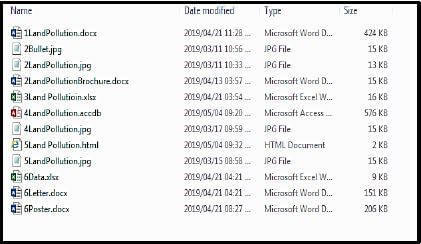
Adele
Economics P2 Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Exams Past Papers and Memos September 2019 Preparatory Examinations
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1.1.1 B √√ structure
1.1.2 B √√ technical
1.1.3 C √√ interdependent
1.1.4 A √√ packaging
1.1.5 D √√ taxation
1.1.6 D √√ mortgage
1.1.7 C √√ transit
1.1.8 A √√ non-renewable (8 x 2) (16)
1.2 MATCHING ITEMS
1.2.1 C √ determined by the interaction between demand and supply
1.2.2 E √ additional remuneration for entrepreneurship
1.2.3 I √ the value of what you have to give up in order to choose something else
1.2.4 A √ has a hybrid structure
1.2.5 D √ traditional way of doing things that are unique to a given culture
1.2.6 G √ used to calculate all-inclusive inflation
1.2.7 H √ visiting art galleries, museums, archaeological sites etc.
1.2.8 F √ when heat is trapped by CO2 layer in the atmosphere (8 x 1) (8)
1.3 GIVE ONE TERM
1.3.1 Explicit costs √
1.3.2 Long run √
1.3.3 Externalities √
1.3.4 Deflation √
1.3.5 World heritage sites √
1.3.6 Biodiversity √ (6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer TWO of the three questions from this section in your ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 2: MICROECONOMICS
2.1
2.1.1 Give any TWO examples of variable costs.
- Water √
- Electricity √
- Raw materials √
- Sales commissions √
- Direct labour costs √
- Packaging √
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 Why are individual market participants in a perfect market insignificant to the market as a whole?
- They have no power in the market√√
- They cannot influence the prices of products √√
- They accept the market price as given by the market as a whole √√
- They act completely independent of one another√√
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.2
2.2.1 Provide a suitable label for curve A (1) Average Revenue / Demand curve √
2.2.2 What is the selling price for the business above?
- 100 √ (1)
2.2.3 Briefly describe the term monopoly.
- Monopoly is a market structure where only one seller operates with blocked entry. √√
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.2.4 Explain a reason for the shape of total revenue curve.
- The slope of this curve rises as more output is produced, eventually reaching a peak, then becoming negative √√
- The changing slope of this curve is due to the changing price √√
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
2.2.5 Redraw Graph 1 in your answer book and show how a monopoly will make economic profit. 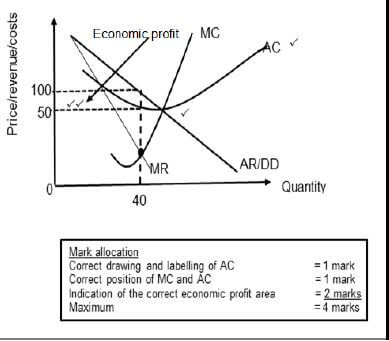
(4)
2.3 DATA RESPONSE
2.3.1 Name the market structure that led to the implementation of competition policy.
- Imperfect market /Monopoly/Monopolistic Competition/Oligopoly √ (1)
2.3.2 Which institution provides final decisions when parties are dissatisfied with rulings of the Competition Tribunal?
- Competition Appeal Court √ (1)
2.3.3 Briefly describe the term regulation in economics.
- It is the imposition of rules by the government, backed by use of penalties that are intended to modify economic behaviour of firms. √√
(Accept any other relevant correct response) (2)
2.3.4 What is the role of the Competition Commission?
- It is to investigate, control and evaluate restrictive business practices √√ (2)
2.3.5 Why is it important for the South African government to control competition among businesses?
It is important because the government would like to:
- promote efficiency, adaptability and development of the economy √√
- provide consumers with competitive prices and product choices √√
- promote employment and advance social and economic welfare of SA √√
- expand opportunities for SA participation in world market√√
- ensure that SMMEs have equal opportunities to participate in the economy√√
(Accept any other relevant correct response) (2 x 2) (4)
2.4 Briefly explain entry and perfect knowledge as characteristics of a perfect competitor.
Entry
- There is freedom of entry and exit in the market, i.e the market is fully accessible √√
- Entry is not subject to any restrictions e.g. financial, technological barriers √√
- If an individual business observes another business making a large profit in a specific market, it can open a similar business that supplies the same product √√
- New firms will enter and compete in a specific market as long as there are opportunities to make a profit √√
Perfect knowledge
- Both buyers and sellers have complete information about the prevailing market conditions √√
- There is no information failure or time lag in the flow of information √√
- Given that producers and consumers have perfect knowledge, it is assumed that they make rational decisions to maximise their self-interest
- consumers look to maximise their utility, and producers look to maximise their profits√√
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 4) (8)
2.5 What positive impact will an increase in suppliers of electricity have on South Africa?
The economy will benefit because this will result in:
- improving competition as more firms will enter the market and produce electricity √√
- lowering price of electricity for both consumers and producers in the economy √√
- improving the quality of service provided by electricity suppliers √√
- increasing production in the economy as a whole as there will be reduction in production costs
- creating more jobs for the people therefore improving the welfare of the consumers
- increasing economic growth due to increased number of suppliers in the economy
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (4 x 2) (8) [40]
QUESTION 3: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
3.1 3.1.1 Name any TWO negative effects of tourism.
- Damage to the landscape
- Litter
- Erosion
- Fires
- Traffic congestion
- Pollution
- Expensive local goods (2 x 1) (2)
3.1.2 Why is the preservation of natural resources important?
- It is essential for promoting sustainable development
- It is important for the alleviation of poverty
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
3.2 DATA RESPONSE
3.2.1 Name the economic sector that is represented by tourism. - Tertiary/service sector (1)
3.2.2 Which type of tourism is depicted in the data above?
- Domestic tourism/local tourism (1)
3.2.3 Briefly explain the term tourism.
- Tourism refers to the activities of people travelling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for no more than one consecutive year for leisure, business and other purposes
(Accept any other relevant correct response) (2)
3.2.4 Explain a reason for the growth of foreign tourism in South Africa.
- SA is a peaceful and prosperous democratic country
- It is cheaper for foreigners to visit South Africa because of the low value of rand
- SA offers a wide variety of tourism attraction – it is a world in one
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
3.2.5 How can tourism alleviate poverty in rural areas?
Tourism can alleviate poverty by:
- providing rural people with direct and indirect jobs
- hiring rural people who work directly in the sector as tour operators, travel agents, flight attendants etc.
- providing income to rural people through spending by tourists on goods and services
- allowing rural people to benefit from the infrastructure built for tourists
- acquiring skills needed in tourism industry
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 2) (4)
3.3 DATA RESPONSE
3.3.1 Name the organisation which has facilitated a number of agreements regarding disposal of toxic chemical waste.
- United Nations (1)
3.3.2 What could be the cause of global warming? (1)
- Emission of gases/greenhouse gases
3.3.3 Briefly describe the term climate change.
- It is the change in the composition of the atmosphere that is related to human activities
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.3.4 Why does the government provide environmental subsidies to businesses?
- To encourage businesses to produce environmentally friendly products
- For the development of new techniques and technology so as to reduce pollution
- To promote recycling of waste products
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
3.3.5 How are farmers affected by acid rain?
Farmers are negatively affected by acid rain because:
- crop production will decrease
- the price of agricultural products will be high
- animal husbandry will decrease as it will be affected by lack of water and food
(Accept any other relevant correct response) (2 x 2) (4)
3.4 Briefly explain the economic benefits of tourism for the government.
The government will benefit from tourism through:
- increased revenue because tourism makes direct and indirect contribution to the government revenue through taxes, e.g. airport departure tax, air tickets etc.
- advertising and excellent service delivered to tourists, thus creating a good image of the country.
- job creation and relieve poverty especially in the informal sector e.g. musicians
- earning of foreign exchange for the country thereby increasing the foreign reserves
- recovering external costs, as the government is able to recover from tourists a portion of what serves as a compensation for providing the infrastructure
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (4 x 2) (8)
3.5 How can environmental degradation be prevented?
It can be prevented by:
- planting trees as they can absorb carbon dioxide thereby providing a cleaner environment
- avoiding littering by people as it may lead to global warming
- educating people about the importance of recycling items or reusing them instead of throwing away
- avoiding burning of paper and other material as this may result into pollution
- avoiding intense agricultural practices which destroy fertile land
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (4 x 2) (8) [40]
QUESTION 4: MICROECONOMICS AND CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
4.1
4.1.1 Name any TWO major international protocols and agreements on sustainable development.
- Rio de Janerio summit (UNCED)
- Johannesburg summit
- Rio + 20 summit
- Kyoto Protocol
- Millennium development goals
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
- Conference of the Parties (2 x 1) (2)
4.1.2 How are consumers affected by maximum prices?
- They will buy goods and services at a price lower than the market price
(Accept any relevant correct response) (1 x 2) (2)
4.2 DATA RESPONSE
4.2.1 What is the nature of the service offered by the firms above?
- Homogenous / Differentiated (1)
4.2.2 How is the shape of the demand curve of the oligopoly?
- Kinked (1)
4.2.3. Briefly describe the term oligopoly.
- A market structure where only a few sellers operate
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
4.2.4 What does it mean for Vodacom to be a dominant firm?
- It has a significantly larger market share than its competitors or rivals
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
4.2.5 How do oligopoly competitors benefit from collusion?
Oligopoly competitors benefit by:
- having their performance increased
- preventing uncertainties that may occur
- having a large market share by preventing entry of new organisation
(Accept any relevant correct response) (2 x 2) (4)
4.3 DATA RESPONSE
4.3.1 What is the group of animals in the picture above called?
- The Big FIVE (1)
4.3.2 Which international treaty is concerned with endangered species?
- The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) (1)
4.3.3 Briefly describe the term endangered species.
- A species of animal or plant that is seriously at risk of extinction.
(Accept any other correct relevant response). (2)
4.3.4 How can education be used as a measure to ensure sustainability?
- People should be made aware of environmental issues and the consequences of their actions
- Innovative approaches can be tried to educate people, e.g. setting up community wildlife reserves
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
4.3.5 Why were the Millennium Development Goals not achieved? Millennium development Goals were not achieved because:
- of a lack of proper monitoring systems
- the earth forest areas still continue to shrink
- there are declining trends in productivity
- illicit poaching and tracking wildlife continue to prevent conservation
(Accept any relevant correct response) (2 x 2) (4)
4.4 With the aid of a well labelled graph, explain economic loss in a perfect market. 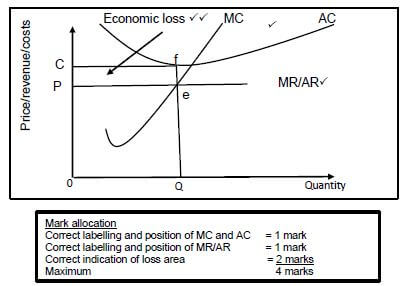
- The business is in equilibrium at point e where MR=MC and optimal quantity produced is Q at price P and cost C
- Economic loss is made where AR is less than AC which is indicated by the CPef area (8)
4.5 Examine the success of marketing as a strategy to promote tourism in South Africa.
Marketing has been successful in promoting tourism by:
- having a modern looking website which has been used to build the brand for tourist services and has attracted many tourists to South Africa
- utilising the online bookings and payments ensures that tourists pay for their hotel rooms and book recreational activities online prior their travel
- providing information to tourists about their safety and security through reduction of crime and violence on tourists, has attracted many visitors to the country through tourism indabas
- devoting adequate resources to provide for safety of tourists through speedy and effective legal procedures
- emphasising the diversity of the tourism products which include, cruise tourism, sports, wildlife safari’s etc. has attracted tourists both nationally and internationally
- making travel more accessible and affordable to all through Sho’t left campaign
- providing reliable and affordable mode of transportation in accordance with tourist demand and tourism has provided services that are tailor made to the needs of the tourists, for example Gautrain
- maintaining and upgrading infrastructure to improve accessibility and mobility to tourist destination, has improved the tourism sector e.g. information centres, rail and road network, telecommunication etc.
(Accept correct and relevant response) (8) [40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer ONE of the two questions from this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 5
- Discuss in detail the causes of market failure focusing on the following:
- Missing markets
- Lack of information (26)
- Evaluate the success of the government intervention in markets in distributing wealth. (10)
INTRODUCTION
Market failure means that the best available/optimal production outcome has not been achieved.
Markets fail when they are unable to allocate resources efficiently.
(Accept any other correct response) (Max.2) (2)
MAIN PART
Missing markets
Markets are incomplete and cannot meet the demand for all goods.
Public goods
- Free market does not want to supply these goods, hence government supply them
- Businesses in the free market will not charge a price for these goods based on their use, so they will not supply them
- Public goods include:
- Community goods
These are goods such as defence, police services, street lighting, flood control etc.
Features of community goods: - Non-rivalry
Consumption by one person does not in any way reduce consumption by another person. E.g. street lighting, lighthouse
Consumption by one person may not prevent others from enjoying it too - Non-excludability
Consumption of a good cannot be confined to those who have paid for it, so there are free riders
They are provided for all users even those who did not pay for it, e.g. television and radio - Social benefits outstrip private benefits
Community goods often have large social benefits relative to private benefits, e.g. health care and education - Infinite consumption
Once they are provided the marginal costs of supplying one more individual is zero, e.g. traffic lights - Non-rejectability
Individuals may not be able to abstain from consuming them even if they want to, e.g. street lighting
- Community goods
- Collective goods
- These are goods like beach facilities, streets, pavements, roads, bridges etc.
- They are provided for a user fee
- Provision of some collective goods is subsidised, e.g. public transport and clean water
Merit and demerit goods
Merit goods
- They have important benefits to the user and to the general welfare of the community
- They are highly desirable for the general welfare of the people of a country but are often not highly rated by the market
- If people had to pay market prices for them, relatively little would be consumed
- In this sense, the market will fail to the detriment of the economy and society
- Examples of such goods are health care and education, skills training, safety, inoculations and car seat belts
- Markets do not reflect the full value of merit goods because markets only take the private benefits into account and not social benefits
- Markets undervalue these products and provide too few of them at prices that are too high
- If consumers were to pay a full market price, very little would be consumed and the market therefore would fail
Demerit goods
- They are over consumed by individuals
- Some consumers may be unaware of the true costs of consuming them, i.e. their negative externalities
- Government can ban their consumption or reduce it by means of taxation and provide information about their harmful effects
- Examples include: cigarettes, alcohol, tobacco, non-prescription drugs
- When the market is willing to produce them, it will supply too much of these goods
Lack of information
- Consumers, workers and entrepreneurs do not always have necessary information at their disposal to make rational decisions, hence lack of information makes markets to fail operating well
- Consumers do not have detailed information on advanced technology to be aware of the goods produced so as to maximise their utility
- Workers also need information about all job opportunities and benefits to ensure that they use their labour effectively but they are unaware of such job opportunities outside their current employment, hence markets fail to employ the required labour force
- Entrepreneurs may lack information about costs and availability of factors of production; therefore, they may be operating on the basis of incorrect information and make wrong decisions
(Accept any other relevant response)
(Allocate a maximum of 8 marks for mere listing or examples) (26)
ADDITIONAL PART
Evaluate the success of the government intervention in markets in distributing wealth.
The government has been successful in distributing wealth through:
- providing public goods for collective consumption, e.g. provision of health care services, infrastructure development etc. leading to uplifting of the welfare of individuals
- investing in education and training by providing free education in schools and tertiary institutions resulting in people getting opportunities of being employed and accumulating wealth
- reducing poverty through social transfer to the poor thus improving their welfare
- boosting participation of black entrepreneurs in economic activities thus creating employment for different skills in the economy leading to improved standard of living for all
Unsuccessful by:
- failing to reduce inequality despite the social transfers provided because the grants do not cater for the unemployed
- using an official definition of unemployment which exclude people who have given up looking for jobs
- creating jobs that barely keep up pace with the growth in labour force
- failing to have proper monitoring tools for granting tenders to empower blacks
- failing to bridge the gap between the rich and the poor
(Accept any other relevant correct response) (10)
CONCLUSION
The government is trying to safeguard the interests of the community and improve the efficiency in markets but there is still more to be done.
(Accept any relevant high order conclusion) (2) [40]
QUESTION 6
- Examine in detail the causes of cost-push inflation. (26)
- How effective are interest rates in combating inflation since the introduction of inflation targeting? (10)
INTRODUCTION
- Cost-push inflation is a rise in the general prise level resulting from an increase in the costs of production
- Any costs to businesses is a potential source of cost-push inflation
- Cost-push inflation may be caused by the combination of the various components of production costs
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
BODY
MAIN PART – CAUSES OF COST-PUSH INFLATION
Increase in wages
- Remuneration of labour constitutes almost 60% of the cost of producing the GDP
- Increases in salaries and wages are therefore an important source of cost-push inflation
- When workers demand higher wages than their productivity, the increased costs are recovered by increase in prices
- If trade unions are successful in negotiating wages, the wages will go up and the producers will increase the selling price to compensate for the higher input costs
- Prices of goods/services will go up and inflation may occur
- A vicious cycle then results as labour demand even more higher wages as the cost of living goes up (Max. 6)
Increase in the prices of imported goods/key inputs
- South African manufacturers have to import most of their capital and commodities like oil and aluminium
- When these are raised, it leads to price increases because producers wish to maintain their profits
- When prices of key input goods that are imported increase (e.g. oil, energy, capital goods etc.) the domestic costs of production are pushed upwards
- and the consumer prices increase leading to inflation
- (Max. 4)
Increased profits/profit margins
- When profit margins are increased, it leads to an increase in the prices of goods
- This occurs when firms use their market power to push up prices
- When businesses push up their profit margins, they increase the cost of production and eventually the prices that consumers have to pay (Max. 4)
Low levels of productivity
- When the various factors of production become less productive while receiving the same remuneration, the costs of producing each unit of output increases, wage increases that are not accompanied by similar productivity increases have the effect of increasing inflation (Max. 4)
Natural disasters
- Natural disasters such as floods, fires, drought often occur in South Africa and can cause inflation in food prices because of shortages in agricultural production
- They impact on the costs of producers
- Food prices are one of the most volatile price items in inflation indexes as a result of the effects of weather changes (Max. 4)
Exchange rate depreciation
- Exchange rate depreciation may be the cause of price increases
- E.g. if the rand depreciates in terms of the US dollar, all imported goods and services become more expensive(Max. 4)
Sudden increase in interest rates
Increase in interest payments on loans will lead to higher costs
- Producers will recover these higher costs through increasing prices of their goods and services (Max .4)
Government induced prices
- When government induced price rises, which include increase in direct taxes or indirect taxes, the prices of goods and services are affected
- Producers normally shift the tax burden to consumers by increasing their prices of goods and services thereby leading to inflation (Max. 4)
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(Allocate a maximum of 8 marks for mere listing of facts or examples) (26)
ADDITIONAL PART
How effective are interest rates in combating inflation since introduction of inflation targeting?
The use of interest rates as an instrument to maintain inflation has been effective because:
- Changes in the repo rate have shown a positive effect so far as the inflation is maintained within the targeted range.
- Although the inflation rate was 13,51% in 2002, through the use of interest rates it declined to 6,16% in 2016 which was still outside the target range.
- The 25 basis points increase in November 2018 brought the repo and prime rates to 6,75% and 10,25% and inflation rate was within the target at 5,2%
- Increasing the interest rates will result in less money, credit and expenditure in the economy and it becomes difficult to raise prices and wages
- The repo rate is kept at 6,77% and prime rate at 10,25% in the first quarter of 2019
- The current inflation rate stands at 4,5% from 4,1% in March 2019 and this shows that SARB has effectively managed to maintain the inflation rate through the use of interest rates.
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (10)
CONCLUSION
Inflation can be a threat to the normal functioning of the economy, therefore measures like monetary and fiscal policies are vital to keep the phenomenon under control.
(Accept any relevant higher order conclusion) (2)
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Economics P2 Grade 12 Questions - NSC Exams Past Papers and Memos September 2019 Preparatory Examinations
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Answer FOUR questions as follows in the ANSWER BOOK:
- SECTION A: COMPULSORY
- SECTION B: Answer TWO of the three questions.
- SECTION C: Answer ONE of the two questions.
- Answer only the required number of questions. Answers in excess of the required number will NOT be marked.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write the number of the question above each answer.
- Read the questions carefully.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Leave 2–3 lines between subsections of questions.
- Answer the questions in full sentences and ensure that the format, content and context of your responses comply with the cognitive requirements of the questions.
- Use only black or blue ink.
- You may use a non-programmable pocket calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.9 D.
1.1.1 The elements of a market … include the number of sellers, nature of the product and the extent of differentiation.
- power
- structure
- system
- equilibrium
1.1.2 A(n) … monopoly occurs when a single firm controls manufacturing methods to produce a certain product.
- geographical
- technical
- artificial
- state-owned
1.1.3 In an oligopoly one firm’s actions affect decisions of other competing firms, meaning these firms are …
- unique.
- powerful.
- interdependent.
- special.
1.1.4 Producers make use of … to make their products appealing to the consumers.
- packaging
- prices
- branding
- services
1.1.5 The state can play a significant role in maintaining environmental sustainability through …
- marketing.
- externalities.
- exports.
- taxation.
1.1.6 CPIX is the inflation rate that excludes interest rates on … bonds.
- municipal
- treasury
- government
- mortgage
1.1.7 People travelling through South Africa to get to another country are called … tourists.
- outbound
- inbound
- transit
- domestic
1.1.8 Finite resources are also known as … resources.
- non-renewable
- renewable
- non-depleted
- limitless (8 x 2) (16)
1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.9 K.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.2.1 Market price |
|
(8 x 1) (8)
1.3 Give ONE term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK.
Abbreviations, acronyms and examples will NOT be accepted.
1.3.1 The actual cost that a business incurs in conducting an activity, e.g. salaries, wages, materials etc.
1.3.2 The period during which all factors of production are variable
1.3.3 The cost or benefit of a transaction that affects economic agents who are not directly involved in the transaction
1.3.4 A continuous decrease in the general prices of goods and services
1.3.5 A landmark or area which is selected by the United Nations as having cultural, historical or other form of significance
1.3.6 The variety of plant and animal life in a particular habitat (6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer any TWO of the three questions from this section in your ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 2: MICROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
2.1 Answer the following questions.
2.1.1 Give TWO examples of variable costs. (2)
2.1.2 Why are individual market participants in a perfect market insignificant to the market as a whole? (2)
2.2 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow. 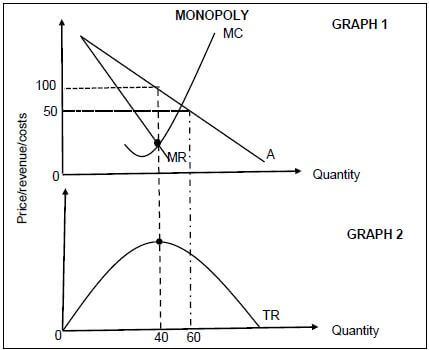
2.2.1 Provide a suitable label for curve A. (1)
2.2.2 What is the selling price for the business above? (1)
2.2.3 Briefly describe the term monopoly. (2)
2.2.4 Explain a reason for the shape of the total revenue curve. (2)
2.2.5 Redraw Graph 1 in your ANSWER BOOK and show how the monopoly will make economic profits. (4)
2.3 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
COMPETITION POLICY AND SECTOR SPECIFIC REGULATIONS Competition policy and regulation are often regarded as two important and inter-related areas of regulatory policy. The policies are designed to address weaknesses within the market system. If used efficiently and complementary to each other, competition policy and regulation can both play a key role in improving the quality of regulation thus creating competitive markets. The policy uses three authorities; the Competition Commission, Competition Tribunal and the Competition Appeal court. [Adapted from www.law.ufi.edu] |
2.3.1 Name the market structure that led to the implementation of a competition policy. (1)
2.3.2 Which institution provides final decisions when parties are dissatisfied with rulings of the Competition Tribunal? (1)
2.3.3 Briefly describe the term regulation in economics. (2)
2.3.4 What is the role of the Competition Commission? (2)
2.3.5 Why is it important for the South African government to control competition among businesses? (2 x 2) (4)
2.4 Briefly explain entry and perfect knowledge as characteristics of a perfect competitor. (2 x 4) (8)
2.5 What positive impact will an increase in suppliers of electricity have on South Africa? (8) [40]
QUESTION 3: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
3.1 Answer the following questions.
3.1.1 Name any TWO negative effects of tourism. (2)
3.1.2 Why is the preservation of natural resources important? (2)
3.2 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.
NUMBER OF MOST RECENT DAY AND OVERNIGHT TRIPS INSIDE SOUTH AFRICA: JANUARY – JUNE 2018
TOTAL NUMBER OF TRIPS (‘000) | ||
TYPE OF TRIP | QUARTER 1 | QUARTER 2 |
Day trip in SA | 3 825 | 4 284 |
Overnight trip in SA | 6 300 | 6 351 |
The number of most recent day trips increased from 4,0 million to 4,3 million between the two quarters of 2018. The number of most recent overnight trips slightly increased from 6,3 million in Quarter 1 to 6,4 million in Quarter 2.
[Adapted from StatsSA survey 2018]
3.2.1 Name the economic sector that is represented by tourism. (1)
3.2.2 Which type of tourism is depicted in the data above? (1)
3.2.3 Briefly explain the term tourism. (2)
3.2.4 Explain a reason for the growth of foreign tourism in South Africa. (2)
3.2.5 How can tourism alleviate poverty in rural areas? (2 x 2) (4)
3.3 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow. 
3.3.1 Name the organisation which has facilitated a number of agreements regarding the disposal of toxic chemical waste. (1)
3.3.2 What could be the cause of global warming? (1)
3.3.3 Briefly describe the term climate change. (2)
3.3.4 Why does the government provide environmental subsidies to businesses? (2)
3.3.5 How are farmers affected by acid rain? (4)
3.4 Briefly explain the economic benefits of tourism for the government. (8)
3.5 How can environmental degradation be prevented? (8) [40]
QUESTION 4: MICROECONOMICS AND CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
4.1 Answer the following questions.
4.1.1 Name any TWO major international protocols and agreements on sustainable development. (2)
4.1.2 How are consumers affected by maximum prices? (2)
4.2 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow. 
4.2.1 What is the nature of the service offered by the firms above? (1)
4.2.2 How is the shape of the demand curve of the oligopoly? (1)
4.2.3 Briefly describe the term oligopoly. (2)
4.2.4 What does it mean for Vodacom to be a dominant firm? (2)
4.2.5 How do oligopoly competitors benefit from collusion? (4)
4.3 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow. 
4.3.1 What is the group of animals in the picture above called? (1)
4.3.2 Which international treaty is concerned with endangered species? (1)
4.3.3 Briefly describe the term endangered species. (2)
4.3.4 How can education be used as a measure to ensure sustainability? (2)
4.3.5 Why were the Millennium Development Goals not achieved? (4)
4.4 With the aid of a well-labelled graph, explain economic loss in a perfect market. (8)
4.5 Examine the success of marketing as a strategy to promote tourism in South Africa. (8) [40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer ONE of the two questions from this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
Ensure that your answer follows the structure indicate below in order to obtain maximum marks.
STRUCTURE OF ESSAY | MARK |
Introduction
| Max. 2 |
Body Additional part: Give own opinion/Critically discuss/Evaluate/Critically evaluate/Draw a graph and explain/Use the graph given and explain/Complete the given graph/Calculate/Deduce/Compare/Explain/Distinguish/Interpret/ Briefly debate/How/Suggest | Max. 26 Max. 10 |
Conclusion
| Max. 2 |
TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 5: MICROECONOMICS
40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
- Discuss the causes of market failure in detail focusing on the following:
- Missing markets
- Lack of information (26 marks)
- Evaluate the success of the government intervention in markets in distributing wealth. (10 marks) [40]
QUESTION 6: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
- Examine in detail the causes of cost-push inflation. (26 marks)
- How effective are interest rates in combating inflation since the introduction of inflation targeting? (10 marks)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Economics P1 Grade 12 Questions - NSC Exams Past Papers and Memos September 2019 Preparatory Examinations
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Answer FOUR questions as follows in the ANSWER BOOK:
SECTION A: COMPULSORY
SECTION B: Answer any TWO of the three questions
SECTION C: Answer ONE of the two questions - Answer only the required number of questions. Answers in excess of the required number will NOT be marked.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write the question number above each answer.
- Read the questions carefully.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Leave 2–3 lines between subsections of questions.
- Answer the questions in full sentences and ensure that the format, content and context of your responses comply with the cognitive requirements of the questions.
- Use only black or blue ink.
- You may use a non-programmable pocket calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY) 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.9 D.
1.1.1 Short term savings and loans are part of the … market.
- factor
- foreign exchange
- money
- capital
1.1.2 The … curve illustrates a trade-off between employment and inflation.
- Laffer
- Lorenz
- Production possibility
- Phillips
1.1.3 The balance on the Financial Accounts in the Balance of Payment (BOP) excludes …
- reserve assets.
- net financial derivatives.
- net portfolio investments.
- net other investments.
1.1.4 The consumption expenditure of households and income of producers is regarded as … flow.
- money
- real
- circular
- capital
1.1.5 The consultations of the South African Reserve Bank (SARB) to convince banks to act in a manner that is desirable, is known as …
- interest rates.
- moral suasion.
- cash reserve requirement.
- open market transaction.
1.1.6 A development policy that works with the Sectoral Education Training Authority (SETA) is …
- Export Processing Zones.
- Joint Initiative on Priority Skills Acquisition.
- Reconstruction and Development Programme.
- Expanded Public Works Programme.
1.1.7 The Department of Trade and Industry implemented … to assist industries to grow by identifying certain cross cutting issues and competitive input sectors.
- Spatial Development Initiative
- Special Economic Zones
- Strategic integrated Projects
- Integrated Manufacturing Strategy
1.1.8 Depreciation of capital as a method used to encourage investment is known as capital ...
- widening.
- deepening.
- formation.
- growth. (8 x 2) (16)
1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the correct letter (A−I) next to the question number (1.2.1−1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.9 K.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.2.1 Expenditure method |
|
(8 x 1) (8)
1.3 Give ONE term/word for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term/word next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.6).
Abbreviation, acronyms and examples will NOT be accepted.
1.3.1 A view that explains that disequilibrium in markets are caused by the incorrect use of policies
1.3.2 The main source of government revenue
1.3.3 Money received without any productive service rendered
1.3.4 Increase in population numbers of cities and towns
1.3.5 The rate at which SARB lends money to banks for short periods
1.3.6 The return of land to those that have lost it due to discriminatory laws in the past. (6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 2: MACROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
2.1 Answer the following questions.
2.1.1 Name any TWO member countries of BRICS. (2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 Why is the GDP at market prices normally higher than the GDP at factor cost? (1 x 2) (2)
2.2 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.
KEYNESIAN ECONOMICS The concept of the multiplier process became important in the 1930s when John Maynard Keynes suggested it as a tool to help governments in decision-making. This ‘demand-management approach’ was designed to help measure the amount needed to reach high levels of national income. Analysts believe that an increase in government spending generally have a multiplier effect on economic growth, while uplifting living standards for affected people and communities. [Adapted from www.tutor2u.net] |
2.2.1 Give an example of a leakage. (1)
2.2.2 What factor influences the size of the multiplier? (1)
2.2.3 Briefly describe the term multiplier. (2)
2.2.4 Explain the effect on national income when injections are more than leakages. (2)
2.2.5 Suppose the South African government spends R250 m on the economy. Calculate the multiplier effect if mpc = 0,7. Show all calculations. (4)
2.3 Study the following information and answer the questions that follow.
AfCTA is a planned free trade area among 49 of 55 African states. It will be the largest in the world in terms of participating countries. [Source: TESFANEWS, 9 February 2019] |  |
2.3.1 Except AfCTA, name any other free trade area in the world. (1)
2.3.2 Which trade protocol is behind the establishment of a single market in Africa? (1)
2.3.3 Briefly describe the term free trade area. (2)
2.3.4 Briefly explain the role of the World Trade Organisation as part of globalisation. (2)
2.3.5 How can Africa benefit from being a single market? (2 x 2) (4)
2.4 Discuss the length and amplitude of a business cycle. (4 x 2) (8)
2.5 Evaluate the effects of a currency depreciation in an economy. (8) [40]
QUESTION 3: ECONOMIC PURSUITS 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
3.1 Answer the following questions.
3.1.1 Name TWO demand side approach policies to growth and development. (2 x 1) (2)
3.1.2 How can interest rates be used by South African Reserve Bank to stimulate production of goods and services? (1 x 2) (2)
3.2 Study the cartoon below and answer questions that follow. 
3.2.1 Name ONE example of a country in the North. (1)
3.2.2 Provide a characteristic of the group of countries represented by ‘South’. (1)
3.2.3 Briefly describe the term globalisation. (2)
3.2.4 Briefly explain trade as a challenge of globalisation. (2)
3.2.5 How do countries in the North contribute to the destruction of the environment? (4)
3.3 Study the table below and answer the questions that follow.
CONTRIBUTIONS TO GROWTH IN REAL GDP (%)
SECTOR | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
Primary sector | -0,6 | 0,7 | -0,1 |
Secondary sector | 0,1 | 0,0 | 0,1 |
Tertiary sector | 1,1 | 0,5 | 0,7 |
Growth in total real GDP | 0,6 | 1,3 | 0,8 |
[Source: SARB: Quarterly Bulletin, December 2018]
3.3.1 Name ONE category of the secondary sector. (1)
3.3.2 What was the trend in the primary sector between 2017 and 2018? (1)
3.3.3 Briefly describe the term Gross Domestic Product. (2)
3.3.4 Explain the use of per capita GDP figures. (2)
3.3.5 How does real growth of 0,8% negatively affect the economy? (4)
3.4 Briefly discuss the cost of doing business as a supply-side approach in promoting growth and development in South Africa. (4 x 2) (8)
3.5 How do international organisations such as the World Bank and United Nations standardise the indicators of member countries? (8) [40]
QUESTION 4: MACRO ECONOMICS AND ECONOMIC PURSUITS 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
4.1 Answer the following questions.
4.1.1 Name TWO types of business cycles. (2 x 1) (2)
4.1.2 How can SMMEs contribute to economic growth? (1 x 2) (2)
4.2 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow. 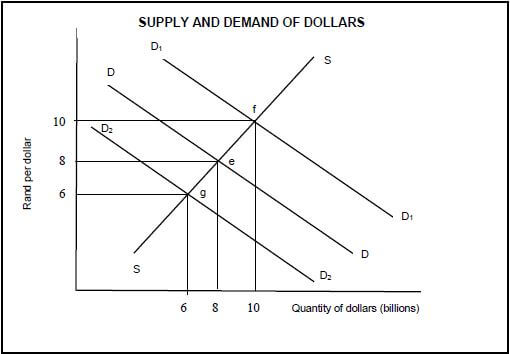
4.2.1 Identify the demand curve that indicates a decrease in the demand for dollars. (1)
4.2.2 What type of exchange rate system is currently used in South Africa? (1)
4.2.3 Briefly describe the term devaluation. (2)
4.2.4 Explain ONE factor that can influence the demand for the dollar. (2)
4.2.5 What is the effect on the rand when there is a decrease in the demand for dollars? (4)
4.3 Read the information below and answer the questions that follow.
The NDP has progressed despite a [Source: fin24, 14 April 2018] |  |
4.3.1 In which year is the NDP aiming to eliminate poverty? (1)
4.3.2 Name ONE way how the government can reduce poverty among the vulnerable groups in South Africa. (1)
4.3.3 Briefly describe the term economic development. (2)
4.3.4 What negative effect can the NDP have on taxpayers? (2)
4.3.5 How will the South African economy benefit from the implementation of the NDP? (2 x 2) (4)
4.4 Briefly discuss the demographic social indicators. (4 x 2) (8)
4.5 How will an increase in export prices and import prices affect the South African economy? (8) [40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer any ONE question of the TWO questions in the ANSWER BOOK. Your answer will be assessed as follows:
STRUCTURE OF ESSAY | MARK |
Introduction
| Max. 2 |
Body: Additional part: Give own opinion/Critically discuss/Evaluate/Critically evaluate/Draw a graph and explain/Use the graph given and explain/ Complete the given graph/Calculate/Deduce/Compare/Explain/ Distinguish/Interpret/Briefly debate/How/Suggest/Use the information and argue, debate, evaluate. | Max. 26 Max. 10 |
Conclusion
| Max. 2 |
TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 5: MACROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
Discuss in detail how the following factors contribute to poor public-sector provisioning:
- Lack of accountability (10)
- Inefficiency (8)
- Difficulty in assessing needs (8) (26)
Suggest solutions on how efficiency of state-owned enterprises can be improved. (10) [40]
QUESTION 6: ECONOMIC PURSUITS 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
Discuss in detail the appropriateness of South Africa’s regional development policies in terms of international benchmark criteria. (26)
How successful has the South African government been in meeting the aims of regional development? (10) [40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Consumer Studies Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Exams Past Papers and Memos September 2019 Preparatory Examinations
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: SHORT QUESTIONS
1.1 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1.1.1 A ✔ (1)
1.1.2 B ✔ (1)
1.1.3 D ✔ (1)
1.1.4 C ✔ (1)
1.1.5 A ✔ (1)
1.1.6 C ✔ (1)
1.1.7 C ✔ (1)
1.1.8 A ✔ (1)
1.1.9 C ✔ (1)
1.1.10 C ✔ (1)
1.1.11 D ✔ (1)
1.1.12 C ✔ (1)
1.1.13 B ✔ (1)
1.1.14 A ✔ (1)
1.1.15 B ✔ (1)
1.1.16 D ✔ (1)
1.1.17 D ✔ (1)
1.1.18 A ✔ (1)
1.1.19 C ✔ (1)
1.1.20 C ✔ (1)
1.2
1.2.1 D ✔ (1)
1.2.2 A ✔ (1)
1.2.3 G ✔ (1)
1.2.4 F ✔ (1)
1.2.5 E ✔ (1)
1.3
1.3.1 C ✔ (1)
1.3.2 B ✔ (1)
1.3.3 A ✔ (1)
1.4 A D F ✔✔✔ (3)
1.5 B D E H ✔✔✔✔ (4)
1.6
1.6.1 tuberculosis ✔ (1)
1.6.2 gastro enteritis ✔ (1)
1.6.3 sell by date ✔ (1)
1.6.4 recycle ✔ (1)
1.6.5 renewable ✔ (1) [40]
QUESTION 2: THE CONSUMER
2.1 Grey goods
2.1.1 Grey goods/parallel imports ✔ (1)
2.1.2 Cheaper/costs less (1)
2.1.3
- If it breaks/is faulty the buyer discovers that there is no guarantee/warranty from the official supplier ✔
- Seller may repair item, but the quality of the repair may be compromised ✔
- If the seller does not display a notice, they are not aware that it is a grey product
- The buyer cannot make an informed choice
- The seller may not explain what a ‘grey goods/product notice’ means
- The seller could alter the product, so it does not resemble the genuine/original product
- The goods are not sold by approved dealers (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.2 Tax/Inflation
2.2.1 Health / less pollution ✔ (1)
2.2.2 South African Revenue Service ✔ (1)
2.2.3
- VAT (value added tax) ✔
- Excise duty (sin tax) (alcohol + cigarettes) ✔
- Petrol/Fuel
- Import duty / custom duties
- Car licence / drivers / learners
- TV licence
- Fishing / hunting
- Air passenger (overseas travel)
- Environmental levy (on plastic bags) (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.2.4
- A gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect ✔
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) and other gases act as a blanket to keep the heat out ✔/blocking heat from earth to space/ to prevent it from escaping ✔
- A greenhouse gas radiates/releases heat in all directions ✔ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.2.5
- Prices go up ✔and you can buy less ✔/ You can cover fewer expenses
- Less disposable income / decreases buying power of money ✔
- Decrease in the standard of living ✔
- Reduces the purchasing power of savings
- Pensioners / people on fixed incomes are affected more
- Investments / savings worth less
- The economy suffers and this impacts on job losses / workers (consumers) retrenched/unemployed
- Petrol price increases and has an impact on food if the price increases (Any 4 x 1) (4)
2.3 Municipal services
- Refuse: If refuse not collected the environment is unsafe/unhealthy ✔
- Electricity: If electricity supply interrupted or / when the 50 kWh free electricity quota not provided to poor households then they will not have basic lighting / cannot use basic electrical appliances / will not be able to have lights ✔
- Water: If access to water not available / if free water to poor households is not provided then health is compromised / survival impacted ✔
Poor quality water is unhealthy - Sanitation: Unhealthy living conditions/ spread of diseases / contamination if basic sanitation not met / access to toilets needed ✔
- Roads: If roads are inaccessible / poor roads will impact on their safety / mobility /ability to earn an income ✔
- Sewage collection: Major health issues / health issues when sewage flows into streets / rivers / polluted drinking water ✔
- Infrastructure: Lack of infrastructure affects community well-being / hinders access to education / health care / inadequate emergency services ✔
- General poor services: Industry/ businesses will not be open, there will be limited job opportunities ✔ Social problems like teenage pregnancies/child neglect/ domestic violence/drug use/crime/ethnic conflict/HIV/Aids
NOTE: Marks are awarded for the discussion and not for the topic. If discussion in-depth, then maximum 2 marks per area.
Question is based on basic services, so at least 3 different areas must be covered. (6) [20]
QUESTION 3: FOOD AND NUTRITION
3.1 Lifestyle behaviours
- Excess alcohol ✔
- Smoking ✔
- Lack of exercise (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.2 Anaemia
3.2.1 Iron deficiency
- Females lose iron through menstruation ✔
- Increased iron requirements which are not met during pregnancy
- A diet lacking in iron when the focus is on weight loss/slimming diets (Any 1 x 1) (1)
3.2.2
- Excessive iron loss ✔e.g. menstruation, blood loss after injury, bleeding ulcer ✔
- Poor iron absorption ✔ e.g. diarrhoea, intestinal disease, medication ✔ (4)
3.2.3 Iron is a component of haemoglobin ✔ in red blood cells (RBC) which carry oxygen to the body. ✔ Oxygen is needed for cells to work properly. ✔ Plays a role in maintaining a healthy immune system ✔ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
3.3 Eating disorders
- Obsession with body weight / Dissatisfaction with body weight ✔
- Distorted body image / Body-image issues / Poor self-esteem and self-image ✔
- Use similar methods to lose weight i.e. overuse of diet pills, using laxatives, diuretics, enemas, exercising excessively ✔ (3 x 1) (3)
3.4 Management of anorexia and bulimia
- Psychotherapy to treat underlying causes ✔
- Hospitalisation (in serious cases / medical and psychological complications) ✔
- Counselling or cognitive behavioural therapy by a mental health specialist ✔
- Nutritional education / counselling
- Medication: anti-depressants
- Join a support group
- Multidisciplinary approach with doctors, psychologists and dieticians
- Medication: anti-depressants
- Physical needs addressed so that normal eating patterns resume
- Behaviour management (Any 3 x 1) (3)
3.5 Graph: blood glucose levels
3.5.1 1 – Hyperglycaemia ✔ 2 – Hypoglycaemia ✔ (2)
3.5.2 Insulin ✔ (1)
3.5.3
- When you skip meals or do not eat enough/irregular eating habits ✔
- If you exercise hard or for a long time without eating extra food ✔
- If you have an underlying disease e.g. tumour on pancreas
- Taking certain medications
- Eating a lot of fat
- Eating high glycaemic index foods (high GI)
(The glucose levels rise very quickly and the body releases a lot of insulin to bring down the glucose level in the blood. Sudden removal of glucose from blood will cause the blood glucose level to drop below the normal level.) (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.5.4
- Glucose levels will not fluctuate / not be too high or too low ✔
- Gives one a continuous supply of energy / there will not suddenly be a large amount of glucose in the blood ✔
- This results in sustained energy levels ✔
- Energy will not be depleted quickly / will not feel tired ✔/resulting in better weight control ✔
- Insulin will not have to be produced continuously ✔ which would overstimulate the pancreas ✔ causing one to develop insulin resistance ✔ (Any 5 x 1) (5) 3.6 Aids and Food safety
3.6.1 Aids sufferers have a weak immune system ✔ and so are more susceptible to infection ✔ (2)
3.6.2 Hygienic practices when working with food:
- Wash your hands for at least 20 seconds in hot soapy water before and after handling raw products
- Wash hands after using the toilet, changing a baby’s nappy or touching nappies
- Clean appliances and surfaces with hot, soapy water after food preparation
- Food preparation areas must be free from flies and cockroaches as these insects can carry pathogens from contaminated food or directly from human waste to other foods (Any 4 x 1) (4)
3.7 Menu – Heart disease
3.7.1 Saturated fat ✔ and cholesterol (LDL) ✔ present in cheeses (cheese/cottage) are low/reduced fat / is limited ✔ as well as unsaturated fat in fat spread. ✔ It is better for a person as less accumulated fat in arteries / no blockage✔/ will not increase blood cholesterol levels ✔ Poly unsaturated ✔ in salmon ✔ that help lower blood cholesterol levels ✔ Monounsaturated ✔ in avocado / peanuts ✔ good plant fats / that help lower blood cholesterol levels ✔ Trans fats ✔ in fat spread ✔ will be limited as not a hard margarine / no saturated fats ✔/Skimmed milk fat free- and soft spread/margarine / not hard brick will have less transfats ✔ so no contribution to cardio vascular disease
NOTE: Do not mark just any ticks. Mark the type of fat and correlate the source and the benefit. (Max. 8) (8) [40]
QUESTION 4: CLOTHING
4.1 Eco-fashion
4.1.1 The’ in’ thing to wear / presently popular / hot and happening ✔ (1)
4.1.2 Has minimal impact on the environment because:
- The resources are not depleted or permanently damaged when the products manufactured ✔
- Few chemicals are used during the growth (cultivation) of the plant and processing (production) of the textile ✔
- Fabrics and fabrics produced from renewable sources such as bamboo and hemp ✔
- Plants that require little water but still yield good crops grown without any damage to the soil ✔
- Grows without pesticides and weed killers and is produced without bleach agents/chemical colourants are used/natural plant colouring
- Is often from recycled or re-usable textiles
NOTE: If not written in a paragraph, -1 mark. (4)
4.2 Imitation and counterfeiting
- Imitation – makes use of brand logo that looks similar to the original brand’s emblem/logo or legal ✔
- Counterfeiting – a copy that looks exactly like the original (replica) or illegal copy of a product ✔ (2)
4.3 Retrospective/fashion
4.3.1
- Clothes that imitate/resemble the style of a previous era/earlier period ✔
- The 2018 (picture B) also has an off the shoulder and short sleeve design ✔
OR
- The design is reinterpreted it with a modern twist ✔
- The 2018 dress has a looser sleeve instead of elasticised and no frill on neckline / plain white fabric ✔
NOTE: Must refer to picture for second mark. (2)
4.3.2 Maturity ✔ (1)
4.3.3 Average fashion / contemporary / standard fashion ✔ (1)
4.4 Fashion change
- Celebrities cause the fashion change to speed up✔ as sales will go up ✔ and more clothes purchased / more popular ✔ /affects the consumer socially/ social factor ✔/ is a positive change. (Any 3 x 1) (3)
4.5 Evaluate outfit
- The outfit cannot be worn for work without a tie / having no tie is not suitable ✔ however, the garments are suitable for workwear ✔ because the colours are neutral ✔ / white, navy, brown
- All garments/outfits are a classic style/ workwear style / professional looking ✔
- Shoes: Closed / colour goes with pants ✔
- Jacket: Style is formal, correct length, navy colour is neutral / classic style ✔
- Shirt: White suitable. Long-sleeved suitable ✔
- Pants: Correct style / classic / formal
NOTE: This outfit may be discussed as a whole or garments separately. Do not mark the same point twice. (Any 6 x 1) (6) [20]
QUESTION 5: HOUSING
5.1 Housing options
5.1.1 The person is the legal owner of the entire property/land ✔and the structures on it ✔ (2)
5.1.2
- Lease ✔
- Landlord/lessor/property owner ✔
- Tenant/lessee/renter ✔ (3)
5.1.3
- If there is any damage to the property ✔
- If rent is outstanding ✔
- If the premises are vacated before the lease period is up (Any 2 x 1) (2)
5.1.4 Option 1: Rent
- The tenant would not be responsible for the maintenance of the pool/ will not pay anything to use the pool✔
- Unless the lease agreement stipulated otherwise ✔
- The owner of the apartment will have to pay for chemicals / maintenance/upkeep ✔ (Max. 2)
Option 2: Sectional title
- The owner will pay a monthly levy ✔/used for the maintenance of the common property ✔
- The pool is common property ✔ (Max. 2) (4)
5.1.5
- Greater security than living on a separate plot/has 24 hour security which you may not be able to afford if living on a separate plot ✔
- Enjoy the use of the pool/ common facilities of the complex without the responsibility of personally maintaining it ✔
- Save money as it has a small garden rather than the maintenance of a larger garden ✔
- These developments are often closer to the city, so you save on travelling costs ✔
- You have fewer responsibilities/less administration as the body corporate must control and manage the complex ✔
- You benefit from shared responsibility as it is in the owner’s interest that the complex is well maintained/run ✔ (Any 4 x 1) (4)
5.1.6
- It is brand new / no one else has owned it before/ the buyer is the first owner ✔
- So no one’s name to transfer it from / never been in someone’s name before ✔
- If the seller is registered as a VAT vendor ✔ (usually, the case when buying property in a new development where the developer is generally VAT registered). The seller must have included VAT in the purchase price. Tax already paid ✔ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
5.1.7
Transfer fee | Transfer duty | |
The main difference | Legal fee/attorney fee ✔ | Government (Tax) ✔ |
Who finally receives the fee | Attorney / conveyancer ✔ | South African Revenue Service/SARS ✔ |
What the fee amount is based on | Depends on property price and law firm / Law Society’s recommended tariffs ✔ | Depends on the property price/value of property The higher the house price, the higher the amount✔ |
NOTE: -1 if answer is not in a table form. (6)
5.1.8
- Deed of sale ✔
- Title deed ✔ (2)
5.2 Household appliance – Microwave
5.2.1
- Needs of the family / what they will use it for / functionality ✔
- Amount of space available / size of the oven ✔
- Budget / cost /do the features and quality justify the price ✔
- Features / good wattage / does it have a turntable / fewer features cheaper to repair ✔
- Warranty /after-sales service
- Easy to operate (Any 3 x 1) (3)
5.2.2 An automatic defrost ✔ and pre-programmed setting ✔ (2)
5.2.3 Human ✔ (1)
5.2.4 Automatic defrost ✔
- It can work out how long the food needs to defrost/auto defrost
OR
- So it will be quicker than if you just guess and have to keep punching in more time/you just enter weight ✔
- Pre-programmed setting ✔
Auto cook mode / automatically works out the cooking time
OR
- You do not need to set the cooking time or power level /so the working out is done for you/ you enter the number for the food type
- 1 000 wattage ability ✔
Higher watt ability warms faster ✔ - Turntable ✔
By not stopping the microwave and turning the dish you will save time ✔
(3 Features and 3 Explanations) (6)
5.2.5
- Spent money wisely / to budget / spent a maximum of R1 200 ✔
- Shopped around/ got a fair deal
- Compared prices ✔
- Went to four retailers ✔
- Checked if the microwave had a return policy ✔
- Read the warranty ✔ (Any 3 x 1) (3) [40]
QUESTION 6: ENTREPRENEURSHIP
6.1
6.1.1 Business idea
- She let her friends try the products (taste the samples)
Her friends loved the unique flavours
Made two different meal samples (Any 1 x 1) (1) - Saved her money from waitressing job / savings ✔ (1)
- Home / online ✔ (1)
6.1.2
- She tried the supermarket brand ✔
- She checked out the online brands / checked her competitors✔
- She chose a catchy trade name
- She knew her meal kits would be more appealing (Any 2 x 1) (2)
6.1.3
- She is creative ✔
- Knowledge from doing Consumer Studies at school ✔
- Can use a computer
- Did a business management course / has knowledge to run a business
- Friends to help her by tasting and giving her feedback
- She can cook
- She has knowledge of trends (eco-friendly packaging/vegan)
- Knowledge of target market
- Has discipline to save
- Has people skills (has waitressed) (Any 2 x 1) (2)
6.1.4
-
- Ingredients locally available ✔
- Has a supplier for packaging boxes ✔ (2)
-
- Environmentally friendly packaging / 100% recycled ✔
- Uses minimal plastic ✔
- Product has 3 options (chicken, beef and beans) ✔
- Unique flavour / combinations / delicious ✔
- Healthy/wholesome ✔
- Vegan option / plant based ✔
- Opportunity to try new flavours / ingredients ✔
- Convenient / time-saving
- Sell it for a good price (Any 6 x 1) (6)
6.1.5 ‘Quikstix’ implies that the meal can be prepared quickly ✔ which goes with the desire to be convenience food and to save time ✔ (2)
6.1.6
- Protect the product ✔
- Be safe ✔
- Be hygienic / keep product clean and fresh
- Convenient for distribution
- Strong for transportation
- Be easy for customers to handle/open/close/well-designed to handle
- Protects the environment against damage
- Easy to carry, display and stack
- Suitable for the target market (Any 2 x 1) (2)
6.1.7
- Must plan ahead ✔
- Plan her time schedule ✔
- Prioritise tasks ✔
- Assign a time to each task ✔
- Follow a routine
- Tidy work area
- Do not procrastinate (Any 4 x 1) (4)
6.1.8
- R21,00 + R5,00 + R7,00 + R2,50 + R6,00 + R30,00 = R71,50 ✔ (1)
- R71,50 x 65 ÷ 100 = R46,48 ✔
R71,50 + R46,48 = R117,98 ✔ = R118 ✔ (3) - R46,48 x 120 ✔ = R5 577,60 ✔ (2)
NOTE: -1 If no R sign in final answer
6.1.9
- Must be a written statement ✔
- Must state it serves four people ✔
- Say it is packaged in a recyclable box ✔
- Instructions for making (recipe) inside ✔ (4)
Example :
The meal kit serves 4. The ingredients are provided in separate packets packaged inside a recyclable box with a recipe insert.
6.1.10
- Box is made from recyclable cardboard ✔
- Minimum plastic used / less packaging ✔
- Box can be reused ✔
- Box can be recycled/taken to recycling depot ✔
- Cardboard is biodegradable ✔
- Supporting local suppliers / not imported / plane pollution ✔
- Saving petrol – product delivered ✔
- Quick to prepare – less electricity in preparation
- Protect environment for future generations
- Only buy necessary ingredients/all ingredients you need in box/no wastage (Any 7 x 1) (7) [40]
TOTAL: 200
Consumer Studies Grade 12 Questions - NSC Exams Past Papers and Memos September 2019 Preparatory Examinations
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions
SECTION
MARKS
TIME
(MINUTES)
QUESTION 1: Short questions (All topics)
40
20
QUESTION 2: The Consumer
20
20
QUESTION 3: Food and Nutrition
40
40
QUESTION 4: Clothing
20
20
QUESTION 5: Housing
40
40
QUESTION 6: Entrepreneurship
40
40
TOTAL:
200
180
- ALL the questions are COMPULSORY and must be answered in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start each question on a NEW page.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Write in black or blue ink only.
- Pay attention to spelling and sentence construction.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: SHORT QUESTIONS
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.20) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.21 D.
1.1.1 A money-back guarantee stipulates that …
- the seller will give the unsatisfied customer his/her money back after a specified number of days.
- the product will be repaired or replaced if it does not meet certain requirements.
- the customer pays a small monthly fee for an extended period of time.
- the customer gets his/her money back if a supplier influences them to do business with it. (1)
1.1.2 Provisional tax is …
- tax paid at the same time as income is earned.
- two payments made per year based on estimated taxable income.
- tax paid on the provision of goods and services.
- a single large sum paid at the end of the tax year. (1)
1.1.3 A pyramid scheme involves members who …
- are recruited to buy and sell products and receive commission for recruiting other members.
- pledge a fixed amount of money to a common fund on a regular basis.
- are unjustly treated by the supplier.
- are paid to recruit new members and promised a high return on their investment. (1)
1.1.4 The consumer price index (CPI) …
- is calculated on the principal (original) amount borrowed.
- measures the interest charged by the Reserve Bank.
- is an instrument used to calculate price increases and the inflation rate.
- is the rate at which prices fluctuate as the demand for money changes. (1)
1.1.5 Factor/factors that increase(s) the risk of osteoporosis:
- Low oestrogen levels
- Larger big-boned people
- Non-smokers
- A diet high in calcium (1)
1.1.6 Which of the following foods should be avoided by a person suffering from lactose intolerance?
- Sardines
- Brown bread
- Full fat ice cream
- Soya milk (1)
1.1.7 A person with high blood pressure is also at risk of developing …
- high blood glucose levels, Aids and kidney failure.
- stroke, osteoporosis and anorexia.
- heart attack, stroke and kidney failure.
- heart attack, anorexia and Aids. (1)
1.1.8 A stabiliser is added to instant pudding to …
- give it an even, smooth consistency.
- prevent the fat from becoming rancid.
- create a lighter colour.
- retard the growth of micro-organisms. (1)
1.1.9 Food irradiation is a technology that …
- uses agricultural methods to sustain the productivity of the eco system.
- introduces characteristics from one species to another.
- improves the safety of food and extends their shelf life.
- enables a country to be self-sufficient. (1)
1.1.10 Food security means that …
- South African farmers produce their own food.
- South African goods are sent for sale or exchange to other countries.
- people eat enough safe food for an active healthy life.
- everyone can afford to buy food. (1)
1.1.11 A fad/fads:
- What is currently popular and worn by the masses
- An expensive, outrageous style
- Lasts for many seasons
- Often seen in accessories (1)
1.1.12 An advantage of a well-planned wardrobe:
- It contains a variety of fashionable and colourful outfits
- Cheaper clothes are enhanced with expensive accessories
- There are many items that can be mixed and matched
- Many fad outfits are included (1)
1.1.13 The type of insurance that is taken out to cover the structure of a home:
- Life insurance
- Home owners’ insurance
- Bond protection insurance
- Household contents insurance (1)
1.1.14 The government offers a housing … for people of the lower-income group who qualify to obtain their own homes.
- subsidy
- collateral
- need
- delivery (1)
1.1.15 A term that refers to costs that buyers do not always take into account when purchasing a house:
- Deposit
- Hidden costs
- Bond costs
- Collateral security (1)
1.1.16 An advantage when interest is calculated according to a fixed rate on the bond repayment:
- You will not benefit when the interest rate drops
- The amount of interest you pay back may fluctuate
- If the interest rates rise, the monthly repayments will also go up
- You will not pay more when interest rates rise (1)
1.1.17 To lower the costs of finance charges for instalment sales transactions:
- Become the owner immediately.
- Use a credit card for payments.
- Know the interest rate.
- Pay off the goods as quickly as you can. (1)
1.1.18 The wages/salaries of workers are usually determined by their …
- skills and experience.
- experience and money available.
- age and working hours.
- attitude and work ethic. (1)
1.1.19 A document that shows the movement of money over a forecast period:
- Revenues
- Best sale scenario
- Cash-flow projection
- Feasibility study (1)
1.1.20 Objectives of advertising include:
- Establishing the costs of your product and communicating information
- Generating interest and choosing a product name
- Creating product awareness and maintaining sales
- Expanding your market and getting feedback from customers (1)
1.2 Choose the food-related disease from COLUMN B that matches the symptoms in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–H) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 I.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.2.1 Excessive weight loss and thirst | A Skin allergy |
(5 x 1) (5)
1.3 Choose the term in COLUMN B that matches the description in COLUMN A. Write only the letters (A–F) next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.3) in your ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.3.4 G.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.3.1 When a contract is not valid or not legally binding |
|
(3 x 3) (3)
1.4 Identify THREE CORRECT statements from the list below for the requirements when applying for a home loan. Write only the letters (A–F) next to the question number (1.4) in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Certified copy of SA identity document or passport
- Proof of a housing subsidy
- Certified copy of your Curriculum Vitae
- Certified copy of the offer to purchase
- Letters from two references
- Income tax reference number (3 x 1) (3)
1.5 Identify FOUR CORRECT statements to retain quality during the storage of products in a business. Write only the letters (A–H) next to the question number (1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Do not overstock through incorrect purchasing
- Use the FIFO principle to ensure that older stock does not deteriorate
- Purchase quality raw materials
- Keep an accurate inventory of all stock
- Keep areas dry to prevent damage to stock
- Do not spend too much money on stock that could have been used more effectively elsewhere
- Keep products safe for clients
- Store frequently used goods as close to the door as possible (4 x 1) (4)
1.6 Choose the correct term/word in brackets. Write only the word/term next to the question number (1.6.1–1.6.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.6.1 (Tuberculosis/Hepatitis) is a bacterial infection that spreads through the air.
1.6.2 (Gastro-enteritis/Dysentery) is a condition that causes inflammation of the stomach and intestines.
1.6.3 The (use by date/sell by date) is the latest date that a product can be sold to a consumer.
1.6.4 Anything that has been made from already existing materials, fabrics, metals or fibres is (reused/recycled).
1.6.5 Bamboo fabric is an example of a (renewable/non-renewable) textile. (5 x 1) (5) [40]
QUESTION 2: THE CONSUMER
2.1 Read the information and answer the questions that follow.
| The Consumer Protection Act states that a person who markets any goods that bear a trademark – but have been imported without the approval of the registered owner of the trademark – must put a notice in a visible place on the product clearly stating that the goods have been imported and explain the meaning of the notice to the consumer. |
2.1.1 What type of goods are referred to in the statement above? (1)
2.1.2 Give ONE advantage for a consumer buying this type of goods. (1)
2.1.3 Discuss the risks involved when a consumer purchases these types of products. (2)
2.2 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
The Carbon Tax Bill was introduced by the Finance Minister, Tito Mboweni, in the National Assembly in October 2018 and is due to take effect from 1 June 2019. “SA intends to play a role in the world, as part of global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 42% by 2025,” Mboweni said. “This will also be beneficial for all of South Africa and the health of individuals as there will be less pollution.” As for the drawbacks, it is another tax being added to an already struggling economy. It will create a further financial burden, as well as an administrative burden, as taxpayers will have to report to SARS. Secondly, as of 31 December 2022, the carbon tax will increase at the rate of inflation + 2%. [Adapted from Fin24, December 2017] |
2.2.1 Give ONE example of how consumers will benefit from carbon tax. (1)
2.2.2 What does SARS stand for? Write out in full. (1)
2.2.3 Name TWO other examples of indirect taxes that South African households have to pay. (2)
2.2.4 What is the effect of greenhouse gases on the environment? (2)
2.2.5 How does inflation affect the SA consumer? (4)
2.3 In our country, many communities resort to protests to air their grievances to their respective municipalities about a lack of service delivery. Discuss how a lack of the different basic services impacts on the community. (6) [20]
QUESTION 3: FOOD AND NUTRITION
3.1 Name TWO lifestyle behaviours that are a contributing cause to most of the food-related health conditions. (2)
3.2 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
Iron-deficiency anaemia (IDA) is globally the most common nutritional deficiency. When iron stores become depleted, this can lead to anaemia. In a recent study of the iron status in a healthy SA adult population, the prevalence of iron deficiency was 39,8% in all participants and as high as 56,6% in women. Apart from inadequate dietary iron, anaemia can stem from excessive iron loss. Poor iron absorption can also be an issue. [Adapted from News24] |
3.2.1 Give ONE reason why iron-deficiency is higher in women. (1)
3.2.2 Iron amounts can be insufficient in the body due to a lack of iron rich foods in the diet. From the extract above, name TWO other causes of inadequate iron in the body and give an example of how this can occur for each one. (4)
3.2.3 Explain the role of iron in the blood. (3)
3.3 Give THREE similarities when considering the characteristics of the eating disorders, anorexia and bulimia. (3)
3.4 The aim in the management of persons who have anorexia and bulimia is for them to become physically and mentally healthy. Suggest THREE management strategies to assist them in their recovery. (3)
3.5 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow. 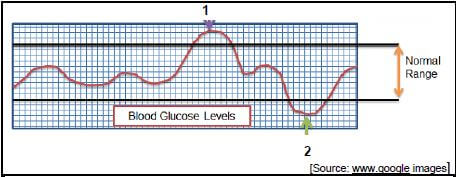
[Source: www.google images]
3.5.1 Use the correct terminology to label number 1 and 2 on the graph. (2)
3.5.2 Name the hormone responsible for ensuring that the glucose level stays within the normal range. (1)
3.5.3 Give TWO situations that would cause a drop in blood sugar levels in a normal situation (person who does not have diabetes). (2)
3.5.4 Discuss in detail how eating low GI foods would help to control the blood glucose levels so that they stay within the normal range. (5)
3.6 Read the statement below and answer the questions that follow.
| Food safety principles are for everyone, especially those living with HIV/Aids. People with Aids should take steps to prevent food-borne illnesses. Personal, kitchen and food hygiene practices must be followed to prevent contamination during food preparation. |
3.6.1 Explain why the above statement is true for people with Aids. (2)
3.6.2 State FOUR hygiene practices when working with food that would be applicable to prevent the spread of food-borne illnesses. (4)
3.7 Study the menu below, which is for one day and answer the questions that follow.
Breakfast: Muesli with skimmed milk and a banana, a glass of unsweetened orange juice |
3.7.1 The menu is suitable for a person with heart disease.
Analyse the types of fat present in the menu, their sources and discuss how the inclusion of this choice of fat would benefit a person with heart disease. (8) [40]
QUESTION 4: CLOTHING
4.1 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
Eco-fashion is now perceived as a modern, rising trend. You can’t really tell the difference between ecologically-friendly fashion and traditional fashion pieces. The big difference is knowing that what you are wearing is manufactured by methods acceptable to mother nature. [Source: https://greenconduct.com/blog/what-is-eco-fashion/] |
4.1.1 Give a phrase to show your understanding of the word trend. (1)
4.1.2 Write a paragraph to indicate how people wearing eco-fashion can have an impact on protecting our environment. (4)
4.2 Explain the difference between imitation and counterfeiting, as these two terms are both forms of brand piracy. (2)
4.3 Study the pictures below and answer the questions that follow. 
4.3 1 Use the illustrations above to explain the term retrospective fashion. (2)
4.3.2 Give the name of the stage in the fashion life cycle when the top in picture B is worn by the masses. (1)
4.3.3 Give the name of the fashion when the top in picture B will last 2–3 years in the fashion life cycle. (1)
4.4 How would a fashion trend worn by a celebrity affect fashion change? (3)
4.5 Evaluate the suitability of the outfit below for professional workwear. 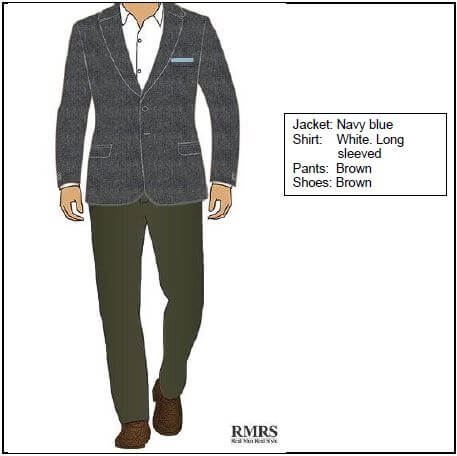 (6)
(6)
[20]
QUESTION 5: HOUSING
5.1 Read the advertisements on accommodation options below and answer the questions that follow.
| 1. Apartment to rent | 2. Apartment to buy | 3. Townhouse to buy |
One bedroomed Neat and spacious
Rental R7 000 per month 2 months’ deposit | Sectional title
R1 150 000,00 | Full title
R1 450 000,00 |
5.1.1 What is meant by the term full title used in the advertisement for the townhouse in option 3? (2)
5.1.2 In the first advertisement, name the contract and the two parties that are required to sign an agreement to rent the apartment. (3)
5.1.3 Name TWO instances where one could lose the deposit paid when the premises in option 1 are vacated. (2)
5.1.4 Discuss the different financial responsibilities for a person renting option 1 as opposed to the people buying the apartment in option 2 with regards to the pool facility. (4)
5.1.5 Give FOUR advantages of buying the townhouse in option 3, rather than buying a similar house that is not situated in a complex. (4)
5.1.6 Why are there no transfer fees or transfer duty in the advertisement for option 3? (2)
5.1.7 Compare the difference between transfer fee and transfer duty under the following headings. Tabulate your answer as follows:
Transfer fees | Transfer duty | |
The main difference | (1) | (1) |
Who finally receives the fee | (1) | (1) |
What the fee amount is based on | (1) | (1) |
(6)
5.1.8 Give the new name that each of these documents are given once a sale of a property is finalised and the house is in the new owner’s name:
- Offer to purchase (1)
- Deed of transfer (1)
5.2 Read the case study and answer the questions that follow.
Billy and Nelly want to buy a new microwave. The space available for a microwave in their kitchen is 35,6 x 61 x 50,8 cm (HWD). They want to use the microwave to defrost food from the freezer, reheat food and do some cooking. The maximum amount they are prepared to spend is R1 200,00. They plan to look at four different retailers and different brands. They read online that the advantage of a microwave with a turntable is that you do not have to stop the microwave and turn the dish while cooking. A 1 000-watt microwave with an automatic defrost and pre-programmed setting would be preferable. They would like the seller to assure them of a return policy and plan to study the warranty. |
5.2.1 Name THREE factors to consider before purchasing the microwave. (3)
5.2.2 Identify the universal design features referred to in the case study. (2)
5.2.3 What type of energy consumption would ‘saving time’ be categorised as? (1)
5.2.4 Identify the features that will save them time and give an explanation of how each feature will accomplish this. (6)
5.2.5 Name THREE responsibilities that Billy and Nelly carried out before purchasing the microwave. (3) [40]
QUESTION 6: ENTREPRENEURSHIP
6.1 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
THE MEAL KIT GAME IS ON Thandi did Consumer Studies at school. When doing practical lessons at school, her teacher always said that she was very creative. After school, when completing a short computer course on Business Management, she discovered South Africa’s four online meal delivery kit services. She decided she would start an online business from home to sell meal kits. She realised that people are too busy and tired from work to think of meals when they get home. She did a SWOT analysis to assess this business opportunity. She made two different meal samples for her friends to try and they loved the unique flavours. She would buy the ingredients locally, measure them out and put them in a box to be delivered to people’s homes. She noted that two local supermarkets sold this ready-to-go meal option. She tried some of them and knew that she could make her meal kits more appealing. She named her business ‘Quikstix’. She found a supplier that could buy boxes that were made from 100% recyclable material and the box contents would be contained in minimal plastic. The size of her box would be able to hold ingredients for four servings She had saved money for the initial outlay of her business from waitressing at the local coffee shop on weekends. She started her meal kit business with three options: a chicken pasta, a beef curry and a bean-and-vegetable stir fry for those customers who are vegan and follow a plant-based diet. On her Facebook page, she described her meal kits as time saving, wholesome delicious meals. She claimed ‘Quikstix’ offered convenience and a chance for customers to try new ingredients and flavours. [Own text] |
[A meal kit is a service that sends customers the recipe and ingredients needed to make a homemade meal. Fresh ingredients are included in the box/packaging.]
6.1.1 Select examples from the scenario to show that Thandi considered the following areas to check if her business idea had the potential to be successful:
- Testing the business concept (1)
- Having start-up capital (1)
- The location (1)
6.1.2 Explain what Thandi researched to ensure that her business would have a competitive edge over other competitors. (2)
6.1.3 Identify TWO strengths that Thandi could list for her SWOT analysis. (2)
6.1.4 Discuss how Thandi considered the following TWO factors when making her choice for a suitable product:
- Available raw materials (2)
- Consumer appeal (6)
6.1.5 How does her business name ‘Quikstix’ suit the concept of meal kits? (2)
6.1.6 Give TWO other requirements for good packaging for this product not mentioned in this scenario. (2)
6.1.7 Suggest ways how Thandi can use her time more efficiently on her production line when preparing and packaging her meal kits. (4)
6.1.8 Use the information below for the calculation questions. 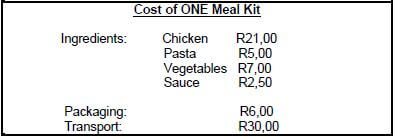
- Calculate the production cost for ONE meal kit. (1)
- Calculate the selling price of the meal kit if she added 65% mark-up. Show ALL calculations and round off the answer to the nearest rand. (3)
- Calculate the profit she will make if she reaches her sales target of selling 120 meal kits per month. Show ALL calculations. (2)
6.1.9 Create a product specification for the meal kit. Use appropriate information from the case study. Incorporate into your answer the ingredients that are provided in separate packets. (4)
6.1.10 The principle of sustainable consumption is not only the responsibility of the producer, but also the consumer. Assess how a consumer buying Thandi’s meal kit demonstrates responsible consumption to protect the environment. (7)
[40]
TOTAL: 200
Computer Technology Application P2 Grade 12 Questions - NSC Exams Past Papers and Memos September 2019 Preparatory Examinations
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of:
SECTION A (25 marks)
SECTION B (75 marks)
SECTION C (50 marks) - Answer ALL the questions.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Do NOT write in the right-hand margin.
- Leave a line after EACH subquestion.
- In general, ONE mark is allocated per fact. A 2-mark question would therefore require TWO facts, et cetera.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1– 1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.11 D.
1.1 Which ONE of the following is NOT web-based software?
- Adobe Photoshop Express
- Office 365
- Linux
- Google Calendar (1)
1.2 Which ONE of the following is an example of a monitor’s refresh rate?
- 5 ms
- 1920 x 1080
- 16:9
- 60 Hz (1)
1.3 Cloud storage refers to ...
- shared data storage on a central server usually managed by a hosting company.
- store and control by a single person over the internet.
- software that allows access to files without an internet connection.
- faster uploading of data. (1)
1.4 How do solid-state drives store data as compared to traditional hard drives?
- Optical
- Electronic
- Magnetic
- Digital (1)
1.5 Which ONE of the following statements about a URL shortener is FALSE?
- A URL shortener is a service used to convert a long URL to a shorter one.
- A website will allow access if you paste a long URL.
- A URL shortener will make a long URL much easier to share.
- All websites prevent URL shorteners from being used. (1)
1.6 Which ONE of the following statement about RAM is FALSE?
- RAM is more expensive per GB than hard drives.
- RAM does not store data and programs when the device is switched off.
- RAM has a much lower capacity than hard drives.
- RAM operates on a mechanical basis and is therefore, relatively slower. (1)
1.7 The automatic movement of text to the next page in a document is known as a ….
- continuous section break.
- soft page break.
- hard page break.
- next page section break. (1)
1.8 The defragmentation utility can be used to ...
- rearrange files in a continuous order.
- remove corrupted files.
- compress unused files.
- increase hard drive space. (1)
1.9 You want to find out how many times a date in 2014 appears in a column of dates consisting of month and year. Look at the screenshot below and complete the formula.
=COUNTIF(B5:B36; ____) 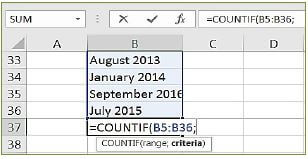
- “>2013”
- 2014
- “*2014”
- =2014 (1)
1.10 If you want to determine how many records appear in a report, you should use the following expression in a calculated field:
- =Sum(([Name of specific field]) + Count([Name of specific field]))
- =Count([Name of specific field])
- =Sum([Name of specific field])
- =Max([Name of specific field]) (1) [10]
QUESTION 2: MATCHING COLUMNS
Choose a term/concept from COLUMN B that matches the description in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–P) next to the question number (2.1–2.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 2.11 Q.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
2.1 A port usually found on portable devices such as smartphones |
|
(10 x 1) [10]
QUESTION 3: TRUE/FALSE ITEM
Indicate whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Write ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the question number (3.1–3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK. Correct the statement if it is FALSE. Change the underlined word(s) to make the statement TRUE. (You may not simply use the word ‘NOT’ to change the statement. NO mark will be awarded if only FALSE is written down.)
EXAMPLES:
QUESTION | ANSWER |
Google is the world’s most popular search engine. | True |
A NIC has slots for hardware components such as the CPU. | False – motherboard |
3.1 A multi-touch screen offers more functionality without using menus. (1)
3.2 A solid state drive is a drive that has no moving parts, thus making it quieter and more robust. (1)
3.3 The term Virtual Reality (VR) is associated with simulation of a 3D-environment. (1)
3.4 ICT refers to the trend whereby all sorts of objects and devices increasingly being connected to one another via the Internet. (1)
3.5 Freeware refers to software that has copyright, but may be copied or shared for the purpose of trying it out, with the understanding that an amount should be paid for continuous use. (1) [5]
TOTAL SECTION A: 25
SECTION B
QUESTION 4: SYSTEM TECHNOLOGIES
4.1 Study the advertisement below and answer the questions that follow. 
4.1.1 Name the TWO hardware components for Device A that are most important for the effective working of a computer, other than the hard drive. (2)
4.1.2 Explain how adding more RAM to a computer can improve the overall system performance of the computer. (2)
4.1.3 Give TWO reasons why solid state drives (SSDs) will in future replace hard disk drives as the main storage device of a computer. (2)
4.1.4 Give TWO benefits of buying Device A, which is an ‘all-in-one’ computer. (2)
4.1.5 Give TWO reasons why HDMI output is better than VGA output. (2)
4.2 The following questions refer to Device B:
4.2.1 Name TWO features/functionalities, which were added to a cell phone when multiple technologies converged as a phablet. (2)
4.2.2 Name ONE way in which you could transfer photos from Device B to your desktop computer. (1)
4.2.3 Give ONE example of an action that can be performed on a ‘multi touch sensing screen’. (1)
4.2.4 Name ONE biometric feature of Device B listed in the advert. (1)
4.2.5 Compare the operating systems found on both devices by referring to:
- Cost of the software (2)
- Support from the developer (2)
4.3 Write down the TWO processes in the information processing cycle that have the least influence on the overall performance of the computer. (2)
4.4 Explain why the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer needs cache memory. (2)
4.5 A buyer considers purchasing a 3D printer. Name TWO advantages of buying a 3D printer. (2) [25]
QUESTION 5: INTERNET AND NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES
5.1 Give TWO reasons for compressing files before uploading them to cloud storage. (2)
5.2 Study the Internet connection package advertised below and answer the questions that follow.
- 30 GB data per month
- 15 Mbps
- Shaped
5.2.1 Give the common term used when an Internet Service Provider slows down your Internet speed when you download huge amounts of data. (1)
5.2.2 Give TWO factors (besides the one in QUESTION 5.2.1) that can influence Internet speed. (2)
5.2.3 Explain the term shaped and provide ONE example of a situation where it would be necessary to ‘shape’ a connection. (2)
5.3 How would RSS-feeds be used to distribute podcasts? (1)
5.4 You are unable to attend a seminar in Limpopo due to protests. A friend suggests you use a video conference.
5.4.1 How can a video conference be used to share information about the seminar in Limpopo? (2)
5.4.2 Give TWO advantages of using a video conference. (2)
5.5 Your friend complained that he was automatically redirected to a fake website, even when he typed in the correct URL for a specific website. Name TWO ways how he can prevent becoming a victim of pharming. (2)
5.6 What is digital migration? (1) [15]
QUESTION 6: INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
6.1 Youth participating in social media has advantages and disadvantages.
6.1.1 Can continuous online participation decrease social interaction between people? Motivate your answer. (2)
6.1.2 Give TWO ways in which social media sites such as Facebook can benefit you in searching for a job. (2)
6.2 A strategy to prevent information overload is to read more accurately and faster. Give TWO more strategies to overcome overload of information. (2)
6.3 Compare plagiarism and copyright infringement by explaining:
6.3.1 What each offence is (2)
6.3.2 How you can avoid being guilty of the offence (2) [10]
QUESTION 7: SOCIAL IMPLICATIONS
7.1 Give TWO reasons why it would be necessary for a school or company that has a policy of BYOD to take extra measures to secure their data. (2)
7.2 Computers on any network can be open to ransomware attacks.
7.2.1 What is a ransomware attack and what is required of a user to do? (2)
7.2.2 What is the best way to safeguard/protect yourself against ransomware? (2)
7.3 Briefly explain how bitcoins work to financially benefit entrepreneurs or individuals. (2)
7.4 Social media has been overflowing with fake news recently. Give TWO ways to spot fake news. (2) [10]
QUESTION 8: SOLUTION DEVELOPMENT
8.1 Name TWO possible data sources to create mailing labels in a mail merge. (2)
8.2 The following message appears when one tries to create a Table of Figures for all images in a document: "No table of figures entries found". What change should you make to the document to ensure a Table of Figures can be generated? (1)
8.3 Study the screenshot below which shows part of a spreadsheet. 
Cell B1 contains the formula =A1 * 5.
Give a possible reason why the answer displayed in cell B1 is not 60. (2)
8.4 Explain the difference between a validation rule and validation text by referring to their functions. (2)
8.5 What is the function of the ‘eye’ icon in the screenshot below? (1)
8.6 The screenshot below shows part of a spreadsheet listing movie titles. 
The function =COUNTIF(A2:A11, “Gold*”) returns a result of 3.
8.6.1 Explain the purpose of the ‘*’ in the criterion “Gold*”. (2)
8.6.2 If the criterion were changed to “Gold”, what would the result be? (1)
8.6.3 If the criterion were changed to “*Gold*”, what would the result be? (1)
8.7 The html code
<table border=“3”>
<tr>
<td>Cell 1</td>
<td>Cell 2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Cell 3</td>
<tr>
</table>
displays the following table in the browser: ![]()
How would you correct the highlighted (bold) line (the third line of code) so that the table will display as shown below?  (2)
(2)
8.8 Mention ONE example of metadata that is saved with a word processing document. (1) [15]
TOTAL SECTION B: 75
SECTION C
QUESTION 9: INTEGRATED SCENARIO
Your cousin is a young man who has just completed his studies in Creative Brand Communication. He wants to start his own business of Branding using the savings he accumulated during his years at university. His type of business needs a ‘powerful’ computer/notebook as he has to use graphic design software like Photoshop.
9.1 Your cousin needs to start shopping for two computers: a notebook for himself and another one for his secretary.
9.1.1 You mention to your cousin that the notebook he needs to buy for the secretary should meet the minimum system requirements. What does this mean? (2)
9.1.2 You recommend to him that he has to buy a notebook with higher specifications for himself than the requirements for his secretary. Give TWO reasons why this is good advice. (2)
9.1.3 Your cousin has been given a trial version of a program by the software developers. Give ONE advantage of using a trial version of software before installing the full version. (1)
9.2 RFID tags and bar codes have similar functions.
9.2.1 What medium does an RFID reader use to read RFID tags? (1)
9.2.2 What medium does a bar code scanner use to read bar codes? (1)
9.3 Give ONE advantage of using a QR code to advertise his business. (1)
9.4 Your cousin has stored a lot of confidential information on his notebook.
9.4.1 Mention TWO practical ways in which he can prevent his notebook from being stolen from his office, besides being locked on the desk. (2)
9.4.2 Give TWO examples of biometric features to ensure secure access to a notebook. (2)
9.5 The secretary wants to telecommute on some days (wants to work from home instead of actually being present at the workplace). Give TWO general advantages of telecommuting or teleworking for the employee. (2)
9.6 Besides social networking sites, your cousin wants to use a blog for the business. Suggest TWO ways in which he can attract or maintain their interest in reading the blog in future. (2)
9.7 Your cousin wants to carefully consider certain aspects when choosing an Internet Service Provider (ISP). List TWO possible aspects to consider when choosing between different Internet Service Providers (ISP). (2)
9.8 The user has a choice of allowing an automatic download of a patch. Mention TWO disadvantages of choosing an automatic download of a patch. (2)
9.9 There will be instances where your cousin would want some of the hard copies to be converted and used electronically on his notebook.
9.9.1 Which device would be suitable to do this? (1)
9.9.2 Which software does the device use and briefly mention how this software works? (2)
9.9.3 Mention TWO disadvantages of using the device you mentioned in QUESTION 9.9.1 to create soft copies. (2) [25]
QUESTION 10
Your school is planning to roll out tablets to be used in the class. The school needs your support to make this transition smooth with the help of ICTs (Information and Communication Technologies).
10.1 The following are specifications of a tablet the school would like to purchase.
Technical Specifications: 1.3GHz Spreadtrum T-Shark quad-core processor |
10.1.1 Give TWO uses for a front camera of a tablet. (2)
10.1.2 What does it mean when the tablet is both Wi-Fi and SIM Card enabled? (2)
10.1.3 Give the name of the specification that 1024 x 600 refers to. (1)
10.1.4 Explain what the term micro SD refers to, and what the purpose of the micro SD is. (2)
10.1.5 What is meant by a quad-core processor and what is the significance of such a processor? (2)
10.2 When used in a classroom, tablets have both advantages and disadvantages.
10.2.1 Name TWO tasks associated with teaching and learning in the class that can best be done by using a tablet. (2)
10.2.2 Give TWO ways in which educators can make sure that their learners are unable to access inappropriate websites while ‘surfing’ the web. (2)
10.2.3 Name TWO ways in which the use of tablets in class can promote ‘green computing’. (2)
10.2.4 Some sight impaired learners are struggling with viewing work on the tablets due to the size of the screen. Recommend TWO solutions how this challenge can be overcome. (2)
10.3 ISPs offer data bundles which provide different limitations in the amounts of data that can be downloaded and uploaded in a month.
10.3.1 Why is it better for the school to have uncapped data? (2)
10.3.2 Explain the difference between a hard cap and a soft cap. (2)
10.4 The school should have a backup policy.
10.4.1 Name TWO measures that should be included in such a policy. (2)
10.4.2 Name TWO advantages of dedicated backup programs. (2) [25]
TOTAL SECTION C: 50
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Computer Technology Application P2 Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Exams Past Papers and Memos September 2019 Preparatory Examinations
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE |
[10]
QUESTION 2: MATCHING COLUMNS |
[10]
QUESTION 3: TRUE/FALSE ITEM
3.1 True (1)
3.2 True (1)
3.3 True (1)
3.4 False Internet of Things (1)
3.5 False Shareware (1) [5]
TOTAL SECTION A: 25
SECTION B
QUESTION 4: SYSTEM TECHNOLOGIES
4.1 | 4.1.1 |
| 2 | 10 | |
4.1.2 |
| 2 | |||
4.1.3 |
| 2 | |||
4.1.4 |
✓✓ (any two or any acceptable answer) | 2 | |||
4.1.5 |
| 2 | |||
4.2 | 4.2.1 |
| 2 | 5 | |
4.2.2 |
| 1 | |||
4.2.3 |
| 1 | |||
4.2.4 |
| 1 | |||
4.2.5 | (a) | Apple software is proprietary and subject to cost, ✔whilst Android is open source free of charge. ✔ | 2 | 4 | |
(b) |
| 2 | |||
4.3 |
| 2 | 2 | ||
4.4 | The CPU needs cache memory to store frequently or recently accessed data ✔ based on the assumption that it will probably be accessed again soon. ✔ | 2 | 2 |
4.5 |
| 2 | 2 |
25 |
QUESTION 5: INTERNET AND NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES
5.1 |
| 2 | 2 | ||
5.2 | 5.2.1 | Throttling ✔ | 1 | 5 | |
5.2.2 |
| 2 | |||
5.2.3 |
OR
| 2 | |||
5.3 | A podcast reader is connected to an RSS feed that contains information about the podcast. ✔ | 1 | 1 | ||
5.4 | 5.4.1 |
OR | 2 | 4 | |
5.4.2 |
| 2 | |||
5.5 |
| 2 | 2 | ||
5.6 | A process in which broadcasting services using traditional analogue technology are replaced with digital technology. | 1 | 1 | ||
15 | |||||
QUESTION 6: INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
6.1 | 6.1.1 | Yes ✔ OR No | 2 | 4 |
6.1.2 |
| 2 | ||
6.2 |
| 2 | 2 | |
6.3 | 6.3.1 |
| 2 | 2 |
6.3.2 |
| 2 | 2 | |
10 | ||||
QUESTION 7: SOCIAL IMPLICATIONS
7.1 |
| 2 | 2 | |
7.2 | 7.2.1 | Definition | 2 | 4 |
7.2.2 |
| 2 | ||
7.3 |
| 2 | 2 | |
7.4 |
| 2 | 2 | |
10 | ||||
QUESTION 8: SOLUTION DEVELOPMENT
8.1 |
| 2 | 2 | |
8.2 | Add an automatic caption ✔ to each image | 1 | 1 | |
8.3 | Cell A1 has been formatted to display a whole number. ✔ | 2 | 2 | |
8.4 | A validation rule is a field property that sets limits or conditions on the values that can be entered in the field ✔ | 2 | 2 | |
8.5 | When the ‘eye’ symbol is clicked the actual password is revealed instead of the placeholder character ✔ | 1 | 1 | |
8.6 | 8.6.1 | It will search ✔ for all text that starts with the word Gold ✔ | 2 | 4 |
8.6.2 | 3 ✔ | 1 | ||
8.6.3 | 10 ✔ | 1 | ||
8.7 | <td rowspan = 2>Cell 1</td> | 2 | 2 | |
8.8 |
| 1 | 1 | |
15 | ||||
TOTAL SECTION B: 75
SECTION C
QUESTION 9: INTEGRATED SCENARIO
9.1 | 9.1.1 | The lowest/minimum possible specifications (hardware/software) ✔ needed for the program to load/run ✔ | 2 | 5 |
9.1.2 |
| 2 | ||
9.1.3 |
| 1 | ||
9.2 | 9.2.1 | RFID uses radio waves ✔ | 1 | 2 |
9.2.2 | Barcodes uses light ✔ | 1 | ||
9.3 |
| 1 | 1 | |
9.4 | 9.4.1 |
| 2 | 4 |
9.4.2 |
| 2 | ||
9.5 |
| 2 | 2 | |
9.6 |
NOTE TO MARKER: (Accept any valid reasons for attracting or maintaining interest in the blog) (✔✔ any two) | 2 | 2 | |
9.7 |
| 2 | 2 | |
9.8 |
| 2 | 2 | |
9.9 | 9.9.1 |
| 1 | |
9.9.2 | OCR ✔ | 2 | ||
9.9.3 |
| 2 | 5 | |
25 | ||||
QUESTION 10
10.1 | 10.1.1 |
| 2 | 9 |
10.1.2 | Data connection via Wi-Fi ✔ or SIM card ✔ | 2 | ||
10.1.3 | Resolution ✔ | 1 | ||
10.1.4 |
| 2 | ||
10.1.5 | It tells you how many (in this instance four) physical CPUs ✔ are on the chip | 2 | ||
10.2 | 10.2.1 |
(✔✔ any two or other acceptable answer) | 2 | |
10.2.2 |
| 2 | ||
10.2.3 |
| 2 |
10.2.4 |
| 2 | 8 | |
10.3 | 10.3.1 |
| 2 | 4 |
10.3.2 | A Hard cap is a type of an account that stops ✔ all Internet access once the cap limit has been reached while with a Soft cap the user is allowed some Internet connectivity ✔ after the limit has been reached | 2 | ||
10.4 | 10.4.1 |
| 2 | 4 |
10.4.2 |
| 2 | ||
25 | ||||
TOTAL SECTION C: 50
GRAND TOTAL: 150
Computer Technology Application P1 Grade 12 Memorandum - NSC Exams Past Papers and Memos September 2019 Preparatory Examinations
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1 File Name: 1LandPollution Total Q1: 29
No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | Candidate Mark | ||
1.1.1 | Cover Page
| 1 | 1 | ||
1.1.2 | Cover Page
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
1.2.1 | Table of Contents
| 1 | 1 | ||
1.2.2 | Table of Contents
| 1 | 1 | ||
1.2.3 | Table of Contents
(Note to marker: All three levels must be inserted correctly in order to obtain the last mark.) | 1 | 1 | ||
1.3.1 | Page Numbering
| 1 | 1 | ||
1.3.2 | Page Numbering
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
1.4.1 | Paragraph Formatting
| 1 | 1 | ||
1.4.2 | Line Formatting
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
1.4.3 | Character Formatting
| 1 | 1 | ||
1.5 | Document Editing
(Note to marker: 2 Occurrences only 2 or 0 marks) | 1 1 | 2 | ||
| No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | Candidates Mark | ||
c | Hyperlink
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
1.7 | Footnote
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
1.8 | Document formatting
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
1.9 | Citation
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
1.10 | Bibliography
| 1 | 1 | ||
1.11 | Quick Parts
| 1 | 1 | ||
Total for QUESTION 1 | [29] | ||||
QUESTION 2 File Name: 2LandPollutionBrochure Total Q2: 23
No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | Candidate Mark | ||
2.1 | Page Orientation
| 1 | 1 | ||
2.2 | Page border
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
2.3 | Columns
| 1 1 1 1 | 4 | ||
2.4 | WordArt
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
2.5 | Bullets
| 1 1 1 1 | 4 | ||
2.6 | Shapes
| 1 1 1 1 | 4 | ||
2.7 | Watermark
| 1 1 1 1 | 4 | ||
Total for QUESTION 2 | [23] | ||||
QUESTION 3 File Name: 3_LandSheet Total Q3: 57
- Mark the questions from the formulae and not the values/answers in the cell.
- Check against candidate's actual work (Cell references may differ, depending on the candidate's response).
- Candidate may use multiple formulae or cells as 'building blocks' to reach answers.
- Named ranges can be used instead of cell references.
- The answers must still be correct even if changes are made to the existing data.
No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | Candidate Mark | ||
Stats per Province worksheet | |||||
3.1.1 | Stats per Province
(Note to marker: Colour was white.) | 1 | 1 | ||
3.1.2 | Merge and Centre
| 1 | 1 | ||
3.1.3 | Fill
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
3.1.4 | Row 4
| 1 | 1 | ||
3.2 | Freeze panes
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
3.3 | Format Date =(dd)-(mm)-( yyyy)
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
3.4 | Cell A5 =CONCATENATE(UPPER(LEFT(B5;2));"-”; LEN(B5))
| 1 1 1 1 1 | 5 | ||
| No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | Candidates Mark | ||
3.5 | Cell C3 =FIND(" ";B5)
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
3.6 | Data Validation
| 1 1 1 1 | 4 | ||
3.7 | Cell E3 =COUNTIFS(D5:D13;">=100000";E5:E13;"<=55")
| 1 1 1 1 1 | 5 | ||
3.8 | Nested IF =IF(E5<51;"Less Dense";
| 1 1 1 1 | 4 | ||
3.9 | Conditional formatting
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
3.10 | Cell Q15 =SUMIF(B5:B13;"*Cape";Q5:Q13)
| 1 1 1 1 | 4 | ||
3.11 | Cell R5 =P5-Q5
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
3.12 | Cell S5 =IF(P5<=Q5,"Top up"," ")
| 1 1 1 1 | 4 | ||
3.13 | Cell T9 =VLOOKUP(B9,Towns!$A$2:$B$10,2, FALSE)
| 1 1 1 1 1 | 5 | ||
3.14 | Graph Worksheet
WasteTreatment. ✔
| 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 | 7 | ||
Total for QUESTION 3 | [57] |
QUESTION 4 File Name: 4_LandPollution Total Q4: 41
No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | Candidate Mark | ||
Table: Waste Pollution | |||||
4.1.1 | Field: ID
| 1 | 1 | ||
4.1.2 | Field: Image
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
4.1.3 | Primary key
| 1 | 1 | ||
4.1.4 | Required Field: Hazardous Waste
| 1 | 1 | ||
4.1.5 | Validation rule and text: Own refuse dump
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
4.1.6 | Budget Field
| 1 | 1 | ||
4.2 | Form: frm4_2
| 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 | 7 | ||
4.3 | Qry4_3
4 Records | 1 1 1 1 1 | 5 | ||
4.4 | Qry4_4
4 Records | 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
4.5 | Qry4_5
2 Records | 1 1 1 1 1 1 | 6 | ||
4.6 | Report4_6
| 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 | 10 | ||
Total for QUESTION 4 | [41] |
QUESTION 5 File Name: 5_MyWebsite Total Q5: 20
- This question should be marked from the HTML code.
- Numerical attribute values do not need to be in inverted commas.
No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | Candidate Mark | ||
5.1 | Title
| 1 | 1 | ||
5.2 | Heading: LandPollution <h1 align ="center"><font color = "Brown"> Land Pollution</font></h1>
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
5.3 | Horizontal line <hr size=7 color="Red"/>
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
5.4 | Ordered list
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
| No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | Candidates Mark | ||
5.5 | Table
Table border set at 2 ✔
| 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 | 9 | ||
5.6 | Link
| 1 1 1 | 3 | ||
Closing tag(s) or triangular brackets omitted | -1 | ||||
Total for QUESTION 5 | [20] | ||||
QUESTION 6 File Name: 6Letter.docx Total Q6: 10
No. | Criteria | Maximum Mark | Candidate Mark | ||
6.1.1 |
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
6.1.2 |
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
6.1.3 |
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
6.1.4 |
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
6.1.5 |
| 1 1 | 2 | ||
Total for QUESTION 6 | [10] | ||||
TOTAL: | 180 | ||||
Computer Technology Application P1 Grade 12 Questions - NSC Exams Past Papers and Memos September 2019 Preparatory Examinations
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Owing to the nature of this three-hour examination, it is important to note that you will NOT be permitted to leave the examination room before the end of the examination period.
- Insert your surname and name in the header of EVERY document that you create or save.
- The invigilator will give you a disk containing ALL the files needed for the examination OR you will be told where the files can be found on the network or computer. If a disk has been issued to you, you must write your centre number and examination number on the label. If you are working on the network, you must follow the instructions provided by the invigilator.
- A copy of the master files will be available from the invigilator. Should there be any problems with a file, you may request another copy from the invigilator.
- This question paper consists of SIX questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Ensure that you save each document using the file name given in the question paper. Save your work at regular intervals as a precaution against possible power failures.
- Read through each question before answering or solving the problem. Do NOT do more than required by the question.
- At the end of the examination you must hand in the disk given to you by the invigilator with ALL the files saved on the disk, OR you should make sure that ALL the files are saved on the network/computer as explained to you by the invigilator/teacher. Make absolutely sure that ALL files can be read.
- During the examination you may make use of the help functions of the programs which you are using. You may NOT use any other resource material.
- If data is derived from a previous question that you cannot answer, you should still proceed with the questions that follow.
- Unless instructed otherwise, you must use formulae and/or functions for ALL calculations in questions involving spreadsheets. Use absolute cell references only where necessary to ensure that formulae are correct when you copy them to other cells in a spreadsheet.
- In all questions involving word processing, you should set the language to English (South Africa). The paper size is assumed to be A4 Portrait, unless instructed otherwise.
- In Annexure A the HTML Tag sheet is provided.
- The examination folder/data disk that you receive with this question paper will contain the folder and files listed below. Ensure that you have the folder and all the files before you begin this examination.

QUESTIONS
SCENARIO
Land pollution is a serious problem that impacts on humans, animals and the earth. Without taking measures now to reduce pollution levels, permanent changes to the land can occur. The adverse changes to the environment due to land pollution are subtle, but the problem is much bigger than it appears. It is therefore important to Save our Land. The school asked the Grade 12 learners to assist in a campaign to promote sustainable living.
QUESTION 1: WORD PROCESSING
A document was created to give an insight about what land pollution is. Edit the document as requested.
Open the 1LandPollution word processing document.
1.1 Insert a cover page in the document. The cover page must display the following:
1.1.1 A “Facet” cover page at the beginning of the document. (1)
1.1.2 Type Land Pollution in the title field, Save our Land in the subtitle field and This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it. in the email field. Delete the abstract field. (3)
1.2 Insert an automatic table of contents below the heading “Table of Contents” as follows:
1.2.1 Use the “Title” style for the level 1 headings. (1)
1.2.2 Use the “Heading 1” style for the level 2 headings. (1)
1.2.3 Use the “Heading 2” style for the level 3 headings. (1)
1.3 Apply automatic page numbering to the document as follows:
1.3.1 Insert the Accent Bar Right page numbers in the document. (1)
1.3.2 Start the page numbering from the second page of the document, numbering the pages from page 1 onwards. (2)
1.4 Format the first paragraph under the heading “Land Pollution”, starting with the text “What’s beneath …” and ending with “… closer look”. as follows:
1.4.1 Change the paragraph spacing to 6 pt before and 6 pt after the paragraph. (1)
1.4.2 Change the line spacing to exactly 16 pt. (2)
1.4.3 Expand the character spacing by 1.5 pt. (1)
1.5 The word “Contaminate” appears twice in this document. Replace the two occurrences of this word with the word “infect”. (2)
1.6 Locate the word ‘In factories and offices’ in the text under the heading ‘Waste disposal’.
Add a hyperlink to this text as follows:
- The hyperlink must link to the website www.explainthatstuff.com/land pollution.html.
- he text “HowStuffWorks” must display when the mouse hovers (is moved) over the hyperlink. (3)
1.7 Attach a footnote to the word “Radioactive Waste” under the heading “Waste Disposal”. Use the symbol (Wingdings character 83) as a custom symbol and type in ‘by-product of nuclear power’ as the footnote text. (3)
1.8 Justify and automatically hyphenate the whole document. (2)
1.9 Add the source displayed at the end of the document to the other sources of the document. (3)
1.10 The bibliography at the end of the document does not display any records. Format the bibliography so that it shows at least ONE source. (1)
1.11 Insert a field next to the text “Date Created” to display the date that this document was created. (1) [29]
QUESTION 2: WORD PROCESSING
You are requested to modify the brochure that was created in Word. This brochure will be distributed to people as a form of awareness.
Open the 2LandPollutionBrochure word processing document and modify it as follows:
2.1 Change the page orientation to landscape. (1)
2.2 Place a 2¼ pt wide, red double-line page border around the document. (3)
2.3 Place the highlighted text of the document into three columns.
- Insert a 1 cm/0.39 inches space between the columns.
- Insert a line between columns.
- Headings must be at the top of each column. (4)
2.4 Change the heading “What is land pollution?” by using a WordArt with a gold colour Accent 4 Soft Bevel. (4)
2.5 Locate the bulleted list under the heading “How to prevent land pollution?”.
- Change the format of the bullets to the picture 2Bullet.jpg found in the data folder.
- Set the indentation of the bullets at 0 cm and the paragraphs must be hanging at 1.5 cm. (4)
2.6 Insert an Oval Callout Shape at the bottom of the first column with the text “Save Our Land!” (3)
2.7 Use the image 2LandPollution.jpg as a watermark WITHOUT any washout effect and set the scaling to 120%. (4) [23]7
QUESTION 3: SPREADSHEET
A spreadsheet file containing results of the event has been stored in the 3_LandPollution spreadsheet.
Open the 3_LandPollution spreadsheet and work in the Stats per Province worksheet.
3.1 Format the worksheet as follows:
3.1.1 Change the tab colour of the Stats per Province worksheet to any colour other than the original. (1)
3.1.2 Merge and centre cells from cell A1 to cell T1. (1)
3.1.3 Apply a thin diagonal stripe pattern style fill effect with a red colour to the merged cell. (2)
3.1.4 Format Row 4 so that all contents is visible without enlarging the cells. (1)
3.2 Freeze the pane in column A so that all columns display when you scroll right. (2)
3.3 The date the land pollution report was created is stored in cell A3. Format the date to display as follows: (28)-(02)-(2019). (3)
3.4 Use suitable functions to create a code in cell A5. The code is created by combining the following:
- First two letters of the province.
- A hyphen (-).
- Number of characters of the province.
- All these in capital letters. (5)
3.5 Insert a function in cell C3 to determine the position of the space in the name ‘Eastern Cape’ in cell B5. (3)
3.6 Use a spreadsheet feature to force the user to enter a whole number that cannot be greater than 999 999 in column D. Add a suitable error message that the user will receive if invalid data is entered. (4)
3.7 Some provinces are densely populated than others; this creates a lot of land pollution.
Insert a function in cell E3 to determine the number of provinces that are bigger than 100000 (Square metres) (column D) AND whose population density is less than 55 (column E). (5)
3.8 The population density of each province is recorded in column E and is expressed in percentages. The percentages can be translated as follows:
Population Density | Density |
<51 | Less Dense |
51 to100 | Dense |
>100 | Highly Dense |
Insert a suitable function in cell F5 to determine the density of the Eastern Cape. (4)
3.9 In column O, daily inflows per province are recorded. Use an appropriate spreadsheet feature to apply a red data bar to represent the value in the cell. The higher the value, the longer the bar. (3)
3.10 Insert a function in cell Q15 to determine the total budget of all the “Cape” provinces. (4)
3.11 The amount budgeted by each province is in column P and expenditure in column Q. Calculate in cell R5 the amount that is left after the expenditure of the province has been paid. Copy the result for all provinces. (3)
3.12 Some provinces used their whole budget for Waste Management. Some have money left in their budget. Use a function in cell S5 to determine whether the province(s) need a Top Up or not. Insert “Top Up” for those provinces that need Top Up and leave cell blank for province(s) that do not need a Top Up. Copy the answer to the rest of the column C. (4)
3.13 A town per province was identified for the study of land pollution. These towns are stored as worksheet Towns.
Insert a function in cell T9 to identify the town in the province of Limpopo. (5)
Work in the Graph worksheet.
3.14 Create a graph using the data in the ranges B5:B13; L5:L13 and M5:M13. The chart/graph must resemble the chart/graph below. Adhere to the instructions that follow. 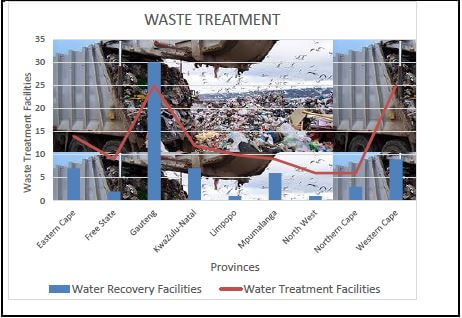
- The graph must have two series points plotted correctly.
- Series 1 (Waste Recovery Facilities) must be a column graph and Series 2 (Waste Treatment Facilities) must be a line graph.
- Legends must be correctly placed and edited.
- Both axes must be renamed.
- Format chart area to picture.
- Use a spreadsheet feature to move the chart to the graph worksheet. (7) [57]
QUESTION 4: DATABASE
A database of all waste management facilities is created. Modify the database and work in the design view.
Open the 4_LandPollution database.
4.1 Edit the Waste Pollution table as follows:
4.1.1 Remove the ID field. (1)
4.1.2 Add a new field named Image after the province field:
- This field must be able to store a picture.
- Provide the field with an appropriate data type. (3)
4.1.3 Set the primary key to a more appropriate field type. (1)
4.1.4 Change the field properties of Hazardous Waste field so that the user is forced to enter a value. (1)
4.1.5 Change the Own refuse dump field so that:
- The user can only enter values greater than 2 or less than 99.
- Appropriate validation text is inserted. (3)
4.1.6 Set the default value of the Budget field to R10 000. (1)
4.2 Create the form frm4_2 based on the LandPollution table.
- Insert only the following fields: Province; Hazardous Waste; Budget and Expenditure.
- Change the background colour of the form header to red.
- Change the content of the label in the form header to Waste.
- Insert the date as a field in the header of the form.
- Insert a calculation in the form footer to determine the total number of provinces. (7)
4.3 Open the query qry4_3 and modify it as follows:
- Edit the qry4_3 to show only Province, Population served by Municipality and Own Refuse dump.
- Only show those who are 50% and above of population served by municipal waste collection.
- Also show those who have a Hazardous Waste.
- Sort them from smallest to biggest of the Own Refuse Dump field. (5)
4.4 Open query qry4_4.
Modify the query so that it displays the total of the provinces whose budget for waste management is R50 000 and more, as shown below. (3)
Province | SumOfBudget |
Eastern Cape | R 105 740.00 |
Free State | R 50 314.00 |
Gauteng | R 236 324.00 |
KwaZulu-Natal | R 209 726.00 |
Western Cape | R 291 920.00 |
4.5 Open query qry4_5.
Create a calculated field called Balance in the query qry4_5. Calculate which province(s) spend more than their budget and have a Hazardous Waste. (6)
4.6 Create a report from the LandPollution table.
- Show all fields other than the ID field.
- Group according to the Licensed facilities and then by Hazardous Waste.
- Sort from the smallest to the biggest budget.
- Page orientation must be landscape.
- Calculate the total amount used in the Licensed Facilities footer.
- The total amount must be in a suitable format.
- Insert the picture 4LandPollution.jpg in the header of the report.
- Save as Report. (10) [41]
QUESTION 5: WEB DESIGN (HTML)
A web page has been created to create an awareness about land pollution.
Open the incomplete 5_LandPollution.html web page in a web browser and in a text editor e.g. Notepad.
NOTE:
- Question numbers are inserted as comments in the coding as guidelines to show approximately where the answer(s) should be inserted.
- An HTML tag sheet has been attached for reference.
Your final web page should look like the example below.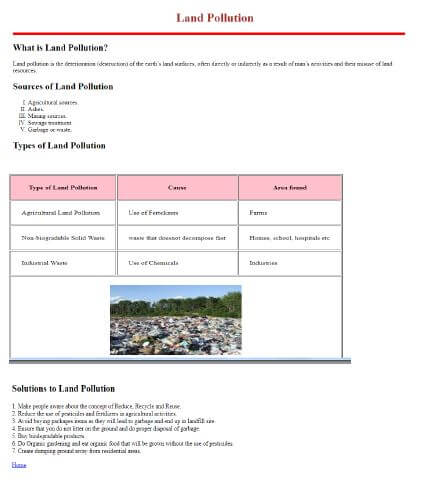
5.1 Insert tags to ensure that the text “Land Pollution” displays in the browser tab. (1)
5.2 Adjust the heading “Land Pollution” as follows:
- The heading “Land Pollution” must be centred.
- Change font colour to brown. (2)
5.3 Change the size of the horizontal line under the heading “Triathlon” to 7 and colour red. (2)
5.4 Change the information under the heading “Sources of Land Pollution” to a bulleted list by using capital Roman figures as shown in the example of the website. (3)
5.5 A table has been created but does not show correctly. Correct it as follows:
- Change the first row as table headings.
- Set the table border to 2.
- Set the space between text and the cell borders to 25.
- The heading row must be shaded in pink colour.
- Merge the cells in the last row of the table and insert the picture 5LandPollution.
- The picture height must be 200 and width 300.
- The picture must be in the centre of the cell.
- The word “Dump” must show if the picture does not display. (9)
5.6 Insert a link on the word Home below the table, to link to the Top of the website. (3) [20]
QUESTION 6: GENERAL
A community member of Waterfall Park has written a letter to the mayor of the city to complain about the land pollution.
Open and edit the file 6Letter.docx.
6.1 The following changes must be done to the letterhead:
6.1.1 There are two pictures in the letterhead. Use a word processing feature to combine the two pictures to appear as one. Move the picture below the heading “Waterfall Community”. (2)
6.1.2 Add a cross reference next to the highlighted “my” in first paragraph that links to the endnote found in the letter. (2)
6.1.3 The graph created had an error where the values of the Plastic pollutants were swapped with Broken Metal pollutants. Correct the graph to show the correct percentages. (2)
6.1.4 Use a paragraph setting to ensure that the lines in the paragraph starting with “There” and ending with “earth” will stay together and not split if the paragraph runs over to another page. (2)
6.1.5 A poster called 6Poster.docx has been created to educate people about land pollution.
Insert 6Poster.docx as an icon in the space provided in the letter. (2) [10]
TOTAL: 180
ANNEXURE A – HTML TAG SHEET
Basic Tags | |
Tag | Description |
<body></body> | Defines the body of the web page |
<body bgcolor="pink"> | Sets the background colour of the web page |
<body text="black"> | Sets the colour of the body text |
<head></head> | Contains information about the document |
<html></html> | Creates an HTML document – starts and ends a web page |
<title></title> | Defines a title for the document |
<!-- --> | Comment |
Text Tags | |
Tag | Description |
<hl></hl> | Creates the largest heading |
<h6></h6> | Creates the smallest heading |
<b></b> | Creates bold text |
<i></i> | Creates italic text |
<font size="3"></font> | Sets size of font, from "1" to "7" |
<font color="green"></font> | Sets font colour |
<font face="Times New Roman"></font> | Sets font type |
Link Tags | |
Tag | Description |
<a href="/URL"></a> | Creates a hyperlink |
<a href="/URL"><img src="/URL"></a> | Creates an image link |
<a name="NAME"></a> | Creates a target location |
<a href="#NAME"></a> | Links to a target location created somewhere else in the document |
Formatting Tags | |
Tag | Description |
<p></p> | Creates a new paragraph |
<p align="left"> | Aligns a paragraph to the "left" (default), can also be "right", or "center" |
<br/> | Inserts a line break |
<ol></ol> | Creates a numbered list |
<ol type="A","a", "I","i","1"></ol> | Defines the type of numbering used |
<ul></ul> | Creates a bulleted list |
<ul type="disc", "square","circle"></ ul> | Defines the type of bullets used |
Formatting Tags continued | |
Tag | Description |
<li></li> | Inserted before each list item, and adds a number or symbol depending upon the type of list selected |
<img src="/name"> | Adds an image |
<img src="/name" align="left"> | Aligns an image: can also be "right", "center"; "bottom", "top", "middle" |
<img src="/name" border="1"> | Sets size of border around an image |
<img src="/name" width="200" height ="200"> | Sets the height and width of an image |
<img src="/name" alt="alternative text"> | Displays alternative text when the mouse hovers over the image or when the image is not found |
<hr/> | Inserts a horizontal line |
<hr size="3"/> | Sets size (height) of line |
<hr width="80%"/> | Sets width of line, in percentage or absolute value |
<hr color="ff0000"/> | Sets the colour of the line |
Table Tags | |
Tag | Description |
<table></table> | Creates a table |
<tr></tr> | Creates a row in a table |
<td></td> | Creates a cell in a table |
<th></th> | Creates a table header (a cell with bold, centered text) |
<table width="50"> | Sets the width of the table |
<table border="1"> | Sets the width of the border around the table cells |
<table cellspacing="1"> | Sets the space between the table cells |
<table cellpadding="1"> | Sets the space between a cell border and its contents |
<tr align="left"> | Sets the alignment for cell(s) (can also be "center" or "right") |
<tr valign="top"> | Sets the vertical alignment for cell(s) (can also be "middle" or "bottom") |
<td colspan="2"> | Sets the number of columns a cell should span |
<td rowspan="4"> | Sets the number of rows a cell should span |
INPUT MASK CHARACTER SHEET
CHARACTER | DESCRIPTION |
0 | Digit (0 to 9, entry required, plus [+] and minus [–] signs not allowed) |
9 | Digit or space (entry not required, plus [+] and minus [–] signs not allowed) |
# | Digit or space (entry not required; spaces are displayed as blanks while in Edit mode, but blanks are removed when data is saved; plus [+] and minus [–] signs allowed) |
L | Letter (A to Z, entry required) |
? | Letter (A to Z, entry optional) |
A | Letter or digit (entry required) |
a | Letter or digit (entry optional) |
& | Any character or a space (entry required) |
C | Any character or a space (entry optional) |
. , : ; - / | Decimal placeholder and thousand, date and time separators (The actual character used depends on the settings in the Regional Settings Properties dialog box in the Windows Control Panel.) |
< | Causes all characters to be converted to lower case |
> | Causes all characters to be converted to upper case to right. You can include the exclamation point anywhere in the input mask. |
! | Causes the input mask to display from right to left, rather than from left to right. Characters typed into the mask always fill it from left to right. You can include the exclamation point anywhere in the input mask. |
\ | Causes the character that follows to be displayed as the literal character (for example, \A is displayed as just A) |
COMPUTER APPLICATIONS TECHNOLOGY P1 – SEPTEMBER 2019
INFORMATION SHEET (to be completed by the candidate AFTER the 3-hour session)
SCHOOL: .........................................................................................................................
NAME: ............................................................................................................................
WORK STATION NUMBER: ............................................................................................
SUITE USED | Microsoft Office 2010 | Microsoft Office 2013 | Microsoft Office 2016 | Office 365 |
WEB BROWSER USED (QUESTION 6) | Mozilla Firefox | Google Chrome | Internet Explorer | Other (Specify) |
FOLDER NAME: .........................................................................................................................
Tick if saved and/or attempted.
Question | File name | Saved (√) | Attempted (√) | Maximum | Maximum | Marker | HOD | Cluster | EM |
1 | 1_1Land Pollution | 29 | |||||||
2 | 2_2LandPollution Brochure | 23 | |||||||
3 | 3_LandSheet | 57 | |||||||
4 | 4_LandPollution | 41 | |||||||
5 | 5_MyWebsite | 20 | |||||||
6 | 6Letter.docx | 10 | |||||||
TOTAL: | 180 | ||||||||
Comment (for marker use only)
BBR or BSR - Economics Grade 12 Study Guides and Notes
BBR or BSR?
BBR: Bank Buying Rate
BSR: Bank Selling Rate
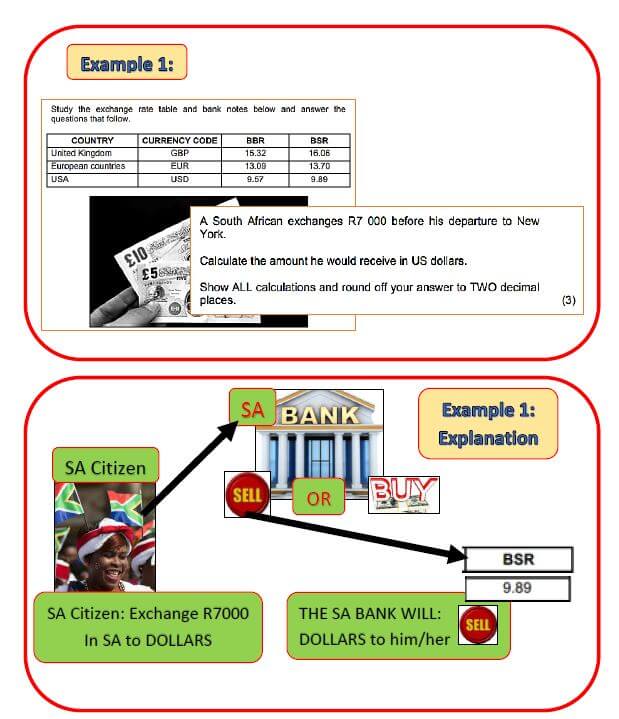
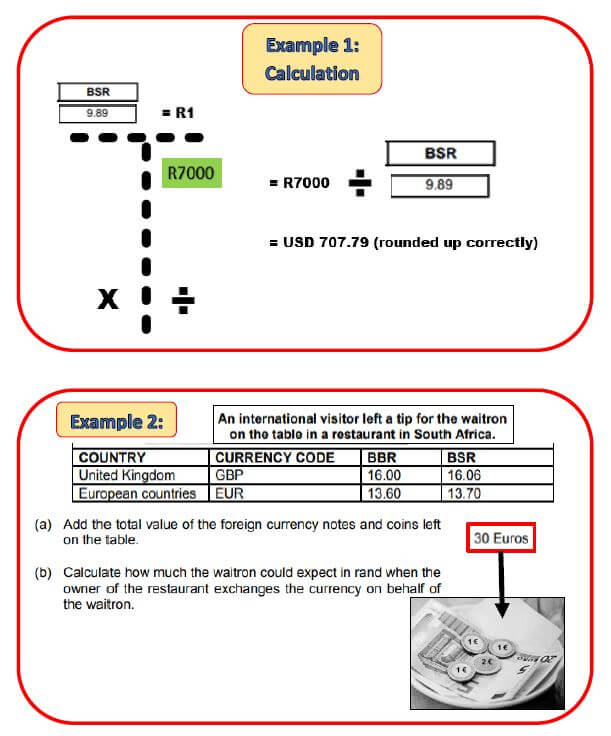
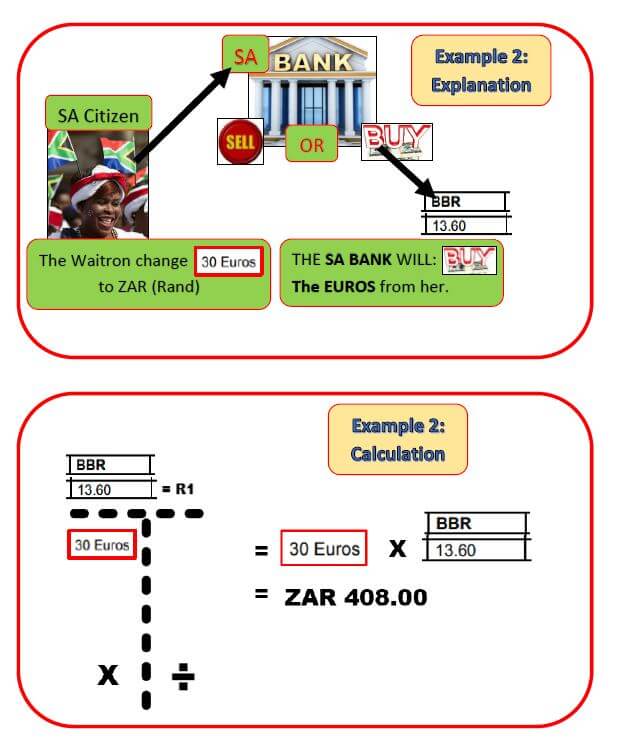
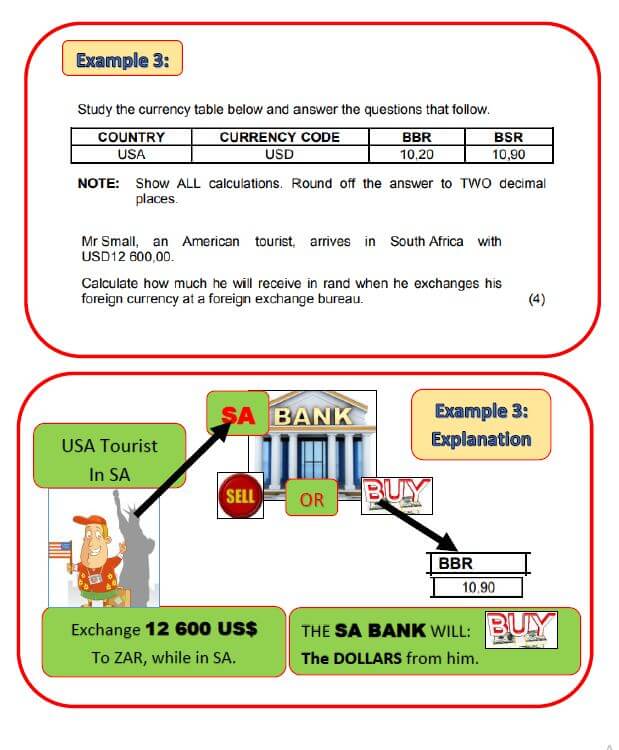
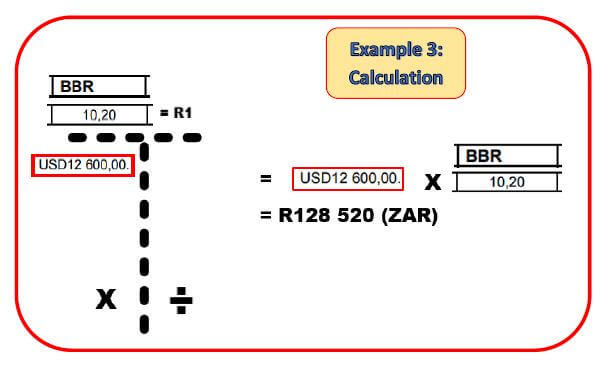
ACTIVITY 1:
Study the picture and the exchange rate table below and answer the questions that follow
| GRATUITIES (TIPPING) An international visitor left a tip for the waitron on the table in a restaurant in South Africa  | |||
| COUNTRY | CURRENCY CODE | BBR | BSR |
| United Kingdom | GBP | 16.00 | 16.06 |
| European countries | EUR | 13,60 | 13.70 |
3.1.1 Identify the currency that was left on the table for the waitron (1)
3.1.2
- Add the total value of the foreign currency notes and coins loft on the table. (1)
- Calculate how much the waitron could expect in rand when the owner of the restaurant exchanges the currency on behalf of the waitron.(3)
3.2 A British tourist left 27 British pounds on the table for the waitron.
3.2.1 Calculate the amount the waitran received in rand. Show ALL calculations and round off your answer to TWO decimal places. (3)
3.2.2
- Compare the two scenarias above in terms of the value of the tips the waitron has received.(2)
- Explain how the gratuities (tips) received by the waitron can add to the multiplier effect in the nearby community. (2) [12]
QUESTION 3
MEMO
3.1
3.1.1 Euro
- EUR
- £
3.1.2
- 30 Euros
- 30 (V) (13.604) = ZAR 408.00
3.2
3.2.1 27 (x) (16.00) = ZAR 432.00
3.2.2
- He received more value in rand from the British tourist than the FX European tourist.
- The amount he received in tips in euro was more than the amount in tips he received in British pounds.
- The gratuities received by the waitron set the multiplier effect in motion and gives the waitron more spending power in the local community, benefitting many business and households
Note: Accept examples related to the application of the multiplier effect
ACTIVITY 2:
Study the information and the forex table below and answer the questions that follow.
| A South African university choir has been invited to perform at an international music festival held in London (UK). The members of the choir each received R610,00 spending money. | |||
| EXCHANGE RATES | |||
| COUNTRY | CURRENCY CODE | BBR | BSR |
| United Kingdom | GBP | 16,09 | 17,18 |
| United States of America | USD | 14.31 | 14.45 |
3.1 Calculate the amount in pounds that each student received when they exchanged R610,00 at the foreign exchange bureau at the OR Tambo International Airport.
NOTE: Round off your answer to TWO decimal places.
Show ALL the steps of your calculation.
3.2 When they returned to South Africa, one of the choir members exchanged £26,35 at a foreign exchange bureau at the OR Tambo International Airport
Calculate the amount in rand he received
NOTE: Round off your answer to TWO decimal places.
Show ALL steps of your calculation.
3.3 List SIX factors that may have an impact on exchange rate fluctuations in South Africa
MEMO
3.1
R610 (+) 17,18V = £›35,51
- £35,51
3.2 GBP26,35 (x) 16,09V = R 423,97
- R423,97
3.3
- Political unrest/ instability
- Natural disasters drought/water crisis
- Negative Credit Ratings/ junk status
- Corruption in government
- Discovery of new/large amounts of mineral resources
- Lack of investor confidence
- Hosting of successful global events
- Impact of major currencies (positive and negative)
- Interest rates
- Acts of terrorism
- Reshuffling of cabinet ministers
- Economic recession
- High crime rates
- Positive / negative image of the country in media reporting
ACTIVITY 3:
Study the information and the forex table below and answer the questions that follow
| Mrs Biggs, who lives in South Africa, went on a trip to the USA. Her son added R600,00 to her spending money, which she exchanged for USD at OR Tambo International Airport before she left South Africa When Mrs Biggs returned to South Africa she had US$219,99 left of all her spending money |
| RANDIUS DOLLAR EXCHANGE RATE TABLE | |||
| COUNTRY | CURRENCY CODE | BBR | BSR |
| USA | USD | 13.25 | 13.57 |
3.1.1
- Calculate the amount in USD that Mrs Biggs received when she exchanged the R600,00.
NOTE: Round off your answer to TWO decimal places
Show ALL the steps of your calculation - Calculate the amount in rand Mrs Biggs received when she exchanged the US$219.99 in South Africa.
NOTE: Round off your answer to TWO decimal places.
Show ALL the steps of your calculation
Refer to the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
MAJOR CURRENCIES TAKE A FALL Europe, including the United Kingdom, has had a decline in the value of their currencies. Some economists have blamed it on Brexit* while others have blamed it on the influx of refugees into Europe. The drop in the value of the najor currencies can impact negatively and positively on South Africans travelling to these countries. |
3.2.1 Name the TWO foreign currencies referred to in the extract above. (2)
3.2.2 Discuss, in a paragraph, THREE ways in which a drop in the exchange rate of the currencies mentioned in QUESTION 3.2.1 will have a positive impact on South Africans visiting Europe. (6) [16]
MEMO
3.1.1
- R600,00 (+) 13,577 = USD44,22
OR
USD44,22- $44,22
Note: Do not penalise candidates if the currency code/symbol is omitted, as it is given in the question.
- $44,22
- USD219,99 (V) 13,257 = ZAR2 914,87
OR
ZAR2 914,87- R2 914,87
Note: Do not penalise candidates if the currency code/symbol is omitted, as it is given in the question
- R2 914,87
3.2.1 Euro 1€
British / Pound
- Great British Pound
- Pound Sterling
Note: Do not accept "Pound".
3.2.2 The South Africans will receive more value for money.
It will give the South Africans greater buying/spending power.
They can afford to stay longer/repeat visits at the destination and visit more attractions/activities.
- Europe can become a value for money destination.
ACTIVITY 4:
Study the cartoon below and answer the questions that follow
3.1.1 Explain what the artist is addressing with regard to the value of the rand in the cartoon above. (2)
3.1.2 Discuss ONE way in which the value of the land has benefitted the American tourist during her visit to South Africa (2)
Study the currency rate table below and answer the questions that follow.
| COUNTRY | CURRENCY CODE | BBR | BSR |
| United States of America | USD | 15.90 | 16.50 |
| Great Britain | GBP | 23.57 | 23.95 |
3.2.1 A British tourist has 2 800,00 GBP and would like to change the GBP to ZAR for a holiday in South Africa. On arrival at OR Tambo International Airport the tourist visits the foreign exchange bureau to exchange the currency.
Calculate how much the tourist will receive in rands. (4)
3.2.2 Pume, a South African, is attending a conference in the United States of America. Her company has given her R15 500,00 for any extra expenses. She goes to a foreign exchange bureau to load this money onto a preloaded foreign currency debit card
Calculate how much she will receive in US dollars on the preloaded card. (4) [12]
MEMO
3.1.1 The sudden decline in the value of the rand
- The drop in the value of the rand.
- The decline in the value of the rand resulted in a decline in the economy of South Africa.
- It advantages inbound international tourists.
3.1.2 The American tourist will receive more rands for his dollars.
- The tourist will have more spending power
- It will be a better value for money destination for the tourist.
3.2.1
- GBP2 800 x 23.577 (BBR)
= ZAR/R65 996,00 (currency must be indicated)
3.2.2
- ZAR15 500 + 16.50 (BSR)
= USD 939, 397 (rounded off correctly)
ACTIVITY 5:
Read the information below and answer the questions that follow.
A South African visited the United Kingdom in 2015 and in 2016. He bought fish and chips from the menu below on both trips.
Compare the value of the rand on both trips in the table below.
| 2015 | 2016 |
| £1 = R22,55 | £1 = R24,69 |
3.1.1 Calculate the cost of the fish and chips in ZAR:
NOTE: Show ALL calculations. Round off the answer to TWO decimal places.
- in 2015 (2)
- in 2016 (2)
3.1.2 State the year in which the tourist received the best value for his rand. (2)
Study the currency table below and answer the questions that follow.
| COUNTRY | CURRENCY CODE | BBR | BSR |
| USA | USD | 10,20 | 10,90 |
NOTE: Show ALL calculations. Round off the answer to TWO decimal places.
3.2.1 Mr Small an American tourist, arrives in South Africa with USD12 600,00. Calculate how much he will receive in rand when he exchanges his foreign currency at a foreign exchange bureau.
3.2.2 Mr Small would like to exchange his remaining rands before he leaves South Africa. He goes to a foreign exchange bureau to exchange R2 750 for US dollar. Calculate the amount that he will receive in US dollar.
MEMO
3.1.1
- 2015: £6,50 (x) 22,55 = R (ZAR) 146,58 (2)
OR
R (ZAR) 146,58
NOTE: Do not penalise candidates if the currency code is omitted because the code appears in the question - 2016. £6,50 (X) 24.69 = R (ZAR) 160,49 (2)
OR
R (ZAR) 160.49
NOTE: Do not penalise candidates if the currency code is omitted because the code appears in the question.
3.1.2 2015 (2)
3.2.1 USD12 600 (X) 10,207 =R (ZAR) 128 52V
OR
R (ZAR) 128 520
NOTE: Do not penalise candidates if the currency code is omitted because the code appears in the question
3.2.2 R2 750 (+) 10,907 = USD (US$) 252,2977
OR
USD (US$) 252,297
NOTE: Do not penalise candidates if the currency code is omitted because the code appears in the question
ACTIVITY 6:
Study the exchange rate table below and answer the questions that follow.
| COUNTRY | CURRENCY CODE | BBR | BSR |
| United Kingdom | GBP | 15.66 | 16.39 |
3.3.1 A Bloodhound team member has £1 300,00. Calculate the amount in rands that he will get for his £1 300,00 (4)
3.3.2 A British tourist pays R550,00 for a Bloodhound T-shirt. Calculate the amount in pounds the tourist will pay for the Bloodhound T-shirt. (4)
3.3.3 Discuss the buying power of the British team in South Africa, taking into account the exchange rate. (4)
MEMO
3.3.1
- £1 300,00 x 15,66 = R20 358,00
OR
R20 358,00
3.3.2
- R550,00 ÷ 16,39 = £33,567
OR
£33,56
3.3.3 The British tourists will get more value for their money.
The Pound is strong in comparison to the rand.
- More spending/buying power.
ACTIVITY 7:
Study the table below and answer the questions that follow.
Round off your answer to TWO decimal places.
| COUNTRY | CURRENCY CODE | BBR | BSR |
| United Kingdom | GBP | 15.66 | 16.39 |
| Peru | PEN - Peruvian nuevo sol | 3.90 | 3.55 |
| TOURS ON OFFER: | |
| LED TOUR | Peru: 7 nights from £1 560 p.p. |
3.1 Calculate the amount in rand that a South African will pay for ONE person for the above tour.(3)
3.2 A South African tourist has R250,00 in cash to pay for a handbag. Calculate the amount of PEN the tourist will pay for the handbag. (3)
3.3 Explain the difference between the buying power of a South African tourist in Peru and his/her buying power in the United Kingdom. (4) [10]
MEMO
3.1 (Using the BBR)
- £1560 (X) 15,66 = R24 429,60
OR - R24 429,604
Note: No marks are awarded if the wrong currency code or symbol was used.
Award the mark if no currency code or symbol was used.
ALTERNATIVE ANSWER
(Using the BSR)
- £1560 (X) 16,39 = R25 568,40
OR
R25 568,407
Note: No marks are awarded if the wrong currency code or symbol was used.
Award the mark if no currency code or symbol was used.
3.2
- R250 (÷) 3,55 = PEN70,42
OR - PEN70,42 V
Note: No marks are awarded if the wrong currency code or syrnbol was used.
Award the mark if no currency code or symbol was used.
3.2 ALTERNATIVE ANSWER
- R250 (÷) 3,90 = PEN64,10
OR - PEN64,10
Note: No marks are awarded if the wrong currency code or symbol was used.
Award the mark if no currency code or symbol was used.
3.3 The PEN is not as strong in value when compared to the strong GBP. A South African tourist will get more value for his money in Peru and therefore have more to spend in Peru when compared to the UK and therefore have less buying power in the UK.
- The South African will get more PEN than GBP for his/her rand; therefore he/she will be able to spend more in Peru.
- It is cheaper to visit Peru which is a better value-for-money destination.
ACTIVITY 8:
3.1 Study the exchange rate table and bank notes below and answer the questions that follow.
| COUNTRY | CURRENCY CODE | BBR | BSR |
| United Kngdom | GBP | 15.32 | 16.06 |
| European countries | EUR | 13.09 | 13.70 |
| USA | USD | 9.57 | 9.89 |

3.1.1 Name the currency represented on the two bank notes in the photograph above. (2)
3.1.2 A South African returns from the country where the currency mentioned in QUESTION 3.1.1 is used. Add the value of the two bank notes together and then calculate the rand value when the South African exchanges his unused foreign currency at the bank. Show ALL calculations and round off your answer to TWO decimal places. (3)
3.1.3 A South African exchanges R7 000 before his departure to New York. Calculate the amount he would receive in US dollars. Show ALL calculations and round off your answer to TWO decimal places. (3)
3.2 Study the South African rand to US dollar exchange rate graph below and answer the questions that follow.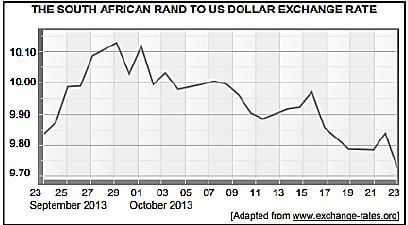
3.2.1 State the value of the South African rand in relation to the US dollar on 8 October 2013 (2)
3.2.2 The line graph shows daily changes in the rate of exchange Give the term used for these changes in the exchange rate. (2)
3.2.3 Determine the date and the value of the exchange rate when:
- The rand was at its weakest (2)
- The rand was at its strongest (2)
3.2.4 Explain TWO ways in which the travel plans and budget of an Inbound international tourist who visits South Africa will be affected by a weakening rand. (4) [20]
MEMO
3.1
3.1.1 British Pounds
- Pound Sterling .
- GBP
- 15 Founds .
- 15 GBP
3.1.2 GBP 15 X 15.32 (BBR) =ZAR 229.807 (two decimal places to indicate cents)
3.1.3 ZAR 7 000 = 9.89 (BSR) =USD 707.79(rounded up correctly)
3.2
3.2.1 R10
3.2.2 fuctuation
3.2.3
- 29 September
- 1 October
More than 10.10
(Any rate between 10.10 and 10.15, including the first and last values in this range is acceptable) - 23 October
less than 9.75
(Any rate between 9.70 and 9.75, including the first and last values in this range is acceptable)
- 1 October
3.2.4 Tourists might extend their length of stay ✓
Tourists can retain their original budget and have more money at their disposal.
- Tourists will be able to reduce their original budget making their trip less expensive.
- Tourists will use this opportunity to purchase more foreign currency needed for the intended joumey.