Adele
ENGLISH FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE PAPER 3 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
ENGLISH FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE
PAPER 3
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
This memorandum must be used together with the attached English FAL assessment rubrics for SECTIONS A, B and C.
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A: ESSAY
QUESTION 1
Instructions to Markers:
- Candidates are required to write on ONE topic only.
- The ideas listed below the topics are only some ways in which the topic could be interpreted.
- Full credit must be given for the candidate's own interpretation.
- Marking must be objective. Give credit for relevant ideas.
- Use the 50-mark assessment rubric to mark the essays. The texts produced by candidates must be assessed according to the following criteria as set out in the assessment rubric:
- Content and planning (30 marks)
- Language, style and editing (15 marks)
- Structure (5 marks)
NOTE:
- Adhere to the length of between 250 and 300 words as prescribed in the CAPS document. However, should the maximum word count be reached mid-sentence, read to the end of that sentence.
- No additional penalties may be imposed as the rubric itself imposes penalties.
1.1 Everything was going according to plan when …
Narrative/Reflective/Descriptive
- If narrative, the essay must have a strong story line and an interesting ending.
- If reflective, the essay should convey emotional reactions and feelings the candidate experiences/experienced.
- If descriptive, the writer should create a picture in words using as many senses as possible to make the description clear.
NOTE: A candidate may write an essay which contains elements of more than one type of essay/any other essay type. [50]
1.2 'We can change the world and make it a better place. It is in your hands to make a difference.' – Nelson Mandela
Reflective/Argumentative/Discursive/Narrative
- If reflective, the essay should convey emotional reactions and feelings the candidate experiences/experienced.
- If argumentative, the essay must reflect a specific argument or viewpoint for or against the topic. The candidate should give a range of arguments to support his/her view. The conclusion should be a strong, clear and convincing statement of the writer's opinion.
- If discursive, the arguments for and against must be well-balanced and clearly analysed in the essay. The candidate must provide supporting evidence for arguments. The candidate may come to a particular conclusion at the end of the essay, which should include recommendations.
- If narrative, the essay must have a strong story line and an interesting ending.
NOTE: A candidate may write an essay which contains elements of more than one type of essay/any other essay type. [50]
1.3 Hidden treasure
Descriptive/Narrative/Reflective
- If descriptive, the candidate should create a picture in words using as many senses as possible to make the description clear.
- If narrative, the essay must have a strong story line and an interesting ending.
- If reflective, the essay should convey emotional reactions and feelings the candidate experiences/experienced.
NOTE: A candidate may write an essay which contains elements of more than one type of essay/any other essay type. [50]
1.4 'Go for it now. The future is promised to no-one.' – Dr Wayne Dyer
Reflective/Argumentative/Discursive/Narrative
- If reflective, the essay should convey emotional reactions and feelings the candidate experiences/experienced.
- If argumentative, the essay must reflect a specific argument or viewpoint for or against the topic. The candidate should give a range of arguments to support his/her view. The conclusion should be a strong, clear and convincing statement of the writer's opinion.
- If discursive, the arguments for and against must be well-balanced and clearly analysed in the essay. The candidate must provide supporting evidence for arguments. The candidate may come to a particular conclusion at the end of the essay, which should include recommendations.
- If narrative, the essay must have a strong story line and an interesting ending.
NOTE: A candidate may write an essay which contains elements of more than one type of essay/any other essay type. [50]
1.5 You do not need someone else's approval to feel good about yourself.
Argumentative/ Discursive/Reflective
- If argumentative, the essay must convey a specific argument or viewpoint for or against the topic. The candidate should give a range of arguments to support his/her view. The conclusion should be a strong, clear and convincing statement of the writer's opinion.
- If discursive, the arguments for and against must be well-balanced and clearly analysed in the essay. The candidate must provide supporting evidence for arguments. The candidate may come to a particular conclusion at the end of the essay, which should include recommendations.
- If reflective, the essay should convey emotional reactions and feelings the candidate experiences/experienced.
NOTE: A candidate may write an essay which contains elements of more than one type of essay/any other essay type. [50]
1.6 Beyond these walls
Descriptive/Narrative/Reflective
- If descriptive, the candidate should create a picture in words using as many senses as possible to make the description clear.
- If narrative, the essay must have a strong story line and an interesting ending.
- If reflective, the essay should convey emotional reactions and feelings the candidate experiences/experienced.
NOTE: A candidate may write an essay which contains elements of more than one type of essay/any other essay type. [50]
1.7 Interpretation of pictures
The candidate:
- must give the essay a suitable title.
- may interpret the pictures in any way, relevant to the picture.
- may choose to write any type of essay, relevant to the picture.
- must link the interpretation to the picture.
- may write in any appropriate tense.
1.7.1 Picture: Computer
Narrative/Descriptive/Reflective/Argumentative/Discursive
- Literal interpretations: Communicating electronically, use of computers, working in an office, electronic learning.
- Figurative interpretations: the effects of technology on our lives, modern life, the world of work. [50]
1.7.2 Picture: Lion
Narrative/Descriptive/Reflective/Argumentative/Discursive
- Literal interpretations: lions as an endangered species, king of the jungle, wildlife.
- Figurative interpretations: survival of the fittest, law of the jungle, power, fear. [50]
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B: LONGER TRANSACTIONAL TEXT
QUESTION 2
Instructions to Markers:
- Candidates are required to answer ONE question.
- Marking must be objective. Give credit for relevant ideas.
- Use the 30-mark assessment rubric to mark the responses in this section. The texts produced by candidates must be assessed according to the following criteria as set out in the assessment rubric:
- Content, planning and format (18 marks)
- Language, style and editing (12 marks)
NOTE:
- Adhere to the length of between 120 and 150 words as prescribed in the CAPS document. However, should the maximum word count be reached mid-sentence, read to the end of that sentence.
- No additional penalties may be imposed as the rubric itself imposes penalties.
2.1 DIALOGUE
A conversation between siblings.
- A brief context must be provided at the beginning of the dialogue.
- The dialogue must be between the siblings.
- The tone must be informal.
- The following aspects of the dialogue format must be included:
- The names of the speakers written on the left side of the page.
- A colon after the name of the character who is speaking.
- A new line to indicate each new speaker.
- Where necessary, actions must be given in brackets before the words are spoken. [30]
2.2 OBITUARY
A learner has recently passed away.
- The tone must be formal.
- The following aspects of format must be included:
- Full name of the deceased
- Date of birth
- Date of death
- Birthplace
- Where the person was living at the time of death
- Key survivors (e.g. parents, siblings) and their names
- The following information may be included:
- Date, time and place of funeral
- Biographical information
- Cause of death.
- The obituary must pay tribute to the deceased. [30]
2.3 NEWSPAPER ARTICLE
An article for a community newspaper.
- The article must have a suitable heading.
- Paragraphs should not be too long.
- The style should be personal, addressing the reader.
- The language may be formal.
- The article should be stimulating to the reader/encourage the reader to recycle.
- The article must provide the reader with suggestions on how residents can recycle at home. [30]
2.4 FORMAL LETTER
Complaint to the manager.
- Allow for acceptable variations of the format, e.g. addresses.
- The letter must be addressed to the manager of the store.
- The tone and register of the letter must be formal.
- The letter must include an introduction, a body and a conclusion.
- The following aspects of format must be included:
- Address of sender
- Date
- Recipient: The Manager
- Address of recipient
- Greeting/Salutation
- Subject line
- Suitable ending
- Signature
- Name of sender
- The following information must be included in the letter, among others:
- Details about the purchase of the garment
- Dissatisfaction with the service [30]
TOTAL SECTION B: 30
SECTION C: SHORTER TRANSACTIONAL TEXT
QUESTION 3
Instructions to Markers:
- Candidates are required to answer ONE question.
- Marking must be objective. Give credit for relevant ideas.
- Use the 20-mark assessment rubric to mark the responses in this section. The texts produced by candidates must be assessed according to the following criteria as set out in the assessment rubric:
- Content, planning and format (12 marks)
- Language, style and editing (8 marks)
NOTE:
- Adhere to the length of between 80 and 100 words as prescribed in the CAPS document. However, should the maximum word count be reached mid-sentence, read to the end of that sentence.
- No additional penalties may be imposed as the rubric itself imposes penalties.
3.1 FLYER
Service to the elderly
- The following aspects should be included in the flyer, among others:
- Eye-catching headline or slogan
- Catchy words and phrases
- Sufficient details of services offered
- Contact details of the person offering the service
- The language may be formal or informal but not slang or colloquial.
NOTE: Do NOT award marks for illustrations or drawings. [20]
3.2 DIARY ENTRIES
The candidate's feelings BEFORE and AFTER informing his/her family of the decision taken.
- There MUST be TWO diary entries with two different dates/times.
- The entries must express the candidate's feelings before and after informing his/her family.
- The diary entries should be written in the first person.
- The language should be simple and informal.
- The tone must reflect suitable emotions. [20]
3.3 DIRECTIONS
Directions to the clinic
- The directions may be in either point or paragraph form.
- Complete sentences are not necessary.
- Directions must be in the correct chronological order.
- Approximate distance, turns and landmarks must be included.
NOTE: Do NOT award marks for illustrations. [20]
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 100
ASSESSMENT RUBRIC FOR ESSAY – FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE [50 MARKS]
Criteria | Exceptional | Skilful | Moderate | Elementary | Inadequate | |
CONTENT & PLANNING (Response and ideas) Organisation of ideas for planning; Awareness of purpose, audience and context 30 MARKS | UPPER LEVEL | 28–30 | 22–24 | 16–18 | 10-12 | 4-6 |
|
|
|
|
| ||
LOWER LEVEL | 25–27 | 19–21 | 13–15 | 7–9 | 0–3 | |
|
|
|
|
| ||
LANGUAGE, STYLE & EDITING Tone, register, style, vocabulary appropriate to purpose/effect and context; Word choice; Language use and conventions, punctuation, grammar, spelling 15 MARKS | UPPER LEVEL | 14–15 | 11-12 | 8- 9 | 5- 6 | 0 – 3 |
|
|
|
|
| ||
LOWER LEVEL | 13 | 10 | 7 | 4 | ||
|
-Well crafted |
|
| |||
STRUCTURE Features of text; Paragraph development and sentence construction 5 MARKS | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 0–1 | |
|
|
|
|
|
ASSESSMENT RUBRIC FOR LONGER TRANSACTIONAL TEXT – FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE [30 MARKS]
Criteria | Exceptional | Skilful | Moderate | Elementary | Inadequate |
CONTENT, PLANNING & FORMAT Response and ideas; Organisation of ideas for planning; Purpose, audience, features/conventions and context 18 MARKS | 15–18 | 11-14 | 8-10 | 5-7 | 0–4 |
|
|
|
|
| |
LANGUAGE, STYLE & EDITING Tone, register, style, purpose/effect, audience and context; Language use and conventions; Word choice; Punctuation and spelling 12 MARKS | 10–12 | 8–9 | 6–7 | 4-5 | 0–3 |
|
|
|
|
| |
MARK RANGE | 25–30 | 19–23 | 14-17 | 9-12 | 0–7 |
ASSESSMENT RUBRIC FOR SHORTER TRANSACTIONAL TEXT – FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE [20 MARKS]
Criteria | Exceptional | Skilful | Moderate | Elementary | Inadequate |
CONTENT, PLANNING & FORMAT Response and ideas; Organisation of ideas; Features/conventions and context 12 MARKS | 10–12 | 8-9 | 6-7 | 4-5 | 0-3 |
|
|
|
|
| |
LANGUAGE, STYLE & EDITING Tone, register, style, vocabulary appropriate to purpose and context; Language use and conventions; Word choice; Punctuation and spelling 8 MARKS | 7–8 | 5-6 | 4 | 3 | 0–2 |
|
|
|
|
| |
MARK RANGE | 17–20 | 13–15 | 10-11 | 7-8 | 0–5 |
ENGLISH FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
ENGLISH FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Candidates are required to answer questions from TWO sections.
- These marking guidelines have been finalised at a marking guideline discussion session at DBE at which all provinces were represented. Any omissions or queries should be referred to Chief Markers/Analytical Moderators/Internal Moderators at marking centres. All protocol must be followed.
- Candidates' responses should be assessed as objectively as possible.
- MARKING GUIDELINES
4.1 A candidate may not answer more than ONE question on the same genre.
4.2 If a candidate gives two answers where the first one is incorrect and the next one is correct, mark the first answer and ignore the next.
4.3 If answers are incorrectly numbered, mark according to the marking guidelines.
4.4 If a spelling error affects the meaning, mark incorrect. If it does not affect the meaning, mark correct.
4.5 If the candidate does not use inverted commas when asked to quote, do not penalise.
4.6 For open-ended questions, no marks should be awarded for YES/NO or I AGREE/I DISAGREE. The reason/substantiation/ motivation is what should be considered.
4.7 No marks should be awarded for TRUE/FALSE or FACT/OPINION. The reason/substantiation/motivation is what should be considered.
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A: NOVEL
NOTE: Candidates are required to answer ONE question on the novel they have studied.
QUESTION 1: CRY, THE BELOVED COUNTRY
Candidates are required to answer BOTH questions, i.e. QUESTIONS 1.1 and 1.2.
1.1
1.1.1
- Ndotsheni
- big cities
- Reverend Msimangu
- Gertrude (4)
1.1.2 His son, Matthew, might escape punishment if a lawyer defends him. (2)
1.1.3
- Matthew Kumalo is an accomplice when they burgle Arthur Jarvis's house.
- Johannes Pafuri attacks Arthur Jarvis' male servant (Richard Mpiring with an iron bar)./Johannes Pafuri masterminds the crime.(2)
1.1.4
- Disbelief/incredulity/shock (1)
- Stephen Kumalo cannot believe that John denies Matthew's involvement in the crime. (1)
1.1.5 Absalom is truthful/honest/remorseful/repentant. Matthew, on the other hand, is selfish/disloyal (turns his back on Absalom)/dishonest.
NOTE: The difference in character traits must be clear for 2 marks to be awarded. (2)
1.1.6 The discussion of the theme of power, should include the following points, among others:
- Power corrupts even John Kumalo, who seems to be working for the cause (the fight against apartheid/for freedom/equality).
- His immunity to conscience is clear. He does not take his brother's feelings into consideration when Stephen tells him about the murder case.
- The power of forgiveness between James Jarvis and Stephen Kumalo. James forgives Stephen, although it is Stephen’s son (Absalom) who kills James’ son (Arthur).
NOTE: For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1–2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The candidate's interpretation must be grounded in the novel. (3)
1.1.7 Open-ended.
- Accept a relevant response which shows an understanding of the following viewpoints, among others:
Yes.
- The young man is disappointed in Absalom.
- He goes to great lengths to rehabilitate Absalom.
- He is not compelled to assist Stephen Kumalo by driving him around.
- He is not obliged to become involved in the conflict between the two brothers.
OR
No.
- The young man should not give up on Absalom that easily.
- He should stand firm in his beliefs.
- He cannot renege on his willingness to have agreed to assist Stephen Kumalo.
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for YES or NO. Credit responses where a combination is given. For full marks, responses must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1–2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The candidate's interpretation must be grounded in the novel. (3)
AND
1.2
1.2.1 Books on Abraham Lincoln/South Africa/Afrikaans/religion/ sociology/crime and criminals/poetry/novels/Shakespeare.NOTE: Accept any TWO of the above. (2)
1.2.2
- Jarvis is shocked by the revelations (the plight of black South Africans) made by Arthur who knew so much about South Africa.
OR - He is hurt because he realises that he (Jarvis) has failed his son because he did not teach him anything about South Africa.
OR - Jarvis is shocked and hurt because his son was murdered by the very people whom he was trying to uplift. (2)
1.2.3
- 'trembling' (1)
- It is the mark of the blood left on the carpet after Arthur Jarvis is shot/killed (by Absalom Kumalo). (2)
1.2.4 C/becomes emotional (1)
1.2.5 It is ironic that Arthur Jarvis, who makes it his mission in life to uplift the South African black people, is killed by a black South African (Absalom Kumalo).
NOTE: BOTH parts should be included to earn the marks. (2)
1.2.6 Absalom is a murderer/criminal/takes an innocent/good man's life. (1)
1.2.7
- Metaphor/Personification (1)
- In the same way that a star is a guiding light, Arthur wants authenticity and not a misguided version of what is really happening in South Africa. He wants to work towards change (and not for personal glory).
OR
The star is given the human quality of guiding him towards uncovering the truth (about life of the black people in South Africa). (2)
1.2.8 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows an understanding of the following viewpoints, among others:
Yes.
- Up to now Jarvis has not really known his son (Arthur).
- He has been unaware of the things that lay close to his heart/were important to Arthur.
- He is indifferent to the plight of black South Africans. He could have helped the villagers of Ndotsheni earlier.
- Arthur is dead and it is now too late for him to witness real change in his father.
OR
No.
- Arthur's writings clearly have an impact on James Jarvis because he now appears to understand Arthur's perspective on the South African situation and the need to change.
- Jarvis' own awareness increases and he resolves to be more tolerant of especially black people.
- He helps the people of Ndotsheni by providing them with milk and arranging for an agricultural expert to teach the farmers.
- He is understanding and forgiving towards Stephen Kumalo and donates money towards the erection of a new church building.
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for YES or NO. Credit responses where a combination is given. For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1–2 marks for a response which is not well substantiated. The candidate's interpretation must be grounded in the novel. (3) [35]
QUESTION 2: STRANGE CASE OF DR JEKYLL AND MR HYDE
Candidates are required to answer BOTH questions, i.e. QUESTIONS 2.1 and 2.2.
2.1
2.1.1
- lawyer
- Mr Enfield
- Dr Jekyll
- Mr Hyde (4)
2.1.2 Mr Utterson is concerned about Dr Jekyllbecause he leaves his estate/property/belongings to Mr Hyde(who is unknown to him). (2)
2.1.3
- Surprise/amazement (1)
- Mr Utterson is surprised to discover that Dr Lanyon and Dr Jekyll are no longer in contact with each other, since they are friends/both scientists. (1)
2.1.4 'balderdash' (1)
2.1.5
- Sir Carew is gentle/kind-hearted/polite.
- Mr Hyde, on the other hand, is heartless/cruel/impolite/vicious.
NOTE: The difference in character traits must be clear for 2 marks to be awarded. (2)
2.1.6 He is loyal: Poole does not reveal to anybody that he suspects Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde is the same person./ He goes out of his way to find the powders to make the potion./He consults with Mr Utterson when he becomes concerned about Dr Jekyll’s behaviour.
2.1.7
- Mr Utterson identifies the cane as the present he has given Dr Jekyll.
- Half of the broken cane/stick which was used to assault Sir Carew is found behind the door of Mr Hyde’s house.
- Utterson finds the stub of a cheque book in the hearth, he links this information with his knowledge of Jekyll’s will.
- The letter written by Mr Hyde to Dr Jekyll, is later discovered (by Mr Guest), to have been written by Jekyll himself.
NOTE: Accept any TWO of the above. (2)
2.1.8 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows an understanding of the following viewpoints, among others:
Yes.
- Mr Utterson and Dr Jekyll have a friendship spanning many years.
- As his lawyer, he is in possession of Dr Jekyll's will and is terribly perturbed/concerned on learning that Mr Hyde is the beneficiary.
- His concern for Dr Jekyll stems from the fact that as a close friend he has never met Mr Hyde.
- Mr Utterson thinks that Mr Hyde is blackmailing Dr Jekyll and he is, therefore, concerned.
- Dr Jekyll's refusal to talk about Mr Hyde prompts Mr Utterson to try and find Mr Hyde/solve the mystery.
OR
No.
- Mr Utterson should respect Dr Jekyll's wish not to speak about Mr Hyde.
- Mr Utterson should contain his curiosity and not meddle in Dr Jekyll's affairs by trying to solve the mystery.
- As Dr Jekyll's lawyer, he should maintain the confidentiality and trust expected from a lawyer.
- Dr Jekyll is a learned man and Mr Utterson should not question his decisions.
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for YES or NO. Credit responses where a combination is given. For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1–2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The candidate's interpretation must be grounded in the novel. (3)
AND
2.2
2.2.1 C/Soho (1)
2.2.2
- Simile (1)
- Dr Jekyll's crying is compared to that of a crying woman/lost soul who experiences intense pain/agony/suffering/distress.
This shows Dr Jekyll's agony as he cannot undo what he has done. (2)
2.2.3
- Mr Utterson and Poole are afraid of what they might find/what is happening in the cabinet. (2)
- Dr Jekyll/Mr Hyde is contemplating suicide. His pacing shows his uncertainty.
OR
He is desperate in the hope of receiving the powder to make the potion. (2)
2.2.4 Mr Utterson calls out repeatedly to see Dr Jekyll, unaware that it is actually Mr Hyde in the cabinet and not Dr Jekyll. NOTE: BOTH parts should be included to earn the marks. (2)
2.2.5 Poole and Utterson find the body of Mr Hyde/a crushed phial/a fire burning/a boiling kettle/cups and saucers/a neat pile of papers/a will/a letter/chemicals/Hyde is dressed in Jekyll’s clothes. NOTE: Accept any TWO of the above. (2)
2.2.6 The discussion of the theme of violence, should include the following points, among others:
- Mr Hyde is violent, with no apparent motive.
- Mr Enfield witnesses Mr Hyde bumping into a little girl and then trampling on her.
- Hyde beats Sir Danvers Carew to death with a walking stick.
- Hyde defaces Dr Jekyll's favourite religious work.
- Jekyll commits the violent act of suicide.
NOTE: For full marks, the response must be well substantiated. A candidate can score 1–2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The candidate's interpretation must be grounded in the novel. (3)
2.2.7 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows an understanding of the following viewpoints, among others:
Yes.
- Dr Jekyll duplicates himself into two different persons with ambivalent qualities.
- He remains respectable in public (as Dr Jekyll).
- He indulges in indecent activities (as Mr Hyde).
- He experiments with several potions and is eventually successful in creating one that transforms him into the evil Mr Hyde and vice versa.
OR
No.
- Dr Jekyll succeeds only in separating his evil half into Mr Hyde while he remains both good and evil.
- Dr Jekyll has to increase his dosages of the potion as Mr Hyde becomes the stronger one.
- Without taking the potion he loses control – Mr Hyde still appears.
- Dr Jekyll is consumed by his own potion which eventually claims his life.
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for YES or NO. Credit responses where a combination is given. For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1–2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The candidate's interpretation must be grounded in the novel. (3) [35]
TOTAL SECTION A: 35
SECTION B: DRAMA
NOTE: Candidates are required to answer ONE question on the drama they have studied.
QUESTION 3: MACBETH
Candidates are required to answer BOTH questions, i.e. QUESTIONS 3.1 and 3.2.
3.1
3.1.1
- Cawdor
- king of Scotland
- Scottish
- happier (4)
3.1.2
- Lady Macbeth should clasp/fidget with her hands.
- She should use hand gestures to show guests the door.
- She should stand next to Macbeth.
NOTE: Accept any TWO RELEVANT responses. (2)
3.1.3 Macbeth pays a servant in the home of every Thane (to spy on whoever he considers to be an enemy). (2)
3.1.4
- Metaphor/Hyperbole (1)
- Macbeth compares his murderous deeds/blood he has shed to a river of blood.He feels that to return would be impossible. (2)
3.1.5 C/ the noblemen from Scotland. (1)
3.1.6 The discussion of the theme of fate versus free will, should include the following points, among others:
- Macbeth goes to the witches because he believes that the witches are the agents of fate, foretelling the future that is already decided.
- It is not fate that determines Macbeth's future, he chooses to murder Duncan.
- Macbeth has made his choice in that he has already killed to secure his position (he cannot undo what he has done).
- The only way he will remain in power is by committing further murders (the planned killing of Macduff), thus it is his choice and not fate.
NOTE: For full marks, the response must be well substantiated. A candidate can score 1–2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The candidate's interpretation must be grounded in the drama. (3)
3.1.7 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows an understanding of the following viewpoints, among others:
Yes.
- Initially Macbeth confides in Lady Macbeth when he tells her about the prophecy of the witches. He calls her 'his dearest partner of greatness,' yet later he excludes her from the plan to murder Banquo.
- They are not as close as they were when they planning Duncan's murder.
- Macbeth is intent on being 'safe' and securing his position as king, that he cannot focus on anything else, not even on Lady Macbeth. As a result, she becomes lonely and self-absorbed.
- Lady Macbeth only finds out later about the cruel deeds her husband has committed (killing of Lady Macduff and her children). This causes her insanity and later her suicide.
OR
No.
- Lady Macbeth is responsible for her own death as she prays to the evil spirits to be filled with evil to commit the deed (the killing of King Duncan) which she later regrets.
- She is the one who directs Macbeth onto the path of destruction and becomes ridden/consumed with guilt.
- She loses her mind as she cannot take the strain anymore (sleepwalking) and commits suicide.
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for YES or NO. Credit responses where a combination is given. For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1–2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The candidate's interpretation must be grounded in the drama. (3)
AND
3.2.1 Macbeth will not be defeated until Birnam Wood moves to Dunsinane (Hill). (2)
3.2.2 Macbeth murders Duncan.
- He kills Duncan's guards.
- He arranges for Banquo to be killed
- He orders the killing of Lady Macduff and her son.
- He kills all those whom he suspects to be against him.
NOTE: Accept any TWO of the above. (2)
3.2.3
- The soldiers/Malcolm and the English army. (1)
- Macbeth compares himself to a bear that is tied to a pole and must fight (dogs) to survive. / Similarly, as a bear tied to a pole there is no escape for him (Macbeth). (2)
3.2.4
- Disgust/contempt/scorn. (1)
- Young Siward disapproves of Macbeth's cruel/evil deeds. (1)
3.2.5 Macbeth is over-confident when he says that he is unafraid of a man born of a woman, yet it is Macduff not born in a natural way/Caesarean birth that kills Macbeth.
NOTE: BOTH parts should be included to earn the marks. (2)
3.2.6 Donalbain flees to Ireland./Malcolm flees to England. (1)
3.2.7
- Malcolm is resourceful/intelligent ─ he comes up with a plan on how to conceal their numbers.
OR - He is strategic/organised ─ he plans the attack
.OR - He is respectful ─ he talks about 'noble' Young Siward and 'worthy' Macduff.
OR - Malcolm is brave – he is prepared to lead the army against Macbeth and his troops.
NOTE: Accept any ONE of the above. (2)
3.2.8 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows an understanding of the following viewpoints, among others:
Yes.
- Macduff flees from Scotland leaving his wife and children unprotected.
- He should have realised what consequences his actions (not attending the coronation and the banquet) would have for his family.
- It appears that he loves his country more than his family ─ his first thoughts should have been to provide his family with security before he flees.
- Macduff is suspicious of Macbeth (killing of Duncan and the guards) and should have known what Macbeth is capable of.
OR
No.
- Macduff wants to serve his king and country before all else.
- He flees to England to request Malcolm's assistance in raising an army to overthrow Macbeth.
- He supports Malcolm, who is the rightful heir to the throne, and wants order to be restored in Scotland.
- He could not have known that Macbeth would go to that extreme to have his (Macduff's) family murdered.
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for YES or NO. Credit responses where a combination is given. For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1–2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The candidate's interpretation must be grounded in the drama. (3)
OR
QUESTION 4: MY CHILDREN, MY AFRICA!
Candidates are required to answer BOTH questions, i.e. QUESTIONS 4.1 and 4.2.
4.1
4.1.1
- literature
- Grahamstown
- English
- tense (4)
4.1.2
- The leaders of the apartheid governmentcould soon be overthrown/lose their power.
OR - There are statues/symbols of the apartheid regime that need to be removed. (2)
4.1.3
- Personificatio (1)
- Thami says that they have no patience and want to expedite the action of overthrowing the government as they want immediate change (2)
4.1.4 The comrades/people who are fighting for freedom/liberation in South Africa (1)
4.1.5
- Sarcastic (1)
- Mr M does not believe that violence, (as advocated by 'The People', will bring about change). (1)
4.1.6 Mr M, being a black person, assumes that the colour of his skin automatically qualifies him to be regarded as a member of the movement/Tshisa Qhumisa (The fight against Bantu Education/for freedom/equality). (2)
4.1.7 C/principal (1)
4.1.8 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows an understanding of the following viewpoints, among others:
Yes.
- Mr M believes that The People/Comrades can be orderly and rational – the destruction of statues is irrational and will not bring about freedom.
- He rejects violence as this can lead to destruction, suffering and pain – the incident where the children cry out to him from the police vehicle.
- He advocates argument and debate as this can achieve change without destruction or loss of lives – when he reads the learners' names from the register, he does not know how many of them have been killed.
- He believes education is the key to free the mind – he persists in going to school during the boycotts in the hope that the children would follow his example.
OR
No.
- Words alone are not enough; drastic action is sometimes needed to achieve certain demands – the school boycotts.
- People run out of patience and the only way for them is to resort to violent action – rioting in Brakwater.
- The unjust political system forces people to take the law into their own hands – the destruction of Zolile High School.
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for YES or NO. Credit responses where a combination is given. For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1–2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The candidate's interpretation must be grounded in the drama. (3)
AND
4.2
4.2.1
- She wants to know if Thami was present when Mr M was killed. Whether Thami has tried to prevent the killing of Mr M.
- Whether Thami was part of the mob who killed Mr M.
- She wants to know why Mr M has been killed.
NOTE: Accept any TWO of the above. (2)
4.2.2
- Thami should shrug his shoulders.
- He should hold his head in his hands.
- He should shake his head from side to side.
- His arms should be half-stretched with his hands open.
NOTE: Accept any TWO RELEVANT responses. (2)
4.2.3 Thami plays an integral part in the boycotts/unrest and now that the police are looking for him, he goes north.NOTE: BOTH parts should be included to earn the marks. (2)
4.2.4 Mr M rents a room from the Reverend (Mbopa). (1)
4.2.5
- Isabel wants to bid her last farewell to Mr Mbut does not know where to go.
OR - The Wapadsberg Pass is where Mr M decides that he wants to be a teacher/wants to make teaching his career. (2)
4.2.6
- Isabel is compassionate – The repetitive questioning shows that Isabel needs answers in order to find closure as she mourns the death of Mr M.
OR - She is caring – she wants to know what Thami's intentions are as the police are looking for him.
OR - She is empathetic – she realises that her questions upset Thami.
OR - She is forgiving – previously she wanted to have nothing to do with Thami/did not want to see him but now she affords him the opportunity to speak with her. (2)
NOTE: Accept any ONE of the above.
4.2.7 The discussion of the theme of the generation clash, should include the following points, among others:
- The younger generation (Thami and his peers) oppose the older generation's (Mr M) approach of non-violence towards attaining freedom.
- They are impatient and want immediate change whereas Mr M (the older generation) believes that change can eventually be brought about through dialogue and negotiation.
- Thami opposes Mr M's way of teaching ('old-fashioned');
- Mr M is dictatorial in his approach to the youngsters ('I teach, Thami learns') allowing them no opportunity to think independently.
- There is a clash between Isabel and her parents, who are not keen on her visiting Thami in the township.
NOTE: For full marks, the response must be well substantiated. A candidate can score 1–2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The candidate's interpretation must be grounded in the drama. (3)
4.2.8 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows an understanding of the following viewpoints, among others:
Yes.
- Isabel's visit to Zolile High is a turning point in her life. Prior to this visit the only contact she has across the colour line is with their domestic worker (Auntie) and her father's delivery man (Samuel).
- Her social and political awareness grows when she befriends Thami and Mr M and learns more about the school boycotts and opposing views.
- When Isabel goes to Mr M's special place she promises him that she will make her life useful/not allow her life to be wasted (Mr M's lament: that the lives of the learners are destroyed).
- This signifies hope for the future of South Africa.
- Isabel is the voice of hope, despite the terrible events that take place.
- She has discovered a new world (her growing sense of the inequalities that exist).
OR
No.
- Isabel lives a sheltered life and is ignorant about the effects of apartheid on the people of colour.
- The debating competition at Zolile High is an isolated event and will not ensure equal opportunities for everyone.
- Isabel is an individual and on her own she will not make a significant change.
- Isabel promises to make a success of her life but does not become actively involved to improve the lot of black people/to make others aware of the inequalities that exist.
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for YES or NO. Credit responses where a combination is given. For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1–2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The candidate's interpretation must be grounded in the drama. (3) [35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 35
SECTION C: SHORT STORIES
QUESTION 5
Candidates are required to answer BOTH questions, i.e.
QUESTIONS 5.1 AND 5.2 THE NEW TRIBE – BUCHI EMECHETA
5.1
5.1.1
- St Simon
- reverend
- Nigerian
- Miss Slater/Miss Slattery (4)
5.1.2
- The children mock him by calling him king of devils. (1)
- Ginny thinks that the role of Orient king suits Chester because of his dark skin./Ginny had already made the costume for Chester./Ginny makes Chester aware of his roots/identity. (1)
5.1.3 Apologetic/remorseful. (1)
5.1.4 B/brave enough to tell Ginny how he feels. (1)
5.1.5 Chester regards Arthur as emotionally strong/dependable/solid. He feels safe with Arthur. (2)
5.1.6
- Chester is considerate/caringwhen he makes her a Christmas card/gives her a diary as a gift.
OR - He is strong-willed/brave/resolutewhen he confirms that he does not want to play the role as King of Orient. (2)
5.1.7 The discussion of the theme of insecurity, should include the following points, among others:
- From a very young age Chester feels that he does not 'belong'.
- The insecurity manifests itself when Chester goes to school and does not want to stay there.
- When Ginny talks about 'your people' are from the East, Chester begins to doubt who he is.
- Chester knows he is 'different' and feels he has to do so much more to be accepted which accentuates his insecurity.
- hen Chester and Julia are told they are adopted, both become insecure. (Chester escapes into his dream world while Julia becomes introverted 'stares into space').
- The theme of insecurity could also relate to Arthur and Ginny. They fear that they will not be accepted as adoptive parents or that the biological parents will return and claim the children.
NOTE: For full marks, the response must be well substantiated. A candidate can score 1–2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The candidate's interpretation must be grounded in the short story. (3)
5.1.8 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows an understanding of the following viewpoints, among others:
Yes.
- Julia is abandoned as a baby and brought to the Arlingtons by the man who delivers the newspaper.
- As the elder child Julia is expected to take care of/protect Chester because he is 'different'/ she knows what he is exposed to at school.
- She develops an inferiority complex/becomes withdrawn/ avoids eye contact with people after her parents tell her that she has been adopted.
OR
No.
- The Arlingtons are loving parents. ∙ Being adopted is no sin; it should not make her feel inferior to others.
- Unlike Chester, she is white and less likely to be mocked at school.
- She now has opportunities to develop which she would otherwise not have had with her biological mother.
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for YES or NO. Credit responses where a combination is given. For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1–2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The candidate's interpretation must be grounded in the short story. (3)
AND
5.2 THE FUR COAT – SEAN O'FAOLAIN
5.2.1
- Molly is frustrated/upset because Paddy is not paying attention to her. (2)
- Simile (1)
- The figure of speech shows Molly's anger. She does not tuck the children into bed gently but does so in a rough manner just as one would throw turf into a cellar. (2)
5.2.2 Paddy is trying to find ways to cut costs/perfect the construction of the pier and is therefore focused on the plan. (2)
5.2.3 Molly hopes that Paddy will show more enthusiasm/interest when she talks about the fur coat./She needs confirmation/ reassurance (from Paddy regarding the fur coat). (2)
5.2.4
- Molly desperately wants a fur coat, yet she considers it to be vulgar.
OR - She says she doesn’t care what others say, yet she’s pestering him about the fur coat.
NOTE: BOTH parts should be included to earn the marks. (2)
5.2.5 Molly:
- She wants to be able to wear the fur coat at any given time and still look well-dressed./She could wear any dress underneath it.
- Without a fur coat, she will be forced to purchase new outfits including the accessories./She would not have to buy a new outfit for each occasion she attends.
- A fur coat will elevate her social status.
Paddy:
- Paddy says a fur coat will keep her warm.
- It will prevent her from getting a cold.
- She could show off in it.
NOTE: Accept any ONE of the above for each character. (2)
5.2.6 Molly tears the cheque (and does not use it to buy the fur coat). (1)
5.2.7 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows an understanding of the following viewpoints, among others:
Yes.
- Paddy agrees to give her the money, but she refuses it.
- Molly spends a long time trying to convince Paddy that a fur coat will be practical, but Paddy has already agreed that she may have it.
- Paddy tries to work on how to change the pier, but Molly persists with her nagging of the fur coat.
- She becomes angry when she thinks that Paddy is indifferent to the buying of the fur coat, but she simultaneously becomes angry with him when he agrees with her.
OR
No.
- Molly asks permission to have the fur coat but is not demanding in her request.
- She gives practical reasons why she needs the fur coat.
- Molly is indecisive: her experience of poverty and having to rely on relatives and the Prisoners' Dependence' Fund, while spending money on the fur coat, might seem extravagant.
- Buying a fur coat is expensive and needs careful consideration and discussion but Paddy appears not to pay attention to the matter.
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for YES or NO. Credit responses where a combination is given. For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1–2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The candidate's interpretation must be grounded in the short story. (3) [34]
TOTAL SECTION C: 34
SECTION D: POETRY
6.1 'SONNET 18' – WILLIAM SHAKESPEARE
6.1
6.1.1
- Elizabethan
- quatrains
- rhyming couplet
- iambic (4)
6.1.2
- Summer has strong/harsh winds.
- It is too brief.
- Sometimes the temperature is too high/the sun is scorching.
- It is often cloudy/overcast.
NOTE: Accept any TWO of the above. (2)
6.1.3
- B / alliteration (1)
- Everything eventually loses its beauty whether by coincidence/ accident or through natural causes. (2)
6.1.4
- Personification (1)
- The speaker personifies Death which falsely boaststhat it will claim the speaker's beloved. (2)
6.1.5
- eternal' (1)
- The speaker will write about his beloved's beauty in this poem/his poetry. (1)
6.1.6 Adoration/devotion/affection (1)
6.1.7 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows an understanding of the following viewpoints, among others:
Yes.
- The speaker claims his beloved is not moody/temperamental like the season of summer.
- She is not harsh like the wind that could be destructive in damaging the buds.
- The beloved's beauty does not change unlike the sun which is either too scorching or at times hidden by the clouds.
- Summer is a short period of time; his beloved's beauty, however, is eternal and not even death can affect it as it will be immortalised in the poem.
OR
No.
- His beloved's beauty cannot be compared to a perfect summer's day.
- Summer is regarded by many as being a beautiful season. However, the speaker's perception of his beloved's beauty is personalised and not shared by everybody.
- Just as summer has imperfections (strong winds, hot sun), so too does the speaker's beloved (bad temper, mood swings).
- Everything is subject to the passage of time.
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for YES or NO. Credit responses where a combination is given. For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1–2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The candidate's interpretation must be grounded in the poem. (3)
AND
6.2 'STILL I RISE' – MAYA ANGELOU
6.2
6.2.1
- The speaker's opinion of history is that it is not a true account of events because it is written from the historians’/current regime’s point of view.
OR - When the speaker reflects on her past, the shameful act of slavery imposed on her ancestors brings back painful memories. (2)
6.2.2
- sassiness'/ ‘pumping’ (1)
- Simile (1) `
- The speaker walks as if she had the world's wealth and walks with an air of self-confidence. /The oil symbolises her success and she walks with pride.(2)
6.2.3 The speaker refers to natural forces/elements that are eternal and cannot be contained/controlled. Likewise, she is certain that she will not give up and cannot be controlled. OR Moon and stars can also refer to achieving success/ambition thus the speaker will not give up but work towards achieving her goals. (2)
6.2.4 When you hurt someone by looking contemptuously/scornfully/ deprecatingly at the person. (2)
6.2.5 Even though the speaker writes about herself/women, the poem is about the atrocities she and her ancestors (males and females) suffered as slaves (lines 39─40). (1)
6.2.6 Accept a relevant response which shows an understanding of the theme of perseverance, among others:
- The speaker portrays the history of racism and brutality to her race and the determination to overcome this wretched treatment.
- The poem depicts the American treatment of African Americans. Despite slavery and prejudice the speaker says/promises that none of that will stop African-Americans in their quest for equality, contentment and success.
- The phrase 'Still I rise' is repeated several times. It reflects the idea that no matter what comes your way, she/African Americans will stand up and try again.
- Throughout the poem the speaker makes the point that nothing that the oppressors have done to African-Americans all these years will stop them from overcoming their obstacles and succeeding. This is resonated in 'like dust…', 'like air I'll rise'.
- The poem reflects the universal idea that no matter what comes your way, the determination to ‘rise’ is evident.
NOTE: For full marks, the response must be well substantiated. A candidate can score 1–2 marks for a response which is not well-substantiated. The candidate's interpretation must be grounded in the poem. (3)
6.2.7 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows an understanding of the following viewpoints, among others:
Yes
- The speaker writes from personal experience.
- She is an African-American woman who is subjected to slavery, discrimination, oppression and wants to empower other women to break free from this bondage.
- Despite her suffering, she has risen above her circumstances.
- She portrays resolution and determination; thus becoming the hope for many other African-Americans.
OR
No
- The speaker writes from her experiences as an African American slave. Slavery no longer exists in America.
- She focuses on prejudice (against black women). Women do have equal opportunities and may not regard her as their role model ('dream').
- African-Americans may not read her poetry/writings or know her background, thus they may not consider her as their dream and hope (the emancipation of women/feminists).
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for YES or NO. Credit responses where a combination is given. For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated. A candidate can score 1–2 marks for a response which is not well substantiated. The candidate's interpretation must be grounded in the poem. (3)
TOTAL SECTION D: 35
GRAND TOTAL: 70
ENGLISH FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
ENGLISH FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS TO MARKERS
- Candidates are required to answer ALL the questions.
- This marking guideline serves as a guide to markers. Some responses may require a marker's discretion, while others may be expanded at the national marking guideline discussion.
- Candidates' responses should be assessed as objectively as possible.
MARKING THE COMPREHENSION
- Because the focus is on understanding, incorrect spelling and language errors in responses should not be penalised unless such errors change the meaning/understanding. (Errors must still be indicated.)
- If a candidate uses words from a language other than the one being examined, disregard those words, and if the answer still makes sense, do not penalise. However, if a word from another language is used in a text and required in an answer, this will be acceptable.
- For open-ended questions, no marks should be awarded for YES/NO or I AGREE/I DISAGREE. The reason/substantiation/motivation is what should be considered.
- When one-word answers are required and the candidate gives a whole sentence, mark correct provided that the correct word is underlined/ highlighted.
- When two/three facts/points are required and a range is given, mark only the first two/three.
- Accept dialectal variations.
- For multiple-choice questions, accept BOTH the letter corresponding with the correct answer AND/OR the answer written out in full.
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A: COMPREHENSION
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 'running shoe'✔ (1)
1.1.2
- These shoes do not make any noise ✔as their soles are soft. ✔ OR
- These shoes allow a person to sneak up on someone noiselessly ✔because of the soft soles. ✔
NOTE: Candidates must use their OWN words. (2)
1.2 The purchase/buying and selling of sneakers have become widespread. ✔ The sneaker industry has grown extensively.✔ (2)
1.3 Sneakerheads are people (who collect/trade/admire sneakers as a hobby). ✔ (1)
1.4
- To advertise/promote their brand. ✔
- To increase sales.✔OR
- People who admire Chuck Taylor as a famous football player will be interested in buying All Star sneakers. ✔✔ (2)
1.5
- Famous musicians/rappers/hip-hop artists wore the sneakers.✔
- A rapper, RUN-DMC, released a song, 'My Adidas'. ✔ (2)
1.6 B/trendiest✔ (1)
1.7
- Television. ✔
- Social media.✔
- Music videos. ✔
NOTE: Accept any TWO of the above answers. (2)
1.8
1.8.1 devotee ✔ (1)
1.8.2 Sneakers allow people wearing them✔ to walk/move (from one point to another with ease).✔ (2)
1.9
1.9.1 The writer states that this practice was introduced just a decade/ 10 years ago. ✔ (1)
1.9.2 Instagram ✔ (1)
1.10
- Information (about sneakers) is easily available online. ✔
- There is a wider choice (of sneakers) available online. ✔
- One can shop (for sneakers online), from anywhere in the world.✔
- Sneakers can be delivered directly to you. ✔
NOTE: Accept any TWO of the above answers. (2)
1.11 Open-ended. Accept a suitable response, e.g.
- Agree.
Sneakers appeal to people from all walks of life regardless of their gender, age and social status. Sneakers are a popular choice for many people around the world.
OR
- Disagree.
There are people who consider sneakers as a form of sportswear. Some people cannot afford to buy sneakers. There are many people who do not even wear sneakers.
NOTE: Accept other suitable responses. A candidate can score 1 mark for an answer that is not well-substantiated. Accept a combination answer. (2)
1.12 Open-ended. Accept a suitable response, e.g.
- The title is suitable because the passage is about sneakers which have soft rubber soles and buyers go online searching for soles (sneakers). The pun on the word sole in relation to soul-searching, reflects the cleverness in which the title has been written.
OR - The title is not suitable because it is misleading. There is a pun on the word sole; sole-searching could refer to searching for a type of fish called sole and the passage has nothing to do with fish/sole refers to individual or singular ownership/mandate etcetera, however, this passage has nothing to do with individual/singular ownership or mandate.
NOTE: Accept other suitable responses. A candidate can score 1 mark for an answer that is not well-substantiated. Accept a combination answer. (2)
1.13
- Driving ✔
- Using a cellphone (e.g. texting, taking a selfie, talking, etc.) ✔ (2)
1.14 The boy's actions of controlling the toy car while using a cellphone, are similar to those of his mother who is using her cellphone while driving.✔ These actions indicate that he has picked up this bad habit from his mother. ✔ (2)
1.15 Open-ended. Accept a suitable response, e.g.
- The text succeeds in conveying the message that children pick up bad habits from their parents. The toy that crashes sends a warning that using a cellphone while driving can be disastrous.✔✔
OR - As much as there are similarities in the woman's and the boy's actions, there is no proof that the boy is the woman's son. /The boy's actions are not posing any danger to him; he is just playing with a toy car and a cellphone./The text does not succeed in conveying a warning against using a cellphone and driving as there is no evidence that the woman's car could have crashed or that she is driving. The car could be stationary. ✔✔
NOTE: Accept other suitable responses. A candidate can score 1 mark for an answer that is not well-substantiated. (2) [10]
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B: SUMMARY
QUESTION 2
The following points form the answer to the question:
QUOTATIONS | FACTS (NOTE: Candidates may phrase the facts differently.) | ||
1. | 'It is important to brush your teeth in the morning and again before you go to bed.' | 1. | Brush your teeth in the morning and at bedtime. |
2. | 'Therefore, flossing before brushing is important.' | 2. | Floss before brushing your teeth. |
3. | 'Brushing your tongue is also necessary to help remove bacteria and prevent bad breath.' | 3. | Brush your tongue (when brushing your teeth). |
4. | 'Use mouthwash after brushing your teeth.' | 4. | Rinse with mouthwash (after brushing your teeth). |
5. | ‘Your toothbrush is often moist and kept in an enclosed storage space that creates an environment for bacterial growth.’ | 5. | Store your toothbrush in an open space. |
6. | 'A good habit would be to change your toothbrush every three or four months or when you notice that the bristles are spreading or changing colour.' | 6. | Replace your toothbrush regularly or when the condition of the bristles deteriorates. |
7. | 'Eating large amounts of sugar loaded foods like sweets, cookies, cakes, pastries, fizzy drinks and dried foods causes tooth decay./Bacteria, which feed on these sugar-loaded foods, damage the tooth enamel.' | 7. | Reduce the amount of sugar you consume. |
8. | 'Water does not stain the teeth, therefore, consume large quantities.' | 8. | Drink large amounts of water. |
9. | 'You should have regular dental check-ups to detect the early signs of tooth decay.' | 9. | Visit your dentist regularly. |
MARKING THE SUMMARY
Marking is on the basis of the inclusion of valid material and the exclusion of invalid material.
The summary should be marked as follows:
- Mark allocation:
- 7 marks for 7 points (1 mark per main point)
- 3 marks for language
- Total marks: 10
- Distribution of language marks when a candidate has not quoted verbatim:
- 1–3 points correct: award 1 mark
- 4–5 points correct: award 2 marks
- 6–7 points correct: award 3 marks
- Distribution of language marks when a candidate has quoted verbatim:
- 6–7 quotes: award no language mark
- 1–5 quotes: award 1 language mark
NOTE:
- Word count:
- Markers are required to verify the number of words used.
- Do not deduct any marks if the candidate fails to indicate the number of words used, or if the number of words used is indicated incorrectly.
- If the word limit is exceeded, read up to the last sentence above the stipulated upper limit and ignore the rest of the summary.
TOTAL SECTION B: 10
SECTION C: LANGUAGE
NOTE:
- One-word answers must be marked correct even if the spelling is incorrect, unless the error changes the meaning of the word.
- In full-sentence answers, incorrect spelling should be penalised if the error is in the language structure being tested.
- entence structures must be grammatically correct and given in full sentences/ as per instructions.
- For multiple-choice questions, accept BOTH the letter corresponding with the correct answer AND/OR the answer written out in full as correct.
- Where an abbreviation is tested, the answer must be punctuated correctly. QUESTION 3: ANALYSING AN ADVERTISEMENT
3.1 To people who enjoy sweet foods/cake/hot beverages.✔ (1)
3.2 To offer a/an healthier/alternate option. (1)
3.3
3.3.1 D/enjoyment✔ (1)
3.3.2
- Huletts provides the opportunity to have moments of enjoyment through a slice of cake/a cup of coffee/biscuits/the presentation. ✔✔✔
OR - The picture of the box of sugar and artificial sweeteners shows that these products from Huletts make the enjoyment of a slice of cake/a cup of coffee/biscuits possible, even for the health-conscious. ✔✔✔ (3)
3.4
- To emphasise how old the company is. ✔
- To emphasise how reputable the company is. ✔ (2)
3.5 Open-ended. Accept a suitable response, e.g.
- Yes.
The advertised products can be used in different ways e.g. coffee. The company has been in existence for more than 125 years and is therefore, reliable. The advertiser has also included artificial sweeteners which are the alternate to sugar for people who are health-conscious/have diabetes.
OR
- No.
Sugar and sweeteners are health hazards and can cause harm/diseases to the body. Products with large amounts of sugar can cause diseases, e.g. diabetes.
NOTE: Do not award a mark for Yes or No. The above are merely examples. A candidate can score 1 mark for an answer that is not well substantiated. (2)
QUESTION 4: ANALYSING A CARTOON
4.1
4.1.1B/anxious✔ (1)
4.1.2
- Amy is reluctant to open the email ✔she receives from Waverly University/Collegeas she does not know whether her application is successful or not./Amy uses the expression, ‘OMG’ to show her anxiety. ✔
OR - Amy’s eyes are wide open.✔
- Amy’s mouth is wide open.✔
- Amy is clutching the phone with both hands. ✔
NOTE: Accept any TWO of the above answers. (2)
4.1.3 Oh My Gosh/Goodness/God✔ (1) NOTE: Accept any other suitable response.
4.2 To emphasise that Amy is crying (loudly). (1)
4.3
4.3.1 By using the word 'cruel',✔ the cartoonist conveys that the mother does not approve of the way in which the response to Amy's application was supposedly worded.✔ (2)
4.3.2 humour✔ (1)
4.4 Open-ended. Accept a suitable response, e.g.
- No.
In frame 2, Amy's father plays a cruel trick on her when he creates the impression that her application is unsuccessful by saying, '… we regret to inform you …'. What he expects to be funny upsets Amy causing her much anxiety. Therefore, playing with someone's emotions is not humorous/funny.
OR
- Yes.
The father creates an expectation that Amy has received an unfavourable response by saying the words, '… we regret to inform you …'. The ellipsis indicates the strategic pauses he makes to build suspense. /The humour lies in the fact that the father creates undue anxiety for both Amy and her mother by saying '… we regret to inform you …' (frame 2) only to reveal later that Amy's application to university has been successful.
NOTE: Do not award a mark for Yes or No. The above are merely examples. A candidate can score 1 mark for an answer that is not well substantiated. (2) [10]
QUESTION 5: LANGUAGE AND EDITING SKILLS
5.1
5.1.1
- difference✔ (1)
- are✔ (1)
- as✔ (1)
- instantly✔ (1)
5.1.2 One thousand nine hundred/nineteen hundred✔ (1)
5.1.3 Emojis do not constitute a language.✔ (1)
5.1.4 separate/split/divide✔ (1)
5.1.5 don't they/do they not✔ (1)
5.1.6 When Siyabonga sent his mother a smiley emoji,✔she responded with a heart emoji.✔ (2)
5.1.7 Elize said that she/he✔ had used✔ emojis the previous day/the day before✔.
NOTE: Award ONE mark for each underlined change and ONE mark for correct punctuation. (4)
5.2
5.2.1 Every leaf is trapping CO2.✔ (1)
5.2.2 for – preposition✔ planet – (common) noun✔ (2)
5.2.3 worse✔ (1) 5.2.4 donation✔ (1)
5.2.5 The leaves did not/didn't fall off the tree during autumn.✔ (1)
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 80
TOURISM GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
TOURISM
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- This question paper consists of FIVE sections.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- In QUESTIONS 3.1 and 3.2, round off your answer to TWO decimal places.
- Show ALL steps for the calculations.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Use the mark allocation of each question as a guide to the length of your answer.
- Write neatly and legibly.
- The table below is a guide to help you allocate your time according to each section.
SECTION | TOPIC | MARKS | TIME (minutes) |
A | Short Questions | 40 | 20 |
B | Map Work and Tour Planning; Foreign Exchange | 50 | 50 |
C | Tourism Attractions; Culture and Heritage Tourism; Marketing | 50 | 50 |
D | Tourism Sectors; Sustainable and Responsible Tourism | 30 | 30 |
E | Domestic, Regional and International Tourism; Communication and Customer Care | 30 | 30 |
TOTAL | 200 | 180 |
QUESTIONS
SECTION A: SHORT QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.20) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.21 D.
1.1.1 This type of visa applied for when travelling to European Union countries:
- Brazilian
- Scottish
- Schengen
- American
1.1.2 A compulsory vaccination required when visiting certain African countries:
- Bilharzia
- Yellow fever
- Hepatitis A
- Malaria
1.1.3 A bank will use the … when a South African tourist at OR Tambo International Airport exchanges R5 000,00 to euro:
- bank buying rate
- bank investment rate
- bank repo rate
- bank selling rate
1.1.4 When practising daylight saving time (DST), participating countries are required to adjust their clocks … 
- backward by ONE hour in summer.
- forward by ONE hour in winter.
- forward by ONE hour in summer.
- backward by TWO hours in summer.
1.1.5 An IDP is required to …
- participate in local cultural activities.
- fly a light aircraft in a foreign country.
- hire a vehicle at certain foreign destinations.
- participate in white water rafting activities.
1.1.6 The difference between an attraction and an icon:
- An attraction is a feature tourists want to experience while an icon is a symbol representing a destination.
- An attraction is a symbol attracting tourists while an icon is an attraction that attracts cultural tourists only.
- An attraction represents a destination whilst an icon contributes to the economy of the country.
- An attraction is a new experience at a destination while an icon is an existing attraction at a destination.
1.1.7 The Jungfrau-Aletsch is a mountain range found in this country:
- Japan
- India
- Brazil
- Switzerland
1.1.8 The TWO icons found in Rome: 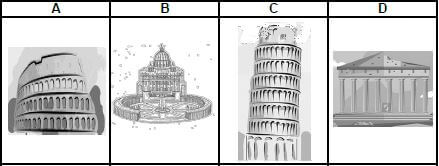
- Icon A and icon B
- Icon A and icon C
- Icon C and icon D
- Icon B and icon D
1.1.9 A stretch of coastline with golden beaches and world-class golf courses:
- Floating Markets
- Algarve
- Blue Mosque
- Petra
1.1.10 The symbol below shows an attraction is universally accessible:
1.1.11 If a tourism business practises the triple bottom-line approach, it will lead to…tourism.
- irresponsible
- practical
- sustainable
- friendly
1.1.12 A payment made to an employee for work done:
- Remuneration
- Bartering
- Trading
- Transaction
1.1.13 An example of ethical staff behaviour:
- Inform the supervisor when you will be absent from work.
- Granting unlimited discounts to family and friends.
- Not paying an employee for all the extra hours worked.
- Taking credit for work that is not considered your own.
1.1.14 An example of a fringe benefit for cabin crew at an airline:
- Monthly salary
- Severance pay
- Uniform allowance
- Reduced tax
1.1.15 The eruption of a volcano on an island relying on tourism as their main source of income will have this negative impact:
- Damaged access roads and fewer tourists visiting the resorts
- Heavy snowfalls and more tourists arriving for a skiing holiday
- Wild flowers to bloom and an increase in eco-tourists visiting the island
- A display of fireworks and fewer volunteers for the opening ceremony
1.1.16 The image of a country hosting a global event will be enhanced when …
- unknown sponsors are involved in the event.
- deadlines during the preparation process are met.
- the event is advertised on one media platform.
- local communities are not allowed to sell their products.
1.1.17 This logo shows tourists that their holiday benefits local communities and economies:
1.1.18 General unrest, protests and strikes in South Africa lead to …
- job creation.
- loss of investor confidence.
- the strengthening of the local currency.
- positive publicity.
1.1.19 Statistical information regarding tourist arrivals in South Africa from countries such as the United States of America and Australia, is classified as …
- land markets.
- water markets.
- air markets.
- rail markets.
1.1.20 Renovations to a hotel room during a guest's stay may …
- decrease GDP growth.
- enhance staff team building.
- inconvenience the guest.
- add costs to the guest's bill. (20)
1.2 Give ONE word(s)/term for each of the following descriptions by choosing a word(s)/term from the list below. Write only the word(s)/term next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
global recession; passport; deduction; FOREX; telegraphic transfer TravelWallet; multiplier effect; single supplement; MasterCard |
1.2.1 An example of a preloaded foreign currency card where the exchange rate is fixed by the bank when purchased
1.2.2 A business will display the logo of this institution to indicate they accept credit card transactions
1.2.3 An electronic method to transfer funds to foreign countries
1.2.4 The additional amount payable when a guest prefers not to share a room
1.2.5 The term reflected on the salary slip of an employee that shows the amount paid to the Unemployment Insurance Fund (UIF) (5)
1.3 Choose the correct word from those given in brackets. Write only the word(s) next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.3.6 passport.
1.3.1 The (educational level/financial status) of a client is an important factor to consider when drawing up a tourist's profile.
1.3.2 A South African tourist returning to OR Tambo International Airport with gift purchases over one hundred thousand rand must go through the (red/green) channel at customs.
1.3.3 A positive impact for the locals of hosting the 2018 FIFA World Cup in Russia is referred to as the (magnetic/multiplier) effect.
1.3.4 When a South African tourist applies for a visa, proof of paid (accommodation/taxes) is a compulsory requirement.
1.3.5 The (Blue Mosque/Dome of the Rock) is a religious structure located in the city of Jerusalem. (5)
1.4 Choose the host (country/province/city) from COLUMN B that matches the global event in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–F) next to the question numbers (1.4.1 to 1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.4.6 G.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.4.1 Comrades Marathon |
(5 x 1) (5) |
1.5 South Africa, like other countries, requires annual statistical information on visitor arrivals in the country. Refer to the key indicators of the statistical information below.
Match the key indicators to the infographics. Write only the letters (A–F) next to the question numbers (1.5.1 to 1.5.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.5.6 G. 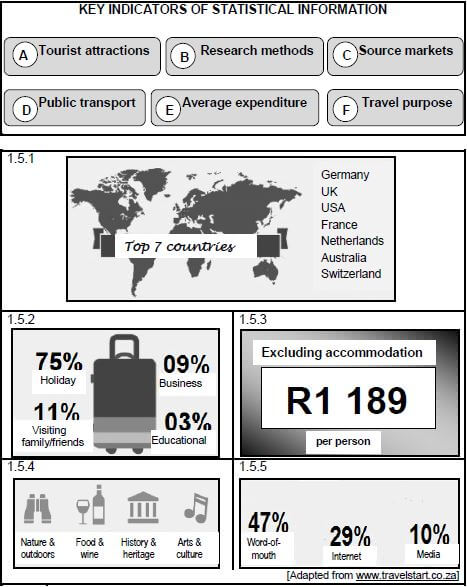 (5)
(5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 40
SECTION B: MAP WORK AND TOUR PLANNING; FOREIGN EXCHANGE
QUESTION 2
2.1 Study the World Time Zone map below, read the information and answer the questions that follow. 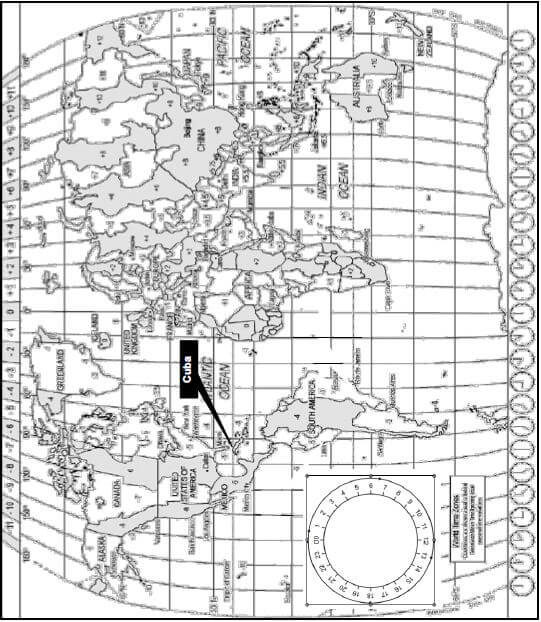
[Adapted from www.paperlesstravel.com]
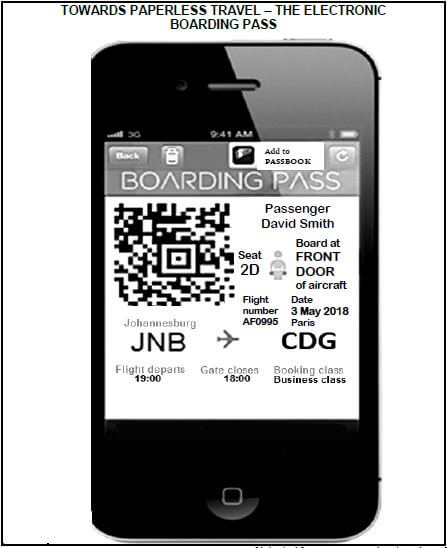
2.1.1 Refer to Mr David Smith's electronic boarding pass on his cellphone and identify the following:
- The flight number (1)
- Mr Smith's seat number (1)
- The airport code for Charles De Gaulle International Airport in Paris (1)
2.1.2 With reference to Mr Smith's boarding pass, give ONE reason why he had to board at the front door of the aircraft. (2)
2.1.3 Explain TWO advantages for airlines using electronic boarding passes. (4)
2.1.4 Discuss the following:
- ONE advantage of using electronic boarding passes for tourists (2)
- ONE disadvantage of using electronic boarding passes for tourists (2)
2.2 Study the itinerary below and answer the questions that follow.
ITINERARY Mr David Smith, a South African engineer, travelled from Johannesburg via Paris to Havana in Cuba to oversee the construction of a new bridge in 2018.
First leg of Mr Smith's trip Second leg of Mr Smith's trip NOTE: At the time of the trip both France and Cuba practised DST. |
2.2.1 There were no directs flights available from Johannesburg to Havana on the dates Mr Smith wanted to travel. The travel agent, who did the flight bookings, considered logical route planning for Mr Smith's trip.
Refer to the route indicated on the map, give ONE reason to support this statement. (2)
2.2.2 First leg of Mr Smith's trip Calculate what time it was in Paris when Mr Smith departed from OR Tambo International Airport at 19:00.
NOTE: France practises DST. Show ALL calculations. (4)
2.2.3 Calculate how many hours Mr Smith was in transit at the Charles De Gaulle International airport. Show ALL calculations. (4)
2.2.4 Second leg of Mr Smith's trip Calculate the flying time of Mr Smith's flight from Paris to Havana. NOTE: Both France and Cuba practise DST. Show ALL calculations. (5) [28]
QUESTION 3
Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.
EXCHANGE RATE TABLE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3.1 With reference to the exchange rate table above, identify the strongest currency. (1)
3.2
3.2.1 Give ONE reason why the bank selling rate of the currencies in the table is higher than the bank buying rate. (2)
3.2.2 In the table above, identify the TWO countries where South Africans will receive the greatest value for their money. (2)
3.3 Ms Nobuhle Maliti lives in South Africa and wants to visit the United States of America (USA). She has R58 000,00 for the trip.
Her return flight ticket will cost R26 000,00, the USA visa and travel insurance will cost R3 800,00 and the tour package for the USA is R23 100.
3.3.1 Calculate, in rand, the total cost of Ms Maliti's trip to the USA. (2)
3.3.2 Will Ms Nobuhle Maliti have enough money for the trip? Give ONE reason for your answer. (2)
3.3.3 Ms Maliti exchanges R58 000 for USD at the OR Tambo International Airport. Using the exchange rate table above, calculate the amount of US dollars Ms Maliti received when she exchanged the R58 000. (3)
3.3.4 When Ms Maliti returned to South Africa she had USD150 left which she exchanged at the OR Tambo International Airport. Calculate the amount of rand she received. (3)
3.4 Study the magazine cover below and answer the questions that follow.
| THE IMPACT OF A WEAK RAND | |
 | A weak rand can have both a negative and a positive impact on the tourism industry and on the South African economy. |
[Adapted from www.financialmail.com]
Refer to the scenario above, write a paragraph in which you discuss how a weak rand can help to alleviate poverty and unemployment in South Africa.
Your discussion must include the following:
- How a weak rand will give international visitors more buying power (2)
- How the scenario will contribute to the multiplier effect (2 x 2)
NOTE: ONE mark will be awarded for the paragraph format containing complete, well-constructed sentences without bullets or numbers. (1) (7) [22]
TOTAL SECTION B: 50
SECTION C: TOURISM ATTRACTIONS; CULTURE AND HERITAGE TOURISM; MARKETING
QUESTION 4
Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.
4.1
| Mr Bean is on a treasure hunt to find the icons and attractions in London. Help him to find his way to the icons and attractions in London using the treasure map below. |
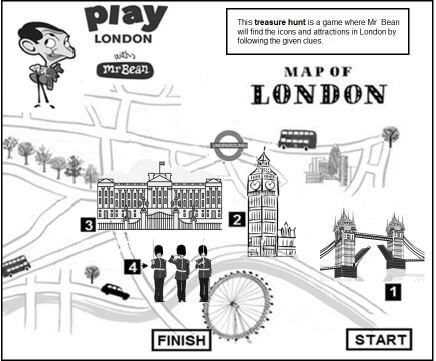
[Adapted from www.pintinterest.com]
4.1.1 Give the name of the country where the treasure hunt takes place. (1)
4.1.2 Mr Bean is using public transport for the treasure hunt. Identify, on the map, the mode of public transport he can use. (2)
4.1.3 Identify the THREE international icons (1, 2 and 3) that Mr Bean needs to find during the treasure hunt. (3)
4.1.4
- Identify the military activity 4 that Mr Bean will watch when visiting icon 3. (2)
- Describe the military activity in QUESTION 4.1.4(a). (2)
- State what icon 3 is mainly used for. (2)
4.1.5 Mr Bean's final clue is to locate the Crown Jewels. Name the icon where he will find this treasure. (1)
4.2 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.
THE AUSTRALIAN CHALLENGE The Australians see this site as a celebrated icon and take pride in its natural beauty. To the Aborigines (indigenous people) it is a sacred site, supporting them financially and spiritually. [Adapted from www.cnn.com] |
4.2.1 Identify the icon in this article. (1)
4.2.2 Name ONE other icon located in Australia. (1)
4.2.3 Do you think the icon named in QUESTION 4.2.1 is a successful tourist attraction? Give ONE reason for your answer. (2)
4.2.4
- Give TWO reasons why the Aborigines are unhappy with the current situation regarding this icon. (4)
- Recommend ONE way in which the Australian authorities can address EACH of the reasons given in QUESTION 4.2.4(a). (4) [25]
QUESTION 5
5.1 Read the information below and answer the questions that follow.
THE ǂKHOMANI CULTURAL LANDSCAPE The ǂKhomani Cultural Landscape being declared a World Heritage Site shows the acknowledgement by UNESCO of the universal value and importance of this site as a living heritage. [Adapted from Sawobona, September 2017 and Indwe, October 2017] |
5.1.1 Give the name of the province where the World Heritage Site in this article is located. (1)
5.1.2 State the type of World Heritage Site of the ǂKhomani Cultural Landscape according to UNESCO's classification. (1)
5.2 Explain ONE reason why this World Heritage Site is referred to as a 'living heritage'. (2)
5.3 In a paragraph, discuss how the ǂKhomani Cultural Landscape being declared a World Heritage Site will support the rural development strategy for the ǂKhomani San.
Your paragraph must include the following:
- Improved quality of life
- Cultural pride and sustainability
- Infrastructural accessibility (3 x 2)
NOTE: ONE mark will be awarded for paragraph format containing complete, well-constructed sentences without bullets or numbers. (1) (7) [11]
QUESTION 6
Study South Africa Tourism's (SATourism's) Marketing Event Calendar 2018 below and answer the questions that follow. 
6.1 Identify TWO international events where SATourism markets South Africa as a destination of choice. (2)
6.2 Explain the purpose of the event from 23 to 25 September 2018. (2)
6.3 State TWO ways in which South African Tourism markets South Africa at all the travel shows above. (4)
6.4 The campaign below takes place in June and is aimed at South Africans. 
Discuss TWO ways in which this campaign encourages:
6.4.1 South African businesses to make a positive contribution to tourism in South Africa. (2)
6.4.2 The South African public to make a positive contribution to tourism in South Africa (2)
6.5 Explain ONE reason why South African Tourism made this calendar available to tourism stakeholders. (2) [14]
TOTAL SECTION C: 50
SECTION D: TOURISM SECTORS; SUSTAINABLE AND RESPONSIBLE TOURISM
QUESTION 7
7.1 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
DISILLUSIONED!!!* Megan has been employed at a restaurant as a waitron for the past six months. A contract of employment was signed after she accepted the position at the restaurant. *Disillusioned: A feeling of disappointment |
7.1.1 Explain the term contract of employment. (2)
7.1.2 Identify ONE way in which Megan is being exploited at her place of employment in the extract above. (2)
7.1.3 Advise Megan and give TWO ways how her grievances in the workplace can be addressed. (4)
7.1.4 Discuss TWO ways in which the current working conditions can impact on Megan's work ethic. (4) [12]
QUESTION 8
8.1 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
BASOTHO CULTURAL VILLAGE – OUR HERITAGE Being a responsible traveller is more than just words and intentions. It involves following a code of ethics and playing your part in creating a sustainable and caring approach to travel. |
8.1.1 Explain what is meant by a code of ethics for responsible tourist behaviour. (2)
8.1.2 Explain the meaning of '… do your children not deserve to see this continent as you do today?'. (2)
8.1.3 International visitors to South Africa want to experience a taste of the African lifestyle and history. Recommend THREE ways in which they can behave responsibly when visiting the Basotho Cultural Village. (6)
8.2 Read the case study below and answer the questions that follow.
| CHANGING LIVES – WITH SOAP | |
The Wilderness Adventure Camp in Namibia offers educational counselling and financial support to a community project in Katutura, run by six HIV positive women. The project involves producing a soap with an olive oil base. |
|
8.2.1
- Identify the TWO pillars of sustainable tourism practices evident in this extract. (2)
- Match each pillar of sustainable tourism identified in QUESTION 8.2.1(a) with ONE example in the extract. (2)
8.2.2 Discuss TWO ways in which the support offered by the Wilderness Adventure Camp is positively changing the lives of the HIV-positive women within the Katutura community. (4) [18]
TOTAL SECTION D: 30
SECTION E: DOMESTIC, REGIONAL AND INTERNATIONAL TOURISM, COMMUNICATION AND CUSTOMER CARE
QUESTION 9
9.1 Read the news article below and answer the questions that follow.
POSSIBLE DISASTER – OR NOT? The outbreak of bird flu and the Robben Island ferry (passenger boat) that almost sank in 2017 had negative consequences for the tourism industry in South Africa. BIRD FLU OUTBREAK
A FERRY STARTED TO SINK [Adapted from www.timeslive.co.za and www.ewn.co.za] |
9.1.1 Give ONE reason why Monte Casino Bird Gardens and the World of Birds temporarily stopped their normal activities. (2)
9.1.2 State ONE positive and ONE negative viewpoint tourists may have of the preventative measures implemented at the Johannesburg Zoo. (4)
9.1.3 Name the type of incident in September 2017 involving the tourists returning from Robben Island. (2)
9.1.4 Discuss TWO ways in which the incident named in QUESTION 9.1.3 will impact on tourists visiting the Western Cape. (4)
9.1.5 Explain TWO ways in which the two incidents in the extract will impact on South Africa's economy. (4)
9.2 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow. 
9.2.1 Identify the group with the highest number of inbound international tourist arrivals. (2)
9.2.2 Travel patterns can contribute to an increase in the average expenditure of tourists. Discuss ONE way in which the following will contribute to an increase in the average expenditure of tourists.
- Only arrivals (2)
- Multiple trips (2)
9.3 Financial institutions reward clients with loyalty points every time they use their credit cards. Explain how tourists can use these accumulated loyalty points when they travel. (2) [24]
QUESTION 10
Study the information below and answer the questions that follow. 
10.1 Recommend ONE way in which EACH of the above can be resolved. Number your answers 10.1.1 and 10.1.2. (2 x 2) (4)
10.2 Name ONE way in which the attraction can measure the successful implementation of the recommendations made in QUESTION 10.1. (2) [6]
TOTAL SECTION E: 30
GRAND TOTAL: 200
TOURISM GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
TOURISM
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
TOPICS IN THE TOURISM CAPS | ABBREVIATION | |
Topic 1 | Tourism sectors | TS |
Topic 2 | Map work and tour planning | MTP |
Topic 3 | Tourism attractions | TA |
Topic 4 | Sustainable and responsible tourism | SR |
Topic 5 | Domestic, regional and international tourism | DRI |
Topic 6 | Culture and heritage tourism | CH |
Topic 7 | Foreign exchange | FX |
Topic 8 | Communication and customer care | KK |
Topic 9 | Marketing | M |
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A: SHORT QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 | C✔/Schengen | MTP |
1.1.2 | B✔/Yellow fever | MTP |
1.1.3 | D✔/Bank selling rate | MTP |
1.1.4 | C✔/forward by ONE hour in summer | MTP |
1.1.5 | C✔/hire a vehicle at certain foreign destinations | MTP |
1.1.6 | A/An attraction is a feature tourists want to experience while an icon is a symbol representing a destination. | TA |
1.1.7 | D/Switzerland | TA |
1.1.8 | A/Icon A and icon B | TA |
1.1.9 | B/Algarve | TA |
1.1.10 | A/picture of sign language | TA |
1.1.11 | C✔/sustainable | SR |
1.1.12 | A✔/Remuneration | TS |
1.1.13 | A✔/Inform the supervisor when you will be absent from work. | TS |
1.1.14 | C✔/Uniform allowance | TS |
1.1.15 | A✔/Damaged access roads and fewer tourists visiting the resorts | DRI |
1.1.16 | B✔/deadlines during the preparation process are met. | DRI |
1.1.17 | C✔/Fair Trade Tourism (FTT) | SR |
1.1.18 | B✔/loss of investor confidence. | DRI |
1.1.19 | C✔/air markets | DRI |
1.1.20 | C✔/inconvenience the guest. | KK |
(20 x 1) [20]
1.2
1.2.1 | TravelWallet | DRI |
1.2.2 | MasterCard | DRI |
1.2.3 | telegraphic transfer | DRI |
1.2.4 | single supplement | MTP |
1.2.5 | deduction | TS (5) |
1.3
1.3.1 | financial status ✔ | MTP |
1.3.2 | red ✔ | MTP |
1.3.3 | multiplier ✔ | FX |
1.3.4 | accommodation ✔ | MTP |
1.3.5 | Dome of the Rock | TA (5) |
1.4
1.4.1 | D/KwaZulu-Natal | DRI |
1.4.2 | E/Canada | DRI |
1.4.3 | A/Australia | DRI |
1.4.4 | B/London | DRI |
1.4.5 | F/Rio de Janeiro | DRI (5) |
1.5
1.5.1 | C✔/Source markets | DRI |
1.5.2 | F✔/Travel purpose | DRI |
1.5.3 | E✔/Average expenditure | DRI |
1.5.4 | A✔/Tourist attractions | DRI |
1.5.5 | B✔/Research methods | DRI (5) |
TOTAL SECTION A: 40
SECTION B: MAP WORK AND TOUR PLANNING; FOREIGN EXCHANGE
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1
-
- AF0995
- Air France 0995
- Note: Do not accept “0095” only. MTP (1)
-
- 2D✔ MTP (1) (c) CDG✔ (1)
2.1.2
- His seat number is 2D which is located in the front of the aircraft. ✔✔
- He is booked in the business class section which is located in the front of the aircraft.
- According to the configuration of the aircraft his seat is in the second row which is located at the front of the aircraft.
- As a business class passenger, he gets priority boarding.
2.1.3
- To save paper for the airline✔✔
- To reduce printing and maintenance costs for the airline✔✔
- To subscribe to sustainable practices
- o speed up the check-in process.
- To be technologically advanced
- Less pressure on the airline staff when it comes to boarding procedures.
2.1.4 (a)
- It is a more convenient option in terms of accessibility (mobile devices) compared to hard copies.✔✔
- It cannot be lost easily – it is on the cell phone.
- It eliminates time spent in long queues at the check-in counters when travelling without checked luggage.
- Tourists who are technologically inclined would prefer to utilise this streamlined check-in process.
(b)
- The cell phone's battery can be flat. ✔✔
- Problems with access to the Internet to download the electronic boarding pass.
- The cell phone/information can be lost/stolen/damaged.
- Tourists/staff who are not technologically inclined will experience difficulty in using the technology.
- Not all cell phones are able to operate the application.
2.2.1
- The flight routes consisted of two direct flights without travelling back and forth unnecessarily. ✔✔
- The flight travelled north directly to Paris where there was a stop-over followed by a direct transatlantic flight westward to Havana.
- It is a 1 stop flight.
- There are no direct flights to Havana, therefore he was in transit in Paris.
2.2.2 (4)
Leg 1 of Mr Smith's trip | Paris (+1) | Johannesburg (+2) |
Time difference: | 1 hours ✔ | |
OR |
Paris (+1) | Johannesburg (+2) | |
Daylight Saving Time: | Paris (+2) ✔ | |
2.2.3 (4)
Arrival time in Paris: Transit time in Paris: | 19:00 (+)✔ 11hours flying time = 06:00✔ |
2.2.4 (5)
Leg 2 of Mr. Smith's trip | Havana (-5) | Paris (+1) |
Time difference: | 6 hours ✔ | |
OR |
Havana (-5) | Paris (+1) | |
Daylight Saving Time added: Time difference: | Havana (-4) Paris (+2) | |
[28]
QUESTION 3
3.1 Euro✔
- € FX (1)
3.2
3.2.1 The bank has to make a profit when it sells currencies/FOREX. ✔✔ FX (2)
3.2.2
- Czech Republic ✔
Czech / Czech koruna - Egypt ✔
Egyptian / Egyptian pound
3.3
3.3.1
- R26 000 + R3 800 + R23 100 = R52 900✔✔
R52 900
3.3.2 R58 000 – R52 900 = R5 100
- Yes
She has not exceeded her budget✔✔ and will have R5 100 extra. Note: Do not award any marks for YES FX (2)
3.3.3
- R58 000 ÷ (✔) 14.11✔ = USD 4 110,56✔ FX (3) OR
USD 4 110,56✔✔✔
3.3.4 USD150 x (✔) 14,07✔ = R 2 110,50✔ FX (3) OR
R 2 110,50✔✔✔
3.4 PARAGRAPH
HOW A WEAK RAND CAN HELP TO ALLEVIATE POVERTY AND UNEMPLOYMENT IN SOUTH AFRICA.
A weak rand will attract more inbound international tourists to South Africa.✔✔ When inbound international tourists spend more in South Africa, a greater demand for tourism products and services is created. ✔✔ They will get more value for their money and therefore more spending within the local economy. ✔✔
- More international tourists will come to South Africa, they will spend more, thus alleviating poverty and reducing unemployment.
- When the rand is weak, inbound international tourists will receive more rand for their currency, giving them greater spending power in South Africa.
- An increased demand will lead to a growth in the GDP.
- More job opportunities are created.
- Improved standard of living for the people of South Africa. FX (6)
Paragraph format
Complete well-constructed sentences were used, written as a complete paragraph without bullets or numbers. (1) [22]
TOTAL SECTION B: 50
SECTION C: TOURISM ATTRACTIONS; CULTURE AND HERITAGE TOURISM; MARKETING
QUESTION 4
4.1
4.1.1 Britain
- UK
- United Kingdom
- Great Britain
- England
4.1.2 Road / Rail / Water transport ✔✔
- Note: Accept a relevant example such as double decker bus bus, metered taxi, underground train, river boat
4.1.3
- 1 - Tower Bridge
- 2 - Big Ben / Palace of Westminster
- 3 - Buckingham Palace
4.1.4
- Changing of the Guards
Note: Accept any reference to military activity at the icon. - The guards at the palace go through a military routine which attracts many tourists.
The changing of the guards and the ceremony of the process has become a tradition and is enjoyed by tourists. - It is the royal residence of the British monarch
Buckingham Palace hosts State functions.
4.1.5 Tower of London TA (1)
4.2
4.2.1
- Ayers Rock
- Uluru-Kata Tjuta National Park
- Uluru-Kata Tjuta
Note: Do not accept “Uluru” only. TA (1)
4.2.2 Sydney Opera House TA (1)
4.2.3 Yes.
- The visitor numbers exceeded the targeted numbers.
- It attracts tourists from all over the world who are interested in culture, heritage and nature.
OR
No.
- They do not have sustainable and responsible management plans in place.
- Tourists are destroying the site through litter and damaging the site through climbing.
- The tourists' disregard the religious significance of the site.
- There is little focus on the general appearance and upkeep of the attraction.
- There are no benefits for the indigenous people and on the environment.
Note: Do not award any marks for YES or NO
4.2.4 (a)
- Tourists climb the rock even though the aborigines do not want them to.✔✔
- The aborigines do not get the benefits from tourists visiting the site even though the land belongs to them.✔✔
- It is a sacred site to the aborigines and should be treated with respect.
- Few Aborigines are employed in the park.
(b) Problems with climbing the rock
- Limit the number of tourists climbing the rock.
- Involve the aborigines in granting permission rights to climbers.
- Use the local aborigines as guides for the climbers.
Do not get benefits from the tourism chain
The Aborigines should be given incentives such as becoming shareholders in the attraction.
- The Aborigines must be involved in the planning and management of the tourist activities in and around the attraction.
Disrespect of the sacred site
- Provide information boards/pamphlets with information on responsible tourist behaviour.
- More stringent regulations should be enforced by the government.
Few Aborigines employed
- Policy on preferential employment for aborigines.
Note: Ensure that the recommendation given in (b) are linked to the reason given in (a). [25]
QUESTION 5
5.1
5.1.1 Northern Cape CH (1)
5.1.2 Cultural CH (1)
5.2 The ǂKhomani San tribes are still living in this area and they still practise some of their ancient cultural traditions.
5.3 Improved quality of life
Increase in tourism will lead to increased revenue and therefore they can spend money on basic necessities to improve their quality of life.
- With the ǂKhomani Cultural Landscape becoming a World Heritage Site it will increase the number of tourists visiting this area which will mean increased revenue for the people.
- Increased revenue will alleviate poverty in this rural part of South Africa and improve their quality of life.
- Job creation.
Cultural pride and sustainability
Due to the traditional practises that come from an ancient culture still being practised today, they will protect their cultural practises.
- Their culture earned them World Heritage Status, so they will now protect and take pride in their culture.
- They will manage the site sustainably as well as their cultural practises as it is an attraction that is earning them an income and bringing tourists to this rural part of South Africa.
Infrastructural accessibility
The ǂKhomani people will now also enjoy and benefit from the upgrades to infrastructure due to increased visitor numbers and increased interest to visit the new World Heritage Site.
- Increase in visitor numbers to the World Heritage Site will set in motion the demand for tourism infrastructure and support services which will set the multiplier effect in motion for the region.
Paragraph format
Complete well-constructed sentences were used, written as a complete paragraph without bullets or numbers. [11]
QUESTION 6
6.1 World Travel Market
- WTM
- ITB
Note: Accept any order
6.2 Tourism businesses in South Africa advertise amongst others, their outdoor products and services to domestic tourists.✔✔
- They showcase tourism products and services on offer in South Afrika.
6.3 Attractive and eye-catching displays of all 9 provinces at the South African Tourism stands.
- Brochures, DVDs and proudly South African branded hand-outs.
- Personnel manning the stand answer questions about South Africa
- Networking with other international role players and promoting the South African brand image to these role players.
- Presentations on South African products and services.
- Sharing posts to social media platforms.
6.4
6.4.1 Tourism businesses are encouraged to maintain high service levels to maintain good publicity.
- Responsible management plans are in place to support the tourism businesses sustainably.
- Tourism businesses must have sound business principles in place to ensure profitability and thus a guarantee of the business succeeding and being in operation for the future.
6.4.2 Locals must become brand ambassadors for the country and always say positive things about South Africa.
- Each South African should play their part in ensuring South Africa is a safe, secure, clean and beautiful country.
- South Africans must act in a responsible way to showcase their pride in their country.
- To encourage South Africans to be responsible travellers in their own country.
- Encourage South Africans to explore their own country.
6.5 Stakeholders can have time in advance to prepare and inform relevant parties of these marketing opportunities.✔✔ [14]
TOTAL SECTION C: 50
SECTION D: TOURISM SECTORS; SUSTAINABLE AND RESPONSIBLE TOURISM
QUESTION 7
7.1
7.1.1 A verbal or written agreement outlining the terms and conditions of employment. ✔✔ Note: Accept examples linked to the Contract of Employment.
7.1.2 Working double shifts with no overtime pay. ✔✔
- Not allowed to sit during shifts.
- Increased responsibilities without extra remuneration.
- Verbally abused by her employer.
- No staff transport available at the end of their late-night shifts.
- No opportunities available to channel grievances.
7.1.3 Raise her grievance to her employer stating the current unacceptable working conditions and suggest ways to improve upon it. ✔✔
Seek legal advice from a labour law expert / CCMA. ✔✔
- Discuss the matter with the union she is affiliated (associated) to.
- Work towards resolving the grievance amicably (politely) between the employer with emphasis to compliance in terms of the employment contract.
- Commence with the restaurant's internal grievance procedures if one is in place.
7.1.4 Lack of concentration/focus on the tasks on hand when at work.✔✔ Not keen in displaying her best efforts when performing her duties at work.✔✔
- Frustration spilling over onto customers that she is attending to.
- Demotivation can lead to tasks left incomplete or not attempted altogether.
- Absenteeism / lack of punctuality will increase.
- Loyalty to the company can be compromised [12]
QUESTION 8
8.1
8.1.1 These are guidelines addressing responsible and appropriate behaviour when visiting a destination. ✔✔
- It includes appropriate behavioural guidelines including the pillars of sustainability and responsible tourism.
8.1.2 Ensuring that the resources in an area are respected and sustained for future generations to benefit and enjoy. ✔✔
8.1.3
- Enquire from local leaders the appropriate behaviour in line with the local customs and religious ceremonies.✔✔
- Respect the dignity/privacy of the locals. ✔✔
- Be sensitive and ask permission before taking photographs. ✔✔
- Do prior research on the culture practised at the attraction in order not to offend the locals.
- Dressing appropriately to avoid offence.
- Participate in the local everyday activities of the local people.
- Tourists should be encouraged to act responsibly towards the environment. (Accept examples in context of the cultural village)
8.2
8.2.1 (a)
- Social Pillar✔
- People pillar
- Economic Pillar✔
- Profit pillar
(b)
- Social pillar (People pillar) - counselling sessions / Supporting the health of HIV positive women.✔
- Economic Pillar (Profit pillar) - financial support✔ / making and selling soap.
Note: If no pillar is given in (a), no marks are to be awarded for (b)
8.2.2 Offering employment and empowerment to the local women who are HIV-positive. ✔✔
The financial gain earned through employment is used to meet the basic needs of these women and their children. ✔✔
- The earnings enable these women to have access to basic health necessities needed to follow a healthy lifestyle e.g. access to medication.
- The counselling builds on their knowledge of the HIV epidemic and assists in maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
- Skills are developed. [18]
TOTAL SECTION D: 30
SECTION E: DOMESTIC, REGIONAL AND INTERNATIONAL TOURISM; COMMUNICATION AND CUSTOMER CARE
QUESTION 9
9.1
9.1.1 Bird flu outbreak✔✔
- Outbreak of H5N8 bird flu virus
- Infected wild birds
- Caused the deaths of many wild birds
- Stopped the spread of the disease
9.1.2 Positive
Tourist may want to educate their children about the preventative measures in place to stop the spreading of a dangerous virus. ✔✔
- Tourists will appreciate the measures put in place by the zoo to safeguard visitors against contracting and spreading the virus.
- Tourists may regard the zoo as a responsible attraction due to its attempts in containing bird flu.
- Chemicals used are not harmful to humans
Negative
Some tourists will view the disinfectants used by the zoo as harmful to humans and the surrounding environment. ✔✔
- Some tourists will not be comfortable in submerging their feet or shoes into a footbath at the exits.
- Visitors will put their trip to the attraction on hold until it is safe therefore causing a decline in ticket sales.
- Bad publicity through word of mouth.
- Engaging in the process can be time consuming
Note: Award marks for ONE answer from EACH category (positive and negative)
9.1.3 Unforeseen occurrence✔✔
- Boating/ferry accident
9.1.4 Tourists will be reluctant to use the ferries to Robben Island due to the element of danger. ✔✔
Tourists may decide not to visit Robben Island but may opt to visit other destinations. ✔✔
- Visitors would be fearful of their safety when visiting other attractions in the Western Cape.
9.1.5 A decline in foreign tourist arrivals to South Africa will result in decreased foreign income. ✔✔
The multiplier effect will be negatively affected due to fewer tourists visiting the attractions. ✔✔
- Domestic travel to the affected areas will decrease resulting in a decrease in visitor numbers and spending.
- Will result in job losses
9.2
9.2.1 Multiple trips ✔✔
- Group 3
- 445 495
- 41,1%
- Tourists who entered and departed South Africa more than once in June 2017.
9.2.2 (a) Only arrivals
- Inbound international tourists continued to spend money during their stay as they remained in the country for an undetermined period. ✔✔
(b) Multiple trips
- The basic expenditure of inbound international tourists is being repeated for every return visit to the country over a one-month period. ✔✔
- Each trip tourists make to South Africa they require accommodation, transport, food etc. thereby increasing the average expenditure of tourists.
9.3 Loyalty points can be used to supplement payment towards purchases, thus making products/services more affordable (discounts). ✔✔
- The tourists will spend their accumulated loyalty point at the loyalty programme partners, thus increasing the financial gains for these businesses.
Note: Do not accept one-word answers.
QUESTION 10
10.1
10.1.1 Make use of technology such as listening devices (audio-tours) and translation Apps. ✔✔
- Employ tourist guides that speak the language of the group.
- Employ multilingual tourist guides (speaking more than one language).
- Tours for smaller groups
- Retraining of tourist guides to improve communication skills.
- Make information available in different languages.
10.1.2 Establish a restaurant at the attraction. ✔✔
- Encourage entrepreneurship by allowing local vendors to trade at the attractions.
- Partner with neighbouring food and beverage outlets.
10.2 The attraction would use different types of feedback methods such as feedback cards, questionnaires etc. to determine how successful the above recommendations were. ✔✔
Note: Accept examples of feedback methods. [6]
TOTAL SECTION E: 30
GRAND TOTAL: 200
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY: ELECTRONICS GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY: ELECTRONICS
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY
1.1
- 'Major incident 'is an occurrence of catastrophic proportion✔ resulting from the use of plant and machinery from activities in the workplace. ✔
- Severe or serious injury or great damage to machinery and persons resulting from the use of plant or machinery in a workplace. (2)
1.2
- Manufacturers must ensure that products are safe ✔
- Not permitting any employee to do any work or to produce any artefact unless precautionary measures are in place. ✔
- Safe to use / without risk to health
- Safety feature
- Instructional manual
- Good state or design without a fault. (2)
1.3
- 'Horseplay' is an unsafe act because it is an inappropriate behaviour by learners ✔ in the workshop that would compromise the safety ✔ of themselves and others.
- It distracts others that could lead to accidents or incidents. (2)
1.4
- Do not touch the person. ✔
- Switch off the supply. ✔
- Help the person by removing him/her with a type of insulation material. (2)
1.5 Qualitative risk analysis defines the levels of threat ✔ and devises counter measures ✔ to eliminate possible risk. (2) [10]
QUESTION 2: RLC CIRCUITS
2.1 The total opposition to the flow of alternating current ✔ in a circuit comprising of resistance and reactance. ✔ (2)
2.2
2.2.1 (2)
(2)
If the learner drew only one signal, it doesn’t show relation. (no marks)
2.2.2  (2)
(2)
NOTE. If the learner drew only one signal, it doesn’t show relation. (no marks)
2.3
2.3.1
- C = 1
2 × π f × XC
= 1
2 × π × 60 × 36
= 73,68μF ✔ (3)
NOTE. Note if the formula is copied directly from the formula sheet a mark must be awarded, there after the substitution, manipulation and the answer must be correct to receive 3 marks.
2.3.2
- L = XL
2 × π × 60
= 22
2 × π × 60
= 58,35 mH ✔ ✔ (3)
NOTE. Note if the formula is copied directly from the formula sheet a mark must be awarded, there after the substitution, manipulation and the answer must be correct to receive 3 marks.
2.3.3 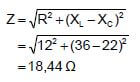 (3)
(3)
2.3.4
- 1 = VS
Z
= 60
18.44
= 3,25 A ✔ ✔ (3)
2.3.5
- Q = V × I × Sinθ
= 60 × 3,25 × Sin(50º) ✔
= 149,38 VA r ✔ (3)
2.4 The value of the inductive reactance will double/increase ✔ because the inductive reactance is directly proportional to the frequency ✔ of the supply voltage.
NOTE. If only the formula is given, no marks.
If the formula is given as a reason, 1 mark will be awarded for the formula. (2)
2.5. The resonant frequency is the frequency at which the inductive reactance ✔ is equal to the capacitive reactance. ✔
NOTE. All characteristics of resonance explained correctly will be accepted. (2)
2.6
- XL = VS
IL
=100
2
= 50 Ω (3) - XC = VS
IC
=100
6
= 16,67 Ω ✔ (3) - IX = IC + IL
= 6 - 2
= 4 A ✔ (3)
NOTE. If the learner stated either one or a difference in reactive currents is stated, the learner must be awarded 3 marks.  ✔ (3)
✔ (3)
2.6.2 Phase angle is leading. ✔ (1)
2.7 A low value of resistance produces a high Q-factor ✔ which results in a low bandwidth ✔ and high selectivity. (2) [40]
QUESTION 3: SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
3.1
- N-channel JFET or NFET ✔
- P-channel JFET or PFET ✔ (2)
3.2 To overcome leakage current between the gate terminal and Drain-Source channel, the gate terminal is electrically isolated from the channel ✔ by means of an extremely narrow layer of metal-oxide-silicon ✔ (MOS). (2)
3.3
3.3.1 Enhancement-mode ✔ N-channel ✔ MOSFET (2)
3.3.2 The lamp will switch ON as soon as the gate voltage VGS is raised ✔ to a sufficient level which will forward bias the internal channel of the MOSFET. ✔ (2)
3.3.3
- If RGS is short circuited, it will cause the internal conductive channel of the MOSFET to disperse, ✔ cutting the current flow ✔ and switching the lamp OFF. ✔ (3)
- If RGS is short circuited, the gate of the MOSFET will be tied directly to ground (0V potential), causing the internal channel to close and switch the lamp off.
3.4
3.4.1 Saturation region ✔ (1)
3.4.2
- At point C the UJT triggers ON. As the UJT is triggered, its internal resistance and voltage ✔ will decrease ✔ while current increases. ✔
- This is contrary to Ohm's law and is called negative resistance. (3)
3.5
3.5.1 Darlington pair ✔ (1)
3.5.2
- Very high current gain ✔
- Improved input impedance ✔
- When used in common collector pair it develops a very low output impedance (2)
3.6
3.6.1 Non-inverting input ✔ (1)
3.6.2
- Dual-in-line package outline (DIP) ✔
- Surface mount package (SMP) (1)
3.6.3 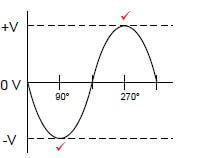 (2)
(2)
Note. If a square wave is drawn and it shows the correct inversion, 2 marks will be awarded.
3.7
- Open loop gain is the gain of an Op-Amp without any feedback ✔ from the output to the input.
- Closed loop gain is the gain of an Op-Amp with feedback ✔ from the output to the input. (2)
3.8 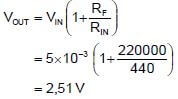 ✔ (3)
✔ (3)
3.9
- Trigger pin 2 is an active low trigger. ✔
- When the voltage on pin 2 is less than 1/3 of the supply voltage, the output goes high. ✔
- When the voltage is higher than 2/3 of the supply voltage, the output resets. ✔ (3) [30]
QUESTION 4: SWITCHING CIRCUITS
4.1
- An astable multivibrator generates a continuous train ✔ of (clock) pulses ✔ without the need of a trigger pulse.
- Continuously changes its state from high to low and back (2 marks)
- Continuously switches something on and off. (2 marks) (2)
4.2
4.2.1 Bistable multivibrator ✔ (1)
4.2.2 Positive feedback ✔ (1)
4.2.3 When a positive pulse (trigger pulse 1) is applied to the Trigger input, the output will change to a negative (-V) ✔ and remain there until a negative pulse (trigger pulse 2) is applied. ✔ When a negative pulse is applied to the trigger input, the output will change to positive. ✔ (3)
4.3
4.3.1
- Clock pulse generator ✔
- Morse code generators
- Timers
- Amateur radio equipment
- Systems that require square wave (1)
4.3.2 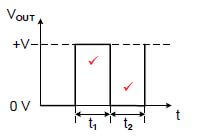 (2)
(2)
4.3.3
- If the value of R1 is increased, the RC time constant of the charging circuit (t1) increases, ✔ keeping the output of the 555 IC high for longer. ✔ This means that the positive output pulse (high) will be longer than the negative output pulse (low). ✔ (3)
- When the first trigger pulse is applied, Pin 7 of the 555 will be pulled (set) high to allow the capacitor to start charging. The charging period of the capacitor will only end once it has reached 2/3 Vcc, and any other further applied pulses during this period will be of no effect.
4.4
4.4.1 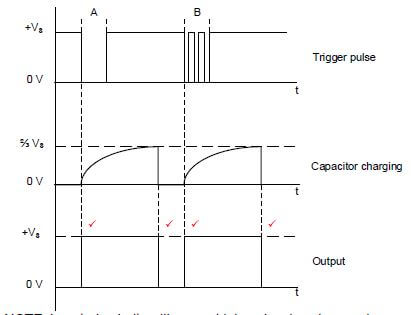 (4)
(4)
NOTE. Inverted polarity with correct intervals minus two marks
4.4.2 Trigger pulse B appears like a train of 'on' - 'off' pulses ✔ which is known as contact switch bounce. ✔ Switch bounce (2 marks) (2)
4.4.3
- The application of additional short pulses, ✔ after the initial set pulse will not affect the mono-stable multivibrator✔ that is already in the set state✔ and hence will not affect the charging of the capacitor (3)
- When the first trigger pulse is applied, Pin 7 of the 555 will be pulled (set) high to allow the capacitor to start charging. The charging period of the capacitor will only end once it has reached 2/3 Vcc, and any other further applied pulses during this period will be of no effect.
4.5
4.5.1
- Thermo-couple ✔
- Piezzo sensor ✔
- Microphone (2)
4.5.2 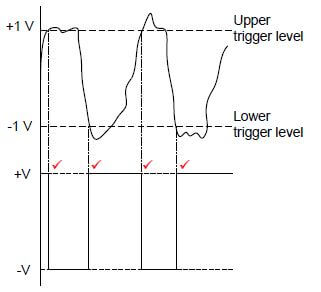 ✔ (4)
✔ (4)
4.5.3 When R1 is decreased the feedback voltage VR1 is decreased. ✔ As a result the positive feedback through R1 is decreased, ✔ lowering the trigger threshold voltage. ✔ (3)
4.6
4.6.1 The purpose of the comparator is to compare two input voltages. ✔ (1)
4.6.2
- A comparator compares the two voltages appearing at the two input terminals. ✔
- When one of its two input voltages is greater than the other, the output will go into one of the two saturation states. ✔
- When the inputs are reversed the output switches to the other saturation state. ✔ (3)
4.6.3 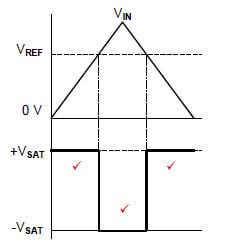 ✔ (3)
✔ (3)
4.7
4.7.1 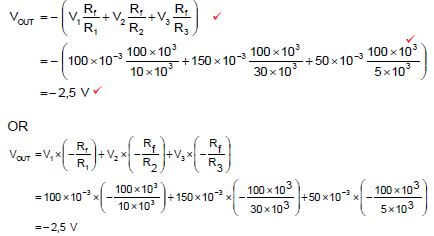 (3)
(3)
4.7.2 The voltage of each signal can be controlled independently by replacing each input resistor ✔ with a variable resistor ✔ (2)
4.7.3 DC blocking capacitors ✔ must be connected at the inputs ✔ to prevent dc current from being fed back to the input voltage sources. (2)
4.7.4 
ONE mark for CORRECT POLARITY
ONE mark for AMPLIFICATION
If the wave form does not depict the wave size but there is reference to the correct value of the wave, a mark must be awarded (2)
4.8
4.8.1 
1 mark for 90° phase shift
Correct orientation of which will be:
- 1 mark for positive half
- 1 mark for negative half (3)
4.8.2 Triangular wave 
1 mark for phase shift ✔
2 marks for correct orientation (3)
4.9
4.9.1  ✔ (3)
✔ (3)
4.9.2
- The textbook only mentioned the passive integrator of which the following will be accepted.
- If the RC time constant is short, the capacitor will charge rapidly ✔ reaching the maximum input voltage and remaining there ✔ until the input falls again. This results in the output having rounded leading and trailing edges ✔ with a flat top resembling a distorted square wave. ✔ (4)
- The following is the correct response for the Op-amp integrator.
- If the RC time constant is short, the output will rise in a linear manner until reaching the maximum output voltage and remaining there until the input falls again. This results in the output having straight sloping leading and trailing edges with flat tops and bottoms.
- It will resemble a triangular wave with its top and bottom peaks cut off. [60]

QUESTION 5: AMPLIFIERS
5.1 Class A - the transistor is biased with the Q-point on the midpoint ✔ of the load line, allowing for the full signal (360°) to be amplified. ✔ (2)
5.2
5.2.1
- To set the operating conditions (points) of the transistor. ✔
- To stabilise the operating point of the transistor. ✔ (2)
5.2.2 Q-point on the DC load line represents the voltages across the transistor ✔ and current through the transistor✔ when no input signal is applied. ✔ (3)
5.2.3 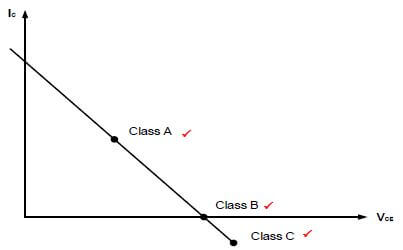 ✔ (3)
✔ (3)
Note. If the reference base biasing current is drawn and Q-point for class B is drawn slightly above line VCE, that mark will be awarded.
5.3 5.3.1 C2 serves as the AC coupling component between the two stages. ✔ C2 also blocks or decouples the DC component of the signal. ✔ (2)
5.3.2
- When an AC voltage is applied to the input of the first amplifier stage, ✔an alternating current will flow in the collector circuit of transistor (Q1). ✔
- An alternating voltage will develop across the collector resistor (RC1). ✔
- The developed alternating voltage across the RC1 will be transferred through capacitor C2 ✔ to the base of the transistor(Q2) in the amplifier 's second stage(stage 2). ✔
- The process will be repeated and the amplified output will measured between C3 and 0 V. ✔ (6)
5.3.3
- Impedance matching ✔
- Correct frequency response ✔
- DC isolation. (2)
5.4
5.4.1 Frequency response is the ability of the circuit ✔ to respond to a range of frequencies applied to the transistor. ✔ (2)
5.4.2 NOTE: The response given in the text book is wrong but marks will be awarded as such:
- Half-power points (-3dB) is the point when the output ✔ is at half the input power. ✔ (2)
- The correct response is as follows:
- The half-power point is the points at which the output power has dropped to half of its peak value; that is, at a level of -3 dB.
5.4.3
- At lower frequencies the reactances of the decoupling capacitors across the emitter resistors rises. ✔
- These reactances each combine with the resistance of their emitter resistors, causing the total impedance to rise ✔ limiting the stage gain. ✔ (3)
5.5
5.5.1 Impedance matching can be achieved by selecting a transformer ✔ with the required number of turns ✔ that will coincide with the impedances of the respective stages. (2)
5.5.2 The reason for using a transformer is that the relatively high output impedance of the second stage ✔ is connected to the relatively low impedance of the speaker ✔ thus matching the output impedance ✔ of the amplifier to the load. (3)
5.5.3 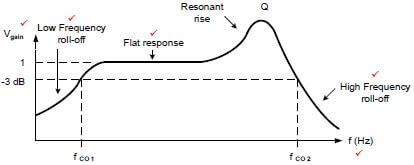 ✔ (6)
✔ (6)
5.6
5.6.1 An oscillator is a device which generates an AC output signal ✔ without any externally applied input signal. ✔ (2)
5.6.2 Sine wave ✔ (1)
5.6.3 Positive feedback ✔ (1)
5.6.4 The resistors R1 and R2 form a voltage divider ✔ to bias the base of the transistor. ✔ (2)
5.6.5
- The Colpitts oscillator uses TWO capacitors and an inductor in the tank circuit. ✔
- The Hartley oscillator uses TWO inductors and a capacitor in the tank circuit. ✔ (2)
5.7
5.7.1
- The transistor is used to amplify the damped oscillating signal ✔ ensuring a gain of 1 thus maintaining oscillation.
- Provide phase shift of 180°. ✔ (2)
5.7.2 The RC-network provides a phase shift of 180° ✔ and the amplifier circuit provides a phase shift of -180°. ✔ (2)
5.7.3  (2)
(2)
5.7.4
- No external input signal is applied to oscillators.✔
- The circuit is self-maintained.
- An input signal is required in the transistor amplifier.✔ (2)
5.8
- The RF-oscillator may be used in:
- Local oscillators ✔
- Radio circuits ✔
- Signal generator (2)
5.9
- 1 mark for constant frequency.
- 3 marks each half cycle with smaller amplitude. (4) [60]
TOTAL: 200
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY: POWER SYSTEMS GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY: POWER SYSTEMS
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS TO THE MARKERS
- All questions with multiple answers imply that any relevant, acceptable answer should be considered.
- Calculations:
2.1 All calculations must show the formulae.
2.2 Substitution of values must be done correctly.
2.3 All answers MUST contain the correct unit to be considered.
2.4 Alternative methods must be considered, provided that the correct answer is obtained.
2.5 Where an incorrect answer could be carried over to the next step, the first answer will be deemed incorrect. However, should the incorrect answer be carried over correctly, the marker has to re calculate the values, using the incorrect answer from the first calculation. If correctly used, the candidate should receive the full marks for subsequent calculations.
2.6 Markers should consider that learner answers may deviate slightly from the guideline; depending on how and where in the calculation rounding off was used. - These marking guidelines are only a guide with model answers. Alternative interpretations must be considered and marked on merit. However, this principle should be applied consistently throughout the marking session at ALL marking centres.
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY
1.1
- 'Major incident 'is an occurrence of catastrophic proportion✔ resulting from the use of plant and machinery from activities in the workplace. ✔
- Severe or serious injury or great damage to machinery and persons resulting from the use of plant or machinery in a workplace. (2)
1.2
- Manufacturers must ensure that products are safe✔
- Not permitting any employee to do any work or to produce any artefact unless precautionary measures are in place.✔
- Safe to use / without risk to health
- Safety feature
- Instructional manual
- In good condition without faults (2)
1.3
- 'Horseplay 'is an unsafe act because it is an inappropriate behaviour by learners✔ in the workshop that would compromise the safety✔ of themselves and others.
- It distracts others that could lead to accidents or incidents. (2)
1.4
- Do not touch the person. ✔
- Switch off the supply. ✔
- Help the person by removing him/her with a type of insulation material. (2)
1.5 Qualitative risk analysis defines the levels of threat ✔ and devises counter measures ✔ to eliminate possible risk. (2) [10]
QUESTION 2: RLC CIRCUITS
2.1 The total opposition to the flow of alternating current ✔ in a circuit comprising of resistance and reactance. ✔ (2)
2.2
2.2.1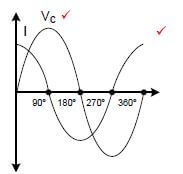 (2)
(2)
If the learner drew only one signal, it doesn’t show relation. (no marks)
2.2.2 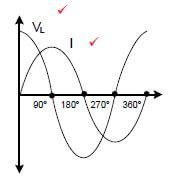 (2)
(2)
NOTE. If the learner drew only one signal, it doesn’t show relation. (no marks)
2.3
2.3.1
- C = 1
2 × π × f × XC
= 1 - 2 × π × 60 × 36
= 73,68μF ✔ (3)
NOTE. Note if the formula is copied directly from the formula sheet a mark must be awarded, there after the substitution, manipulation and the answer must be correct to receive 3 marks.
2.3.2
- L = XL
2 × π × 60
= 22
2 × π × 60
= 58,35 mH ✔ ✔ (3)
NOTE. Note if the formula is copied directly from the formula sheet a mark must be awarded, there after the substitution, manipulation and the answer must be correct to receive 3 marks.
2.3.3 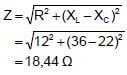 (3)
(3)
2.3.4
- I = VS
Z
= 60
18.44
= 3,25 A ✔ ✔ (3)
2.3.5
- Q = V × I × Sinθ
= 60 × 3,25 × Sin (50 º)✔
= 149,38 VA r ✔ (3)
2.4 The value of the inductive reactance will double/increase ✔ because the inductive reactance is directly proportional to the frequency ✔ of the supply voltage.
NOTE. If only the formula is given, no marks. If the formula is given as a reason, 1 mark will be awarded for the formula. (2)
2.5. The resonant frequency is the frequency at which the inductive reactance ✔ is equal to the capacitive reactance. ✔
NOTE. All characteristics of resonance explained correctly will be accepted. (2)
2.6
- XL = VS
IL
=100
2
= 50 Ω V (3) - XC = VS
IC
=100
6
= 16,67 Ω (3) - IX = IC - IL
= 6 - 2
= 4 A (3)
Note: If the learner sets one or a difference in reactive currents, the learner must get 3 points.  (3)
(3)
2.6.2 Phase angle is leading. ✔ (1)
2.7 A low value of resistance produces a high Q-factor ✔ which results in a low bandwidth ✔ and high selectivity. (2) [40]
QUESTION 3: THREE-PHASE AC GENERATION
3.1 120º ✔ (1)
3.2
3.2.1
- Apparent power is the product of the current and the voltage ✔ not considering reactance in an AC circuit. ✔
- Apparent power is the total power drawn from the supply. (2)
3.2.2 Power factor is the ratio ✔ of the active to the apparent power consumed in an AC circuit. ✔ (2)
3.3
- Thinner supply cables will be required.
- It will minimise the supply current.
- Cost of maintenance will be less (3)
3.4
3.4.1
- For alternator of similar frame size, single phase produces less power than three phase. ✔
- For the same amount of energy generated single phase power is relatively more expensive to generate than three phase. ✔
- Single phase supply can only supply power to single phase loads. ✔
- You can’t do load balancing with single phase loads.
- Single phase loads uses thicker supply cables. (3)
3.4.2 When the coils of a three phase alternator are connected in star, a neutral point is created ✔ and both line as well as phase voltages of different values are available. ✔ The neutral point can be earthed. (2)
3.5 The transmission voltage is inversely proportional to the current therefore by increasing the transmission voltage, ✔ the line current ✔ is decreased and the copper losses are reduced. (2)
3.6
3.6.1 Phase voltage
- VP = VL
√3
= 380
√3
= 219,39 V ✔ ✔ (3)
3.6.2 Line current to the load.  (3)
(3)
3.6.3 Apparent power 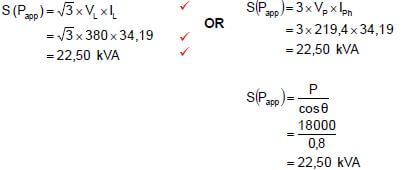 (3)
(3)
3.7
3.7.1 The total input power to the motor.
- PT = P1 + P2
= 1200 + 2300 ✔
= 3,5 kW ✔(3)
3.7.2
- The power factor can be determined. ✔
- The total input power can be measured in a star or delta connected system. ✔
- Only two wattmeters are required instead of three. ✔
- For a given supply voltage the line current can be determined without using an ammeter.
- Power in a balanced and unbalanced system can be measured.
- It is less complicated to connect two wattmeters than three wattmeters. (3) [30]
QUESTION 4: THREE-PHASE TRANSFORMERS
4.1
- Copper losses / I2R losses / heat losses.✔
- Iron losses / eddy current losses / Hysteresis losses / heat losses.✔
- Stray losses / Magnetic field losses.✔
- Dielectric losses. (3)
4.2 Delta-star is used for
- Power distribution in Commercial✔
- Power distribution in Industries ✔
- power distribution for domestic / step down 380 V to 220 V (2)
4.3
- It improves the insulation of the transformer.✔
- Conducts the heat away from the windings.✔ (2)
4.4
- When an alternating voltage is applied to the primary windings ✔ an alternating flux is created in the windings. ✔
- This flux will link with the secondary windings ✔ through the magnetic path of the iron core of the transformer ✔ inducing in it an emf of the same frequency. ✔
NOTE if only mutual induction is mentioned, 1 mark is awarded. (5)
4.5
- Transformers have no moving parts ✔ as a result less losses develops ✔ and it delivers a better power output. ✔
- Transformers are designed efficiently. (3)
4.6 To detect abnormal gas formation in the transformer ✔ and isolate it from the supply to prevent it from being damaged. ✔ (2)
4.7
4.7.1
- VP(S) = VL(S)
√3
= 380
√3
= 219,39V ✔ ✔ (3)
4.7.2
- TR = V1(P)
V2(P)
= 2200
219,39
= 10:1 ✔ ✔ (3)
4.7.3
- V1(P) = N1
V2(P) N2
N2 = 1500 × 219,39
2200
= 149,58 ✔ ✔ (3)
4.8
4.8.1 Is a step down transformer ✔ (because NP > NS) (1)
4.8.2 The secondary windings of the transformer are connected in star ✔ thereby creating a neutral point ✔ to supply single phase and three phase systems. ✔ (3) [30]
QUESTION 5: THREE-PHASE MOTORS AND STARTERS
5.1
5.1.1 1,3 A ✔ (1)
5.1.2 The motor can be used in South Africa because of the supply voltage of 380 V ✔ with a frequency of 50 Hz. ✔ (2)
5.1.3 The 7,5 kW signifies the rated output power ✔ the motor can deliver to drive the load. (1)
5.1.4
- p = 60 × f
ns
= 60 × 50
1500
= 2 polepairsper phase ✔ ✔
∴ Total numberof poles 2 × 2 × 3 ✔
= 12 poles ✔ (5)
5.1.5
- Pin = Pout + Plosses
= 7500 + 1200
= 8,7 kW ✔
η = Pout × 100
Pin
= 7500 × 100 ✔
8700
= 86,21 % (5)
Alternative answer
- η = Pout × 100
Pout + Plosses
= 7500 × 100
7500 + 1200
= 86,21 % ✔✔
5.2
- No-volt protection prevents a motor from restarting ✔ after a power failure ✔ to protect the operator. ✔ (3)
- If the supply voltage drops below a prescribed value, it will switch off the supply.
5.3
- By changing any two✔ of the three supply lines. ✔ (2)
- NOTE mentioning the colour of the lines are accepted.
5.4 Check if the:
- End plates are securely fastened. ✔
- Frame has any cracks. ✔
- Shaft turns freely.
- Bearing works smoothly when the shaft is turned. Cooling fan / fin (2)
5.5
5.5.1 Forward reverse control circuit. ✔ (1)
5.5.2
- In elevators to change the direction of the motor. ✔ (1)
- Conveyor belts
- Lathe
5.5.3The purpose of the overload is to disconnect the supply from the motor ✔, when the current exceeds the pre-set value. ✔ (2)
5.5.4
- When the start button is pressed, current will flow in the circuit and MC1/FWD becomes energised. ✔
- When MC1/FWD is energised, MC1/NO closes and MC1/NC opens and the motor will run forward. ✔
- When the stop button is pressed MC1/FWD de-energised opening contact MC1/NO and closing MC1/NC and the motor stops running. ✔
- When the reverse start button is pressed, current will flow in the circuit and MC2/REV becomes energised. ✔
- When MC2/REV is energised, MC2/NO closes and MC2/NC opens and the motor will run in the reverse. ✔ (5) [30]
QUESTION 6: PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS (PLCs)
6.1
- Requires regular maintenance. ✔
- It takes time to locate a fault. ✔
- It takes longer to re-wire the system when compared to the reprogramming of the PLC. ✔ (3)
6.2
- Input scan/input module .✔ (checks input device state)
- Process ✔ (complete instruction)
- Output module ✔ (update) (3)
6.3 'Scan time' is the time the PLC takes to complete ✔ one scan cycle, ✔ processing in each of the three most important steps. (2)
6.4
6.4.1 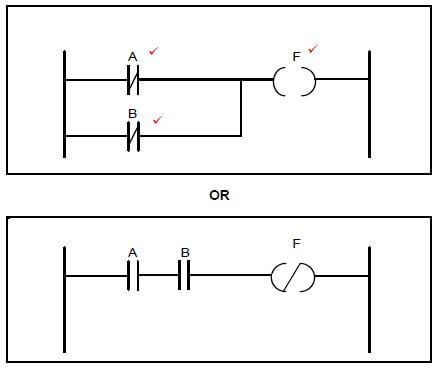 (3)
(3)
6.4.2 (4)
A | B | F |
0 | 0 | 1✔ |
0 | 1 | 1✔ |
1 | 0 | 1✔ |
1 | 1 | 0✔ |
TABLE 6.4.2
6.5 A
- PLC is an industrial computing device that is programmed ✔ to perform a number of tasks as per instruction ✔ and to control various types of machines and processes. ✔ (3)
OR - A PLC is a programmable device capable of interpreting logic for the purpose of controlling a series of output after scanning inputs state and applying the programmed logic.
6.6
6.6.1
- Light sensor. ✔
- Level sensor. ✔
- Overload sensor. ✔
- Temperature sensor. (3)
6.6.2
- A computing device (microprocessors, computers, and logic units) can only interpret the electronic digital/discrete language instructions for processing, monitoring and controlling. ✔ other than an analogue languages, which are highly exposed to noise. ✔ and may cause wrong readings because of its limitations in accuracy ✔and unpredictable behaviour in a control system which might compromise the intended output .✔ (4)
OR - Analogue signals are sampled and converted to definitive digital steps or values to eliminate or avoid any possible misinterpretations or fault state that may arise from noise or interference that could be superimposed on the input signal.
6.7 The output of the PLC sends a positive signal (high logic) to its internal output relay. ✔ This energizes the relay coil which closes its contacts ✔ to drive the motor. ✔ (3)
6.8 The purpose of the timer function is to activate or deactivate a device ✔ after or before a pre-set interval of time. ✔ (2) OR The purpose of the timer function is to run an operation for a predetermined period of time.
6.9 The concept of latching makes it possible for circuit to be triggered 'on'✔ and remain 'on'✔ regardless of whether the activating trigger has been removed.✔ (3)
6.10
6.10.1
- Automatic star delta starter. ✔
- Star delta starter (1)
6.10.2 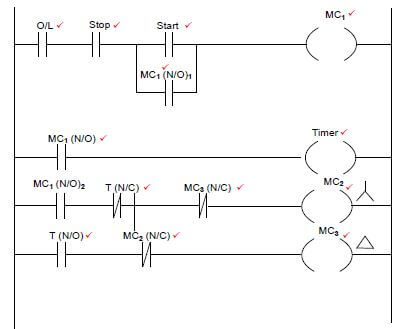 (13)
(13)
Alternative methods are accepted IF the circuit is working correctly.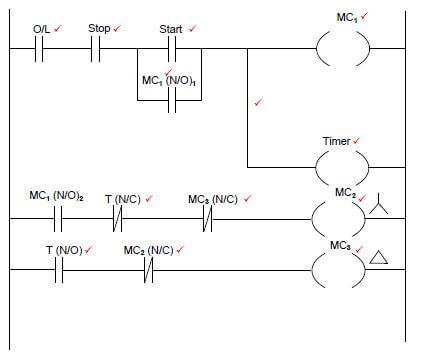
6.10.3 The function of the MC1/NO1 in ladder logic control circuit is to Latch the circuit ✔ and keep the program running even after the start button is released. ✔ (2)
6.10.4 The purpose of MC3 NC is to interlock ✔ and prevents ✔ MC2 from engaging when MC3 is engaged in delta. (2)
6.11
- Induction motors. ✔
- AC synchronous motors. ✔
- AC asynchronous motors. ✔
- DC motors (3)
6.12 A process of changing the frequency of the input voltage ✔ to change the speed and torque of the motor. ✔ (2)
6.13 The purpose of the braking resistor is to stop or slow down the motor through absorption of excess energy ✔ and converting excess energy to heat while in motion by transforming kinetic energy back into electrical energy ✔ through the process of regenerative breaking. (2)
6.14
- The function of the VSD is to control the speed of an AC motor ✔ by varying the frequency of the voltage supplied ✔ to the motor.
- The function of the VSD is to control the speed of a DC motor by varying the voltage supplied to the motor. (2) [60]
TOTAL: 200
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY: POWER SYSTEMS GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY: POWER SYSTEMS
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Answer QUESTIONS 2.2.1 and 2.2.2 on the attached ANSWER SHEET.
- Write your CENTRE NUMBER and EXAMINATION NUMBER on the ANSWER SHEET and hand it in with your ANSWER BOOK, whether you have used it or not.
- Sketches and diagrams must be large, neat and fully labelled.
- Show ALL calculations and round off answers correctly to TWO decimal places.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show the units for ALL answers of calculations.
- A formula sheet is provided at the end of this question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY (GENERIC)
1.1 Define the term major incident with reference to the Occupational Health and Safety Act, 1993 (Act 85 of 1993). (2)
1.2 State TWO general duties of manufacturers with regard to a product that will be used at the workplace. (2)
1.3 Explain why horseplay is an unsafe act in the workshop. (2)
1.4 State TWO procedures to protect yourself when helping a person who is being shocked by electricity. (2)
1.5 Define the term qualitative risk analysis. (2) [10]
QUESTION 2: RLC CIRCUITS (GENERIC)
2.1 Define the term impedance with reference to RLC circuits. (2)
2.2 Illustrate the phase relationship between current and voltage by drawing the waveforms of the following circuits on the ANSWER SHEET:
2.2.1 Pure capacitive circuit (2)
2.2.2 Pure inductive circuit (2)
2.3 FIGURE 2.3 below shows an RLC series circuit that consists of a 12 Ω resistor, an inductor with a reactance of 22 Ω and a capacitor with a reactance of 36 Ω, all connected across a 60 V/60 Hz supply. Answer the questions that follow. 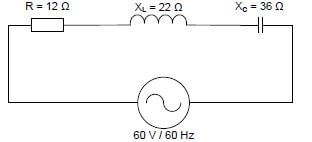
FIGURE 2.3: RLC SERIES CIRCUIT
Given:
R = 12 Ω
XL = 22 Ω
XC = 36 Ω
VS = 60 V
f = 60 Hz
Calculate the:
2.3.1 Capacitance of the capacitor (3)
2.3.2 Inductance of the inductor (3)
2.3.3 Impedance of the circuit (3)
2.3.4 Total current through the circuit (3)
2.3.5 Reactive power at a phase angle of 50° (3)
2.4 Explain how the value of the inductive reactance will be affected if the supply frequency is doubled. (2)
2.5 Define the term resonant frequency. (2)
2.6 Refer to FIGURE 2.6 and answer the questions that follow. 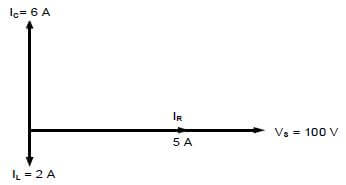
FIGURE 2.6: RLC PHASOR DIAGRAM
2.6.1 Calculate the following:
- Inductive reactance (3)
- Capacitive reactance (3)
- Reactive current (3)
- Total current (3)
2.6.2 State whether the phase angle is lagging or leading. (1)
2.7 Describe how a low resistance value affects the bandwidth of an LC tuned circuit. (2) [40]
QUESTION 3: THREE-PHASE AC GENERATION (SPECIFIC)
3.1 State the size of the angles between the phases of a balanced three-phase AC generated waveform. (1)
3.2 Define the following terms:
3.2.1 Apparent power (2)
3.2.2 Power factor (2)
3.3 State THREE advantages for the supplier when the power factor improves. (3)
3.4 With reference to three-phase power generation:
3.4.1 State THREE disadvantages of single-phase AC generation. (3)
3.4.2 Explain the advantage of connecting a three-phase alternator in star. (2)
3.5 Explain how copper losses are reduced in overhead transmission lines. (2)
3.6 A 380 V three-phase system supplies a star-connected inductive load. The input power to the load is 18 kW with a lagging power factor of 0,8.
Given:
VL = 380 V
Pin = 18 kW
Cos θ = 0,8 lagging
Calculate the:
3.6.1 Phase voltage (3)
3.6.2 Line current to the load (3)
3.6.3 Apparent power (3)
3.7 The two-wattmeter method is used to measure power of a three-phase motor. The readings on the wattmeters are 1,2 kW and 2,3 kW respectively. Answer the questions that follow.
Given:
P1 = 1,2 kW
P2 = 2,3 kW
3.7.1 Calculate the total input power to the motor. (3)
3.7.2 State THREE advantages of the two-wattmeter method over the three-wattmeter method. (3) [30]
QUESTION 4: THREE-PHASE TRANSFORMERS (SPECIFIC)
4.1 Name THREE losses that occur in transformers. (3)
4.2 State TWO applications of a delta-star transformer. (2)
4.3 State TWO functions of the oil used in transformers. (2)
4.4 Describe the operation of a transformer. (5)
4.5 Explain why transformers have a better efficiency in comparison to other machines. (3)
4.6 State the purpose of the Buchholz relay in transformers. (2)
4.7 A three-phase transformer with 1 500 primary turns is connected in delta-star to a supply voltage of 2,2 kV. The primary line current is 30 A and the secondary line voltage is 380 V with a power factor of 0,9.
Given:
NP = 1 500 turns
VP = 2,2 kV
I L(P) = 30 A
V L(S) = 380 V
Cos θ = 0,9 lagging
Calculate the:
4.7.1 Secondary phase voltage (3)
4.7.2 Transformation ratio (3)
4.7.3 Number of secondary turns (3)
4.8 A three-phase transformer with a turns ratio of 30 : 1 is connected in delta star. Answer the questions that follow.
4.8.1 Determine whether the transformer is a step-down or a step-up transformer. (1)
4.8.2 Describe why the transformer can be used for distributing electrical power to domestic and industrial loads. (3) [30]
QUESTION 5: THREE-PHASE MOTORS AND STARTERS (SPECIFIC)
5.1 TABLE 5.1 below shows the name plate of a three-phase induction motor. Answer the questions that follow.
TABLE 5.1: NAME PLATE OF A THREE-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR
MOTOR MANUFACTURER SPECIFICATION | |
Phase | 3 |
Voltage | 380 V |
Current | 1,3 A |
Speed | 1 500 r/min |
Power | 7,5 kW |
Frequency | 50 Hz |
Cos θ | 0,8 lagging |
Frame No. | 22SP27 |
5.1.1 State the amount of current the motor will draw from the supply at full load. (1)
5.1.2 Explain why the motor is suitable for use in South Africa. (2)
5.1.3 State what the 7,5 kW on the name plate indicates. (1)
5.1.4 Determine the total number of poles. (5)
5.1.5 Calculate the efficiency of the motor at full load if the total loss is 1,2 kW. (5)
5.2 Explain the purpose of no-volt protection with reference to motor control circuits. (3)
5.3 Explain how the direction of rotation of a three-phase induction motor can be changed. (2)
5.4 State TWO mechanical inspections that must be carried out on an induction motor before commissioning. (2)
5.5 Refer to the control circuit diagram in FIGURE 5.5 and answer the following questions. 
FIGURE 5.5: CONTROL CIRCUIT
5.5.1 Identify the control circuit in FIGURE 5.5. (1)
5.5.2 State ONE application of the control circuit. (1)
5.5.3 State the purpose of the overload relay. (2)
5.5.4 Describe the operation of the control circuit. (5) [30]
QUESTION 6: PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC CONTROLLERS (PLCs) (SPECIFIC)
6.1 State THREE disadvantages of hard wiring. (3)
6.2 Name the THREE steps that a PLC has to undergo to complete one programmed scan cycle. (3)
6.3 Explain the term scan time with reference to the scan cycle of a PLC. (2)
6.4 Refer to FIGURE 6.4 below and answer the questions that follow. ![]()
FIGURE 6.4: NAND gate
6.4.1 Draw the ladder logic diagram. (3)
6.4.2 Draw the truth table for the NAND gate. (4)
6.5 Describe how a PLC achieves its function. (3)
6.6 With reference to analogue and digital inputs:
6.6.1 Give THREE examples of analogue input devices. (3)
6.6.2 Explain why an analogue input may be converted to a digital input. (4)
6.7 Describe how a PLC uses a relay to drive a motor. (3)
6.8 State the purpose of the timer function. (2)
6.9 Explain the latching concept with reference to retaining circuits. (3)
6.10 Refer to FIGURE 6.10 below and answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 6.10: CONTROL CIRCUIT
6.10.1 Identify the control circuit in FIGURE 6.10. (1)
6.10.2 Draw a ladder logic diagram that executes the same function as the one in FIGURE 6.10. (13)
6.10.3 State the function of the MC1/NO1 as used in ladder logic circuits. (2)
6.10.4 State why the N/C contact of MC3 is connected in series with the star contactor. (2)
6.11 Name THREE types of motors used with variable speed drives (VSD). (3)
6.12 Explain voltage frequency control with reference to VSD. (2)
6.13 Explain the purpose of the braking resistor with reference to regenerative braking. (2)
6.14 Explain the function of the VSD when used in motors. (2) [60]
TOTAL: 200
FORMULA SHEET
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET
QUESTION 2.2 
FIGURE 2.2.1 (2) 
FIGURE 2.2.2 (2)
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY: ELECTRONICS GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY: ELECTRONICS
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of FIVE questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Answer the following questions on the attached ANSWER SHEETS:
QUESTIONS 2.2.1 and 2.2.2
QUESTION 3.6.3
QUESTIONS 4.3.2, 4.4.1, 4.5.2, 4.6.3, 4.7.4, 4.8.1, 4.8.2 and 4.9.1 QUESTIONS 5.2.3, 5.5.3, 5.7.3 and 5.9 - Write your CENTRE NUMBER and EXAMINATION NUMBER on every ANSWER SHEET and hand them in with your ANSWER BOOK, whether you have used them or not.
- Sketches and diagrams must be large, neat and fully labelled.
- Show ALL calculations and round off answers correctly to TWO decimal places.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show the units for ALL answers of calculations.
- A formula sheet is attached at the end of this question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY (GENERIC)
1.1 Define the term major incident with reference to the Occupational Health and Safety Act, 1993 (Act 85 of 1993). (2)
1.2 State TWO general duties of manufacturers with regard to a product that will be used at the workplace. (2)
1.3 Explain why horseplay is an unsafe act in the workshop. (2)
1.4 State TWO procedures that you have to follow to protect yourself when you help a person who is being shocked by electricity. (2)
1.5 Define the term qualitative risk analysis. (2) [10]
QUESTION 2: RLC CIRCUITS (GENERIC)
2.1 Define the term impedance with reference to RLC circuits. (2)
2.2 Illustrate the phase relationship between current and voltage by drawing the waveforms of the following circuits on ANSWER SHEET 2.2:
2.2.1 Pure capacitive circuit (2)
2.2.2 Pure inductive circuit (2)
2.3 FIGURE 2.3 below shows a RLC series circuit that consists of a 12 Ω resistor, an inductor with a reactance of 22 Ω and a capacitor with a reactance of 36 Ω, all connected across a 60 V/60 Hz supply. Answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 2.3: RLC SERIES CIRCUIT
Given:
- R = 12 Ω
XL = 22 Ω
XC = 36 Ω
VS = 60 V
f = 60 Hz
Calculate the:
2.3.1 Capacitance of the capacitor (3)
2.3.2 Inductance of the inductor (3)
2.3.3 Impedance of the circuit (3)
2.3.4 Total current through the circuit (3)
2.3.5 Reactive power at a phase angle of 50° (3)
2.4 Explain how the value of the inductive reactance will be affected if the supply frequency is doubled. (2)
2.5 Define the term resonant frequency. (2)
2.6 Refer to FIGURE 2.6 below and answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 2.6: RLC PHASOR DIAGRAM
2.6.1 Calculate the following:
- Inductive reactance (3)
- Capacitive reactance (3)
- Reactive current (3)
- Total current (3)
2.6.2 State whether the phase angle is lagging or leading. (1)
2.7 Describe how a low resistance value affects the bandwidth of an LC tuned circuit. (2) [40]
QUESTION 3: SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES (SPECIFIC)
3.1 Name TWO types of junction field effect transistors (JFETs). (2)
3.2 Explain how the construction of the JFET was modified to overcome the leakage current between the gate terminal and drain-source channel. (2)
3.3 Refer to FIGURE 3.3 below and answer the questions that follow. +VDD 
FIGURE 3.3: MOSFET AS A SWITCH
3.3.1 Identify the type of MOSFET used in this circuit. (2)
3.3.2 Explain when the lamp in this circuit will switch ON. (2)
3.3.3 Describe what will happen if RGS is short-circuited. (3)
3.4 FIGURE 3.4 below shows the characteristic curve of a UJT. Answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 3.4: UJT CHARACTERISTIC CURVE
3.4.1 Identify region E. (1)
3.4.2 Explain what happens in the UJT between points C and D of the characteristic curve. (3)
3.5 Refer to FIGURE 3.5 below and answer the questions that follow. C 
FIGURE 3.5: TRANSISTOR
3.5.1 Identify the configuration in which the transistors are connected. (1)
3.5.2 State TWO advantages of the transistor configuration in FIGURE 3.5. (2)
3.6 FIGURE 3.6 below shows the 741 op amp. Answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 3.6: 741 OP AMP
3.6.1 Label pin 3. (1)
3.6.2 Name the type of package in which the integrated circuit (IC) above is constructed. (1)
3.6.3 Draw the output signal on ANSWER SHEET 3.6.3 if the signals in FIGURE 3.6.3 below are applied to the inputs of an op amp. 
FIGURE 3.6.3: SIGNALS (2)
3.7 Explain the difference between open-loop gain and closed-loop gain with reference to op amps. (2)
3.8 Calculate the output voltage of the op amp in FIGURE 3.8 below. 
FIGURE 3.8: OP AMP
Given:
VIN = 5 mV
RIN = 440 Ω
RF = 220 kΩ (3)
3.9 Refer to FIGURE 3.9 below and explain the operation of the 555 timer when connected in monostable mode. 
FIGURE 3.9: MONOSTABLE MULTIVIBRATOR (3) [30]
QUESTION 4: SWITCHING CIRCUITS (SPECIFIC)
4.1 Explain the purpose of an astable multivibrator. (2)
4.2 Refer to FIGURE 4.2 below and answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 4.2: MULTIVIBRATOR
4.2.1 Identify the multivibrator in FIGURE 4.2. (1)
4.2.2 Name the type of feedback provided by R2. (1)
4.2.3 Describe the change in the output signal with reference to input trigger pulses 1 and 2. (3)
4.3 FIGURE 4.3 below shows the 555 IC astable multivibrator and the voltage graph of capacitor C1. Answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 4.3: 555 IC ASTABLE MULTIVIBRATOR
4.3.1 Name ONE application of an astable multivibrator. (1)
4.3.2 Draw the output signal with reference to signal VC1 on ANSWER SHEET 4.3.2. (2)
4.3.3 Describe how an increase in the value of R1 will affect the output signal. (3)
4.4 FIGURE 4.4 below shows input trigger pulses A and B to a 555 monostable multivibrator. Answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 4.4: MONOSTABLE MULTIVIBRATOR TRIGGER PULSES
4.4.1 Draw the output signal on ANSWER SHEET 4.4.1. (4)
4.4.2 Describe the condition that occurred at trigger pulse B. (2)
4.4.3 Explain why the condition that occurs at trigger pulse B does NOT affect the capacitor charging. (3)
4.5 Refer to FIGURE 4.5 below and answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 4.5: INVERTING SCHMITT TRIGGER
4.5.1 Name TWO transducers that can be used as input devices to the Schmitt trigger. (2)
4.5.2 Draw the output signal on ANSWER SHEET 4.5.2 if the input signal in FIGURE 4.5.2 below is applied to the circuit. 
FIGURE 4.5.2: INPUT SIGNAL (4)
4.5.3 Describe how a decrease in the value of R1 will affect the trigger voltage level of the Schmitt trigger. (3)
4.6 FIGURE 4.6 shows the 741 op amp as a comparator. Answer the questions that follow. 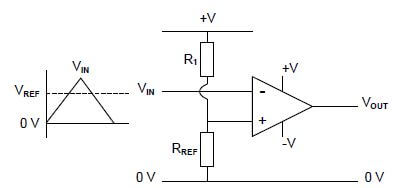
FIGURE 4.6: COMPARATOR
4.6.1 State the purpose of the comparator. (1)
4.6.2 Briefly explain how the comparator achieves its function. (3)
4.6.3 Draw the output signal on ANSWER SHEET 4.6.3, with reference to the input signal in FIGURE 4.6. (3)
4.7 Refer to FIGURE 4.7 below and answer the questions that follow. 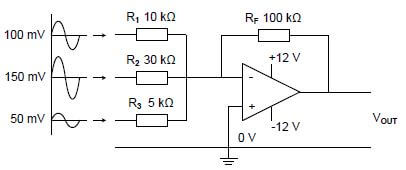
FIGURE 4.7: INVERTING SUMMING AMPLIFIER
4.7.1 Calculate the output voltage. (3)
4.7.2 Explain how this circuit can be modified to control the input voltage of each signal independently. (2)
4.7.3 Describe how this circuit can be modified to prevent DC from being fed back to the input voltage sources. (2)
4.7.4 Draw the output signal on ANSWER SHEET 4.7.4. (2)
4.8 FIGURE 4.8 below shows an op amp as a differentiator. Draw the output signals on ANSWER SHEET 4.8 when the signals, shown in QUESTIONS 4.8.1 and 4.8.2, are applied to the input of the circuit. 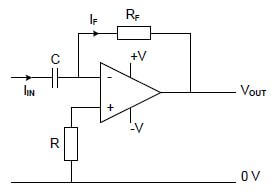
FIGURE 4.8: OP AMP AS DIFFERENTIATOR
4.8.1 Sine wave (3)
(3)
4.8.2 Triangular wave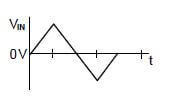 (3)
(3)
4.9 Refer to FIGURE 4.9 below and answer the questions that follow. 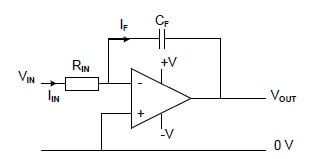
FIGURE 4.9: OP AMP AS INTEGRATOR
4.9.1 Draw the output signal on ANSWER SHEET 4.9.1, when the input signal in FIGURE 4.9.1 below is applied. 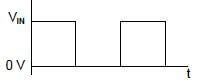
FIGURE 4.9.1: INPUT SIGNAL (3)
4.9.2 Describe what will happen to the output signal if the RC time constant is short. (4) [60]
QUESTION 5: AMPLIFIERS (SPECIFIC)
5.1 Describe class A amplification with reference to the biasing of a transistor. (2)
5.2 Refer to FIGURE 5.2 below and answer the questions that follow. 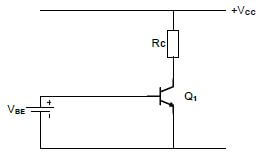
FIGURE 5.2: TRANSISTOR BIASING
5.2.1 Give TWO reasons for biasing a transistor. (2)
5.2.2 Explain the term Q-point on a DC load line. (3)
5.2.3 Indicate the Q-point of a class A, class B and class C amplifier on ANSWER SHEET 5.2.3. (3)
5.3 Refer to FIGURE 5.3 below and answer the questions that follow. 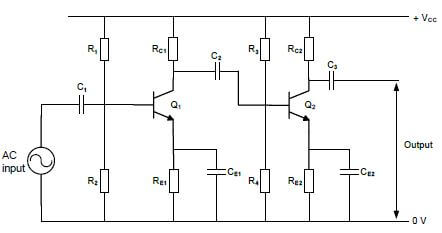
FIGURE 5.3: RC-COUPLED AMPLIFIER
5.3.1 State TWO functions of capacitor C2. (2)
5.3.2 Describe the operation of an RC-coupled amplifier. (6)
5.3.3 State TWO requirements of the coupling of amplifier stages. (2)
5.4 Analyse FIGURE 5.4 below and answer the questions that follow. 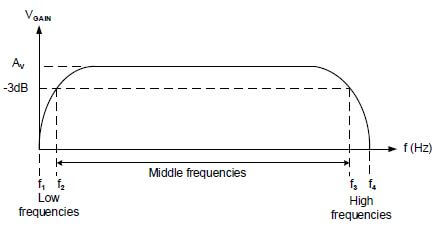
FIGURE 5.4: FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF RC-COUPLED AMPLIFIER
5.4.1 Define the term frequency response with reference to amplifiers. (2)
5.4.2 Explain the term half-power points with reference to a frequency response curve. (2)
5.4.3 Describe how the voltage gain of an RC-coupled amplifier is affected at low frequencies. (3)
5.5 Refer to FIGURE 5.5 below and answer the questions that follow. 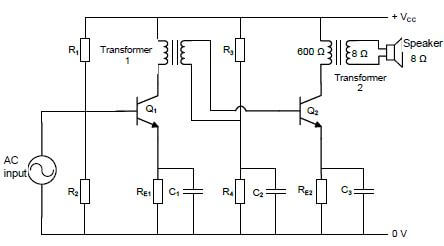
FIGURE 5.5: TRANSFORMER-COUPLED AMPLIFIER
5.5.1 Describe how proper impedance matching can be achieved between the transistor of the first stage and the transistor of the second stage. (2)
5.5.2 Explain why a transformer is used at the output of the amplifier. (3)
5.5.3 Draw the output frequency response curve of the amplifier circuit on ANSWER SHEET 5.5.3. (6)
5.6 Refer to FIGURE 5.6 below and answer the questions that follow. 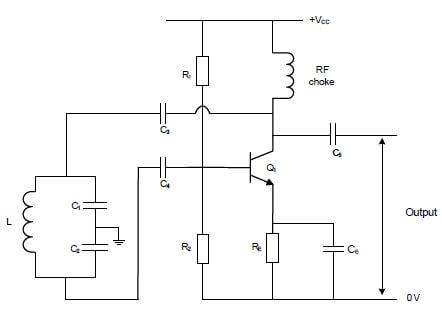
FIGURE 5.6: COLPITTS OSCILLATOR
5.6.1 Define the term oscillator. (2)
5.6.2 Name the type of waveform that is generated by an oscillator. (1)
5.6.3 Name the type of feedback used in FIGURE 5.6. (1)
5.6.4 State the purpose of resistors R1 and R2 in the circuit. (2)
5.6.5 Differentiate between the Hartley oscillator and the Colpitts oscillator with reference to the tank circuits. (2)
5.7 FIGURE 5.7 below shows an RC phase-shift oscillator circuit diagram. Answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 5.7: RC-PHASE-SHIFT OSCILLATOR
5.7.1 State TWO functions of the transistor in the circuit. (2)
5.7.2 Explain why the total phase shift of the oscillating circuit is zero. (2)
5.7.3 Draw the output waveform of the RC-oscillator on ANSWER SHEET 5.7.3. (2)
5.7.4 Differentiate between oscillator circuits and transistor amplifier circuits with reference to input signals. (2)
5.8 Give TWO examples of where an RF-oscillator can be used. (2)
5.9 Draw TWO cycles of damped oscillation on ANSWER SHEET 5.9. (4) [60]
TOTAL: 200
FORMULA SHEET
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 2.2 
FIGURE 2.2.1 (2)
FIGURE 2.2.2 (2)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 3.6.3 
FIGURE 3.6.3 (2)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 4.3.2 Input 
FIGURE 4.3.2 (2)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 4.4.1 
FIGURE 4.4.1 (4)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 4.5.2 +1 V 
FIGURE 4.5.2 (3)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 4.6.3 
FIGURE 4.6.3 (3)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 4.7.4 
FIGURE 4.7.4 (2)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 4.8 
FIGURE 4.8.1 (3) 
FIGURE 4.8.2 (3)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 4.9.1 
FIGURE 4.9.1 (3)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 5.2.3 
FIGURE 5.2.3 (3)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 5.5.3 
FIGURE 5.5.3 (6)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 5.7.3 
FIGURE 5.7.3 (2)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 5.9 
FIGURE 5.9 (4)
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY: DIGITALS GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY: DIGITALS
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of FIVE questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Answer the following questions on the attached ANSWER SHEETS:
QUESTION 2.3.2
QUESTIONS 2.4.1, 2.5.2, 2.6.3, 2.7.4, 2.8.1, 2.8.2 and 2.9.1
QUESTION 3.1.3
QUESTIONS 4.3 and 4.5.2 - Write your CENTRE NUMBER and EXAMINATION NUMBER on every ANSWER SHEET and hand them in with your ANSWER BOOK, whether you have used them or not.
- Sketches and diagrams must be large, neat and fully labelled.
- Show ALL calculations and round off answers correctly to TWO decimal places.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show the units for ALL answers of calculations.
- A formula sheet is attached at the end of this question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY (GENERIC)
1.1 Define the term major incident with reference to the Occupational Health and Safety Act, 1993 (Act 85 of 1993). (2)
1.2 State TWO general duties of manufacturers with regard to a product that will be used at the workplace. (2)
1.3 Explain why horseplay is an unsafe act in the workshop. (2)
1.4 State TWO procedures that you have to follow to protect yourself when you help a person who is being shocked by electricity. (2)
1.5 Define the term qualitative risk analysis. (2) [10]
QUESTION 2: SWITCHING CIRCUITS (SPECIFIC)
2.1 Explain the purpose of an astable multivibrator. (2)
2.2 Refer to FIGURE 2.2 below and answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 2.2: MULTIVIBRATOR
2.2.1 Identify the multivibrator in FIGURE 2.2. (1)
2.2.2 Name the type of feedback provided by R2. (1)
2.2.3 Describe the change in the output signal with reference to input trigger pulses 1 and 2. (3)
2.3 FIGURE 2.3 below shows the 555 IC astable multivibrator and the voltage graph of capacitor C1. Answer the questions that follow. 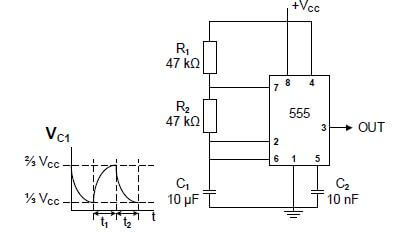
FIGURE 2.3: 555 IC ASTABLE MULTIVIBRATOR
2.3.1 Name ONE application of an astable multivibrator. (1)
2.3.2 Draw the output signal with reference to signal VC1 on ANSWER SHEET 2.3.2. (2)
2.3.3 Describe how an increase in the value of R1 will affect the output signal. (3)
2.4 FIGURE 2.4 below shows input trigger pulses A and B to a 555 monostable multivibrator. Answer the questions that follow. 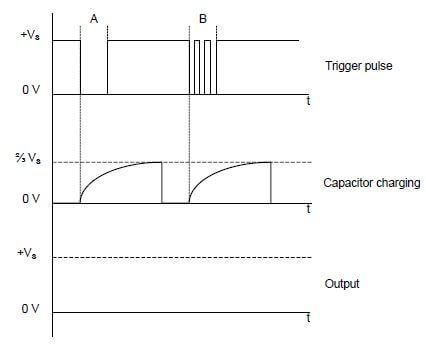
FIGURE 2.4: MONOSTABLE MULTIVIBRATOR TRIGGER PULSES
2.4.1 Draw the output signal on ANSWER SHEET 2.4.1. (4)
2.4.2 Describe the condition that occurred at trigger pulse B. (2)
2.4.3 Explain why the condition that occurs at trigger pulse B does NOT affect the capacitor charging. (3)
2.5 Refer to FIGURE 2.5 below and answer the questions that follow. 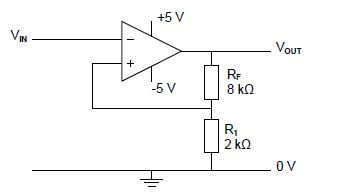
FIGURE 2.5: INVERTING SCHMITT TRIGGER
2.5.1 Name TWO transducers that can be used as input devices to the Schmitt trigger. (2)
2.5.2 Draw the output signal on ANSWER SHEET 2.5.2 if the input signal in FIGURE 2.5.2 below is applied to the circuit. 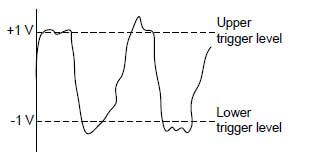
FIGURE 2.5.2: INPUT SIGNAL (4)
2.5.3 Describe how a decrease in the value of R1 will affect the trigger voltage level of the Schmitt trigger. (3)
2.6 FIGURE 2.6 shows the 741 op amp as a comparator. Answer the questions that follow. 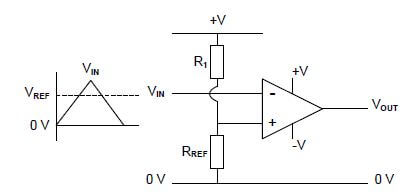
FIGURE 2.6: COMPARATOR
2.6.1 State the purpose of the comparator. (1)
2.6.2 Briefly explain how the comparator achieves its function. (3)
2.6.3 Draw the output signal on ANSWER SHEET 2.6.3, with reference to the input signal in FIGURE 2.6. (3)
2.7 Refer to FIGURE 2.7 below and answer the questions that follow. 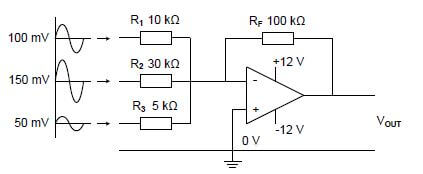
FIGURE 2.7: INVERTING SUMMING AMPLIFIER
2.7.1 Calculate the output voltage. (3)
2.7.2 Explain how this circuit can be modified to control the input voltage of each signal independently. (2)
2.7.3 Describe how this circuit can be modified to prevent DC from being fed back to the input voltage sources. (2)
2.7.4 Draw the output signal on ANSWER SHEET 2.7.4. (2)
2.8 FIGURE 2.8 below shows an op amp as a differentiator. Draw the output signals on ANSWER SHEET 2.8, when the signals shown in QUESTIONS 2.8.1 and 2.8.2, are applied to the input of the circuit. 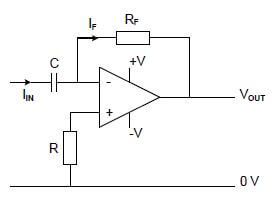
FIGURE 2.8: OP AMP AS DIFFERENTIATOR
2.8.1 Sine wave (3)
(3)
2.8.2 Triangular wave  (3)
(3)
2.9 Refer to FIGURE 2.9 below and answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 2.9: OP AMP AS INTEGRATOR
2.9.1 Draw the output signal on ANSWER SHEET 2.9.1, when the input signal in FIGURE 2.9.1 below is applied. 
FIGURE 2.9.1: INPUT SIGNAL (3)
2.9.2 Describe what will happen to the output signal if the RC time constant is short. (4) [60]
QUESTION 3: SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES (SPECIFIC)
3.1 FIGURE 3.1 below shows the 741 op amp. Answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 3.1: 741 OP AMP
3.1.1 Label pin 3. (1)
3.1.2 Name the type of package in which the integrated circuit (IC) above is constructed. (1)
3.1.3 Draw the output signal on ANSWER SHEET 3.1.3 if the signals in FIGURE 3.1.3 below are applied to the inputs of an op amp. 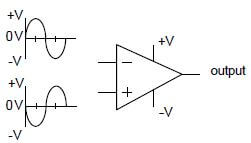
FIGURE 3.1.3: SIGNALS (2)
3.2 State the typical operating voltages of a 741 op amp. (2)
3.3 State TWO characteristics of an ideal op amp. (2)
3.4 Explain the difference between open-loop gain and closed-loop gain with reference to op amps. (2)
3.5 Calculate the output voltage of the op amp in FIGURE 3.5 below. 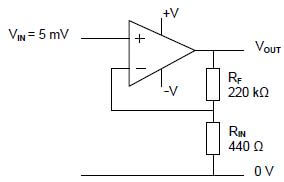
FIGURE 3.5: OP AMP
Given:
VIN = 5 mV
RIN = 440 Ω
RF = 220 kΩ (3)
3.6 FIGURE 3.6 below shows the 555 IC. Answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 3.6: 555 IC
3.6.1 Explain how the trigger input pin on a 555 IC achieves its function. (3)
3.6.2 Refer to FIGURE 3.6.2 below and explain the operation of the 555 timer when connected in monostable mode. 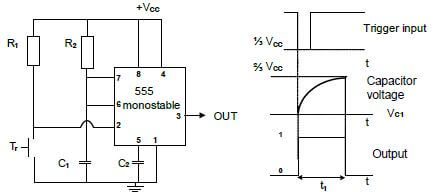
FIGURE 3.6.2: MONOSTABLE MULTIVIBRATOR (4) [20]
QUESTION 4: DIGITAL AND SEQUENTIAL DEVICES (SPECIFIC)
4.1 Briefly explain how a liquid crystal display (LCD) controls the passing of light through it. (3)
4.2 Refer to an LED seven-segment display and illustrate the difference between a sinking output and a sourcing output using TWO simple diagrams. (4)
4.3 Study FIGURE 4.3 below of a decimal-to-binary encoder. Use the table on ANSWER SHEET 4.3 to complete the truth table. 
FIGURE 4.3: DECIMAL-TO-BINARY ENCODER (10)
4.4 Draw the block diagram of a four-bit parallel adder that will be able to add the following two numbers:
A3A2A1A0 + B3B2B1B0 (7)
4.5 FIGURE 4.5 below represents the logic symbol of a J-K flip-flop. 
FIGURE 4.5: LOGIC SYMBOL OF J-K FLIP-FLOP
4.5.1 Draw the logic circuit of this flip-flop using AND gates and NOR gates. (7)
4.5.2 Complete the truth table of the flip-flop below on ANSWER SHEET 4.5.2. (4)
TABLE 4.5.2: TRUTH TABLE
INPUTS | OUTPUTS | |||
CLOCK | J | K | Q | Ò |
| | 0 | 0 | ||
| | 0 | 1 | ||
| | 1 | 0 | ||
| | 1 | 1 | ||
4.6 Describe the difference between a synchronous counter and an asynchronous counter. (2)
4.7 FIGURE 4.7 below shows a three-stage synchronous self-stopping up-counter. Explain the operation of this counter. 
FIGURE 4.7: THREE-STAGE SYNCHRONOUS SELF-STOPPING UP-COUNTER (8)
4.8 Draw a neatly labelled sketch of a 4-bit serial-in parallel-out shift register using D-type flip-flops. Show ALL inputs and outputs. (10) [55]
QUESTION 5: MICROCONTROLLERS (SPECIFIC)
5.1 State TWO uses of a microcontroller in commercial devices. (2)
5.2 State TWO advantages of a microcontroller. (2)
5.3 Explain the basic process that a microcontroller follows to fulfil its function. (4)
5.4 Refer to the block diagram of communication in a microcontroller in FIGURE 5.4 below. Answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 5.4: COMMUNICATION IN A MICROCONTROLLER
5.4.1 Label the following blocks in FIGURE 5.4:
- A (1)
- C (1)
5.4.2 Identify the following bus connections:
- X (1)
- Y (1)
5.5 Define the following elements in a microcontroller:
5.5.1 Protocol (1)
5.5.2 Communication protocol (2)
5.5.3 Hardware interface (2)
5.6 Refer to registers within the CPU and answer the questions that follow.
5.6.1 Briefly define a register. (2)
5.6.2 Describe the function of a register. (2)
5.6.3 Name TWO types of registers that are used in the CPU of a microcontroller. (2)
5.6.4 Explain the function of the memory data register. (2)
5.7 Discuss the read-only memory (ROM) with reference to the CPU of a microcontroller. (4)
5.8 Draw the serial communication block diagram for:
5.8.1 Synchronous communication (4)
5.8.2 Asynchronous communication (4)
5.9 Name THREE types of communication peripherals. (3)
5.10 Give the reason why the RS-485 communication protocol is used in industrial applications. (2)
5.11 Identify the following flow diagram symbols:  @ (1)
@ (1)
5.12 Design a flow diagram of a home security system that has THREE sensors in different parts of the house. If any one of the sensors is activated, the alarm will be activated. The alarm must include a reset function. No timing function is required. (10) [55]
TOTAL: 200
FORMULA SHEET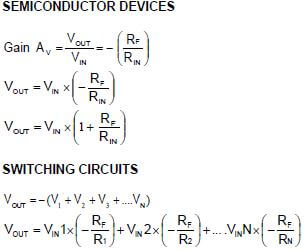
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 2.3.2 Input 
FIGURE 2.3.2 (2)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 2.4.1 
FIGURE 2.4.1 (4)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 2.5.2 +1 V 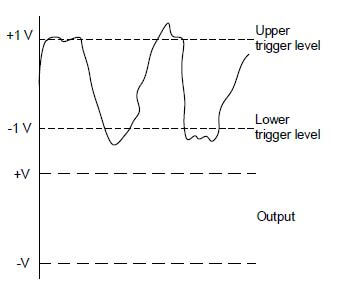
FIGURE 2.5.2 (3)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 2.6.3 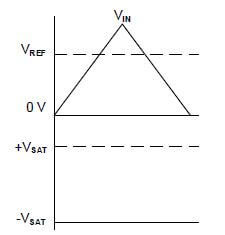
FIGURE 2.6.3 (3)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 2.7.4 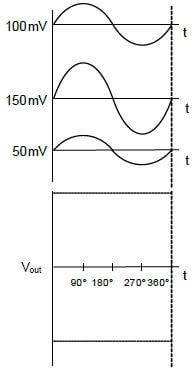
FIGURE 2.7.4 (2)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 2.8 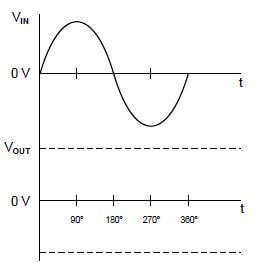
FIGURE 2.8.1 (3)
FIGURE 2.8.2 (3)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 2.9.1 
FIGURE 2.9.1 (3)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 3.1.3 
FIGURE 3.1.3 (2)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 4.3
INPUTS | OUTPUTS | ||||||||||||
0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A3 | A2 | A1 | A0 |
1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | ||||
1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||||
1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||||
TABLE 4.3 (10)
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 4.5.2
INPUTS | OUTPUTS | |||
CLOCK | J | K | Q | Ô |
| | 0 | 0 | ||
| | 0 | 1 | ||
| | 1 | 0 | ||
| | 1 | 1 | ||
TABLE 4.5.2 (4)
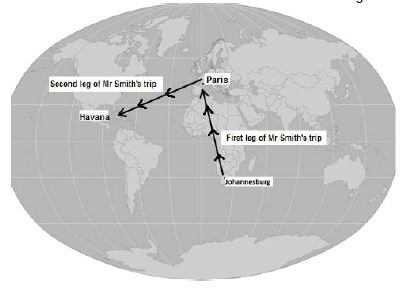




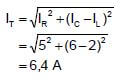 ✔ (3)
✔ (3) 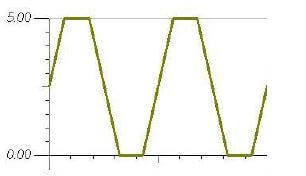
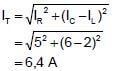 (3)
(3)