Adele
ECONOMICS GRADE 12 PAPER 2 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
ECONOMICS
GRADE 12
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A(COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1.1.1 D ✓✓ social benefits exceed social costs.
1.1.2 B ✓✓ explicit
1.1.3 D ✓✓ normal
1.1.4 A ✓✓ suffering an economic loss.
1.1.5 C ✓✓ inbound
1.1.6 B ✓✓ unadjusted CPI
1.1.7 C ✓✓ low growth, high unemployment and high inflation.
1.1.8 C ✓✓ eradicate (8 × 2) (16)
1.2 MATCHING ITEMS
1.2.1 F ✓ occurs when average revenue is less than average variable costs
1.2.2 H ✓ transfer of ownership of assets from the private sector to the public sector
1.2.3 G ✓ set by governments to protect consumers against exploitation
1.2.4 A ✓ paid by society which is not included in the actual price of goods and services
1.2.5 B ✓ occurs when the marginal rate of taxation is higher, even when real income remains unchanged
1.2.6 C ✓ an American travelling through South Africa to Kenya
1.2.7 D ✓ it is about to keep the resources that are non-renewable intact
1.2.8 I ✓ Vredefort dome (8 × 1) (8)
1.3 GIVE A CONCEPT
1.3.1 Minimum wages ✓
1.3.2 Biodiversity ✓
1.3.3 Pollution / Air Pollution / Green house gases ✓
1.3.4 Collusion ✓
1.3.5 Administered prices ✓
1.3.6 Price taker ✓ (6 × 1) (6)
[30]
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer any TWO of the three questions from this section in your ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 2: MICRO ECONOMICS
2.1 2.1.1 Name any TWO characteristics of oligopolistic markets.
- Products can be homogenous or differentiated ✓
- Barriers make it difficult to enter the market ✓
- Producers have considerable control over prices ✓
- Oligopolies are interdependent ✓
- Buyers and sellers have incomplete information ✓
(Accept any other relevant response) (Any 2 × 1) (2)
2.1.2 Why is it only possible in the long run to vary all factors of production?
- In the long run firms shall have acquired profit to enable them to expand their plant ✓✓
- There will be enough time for new business to enter into the market ✓✓
- The mobility of factors of production improve in the long-run ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant answer) (Any 1 × 2) (2)
2.2
| SHORT RUN EQUILIBRIUM OF A PERFECT MARKET |
2.2.1 Which market structure is depicted in the graph above?
- Perfect market ✓ (1)
2.2.2 Identify profit maximisation point in the above graph.
- Point a ✓ (1)
2.2.3 Briefly describe the demand curve in the graph above.
- The demand curve is horizontal / perfectly elastic ✓✓ (2)
2.2.4 Briefly explain the output level of a perfect competitor.
- A perfectly competitive firm can sell any number of units of output at exactly the same price ✓✓
- The firm can sell more / less than100 units at price R6 ✓✓
(Accept any other correct answer) (Any 1 × 2) (2)
2.2.5 Calculate the profit/loss of the individual firm above. Show ALL calculations.
- Profit = TR – TC ✓
= (100 × 6) –(100 x 4) ✓
= 600 – 400
= 200 ✓✓OR
AR – AC × units
= 6 – 4 x 100 ✓✓
= 200 ✓✓ (4)
2.3 DATA RESPONSE
MARKET FAILURE Unemployment has been rising in South Africa for the past three decades, leading to an official unemployment rate of 27,7%. This implies a jobless total of 8,49 million, with more than 40% of the rural population unemployed and the development of a growing pool of workers who are excluded from the labour market. [Source: htp//www.opensadnu.uct.ac.za] |
2.3.1 What is the official unemployment rate in South Africa?
- 27,7% ✓ (1)
2.3.2 Identify a reason for market failure mentioned in the extract above.
- Lack of information ✓ (1)
2.3.3 Explain why more labourers are being excluded from the labour market.
- More companies are closed down due to economic decline ✓✓
- Mining sector is laying off workers ✓✓
- The farming sector is affected by drought as a result workers lose their jobs ✓✓
- Unfair competition in the textile industry✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Any 2 × 2) (4)
2.3.4 How can the market failure mentioned in the extract above be resolved?
- The DTI provides information and assistance to broaden the participation. ✓✓
- The government makes businesses supply certain information on the packaging of their products. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Any 2 × 2) (4)
2.4 Explain free competition and nature of the product as characteristics of perfect markets.
FREE COMPETITION:
- Buyers must be free to buy whatever they want from any firm and in any quantity ✓✓
- Sellers must be free to sell what, how much and where they wish ✓✓
- There should be no state interference and no price control ✓✓
- Buyers should not form groups to obtain lower prices ✓
- Sellers should not combine to enforce higher prices ✓✓ (max 2 × 2)(4)
NATURE OF THE PRODUCT:
- All products sold in a specific market are homogenous ✓✓
- They are exactly the same in quality and appearance ✓✓
- It makes no difference to a buyer where or from whom he / she buys the product ✓✓ (max 2 × 2)(4)
(Accept any other correct relevant answer) (2 × 4) (8)
(Allocate a maximum of 4 marks for the mere listing of facts / examples)
2.5 With the aid of a diagram explain why oligopolists are reluctant to participate in price competition.
KINKED DEMAND CURVE |
Maximum 4 marks for graph
- Suppose the oligopolist is selling at the original / present price of R10 and 10 units of output are sold. Total revenue is R20 × 10 = R200 ✓✓
- If the firm tries to increase profit by increasing the price by R2 to R22, quantity demanded would fall to 8 units and total revenue would decrease to R176 (R22 × 8) ✓✓
- If the firm tries to increase profit by reducing the price by R12 to R8 and increasing its total sales, total revenue would be R88 ✓✓
- The oligopolist is therefore faced with a difficult decision because in both instances it will not benefit ✓✓
- Increasing the price of goods or reducing the price to increase sales will not lead to greater revenue earned ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant answer)
(Allocate a maximum of 2 marks for the mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
3.1 3.1.1 Name TWO positive effects that tourism will have on our economy.
It will increase the following:
- economic growth / GDP ✓
- employment opportunities ✓
- investment ✓
- the standard of living of the poor ✓ (Any 2 × 1) (2)
3.1.2 How does air pollution effect the environment?
Air pollution contributes towards:
- global warming ✓✓
- depletion of the ozone layer ✓✓
- acid rain ✓✓
- greenhouse gases ✓✓ (Any 1 × 2) (2)
3.2 Study the information below and answer questions that follow.
CULTURAL TOURISM AT ITS BEST The world tourism organisation claims that cultural tourism accounts for 37% of global tourism and continues to grow at 15% per year. Destinations should leverage what makes their societies unique and invest in developing cultural tourism, because it allows travellers to enjoy local rituals and taking home photos of shared memories and unique experiences. By embracing cultures, South Africa can boost economic growth. [www.solimarinternational.com June 2015] |
3.2.1 What type of tourism is portrayed in the picture above?
- Cultural tourism ✓ (1)
3.2.2 At what rate is cultural tourism growing worldwide?
- 15% ✓ (1)
3.2.3 Briefly describe the term Indigenous Knowledge Systems. Indigenous knowledge systems refers to local knowledge or a traditional way of doing things that is unique to a given culture or
- society ✓✓ (2)
3.2.4 Explain ONE reason for growth in the tourism industry.
- Increased disposable income ✓✓
- Less working hours; so more time to travel ✓✓
- An awareness of leisure and recreation ✓✓
- Improved transport, communication and accommodation facilities ✓✓
- Increased advertising and promotion ✓✓
- Enjoying the benefits of holidays and travel ✓✓
- Easily obtainable foreign exchange ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant answer) (Any 2 × 1) (2)
3.2.5 How can South Africa use its world heritage sites more effectively to promote tourism?
World heritage sites can be promoted by:
- advertising through various types of media ✓✓
- advertising sites domestically and abroad ✓✓
- create excitement around these sites, by for example inviting well known artists ✓✓
- keeping the sites well cared for ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant answer) (Any 2 × 2) (4)
3.3 Study the information below and answer questions that follow.
ENEMY NUMBER ONE FOR OUR ECONOMY Rising prices for energy, food, commodities and other goods and services affect the entire economy. Inflation impacts the cost of living, cost of doing business, borrowing money and every other facet of the economy. When the economy is healthy, there is low unemployment and wage increases as business demand labour to meet the growing economy. [Adapted from: www.Cartoons] |
3.3.1 Who is the number one enemy for our economy depicted in the cartoon above?
- Inflation ✓ (1)
3.3.2 What happens to the economy according to the cartoon above?
- It decreases / slows down ✓ (1)
3.3.3 Briefly describe the term hyperinflation?
- An inflation rate above 50% / People lose confidence in the value of money and start bartering goods and services ✓✓ (2)
3.3.4 How can taxation be used to reduce inflation?
- Taxes are increased to reduce the buying power ✓✓ (2)
3.3.5 What is the relation between inflation and wage demands?
- as prices increases the real wage decreases ✓✓
- as a result workers demand higher wages ✓✓
- the higher the inflation the higher the demand for wages ✓✓
(Accept any other relevant answer) (Any 2 × 2) (4)
3.4 Discuss income and infrastructure as benefits of tourism to households.
Households:
- Income: members of households receive income by acquiring jobs in the tourism industry ✓✓
- Many households are indirectly involved in tourism as employees in the hotel industry, financial institutions, transport and trading industries, businesses that provide services to tourists. ✓✓ So tourism also contributes to the incomes of these households. ✓✓
- Entrepreneurs from households that operate as curio producers, musicians, interpreters and tour guides also earn income from tourism. (2 x 2) (4)
- Infrastructure: infrastructure built for tourists is available both for tourists and local people’s use. ✓✓
- Infrastructure is built to promote tourism, but is ultimately used by households. ✓✓
- for e.g., roads that are built to improve access to a region for a special event will continue to benefit the local population long after the event is over. ✓✓ (2 x 2) (4)
(Accept any other correct relevant answer)
(Allocate a maximum of 4 marks for the mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
3.5 What role does South Africa play in alleviating the negative effects of global warming?
South Africa alleviates the effects by:
- committing voluntary commitment to combat climate change.✓✓
- reducing greenhouse gases by 34% by 2020 ✓✓
- playing a leading role in international climate negotiations ✓✓
- greening its cities with actions like reducing energy load in buildings ✓✓
- creating a recycling economy ✓✓
- restoring wetlands and protecting previous water resources ✓✓
- supporting programmes also forms part of international climate initiative ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant answer)
(Allocate a maximum of 2 marks for the mere listing of facts / examples) (Any 4 × 2) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4 MICROECONOMICS AND CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
4.1 4.1.1 Name TWO examples of renewable resources.
- Timber ✓
- Agricultural products ✓
- Recycling water ✓
- Electricity generated by wind ✓ (Any 2 × 1) (2)
4.1.2 What is the purpose of inflation targeting?
- The purpose of inflation targeting is to create price stability ✓✓ (1 × 2) (2)
4.2 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
WATER CRISIS IN THE EASTERN CAPE Large parts of the Eastern Cape have been gripped by drought and water shortage so severe that rivers, dams and boreholes are bone-dry. [Source: http//www.heraldlive.co.za] |
4.2.1 Which serious problem is currently experienced in the Eastern Cape?
- Shortage of water ✓ (1)
4.2.2 Why is food security threatened in the country?
- Maize and lucerne crops have been destroyed ✓ (1)
4.2.3 How can the public sector use education to ensure environmental sustainability?
- Incorporating topics on the protection of the environment in the school curriculum ✓✓
- People should be made aware of environmental issues and the consequences of their actions ✓✓
- Education play an important role in improving people’s ability to manage the environment ✓✓ (Any 2 × 2) (4)
4.2.4 What can the government do to solve the water crisis in the country?
- The government should ensure speedily leak detection and repair ✓✓
- There should be pressure management of water to avoid bursting of pipes ✓✓
- Pipes should be protected from any danger ✓✓
- There should be water management programme to avoid unauthorised connection ✓✓
- Encourage water harvesting – install water tanks to conserve rain water ✓✓
- Municipalities should encourage wise use of water, e.g. not to wash cars with hosepipes ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant answer) (Any 2 × 2) (4)
4.3 Study the extract below and answer questions that follow.
MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION Monopolistic competition as a market structure was first identified in the 1930s by the economist Edward Chamberlin. [Adapted from: www.economicsonlinne.co.uk] |
4.3.1 Who was the first economist to identify monopolistic competition?
- Edward Chamberlin ✓ (1)
4.3.2 Give an example of a business operating in a monopolistic market.
- Restaurants ✓
- Kentucky fried chicken ✓
- Link Pharmacy ✓
(Accept any correct relevant answer) (1)
4.3.3 Briefly describe the hybrid structure as a feature of monopolistic competition.
- Monopolistic competition is a combination of perfect competition and a monopoly✓✓
- There are many sellers of differentiated products, and that each market is a relatively small in relation to the market as a whole ✓✓
- Every monopolistic competitive business has a certain degree of monopolistic power and is actually a mini monopoly in that it is the only producer of that specific brand or variant product ✓✓ (Any 2 × 2) (4)
4.3.4 How can restaurants use differentiated strategies to attract more customers?
- Quick and better service to customers ✓✓
- Clean and healthy environment ✓✓
- Consistent and good preparation of recipe ✓✓
- Awarding of discounts and loyalty points to regular customers ✓✓
- Special programs for children for example playing games and birthday parties ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant answer) (Any 2 × 2) (4)
4.4 Explain externalities as a cause of market failures without a graph.
- Externalities are costs not included in the pricing of goods / services, and consequently there is a difference between the private costs / benefits and the social costs / benefits of production.✓✓
- Private costs / internal costs are cost of producing the good or service which translates into the prices that consumers pay.✓✓
- Private benefits are internal benefits that accrue to those who produce goods and buy these goods, e.g. producing a bicycle (for producer) and using the bicycle(consumer).✓✓
- Social costs these are total costs incurred by society as a whole. Social cost = private costs plus external costs.✓✓
- Social benefits include the total benefit experienced by society as a whole. Social benefits = private benefits plus external benefits.✓✓
- Negative externalities are things like pollution, tobacco smoking and alcohol abuse. ✓✓The costs of negative externalities are paid by society rather than by the producers. ✓✓
- Positive externalities are the positive effects of products to third parties which are not paid for.✓✓
- Negative externalities are often over-produced while positive externalities are under-produced. This leads to market failure.✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant answer)
(Allocate a maximum of 4 marks for the mere listing of facts / examples (Any 4 × 2) (8)
4.5 How has the implementation of minimum wages benefited workers in South Africa?
Minimum wages benefited workers by:
- Increasing their buying power to afford more goods and services ✓✓
- Improving their living standards by being able to satisfy more wants✓✓
- Improving the distribution of income to those people who received very low wages in the past✓✓
- Protecting workers from being exploited by employees ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant answer)
(Allocate a maximum of 2 marks for the mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer ONE of the two question from this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
STRUCTURE OF ESSAY: | MARK ALLOCATION: |
Introduction
| Max. 2 |
Body:
| Max. 26 Max. 10 |
Conclusion
| Max. 2 |
TOTAL NUMBER OF MARKS | 40 |
QUESTION 5: MICROECONOMICS
A monopoly is one of the extreme ends of our market structures and is an integral part of our economy.
- Examine the characteristics of a monopoly as a market structure. (26)
- Why, in your opinion, is a monopoly an undesirable type of market structure? (10)
INTRODUCTION
A monopoly exists when there is one seller of a good or service for which there is no close substitute. ✓✓
(Accept any relevant introduction) (2)
BODY
- Number of businesses ✓
- Exists when one large business can supply the entire market at a lower price than two or more similar ones.✓✓
- It represents the entire industry ✓✓
- Nature of product ✓
- The product of the monopoly is unique and has no close substitutes ✓✓
- e.g. Eskom and the rail transport ✓✓
- Entrance and exit ✓
- There are barriers to entry, some producers are unable to enter the market. ✓✓
- Government sometimes use patents, which are licences and copy rights for people who invent products, to protect them against competition. ✓✓
- Legal restrictions are also used to give one firm exclusive rights to produce a particular product or to provide a particular service✓✓
- e.g. Post Office ✓
- Control over prices ✓
- A monopoly has full control over price of product or a service. ✓✓
- They control price by manipulating output and can restrict their output to create a shortage which causes an increase in price. ✓✓
- The monopolist also withholds information from consumers ✓✓
- Demand Curve ✓
- Monopolists are faced with demand curves for their product, because the law of demand applies✓✓
- As the monopolist is the only supplier, it can decide on what point on the demand curve they wish to be.✓✓
- Economic Profit ✓
- It is possible for the monopolist to make economic profit both in the short and the long run. ✓✓
- This is because it faces no completion from new entrance as a result of barriers to entry. ✓✓
(A maximum of 8 marks may be allocated for mere listing of facts / examples) (Accept any other correct relevant response) (26)
ADDITIONAL PART
Monopolies may be undesirable because:
- they sets a price higher than in a competitive market, leading to a fall in consumer surplus.✓✓
- they are allocative inefficient because at the quantity it sells, price is greater than marginal cost.✓✓
- it is also productively inefficient because it is not the lowest point on the average cost curve. ✓✓
- it may also have fewer incentives to cut costs because of a lack of competitors.✓✓
- the cost curves of a monopoly will be higher than they would if there was more competitive pressure.✓✓
- they lack the incentives to develop new products and offer a good quality service✓✓
- they make supernormal profit and this can be said to be an inequitable and unfair distribution of resources in society.✓✓
- they tend to exploit the consumers because they rely only on the firm for the product / service since there are no close substitutes for the product.✓✓
(Accept any other relevant correct response) (Max 10) (10)
CONCLUSION:
Monopolies are crucial in as far as providing unique goods and services, but inefficient in that they tend to provide less at high prices and exploit consumers in the process✓✓
(Accept any relevant conclusion) (2)
[40]
QUESTION 6: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUE
In today’s declining economic climate, all the sectors of the economy are adversely affected by the negative effects of inflation.
- Analyse the causes of cost push inflation. (26)
- What impact does inflation have on the households? (10)
INTRODUCTION
Cost push Inflation is caused by an increase in the costs of goods and services that are important in the economy and which no alternative exists.✓✓ (2)
MAIN BODY
CAUSES OF COST-PUSH INFLATION
- Increase in Wages: ✓
- In South Africa, increase in wages constitute more than 50% of Gross Value Added at basic prices✓✓
- If the increase in wages is not accompanied by an increase in production, the cost of production will rise ✓✓
- Producers will increase the prices of their products to offset the high cost of production✓✓
- Key inputs / increase in prices of imported capital goods ✓
- When the prices of key inputs that are imported increase, domestic cost of production increases especially in the manufacturing sector ✓✓
- Exchange rate depreciation ✓
- A decrease in the value of the rand will result in an increase in prices of imports ✓✓
- Profit margins ✓
- When firms increase profit margins, the prices that consumers pay also increase ✓✓
- Sometimes firms use their market power to push up prices ✓✓
- Productivity ✓
- Less productive factors of production will lead to increased cost per unit ✓✓
- Strikes and stay-aways often reduce production output and can result in price increases ✓✓
- Natural disasters ✓
- Natural disasters such as drought, flood and global warming can increase the cost of production ✓✓
- This is often the case in relation to food prices ✓✓
(A maximum of 8 marks may be allocated for mere listing of facts / examples) (26)
ADDITIONAL PART
What impact does inflation have on the households?
Households are often stressed by the high rates of inflation because of the following:
- inflation affects the distribution of real income.✓✓
- people on fixed incomes suffer as the purchasing power of their incomes(their real income) decrease as price levels rise.✓✓
- people whose incomes rise faster than the rate of inflation experience an increase in their real wage✓✓
- inflation tends to result in a more unequal distribution of income as those on lower incomes find their wages do not rise as quickly as those on higher incomes.✓✓
- in times of high inflation households tend to purchase real assets(e.g. houses, gold, antiques, paintings etc) that retain their real value since their prices rise faster than the inflation rate.✓✓
- as employees nominal wages increase with inflation their real wage(the purchasing power of nominal wages) may remain constant. ✓✓
- under progressive tax system increased nominal wages may put wage earners into higher tax brackets(higher marginal tax rate).✓✓
- the percentage on income paid in tax rises even though real wages remain constant.✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant answer) (Max 10) (10)
CONCLUSION
Inflation is very detrimental to the economy, amongst other things it leads to the depreciation of the rand and it hits hard on the poor, lowering the standard of living in the process. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant higher order conclusion) (2)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
ECONOMICS GRADE 12 PAPER 1 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
ECONOMICS
GRADE 12
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1.1.1 C leakages ✔✔
1.1.2 B reducing production costs ✔✔
1.1.3 A provide merit goods ✔✔
1.1.4 D an embargo ✔✔
1.1.5 A the prevention of dumping ✔✔
1.1.6 D wealth ✔
1.1.7 C repo rate ✔✔
1.1.8 B interdependent ✔✔ (8 x 2) (16)
1.2 MATCHING ITEMS
1.2.1 G Value of all final goods and services produced by the permanent residents of the country for a specific year ✔
1.2.2 A Financial grants to support the production of exports goods✔
1.2.3 D Money received without any productive service rendered ✔
1.2.4 F Business owned by the state and run by public authorities ✔
1.2.5 H An inter-government organisation that aim to promote socio-economic cooperation and integration ✔
1.2.6 I The total amount of money in circulation in the economy ✔
1.2.7 B Focuses on improving the competitiveness of the manufacturing industries ✔
1.2.8 E Are used to analyse the changes in a series of data over a period of time ✔ (8 x 1) (8)
1.3 IDENTIFY THE CONCEPT
1.3.1 Consumption spending✔
1.3.2 Exogenous / Monetarist ✔
1.3.3 Exchange rate ✔
1.3.4 Corridor ✔
1.3.5 Devaluation ✔
1.3.6 RDP ✔ (6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer TWO of the three questions from this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 2: MACROECONOMICS
2.1 2.1.1 Name the TWO periods in a business cycle.
- Contraction/downswing ✔
- Expansion/upswing ✔ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 What is the impact of the multiplier, if the equilibrium income increases by more than the increase in initial expenditure?
- The total income and expenditure increase the multiplier will also increase. ✔✔(1 x 2) (2)
2.2 DATA RESPONSE
2.2.1 Which source was used to compile the data in the above table?
- Quarterly bulletin, March 2017 ✔ (1)
2.2.2 Which year is currently used as the base year by the Reserve Bank?
- 2015 ✔ (1)
2.2.3 Briefly explain the difference between nominal GDP and real GDP.
- Nominal GDP
- Referred to as GDP at current price. ✔✔
- Also known as market or money value. ✔✔
- Inflation has not yet been taken into account. ✔✔
- These prices do not reflect whether economic activity has increased. ✔✔
- Real GDP
- Referred to GDP at constant prices.✔✔
- Real prices are adjusted for price changes.✔✔
- Real national product is the national product expressed in prices which applied in a certain base year. ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant responses.) (Any 2 x 2) (4)
2.2.4 Calculate the deflator for 2016. Show all your calculations.
- Deflator: Nominal GDP ÷ Real GDP x 100
- Deflator for 2016 = 4 336 988 ✔ ÷ 3 009 860 ✔ x 100 ✔
= 144 ✔ (4)
2.3 DATA RESPONSE
2.3.1 At which point will the government maximise revenue? (1)
- A ✔
2.3.2 What curve is depicted above?
- Laffer ✔ (1)
2.3.3 What effect will point C have on government revenue?
- Tax revenue will increases ✔✔ (2)
2.3.4 What are the dangers of high personal income tax rates?
- Tax avoidance ✔✔
- Tax evasion ✔✔
- People will be discouraged to work ✔✔ (Any 1 x 2) (2)
2.3.5 How can the South African government avoid public – sector failure?
- Improving the quality of management skills in the public sector ✔✔
- Reducing corruption, including nepotism when hiring public sector employees ✔✔
- Reducing bureaucracy by investing in modern systems such as a IT system✔✔
- Increasing accountability ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) (Any 2 x 2) (4)
2.4 Briefly explain how a deficit on a balance of payment will automatically be corrected under a free floating exchange rate system.
- There is an excess demand for foreign currency on the foreign exchange market. ✔✔
- Exports will become cheaper and will increase.✔✔
- Imports will become more expensive and decrease. ✔✔
- The deficit will decrease. ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) (Any 4 x 2) (8)
2.5 How does the entry of domestic businesses into foreign markets benefit South Africa?
South Africa will benefit from entering foreign markets by:
- Local businesses becoming more competitive. ✔✔
- Improving quality and decreasing prices. ✔✔
- Earning foreign exchange. ✔✔
- Enabling us to import products from other countries that we are not able to produce for ourselves. ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) Max. 8 (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: ECONOMIC PURSUITS
3.1 3.1.1 Name TWO instruments that the SARB can use to influence the economy.
- Interest rates ✔
- Open market transactions ✔
- Moral persuasion ✔
- Cash reserve requirements ✔
- Exchange rate policy ✔ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.1.2 What effects will a huge increase in electricity costs have on smaller businesses in South Africa?
- Businesses will run at a loss / closing down / more will be forced into bankruptcy. ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) (Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.2 DATA RESPONSE
3.2.1 What does the abbreviation IPAP stand for?
- Industrial Policy Action Plan ✔ (1)
3.2.2 Name ONE focus area of this policy for 2017/2018.
- Education and skills ✔
- Infrastructure ✔ and regulatory environment ✔
- The labour relations environment ✔
- Inclusive growth ✔ (Any 1 x 1) (1)
3.2.3 Explain ONE reason for industrial development
- Job creation ✔✔
- Maintain macroeconomic stability. ✔✔
- Develop and maintain appropriate incentives to attract investors. ✔✔
- Diversification of the economy ✔✔
- Contribute to the industrial development of the African continent. ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.2.4 How successful is the industrial development policies in South Africa?
- Promotes incentives for investors to establish industries. ✔✔
- Promote industrialisation by manufacturing developments policies which offer incentives ✔✔ such as loans, export promotion, subsidies and establishment allowances.
- Promote globalisation by having a liberal policy towards foreign investment. ✔✔
- Improve infrastructure of transport, power and modern communication including access to the internet. ✔✔
- Innovation and technology. ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) (Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.2.5 What impact might IPAP have on industrial development in the private sector of South Africa?
- Rapid increase in the price of electricity and petrol which increase business costs. ✔✔
- Labour unrest which has led to reduced productivity ✔✔
- Structural unemployment as new skills are needed and others become outdated. ✔✔
- The global financial crisis and the continuing instability resulting in low foreign demand for South African exports. ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Any 2 x 2) (4)
3.3 DATA RESPONSE
3.3.1 Name the method used to measure economic development of a country.
- Human development Index (HDI) ✔ (1)
3.3.2 Which country has the highest HDI in the table above?
- Norway ✔(0,955) (1)
3.3.3 Explain the term human development.
- Is the improvement of the opportunities facing a country’s people so that they can lead long, full educated and healthy lives, accessing resources and participating in their communities. ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) (2)
3.3.4 Why is South Africa’s economic development underperforming?
- Decline in life expectancy due to HIV and Aids epidemic ✔✔
- Underperforming education system ✔✔
- Decline in employment rate ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.3.5 How can the South African government help to improve economic development?
Government plan to maintain economic development include:
- Job creation ✔✔
- Subsidies to no-fee schools ✔✔
- Access to basic services such as a provision of solar water geysers ✔✔
- Upgrading of informal settlements and water structures ✔✔
- Spending on health and social assistance ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) (Any 2 x 2) (4)
3.4 Compare the standard of living between the North-South countries.
North | South | |
Real GDP per capita : | Produces 78% of world income – have much higher per capita income. ✔✔ | Produces 22% of world income – the per capita is much lower. ✔✔ |
Life expectancy : | Is over 75 years and over 80 in some countries. ✔✔ | Is about 50 years, and 40 years in some African countries. ✔✔ |
Education: | Literacy levels are about 95%. ✔✔ Max. 4 | Literacy levels are as low as 50% in some developing countries in Africa. ✔✔ Max. 4 |
(8)
3.5 How successful is Black Economic Empowerment in the South African economy?
- Number of black people who own, manage and control businesses in the country increases significantly. ✔✔
- Income and inequalities decreases substantially.✔✔
- Businesses spend money on projects that empower workers and other member of disadvantaged communities. ✔✔
- It brings about transformation of the ownership, management and employment equity aspect of businesses in S.A. ✔✔
- Ensures employees are not placed in position within a company because of their race. ✔✔
- They are promoted and encouraged to move up the ranks if they meet the minimum criteria. ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) Max. 8 (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4
4.1 4.1.1 List TWO problems of public sector provisioning.
- Accountability ✔
- Efficiency ✔
- Assessing needs ✔
- Parastatals ✔
- Pricing policy ✔
- Privatisation/ Nationalisation ✔ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.1.2 How does economic growth relate to economic development?
- Economic growth is concerned with goods and services ✔ and economic development is concerned with people and human development. ✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) (1 x 2) (2)
4.2 DATA RESPONSE
4.2.1 What international trade policy is reflected in the graph above?
- Free trade ✔ (1)
4.2.2 What happens to the supply when the country engages in free trade?
- Increases ✔ (1)
4.2.3 Describe the term free trade.
- Is when producers and consumers are free to buy goods and services from anywhere in the world, without the interference of government.✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) (2)
4.2.4 Explain why trade protocols are necessary for the economy.
- They have a combined effect of increasing the amount of trade between countries. ✔✔
- They restrict trade by laying down rules for the way in which it occurs. ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) (Any 1 x 2) (2)
4.2.5 How does the society experience an increase in welfare through free trade?
- Need to examine the costs of trade barriers.✔✔
- Tariffs and quotas reduce the quantity and variety of gods available to consumers. ✔✔
- The foreign which are imported are more expensive due the excise taxes and customs duties. ✔✔
- Free trade increases the range of choice that is available to consumers and reduces the general price level. ✔✔
(Any 2 x 2) (4)
4.3 DATA RESPONSE
4.3.1 What economic problem is illustrated in the picture above?
- Inflation ✔ (1)
4.3.2 How might inflation affect the consumers buying power?
- Decreasing/decline ✔ (1)
4.3.3 Briefly describe the term inflation.
- Inflation can be described as an increase in the general level of prices in an economy, that is sustained over a period of time. ✔✔ (2)
4.3.4 How would an investor be influenced by inflation?
- Profits / return on investment might decline. ✔✔
- Assets with a fixed nominal value have a fixed return and ✔✔
- Lower purchasing power as prices increases ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) (Any 1 x 2) (2)
4.3.5 Why is important for the South African government to monitor the performance of the economy?
- Is to make decisions and form policies ✔✔
- Show whether targets have been met ✔✔
- Compare conditions between areas and in different periods. ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) (Any 2 x 2) (4)
4.4 Briefly explain the critical infrastructure and skill support programme as the incentives used by the South African government to improve industrial development.
- Critical infrastructure Programme
- Is a cost-sharing grant for projects designed to improve critical infrastructure in South Africa.✔✔
- Covers a qualifying development cost between 10% and 30% towards the total development costs. ✔✔
- Becomes available on completion of the project. ✔✔
- It extends to both the public sector and private sector ✔✔
- The programme deems infrastructure to be critical if investment had not taken place or would not work optimally without the infrastructure.✔✔
- Government supplies financial incentives to large enterprises requiring critical infrastructure.✔✔ such as roads, electricity and water purification. ✔✔ (Any 2 x 2)
- Skill support programme
- Is a cash incentive scheme to encourage greater investment in skills training in general. ✔✔
- To introduce new, advance skills to the immediate benefit of the South African labour force. ✔✔
- A maximum of 50% of a company’s trading costs are covered. ✔✔ (Any 2 x 2) (8)
4.5 How can climate changes influence international trade?
A change in climatic conditions might influence international trade by:
- Leading to different products being produced and exported to other countries than before. ✔✔
- Leading to imports of different products produced locally and exported before. ✔✔
- Causing other types of industries to arise due a change in production pattern and types of products delivered. ✔✔
- Causing a serious need for research in unknown fields of production to ensure international trade. ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer ONE question from this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
STRUCTURE OF ESSAY: | MARK ALLOCATION: |
Introduction
| Max. 2 |
Body:
| Max. 26 Max. 10 |
Conclusion
| Max. 2 |
TOTAL NUMBER OF MARKS | 40 |
QUESTION 5: MACROECONOMICS 40 MARK − 40 MINUTES
The business cycle plays a key role in enabling economists to make educated guesses about the future growth of the economy.
- Discuss indicators as features underpinning forecasting business cycles. (26 marks)
- Why is it important that the Reserve Bank maintains price stability in the South African economy? (10 marks)
INTRODUCTION
Economic indicators are statistics used to measure some aspect of the economy. ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant introduction.) Max. 2
BODY: MAIN PART
Economic indicators:
⮚ Leading economic indicators ✔
- Changes before the economy changes. ✔✔
- They peak before the peak in aggregate economic activity is reached and they reach a trough before aggregate economic activity reaches a trough. ✔✔
- They give advance warning of changes in aggregate economic activity. ✔✔
- They give consumers, business leaders and policy makers a glimpse into where the economy might be headed. ✔✔
- If leading indicators rise today, then the rest of the economy is likely to rise in the coming year. ✔✔
- Examples of leading economic indicators: Job advertising space, average manufacturing hours worked, building plans approval.✔ (Max. 8)
⮚ Lagging economic indicators ✔
- Do not change direction until after the business cycle has changed its direction.✔✔
- They reach a peak/trough months after the business cycle has reached a peak/trough. ✔✔
- Follow coincident indicators after a further time elapse ✔✔
- They therefore may serve to confirm the behaviour of the coincident indicators. ✔✔
- If they do not confirm an upswing or a downswing, this signals that the upswing or downswing is weak and will mostly end at an early stage. ✔✔
- Economists use them to estimate whether individual indicators gave false signals. ✔✔
- Examples of lagging economic indicators: Unemployment rate, Number of commercial vehicles sold, Real machinery and equipment sold, Number of hours worked in construction. ✔ (Max. 8)
⮚ Coincident economic indicator ✔
- Move together with the aggregate economic activity. ✔✔
- They indicate actual state of the economy ✔✔
- Coincidence indicator change at the same time as the economy. ✔✔
- They reach a peak / trough at the same time as the business cycle. ✔✔
- Economists use them to compile the business cycle. ✔✔
- They follow leading indicator after some time has elapsed but they tend to confirm the turning points of the leading indicator.✔✔
- Examples of coincident indicator: Industrial production index, Volume of imports, Value of wholesale, retail and new vehicle sales ✔(Max. 8)
⮚ Composite economic indicator ✔
- A summary of various indicators of the same type into a single value.✔✔
- The three composite indicators are often used to calculate a single composite indicator, ✔✔ that is single number to benchmark a country’s economic performance. ✔✔ (Max. 4)
(Accept any other correct relevant response.)
(A maximum of 8 marks may be allocated for mere listing of facts/examples) (Max. 26)
ADDITIONAL PART
It is important that the Reserve Bank maintains price stability in the South African economy by:
- Ensuring that markets can function optimally and the government can promote economic growth and development more effectively. ✔✔
- Avoiding frequent fluctuations in the level of consumer and producer goods ✔✔ ∙ Making it easy for consumers and producers to plan and budget ✔✔ so that consumers might be aware of costs of goods and services. ✔✔
- Boosting investors’ confidence and foreign investors who would be likely to invest in local businesses if they were sure what production costs. ✔✔ / revenue was going to be from one month to the next. ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) (Max. 10)
Conclusion
It is difficult to do accurate economic forecasting because there are many factors that influence the dynamics of the economy. ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant conclusion.) (Max. 2)
[40]
QUESTION 6: ECONOMIC PURSUITS
Many people are interested in the performance of an economy, such as ordinary citizens, businesses, investors and the government.
- Discuss the following social indicators:
- Nutrition and health (16 marks)
- Demographics (10 marks ) (26 marks)
- How can the economic development be improved through the use of these social indicators? (10 marks)
INTRODUCTION
Social indicators are statistics that show the level and progress of human development in a country. ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant introduction.) Max. 2
BODY: MAIN PART
⮚ Nutrition and health
- The health of a population and of the labour force of a country is very important for the economic growth and development. ✔✔
- Healthy citizens are more productive, earn more, consume more and work longer. ✔✔
Infant mortality rate. ✔
- It measures the number of infants who died before reaching one year of age per thousand live births in a given year. ✔✔
- The infant mortality rate in South Africa is still high compared to other countries. ✔✔
- Infant mortality is often connected to a low birth weight, which can be caused by pregnant mother’s malnutrition, stress or by her smoking, alcohol or drug abuse. ✔✔
⮚ Under five mortality ✔
- Is often connected to malnutrition, diarrhoea, measles, malaria and respiratory infections. ✔✔
- he under-five mortality rate is normally given as the number of deaths per 1 000 live births. ✔✔
- The number of children that will die before the age of five years. ✔✔
⮚ Access to health service ✔
- South Africa compares well in terms of indicators measuring access to primary health services ✔✔ and ∙ The amount of health expenditure as a percentage of GDP. ✔✔
⮚ Access to clean drinking water ✔
- Means that people have safe drinking water out of taps in their houses. ✔✔
- The percentage of a population that has a reasonable access to safe drinking water ✔✔
⮚ Access to sanitation facilities ✔
- Means that people have access to toilets or improved sanitation facilities that keep them away from other humans, animals and insects.✔✔
- The percentage of a population with at least adequate sanitation facilities ✔✔
⮚ Nutrition
- Is a process of a person‘s body getting the food necessary for health and growth. ✔✔
⮚ Child malnutrition ✔
- Malnutrition is expressed in two ways: weight of age and height of that age. ✔✔
- A person’s body weight is compared to an ideal for a person of that age, sex and height. ✔✔
- Physical signs also need to be taken into account as people of normal weight, or people who are overweight, can still be suffering from deficiencies in particular nutrients.✔✔
⮚ Overweight children ✔
- There is an association between obesity of children and other diseases. ✔✔
- A person is considered obese if his / her BMI is more than 30 kg.✔✔ (Max. 16)
⮚ Demographics
- Is the study of population relating to elements such as its total size, population changes over time, age and gender distribution and geographical distribution. ✔✔
⮚ The population growth ✔
- South Africa has a relatively high population growth compared with that of developed countries.✔✔
- The population growth rate is an important indicator to the government in terms of the number of social services that are needed. ✔✔
⮚ Life expectancy ✔
- Expresses the number of years a newborn infant may live ✔✔ if the prevailing patterns of mortality remained the same throughout his or her life. ✔✔
- Mortality rates in South African have been affected by the prevalence of HIV, which has been increasing significantly. ✔✔
- It is important for government to know what the average life expectancy is, ✔✔ because working humans require a range of social services. ✔✔
- Assurance companies in particular are interested in life expectancy. ✔✔ (Max. 10) (Accept any other correct relevant response)
(A maximum of 8 marks may be allocated for mere listing of facts/examples) (Max. 26)
ADDITIONAL PART
Economic development can be improved by:
- Spending more on the improvement of the quality of life of the general population and reduce social tension. ✔✔
- Investing more in the future quality labour force for the progression of the economy. ✔✔
- Improving health and educational facilities.✔✔
- Focusing on the areas that needs development in communities and spend on them. ✔✔
- Improving social cohesion and interdependence. ✔✔
- Assisting the government to look into other areas of need through the budget. ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) (Max. 10)
CONCLUSION
Social indicators are directing government expenditure on issues that will guarantee social development and a quality lifestyle. ✔✔
(Accept any other correct, relevant conclusion) (Max. 2)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL 150
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES GRADE 12 PAPER 1 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
GRADE 12
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 D √√
1.1.2 B √√
1.1.3 C √√
1.1.4 C √√
1.1.5 D √√
1.1.6 A √√
1.1.7 C √√
1.1.8 A √√
1.1.9 B √√
1.1.10 A √√ (10 × 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 B only √√
1.2.2 A only √√
1.2.3 B only √√
1.2.4 Both A and B √√
1.2.5 None √√ (5 × 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 Ad lib √√
1.3.2 Topical √√
1.3.3 Bunching √√
1.3.4 An-oestrus/sub-oestrus √√
1.3.5 Semen √√ (5 × 2) (10)
1.4
1.4.1 Amylase √
1.4.2 Optimum √
1.4.3 Leydig √
1.4.4 Resorption √
1.4.5 Implantation √ (5 × 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: ANIMAL NUTRITION
2.1
2.1.1 Cattle/Sheep/Goat √ (1)
2.1.2
- A √ (1)
- B √ (1)
- A √ (1)
2.1.3 Presence of leaves √ where food particles are grinded finely √ (2)
2.1.4 Presence of rumen micro-organisms √ which break down cellulose√ into volatile fatty acids √ (3)
2.2
2.2.1
- Protein rich roughage √ Lucerne hay √
- Carbohydrate rich roughage √ oat hay √ (4)
2.2.2 Maize meal √ (1)
2.2.3 Ration cannot be fed to pigs √ (1)
2.2.4 Ration contains urea √ which cannot be digested by pigs. √ (2)
2.3
2.3.1 Non-ruminant √ (1)
2.3.2
- Crude fibre √ was poorly digested √
- High/73% √ of crude fibre was excreted √ (Any 1) (2)
2.3.3
- 7kg - 4kg × 100 √ = 42,8 % √ (2)
7kg
2.3.4 Only 42,8 % of feed √ has been digested and absorbed √ (2)
2.4
2.4.1
- Roughage have a higher crude fibre content √
- Concentrates have low crude fibre √ (2)
2.4.2
- Roughage – less than 60% TDN √
- Concentrates – More than 60% TDN √ (2)
2.5
2.5.1 15 t/ha × 19,6 (ha) √ = 294 tons √ (2)
2.5.2 August √ (1)
2.5.3
- Feed required is 65t and feed available is 35t √√
- There is a shortage of 30t √√ (Any 1) (2)
2.5.4 56 + 60 + 85 √ = 201 tons √ (2)
[35]
QUESTION 3: ANIMAL PRODUCTION, PROTECTION AND CONTROL
3.1
3.1.1
- : Extensive production system √
- : Intensive production system √ (2)
3.1.2
- : Few animals in a large space/low stocking density √
- Many animals in small space/high stocking density √ (2)
3.1.3
- Extensive production system: Subsistence farming √
- Intensive production system: Commercial farming √ (2)
3.1.4
- Nutrition/feeding √
- Environment √
- Breeding/reproduction √
- Management √ (Any 2) (2)
3.2
3.2.1 Crush √ (1)
3.2.2
- Administration of medication/dipping/dosing √
- Determining the age of animal √
- Normal management programme (dehorning/docking/castration/marking) √
- Pregnancy testing √
- Transportation √ (Any 2) (2)
3.2.3
- High solid sides √
- Narrow and curved √
- Wide and straight to provide clear path √ (Any 2) (2)
3.3
3.3.1 Always have a red flag √ (1)
3.3.2 Should be in possession of a permit √ (1)
3.3.3 Loading ramp √ (1)
3.4
3.4.1
- Bacterial √
- Blisters on the tongue ,nose, lips in the mouth √
- Protozoan √
- Bont tick √
- Ringworm √ (5)
3.4.2 Notifiable √ (1)
3.4.3 Foot-and-mouth disease √ (1)
3.4.4
- Restricting the movement of animals/control measures√
- Quarantine the affected animals √
- Vaccination programmes/Veterinary services √
- Import bans √
- Legislation √ (Any 2) (2)
3.5
3.5.1 Internal parasite/endoparasite √ (1)
3.5.2 Liver fluke √ (1)
3.5.3 Snail √ (1)
3.5.4 Animal get infested during grazing √ (1)
3.5.5 Anaemia/fasciolosis √ (1)
3.5.6
- Rotation grazing/resting veld √
- Avoiding wet places during grazing √
- Allow animals to graze on clean pastures √
- Integrated pasture management √ (Any 2) (2)
3.6
3.6.1
- Excessive salivation √
- Increased thirst √
- Vomiting and regurgitation √
- Constipation √
- Aggressiveness √
- Hypersensitivity to touch √
- Red and dry mucous membranes of mouth √
- Increased urination and defecation √
- Abnormal pain and diarrhoea √ (Any 1) (1)
3.6.2
- Provision of fresh water in small amounts at short intervals √
- Give young animals isotonic saline solution/hypertonic dextrose √
- Remove the source of salt poisoning √ (Any 2) (2)
[35]
QUESTION 4: ANIMAL REPRODUCTION
4.1
4.1.1 Identical twin √ (1)
4.1.2 They are formed from the fertilisation of one egg cell by one sperm cell √ (1)
4.1.3
- Gender They are of the same sex √ (1)
- Physical appearance They are identical √ (1)
4.1.4 Hailurodinase √ (1)
4.1.5 Ovum stage √ (1)
4.2
4.2.1 Table showing number of cows in oestrus during different time period
Number of cows | Time |
25 | 06:00 – 12:00 |
10 | 12:00 – 18:00 |
20 | 18:00 – 00:00 |
45 | 00:00 – 06:00 |
Marking table with the following checklist:
Criteria | Yes: 1 mark | No: 0 mark |
1. Table | 1 | 0 |
2. Labelling: No. of cows | 1 | 0 |
3. Labelling: Time | 1 | 0 |
4. Data correctly captured (time and no .of cows) | 2 | 0 |
5. Correct heading | 1 | 0 |
(6)
4.2.2 06:00–08:00 √ (1)
4.2.3 It is 12 hours √ after oestrus signs have disappeared √ (2)
4.3
4.3.1
- Oogenesis primary oocytes √
- Spermatogenesis primary spermatocytes √ (2)
4.3.2
- Oogenesis ootids √
- Spermatogenesis primary spermatids √ (2)
4.3.3
- Oogenesis ovary √
- Spermatogenesis testicles/testes √ (2)
4.4
4.4.1 Vas deferens/seminal tube √ (1)
4.4.2 Prostate gland √ (1)
4.4.3 Epididymis √ (1)
4.5
4.5.1 Dystocia √ (1)
4.5.2
- Deviation of the head √
- Flection of the elbow √
- Retention of one or both forelegs √
- Hydrocephalus √
- Congenital defects √
- Posterior presentation/position and posture √
- Torsion of the uterus √ (Any 2) (2)
4.6
4.6.1 Cloning √ (1)
4.6.2
- Sheep 1 Donor √
- Sheep 2 Recipient √ (2)
4.6.3
- Reproductive cloning √
- Therapeutic cloning √ (2)
4.6.4 For the production of medicines to treat different diseases √ (1)
4.6.5
- High quality products ( meat, wool, et cetera) √
- Farmers farm with best animals with desirable characteristics √
- Animals can be bred for disease resistance thus, decreasing the cost of treatment √
- Extinct and endangered species can be revived √
- One female can produce many clones √ (Any 2) (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES GRADE 12 PAPER 2 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
GRADE 12
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
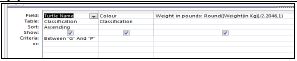
| QUESTION 1.1 | QUESTION 1.2 |
| 1.1.1 A √√ 1.1.2 C √√ 1.1.3 B √√ 1.1.4 A √√ 1.1.5 D √√ 1.1.6 A √√ 1.1.7 B √√ 1.1.8 C √√ 1.1.9 C √√ 1.1.10 D √√ (10 x 2) (20) | 1.2.1 G √√ 1.2.2 D √√ 1.2.3 A √√ 1.2.4 J √√ 1.2.5 B √√ (5 x 2) (10) |
| QUESTION 1.3 | QUESTION 1.4 |
1.3.1 Selective breeding √√ (5 x 2) (10) | 1.4.1 Sex linkage √ (5 x 1) (5) |
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
2.1
2.1.1 Reasons why tomatoes are protected in boxes
- For easy handling during distribution/transportation. √
- For protection against mechanical damage. √
- For easy storage and packaging. √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 Important packaging information that could attract tomato buyers.
- Produce name √
- Brand of the produce √
- Size √
- Variety √
- Net weight √
- Count √
- Producer √
- Shipper √
- Country of origin √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.1.3 Reason why materials used for packaging vegetables must not contain chemicals.
- Toxic chemicals can be transferred to the vegetables. √
- Vegetables may contaminate/absorb chemical odour/unpleasant smell. √ (Any 1 x 1) (1)
2.2 2.2.1 The law of supply
- The higher the supply, the more goods will be supplied. √√ (2)
2.2.2 Functions of agricultural marketing factors affecting supply
- Price of the product – the higher the price, the more producers will be willing to supply. √
- Competitive products – if cheaper products enter the market, the farmer may reduce production. √
- Environmental conditions such as pest infestation can affect supply. √
- Political instability such as war. √
- Expectation of future price changes. √
- When the demand for the product declines, producers will switch to produce other things. √
- Technology – new technology may increase production. √
- Production cost – the higher the cost of production, the less profit will be made. √
- If government subsidies production, supply is likely to increase. √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.2.3 How the following factors affect the demand of a product.
- Advertisement
- Advertisement can inform consumers of a new or improvement in a product. √ This can increase the demand for that product. √ (2)
- Quality of a product
- Demand of a product will increase if the quality of the product is good. √ If the quality is bad, the demand will decrease/decline. √ (2)
2.3 2.3.1 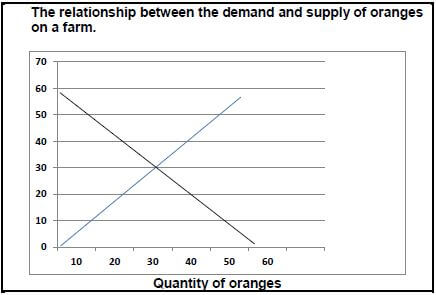
- Correct heading √
- Correct plotting of values √
- Labelling and units (Price in Rands) on Y-axis √
- Labelling and units (Quantity of oranges) on X-axis √
- Demand and supply curves √ (5)
2.3.2 Price at market equilibrium
- R30,00 √ (1)
2.3.3 Why demand for oranges is low at R50,00
- The price is very high / the higher the price, the lower the demand. √ (1)
2.4 2.4.1 Free marketing
- It is the marketing of products in an uncontrolled way. √√ (2)
2.4.2 The main channels of free marketing
- Farm gate marketing √
- Fresh produce markets
- Stock sales √
- Direct marketing √
- Internet marketing √
- Auction √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.4.3 Disadvantages of free marketing.
- Price fluctuates considerably √
- Market cost are high √
- The producer is responsible for the marketing of the products √
- The producer has limited bargaining power √
- Producer decision may lead to big financial loss
- Very often cartels are formed and the consumers are exploited √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.5 2.5.1 Marketing cost that could affect the price of the product
- Product preparation and packaging costs √
- Handling cost √
- Transport cost √
- Product cost √ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
2.5.2 Factors that hamper the marketing of agricultural products
- Perishability nature of farm produce like meat √
- Agricultural products have high volume with relative low unit value √
- Seasonal fluctuations in production √
- Standardisation of size, taste and appearance vary √
- Local restrictions of agricultural production √
- Intermediaries required for the marketing of agricultural products √
- Long production time of certain crops such as wood √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.5.3 Ways to streamline and improve the agri-business chain
- Improve the competiveness of commercial farmers √
- Increase government control over inferior agricultural products from overseas √
- Improve transportation √
- Promote farmer cooperatives √
- Provide access to market information √
- Improve access to storage facilities √
- Improve training and skill development √
- Improve local marketing infrastructure and local marketing networks √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.6 Possible problems that may arise when compiling agri-business plan.
- Insufficient research √
- Leaving gaps / being vague / providing too much information √
- Insufficient technical detail √
- Overambitious or unrealistic assumptions and projections √
- Incomplete financials √
- Not highlighting potential competition √
- Hiding weakness and risks √
- Using the incorrect format √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
[35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
3.1 3.1.1 Production factor that could be used as a collateral Land √ (1)
3.1.2 Justification
- The value of land appreciates with time √
- Land ownership is easily transferable √
- The value of land can be convertible √
- Land can easily be sold at any time √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.1.3 Explanation of “the availability of land for agricultural purposes is limited”.
- Land for cultivation/tillage/production or agricultural purposes is restricted √ to specific areas. √
- Land for agricultural purposes cannot be produced. √
- It is fixed. √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.1.4 Economic characteristics of land
- It is a primary factor of production √
- It is indestructible √
- It varies in production potential √
- It can be bought and sold √
- Its value appreciates √
- It is a passive factor of production √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.2 3.2.1 (3)
Skilled labourer | Semi-skilled labourer | Unskilled labourer |
Veterinarian √ | Unqualified mechanic √ | Apple picker √ |
3.2.2 Worker who could be in highest demand by a livestock farmer
- Veterinarian √ (1)
3.2.3 Reason
- Skilled workers are scarce and demand for them is high. √
- It takes a long time to train a veterinarian. √
- Only the veterinarian is more useful to the livestock farmer. √ (Any 1 x 1) (1)
3.2.4 Methods to improve the economic conditions of the apple picker
- Provide him with incentives √
- Pay higher salary √
- Pay bonuses √
- Entering into partnership deals with the worker √
- Provide medical insurance √
- Supply farm products such as milk √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.2.5 The legislation that can best help the apple picker
- Basic Conditions of Employment Act/Skills Development Act √ (1)
3.3 3.3.1 The type of document in 3.3.
- Enterprise budget √ (1)
3.3.2 Justification of answer to QUESTION 3.3.1.
- The record is a plan or a record of the money spent on and earned √ by only one enterprise (tomato). √ (2)
3.3.3 Two types of capital with examples
- Movable capital e.g. tractor √
- Working capital e.g. fertiliser, tomato seedlings, insecticides storage boxes √ (2)
3.3.4 Profit or loss of the farmer.
- Total income = 15 250,92 √
Expenditure = 4 521,25 √
Profit = R15 250,92 – R4 521,25 = R10 729,67 √ (3)
3.3.5 Sources of capital to the farm worker
- A commercial bank that supplies credit to the general public √
- Financial institutions such as land bank or Ithala Development Finance Corporation Ltd √
- A trust company √
- A potential business partner √
- Agricultural cooperatives and agribusinesses √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.4 3.4.1 Definition of farm management
- Application of basic business principles and scientific principles of agriculture √ to the farm business. √ (2)
3.4.2 Components of strategic management
- Developing a vision √
- Developing a mission √
- Setting goals and objectives √ (3)
3.4.3 Explanation of conceptual skills
- Conceptual skills allow you to reflect on changes in the industry or in farm circumstances √ and develop strategies to address them. √ (2)
3.4.4 Socio-cultural forces that affect businesses
- Population demographics – age, gender and race composition √
- Education levels can affect the labour availability to the farm √
- Culture and religion and the values and lifestyle choices of your customers √
- Attitudes to environmental issues will affect demand for your product √
- HIV and Aids can affect your consumers available cash and the availability of labour √ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
[35]
QUESTION 4: GENETICS
4.1 4.1.1 Genotype in K
- SsQq √ (1)
4.1.2 Phenotype in L
- Black Short √ (1)
4.1.3 Ratio of white and long hair in the crosses
- 1 √ : 16 √ (2)
4.1.4 Percentage of black and short hair in the phenotype
- Total of the phenotypes = 9 + 3 + 3 + 1 √ = 16 √
Black and short hair = 9
Percentage of black and short hair = 9/16 x 100 √
= 56,25% or 56,3% √ (4)
4.2 4.2.1 Qualitative characteristics
- These are characteristics that can take only a few fixed forms. √
- They are controlled by one pair of genes. √ (2)
Quantitative characteristics
- Quantitative characteristics can take on a whole series of values without clear boundary lines between the different classes. √
- They are usually determined by a number of genes. √ (2) (4)
4.2.2
- Gender of a bull – qualitative characteristic √ (1)
- Body size of the bull – quantitative characteristic √ (1)
4.3 4.3.1 Limitations of traditional breeding
- It is not precise. √
- Many unwanted traits can be transferred. √
- Not suitable for the production of vaccines. √
- Recombined genetic traits within species and between related ones. √
- It is time-consuming – takes several years. √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.3.2 Current uses of genetically modified plants
- Improving the shell life of many fruiting plants. √
- Improving the nutritional value of food. √
- Improving resistance to diseases and pests. √
- Improving resistance to weed killers. √
- Improving resistance to viral disease.√
- Increasing resistance of plants to negative environmental influences such as drought. √ (2)
4.4
- Prepotency
- The ability of a parent to pass its genetic characteristics √ on to its offspring. √ (2)
- Pedigree selection
- Pedigree selection focuses on the quality of the ancestors, √ rather than on the individual. √ (2)
4.5 4.5.1 The type of breeding that could take place on the farm.
- Cross breeding √ (1)
4.5.2 Reason for answer in QUESTION 4.5.1.
- It involves the mating of two pure-bred animals √ of different breeds. √ (2)
4.5.3 Characteristics of crossbred animals
- They produce heterosis/hybrid vigor √
- The offspring are heterozygous √
- It helps to improve characteristics that have low heritability √
- Progeny is more resistant to diseases √
- Offspring have more vitality √
- Better adaptability to varying environmental conditions √ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
4.5.4 One genetic terminology for the offspring
- Progeny √ (1)
4.6 4.6.1 Calculation of milk yield
- aabbcc = 3 000 litres of milk
B = 200 litres of milk √
C = 200 litres of milk √
AaBbcC = 3 000 + 200 + 200
= 3 400 √ litres of milk √ (4)
4.7 4.7.1 Crossing over √√ (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES GRADE 12 PAPER 2 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
GRADE 12
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show ALL your calculations, including formulae, where applicable.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write ONLY the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 In sex-linked characteristics, maleness or femaleness is considered a …
- genetic phenotype.
- genetic genotype.
- polygenic appearance.
- single base loss.
1.1.2 ... refers to the money from the profit of a business that is shared among the owners of the business.
- Savings
- Credits
- Dividends
- Cash flow
1.1.3 Labourers in a commercial farming enterprise can cause losses in production if they:
- Are not skilled to perform their jobs
- Are not supervised
- They are not motivated
- Are not transferred frequently to other farms
Choose the correct combination:
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
1.1.4 The agricultural legislation that ensures fair, transparent and efficient financial markets is the …
- Security Services Board Act No. 36 of 2004.
- Agricultural Produce Agents Act of 1952.
- Consumer Protection Act of 2008.
- Agricultural Produce Amendment Act of 2004.
1.1.5 Some of the attributes of selling farm produce are that:
- hey are product oriented
- They emphasise consumers’ needs and satisfaction
- Cost are reduced to achieve maximum sales and profits
- Technological innovation is important
Choose the correct combination:
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i) and (iii)
1.1.6 The relationship between a change in quantity demanded and the change in supply in the diagram below is an indication of ...
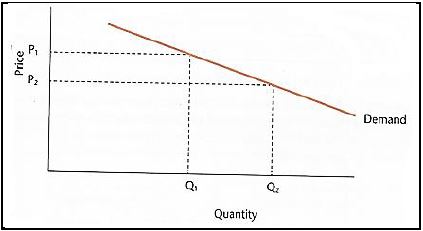 |
- elasticity of demand.
- inelastic demand.
- elasticity of supply.
- supply schedule.
1.1.7

The letter X represents …
- agricultural inputs.
- agricultural outputs.
- economies of business enterprises.
- input alternatives.
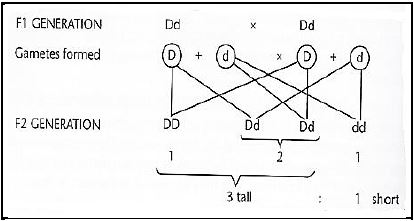
1.1.8 The percentage of the plants that are tall in the crossing below is …
- 1.1.9 An event where different buyers come together to bid on farm produce available. 25%.
- 50%.
- 75%.
- 100%.
- Cooperative farming
- Agricultural show
- Auction
- Liquidity
1.1.10 Cells that contain foreign genes that were deliberately transferred to its host are …
- somatic cells.
- transgenic cells.
- mutagenic cells.
- osteoclast cells. (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Choose a term/phrase from COLUMN B that matches a term in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–J) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 K.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.2.1 Motivation |
|
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Write the agricultural term/phrase for each of the following descriptions next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 Breeding of plants and animals that are chosen for certain desirable characteristics
1.3.2 When the price of a product settles at the point where demand is equal to supply
1.3.3 Entering into future contracts to ensure a secure market and price
1.3.4 A legally binding agreement between an employer and an employee
1.3.5 A type of mutation in which an individual has more than two whole sets of homologous chromosomes (5 x 2) (10)
1.4 Change the UNDERLINED WORD/S in the following statements to make them TRUE. Write only the appropriate word(s) next to the question number (1.4.1–1.4.5) on the ANSWER SHEET.
1.4.1 Variation is a mechanism of inheritance resulting from genes relating to sex chromosomes.
1.4.2 Capitalisation is when a business gives certain activities or functions to another business to perform on its behalf.
1.4.3 An entity’s income minus expenses for an accounting period is liabilities.
1.4.4 Items or products that are seen to not cause damage to the environment, are mass products.
1.4.5 The sequence of steps involved in transferring produce from the farm to the consumer is processing. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 The picture below shows the packaging of tomatoes on a commercial farm.
 |
2.1.1 State TWO reasons why the tomatoes are protected in boxes. (2)
2.1.2 Mention TWO important packaging information that could attract tomato buyers. (2)
2.1.3 Give ONE reason why materials used for packaging must not contain chemicals. (1)
2.2
| The connection between the price of goods and the quantity of goods supplied to the market, is known as the supply relationship. The price at which a product is eventually sold, is a reflection of both supply and demand. If prices are high, farmers and suppliers are likely to offer more goods for sale. |
2.2.1 Deduce the law of supply from the scenario in 2.2. (2)
2.2.2 State TWO factors that can affect the supply of meat in South Africa. (2)
2.2.3 State how the following factors can affect the demand of a product:
- Advertisement (2)
- Quality of a product (2)
2.3 The illustration below indicates the relationship between the demand and supply of oranges on a farm.
| Price in Rand | 5 | 10 | 15 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 45 | 50 |
| Quantity of oranges in bags | 60 | 50 | 45 | 40 | 30 | 25 | 25 | 20 |
2.3.1 Plot the information on a demand and supply curve graph. (5)
2.3.2 Determine the price at the market equilibrium. (1)
2.3.3 State ONE reason why the demand for oranges is lowest at R50. (1)
2.4
| There are various marketing channels available to move a product from the producer to the consumer. Farmers operating in a free market system will usually adopt a free marketing system that best suit their situation. |
2.4.1 Explain the concept “free marketing” to your classmate. (2)
2.4.2 Recommend TWO channels/options of free marketing to a farmer. (2)
2.4.3 State TWO disadvantages of a free marketing system. (2)
2.5 The illustration below represents the distribution of milk from a dairy farm to the consumer. 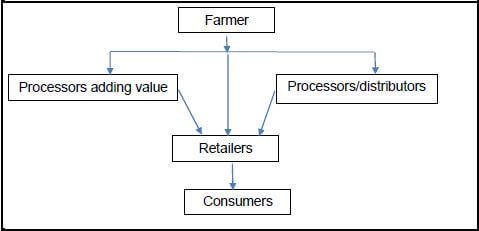
2.5.1 State THREE major marketing costs that could increase the price of the product to the consumer. (3)
2.5.2 Mention TWO major factors that can hamper the marketing of the milk by the distributer. (2)
2.5.3 Recommend TWO ways to improve and streamline the agric business chain. (2)
2.6 State TWO possible problems that may arise when compiling an agri business plan. (2)
[35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 For production of any product to take place, the following factors should be in place. Land is a permanent economic factor in agricultural science, however the availability of land for agricultural purposes is limited. 
3.1.1 Indicate the production factor that could be used as collateral from 3.1 above. (1)
3.1.2 Justify your answer to QUESTION 3.1.1 with TWO reasons. (2)
3.1.3 Explain the underlined economic characteristic of land in the scenario in 3.1. (2)
3.1.4 Name TWO other economic characteristics of land apart from the underlined one in 3.1 to the entrepreneur. (2)
3.2
| Labour can be described as the sum total of human, physical and mental effort used to create goods and services. The labour market is a pool or group of people, skilled, semi-skilled and unskilled labourers who offer their labour to the highest bidder. |
3.2.1 Tabulate the following labourers into skilled, semi-skilled and unskilled labourers:
- Unqualified mechanic
- Veterinarian
- Apple picker (3)
3.2.2 Identify the labourer in QUESTION 3.2.1 who could be the highest in demand by a livestock farmer. (1)
3.2.3 Give ONE reason to justify your answer in QUESTION 3.2.2. (1)
3.2.4 Recommend TWO methods that could improve the economic conditions of the apple picker. (2)
3.2.5 State the labour legislation that could assist an unqualified mechanic to become qualified on a commercial farm. (1)
3.3 The document below was found by a worker in the drawer of the desk of a commercial farm manager. The worker approached you with some questions to find out what the document could be.
Income | R | C | Expenditure | R | C | ||
Sales | 15 000 | 85 | Tomato seedlings | 600 | 00 | ||
Interest on credits | 250 | 07 | Fertiliser | 750 | 00 | ||
Insecticides | 370 | 30 | |||||
Harvesting | 1 350 | 45 | |||||
Storage boxes | 650 | 80 | |||||
Transport by tractor | 800 | 00 | |||||
Total | Total |
3.3.1 Mention the type of document in QUESTION 3.3. (1)
3.3.2 Give TWO reasons for your answer in QUESTION 3.3.1. (2)
3.3.3 Identify TWO types of capital mentioned in the document in QUESTION 3.3, with examples of each. (2)
3.3.4 Calculate the profit or loss of the farmer according to the document in QUESTION 3.3. (3)
3.3.5 Mention TWO sources of capital to the farm worker. (2)
3.4
 |
3.4.1 Define the concept “farm management”. (2)
3.4.2 Indicate THREE components of strategic management. (3)
3.4.3 Explain conceptual skills as used in business management skills. (2)
3.4.4 State THREE socio-cultural forces that affect agricultural enterprises. (3)
[35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1
| The illustration below is a Punnett square diagram showing the F2 generation of the dihybrid cross between a pure-breed monkey with black short hair and a pure-breed monkey with white long hair. |
Key:
S = black s = white | Q = short q = long |
| SQ | Sq | sQ | sq |
SQ | SSQQ | SSQq | SqQQ | SsQq |
Sq | SSQq | SSqq | K | Ssqq |
sQ | L | SsQq | ssQQ | ssQq |
Sq | SsQq | Ssqq | ssQq | ssqq |
4.1.1 Name the genotype represented by K in the Punnet square above. (1)
4.1.2 State the phenotype that could appear in L in the Punnet square above. (1)
4.1.3 Determine the ratio of white and long hair to all the possible phenotypes. (2)
4.1.4 Calculate the percentage of black and short hair in the phenotypes. (4)
4.2
| Some genetic traits found in animals are characterised by segregation in the classical Mundelein ratios. Others can take on a whole series of values without clear boundary lines. These characteristics are classified as qualitative or quantitative. |
4.2.1 Distinguish between qualitative and quantitative genetic characteristics of organisms. (4)
4.2.2 Categorise the following into quantitative or qualitative characteristic of a bull:
- Gender of a bull (1)
- Body size of the bull (1)
4.3
| In traditional breeding, plants and animals from an existing stock that have the desired characteristics are selected and allowed to breed. The offspring will hopefully display the characteristics required. The best offspring are then allowed to breed, until all offspring display the desired characteristics. |
4.3.1 State TWO limitations of the breeding method mentioned in the scenario. (2)
4.3.2 Mention TWO current uses of genetically modified plants in South Africa. (2)
4.4 Define the following terminologies:
- Prepotency (2)
- Pedigree selection (2)
4.5 A farmer went to an agricultural show and bought two breeds of cattle. The photos of the cattle are shown in the picture below. The cow is a Scottish breed and the bull is a Sudan Abigcer. He intends breeding the cattle on his farm.
 |
4.5.1 From the scenario, deduce the type of breeding that will take place on the farm. (1)
4.5.2 Give ONE reason for your answer to QUESTION 4.5.1. (2)
4.5.3 State THREE possible characteristics the farmer could expect from the offspring. (3)
4.5.4 Give ONE genetic terminology for the offspring. (1)
4.6
| Polygenic inheritance is mechanism of inheritance in which a genetic characteristic is controlled by many pairs of genes, instead of only a single pair of genes. The genotype aabbcc gives a milk yield of 3 000 litres. Imagine that each dominant gene adds a further 200 litres to the yield: |
4.6.1 Calculate the milk yield for the genotype aaBbcC, without using a calculator. (4)
4.7 The illustration below is one of the factors that cause mutation in genetics.
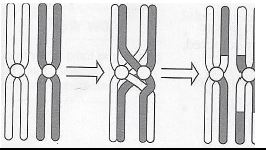 |
4.7.1 Make a prediction with regard to the process in the scenario in 4.7. (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES GRADE 12 PAPER 1 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
GRADE 12
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Read ALL the questions correctly and answer only what is asked.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Non-programmable calculators may be used.
- Show ALL your calculations, including units and formula, where applicable.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 A.
1.1.1 The process whereby the waste matter is separated and expelled from the body through the anus is known as ...
- eructation.
- ingestion.
- regurgitation.
- excretion.
1.1.2 The gross energy value of a feed minus the energy lost through manure, urine and gases:
- Digestible
- Metabolic
- Net
- Gross
1.1.3 The ratio of maize meal to sunflower meal is 22 : 7. The percentage of maize meal in this mixture is ...
- 24,1.
- 67,8.
- 75,9.
- 7,59.
1.1.4
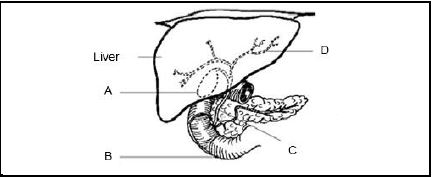 |
The fluid secreted from the part labelled A assist in digestion by …
- changing the pH from acidic to alkaline.
- promoting the absorption of fatty acids and glycerol.
- stimulating the conversion of glucose to glycogen.
- creating an alkaline medium for the functioning of enzymes.
Choose the correct combination:
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
1.1.5 A tool used in a bloodless method to castrate ONLY young animals:
- Burdizzo
- Tail docker
- Electric knife
- Elastrator
1.1.6 A supplementary feed given to young suckling animals for fast growth and high weaning weight:
- Creep
- Flush
- Finisher
- Weaner
1.1.7 Diseases that are contagious:
- Some are zoonotic
- Some are enzootic
- All virus diseases
- All are bacteria diseases
Choose the correct combination:
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
1.1.8 The membrane that grows out of the urinary system of the embryo and collects the urine from the unborn calf is the ...
- allantois.
- chorion.
- placenta.
- amnion.
1.1.9 The following statement is NOT a disadvantage of Embryo transplantation:
- It is more expensive than conventional breeding methods.
- Top genetics are introduced into a herd rapidly.
- Recipients could abort the eggs after being inseminated.
- Level of expertise is required in embryo handling procedures.
1.1.10 The spermatozoa receive nutrition from the secretion of ...
- seminal vesicles.
- Cowper's gland.
- prostate gland.
- bulbo-urethral gland. (10 × 2) (20)
1.2 Indicate whether each of the descriptions in COLUMN B applied to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A and B or NONE of the items in COLUMN A. Write A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A and B or NONE next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 B only.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
1.2.1 | A | Production ration | The feed given to an animal when it produces no product |
B | Maintenance ration | ||
1.2.2 | A | Pearson square | A method of balancing the ration to determine the required value of a particular nutrient in a feed mixture |
B | Punnet square | ||
1.2.3 | A | Marbling | The stiffness of the meat after slaughtering |
B | Rigor mortis | ||
1.2.4 | A | Thorn apple | Administer tannic acid to neutralise its effects |
B | Maize fungus | ||
1.2.5 | A | Maceration | Hardening and drying of the dead foetus after skeleton has been formed |
B | Absorption |
(5 × 2) (10)
1.3 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 A labour saving feeding approach where animals have unlimited access to feed
1.3.2 The application of an ointment to the open wound
1.3.3 A tendency by animals to come close to each other on hot days in an attempt to seek shade
1.3.4 The condition when the sexually ripe female animal shows no sign of oestrus
1.3.5 The mixture of the sperms and the fluids that are expelled during ejaculation (5 × 2) (10)
1.4 Change the underlined word(s) in each of the following statements to make it TRUE. Write only the correct word(s) next to the question number
(1.4.1–1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 Pepsin is an enzyme in the saliva of pigs that changes starch into maltose.
1.4.2 Lower critical temperature is the most suitable temperature for the animal to produce.
1.4.3 Sertoli cells are responsible for the production of testosterone in the male reproductive system.
1.4.4 Abortion is the termination of pregnancy without the visible loss of the foetus.
1.4.5 Fertilisation is the process when blastocyst attaches to the wall of the uterus. (5 × 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: ANIMAL NUTRITION
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 The pictures below show the stomach compartments in farm animal.
2.1.1 Indicate the example of an animal with the stomach compartments in the picture above. (1)
2.1.2 Identify the letter from the pictures representing the compartment where the following occurs:
- Microbial fermentation (1)
- Grinding of food (1)
- Heating rods keep the temperature constant (1)
2.1.3 Explain how the compartment labelled B is structurally suited to perform its function. (2)
2.1.4 The compartments above assist the animal to live mainly on feed with a high crude fibre content. Refer to the compartment labelled A to justify this statement. (3)
2.2 The graph below shows the feed components and their quantities that are included in a ration prepared for animals: 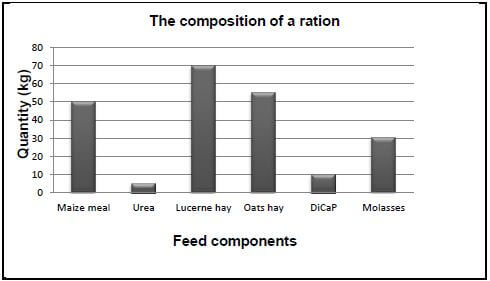
2.2.1 Indicate TWO types of roughages and give an example for each from the graph above. (4)
2.2.2 Provide the feed component that is an energy rich concentrate. (1)
2.2.3 Suggest whether the ration above can be fed to pigs. (1)
2.2.4 Give a reason for the suggestion in QUESTION 2.2.3. (2)
2.3 The table below shows the feed composition, feed intake and feed excreted by an animal in a feed trial. The animal consumed 7 kg of feed and excreted 4 kg.
FEED COMPOSITION | FEED INTAKE (%) | FEED EXCRETED (%) |
Crude protein | 5,0 | 3,0 |
Crude fiber | 78 | 73 |
2.3.1 Indicate whether the trial was done from the ruminant or non ruminant. (1)
2.3.2 Refer to the data in the table above to justify the answer in QUESTION 2.3.1. (2)
2.3.3 Calculate the amount of feed digested by an animal as a percentage. (2)
2.3.4 Explain the implication of the calculated figure in QUESTION 2.3.3. (2)
2.4 Compare roughages and concentrates with regard to the following: 2
.4.1 Crude fibre content (2)
2.4.2 Percentage of Total Digestible Nutrients (2)
2.5 The table below shows a fodder flow programme for a period of six months.
Criteria | Yield (t/ha) | Area (ha) | July (t) | Aug (t) | Sep (t) | Oct (t) | Nov (t) | Dec (t) | DM Total |
Veld supply | 5 | 26,2 | ---- | ---- | --- | 10 | 18 | 25 | |
Teff grass | 10 | 30 | 25 | 30 | |||||
Lucerne | 15 | 19,6 | 40 | 35 | 54 | 46 | 17 | 30 | |
Total feed | 40 | 35 | 54 | 56 | 60 | 85 | |||
Feed requirement | 63 | 65 | 66 | 60 | 72 | 84 |
2.5.1 Calculate the total quantity of Lucerne produced in tons. (2)
2.5.2 Identify the month with the most shortage of feed. (1)
2.5.3 Give a reason for the answer in QUESTION 2.5.2. (2)
2.5.4 Calculate the total dry matter (DM) available from October to December. (2)
[35]
QUESTION 3: ANIMAL PRODUCTION, PROTECTION AND CONTROL
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 The pictures below illustrate animal production systems commonly used by farmers. 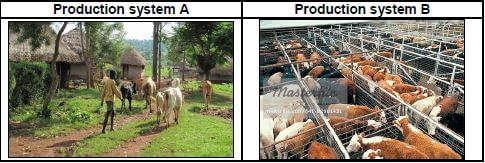
3.1.1 Identify the animal production systems labelled A and B. (2)
3.1.2 Give a reason visible in the pictures for identified production systems in QUESTION 3.1.1. (2)
3.1.3 Link each of the production system in QUESTION 3.1.1 with a farming system. (2)
3.1.4 Name TWO factors a farmer can put in place to ensure the increased production in picture B. (2)
3.2 The picture below shows the handling facility used to handle farm animals. 
3.2.1 Identify the facility in the picture above. (1)
3.2.2 Name TWO possible reasons for handling sheep in a facility illustrated in the picture above. (2)
3.2.3 State TWO features of the facility above to ensure that the animals are not injured. (2)
3.3 There are basic guidelines stipulated when transporting animals from farm to farm. Indicate the guideline stipulated when transporting animals under the following:
3.3.1 To alert motorists about animals on the road (1)
3.3.2 To avoid suspicion by police that the animals transported are stolen (1)
3.3.3 To ensure easy loading and offloading of animals in a truck (1)
3.4 The table below show diseases affecting farm animals, their symptoms and mode of transmission.
Disease | Pathogenic organism | Main symptom | Vector transmitting the disease |
Mastitis | A | Udder inflammation | Flies |
Foot-and-mouth disease | Virus | B | ---- |
Heartwater | C | Nervousness, frothy from the mouth and nose | D |
E | Fungus | Hair loss, itchy grey white scabs | Flies |
3.4.1 Complete the table by filling the missing information from A to E. (Do not redraw the table, just write the correct answer for A to E) (5)
3.4.2 Farmers are required to report to government authorities some diseases once they are detected. Give a term referring to those diseases. (1)
3.4.3 Identify the disease from the table above that needs to be reported once detected. (1)
3.4.4 Indicate TWO measures the State can take to control further spread of the disease in QUESTION 3.4.3 once it has been reported. (2)
3.5 The illustration below shows the lifecycle of a parasite affecting farm animals. 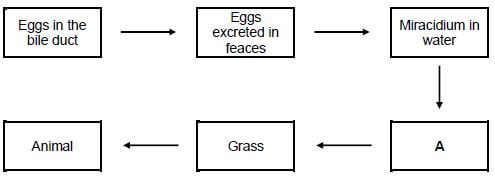
3.5.1 Classify the parasite illustrated above. (1)
3.5.2 Give the name of the parasite classified in QUESTION 3.5.1. (1)
3.5.3 The parasite illustrated above need an intermediate host to complete its life cycle. Name the intermediate host in label A. (1)
3.5.4 Indicate how the animal get infested by the parasite in QUESTION 3.5.2. (1)
3.5.5 Indicate the metabolic disease caused by the parasite on animal. (1)
3.5.6 Suggest TWO management practices that the farmer can put in place to control the parasite infestation on pasture. (2)
3.6 Salt is one of the essential minerals needed by animals but the consumption of large amount can be fatal to livestock.
3.6.1 Indicate ONE symptom of salt poisoning. (1)
3.6.2 Suggest TWO measures the farmer can take to treat animals with salt poisoning. (2)
[35]
QUESTION 4: ANIMAL REPRODUCTION
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 The diagram below illustrates the development of twins in a cow.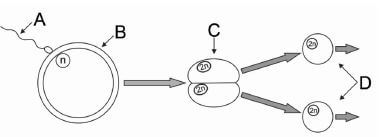
4.1.1 Identify the type of multiple birth illustrated in the diagram above. (1)
4.1.2 Give a reason for the answer in QUESTION 4.1.1. (1)
4.1.3 Indicate TWO characteristics of the twins illustrated in the diagram with regard to:
- Gender (1)
- Physical appearance (1)
4.1.4 Indicate an enzyme released by the sperm cell to facilitate its penetration in part B. (1)
4.1.5 Name the stage of gestation during which part C is formed. (1)
4.2 The graph below shows the number of cows in oestrus during different time periods.
4.2.1 Translate the data from the graph above to a table. (6)
4.2.2 Suggest the appropriate time to inseminate 10 cows. (1)
4.2.3 Give a reason for the answer in QUESTION 4.2.1. (2)
4.3 During the process of oogenesis and spermatogenesis, the cells undergo mitosis and meiosis, but these divisions give rise to different cells. Differentiate between oogenesis and spermatogenesis with regard to the following:
4.3.1 Cells formed during mitosis (2)
4.3.2 Cells formed during meiosis 2 (2)
4.3.3 Organs where they are formed (2)
4.4 After the process of spermatogenesis has been completed, sperms move through various primary and secondary organs until they reach the mating organ. Indicate the organ responsible for each of the following functions.
4.4.1 Transports sperms from the epididymis to the urethra (1)
4.4.2 Secretes a sticky alkaline mucus that gives semen a characteristic smell (1)
4.4.3 Secretes a buffer that protects sperms against pH changes (1)
4.5 Difficult birth is a challenge for farmers but can be corrected in some cases by proper management:
4.5.1 Give the term referring to the condition above. (1)
4.5.2 Indicate TWO reasons leading to the condition in QUESTION 4.5.1. (2)
4.6 The illustration below show processes occurring during a reproductive technique in female animals. 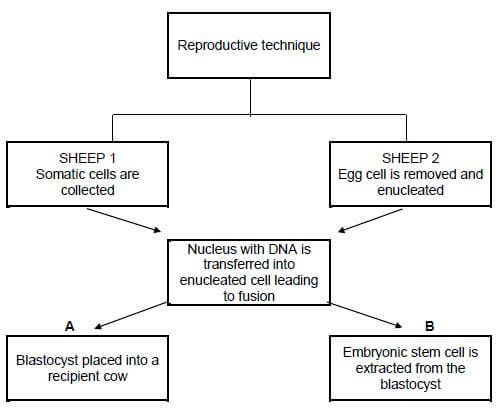
4.6.1 Identify the reproductive technique illustrated above. (1)
4.6.2 Indicate an appropriate name given to an animal represented by sheep 1 and sheep 2. (2)
4.6.3 There are TWO main types of the technique mentioned in QUESTION 4.6.1. Indicate these main types as labelled in A and B. (2)
4.6.4 Indicate the purpose for which the technique labelled B is done. (1)
4.6.5 The technique in A has an economic benefit for the farmer. Validate this statement by mentioning TWO economic benefits of this technique to the farmer. (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
COMPUTER APPLICATIONS TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 PAPER 1 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
COMPUTER APPLICATIONS TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Owing to the nature of this three-hour examination, it is important to note that you will NOT be permitted to leave the examination room before the end of the examination period.
- Insert your surname and name in the header of EVERY document that you create or save.
- The invigilator will give you a disk containing all the files needed for the examination OR you will be told where the files can be found on the network or computer. If a disk has been issued to you, you must write your centre number and examination number on the label. If you are working on the network, you must follow the instructions provided by the invigilator.
- A copy of the master files will be available from the invigilator. Should there be any problems with a file, you may request another copy from the invigilator.
- This question paper consists of SEVEN questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Ensure that you save EACH document using the file name given in the question paper. Save your work at regular intervals as a precaution against possible power failures.
- Read through each question before answering or solving the problem. Do NOT do more than required by the question.
- At the end of the examination you must hand in the disk given to you by the invigilator with ALL the files saved on the disk, OR you should make sure that ALL the files are saved on the network/computer as explained to you by the invigilator/teacher. Make absolutely sure that all files can be read.
- During the examination you may make use of the help functions of the programs which you are using. You may NOT use any other resource material.
- If data is derived from a previous question that you cannot answer, you should still proceed with the questions that follow.
- Unless instructed otherwise, you must use formulae and/or functions for ALL calculations in questions involving spreadsheets. Use absolute cell references only where necessary to ensure that formulae are correct when you copy them to other cells in a spreadsheet.
- In ALL questions involving word processing, you should set the language to English (South Africa). The paper size is assumed to be A4 Portrait, unless instructed otherwise.
- In Annexure A the HTML tag sheet is provided.
- The examination folder/data disk that you receive with this question paper will contain the folder and files listed below. Ensure that you have the folder and all the files before you begin this examination.
QUESTIONS
SCENARIO
Turtles are found throughout most of the temperate and tropical world and in the open ocean. 42% of the 270-known species are rare or threatened with extinction. Many turtles and their eggs are valued as food. Edible species include several marine turtles, the green turtle (traditional ingredient of turtle soup), the diamondback terrapin and the soft-shelled turtle. Catching females when they lay eggs on land has contributed to a serious decline in many species, since it can take 10 to 30 years for some turtles to reach sexual maturity. |
QUESTION 1 WORD PROCESSING
A document was created to give some basic facts about Sea Turtles. Open the 1_Turtle Facts word processing document.
1.1 Set the left-hand and bottom margins of the document to 1.5 cm. (1)
1.2 This document has a cover page. Make the following changes to the cover page.
1.2.1 Add the heading “Save The Sea Turtles” in the Title control on the cover page. (1)
1.2.2 Locate the AutoShape on the cover page:
- Fill the AutoShape with the image 1_Save The Turtle (1)
- Ensure that the height and width is exactly 8 cm (2)
1.3 Apply a condensed spacing of 1.5 pt for the heading "BASIC FACTS ABOUT SEA TURTLES” on page 3. (2)
1.4 Locate the highlighted letter “S” on page 3.
- Add a drop cap effect for the letter “S” to drop over 4 lines
- Distance from the text is 0.5 cm (2)
1.5 Modify the existing style Sub Turtle so that the paragraph shading appears in yellow and that all text in this style will be formatted to update automatically. (2)
1.6 Locate the four paragraphs (highlighted in green) under the heading Reproduction and do the following:
- Place them in 2 columns with a line in between
- The spacing between the columns should be 1.5 cm
- The first paragraph should be in the first column and the other three paragraphs should be in the second column (3)
1.7 Apply any glow effect to the text box containing the tip “Did you know?...” on page 5. (1)
1.8 Locate the footnote on page 6 that’s added to the word mating and make the following changes:
- Convert the footnote to an endnote
- Change the endnote symbol to a ‘ * ’ symbol (2)
1.9 A table representing the population status of different turtle species is listed on page 7 of the document. Alter the table so that:
- The spacing between the cells is 0.5 cm (1)
- Insert a function in the highlighted area (replace the highlighted region) to determine how many turtle species are listed under the population status (2)
1.10 Apply multilevel bullets to the Glossary listed on page 8 as shown below:
- Use Bullet 1.jpg as the first level
- Bullet 2.jpg as the second level

1.11 Edit the bibliography inserted on page 8 to include:
- The month the website was updated is August and not February (1)
- Include a comment that reads “Save Sea Turtles” (1)
NB: Make sure to display the updated contents in the bibliography.
1.12 Change the orientation of only the last 2 pages to landscape. (1)
1.13 Locate the table displayed on the last 2 pages of the document and do the following:
- Change the outer border of the table to dashed line and 4½ pt thickness (2)
- Insert a caption for the image displayed next to “Green Sea Turtle” so that it reads “Figure 1: Green Sea Turtle” (1)
NB: Update the table of figures so that the caption for Figure 1 is included as well.
1.14 Add automatic page numbering to the last 2 pages of the document as follows:
- Place the page numbers in the page header in any format (1)
- Ensure that page number restarts from 1 onwards (2)
1.15 Create a hyperlink to the word <<TOP OF THE DOCUMENT >> found on the last page so that the link is created to the top of the document. (2)
1.16 Insert a watermark on the cover page only that reads Billion Baby Turtles. (2)
[36]
QUESTION 2 WORD PROCESSING
An observation form was created in Word for people to fill in information about Sea Turtles if they come across any during their visit to the seashore or any other place.
Open the 2_Observation Form word processing document.
2.1 Insert a paragraph shading to the heading "Sea Turtle Observation Form” with any shade of green. (2)
2.2 Format the text form field for the heading “How many turtles…” so that:
- The maximum length is 2
- It does not display any decimals (2)
2.3 Edit the drop down form next to “What was the health condition…” field so that:
- The option “Select One Below” is added (1)
- Appear as the first option in the list (1)
2.4 Format the date field next to “Date Of Observation” so that the date will be displayed in d MMMM yyyy format. (1)
2.5 Crop the image shown in the document so that it resembles image/picture below. 
2.6 Add a help text to the “Cell No” field so that it reads “Please Enter only 10 Digits”. (2)
2.7 Set and apply a 14 cm right aligned solid leader tab after the headings “Name, Surname and Address” after the heading “Contact Details" to resemble like shown below: 
2.8 Locate the email address This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. shown on the last line of the document. Use a feature in Word to display the message “Help Us To Save SEA Turtles” when you move your mouse pointer on to the email address. (2)
[14]
QUESTION 3 SPREADSHEET
A spreadsheet file containing the different ongoing campaigns to save the Sea Turtles has been stored in the 3_Turtle Campaign spreadsheet.
Open the 3_Turtle Campaign spreadsheet and work in the Info worksheet.
3.1 Insert today’s date in cell H1 in the format dd mmm YY. (1)
3.2 Merge and centre the cells A1 to G2. (1)
3.3 Insert a thick border on the left and right side of each cell from A3 to O3.
NB: The top and the bottom borders remains the same as shown below.
3.4 Freeze row 3. (1)
3.5 Use suitable text functions to create a member code in cell A4.
The code is created by combining the following:
- Whole contents of Name field
- Followed by the length of the Membership Status field
- Followed by the text ‘#code’
Example: The member code for 'Jacob' will be Jacob4#code. (5)
3.6 The membership status is given to the members based on the years of service that each member has under their respective campaign.
Insert a function/formula in cell H4 to determine the Years Of Service since he/she joined the campaign using the column G (Active Member Since) and cell H1, rounded up to no decimal place. (6)
3.7 The management has conducted an annual fundraising for its members. The amount to be paid individually for each fundraising event is displayed in cells I2:M2.
Use a formula/function in cell N20 to find the total amount raised by James as a member during the fundraising event. (3)
3.8 Apply conditional formatting to the Amount Raised values given in column N.
- Only amount raised between R 200 and R 250 should be shaded
- Apply any 2 colour shading of your choice (3)
3.9 The management is planning on rewarding the members for their effort and help that they have offered for conserving the Sea Turtles.
The reward is decided after finding the difference between the target amount for adopting a turtle hatchling (cell P1) and the amount raised by the members displayed in column N. Use a function in cell O4 to find the type of reward for Jacob.
NB: Find the difference in the same calculation and make use of cell referencing wherever necessary.
| Reward | |
| If the difference is 0 or less | Adoption Cert |
| If the difference is between 1 and 100 | - |
| If the difference is more than 100 | Participation Cert |
Copy the function you added in cell O4 to cells O5:O49. Ensure that it works correctly. (6)
3.10 Calculate in cell E51, the total amount raised by all the platinum members. (4)
3.11 Calculate the number of members who belong to SEE Turtles Campaign, in cell E52. (3)
3.12 Calculate the average age of all the female members in cell E53. (4)
3.13 Use a function or combination of functions in cell E54 to find the number of Members who did not participate in Sea Turtle Garden Flag and Turtle Goodies event. (3)
Work in the Spotted worksheet.
3.14 The management would like to find the name of the turtle spotted by the different members who came for the event.
Use the LOOKUP function in cell B2 on the Spotted worksheet together with the LOOKUP worksheet to display the name of the turtle spotted by the member Jacob. (5)
Work in the Graph worksheet.
3.15 Change the graph to appear as follows:
NOTE:
- Include the data set for the year 2014 in the graph
- Make the series overlap at -50°
- Display the x-axis name as shown in the screenshot above
- Display the data labels at the top of each bar
- Set the minimum value of the y-axis to be 5 (5)
[52]
QUESTION 4 DATABASE
A database was created showing the different classifications and other features of Turtles.
Open the 4_Turtle Classification database.
4.1 Format the Classification table as follows:
4.1.1 Change the row height to the standard height (1)
4.1.2 Ensure that gridlines are changed to red colour (1)
4.1.3 Edit the value list for the Listed As field so that the option Threatened will be listed as the third option (2)
4.1.4 Change the data type of Diet field to a more appropriate type (1)
4.1.5 Ensure that the Scientific Name field is not left empty and is displayed in uppercase even if it is typed in lowercase (2)
4.1.6 Create an input mask on the Turtle ID field to ensure that the user inserts a code made up as follows:
- One compulsory letter
- Followed by two compulsory numbers
- Followed by an asterisk (*)
- Followed by an optional digit or space
- Then an optional letter or digit
Example: L78*1K or j89* K or k78*16 can be entered (5)
4.2 Work with the Turtle Images table and the frm4_2 form.
4.2.1 The form frm4_2 was created to include the images of the six turtles in the form. Unfortunately the image for the Green Sea Turtle was not displayed. Make the necessary changes in the Turtle Images table so that the image Green sea turtle.jpg will be displayed in the form. (2)
4.2.2 Export the Turtle images table as a PDF file and save it in the examination folder as Export4_2. (2)
4.3 Open the query qry4_3. Display only the records where:
- The total species is 399 or less
- Whose diet contains jelly fish and crab (4)
4.4 Create a query called qry4_4 based on the Classification table.
- Display only the Turtle Name and Colour
- Insert a calculated field called Weight in pounds, which is calculated by dividing the weight in kilogram by 2.2046
- Use a function to round off the answer to one decimal place
- The starting letter of the turtle name should be between G and O and sorted in the ascending order of their names (7)
4.5 Open the form frm4_5 and make the following changes:
- Add a border width of 4pt and a shadow effect to the image in the form header
- Insert a command button in the form footer to exit the form
- Ensure that the dividing lines are not visible
- Make the default view of the form to be continuous (6)
4.6 Create a report called rpt4_6 based on the Classification table so that it resembles as follows:
- Display only the fields Turtle Name, Turtle ID, Colour, Weight (in kg) & Listed As
- Group the records based on the Weight (in kg) field and set the grouping intervals to 50s
- Ensure that the page number does not display on the first page
- Add a calculation in the report footer to count the number of Critically Endangered turtles. Make sure a proper label is given for the calculation (9)
[42]
QUESTION 5 WEB DESIGN (HTML)
A web page has been created to give some people facts about the most endangered turtle species, the threats faced by them and the ways to save the turtles.
Open the incomplete 5_Save Us web page in a web browser and also in a text/HTML editor for e.g. Notepad (NOT a word processing program such as Word).
NOTE:
- Question numbers are inserted as comments in the coding as guidelines to show approximately where the answer(s) should be inserted.
- An HTML tag sheet has been attached for reference.
Your final web page should look like the example below.
5.1 Add the HTML code so that the text Save Sea Turtles appear in the browser tab. (2)
5.2 Change the size of the horizontal lines that comes within the heading “7 Things You Can Do To Save Sea Turtles” to 6. (1)
5.3 Insert the image Baby Turtle found in the exam folder after the heading “7 Things You…” so that the width and the height of the image is 100 and 45 percent and the text “Baby Turtle” to display if the image does not display in the browser. (5)
5.4 Change the word SEVEN in the first paragraph to bold. (1)
5.5 Change the unordered list displayed after the first paragraph to a square pattern. (2)
5.6 Change the heading “Most Endangered…” so that it becomes the heading for the whole table as shown in the screenshot. (3)
5.7 Make the following changes to the second row of the table containing the headings Turtle Name and Scientific name so that:
- The row colour is green
- The font colour is white for both the headings (2)
5.8 Insert a caption at the end of the table displayed in the webpage so that it displays “Table 1: List Of Endangered Turtle Species” as shown in screenshot (centred). (3)
5.9 Correct the hyperlink tag created to the word SEETurtles.org found in the last paragraph so that it links to the www.SEETURTLES.ORG website. (1)
[20]
QUESTION 6 GENERAL
Open the 6_Spotted By & Scientific Info spreadsheet and work in the Spotted By & Scientific Info worksheet.
6.1 Hide the worksheets 2 and 3 as it is no longer needed. (1)
6.2 Column D contains the name of the different turtles. Replace all the occurrences of the word turtle with uppercase TURTLE.
NB: Any method can be used. (2)
6.3 Column B contains the name of the person who spotted different turtles. Use any appropriate method to find the name that is not repeated the second time.
Enter the name of the person in cell G3. (2)
6.4 Sort the contents of the worksheet first by Scientific Name in the descending order and then by Spotted By in the ascending order. Write down the name of the turtle in the first row of the worksheet after the sorting is done in cell G9. (3)
6.5 Protect the cells A1:D1 with the password 2017. Ensure that only these four cells are protected. (2)
[10]
QUESTION 7 INTEGRATION
The name of the adoption certificate winners are stored in the 7_Winners List spreadsheet, in the Winners worksheet.
7.1 Create a mail merge as follows:
- Link the document 7_Certificate to the Winners worksheet in the 7_Winners List spreadsheet file.
- Link the placeholders shaded in yellow to the appropriate fields.
- Only the platinum members with an adoption certificate should receive the certificates. (4)
DO NOT complete the merge yet.
Save the document 7_Certificate. - Complete the merge and save the merged document in your examination folder as 7_CertificateMerged. (2)
[6]
TOTAL: 180
ANNEXURE A – HTML TAG SHEET
Basic Tags | |
Tag | Description |
<body></body> | Defines the body of the web page |
<body | Sets the background colour of the web page |
<body text="black"> | Sets the colour of the body text |
<head></head> | Contains information about the document |
<html></html> | Creates an HTML document – starts and ends a web page |
<title></title> | Defines a title for the document |
<!-- --> | Comment |
Text Tags | |
Tag | Description |
<hl></hl> | Creates the largest heading |
<h6></h6> | Creates the smallest heading |
<b></b> | Creates bold text |
<i></i> | Creates italic text |
<font size="3"></font> | Sets size of font, from "1" to "7" |
<font color="green"></font> | Sets font colour |
<font face="Times New Roman"></font> | Sets font type |
Link Tags | |
Tag | |
<a href="/URL"></a> | Creates a hyperlink |
<a href="/URL"><img src="URL"></a> | Creates an image link |
<a name="NAME"></a> | Creates a target location |
<a href="#NAME"></a> | Links to a target location created somewhere else in the document |
Formatting Tags | |
Tag | |
<p></p> | Creates a new paragraph |
<p align="left"> | Aligns a paragraph to the "left" (default), can also be "right", or "center" |
<br/> | Inserts a line break |
<ol></ol> | Creates a numbered list |
<ol type="A","a", "I","i","1"></ol> | Defines the type of numbering used |
<ul></ul> | Creates a bulleted list |
<ul type="disc", "square","circle"></ ul> | Defines the type of bullets used |
Formatting Tags continued | |
Tag | Description |
<li></li> | Inserted before each list item, and adds a number or symbol depending upon the type of list selected |
<img src="/name"> | Adds an image |
<img src="/name" align="left"> | Aligns an image: can also be "right", "center"; "bottom", "top", "middle" |
<img src="/name" border="1"> | Sets size of border around an image |
<img src="/name" width="200" height ="200"> | Sets the height and width of an image |
<img src="/name" alt="alternative text"> | Displays alternative text when the mouse hovers over the image or when the image is not found |
<hr/> | Inserts a horizontal line |
<hr size="3"/> | Sets size (height) of line |
<hr width="80%"/> | Sets width of line, in percentage or absolute value |
<hr color="ff0000"/> | Sets the colour of the line |
Table Tags | |
Tag | Description |
<table></table> | Creates a table |
<tr></tr> | Creates a row in a table |
<td></td> | Creates a cell in a table |
<th></th> | Creates a table header (a cell with bold, centered text) |
<table width="50"> | Sets the width of the table |
<table border="1"> | Sets the width of the border around the table cells |
<table cellspacing="1"> | Sets the space between the table cells |
<table cellpadding="1"> | Sets the space between a cell border and its contents |
<tr align="left"> | Sets the alignment for cell(s) (can also be "center" or "right") |
<tr valign="top"> | Sets the vertical alignment for cell(s) (can also be "middle" or "bottom") |
<td colspan="2"> | Sets the number of columns a cell should span |
<td rowspan="4"> | Sets the number of rows a cell should span |
COMPUTER APPLICATIONS TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 PAPER 2 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
COMPUTER APPLICATIONS TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of:
SECTION A (25 marks)
SECTION B (75 marks)
SECTION C (50 marks) - Answer ALL the questions.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Do NOT write in the right-hand margin.
- Leave a line between each sub-question.
- In general, one mark is allocated per fact. A 2-mark question would therefore require TWO facts, et cetera.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1: MATCHING ITEMS
Choose a term/concept from COLUMN B that best matches a description in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–P) next to the question number (1.1–1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.11 Q.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.1 A test to determine whether it is a human being interacting with the computer |
|
(10 x 1) [10]
QUESTION 2: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Various options have been provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the most appropriate answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (2.1–2.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 2.11 E.
2.1 The technology that is used to get information from different websites automatically, is called …
- RSI.
- EULA.
- RSS.
- FAT. (1)
2.2 Which ONE of the following would be the most suitable for creating a library management system?
- Word processor
- Database
- Spreadsheet
- Presentation program (1)
2.3 Which ONE of the following Internet websites does NOT require a password, user name and/or pin code in order to use its functions?
- Internet banking site
- Wikipedia (1)
2.4 Many libraries save money by installing and using inexpensive networked computers known as thin client computers. What main computer part do these thin client computers often NOT have?
- Motherboard
- Hard drive
- Power supply
- RAM (1)
2.5 The school library promotes green computing. Which ONE of the following is NOT directly associated with green computing?
- Recycling paper
- Sleep mode
- Security webcam
- Paperless office (1)
2.6 A learner did a Google web search and found information on a web page. Which ONE of the following would be the best option for the bibliography?
- Gates, Bill. The future of technology. http://microsoft.gates.htm. Accessed 20 October 2016.
- Gates, Bill. The future of technology.
- http://microsoft.gates.htm. Gates, Bill. The future of technology. (1)
2.7 A public location where wireless Internet access can be obtained for mobile computers is called a ...
- Wi-Fi.
- Hot spot.
- MySpace.
- Cyber café. (1)
2.8 A code in Access which forces data capturers to enter data in a specific format is known as a ...
- validation rule.
- primary key.
- input mask.
- validation text. (1)
2.9 Which ONE of the following specifications is the most likely to indicate that a computer is a notebook?
- 1 TB HDD
- Touchpad
- Windows 10 Home (64 bit)
- USB 3.0 (1)
2.10 Which ONE of the following components forms an integral part of the motherboard?
- DIMM slots
- DVD-ROM
- USB drivers
- HDD (1)
[10]
QUESTION 3: TRUE/FALSE
Indicate whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Choose the answer and wrtie ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the question number (3.1–3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK. Correct the statement if it is FALSE. Change the underlined word(s) to make the statement TRUE. (You may not simply use the word ‘NOT’ to change the statement. NO mark will be awarded if only FALSE is written down.)
EXAMPLES:
QUESTION | ANSWER |
Google is the world’s most popular search engine. | True |
An NIC has slots for hardware components such as the CPU. | False − motherboard |
3.1 File sharing is a system whereby the resources of different computers are shared and used at the same time to solve a single problem. (1)
3.2 Aspect ratio is the number of steps between the darkest black and the brightest white that a display device can produce. (1)
3.3 A patch is a collection of software updates over the past period of time put into one big unit for easier installation. (1)
3.4 DOTX is the file extension for a Microsoft Word Template. (1)
3.5 A switch is a network device used to connect two or more networks to each other. (1)
[5]
TOTAL SECTION A: 25
SECTION B
QUESTION 4: SYSTEM TECHNOLOGIES
4.1 The managers at Spar were given a choice to use one of the following two devices to perform their tasks during the countrywide Angry Birds competition.
DEVICE | SPECIFICATIONS |
Laptop |
|
Tablet |
|
4.1.1 Give TWO reasons why the managers requested to be issued with the laptop rather than the tablet. (2)
4.2 A tablet uses an SSD for the storage of data and files.
4.2.1 What does the acronym SSD stand for? (1)
4.2.2 List THREE comparative differences between the features and performance of an SSD and an HDD in table format. (3)
4.2.3 Why have SSDs not completely replaced HDDs, even though they have so many benefits? Do NOT refer to cost in your answer. (1)
4.3 Both a tablet and a laptop use cache memory. Explain the purpose of cache memory in a computer system. (3)
4.4 Give TWO reasons why a tablet and a laptop cannot use the same type of RAM. (2)
4.5 The managers have been told that they can use FireWire 800 or USB 3.0 to upload video material of the performances of contestants to the competition’s website.
4.5.1 State TWO advantages of USB over FireWire. (2)
4.5.2 Would the software used for the editing of videos be considered application software or system software? (1)
4.6 Cellular modems are used to connect to the Internet and upload the results of the competition each week. The results are stored in a ‘cloud’.
4.6.1 Name the type of connection the modem will use with the uploading of the results. (1)
4.6.2 Explain what is meant by the term cloud in this context. (2)
4.7 Each week the managers have a group conference call to discuss results and some of the outstanding performances. It is suggested that they use VoIP in order to save costs.
4.7.1 Briefly explain the basic concept VoIP. (2)
4.7.2 Name a VoIP client that the managers could use to host the conference call. (1)
4.7.3 Name ONE other way (besides a conference call), in which the managers could have discussions and collaborate online. (1)
4.8 Identify the image below that appears on Spar’s newsletter AND explain how it would be used, by referring to a suitable example.  (3)
(3)
[25]
QUESTION 5: INTERNET AND NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES
5.1 Friends and family of the contestants requested the managers to e-mail them the video footage as an attachment. Give TWO reasons why this request is possibly not feasible. (2)
5.2 The managers made the videos available as podcasts.
5.2.1 Explain the concept of podcasting. (1)
5.2.2 Name TWO examples of an electronic medium that can be used to inform friends and family when a new podcast is available. (2)
5.3 Friends and family who want to download multimedia files of all the events, must preferably have a broadband Internet connection.
5.3.1 Explain the term broadband. (1)
5.3.2 ADSL is an example of a wired broadband connection.
- Is ADSL a digital or an analogue connection? (1)
- Give an example of another wired broadband connection. (1)
5.4 One of the managers is not familiar with using e-mail and has a few questions regarding the e-mail window.
5.4.1 What is the function of the paperclip icon next to the “send” icon? (1)
5.4.2 He noticed that there is an option between Plain Text and Rich Text. Explain the difference between these two options. (2)
5.5 How does a social network such as Facebook make most of its money? (1)
5.6 Explain TWO advantages of e-books compared to printed versions of books. (NOTE: Cost factors should NOT form part of your answer.) (2)
5.7 What is the purpose of the ‘History’ button or tab in a web browser? (1)
[15]
QUESTION 6: INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
6.1 The regional manager of Spar has to coordinate a number of meetings with local Spar managers regarding the competition. He has found that there is a great deal of administration involved regarding the competition and that it is quite difficult to set up these meetings.
6.1.1 Mention TWO ways an e-mail calendar function will help in this context. (2)
6.1.2 The manager finds that he often has to scribble reminders of tasks on slips of paper.
Give the general or generic name given to the e-mail function that can be used to remind the user of tasks and the due dates of these tasks. (1)
6.2 State TWO advantages of using electronic forms when gathering data in a survey. (2)
6.3 Give ONE reason for using a table on a form to fill in numbers, such as an ID number, as shown below. (1)
6.4 State ONE feature of a spreadsheet that can be used to meaningfully arrange large quantities of data. (1)
6.5 Give TWO examples where you would use a database instead of a spreadsheet to process data. (2)
6.6 Briefly explain the concept of plagiarism. (1)
[10]
QUESTION 7: SOCIAL IMPLICATONS
7.1 Name ONE legally acceptable use of a file-sharing application, such as BitTorrent. (1)
7.2 Give your opinion regarding the following statement by giving TWO reasons or examples to support your answer:
'The Internet offers its users some privacy.' (2)
7.3 Many cameras have the capability to ‘geotag’ photographs.
7.3.1 Explain the term geotagging. (1)
7.3.2 Why do some game reserves discourage visitors from placing geotagged photographs of rhinos on social media? (1)
7.4 State ONE possible way of preventing other users from tagging you in photographs on Facebook. (1)
7.5 State TWO advantages of cars that are connected to the Internet. (2)
7.6 State TWO typical ways in which your computer may be misused by cybercriminals, if they use your computer as part of their botnet. (2)
[10]
QUESTION 8: SOLUTION DEVELOPMENT
8.1 Some of the learners in your school are planning a field trip to a book fair. Below is a spreadsheet of their budget.
8.1.1 In the calculation for the Total cost for transport, in cell C4, the formula was: =B4*$E$1. The formula was then copied down (Autofill) for the other items.
Name the TWO types of cell references used in the formula and explain the difference between the two. (4)
8.1.2 When the data was formatted for currency, the $-sign appeared instead of the R-sign. Explain TWO ways in which this can be corrected. (2)
8.1.3 The pie chart represents the breakdown of costs for each learner for the field trip. Name THREE items that should be added to the pie chart, to make it meaningful and easy to interpret. (3)
8.2 Many modern businesses make use of databases.
8.2.1 Indicate in which section the function =Count(*) must be placed in a database report, in order to count the number of records for each group of records in the report. (1)
8.2.2 Identify the type of database object in which you are likely to find the formula below. Total:[Price]*[Quantity] (1)
8.2.3 The database formula VAT:[Price*0.14] currently produces an error. Correct the formula for it to work properly. (1)
8.3 What is a citation in a document and when should it be used? (2)
8.4 Name the word processing feature that must first be used or applied, before an automatic table of contents will work. (1)
[15]
TOTAL SECTION B: 75
SECTION C
QUESTION 9: INTEGRATED SCENARIO
| During the final round of the Idols competition the audience in the State Theatre votes for contestants to determine a winner. They have been provided with remote voting controllers that allow them to press a button to transmit their vote wirelessly via Bluetooth technology to a local server at the Theatre. |
9.1 Is Bluetooth a suitable technology to use in this scenario? Motivate your answer. (2)
9.2 A member’s voting controller does not connect to the wireless network, although the member is within range of the server. Name TWO troubleshooting steps that can be followed to solve the problem. Replacing the voting controller is not an option. (2)
9.3 The live broadcast of the final round of the event can be streamed.
9.3.1 Explain what is meant by streamed. (2)
9.3.2 Name TWO components that are required to be able to stream a live event. (2)
9.3.3 State ONE potential disadvantage of using live streaming. (1)
9.3.4 Which type of software can be used for input by visually impaired users? (1)
9.4 A cabled network is used at the event theatre to transmit the scores electronically to the server. The organisers are planning to use a wireless network for this purpose in future.
9.4.1 State TWO advantages of a wireless network over a cabled network. (2)
9.4.2 State TWO additional hardware components that are required to create the wireless network. (2)
9.4.3 Which upgraded version of Wi-Fi will be suitable to use for the wireless network? (1)
9.4.4 Give TWO examples of what NFC (near field communication) can be used for. (2)
9.4.5 Describe TWO ways in which the organisers can prevent their computers from being accessed by unauthorised software. (2)
9.4.6 What is the function of a driver? (1)
9.5 ICT provides more effective solutions for the capturing of data and generating results than a paper-based voting system.
9.5.1 Motivate why the above statement is valid by referring to the following TWO aspects:
- Faster and improved data processing (2)
- Improved data storage (2)
[24]
QUESTION 10
The organisers of the Idols competition will be responsible for the accuracy of all information, as well as to create surveys.
10.1 Explain the difference between a survey and an interview. (2)
10.2 Give TWO reasons why one should always check the reliability and accuracy of information found on the Internet. (2)
10.3 Explain what information overload is. (1)
10.4 Which social networking service is associated with the term ‘hash-tags’? (1)
10.5 One of the organisers received the following e-mail, which was supposedly sent by an official at Empire Bank. Examine the e-mail carefully and answer the questions below.
From: Empire Bank [mailto:This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.] This e-mail was sent by the Empire Bank server to verify your e-mail address. You must complete this process by clicking on the link below and entering in the small window your Empire Bank and Password. Click here to update your data. |
10.5.1 What general name is given to this kind of scam? (1)
10.5.2 Should the organiser click on the link? Motivate your answer by explaining what would happen if he did. (2)
10.5.3 What is the generic name given to techniques that rely on convincing people to give out information or to grant access by pretending to be someone who has the right to access this information? (1)
10.5.4 Banks offer their online banking clients peace of mind by providing a number of security measures designed to make online banking as safe as possible.
Give TWO of these measures, besides the use of encryption. (2)
10.5.5 Briefly explain what a computer virus is by referring to TWO of its general aims in your answer. (2)
10.5.6 What is a Trojan? (2)
10.6 The organiser of the Idols has tried to create a basic website to advertise the event for next year. Study the HTML code below.
<title> Idols <hr /> </title> <body> <h1> DATES FOR THE IDOLS AUDITIONS </h1> <font colour=”red”> </font> <br /> Auditions kick off in Cape Town! </body> |
Explain how you would correct the following mistakes:
10.6.1 The horizontal line is not displayed. (1)
10.6.2 The heading ‘DATES FOR THE IDOLS AUDITIONS’ should be smaller. (1)
10.6.3 The text ‘Auditions kick off in Cape Town!’ should be displayed in red font, but it is displayed in black. (1)
10.7 A database was created to keep track of the current entries for the competition.
10.7.1 Study the screenshot below and name the data type that should be used for the Specifications field to enter a large amount of text.
10.7.2 Why is the AutoNumber data type always suitable to use for a primary key field? (1)
10.7.3 The query below was designed to show all the names that start with an S, and the age is either less than 20 or more than 30.
Identify TWO errors in the design of this query that are causing it to display the incorrect information. (2)
10.8 Briefly explain what each of the following would be used for in a word processing application:
10.8.1 Continuous section break (2)
10.8.2 Bookmark (1)
[26]
TOTAL SECTION C: 50
GRAND TOTAL: 150
COMPUTER APPLICATIONS TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 PAPER 2 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
COMPUTER APPLICATIONS TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A: SHORT QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MATCHING ITEMS |
[10]
QUESTION 2: MULTIPLE-CHOICE |
[10]
QUESTION 3: MODIFIED TRUE/FALSE
3.1 False − Grid computing (1)
3.2 False − Contrast ratio (1)
3.3 False − service pack (1)
3.4 True (1)
3.5 False − router (1)
[5]
TOTAL SECTION A: 25
SECTION B
QUESTION 4: SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGIES
4.1. | 4.1.1 - | Any TWO of ✔✔
Also accept any other correct sensible reason.
| 2 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
4.2 | 4.2.1 | SSD: Solid State Drive/Disc OR Static State Drive ✔ | 1 | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
4.2.2 | Any THREE comparative differences ✔✔✔
| 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
4.2.3 | Currently/generally SSDs are not readily available in as large a storage capacity as a traditional HDD. ✔ | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
4.3 | 4.3.1 | Any ONE for THREE marks: ✔✔✔ OR Cache memory increases the speed of the system ✔ by using its high speed memory that stores instructions and data that will probably be used next ✔ by the CPU. ✔ OR Cache memory increases the speed of the system ✔ by preventing the CPU having to wait ✔ for data from the slower RAM. ✔ | 3 | 3 | |
4.4 | Any TWO reasons: ✔✔
| 2 | 2 | ||
4.5 | 4.5.1 | Any TWO advantages of USB over Firewire ✔✔
| 2 | 3 | |
4.5.2 | Application software. ✔ | 1 | |||
4.6 | 4.6.1 | Any ONE of: ✔
| 1 | 3 | |
4.6.2 | The cloud refers to storage/services/space ✔ located on the Internet/on-line/external. ✔ | 2 | |||
4.7 | 4.7.1 | VoIP converts voice/video/images data into (digital) data ✔ that can be sent over a network/Internet. ✔ OR VoIP can use a standard Internet connection ✔ to make telephone calls. ✔ | 2 | 4 |
4.7.2 | Any ONE of: ✔
| 1 | ||
4.7.3 | Any ONE of: ✔
| 1 | ||
4.8 |
| 3 | 3 | |
[25] | ||||
QUESTION 5: INTERNET AND NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES
5.1 | Any TWO reasons for not being feasible: ✔✔
| 2 | 2 | |
5.2 | 5.2.1 | Podcasting is when video/audio clips are made available/published online for downloading purposes. The format cater for portable media devices. | 1 | 3 |
5.2.2 | Any TWO of: ✔✔
| 2 | ||
5.3 | 5.3.1 | Broadband is any high speed/high bandwidth connection to the Internet. | 1 | 3 |
5.3.2 | (a) Digital | 1 | ||
(b) Any ONE EXAMPLE
| 1 | |||
5.4 | 5.4.1 | Click on this icon to add any files to the e-mail message. | 1 | 3 |
5.4.2 | Rich text option: Allows you to format the e-mail message. Plain text: Message is sent without any formatting. Even formatting that has been done, will be lost. | 2 | ||
5.5 | (Online) Advertising/ads | 1 | 1 | |
5.6 |
| 2 | 2 | |
5.7 | Keeps track of pages visited. | 1 | 1 | |
[15] | ||||
QUESTION 6: INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
6.1 | 6.1.1 | Any TWO ways: ✔✔
| 2 | 3 |
6.1.2 | A to-do list. | 1 | ||
6.2 | Any TWO: ✔✔
| 2 | 2 | |
6.3 | Any ONE: ✔
| 1 | 1 | |
6.4 | Any ONE: ✔
| 1 | 1 | |
6.5 | Any TWO: ✔✔
| 2 | 2 |
6.6 | The use of another author’s expression of thoughts and ideas and passing them off as one’s own without permission. | 1 | 1 |
[10] |
QUESTION 7: SOCIAL IMPLICATIONS
7.1 | Any ONE: ✔
| 1 | 1 |
7.2 | Any TWO: ✔✔
AND/OR
| 2 | 2 |
7.3 | 7.3.1 | The GPS coordinates of where the photograph was taken, is added to the photograph’s metadata. | 1 | 2 |
7.3.2 | The inclusion of the GPS coordinates may alert poachers where to find the rhino. | 1 | ||
7.4 | Adjust the settings (Privacy settings) of your Facebook account to prevent being tagged (without permission) in photographs. | 1 | 1 | |
7.5 | Any TWO: ✔✔
| 2 | 2 | |
7.6 | Any TWO: ✔✔
| 2 | 2 | |
[10] | ||||
QUESTION 8: SOLUTION DEVELOPMENT
8.1 | 8.1.1 |
| 4 | 9 |
8.1.2 |
| 2 | ||
8.1.3 |
| 3 | ||
8.2 | 8.2.1 | Group Footer or Group Header | 1 | 3 |
8.2.2 | Query | 1 | ||
8.2.3 |
| 1 |
8.3 | A feature to reflect information regarding the reference to a book or academic work. ✔
| 2 | 2 |
8.4 | Styles | 1 | 1 |
[15] | |||
TOTAL SECTION B: | 75 | ||
SECTION C
QUESTION 9: INTEGRATED SCENARIO
9.1 | NOTE: Any ONE correct motivation ✔✔
If answered No:
| 2 | 2 | |
9.2 | Any TWO of: ✔✔
| 2 | 2 | |
9.3 | 9.3.1 | Any ONE of: ✔✔ | 2 | |
9.3.2 |
| 2 | ||
9.3.3 |
| 1 | ||
9.3.4 | Speech to text/speech recognition | 1 | 6 | |
9.4 | 9.4.1 | Any TWO advantages of wireless network over a cabled network: ✔✔
| 2 | 10 |
9.4.2 |
| 2 | ||
9.4.3 | WiMAX | 1 | ||
9.4.4 | Any TWO of: ✔✔
| 2 | ||
9.4.5 | Any TWO of: ✔✔
| 2 | ||
9.4.6 | The driver translates instructions from the operating system into the actual signals that controls the hardware of the device./Software that enables your computer to communicate with the hardware. | 1 |
9.5 | 9.5.1 | Any TWO aspects: ✔✔
| 2 2 | 10 |
[24] |
QUESTION 10
10.1 | Survey – A set of written/typed questions given to many or a group of people. ✔ | 2 | ||
10.2 | Any TWO: ✔✔
| 2 | ||
10.3 | Information overload is what happens when people cannot cope with the amount of information that they are exposed to every day. | 1 | ||
10.4 | 1 | |||
10.5 | 10.5.1 | Phishing | 1 | |
10.5.2 | No, he should not click on the link, because he would probably be directed to a website that is a replica of the actual banking website, where she would be prompted to log on. He would thus be giving out personal, confidential details such as PIN numbers and passwords. | 2 | ||
10.5.3 | Social engineering | 1 | ||
10.5.4 | Any TWO of: ✔✔
| 2 | ||
10.5.5 |
| 2 2 | ||
10.5.6 | A Trojan is a form of malware which is a destructive program disguised as a useful application/program. It can be used to install malware on a computer. | 10 | ||
10.6 | 10.6.1 | Place the <hr /> tag in the body of the HTML document. | 1 | 10 |
10.6.2 | Any ONE of: ✔
| 1 | ||
10.6.3 | Colour should be color. | 1 | ||
9.8 | 10.7.1 | Memo/Long Text | 1 | |
10.7.2 | Unique numbers are automatically assigned so that there can be no duplicate values. | 1 | ||
10.7.3 |
| 2 | ||
10.8 | 10.8.1 | Starting a new section ✔ that allows different page formatting/settings on the same page. ✔ | 2 | |
10.8.2 | Assign a name/link to a specific point in the document for quicker access/to which a hyperlink can be linked. | 1 | ||
TOTAL SECTION C: | 50 | |||
GRAND TOTAL: | 150 | |||
COMPUTER APPLICATIONS TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 PAPER 1 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
COMPUTER APPLICATIONS TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1 File Name: 1_Turtle Facts
No | Criteria | Max | ✔ | Mark | |
1.1 |
| 1 | |||
1.2 | 1.2.1 |
| 1 | ||
1.2.2 |
| 3 | |||
1.3 |
∙ Spacing is 1.5 pt. ✔ | 2 | |||
1.4 | ∙ Drop Cap effect applied to the highlighted letter “S” dropped over 4 lines. ✔ Distance from the text is 0.5 cm.✔ | 2 | |||
1.5 | Style
| 2 | |||
1.6 | Columns
| 3 | |||
1.7 |
| 1 | |||
1.8 |
| 2 | |||
1.9 |
| 3 | |||
1.10 |
| `3 | |||
1.11 | Bibliography
| 2 | |||
1.12 | Page orientation
| 1 | |||
1.13 | Table and Image caption
| 3 | |||
1.14 |
| 3 | ||
1.15 |
| 2 | ||
1.16 |
| 2 | ||
Total for QUESTION 1 [36]
QUESTION 2 File Name: 2_Observation Form
No | Criteria | Max | ✔ | Mark |
2.1 |
| 2 | ||
2.2 | Text form field for the heading “How many turtles…” formatted:
| 2 | ||
2.3 |
| 2 | ||
2.4 |
| 1 | ||
2.5 |
| 1 | ||
2.6 |
| 2 | ||
2.7 |
| 2 | ||
2.8 |
| 2 | ||
Total for QUESTION 2 [14]
QUESTION 3 File Name: 3_Turtle Campaign
No | Criteria | Max | ✔ | Mark |
Info worksheet | ||||
3.1 | Cell H1:
| 1 | ||
3.2 |
| 1 | ||
3.3 | Cell A3:O3 :
| 2 | ||
3.4 | Row 3 freezed✔ | 1 | ||
3.5 | Cell A4: OR =B4&LEN(E4)& "#code")
| 5 | ||
3.6 | Cell H4:
| 6 | ||
3.7 | Cell N20: OR =I20*$I$2+J20*$J$2+K20*$K$2+L20*$L$2+M20*$M$2
| 3 | ||
3.8 | Conditional formatting:
| 3 | ||
3.9 | Cell O4:
| 6 | ||
3.10 | Cell E51: OR =SUMIF(E4:E49, “Platinum”,N4:N49)
| 4 | ||
3.11 | Cell E52: OR =COUNTIF(F4:F49, “SEE Turtles”)
| 3 | ||
3.12 | Cell E53: OR =AVERAGEIF(D4:D49, “F”,C4:C49)
| 4 | ||
3.13 | Cell E54:
| 3 | ||
Spotted worksheet | ||||
3.14 | Cell B2:
| 5 | ||
Graph worksheet | ||||
3.15 | Graph
| 5 | ||
Total for QUESTION 3 [52]
QUESTION 4 File Name: 4_Turtle Classification
No | Criteria | Max | ✔ | Mark |
Table: Patient Details | ||||
4.1.1 |
| 1 | ||
4.1.2 |
| 1 | ||
4.1.3 |
| 2 | ||
4.1.4 |
| 1 | ||
4.1.5 | Scientific Name field:
| 2 | ||
4.1.6 | Input mask for Turtle Id field:
| 5 | ||
Turtle Images table and the frm4_2 form | ||||
4.2.1 |
| 2 | ||
4.2.2 |
| 2 | ||
Query: qry4_3 | ||||
4.3 |
OR <=399
(Answer: 3 records) | 4 | ||
Query: qry4_4 | ||||
4.4 |
| 7 | ||
Form: frm4_5 | ||||
4.5 |
| 6 | ||
Report: rpt4_6 | ||||
4.6 | Report rpt4_6 created based on Classification Table
| 9 | ||
Total for QUESTION 4 [42]
QUESTION 5 File Name: 5_Save Us
- This question should be marked from the browser as far as possible, unless otherwise indicated or if it cannot be seen on the browser.
- A maximum of 1 mark will be deducted if one or more closing tags are omitted.
No | Criteria | Max | ✔ | Mark |
5.1 | Title
| 2 | ||
5.2 | Horizontal Line Size
| 1 | ||
5.3 | Image Tag
| 5 | ||
5.4 | Bold formatting
| 1 | ||
5.5 | Unordered List Type
| 2 | ||
5.6 | Table Heading <th colspan="2"> <h1>Most Endangered Sea Turtles In The World</h1> </th> </tr>
| 3 | ||
5.7 | Table Row color and font color:
| 2 | ||
5.8 | Caption tag
| 3 | ||
5.9 | Link
| 1 |
Total for QUESTION 5 [20]
QUESTION 6 File Name: 6_Spotted By & Scientific Info
No | Criteria | Max | ✔ | Mark |
6.1 | Spotted By & Scientific Info worksheet
| 1 | ||
6.2 | Find and Replace
| 2 | ||
6.3 | Unique name
| 2 | ||
6.4 | Sorting
| 3 | ||
6.5 | Password
| 2 | ||
Total for QUESTION 6 [10]
QUESTION 7 File Name: 7_Winners List 7_Certificate
7_Certificate (Word processing document) | ||||
No | Criteria | Max | ✔ | Mark |
7.1 | Mail Merge:
| 6 | ||
Total for QUESTION 7 [6]
TOTAL: 180