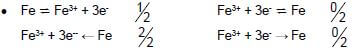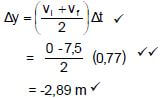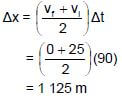Adele
PHYSICAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
PHYSICAL SCIENCES
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your examination number and centre number in the appropriate spaces on the ANSWER BOOK.
- This question paper consists of TEN questions. Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Leave ONE line between two subquestions, e.g. between QUESTION 2.1 and QUESTION 2.2.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- You may use appropriate mathematical instruments.
- Show ALL formulae and substitutions in ALL calculations.
- Round off your FINAL numerical answers to a minimum of TWO decimal places.
- Give brief motivations, discussions, etc. where required.
- You are advised to use the attached DATA SHEETS.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A-D) next to the question numbers (1.1 to 1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.11 D.
1.1Which ONE of the following is the structural formula of the functional group of the KETONES?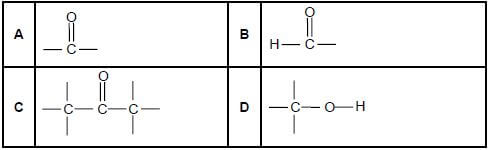 (2)
(2)
1.2 Which ONE of the formulae below represents an ALKANE?
- C2H4
- C5H10
- C14H30
- C8H14 (2)
1.3 Consider the organic compound below.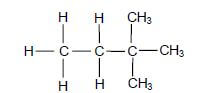
The IUPAC name of this compound is …
- 2,3-dimethyl butane.
- 3,3-dimethyl butane.
- 2,2-dimethyl butane.
- 1,1,1-trimethyl propane. (2)
1.4 Activation energy can best be described as the minimum energy required to …
- cause effective collisions.
- make reactant molecules collide.
- change the orientation of reactant molecules.
- increase the kinetic energy of reactant molecules. (2)
1.5 Which statement is CORRECT for a system in DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM?
- All reactants are used up.
- The forward reaction is equal to the reverse reaction.
- All substances in the reaction are of equal concentration.
- The concentration of the reactants and products remain constant. (2)
1.6 Initially, a certain amount of P(g) was placed in an empty container. The hypothetical reaction reaches equilibrium in a closed container according to the following balanced equation:
P(g) ⇌ 2Q(g) ΔH < 0
At time t, the temperature is increased. Which graph below best illustrates the resulting changes in the rates of the forward and reverse reactions after the temperature is increased?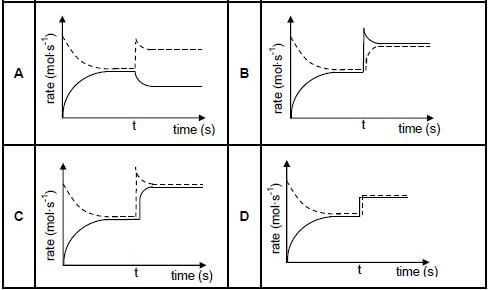
1.7 Reactions I and II below have equilibrium constants (Kc) greater than 1.
- : H3X + HCO-3 ⇌ H2X− + H2CO3 Kc > 1
- : H3O+ + H2X− ⇌ H2O + H3X Kc > 1
Based on the reactions above, the ACIDS in order of INCREASING STRENGTH (weakest to strongest) are …
- H3X, H2X−, H3O+
- H2CO3, H3X, H3O+
- H3X, H2CO3, H3O+
- H3X, H3O+, H2CO3 (2)
1.8 Consider the cell notation for a galvanic cell below.
Ni(s) | Ni2+(aq) || H+(aq) | H2(g) | Pt(s)
Which ONE of the following half-reactions takes place at the ANODE of this cell?
- 2H+(aq) + 2e− → H2(g)
- H2(g) → 2H+(aq) + 2e−
- Ni2+(aq) + 2e− → Ni(s)
- Ni(s) → Ni2+(aq) + 2e− (2)
1.9 Which ONE of the following is applicable to an ELECTROLYTIC CELL?
- Reduction takes place at the anode.
- Oxidation takes place at the cathode.
- It uses alternating current.
- A battery is used for the cell to function. (2)
1.10 The flow diagram below shows four stages (A, B, C and D) in the conversion of sulphur to sulphuric acid.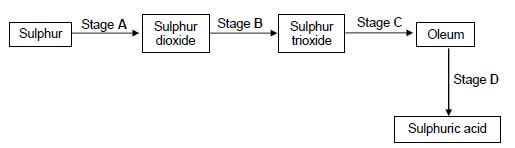
At which stage is a catalyst used?
- A
- B
- C
- D (2) [20]
QUESTION 2 (Start on a new page.)
A test tube containing a straight chain organic acid X, ethanol and a catalyst is heated in a water bath, as illustrated below.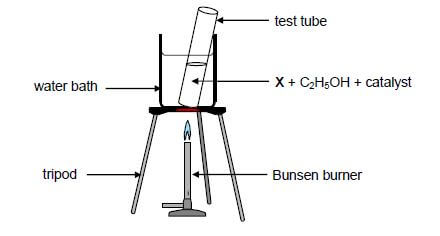
Organic compound Y is produced according to the following equation:
X + C2H5OH ⟶ Y + H2O
2.1 Give a reason why the test tube is heated in a water bath instead of directly over the flame. (1)
2.2 Write down the:
2.2.1 Type of reaction that takes place here (1)
2.2.2 FORMULA of the catalyst needed (1)
2.2.3 Homologous series to which compound Y belongs (1)
The molecular mass of compound Y is 144 g∙mol-1 and its empirical formula is C4H8O.
2.3 Determine the molecular formula of compound Y. (2)
2.4 Write down the IUPAC name of compound Y. (2)
2.5 Write down the structural formula of the organic acid X. (2) [10]
QUESTION 3 (Start on a new page.)
The boiling points of different organic compounds are given below.
COMPOUND | BOILING POINT (°C) | |
A | HCOOH | 101 |
B | CH3COOH | 118 |
C | CH3CH2COOH | 141 |
D | CH3CH2CH2COOH | 164 |
3.1 Define boiling point. (2)
3.2 Write down the:
3.2.1 Name of the FUNCTIONAL GROUP of these compounds (1)
3.2.2 IUPAC name of compound C (1)
3.2.3 Structural formula of the FUNCTIONAL isomer of compound B (2)
3.3 Which ONE of the compounds, A or B or C, has the highest vapour pressure? Refer to the data in the table to give a reason for the answer. (2)
3.4 The boiling point of compound B is now compared with of compound X.
COMPOUND | BOILING POINT (°C) | |
B | CH3COOH | 118 |
X | CH3CH2CH2OH | 98 |
3.4.1 Besides the conditions used to determine boiling points, give a reason why this is a fair comparison. (1)
3.4.2 Is compound X a PRIMARY, SECONDARY or TERTIARY alcohol? Give a reason for the answer. (2)
3.4.3 Fully explain the difference between the boiling points by referring to the types of intermolecular forces present in each of these compounds. (4) [15]
QUESTION 4 (Start on a new page.)
4.1 Three reactions of organic compounds from the same homologous series are shown below.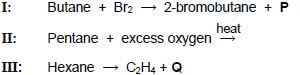
4.1.1 Define a homologous series. (2)
4.1.2 Name the type of reaction represented by I. (1)
4.1.3 Write down the formula of the inorganic compound P. (1)
4.1.4 Give the structural formula of a POSITIONAL isomer of 2-bromobutane. (2)
4.1.5 Using molecular formulae, write down the balanced equation for reaction II. (3)
Reaction III is an example of a cracking reaction.
4.1.6 Define a cracking reaction. (2)
4.1.7 Give the structural formula of organic compound Q. (2)
4.2 Study the flow diagram below.![]()
4.2.1 Write down the IUPAC name of compound R. (2)
4.2.2 Compound R reacts in the presence of concentrated phosphoric acid to form an alkene. Write down the structural formula of the MAJOR PRODUCT in this reaction. (2) [17]
QUESTION 5 (Start on a new page.)
The reaction of zinc and EXCESS dilute hydrochloric acid is used to investigate factors that affect reaction rate. The balanced equation for the reaction is:
Zn(s) + 2HCℓ(aq) ⟶ ZnCℓ2(aq) + H2(g)
The reaction conditions used and the results obtained for each experiment are summarised in the table below. The same mass of zinc is used in all the experiments. The zinc is completely covered in all reactions. The reaction time is the time it takes the reaction to be completed.
EXPERIMENT | CONCENTRATION OF HCℓ (mol∙dm-3) | VOLUME OF HCℓ (cm3) | STATE OF DIVISION OF Zn | TEMPERATURE OF HCℓ (°C) | REACTION TIME (min.) |
1 | 2,0 | 200 | powder | 25 | 7 |
2 | 1,5 | 200 | granules | 25 | 14 |
3 | 5,0 | 200 | powder | 25 | 5 |
4 | 1,5 | 400 | granules | 25 | x |
5 | 2,0 | 200 | powder | 35 | 4 |
5.1 Experiment 1 and experiment 5 are compared. Write down the independent variable. (1)
5.2 Define reaction rate. (2)
5.3 Write down the value of x in experiment 4. (2)
5.4 The Maxwell-Boltzmann energy distribution curves for particles in each of experiments 1, 3 and 5 are shown below.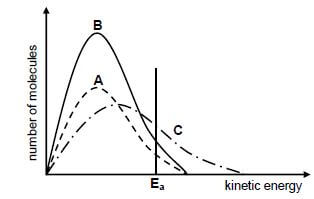
Identify the graph (A or B or C) that represents the following:
5.4.1 Experiment 3 Give a reason for the answer. (2)
5.4.2 Experiment 5 Give a reason for the answer. (2)
5.5 Experiment 6 is now conducted using a catalyst and the SAME reaction conditions as for Experiment 1.
5.5.1 What is the function of the catalyst in this experiment? (1)
5.5.2 How will the heat of reaction in experiment 6 compare to that in experiment 1? Choose from: GREATER THAN, EQUAL TO or LESS THAN. (1)
5.6 Calculate the average rate of the reaction (in mol·min-1) with respect to zinc for experiment 2 if 1,5 g of zinc is used. (4) [15]
QUESTION 6 (Start on a new page.)
Dinitrogen tetraoxide, N2O4(g), decomposes to nitrogen dioxide, NO2(g), in a sealed syringe of volume 2 dm3.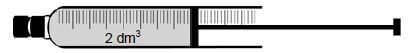
The mixture reaches equilibrium at 325 °C according to the following balanced equation:
- N2O4(g) ⇌ 2NO2 (g)
colourless brown
When equilibrium is reached, it is observed that the colour of the gas in the syringe is brown.
6.1 State Le Chatelier's principle. (2)
6.2 The syringe is now dipped into a beaker of ice water. After a while the brown colour disappears. Is the forward reaction EXOTHERMIC or ENDOTHERMIC? Explain the answer using Le Chatelier's principle. (3)
6.3 The volume of the syringe is now decreased while the temperature is kept constant. How will EACH of the following be affected? Choose from: INCREASES, DECREASES or REMAINS THE SAME.
6.3.1 The number of moles of N2O4(g) (1)
6.3.2 The value of the equilibrium constant (1)
6.3.3 The rate of the forward and reverse reactions (1)
6.4 Initially X moles of N2O4(g) were placed in the syringe of volume 2 dm3. When equilibrium was reached, it was found that 20% of the N2O4(g) had decomposed. If the equilibrium constant, Kc, for the reaction is 0,16 at 325 °C, calculate the value of X. (8) [16]
QUESTION 7 (Start on a new page.)
7.1 Sulphuric acid is a strong acid present in acid rain. It ionises in two steps as follows:
- : H2SO4(aq) + H2O(ℓ) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + HSO-4 (aq)
- : HSO-4 (aq) + H2O(ℓ) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + SO2-4 (aq)
7.1.1Define an acid in terms of the Lowry-Brønsted theory. (2)
7.1.2 Write down the FORMULA of the conjugate base of H3O+(aq). (1)
7.1.3 Write down the FORMULA of the substance that acts as an ampholyte in the ionisation of sulphuric acid. (2)
7.2 Acid rain does not cause damage to lakes that have rocks containing limestone (CaCO3). Hydrolysis of CaCO3 results in the formation of ions, which neutralise the acid.
7.2.1 Define hydrolysis of a salt. (2)
7.2.2 Explain, with the aid of the relevant HYDROLYSIS reaction, how limestone can neutralise the acid. (3)
7.3 The water in a certain lake has a pH of 5.
7.3.1 Calculate the concentration of the hydronium ions in the water. (3)
The volume of water in the lake is 4 x 109 dm3. Lime, CaO, is added to the water to neutralise the acid according to the following reaction:
CaO + 2H3O+ ⇌ Ca2+ + 3H2O
7.3.2 If the final amount of hydronium ions is 1,26 x 103 moles, calculate the mass of lime that was added to the lake. (7) [20]
QUESTION 8 (Start on a new page.)
8.1Corrosion is a redox reaction that takes place in the presence of oxygen and water. Rusting is the corrosion of iron leading to the formation of iron(III) ions.
8.1.1 Define oxidation in terms of electron transfer. (2)
A cleaned copper rod and a cleaned iron nail are placed in a beaker containing water at 25°C, as shown below.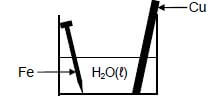
After a while it was observed that the iron nail was coated with rust. The copper rod showed no visible signs of corrosion.
8.1.2Write down the half-reaction for the iron nail. (2)
8.1.3 Does iron act as REDUCING AGENT or OXIDISING AGENT in the beaker? (1)
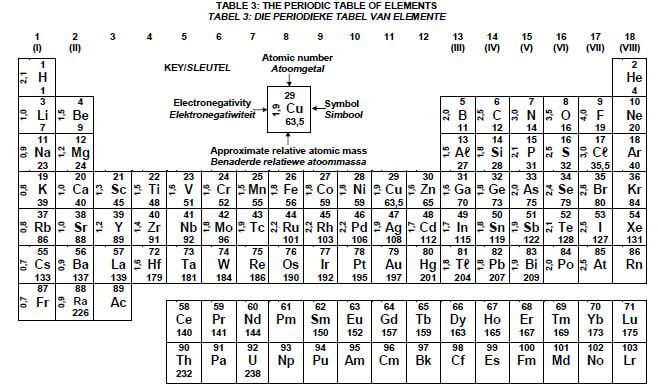
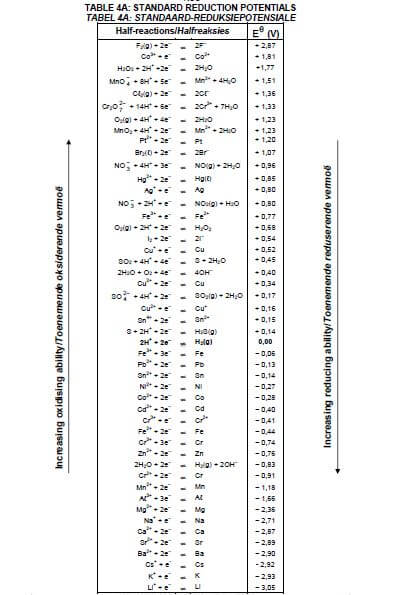
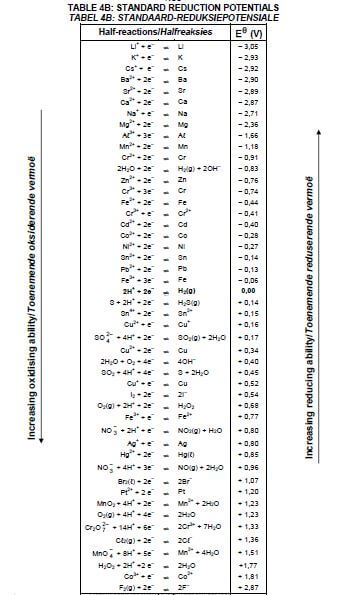
8.1.4 Explain the above observation by referring to the Table of Standard Reduction Potentials. (3)
To prevent rusting of an underground iron pipe, the pipe is connected to a metal (Q) that corrodes easily.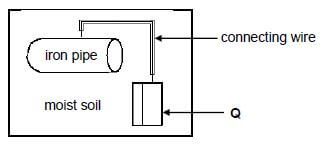
8.1.5 You are given two metals, Zn and Cu, to use as metal Q. Which metal would more suitable? Give a reason. (2)
8.2 A galvanic cell is constructed using a Fe | Fe3+ half-cell and a Cu | Cu2+ half-cell.
8.2.1 Write down the overall (net) cell reaction that takes place when the cell is functioning. (3)
8.2.2 Calculate the cell potential of this cell under standard conditions. (4) [17]
QUESTION 9 (Start on a new page.)
The electrolytic cell below is set up to obtain pure copper from a piece of impure copper.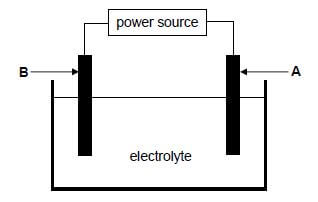
The impure copper contains other metals, such as platinum, iron, cobalt, silver and nickel.
The cell potential of the power source is adjusted so that only copper is deposited on electrode B.
9.1 Define an electrolytic cell. (2)
9.2 Write down the FORMULA of a suitable electrolyte for this cell. (1)
9.3 Which electrode (A or B) is the cathode? Write down the relevant half-reaction taking place at this electrode. (3)
9.4 Sludge forms below one of the electrodes while the cell above is in operation. Which of the metals, PLATINUM, IRON, COBALT, SILVER or NICKEL, will be present in the sludge? (2) [8]
QUESTION 10 (Start on a new page.)
In the flow diagram below, I and II represent industrial processes used in the fertiliser industry. P and Q are chemical reactions that take place to produce ammonium sulphate and fertiliser Y respectively.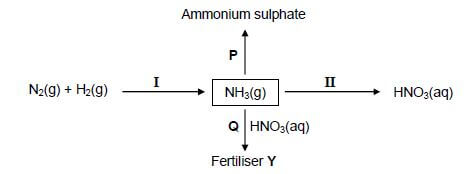
10.1 Write down the name of the industrial process:
10.1.1 I (1)
10.1.2 II (1)
10.2 Write down the NAME or FORMULA of:
10.2.1 Fertiliser Y (1)
10.2.2The catalyst used in process I (1)
10.3 In reaction P, NH3(g) reacts with another substance. Write down a balanced equation for this reaction. (3)
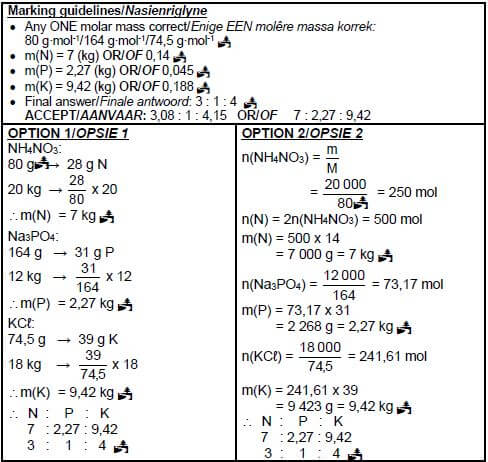
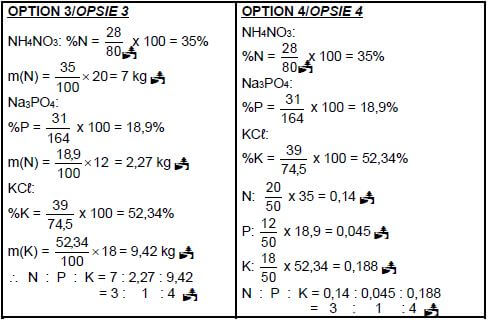
10.4 The following substances are present in a bag of fertiliser:
- 20 kg ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3)
- 12 kg sodium phosphate (Na3PO4)
- 18 kg potassium chloride (KCℓ)
Calculate the NPK ratio of the fertiliser. (5) [12]
TOTAL: 150
DATA FOR PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 12 PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY)
TABLE 1: PHYSICAL CONSTANTS
NAME | SYMBOL | VALUE |
Standard pressure | pθ | 1,013 x 105 Pa |
Molar gas volume at STP | Vm | 22,4 dm3∙mol-1 |
Standard temperature | Tθ | 273 K |
Charge on electron | e | -1,6 x 10-19 C |
Avogadro's constant | NA | 6,02 x 1023 mol-1 |
PHYSICAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
PHYSICAL SCIENCES
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1 C ✔✔ (2)
1.2 C ✔✔ (2)
1.3 C ✔✔ (2)
1.4 A ✔✔ (2)
1.5 D ✔✔ (2)
1.6 B ✔✔ (2)
1.7 B ✔✔ (2)
1.8 D ✔✔ (2)
1.9 D ✔✔ (2)
1.10 B ✔✔ (2) [20]
QUESTION 2
2.1 ANY ONE
- (Alcohol/ethanol) is flammable/catches fire easily.
- To heat it evenly.
- Water bath is used for low heat/low temperature.
- Alcohol/ethanol will evaporate too quickly.
Accept/
(Alcohol/ethanol) is volatile. (1)
2.2
2.2.1 Esterification/condensation (1)
2.2.2 H2SO4 (1)
2.2.3 Esters (1)
2.3
- M(ester) = 144 = 2
M(C4H8O) 72
∴ 2 x C4H8O = C8H16O2
Marking guidelines:
- If only answer given, award 2 marks on final
- If 72 g·mol-1 calculated without substituting, no mark is awarded (2)
2.4 Ethyl hexanoate (2)
Note
- Accept any other ethyl ESTER from QUESTION 2.3.
2.5 POSITIVE MARKING FROM QUESTION 2.4.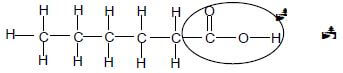
Marking criteria
- Whole structure correct 2/2
- Only functional group correct : Max: 1/2
- Accept -OH as condensed (2)[10]
QUESTION 3
3.1 Marking guidelines/
- If any one of the underlined key phrases in the correct context is omitted, deduct 1 mark
- The temperature at which the vapour pressure of a substance equals atmospheric/external pressure. (2)
3.2
3.2.1Carboxyl (group)
Accept
- Carboxylic (1)
3.2.2 Propanoic acid/propanoësuur (1)
3.2.3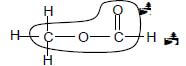
Marking criteria
- Whole structure correct: 2/2
- Only functional group correct: 1/2
IF
- More than one functional group/wrong functional group 0/2
- If condensed structural formulae used: Max: 1/2
3.3 A - Lowest boiling point./Shortest chain length.
3.4
3.4.1 The same molecular mass/molecular size.
3.4.2 Primary
- OH group is bonded to a C atom bonded to one other C atom.
OR - OH group is bonded to a C atom that has two H atoms.
3.4.3 Marking guidelines
- BOTH have hydrogen bonding.
- Compare number of sites for hydrogen bonding.
- Compare strength of IMFs.
- Compare energy required.
- Both compounds/X and B have (in addition to London forces and dipole-dipole forces) hydrogen bonding.
- Compound X/CH3CH2CH2OH/propan-1-ol/alcohol has one site for hydrogen bonding and compound B/ethanoic acid/carboxylic acid has two/more sites for hydrogen bonding OR B/ethanoic acid/carboxylic acid has two/more sites for hydrogen bonding.
- Intermolecular forces in compound B/ethanoic acid/carboxylic acid are stronger than intermolecular forces in compound X/CH3CH2CH2OH/ propan-1-ol/alcohol.
OR
Intermolecular forces in compound X/CH3CH2CH2OH/ propan-1-ol/alcohol are weaker than intermolecular forces in compound B/ethanoic acid/carboxylic acid. - More energy is needed to overcome/break intermolecular forces in compound B/ethanoic acid/carboxylic acid than in compound X/CH3CH2CH2OH/ propan-1-ol/alcohol.
OR
Less energy is needed to overcome/break intermolecular forces in compound X/CH3CH2CH2OH/propan-1-ol/alcohol than in compound B/ethanoic acid/carboxylic acid. (4) [15]
QUESTION 4
4.1
4.1.
- (A series of organic) compounds that can be described by the same general formula/functional group. (2 or 0)
OR
(A series of organic) compounds in which one member differs from the next by a CH2 group (2)
4.1.2 Substitution/halogenation/bromination (1)
4.1.3 HBr (1)
4.1.4 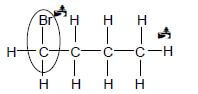
Marking criteria
- Br on first C atom: Max: 1/2
- Whole structure correct 2/2
IF
- Br2 but rest of structure correct (2)
4.1.5 C5H12 + 8O2 → 5CO2 + 6H2O Bal
Marking guidelines
- Reactants Products Balancing
- Ignore double arrows and phases.
- Marking rule 6.3.10/Nasienreël 6.3.10.
- If condensed structural formulae used : Max: 2/3 (3)
4.1.6 Marking guidelines/Nasienriglyne
- If any one of the underlined key phrases in the correct context is omitted, deduct 1 mark
The (chemical) process in which longer chain hydrocarbons/longer chain alkanes are broken down to shorter/more useful hydrocarbons/molecules/ chains/alkanes and alkenes. (2)
4.1.7 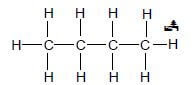
Marking guidelines
- One or more H atoms omitted : Max: 1/2
- Condensed or semi-structural formula:Max: 1/2 (2)
4.2
4.2.1 Butan-2-ol OR 2-butanol
IF:
- Butanol or butan-1-ol 1/2 (2)
4.2.2 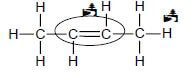
Marking criteria
- Only functional group correct: Max/Maks: 1/2
- Whole structure correct: 1/2 (2) [17]
QUESTION 5
5.1Temperature (1)
5. 2 NOTE
Give the mark for per unit time only if in context of reaction rate.
ANY ONE
- Change in concentration of products/reactants per (unit) time.
- Change in amount/number of moles/volume/mass of products or reactants per (unit) time.
- Amount/number of moles/volume/mass of products formed/reactants used per (unit) time.
- Rate of change in concentration/amount/number of moles/volume/mass. (2 or/of 0) (2)
5.3 14 (min) (2)
5.4
5.4.1 Graph B
- (Experiment 3) has the highest (acid) concentration/more particles/higher number of moles. (2)
5.4.2 (Graph/grafiek) C
- (Experiment 5) is at highest temperature/more particles with sufficient kinetic energy/HCℓ is at 35oC (2)
5.5
5.5.1 Speeds up the reaction./Increases the reaction rate./Provides alternate pathway./Lowers the (net) activation energy. (1)
5.5.2 Equal to (1)
5.6 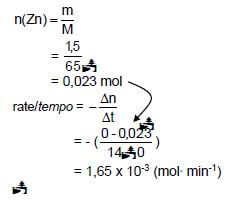
Marking guidelines
- Substitute 65 g∙mol-1 in n = m
M - Substitute change in mol to calculate rate.
- Substitute change in time to calculate rate.
- Final answer:
1,65 x 10-3 mol∙min-1
Range/Gebied:
1,43 x 10-3 to/tot 1,65 x 10-3 (mol∙min-1)
Notes
- Ignore if zeros omitted in calculation of reaction rate.
- Accept negative answer i.e. -1,65 x 10-3 mol·min-1 (4) [15]
QUESTION 6
6.1
- When the equilibrium in a closed system is disturbed, the system will re- instate a (new) equilibrium by favouring the reaction that will cancel/oppose the disturbance. (2)
6.2 Endothermic
- Decrease in temperature favours the exothermic reaction.
- The reverse reaction is favoured.
OR
Number of moles/amount/concentration of N2O4/colourless gas increases.
OR
Number of moles/amount of NO2/brown gas decreases. (3)
6.3
6.3.1 Increases (1)
6.3.2 Remains the same (1)
6.3.3 Increases (1)
6.4 CALCULATIONS USING NUMBER OF MOLES
Marking guidelines/Nasienriglyne
- ∆n(N2O4) = 20% of x/0,2x.
- USE ratio: N2O4 : NO2 : = 1 : 2.
- n(N2O4)eq/ewe = n(N2O4)initial/begin - ∆n(N2O4).
- n(NO2)eq/ewe = n(NO2)initial/begin + ∆n(NO2).
- Divide equilibrium moles by 2 dm3
- Correct Kc expression (formulae in square brackets).
- Substitution of Kc value
- Substitution of concentrations into correct Kc expression.
- Final answer/Finale antwoord: 1,6 (mol)
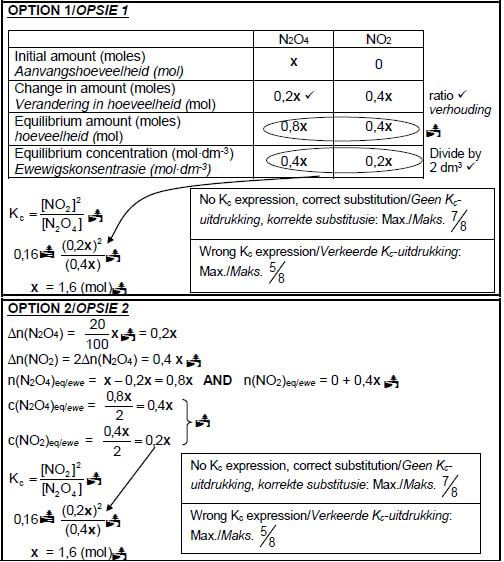
CALCULATIONS USING CONCENTRATION
Marking guidelines
- Initial n(N2O4)/x divide by 2 dm3.
- ∆c(N2O4) = 20% of initial concentration/0,1x.
- USE ratio/GEBRUIK verhouding: c(N2O4) : c(NO2) = 1 : 2.
- c(N2O4)eq/ewe = c(N2O4)initial/begin - ∆c(N2O4).
- c(NO2)eq/ewe = c(NO2)initial/begin + ∆c(NO2).
- Correct Kc expression (formulae in square brackets).
- Substitution of Kc value/Vervanging van Kc-waarde.
- Substitution of concentrations into Kc expression.
- Final answer/Finale antwoord: 1,6 (mol)
OPTION 3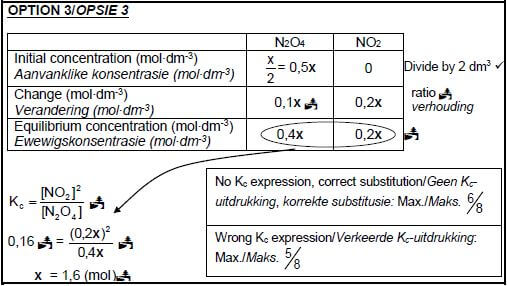 (8) [16]
(8) [16]
QUESTION 7
7.1
7.1.1 An acid is a proton donor. (2)
7.1.2 H2O (1)
7.1.3 HSO-4 (2)
7.2
7.2.1 Reaction of a salt with water/H2O.
Accept
- Reaction of cations or anions with water (2)
7.2.2 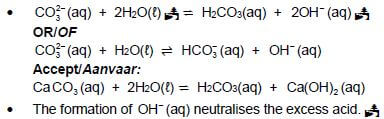
Marking guidelines
- Reactants Products
- The formation of OH (aq) neutralises the excess acid.
- Ignore single arrows and phases
- Marking rule 6.3.10
- Ignore balancing.
7.3
7.3.1
- pH = -log[H3O+]
5 = -log[H3O+]
[H3O+] = 1 x 10-5 mol·dm-3 (3)
7.3.2 POSITIVE MARKING FROM QUESTION 7.3.1.
Marking guidelines
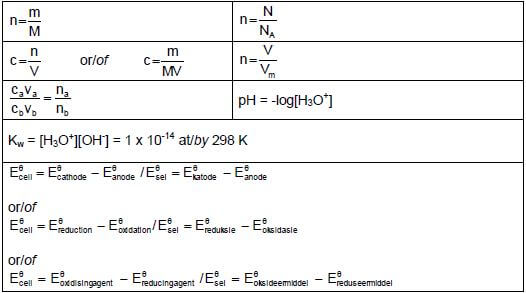
- Any formula : c = n / n = m / Ca x Va =na /c = m
V M Cb x Vb nb MV - Substitute V = 4 x 109 dm3
- Calculate na(reacted) = na(initial) - na(final)
- Use n(CaO) : n(H3O+) = 1:2
- Substitution of 56 g∙mol-1
- Final answer : m = 1,08 x 106 g to/tot 1,09 x 106 g
IF final answer is negative: Max: 6/7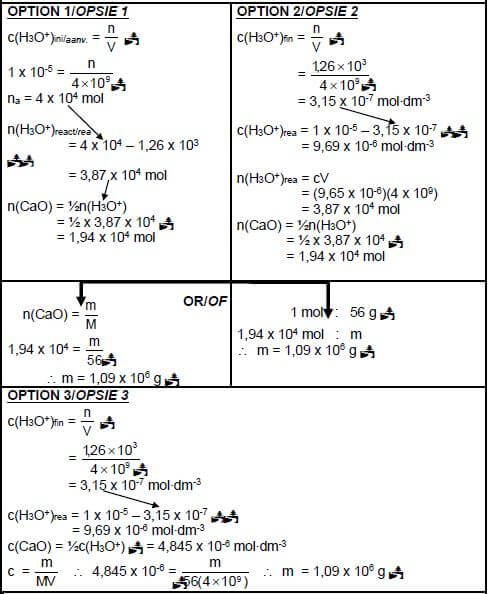 (7) [20]
(7) [20]
QUESTION 8
8.1
8.1.1 Loss of electrons./Verlies aan elektrone. (2 or/of 0) (2)
8.1.2 Fe → Fe3+ + 3e-
Marking guidelines
-

- Ignore if charge omitted on electron.
- If charge (+) omitted on Fe3+: Example: Fe → Fe3 + 3e-
Max1/2 (2)
8.1.3 Reducing agent (1)
8.1.4
- Fe is a stronger reducing agent than Cu and (Fe) will be oxidised (to Fe3+).
OR - Cu is a weaker reducing agent than Fe and (Cu) will not be oxidised (to Cu2+). (3)
8.1.5 Zinc/Zn
- Stronger reducing agent (than Fe).
OR - Zn will undergo oxidation (before Fe).
OR - Cu is a weaker reducing agent (than Fe). (2)
8.2
8.2.1 3Cu2+ + 2Fe → 3Cu + 2Fe3+ Bal.
Marking guidelines/Nasienriglyne
- Reactants Products Balancing
- Ignore double arrows.
- Marking rule 6.3.10 (3)
8.2.2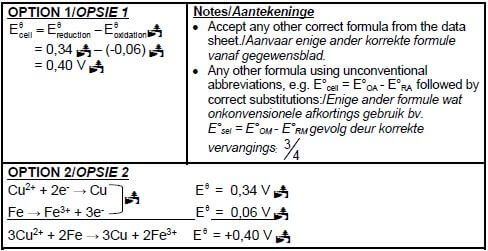
(4) [17]
QUESTION 9
9.1
- A cell in which electrical energy is converted to chemical energy. (2 or 0)
OR - A cell in which electrical energy/electricity is used to obtain a chemical change/reaction. (2 or 0) (2)
9.2 Any soluble copper(II) salt e.g
- CuSO4/Cu(NO3)2/CuCℓ2 (1)
9.3 Marking guidelines

- Ignore if charge on electron is omitted.
- If a charge of an ion is omitted e.g. Cu2 + 2e- → Cu Max.: 1/2 (3)
9.4 Platinum/Pt AND silver/Ag/ (2) [8]
QUESTION 10
10.1
10.1.1 Haber (process)
10.1.2 Ostwald (process)
10.2
10.2.1Ammonium nitrate/Ammoniumnitraat/NH4NO3
10.2.2 Iron/iron oxide/Fe/FeO
10.3
- 2NH3 + H2SO4 → (NH4)2SO4 Bal
Marking guidelines
- Reactants Products Balancing
- Ignore double arrows.
- Marking rule 6.3.10
 (5)
(5)
[12]
TOTAL: 150
PHYSICAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
PHYSICAL SCIENCES
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1 C /D✔✔ (2)
1.2 C ✔✔ (2)
1.3 C ✔✔ (2)
1.4 B ✔✔ (2)
1.5 B ✔✔ (2)
1.6 A ✔✔ (2)
1.7 A ✔✔(2)
1.8 D ✔✔ (2)
1.9 D ✔✔ (2)
1.10 C ✔✔ (2) [20]
QUESTION 2
2.1 (2)
When a (non-zero) resultant/net force acts on an object, the object will accelerate in the direction of the force with an acceleration that is directly proportional to the force and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. ✔✔ |
NOTE
|
2.2  (4)
(4)
Notes
|
Accept the following symbols | |
N | FN; Normal;Normal force ✔ |
f | Ff / fk / frictional force ✔ |
w | Fg; mg; Weight;FEarth on block;Fw ;Gravitational force ✔ |
T | Tension ; FT /FA, F /16,96 N ✔ |
2.3.1 (1)
The 2/8 kg block /system is accelerating ✔
|
2.3.2 (3)
For 2 kg |
2.3.3 (4)
POSITIVE MARKING FROM 2.3.2 |
2.4 (1)
|
2.5 (2) [17]
Yes✔ |
QUESTION 3
3.1 (2)
Downwards ✔
|
OPTION 1 Downward positive |
3.2 (3)
OPTION 2 | OPTION 2 |
OPTION 3 | OPTION 3 |
OPTION 4 | OPTION 4 |
OPTION 5 | OPTION 5 |
NOTES for marking QUESTION 3.3 | |
Formula mark | ✔ |
Substitution mark | ✔✔ |
Mark for height/distance | ✔ |
Mark for comparison | ✔ |
Mark for conclusion | ✔ |
3.3 (6)
OPTION 1 Downward positive |
OPTION 2 |
OPTION 3 |
OPTION 4 |
OPTION 5 Yes ✔ ✔ Downward positive |
OPTION 6 (POSITIVE MARKING FROM 3.2) Downward positive |
OPTION 7 (POSITIVE MARKING FROM 3.2) | OPTION 7(POSITIVE MARKING FROM 3.2 |
OPTION 8
Downward positive
|
OPTION 9 |
OPTION 10 Downward positive 2,1✔ = (7,5)Δt + ½ (-9,8)Δt2 ✔ |
OPTION 11 Downward positive |
OPTION 12 Downward positive Velocity at T is -3,88 m·s-1therefore the ball is still moving towards its maximum height ✔✔ |
3.4 POSITIVE MARKING FROM 3.2 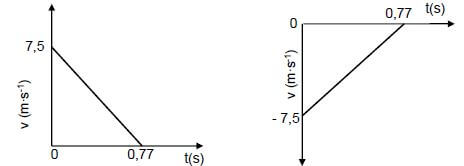 (2) [13]
(2) [13]
Notes | |
Initial velocity and time for final velocity shown | ✔ |
Correct straight line (including orientation) drawn | ✔ |
QUESTION 4
4.1 Momentum is the product of the mass of an object and its velocity ✔✔
[NOTE: 2 or/of 0] (2)
4.2 To the left ✔
Newton's third law✔
ACCEPT:
- Principle of conservation of linear momentum / law of action-reaction✔
- Newton's third law and Newton’s second law ✔ (2)
NOTE: For QUESTION 4.3 and 4.4 motion to the right has been taken as positive. Candidates may use the opposite direction. 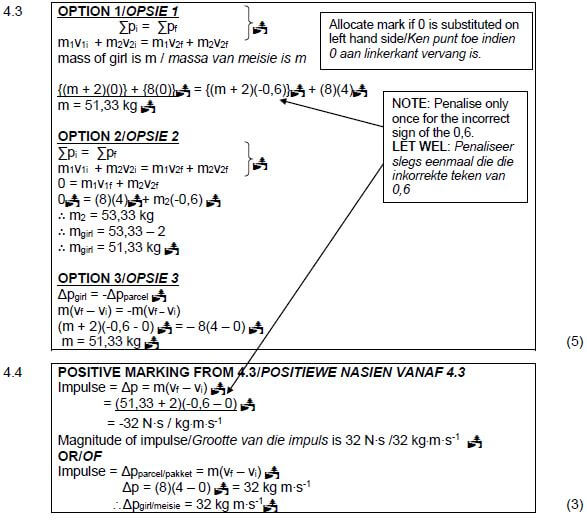
4.5 (2) [14]
POSITIVE MARKING FROM 4.4 /POSITIEWE NASIEN VANAF 4.4 32 kg⋅m⋅s-1/ N·s to the right/opposite direction /na regs /teenoorgestelde rigting |
QUESTION 5
5.1
- A force is non-conservative if the work it does on an object which is moving between two points depends on the path taken✔✔
OR - A force is non-conservative if the work it does on an object depends on the path taken.✔✔
OR - A force is non-conservative if the work it does in moving an object around a closed path is non-zero ✔✔. (2)
NOTE
|
5.2 No ✔ (1)
5.3 (3)
OPTION 1 OPTION 2 |
5.4
- The net/total work done on an object is equal to the change in the object's kinetic energy✔✔
OR
The work done on an object by a net force ✔is equal to the change in the object's kinetic energy. ✔ (2)
NOTE If any of the underlined key words/phrases in the correct context is omitted deduct 1 mark. . |
5.5 (5) (5)
OPTION 1 OR Wnet = ΔK✔ -ΔEp + Wf + WF = ½ mvf2- ½ mvi2 |
NOTE
|
OPTION 2 OR 1 mark for any of these |
ACCEPT THE FOLLOWING FOR: 3 /5 |
(5) [13]
QUESTION 6
6.1
- The change in frequency (or pitch), of the sound detected by a listener because the sound source and the listener have different velocities relative to the medium of sound propagation.
OR - An (apparent) change in observed/detected frequency (pitch), as a result of the relative motion between a source and an observer (listener). (2)
NOTE If any of the underlined key words/phrases in the correct context is omitted deduct 1 mark. |
6.2 Away from✔
Observed frequency lower (2)
6.3 (3)
v = fλ ✔ |
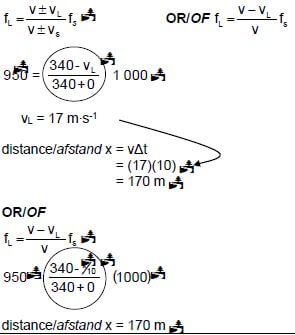
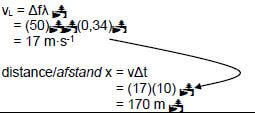
6.4
POSITIVE MARKING FROM 6.3 |
(6) [13]
QUESTION 7
7.1 (2)
Qnet = Q1 + Q2 + Q3
|
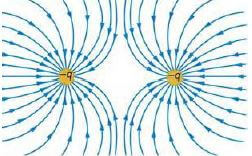
NOTES
- Correct shape ✔
- Correct direction ✔
- Lines must not cross and must touch spheres ✔ (3)
7.3 The magnitude of the electrostatic force exerted by one point charge (Q1) on another point charge (Q2) is directly proportional to the product of the (magnitudes) of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (r) between them ✔✔ (2)
NOTE
|
7.4 (5)
OPTION 1
OPTION 2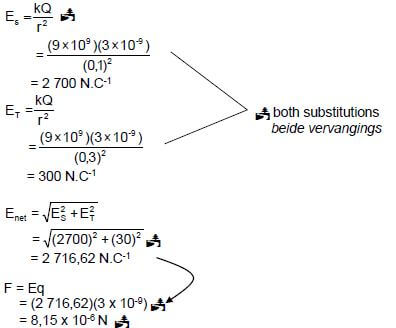
7.5 (3)
POSITIVE MARKING FROM 7.4 |
OPTION 2 ET = KQ Enet = √ (ES2 + ET2) NOTE
If calculation done in 7.4 award full marks for answer written here. |
7.6.1 Sphere P or/of T✔ (1)
7.6.2 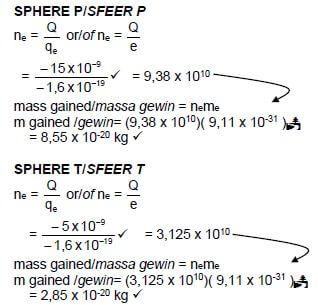 (3)[19]
(3)[19]
QUESTION 8
8.1
- The battery supplies 12 J per coulomb/12 J per unit charge. ✔ ✔OR
- The potential difference of the battery in an open circuit is 12 V. ✔ ✔OR
- The battery does 12 J of work per coulomb of charge.✔ ✔ OR
- Maximum work done by the battery per unit charge is 12 J ✔ ✔ OR
- Maximum energy supplied by the battery per unit charge is 12 J ✔ ✔ OR
- The battery supplies 12 J of energy per coulomb/ 12 J of energy per unit charge ✔ ✔ OR
- The greatest potential difference that can be generated by a battery is 12V ✔ ✔ OR
- The total energy transferred by a battery to a unit electric charge is 12 J ✔ ✔ OR
- The total amount of electric energy supplied by the battery per coulomb/per unit charge is 12 J ✔ ✔ (2)
NOTE |
8.2.1 (3)
OPTION 1 |
OPTION 2 |
OPTION 3 |
8.2.2 (2)
POSITIVE MARKING FROM 8.2.1 |
OPTION 2 |
OPTION 3 |
OPTION 4 |
OPTION 5 |
8.3 Decreases
- Total resistance decreases ✔
- Current increases ✔
- "Lost volts" increases, (emf the same) ✔
- External potential difference decreases ✔
OR - Decreases ✔
- Total resistance decreases ✔
- Current increases ✔
- ε = Vext + Ir ✔
- Ir increases ✔
- ε is constant ✔
∴Vext/eks decreases (4) [11]
QUESTION 9
9.1 Temperature/Temperatuur ✔ (1)
9.2.1 r = 3 Ω or/of 1,5 Ω ✔✔
- Accept for one mark only:
r = -3 Ω ✔ or -1,5 Ω (2)
9.2.2 (3) [6]
ε = slope (gradient) of the graph✔
ε = 7,5 -(-3) OR POSITIVE MARKING FROM 9.2.1
7,5 = 1,5ε -3 OR ε = I(R + r) |
QUESTION 10
10.1.1 Y to/na X ✔ (1)
10.1.2
- Faraday’s Law Electromagnetic Induction ✔
OR - Electromagnetic induction/Faraday's Law (1)
10.1.3 Mechanical (kinetic) energy ✔to electrical energy ✔(2)
10.2.1 340 V ✔(1)
Accept -340 V
10.2.2 POSITIVE MARKING FROM 10.2.1 (3)
(3)
10.2.3 POSITIVE MARKING FROM 10.2.2 (3) [11]
OPTION 1 OPTION 2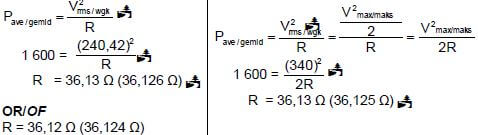
OPTION 3 (Do not penalise if rms is omitted V) in R = Vrms | OPTION 4 = 340 (Do not penalise if rms is omitted V) in R = Vrms |
QUESTION 11
11.1 (2)
Work function of a metal is the minimum energy needed to eject an electron from the metal surface ✔✔ |
NOTE |
11.2 (2)
Potassium / Kalium / K ✔ Wo α fo |
11.3 (3)
OPTION 1 |
OPTION 2 = 3,6164 x 10-19 J
|
OPTION 3 |
11.4 (5)
OPTION 1 NOTE: If EK of the incorrect photocell is calculated, candidate forfeit the mark for the final answer. |
OPTION 2 NOTE: If EK of the incorrect photocell is calculated, candidate forfeit the mark for the final answer. |
11.5 Remains the same (1) [13]
TOTAL: 150
ADDENDUM
QUESTION 7.2
Accept the following electric field diagram which would be formed if the effect of the third charge is considered. 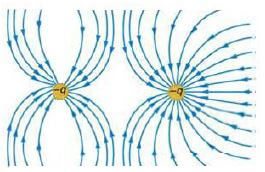
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of FOUR questions. Answer ALL the questions.
- 2.1 Use the ANNEXURES in the ADDENDUM to answer the following questions:
- ANNEXURE A for QUESTION 1.2
- ANNEXURE B for QUESTION 2.1
- ANNEXURE C for QUESTION 3.1
- ANNEXURE D for QUESTION 4.1
2.2 Answer QUESTION 2.1.5 on the ANSWER SHEET attached. Write your centre number and examination number in the spaces on the ANSWER SHEET. Hand in the ANSWER SHEET with your ANSWER BOOK.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in thisquestion paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- You may use an approved calculator (non-programmable and non-graphical), unless stated otherwise.
- Show ALL calculations clearly.
- Round off ALL final answers appropriately according to the given context, unless stated otherwise.
- Indicate units of measurement, where applicable.
- Maps and diagrams are NOT drawn to scale, unless stated otherwise.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1 Mapotjo plans to purchase a bakkie (motor vehicle). She received the followingquotation from a car dealer on 28 February 2018:
Extract of a quotation for a bakkie from a dealer:
| Rand (R) | |
| Selling price (excluding VAT) without accessories (extras) | 160 087,72 |
| Discount | 6 140,00 |
| ACCESSORIES (EXTRAS) | |
| Smash-and-grab film | 3 500,00 |
| Door protector | 3 500,00 |
| OTHER CHARGES | |
| On-road charges | 4 298,25 |
| Transaction fee | 1 315,79 |
| SUBTOTAL | 166 561,76 |
| VALUE-ADDED TAX | 14% |
| TOTAL DUE | 189 880,41 |
[Source: Group 1 Nissan and The Glen]
Use the information above to answer the questions that follow.
1.1.1 Calculate (rounded off to ONE decimal place) the percentage discountgiven on the bakkie's selling price, excluding VAT. (3)
1.1.2 Show how the amount of R166 561,76 was calculated. (3)
1.1.3 Give ONE reason why customers would prefer to install the accessories(extras), as shown in the quotation. (2)
1.1.4 Mapotjo has an investment of R1,25 million. The money was invested as follows:
- Twenty-seven (27) months investment period
- 6% interest per annum, compounded annually
Show whether the interest earned on this investment is sufficient to cover the total purchase price of R189 880,41. (9)
1.1.5 VAT in South Africa increased to 15% with effect from 1 April 2018.
The following shows how the dealer calculated the new increased VAT incorrectly:
- Selling price, including 14% VAT
= R160 087,72 + 14% of R160 087,72
= R160 087,72 + R22 412,28
= R182 500 - VAT increased with 1%.
New selling price, including 15% VAT = R182 500 + R182 500 x 1%
= R182 500 + R1 825
= R184 325
Identify the mistake the dealer has made in calculating the new selling price. Hence, calculate the new selling price, including 15% VAT (excluding accessories and other charges). (4)
1.2
| After Mapotjo had purchased the bakkie, she decided to paint the cargo bin (loading box) of her bakkie with rubberising paint. The spread rate of the paint is 0,25 m2/f. The rubberising paint is sold in 5 f tins. A photograph of the cargo bin of a bakkie and a simplified model of the cargo bin with dimensions are given in ANNEXURE A. NOTE: Rubberising paint — a special paint used to coat the surface of a cargo bin |
Use the information above and ANNEXURE A to answer the questions that follow.
1.2.1 The cargo bin does not have a flat surface area and therefore the surface area must be increased by 2% to accommodate the uneven surface area.
- Calculate how many litres of rubberising paint Mapotjo needs to purchase in order to rubberise the cargo bin of her bakkie.
You may use the formula:- Surface area of an open box
= Width x length + 2(length x height + width x height)
- Surface area of an open box
- Calculate the cost of applying TWO coats of rubberising paint (excluding labour) if a 5 f tin costs R549, including VAT.
1.2.2 Explain the significance of applying rubberising paint to the cargo bin of a bakkie.
1.3 It takes 20 minutes to apply a layer of rubberising paint. There is a 4-hour waiting period before the second coat of rubberising paint can be applied. In addition, a further drying time of 2 hours is required after the second coat has been applied.
Determine, with calculations, at what time the bakkie would be ready if the workshop started rubberising the cargo bin at 08:15. (4) [38]
QUESTION 2
2.1 TABLE 1 in ANNEXURE B shows data relating to the import of personal care and cosmetic products in Australia for the period 2013 to 2015.
Use the information in ANNEXURE B to answer the questions that follow.
2.1.1 Determine:
- Missing value A (rounded off to a whole percentage) using the following formula:
- % change (A) = 2015 imports - 2013 imports x 100% (4)
2013 imports
- % change (A) = 2015 imports - 2013 imports x 100% (4)
- The median of the percentage change for the period 2013 to 2015. (3)
2.1.2 Describe the trend in the imports of make-up and skincare products. (2)
2.1.3 The negative value of the percentage change does not necessarily imply that the import value of the products decreased continuously over the three-year period. Name TWO different products in TABLE 1 and explain how they support the statement above. (4)
2.1.4 State, with a reason, whether the data in TABLE 1 can be represented using a single pie chart. (2)
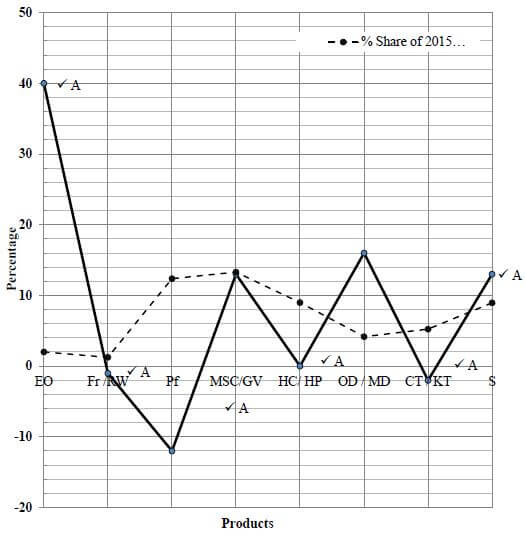
2.1.5 A line graph showing the % share of 2015 imports for the first eight products in TABLE 1 has been drawn on the ANSWER SHEET. On the same grid, draw another line graph representing the percentage change for the period 2013 to 2015 for the same eight products. (6)
2.2 Nomsa plans to visit Los Angeles for an educational conference. She will be travelling from her hotel to the conference venue with an Uber taxi.
An Uber taxi is operated using two options, as shown below.
- Option 1: UPFRONT fare
= base fare (call-out fee) + (number of miles x per mile fare) - Option 2: POST-TRIP fare
= (number of minutes x per minute fare) + (number of miles x per mile fare)
TABLE 2 below shows the different Uber taxis and their respective rates in Los Angeles for both UPFRONT and POST-TRIP fare options, including an example of a 10-mile trip using the UPFRONT fare option.
COST | UberX | UberBLACK | UberLUX |
| Base fare (call-out fee) | $0,00 | $ 8,00 | $20,00 |
| Per minute fare | $0,15 | $ 0,45 | $ 0,60 |
Per mile fare | $0,90 | $ 3,55 | $ 5,00 |
| *Minimum fare | $4,65 | $15,00 | $30,00 |
| Cancellation fee | $5,00 | $10,00 | $10,00 |
| Total fare (for a 10-mile trip using the UPFRONT option) | $9,00 | $43,50 | B |
[Adapted from www.uber.com, March 2016]
*Minimum fare: the lowest fare one would be charged per trip
Use the information above to answer the questions that follow.
2.2.1 Calculate the missing value B. (3)
2.2.2 Calculate (rounded off to the nearest mile) the maximum distance for which a person can use the UberX taxi if you pay the minimum upfront fare. (4)
2.2.3 Nomsa travelled a distance of 29,73 miles with UberBLACK. The post-trip fare option Was used and the trip took 1 hour and 9 minutes to complete. Nomsa stated that she would have saved more than $20,00 if she had used the upfront fare option. Show, with calculations, whether her statement is correct. (8)
2.2.4 Explain the importance of a cancellation fee for the Uber service provider. (2) [38]
QUESTION 3
3.1
The Big Five Marathon is an annual event in South Africa. It can be run as a full 42 km marathon or as a half-marathon of 21 km.
[Source: http://aublog.southafrica] ANNEXURE C contains the Big Five 42 km full marathon map. | ||||||||||||||||
Use the information above and ANNEXURE C to answer the questions that follow.
3.1.1 Determine (as a decimal fraction) the probability of a runner of the Big Five marathon route accessing a refreshment station that offers ONLY Coke and water. (3)
3.1.2 Give the general direction in which a marathon runner is heading when passing the 20 km mark. (2)
3.1.3 Consider the heights above sea level for this race.
- Explain why a runner was CORRECT when he stated that he was running uphill from the start to the 10 km mark. (2)
- Express, in the form 1 : ..., the lowest possible height above sea level to the highest height above sea level. (3)
3.1.4 Explain why there are cut-off times for a marathon. (2)
3.1.5 For the half-marathon a runner must cover a distance of 16,5 km in a time of 5 hours from the start of the race to beat the cut-off 2 time for the half-marathon. A runner of the full marathon compared his speed with the speed of a half-marathon runner and stated that he had to run 2,7 km/h faster in order to beat the cut-off 2 time of the full marathon.
Verify, showing ALL calculations, whether he is CORRECT. You may use the formula:
- Distance = speed x time (6)
3.2
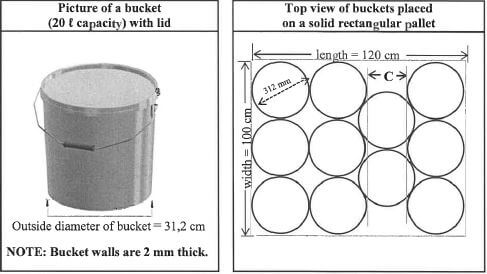
More water must be taken to the refreshment stations. The water will be transported in cylindrical buckets (with lids) with a maximum capacity of 20 litres of water. [Source: www.meyaplast.co.uk] |
Use theinformation and picture above to answer the questions that follow.
3.2.1 Determine the maximum height (in cm) of the water in the bucket if the outside diameter of the bucket is 31,2 cm.
You may use the formula:
- Volume of a cylinder = n x (radius)2 x height
where π = 3,142 and 1 f = 1 000 cm3 (7)
3.2.2 Buckets are placed on the pallet, as shown in the diagram above.
- Calculate the unused area (in cm2) of the rectangular floor of the solid pallet.
You may use the formula:- Area of a circle = 7 x (radius)2, where π = 3,142 (6)
- Determine length C, as shown in the diagram above. (3)
3.2.3 The organiser would have preferred each pallet to have 12 buckets arranged in three rows of four each, as shown in the diagram alongside.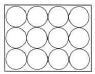
Calculate the percentage by which the length of the pallet should be increased to accommodate this new arrangement. (5) [39]
QUESTION 4
4.1 ANNEXURE D shows photographs of the London Eye, which is a *Ferris wheel.
The following information represents features of the Ferris wheel:
- The structure is 443 feet tall.
- The radius of the wheel is 197 feet.
- It has 32 capsules that are spaced apart evenly.
- Each capsule can carry a maximum of 28 passengers.
- Ticket prices for all capsules are identical.
The following are the ticket prices per person:
| TICKET CATEGORY | PRICE |
| Adults (16+) | £27,00 |
| Children aged 3-15 | £22,00 |
| Senior citizens | £25,50 |
| 10% discount for tickets bought online | |
[Source: www.londoneye.com]
- Conversions: 1 pound (£) = R16,58
1 metre = 3,28 feet
*Ferris wheel: a very large upright wheel with capsules on its circumference for people to ride in
Use the information above to answer the questions that follow.
4.1.1 Capsule 24 and capsule 30 have the following number of occupants.
| ADULTS (16+) | CHILDREN AGED 3-15 | SENIOR CITIZENS | |
| Capsule 24 | 18 | 7 | 2 |
| Capsule 30 | 10 | 1 | 5 |
Only 5 adults of the total number of occupants in the table above bought tickets online. A South African tourist at the London Eye remarked that more than R18 400 was spent on these tickets. Verify, with calculations, whether this remark is CORRECT. (8)
4.1.2 The capsules are mounted on the circumference of the wheel.
- Calculate (in feet) the circumference of the wheel.
You may use the formula:- Circumference = 2 x π x radius, where π = 3,142 (2)
- Hence, calculate the distance (to the nearest metre) on the circumference between any TWO capsules right next to each other. (3)
4.2 Tourism creates many employment opportunities in the United Kingdom. Tourists are most likely business visitors, holiday visitors or visitors to friends and relatives (VFR).
TABLE 3 below shows information regarding the number of visitors (in thousands) and the reasons for their visits. It also shows the number of employment opportunities for the different tourist regions.
TABLE 3: NUMBER OF VISITORS (IN THOUSANDS) AND THE REASONS FOR VISITS TO DIFFERENT TOURISM REGIONS IN THE UNITED KINGDOM AND OPPORTUNITIES
| REGIONS | NUMBER OF VISITORS (IN THOUSANDS) ACCORDING TO REASON FOR VISIT | DIRECT EMPLOYMENT | ||
| HOLIDAY | VFR | BUSINESS | ||
| London | 7 575,9 | 3 556,0 | 3 092,2 | 471 928 |
| North East | 115,3 | 175,1 | 115,3 | ... |
| North West | 624,0 | 762,6 | 531,5 | 170 113 |
| Yorkshire | 273,0 | 480,5 | 273,0 | 119 639 |
| West Midlands | 312,6 | 562,7 | 609,6 | 107 230 |
| East Midlands | 166,0 | 405,7 | 295,0 | 76 496 |
| East of England | 467,0 | 856,2 | 447,6 | 120 343 |
| South West | 766,5 | 806,8 | 302,6 | 179 450 |
| South East | 1 335,5 | 1 594,0 | 1 033,9 | 226 003 |
| Scotland | 1 157,0 | 600,8 | 378,3 | 172 282 |
| Wales | 324,5 | 324,5 | 87,6 | ... |
| TOTAL | 13 117,3 | 10 124,8 | 7 146,6 | ... |
[Adapted from visitbritain.org/research]
Use the information above to answer the questions that follow.
4.2.1 Calculate the difference between the number of holiday visitors to the North West and the number to the West Midlands. (3)
4.2.2 Determine (as a percentage) the probability of randomly selecting a business visitor to the Midlands from the total business visitors. (4)
4.2.3 A visitor stated that there are more than 3 times more holiday visitors than business visitors to Scotland. Verify, with a calculation, whether this statement is valid. (3)
4.2.4 Calculate the interquartile range for VFR visitors. (5)
4.2.5 Give ONE other reason, besides employment opportunities, why tourism is important to a country. (2)
4.2.6 The mean direct employment in the United Kingdom is 162 666,5455. The North East employs 30 440 fewer people than Wales. Calculate the direct employment for the North East. (5) [35]
TOTAL: 150
ANSWER SHEET QUESTION 2.1.5
CENTRE NUMBER
EXAMINATION NUMBER
Percentage imports and average growth of personal care and cosmetic products in Australia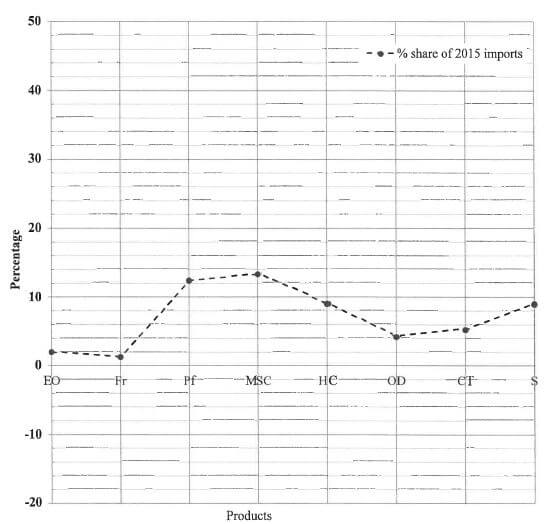
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of FIVE questions. Answer ALL the questions.
- 2.1 Use the ANNEXURES in the ADDENDUM to answer the following questions:
- ANNEXURE A for QUESTION 2.1
- ANNEXURE B for QUESTION 3.1
- ANNEXURE C for QUESTION 4
2.2 Answer QUESTION 5.2.7 on the attached ANSWER SHEET.
2.3 Write your centre number and examination number in the spaces on the ANSWER SHEET. Hand in the ANSWER SHEET with your ANSWER BOOK.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- You may use an approved calculator (non-programmable and non-graphical), unless stated otherwise.
- Show ALL calculations clearly.
- Round off ALL final answers appropriately according to the given context, unless stated otherwise.
- Indicate units of measurement, where applicable.
- Maps and diagrams are NOT necessarily drawn to scale, unless stated otherwise.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1 Happy Life Superstore advertised the specials below for the annual Black Friday in 2017.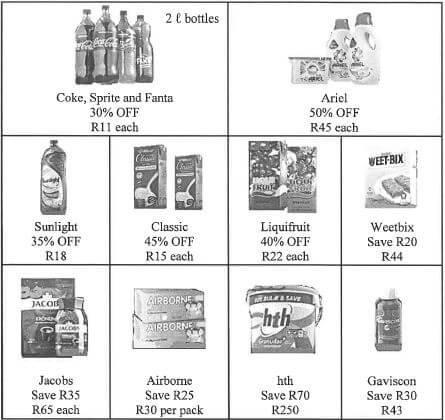
NOTE:
- 1 L =1000ML
- ALL amounts given INCLUDE the discount
Study the advertisement above to answer the questions that follow.
1.1.1 Write down the number of day(s) on which these prices are valid. (2)
1.1.2 Calculate the original price of hth before the saving. (2)
1.1.3 Write down the name of the product which is now half price. (2)
1.1.4 Convert 750 mt to litres. (2)
1.1.5 Calculate the total price of ONE 2 L-bottle of Coca Cola and TWO 2 L-bottles of Fanta. (2)
1.1.6 Arrange ALL the sale prices in ascending order. (2)
1.2 The picture below is a scaled drawing of a T-shirt for Grade 12 learners.
Scale = 1 : 25
1.2.1 Calculate the number of letters needed to print the logo on the front of the T-shirt. (2)
1.2.2 Write down the temperature displayed on the thermometer in 'C. (2)
1.2.3 Explain the meaning of the scale in the drawing above. (2)
1.2.4 Measure the length of the back of the T-shirt in mm, as indicated in the drawing. (2)
1.3 The Two Oceans Marathon and the Comrades Marathon are two of the most popular ultramarathons in the world.
TABLE 1 below shows the dates, distances and entry fees of these marathons.
TABLE 1: TWO OCEANS MARATHON VS COMRADES MARATHON
| TWO OCEANS | COMRADES | |
| Date (2017) | 15 April 2017 | 4 June 2017 |
| Distance | 56 km | 89 km |
| Entry fee | R520,00 | R460,00 |
[Adapted from www.capetownmagazine.com and www.news.comrades.com]
Use TABLE 1 above to answer the questions that follow.
1.3.1 Which race took place first? (2)
1.3.2 Which one of the two races had the longest distance? (2)
1.3.3 Determine the difference between the entrance fee of the Two Oceans Marathon and the entrance fee of the Comrades Marathon. (2)
1.4
The Comrades Marathon Association (CMA) has issued its medical statistics for the
|
[Adapted from http://www.runnersworld.co.za]
Use TABLE 2 above to answer the questions that follow.
1.4.1 Write down the maximum time given to the athletes to complete the Comrades Marathon. (2)
1.4.2 State if the medical statistics data is discrete or continuous. (2)
1.4.3 Write down the ratio of athletes starting the race to the athletes finishing the race. (2) [32]
QUESTION 2
2.1 ANNEXURE A shows the student fees statement for Tamryn Abrahams, a second-year Architecture student at the University of Cape Town (UCT).
Use ANNEXURE A to answer the questions that follow.
2.1.1 Explain the meaning of the term interest with reference to the student fees statement. (2)
2.1.2 Write down the balance (excluding interest) that was brought forward on the last day of the previous year. (2)
2.1.3 Calculate the monthly interest rate that was used on the overdue fees for the previous year. (3)
2.1.4 Write down the code and the name of the module/course that is the most expensive. (2)
2.1.5 Show how the amount of R6 317,70 was calculated. (2)
2.1.6 Calculate the total amount debited to this account for the courses studied in the 2017 academic year including interest on overdue fees in 2017. (3)
2.1.7 State the payment method used to transfer money into this account. (2)
2.1.8 A family friend paid the balance of R40 386,60 on condition that the amount could be paid back in equal monthly instalments, interest free. Show how the monthly instalment of R8 077,32 was calculated if the first payment was due on 1 November 2017 and the last payment was due on 1 March 2018. (2)
2.2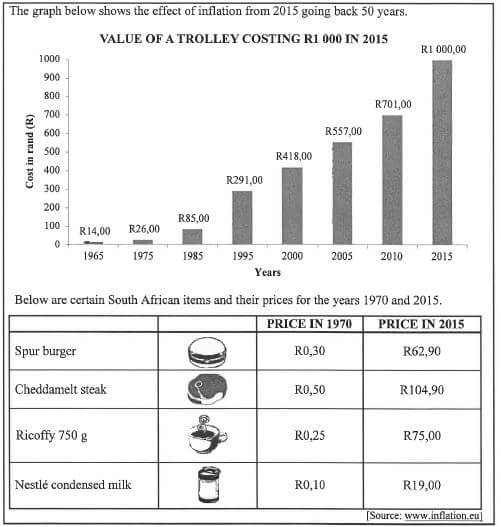
Use the information above to answer the questions that follow.
2.2.1 Explain the term inflation within the given context. (2)
2.2.2 Write down the price of a Spur burger in 1970. (2)
2.2.3 Calculate by how much the cost, in rand, of a trolley had increased from 2000 to 2005. (3)
2.2.4 Calculate the percentage increase of Ricoffy from 1970 to 2015. You may use the following formula:
- Percentage increase = new amount - original amount x 100 % (3)
original amount
2.2.5 A cheddamelt steak was sold for R104,90 at a percentage profit of 17,5%. Determine the cost price. (2)
2.3 TABLE 3 below shows the national budget and education budget of South Africa for 2017/18.
TABLE 3: NATIONAL BUDGET AND EDUCATION BUDGET OF SOUTH AFRICA FOR 2017/2018
| NATIONAL BUDGET OF SOUTH AFRICA (IN RAND) | EDUCATION BUDGET OF SOUTH AFRICA (IN RAND | ||
Economic affairs and agriculture | 241,6 billion | Basic education | 216,7 billion |
Defence and public safety | 198,7 billion | University subsidies | 31,6 billion |
Health | 187,5 billion | Education administration | 15,8 billion |
General admin | 70,7 billion | Skills development levy institutions | 21,1 billion |
Local development and infrastructure | 195,8 billion | National student financial aid scheme (NSFAS) | 15,3 billion |
Debt service costs | 162,4 billion | Technical and vocational education and training | 7,5 billion |
Socialprotection | 180,0 billion | Other | 12,5 billion |
| Education | 320,5 billion | ||
[Adapted from www.graphics24.com]
Use TABLE 3 above to answer the questions that follow.
2.3.1 Which of the amounts below represents the economic affairs and agriculture budgets?
- 24 160 000
- 241 600 000 000
- 241 600 000
- 24 160 000 000 000 (2)
2.3.2 Explain the term budget within the context above. (2)
2.3.3 Write down the item which receives the third most money from the education budget. (2)
2.3.4 Calculate the percentage of the total education budget that is allocated to the NSFAS. (3)
2.3.5 University subsidies comprise about 9,86% of the total education budget. Estimate the combined budget, as a percentage, for education administration and the NSFAS. (2) [41]
QUESTION 3
3.1 Liam and Amy are planning their wedding. Amy wants a four-layer red velvet wedding cake. She must still decide between a cylindrical or rectangular cake as shown on ANNEXURE B.
Use ANNEXURE B to answer the questions that follow.
3.1.1 Determine the total height of the cylindrical cake in millimetres.
3.1.2 The base (bottom) layer of the cylindrical cake has a radius of 14 cm.
- Determine the diameter of the base layer in cm.
- Calculate the volume (in cm3) of the base layer.
You may use the following formula:
- Volume of a cylinder = π x (radius)2 × height, and using π = 3,142 (3)
3.1.3 Define the term perimeter. (2)
3.1.4 Calculate the area (in cm2) of the base of the pan needed to bake the top layer of the rectangular cake.
You may use the following formula:
- Area = length x width (2)
3.2 Aunt Abby will bake the wedding cake. She will be using a recipe from a recipe book published in England.
NOTE:
- 1 kg = 2,25 pounds
- 1 ml flour = 0,7 g flour
3.2.1 Aunt Abby needs 3 and a half pounds of butter. Determine the mass of butter, in kilogram. (2)
3.2.2 Aunt Abby only has a kitchen scale available. If aunt Abby needs 625 ml, of flour, determine the mass of the flour in grams. (2)
3.2.3 The cake must be baked at 356 °F. Determine to what degree Celsius the oven should be turned. You may use the following formula:
- ºC = (ºF - 32º) ÷ 1,8 (2) [18]
QUESTION 4
4.1 A parkrun is a weekly 5 km run. A group of runners drove from Upington to Springbok to take part in the weekly parkrun in Springbok.
ANNEXURE C shows a route map from Upington to Springbok.
Use ANNEXURE C to answer the questions that follow.
4.1.1 Give the general direction from Upington to Springbok. (2)
4.1.2 Write down the name of the national park close to Kamieskroon. (2)
4.1.3 Name TWO towns the runners will pass through on their way to Springbok, following the N14. (3)
4.1.4 Identify the type of scale used on the map. (2)
4.1.5 Use the given scale to determine the actual distance (to the nearest km) between Upington and Springbok. (4)
4.2
| On arrival in Springbok the runners must first pick up Joe, a fellow runner, before heading to the parkrun (B). ANNEXURE C shows a street map indicating the route from entering Springbok (A) to the parkrun (B). |
Use ANNEXURE C to answer the questions that follow.
4.2.1 Name the road by which they will enter Springbok. (2)
4.2.2 Joe gives them the following directions to his home:
- Enter Springbok from Upington.
- Turn right into Uitspan Street.
- Turn left into Lukhof Street.
- Turn left into the first street.
Use the directions above to determine in which street Joe lives. (2)
4.2.3 Name of the lodge near the parkrun. (2)
4.2.4 The distance from Joe's house to the parkrun is 2,34 km. They travel at an average speed of 40 km/h. Determine how long it will take them (in minutes) to get from Joe's house to the parkrun.
You may use the following formula:
- Time = distance (3)
speed
4.2.5 29 of the 42 athletes who participated in the parkrun were female. Determine the probability of randomly selecting a male athlete from this group. (2) [24]
QUESTION 5
5.1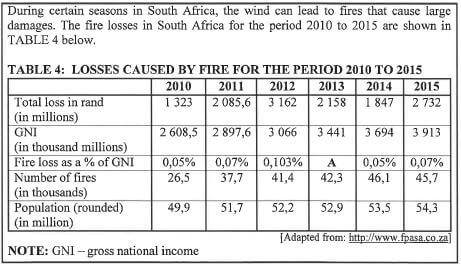
[Adapted from: http://www.fpasa.co.za]
Study TABLE 4 above to answer the questions that follow.
5.1.1 Write down the total loss, in rand, caused by fire during 2011. (2)
5.1.2 Calculate the mean total loss, in rand, caused by fires for the period 2010 to 2015. (3)
5.1.3 Identify the maximum number of fires for the period 2010 to 2015. (2)
5.1.4 Calculate the value of A, the fire loss as a percentage of the GNI for 2013. Round your answer to TWO decimal places. (4)
5.2 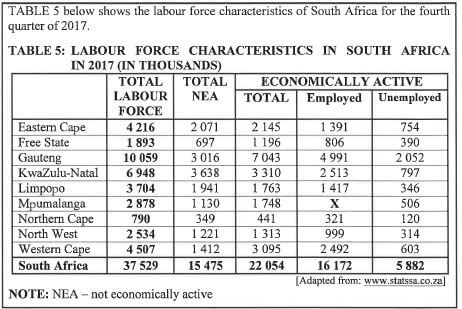
[Adapted from: www.statssa.co.za]
Use TABLE 5 above to answer the questions that follow.
5.2.1 Explain the meaning of the term unemployed within the context of the table above. (2)
5.2.2 Determine the value of X, the number of people employed in Mpumalanga. (2)
5.2.3 Name ONE data collection instrument that could be used to collect the data above. (2)
5.2.4 Calculate the percentage of people in the Western Cape who are NOT economically active (NEA). (3)
5.2.5 Write down the ratio of employed people to unemployed people in South Africa in the form ... : 1. (2)
5.2.6 Determine the probability (as a decimal) of randomly selecting a person in the Free State who is NOT economically active (NEA). (3)
5.2.7 The graph on the ANSWER SHEET represents the number of economically active people, as well as those who are not economically active (NEA) in South Africa. The bars for ALL economically active persons and only the bar for the people in the Eastern Cape who are NOT economically active (NEA) are drawn.
Use the ANSWER SHEET to draw the graphs for the rest of the provinces. (6)
5.2.8 Determine the probability, as a simplified fraction, of selecting a province where fewer than 350 000 people are unemployed. (4) [35]
TOTAL: 150
ANSWER SHEET
QUESTION 5.2.7
CENTRE NUMBER:
EXAMINATION NUMBER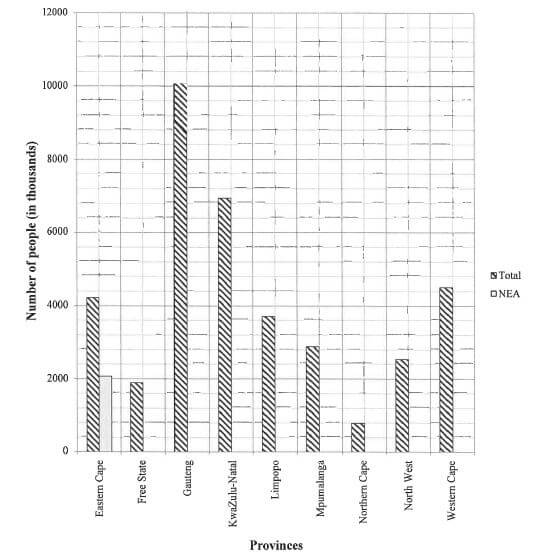
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MARKS: 150
Symbol | Explanation |
M | Method |
MA | Method with accuracy |
CA | Consistent accuracy |
A | Accuracy |
C | Conversion |
S | Simplification |
RT | Reading from a table/graph/document/diagram |
SF | Correct substitution in a formula |
O | Opinion/Explanation |
P | Penalty, e.g. for no units, incorrect rounding off, etc. |
R | Rounding off |
NPR | No penalty for rounding |
AO | Answer only |
MCA | Method with constant accuracy |
NOTE:
- If a candidate answers a question TWICE, only mark the FIRST attempt.
- If a candidate has crossed out (cancelled) an attempt to a question and NOT redone the solution, mark the crossed out (cancelled) version.
- Consistent accuracy (CA) applies in ALL aspects of the marking guidelines; however it stops at the second calculation error.
- If the candidate presents any extra solution when reading from a graph, table, layout plan and map, then penalise for every extra incorrect item presented.
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1 [32 MARKS] ANSWER ONLY FULL MARKS | |||
Q/V | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
1.1.1 | ✔✔A 1 / one | 2A for correct day (2) | M L1 |
1.1.2 | Price before saving ✔M | 1M adding correct values | F L1 |
1.1.3 | Ariel ✔✔A | 2A product (2) | F L1 |
1.1.4 | ✔MA | 1MA for dividing by 1 000 OR 1MA for multiplying by 0,001 | M L1 |
1.1.5 | Price | 1MA multiplying correct values 1CA simplification (only if R7,70× 3) (2) | F L1 |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
1.1.6 | R11; R15; R18; R22; R30; R43; R44; R45; R65; R250✔✔A | 2A arranging in correct order | D L1 |
1.2.1 | English = 35 letters OR 15 letters ✔✔A | 2A correct number WC, FS, NC Provinces accept both (2) | M L1 |
1.2.2 | 44 0C ✔✔A | 2A correct reading Accept 44 - 45 0C (2) | M L1 |
1.2.3 | One unit on the drawing represents twenty five units in reality ✔✔A | 2A correct definition | MP L1 |
1.2.4 | ± 61 mm ✔✔A | 2A correct measurement (Accept 59 mm – 64 mm) \ | M L1 |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
1.3.1 | Two Oceans Marathon ✔✔RT | 2RT reading from table
| M L1 |
1.3.2 | Comrades Marathon ✔✔RT | 2RT reading from table
| M L1 |
1.3.3 | R520,00 – R460,00 ✔RT | 1RT correct values from the table | F L1 |
1.4.1 | 12 Hours ✔✔A OR Half a day ✔✔A | 2A correct time
Max 1 mark (2) | M L1 |
1.4.2 | Discrete ✔✔A | 2A discrete (2) | D L1 |
1.4.3 | ✔RT ✔A | 1RT correct values from table
Accept answer in fraction form NPR (2) | D L1 |
[32] |
QUESTION 2 [41 MARKS] | |||
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
2.1.1 | Interest refers to the amount that will be added to an ✔A account that is not settled yet | 1A amount charged | F L1 |
2.1.2 | R14 819,50 ✔✔RT | 2RT balance (2) | F L1 |
2.1.3 | ✔RT | 1RT correct values | F L2 |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
2.1.4 | ✔RT | 1RT code | F L1 |
2.1.5 | ✔RT ✔M | 1RT correct values | F L1 |
2.1.6 | ✔RT ✔M | AO OR 1RT reading all correct values OR 1RT reading all correct values OR 1RT reading all correct values OR 1RT reading all correct values OR 1RT reading all correct values | F L1 |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
2.1.7 | Direct deposit \ ✔✔RT | 2RT reading correctly | F L1 |
2.1.8 | Monthly instalment | 1A calculating 5 | F L1 |
2.2.1 | Inflation is a measure of rate at which the cost of goods is changing over a period of time and is usually ✔A expressed as a percentage ✔A | 1A percentage increase | F L1 |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
2.2.2 | R0,30 OR/OF 30c ✔✔RT | 2RT correct value | F L1 |
2.2.3 | ✔M R557,00 – R418,00 ✔RG | AO | F L1 |
2.2.4 | Percentage change | AO | F L2 |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
2.2.5 | Cost price | AO | F L2 |
2.3.1 | B OR/OF R241 600 000 000 ✔✔A | 2A correct value (2) | F L1 |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
2.3.2 | Budget is the proposed way in which money will be spent on different items ✔✔A | 2A definition (2) | F L1 |
2.3.3 | Skills development levy institutions s✔✔RT | 2RT correct sector (2) | F L1 |
2.3.4 | Percentage of the total education budget | 1RG/RT correct values | F L2 |
Q | Solution | Explanation/ | T&L |
2.3.5 | Education Administration plus NSFAS amount to 31,1 billion rand | AO | F L2 |
[41] |
QUESTION 3 [18 MARKS] | |||
Q/V | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
3.1.1 | 15 cm + 17 cm + 19 cm + 21 cm ✔A | 1A adding of correct values | M L1 |
3.1.2a | Diameter = 2 × radius | AO | M L1 |
3.1.2b | Volume of a cylinder = π × r2 × height | AO | M L2 |
3.1.3 | The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around the edges defining the outline of that shape ✔✔A | 2A explanation (2) | M L1 |
3.1.4 | Area of a rectangle = length × width ✔SF | 1SF correct substitution
| M L2 |
3.2.1 | Amount in kg = 3,5 ÷ 2,25 ✔C | 1C conversion
| M L2 |
Q | Solution/ | Explanation | T&L |
3.2.2 | 1 mℓ flour = 0,7 g flour | 1C conversion | M L2 |
3.2.3 | °C = (°F – 32°) ÷ 1,8 | 1SF correct substitution | M L2 |
[18] |
QUESTION [24 MARKS] | |||
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
4.1.1 | South West OR SW ✔✔A | 2A direction (2) | MPL 2 |
4.1.2 | Namaqua National Park✔✔RM | 2RM national Park (2) | MPL 1 |
4.1.3 | ✔✔RM ✔RM | 2RM first correct town | MPL 1 |
4.1.4 | Ratio scale OR number scale OR numerical scale ✔✔A | 2A ratio / number / numerical | MP L1 |
4.1.5 | Measured distance /Gemete afstand = 135 mm ✔A | 1A measures distance | MPL 3 |
4.2.1 | Voortrekker Road ✔✔RM | 2RM correct road (2) | MPL 1 |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
4.2.2 | Rivier Street ✔✔RM | 2RM correct road (2) | MP L2 |
4.2.3 | Debs-Lodge ✔✔RM | 2RM correct road (2) | MP L2 |
4.2.4 | Time = 2,34 km ✔SF | 1SF calculating time | MP L2 |
4.2.5 | P = 13 ✔A | 1A numerator (independent) | P L2 |
[24] |
QUESTION 5 [35 MARKS] | |||
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
5.1.1 | R2 085 600 000 ✔✔RT | 2RT correct amount | D L1 |
5.1.2 | R1 323+ R2 085,6 +R3 162+R2 158 +R1 847 + R2 732 million ✔RT ✔CA | AO | D L2 |
5.1.3 | ✔A ✔A | 1A correct value | D L1 |
5.1.4 | ✔RT | AO | D L2 |
5.2.1 | A person who is able and willing to work, but cannot find work ✔✔A | 2A explanation | D L1 |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
People who are without work ✔✔A | 2A explanation (2) | ||
5.2.2 | X = 1 748 – 506 ✔M | 1M subtracting correct values | D L1 |
5.2.3 | Questionnaire ✔✔A | 2A correct answer (2) | D L1 |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
5.2.4 | Percentage of people | 1RT using both correct values | D L2 |
5.2.5 | 16 172 000 : 5 882 000 ✔RT | 1RT both correct values
| D L2 |
5.2.6 | ✔RT | AO | P L2 |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
5.2.7 | Do not mark this question. | ||
5.2.8 | 3 ✔✔A | AO | P L3 |
[35] | |||
TOTAL: 150 | |||
Upscaling of Question 5 mark
QUESTION 5 | |
Mark out of 29 | Mark out of 35 |
29 | 35 |
28 | 34 |
27 | 33 |
26 | 31 |
25 | 30 |
24 | 29 |
23 | 28 |
22 | 27 |
21 | 25 |
20 | 24 |
19 | 23 |
18 | 22 |
17 | 21 |
16 | 19 |
15 | 18 |
14 | 17 |
13 | 16 |
12 | 14 |
11 | 13 |
QUESTION 5 | |
Mark out of 29 | Mark out of 35 |
10 | 12 |
9 | 11 |
8 | 10 |
7 | 8 |
6 | 7 |
5 | 6 |
4 | 5 |
3 | 4 |
2 | 2 |
1 | 1 |
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
Symbol/ | Explanation |
M | Method |
MA | Method with accuracy |
CA | Consistent accuracy |
A | Accuracy |
C | Conversion |
S | Simplification |
RT | Reading from a table/graph/document/diagram |
SF | Correct substitution in a formula |
O | Opinion/Explanation |
P | Penalty, e.g. for no units, incorrect rounding off, etc. |
R/RCA | Rounding off /Rounding with CA |
NPR | No penalty for rounding |
AO | Answer only |
MCA | Method with constant accuracy |
NOTE:
- If a candidate answers a question TWICE, only mark the FIRST attempt.
- If a candidate has crossed out (cancelled) an attempt to a question and NOT redone the solution, mark the crossed out (cancelled) version.
- Consistent accuracy (CA) applies in ALL aspects of the marking guidelines; however it stops at the second calculation error.
- If the candidate presents any extra solution when reading from a graph, table, layout plan and map, then penalise for every extra incorrect item presented.
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1 [38 MARKS] | |||
Q/V | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
1.1.1 | Discount percentage | 1RT numerator and denominator | F L2 |
1.1.2 | Sub Total | 1M subtracting discount | F L2 |
1.1.3 | ✔✔ O | 2O reason (2) | F L4 |
Q/V | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
1.1.4 | Interest Year 1 It is not enough / not sufficient | 1MA calculating interest OR 1C conversion to years OR 2M multiply the principal with 106 % | F L3 |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
1.1.5 | ✔O OR The dealer added 1% on the VAT inclusive price of ✔ O R182 500 / Calculating VAT on VAT OR Mistake is calculating the increased 1% on the VAT inculsive amount. ✔ O | 1O reason OR 1O stating the error or the solution OR 1O describing the error | F L4 |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
1.2.1 (a) | Surface area of an open box ✔SF Or = 1,02 × 5,886488 m2 | 1SF Substitution | M L3 |
1.2.1 (b) | Cost = Number of 5 litre × 2 coats × Price per 5 litre ✔ CA OR | CA from 1.2.1(a) OR 1MCA multiply by 2 | F L2 |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
1.2.2 | To protect the cargo bin's surface from scratching/rusting/ being damaged. ✔✔O OR Extend the life span of a bakkie's loading box ✔✔O OR To stop goods from slipping/protection of goods ✔✔O | 2O reason (2) | M L4 |
1.3 | Time:
Total time needed OR Apply 1st coat (20 min) 8:15 - 8:35 ✔M Apply 2nd coat (20 min) 12:35 - 12:55 ✔ MCA | 1C converting OR 1M adding times | M L2 |
[38] |
QUESTION2 [38MARKS] | |||
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
2.1.1 (a) | ✔ MA | 1MA subtracting correct values | D L2 |
2.1.1 (b) | ✔MCA | CA from 2.1.1(a) | D L3 |
2.1.2 | ✔ A | 1A year increased | D L4 |
2.1.3 | ✔A ✔O | 1A product | D L4 |
2.1.4 | ✔O ✔O | 1O No | D L4 |
Q/V | Solution/Oplossing | Explanation/Verduideliking | T&L |
2.1.5 | Percentage imports and average growth of Personal Care and Cosmetics to Australia | D L3 | |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
2.2.1 | Total cost = Basefare+ 10 × cost per mile | 2RT using correct values | F L2 |
2.2.2 | Maximum distance (in miles)/Maksimum afstand(in myl) | 1RT reading correct values from table | F L3 |
2.2.3 | 1 hour 9 minutes = 69 minutes ✔ C OR Difference = Post trip cost - Upfront cost | 1 C converting to minutes OR 1C time to minutes | F L4 |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
2.2.4 | To cover cost for idle/wasted time when a vehicle could have been used to assist someone when you cancel the booking. ✔✔O | 2O reasoning (2) | F L4 |
[38] |
QUESTION 3 [39MARKS] | |||
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
3.1.1 | P(Coke & water) = [4/9] ✔A | 1A numerator | P L2 |
3.1.2 | South East OR East of South OR SE. ✔✔A | 2A direction (2 | MP L2 |
3.1.3 (a) | ✔A | 1A for height 1 400 m | MP L4 |
3.1.3 (b) | Lowest point : highest point | 2RT correct values | MP L2 |
3.1.4 | To take struggling runners out of the race because they are not coping. ✔✔O | 2O understanding/reason (2) | MP L4 |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
3.1.5 | The average speed required to beat the cut-off 2: Increased speed for full marathon = (3,3 + 2,7) km/h = 6km/h ✔MA ✔M ✔CA | 1RT correct values (dist. & time) OR 1M calculating speed / change the subject OR 1M calculating speed / change the subject (6) | MP L4 |
3.2.1 | 20 ℓ = 20 × 1 000 cm3 ✔ C | 1C conversion | M L3 |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
3.2.2 (a) | Area of base of 1 bucket = 3,142 × (15,6 cm)2 | 1A radius | M L3 |
3.2.2 (b) | ✔A | 1A 120 cm | M L4 |
3.2.3 | Length occupied by 4 buckets OR Length occupied by 4 buckets | 1MA multiplying OR 1MA multiplying | MP L3 |
[39] |
QUESTION 4 [35 MARKS] | |||
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
4.1.1 | Total for these capsules OR Without discount for 5 OR Cost of Capsule 24 + Cost of Capsule 30 - Discount for 5 Adults | 3MA multiply tickets by price OR 3MA multiply tickets by price OR 2MA multiply tickets by price | F L4 |
Q/V | Solution/Oplossing | Explanation/Verduideliking | T&L |
OR | OR 1C conversion | ||
4.1.2 (a) | Circumference of the wheel | 1SF correct values | M L2 |
4.1.2 (b) | Distance = 1237,948 feet ✔ MA OR Circumference in metre | CA from 4.1.2(a) OR 1C conversion | M L2 |
4.2.1 | ✔ M ✔ RT | 1RT correct values | D L2 |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
4.2.2 | ✔RT | 1RT numerator & denominator | P L3 |
4.2.3 | Ratio =1 157,0 ✔RT OR Number of business visitors = 378,3 thousand OR | 1RT values OR 1RT values OR 1RT values | D L4 |
4.2.4 | 175,1 324,8 405,7 480,5 562,7 600,8 ✔MA | 1MA order, ascending or descending | D L3 |
Q | Solution | Explanation | T&L |
4.2.5 | Tourism boosts the economy (selling and buying) of the country. ✔✔O | 2O reason financial | D L4 |
4.2.6 | ✔M OR | 1M multiplying with 11 1R rounding 1A known total 1MA two unknowns 1CA simplification OR/OF 1M concept of mean 1MA two unknowns 1S simplification 1M dividing by 2 1R rounding (5) | D L4 |
[35] | |||
TOTAL:150 | |||
Notes to the Marking Guideline Mathematical Literacy P2 November 2018
Note: In any verification/opinion question, some form of calculation must be shown in order to give a mark for conclusion.
1.1.1 | If the values are swopped, give only 1 mark |
1.1.2 | If the candidate starts with R153 947,72 and not show how it was calculated, Max 2 marks |
1.1.5 | Only calculation done and no explanation, Max 3 marks |
1.2.1 (a) | Early rounding leading to a surface area of 6 and the litres required 24, Max 6 marks |
1.2.1 (a) | Changing the formula by replacing a + with a ×, max 6 |
1.3 | 14:35 is worth 3 marks showing calculations; 18:55 is worth 3 marks with calculations. No calculations shown for these answers, 0 marks. |
2.1.1 (b) | Omitting the value of A, max 2 marks provided it is arranged. |
2.1.2 | "constantly increasing" is worth 1 mark. |
2.1.3 | "Both Pf and Fr fluctuate", max 3 marks. |
2.1.5 | One or two points plotted wrong, max 5 marks. Three or four plotted wrong, max 4 marks etc. |
2.2.1 | Adding the costs on the table is a break-down,0 marks. |
2.2.2 | Wrong formula,0 marks. Two wrong values,0 marks. |
2.2.3 | Converting mark must be given if it is substituted without showing the time conversion. |
2.2.3 | After calculating both Post and Upfront costs the difference need not be shown, then the conclusion carries 2 marks. |
3.1.1 | Written as 4:9 or 4 out of 9, give 2 marks, |
3.1.3 (b) | If ratio values are swopped, max 2 marks. |
3.1.5 | If they use 42km and 7 hours or 25,5 km and 4h15min, max 4 marks. |
3.2.1 | If both thicknesses not subtracted, H = 26,156 cm, max 6 marks |
3.2.2(a) | Max of 4 marks if only one bucket's area is subtracted from pallet's area. |
3.2.2(b) | No unit was specified, answer can be in mm or cm, thus 264mm is accepted. |
4.1.1 | Calculating discount on senior citizen, max 7 marks.
|
4.2.1 | If the values are swopped and the answer is negative, max 2 marks |
4.2.2 | With only 1 value in the numerator, max 2 marks. |
4.2.4 |
|
The following tolerance range was agreed upon during marking guideline discussions: Questions 1.1.4 , 1.2.1 , 3.2.1 , 4.1.1 (1 mark each)
RELIGION STUDIES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
RELIGION STUDIES
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SECTION A and SECTION B.
- SECTION A: COMPULSORY
SECTION B: Answer any TWO questions in this section. - Read ALL the questions carefully.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- The length of your answers must be in accordance with the marks allocated to each question.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 The Tao Te Ching was written by …
- Chuang Tzu.
- Yang.
- Lao Tzu.
- Confucius. (1)
1.1.2 In the African Traditional Religion this person may throw bones in the performance of certain rituals:
- Induna
- Chief
- Sangoma/Isangoma
- Intlabi (1)
1.1.3 The oldest branch of Buddhism is …
- Theravada Buddhism.
- Zen Buddhism.
- Mahayana Buddhism.
- Tibetan Buddhism. (1)
1.1.4 The great Hindu sage, Krishna Dwipayana, compiled these sacred books:
- The Kitáb-i-Aqdas and the Mahabharata
- Ecclesiastes and the Apocalypse
- The Pali Canon and the Tripitaka
- The Rig-Veda and the Samaveda (1)
1.1.5 Holding on to traditional, conventional values:
- Conservatism
- Secularism
- Confucianism
- Heresy (1)
1.1.6 The Tenach in Judaism corresponds with this part of the Christian Bible:
- The New Testament
- The Pentateuch
- The Acts of the Apostles
- The Old Testament (1)
1.1.7 A spiritual exercise to attain moksha, which includes breath control and specific body postures:
- Mysticism
- Meditation
- Mantra
- Yoga (1)
1.1.8 Every person in the universe controls his/her own destiny and is not controlled by any other person or any superior being, like a god. This is a teaching of …
- the African Traditional Religion.
- Hinduism.
- Buddhism.
- the Bahá'i faith. (1)
1.1.9 A declaration of the Parliament of the World's Religions adopted in 1993:
- The Charter for Compassion
- Towards a Global Ethic
- Millennium Development Goals
- The Freedom Charter (1)
1.1.10 Two leaders of the Bahá'i faith were …
- Abdu'l-Baha and Bahá'u'lláh.
- Abdu'l-Baha and Abu Bakr.
- Bahá'u'lláh and Hermann Zimmer.
- Bahá'u'lláh and Maimonides. (1)
1.2 Choose the word in each list below that does NOT match the rest. Write down the word next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK and give a reason why it does NOT fit.
EXAMPLE: Banana; Apple; Potato; Grape
ANSWER: 1.2.6 Potato. The others are all fruit.
1.2.1 Roman Catholic; Baptist; Presbyterian; Methodist (2)
1.2.2 Fatwa; Shahada; Ilima; Wudu (2)
1.2.3 Psalms; Myths; Parables; Legends (2)
1.2.4 Copernicus; Darwin; Galileo; Kepler (2)
1.2.5 Imam; Dominee; Rabbi; Martyr (2)
1.3 Choose an item from COLUMN B that matches the description in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–H) next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK. Do NOT use any letter more than ONCE.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.3.1 On this mountain the Ten Commandments were given to Moses |
(6 x 1) (6) |
1.4 Indicate whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Write 'true' or 'false' next to the question numbers (1.4.1 to 1.4.6) in the ANSWER BOOK. Correct the statement if it is FALSE.
1.4.1 Martin Luther King started the Reformation. (2)
1.4.2 The Archbishop of Canterbury is the hereditary head of the Anglican Church. (2)
1.4.3 Mixing elements of one religion with elements of another to form a new religion, is called fundamentalism. (2)
1.4.4 The Bahá'i faith is a clan-based religion. (2)
1.4.5 Conservative Judaism is the oldest subdivision of Judaism. (2)
1.4.6 Compassion is a religious observance intended to remind of a sacred occasion. (2)
1.5 Complete the following sentences by filling in the missing word. Write only the word next to the question numbers (1.5.1 to 1.5.6) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.5.1 The Crusades of the Middle Ages were religious wars fought between the Muslims and the … (2)
1.5.2 The followers of Hinduism call their divinity … (2)
1.5.3 In the 4th century, Christianity became the official religion of the Roman Empire under Emperor … (2)
1.5.4 A statement about how something is observed to be in a religion, is called a descriptive statement, but a statement about how something ought to be, is called a … statement. (2)
1.5.5 According to Taoism, the 'ten thousand things' are produced by the Three and the Three are produced by the Two. The Two are the … and … (2)
1.5.6 The primary source of the Sharia is the holy scripture called the … (2)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
Answer any TWO questions in this section.
QUESTION 2
2.1 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
PARLIAMENT OF THE WORLD'S RELIGIONS The first session Parliament of the World's Religions was held in Chicago in 1893 with the aim of creating a global dialogue of faiths. Since that event, there have been several further Parliament session. [Source: Shuters Top Class Religion Studies Grade 12] |
2.1.1 What are THREE positive outcomes of the first Parliament of the World's Religions? (6)
2.1.2 In TWO sentences, explain the phrase 'global dialogue of faiths'. (4)
2.1.3 How is the parliament of a country different from the Parliament of the World's Religions? (6)
2.1.4 The Parliament of the World's Religions is but one interreligious organisation. Name ONE other interreligious organisation and discuss its successes and failures. (12)
2.1.5 The Parliament of the World's Religions was held in Cape Town in 1999. Give THREE reasons why Cape Town was chosen. (6)
2.2 Explain the relationship between religious teaching and religious belief. (4)
2.3 State TWO differences between doctrine and dogma. (4)
2.4 Explain the following in the context of religion:
2.4.1 Uniqueness (2)
2.4.2 Unity (2)
2.5 Give ONE example of the following:
2.5.1 Unity within a religion (2)
2.5.2 Unity between different religions (2) [50]
QUESTION 3
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
RELIGION AND MEDIA In several studies of religious coverage in the media the main conclusions were the following:
[Adapted from Religion Studies Grade 12, Steyn et al.] |
3.1 What do you understand by the word media? Include TWO different kinds of media in your answer. (6)
3.2 Discuss conclusion (a) in the extract above, and indicate whether it is beneficial to religion. (6)
3.3 Refer to conclusion (b) in the extract above and answer the following questions:
3.3.1 Explain, in your own words, what is meant by orthodox faiths and minority religions in this context. (4)
3.3.2 Suggest TWO reasons why 'the tone is mostly hostile' towards orthodox faiths, but 'favourable' towards minority religions. (4)
3.4 Refer to conclusion (f) in the extract above. Discuss ONE example of this you have noticed in the media. (10)
3.5 With regard to religious coverage in the media, explain what is meant by EACH of the following and give a suitable example in EACH case:
3.5.1 Stereotyping (4)
3.5.2 Bias (4)
3.5.3 Impartiality (4)
3.5.4 Sensationalism (4)
3.5.5 Factual account (4) [50]
QUESTION 4
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
HUMAN RIGHTS In 1948 the United Nations' Universal Declaration of Human Rights was produced and signed by governments all over the world. In this document human rights are based on the inherent dignity of human beings. [Source: Religion Studies Grade 12, Steyn et al.] |
4.1 Religious freedom is a human right. Name any TWO other human rights and discuss the responsibilities associated with EACH of them. (8)
4.2 What does the South African Constitution say about religious freedom? (8)
4.3 How does South Africa demonstrate religious freedom? (10)
4.4 Name ONE country in the world where religious freedom has been violated. Explain the nature of the violation. (8)
4.5 With reference to ANY of the religions you have studied, state FOUR teachings that show support for EACH of the following:
4.5.1 Human rights (8)
4.5.2 Religious freedom (8) [50]
QUESTION 5
5.1 Explain EACH of the following and name ONE religion with which it is associated:
5.1.1 Monotheism (4)
5.1.2 Sannyasin (4)
5.1.3 Ubuntu (4)
5.1.4 Dharma (4)
5.2 Identify ONE common feature of EACH of the following groups:
5.2.1 Christianity, Islam and Judaism (2)
5.2.2 Hinduism and Buddhism (2)
5.2.3 African Traditional Religion and the African Initiated Churches (2)
5.3 All Muslims share a common set of beliefs (imaan). List SIX of these beliefs. (12)
5.4 Compare the concepts of religion and ideology. (4)
5.5 Choose ONE religion and discuss THREE of its unique features. (12) [50]
TOTAL SECTION B: 100
GRAND TOTAL: 150
RELIGION STUDIES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
RELIGION STUDIES
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of FIVE questions.
- Answer any THREE questions.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Read ALL the questions carefully.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- The length of your answers must be in accordance with the marks allocated to each question.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
EUTHANASIA Euthanasia is normally thought of as providing a gentle and easy death to someone suffering from a painful, terminal disease, which results in a poor quality of life. Euthanasia can be done by assisted suicide, voluntary euthanasia or non-voluntary euthanasia. [Source: Religion and Life by V Watton] |
1.1.1 Briefly explain TWO forms of euthanasia. (4)
1.1.2 List THREE advantages and THREE disadvantages of euthanasia. (12)
1.1.3 With reference to the relevant teachings of any ONE religion you have studied, discuss its response to euthanasia. (10)
1.2 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
Not only are religions different from each other, but there are also internal differences within religions themselves. [Source: Focus on Religion Studies, Grade 12] |
Name any TWO branches that exist within ONE religion and discuss their differences in terms of:
1.2.1 Teachings (12)
1.2.2 Practices (12) [50]
QUESTION 2
2.1 Discuss the central teachings of any ONE religion under the following headings:
2.1.1 The nature of the world (10)
2.1.2 Reward and punishment (10)
2.2 Compare the role of sacred texts in Abrahamic and non-Abrahamic religions. (14)
2.3 Name and discuss any FOUR hermeneutical principles. (16) [50]
QUESTION 3
3.1 What is the role of inspiration in the African Traditional Religion? (10)
3.2 Name and discuss the teachings of any ONE secular worldview. (14)
3.3 What influence did secularism have on the current South African Constitution? (10)
3.4 Do you think secularism has a negative impact on the moral values of society? Give reasons for your answer. (16) [50]
QUESTION 4
Read the statement below and answer the questions that follow.
I don't see why my religion and science can't work together positively. |
4.1 Compare the scientific and the religious accounts of how the universe came into being. (10)
4.2 Discuss the scientific explanation of how human beings came into existence. (14)
4.3 Discuss the different responses of the following religions to Darwin's theory evolution:
4.3.1 Hinduism (12)
4.3.2 Christianity (14) [50]
QUESTION 5
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
In many countries around the world today we find people living together who have different beliefs and practices. This can sometimes cause conflict between religious communities, especially if one of them has more power or authority in a society. [Source: Focus on Religion Studies, Grade 12] |
5.1 Identify ONE area of possible religious conflict anywhere in the world. (2)
5.2 Briefly discuss the causes of conflict in the area you identified in QUESTION 5.1. (12)
5.3 Does religion play a major role in the conflict? Give reasons for your answer. (10)
5.4 Describe the current situation in this conflict. (10)
5.5 What practical steps can religious organisations follow to resolve this conflict? (16) [50]
TOTAL: 150
RELIGION STUDIES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
RELIGION STUDIES
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1.1
- Non-voluntary euthanasia means ending someone's life painlessly when they are unable to ask for death, but there is sound medical reason for thinking they would want death.
- Voluntary euthanasia refers to the situation where a person who is terminally ill and dying in pain, asks another person to end his/her life painlessly.
- Assisted suicide refers to providing a terminally ill person with the means to commit suicide. (4)
1.1.2 ADVANTAGES
It may help the following patients:
- People who are terminally ill and for whom there is no relief from excruciating pain. Such a person's suffering will be ended.
- It can also help those who are too weak to ask for voluntary euthanasia.
- It can help those who cannot respond to treatment as a result of organ failure.
In addition:
- It will ease the stress of people who have been bedridden for a very long time.
- The economic benefit is that this may help save the family and the state money, as some people will never recover, based on medical evidence.
- Medicine and medical treatment are very expensive, and the resources can be used for those who have a better chance of recovery.
- The family is relieved from helplessly watching the suffering of their loved one.
DISADVANTAGES
- Conflict often arises due to differing opinions and beliefs of various family members.
- The family of the terminally ill person may choose euthanasia and assisted suicide for economic and inheritance reasons, and benefit from the inheritance.
- Some people may regret their decision at a later date, leading to unresolved grieving and guilt.
- Euthanasia could be used by unscrupulous doctors as an excuse for organ harvesting.
- Euthanasia and assisted suicide may send signals to other family members that choosing death is an acceptable action, and lead to suicides.
- Doctors may refuse to perform euthanasia on the basis of their religious beliefs.
NOTE: Other relevant responses must be credited. (12)
1.1.3 EXAMPLE 1: CHRISTIANITY
- Christianity is against euthanasia because it values the sanctity of life.
- It teaches that life is created by God.
- The sacredness of life is embedded in the Word, so no one can tamper with life in any way.
- It is up to God, not humans, to determine when people would die.
- Euthanasia is to put oneself on par with God. This is condemned in the Bible.
- In the Christian faith the option of euthanasia is regarded as murder.
- 'Why should you die before your time?' (Ecclesiastes 7:17).
- This means euthanasia is against God's will because it causes somebody to die before his/her time.
- 'Your eyes saw my unformed substance; in your book were written, even one of them, the days that were formed for me, when as yet there was none of them'. (Psalm 139:16).
- This means that God alone determines the time of death for every one of us. Therefore euthanasia is against God's plan for men.
- Thou shall not commit murder' (Exodus 20:13). This commandment forbids euthanasia.
EXAMPLE 2: HINDUISM
- In Hinduism, there are differences of opinion, due to different traditions.
- Hindus embrace karma (a belief that every action has a consequence, which may show up only in a later reincarnation). If one practises euthanasia there will be negative consequences for the soul.
- Hindus believe that whatever suffering a person experiences in his/her current life is the result of something one did in a past life.
- If one circumvents karma by taking action to stop suffering, one will pay for it later.
- Some Hindus believe that there are circumstances that justify a hastening of death.
- Some believe that if a person has reached a stage in life in which s/he can no longer worship God, s/he may ask a doctor to hasten the end of his/her life.
- However, most Hindus do not subscribe to the concept of euthanasia.
- In general, Hinduism is against euthanasia because it breaches the teaching of ahimsa (doing no harm).
NOTE: Other relevant responses must be credited.
Credit is given for teachings from only the first religion identified. (10)
1.2
1.2.1 NOTE: A total of FOUR marks may be awarded for naming the two branches in either 1.2.1 or 1.2.2, but not both. The same two branches must be discussed in 1.2.1 and 1.2.2.
EXAMPLE 1: BUDDHISM
The learner may choose any TWO of the following branches:
- Theravada Buddhism
- Theravada Buddhism believes in the doctrine of anatman.
- 'Anatman' means that the ego/self prevents us from becoming enlightened and reaching nirvana.
- Theravada Buddhism teaches that enlightenment comes through an individual's efforts, and not by the intervention of others or any gods.
- Mahayana Buddhism
- This branch believes that there is no such thing as an individual, autonomous self. All beings are connected.
- Followers of Mahayana believe in collective enlightenment.
- Mahayana Buddhism teaches that the motivation for enlightenment is compassion for all living things.
- The followers strive to become bodhisattva, (one who is at the service of the enlightenment of others).
- Tibetan Buddhism
- The followers of Tibetan Buddhism believe in the reincarnation of lineage of certain lamas (teachers), such as the Dalai Lama.
- They believe that Buddha can be shown in human form.
- They believe in a pantheon of Buddhas, bodhisattvas and dharma protectors.
- Zen Buddhism
- They teach that direct communication, and not scriptural study, is the way of experiencing enlightenment.
- They believe that Zen is the way of life and not solely a state of conscience.
- They believe that Buddha can be shown in a human form, such as in the person of Padmasambhava (one who brought Zen Buddhism in Tibet).
NOTE: Other relevant responses must be credited. (12)
1.2.2 EXAMPLE 1: BUDDHISM
Theravada Buddhism
- Monks live in monasteries, they beg for their food and meditate most of the day.
- Theravada monks also assist and co-operate with laity in important life events such as births, weddings and funerals.
- Building stupas (tower- like structures) is a widespread practice.
- Most practices are performed in the home although there is also individual and communal meditation and chanting in temples.
- They leave altar offerings of food, incense, candles and flowers at the temple, in front of the statue of Buddha.
Mahayana Buddhism
- They practise more ritual elements than Theravada Buddhism, such as prostrating themselves.
- Only people who live in monasteries are allowed to practise meditation.
- Lay people are allowed to practise chanting and prayer.
Tibetan Buddhism
- Practices used include meditation, rituals and chanting.
- They use methods like trances to recover hidden ancient scriptures.
- Tibetan Buddhist monks wear orange robes in their temples.
Zen Buddhism
- They practise meditation in order to attain enlightenment.
- They choose Zen teachers to guide students in meditation and performing rituals.
- They practise dharma transmission (passing of Buddha's teachings from the master to the students).
NOTE: Other relevant responses must be credited (12)
1.2.1 EXAMPLE 2: CHRISTIANITY
- Roman Catholic Church
- This branch sees itself as the original church of Christ.
- The Holy Spirit comes from God the Father and the Son.
- Eastern Orthodox Church
- According to the Eastern Orthodox Church, the Holy Spirit comes from God the Father only, and not the Son.
- They believe that they are the rightly guided church.
- They teach that no one has the power to change Christian teachings and traditions.
- They see the Bible as canonical.
- Protestantism
- In Protestantism, the Bible has more authority than the Pope.
- Rituals are less important than belief.
- They believe that faith is the key to salvation.
- Salvation is a gift given freely through the work of Jesus Christ, who died for sinners.
NOTE: Other relevant responses must be credited. (12)
1.2.2 EXAMPLE 2: CHRISTIANITY
The learner may choose any TWO of the following branches: Roman Catholic Church
- They ordain their priests, who practise celibacy.
- They confess their sins to a priest.
- Nuns and monks do not marry.
- There is no dissolution of marriage.
- They practise last rites before the death of a person.
Eastern Orthodox Church
- They express piety by kissing images of Saints, called icons.
- They see the entire Bible as canonical.
- Ordained priests can get married.
Protestantism
- Attendance of Sunday services is important in Protestantism.
- Holy Communion service is also practised in many forms of Protestantism.
- Speaking in tongues in the Pentecostal/Charismatic churches is a characteristic.
- They have revival tent crusades with the gospel,to reach the lost.
- Healing services are also common.
- Charity is seen as an outward sign of inner grace, and not as 'buying one's way to heaven'.
NOTE: Other relevant responses must be credited. (12) [50]
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1 EXAMPLE 1: AFRICAN TRADITIONAL RELIGION
- For the indigenous traditional African, the nature of the world includes all that exists.
- The world is understood more as the cosmos than simply as the planet Earth.
- All that exists is looked upon as a living wholeness manifesting itself in a variety of forms and phases.
- Life is understood as a perpetual exchange of interconnected forces among and between all beings.
- According to this understanding, the cosmos or the universe does not have a centre.
2.1.2 NOTE: If ONLY reward or ONLY punishment is discussed, award a maximum of SIX marks.
EXAMPLE 1: AFRICAN TRADITIONAL RELIGION
- Reward and punishment in ATR occurs in the present life, not after death.
- The living dead/ancestors are believed to be able to punish evildoers and reward those who do good.
- Punishment from the living dead, comes in various forms of affliction.
- The person experiencing these afflictions, is said to have bad blood.
- The remedy for bad blood is an appropriate form of cleansing which is intended to appease the living dead.
- Whenever these rituals are needed, the traditional healer holds the remedy for the cleansing of bad blood.
- Those who lived a good life are rewarded by becoming ancestors.
- Those who venerate the ancestors are rewarded by prosperity and a good life.
2.1.1 EXAMPLE 2: ISLAM
- According to the Qur'an, Allah created the universe in six phases.
- Allah also provides the energy that everything in the universe needs for survival and growth.
- The existence of the universe is not accidental and life is not purposeless, but planned and purposeful.
- The universe, having been created in time, is not eternal but has a fixed time span.
- Since Allah alone is eternal, to believe in the eternity of the universe would mean equating creation to the Creator. This is a major sin (shirk).
- NOTE: Other relevant responses must be credited. (10)
2.1.2 EXAMPLE 2: ISLAM
- Islam teaches that reward and punishment exist in the present world and after death.
- On the Day of Judgment all humanity will be resurrected to be judged by Allah.
- Those who believe in Allah and have fulfilled their obligations to the Creator, as well as to humanity, will be rewarded and admitted to paradise.
- Those who deny the existence of Allah will be punished and consigned to hell.
- Those who believe but have failed to fulfill their obligations, will be either forgiven or punished in accordance with the nature of their wrongdoing.
- The giving of alms to the poor is said to bring a person closer to Allah and will be rewarded with Allah's mercy and kindness.
- NOTE: Other relevant responses must be credited. (10)
2.2 NOTE: If there is no comparison, award a maximum of EIGHT marks.
- In Abrahamic religions sacred texts are central to their practices and beliefs. That is why they are called 'religions of the Book'.
- Abrahamic religions' teachings are fixed in their written sacred scriptures.
- In non-Abrahamic religions, like Hinduism, absolute authority is awarded to the original sound of the spoken word, not to the text.
- Therefore non-Abrahamic religions see their beliefs and teachings as being objects of fluidity/seeking.
- In Abrahamic religions sacred texts evoke a deeper connection with the Divine.
- In non-Abrahamic religions, such as Buddhism, scriptures are not seen as divine dictates.
- The Abrahamic religions are characteristically exclusivist because their religion is fundamentally rooted in their holy scriptures.
- The non-Abrahamic religions are characteristically pluralist, e.g. Hinduism.
- In Abrahamic religions, sacred texts foster communal identity, while in religions like Hinduism, there is a variety of texts and one can follow any text.
- NOTE: Other relevant responses must be credited. (14)
2.3
- Historical context
- This means that the writings must be understood within the context of the time and circumstances in which the text was written.
- Clearest meaning
- The meaning that is clearest to the reader should be considered.
- Plan, purpose and context
- The writing plan or structure of the whole document must be taken into account.
- An extract must be seen as part of the whole.
- E.g. Is the writing in the form of poetry or prose?
- Meaning of words
- The meaning of words often changes over time and context.
- For the correct interpretation the original meaning must be considered.
- Figurative language
- Figurative language is used widely in sacred texts.
- This must be identified as such, so that it is not interpreted literally.
- Figurative language requires the application of all the other hermeneutical principles for correct interpretation.
- Other sacred texts
- One sacred text may be used to interpret other sacred texts from the same religion.
- This is because there is consistency between the teachings of the religion and its sacred texts. (16) [50]
QUESTION 3
3.1
- In ATR, people communicate with their ancestors through inspiration.
- Mediums and diviners specialise in communicating with the ancestors and spirits.
- Mediums often go through a process of death and rebirth during their training. This happens because of inspiration.
- In this process, they believe that personality is terminated and the medium receives a new personality, dedicated to the supernatural forces.
- Such mediums have an intermediary function. African Traditional Religion includes contemporary and divine inspiration. NOTE: Other relevant responses must be credited. (10)
3.2 EXAMPLE 1:
AGNOSTICISM
- Agnosticism comes from the Greek, 'a', which means 'without' and 'gnosis' which means 'knowledge'.
- This term was first used by a philosopher called TH Huxley in 1869.
- Agnostics believe that it is not possible to either prove or disprove the existence of God or a supernatural being.
- This refers to uncertainty about God-knowledge.
- Agnostics are sceptical of religious teachings.
- They reject religious doctrine, especially religions that claim to have spiritual knowledge.
EXAMPLE 2:
ATHEISM
- Atheists reject the belief that divine or supernatural powers exist.
- There are different degrees of atheism.
- Soft or neutral atheists do not actively reject the existence of a supernatural being.
- Strong or positive atheists believe there is evidence to support their atheistic views.
- In some cases soft atheists reject both theism and strong atheism.
- This is because they feel both world views depend on proof to support their claims.
- Atheists often turn to science to explain the nature of the universe, rather than relying on faith. (14)
- NOTE: Other relevant responses must be credited.
3.3
- The Constitution of South Africa is not based on any religious teachings.
- The Constitution of South Africa promotes equal recognition of all religions.
- The Constitution also promotes religious freedom.
- Secularism helped South Africans to design a constitution that promotes religious tolerance.
- Freedom of religions, beliefs and opinion are enshrined in the Constitution.
- In the South African Constitution, morals and ethical values are based on reasoning and not on religious teachings.
- There is no state religion.
- NOTE: Other relevant responses must be credited. (10)
3.4 YES
- Today society relies on the faculty of reason in order to make decisions.
- They ignore the authority of the Supreme Being.
- They rely on reason, evidence and scientific approach in dealing with life.
- They undermine the dictates of sacred texts.
- Religious places of worship are no longer respected.
- The majority of youth do not attend religious celebrations and rituals, because these are not based on human reasoning.
- Secular humanists put more emphasis on liberal views of human rights than traditional religious beliefs.
- As a result there is an increase in social challenges, such as crime and teenage pregnancy, which result from a degeneration of moral values.
NO
- Secularism promoted the development of the Bill of Human Rights that promote moral values.
- Moral values are promoted through the Constitution in secular states.
- There is no need for sacred texts to develop a moral code. The rule of law will enforce moral values.
- Families have the responsibility of developing moral values in their children. This can be done independently of religion.
- Secularism has contributed through secular states to end religious wars, thus restoring human dignity.
- Today people of different faiths are able to coexist and help each other during difficult times because one religion does not dominate another.
- This does not mean that people who hold a secular worldview do not have morals and values.
- Secularism instils a sense of self awakening. Some people do not belong to any religion, but still have a deep concern for their soul or spirit, thus developing high moral values. (16)
- NOTE: Other relevant responses must be credited. A combination of both perspectives may be accepted. [50]
QUESTION 4
4.1 NOTE: If there is no comparison, award a maximum of FOUR marks.
- The Big Bang Theory teaches that there was an enormous explosion from which the different planets were formed.
- This happened about 13,7 billion years ago.
- Small temperature differences in the initial explosion led to varying densities through the universe.
- These eventually formed into clusters of matter and energy.
- The clusters continued to condense in a lumpy way and formed the vast collection of stars called galaxy.
- Some of the lumps in galaxies condensed into a combination of stars and planets.
- Earth was formed about 4,5 billion years ago.
- Traditional religions maintain that the universe was created perfect.
- In Abrahamic religions the Creator is male.
- At first, only the Creator exists. The Creator then makes the universe from nothing.
- Abrahamic religions believe that God/Allah/Yahweh created the universe in six days.
- For Hindus the Creator exists in either an active or passive state.
- The passive state is a state of rest when nothing happens.
- At rest, the universe has no form, is undifferentiated, and 'flat' all over.
- After a long time, the Creator stirs and become active. This is when the creation begins.
- Hinduism upholds both physical and spiritual evolution but science is limited to physical evolution.
- NB: Any relevant response must be awarded (10)
4.2
- The theory proposes that all life evolved from primitive forms and continues to adapt and evolve.
- It asserts that humans have evolved from an ancestor shared with apes.
- The theory of evolution, according to Charles Darwin, consists of the following ideas:
- Species contain a great variety of minor differences.
- In the fight for survival, better adapted variations will be favoured while those that are not fit will struggle to survive.
- This applies to change in humans as well.
- In the fight for survival, humans adapted and gradually change from apes to human beings.
- The process of change and adaptation happened over a very long period of time.
- Science offers no explanation of creation as part of a divine plan. (14)
- NB: Other relevant response must be awarded.
4.3 4.3.1 HINDUISM
- Hindus have no problem with evolution.
- They believe that the universe is based on evolution.
- They believe that they have a more advanced theory of evolution than the scientific one.
- The scientific theory is limited.
- It focuses only on the physical perspective of creation.
- Hindus believe that humans have control over their spiritual and physical evolution.
- Hindus believe that if one lives a good life one will evolve through many rebirths until one is physically and spiritually advanced.
- Ultimately, one will achieve liberation from the physical and be one with God.
- Hindus believe that there is an intelligent designer behind everything like evolution of humanity and of the universe. (12)
4.3.2 CHRISTIANITY
- In contrast, there is no connection between the traditional Christians and the theory of evolution.
- Traditional Christians only accept that God created Adam and Eve as it is narrated in the Book of Genesis.
- They argue that there is no evidence in history of human beings evolving from apes.
- God created perfect human beings and gave them authority to rule and manage the world.
- However there is a connection between the theory of evolution and liberal/progressive Christians.
- They argue that everything in the universe was created by God, and the process of evolution is also part of the Divine Plan. (It is referred as 'intelligent design')
- They say God was responsible for the Big Bang.
- Progressive Christians accept the idea of guided/theistic evolution, and add that the creation myth must be seen as symbolic.
- They admit that there were some stages of creation which involved evolution, as explained by scientists. (14) [50]
QUESTION 5
5.1 EXAMPLE 1: WORLD CONFLICT (2)
- Israel-Palestine Conflict
5.2
- The on-going conflict started with the establishment of Israel in 1948.
- Hard-line Israelis and Zionists claim that, according to their scripture, Palestine rightfully belongs to the Jews.
- This claim is rejected by Palestinians, as well as many Jewish organisations, including some Orthodox Jews.
- The land of Israel is sacred to Jews, Christians and Muslims.
- The Al Aqsa Mosque in Jerusalem is Islam's third holiest site.
- Jerusalem is also sacred to Christians, as it is where Christ was crucified.
- Jews regard Jerusalem as the location of the Temple Mount/Temple of Solomon.
- All these sites existed long before the creation of the state of Israel, and were occupied by various tribes throughout history.
- Jews and Palestinians are fighting for the control over land. (12)
5.3
- Religion does not play a major role in this conflict.
- Religion is used as an excuse for the conflict.
- There is no attempt by any side to convert people to their faith.
- The continuous occupation of Palestinian land by Jewish settlers is a major factor in the conflict.
- The building of illegal settlements on this land is also a major factor.(10)
5.4
- Numerous UN resolutions have been passed condemning this occupation.
- However, Israel continues to defy UN resolutions and is building more settlements on Palestinian land.
- There are sporadic attacks on Palestinians, as well as on Jews.
- The American president, Donald Trump, recently declared that America recognises Jerusalem as the capital city of Israel.
- This has stirred up the conflict between the Israelis and Palestinians.
- Most of the world does not accept Trump's declaration. (10)
5.5 NOTE: A maximum of EIGHT marks may be awarded for social intervention.
- Religious leaders can call an inter-religious summit to discuss the conflict.
- The dialogue should lead to practical steps that can be taken on both sides, regardless of religion, towards alleviating the situation.
- Religious leaders are still respected and can act as mediators between conflicting parties.
- Religious organisations can use their religious conviction about peace in the world and the sacredness of life, to lead and model peaceful behaviour.
- Religious leaders can mediate and hold a dialogue with all parties with influence over the situation in Israel/Palestine. E.g. America, which is not one of the parties in the conflict, but has huge influence over the situation.
- Religious organisations can co-operate to alleviate human suffering such as shortage of food, medical supplies or other necessities.
- Religious organisations have a network of contacts with other parts of the world, and can publicise the situation. (16)
- They can mobilise people to pray for and support the affected people.
5.1 EXAMPLE 2: AFRICA
- Darfur in Sudan (2)
5.2
- Fault lines in Darfur society can be traced back well over 100 years.
- The main divisions in this country are ethnic and cultural.
- Religion does not seem to be the main source of conflict although it is always perceived.
- Two broad groupings can be found in Darfur, namely Arab tribes called Baggara and many African tribes.
- The African groups include the Fur, the Masalit and the Zaghawa.
- Another set of divisions relates to issues of culture.
- Most people in the area are Sunni Muslims.
- There are also Christians and animists.
- For many centuries, nomads and farmers made an effort to coexist, but when food became scarce, competition for scarce resources led to conflict.
- The oil resources of the Heglig fields are also a major factor in the conflict.
- Darfur was also the centre of the slave trade in North East Africa. (12)
5.3
- Religion plays only a minor role in the conflict, and therefore this is not a religious war. No attempt is made by one religion to convert another.
- Muslims also enlisted in the SPLA.
- There was also evidence of infighting in the SPLA soon after it was formed.
- The conflict in Sudan is known as the longest running civil war in history. (Focus p. 94). The imposition of Sharia law (1983) was therefore not the cause of the conflict, but it worsened the fragile situation.
- Civil war had started as far back as 1955.
- There are numerous other divisions (economic, cultural and tribal), which continue even after establishment of South Sudan.
- Even after South Sudan gained independence from Khartoum in 2011, armed conflict still continues in the region. (10)
5.4
- There is still conflict in South Sudan, even after independence which was gained on 9 July 2011.
- The 2013–2015 civil war displaced 2,2 million people to many parts of the world.
- Around 6 million people are currently at risk of going hungry.
- About 70% of schools have been closed due to fighting.
- There is a new element of ethnic hatred and conflict adding to what had been going on before.
- There are disturbing indicators of potential impending genocide inside the country.
- Human rights groups say the evidence of war crimes grows by the day.
- The people in South Sudan are now totally dependent on aid groups. (10)
5.5
- Religious leaders can mediate and have dialogue with all parties.
- Religious leaders are respected and through their religion usually have contacts and connections in many parts of the world.
- They must liaise with political parties to find a solution, as the conflict is not religious.
- They have access to a network of people from other parts of the world that can assist in the resolution of the conflict.
- Most religions teach peace and compassion. Therefore members are willing to contribute materially and financially to the victims of conflict.
- Religious leaders can call an inter-religious summit for dialogue on the conflict.
- Dialogue means to talk and listen with respect so as to try and understand the problem and seek a solution.
- The dialogue should lead to practical steps that can be taken on both sides, regardless of religion, towards alleviating the situation.
- Religious organisations can use their religious conviction about peace in the world and the sacredness of life, to lead and model peaceful behaviour.
- Religious organisations can co-operate to alleviate human sufferings such as shortage of food, medical supplies or other necessities.
- The African Union, the United Nations and many international aid agencies must try to protect and support civilians.
- Organisations like the Islamic Relief Agency and the Catholic Agency for Overseas Development should focus on practical support, such as medical supply, shelter for victims and the supply of food. (16) [50]
TOTAL: 150