Adele
MUSIC PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MUSIC
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MEMORANDUM
Note to the marker: Candidates must be credited for any correct answers not given in the marking guidelines. |
SECTION A: AURAL
QUESTION 1
1.1 Listen to the melodic and rhythmic phrase. Notate the rhythm of the missing notes in bars 2–3 below.
Answer: ![]() (3)
(3)
1½ mark per bar as indicated = 3 marks |
1.2 Which ONE of the notations below best represents the solo voice part? Make a cross (X) in the appropriate block.  (1) [4]
(1) [4]
QUESTION 2
Listen to the extract below and answer the questions that follow. 
2.1 Name the interval formed between the Db note and the missing note in bar 24.
- Answer: Perfect 4th (1)
2.2 Which type of non-chordal note do you hear in bar 54?
- Answer: Anticipation (1)
2.3 Name the cadence at bars 11 to 12.
- Answer: Perfect cadence (1)
2.4 Listen to the music from bars 1 to 6. Some of the notation in bar 4 has been omitted from the score. Fill in the missing pitches and note values that correspond with the music that you hear.
- Answer: See score (2)
Correct pitches and note values = ½ mark each No mark for correct pitch or note value only |
2.5 Name the solo instrument that plays the melody line in this extract.
- Answer: Trumpet (1) [6]
TOTAL SECTION A: 10
SECTION B: RECOGNITION OF MUSIC CONCEPTS
QUESTION 3: GENERAL LISTENING (COMPULSORY)
Listen to the following tracks and answer the questions that follow.
Note to marker: if a candidate selected more items than requested, only the first answers must be marked. |
3.1 With which items in COLUMN A do you associate the music that you hear in Track 7? Make a cross (X) in THREE appropriate blocks.
Answer:
COLUMN A | Track 7 |
Chromatic passage | X |
Adagio | |
Duet | |
Allegretto | X |
String and wind quartet | |
Major key | X |
String quartet | X |
3x1 = 3 marks |
3.2 Which ONE of the following statements is correct? Make a cross (X) in the appropriate block.
Answer:
Statement | |
The extract consists of a motif, an imitation and an imperfect cadence | X |
The extract consists of a motif, inversion and an imperfect cadence | |
The extract consists of a motif, repetition and an imperfect cadence |
1 mark |
3.3 With which items in COLUMN A do you associate the music that you hear in Track 9? Make a cross (X) in THREE appropriate blocks.
Answer:
COLUMN A | Track 9 |
Vocal melody starts with an anacrusis | X |
Triple time | |
Quadruple time | X |
Swing/shuffle rhythm | X |
Guitar introduction | |
12-bar blues | |
Syllabic word setting | X |
3x1 = 3 marks |
3.4 With which items in COLUMN A do you associate the music that you hear in Track 10? Make a cross (X) in THREE appropriate blocks.
Answer:
COLUMN A | Track 10 |
Chordal accompaniment | X |
Allegro | |
Simple quadruple | X |
Compound triple | |
Guitar introduction | X |
Straight rhythm | X |
Alto voice | X |
3x1 = 3 marks |
3.5 Choose any TWO items in COLUMN A and identify what you hear, in COLUMN B.
Answer:
COLUMN A | COLUMN B (IDENTIFY) |
Solo instrument | Pennywhistle |
Prominent compositional technique | Repetition |
Musical genre | Kwela |
Texture | Homophonic |
2x1 = 2 marks |
(12 ÷ 3 =) [4]
Answer QUESTION 4 (WAM) OR QUESTION 5 (JAZZ) OR QUESTION 6 (IAM).
QUESTION 4: WAM
4.1 With which ONE of the following characters in COLUMN A do you associate EACH track? Make a cross (X) in the appropriate block for each track.
Answer:
COLUMN A | Track 12 | Track 13 | Track 14 |
Papageno | X | ||
Tamino | X | ||
Sarastro | X | ||
Monastatos | |||
Pamina |
3x1 = 3 marks |
4.2 Give a suitable Italian term to describe the tempo of the music in this extract.
- Answer: Largo/Larghetto/Adagio (1)
4.3 Name the wind instrument heard at the end of this extract.
- Answer: Flute (1)
4.4 Which item describes the compositional technique used in this extract? Choose from the list below. Make a cross (X) in the appropriate block.
Answer: ![]() (1)
(1)
4.5 What is the title of the movement from which this extract is taken?
- Answer: Awakening of cheerful feelings upon arrival in the countryside (1)
4.6 Which solo wind instrument plays the melody?
- Answer: Clarinet (1)
4.7 Which wind instrument plays an accompaniment to this melody at the start of this extract?
- Answer: Bassoon (1)
4.8 Describe how Beethoven employs the string section in this extract.
Answer:
- Forms part of the accompaniment
- Interjecting/punctuating two chords at the end of each subphrase (cadences)
- The two chords are played accented or > or detached
- Decrescendo/Diminuendo at the end of the track
- Features in the Introduction
- Alternating playing between strings and winds
- Employs homophonic texture
2x1 = 2 marks |
4.9 Choose THREE statements below that best describe the music that you hear. Make a cross (X) in THREE appropriate block.
Answer:
All instruments play in unison | |
Ascending legato passages | X |
Ascending chromatic scale passages | X |
Ascending chromatic sequences in clarinets | |
Long sustained note | X |
Clarinet solo |
3x1 = 3 marks |
4.10 Write down the title of the work from which this extract is taken.
- Answer: Hebrides Overture/Fingal's Cave (3)
(Lonely Island) = ½ mark(1)
4.11 Identify from which part of the work this extract is taken. Choose from the list below and make a cross (X) in the appropriate block.
Answer:
Part of work | Answer |
First subject/theme | |
Second subject/theme | |
End of the development | X |
Beginning of the coda |
1x1 = 1 mark |
(16 ÷ 2=) [8]
TOTAL SECTION B: 12
OR
QUESTION 5: JAZZ
5.1 With which FOUR items in COLUMN A do you associate the music that you hear? Make a cross (X) in FOUR appropriate blocks.
Answer:
COLUMN A | Answers |
Mbaqanga | |
Pentatonic | |
Major | X |
Simple quadruple | X |
12-bar blues | |
Cape Jazz | X |
| X |
Kwela | |
Harmonic chord cycle | X |
4x1 = 4 marks |
5.2 Which item describes the melodic movement of the horn section? Make a cross (X) in the appropriate block.
Answer:
Chromatic passage | |
Group improvisation | |
Ascending sequences | |
Descending sequences | X |
1 mark |
5.3 Apart from the drum kit, name ONE other instrument that forms part of the rhythm section in this extract.
- Answer: Bass guitar/Rhythm guitar/Piano (1)
5.4 With which one of the South African solo artists do you associate this extract? Make a cross (X) in the appropriate block.
Answer: ![]()
5.5 With which THREE items in COLUMN A do you associate the music that you hear? Make a cross (X) in THREE appropriate blocks.
Answer:
COLUMN A | Answers |
Fuses Xhosa songs with blues | |
Abdullah Ibrahim influences | X |
Idiophone | X |
Modal chord progression | X |
Improvisation | |
Ceremonial atmosphere | X |
Answer:
3x1 = 3 marks |
5.6 Describe the role of the piano in this extract.
Answer:
- Provides short introduction
- Plays the ostinato
- Plays short melodic riffs
- Provides rhythmic drive
- Provides an African percussive timbre
- Provides harmonic basis (modal chords)
Any TWO correct answers = 2 marks |
5.7 Name the instrument that plays the accompaniment in the introduction of this extract.
- Answer: (Rhythm) guitar/banjo/double bass (1)
5.8 Describe the role of the backing singers.
Answer:
- provides harmonic support
- Adds tone colour (male voices)
- Thickens texture (new layer of sound)
Any TWO correct answers = 2 marks |
5.9 Name ONE group that you associate with this jazz style.
Answer:
- The Manhattan Brothers
- The Merry Blackbirds
Any ONE correct answer = 1 mark |
OR
(16 ÷ 2=) [8]
TOTAL SECTION B: 12
QUESTION 6: IAM
6.1 With which FOUR items in COLUMN A do you associate the music that you hear? Make a cross (X) in FOUR appropriate blocks.
Answer:
COLUMN A | Answer |
Mbaqanga | |
Modal | X |
Malombo | |
Umrhube | X |
Ululation | X |
Major | |
Aerophone | X |
Concertina | |
Repetition | X |
4x1 = 4 marks |
6.2 Describe the whistling that you hear.
Answer:
- Provides melodic material over marimba accompaniment
- Has an improvisational character
- Glissandi
- There are multiple (3-4) whistles (polyphonic)
- Call and response
Any correct answer = 1 mark |
6.3 Write down a suitable term to describe the rhythmic feature in the accompaniment.
Answer:
- Polyrhythms/Cross rhythms
- Repetitive overlapping rhythmic pattern.
Any correct answer = 1 mark |
6.4 With which THREE items in COLUMN A do you associate the music that you hear? Make a cross (X) in THREE appropriate blocks.
Answer:
COLUMN A | Answer |
Blues | |
Batswana | X |
Idiophone | X |
Malombo drum | |
Chord cycle | X |
Tshikona |
Correct answers = 3 marks |
6.5 Identify the differences between Track 29 and Track 30. Choose only TWO items in column A for your comparison.
Answer:
COLUMN A | Track 29 | Track 30 |
Introduction | Organ/Keyboard prominent | Guitar prominent ` |
Drum kit enters later during the introduction | Drum kit features from the beginning | |
Voice type | Male singers only (solo and backing vocals) | Female singers (SSA) and a solo male singer (baritone/Idoshaba/Umngqokolo) |
Tempo/Beat | Relaxed beat | Energetic driving beat |
(Medium tempo) | (Fast tempo) |
Any TWO correct correlated differences = 2 x 2 = 4 marks No marks awarded if direct comparison is not made |
6.6 Name the style that you associate with both extracts.
- Answer: Mbaqanga (1)
6.7 With which artists/bands do you associate each track?
Answer:
- Track 29: Soul Brothers
- Track 30: Mahlathini and the Mahotella Queens/Cool Crooners
2x1 = 2 marks |
(16 ÷ 2=) [8]
TOTAL SECTION B: 12
SECTION C: FORM
QUESTION 7
Read and study the questions for ONE minute.
Listen to the piece below while you study the score.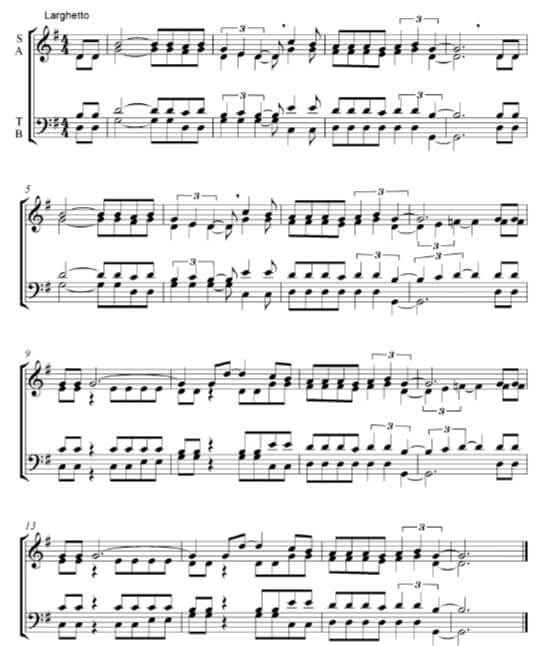
7.1 Name the form type of this piece?
- Answer: AB/Binary (1)
7.2 Motivate your answer to QUESTION 7.1 by giving a schematic layout of the form of this piece. Use the table below.
Answer:
Section | Bar numbers |
A | 1–8 or 04–83 |
B | 84 – 163 |
1 mark for each correct section = 2 marks 1 mark for correct bar numbers of each section = 2 marks |
7.3 Name the texture type of this extract.
- Answer: Homophonic (1)
7.4 What is the function of the F natural in bar 8?
Answer:
- It shows a temporary/short modulation to C Major
- The lowered leading note of G major suggests a secondary dominant, V7/IV
Any correct answer = 1 mark Modulation = ½ mark |
7.5 Which ONE of the following features is used in this piece? Make a cross (X) in the appropriate block.
Answer: ![]() (1) [8]
(1) [8]
TOTAL SECTION C: 8
GRAND TOTAL: 30
MUSIC PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MUSIC
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A: THEORY OF MUSIC (COMPULSORY) (90 minutes)
Answer QUESTION 1
AND QUESTION 2.1 OR 2.2
AND QUESTION 3.1 OR 3.2
AND QUESTION 4.1 OR 4.2.
QUESTION 1 (25 minutes)
Study the extract and answer the questions that follow.
1.1 Name the submediant minor key of this piece.
- Answer: F (minor) (1)
1.2 Name the related dominant major key of this piece:
- Answer: Eb(major) (1)
1.3 Name the intervals at (a) and (b) according to type and distance. Answer:
- Compound Perfect 5th/Perfect 12th
- Minor 3rd (2)
1.4 Transpose the bass part of bar 1 at X a perfect 5th lower. Insert the new key signature.
Answer: 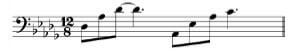 (3)
(3)
Correct key signature = 1 mark |
1.5 Describe the triads at (c) and (d) according to type and position.
Answer:
(c) Minor, First inversion
(d) Minor, Root position(2)
2x½ = 1 mark |
1.6 Halve the note values and rewrite the bass clef part at Y in bar 4. Insert the new time signature.
Answer:  (3)
(3)
Time signature = 1 mark |
1.7 Complete the melody below by writing ascending sequences as indicated.
Answer:  (4)
(4)
Motif A = 2 marks |
1.8 Select the scale/mode on which each of the following TWO extracts is based. Make a cross (X) in the appropriate block.
1.8.1 Answer: Dorian mode (1)
1.8.2 Answer: Whole-tone scale (1)
1.9 Write F# melodic minor scale ascending and descending without key signature in the given clef. Use only semibreves and indicate the semitones.
Answer: ![]() (2) [20]
(2) [20]
Ascending = 1 mark |
QUESTION 2 (25 minutes)
Answer EITHER QUESTION 2.1 OR QUESTION 2.2.
2.1 Complete the opening below to form a twelve-bar melody in ternary form for any single-line melodic instrument of your choice. Name the instrument and supply a suitable tempo indication. Add dynamic and articulation indications where applicable.
Concept answer: Instrument: Saxophone/Clarinet/Trumpet/Violin/Flute/Oboe/Horn, etc. Allegretto 
OR
2.2 Complete the opening below to form a twelve-bar melody in ternary form for any single-line melodic instrument of your choice. Name the instrument and supply a suitable tempo indication. Add dynamic and articulation indications where applicable.
Concept answer: Instrument: Saxophone/Clarinet/Trumpet/Violin/Flute/Oboe/Horn, etc. 
The melody will be marked according to the following criteria: [15]
DESCRIPTION | MARK ALLOCATION | ||
Form and cadential points | 1 mark per phrase x 3 | 3 | |
Correctness | Minus ½ mark per error up to 2 marks | 2 | |
Quality
| 9–10 | Excellent | 10 |
7–8 | Good | ||
4–6 | Average | ||
0–3 | Not acceptable | ||
TOTAL | Markers may use ½ marks | 15 | |
QUESTION 3 (10 minutes) Answer EITHER QUESTION 3.1 OR QUESTION 3.2.
3.1 Study the extract and answer the questions.
Answer: 
3.1.1 Name the new key to which the piece modulates in bars 5–8. Write the answer on the score.
- Answer: See score (1)
3.1.2 Figure the chords at (a)–(e) with Roman numerals on the score, e.g. iii6/iiib
- Answer: See score (5)
1 mark per chord = 5 marks |
3.1.3 Identify the cadence at (f) in bars 12–13 on the score. Indicate the key and figure the chords with Roman numerals.
- Answer: See score (2)
½ mark for key | = 2 marks |
3.1.4 Name the type of non-chordal notes at (i) and (ii).
- Answer (i) Passing note
(ii) Auxiliary note/Neighbouring note(2) [10]
OR
3.2 Study the extract and answer the questions.
Answer: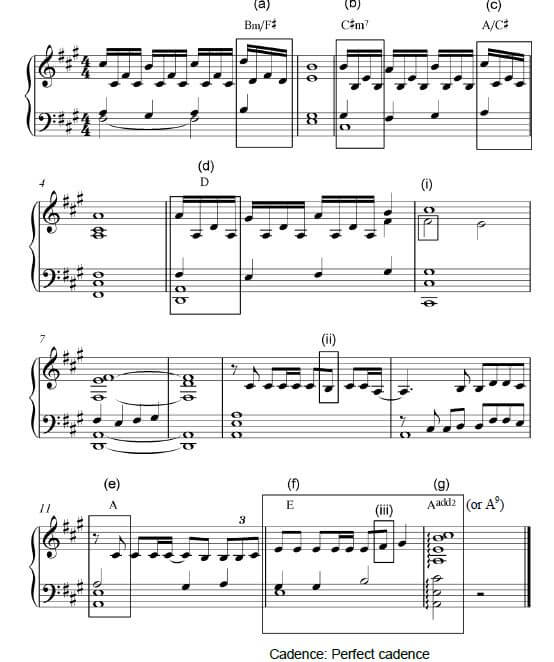 
3.2.1 Identify the chords (a)–(e) and write chord symbols in the spaces provided on the score, e.g. Bb/D.
- Answer: See score (5)
1 mark per chord = 5 marks |
3.2.2 Name the types of non-chordal notes at (i)–(iii).
- Answer: (i) Suspension
(ii) Auxiliary/Neighbouring note
(iii) Passing note(3)
3.2.3 Name the cadence which is formed in bars 12–13 on the score. Indicate the chord symbols at (f) and (g).
- Answer: Perfect cadence, E – Aadd2 (or A9) (2) [10]
Cadence = 1 mark | = 2 marks |
QUESTION 4 (30 minutes)
Answer EITHER QUESTION 4.1 OR QUESTION 4.2.
4.1 Complete the four-part vocal harmonisation below by adding the alto, tenor and bass parts.
Concept answer: 
The harmonisation will be marked according to the following criteria:
DESCRIPTION | MARK ALLOCATION | |
Chord progression | 1 mark between each pair of chords (except between bars 4, 5 and 8) | 12 |
Correctness | Minus ½ mark per error but not more than 1 mark per chord | 14 |
Quality | Excellent = 3½–4 marks | 4 |
Note to marker: | 30 (÷ 2) | |
TOTAL | 15 | |
Candidates must be credited for a different/creative and correct harmonisation not given in the marking guidelines. The figuring serves as a guide for the marker, but no marks are allocated for the symbols as such.
OR
4.2 Complete the piece below by adding suitable harmonic material in the open spaces on the stave. Continue in the style suggested by the given material in bars 1 and 2.
Concept answer: 
The answer will be marked according to the following criteria:
DESCRIPTION | MARK ALLOCATION | |
Chord progression | 1 mark between each pair of chords | 14 |
Correctness | Minus ½ mark per error but not more than 1 mark per chord | 12 |
Quality | Excellent = 3½–4 marks | 4 |
Note to marker: | 30 (÷ 2) | |
TOTAL | 15 | |
Candidates must be credited for a different/creative and correct harmonisation not given in these marking guidelines. The figuring serves as a guide for the marker, but no marks are allocated for the chord symbols as such.
TOTAL SECTION A: 60
SECTIONS B, C, D, E: GENERAL MUSIC KNOWLEDGE (90 minutes)
Answer SECTION B
AND SECTION C (Western Art Music)
OR SECTION D (Jazz)
OR SECTION E (Indigenous African Music).
Note to marker: One mark will be allocated for each correct fact. Candidates must be credited for any correct answer not given in these marking guidelines. Regardless of the fact that this marking guideline is constructed in bullet form, it is expected that the candidate answers the questions in paragraph/essay form where required. |
SECTION B: GENERAL (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 5
5.1
5.1.1 B
5.1.2 C
5.1.3 D
5.1.4 B
5.1.5 D
5.1.6 D
5.1.7 D
5.1.8 B
5.1.9 C
5.1.10 B (10)
5.2
5.2.1 B
5.2.2 A
5.2.3 E
5.2.4 C
5.2.5 D (5)
FIVE correct answers = 5 marks |
5.3 ∙ Song writer/composer
- Performer/singer/band member/session musician
- Sound engineer
- Editor/director
- Recording engineer
- Producer/recording company
- Arranger
- Lyricist (5)
Any FIVE correct answers = 5 marks |
[20]
TOTAL SECTION B: 20
Answer SECTION C (WAM)
OR SECTION D (JAZZ)
OR SECTION E (IAM).
SECTION C: WESTERN ART MUSIC (WAM) QUESTION 6
6.1
- Clarinet
- French Horn
- Trumpet (2)
TWO correct answers = 2 marks |
6.2 Clarinet (1)
6.3
- Two
- Timpani/Kettle drums(1)
6.4 (3)
Codetta | Coda | |
Where in the work | Found at the end of the exposition | Found at the end of the recapitulation |
Key | Ends in a related key | Ends in the tonic key |
Function | Tail section as ending and rounding off the exposition | Tail section to end off the movement |
Length | Usually a short section | Sometimes short, but often an extensive section |
Structural function | Usually in the form of a repeated (extended) cadence (in new key) | New material introduced or previously stated material may be developed with extended cadence at the end |
Any THREE correct correlated differences = 3 marks Candidates may answer in table format |
6.5
6.5.1  [10]
[10]
QUESTION 7
7.1 In Diesen Heil'gen Hallen/Within these Hallowed Halls (1)
7.2
- Sung by Sarastro – a symbol of good
- Bass voice – reinforces stable attitude
- Act 2 – contrasts with the Queen of the Night's vengeful second aria
- Fairly slow tempo: Larghetto – to reinforce 'holiness' of the temple
- Key: E major – to establish a positive, reassuring atmosphere
- Form: 2 verses – simplicity of form reinforces calm, stable mood
- Use of melismas
- Mood: serious, calm and reassuring
- Sarastro sings of love, duty and forgiveness / ideals of brotherhood
- Instrumentation: 2 flutes, 2 bassoons, 2 horns, string section
FOUR correct facts = 4 marks |
QUESTION 8
- Established the layout of the standard Classical orchestra
- Arrangement of the standard Classical orchestra into 4 instrument groups
- Each section of orchestra given a particular role
- Large string section with violins playing the principle melody
- Doubled instruments in woodwinds (excluding clarinet) as a binding/filling role
- Woodwinds as melodic instruments
- Restricted use of brass and percussion (two timpani) for the ff sections
- Basso continuo was omitted
- The bass part is given a stronger forward rhythmic drive
- French Horns act as a harmonic binding agent
- Introduced the four movement symphony
- Performance techniques developed
- Tremolo
- Sudden sfz
- Opening arpeggios
- Crescendos and decrescendos
- Playing techniques: The rocket- and sigh-motives [5]
Any FIVE correct facts |
QUESTION 9
Instrumentation
- Increases number of instruments in orchestra
- Use of timpani more for dramatic effect than for harmonic reinforcement
- Piccolo adds colour to the exhilaration and tension
- Trombones added for intensity and power of sound colour and range Dynamics
- Greater range and extremes of dynamics are used than before (pp – ff)
- ff in tremolos of string passages
- pp string passage at end of the symphony
- Sudden changes in dynamics for dramatic purposes e.g. fortepiano fp
- More use of accents (sf) and climaxes
- Extensive use of crescendi and decrescendi in successive 'waves'
- Extended orchestration to increase dynamic possibilities [5]
Any FIVE facts as long as both dynamics and instrumentation are included = 5 marks |
QUESTION 10
Answer:
Origin
- Composed as a result of a visit to Scotland – the Hebrides islands
- Inspired by a cavern known as Fingal's Cave and the surrounding seascape, even made sketches of the island
- A boat ride to these islands had a huge impact on him
- He wrote letters to his sister describing this emotional experience
- Completed in 1830 (The Lonely Island), revised and renamed in 1833
Any THREE correct facts = 3 marks |
Description of composition
Form
- Concert overture
- An independent single movement work
- Sonata form OR Allegro-Sonata form
- Exposition: B minor - D Major
- Development: D Major
- Recapitulation: starts in B minor; includes new material in bridge; 2nd subject in B Major; extended Coda
- The bridge passages are greatly extended
Only 1 mark for keys |
Instrumentation/Orchestration
- A work for standard Classical orchestra
- Innovative orchestration resulted in new combinations of colour and mood e.g. use of upper pedal points
- No additional instruments as was the case in most other Romantic orchestral works
- Both themes are played by the lower register instruments (cello, bassoon, viola)
- Demands greater technical competence from the orchestral players
- Instrumentation/orchestration contribute to the mood
- the murmur of the sea depicted by the tremolo in the strings
- the crashing waves depicted by sforzandi chords for the orchestra tutti
- the sea swells depicted by the movement of the opening theme played by cello, viola and bassoon
Any THREE correct facts = 3 marks |
Style
- Use of chromaticism
- Extreme dynamic contrasts
- A dramatic symphonic work with programmatic content
- Texture: Mostly homophonic
- Tempo: Allegro moderato
- Tempo fluctuations - rubato
- Programmatic nature and sets a scene but does not tell a story
Any THREE correct facts = 3 marks |
Logical presentation and structure of the essay = 3 marks |
The essay will be marked according to the following criteria:
CRITERIA | MARK ALLOCATION | ||
Origins | 3 marks | 3 | |
Form | 3 marks | 3 | |
Instrumentation/ Orchestration | 3 marks | 3 | |
Style | 3 marks | 3 | |
Logical presentation and structure of the essay | Excellent | = 3 marks | 3 |
Good | = 2–2½ marks | ||
Average | = 1½ marks | ||
Below average | = 1 mark | ||
Weak | = ½ mark | ||
Not acceptable | = 0 marks | ||
TOTAL | 15 | ||
[15]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
SECTION D: JAZZ
QUESTION 11
11.1
- Trumpet
- Saxophone
11.2
- Keyboard/organ
- Guitar
- Bass guitar
- Drum kit
Any TWO correct answers = 2 marks |
11.3 (4)
POPULAR SONG FORM | BLUES FORM |
32 bars | 12 bars (with lyrics in AAB form) |
AABA form/Verse and chorus | One part form |
Diatonic chord progression e.g. A: I-vi-IV-V B: V7/vi - V7/ii - V7/V - V7 | I7, IV7 and V7in a 12-bar cyclic scheme (All chords have a minor seventh added) F7(4 bars), Bb7(2 bars), F7(2 bars), C7(1 bar), Bb7(1 bar), F7(2 bars) |
Two contrasting themes | One theme |
Any TWO correct correlated differences 2 x 2 = 4 marks Candidates may answer in table format |
11.4
11.4.1 Improvisation/Jamming (1)
11.4.2
- Comping
- Improvisational chordal accompaniment (1)
Correct fact = 1 mark |
11.4.3 Substitution (1) [10]
QUESTION 12
Answer:
Characteristics
- A unique fusion of African jazz with rhythms and melodies of traditional vhaVenda and baPedi music
- Melodies, percussion and language derived from baPedi and vhaVenda cultures ∙ Prominent use of African polyrhythms
- African rhythms supplied by the bongo, malombo and meropa
- Lyrical, lilting guitar and flute melodies are extensively used
- Free jazz, blues and rock influences from North America
- Guitar arrangements and improvisatory style are borrowed from musicians such as Wes Montgomery and John McLaughlin
- 12-bar blues structure employed in some compositions
Any FOUR characteristics = 4 marks |
Artist/Band
- Philip Tabane
- Julian Bahula
- Malombo Men
- Malombo Jazz [5]
Any ONE artist/band = 1 mark |
QUESTION 13
Answer:
Marabi
- Both vocal and instrumental music
- Primarily a keyboard style
- Influenced by Duke Ellington (Afro-American fusion)
- Other instruments: piano, pedal organ, guitar/banjo, bass guitar, percussion and voice in a small instrumental ensemble
- Voice and piano have melodic role
- Songs often start with a brief introduction featuring the guitar or piano OR
Kwela
- Instrumental music mostly
- Guitar and banjo outline the chord progression and give rhythmic drive
- The guitar plays the skiffle-like rhythm
- Penny-whistle often used as lead instrument (saxophone added later)
- Songs usually start with a pennywhistle introduction
- Penny-whistle used as a warning signal during apartheid-era [5]
Any FIVE facts = 5 marks |
QUESTION 14
Abdullah Ibrahim
Melody
- Folk-like melodies
- Hymn-like/Chorale style
- Ghoema/Cape Malay characteristics
- Modal melodies
- Extensive improvisational style
- Melodies are often realised on the piano
Any FOUR correct facts = 4 marks |
Relevant example
- Mannenberg, Soweto is where it's at, Tsakwe (Royal Blue) [5]
Any correct example = 1 mark |
OR
Robbie Jansen
Melody
- Folk-like melodies
- Khoisan/Cape Malay melodies interwoven with Malaysian/Indonesian melismatic styles
- Saxophone melody produced with a nasal tone with vibrato at the end of phrases
- Lead-saxophone (alto) mostly plays the melody
- Extensive improvisation for all instruments, blending various styles (eclectic)
Any FOUR correct facts = 4 marks |
Relevant example
- Hoija Tjie Bonga, Tsakwe, Sommer Ghoema [5]
Any correct example = 1 mark |
OR
Winston Mankunku Ngozi
Melody
- Lead-saxophone (tenor) plays the melody
- Folk-like melodies
- Khoi-Khoi and San melodies intertwined
- Malaysian and Indonesian melismatic styles are fused
- Extensive improvisation for all instruments, blending various styles
- Call and response between lead saxophone and other instruments
Any FOUR correct facts = 4 marks |
Relevant example
- Abantwana be Afrika, Crossroads [5]
Any correct example = 1 mark |
QUESTION 15
Reasons for popularity:
- The very popular traditional Zulu Indlamu dance rhythms are prominently part of mbaqanga and that is the reason that it is popular. The modern style mbaqanga is based on the traditional music
- The music style mbaqanga is associated with the popular staple food, 'maize bread'
- A fusion of popular American jazz, mbube, kwela and marabi music caused more people to be drawn to this mixed style
- Introduction of Radio Bantu ensured that many musicians recorded their music for airplay
- The 'spirit of competition' around releasing new recordings made this style popular
- One of the reasons why it became popular is that it was an easy way for musicians to make a quick buck (money)
Any THREE reasons = 3 marks |
Style characteristics
- Use of both traditional and Western instruments
- Fuses traditional and Western music elements
- Electric guitar very important in mbaqanga, e.g. by Mahlathini and the Mahotella Queens
- Electronic organ more important in mbaqanga than in preceding styles of music, e.g. the Soul Brothers
- Sometimes a male-only vocal style: Soul Brothers
- Usually starts with a brief guitar introduction (or in the case of Soul Brothers, the introduction is done by the electronic organ)
- Heavy bass line and rock beat are prominent features
- Chord progression I – IV – V – I cycle over a bouncy 8/8 rhythm
- Music has a repetitive character
- Call and response used between the lead singer/guitarist and the backing singers/band
Any SEVEN style characteristics = 7 marks |
Artist/Band:
- Mahlathini and the Mahotella Queens
- Soul Brothers
- The Cool Crooners
- Makgona Tsohle Band
Any TWO artists/bands = 2 marks |
The essay will be marked according to the following criteria:
CRITERIA | MARK ALLOCATION | ||
Reasons for popularity | 1 mark for each correct fact | 3 | |
Style characteristics | 1 mark for each correct fact | 7 | |
Artists | 1 mark for each correct fact | 2 | |
Logical presentation and structure of the essay | Excellent | = 3 marks | 3 |
Good | = 2-2½ marks | ||
Average | = 1½ marks | ||
Below average | = 1 mark | ||
Weak | = ½ mark | ||
Not acceptable | = 0 marks | ||
TOTAL | 15 | ||
[15]
TOTAL SECTION D: 40
OR
SECTION E: INDIGENOUS AFRICAN MUSIC (IAM)
QUESTION 16
16.1
- vhaVenda drums
- Mbila mutondo
- Mbila dzamedza
- Ngoma
- Tshikona pipes (2)
Any TWO instruments = 2 marks |
16.2 Flute (1)
16.3
- Keyboard/organ
- Guitar
- Bass guitar
- Drum kit (1)
16.4 (3)
Any correct answer = 1 mark |
Indlamu | Mokhibo |
amaZulu dance | baSotho dance |
Fast and energetic | Can be moderate and calm |
Uses mostly the lower body and includes stomping of feet | Uses mostly the upper body and includes the shaking of the back and shoulders |
Performed, using feet | Performed while kneeling |
Any THREE correct correlated differences = 3 marks Candidates may answer in table format |
16.5 16.5.1 Ululation (1)
16.5.2 Izibongo (1)
16.5.3 Chordophone (1) [10]
QUESTION 17
- Traditional elements which were retained are the following:
- Kiba polyrhythms
- Always in Sepedi language
- Call and response between voices and instruments
- Ululation, crepitations and vocal lilting
- Changes which were introduced:
- Modern jazz rhythms are added
- Any modern instruments (guitar, keyboard, drum kit) can be used
- Any African language can be used
- Free kiba is recorded and sold for commercial gain. [5]
Any TWO facts relating to traditional elements = 2 marks Any THREE facts on transformation of elements to modern style = 3 marks | = 5 marks |
QUESTION 18
- He has created a modern version of the malombo style
- He employs various indigenous African languages
- He replaces the original reed flute with a Western flute
- Cyclical chord structures are employed
- Call and response between voice and instrument is used extensively ∙ Vocals, bass guitar, drum kit, indigenous drums and rattles are used [5]
Any FIVE correct facts = 5 marks |
QUESTION 19
- Ancestral worship
- Certain songs and dances exist exclusively to communicate with the ancestors e.g. at funerals and weddings
- Certain songs and dances induce a trance through which contact is established
- Through music and dance the assistance and blessing of the ancestors are sought e.g. during initiation ceremonies
- The participation of the community in the musical activity often signifies the joy of connecting with the ancestral spirits successfully
- Traditional Healers (Sangomas)
- Sangomas are agents and conduits of divinity, e.g. 'Saane' and 'Leepo'
- Sangomas will initiate the process of contacting the ancestral spirits by using invocative singing and praise poetry
- Sangomas will incite the community/people to participate in ceremony
- Singing, drums and whistles are employed during ritualistic performances to provide the link between the worshippers and the divine [5]
Any FIVE correct facts = 5 marks |
QUESTION 20
Playing techniques on guitar
- Ukuvamba technique:
- strumming chords percussively
- Ukupika technique:
- a finger-picking style
- the thumb plays the lower strings ('amadoda', the Zulu word for 'men')
- the other fingers in the right hand (mainly the index finger) plays a melody on the upper strings ('amatombazane', the Zulu word for 'women')
- A plectrum (called ikati) is often used
Any THREE correct facts = 3 marks |
Tuning of the guitar
- Different maskandi use different tunings depending on the specific style of dance/song
- Standard maskanda guitar tuning is called isiZulu-style
- strings are tuned as: EADGBD
- Isishameni-style
- strings are tuned as: DADABD
- Isichunu style
- strings are tuned as: DADABD (as in Isishameni)
- Isigeyane-style
- Uses isiZulu (standard maskanda tuning) but different rhythmic patterns
- Isimandolini style
- strings are tuned as: EBBC#F#G#
Any TWO correct facts = 2 marks |
Style of singing
- Based on amahubo (using the pentatonic scale)
- Umaskanda melody is an authentic remnant of the Zulu amahubo music, the foundation of all Zulu vocal music
- Range of voices is not wide: between a 5th and 11th
- Singers switch between singing and speaking
- Vocal glissandi or pitch bending is used
- Text for umaskanda music is in isiZulu
- Formal design of umaskanda music imitates the vocal style of isiZulu music which in turn is based on Zulu-speech
- Leader (call) and backup singers (response)
Any FIVE correct facts = 5 marks |
Izihlabo
- An instrumental introduction based on a descending motive played on guitar or concertina
- Consists of short bursting motifs
- It sounds like an 'improvised sound check' to check the tuning
- Uses free rhythm and metre
Any TWO correct facts = 2 marks |
The essay will be marked according to the following criteria:
CRITERIA | MARK ALLOCATION | ||
Playing techniques on the guitar | 1 mark for each correct fact | 3 | |
Tuning of guitar | 1 mark for each correct fact | 2 | |
Style of singing | 1 mark for each correct fact | 5 | |
Izihlabo | 1 mark for each correct fact | 2 | |
Logical presentation and structure of the essay | Excellent | = 3 marks | 3 |
Good | = 2-2½ marks | ||
Average | = 1½ marks | ||
Below average | = 1 mark | ||
Weak | = ½ mark | ||
Not acceptable | = 0 marks | ||
TOTAL | 15 | ||
[15]
TOTAL SECTION E: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 120
MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY: AUTOMOTIVE GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY: AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (GENERIC)
1.1 A ✔ (1)
1.2 C ✔ (1)
1.3 A ✔ (1)
1.4 B ✔ (1)
1.5 D ✔ (1)
1.6 A ✔ (1)
TOTAL QUESTION 1: [6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 Angle grinder: (Before using)
- The safety guard must be in place before starting. ✔
- Protective shields must be placed around the object being grinded to protect the people around. ✔
- Use the correct grinding disc for the job. ✔
- Make sure that there are no cracks in the disc before you start. ✔
- Protective clothing and eye protection are essential. ✔
- Check electrical outlets and cord/plugs for any damages. ✔
- Ensure that lockable switch is disengaged. ✔
- Ensure that the disc and the nut are well secured. ✔
- Ensure that the removable handle is secured. ✔
- Remove all flammable material from the area. ✔
- Secure the work piece. ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.2 Welding goggles:
- To protect your eyes against sparks ✔
- To protect your eyes against heat ✔
- To be able to see where to weld ✔
- To protect your eyes from UV rays / bright light ✔
- To protect your eyes from smoke ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.3 PPE for Hydraulic press:
- Overall ✔
- Safety shoes ✔
- Safety goggle ✔
- Leather gloves ✔
- Leather apron ✔
- Face shield ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.4 Workshop layouts:
- Process layout ✔
- Product layout ✔ (2)
2.5 Employer’s responsibility regarding first-aid:
- Provision of first-aid equipment ✔
- First aid training ✔
- First-aid services by qualified personnel ✔
- Any first aid procedures ✔
- Display first aid safety signs ✔
- First aid personnel must be identified by means of arm bands or relevant personal signage ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
TOTAL QUESTION 2: [10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1 Bending test:
- Ductility ✔✔
- Malleability ✔✔
- Brittleness ✔✔
- Flexibility ✔✔
- (Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.2 Heat-treatment:
3.2.1 Annealing:
- To relieve internal stresses ✔
- To soften the steel ✔
- To make the steel ductile ✔
- To refine the grain structure of the steel ✔
- To reduce the brittleness of the steel ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.2.2 Case hardening:
- To produce a wear resistant surface ✔ and it must be tough enough internally ✔ at the core to withstand the applied loads.
- Hard case ✔ and tough core. ✔
- (Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.3 Tempering process:
- To reduce ✔ the brittleness ✔ caused by the hardening process.
- Relieve ✔ strain ✔ caused during hardening process.
- Increase ✔ the toughness ✔ of the steel.
- (Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.4 Factors for heat-treatment processes:
- Heating temperature / Carbon content ✔
- Soaking (Time period at temperature) / Size of the work piece ✔
- Cooling rate / Quenching rate ✔ (3)
3.5 Hardening of steel:
- Steel is heated to 30 – 50°C above the higher critical temperature. (AC3) ✔
- It is then kept at that temperature to ensure (soaking) that the whole structure is Austenite. ✔
- The steel is then rapidly cooled by quenching it in clean water, brine or oil. ✔ (3)
TOTAL QUESTION 3: [14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (SPECIFIC)
4.1 C ✔ (1)
4.2 B ✔ (1)
4.3 D ✔ (1)
4.4 D ✔ (1)
4.5 A ✔ (1)
4.6 C ✔ (1)
4.7 A ✔ (1)
4.8 D ✔ (1)
4.9 A / C ✔ (1)
4.10 A ✔ (1)
4.11 D ✔ (1)
4.12 D ✔ (1)
4.13 A ✔ (1)
4.14 A ✔ (1)
TOTAL QUESTION 4: [14]
QUESTION 5: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
5.1 Equipment:
5.1.1 Compression tester ✔ (1)
5.1.2
- A – Flexible piping / hose / tubing ✔
- B – Adaptor screw / Fitting / Attachment / Connector ✔
- C – Gauge ✔
- D – Pressure release valve ✔ (4)
5.1.3 Compression Tester:
- It measures the pressure created, ✔ when the piston is at top dead centre on power stroke. ✔ (2)
5.2 Cylinder leakage:
- To check whether the engine leaks gases ✔ from the cylinder during the compression stroke. ✔ (2)
5.3 Gas Analyser:
- To ensure ✔ an accurate reading. ✔
- o prevent ✔ a lean reading. ✔
- (Any 1 x 2 ) (2)
5.4 Function of a computerized diagnostic scanner:
- Scans all systems ✔ on the vehicle.
- Informs what adjustments can be made after diagnosis ✔
- (Any 1 x 1 ) (1)
5.5 Bubble gauge camber procedure:
- Mount the bubble gauge on to the straightened wheel ✔
- Zero the bubble gauge at the gauge zero scale ✔
- Take the reading on the camber scale ✔
- Do the same for the other wheel ✔ (4)
5.6 Dynamic balance on wheels:
- The plane of imbalance ✔
- The extent of the unbalancing forces ✔
- The sense of direction of these forces (clockwise or counter clockwise) ✔
- Determine the location of weight placement ✔
- Magnitude of the weights ✔
- The run-out of the tyre and wheel assembly ✔
- (Any 3 x 1 ) (3)
5.7 Purpose of turn tables:
- To make it possible to turn ✔ the front wheels in or out ✔ to check ✔ the wheel angles. ✔ (4)
TOTAL QUESTION 5: [23]
QUESTION 6: ENGINES (SPECIFIC)
6.1 Static balancing of the crankshaft:
- The crankshaft is in static when the mass in all directions ✔ from the centre of rotation is equal while it is at rest. ✔ (2)
6.2 Cylinder layouts:
6.2.1 V - engine layout ✔ (1)
6.2.2 In line (straight) engine layout ✔ (1)
6.3 Firing order in an engine:
- By removing the tappet cover and determining which are intake valves and which are exhaust valves ✔
- Rotating the engine in the direction in which it turns. ✔
- Watch the order in which one set of valves, inlet or exhaust operates ✔
- This will give the order in which the inlet stroke or exhaust stroke occurs ✔
- The power strokes occur in the same order ✔
OR - Cylinder 1 must be at TDC on power stroke ✔
- Remove the distributor cap ✔
- Ensure to turn the engine in the correct direction of rotation ✔
- Determine the direction of rotation of the rotor ✔
- Trace the firing order by the HT leads ✔
- (Any 1 x 5 ) (5)
6.4 Firing order of engines:
6.4.1 Four cylinder in-line engine:
- 1,3,4,2; or ✔
- 1,2,4,3 ✔
- (Any 1 x 1 ) (1)
6.4.2 V6-cylinder engine:
- 1,4,2,5,3,6 ✔
- 1,2,3,4,5,6 ✔
- 1,6,5,4,3,2 ✔
- 1,4,5,6,3,2 ✔
- (Any 1 x 1 ) (1)
6.5 Turbo charger:
6.5.1 Turbocharger:
- A – Compressor air inlet ✔
- B – Turbine housing ✔
- C – Turbine exhaust gas outlet ✔
- D – Turbine wheel ✔
- E – Turbine exhaust gas inlet ✔
- F – Compressed air outlet ✔
- G – Compressor wheel ✔ (7)
6.5.2 Turbocharger advantages:
- More power / speed / boost is obtained from an engine with the same capacity ✔
- There is no power loss as the turbocharger is driven by exhaust gasses ✔
- Improved fuel consumption ✔
- The effect of height above sea level is eliminated ✔
- Generally, cheaper than superchargers ✔
- Any ( 2 x 1) (2)
6.6 Terminology:
6.6.1 Boost:
- Refers to the increase in manifold pressure ✔ that is generated by the turbocharger in the intake that exceeds the normal atmospheric pressure. ✔ (2)
6.6.2 Turbo lag:
- It is a delay ✔ between pushing on the accelerator and feeling turbo kick in. ✔ or
- The time ✔ it takes the turbo charger to reach operating speed. ✔
- (Any 1 x 2) (2)
6.7 Purpose of waste gate:
- It diverts exhaust gases ✔ away from the turbine wheel to regulate the turbine speed ✔ and consequently boost pressure. (2)
6.8 Oil cooler:
- To cool (prevent overheating) the oil ✔ that lubricates the turbocharger bearings and shaft. ✔ (2)
TOTAL QUESTION 6: [28]
QUESTION 7: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
7.1 Torque:
- Torque is the twisting effort ✔ transmitted by a rotating shaft or wheel. ✔
- Turning force applied ✔ over a centre of a round object. ✔
- (Any 1 x 2) (2)
7.2 Clearance volume:
- This is the volume of the space ✔ above the crown of the piston at TDC. ✔ (2)
7.3 Method to increase compression ratio:
Remove shims between the cylinder block and cylinder head. ✔
- Fit thinner cylinder head gasket. ✔
- Machine metal from cylinder head. ✔
- Skim metal from cylinder block. ✔
- Fit a piston with a higher crown. ✔
- Fit a crankshaft with a longer stroke. ✔
- Increase the bore of the cylinders. / bigger pistons. ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
7.4 Calculation of compression ratio:
7.4.1
- Swept Volume = πD2 × L ✔
4
= π (7,5)2 8,0 ✔
4
353,43 cm3 ✔ (3)
7.4.2
- Compression Ratio = SV + CV
CV
CV = SV
CR - 1
= 353,43
8,5 1
= 353,43
7,5
= 47,12 cm ✔ (3)
7.4.3 New compression ratio:
- Sweptvolume = πD2 × L
4
= π7,82 × 8
4
= 382,27 cm ✔ - New compression Ratio = SV + 1
CV
= 382,27 + 1
47,12
= 8,11 + 1:1
= 9.11:1
OR - New compression Ratio = SV + CV
CV
= 382.27 + 47.12
47.12
= 9.11:1 ✔(6)
7.5 Calculations: Power:
7.5.1 IndicatedPower = P × L × A × N × n
- P = 1400 kPa
L = 110
1000
= 0,11 m - A = πD2
4
= π0,102
4
= 7,85 x 10-3m2 ✔ ✔ - N = 3600
60 × 2
= 30 r/s ✔ ✔
n 4 cylinders - IndicatedPower = P × L × A × N × n
= [1400 × 103] × 0,11 × [7,85 × 10-3] × 30 × 4
= 145068 W
= 145,07 kW (8)
7.5.2 T = F × r
- (75 × 10) × 0,45
= 337,5N.m ✔ - Brake power = 2π × N × T
= 2π × 60 × 337,5 ✔
= 127234,5 W
= 127,23 kW ✔ (4)
7.5.3 Mechanicalefficiency = BP 100%
IP
- = 127,23 × 100%
145,07 00 %
= 87,70% ✔ (2)
TOTAL QUESTION 7: [32]
QUESTION 8: MAINTENANCE (SPECIFIC)
8.1 Gas analyser:
- Exhaust gasses ✔
- CO gasses ✔
- CO2 gasses ✔
- SO2 gasses ✔
- NOx gasses ✔
- HC gasses ✔
- O2 gasses ✔
- (Any 1 x 1) (1)
8.2 Specification for gas analysis:
- % Hydrocarbon / HC ✔
- % Carbon monoxide / CO ✔
- % Carbon dioxide / CO2 ✔
- % Nitrogen oxide / NOx ✔
- % Sulphur dioxide / SO2 ✔
- (Any 3 x 1) (3)
8.3 Cylinder leakage test: (Results)
- Hissing noise at air intake ✔
- Hissing noise at exhaust pipe ✔
- Hissing noise in dipstick hole ✔
- Hissing noise under tappet cover ✔
- Bubbles in radiator water ✔
- Hissing noise at adjacent cylinders ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
8.4 Cylinder Leakage test: (Causes)
- Worn cylinders ✔
- Worn piston ✔
- Worn piston rings ✔
- Leaking inlet valve ✔
- Leaking exhaust valve ✔
- Leaking cylinder head gasket ✔
- Cracked cylinder head / block ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
8.5 Compression test procedures:
- Get the engine to normal operating temperature. ✔
- Disconnect the fuel supply and ignition system. ✔
- Remove spark plugs. ✔
- Fit the compression tester ✔
- Depress the throttle and crank the engine a few revolutions. ✔
- Record and compare the pressure reading for each cylinder with manufacturers specifications. ✔ (6)
8.6 Reasons for low oil pressure:
- Worn oil pump ✔
- Blocked oil pump screen/filter/strainer in the sump ✔
- Worn main, big-end and camshaft bearings ✔
- Blocked or restricted oil filter ✔
- Dirty or contaminated oil ✔
- Oil leaks ✔
- Too little oil in engine ✔
- Incorrect grade (viscosity) of oil ✔
- Pressure relief valve spring too weak or damaged ✔
- Plunger / Ball stuck in open position ✔
- Dirt stuck between ball and seat ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
8.7 Cooling system pressure test:
- Start engine and allow to heat up. Fit radiator pressure tester to radiator. ✔
- Pressurize the cooling system according to manufacture’s specification. ✔
- Watch the pressure for a while, if it drops there is a leak. ✔
- Make a visual check for leaks. ✔
- Install radiator cap to tester and pump tester, the cap should release air at its rated pressure. ✔
- Check the rubber seal for cracks and damage. ✔
- Check the vacuum valve for free movement and operation. ✔ (7)
TOTAL QUESTION 8: [23]
QUESTION 9: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL (AUTOMATIC GEARBOX) (SPECIFIC)
9.1 Differences between an automatic and manual gearbox:
- There is no clutch pedal in a motor vehicle with an automatic gearbox. / There is a clutch pedal in a motor vehicle with a manual gearbox. ✔
- There is no need to change gears, the shifting of the gears happens automatically. ✔
- Automatic transmission uses thin oil while manual gearbox uses thicker oil. ✔
- Automatic transmission uses torque converter while manual gearbox uses clutch assembly. ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.2 Advantages of automatic gearbox:
- It reduces driver fatigue ✔
- It ensures great reduction of wheel spin under bad road conditions ✔
- The vehicle can be stopped suddenly without the engine stalling ✔
- The system dampens all engine torsional vibrations ✔
- Easier to drive (e.g. Disabled person with one leg) ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.3 Torque converter:
9.3.1 Torque converter function:
- Transfers engine torque to the transmission. ✔
- It multiplies the engine torque to the transmission. ✔
- Provides a direct-drive, or mechanical link from the engine to the transmission. ✔
- The torque converter dampens all engine torsional vibrations. ✔
- The torque converter acts as a flywheel. ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.3.2 Parts:
- A – One-way clutch / Turbine ✔
- B – Turbine / Impeller ✔
- C – Pump ✔
- D – Turbine shaft ✔
- E – Gearbox housing ✔ (5)
9.4 Single epicyclic gear train:
- Overdrive forward ✔
- Overdrive reverse ✔
- Gear reduction forward ✔
- Gear reduction reverse ✔
- Direct drive ✔
- Neutral ✔
- (Any 5 x 1) (5)
9.5 Purpose of gear ratio in the gearbox:
- It is used in order to utilise the usable torque ✔ developed in a relatively limited speed range of the engine over a greater road speed range. ✔
- Allows different speeds ✔ depending on the different loads. ✔
- (Any 1 x 2) (2)
TOTAL QUESTION 9: [18]
QUESTION 10: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL (AXLES, STEERING GEOMETRY AND ELECTRONICS) (SPECIFIC)
10.1 Preliminary wheel alignment checks:
- Kerb mass (tank full of petrol, spare wheel and tools) against the manufacturer’s specifications. ✔
- Uneven wear on the tyre. ✔
- Tyre pressure. ✔
- Run-out on the wheels; check wheel nuts with torque wrench. ✔
- Correct preload on the wheel (hub) bearings. ✔
- Kingpins and bushes. ✔
- Suspension ball joints for wear, locking and lifting. ✔
- Suspension bushes for excessive free movement. ✔
- Steering box play and whether secure on chassis. ✔
- Tie-rod ends. ✔
- Sagged springs, this includes riding height. ✔
- Ineffective shock absorbers. ✔
- Spring U-bolts. ✔
- Chassis for possible cracks and loose cross-members. ✔
- Wheels must be balanced ✔
- Wheel alignment specifications ✔
- Drive shafts / CV-joints ✔
- (Any 5 x 1) (5)
10.2 Caster
10.2.1 Negative ✔ Caster ✔ (2)
10.2.2 Parts:
- A – Contact point of king pin centre line ✔
- B – King pin ✔
- C – Perpendicular line / vertical line / normal line ✔
- D – Negative caster angle ✔
- E – Centre line of king pin ✔
- F – Front of vehicle / Direction of wheel motion ✔
- G – Point of wheel contact / Wheel ✔ (7)
10.2.3 Negative caster angle is the forward tilt ✔ of the kingpin at the top, ✔ viewed from the side. ✔ (3)
10.3 Toe-out: 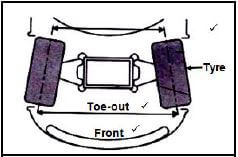 (3)
(3)
10.4 Purpose of the king pin inclination:
- To bring the front wheels back to the straight-ahead position ✔ after rounding a corner without any driver effort. ✔
- Reduce ✔ the scrub radius. ✔
- (Any 1 x 2) (2)
10.5 Catalytic converter:
- Oxidation ✔
- Reduction ✔
- (Any 1 x 1) (1)
10.6 Purpose of the speed control system:
- The purpose of the speed control system is to control the throttle opening ✔ and to keep the vehicle speed constant. ✔ (2)
10.7 Advantage of speed control:
- Driver fatigue is reduced. ✔
- The set speed is controlled constantly. ✔
- Improved fuel consumption. ✔
- A consistently controlled speed helps to prevent speeding fines. ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
10.8 Fuel pressure regulator:
- Fuel pressure regulator regulates the fuel pressure in relation to the manifold pressure. ✔ (1)
10.9 Output frequency of an alternator:
- Increase the turns of wire on the stationary coil. ✔
- Increase the magnetic fields. ✔
- Increase the rotational frequency at which the magnet rotates. ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
10.10 Stator and stator windings:
- To provide a core which concentrates the magnetic lines of force onto the stator windings ✔
- To provide a coil into which a voltage is induced which is used to charge the battery. ✔
- (Any 1 x 1) (1)
10.11 Function of rotor assembly:
- Is to provide a rotating electro-magnet. ✔ (1)
TOTAL QUESTION 10: [32]
TOTAL: 200d
MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY: FITTING AND MACHINING GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY: FITTING AND MACHINING
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (GENERIC)
1.1 A ✔ (1)
1.2 C ✔ (1)
1.3 A ✔ (1)
1.4 B ✔ (1)
1.5 D ✔ (1)
1.6 A ✔ (1)
TOTAL QUESTION 1: [6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 Angle grinder: (Before using)
- The safety guard must be in place before starting. ✔
- Protective shields must be placed around the object being grinded to protect the people around. ✔
- Use the correct grinding disc for the job. ✔
- Make sure that there are no cracks in the disc before you start. ✔
- Protective clothing and eye protection are essential. ✔
- Check electrical outlets and cord/plugs for any damages. ✔
- Ensure that lockable switch is disengaged. ✔
- Ensure that the disc and the nut are well secured. ✔
- Ensure that the removable handle is secured. ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.2 Welding goggles:
- To protect your eyes against sparks ✔
- To protect your eyes against heat ✔
- To be able to see where to weld ✔
- To protect your eyes from UV rays ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.3 PPE for Hydraulic Press:
- Overall ✔
- Safety shoes / boots✔
- Safety goggle ✔
- Leather gloves ✔
- Face shield ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.4 Workshop layouts:
- Process layout ✔
- Product layout ✔ (2)
2.5 Employer’s responsibility regarding first-aid:
- Provision of first-aid equipment ✔
- First aid training ✔
- First-aid services by qualified personnel ✔
- Any first aid procedures / treatment ✔
- Display first aid safety signs ✔
- First aid personnel must be identified by means of arm bands or relevant personal signage ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
TOTAL QUESTION 2: [10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1 Bending test:
- Ductility ✔✔
- Malleability ✔✔
- Brittleness ✔✔
- Flexibility ✔✔
- (Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.2 Heat-treatment:
3.2.1 Annealing:
- To relieve internal stresses ✔
- To soften the steel ✔
- To make the steel ductile ✔
- To refine the grain structure of the steel ✔
- To reduce the brittleness of the steel ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.2.2 Case hardening:
- To require a wear resistant surface ✔ and it must be tough enough internally ✔ at the core to withstand the applied loads.
- Hard case ✔ and tough core. ✔
- (Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.3 Tempering process:
- To reduce ✔ the brittleness ✔ caused by the hardening process.
- Relieve ✔ strain ✔ caused during hardening process.
- Increase ✔ the toughness of the steel. ✔
- (Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.4 Factors for heat-treatment processes:
- Heating temperature / Carbon content ✔
- Soaking (Time period at temperature) / Size of the work piece ✔
- Cooling rate / Quenching rate ✔ (3)
3.5 Hardening of steel:
- Steel is heated to 30 – 50°C above the higher critical temperature. (AC3) ✔
- It is then kept at that temperature to ensure (soaking) that the whole structure is Austenite. ✔
- The steel is then rapidly cooled by quenching it in clean water, brine or oil. ✔ (3)
TOTAL QUESTION 3: [14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (SPECIFIC)
4.1 C ✔ (1)
4.2 A ✔ (1)
4.3 D ✔ (1)
4.4 A ✔ (1)
4.5 B ✔ (1)
4.6 A ✔ (1)
4.7 B ✔ (1)
4.8 B ✔ (1)
4.9 D ✔ (1)
4.10 C ✔ (1)
4.11 B ✔ (1)
4.12 D ✔ (1)
4.13 D ✔ (1)
4.14 C ✔ (1)
TOTAL QUESTION 4: [14]
QUESTION 5: TERMINOLOGY (LATHE AND MILLING MACHINE) (SPECIFIC)
5.1 Advantages of using the tailstock to cut an external taper:
- Long an accurate taper can be cut. ✔
- The automatic feed can be used which result in a good finish. ✔ (2)
5.2 Calculate the compound slide set-over:
- Tan θ = D - d
2 2L
Tan θ = 60 - 28
2 2 × 85
= 0,188 ✔ ✔
θ = 10,66 º
2
OR 
- X = D - d
2
= 60 - 28
2
= 16 mm - Tan θ = 16
2 85
θ = 10,66 º (5)
2
5.3 Centre gauge:
- To measure the form and angle of the screw cutting tool angle while grinding the tool ✔
- To set the screw cutting tool square/perpendicular to the axis of the work piece ✔ (2)
5.4 Parallel key:
Length:
- Length = 1,5 × diameter
= 1,5 × 42 ✔ ✔
= 63 mm ✔ (3)
5.5 Advantages of up-cut milling:
- Deeper cuts can be made as the cutting pressure on the cutter is lower than down cut milling. ✔
- The process enables hard steel to be cut, because the total cutting pressure is absorbed by the material at the back of the edge. ✔
- Metal with hard scale, such as castings or forgings, the cut is started under the scale where the material is softer which extends the life of the cutter. ✔
- A quicker/course feed can be used. ✔
- The strain on the cutter and arbour will be less. ✔
- Vibration is limited ✔
- Good finish ✔
- Low noise level ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
5.6 Disadvantage of down-cut milling:
- Vibration in the arbour is unavoidable. ✔
- A fine feed must be used. ✔
- When milling a material with hard scale the milling cutter will be damaged. ✔
- Process takes time because of slower feed. ✔
- Noisy process. ✔
- Bad finish because of vibration. ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
5.7 Methods of centring a milling cutter:
- Square and ruler method. ✔
- Set-over method by milling machine dial. ✔
- Dial indicator method ✔
- Using reference points on digital read out equipment ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
TOTAL QUESTION 5: [18]
QUESTION 6: TERMINOLOGY (INDEXING) (SPECIFIC)
6.1 Spur gear:
Chordal tooth thickness: 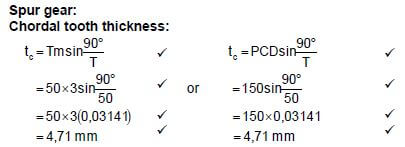 (4)
(4)
6.2 Calculate simple indexing:
- Simple Indexing = 40
N
= 40
13
= 3 1
13
= 3 1 × 3
13 3 - = 3 3
39
3 full turns and 3 holes in a 39 hole circle (4)
6.3 Differential indexing:
6.3.1 Indexing required:
- Indexing = 40 = 40
n 127
= 40 = 40 ÷ 5
A 125 5
= 8
25
Indexing 8 holes on the 25 hole circle (3)
6.3.2 Change gears required:
- Dr = A-n × 40
Dn A 1
= 125 - 127 × 40
125 1
= 2 × 40
125 1
= -80 ÷ 5
125 5
= -16 × 4
25 4
= -64
100 (5)
6.3.3 Direction of rotation of index plate:
- The index plate will turn the opposite ✔ direction as the index crank handle. (1)
6.4 Calculate distance “x” between rollers:
- "x"=150 +2(AB)− 2(CD)− 2r
tanθ = BC
AB
AB = BC
tanθ
= 35
tan 60º
= 20,207 mm
= 20,21 mm - tanθ = DE
CD
CD = 15
tanθ
CD = 15
tan30º
= 25,98 mm 
- " x" = 150 + 2(AB) - 2(CD) - 2r
= 150 + 2 (20,21) - 2 (25,98) - 2 (15)
= 150 + 40,42 - 51,96 - 30
= 108,454m m
= 108,45 m m ✔ (9)
6.5 Reasons for balancing work piece on a centre lathe:
- Prevent unnecessary bearing loads ✔
- Prevent excessive vibration ✔
- To obtain a good finish ✔
- To prevent clatter on the gear teeth ✔
- To prevent the spindle from bending ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
TOTAL QUESTION 6: [28]
QUESTION 7: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
7.1 Hardness testers:
- Brinell-hardness tester ✔
- Rockwell-hardness tester ✔
- Vickers ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
7.2 Moment tester:
- To determine the reactions ✔ on either side of a simply loaded beam. ✔ (2)
7.3 Tensile test:
- A piece of material is subjected to an increasing axial load ✔ while measuring ✔ the corresponding elongation ✔ of the material. (3)
7.4 Depth micro-meter:
- Reading = 100 + 11,00 + 0,50 + 0,09 ✔
= 111,59 mm (5)
7.5 Measure depth:
- Vernier calliper ✔ (1)
TOTAL QUESTION 7: [13]
QUESTION 8: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
8.1 Forces: 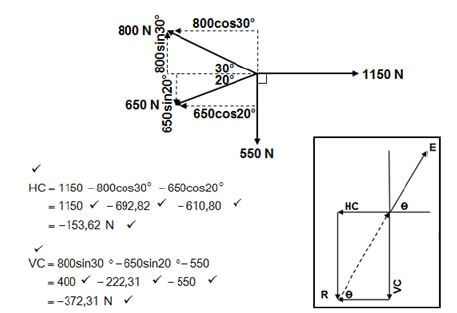 (15)
(15)
Horizontal Components | Magnitudes | Vertical Components | Magnitudes |
1150cos0° | 1150N | 1150sin0° | 0N |
800cos150° | -692,82N | 800sin150° | 400N |
650cos200° | -610,80N | 650sin200° | -222,31N |
550cos270° | 0N | 550sin270° | -550N |
TOTAL: | -153,62N | TOTAL: | -372,31N |
- E2 = HC2 + VC2
√E2 = √(53,62 + 372,312)
E = 402,76N
Tanθ = VC
HC
= 372.31
153,62
θ = 67,58º
Equilibrant = 402,76N en 67,58º North from East (15)
8.2 Moments: 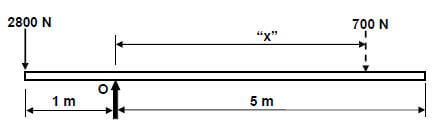
Calculate “x”:
Take moments about O.
- ∑RHM = ∑LHM
700 × "x" 2800 × 1
700 × "x" 2800
"×" = 2800
700
"x" = 4m ✔ ✔ (4)
8.3 Stress and Strain:
8.3.1 Type of stress:
- Compressive stress ✔ (1)
8.3.2 Stress:
- A = π(D2 -d2)
4
= π(0,042 - 0,032)
4
= A = 0,55 × 10σ m2
σ = F
A
= 50 × 10σ
0,55 ×10σ
σ = 90,91 × 10σ Pa
σ = 90,91 MPa ✔
(NO UNIT – NO MARK) (5)
8.3.3 Change in length:
- E = σ
ε
ε = σ
E
= 90,91 × 106 ✔
90 × 109
= 1,01 × 10-3 ✔
(IF ANY UNIT IS GIVEN – NO MARK)
- ε = ΔL
L
ΔL = ε × L
= (1,01 × 10-3) × 80
= 0,08 mm ✔ (5)
8.3.4 Safety factor:
- Safety factor = Break stress
Safe workingstress
Safe workingstress = Break stress
Safety factor
= 600 × 106
4
= 150 × 106 Pa
= 150 MPa ✔(3)
TOTAL QUESTION 8: [33]
QUESTION 9: MAINTENANCE (SPECIFIC)
9.1 Lack of preventative maintenance:
- Risk of injury or death. ✔
- Financial loss due to damage suffered as a result of part failure and the waste of material. ✔
- Loss of valuable production time. ✔ (3)
9.2 Causes for the malfunctioning of chain drive systems:
- Lack of or incorrect lubrication ✔
- Lack of maintenance ✔
- Overloading ✔
- Misalignment of sprockets ✔
- Incorrect chain tension ✔
- Contamination of chain drive system such as dust or sand ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.3 Procedures to reduce the physical wear on a belt drive system:
- Check the belt alignment. ✔
- Checking the belt tension. ✔
- Prevent overloading of the system. ✔
- Keep the pulleys and belt clean. ✔
- Check that all covers are secure. ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.4 Procedures to replace the belt on a belt drive system:
- Ensure that the machine is switched off ✔
- Release the tension on the belt ✔
- Remove the belt from the pulleys ✔
- Fit the correct size replacement belt onto the pulleys ✔
- Check the pulley alignment ✔
- Apply adequate tension according to specification and lock the system ✔
- (Any 5 x 1) (5)
9.5 Properties of materials:
9.5.1 Poly vinyl chloride (PVC):
- Flexible ✔
- Rubber-like substance ✔
- Makes a dull sound when dropped ✔
- Tough ✔
- Act as an insulator ✔
- It is durable ✔
- Highly resistant to oxidative material ✔
- Oil, water and chemical resistant ✔
- (Any 1 x 1) (1)
9.5.2 Carbon fibre:
- Strong ✔
- Tough ✔
- Light weight ✔
- Good electrical conductor ✔
- (Any 1 x 1) (1)
9.6 Difference between “Thermoplastic” and “Thermo hardened (thermosetting)” composites:
- Thermoplastics can be reheated and deformed. / Recyclable ✔
- Thermo hardened cannot be reheated. / Non-recyclable ✔ (2)
9.7 Examples of thermo hardened composites:
- Carbon fibre or (Any application) ✔
- Glass fibre or (Any application) ✔
- Bakelite or (Any application) ✔
- Teflon or (Any application) ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
TOTAL QUESTION 9: [18]
QUESTION 10: JOINING METHODS (SPECIFIC)
10.1 Square thread:
10.1.1 The lead of the thread:
- Lead = pitch × no of starts
= 5 × 2 ✔
= 10 mm ✔ (2)
10.1.2 The helix angle of the thread:  (5)
(5)
10.1.3 The leading tool angle:
- Leadingtoolangle 90º helix angle + clearanceangle
= 90º - (2,29º + 3º)
= 84,71º /84º 42'36"
OR - Leadingtoolangle 90º helix angle + clearanceangle
= 90º - (7,17º + 3º)
79,83º / 79º 49'48" (2)
10.1.4 The following tool angle:
- Followingtoolangle = 90º + (helix angle - clearanceangle)
= 90º + (2,29º - 3º)
= 89,29º /89º 17'24"
OR - Following toolangle = 90º + (helix angle - clearanceangle)
= 90º + ( 7,17º - 3º)
= 94,17º / 94º 10'12" (2)
10.2 Measurements of a screw thread :
10.2.1 Metric screw thread ✔ (1)
10.2.2 Crest / Major / External / Basic / Nominal / Outside diameter ✔ (1)
10.2.3 Pitch ✔ (1)
10.3 Angles of a square thread cutting tool:
- A – Helix angle ✔
- B – Clearance angle ✔
- C – Leading tool angle ✔
- D – Following tool angle ✔ (4)
TOTAL QUESTION 10: [18]
QUESTION 11: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL (DRIVE SYSTEMS) (SPECIFIC)
11.1 Advantages of a belt drive system compared to a chain drive system:
- Silent operation ✔
- Less expensive ✔
- Drive can take place over a longer distance ✔
- No lubrication needed ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
11.2 Hydraulics:
11.2.1 Fluid pressure:  (4)
(4)
11.2.2 Diameter of the ram:  (6)
(6)
11.3 Hydraulic symbols: One-way valve  (1)
(1)
11.4 Belt drives:
Rotation frequency of the drive pulley:
- NDRDDR = NDNDDN
NDR = NDN × DDN
DDR
= 80 × 240
75
= 256 r/min ✔ ✔ ✔ (4)
11.5 Gear drives:
11.5.1 Rotation frequency of the output:
- NA = Product of Driven gears
ND Product of Driver gears
ND = TA × TC
NA TB × TD
ND = TA × TC × NA
TB × TD
= 20 × 25 × 3000
35 × 30
ND = 1428,57 r/min
60
= 23,81 r/sec ✔
OR  (6)
(6)
11.5.2 Gear ratio:
- Gear ratio = Product of the number of teeth on driven gears✔
Product of the number of teeth on driver gears
=35 × 30
20 25
= 2,1 : 1 (3)
11.6 Work done:
- Work done F × s
= 250 × 15
= 3750 Jouleor N.m ✔(2)
TOTAL QUESTION 11: [28]
TOTAL: 200
MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY: WELDING AND METALWORK GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY: WELDING AND METALWORK
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (GENERIC)
1.1 A ✔ (1)
1.2 C ✔ (1)
1.3 A ✔ (1)
1.4 B ✔ (1)
1.5 D ✔ (1)
1.6 A ✔ (1)
TOTAL QUESTION 1: [6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 Angle grinder: (Before using)
- The safety guard must be in place before starting. ✔
- Protective shields must be placed around the object being grinded to protect the people around. ✔
- Use the correct grinding disc for the job. ✔
- Make sure that there are no cracks in the disc before you start. ✔
- Protective clothing and eye protection are essential. ✔
- Check electrical outlets and cord/plugs for any damages. ✔
- Ensure that lockable switch is disengaged. ✔
- Ensure that the disc and the nut are well secured. ✔
- Ensure that the removable handle is secured. ✔
- Remove all flammable material from the area. ✔
- Secure the work piece. ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.2 Welding goggles:
- To protect your eyes against sparks ✔
- To protect your eyes against heat ✔
- To be able to see where to weld ✔
- To protect your eyes from UV rays / bright light ✔
- To protect your eyes from smoke ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.3 PPE for Hydraulic press:
- Overall ✔
- Safety shoes ✔
- Safety goggle ✔
- Leather gloves ✔
- Leather apron ✔
- Face shield ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.4 Workshop layouts:
- Process layout ✔
- Product layout ✔ (2)
2.5 Employer’s responsibility regarding first-aid:
- Provision of first-aid equipment ✔
- First aid training ✔
- First-aid services by qualified personnel ✔
- ∙ Any first aid procedures ✔
- Display first aid safety signs ✔
- First aid personnel must be identified by means of arm bands or relevant personal signage ✔
- Any 2 x 1) (2)
TOTAL QUESTION 2: [10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1 Bending test:
- Ductility ✔✔
- Malleability ✔✔
- Brittleness ✔✔
- Flexibility ✔✔
- Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.2 Heat-treatment:
3.2.1 Annealing:
- To relieve internal stresses ✔
- To soften the steel ✔
- To make the steel ductile ✔
- To refine the grain structure of the steel ✔
- To reduce the brittleness of the steel ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.2.2 Case hardening:
- To produce a wear resistant surface ✔ and it must be tough enough internally ✔ at the core to withstand the applied loads.
- Hard case ✔ and tough core. ✔
- (Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.3 Tempering process:
- To reduce ✔ the brittleness ✔ caused by the hardening process.
- Relieve ✔ strain ✔ caused during hardening process.
- Increase ✔ the toughness ✔ of the steel.
- (Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.4 Factors for heat-treatment processes:
- Heating temperature / Carbon content ✔
- Soaking (Time period at temperature) / Size of the work piece ✔
- Cooling rate / Quenching rate ✔ (3)
3.5 Hardening of steel:
- Steel is heated to 30 – 50°C above the higher critical temperature. (AC3) ✔
- It is then kept at that temperature to ensure (soaking) that the whole structure is Austenite. ✔
- The steel is then rapidly cooled by quenching it in clean water, brine or oil. ✔ (3)
TOTAL QUESTION 3: [14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (SPECIFIC)
4.1 B ✔ (1)
4.2 A ✔ (1)
4.3 B ✔ (1)
4.4 B ✔ (1)
4.5 A ✔ (1)
4.6 B ✔ (1)
4.7 D ✔ (1)
4.8 D ✔ (1)
4.9 C ✔ (1)
4.10 C ✔ (1)
4.11 A ✔ (1)
4.12 D ✔ (1)
4.13 B ✔ (1)
4.14 B ✔ (1)
TOTAL QUESTION 4: [14]
QUESTION 5: TERMINOLOGY (TEMPLATES) (SPECIFIC)
5.1 Template loft:
The template loft is separated from the workshop because…
- it is quieter. ✔
- the lighting is better. ✔
- all equipment is at hand. ✔
- it is a permanent base. ✔
- marking on the floor enhance accuracy. ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
5.2 Purpose of purlins:
- The purlins support ✔ the roof covering ✔
- Stabilizes ✔ the trusses. ✔
- (Any 1 x 2) (2)
5.3 A steel ring calculation:
5.3.1 Dimensions of the required material:
- Mean diameter = Outside diameter - plate thickness
= 880 - 50
= 830mm - Mean circurmference = π × Meandiameter = ×
= π × 830
= 2607,52mm ✔ - 2608 mm of 50 x 50 mm ✔ square steel bar is required to fabricate the ring. (7)
5.3.2 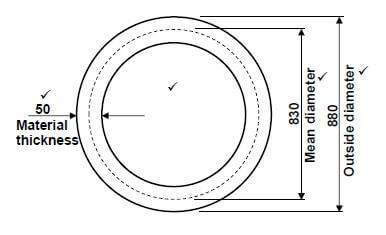
5.4 Resistance weld symbols:
5.4.1 Spot weld ✔ (1)
5.4.2 Seam weld ✔ (1)
5.5 Welding symbols:
- A. Tail ✔
- B. Weld symbol (Fillet weld) ✔
- C. Pitch of weld ✔
- D. Site weld ✔
- E. Arrow ✔
- F. Weld all round ✔ (6)
TOTAL QUESTION 5: [23]
QUESTION 6: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
6.1. Working Principles:
6.1.1 Guillotine:
- A bottom cutting blade is fixed horizontally. ✔
- With a top cutting blade moving downwards. ✔
- It is driven by an electric motor, flywheel, gearbox and axle ✔ by eccentric motion / action / hydraulic action. ✔
- OR
- It is activated manually by foot ✔ with lever action. ✔ (4)
6.1.2 Bending rolls:
- A bending roll has two fixed rollers next to each other rotating in unison (Manually or Electrical motor). ✔
- A third roller is adjustable, moving in between the two rollers. ✔
- The third roller applies downward pressure onto the metal. ✔
- That causes the metal to deflect and ultimately form the round shape desired. ✔ (4)
6.2. Regulators on gas cylinders:
- Regulators reduce ✔ the cylinder pressure ✔ to operating or working pressure. ✔ (3)
6.3 Press machine:
- The press machine is used for installing ✔ or removing ✔ components on mechanical devices / machines. ✔
- To press ✔ profiles ✔ onto material ✔
- (Any 1 x 3) (3)
6.4 MIGS/MAGS welding process:
- A – Weld pool / weld bead / molten metal ✔
- B – Electrode wire / electrode ✔
- C – Gas shroud / electrical contact / nozzle / contact tip ✔
- D – Shielding gas ✔ (4)
TOTAL QUESTION 6: [18]
QUESTION 7: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
7.1 Forces in members:
SCALE: Vector diagram 1 mm = 5 N 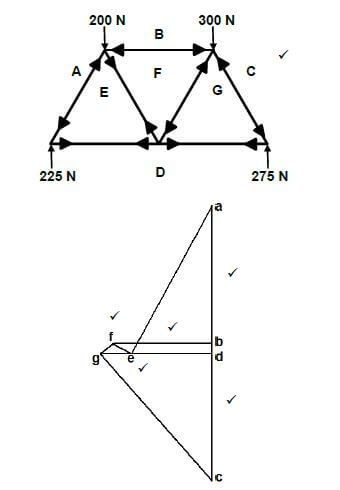 (20)
(20)
MEMBER | MAGNITUDE | NATURE |
AE | 260 N ✔ | STRUT ✔ |
BF | 135 N ✔ | STRUT ✔ |
CG | 317,5 N ✔ | STRUT ✔ |
FG | 27,5 N ✔ | STRUT ✔ |
ED | 130 N ✔ | TIE ✔ |
EF | 27,5 N ✔ | TIE ✔ |
GD | 160 N ✔ | TIE ✔ |
NOTE:
- Use a tolerance of 2 mm + and – on the vector diagram.
- = a tolerance of 10 N + and – on the answer.
7.2 Bending moments: 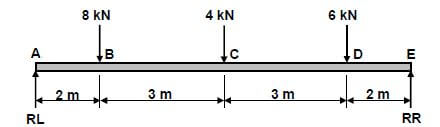
7.2.1 Moments about RR
- RL × 10 = (8× 8)+ (4× 5) +(6× 2)
RL = 96
10
= RL 9,6kN ✔
Moments about RL - RR × 10= (6× 8) +(4 × 5) +(8×2)
RR = 84
10
= RR 8,4kN (8)
7.2.2 Bending moments at point A, B, C, D and E:
- Scale2 mm = 1 kN.m
Momentat A = 0 kN.m
B = RL × 2 = 19,2 kN.m
C = (RL × 5) - (8×3) = 24 kN.m
D =(RL×8) -(8×6) - (4×3) = 16,8 kN.m
E = (RL×10) -(8×8) - (4×5) - (6×2) = 0 kN.m (5)
7.2.3 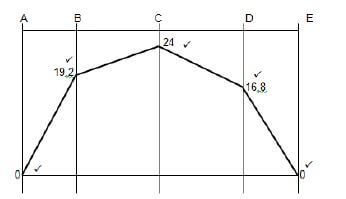 (5)
(5)
NOTE:
- Use a tolerance of 2 mm + and – on the bending moment diagram.
7.3 Stress and strain:
- A = πd2
4
A = π(0,02)2
4
A = 0,314 ×10-3m2 - Stress = Load
Area
Load = Stress c Area
Load = (80 × 106) × (0,314 × 10-3)
Load = 25,133kN ✔(7)
TOTAL QUESTION 7: [45]
QUESTION 8: JOINING METHODS (WELD INSPECTION) (SPECIFIC)
8.1 Factors to be observed during oxy-acetylene welding:
- Correct flame for the work on hand. ✔
- Correct angle of welding torch and welding rod. ✔
- Depth penetration and amount of fusion. ✔
- The rate of progress along the joint. ✔
- The distance of the nozzle from the parent metal. ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
8.2 Abbreviation 'HAZ':
- Heat Affected Zone ✔ (1)
8.3 Causes of weld defects:
8.3.1 Spatter:
- Disturbance in the molten weld pool. ✔
- Too low welding voltages. ✔
- Too high welding current / amps. ✔
- Inadequate shielding gas flow. ✔
- Too fast travel speed ✔
- Arc length too long ✔
- Wet electrode ✔
- Wrong polarity ✔
- Arc length too short ✔
- Wrong included electrode angle ✔
- Wrong electrode used ✔
- Arc blow ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
8.3.2 Undercutting:
- Too fast travel speed ✔
- Rapid solidification ✔
- Too low arc voltage ✔
- Arc length too long ✔
- Excessive welding current ✔
- Too slow movement over weld ✔
- Current / amps too high ✔
- Electrode too big ✔
- Wrong electrode ✔
- Wrong included electrode angle ✔
- Excessive weaving ✔
- Wrong joint design ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
8.3.3 Incomplete penetration:
- Welding current too low ✔
- Too fast travel speed ✔
- Incorrect electrode angle ✔
- Poor edge preperation ✔
- Insufficient root gap ✔
- Electrode too big ✔
- Wrong electrode ✔
- No pre-heating done ✔
- Wrong shielding gas used ✔
- Too long arc ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
8.4 Types of cracks:
8.4.1 Transverse cracks:
- Pre-heating the base metal ✔
- Using lower strength consumables / welding rod ✔
- Slow cooling after welding ✔
- Use clamping device. ✔
- Weld toward the unrestrained side of the weld. ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
8.4.2 Centreline cracks:
- Ensure that width-to-depth ratio is 1:1. ✔
- Decrease the current to decrease excess penetration. ✔
- Decreasing welding voltage setting or slowing travel speed to achieve a flat to convex weld surface. ✔
- Use clamping device. ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
8.5 Differences between non-destructive and destructive tests: ∙ Non-destructive test does not destroy the welded joint. ✔
- Destructive test destroys the welded joint. ✔ (2)
8.6 Ultrasonic test:
- No defects will occurs during a ultrasonic test ✔✔
- Detect internal ✔ flaws as well as surface flaws. ✔
- Porosity ✔✔
- Slag inclusions ✔✔
- Cracks ✔✔
- Any 1 x 2) (2)
8.7 Nick break test for internal defects:
- Slag inclusion ✔
- Porosity ✔
- Lack of fusing ✔
- Oxidised metal ✔
- Burned metal ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
8.8 Machinability test:
- To determine the hardness ✔ and strength ✔of the welded joint.
- To determine ✔ the machinability. ✔
- Any 1 x 2) (2)
8.9 Visual requirements of welds:
- Shape of the profile ✔
- Uniformity of the surface ✔
- Overlap ✔
- Free from any external defects ✔
- Penetration bead ✔
- Root groove ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
TOTAL QUESTION 8: [23]
QUESTION 9: JOINING METHODS (STRESSES AND DISTORTION) (SPECIFIC)
9.1 Residual stress:
- Residual stresses are stresses that exist ✔ in a metal after cooling / welding. ✔ (2)
9.2 Factors affecting grain size:
- The amount of cold work. ✔
- The temperature and time of annealing process. ✔
- The composition and constitution. ✔
- The recrystallisation temperature of cold worked metal. ✔
- The melting point. ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.3 Quenching medias:
- Oil ✔
- Water ✔
- Sand ✔
- Air ✔
- Brine / Salt water ✔
- Lime ✔
- Liquid salts ✔
- Molten lead ✔
- Ash ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
9.4 Weld distortion:
- Distortion in a weld results from the uneven expansion and contraction (warping) ✔ of the weld metal ✔ and adjacent base metal ✔ during the heating and cooling cycle ✔ of the welding process. (4)
9.5 Factors that affect distortion and residual stress:
- If the expansion that occurs when metal is heated is resisted ✔ then deformation will occur. ✔
- When contraction that occurs on cooling is resisted ✔then a stress will be applied. ✔
- If this applied stress causes movement ✔ then distortion occurs. ✔
- If the applied stress does not cause movement ✔ then there will be residual stress in the welded joint. ✔
- (Any 2 x 2) (4)
9.6 Result when metal is cooled rapidly:
- Rapid cooling of metal results in large temperature differences ✔ between the internal and external areas ✔ of the metal that set up stresses, ✔ which cause cracks ✔ on the surface.
- It will harden ✔✔ and the grain structure ✔ will change. ✔
- (Any 1 x 4) (4)
TOTAL QUESTION 9: [18]
QUESTION 10: MAINTENANCE (SPECIFIC)
10.1 Reasons maintenance:
- Promote cost saving ✔
- Improves safety ✔
- Increases equipment efficiency ✔
- Fewer equipment failure ✔
- Improves reliability of equipment ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
10.2 Lockout on machines:
- To ensure that nobody can turn on the machine ✔ while maintenance is being carried out. ✔ (2)
10.3 Reasons for service records:
- Assist in the monitoring of the condition of the machines. ✔
- Assist in upholding warrantees. ✔
- Assist in keeping a history of maintenance and repairs. ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
10.4 Methods of reducing friction:
- By reducing both drill speed and feed speed. ✔
- By applying lubrication. (cutting fluid) ✔
- Use the correct drill bit ✔
- Drill a pilot hole ✔
- (Any 2 x 1) (2)
TOTAL QUESTION 10: [8]
QUESTION 11: TERMINOLOGY (DEVELOPMENT) (SPECIFIC)
11.1 Use of transformers:
- Transformers are used to connect ✔ ducting sections of dissimilar ✔ shapes to each other. ✔ (3)
11.2 @1
@1
11.3 Truncated cone: 
11.3.1 Base circumference:
- Circumference = π × Basediameter
= π × 1400
= 4398,23 mm ✔(3)
11.3.2 Main radius (AC):
- Triangles ABC and CED has the same shape:
AC : DC BC :EC
Thus AC = BC
DC EC
From where AC = BC × DC
EC
and CE = Base Dia - 800
2
= 1400 - 800
2
CE = 300 mm
For : DC
DC2 = DE2 + CE2
DC = √12002 + 3002
DC = 1236,93mm
rounded = 1237mm
AC = BC × DC
EC
= 700 × 1237
300
= 2886,17mm ✔ ✔
rounded 2886mm (10)
11.3.3 Small radius (AD):
- AD = AC - DC
= 2886 - 1237
AD = 1649 mm(1649,24mm) ✔ (3)
TOTAL QUESTION 11: [21]
GRAND TOTAL: 200
MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY: WELDING AND METALWORK GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY: WELDING AND METALWORK
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your examination number and centre number in the spaces provided on the ANSWER BOOK.
- Read ALL the questions carefully.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Show ALL calculations and units. Round off final answers to TWO decimal places.
- Candidates may use non-programmable scientific calculators and drawing instruments.
- The value of gravitational acceleration should be taken as 10 m/s2.
- All dimensions are in millimetres, unless stated otherwise in the question.
- Write neatly and legibly.
- A formula sheet is attached to the question paper.
- Use the criteria below to assist you in managing your time.
QUESTION | CONTENT | MARKS | TIME in minutes |
GENERIC | |||
1 | Multiple-choice questions | 6 | 6 |
2 | Safety | 10 | 10 |
3 | Materials | 14 | 14 |
SPECIFIC | |||
4 | Multiple-choice questions | 14 | 10 |
5 | Terminology (Templates) | 23 | 20 |
6 | Tools and Equipment | 18 | 15 |
7 | Forces | 45 | 40 |
8 | Joining Methods (Inspection of Weld) | 23 | 20 |
9 | Joining Methods (Stresses and Distortion) | 18 | 20 |
10 | Maintenance | 8 | 10 |
11 | Terminology (Developments) | 21 | 15 |
TOTAL | 200 | 180 | |
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (GENERIC)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1 to 1.6) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.7 E.
1.1 What is the purpose of the Occupational Health and Safety Act, 1993 (Act 85 of 1993) with regard to HIV/Aids awareness?
- The Act on safety states that all employers must make sure that the workplace is safe and that employees are not at risk of becoming infected with HIV at work.
- The Act contains common guidelines on how employers, employees and trade unions should respond to HIV in the workplace.
- Employers may not demote or promote an employee based on his/her HIV status.
- Employers cannot simply dismiss a person who has HIV. (1)
1.2 Which ONE of the following items of personal protective equipment (PPE) is applicable when arc welding is performed on a work piece?
- Hard hat
- Welding goggles
- Welding helmet
- Face shield (1)
1.3 Who is responsible for the provision of safety equipment in the workplace?
- Employer
- Employee
- Customer
- Foreman (1)
1.4 Which ONE of the following properties of solid steel will change if the steel is subjected to a heat treatment process?
- Length
- Hardness
- Size
- Shape (1)
1.5 The purpose of normalising steel is to …
- harden.
- temper.
- harden the core.
- relieve internal stresses. (1)
1.6 If a sound test is performed on high-carbon steel, which ONE of the following sounds will help one to identify the metal?
- Loud clear sound
- Dull sound
- Soft ringing sound
- Low ringing sound (1) [6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 An angle grinder is used to smoothen a welded joint. State TWO safety measures that must be observed before using the angle grinder. (2)
2.2 Give TWO reasons why it is important to wear welding goggles during oxy-acetylene gas welding. (2)
2.3 Name TWO items of personal protective equipment (PPE) that one will use when working with a hydraulic press. (2)
2.4 Name TWO types of workshop layouts. (2)
2.5 Name TWO responsibilities of the employer when applying first aid in the workplace. (2) [10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1 Name ONE property of steel that is tested by conducting a bending test. (2)
3.2 Give TWO reasons for conducting EACH of the following heat-treatment processes on steel:
3.2.1 Annealing (2)
3.2.2 Case hardening (2)
3.3 Explain why the tempering of steel is done after the hardening process. (2)
3.4 State the THREE factors that must be considered during all heat-treatment processes. (3)
3.5 Explain the hardening process of steel. (3) [14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (SPECIFIC)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (4.1 to 4.14) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 4.15 E.
4.1 FIGURE 4.1 below shows a section of a plate girder. Identify part Y. 
FIGURE 4.1
- Top flange
- Web plate
- Centre plate
- Middle flange (1)
4.2 FIGURE 4.2 below shows a roof truss. Identify component X. 
FIGURE 4.2
- Gusset plate
- Rafter
- Plate girder
- Lattice girder (1)
4.3 Which ONE of the following is a tool used to cut a complete screw thread in a blind hole?
- Taper or first tap
- Plug or bottoming tap
- Intermediate tap or second tap
- Starting tap (1)
4.4 The type of deformation that causes permanent elongation is known as …
- longitudinal deformation.
- elastic deformation.
- shrinkage deformation.
- plastic deformation. (1)
4.5 One advantage of plasma cutting when compared to oxy-acetylene cutting is that …
- high-speed and precision cuts are possible.
- non-conductive materials can also be cut.
- it uses only oxygen.
- no skill is needed to operate it. (1)
4.6 What is the magnitude of force X shown in FIGURE 4.6 below? 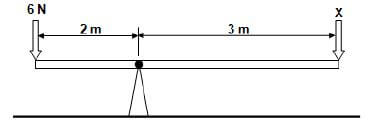
FIGURE 4.6
- 6 N
- 4 N
- 8 N
- 12 N (1)
4.7 What does FIGURE 4.7 below represent regarding points X–X? 
FIGURE 4.7
- Shear moment
- Bending moment
- Bending force
- Shear force (1)
4.8 A strut is defined as a member of a framework designed to …
- hold parts together.
- support beams.
- resist shearing.
- resist compression. (1)
4.9 Which ONE of the following pieces of equipment is associated with oxy acetylene welding?
- Electrode holder
- Earth clamps
- Welding nozzle
- Welding helmet (1)
4.10 Which testing process is represented in FIGURE 4.10 below? 
FIGURE 4.10
- Ultrasonic
- Machinability
- X-ray
- Dye penetrant (1)
4.11 Which ONE of the following is a destructive test on a welded joint?
- Nick-break test
- X-ray test
- Light test
- Sound test (1)
4.12 The maximum gap between the tool rest and the grinding wheel on a bench grinding machine is …
- 6 mm.
- 4 mm.
- 5 mm.
- 3 mm. (1)
4.13 Which ONE of the following is a factor to be considered when selecting the cutting speed of a drill bit?
- The use of cutting fluid
- Type of material
- Cutting angle
- Spindle size (1)
4.14 Calculate the value of X as indicated in FIGURE 4.14 below. 
FIGURE 4.14
- 7 cm
- 5 cm
- 6 cm
- 25 cm (1) [14]
QUESTION 5: TERMINOLOGY (TEMPLATES) (SPECIFIC)
5.1 Give TWO reasons why the template loft is separated from the workshop in most cases. (2)
5.2 Describe the purpose of purlins as used on roof trusses. (2)
5.3 A steel ring with an outside diameter of 880 mm must be fabricated from a 50 x 50 mm square steel bar.
5.3.1 Calculate the dimensions of the required material. (7)
5.3.2 Make a neat sketch of the steel ring indicating the mean diameter, outside diameter and the thickness of the material. (4)
5.4 Identify the following resistance weld symbols: 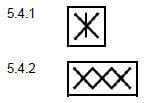 (1)
(1)
5.5 FIGURE 5.5 below shows a welding symbol. Label parts A–F on the welding symbol. 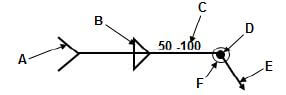
FIGURE 5.5 (6) [23]
QUESTION 6: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
6.1 Briefly describe the working principle of the following machines used in the welding workshop:
6.1.1 Guillotine (4)
6.1.2 Bending rolls (4)
6.2 What is the primary function of the regulators fitted to the gas cylinders of the oxy-acetylene equipment? (3)
6.3 What is the press machine used for in the mechanical workshop? (3)
6.4 FIGURE 6.4 below shows the MIG/MAGS welding process. Label A–D.
FIGURE 6.4 (4) [18]
QUESTION 7: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
7.1 Determine graphically (Bow's notation) the magnitude and nature of ALL the members of the framework in FIGURE 7.1 below.
SCALE: Vector diagram 1 mm = 5 N 
FIGURE 7.1 (20)
7.2 FIGURE 7.2 below shows a simply supported beam that is subjected to THREE point loads. 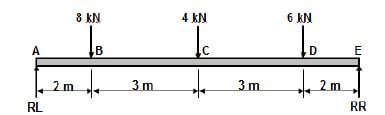
FIGURE 7.2
7.2.1 Calculate the reactions at the supports RL and RR. (8)
7.2.2 Calculate the bending moments at points A, B, C, D and E. (5)
7.2.3 Draw a bending moment diagram of the beam. SCALE: 2 mm = 1 kN.m (moments) and 1 : 100 (distances) (5)
7.3 Calculate the load that needs to be applied to a round stainless steel bar to cause a tensile stress of 80 MPa in the material. The diameter of the bar is 20 mm. (7) [45]
QUESTION 8: JOINING METHODS (WELD INSPECTION) (SPECIFIC)
8.1 Name TWO factors that should be taken into account during oxy-acetylene welding to ensure high quality welding. (2)
8.2 What does the abbreviation HAZ stand for with regard to welded joints? (1)
8.3 State TWO causes of EACH of the following arc-welding defects:
8.3.1 Spatter (2)
8.3.2 Undercutting (2)
8.3.3 Incomplete penetration (2)
8.4 State TWO methods to reduce EACH of the following types of cracks during arc-welding:
8.4.1 Transverse cracks (2)
8.4.2 Centre-line cracks (2)
8.5 Explain the difference between a non-destructive test and a destructive test that are conducted on welded joints. (2)
8.6 What type of welding defect occurs when conducting an ultrasonic test on a welded joint? (2)
8.7 Name TWO internal defects that may be detected when conducting a nick break test on a welded joint. (2)
8.8 Explain why a machinability test is conducted on a welded joint. (2)
8.9 State TWO visual requirements for an acceptable weld. (2) [23]
QUESTION 9: JOINING METHODS (STRESSES AND DISTORTION) (SPECIFIC)
9.1 What is residual stress? (2)
9.2 State TWO factors that affect the grain size of cold-worked metals. (2)
9.3 Name TWO quenching media used during the heat treatment of steel. (2)
9.4 Define distortion of the metal that takes place during the welding process. (4)
9.5 Describe TWO factors that affect distortion and residual stress in welding. (4)
9.6 Explain the result when metal is cooled rapidly. Refer to the internal and external areas of the metal. (4) [18]
QUESTION 10: MAINTENANCE (SPECIFIC)
10.1 Give TWO reasons for the maintenance of machines in the welding workshop. (2)
10.2 Give the reason why one applies lock-out on machines during maintenance. (2)
10.3 Give TWO reasons why it is important to keep service records of the machines. (2)
10.4 Name TWO methods to reduce friction when drilling holes. (2) [8]
QUESTION 11: TERMINOLOGY (DEVELOPMENT) (SPECIFIC)
11.1 Describe the function of transformers used in ventilation ducts. (3)
11.2 Use freehand sketches to indicate the difference between an on-centred hopper and an off-centred hopper. (2)
11.3 FIGURE 11.3 below shows a truncated cone. 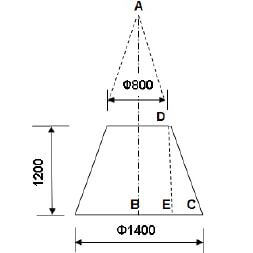
FIGURE 11.3
Calculate the following:
11.3.1 Base circumference (3)
11.3.2 Main radius (AC) (10)
11.3.3 Small radius (AD) (3) [21]
TOTAL: 200
FORMULA SHEET FOR MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY (WELDING AND METALWORK) 
MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY: FITTING AND MACHINING GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY: FITTING AND MACHINING
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your centre number and examination number in the spaces provided on the ANSWER BOOK.
- Read ALL the questions carefully.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Show ALL calculations and units. Round off final answers to TWO decimal places.
- Candidates may use non-programmable scientific calculators and drawing instruments.
- The value of gravitational acceleration should be taken as 10 m/s2.
- All dimensions are in millimetres, unless stated otherwise in the question.
- Write neatly and legibly.
- A formula sheet is attached to the question paper.
- Use the criteria below to assist you in managing your time.
QUESTION | CONTENT | MARKS | TIME in minutes |
GENERIC | |||
1 | Multiple-choice questions | 6 | 6 |
2 | Safety | 10 | 10 |
3 | Materials | 14 | 14 |
SPECIFIC | |||
4 | Multiple-choice questions | 14 | 10 |
5 | Terminology (Lathe and Milling Machine) | 18 | 20 |
6 | Terminology (Indexing) | 28 | 25 |
7 | Tools and Equipment | 13 | 10 |
8 | Forces | 33 | 33 |
9 | Maintenance | 18 | 12 |
10 | Joining Methods | 18 | 12 |
11 | Systems and Control (Drive Systems) | 28 | 28 |
TOTAL | 200 | 180 | |
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (GENERIC)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1 to 1.6) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.7 E.
1.1 What is the purpose of the Occupational Health and Safety Act, 1993 (Act 85 of 1993) with regard to HIV/Aids awareness?
- The Act on safety states that all employers must make sure that the workplace is safe and that employees are not at risk of becoming infected with HIV at work.
- The Act contains common guidelines on how employers, employees and trade unions should respond to HIV in the workplace.
- Employers may not demote or promote an employee based on his/her HIV status.
- Employers cannot simply dismiss a person who has HIV. (1)
1.2 Which ONE of the following items of personal protective equipment (PPE) is applicable when arc welding is performed on a work piece?
- Hard hat
- Welding goggles
- Welding helmet
- Face shield (1)
1.3 Who is responsible for the provision of safety equipment in the workplace?
- Employer
- Employee
- Customer
- Foreman (1)
1.4 Which ONE of the following properties of solid steel will change if the steel is subjected to a heat treatment process?
- Length
- Hardness
- Size
- Shape (1)
1.5 The purpose of normalising steel is to …
- harden.
- temper.
- harden the core.
- relieve internal stresses. (1)
1.6 If a sound test is applied to high-carbon steel, which ONE of the following sounds will help one to identify the metal?
- Loud and clear sound
- Dull sound
- Soft ringing sound
- Low ringing sound (1) [6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 An angle grinder is used to smoothen a welded joint. State TWO safety measures that must be observed before using the angle grinder. (2)
2.2 Give TWO reasons why it is important to wear welding goggles during oxy-acetylene gas welding. (2)
2.3 Name TWO items of personal protective equipment (PPE) that one will use when working with a hydraulic press. (2)
2.4 Name TWO types of workshop layouts. (2)
2.5 Name TWO responsibilities of the employer when applying first aid in the workplace. (2) [10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1 Name ONE property of steel that is tested by conducting a bending test on steel. (2)
3.2 Give TWO reasons for conducting EACH of the following heat-treatment processes on steel:
3.2.1 Annealing (2)
3.2.2 Case hardening (2)
3.3 Explain why the tempering of steel is done after the hardening process. (2)
3.4 State the THREE factors that must be considered during all heat-treatment processes. (3)
3.5 Explain the hardening process of steel. (3) [14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (SPECIFIC)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (4.1 to 4.14) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 4.15 E.
4.1 Which ONE of the following is an advantage of the compound slide set-over method for taper turning on the centre lathe?
- Long tapers can be cut.
- Only internal tapers can be cut.
- Tapers with large angles can be cut.
- Good finishing is obtained. (1)
4.2 Identify the milling process in FIGURE 4.2 below.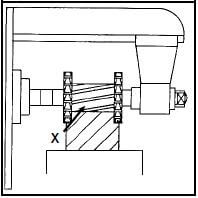
FIGURE 4.2
- Gang milling
- Slab milling
- Slot milling
- Straddle milling (1)
4.3 Which indexing process uses change gears to do indexing?
- Rapid indexing
- Simple indexing
- Angular indexing
- Differential indexing (1)
4.4 What is meant by the term incremental programming on a three-axis digital read-out system?
The point of reference is taken from …
- the previous point.
- the zero point.
- a common point.
- any point. (1)
4.5 If the addendum of a spur gear is 3 mm, what will be the module?
- 6
- 3
- 1,5
- 9 (1)
4.6 Which ONE of the following statements describes the function of a force tester?
- To illustrate the concept of the triangle of forces
- To determine the reactions on either side of a loaded beam
- To illustrate the concept of the friction forces
- To determine the reaction on one side of a loaded beam (1)
4.7 What is the measure unit for stress?
- Newton
- Pascal
- No unit
- Newton per metre (1)
4.8 Which ONE of the following represents the same value as 1 Pa?
- 1 Pa = 1N/m3
- 1 Pa = 1N/m2
- 1 Pa = 1kg/m2
- 1 Pa = 1N.m (1)
4.9 Which ONE of the following materials is classified as a thermoplastic composite?
- Bakelite
- Fibreglass
- Carbon fibre
- Vesconite (1)
4.10 The friction coefficient will … when lubricant is added between two surfaces.
- increase
- be eliminated
- decrease
- have no effect (1)
4.11 Which ONE of the following is an advantage of multiple-start screw threads?
- More locking power
- Produce faster movement
- Produce slower movement
- Use more power due to friction (1)
4.12 Which clearance angle is normally used, unless stated otherwise, to calculate the leading and following tool angles of a square-thread cutting tool?
- 90°
- 45°
- 5°
- 3° (1)
4.13 Which ONE of the following is an advantage of a gear drive system over a belt drive system?
- Drive can take place over a longer distance.
- Less expensive parts are used.
- No lubrication is needed.
- Transmission of power without slip is possible. (1)
4.14 Which ONE of the following symbols is used to indicate a pump in a hydraulic flow diagram?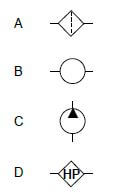 (1) [14]
(1) [14]
QUESTION 5: TERMINOLOGY (LATHE AND MILLING MACHINE) (SPECIFIC)
5.1 State TWO advantages of using the tailstock set-over method to cut an external taper on the centre lathe. (2)
5.2 An 85 mm long external taper, with a large diameter of 60 mm and a small diameter of 28 mm, needs to be cut on a centre lathe. Calculate the angle at which the compound slide must be set to cut this taper. (5)
5.3 State TWO uses of the centre gauge when cutting screw thread on a centre lathe. (2)
5.4 Calculate the length of a parallel key suitable for a 42 mm diameter shaft. (3)
5.5 State TWO advantages of up-cut milling. (2)
5.6 State TWO disadvantages of down-cut milling. (2)
5.7 State TWO methods of centring a milling cutter to the axis of a work piece. (2) [18]
QUESTION 6: TERMINOLOGY (INDEXING) (SPECIFIC)
6.1 A spur gear with 50 teeth has a module of 3. Calculate the cordal tooth thickness of the gear teeth. (4)
6.2 Calculate the required simple indexing to cut a gear with 13 teeth. (4)
6.3 A gear with 127 teeth must be cut on a universal milling machine, using a 40 : 1 Cincinnati-dividing head. Calculate the following:
6.3.1 The differential indexing required (Choose 125 teeth.) (3)
6.3.2 The change gears required (5)
6.3.3 The direction of rotation of the index plate in relation to the index crank handle. (1)
6.4 FIGURE 6.4 below shows a dovetail groove. Calculate distance X between the rollers in FIGURE 6.4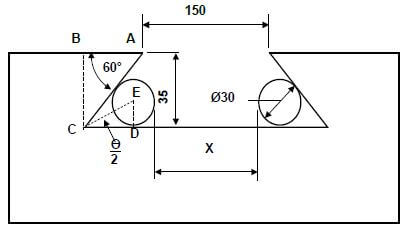
FIGURE 6.4 (9)
6.5 Give TWO reasons why a work piece must be balanced on a centre lathe when a face plate is used. (2) [28]
QUESTION 7: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
7.1 Name the TWO hardness testers that are used to determine the hardness of a metal. (2)
7.2 State the purpose of a moment tester. (2)
7.3 Describe the tensile test applied on steel. (3)
7.4 What is the reading on the depth micrometer, as shown in FIGURE 7.4 below?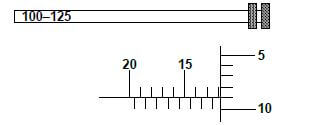
FIGURE 7.4 (5)
7.5 A depth micrometer can accurately measure the depth of a hole. Name another precision measuring tool that can also measure the depth of a hole accurately. (1) [13]
QUESTION 8: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
8.1 FIGURE 8.1 below shows a system of forces with four coplanar forces acting on the same point. Calculate the magnitude and direction of the equilibrant of this system of forces. 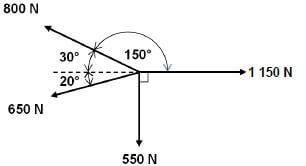
FIGURE 8.1 (15)
8.2 The diagram in FIGURE 8.2 below shows a beam with two vertical point loads of 2 800 N and 700 N acting on it. The beam is supported at point O. Calculate distance X from O to place the 700 N load to ensure that the beam is in equilibrium.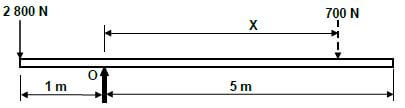
FIGURE 8.2 (4)
8.3 A mild steel bush, 80 mm long, with an inner diameter of 30 mm and an outside diameter of 40 mm, is used in a hydraulic press to press out bearings from a hub. A force of 50 kN is exerted on the bush.
8.3.1 State the type of stress in the steel bush. (1)
8.3.2 Calculate the stress in the material. Give your answer in megamagnitude. (5)
8.3.3 Calculate the change in length caused by the force if Young's modulus E = 90 GPa. (5)
8.3.4 Calculate the safe working stress if the break stress of the material is 600 MPa and a safety factor of 4 is used. (3) [33]
QUESTION 9: MAINTENANCE (SPECIFIC)
9.1 State THREE results of a lack of preventative maintenance on mechanical systems. (3)
9.2 State TWO causes of the malfunctioning of chain drive systems. (2)
9.3 State TWO procedures to reduce wear on a belt drive system. (2)
9.4 Explain the procedure to replace the belt on a flat belt drive system. (5)
9.5 State ONE property of EACH of the following materials:
9.5.1 Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) (1)
9.5.2 Carbon fibre (1)
9.6 State the main difference between thermoplastic composites and thermo hardened (thermosetting) composites. (2)
9.7 Give TWO examples of thermo-hardened composites. (2) [18]
QUESTION 10: JOINING METHODS (SPECIFIC)
10.1 A two-start square thread with a 5 mm pitch must be cut on a lathe. The crest diameter of the thread is 82 mm and the clearance angle 3°.
Calculate the following:
10.1.1 The lead of the thread (2)
10.1.2 The helix angle of the thread (5)
10.1.3 The leading tool angle (2)
10.1.4 The following tool angle (2)
10.2 The measurement of a screw thread is given as M24 x 2,5. What does the following mean:
10.2.1 M (1)
10.2.2 24 (1)
10.2.3 2,5 (1)
10.3 FIGURE 10.3 below shows a left-hand square screw thread cutting tool. Label angles A–D.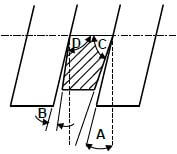
FIGURE 10.3 (4)[18]
QUESTION 11: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL (DRIVE SYSTEMS) (SPECIFIC)
11.1 State TWO advantages of a belt drive system compared to a chain drive system. (2)
11.2 Study FIGURE 11.2 below. An artisan was instructed to design a hydraulic system that will be used to press out bearings. The force that should be exerted on the bearing is 18 kN. The maximum force exerted on the 32 mm plunger is 120 N.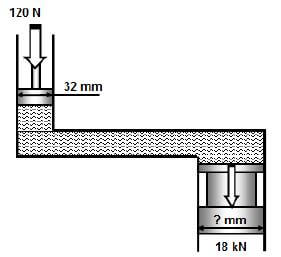
FIGURE 11.2
Calculating the following:
11.2.1 The fluid pressure in the hydraulic system (4)
11.2.2 The diameter of the ram so that the maximum force of 18 kN can be exerted on the bearing. (6)
11.3 Draw the symbol for a one-way spring-loaded valve used in a hydraulic flow diagram. (1)
11.4 The driven pulley of a belt drive system must rotate at a speed of 80 r/min. The driven pulley has a diameter of 240 mm and the driver pulley a diameter of 75 mm. Calculate the rotation frequency of the driver pulley in r/min. (4)
11.5 Study FIGURE 11.5 below. The gear box of a motor vehicle is in second gear. The input shaft rotates at 3 000 r/min. The input shaft is equipped with driver gear A with 20 teeth, which mesh with gear B with 35 teeth. The second acceleration gear C on the countershaft has 25 teeth and meshes with the final driven gear D with 30 teeth.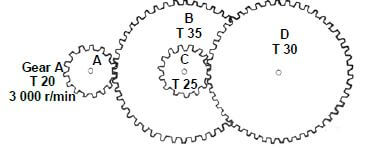
FIGURE 11.5
Calculate:
11.5.1 The rotation frequency of the output shaft in revolutions per second (6)
11.5.2 The gear ratio (3)
11.6 A force of 250 N moves an object over a distance of 15 m. Calculate the work done by this force. (2) [28]
TOTAL: 200
FORMULA SHEET FOR MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY (FITTING AND MACHINING)

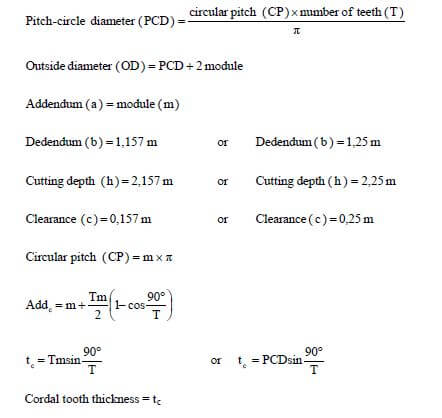

MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY: AUTOMOTIVE GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY: AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your centre number and examination number in the spaces provided on the ANSWER BOOK.
- Read ALL the questions carefully.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Show ALL calculations and units. Round off final answers to TWO decimal places.
- Candidates may use non-programmable scientific calculators and drawing instruments.
- The value of gravitational acceleration should be taken as 10 m/s2.
- All dimensions are in millimetres, unless stated otherwise in the question.
- Write neatly and legibly.
- A formula sheet is attached to the question paper.
- Use the criteria below to assist you in managing your time.
QUESTION | CONTENT | MARKS | TIME in minutes |
GENERIC | |||
1 | Multiple-choice questions | 6 | 6 |
2 | Safety | 10 | 10 |
3 | Materials | 14 | 14 |
SPECIFIC | |||
4 | Multiple-choice questions | 14 | 10 |
5 | Tools and Equipment | 23 | 20 |
6 | Engines | 28 | 25 |
7 | Forces | 32 | 25 |
8 | Maintenance | 23 | 20 |
9 | Systems and Control (Automatic Gearbox) | 18 | 20 |
10 | Systems and Control (Axles, Steering Geometry and Electronics) | 32 | 30 |
TOTAL | 200 | 180 | |
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (GENERIC)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1 to 1.6) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.7 E.
1.1 What is the purpose of the Occupational Health and Safety Act, 1993 (Act 85 of 1993) with regard to HIV/Aids awareness?
- The Act on safety states that all employers must make sure that the workplace is safe and that employees are not at risk of becoming infected with HIV at work.
- The Act contains common guidelines on how employers, employees and trade unions should respond to HIV in the workplace.
- Employers may not demote or promote an employee based on his/her HIV status.
- Employers cannot simply dismiss a person who has HIV. (1)
1.2 Which ONE of the following items of personal protective equipment (PPE) is applicable when arc welding is performed on a work piece?
- Hard hat
- Welding goggles
- Welding helmet
- Face shield (1)
1.3 Who is responsible for the provision of safety equipment in the workplace?
- Employer
- Employee
- Customer
- Foreman (1)
1.4 Which ONE of the following properties of solid steel will change if the steel is subjected to a heat treatment process?
- Length
- Hardness
- Size
- Shape (1)
1.5 The purpose of normalising steel is to …
- harden.
- temper.
- harden the core.
- relieve internal stresses. (1)
1.6 If a sound test is applied to high-carbon steel, which ONE of the following sounds will help one to identify the metal?
- Loud and clear sound
- Dull sound
- Soft ringing sound
- Low ringing sound (1) [6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 An angle grinder is used to smoothen a welded joint. State TWO safety measures that must be observed before using the angle grinder. (2)
2.2 Give TWO reasons why it is important to wear welding goggles during oxy-acetylene gas welding. (2)
2.3 Name TWO items of personal protective equipment (PPE) that one will use when working with a hydraulic press. (2)
2.4 Name TWO types of workshop layouts. (2)
2.5 Name TWO responsibilities of the employer when applying first aid in the workplace. (2) [10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1 Name ONE property of steel that is tested by conducting a bending test on steel. (2)
3.2 Give TWO reasons for conducting EACH of the following heat-treatment processes on steel:
3.2.1 Annealing (2)
3.2.2 Case hardening (2)
3.3 Explain why the tempering of steel is done after the hardening process. (2)
3.4 State the THREE factors that must be considered during all heat-treatment processes. (3)
3.5 Explain the hardening process of steel. (3) [14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (SPECIFIC)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (4.1 to 4.14) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 4.15 E.
4.1 Which ONE of the following pieces of equipment is used to set the wheel alignment of a motor vehicle?
- Pressure tester
- Torsion tester
- Bubble gauge
- Wheel gauge (1)
4.2 What is the purpose of a wheel balancer? To balance …
- the angles of a motor vehicle
- the wheels for static and dynamic balance
- the steering control for better road grip
- engine torque delivered to the wheels (1)
4.3 Identify the type of supercharger shown in FIGURE 4.3 below. 
FIGURE 4.3
- Twin screw supercharger
- Roots supercharger
- Centrifugal supercharger
- Vane type supercharger (1)
4.4 What is the purpose of a vibration damper on the engine of a motor vehicle?
- To check whether the valve lifter is resting on the cam
- To obtain static balance of the crankshaft
- To balance the crank arms and pistons
- To counteract the torsional vibrations of the crankshaft (1)
4.5 The power of an engine may be defined as …
- the rate of doing work within a certain time slot.
- a force that overcomes resistance and causes movement.
- the twisting effect transmitted by a rotating shaft.
- the measure to determine the force developed by burning fuel in a cylinder. (1)
4.6 What will be the brake power of an engine if the engine develops torque of 180 N.m at 3 000 r/min?
- 0,56 kW
- 5,65 kW
- 56,55 kW
- 6,67 kW (1)
4.7 The relationship between the total volume of a cylinder when the piston is at bottom dead centre to the combustion chamber volume in the cylinder is known as the …
- compression ratio.
- clearance volume.
- swept volume.
- clearance ratio. (1)
4.8 Which device controls the modern electronic automatic transmission of a vehicle?
- Electronic control unit
- Automatic transmission unit
- Electronic automatic transmission
- Transmission control unit (1)
4.9 What is the effect of the gear ratio on the road speed of a motor vehicle?
- A lower gear ratio decreases the road speed.
- A higher gear ratio decreases the road speed.
- A higher gear ratio increases the road speed.
- A lower gear ratio increases the road speed. (1)
4.10 What type of gear train is shown in FIGURE 4.10 below? 
FIGURE 4.10
- Epicyclic gear train
- Ring gear train
- Circular gear train
- Helical gear train (1)
4.11 What is the effect of a large positive caster angle on the wheels of a vehicle?
- The pressure increases.
- The pressure decreases.
- The wheels will stop rotating.
- The wheels will wobble. (1)
4.12 What is the definition of static balance of a wheel and tyre assembly? … around the axis of rotation in the rotation plane.
- Equal distribution of less weight
- Unequal distribution of little weight
- Unequal distribution of all weight
- Equal distribution of all weight (1)
4.13 Which exhaust emission control device is used to convert toxic gases and pollutants to less toxic gases from the exhaust gases of an internal combustion engine?
- Catalytic converter
- Toxic converter
- Exhaust converter
- Pollution converter (1)
4.14 Which ONE of the following safety measures must be taken into consideration when testing or repairing an alternator?
- Always connect the positive and negative cables of the tester to the relevant poles of the battery.
- Let the alternator run in an open circuit.
- Make sure that all battery cables are connected to the alternator.
- Connect the battery and alternator before arc welding is done on the motor vehicle. (1) [14]
QUESTION 5: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
5.1 FIGURE 5.1 below shows equipment that is used in the automotive workshop. Answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 5.1
5.1.1 Identify the equipment in FIGURE 5.1. (1)
5.1.2 Label parts A–D. (4)
5.1.3 Describe the purpose of the equipment. (2)
5.2 What is the function of the cylinder leakage tester? (2)
5.3 A gas analyser is used to analyse the exhaust gases of a motor vehicle. Give ONE reason why it is important to make sure that there are no leakages in the exhaust pipe. (2)
5.4 State ONE function of a computerised diagnostic scanner. (1)
5.5 Explain the procedure to follow when checking the camber using a bubble gauge. (4)
5.6 Name THREE faults that can be established when performing dynamic wheel balancing. (3)
5.7 What is the purpose of the turn-tables used to adjust the wheel alignment on a motor vehicle? (4) [23]
QUESTION 6: ENGINES (SPECIFIC)
6.1 What you understand by static balancing of a crankshaft? (2) 6.2 Identify the cylinder layouts as illustrated in FIGURES 6.2.1 and 6.2.2 below.
6.2.1 (1) 
FIGURE 6.2.1
6.2.2 (1) 
FIGURE 6.2.2
6.3 Explain how you will determine the firing order of a four-cylinder petrol engine if it is not marked on the crankshaft pulley and the manual is not available. (5)
6.4 State the firing order of the following types of engines:
6.4.1 Four-cylinder in-line engine (1)
6.4.2 V6-cylinder engine (1)
6.5 A turbocharger is shown in FIGURE 6.5 below. Answer the questions that follow. 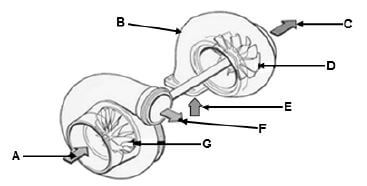
FIGURE 6.5
6.5.1 Label parts A–G. (7)
6.5.2 State TWO advantages of the turbocharger. (2)
6.6 Explain the following terms:
6.6.1 Boost (2) 6.6.2 Turbo lag (2)
6.7 What is the purpose of the waste gate in the turbocharger? (2)
6.8 What is the purpose of an oil cooler fitted to a turbocharged engine? (2) [28]
QUESTION 7: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
7.1 Define the term torque. (2)
7.2 What is meant by the term clearance volume of an engine? (2)
7.3 State TWO methods to increase the compression ratio of an internal combustion engine. (2)
7.4 The bore and stroke of an engine are 75 mm and 80 mm respectively. It has a compression ratio of 8,5 : 1.
Calculate:
7.4.1 The swept volume in cm3 (3)
7.4.2 The original clearance volume in cm3 (3)
7.4.3 The engine has been rebored to 78 mm. What will be the new compression ratio if the clearance volume remains unchanged? (6)
7.5 The following data was recorded during a test carried out on a four-stroke four-cylinder petrol engine:
Mean effective pressure: 1 400 kPa
Stroke: 110 mm
Bore diameter: 100 mm
Engine revolutions: 3 600 r/min
Brake arm length: 450 mm
Scale reading: 75 kg
Calculate:
7.5.1 Indicated power in kW (8)
7.5.2 Brake power in kW (4)
7.5.3 Mechanical efficiency (2) [32]
QUESTION 8: MAINTENANCE (SPECIFIC)
8.1 Which gases are analysed with a gas analyser? (1)
8.2 State THREE manufacturer's specifications that must be obtained for a specific engine when conducting a gas analysing test. (3)
8.3 State TWO possible results observed when a cylinder leakage test is conducted on an internal combustion engine. (2)
8.4 State TWO causes of cylinder leakages that can be determined when conducting a cylinder leakage test on an internal combustion engine. (2)
8.5 Explain the procedures to be followed when conducting a compression test on an internal combustion engine. (6)
8.6 Give TWO reasons for low oil pressure in an internal combustion engine. (2)
8.7 Explain in point form how you conduct a cooling system pressure test. (7) [23]
QUESTION 9: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL (AUTOMATIC GEARBOX) (SPECIFIC)
9.1 State TWO main differences between an automatic gearbox and a manual gearbox. (2)
9.2 State TWO advantages of an automatic gearbox. (2)
9.3 FIGURE 9.3 below shows a torque converter used in an automatic transmission. Answer the questions that follow. 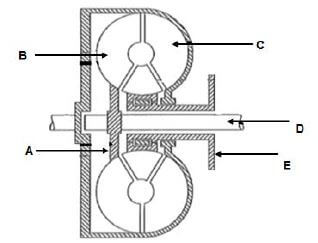
FIGURE 9.3
9.3.1 State TWO functions of a torque converter. (2)
9.3.2 Label parts A–E of the torque converter. (5)
9.4 State FIVE different gear drives that can be obtained with the help of a single epicyclic gear train. (5)
9.5 What is the purpose of gear ratios in the gearbox of a motor vehicle? (2) [18]
QUESTION 10: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL (AXLES, STEERING GEOMETRY AND ELECTRONICS) (SPECIFIC)
10.1 State FIVE factors that need to be taken into account before any wheel alignment adjustments can be done. (5)
10.2 FIGURE 10.2 below shows a wheel alignment angle. Answer the questions that follow. 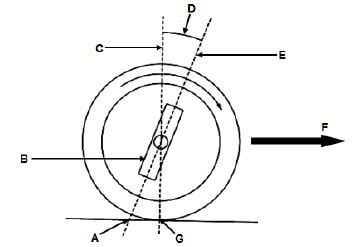
FIGURE 10.2
10.2.1 Identify the wheel alignment drawing in FIGURE 10.2. (2)
10.2.2 Label A–G. (7)
10.2.3 Define the wheel alignment angle, as indicated in FIGURE 10.2. (3)
10.3 Use a labelled sketch to show toe-out of the front wheels of a vehicle. (3)
10.4 State the purpose of kingpin inclination. (2)
10.5 State TWO chemical processes on which the operating principle of the catalytic converter is based. (1)
10.6 Describe the purpose of the speed-control system fitted to a motor vehicle. (2)
10.7 State TWO advantages of the speed-control system fitted to a motor vehicle. (2)
10.8 What is the purpose of the pressure regulator in the fuel system of a motor vehicle? (1)
10.9 State TWO methods to increase the output frequency of an alternator to increase the current output. (2)
10.10 State ONE function of the stator and stator windings in an alternator. (1)
10.11 State the function of the rotor assembly in an alternator. (1) [32]
TOTAL: 200
FORMULA SHEET FOR MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY (AUTOMOTIVE) 
MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 ANNEXURE A WELDING - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
ANNEXURE A : WELDING
Question 7.1
The CM need to redraw to check the scale and to photocopy it to a transparency.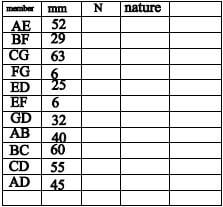
Question 7.2.3
PHYSICAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
PHYSICAL SCIENCES
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your examination number and centre number in the appropriate spaces on the ANSWER BOOK.
- This question paper consists of 11 questions. Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Leave ONE line between two subquestions, e.g. between QUESTION 2.1 and QUESTION 2.2.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- You may use appropriate mathematical instruments.
- Show ALL formulae and substitutions in ALL calculations.
- Round off your FINAL numerical answers to a minimum of TWO decimal places.
- Give brief motivations, discussions, etc. where required.
- You are advised to use the attached DATA SHEETS.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A-D) next to the question numbers (1.1 to 1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.11 D.
1.1 Inertia is the tendency of an object to …
- maintain its mass.
- continue in a state of non-uniform motion.
- remain at rest or in the state of uniform motion.
- maintain its velocity when a non-zero net force is acting on it. (2)
1.2 A person stands on a bathroom scale that is fixed to the floor of a lift, as shown in the diagram below.
The reading on the scale is largest when the lift moves …
- upwards at a constant speed.
- downwards at a constant speed.
- upwards at a increasing speed.
- downwards at a increasing speed. (2)
1.3 An object is projected vertically upwards. Ignore air resistance.
As the object rises, its velocity …
- and acceleration are both directed upwards.
- and acceleration are both directed downwards.
- is directed upwards, but its acceleration is directed downwards.
- is directed downwards, but its acceleration is directed upwards. (2)
1.4 Ball P and ball Q, of the same mass, are dropped onto a concrete floor. Both balls hit the concrete floor at the same speed, v. Ball P rebounds with the same vertical speed, v, but ball Q rebounds with speed ½v.
Refer to the diagram below. Ignore air resistance.
Which ONE of the following statements regarding the collision of EACH ball with the concrete floor is CORRECT?
- Kinetic energy is conserved for both balls P and Q.
- The change in momentum of ball P is greater than that of ball Q.
- The contact time with the floor is the same for both balls P and Q.
- Momentum is conserved for the collision of ball P, but not for that of ball Q. (2)
1.5 If the net work done on a moving object is POSITIVE, then we can conclude that the kinetic energy of the object …
- is zero.
- has increased.
- has decreased.
- has not changed. (2)
1.6 The spectrum produced by a moving asteroid, as observed from Earth, indicates that the light has shifted towards the blue end of the spectrum.
Which ONE of the following frequency combinations of the observed light and the distance between the asteroid and Earth is CORRECT? (2)
| FREQUENCY OF OBSERVED LIGHT | DISTANCE BETWEEN ASTEROID AND EARTH | |
| A | Increased | Decreases |
| B | Increased | Increases |
| C | Decreased | Decreases |
| D | Decreased | Increases |
1.7 Three charged spheres X, Y and Z, supported by insulating threads of equal length, hang from a beam, as shown in the diagram below.
Sphere X is negatively charged.
Sphere X attracts sphere Y, but repels sphere Z.
Which ONE of the following conclusions is CORRECT?
- Sphere Y is positively charged and sphere Z is negatively charged.
- Sphere Y is positively charged and sphere Z is positively charged.
- Sphere Y is negatively charged and sphere Z is negatively charged.
- Sphere Y is negatively charged and sphere Z is positively charged. (2)
1.8 In the circuit diagrams below, the cells and resistors are identical. The cells have negligible internal resistances.
The power dissipated in resistor X is P. The power dissipated in resistor Y is …
- ¼P.
- ½P.
- 2P.
- 4P. (2)
1.9 Which ONE of the following actions will NOT cause an increase in the induced emf in a coil if the coil is rotated in a uniform magnetic field?
- Rotating the coil faster
- Increasing the strength of the magnetic field
- Increasing the number of turns of the coil
- Replacing the coil with a coil of lower resistance (2)
1.10 A learner writes the following statements about the emission spectrum of light in a notebook:
- An emission spectrum is formed when certain frequencies of electromagnetic radiation pass through a cold gas.
- The lines in the emission spectrum of an atom have the same frequency as the corresponding lines in the atom's absorption spectrum.
- An emission spectrum is formed when the atom makes transitions from a high-energy state to a lower energy state.
Which ONE of the following combinations of the statements above is CORRECT?
- (i) only
- (ii) only
- (ii) and (iii) only
- (i) and (iii) only (2) [20]
QUESTION 2 (Start on a new page.)
A block, of mass 8 kg, is placed on a rough horizontal surface. The 8 kg block, which is connected to a 2 kg block by means of a light inextensible string passing over a light frictionless pulley, starts sliding from point A, as shown below.
2.1 State Newton's Second Law in words. (2)
2.2 Draw a labelled free-body diagram for the 8 kg block. (4)
2.3 When the 8 kg block reaches point B, the angle between the string and the horizontal is 15° and the acceleration of the system is 1,32 m·s-2.
2.3.1 Give a reason why the system is NOT in equilibrium. (1)
2.3.2 Use the 2 kg mass to calculate the tension in the string. (3)
2.3.3 Calculate the kinetic frictional force between the 8 kg block and the horizontal surface. (4)
2.4 As the 8 kg block moves from B to C, the kinetic frictional force between the 8 kg block and the horizontal surface is not constant. Give a reason for this statement. (1)
The horizontal surface on which the 8 kg block is moving, is replaced by another horizontal surface made from a different material.
2.5 Will the kinetic frictional force, calculated in QUESTION 2.3.3 above, change?Choose from: YES or NO. Give a reason for the answer. (2) [17]
QUESTION 3 (Start on a new page.)
In a competition, participants must attempt to throw a ball vertically upwards past point T, marked on a tall vertical pole. Point T is 3,7 m above the ground. Point T may, or may not, be the highest point during the motion of the ball.
One participant throws the ball vertically upwards at a velocity of 7,5 ms-1 from a point that is 1,6 m above the ground, as shown in the diagram below. Ignore the effects of air resistance.
3.1 In which direction is the net force acting on the ball while it moves towards point T? Choose from: UPWARDS or DOWNWARDS. Give a reason for the answer. (2)
3.2 Calculate the time taken by the ball to reach its highest point. (3)
3.3 Determine, by means of a calculation, whether the ball will pass point T or not. (6)
3.4 Draw a velocity-time graph for the motion of the ball from the instant it is thrown upwards until it reaches its highest point.
Indicate the following on the graph:
- The initial velocity and final velocity
- Time taken to reach the highest point (2) [13]
QUESTION 4 (Start on a new page.)
Initially a girl on roller skates is at rest on a smooth horizontal pavement. The girl throws a parcel, of mass 8 kg, horizontally to the right at a speed of 4 m.s-1. Immediately after the parcel has been thrown, the girl-roller-skate combination moves at a speed of 0,6 m.s-1. Ignore the effects of friction and rotation.
4.1 Define the term momentum in words. (2)
4.2 Will the girl-roller-skate combination move TO THE RIGHT or TO THE LEFT after the parcel is thrown? NAME the law in physics that can be used to explain your choice of direction. (2)
The total mass of the roller skates is 2 kg.
4.3 Calculate the mass of the girl. (5)
4.4 Calculate the magnitude of the impulse that the girl-roller-skate combination is experiencing while the parcel is being thrown. (3)
4.5 Without any further calculation, write down the change in momentum experienced by the parcel while it is being thrown. (2) [14]
QUESTION 5 (Start on a new page.)
The diagram below, not drawn to scale, shows a vehicle with a mass of 1 500 kg starting from rest at point A at the bottom of a rough incline. Point B is 200 m vertically above the horizontal.
The total work done by force F that moves the vehicle from point A to point B in 90 s is 4,80 x 106 J.
5.1 Define the term non-conservative force. (2)
5.2 Is force F a conservative force? Choose from: YES or NO. (1)
5.3 Calculate the average power generated by force F. (3)
The speed of the vehicle when it reaches point B is 25 m∙s-1.
5.4 State the work-energy theorem in words. (2)
5.5 Use energy principles to calculate the total work done on the vehicle by the frictional forces. (5) [13]
QUESTION 6 (Start on a new page.)
The alarm of a vehicle parked next to a straight horizontal road goes off, emitting sound with a wavelength of 0,34 m. A patrol car is moving at a constant speed on the same road. The driver of the patrol car hears a sound with a frequency of 50 Hz lower than the sound emitted by the alarm. Take the speed of sound in air as 340 m∙s-1.
6.1 State the Doppler effect in words. (2)
6.2 Is the patrol car driving TOWARDS or AWAY FROM the parked vehicle? Give a reason for the answer. (2)
6.3 Calculate the frequency of the sound emitted by the alarm. (3)
6.4 The patrol car moves a distance of x metres in 10 seconds. Calculate the distance x. (6) [13]
QUESTION 7 (Start on a new page.)
Three small identical metal spheres, P, S and T, on insulated stands, are initially neutral. They are then charged to carry charges of -15 x 10-9 C, Q and +2 x 10-9 C respectively, as shown below.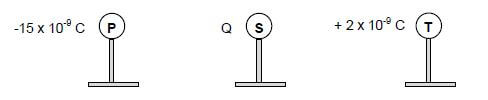
The charged spheres are brought together so that all three spheres touch each other at the same time, and are then separated. The charge on each sphere, after separation, is -3 x 10-9 C.
7.1 Determine the value of charge Q. (2)
7.2 Draw the electric field pattern associated with the charged spheres, S and T, after they are separated and returned to their original positions. (3)
The spheres, each with the new charge of -3 x 10-9 C, are now placed at points on the x-axis and the y-axis, as shown in the diagram below, with sphere P at the origin.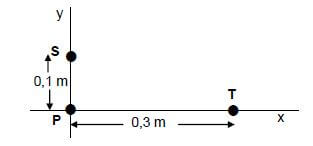
7.3 State Coulomb's law in words. (2)
Calculate the magnitude of the:
7.4 Net electrostatic force acting on sphere P (5)
7.5 Net electric field at the origin due to charges S and T (3)
7.6 ONE of the charged spheres, P and T, experienced a very small increase in mass after it was charged initially.
7.6.1 Which sphere, P or T, experienced this very small increase in mass? (1)
7.6.2 Calculate the increase in mass by the sphere in QUESTION 7.6.1. (3) [19]
QUESTION 8 (Start on a new page.)
The battery in the circuit diagram below has an emf of 12 V and an internal resistance of 0,5 Ω. Resistor R has an unknown resistance.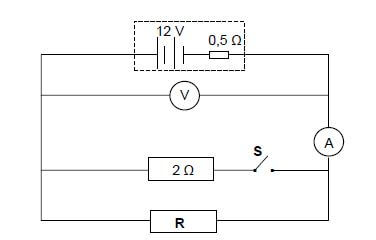
8.1 What is the meaning of the following statement? The emf of the battery is 12 V. (2)
The reading on the ammeter is 2 A when switch S is OPEN.
8.2 Calculate the:
8.2.1 Reading on the voltmeter (3)
8.2.2 Resistance of resistor R (2)
Switch S is now CLOSED.
8.3 How does this change affect the reading on the voltmeter? Choose from: INCREASES, DECREASES or REMAINS THE SAME. Explain the answer. (4) [11]
QUESTION 9 (Start on a new page.)
Learners perform an experiment to determine the emf (ε) and the internal resistance (r) of a battery using the circuit below.
The learners use their recorded readings of current and resistance, together with the equation R = ε - r, to obtain the graph below.
I
9.1 Which variable has to be kept constant in the experiment? (1)
9.2 Refer to the graph.
9.2.1 Write down the value of the internal resistance of the cell. (2)
9.2.2 Calculate the emf of the battery. (3) [6]
QUESTION 10 (Start on a new page.)
10.1 In the simplified AC generator below, the coil is rotated clockwise.
10.1.1 In which direction does the induced current flow in the coil? Choose from: X to Y or Y to X. (1)
10.1.2 On which principle or law is the working of the generator based? (1)
10.1.3 State the energy conversion that takes place while the generator is in operation. (2)
10.2 The voltage output for an AC generator is shown below.
10.2.1Write down the maximum (peak) output voltage of the generator. (1)
A stove is connected to the generator above, and delivers an average power of 1 600 W.
10.2.2 Calculate the rms voltage delivered to the stove. (3)
10.2.3 Calculate the resistance of the stove. (3) [11]
QUESTION 11 (Start on a new page.)
The threshold frequencies of caesium and potassium metals are given in the table below.
METAL | THRESHOLD FREQUENCY |
Caesium | 5,07 x 1014 Hz |
Potassium | 5,55 x 1014 Hz |
11.1Define the term work function in words. (2)
11.2 Which ONE of the two metals in the table has the higher work function? Give a reason for the answer by referring to the information in the table. (2)
The simplified diagrams below show two circuits, A and B, containing photocells. The photocell in circuit A contains a caesium metal plate, while the photocell in circuit B contains a potassium metal plate.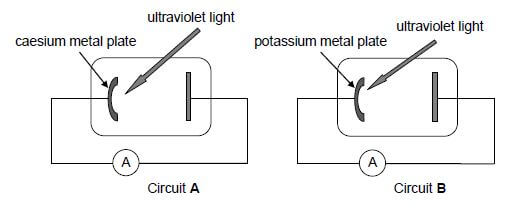
Ultraviolet light with the same intensity and wavelength of 5,5 x 10-7 m is incident on the metal plate in EACH of the photocells and the ammeter in circuit A registers a current.
11.3 By means of a calculation, determine whether the ammeter in circuit B will also register a current. (3)
11.4 Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of an ejected electron in circuit A. (5)
11.5 How will the maximum kinetic energy of the ejected electron, calculated in QUESTION 11.4, change when the intensity of the incident light increases? Choose from: INCREASES, DECREASES or REMAINS THE SAME. (1) [13]
TOTAL: 150
DATA FOR PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 12 PAPER 1 (PHYSICS)
TABLE 1: PHYSICAL CONSTANTS
NAME | SYMBOL | VALUE |
Acceleration due to gravity | g | 9,8 m·s-2 |
Universal gravitational constant | G | 6,67 x 10-11 N·m2·kg-2 |
Radius of Earth | RE | 6,38 x 106 m |
Mass of Earth | ME | 5,98 x 1024 kg |
Speed of light in a vacuum | c | 3,0 x 108 m·s-1 |
Planck's constant | h | 6,63 x 10-34 J·s |
Coulomb's constant | k | 9,0 x 109 N·m2·C-2 |
Charge on electron | e | -1,6 x 10-19 C |
Electron mass | me | 9,11 x 10-31 kg |
TABLE 2: FORMULAE
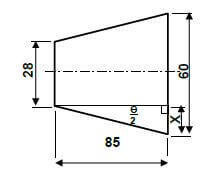
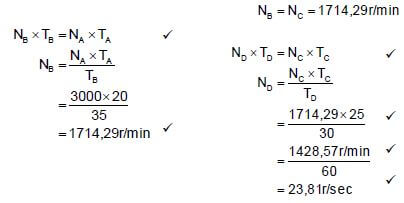 (6)
(6)