways, in which data integration could have assisted the farmer in making his farm at Kleinplaas, block E8, economically viable.
- Availability of water ✔
- Fertility of soil ✔
- Relief of the land (slope) ✔
- Microclimate ✔
- Access to infrastructure ✔
- Access to transport ✔
[Any ONE] (2 x 1) (2)
[15]
TOTAL: 75
GEOGRAPHY GRADE 12 PAPER 1 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
GEOGRAPHY
GRADE 12
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A: CLIMATE, WEATHER AND GEOMORPHOLOGY
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 C (off shore) ✔
1.1.2 D (1012) ✔
1.1.3 B ✔
1.1.4 A (Winter) ✔
1.1.5 D (southwest) ✔
1.1.6 B (weaker) ✔
1.1.7 C (southeast) ✔ (7 x 1) (7)
1.2
1.2.1 Confluence ✔
1.2.2 Interfluve ✔
1.2.3 Water table ✔
1.2.4 River system ✔
1.2.5 Watershed ✔
1.2.6 Abstraction ✔
1.2.7 Stream orders ✔
1.2.8 Infiltration ✔ (8 x 1) (8)
1.3
1.3.1
- Warm moist air. ✔
- Ocean temperatures above 26,5 °C. ✔ (2 x 1) (2)
1.3.2
- A – Eye ✔
B – Eye wall ✔ (2 x 1) (2) - The air is descending at A, and rising/ascending at B. ✔✔ (1 x 2) (2)
- A – High pressure in the upper layers of the atmosphere is causing some of the air to descend. ✔
B – Convergence of air on the surface because of low pressure is forcing the air to rise. ✔ (2 x 1) (2)
1.3.3
- 1 mark for air pressure below 1 000 hPa
- 1 mark for name
- 1 mark for sign of the eye (3 x 1) (3)
1.3.4
- Fishing industry will suffer because the boats cannot go out to sea ✔✔
- Harbour will be destroyed and repairs will have to be done ✔✔
- Businesses and Industries will suffer severe losses ✔✔
- Property and Infrastructure will be damaged ✔✔
- Tourism industry will suffer loses ✔✔
- Flooding will have a negative ripple effect on farming ✔✔
- Destruction will lead to unemployment ✔✔
(Any TWO) (2 x 2) (4)
1.4
1.4.1 Temperature inversion ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
1.4.2
- During clear, windless nights, air on the high grounds at the sides of the valley, cools down ✔✔
This is due to terrestrial radiation ✔✔
Cold air drains down the slopes and accumulates at the valley bottom, ✔✔ forcing warmer air to rise ✔✔
The rising warm air forms a thermal belt midway up the valley ✔✔
This causes a temperature inversion layer, where temperature increases with height ✔✔ (Any TWO) (2 x 2) (4)
1.4.3Slope A is in the shadow zone and therefore experience less evaporation, with the moisture content of the soil higher encouraging faster and lusher growth of vegetation. ✔✔ (1 x 2) (2)
1.4.4 Reasons for the temperature at B
- Sunrays strike the area more slanted/obliquely, therefore less heating during the day ✔✔
- Larger area to be heated ✔✔
- Sunrays penetrates a denser atmospheric layer causing more heat to be absorbed or dispersed, before it reaches the slope, therefore less heating ✔✔
- Katabatic flow during the night causes cold air to accumulate on the valley floor
- Temperatures drop to below freezing point (0 °C) ✔✔
Influence on crops - Oranges are frost resistant, therefore they are grown on the valley floor where cold air accumulates ✔✔
(Any FOUR – BOTH REASONS FOR TEMPERATURE AND INFLUENCE ON CROPS MUST BE MENTIONED.) (4 x 2) (8)
1.5
1.5.1 The manner in which the streams are arranged in a particular drainage basin. ✔ (Concept) (1 x 1) (1)
1.5.2
- – Rectangular ✔
- – Trellis ✔ (2 x 1) (2)
1.5.3
- – The mainstream and its tributaries have right angled bends ✔✔
- – The mainstream flows in a valley area and the tributaries join the mainstream at right angles from a high lying area. ✔✔ (2 x 2) (4)
1.5.4
- Developed due to underlying horizontally layered igneous rocks which has cracked or jointed. ✔✔
- The cracks and joints are exposed to erosion, and the water from stream/river will flow/incise along the cracks and joints. ✔✔ (2 x 2) (4)
1.5.5
- – Hard resistant rocks are causing less channels to be eroded and fewer streams in the basin will result in low density. ✔✔
- – Softer less resistant rocks can easily be eroded as a result more channels are created for stream flow and higher drainage density is the result. ✔✔ (2 x 2) (4)
1.6
1.6.1 Upper course ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
1.6.2 Narrow ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
1.6.3
- Turbulent ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
- Resistant layer or outcrop is dipping upstream. ✔✔
The bedrock upstream and downstream is less resistant and is easily eroded, exposing the outcrop. ✔✔
The slope created on the more resistant bedrock is causing the stream water to flow faster. ✔✔
(Any TWO) (2 x 2) (4)
1.6.4
- In the upper course of the river, there will be downward erosion and deep, V-shaped valleys occurs. ✔✔
- Temporary base levels of erosion like rapids and waterfalls will be eroded away through headward erosion. ✔✔
- In the middle course lateral erosion dominates. ✔✔
- This will widen the river valley and will remove the remaining spurs and other high lying areas. ✔✔
- The lower course is dominated by deposition. ✔✔
- The area is relatively flat in the lower course and this gentle gradient is maintained through deposition. ✔✔
(Any FOUR) (4 x 2) (8)
[75]
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1 B to A ✔
2.1.2 B ✔
2.1.3 A ✔
2.1.4 A ✔
2.1.5 B ✔
2.1.6 A ✔
2.1.7 B ✔
2.1.8 A ✔ (8 x 1) (8)
2.2
2.2.1 Laminar ✔
2.2.2 Turbulent ✔
2.2.3 Turbulent ✔
2.2.4 Laminar ✔
2.2.5 Turbulent ✔
2.2.6 Turbulent ✔
2.2.7 Laminar ✔ (7 x 1) (7)
2.3
2.3.1 Winter ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
2.3.2 Mid-latitudes are low pressure systems ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
2.3.3
- From Friday to Monday heavy rain and cold conditions are forecasted. ✔✔
- As one mid latitude cyclone moves away from Cape Town another approaches ✔✔
- This results in continuous frontal conditions. ✔✔
(Any TWO) (2 x 2) (4)
2.3.4  (Any ONE)
(Any ONE)
(2 x 1) (2)
2.3.5
- Backing ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
- The wind changes in an anti-clockwise direction in a system where the air movement is clockwise. ✔✔ (1 x 2) (2)
- During Monday the warm sector is dominated by North westerly winds driven by the westerly wind belt ✔✔
As the cold front moves over the area is dominated by the cold sector, with south westerly winds which is driven by the Polar easterlies ✔✔ (2 x 2) (4)
2.4
2.4.1 Direct short wave sunrays ✔ /Incoming solar radiation ✔ (CONCEPT) (1 x 1) (1)
2.4.2 Urban areas receive 13–17% less insolation. ✔✔ (1 x 2) (2)
2.4.3
- Insolation is less in urban areas because of more smoke, dust and pollution particles reflecting sunrays away from the surface. ✔✔
- The dust particles also limits terrestrial radiation ✔✔
- Artificial surfaces, artificial production of heat units, high buildings etc. either absorbs or creates more heat over the urban areas. ✔✔
(Any TWO) (2 x 2) (4)
2.4.4 Higher precipitation
- Urban areas have more condensation nuclei (dust and pollution particles) around which condensation occur. ✔✔
- Greater thermal convection due to heat island effect is causing higher rainfall. ✔✔
- When the wind hits the tall buildings it rises, cools off and condense to form clouds and eventually rainfall. ✔✔
Lower relative humidity
- Less vegetation over urban areas decreases the transpiration rate ✔✔
- Storm water drainage systems carries runoff away, therefore evaporation decreases ✔✔
(Any FOUR – MUST MAKE MENTION OF BOTH.) (4 x 2) (8)
2.5
2.5.1 Meander neck ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
2.5.2
- X – Erosion ✔
Y – Deposition ✔ (2 x 1) (2) -
- The river flows faster at the outer bank and is undercutting the area ✔✔
- Repetition of undercutting will eventually cause the top part of the bank to tumble ✔✔
- The bank will start to retreat ✔✔
(Any TWO) (2 x 2) (4)
2.5.3
- The river bend in STAGE 2 is very pronounced reducing the speed of the river, hence causing water to build-up because of the delay and will eventually overflow. ✔✔
- A straighter channel in STAGE 4 will increase the speed of the river, therefore no accumulation of water takes place. ✔✔ (2 x 2) (4)
2.5.4
- During heavy rainfall periods or flooding the river will cut through the neck of the meander. ✔✔
- Deposition next to the bank will eventually block off the meander completely. ✔✔ (2 x 2) (4)
2.6
2.6.1
- – Wind gap ✔
- – Elbow of capture ✔ (2 x 1) (2)
2.6.2
- Watershed ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
- Due to headward erosion the watershed will be removed or lowered ✔✔
River at D will eventually cut through the watershed due to headward erosion ✔✔
(Any ONE) (1 x 2) (2)
2.6.3 Transport routes can be constructed through the gap in the mountain, which was the result of river capture. This will shorten the distance to either side of the mountain. ✔✔ (1 x 2) (2)
2.6.4
- The environment will be negatively affected
- Biodiversity will be destroyed ✔✔
- Aquatic life will be reduced or will totally disappear ✔✔
- Ecosystems disturbed ✔✔
- Natural habitats will be destroyed ✔✔
- The river will eventually dry up if extensive periods of low rainfall occur ✔✔
- The water table will be lowered ✔✔
(Any FOUR) (4 x 2) (8)
[75]
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1 Ribbon development ✔
3.1.2 CBD ✔
3.1.3 Regional shopping centre ✔
3.1.4 Isolated shops ✔
3.1.5 CBD ✔
3.1.6 Outlying business centre ✔
3.1.7 Neighbourhood shopping centre ✔ (7 x 1) (7)
3.2
3.2.1 Gross Domestic Product ✔
3.2.2 Informal sector ✔
3.2.3 Beneficiation ✔
3.2.4 Footloose ✔
3.2.5 Import replacement ✔
3.2.6 Food security ✔
3.2.7 Decentralisation ✔
3.2.8 Foreign Exchange ✔ (8 x 1) (8)
3.3
3.3.1 It is unifunctional because primary economic activities dominate ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
3.3.2 Isolated / Dispersed ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
3.3.3
- Relief
Hilly and mountainous areas influenced the isolated pattern. ✔✔ - Water availability
When water is readily and easy available it encourages dispersed settlements. ✔✔ (2 x 2) (4)
3.3.4
- Its extensive because a large area is being used for farming ✔✔
AND ANY ONE OF COMMERCIAL- It is commercial because outbuildings for the storage of either equipment or products can be identified ✔✔
- It is commercial because the farm area is divided into camps to reduce soil erosion ✔✔
[LEARNERS MUST REFER TO BOTH ASPECTS TO OBTAIN MAXIMUM MARKS.] (2 x 2) (4)
3.3.5
- Farmer can use his machinery extensively ✔✔
- The farmer does not need to share any of his equipment ✔✔
- The farmer’s land is not fragmented ✔✔
- The farmer decides on his own how he want to manage the farm ✔✔
- Makes his own decisions ✔✔
(Any TWO) (2 x 2) (4)
3.4
3.4.1 It is a situation on the public roads that occurs because of more vehicles than the road can handle. ✔ (Concept) (1 x 1) (1)
3.4.2
- Separation between residence and workplace ✔
- Commuter population
- Overconcentration of activities in the CBD of cities ✔
- Outdated street plan and pattern ✔
- Rapid urbanisation ✔
- Rural-urban migration ✔
(Any TWO) (2 x 1) (2)
3.4.3 If people used public transport it would decrease traffic congestion ✔✔ The driver expects others to use public transport when he himself is not ✔✔ (1 x 2) (2)
3.4.4
- Road rage / Frustration / Anger
(ANY NEGATIVE EMOTION) (1 x 1) (1) - Health problems like heart attacks, respiratory problems etc. may occur. ✔✔
Because of frustration more accidents may happen ✔✔
Conflict between drivers may result in violence ✔✔
(Any ONE) (1 x 2) (2)
3.4.5
- Building of ring roads around the congested area ✔✔
- Synchronised robots ✔✔
- One way streets ✔✔
- Subsidise public transport so that more people are encouraged to use it ✔✔
- Designated lanes for busses and other public transport services to encourage faster travelling ✔✔
- Use of flexitime for businesses to encourage different start and closing times to regulate the in- and outflow of traffic in the CBD ✔✔
- Encourage lift clubs ✔✔
- Park and ride schemes ✔✔
(Any FOUR) (4 x 2) (8)
3.5
3.5.1
- 2014 ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
- Construction ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
3.5.2
- Decrease ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
- 1,8% ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
- Negative growth rate because both the primary and secondary sectors experienced a huge (14%) negative growth rate ✔✔ compared to the 1,1% positive growth rate of the tertiary sector ✔✔ (2 x 2) (4)
3.5.3
- There might have been more imports than exports ✔✔
- Exports decreased because of decrease in primary and secondary production ✔✔
(Any ONE) (1 x 2) (2)
3.5.4 Food prices will increase and will affect the poorest the most ✔✔ Increased unemployment because of job losses directly linked to agriculture ✔✔ (2 x 2) (4)
3.6
3.6.1 Rooibos tea✔ (1 x 1) (1)
3.6.2
- Koeberg nuclear power plant (1 x 1) (1)
- Cheaper electricity is available if the industry is stationed near Koeberg ✔✔
Decreases production costs of goods ✔✔
Koeberg’s nuclear energy provides alternative energy as coal generated energy is expensive ✔✔
(Any ONE) (1 x 2) (2)
3.6.3
- The cold Benguela current is causing upwelling, bringing nutrients to the water surface ✔✔
- Increases phytoplankton and zooplankton which attracts larger fish ✔✔
- Fishing flourishes because of this upwelling ✔✔
- Huge shoals pass along the Cape coast ✔✔
(Any TWO) (2 x 2) (4)
3.6.4
- There is a lack or shortage of minerals ✔✔
- The region is very far from the power stations of Mpumalanga, making electricity very expensive despite Koeberg being in the region ✔✔
- Initial slow development caused lack of job opportunities for the fast growing population ✔✔
- High transport costs and the large distance to the Gauteng market places disadvantages the SW Cape compared to the other industrial regions ✔✔
- The availability of fresh water can become a problem in the future ✔✔ The region has not attracted new industries because salaries are generally lower, and the buying power of the growing population is reduced ✔✔
- Large, flat industrial sites are limited close to Cape Town, and therefore land is expensive ✔✔
- Many of the sites set aside for industrial use have been taken over by informal settlements ✔✔
(Any FOUR) (4 x 2) (8)
[75]
QUESTION 4
4.1
4.1.1 F (Specialisation) ✔
4.1.2 K (Rural depopulation) ✔
4.1.3 J (Rural-urban migration) ✔
4.1.4 E (Mechanisation) ✔
4.1.5 G (Market orientated) ✔
4.1.6 H (Push factors) ✔
4.1.7 A (Fragmentation) ✔
4.1.8 C (Consolidation) ✔ (8 x 1) (8)
4.2
4.2.1 A ✔
4.2.2 B ✔
4.2.3 A ✔
4.2.4 A ✔
4.2.5 B ✔
4.2.6 B ✔
4.2.7 A ✔ (7 x 1) (7)
4.3
4.3.1 The process of compensating people for the land they lost due to forced removals ✔ (Concept) (1 x 1) (1)
4.3.2
- To redress the injustices of apartheid ✔
- For national reconciliation and stability ✔
- To promote economic growth ✔
- To alleviate poverty ✔
(Any TWO) (2 x 1) (2)
4.3.3
- Beneficiaries have been neglected by the government ✔
- The people lack support to start ploughing ✔
- The people do not have the finances ✔ (3 x 1) (3)
4.3.4
- People were given land simply to redress the injustices of past policies, but no support to generate income and make an adequate and meaningful living ✔✔ (1 x 2) (2)
4.3.5
- Provide financial assistance to make sure that farmers can buy the basic equipment ✔✔
- Have workshops and training services available to make sure that the skills in farming and business management is on par ✔✔
- Help the farmers understand how the labour policies should be implemented ✔✔
- The development of local community forums so that the community can discuss how land should be developed and maintained ✔✔
- Provision of proper infrastructure like roads, electricity, computer literacy etc. ✔✔
- Government/NGO support ✔✔
(Any FOUR) (4 x 2) (8)
4.4
4.4.1 Rural-urban fringe ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
4.4.2 Area in the photo has mixed functions of rural and urban ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
4.4.3
- Land is cheaper ✔
- There is more space for further expansion ✔
- Factory will be near to raw materials ✔
- Close to labour force ✔
- Close to transport networks ✔
(Any TWO) (2 x 1) (2)
4.4.4
- The market is nearby so transport costs of products will decrease ✔✔
- The farmer has the advantages of the urban services, without paying for it ✔✔
- Demand/competition for land increases the land value ✔✔
(Any TWO) (2 x 2) (4)
4.4.5
- Rural areas and life will be destroyed and could result in a decrease in food production ✔✔
- Biodiversity and aesthetic appeal will be destroyed ✔✔
- The balance of climatic conditions may be destroyed ✔✔
- Informal settlements may develop, which can increase the social and economic problems in the area ✔✔
- To prevent neighbouring towns from merging into one another ✔✔
- To preserve the special character of historic rural life ✔✔
(Any THREE) (3 x 2) (6)
4.5
4.5.1 When raw materials are being transformed into finished goods on a large scale/Add value to an article ✔ (Concept) (1 x 1) (1)
4.5.2 Secondary sector ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
4.5.3
- Employment creation ✔
- Economic empowerment ✔
(Any ONE) (1 x 1) (1)
4.5.4
- Upgrading of skills and knowledge in the production of manufactured goods ✔✔
- More beneficiation of raw materials improving the quality of manufactured goods ✔✔
- Foreign exchange can be earned ✔✔
- Creation of higher paid employment opportunities ✔✔
(Any TWO) (2 x 2) (4)
4.5.5 Labour supply
- South Africa consists of a very large unschooled labour force, with very few entrepreneurs ✔✔
- Production per worker in South Africa is very low ✔✔
- Strikes and stay away actions for higher wages and salaries hinders production ✔✔
International competition
- South Africa finds it very difficult to compete against countries like China, which produces low cost products ✔✔
- South Africa in some instances has had to implement trade restrictions in order to protect local markets, which hinders trade relationships ✔✔
(Any FOUR)
[LEARNER MUST MENTION AT LEAST ONE FACT FROM LABOUR SUPPLY OR INTERNATIONAL COMPETITION.] (4 x 2) (8)
4.6
4.6.1 It is an integrated network of infrastructure within a geographical area designated to stimulate economic development and growth ✔ (Concept) (1 x 1) (1)
4.6.2 Swaziland ✔ (1 x 1) (1)
4.6.3
- Maputo is the nearest export harbour to Johannesburg ✔
- To strengthen relationships between South Africa and Mozambique ✔
(Any ONE) (1 x 1) (1)
4.6.4 The upgrading of infrastructure made it easier to visit major tourist destinations along the corridor ✔✔ (1 x 2) (2)
4.6.5
- To rehabilitate the core infrastructure along the corridor ✔✔
- To maximise investment with the corridor area ✔✔
- To ensure development in previously disadvantaged communities ✔✔
- To promote sustainable job creation for people living in underdeveloped areas along the corridor ✔✔
[Any THREE] (3 x 2) (6)
4.6.6
- A large bulk of the coal mined in Mpumalanga is exported to the Maputo harbour ✔✔
- The corridor passes through vast primary and industrial production areas ✔✔
- Mpumalanga has many international tourist destinations through which the corridor passes ✔✔
- The largest national conservation area, the National Kruger Park can also be found along the corridor ✔✔
(Any TWO) (2 x 2) (4)
[75]
GRAND TOTAL: 225