Adele
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY PAPER 1 GRADE 12 ADDENDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
ADDENDUM
ANNEXURE A
QUESTION 1.3
ANNEXURE B
QUESTION 2.2
ELECTRICITY BILL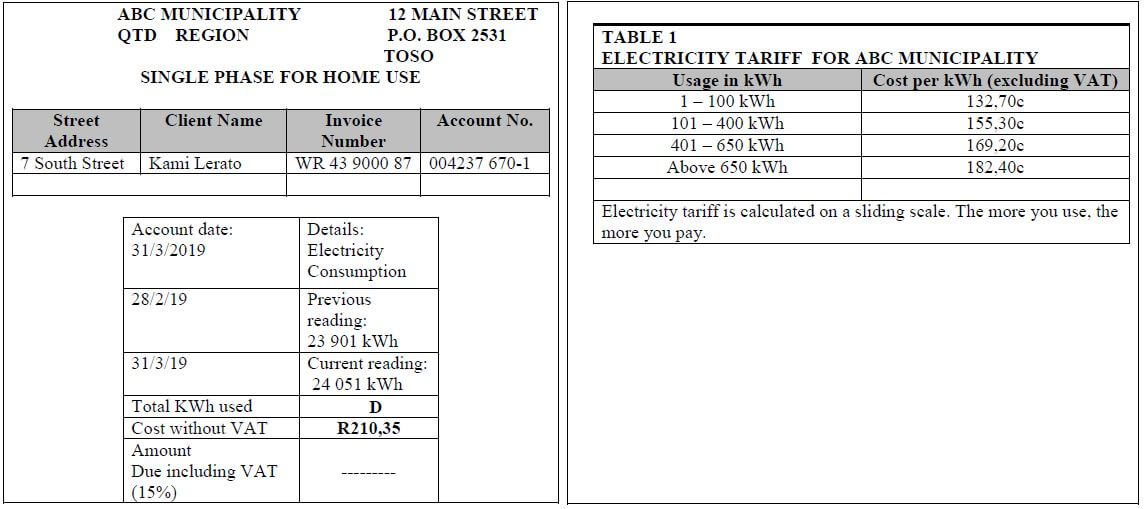
ANNEXURE C
QUESTION 4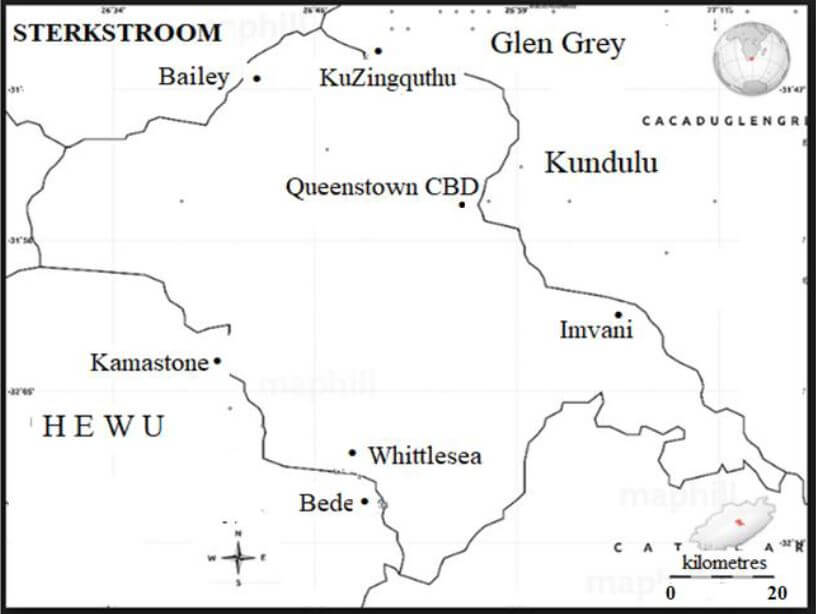
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions before answering the question;
- This question paper consists of FIVE questions. Answer ALL the questions.
- Use the ANNEXURES in the ADDENDUM to answer the following questions:
- ANNEXURE A for QUESTION 1.3
- ANNEXURE B for QUESTION 2.2
- ANNEXURE C for QUESTION 4
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Maps and diagrams are not necessarily drawn to scale, unless stated otherwise.
- Round off ALL final answers according to the context used, unless stated otherwise.
- Indicate units of measurement, where applicable.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Show ALL calculations clearly.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1 A travel agency booked a flight and accommodation for Nomonde’s trip to Pretoria. Study the travel arrangements voucher below and answer the questions that follow.
TRAVEL ARRANGEMENTS VOUCHER
DM Row Travel Agency | Accommodation Client Copy |
Twilight Hotel, | Client details |
Date and Times | Booking References |
1.1.1 Write down the name of the travel agency that issued the voucher. (2)
1.1.2 Write down the client reference number shown on the voucher. (2)
1.1.3 Determine the number of nights Nomonde spent at the hotel. (2)
1.1.4 Calculate the total cost for the duration of Nomonde’s stay at the hotel. (2)
1.2
Fizzy drinks like Coca-Cola are be bottled in different containers with different capacities. Examples of the containers are shown below.
|
1.2.1 Calculate the total capacity in all the containers if they are full. Give your answer in litres. (2)
1.2.2 Determine the number of A containers, filled to capacity, that would completely fill container E. (2)
1.3
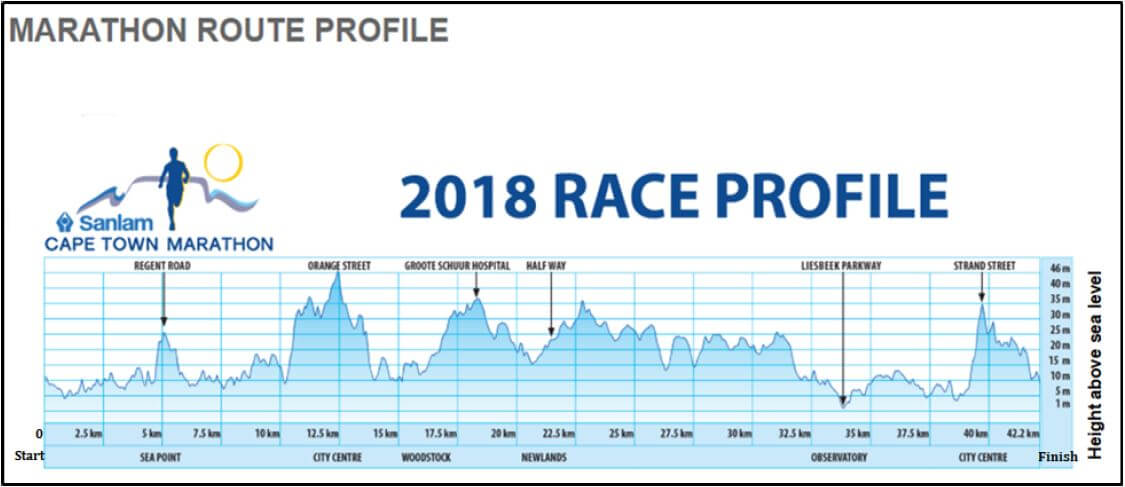
| ANNEXURE A shows the 2018 Cape Town Marathon route profile. Use ANNEXURE A to answer the questions that follow. |
1.3.1 Determine the total distance of the Cape Town marathon route. (2)
1.3.2 Determine the difference in height above sea level between Orange Street and Strand Street. (2)
1.4 The examination results expressed in percentage (%) for a Grade 12 Mathematical Literacy class at Bongo Senior Secondary School at the end of 2018 are shown below:
| 28 18 47 56 86 35 75 47 43 57 61 82 47 61 51 74 61 84 33 43 25 |
1.4.1 Determine the mode percentage of the class. (2)
1.4.2 Calculate the range of the given data. (2)
1.4.3 The examination paper was set out of 150 marks. Calculate the actual marks of the learner that obtained the highest percentage. (2) [22]
QUESTION 2
2.1
| Bazze Secondary School organised a tour for 60 Grade 12 learners costing R20 000. Each learner paid R200 and the school paid 30% of the cost of the tour. T-shirts donated by a charitable organisation were sold to raise the balance of R2 000. |
2.1.1 Calculate the total amount the learners paid. (2)
2.1.2 Determine the school’s contribution towards the cost of the tour. (2)
2.1.3 Show that the ratio of amount raised from the sale of T-shirts to the total cost of the tour is 1 : 10. (2)
2.1.4 Determine the total number of T-shirts donated if 10 of them were sold at R50 each and the rest of the T shirts were sold at R30 each. (3)
2.2
| Ms Lerato lives in ABC Municipality. She needs assistance to understand the calculations involved in her electricity bill. ANNEXURE B contains the electricity bill and TABLE 1 shows the electricity tariffs. |
Use ANNEXURE B to answer the questions that follow.
2.2.1 Determine the value of D, the amount of kilowatt (kWh) used in March 2019. (2)
2.2.2 Show how the cost of R210,35 was calculated. (3)
2.2.3 Determine the Value Added Tax (VAT) amount payable. (2)
2.3
| Lerato is a teacher at Bongo SSS. The distance from her home to school is 50 km. She drives to school daily and her car uses on average 12,5 km per litre of petrol. TABLE 2 below shows the cost per litre of petrol for month of July and August 2018. |
TABLE 2: COST PER LITRE OF PETROL
July 2018: Official price per litre | August 2018 price per litre | |
| Petrol | R16,02 | R16,21 |
Use TABLE 2 above to answer the questions that follow.
2.3.1 Explain the term inflation in the above context. (2)
2.3.2 Determine the difference in the price of petrol for the two months. (2)
2.3.3 Calculate the increase in cost of fuel she paid 5 days after the price increase. (5)
2.4 Ms Lerato’s bank statement for the month of March 2018 is shown in TABLE 3 below.
TABLE 3: MS LERATO’S BANK STATEMENT
GOODWILL BANK 15 March 2018 Lerato | |||||
Details | Service Fee | Debits | Credits | Date | Balance (Rands) |
Balance brought forward | 02 15 | 2 875,77- | |||
Statement fee | # | 20,18- | 02 17 | 2 895,95- | |
Card Purchase | 296,10- | 02 20 | 3 192,05- | ||
Salary | 18 953,85 | 02 21 | 15 761,80 | ||
Insurance premium | 187,27- | 02 25 | 15 574,53 | ||
Dividend YY4098 shares | 840,00 | 02 28 | 16 414,53 | ||
Bond | 4 069,52- | 03 02 | 12 345,01 | ||
Auto Bank deposit | 1 200,00 | 03 05 | 13 545,01 | ||
Fee Cheque Deposit | # | 42,37- | 03 05 | 13 502,64 | |
Fuel CLTX Garage | 729,45- | 03 07 | 12 773,19 | ||
ATM withdraw | 1800,00- | 03 10 | 10 973,19 | ||
Withdrawal fee | # | 17,47- | 03 10 | 10 955,72 | |
Fixed monthly fee | # | 100,88- | 03 11 | 10 854,84 | |
Balance carried forward | 03 15 | 10 854,84 | |||
Use TABLE 3 above to answer the questions that follow.
2.4.1 Write down the closing balance amount on 6th March 2018. (2)
2.4.2 Calculate the total bank fees charged in March 2018. (2) [29]
QUESTION 3
3.1 John, a student at Bongo SSS runs around the school’s playground and keeps a record of his distances and fitness from his fitness tracker watch. The diagram below shows the layout of the playground and TABLE 4 shows data from his fitness tracker watch. 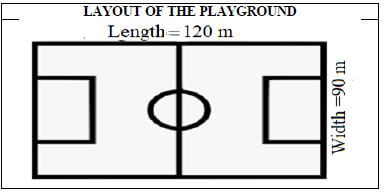
TABLE 4: TARGET SET AT 6 000 STEPS
THE DATA
DATE | STEPS | DISTANCE (KM) | GOAL (%) |
1/1/2019 | 2 444 | 1,6 | 40,73 |
2/1/2019 | 8 710 | 6,3 | 145,17 |
3/1/2019 | 19 210 | 13,02 | 320,17 |
4/1/2019 | 3 245 | 2,10 | 54,08 |
5/1/2019 | 5 859 | 4,2 | ------- |
6/1/2019 | 4896 | 3,36 | 81,60 |
7/1/2019 | 4461 | 2,94 | 74,35 |
8/1/2019 | 3996 | 2,73 | 66,60 |
9/1/2019 | 7561 | 5,04 | 126,02 |
10/1/2019 | 5286 | 3,57 | 88,10 |
Use the layout and TABLE 4 above to answer the questions that follow.
3.1.1 Determine the total distance covered on the days he met the target. (2)
3.1.2 Calculate the perimeter of the playground. (2)
3.1.3 Calculate the number of completed rounds he ran around the playground on the first day of practice. (5)
3.1.4 Calculate the goal percentage on the 5/1/2019.
Use the formula:
- Goal(%) = Steps covered × 100%
Target set
3.1.5 Calculate the distance of one step in metres on the 9/1/2019. Give your answer to 2 decimal places. (4)
3.2 John drinks juice he buys from a local café after running. He wants to determine how much energy he takes in from one can, so he measured the radius and height of the can and read the nutritional information. The picture of the can is shown below. 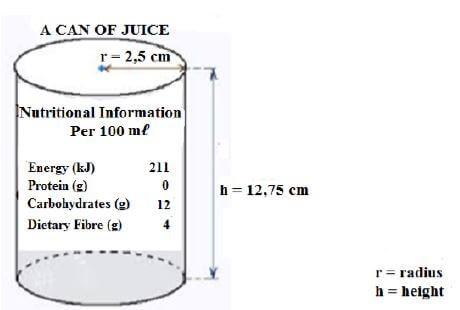
3.2.1 Show that the volume of juice in the can is 250,38 cm3 when full. (2)
Use the following formula:
- Volume = π × radius × radius × height, where π = 3,142
3.2.2 Calculate the energy he takes in when he drinks one can of juice.
NOTE: 1 cm3 = 1 mℓ (3) [20]
QUESTION 4
| ANNEXURE C shows a map of Queenstown and surrounding areas. |
Use ANNEXURE C to answer the questions that follow.
4.1 Name the general direction of Bailey from Kamastone. (2)
4.2 Express the scale in the form 1 : … (3)
4.3 Use the scale in QUESTION 4.2 to determine the distance between Queenstown’s CBD and Whittlesea. (4)
4.4 Name another type of scale that can be used on a map. (2) [11]
QUESTION 5
The data shown in TABLE 5 below gives the number of radio listeners and the population of South African provinces in 2017.
TABLE 5: RADIO LISTENERS AND SOUTH AFRICAN POPULATION IN 2017
Province | Population of the province | Number of radio listeners | % of the listeners to the population |
Eastern Cape | 6 562 053 | 6 233 950 | 95 |
Free State | 2 745 590 | 2 388 663 | 87 |
Gauteng | 12 272 263 | 11 162 759 | 91 |
Kwazulu-Natal | 10 267 300 | 9 856 608 | 96 |
Limpopo | 5 404 868 | 4 918 430 | 91 |
Mpumalanga | 4 039 939 | 3 555 146 | 88 |
Northern Cape | 1 145 861 | 916 689 | 80 |
North West | 3 509 953 | --------- | 90 |
Western Cape | 5 822 734 | 5 240 461 | 90 |
TOTAL |
Use TABLE 5 to answer the questions that follow.
5.1 Name the province with the highest number of radio listeners. (2)
5.2 Arrange the population of the provinces in ascending order. (2)
5.3 Determine the province in the median position as per population. (2)
5.4 Identify the province(s) whose population data would be used to determine the following:
5.4.1 Quartile 1 (2)
5.4.2 Quartile 3 (2)
5.5 Give the percentage of the data represented by the Interquartile Range (IQR). (2)
5.6 Calculate the number of radio listeners in the North West Province. (3)
5.7 Determine the mean percentage of radio listeners. (3) [18]
TOTAL: 100
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- This question paper consists of FOUR questions. Answer ALL the questions.
- Use the ADDENDUM with ANNEXURES for the following questions:
ANNEXURE A for QUESTION 1
ANNEXURE B for QUESTION 2.1
ANNEXURE C for QUESTION 3.1
ANNEXURE D for QUESTION 4.1
ANNEXURE E for QUESTION 4.2 - Number the questions correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- An approved calculator (non-programmable and non-graphical) may be used, unless stated otherwise.
- Show ALL calculations clearly.
- Maps and diagrams are NOT drawn to scale, unless otherwise stated.
- Indicate units of measurement, where applicable.
- Round off ALL final answers appropriately according to the given context, unless stated otherwise.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1
| ANNEXURE A shows a statement for fees payable for courses offered by a student at a university for Semester 1 and Semester 2. Explanations in the statement are in both English and Afrikaans. Use the information in ANNEXURE A to answer the questions below. |
1.1.1 With the necessary calculations, show how the amount overdue was calculated. (2)
1.1.2 Determine the probability of having a course with a study guide in both semesters. Give your final answer as a decimal fraction rounded to two decimal places. (3)
1.1.3 Nancy claims that her tuition fees for EBUS 2715 are R1 000 more than her tuition fees for KOM 234. Show, with the necessary calculations, whether her statement is valid or not. (6)
1.1.4 Calculate the fee for registration as a percentage of the current amount. (3)
1.2
1.2.1 Show, with the necessary calculations, that the difference in the mean amounts for the tuition fees payable in Semester 1 and Semester 2 (excluding study guide fees) is less than R500. (6)
1.2.2 University fees for ALL courses have increased by 5% from the previous year. Calculate the amount of tuition fees for ESBM 2724 in 2017. (3) [23]
QUESTION 2
2.1
| The strip chart in ANNEXURE B shows the route between Cape Town and Springbok. Answer the questions below on the strip chart in ANNEXURE B. |
2.1.1 When looking at the map, the distance between Vanrhynsdorp and Garies, and the distance between Kamieskroon and Springbok seems equal. Show, by using calculations, whether it is correct or not. Give a reason for your findings. (5)
2.1.2 A family from Malmesbury will be attending a birthday party in Calvinia. They leave Malmesbury at 7:00 and have breakfast for 45 minutes at a Wimpy (fast food restaurant) on their way. Determine at what time they will arrive in Calvinia, if they travel at an average speed of 95 km per hour. You may use the following formula:
- Distance = Speed × Time (7)
2.2 Invitation cards for the party are in a rectangular shape, with a circular photo of the birthday girl in the middle of the invitation card and dimensions as shown below. 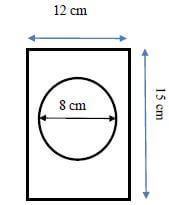
2.2.1 Calculate the area of the invitation card without the photo. Give your final answer to the nearest mm2.
You may use the following formulae:
- Area of invitation card = length × width
- Area of photo = π × radius × radius (7)
2.2.2 One of the guests buys a gift that is packaged in a rectangular box as shown below. She must wrap the gift with gift wrapping paper. 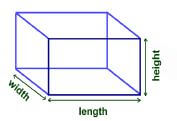
Dimensions of the box are:
- Length = 390 cm
- Width = 270 cm
- Height = 300 cm
Calculate the total area of the paper that is needed for wrapping the box in cm2. You may use the formula:
- Surface area of the gift box = 2(length × width + width × height + length × height) (4)
2.3 Three companies have their sales plotted as box and whisker charts as shown below. 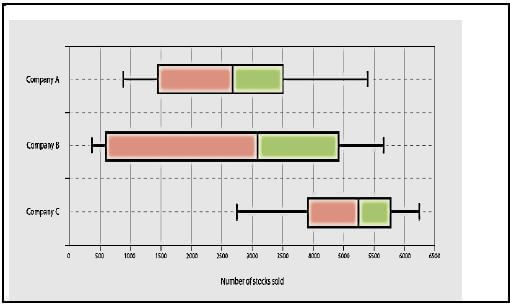
Use the box and whisker charts to answer the following question.
With the use of calculations, compare and comment on the interquartile ranges and ranges on the number of stocks sold by Company A and Company C respectively. (6) [29]
QUESTION 3
3.1 The table in ANNEXURE C represents matches played by the 16 soccer teams in the Premier Soccer League with their scores as on 5 December 2018.
NOTE:
- For every win, a team gets 3 points.
- For every draw, a team gets 1 point.
- For a loss, a team gets 0 points.
3.1.1 Calculate the missing values A and B respectively on the table. (4)
3.1.2 Calculate the probability of choosing a team, which has won more than six games from the teams that have played twelve or more games. (2)
3.1.3 A player for Mamelodi Sundowns claims that out of the remaining matches that they have to play, to get to the same number of matches as already played by Orlando Pirates, and to have five points more than Orlando Pirates, they must win two and draw one. Show, with the necessary calculations, whether his statement is valid or not. (4)
3.2
3.2.1 The Curriculum and Policy Statement (CAPS) document stipulates that Mathematical Literacy needs to be taught for 4,5 hours during a 5-day cycle.There are two schools: School A has 45 minute periods with 3 double periods and 2 single periods for Mathematical Literacy, while School B has 30 minute periods with 4 double periods and 1 single period per week. Show, with the necessary calculations, which school complies with the CAPS document. (5)
3.2.2 In one of the schools, a Mathematical Literacy teacher is giving textbooks to her Grade 10, Grade 11 and Grade 12 classes in the ratio 4 : 3 : 2. If she hands out 62 books to the Grade 12 class, determine how many books she handed out altogether. (3) [18]
QUESTION 4
4.1 ANNEXURE D represents a seating plan for an American Airbus plane. Answer the questions below that are based on ANNEXURE D.
4.1.1 Give a possible reason for a bigger space between row 8 and row 9. (2)
4.1.2 Determine the number of seats in the economy class. (3)
4.1.3 Mention ONE advantage of being a passenger in the first-class seats of the plane. (2)
4.2
| ANNEXURE E shows the program and costs for Wimbledon tickets for 2007 and 2019 tournaments. NOTE: Wimbledon is a tennis championship tournament, which is played annually at Wimbledon in England. Answer the following questions based on ANNEXURE E. |
4.2.1 A couple from America is planning to attend the 2019 Wimbledon tennis championship tournament. They are planning to watch the quarterfinals as well as the finals for both men and women. The couple claim that 30 000 American dollars will be enough to watch all their planned matches. Show, with the necessary calculations, whether their claim is valid or not. (8)
4.2.2 The couple researched the ticket prices for 2007, as they were interested in the effect of inflation. Show, with the necessary calculations, that the percentage increase for ticket prices for the men’s finals from 2007 to 2019 is more than 40%. (4)
4.2.3 The couple started saving three years ago for the 2019 tournament. They invested 20 000 American dollars at an institution offering 6,5% interest compounded annually. Calculate the total in American dollars after 33 months. (5)
4.2.4 Give a possible reason why the price of tickets for the men’s matches are more expensive than the price of tickets for the women’s matches. (2)
4.2.5 Describe the trend observed for the ticket costs of men’s matches during the tournament and give a possible reason for the trend. (4) [30]
TOTAL: 100
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
MARKS: 100
SYMBOL | EXPLANATION |
M | Method |
MA | Method with accuracy |
CA | Consistent accuracy |
A | Accuracy |
C | Conversion |
S | Simplification |
RT/RG/RM | Reading from a table OR reading from a graph OR diagram OR from map a OR a plan |
F | Choosing the correct formula |
SF | Substitution in a formula |
J | Justification |
P | Penalty, e.g. for no units, incorrect rounding off etc. |
R | Rounding Off/Reason |
AO | Answer only |
NPR | No penalty for rounding |
O | Opinion |
D | Define |
NOTE:
- If a candidate answer a question TWICE, only mark the FIRST attempt.
- If a candidate has crossed out (cancelled) an attempt to a question and NOT redone the solution, mark the crossed out (cancelled) version.
- Consistent accuracy (CA) applies in ALL aspects of the marking guidelines; however it stops at the second calculation error.
- If the candidate presents any extra solution when reading from a graph, table, layout plan and map, then penalise for every extra incorrect item presented.
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1 [23 MARKS] | |||
Ques. | Solution | Explanation | Level |
1.1.1 | Amount overdue OR Amount overdue | 1 RT Correct values OR 1 RT Correct values | L2 F |
1.1.2 | Probability | 1A Numerator | L2 P |
1.1.3 | EBUS 2715 fees | 1 RT All correct values | L4 F |
1.1.4 | % Registration fee = 1020 ✔ RT x 100 ✔M | 1RT Correct values | L2 F |
1.2.1 | Semester 1 = ( 3 715 x 4) + 4280 + 5345 ✔M | CA from 1.1.3 | L3 D |
1.2.2 | Amount for 2017 = 4280 × 100 ✔M✔M | 1M Multiplying by 100 | L2 F |
[23] |
QUESTION 2 [29 MARKS] | |||
Ques. | Solution | Explanation | Level |
2.1.1 | Distance from Vanrhynsdorp to Garies | 1 RT Correct values | L4 M&P |
2.1.2 | Distance = (289 – 52) + 121 ✔M | 1M Add correct distances | L2 M&P L3 M |
2.2.1 | Area of rectangle = length x width | 1C Convert to mm | L3 M |
2.2.2 | Surface area = 2(length ൈ width + width ൈ height + length ൈ height) = 2(390 ൈ 270 + 270 ൈ 300 +390 ൈ 300)✔SF✔A = 2(105 300 + 81 000 + 117 000) S✔ = 606 600 cm2 ✔CA | 1SF Substitution | L3 M |
2.3 | Company A OR | 1RT Correct values 1CA IQR (C)
(6) | L3 Data |
[29] |
QUESTION 3 [18 MARKS] | |||
Ques. | Solution | Explanation | Level |
3.1.1 | Value of A = 6 × 3 + 1 × 6 ✔M | 1MA Matches won and drawn | L2 D |
3.1.2 | Probability = 1 ✔A✔A | CA from 3.1.1 | L2 P |
3.1.3 | Points = 2 × 3 + 1 | CA from 3.1.1 | L4 D |
3.2.1 | School A = 45 × 2 × 3 = 270 ✔M | 1M No. of minutes | L4 M |
3.2.2 | Ratio = 62 ✔MA | 1MA Concept of ratio | L3 D |
[18] |
QUESTION 4 [30 MARKS] | |||
Ques. | Solution | Explanation | Level |
4.1.1 | There are emergency exit points between row 8 and row 9 ✔✔A | 2A Reason (2) | L4 M&P |
4.1.2 | Seats in the economy class | 1MA Seats per row | L2 M&P |
4.1.3 | There is more space ✔✔R | 2R Reason (2) | L4 M&P |
4.2.1 | Quarter finals = (1 412 × 2) + (4 249 × 2) ✔RT | 1RT Correct values for both matches × 2 | L4 F |
4.2.2 | % change = 5538 - 3918 × 100% ✔RT✔M✔M | 1RT Correct values | L2 F |
4.2.3 | Year 1 = 20 000 × 1,065 ✔M | 1M Increasing by 6,5% | L3 F |
4.2.4 | Men play more vigourously ✔✔R | 2R Reason (2) | L4 F |
4.2.5 | Ticket prices increase from day 1 to the final day ✔✔O | 2O Trend | L4 D |
[30] | |||
TOTAL: | 100 |
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
MATHEMATICAL LITERACY
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
MARKS: 100
Symbol | Explanation |
M | Method |
MA | Method with accuracy |
CA | Consistent accuracy |
A | Accuracy |
C | Conversion |
S | Simplification |
RT/RG/RM | Reading from a table/Reading from a graph/Reading from a map |
F | Choosing the correct formula |
SF | Substitution in a formula |
J | Justification |
P | Penalty, e.g. for no units, incorrect rounding off etc. |
R | Rounding Off/Reason |
AO | Answer only |
NPR | No penalty for rounding |
NOTE:
- If a candidate answers a question TWICE, only mark the FIRST attempt.
- If a candidate has crossed out (cancelled) an attempt to a question and NOT redone the solution, mark the crossed out (cancelled) version.
- Consistent accuracy (CA) applies in ALL aspects of the marking guidelines; however it stops at the second calculation error.
- If the candidate presents any extra solution when reading from a graph, table, layout plan and map, then penalise for every extra incorrect item presented.
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1 [22 MARKS] INTEGRATED QUESTION | ||||
Question | Solution | Explanation/Marks | Topic/L | |
1.1 | 1.1.1 | DM Row Travel Agency ✔✔ RT | 2 RT correct agency (2) | F |
1.1.2 | Reference Number: 0674582 ✔✔ RT | 2 RT correct Voucher no. (2) | F | |
1.1.3 | 3 nights ✔✔ RT | 2RT correct no of nights (2) | F | |
1.1.4 | 3 × R1 440,00 ✔ M | 1M×1 440,00 | F | |
1.2 | 1.2.1 | 250 + 330 + 450 + 500 + 1 000 + 1500 + 2 000 | 1M addition all values | M |
1.2.2 | No. of A containers= 1 500 ✔M = 6 ✔ CA | 1M division correct values | M | |
1.3 | 1.3.1 | 42,2 km ✔✔ RT | 2 RT distance (2) | M&P |
1.3.2 | Difference in height above sea level | 1RT correct values | M&P | |
1.4 | 1.4.1 | Mode = 61 ✔ RT | 2RT mode (2) | D |
1.4.2 | Range = 86 – 18 ✔ MA | 1MA subtracting correct values | D | |
1.4.3 | Raw mark = 86 × 150 ✔ MA | 1MA % of 150 | D | |
[22] | ||||
QUESTION 2 [29 MARKS] FINANCE | ||||
Question | Solution | Explanation/Marks | Topic /L | |
2.1 | 2.1.1 | Total amount = 1 200 × 60 ✔ M | 1M multiplication | F |
2.1.2 | 30 × 20 000 = R6 000 ✔M ✔ CA | 1M multiplication of correct values | F | |
| 2.1.3 | Ratio 2 000 : 20 000 ✔MA ✔A | 1MA for ratio and 2000 | F | |
2.1.4 | Balance = 2 000 – (10 × 50) | 1M balance after sale of 10 T shirts | F | |
2.2 | 2.2.1 D = 24 901 – 23 901 ✔M | 1M subtracting values 1A simplifying (2) | F L1 | |
2.2.2 | Costs = 100 × 132,70 + 50 × 155,30 ✔M | 1M multiplication and addition 1M simplification 1CA dividing by 100
(3) | F L2 | |
2.2.3 | VAT amount= 15 × 210,35 ✔M | 1M multiplication of 15% by 210,35 1A simplification (2) | F L1 | |
2.3 | 2.3.1 | Inflation is the increase in price of goods and services e.g. the price of petrol increases with time. ✔✔ O | 2 Explanation (2) | F L1 |
2.3.2 | Price increase = 16,21 – 16,02 ✔M | 1M subtraction of values 1A difference (with units cents or Rands) (2) | F L1 | |
2.3.3 | Distance = 5 × 50 × 2 = 500 km ✔M | 1CA from 2.3.2 | F L3 | |
2.4 | 2.4.1 Balance = R13 502,64 ✔✔RT | 2 RT (2) | F L1 | |
2.4.2 | Fee = 42,37+17,47+100,88 = R160,72 ✔ RT✔CA | 1 RT adding correct values | F L1 | |
[29] |
QUESTION 3 [20 MARKS] MEASUREMENT | |||
Ques. | Solution | Explanation/Marks AO: FULL MARKS | Level |
3.1.1 | Total distance = 6,3 + 13,02 + 5,04 ✔M | 1M Addition of correct values | M |
3.1.2 | Perimeter = 120 × 2 + 90 × 2 ✔M | 1M distance around | M |
3.1.3 | No of rounds = 1,6 km ✔RT ✔M | 1 RT value of 1,6 km | M |
3.1.4 | : Goal(%) = steps run × 100% | 1M substitution | M |
3.1.5 | Distance = 5,04 × 1000 ✔M | 1M conversion to m | M |
3.2.1 | V = πr2h ✔M | 1M substituting radius | M |
3.2.2 | 100 mℓ : 211 KJ ✔M | 1Mconcept of ratio | M |
[20] | |||
QUESTION 4 [11 MARKS] MAPS AND REPRESENTATIONS | |||
Ques. | Solution | Explanation/Marks AO: FULL MARKS | Level |
4.1 | South ✔✔RT | 2RT correct direction (2) | M&p |
4.2 | ✔RT | 1RT measuring scale 1CA expressing in unit ratio (3) | M &p |
4.3 | 2,5 cm : 20 km | 1CA from 4.2 1M measuring | M &p |
4.4 | Numeric scale ✔✔ A | 2A Correct scale (2) | M &p |
[11] | |||
QUESTION 5 [18 MARKS] DATA HANDLING | |||
Ques. | Solution | Explanation/Marks AO: FULL MARKS | Level |
5.1 | Gauteng ✔✔RT | 2RT correct province (2) | D L1 |
5.2 | 1 145 861; 2 745 590; 3 509 953; 4 039 939; 5 404 868; 5 822 734; 6 562 053; 10 267 300; 12 272 263 ✔✔RT | 2RT arranging all values starting with smallest. (2) | D L1 |
5.3 | Limpopo ✔✔RT | 2RT middle position CA from 5.2 and check province (2) | D L1 |
5.4 | 5.4.1 Free State and North West ✔✔CA | CA from 5.2 1 mark for each province (2) | D L1 |
5.4.2 Eastern Cape and KwaZulu-Natal ✔✔CA | CA from 5.2 1 mark for each province (2) | D L1 | |
5.5 | IQR represents 50% ✔✔A | 2A (2) | D L1 |
5.6 | No. of listeners in NW = 90 × 3 509 953✔M | 1M 90 % of the population | D L2 |
5.7 | % Mean = 95 + 87 + 91 + 96 + 91 + 88 + 80 + 90 + 90 ✔M | 1M adding the percentages | D L2 |
[18] | |||
TOTAL: | 100 | ||
LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
LIFE SCIENCES
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Write ALL the answers in your ANSWER BOOK.
- Start the answers to EACH question at the top of a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Present your answers according to the instructions of each question.
- ALL drawings must be done in pencil and labelled in blue or black ink.
- Draw diagrams, flow charts or tables only when asked to do so.
- The diagrams in this question paper are NOT necessarily drawn to scale.
- Do NOT use graph paper.
- You must use a non-programmable calculator, protractor and a compass where necessary.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are given as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the correct answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.9) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.0 D.
1.1.1 The term used to describe the observable features of an organism:
- Alleles
- Genes
- Genotype
- Phenotype
1.1.2 A cell divides to produce gametes. This process will …
- supply cells for the replacement of damaged tissue.
- produce cells that are genetically identical.
- involve one nuclear division.
- produce haploid cells.
1.1.3 Trisomy 21 is a genetic disorder in which an individual has an extra copy of chromosome 21. Which process could cause Trisomy 21?
- Failure of a chromosome to replicate during mitosis
- Failure of chromosome pairs to join during fertilisation
- Failure of chromosome pairs to separate properly during meiosis
- Failure of a chromosome to cross over during replication
1.1.4 A piece of DNA has 1 500 bases. 400 of these bases are guanine. How many adenine bases would there be in this piece of DNA?
- 400
- 350
- 700
- 750
1.1.5 The diagram below represents a simple reflex arc. What is the correct sequence of nerve cells through which an impulse passes during a reflex action? 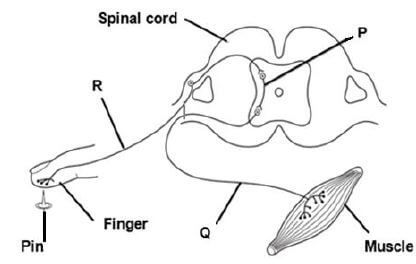
- P → Q → R
- Q → R → P
- Q → P → R
- R → P → Q
1.1.6 The following information shows the alleles belonging to a married couple.
XH – Dominant allele for normal blood
Xh – Recessive allele for haemophilia
Which of the following crosses will produce male offspring who are all haemophiliacs?
- XHY x XhXh
- XHY x XHXh
- XhY x XHXh
- XhY x XHXH
1.1.7 A study was carried out on a lion (male), a lioness (female) and a group of cubs. Samples of DNA were extracted from the animals and analysed. The results are shown in the diagram below, in which the dark bands represent fragments of DNA of a specific length. 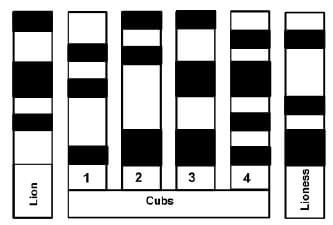
Which of the cubs could be the offspring of the lion and lioness studied?
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1, 2 and 4
- 2, 3 and 4
- 1, 3 and 4
1.1.8 Which sequence correctly shows the path of sound transmission in the ear?
- Tympanic membrane →Eustachian tube → semicircular canals → cochlea
- Tympanic membrane → semicircular canals → Eustachian tube → cochlea
- Auditory canal → ossicles → tympanic membrane → organic of Corti
- Auditory canal → tympanic membrane → ossicles → organ of Corti
1.1.9 A diploid sheep’s nucleus X is inserted into an ovum without nucleus of sheep Y to form a zygote. The zygote is then implanted into the uterus of a surrogate mother sheep. What is the genetic composition of the lamb produced?
- Sheep X
- Sheep Y
- Sheep Z
- Sheep X and Sheep Y (9 x 2) (18)
1.2 Give the correct biological term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.7) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 The organelle which is the site of protein synthesis
1.2.2 The basic unit of inheritance of a particular characteristic
1.2.3 A change in the genetic composition of an organism
1.2.4 Having different alleles for a characteristic
1.2.5 A rapid, automatic response to an external stimulus
1.2.6 Protective membrane situated over the cornea of the eye
1.2.7 A disease that is characterised by a loss of the myelin sheath of neurons in the brain (7 x 1) (7)
1.3 Indicate whether each of the statements in COLUMN І applies to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A and B or NONE of the items in COLUMN ІІ. Write A only, B only, both A and B or NONE next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.3) in the ANSWER BOOK. (3 x 2) (6)
COLUMN І | COLUMN ІІ |
1.3.1 Location of DNA in a human | A: Chloroplasts |
1.3.2 The scientist(s) who discovered the structure of DNA | A: Darwin |
1.3.3 The division of the nervous system that controls reactionof the body to an emergency | A: Sympathetic |
1.4 The diagram below shows part of the process of DNA replication.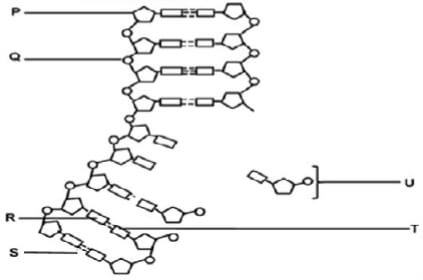
1.4.1 Identify the:
- Structure labelled P (1)
- Structure labelled Q (1)
- Bond labelled S (1)
- Molecule labelled U (1)
1.4.2 Name the base labelled T on the new DNA molecule if the base labelled R on the parent DNA molecule is guanine. (1)
1.5 In tomato plants, the genes for stem colour and presence of epidermal hairs are found on different chromosomes. The allele for purple stem P is dominant to the allele for green stem p and the allele for hairy stem H is dominant to the allele for smooth stem h. The Punnett square below shows a part of the cross between two plants. Genotype (i) has been left out. 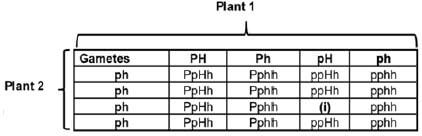
1.5.1 Give the:
- Genotype of plant 1 (2)
- Phenotype of plant 2 (2)
- Genotype of offspring (i) (1)
1.5.2 What percentage of offspring is having green and smooth stems? (1)
1.5.3 State the genotypes of TWO gametes from the table that will result in offspring that are heterozygous for both traits, if fertilisation occurs. (2)
1.6 The brain acts as the main coordinated centre for nervous activity. It receives information, interprets it and responds accordingly. 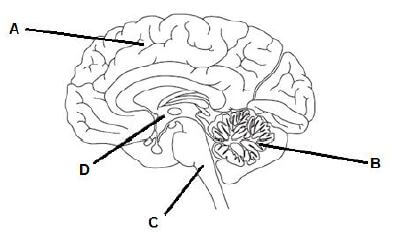
1.6.1 Give the LETTER only of the part of the brain that controls the following:
- Breathing (1)
- Memory (1)
1.6.2 The part labelled A is made up of two similar halves. How are these two halves attached to each other? (1)
1.6.3 State ONE way in which the brain is protected. (1)
1.6.4 State TWO reasons why humans need a nervous system. (2)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1 The diagram below shows some of the changes that occur during the menstrual cycle. 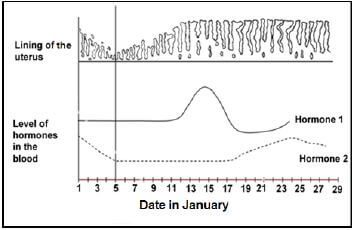
2.1.1 Between which dates did menstruation take place? (1)
2.1.2 On which date did ovulation take place? (1)
2.1.3 Identify hormones 1 and 2, respectively. (2)
2.1.4 Describe the relationship between the level of hormone 1 and ovulation. (2)
2.1.5 Explain what will happen to the lining of the uterus after 28 January. (2)
2.2 Read the passage below.
Seahorses are strange but interesting animals in which the male seahorses undergo pregnancy and give birth to young seahorses. The male seahorse has a pouch (bag) on its stomach in which to carry babies. |
2.2.1 Identify the type of reproduction seahorses have. (1)
2.2.2
- What type of fertilisation does the seahorse have? (1)
- Explain your answer to QUESTION 2.2.2(a). (1)
2.2.3 Why is the seahorse reproductive strategy considered to be ovovivipary? (2)
2.3 The hormone insulin is a relatively small protein made up of 110 amino acids. Researchers studying the production of insulin in the cells of the pancreas noted that one of the early steps in this process was the formation of a polypeptide called preproinsulin. Researchers noted that the formation of this polypeptide required repeated use of different types of molecule X, as shown below. 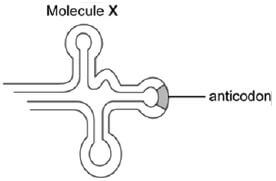
2.3.1 Name molecule X. (1)
2.3.2 Briefly describe how molecule X plays a role in the production of the polypeptide, preproinsulin. (5)
2.3.3 The table below shows mRNA codons and the amino acids they code for.
mRNA CODON | AMINO ACID |
AAC | Asparagine (Asn) |
UGU | Cysteine (Cys) |
CAG | Glutamine (Gln) |
CAU | Histidine (His) |
UUA | Leucine (Leu) |
UUU | Phenylalanine (Phe) |
UCU | Serine (Ser) |
GUC | Valine (Val) |
The sequence of amino acids 1 to 8 in the preproinsulin polypeptide is shown below.
phe-val-asn-gln-his-leu-cys-ser
Use the table shown above to determine the:
- mRNA codon coding for the 4th amino acid from left to right (1)
- Anticodon on molecule X if the amino acid carried is asparagine (1)
2.3.4 A mutation occurred during the formation of preproinsulin resulting in the formation of the following molecule:
phe-val-asn-gln-his-phe-cys-ser
Use the table above to describe how this mutation occurred. (3)
2.4 Huntington’s disease damages the nervous system. It is an inherited condition caused by a dominant allele (H). Only individuals who are homozygous for the recessive allele (h) are protected from the disease. The diagram shows the inheritance of Huntington’s disease in a family. 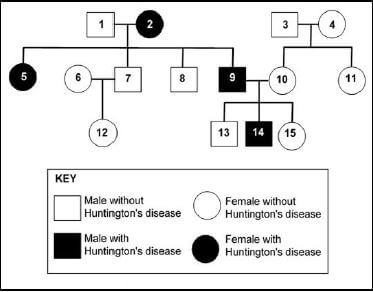
2.4.1 How many individuals in this family each fit the description given below?
- Females with Huntington’s disease (1)
- Homozygous recessive (1)
2.4.2 Determine the:
- Phenotype of individual 3 (1)
- Genotype of individual 2 (1)
2.4.3 Individual 1 and 2 both have male and female children. Use a genetic cross to show how they can produce both male and female children. (6)
2.5 The diagram below represents the phases during meiosis. 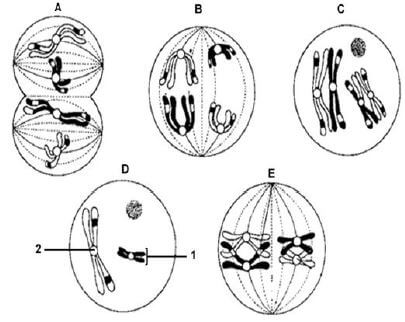
2.5.1
- State whether the diagrams represent meiosis I or meiosis II. (1)
- Give ONE reason for your answer in QUESTION 2.5.1 (a). (1)
2.5.2 Identify structures labelled 1 and 2. (2)
2.5.3 Arrange the phases in the correct sequence using LETTERS (A–E) only. (2) [40]
QUESTION 3
3.1 Human blood groups are controlled by multiple alleles.
3.1.1 Name ALL the alleles that controls human blood groups. (3)
3.1.2 How many of the alleles named in QUESTION 3.1.1 can any individual inherit? (1)
3.1.3 Give a reason for your answer in QUESTION 3.1.2. (2)
3.1.4 A man has blood group A and his wife has blood group B. Their first child has blood group AB and the second child has blood group O. What can one conclude about the blood groups of their future children? (3)
3.2 The iris of the eye has the ability to regulate the amount of light entering the eye in order to prevent damage to the eye. It does so by regulating the size of the pupil when it is exposed to varying light intensities. Scientists did an investigation to determine the effect of dim light on the diameter of the pupil. The procedure was as follows:
- A person in a darkened room was asked to cover one eye.
- A dim electric bulb positioned at varying distances from the person was switched on at one-minute intervals for a period of 10 seconds. (Not all measurements were at different distances from the person’s eye.)
- During this period the diameter of the pupil was measured.
The results obtained are shown in the table below.
| Time intervals (in minutes) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| Diameter of pupil (in mm) | 2 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 8 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 6 |
3.2.1 Name the mechanism by which the iris regulates the amount of light entering the eye. (1)
3.2.2 Identify the:
- Independent variable (1)
- Dependent variable (1)
3.2.3 Plot a line graph to show the above results. (6)
3.2.4 Between which two measurements did the largest decrease in the diameter of the pupil occur? (1)
3.2.5 Explain why the diameter of the pupil remained the same during the third- and fourth-time interval. (2)
3.2.6 List ONE way how the scientists ensured the validity of this investigation. (1)
3.2.7 Explain why the results of this investigation cannot be considered to be reliable. (2)
3.3 Genetic engineering uses biotechnology to satisfy human needs. One form of this is in stem cell research.
- Define stem cells. (2)
- State THREE sources of stem cells. (3)
- Explain the significance of stem cells. (3)
3.4 The diagram below represents structures in the inner ear. 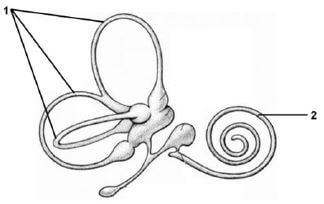
3.4.1 Identify structures labelled 1 and 2. (2)
3.4.2 Explain the significance of the structure labelled 2 being coiled. (2)
3.4.3 Describe the role of the structure above in maintaining balance. (4) [40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
Describe the process responsible for the formation of gametes in human males and females as well as the development of the embryo from fertilisation until implantation.
Content: (17)
Synthesis: (3)
NOTE: NO marks will be awarded for answers in the form of tables, flow charts or diagrams.
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150
LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
LIFE SCIENCES
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
PRINCIPLES RELATED TO MARKING LIFE SCIENCES
- If more information than marks allocated is given.
Stop marking when maximum marks is reached and put a wavy line and ‘max’ in the right-hand margin. - If, for example, three reasons are required and five are given. Mark the first three irrespective of whether all or some are correct/ incorrect.
- If whole process is given when only a part of it is required. Read all and credit the relevant part.
- If comparisons are asked for, and descriptions are given. Accept if the differences/similarities are clear.
- If tabulation is required but paragraphs are given.
Candidates will lose marks for not tabulating. - If diagrams are given with annotations when descriptions are required. Candidates will lose marks.
- If flow charts are given instead of descriptions.
Candidates will lose marks. - If sequence is muddled and links do not make sense. Where sequence and links are correct, credit. Where sequence and links are incorrect, do not credit. If sequence and links become correct again, resume credit.
- Non-recognised abbreviations.
Accept if first defined in answer. If not defined, do not credit the unrecognised abbreviation, but credit the rest of the answer if correct. - Wrong numbering.
If answer fits into the correct sequence of questions, but the wrong number is given, it is acceptable. - If language used changes the intended meaning.
Do not accept. - Spelling errors.
If recognisable, accept the answer, provided it does not mean something else in Life Sciences or if it is out of context. - If common names are given in terminology.
Accept, provided it was accepted at the national memo discussion meeting. - If only the letter is asked for, but only the name is given (and vice versa).
Do not credit. - If units are not given in measurements.
Candidates will lose marks. Marking guideline will allocate marks for units separately. - Be sensitive to the sense of an answer, which may be stated in a different way.
- Caption
All illustrations (diagrams, graphs, tables, etc.) must have a caption. - Code-switching of official languages (terms and concepts) A single word or two that appear(s) in any official language other than the learners' assessment language used to the greatest extent in his/her answers should be credited, if it is correct. A marker that is proficient in the relevant official language should be consulted. This is applicable to all official languages.
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 D ✓✓
1.1.2 D ✓✓
1.1.3 C ✓✓
1.1.4 B ✓✓
1.1.5 D ✓✓
1.1.6 A ✓✓
1.1.7 C ✓✓
1.1.8 D ✓✓
1.1.9 A ✓✓ (9 x 2) (18)
1.2
1.2.1 Ribosome ✓
1.2.2 Gene ✓
1.2.3 Mutation ✓
1.2.4 Heterozygous ✓
1.2.5 Reflex action ✓
1.2.6 Conjunctiva ✓
1.2.7 Multiple sclerosis ✓ (7 x 1) (7)
1.3
1.3.1 B only ✓✓
1.3.2 None ✓✓
1.3.3 A only ✓✓ (3 x 2) (6)
1.4
1.4.1
- Deoxyribose ✓ (1)
- Phosphate ✓ group (1)
- Hydrogen bond ✓ (1)
- Nucleotide ✓ (1)
1.4.2 Cytosine ✓/C (1)
1.5.1
- PpHh ✓✓ (2)
- green ✓ and smooth ✓ stem (2)
- ppHh ✓ (1)
1.5.2 25 ✓% (1)
1.5.3 ph ✓, PH ✓ (2)
1.6 1.6.1
- C ✓ (1)
- A ✓ (1)
1.6.2 By the corpus callosum ✓ (1)
1.6.3 The brain is protected from injury by:
- the skull, ✓
- meninges ✓ and
- cerebrospinal fluid ✓
(Mark first ONE only) (Any 1) (1)
1.6.4 The nervous system is needed to:
- detect changes ✓ in the environment (external and internal) and
- to react ✓ to these changes as well as
- coordinating ✓ the various activities of the body.
(Mark first TWO only) (Any 2) (2)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1 1 January to 5 January ✓ (1)
2.1.2 14 January ✓ (1)
2.1.3 Oestrogen ✓ and progesterone ✓ (2)
2.1.4
- Ovulation occurs when hormone 1 (oestrogen) is rising ✓✓/ near its peak (2) OR
- (Hormone 1) Oestrogen encourages/stimulates ovulation ✓✓
2.1.5
- Due to a decrease in the level of hormone 2 ✓ /progesterone
- The lining breaks down ✓/will be shed from the body (2)
2.2
2.2.1 Sexual reproduction ✓ (1)
2.2.2
- Internal fertilisation ✓ (1)
- Female eggs are deposited into the male pouch and fertilised inside the pouch ✓ (1)
2.2.3
- The fertilised eggs / embryo are nourished by the thickened skin inside the pouch ✓/ are not fed by the placenta as in humans
- until they are ready to hatch into live young. ✓ (2)
2.3
2.3.1 tRNA ✓/transfer RNA (1)
2.3.2
- During translation ✔
- the anticodon on the tRNA✔/ molecule X
- matches the codon on the mRNA ✔
- bringing the required amino acid ✔
- to the ribosome. ✔
- Amino acids become attached by peptide bonds ✔
- to form the polypeptide ✔preproinsulin (Any 5) (5)
2.3.3
- CAG ✓ (1)
- UUG ✓ (1)
2.3.4
- Mutation occurred in 6th codon ✔coding for leucine
- A was replaced with U ✔/ UUA changed to UUU
- resulting in the amino acid phenylalanine ✔ being picked up. (3)
2.4
2.4.1
- 2 ✓ (1)
- 11 ✓ (1)
2.4.2
- Male without Huntington’s disease ✓ (1)
- Hh ✓ (1)
2.4.3 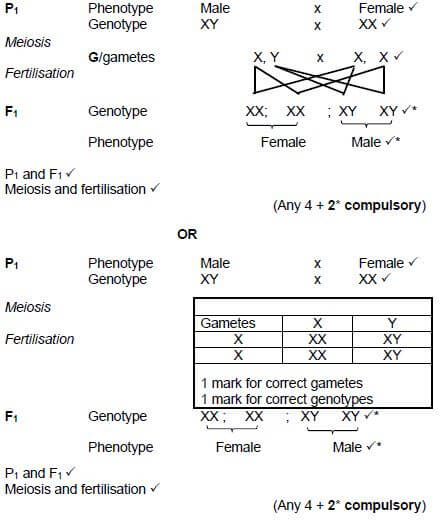 (6)
(6)
2.5.1
- Meiosis I ✓ (1)
-
- Chromosomes are arranged in homologous pairs at the equator ✓
- crossing over is taking place. ✓ (Any 1) (1)
2.5.2 1- Chromosome ✓ 2- Centromere ✓ (2)
2.5.3 C, E, B, A, D ✓✓ (NOTE: correct sequence) (2) [40]
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1 IA ✓, IB ✓, i ✓ (3)
3.1.2 2 ✓ (1)
3.1.3
- A child inherits one allele ✓ for each gene
- from each of the parents ✓ (2)
3.1.4
- In any fertilisation between two parents ✓
- who are heterozygous for blood group A and blood group B ✓
- there is a 25% chance of their children having blood group A, B, AB or O ✓/ their future children can have any one of the four blood groups (A, B, AB and O). (3)
3.2
3.2.1 Pupillary mechanism ✓ (1)
3.2.2
- Distance of the light bulb ✓ from the eye (1)
- Diameter of the pupil ✓ (1)
3.2.3 Diameter of the pupil exposed to varying distances of dim light in one-minute time intervals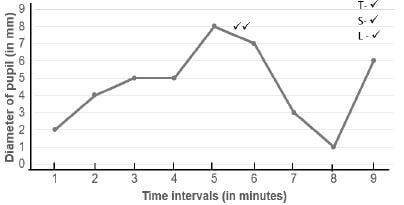
Criteria for assessing the graph: Mark (6)
Type: Line graph drawn (T) | 1 |
Title of graph | 1 |
Correct:
| 1 |
Correct:
| 1 |
Plotting of points | 1–1 to 8 points plotted correctly |
3.2.4 Between 6 and 7 minutes ✓ (1)
3.2.5
- Since measurements were not all done at different distances ✓
- the light source was at the same distance ✓ from the person’s eye. (2)
3.2.6
- Time intervals were the same ✓/ one-minute time intervals
- Same time period of exposure to light ✓/ 10 seconds
(Mark first ONE only) (Any 1) (1)
3.2.7
- Only one person was used in this investigation ✓/ small sample size used
- The investigation was only done once ✓/ not repeated (2)
3.3
- Stem cells are non-specialised cells ✓that have the ability to develop into any type cell in the body. ✓ (2)
-
- embryo ✓
- umbilical cord ✓
- bone marrow ✓
(Mark first THREE only) (3)
-
- Can be used to treat a variety of human diseases ✓/ examples Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, diabetes, spinal cord injury, heart disease, stroke, arthritis, cancer and burns.
- Generation of new tissues ✓
- Stem cells could also be used to understand why some cells develop abnormally and lead to medical problems ✓
- Stem cells may be useful in the testing and development of drugs ✓ (Any 3) (3)
3.4.1 1
- Semi-circular canals ✓ 2
- Cochlea ✓ (2)
3.4.2
- It increases the surface area✓of the inner ear/ saves space
- thereby helping to boost low frequency sounds ✓/ allowing soft sounds to be heard (2)
3.4.3
- A change in speed/direction of movement ✓
- stimulates the cristae ✓
- in the semi-circular canals ✓
- The stimulus is converted to an impulse ✓
- The impulse is transmitted to the cerebellum ✓
- via the auditory nerve ✓
- The cerebellum sends impulses to the muscles to restore balance ✓ (Any 4) (4) [40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
- The process by which gametes are formed is called gametogenesis ✔ (1)
Spermatogenesis:
- Male gametes are formed by spermatogenesis ✔
- under the influence of testosterone ✔
- Diploid cells in the seminiferous tubules of testes ✔
- undergo meiosis ✔
- to form haploid sperm cells ✔ (Max. 4) (4)
Oogenesis
- Female gametes are formed by oogenesis ✔
- Under the influence of FSH ✔
- diploid cells in the ovary ✔
- undergo mitosis ✔
- to form numerous follicles ✔
- One cell inside the follicle enlarges ✔ and
- undergoes meiosis ✔
- Of the four cells that are produced, only one survives ✔
- to form a mature haploid ovum ✔ (Max. 7) (7)
Development of the zygote from fertilisation to implantation
- The zygote divides by mitosis ✔ numerous times
- to form an embryo ✔
- The embryo develops into a ball of cells ✔
- called the morula ✔
- which then develops into a hollow ball of cells ✔
- called the blastula ✔/blastocyst.
- It embeds itself into the uterus lining ✔/endometrium (Max. 5) (5)
Assessing the presentation of the essay
Criterion | Relevance (R) | Logical sequence (L) | Comprehensive (C) |
Generally | All information provided is relevant to the topic. | Ideas are arranged in a logical/cause-effect sequence. | All aspects required by the essay have been sufficiently addressed. |
In this essay | Only information relevant to the description of spermatogenesis and oogenesis and the development of the embryo from fertilisation until implantation is given. There is no irrelevant information. | All the information regarding the spermatogenesis and oogenesis and the development of the embryo from fertilisation until implantation is given in a logical manner. | At least:
|
Mark | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Content: (17)
Synthesis: (3)
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150
PHYSICAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
PHYSICAL SCIENCES
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of 11 questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- You may use appropriate mathematical instruments.
- Number the questions correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You are advised to use the attached DATA SHEETS.
- The formulae and substitutions must be shown in ALL calculations.
- Give brief motivations, discussions, etc. where required.
- Round off your final numerical answers to a minimum of TWO decimal places.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- All diagrams are not necessarily drawn according to scale.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Four possible options are provided as answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write down (A–D) next to the question number (1.1–1.10) on your ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.11 D.
1.1 A girl placed her pencil on a dashboard of a car while the car is stationary. When the car starts to move, which ONE of the following statements will be TRUE regarding the motion of the pencil?
- It will remain stationary.
- It will move forward with the car.
- It will move backwards as the car moves forward.
- It will first move forward and then backwards. (2)
1.2 A lady applied a force F on a shopping trolley and the trolley moves forward while the lady remained stationary. Which ONE of the following statements is correct?
- The force exerted on the trolley by the lady is equal to the force exerted on the lady by the trolley.
- The lady did not experience a force exerted on her.
- The force exerted on the trolley by the lady is smaller than the force exerted on the lady by the trolley.
- The force exerted on the trolley by the lady is bigger than the force exerted on the lady by the trolley. (2)
1.3 The product of the net force acting on an object and the time that the net force acts on the object is the …
- rate of change of momentum of the object.
- impulse on the object.
- momentum of the object.
- acceleration of the object. (2)
1.4 The graph below represents the velocity versus momentum of an object. 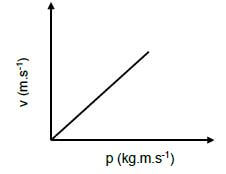
Which ONE of the following quantities is represented by the gradient of this graph?
- Impulse
- Net force
- Mass of the object
- Inverse of mass of the object (2)
1.5 Which ONE of the following acceleration versus time graphs represents the motion of a ball thrown vertically upwards to reach a maximum height after 6 s? Take upwards as positive.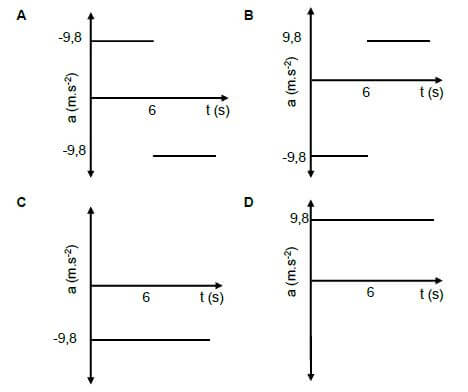 (2)
(2)
1.6 A projectile is moving upwards until it reaches its maximum height. Which ONE of the following statements is correct about the velocity?
- Velocity is zero at the maximum height.
- Velocity increases upwards.
- Velocity at maximum height is equal to velocity at point of projection.
- Velocity remain constant during its motion. (2)
1.7 Which ONE of the following statements regarding mechanical energy of an isolated is correct?
- Kinetic energy is always equal to potential energy.
- The change in kinetic energy is always equal to the change in potential energy.
- The sum of kinetic energy and potential energy is always equal to zero.
- The sum of kinetic energy and potential energy is always maximum at the maximum height. (2)
1.8 A block is moving on a horizontal surface. The work done by the gravitational force on the block is equal to zero because the …
- gravitational force on the object is equal to zero.
- gravitational force is in equilibrium with the normal force.
- angle between the gravitational force and the displacement is equal to 0°.
- angle between the gravitational force and the displacement is equal to 90°. (2)
1.9 An observer is moving relative to a stationary sound source which is emitting sound of frequency 800 Hz. As the observer moves towards the sound source, the detected frequency is 950 Hz. This observation is because the:
- Sound waves between the source and observer become compressed
- Sound waves between the source and observer become stretched out
- The amplitude of the sound waves between the source and observer increases
- The amplitude of the sound waves between the source and observer decreases (2)
1.10 The electrostatic force between two point charges which are a distance of r apart, is F. The charges are then moved to new positions such that the electrostatic force changes to 1/16F. The new distance in terms of r is …
- 4r
- 1r
4 - 8r
- 1(2) [20]
8
QUESTION 2 (Start on a NEW page.)
Two boxes, with masses of 5 kg and 4 kg, are connected by a light inextensible string passing over a frictionless pulley. The 4 kg box experiences a frictional force of 8,14 N due to the surface as it is pulled by Jane with a force of 80 N. The force applied by Jane makes an angle of 30° with the horizontal as shown in the diagram below. 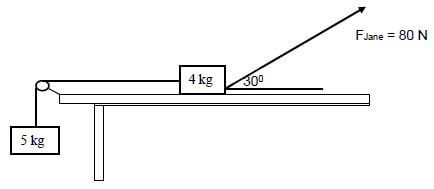
2.1 State Newton’s Second Law of motion in words. (2)
2.2 Draw a labelled free-body diagram of all the forces acting on the 4 kg box. (5)
2.3 Calculate the tension experienced in the string connecting the boxes. (5) [12]
QUESTION 3 (Start on a NEW page.)
A man of mass m, has a weight of 126,30 N on the moon. The mass and radius of the moon are 7,35 x 1022 kg and 1,74 x 103 km respectively.
3.1 State Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation in words. (2)
3.2 Calculate the mass of the man while he stands on the moon. (4) [6]
QUESTION 4 (Start on a NEW page.)
A boy lies on a balcony of a building which is at a height h above the ground. He throws a ball vertically upwards at a velocity of 13 m.s-1. The ball reached its maximum height at the top of the building. Ignore the effects of air resistance. 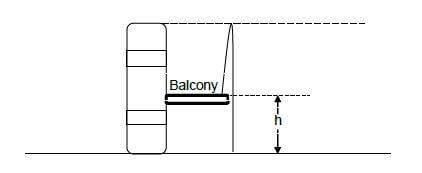
4.1 Define the term projectile motion. (2)
4.2 Calculate the time it took the ball to reach the maximum height. (3)
4.3 Calculate the magnitude of the displacement of the ball from the point of projection to its maximum height. (4)
4.4 It took the ball 3,28 s to reach ground surface from the point of projection. Calculate the:
4.4.1 Velocity with which the ball hits the ground surface (3)
4.4.2 Height of the building (6) [18]
QUESTION 5 (Start on a NEW page.)
The graph below represents the motion of a basketball ball which is dropped from a height of 8 m above the ground. The ball bounced a number of times on the ground. 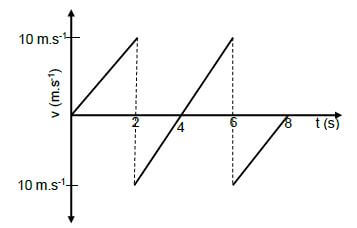
5.1 Which direction is taken as positive? (Upwards or Downwards) (1)
5.2 How many times did the ball bounce? (1)
5.3 Is the collision of the ball with the ground elastic or inelastic? (1)
5.4 At what time(s) was the ball at a maximum height after it was dropped? (2)
5.5 Draw a corresponding position vs time graph for the entire motion of the basketball from the time it was dropped.
Indicate the following:
- The height from which the ball was dropped
- The time(s) when the ball was at its maximum height (3) [8]
QUESTION 6 (Start on a NEW page.)
A traffic officer, driving a van of mass 1 500 kg at a velocity of 30 m.s-1, chased after a driver of a car of mass 1 200 kg travelling at 80 km.h-1, who did not stop at a red traffic light (robot). He accidentally hit the back of the driver’s car. After the collision the driver’s car continued to move forward at a velocity of 25 m.s-1. Ignore the effects of friction.
6.1 State the Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum in words. (2)
6.2 Calculate the velocity of the van after collision. (5)
6.3 Calculate the change in momentum of the car. (3)
6.4 By means of calculations, determine whether the collision was elastic or inelastic. (5) [15]
QUESTION 7 (Start on a NEW page.)
Two trolleys, A and B, of masses 500 g and 750 g respectively are at rest and connected to each other by means of a compressed spring as shown on the diagram below. When the spring is released, trolley A moves at a constant velocity of 2,5 m.s-1to the left. Ignore the effects of friction. 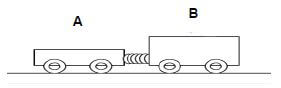
7.1 In which direction will trolley B move? Explain your answer. (3)
7.2 Calculate the magnitude of the velocity of trolley B. (4)
7.3 Trolley A continues to move to the left until it hits a wall at a velocity of 2,5 m.s-1. The wall exerts a net force of 21,5 N on trolley A over a period of 0,1 s. Ignore the effects of friction.
7.3.1 What is the magnitude of the net force exerted by trolley A on the wall? Explain your answer. (3)
7.3.2 Calculate the velocity of trolley A after colliding with the wall. (5)
7.3.3 An identical trolley C, of the same mass and velocity as trolley A collides with the same wall. The wall exerts a net force on trolley C in an increased contact time compared with contact time of trolley A. How will the impulse of trolley C compare with that of trolley A? Write down only INCREASE, DECREASE or STAYS THE SAME. Give a reason for your answer. (3) [18]
QUESTION 8 (Start on a NEW page.)
A steel ball of mass 0,2 kg rolls from point A to C and comes to rest at C, as shown on the diagram below. From A to B is a rough horizontal surface while from B to C it is frictionless. Point C is 1,2 m vertically above ground. 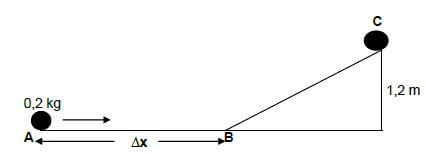
8.1 State the principle of conservation of mechanical energy in words. (2)
8.2 Use ENERGY PRINCIPLES to calculate the velocity of the ball at point B. (4)
8.3 If the initial velocity of the ball at point A is 6 m.s-1 and it took the ball 0,82 s to reach point B, calculate the distance ∆x indicated on the diagram. (3) [9]
QUESTION 9 (Start on a NEW page.)
A box, with a mass of 25 kg, is pulled with a force of 260 N up a rough inclined surface that makes an angle of 40° with the horizontal as shown in the diagram below. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0,16 between the box and the surface. 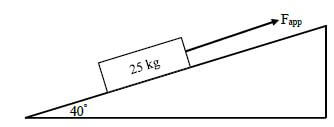
9.1 Define work-energy theorem in words. (2)
9.2 Draw a labelled free-body diagram of all the forces acting on the box. (4)
9.3 If the box started moving from rest, calculate its velocity after it had covered a distance of 8 m up the slope. (6)
9.4 Calculate the power dissipated in moving the box over a distance of 8 m. (4) [16]
QUESTION 10 (Start on a NEW page.)
10.1 Khosi detected two different frequencies, 750 Hz and 700 Hz, as he moved at constant velocity relative to a stationary ambulance which was emitting a sound through its siren.
10.1.1 State Doppler effect in words. (2)
10.1.2 Which ONE of the frequencies was detected while Khosi was moving towards the ambulance? (1)
10.1.3 Explain your answer in QUESTION 10.1.2 in terms of wavelength. (3)
10.1.4 Calculate the velocity at which Khosi was moving if the speed of sound in the air is 340 m.s-1. (6)
10.1.5 Calculate the frequency of the sound of the source. (3)
10.2 The diagrams below show two stars moving relative to each other. 
10.2.1 Is star B moving towards or away from star A? Explain your answer in terms of shift, wavelength and frequency. (4)
10.2.2 How does astronomers describe the phenomenon explained in QUESTION 10.2.1 above? (1) [20]
QUESTION 11 (Start on a NEW page.)
Two point charges of +6 μC and +4 μC are placed 200 mm apart in a vacuum.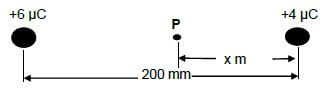
11.1 Define electric field at a point in words. (2)
11.2 Calculate the value of x when the net electric field at point P is 1,88 x 106 N.C-1to the left. (6) [8]
TOTAL: 150
DATA FOR PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 12
PAPER 1 (PHYSICS)
TABLE 1: PHYSICAL CONSTANTS
NAME | SYMBOL | VALUE |
Acceleration due to gravity | g | 9,8 m•s-2 |
Universal gravitational constant | G | 6,67 x 10-11 N•m2•kg-2 |
Speed of light in a vacuum | c | 3,0 x 108 m•s-1 |
Planck's constant | h | 6,63 x 10-34 J•s |
Coulomb's constant | k | 9,0 x 109 N•m2•C-2 |
Charge on electron | e | -1,6 x 10-19 C |
Electron mass | me | 9,11 x 10-31 kg |
Mass of earth | M | 5,98 x 1024 kg |
Radius of earth | RE | 6,38 x 103 km |
TABLE 2: FORMULAE
MOTION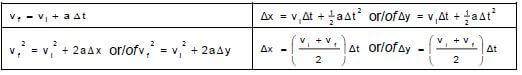
FORCE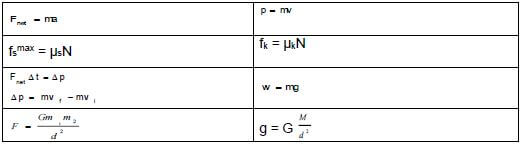
WORK, ENERGY AND POWER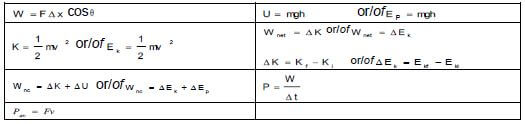
WAVES, SOUND AND LIGHT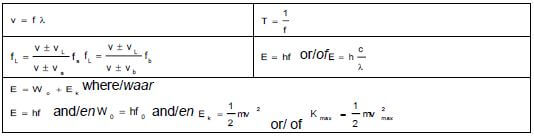
ELECTROSTATICS![]()
ELECTRIC CIRCUITS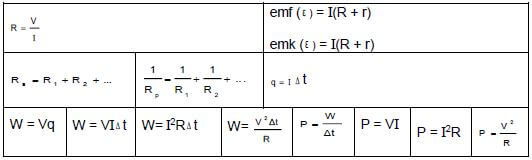
ALTERNATING CURRENT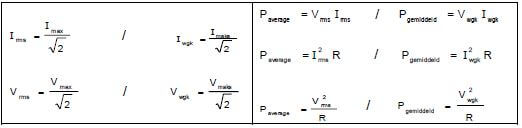
PHYSICAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
PHYSICAL SCIENCES
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your full NAME and SURNAME in the appropriate spaces on the ANSWER BOOK.
- This question paper consists of SEVEN questions.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Leave ONE line between two sub-questions, for example between QUESTION 2.1 and QUESTION 2.2.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- You may use appropriate mathematical instruments.
- You are advised to use the attached DATA SHEETS.
- Show ALL formulae and substitutions in ALL calculations.
- Round off your FINAL numerical answers to a minimum of TWO decimal places.
- Give brief motivations, discussions, et cetera where required.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Four options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Each question has only ONE correct answer. Write only the letter (A–D), corresponding to the correct answer of your choice, next to the question number (1.1–1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.11 D.
1.1 Which ONE of the following compounds has a DOUBLE BOND in its structure?
- Ethane
- Ethene
- Polyethene
- Bromoethane (2)
1.2 By definition the boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which …
- a liquid changes to vapour.
- the vapour pressure equals atmospheric pressure.
- the vapour pressure is less than the atmospheric pressure.
- the vapour pressure is greater than the atmospheric pressure. (2)
1.3 Which ONE of the following is the CORRECT IUPAC name of the compound shown below? 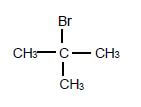
- 2-bromobutane
- 2-methyl-2-bromopropane
- 2-bromo-2-methylpropane
- 2,2,2-trimethylbromomethane (2)
1.4 Consider the reaction represented by the equation below:
CH3Br + H2O → CH3OH + HBr
The TYPE of reaction shown above is …
- substitution.
- combustion.
- esterification.
- polymerisation. (2)
1.5 The boiling points of propanal and propanone are compared.
Which ONE of the following is the INDEPENDENT variable in this comparison?
- Molar mass
- Chain length
- Hydrogen bonds
- Homologous series (2)
1.6 Which ONE of the following factors will change the value of the equilibrium constant, Kc?
- Pressure
- Surface area
- Temperature
- Concentration (2)
1.7 The reaction of magnesium powder and hydrochloric acid is used to investigate the factors that affect reaction rate. The balanced equation for the reaction is:
Mg(s) + 2HCℓ (aq) → MgCℓ2(aq) + H2(g)
In ALL the experiments the hydrochloric acid is in EXCESS and the magnesium powder is completely covered.
The results of the experiments are shown in the table below:
Experiment | Concentration of HCℓ | Volume of | Mass of |
P | 1,5 | 200 | 1,8 |
Q | 1,2 | 400 | 1,8 |
R | 0,8 | 200 | 1,4 |
S | 1,5 | 200 | 1,5 |
Which experiments will produce the SAME amount of hydrogen at same temperature and pressure?
- P and Q
- Q and R
- R and S
- P and S (2)
1.8 Diluted hydrochloric acid is spilt on floor tiles in the laboratory. Which ONE of the following substances can be used to neutralise the acid?
- NaCℓ
- NH4Cℓ
- H2SO4
- Na2CO3 (2)
1.9 Study the ionisation reactions given below:
H3PO4 + H2O → H2PO4- + H3O+
H2PO4- + H2O → HPO42- + H3O+
In the reactions H2O acts as a(n) …
- base.
- ampholyte.
- weak acid.
- strong acid. (2)
1.10 The potential energy diagram shown below is for the reversible hypothetical reaction shown below:
2 AB(g) ⇌ A2B2(g) 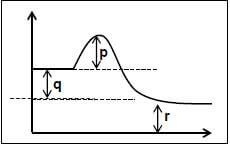
Consider the following statements about the reaction:
- The forward reaction is endothermic
- The value of ΔH for the REVERSE reaction is equal to q
- The activation energy for the reverse reaction is equal to p + q Which of the above statements is/are TRUE?
- I only
- I and II
- III only
- II and III (2) [20]
QUESTION 2
A test tube containing an alcohol P, carboxylic acid R and sulphuric acid is heated in a water bath, as illustrated below. A piece of wet cotton wool is placed at the mouth of the test tube.
Alcohol P + Carboxylic acid R Ester + X 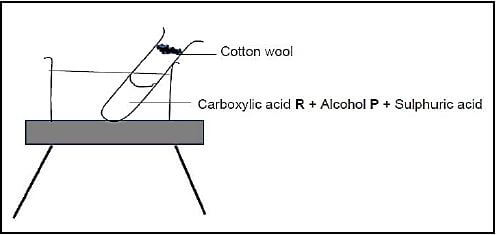
2.1 Is the sulphuric acid that is used CONCENTRATED or DILUTE? (1)
2.2 What is the purpose of placing cotton wool at the mouth of the test tube? (1)
2.3 Write down the molecular formula of the inorganic product, X. (1)
2.4 Alcohol P is a positional isomer of propan-2-ol. Write down the IUPAC name of alcohol P. (2)
2.5 Chemical analysis shows that carboxylic acid R contains 54,55% C, 9,1% H and x % O. The molar mass of the ester produced is 130 g·mol-1. Determine by calculation the MOLECULAR formula of carboxylic acid R. (8) [13]
QUESTION 3
3.1 The boiling points of three compounds (A, B and C) are compared in the table below:
COMPOUND | BOILING POINT (°C) | |
A | Pentan-1-ol | 138 |
B | Butanoic acid | 164 |
C | Methyl propanoate | 68 |
3.1.1 For compound C write down the:
- Name of the homologous series to which it belongs (1)
- STRUCTURAL formula (2)
3.1.2 Give a reason why this is a fair comparison. (2)
3.1.3 Explain why hydrogen bonds are stronger in compound B than in compound A. (2)
3.2 The vapour pressure values of a secondary and a tertiary alcohol are compared in the table below:
COMPOUND | MOLECULAR FORMULA | VAPOUR PRESSURE | |
D | Secondary alcohol | C4H10O | X |
E | Tertiary alcohol | C4H10O | Y |
3.2.1 Are compounds D and E STRUCTURAL isomers? Write down Yes or No. Give a reason for the answer. (3)
3.2.2 Which ONE of the two values, X or Y is HIGHER? Fully explain the answer. (4) [14]
QUESTION 4
4.1 Study the two reactions shown below. P is an inorganic compound. R is an organic compound.
- : 3-methylbut-1-ene + P 1,2-dichloro-3-methylbutane
- : 2-bromobutane + Base R + NaBr + H2O
4.1.1 Write down the TYPE of reaction represented by:
- Reaction I (1)
- Reaction II (1)
4.1.2 Write down the:
- STRUCTURAL formula of 1,2-dichloro-3-methylbutane (3)
- Name of the inorganic reactant P (1)
4.1.3 For reaction II write down:
- The structural formula and IUPAC name of the major product, R (4)
- ONE reaction condition (1)
4.2 The equation shown below shows n molecules of H2C=CH2 reacting to produce a polymer. H2C=CH2 in the equation below represents small organic molecules that can be covalently bonded to each other in a repeating pattern
Polymerisation
n H2C=CH2 → [CH2CH2] 1000
4.2.1 Is this reaction an example of ADDITION or CONDENSATION polymerisation? (1)
Write down:
4.2.2 The value of n (1)
4.2.3 A term used for the underlined phrase (1)
4.2.4 ONE use of the polymer produced in this reaction (1)
4.3 The following equation represents the cracking reaction of octane (C8H18). Y is a straight chain organic compound.
High temperature/High pressure
C8H18 → Y + C2H4
4.3.1 Define the term cracking reaction. (2)
4.3.2 Is this reaction an example of THERMAL CRACKING or CATALYTIC CRACKING? (1)
4.3.3 Write down the STRUCTURAL FORMULA and IUPAC name of compound Y. (4) [22]
QUESTION 5
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) decomposes according to the following equation:
2H2O2(aq) 2H2O(ℓ) + O2(g)
5.1 State THREE factors that can INCREASE the rate of this reaction. (3)
5.2 Define the term reaction rate. (2)
The rate of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide is investigated in THREE experiments. The initial temperature of H2O2 is the same in ALL the experiments.
The reaction runs to completion in ALL the experiments.
5.3 In experiment 1 a solution of hydrogen peroxide is heated to 35 °C. The concentration of H2O2 was measured at different time intervals during the experiment. The following results were obtained:
TIME (MINUTES) | H2O2 CONCENTRATION (mol·dm-3) |
0 | 1,9 |
15 | 1,45 |
55 | 1,10 |
100 | 0,85 |
215 | 0,60 |
5.3.1 Calculate the average reaction rate, in mol·dm-3·min-1 during the first 15 minutes. (3)
5.3.2 Give a reason why the average reaction rate is HIGHER during the first 15 minutes, compared to the time interval 100 to 215 seconds. (2)
5.4 In experiment 2, a small amount of manganese dioxide is added to the same H2O2 solution (used in experiment 1) and the mixture is heated to 35 °C. 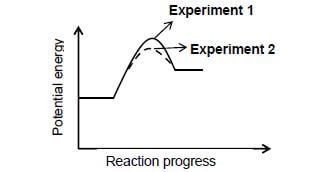
5.4.1 Is the reaction EXOTHERMIC or ENDOTHERMIC? (1)
5.4.2 Use the collision theory to explain the effect of manganese dioxide on the rate of decomposition of H2O2. (4)
5.5 In experiment 3 the same volume of the solution of H2O2 (used in experiment 1) is used but ONLY the temperature to which the solution is heated is changed. The Maxwell-Boltzman distribution curves for experiment 1 and 3 are shown below: 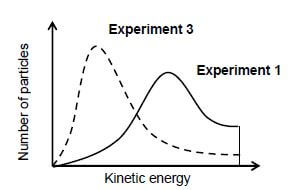
5.5.1 Which experiment (1 or 3) was carried out at a HIGHER temperature? Give a reason for the answer. (2)
5.5.2 How does the area under the graph of experiment 1 compare to the area under the graph of experiment 3? Write down GREATER THAN, EQUAL TO or LESS THAN. Explain the answer. (2)
5.6 In experiment 2 the total volume of oxygen produced at 35 °C is 0,2 dm3. Calculate the mass of H2O2 that decomposed in experiment 2 if the molar volume of oxygen at 35 °C is 24,8 dm3·mol-1. (5)
5.7 The graphs below show how the concentration of H2O2 changes with time in the experiments. 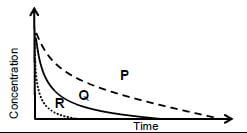
Which graph (P, Q or R) represents the results of:
5.7.1 Experiment 1 (1)
5.7.2 Experiment 2 (1)
5.7.3 Experiment 3 (1) [27]
QUESTION 6
Carbon dioxide gas, CO2(g), reacts with carbon, C(s), according to the following balanced equation:
CO2(g) + C(s) ⇌ 2CO(g)
The system reaches equilibrium at 1 000 °C.
6.1 Define the term chemical equilibrium. (2)
6.2 How will EACH of the following changes affect the number of moles of CO(g) at equilibrium? Choose from INCREASES, DECREASES or REMAINS CONSTANT.
6.2.1 The addition of more carbon, C (1)
6.2.2 The addition of more CO2 (1)
6.2.3 Decreasing the pressure by increasing the volume (1)
6.3 Use Le Chatelier’s principle to explain the answer to QUESTION 6.2.3 above. (3)
6.4 The sketch graph given below shows the changes in the rates of reaction from the moment the reagents are introduced into the container. The reaction reaches equilibrium for the first time at t1. A change is made to the equilibrium mixture at t2. 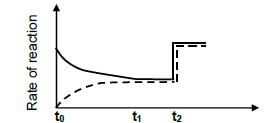
6.4.1 Which reaction (FORWARD or REVERSE) is represented by the broken line? (1)
6.4.2 What change was made at t2? (2)
Initially 104,72 g of CO2 was heated with EXCESS carbon C in a sealed flask of volume 250 cm3. The equilibrium mixture was found to contain 1,90 mol of CO2.
6.5 Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant, Kc at 1 000 °C. (8)
6.6 The value of Kc for the reaction decreases to 0,333 when the temperature is changed to 25 oC.
6.6.1 Is there a HIGH or LOW yield at 25 oC? Give a reason for the answer. (2)
6.6.2 Is the FORWARD reaction ENDOTHERMIC or EXOTHERMIC? Explain the answer fully. (4) [25]
QUESTION 7
7.1 The hydrogen carbonate ion (HCO3-) undergoes hydrolysis according to the equation:
HCO3-(aq) + H2O(ℓ) ⇌ CO32-(aq) + H3O+(aq)
7.1.1 Define the term hydrolysis. (2)
7.1.2 Give a reason why HCO3-is regarded as an ampholyte. (2)
Write down the FORMULA of the:
7.1.3 Conjugate acid of CO32-(1)
7.1.4 Conjugate acid of HCO3-(not in the equation) (1)
7.2 A weak monoprotic acid is dissolved in water to produce a solution of accurately known concentration.
7.2.1 Write down a term for the underlined phrase. (1)
7.2.2 Which ONE of the following is an example of a weak monoprotic acid?
CH3COOH | HCℓ | H2CO3 |
The weak monoprotic acid has a concentration of 0,2 mol.dm-3. (2)
7.2.3 Calculate the volume to which 20 cm3 of the acid must be diluted to produce a solution with a concentration of 0,16 mol·dm-3. (3)
7.3 During a titration a learner adds 30 cm3 of NaOH solution of concentration 0,1 mol.dm-3 to an Erlenmeyer flask and titrates this solution with 25 cm3 HCℓ solution. The balanced equation for the reaction that takes place is:
NaOH + HCℓ NaCℓ + H2O
7.3.1 Name this type of reaction. (1)
7.3.2 At what pH range will a suitable indicator for this titration change colour? Choose from:
6,8 to 7,2 | 3 to 5 | 8,6 to 10 |
Give a reason for the answer. (3)
7.3.3 Calculate the concentration of the HCℓ that was used to neutralise the NaOH in the Erlenmeyer flask. (4)
The learner passes the endpoint by adding an extra 8 cm3 of the HCℓ solution.
7.3.4 Define the term endpoint. (2)
7.3.5 Calculate the pH of the solution in the flask after the addition of the extra 8 cm3 of HCℓ. (7) [29]
TOTAL: 150
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE
DATA FOR PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 12
PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY)
TABLE 1: PHYSICAL CONSTANTS
NAME | SYMBOL | VALUE |
Standard pressure | pθ | 1,013 × 105 Pa |
Molar gas volume at STP | Vm | 22,4 dm3∙mol-1 |
Standard temperature | Tθ | 273 K |
Charge on electron | e | -1,6 × 10-19 C |
Avogadro’s constant | NA | 6,02 × 1023 mol-1 |
TABLE 2: FORMULAE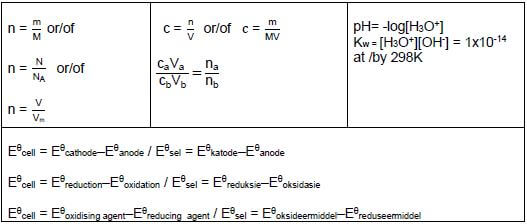
TABLE 3: THE PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS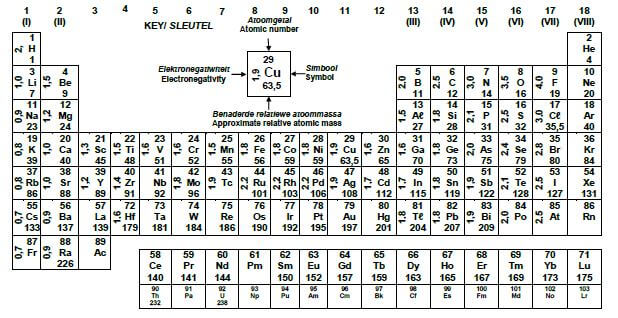
PHYSICAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
PHYSICAL SCIENCES
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2019
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1 B √√ (2)
1.2 B √√ (2)
1.3 C √√ (2)
1.4 A √√ (2)
1.5 D √√ (2)
1.6 C √√ (2)
1.7 A √√ (2)
1.8 D √√ (2)
1.9 A √√ (2)
1.10 D √√ (2) [20]
QUESTION 2
2.1 CONCENTRATED √ (1)
2.2 To prevent reagents escaping √ /To smell the ester/Acts as a condenser (1)
2.3 H2O √ (1)
2.4 propan-1-ol √√ Accept 1-propanol propanol (1/2) (2)
2.5
- n= 54,55/12 √ = 4,55 n = 9,1/1 √= 9,1 n =(100-54.55-9.1) √ /16 √ = 2.27
= 2 = 4- Empirical formula C2H4O √
- Molar mass(R) = 130 + 18 - 60= 88 √
- MMolar Mass (Empirical formula) = 2 x 12 + 4 x 1 + 1 x 16 = 44 √
- Molecular formula = C4H8O2 √ (8) [13]
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1
- Esters √ (1)
-
 (2)
(2)
Marking Criteria
- Whole structure correct2/2
- Only functional group correct ½
3.1.2 Same molecular mass √√ /Same molar mass (2)
3.1.3 B has two sites for hydrogen bonding √. A has one site for hydrogen bonding √ (2)
3.2
3.2.1 Yes √
- Same molecular formula √ but different structural formulae √ (3)
3.2.2 Y √
- D has a larger surface area/chain length than E √
- London forces/Induced-dipole forces √/Dispersion forces stronger√ in D than in E
- More energy needed to break/overcome forces in √
OR
Y √
- E has a smaller surface area/chainlength than D √
- London forces/Induced-dipole forces √/Dispersion forces weaker in E than in D
- Less energy needed to break forces in E √(4)[14]
QUESTION 4
4.1
4.1.1
- Addition √ /Halogenation/Bromination √ (1)
- Elimination √/Dehydrohalogenation √ (1)
4.1.2
 (3)
(3) - Marking criteria
- Whole structure correct 3/3
- Two Br atoms in structure 1/3
- Marking criteria
- Chlorine √ (1)
4.1.3
 (4)
(4) - Marking criteria
- Whole structure correct 2/2
- Only functional group correct ½
- Marking criteria
- Strong heat √ OR Concentrated strong base (1)
4.2
4.2.1 ADDITION √ (1)
4.2.2 n = 1000 √ (1)
4.2.3 Monomer √ (1)
4.2.4 Make plastics√/ (Any other correct answer) (1)
4.3
4.3.1 Breaking down of a long chain √ /hydrocarbon/alkane into more useful shorter chains √ (2)
4.3.2 THERMAL CRACKING √
TERMIESE KRAKING (1)
4.3.3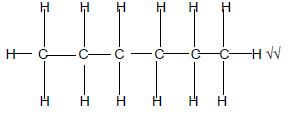 Hexane √√ (4)
Hexane √√ (4)
Marking criteria
- Whole structure correct 2/2
- If one or more hydrogens are omitted ½[22]
QUESTION 5
5.1 Temperature√/Concentration √ (of H2O2)/Add a catalyst √(3)
5.2 Change in concentration per unit time/Rate of change of concentration √√ OR change in amount/volume/mass of reactant/product per unit time. (2)
5.3
5.3.1 Average rate
- = - ∆c/∆t= - (1,45-1,9) √ /(15-0) √
= 0,03√ (mol·dm-3·min-1) (3)
5.3.2 High concentration √√ ( of H2O2 initially)(2)
5.4
5.4.1 ENDOTHERMIC √ (1)
5.4.2 Catalyst increases rate of reaction√
- By lowering activation energy /Deur aktiveringsenergie te verlaag √
- More particles have sufficient Ek to react √/More particles have Ek greater or equal to Ea (4)
5.5
5.5.1 Experiment 1 √ : More particles have higher Ek √(2)
5.5.2 EQUAL TO √Same amount of H2O2 used in both experiments √ (2)
5.6
- nO2 = V/Vm = 0,2/24,8 √ = 8,065 x 10-3 mol
nH2O2 = 2 √ x 8,065 x 10-3
= 0,061 mol
m H2O2 = nM √= 0,0161 x (2+32) √
= 0,547g√ (0,55 g ) (5)
5.7
5.7.1 Q √ (1)
5.7.2 R √ (1)
5.7.3 P √ (1) [27]
QUESTION 6
6.1 Stage reached by a chemical reaction where the rate of forward reaction equals the rate of reverse reaction √√ (2)
6.2 6.2.1 REMAINS THE SAME √ (1)
6.2.2 INCREASES √ (1)
6.2.3 INCREASES √ (1)
6.3 Decreasing pressure is opposed √Reaction which produces more gas moles is favoured √ Forward reaction is favoured √ (3)
6.4 6.4.1 REVERSE √(1)
6.4.2 Catalyst √√ (added)(2)
OPTION 1
6.5 CALCULATIONS USING NUMBER OF MOLES
- Divide by 44 in n = m/M √
- Divide nCO2 equilm & nCO equilm by 2 √
- ∆n(CO2) = ninitial -neq √
- Ratio CO2 : CO 1 : 2 √
- nequil CO = nCOinitial+ ∆n(CO) √
- Kc expression √
- Substituting cequilmCO en cequilimCO2 √
- Final answer √
OPTION 1
ninitial CO2= m/M = 104,72/44 √ = 2,38 mol
| CO2 | C | CO | |
| ninitial | 2,38 | 0 | |
| ∆n | 0,48 | 0,95 (Ratio) | |
| nequilm | 1,9 | 0,96 | |
| 7,6 | 3,84√(Division by 0,25) |
- Kc = [CO]2/[CO2] √
= 3,842/7,6 √
= 1,94 √
OPTION 2
CALCULATIONS USING CONCENTRATION
- Substitute into C=m/MV
- Substitute into c=n/V√
- ∆c(CO2) = cinitial -ceq √
- Ratio CO2 : CO 1:2 √
- cequil CO = cCOinitial+ ∆c(CO) √
- Kc expression√
- Substituting cequilmCO and cequilimCO2 √
- Final answer √
| Initial Concentration of CO2 | Equilibrium concentration of CO2 |
| c= m MV C = 104,72 (44)(0,25) c = 9,52mol.dm-3 | c = n v c = 1,9 0,25 c=3,84mol.dm-3 |
| CO2 | C | CO | |
| Cinitial | 9,52 | - | 0 |
| ∆c | 1,90√ | - | 3,84√(Ratio) |
| c equilm | 7,60 | - | 3,84√ |
- Kc = [CO]2/[CO2] √
= 3,842/7,6 √
= 1,94 √ (8)
6.6
6.6.1 Low √ Yield/
Kc is low √/ Kc is less than 1/ [REACTANTS] > [PRODUCTS]2)
6.6.2 Exothermic √
- As temperature decreases, Kc decreases, [Products]decreases √OR [Reactants increases]
- Reverse reaction is favoured √
- Decrease in temperature favours exothermic reaction √ (4) [25]
QUESTION 7
7.1
7.1.1 Reaction of a salt with water √√ (2)
7.2
7.1.2 Can act as acid and as a base √√/Can donate H+ and accept H+(2)
7.1.3 HCO3- √ (1)
7.1.4 H2CO3 √ (1)
7.2 7.2.1 Standard √ (solution) (1)
7.2.2 CH3COOH √√ (2)
7.2.3
- c1V1=c2V2 n=cV=(0,2)(0.02) √ =0,004 mol
0,2 x 20 √ = 0,16 x V2 √ V=n/c= (0,004)/(0,16) √
V2 = 25 cm3√ OR 0,025 dm3 V=25 cm3 √ OR 0,025 dm3 (3)
7.3 7.3.1 Neutralisation √ (1)
7.3.2 6,8 to 7,2 √ Titration between strong base and a strong acid √ Solution at endpoint is neutral √ (3)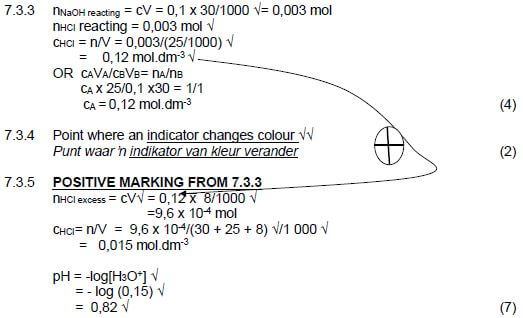
TOTAL: 150

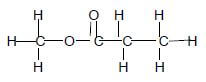 (2)
(2)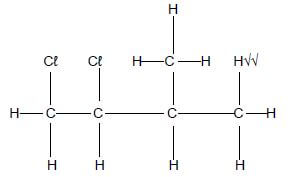 (3)
(3) 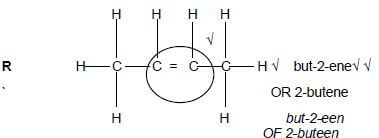 (4)
(4)