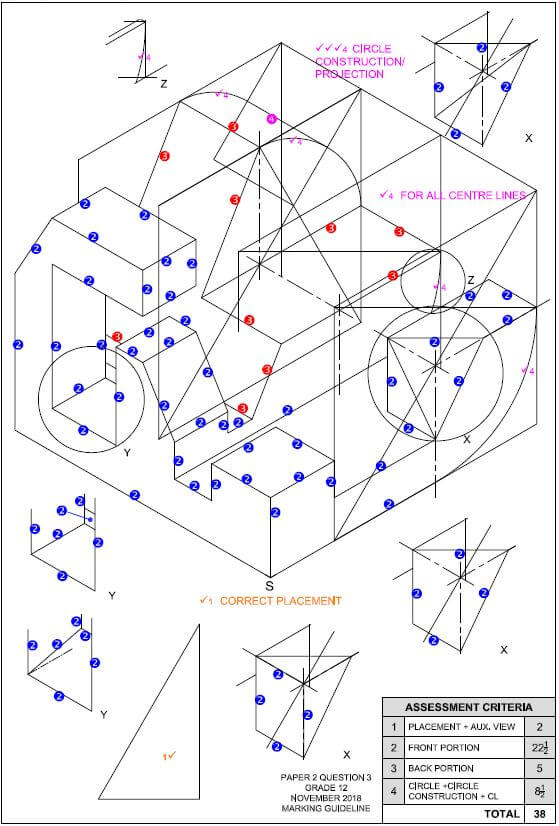
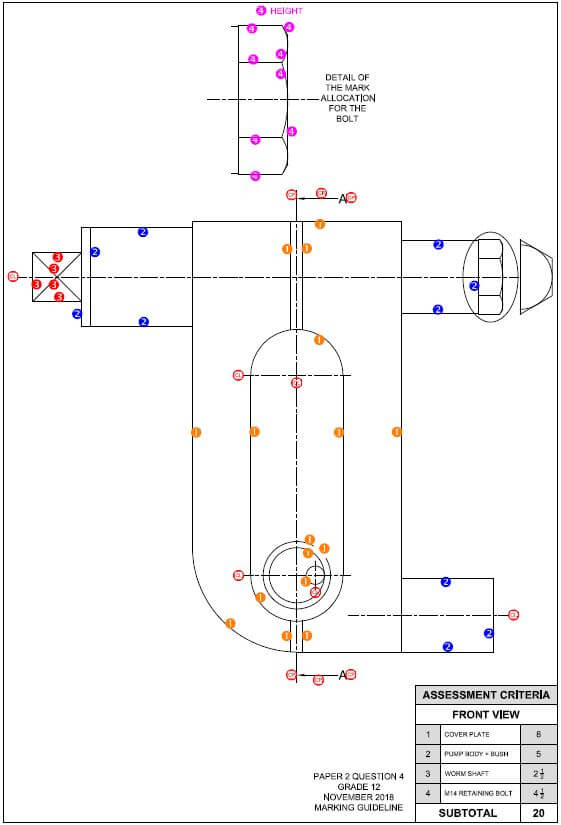
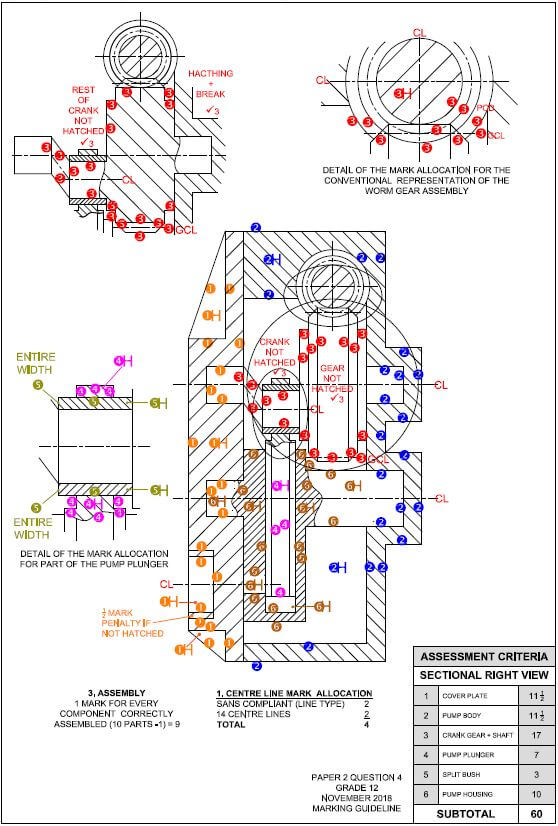
Adele
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY: WOODWORKING GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY: WOODWORKING
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2018
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: OHSA, MATERIALS, TOOLS, EQUIPMENT AND JOINING (GENERIC)
1.1
1.1.1 F ✔ (1)
1.1.2 A ✔ (1)
1.1.3 G ✔ (1)
1.1.4 E ✔ (1)
1.1.5 B ✔ (1)
1.2
- Do not throw any tools or materials from a scaffold. ✔
- Never jump on to and off a scaffold. ✔
- Never overload a scaffold.
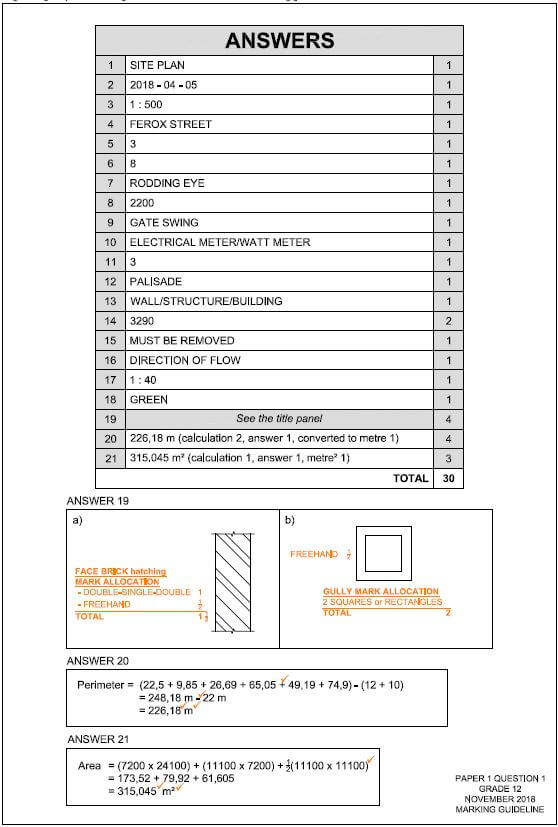
- Remove or cover sharp edges or corners.
- Always attach free-standing scaffoldings to a building.
- Use a ladder to get on and off a scaffold.
- Keep free of waste or any other obstruction.
- Never jump on a scaffold while working on it.
- Responsible/qualified person must ensure that scaffolding is safe, rigid, stable and firm or has no defects.
- Scaffold must be supplied with guard rails/toe boards.
- Scaffolds must be levelled on uneven ground.
- Do not work on a scaffold in bad weather.
- Wear a safety harness when working on scaffolding.
- Do not throw tools on/off a scaffold.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
1.3
- It prevents workers from falling off the scaffold. ✔
- It is used as a handrail. ✔
- It is used to strap on safety harnesses.
- To protect the worker working on the scaffold.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
1.4
- The primary purpose of painting is to protect metals, wood and other material against corrosion and decay. ✔
- Provides a decorative/aesthetic appearance/finishing. ✔
- Protects surfaces from moisture penetration.
- Protects surfaces from rust/uv rays.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
1.5 The curing of concrete:
- Increases the strength of concrete. ✔
- Decreases the permeability of hardened concrete.
- Improves durability of concrete by reducing cracks.
- Makes concrete more watertight.
- Minimises shrinkage cracks in concrete.
- Provides volume stability.
- Cured concrete can carry more weight without breaking/crumbling than uncured concrete.
- Prevents rapid drying of concrete.
- Curing ensures that the hydration process continues.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
1.6
1.6.1 Multi detector ✔ (1)
1.6.2 Tool A is used:
- to detect materials found in/behind walls, ceilings and underneath floors, including ferrous and non-ferrous metals, electrical wiring, wood and metal studs. ✔
- to locate steel bars and copper pipes. ✔
- in carpentry, plumbing, and construction.
- to measure the distance to/from covered objects.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
1.6.3 The batteries must be removed from the tool:
- to prevent the battery from running flat/battery can die. ✔
- to prevent acid leaks from batteries damaging the tool.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
1.7
1.7.1
A – Bolt and nut/Bolt ✔
B – Rawl bolt ✔ (2)
1.7.2 Bolt and nut
- Bolts and nuts are used to secure pipe supports to metal parts. ✔
- To join components together.
Rawl bolt
- A Rawl bolt is used to fix a truss hanger to a wall. ✔
- To fix brackets/structures/panels to a wall/concrete.
- For construction, renovation and industrial work
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2) [20]
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS AS METHOD OF COMMUNICATION (GENERIC)
ANSWER SHEET 2
NO. | QUESTIONS | ANSWERS | MARKS |
1 | Identify FIGURE A. | South Elevation/Elevation ✔ | 1 |
2 | Identify FIGURE B. | Ground floor plan/Floorplan ✔ | 1 |
3 | Identify number 4. | First floor level/Second floor level/Suspended floor/Floor level/ Dash line/ FFL/Expansion joint ✔ | 1 |
4 | Identify number 5. | Window Sill ✔ | 1 |
5 | Identify number 9. | Hand wash basin/Wash basin/Washing basin/HWB/Basin ✔ | 1 |
6 | Identify number 10. | Water closet/WC/Toilet pan ✔ | 1 |
7 | Identify number 11. | Bath/B ✔ | 1 |
8 | On what date was the plan printed? | 2018/10/02 ✔ | 1 |
9 | Who drew the building plan? | JP Maloi ✔ | 1 |
10 | Name the feature in the column for the notes in FIGURE 2 that must be installed in front of the sliding door. | Ramp ✔ | 1 |
11 | Name the feature in the column for the notes in FIGURE 2 that must give access to the first floor. | Staircase/Stairs/Stairway✔ | 1 |
12 | Identify the type of roof that is used for the building in FIGURE A. | Gable roof ✔ | 1 |
13 | Explain the purpose of number 1. | To cover the opening/close the gap between the two slopes of the roof. ✔ | 1 |
14 | Explain the purpose of number 2. |
| 1 |
15 | Explain the abbreviation FFL at number 6. | Finished floor level ✔ | 1 |
16 | Explain the purpose of number 7. | To channel the water from the gutter to the ground. ✔ | 1 |
17 | Explain the meaning of the arrow on the feature that must be installed in front of the sliding door. | It indicates the direction of the slope of the ramp/it indicates the slope. ✔ | 1 |
18 | Explain what is meant by 1:10 indicated on the symbol in the notes. | It indicates the slope or the gradient of the ramp/for every 10 metres horizontally rises 1 metre vertically.✔ | 1 |
19 | Which room will feature 15 serve? | The bathroom. ✔ | 1 |
20 | Explain the short dash lines on the windows. |
| 1 |
21 | Deduce the height of window 2 from the window schedule. | 1,2 m or 1 200 mm ✔(Ignore units) | 1 |
22 | Deduce the width of window 3 from the window schedule. | 2 m or 2 000 mm ✔(Ignore units) | 1 |
23 | On what elevation of the building is the bathroom window situated? | Western elevation/Western side ✔ | 1 |
24 | Differentiate between component number 3 and component number 8. | 3 – window/window frame/reveal frame stile/casement stile ✔ | 2 |
25 | Differentiate between the light in the lounge and the light in the bathroom. | The light in the lounge is a fluorescent light/1 x 40W-/2x40- /3x40 fluorescent light ✔ and the light in the bathroom is a normal ceiling light ✔ | 2 |
26 | Recommend a suitable floor covering for the bathroom. | Tile/ Vinyl flooring(Novilon)/ Coloured screed/Polished or stained concrete flooring/Water proof laminated floor/carpet. ✔ | 1 |
27 | Recommend an appropriate scale to which FIGURE A should be drawn, according to SANS. | 1:50/100/200 ✔ | 1 |
28 | Recommend an alternative sanitary fitment to replace number 11 that will serve a similar purpose. | Shower ✔ | 1 |
29 | Calculate the internal area of the office in m² Show ALL calculations. | 4 m ✔ x 3 m ✔ = 12 m² ✔ OR 12 | 3 |
30 | Calculate the perimeter of the building. Show ALL calculations. | Positive marking | 7 |
TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 3: CASEMENTS, CUPBOARDS, WALL-PANELLING AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
3.1
3.1.1 Tongue and groove boards ✔ (1)
3.1.2 520 mm - 570 mm ✔ (1)
3.1.3 Cornice ✔ (1)
3.1.4 Drip groove ✔ (1)
3.1.5 Fanlight ✔ (1)
3.2
3.2.1
- A – Wood/Timber ✔ (1)
- B – Glass/Perspex ✔ (1)
3.2.2 This part is holding the glass/pane in its place. ✔ (1)
3.3
3.3.1
- A Storage space/top unit ✔
- B Hanging space ✔
- C Shelves/storage space/shelf ✔
- D Drawers ✔ (4)
3.3.2 Melamine:
- is waterproof. ✔
- is easier to clean.
- is more durable.
- enhance inside appearance.
- has a smooth finish.
OR
Chipboard:
- Is not water proof
- Is not easy to clean
- Is less durable
- Does not enhance the inner appearance
- Is not as smooth (1)
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE
3.3.3
- E – Front rail/Top rail ✔
- F – Oval hanging rail/Hanging rail/Pipe rail ✔
- G – Side ✔
- H – Kick plate/base/Bottom rail/Plinth ✔ (4)
3.4
3.4.1
- A – Cornice ✔
- B – Horizontal rough grounds ✔ (3)
- C – Quarter round/Quadrant ✔
3.4.2
- To enhance appearance. ✔
- To give an aesthetic appearance. ✔
- There is no need to plaster the wall where panelling is to be done.
- It serves as insulation against sound and heat.
- For durability
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE(2)
3.5
A | B | C | D | ||
| 3.5.1 | Internal measurements of long walls: | ||||
= 9 000 – 2/220 = 8 560 mm ✔ | |||||
OR | |||||
= 9 000 - 440 = 8 560 mm | |||||
Length of wall plates needed: | (4) | ||||
| 3.5.2 | 2/✔ | 8,56 ✔ | 17,12 ✔ | 17,12 m wall plate needed | |
Number of purlins needed | |||||
Number of purlins = Length of rafter + 1 | |||||
= 3,6 ✔ + 1 OR 3 600 + 1 | |||||
= (4 + 1) ✔2 ✔OR (5x2) | |||||
= 10 purlins ✔ | (4) |
[30]
QUESTION 4: ROOFS, CEILINGS, TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT, AND MATERIALS (SPECIFIC)
4.1
4.1.1 C ✔ (1)
4.1.2 A ✔ (1)
4.1.3 D ✔ (1)
4.1.4 E ✔ (1)
4.1.5 F ✔ (1)
4.2
4.2.1
- A Hipped end ✔
- B Purlin ✔
- C Ridge/Ridge plate ✔
- D Valley rafter/Valley ✔
- E Overhang/Eaves overhang ✔
- F Gable end/Gable wall/Wall/Side of building ✔ (6)
4.2.2
- 76 mm x 50 mm ✔
- 76 mm x 76 mm
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
4.3
- It allows rain water to be directed into the gutter. ✔
- So that water does not damage the end of the rafters. (1)
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE
4.4
- A good roof covering must be able to resist weather conditions such as rain and wind/resistance against corrosion. ✔
- Should look durable and enhances the appearance of the building. ✔
- Should be fire resistant.
- Should provide insulation against heat and cold.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
4.5 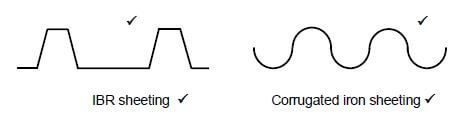 (4)
(4)
4.6
- The installation of steel roofing is faster. ✔
- The installation of steel roofing is more economical. ✔
- The installation of steel roofing is simpler.
- Steel roof covering is cheaper than tiles.
- Steel roof covering is environment friendly.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
4.7
- If roof underlay is not installed there will be more dust inside the roof space. ✔
- If roof underlay is not installed, the roof may not be fully waterproof. ✔
- The risk of wind lifting tiles becomes greater.
- Insulating would not be good.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
4.8
- A - Tie beam ✔
- B - Brandering ✔
- C - Trapdoor ✔
- D - Cover strip ✔ (4)
4.9.1
- A – Router ✔
- B – Combination belt and disc sander. ✔ (2)
4.9.2
- Store in a safe, dry place. ✔
- Store it in a wooden or plastic box away from moisture. ✔ (2)
4.9.3
- Maintain like all machinery – lubricate and adjust according to the manufacturer’s instructions. ✔
- Clean the belt/disc sander after use. ✔
- Repair or replace damaged electrical cords.
- Handle the sander so as not to damage or impair its accuracy.
- Use machinery only for the intended purpose.
- Do not force material onto the belt/disc of the sander.
- Avoid the use of worn out (clogged) belts and discs.
- ervice the machine regularly.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
4.9.4
- Table saw/Circular saw/Mitre saw ✔
- Band saw ✔
- Radial arm saw ✔
- Jigsaw
- Scroll saw
ANY THREE OF THE ABOVE (3)
4.10.1
- M – Mechanical grading ✔
- V – Visual grading ✔ (2)
4.10.2 6 - The number indicates the strength. ✔ (1)
4.10.3 The SABS symbol. ✔  (1)
(1)
[40]
QUESTION 5: CENTERING, FORMWORK, SHORING AND GRAPHICS AS MEANS OF COMMUNICATION (SPECIFIC)
5.1
- A - Concrete beam/Concrete ✔
- B - Brace/Strut ✔
- C - Prop/Adjustable prop ✔
- D - Sole plate ✔ (4)
5.2
- Block board ✔
- Laminated board ✔
- Shutter board ✔
- Plywood ✔
- Timber
- Hard board/Masonite
ANY FOUR OF THE ABOVE (4)
5.3
- Wedges are inserted under the bearers and props to support the formwork. ✔
- Wedges keep the different formwork components sturdy and fixed. ✔
- Wedges help with the lowering and raising of the formwork. ✔
- Wedges are used for the levelling of the formwork.
- Wedges ease the striking of formwork.
ANY THREE OF THE ABOVE (3)
5.4
- It supports more weight. ✔
- Support the weight of the fresh concrete.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
5.5
5.5.1
- A – Laggings ✔
- B – Ribs ✔
- C – Bearer ✔ (3)
5.5.2 Brick arches because they have a solid surface. ✔ (1)
5.5.3
- Openly spaced laggings/Open laggings/Open ✔
- Laggings are not close to each other. (1)
- There are spacing’s between the openings of the laggings.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE
5.6
5.6.1
- Dead shores are used to support structures. ✔
- Dead shores carry dead weight above the dead shores, e.g. walls, floors.
- Support existent walls if openings are made.
- Transfer the weight of the structure to firm ground during structural renovations.
- Support a wall if alterations are made.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
5.6.2
- Double flying shores provide temporary support to TWO parallel walls where one or two walls show signs of failure. ✔
- Double flying shores give temporary support to TWO parallel defective walls.
- Double flying shores can only be used with TWO parallel defective walls between 9 and 15 meters.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
5.7
5.7.1 The steel dog is used to secure the joint between prop and needle. ✔ (1)
5.7.2 Props are used to strengthen or brace the floors and ceiling. ✔ (1)
5.7.3
- Sole plates spread the weight transferred by the props over a wider area.✔
- Prevent vertical props/pipes from sinking into the ground.
- The soleplate create a level area where the props rest on. (1)
5.8 45° ✔ (1)
5.9  (7)
(7)
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Span | 1 | |
Wall plates | 2 | |
Rafters | 2 | |
Ridge beam | 1 | |
Slope of the roof 45° | 1 | |
TOTAL: | 7 |
[30]
QUESTION 6: SUSPENDED FLOORS, STAIRCASES, IRONMONGERY, DOORS AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
6.1
6.1.1 D ✔ (1)
6.1.2 C ✔ (1)
6.1.3 B ✔ (1)
6.1.4 A ✔ (1)
6.1.5 A ✔ (1)
6.2 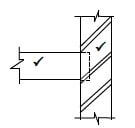
Joist built into wall
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Joist | 1 | |
Built into wall | 1 | |
TOTAL | 2 |
Joist secured to wall with truss/joist hanger (4)
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Joist | 1 | |
Truss/Joist hanger | 1 | |
TOTAL: | 2 |
6.3 Alternative drawing will also be acceptable 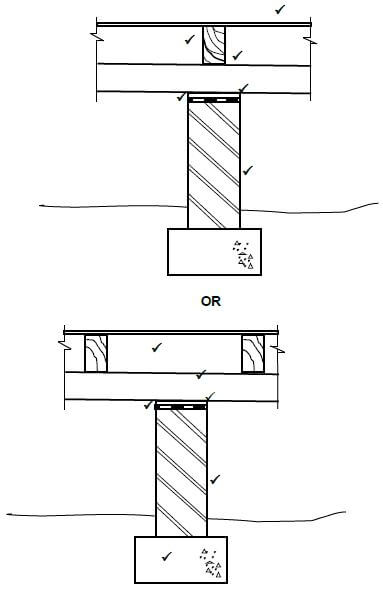 (6)
(6)
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
ONE one-brick pier | 1 | |
DPC/Proportion | 1 | |
Ant guard | 1 | |
Bearer | 1 | |
Joist | 1 | |
Floor boards | 1 | |
TOTAL | 6 |
6.4 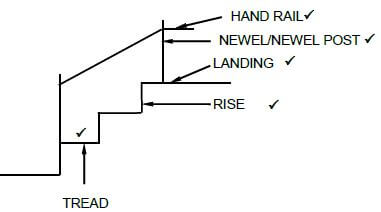 (5)
(5)
2 OR 3 DIMENSIONAL DRAWINGS WILL BE ACCEPTED
6.5
- Serves as a place of rest. ✔
- For safety in case of a falling accident.
- Facilitates a change in direction when moving up or down stairs.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
6.6
6.6.1 Door stile/Lock rail ✔ (1)
6.6.2 Frame stile/Door frame/Stile ✔ (1)
6.6.3 Frame stile/Door frame/Stile ✔ (1)
6.6.4 Door stile ✔ (1)
6.7
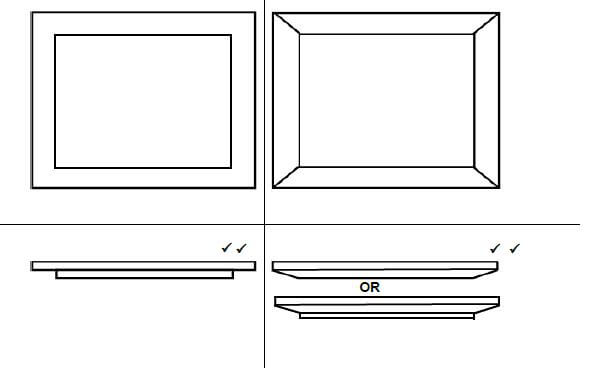 (4)
(4)
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Raised panel top view | 2 | |
Raised and fielded panel top view | 2 | |
TOTAL | 4 |
6.8 The opening allows shrinkage ✔ and expansion of the panel/wood. (1)
6.9
- A – Brace/Strut ✔
- B – Tongue and groove battens/V- Tongue and groove battens ✔
- C – Stile ✔ (3)
6.10
6.10.1 Hinge (Any hinge accepted) ✔ (1)
6.10.2 Clout nail/Chipboard screws/Drywall screw ✔ (1)
6.10.3 Nail/Skew nail/Perm fix nail ✔ (1)
6.10.4 Gang nail/Bolt and nut/Nails ✔ (1)
6.11
- Hinges ✔
- Casement fasteners ✔
- Casement stays
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2) [40]
TOTAL: 200
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY: WOODWORKING GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY: WOODWORKING
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2018
REQUIREMENTS:
- Drawing instruments
- A non-programmable calculator
- ANSWER BOOK
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Answer each question as a whole. Do NOT separate subsections of questions.
- Start the answer to EACH question on a NEW page.
- Do NOT write in the margins of the ANSWER BOOK.
- You may use sketches to illustrate your answers.
- Write ALL calculations and answers in the ANSWER BOOK or on the attached ANSWER SHEETS as required.
- Use the mark allocation as a guide to the length of your answers.
- Make drawings and sketches in pencil, fully dimensioned and neatly finished off with descriptive titles and notes to conform to the SANS/SABS Code of Practice for Building Drawings.
- For the purpose of this question paper, the size of a brick should be taken as 220 mm x 110 mm x 75 mm.
- Use your own discretion where dimensions and/or details have been omitted.
- Answer QUESTIONS 2, 3.5, 5.9, 6.3 and 6.7 on the attached ANSWER SHEETS using drawing instruments, where necessary.
- Write your CENTRE NUMBER and EXAMINATION NUMBER on every ANSWER SHEET and hand them in with your ANSWER BOOK, whether you have used them or not.
- Drawings in the question paper are NOT to scale due to electronic transfer.
- Google Images was used as the source of all photographs and pictures.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: OHSA, MATERIALS, TOOLS, EQUIPMENT AND JOINING (GENERIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
1.1 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–G) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.6 H.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.1.1 Sole plate |
(5 x 1) (5) |
1.2 Describe TWO safety precautions that must be adhered to when working on a scaffold. (2)
1.3 What is the purpose of the guard rail of a scaffold in terms of safety? (2)
1.4 Explain the purpose of painting. (2)
1.5 Describe ONE advantage of the curing process of concrete. (1)
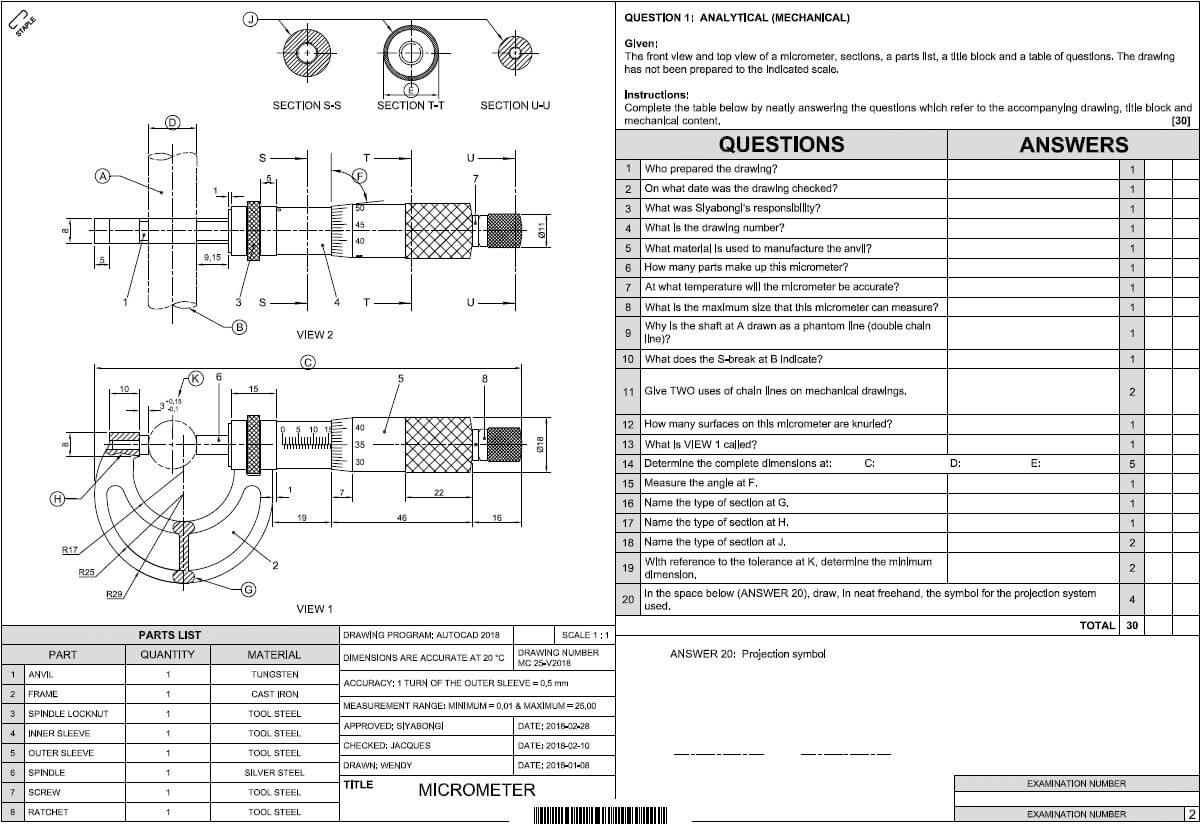
1.6 FIGURE 1.6 below shows a tool that is used in the building construction industry. 
FIGURE 1.6
1.6.1 Identify tool A. (1)
1.6.2 Explain TWO uses of tool A. (2)
1.6.3 Explain why the batteries should be removed from the tool if the tool is not going to be used for a long time. (1)
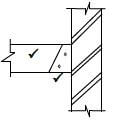
1.7 FIGURE 1.7 below shows joining fixtures that are used on building sites and in workshops. 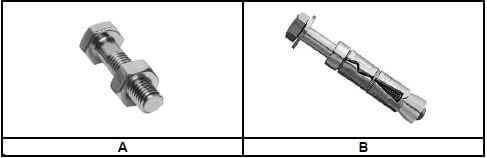
FIGURE 1.7
1.7.1 Identify fastener A and fastener B. (2)
1.7.2 Explain ONE use of fastener A and fastener B respectively. (2) [20]
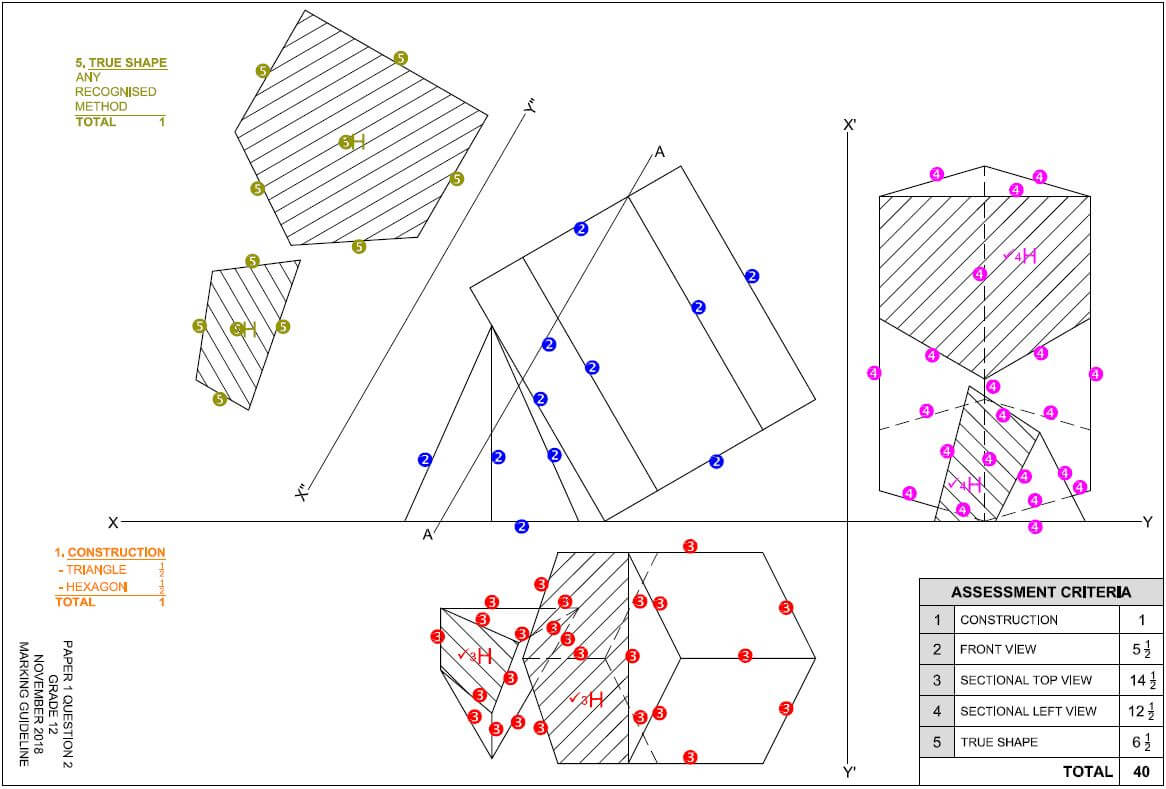
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS AS METHOD OF COMMUNICATION (GENERIC)
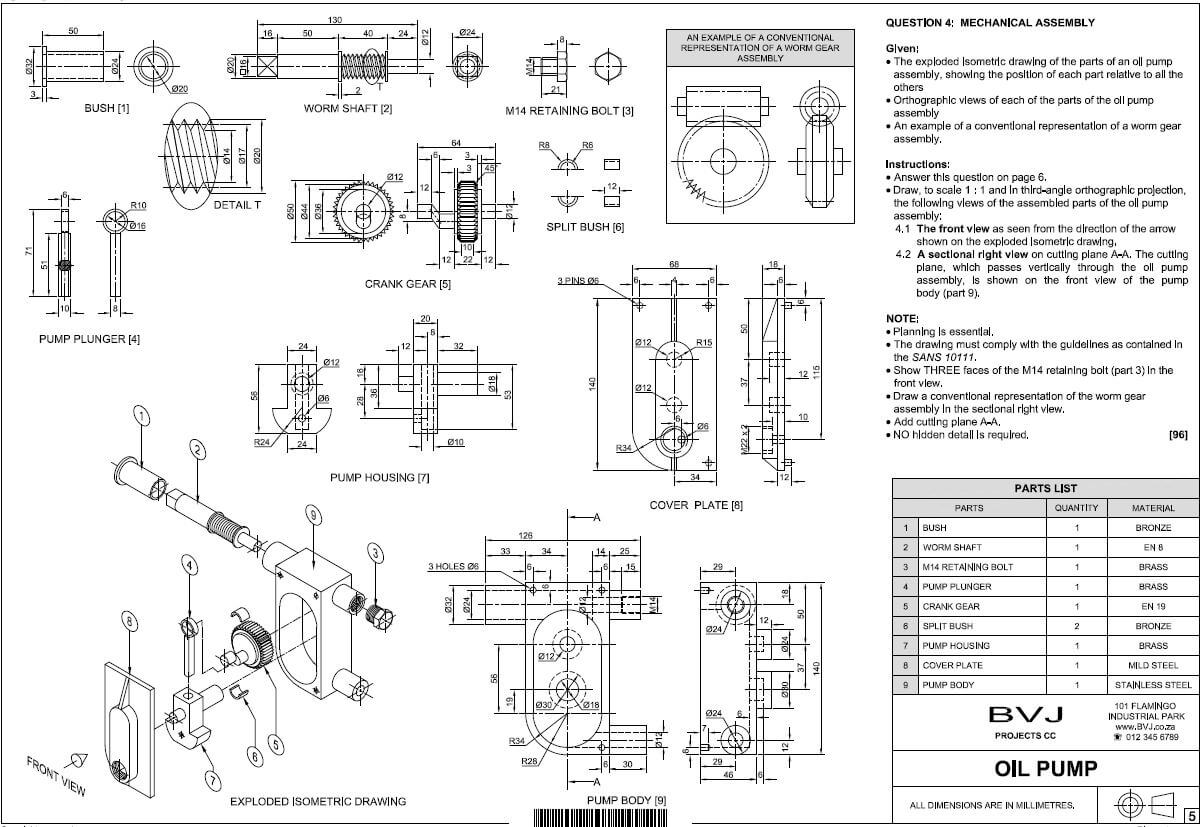
FIGURE 2 on the next page shows different drawings that appear on a building plan. Analyse the drawings and complete the table on ANSWER SHEET 2. 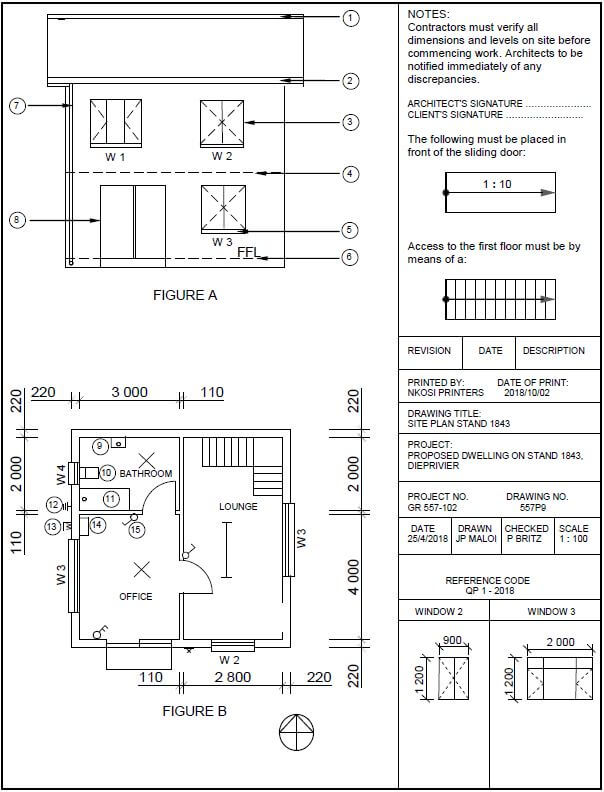
FIGURE 2 [40]
QUESTION 3: CASEMENTS, CUPBOARDS, WALL-PANELLING AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 Give ONE word/term for EACH of the following descriptions by choosing a word/term from the list below. Write only the word/term next to the question numbers (3.1.1 to 3.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 3.1.6 Casement.
| fanlight; 600 mm–650 mm; skirting; tongue and groove boards; frame head; 520 mm–570 mm; window; cornice; melamine boards; drip groove |
3.1.1 Boards that are usually made of knotty pine and fit easily into one another by means of a specific feature on each side of the board (1)
3.1.2 The recommended depth of free-standing cupboards (1)
3.1.3 To close the opening between the wall and the ceiling (1)
3.1.4 Prevent rainwater from being blown into the casement and penetrating the room (1)
3.1.5 The small window that is built above the opening of a door or window (1)
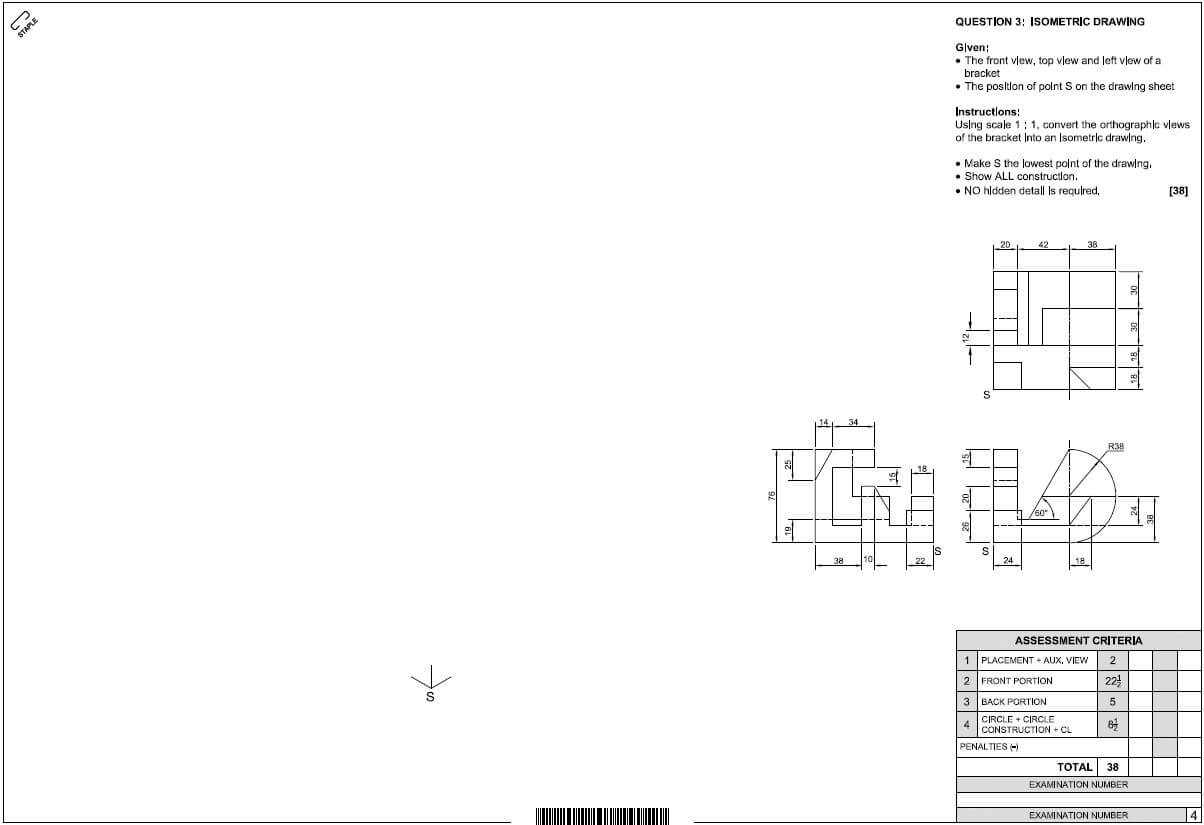
3.2 FIGURE 3.2 below shows an external elevation of a double casement with fanlights. Study the picture and answer the questions that follow. 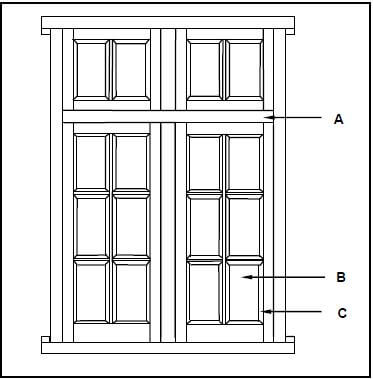
FIGURE 3.2
3.2.1 What type of material can be used for part A and part B respectively? (2)
3.2.2 Explain the purpose of C. (1)
3.3 FIGURE 3.3 below shows the inside of a built-in cupboard without doors. Study the drawing and answer the questions that follow. 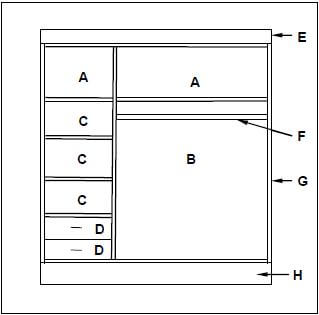
FIGURE 3.3
3.3.1 A well-designed cupboard should consist of four main parts/units. Name parts/units A to D in the drawing above. (4)
3.3.2 Justify the use of melamine rather than plain chipboard for the inside of a built-in cupboard. (1)
3.3.3 Identify parts E to H. (4)
3.4 FIGURE 3.4 below shows the sectional view of a tongue and groove wall panel from the floor to the ceiling, fastened to a 110 mm thick wall. Study the drawing and answer the questions that follow. 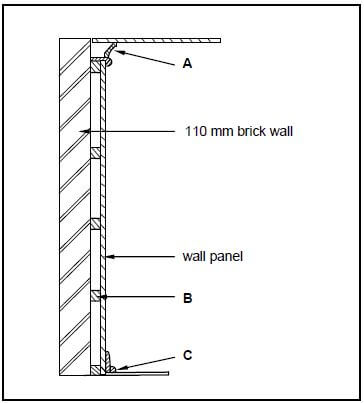
FIGURE 3.4
3.4.1 Identify parts A to C. (3)
3.4.2 Give TWO reasons for panelling a wall. (2)
3.5 FIGURE 3.5 below shows the floor plan of a building with a gable roof. The external measurements are 9 000 mm x 5 000 mm. 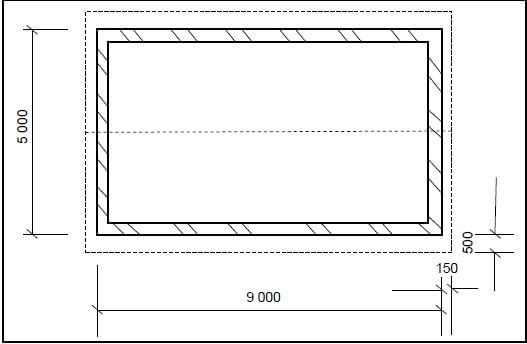
FIGURE 3.5
Use the following specifications:
- Walls are 220 mm thick
- Type of roof – South African (Howe) roof
- Centre-to-centre spacing between purlins = 900 mm
- True length of rafter (principal rafter) = 3 600 mm
Use ANSWER SHEET 3.5 and calculate the following:
3.5.1 Length of the wall plates (4)
3.5.2 Number of purlins needed (4) [30]
QUESTION 4: ROOFS, CEILINGS, TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT, AND MATERIALS (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–H) next to the question numbers (4.1.1 to 4.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 4.1.6 J.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
4.1.1 King post 4.1.2 Purlin 4.1.3 Eaves 4.1.4 Jig saw 4.1.5 Wax |
(5 x 1) (5) |
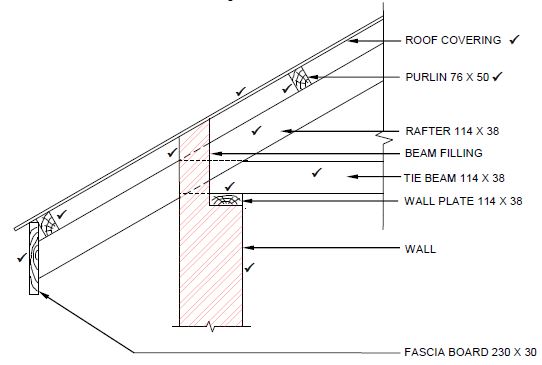
4.2 FIGURE 4.2 below shows a pictorial view of a roof with a hipped end and a gable end with a valley. The roof will be covered with corrugated iron sheeting. Study FIGURE 4.2 below and answer the questions that follow. 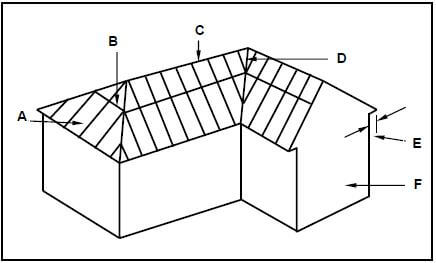
FIGURE 4.2
4.2.1 Identify members A to F. (6)
4.2.2 What are the breadth and thickness of part B in mm? (1)
4.3 Explain why the corrugated iron sheeting is protruding 50 mm over the end of the rafter. (1)
4.4 Explain TWO characteristics of a good roof covering. (2)
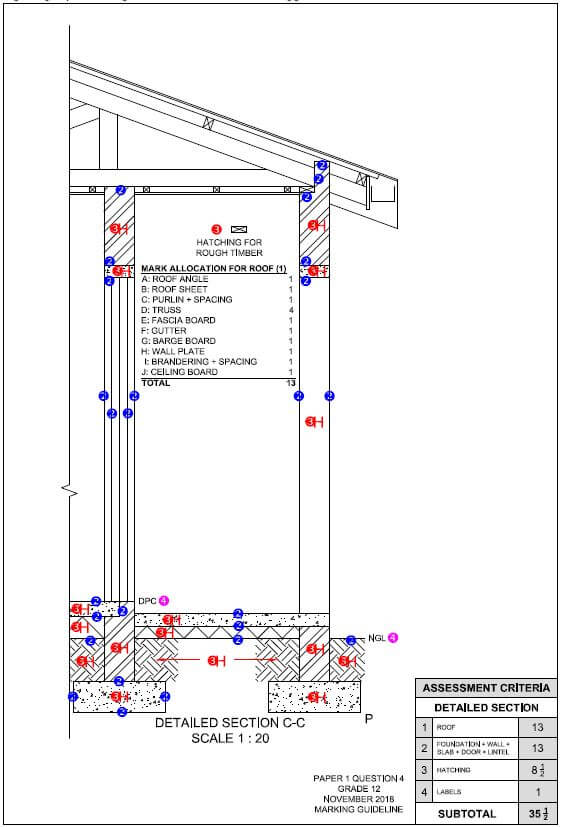
4.5 Differentiate between the profiles of IBR sheeting and corrugated iron sheeting by means of single-line sketches. Name EACH sketch. (4)
4.6 Describe TWO advantages a steel roof sheet. (2)
4.7 Explain the consequences if roof underlay is not installed under roof covering. (2)
4.8 FIGURE 4.8 below shows a sectional view of a conventional trap door. Study the sketch en give ONE word/term for each letter (A to D) by choosing a word/term from the list below. Write only the word/term next to the letter (A–D) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. E – Rafter.
| tie beam; rafter; strut; brandering; trap door; ceiling board; cover strip |
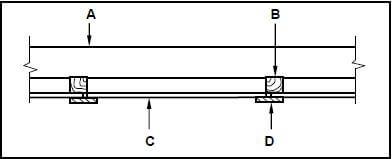
FIGURE 4.8 (4)
4.9 FIGURE 4.9 below shows two woodworking machines. Study the pictures and answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 4.9
4.9.1 Identify machines A and B. (2)
4.9.2 Recommend TWO ways of storing A after use. (2)
4.9.3 What aspects would you take into consideration when taking care of B? (2)
4.9.4 Name THREE types of woodworking machines that you can use to cut wood. (3)
4.10 FIGURE 4.10 below shows two graded wooden planks. 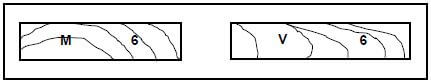
FIGURE 4.10
4.10.1 Explain the grading of each plank as indicated by the letters. (2)
4.10.2 Explain the number on each plank. (1)
4.10.3 Name the symbol that indicates that grading has been done, but which is missing on each plank. (1) [40]
QUESTION 5: CENTERING, FORMWORK, SHORING AND GRAPHICS AS MEANS OF COMMUNICATION (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
5.1 FIGURE 5.1 below shows a vertical sectional view through formwork for two concrete beams. Study FIGURE 5.1 and identify members A to D. Write only the answer next to the letter (A–D) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. E – Rib. 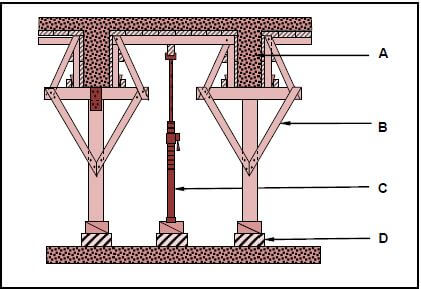
FIGURE 5.1 (4)
5.2 Recommend FOUR wooden board products that can be used as sides for formwork. (4)
5.3 Explain the purpose of folding wedges during the construction of formwork. (3)
5.4 Explain the reason why the bottom soffit board in the construction of formwork for a concrete beam is thicker than the sides of the formwork. (1)
5.5 FIGURE 5.5 below shows a pictorial view of closed laggings. Study the picture and answer the questions that follow. 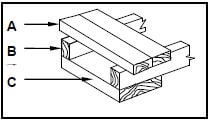
FIGURE 5.5
5.5.1 Identify parts A to C. (3)
5.5.2 Explain ONE use of A if it is used in a closed position, as shown in FIGURE 5.5. (1)
5.5.3 Name ONE other position in which A can be used in laggings. (1)
5.6 Explain ONE use of the following shores:
5.6.1 Dead shore (1)
5.6.2 Double-flying shore (1)
5.7 Describe the function of the following components of a dead shore:
5.7.1 Steel dog (1)
5.7.2 Prop/Strut (1)
5.7.3 Sole plate (1)
5.8 At what angle must the braces above and beneath the horizontal shores be placed on a double-flying shore? (1)
5.9 Use ANSWER SHEET 5.9 and draw a neat line diagram of a couple roof truss on top of the indicated walls. The slope of the roof truss is 45°.
Show the following on the drawing:
- The span by means of dimension lines
- Wall plates
- Rafters
- Ridge beam
- Slope of the roof (7) [30]
QUESTION 6: SUSPENDED FLOORS, STAIRCASES, IRONMONGERY, DOORS AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
6.1 Various options are given as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (6.1.1 to 6.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 6.1.6 C.
6.1.1 The spacing between the floor joists …
- will not affect the strength of the suspended floor.
- depends on the thickness of the joist.
- depends on the availability of timber planks.
- should be 400 mm to 600 mm from centre to centre. (1)
6.1.2 Suspended timber floors …
- can only be used on upper levels.
- can be placed directly on the floor.
- can be used on ground levels or upper levels.
- do not need any air bricks or vents underneath the floor. (1)
6.1.3 Floorboards should have a ...
- mortice and tenon joint along the edges.
- tongue along the one edge and a groove along the other edge.
- clearance of at least 50 mm from the plaster or the wall.
- width of at least 40 mm and not exceed 180 mm. (1)
6.1.4 A framed ledged and braced batten door …
- can be used for back doors (kitchen).
- has solid panels.
- has braces of 40 mm.
- can be made of board products. (1)
6.1.5 A three-panel door with raised and fielded panels …
- is ideal for the front entrance of a house.
- should not be less than 1 000 mm away from the wall.
- should have a total length of 1 800 mm.
- has no lock rail. (1)
6.2 At suspended floors of multistorey buildings there are two methods that are commonly used to fix the ends of the floor joist to the walls.
Differentiate between the TWO methods by means of neat freehand sketches. Write the name of the method below EACH drawing. (4)
6.3 FIGURE 6.3 on ANSWER SHEET 6.3 shows the foundation, NGL and the starting point of the wall of a brick pier. Use ANSWER SHEET 6.3 and draw a neat sketch, in good proportion, of a sectional view of a suspended timber floor that is supported by brick piers.
Show the following on your drawing:
- One-brick pier
- DPC
- Antguard
- Bearer
- Part of the floor joist on both sides of the brick pier
- Floor boards (6)
6.4 Draw a neat line diagram, in good proportion, of a staircase in your ANSWER BOOK.
Show the following on your drawing:
- Landing
- Rise
- Tread/Going
- Newel/Newel post
- Handrail (5)
6.5 Explain the purpose of the landing in a staircase. (2)
6.6 The lock is an important part of a door. On which part of a three-panel door or door frame will you mount the following parts of a lock?
6.6.1 Box lock/Casing (1)
6.6.2 Back plate/Striker plate (1)
6.6.3 Keeper (1)
6.6.4 Night lock (1)
6.7 Use ANSWER SHEET 6.7 and draw neat top views of a raised panel and a raised and fielded panel in the given spaces. (4)
6.8 Explain the purpose of opening A in FIGURE 6.8 below. 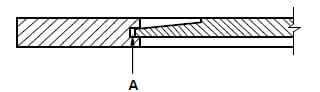
FIGURE 6.8 (1)
6.9 Study FIGURE 6.9 below which shows the inside bottom corner of a framed ledge and braced batten door. Identify members A to C. 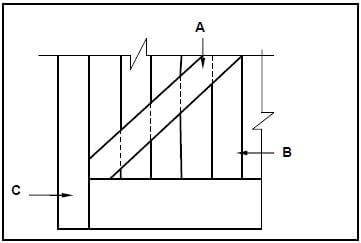
FIGURE 6.9 (3)
6.10 Use the descriptions below and explain the method of joining the components. Write only the answer next to the question number in your ANSWER BOOK.
6.10.1 Door to door frame (1)
6.10.2 Ceiling board to ceiling battens/brandering (1)
6.10.3 Brandering to tie beam (1)
6.10.4 Adjacent members of a roof truss (1)
6.11 State TWO methods that can be used to fix opening window frames to the jambs of casements. (2) [40]
TOTAL: 200
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 2
NO. | QUESTIONS | ANSWERS | MARKS |
1 | Identify FIGURE A. | 1 | |
2 | Identify FIGURE B. | 1 | |
3 | Identify number 4. | 1 | |
4 | Identify number 5. | 1 | |
5 | Identify number 9. | 1 | |
6 | Identify number 10. | 1 | |
7 | Identify number 11. | 1 | |
8 | On what date was the plan printed? | 1 | |
9 | Who drew the building plan? | 1 | |
10 | Name the feature in the column for the notes in FIGURE 2 that must be installed in front of the sliding door. | 1 | |
11 | Name the feature in the column for the notes in FIGURE 2 that must give access to the first floor. | 1 | |
12 | Identify the type of roof that is used for the building in FIGURE A. | 1 | |
13 | Explain the purpose of number 1. | 1 | |
14 | Explain the purpose of number 2. | 1 |
15 | Explain the abbreviation FFL at number 6. | 1 | |
16 | Explain the purpose of number 7. | 1 | |
17 | Explain the meaning of the arrow on the feature that must be installed in front of the sliding door. | 1 | |
18 | Explain what is meant by 1 : 10 indicated on the symbol in the notes. | 1 | |
19 | Which room will feature 15 serve? | 1 | |
20 | Explain the short dashed lines on the windows. | 1 | |
21 | Deduce the height of window 2 from the window schedule. | 1 | |
22 | Deduce the width of window 3 from the window schedule. | 1 | |
23 | On what elevation of the building is the bathroom window situated? | 1 | |
24 | Differentiate between component number 3 and component number 8. | 2 | |
25 | Differentiate between the light in the lounge and the light in the bathroom. | 2 | |
26 | Recommend a suitable floor covering for the bathroom. | 1 | |
27 | Recommend an appropriate scale to which FIGURE A should be drawn, according to SANS. | 1 | |
28 | Recommend an alternative sanitary fitment to replace number 11 that will serve a similar purpose. | 1 |
29 | Calculate the internal area of the office in m². Show ALL calculations. | 3 | |
30 | Calculate the perimeter of the building. Show ALL calculations. | 7 | |
TOTAL | 40 |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 3.5 (8)
A | B | C | D | |
| 3.5.1 | Internal measurements of long walls: | |||
= _________ - _________ = | ||||
Length of wall plates needed: | ||||
__/ | _______ | _______ | ||
| 3.5.2 | Number of purlins needed | |||
Number of purlins = Length of rafter + 1 | ||||
= __________ | ||||
= __________ | ||||
= purlins | ||||
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 5.9 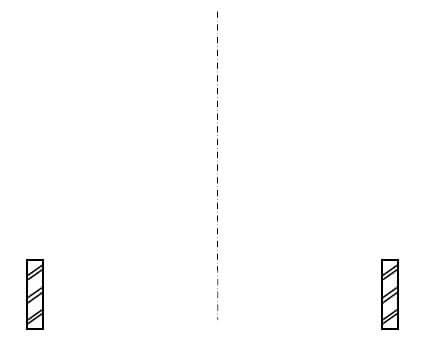
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Span | 1 | |
Wall plates | 2 | |
Rafters | 2 | |
Ridge beam | 1 | |
Slope of roof | 1 | |
TOTAL: | 7 |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 6.3 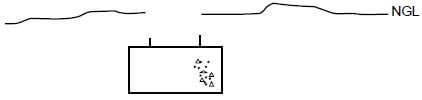
DRAWING NOT TO SCALE
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
ONE one-brick pier | 1 | |
NGL | 1 | |
Ant guard | 1 | |
Bearer | 1 | |
Joist | 1 | |
Floor boards | 1 | |
TOTAL: | 6 |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 6.7 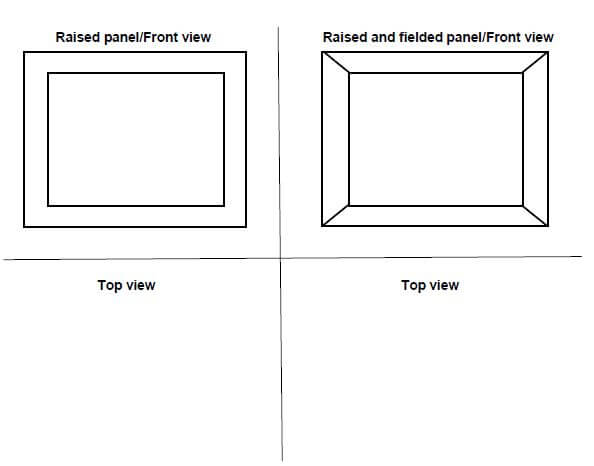
DRAWING NOT TO SCALE
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Raised panel top view | 2 | |
Raised and fielded panel top view | 2 | |
TOTAL: | 4 |
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY: CIVIL SERVICES GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY: CIVIL SERVICES
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2018
REQUIREMENTS:
- Drawing instruments
- A non-programmable calculator
- ANSWER BOOK
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Answer each question as a whole. Do NOT separate subsections of questions.
- Start the answer to EACH question on a NEW page.
- Do NOT write in the margins of the ANSWER BOOK.
- You may use sketches to illustrate your answers.
- Write ALL calculations and answers in the ANSWER BOOK or on the attached ANSWER SHEETS.
- Use the mark allocation as a guide to the length of your answers.
- Make drawings and sketches in pencil, fully dimensioned and neatly finished off with descriptive titles and notes to conform to the SANS/SABS Code of Practice for Building Drawings.
- For the purpose of this question paper, the size of a brick should be taken as 220 mm x 110 mm x 75 mm.
- Use your own discretion where dimensions and/or details have been omitted.
- Answer QUESTIONS 2, 3.2, 3.6, 5.2, 5.3 and 6.3 on the attached ANSWER SHEETS using drawing instruments where necessary.
- Write your CENTRE NUMBER and EXAMINATION NUMBER on every ANSWER SHEET and hand them in with your ANSWER BOOK, whether you have used them or not.
- Drawings in the question paper are NOT to scale due to electronic transfer.
- Google Images was used as the source for all photographs and pictures.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: OHSA, MATERIALS, TOOLS, EQUIPMENT AND JOINING (GENERIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
1.1 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–G) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.6 H.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.1.1 Sole plate 1.1.2 Aluminium ladder 1.1.3 Scaffold 1.1.4 Safety net 1.1.5 Galvanising |
(5 x 1) (5) |
1.2 Describe TWO safety precautions that must be adhered to when working on a scaffold. (2)
1.3 What is the purpose of the guard rail of a scaffold in terms of safety? (2)
1.4 Explain the purpose of painting. (2)
1.5 Describe ONE advantage of the curing process of concrete. (1)
1.6 FIGURE 1.6 below shows a tool that is used in the building construction industry. 
FIGURE 1.6
1.6.1 Identify tool A. (1)
1.6.2 Explain TWO uses of tool A. (2)
1.6.3 Explain why the batteries should be removed from the tool if the tool is not going to be used for a long time. (1)
1.7 FIGURE 1.7 below shows joining fixtures that are used on building sites and in workshops. 
FIGURE 1.7
1.7.1 Identify fastener A and fastener B. (2)
1.7.2 Explain ONE use of fastener A and fastener B respectively. (2) [20]
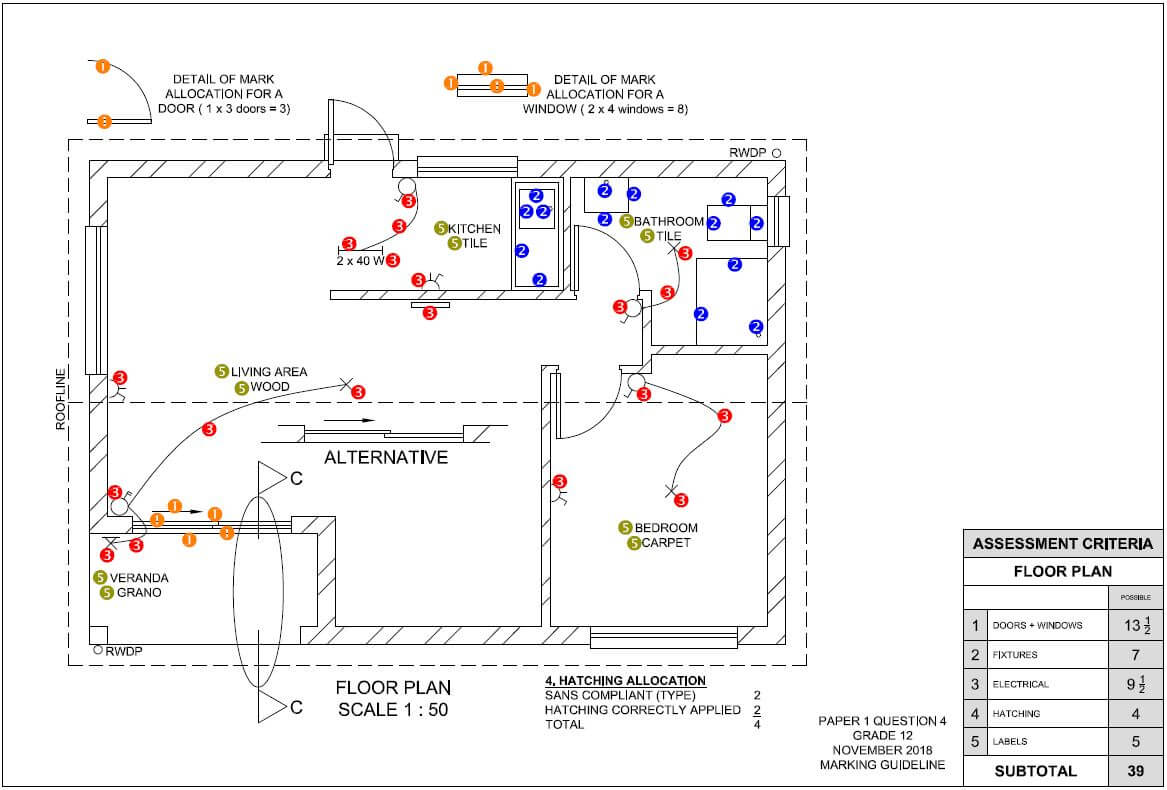
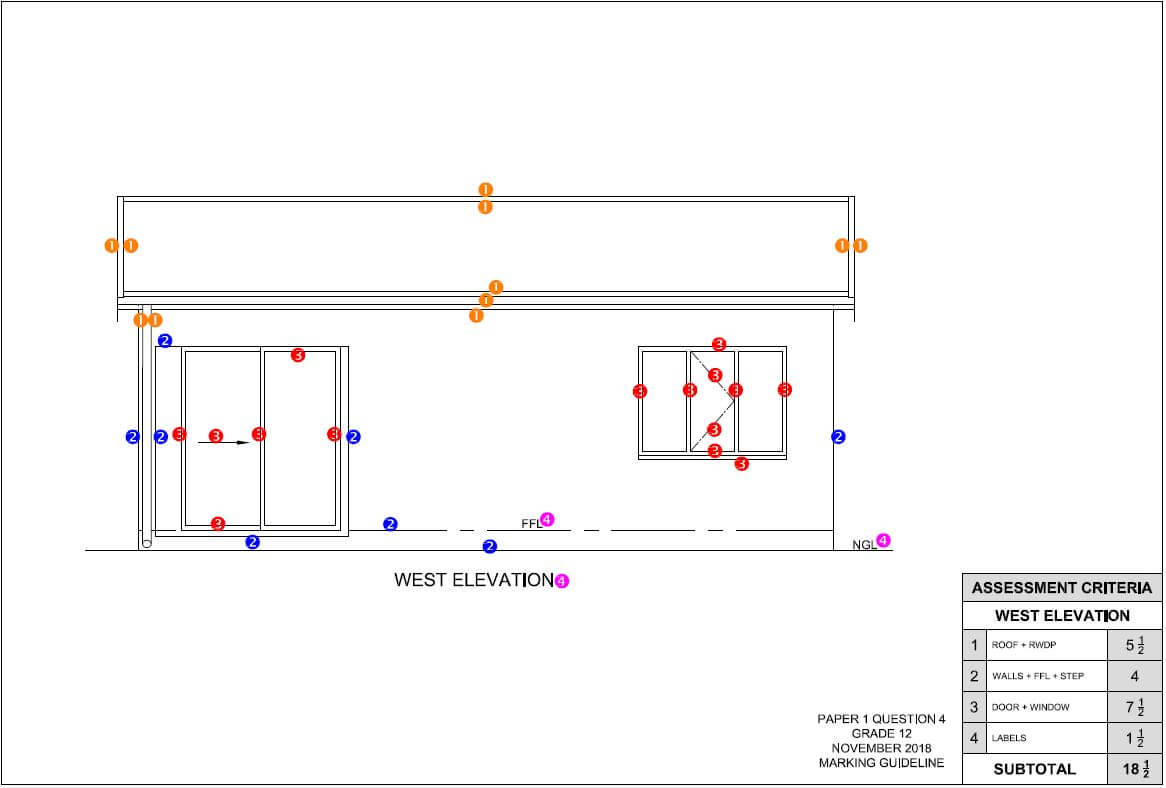
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS AS METHOD OF COMMUNICATION (GENERIC)
FIGURE 2 on the next page shows different drawings that appear on a building plan. Analyse the drawings and complete the table on ANSWER SHEET 2. 
FIGURE 2 [40]
QUESTION 3: CONSTRUCTION ASSOCIATED WITH CIVIL SERVICES, OHSA AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 FIGURE 3.1 below shows a sectional view of a manhole. Study the drawing and answer the questions that follow. 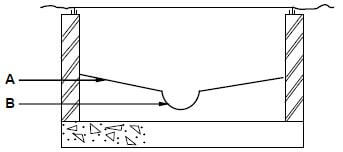
FIGURE 3.1
3.1.1 What is the main function of a manhole? (1)
3.1.2 Identify A. (1)
3.1.3 Identify B. (1)
3.1.4 Manholes that are deeper than 750 mm should be set in frames and have greased double seals. Give TWO reasons why greased double seals are installed. (2)
3.2 ANSWER SHEET 3.2 shows a top view of a T-junction of a half-brick wall in stretcher bond built with common bricks. Draw the sectional front view on section A-A by projecting it from the top view. The front view must have FIVE brick courses. (10)
3.3 State THREE regulations that protect workers during excavations. (3)
3.4 FIGURE 3.4 below shows TWO different types of shoring/shuttering. 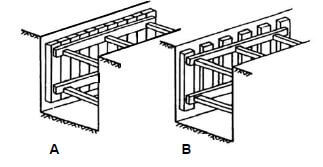
FIGURE 3.4
3.4.1 Different types of shoring are used for different soil types. Which type of shoring, A or B, will be suitable to use in loose or water-logged soil? (1)
3.4.2 Motivate your answer to QUESTION 3.4.1. (1)
3.5 Choose the correct word(s)/term in brackets. Write only the word(s)/term next to the question numbers (3.5.1 to 3.5.2) in the ANSWER BOOK.
3.5.1 Working in confined spaces, such as a (manhole/french drain/excavation), is one of the most dangerous tasks. (1)
3.5.2 A safety harness is clipped to a rope known as a (safety rope/ lifeline). (1)
3.6 FIGURE 3.6 below shows an incomplete sectional view through the bricks and concrete floor slab of a manhole.
Use ANSWER SHEET 3.6 and answer the following questions. 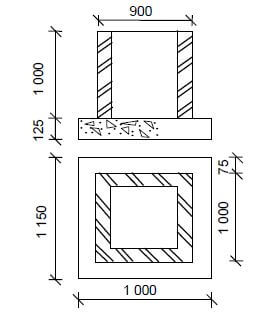
FIGURE 3.6
3.6.1 Calculate the volume of concrete that will be used for the foundation. Round off your answer to TWO decimals. (4)
3.6.2 Calculate the number of bricks needed for the manhole.
Specifications:
- The wall is a one-brick wide wall
- The centre line for the brickwork of the manhole is 4,96 m
- 100 bricks per square metre (m²) are needed for a one-brick wall (4)
[30]
QUESTION 4: COLD AND HOT-WATER SUPPLY, TOOLS, EQUIPMENT AND MATERIALS (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 FIGURE 4.1 below shows a geyser. 
FIGURE 4.1
4.1.1 Identify the type of geyser in FIGURE 4.1 above. (1)
4.1.2 Which part inside the geyser heats the water? (1)
4.1.3 Geysers use a lot of electricity. Recommend ONE other device that can be used to heat water without using electricity. (1)
4.2 Many different faults can occur in hot-water systems. Describe ONE cause of the following faults in hot-water systems:
4.2.1 Dripping geyser overflow (1)
4.2.2 No hot water (1)
4.2.3 Water leaking through the ceiling (1)
4.3 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–G) next to the question numbers (4.3.1 to 4.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 4.3.6 H.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
4.3.1 Vacuum breaker 4.3.2 Heat pump 4.3.3 Pressure control valve 4.3.4 Electrical isolator 4.3.5 Water tank |
(5 x 1) (5) |
4.4 Draw the SANS approved symbols for the followings fittings used in hot water systems:
4.4.1 Automatic shut-off valve (2)
4.4.2 Non-return valve (2)
4.4.3 Pressure reducing valve (2)
4.5 Explain, in FOUR steps, how you would fix a leaking copper pipe with compression joints. The water supply is already shut off. (4)
4.6 FIGURE 4.6 below shows a fitting that can be used under a wash basin. 
FIGURE 4.6
4.6.1 Identify the fitting in FIGURE 4.6. (1)
4.6.2 Name the material that is used to manufacture this fitting. (1)
4.6.3 Which part, A or B, will be connected to the bottom of the wash basin? (1)
4.6.4 Describe the purpose of the seal at C. (1)
4.7 FIGURE A and FIGURE B below show two different types of taps. 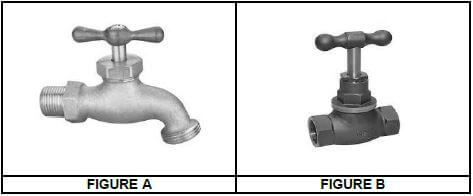
4.7.1 Identify the taps in FIGURES A and B respectively. (2)
4.7.2 Describe where you would use EACH of the taps above. (2)
4.7.3 Explain the advantage of plastic taps over brass taps on the outside of a building. (1)
4.8 Explain the purpose of installing a water meter on the incoming supply pipe of a house. (1)
4.9 Materials react differently when used.
4.9.1 Describe dezincification. (2)
4.9.2 Describe the problems dezincification can cause. (3)
4.10 Recommend ONE method to remove scale or corrosion from a metal surface. (1)
4.11 One function of a centrifugal pump is to convert kinetic energy to another type of energy. Name this type of energy. (1)
4.12 Which tool would you use to clear blockages in drains? (1)
4.13 Recommend ONE tool that can be used to test for leakages in a below ground drainage system. (1) [40]
QUESTION 5: GRAPHICS AS MEANS OF COMMUNICATION, ROOF WORK AND STORM WATER (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
5.1 Give ONE word(s)/term for EACH of the following descriptions by choosing a word(s)/term from the list below. Write only the word(s)/term next to the question numbers (5.1.1 to 5.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 5.1.6 Vacuum breaker.
length of the roof; galvanised sheet metal; gutter seal; concrete shoe; manhole; pitch of the roof; stop end; gutter; kerb |
5.1.1 This fitting can be used to seal off the gutter at the ends (1)
5.1.2 One factor to consider before installing a flashing (1)
5.1.3 A material that can be used for flashings (1)
5.1.4 This part collects rainwater flowing from the roof (1)
5.1.5 A raised edge on the road that guides water to storm-water drains (1)
5.2 FIGURE 5.2 on ANSWER SHEET 5.2 shows an incomplete drawing of a roof construction. Complete the drawing of the roof by drawing the following parts:
5.2.1 Square gutter (2)
5.2.2 Down-pipe with offset (3)
5.2.3 Holderbat (2)
5.3 ANSWER SHEET 5.3 shows the front and top view of a frustrum of a cone where the top is not parallel to the base.
Use the drawing and information on the ANSWER SHEET and draw the development of the cone. The development must have a 3 mm seam on both sides.
Show ALL construction lines. Do NOT redraw the drawing, project the development from the given drawing. (18) [30]
QUESTION 6: SEWERAGE, SANITARY FITTINGS AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
6.1 Various options are given as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (6.1.1 to 6.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 6.1.6 C.
6.1.1 An inspection eye is placed at … in the drainage system.
- rodding eyes
- junctions
- gully's
- All the above-mentioned (1)
6.1.2 Glue can be used to join … pipes.
- PVC
- copper and PVC
- copper and galvanised
- copper, PVC and galvanised (1)
6.1.3 A straight pan collar is used to join the … to the discharge pipe.
- toilet pan
- T-junction
- straight couplings
- cross junction (1)
6.1.4 The … allows odours and gases to escape from the drainage system.
- wastewater pipe
- soil pipe
- soil vent pipe
- All the above-mentioned (1)
6.1.5 All branch pipes should join the main drain at an angle of …
- 90°
- 135°
- 120°
- None of the above-mentioned (1)
6.2 FIGURE 6.2 below shows a part of a sewerage system. Study the drawing and answer the questions that follow. 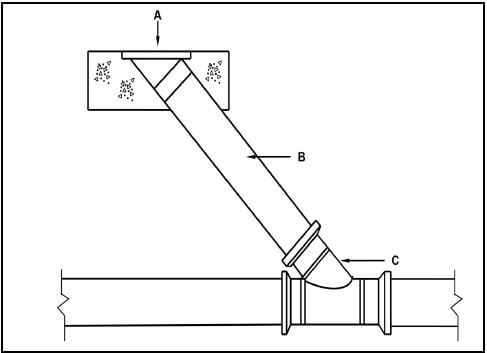
FIGURE 6.2
6.2.1 Identify component C. (1)
6.2.2 Describe ONE purpose of A. (1)
6.2.3 Explain why B is at an angle with the main pipe. (1)
6.3 FIGURE 6.3 on ANSWER SHEET 6.3 shows the line diagram of part of a building with sanitary fitments and sewerage components. Use ANSWER SHEET 6.3 and develop and draw a one-pipe sewerage layout for this building up to the indicated manhole. ALL regulations and design principles of a good drainage (sewerage) system must be considered and appropriate symbols and abbreviations must be used.
The drainage system should consist of:
- 2 x rodding eyes
- 5 x inspection eyes
- 1 x ventilation pipe
- Main sewerage pipes
- Branch pipes (10)
6.4 FIGURE 6.4 below shows the incomplete sectional view of a shower installation.
Study FIGURE 6.4 and answer the questions that follow. 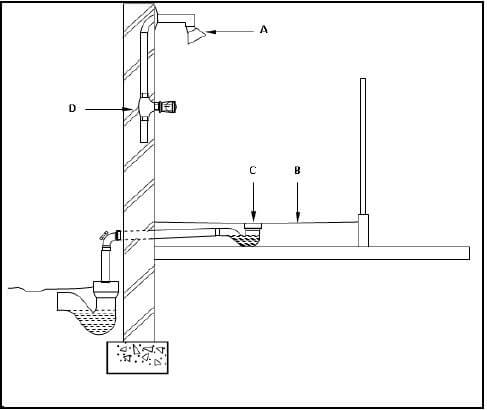
FIGURE 6.4
6.4.1 What is the diameter of the water pipes that are usually used for a shower? (1)
6.4.2 Identify A. (1)
6.4.3 Why is the surface B sloped towards C? (1)
6.4.4 Describe the function of C. (1)
6.4.5 The pipework from fitting A to fitting D consists of copper pipes. Name ONE method of joining these pipes if you are unable to use a compression joint. (1)
6.5 Explain the function of an anti-siphonage pipe. (1)
6.6 Differentiate between FIGURE A and FIGURE B below in terms of their use. 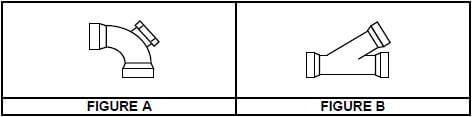 (2)
(2)
6.7 Name ONE sanitary appliance that discharges soil water. (1)
6.8 Draw the SANS approved symbols for the following components:
6.8.1 Urinal (2)
6.8.2 Grease trap (2)
6.8.3 Shower (2)
6.9 Name TWO materials that are commonly used in the manufacturing of sanitary fittings. (2)
6.10 Name TWO types of solder that can be used in the building industry. (2)
6.11 Give ONE use of a chemical anchor. (1)
6.12 FIGURE 6.12 below shows a joint between two pieces of metal. Study the drawing and answer the questions that follow. 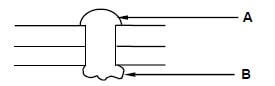
FIGURE 6.12
6.12.1 Identify A. (1)
6.12.2 Explain the function of B. (1) [40]
TOTAL: 200
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 2
NO. | QUESTIONS | ANSWERS | MARKS |
1 | Identify FIGURE A. | 1 | |
2 | Identify FIGURE B. | 1 | |
3 | Identify number 4. | 1 | |
4 | Identify number 5. | 1 | |
5 | Identify number 9. | 1 | |
6 | Identify number 10. | 1 | |
7 | Identify number 11. | 1 | |
8 | On what date was the plan printed? | 1 | |
9 | Who drew the building plan? | 1 | |
10 | Name the feature in the column for the notes in FIGURE 2 that must be installed in front of the sliding door. | 1 | |
11 | Name the feature in the column for the notes in FIGURE 2 that must give access to the first floor. | 1 | |
12 | Identify the type of roof that is used for the building in FIGURE A. | 1 | |
13 | Explain the purpose of number 1. | 1 | |
14 | Explain the purpose of number 2. | 1 |
15 | Explain the abbreviation FFL at number 6. | 1 | |
16 | Explain the purpose of number 7. | 1 | |
17 | Explain the meaning of the arrow on the feature that must be installed in front of the sliding door. | 1 | |
18 | Explain what is meant by 1 : 10 indicated on the symbol in the notes. | 1 | |
19 | Which room will feature 15 serve? | 1 | |
20 | Explain the short dashed lines on the windows. | 1 | |
21 | Deduce the height of window 2 from the window schedule. | 1 | |
22 | Deduce the width of window 3 from the window schedule. | 1 | |
23 | On what elevation of the building is the bathroom window situated? | 1 | |
24 | Differentiate between component number 3 and component number 8. | 2 | |
25 | Differentiate between the light in the lounge and the light in the bathroom. | 2 | |
26 | Recommend a suitable floor covering for the bathroom. | 1 | |
27 | Recommend an appropriate scale to which FIGURE A should be drawn, according to SANS. | 1 | |
28 | Recommend an alternative sanitary fitment to replace number 11 that will serve a similar purpose. | 1 |
29 | Calculate the internal area of the office in m². Show ALL calculations. | 3 | |
30 | Calculate the perimeter of the building. Show ALL calculations. | 7 | |
TOTAL | 40 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 3.2 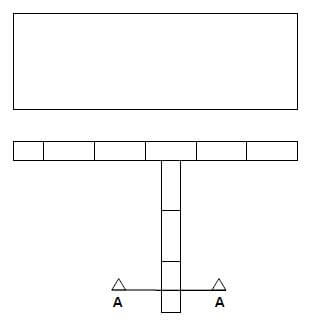
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
FIVE courses of bricks in stretcher bond correctly drawn | 5 | |
Alternate corner bricks on left side | 3 | |
Section correctly drawn | 1 | |
Hatching lines | 1 | |
TOTAL: | 10 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 3.6
A | B | C | D | ||
3.6.1 | Volume of concrete for foundation: | ||||
Volume = ℓ x b x h | |||||
1/ | ________ | ||||
________ | |||||
________ | ________ | ________ m³ of concrete is needed | (4) | ||
3.6.2 | Number of bricks needed for the manhole: | ||||
1/ | ________ | Centre line of wall = 4,96 m | |||
________ | |||||
________ | ________ | ________ bricks are needed | (4) | ||
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 5.2 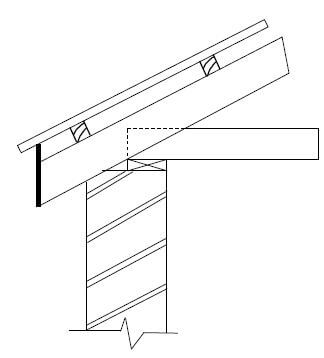
FIGURE 5.2
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Square gutter | 2 | |
Down-pipe with offset | 3 | |
Holderbat | 2 | |
TOTAL: | 7 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 5.3 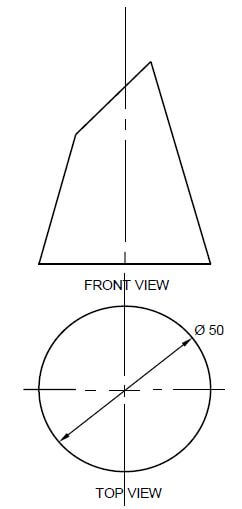
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CM |
Construction lines to top of cone | 2 | |
Construction lines of outer circle | 2 | |
Divide outer circle in 12 parts | 1 | |
Construction lines from top of cone to outer circle | 3 | |
Cone measurement (marked/transferred) from front view to determine top part of development | 6 | |
Outside lines of development | 2 | |
3 mm seam on both sides | 2 | |
TOTAL: | 18 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 6.3 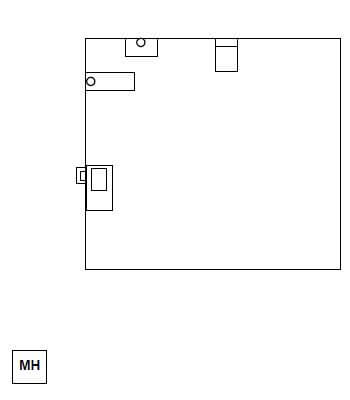
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
2 x rodding eyes correctly positioned | 2 | |
5 x inspection eyes correctly positioned | 5 | |
1 x ventilation pipe correctly positioned | 1 | |
Drain pipes drawn correctly (main and branch pipes) | 2 | |
TOTAL | 10 |
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY: CIVIL SERVICES GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY: CIVIL SERVICES
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2018
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: OHSA, MATERIALS, TOOLS, EQUIPMENT AND JOINING (GENERIC)
1.1
1.1.1 F ✔ (1)
1.1.2 A ✔ (1)
1.1.3 G ✔ (1)
1.1.4 E ✔ (1)
1.1.5 B ✔ (1)
1.2
- Do not throw any tools or materials from a scaffold. ✔
- Never jump on to and off a scaffold. ✔
- Never overload a scaffold.
- Remove or cover sharp edges or corners.
- Always attach free-standing scaffoldings to a building.
- Use a ladder to get on and off a scaffold.
- Keep free of waste or any other obstruction.
- Never jump on a scaffold while working on it.
- Responsible/qualified person must ensure that scaffolding is safe, rigid, stable and firm or has no defects.
- Scaffold must be supplied with guard rails/toe boards.
- Scaffolds must be levelled on uneven ground.
- Do not work on a scaffold in bad weather.
- Wear a safety harness when working on scaffolding.
- Do not throw tools on/off a scaffold.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
1.3
- It prevents workers from falling off the scaffold. ✔
- It is used as a handrail. ✔
- It is used to strap on safety harnesses.
- To protect the worker working on the scaffold.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
1.4
- The primary purpose of painting is to protect metals, wood and other material against corrosion and decay. ✔
- Provides a decorative/aesthetic appearance/finishing. ✔
- Protects surfaces from moisture penetration.
- Protects surfaces from rust/uv rays.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
1.5 The curing of concrete:
- Increases the strength of concrete. ✔
- Decreases the permeability of hardened concrete.
- Improves durability of concrete by reducing cracks.
- Makes concrete more watertight.
- Minimises shrinkage cracks in concrete.
- Provides volume stability.
- Cured concrete can carry more weight without breaking/crumbling than uncured concrete.
- Prevents rapid drying of concrete.
- Curing ensures that the hydration process continues.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
1.6
1.6.1 Multi detector ✔ (1)
1.6.2 Tool A is used:
- to detect materials found in/behind walls, ceilings and underneath floors, including ferrous and non-ferrous metals, electrical wiring, wood and metal studs. ✔
- to locate steel bars and copper pipes. ✔
- in carpentry, plumbing, and construction.
- to measure the distance to/from covered objects.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
1.6.3 The batteries must be removed from the tool:
- to prevent the battery from running flat/battery can die. ✔
- to prevent acid leaks from batteries damaging the tool.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
1.7
1.7.1
- A – Bolt and nut/Bolt ✔
- B – Rawl bolt ✔ (2)
1.7.2 Bolt and nut
- Bolts and nuts are used to secure pipe supports to metal parts. ✔
- To join components together.
Rawl bolt
- A Rawl bolt is used to fix a truss hanger to a wall. ✔
- To fix brackets/structures/panels to a wall/concrete.
- For construction, renovation and industrial work
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2) [20]
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS AS METHOD OF COMMUNICATION (GENERIC)
ANSWER SHEET 2
NO. | QUESTIONS | ANSWERS | MARKS |
1 | Identify FIGURE A. | South Elevation/Elevation ✔ | 1 |
2 | Identify FIGURE B. | Ground floor plan/Floorplan ✔ | 1 |
3 | Identify number 4. | First floor level/Second floor level/Suspended floor/Floor level/ Dash line/ FFL/Expansion joint ✔ | 1 |
4 | Identify number 5. | Window Sill ✔ | 1 |
5 | Identify number 9. | Hand wash basin/Wash basin/Washing basin/HWB/Basin ✔ | 1 |
6 | Identify number 10. | Water closet/WC/Toilet pan ✔ | 1 |
7 | Identify number 11. | Bath/B ✔ | 1 |
8 | On what date was the plan printed? | 2018/10/02 ✔ | 1 |
9 | Who drew the building plan? | JP Maloi ✔ | 1 |
10 | Name the feature in the column for the notes in FIGURE 2 that must be installed in front of the sliding door. | Ramp ✔ | 1 |
11 | Name the feature in the column for the notes in FIGURE 2 that must give access to the first floor. | Staircase/Stairs/Stairway✔ | 1 |
12 | Identify the type of roof that is used for the building in FIGURE A. | Gable roof ✔ | 1 |
13 | Explain the purpose of number 1. | To cover the opening/close the gap between the two slopes of the roof. ✔ | 1 |
14 | Explain the purpose of number 2. |
| 1 |
15 | Explain the abbreviation FFL at number 6. | Finished floor level ✔ | 1 |
16 | Explain the purpose of number 7. | To channel the water from the gutter to the ground. ✔ | 1 |
17 | Explain the meaning of the arrow on the feature that must be installed in front of the sliding door. | It indicates the direction of the slope of the ramp/it indicates the slope. ✔ | 1 |
18 | Explain what is meant by 1:10 indicated on the symbol in the notes. | It indicates the slope or the gradient of the ramp/for every 10 metres horizontally rises 1 metre vertically.✔ | 1 |
19 | Which room will feature 15 serve? | The bathroom. ✔ | 1 |
20 | Explain the short dash lines on the windows. |
| 1 |
21 | Deduce the height of window 2 from the window schedule. | 1,2 m or 1 200 mm ✔(Ignore units) | 1 |
22 | Deduce the width of window 3 from the window schedule. | 2 m or 2 000 mm ✔(Ignore units) | 1 |
23 | On what elevation of the building is the bathroom window situated? | Western elevation/Western side ✔ | 1 |
24 | Differentiate between component number 3 and component number 8. | 3 – window/window frame/reveal frame stile/casement stile ✔ | 2 |
25 | Differentiate between the light in the lounge and the light in the bathroom. | The light in the lounge is a fluorescent light/1 x 40W/2x40/3x40 fluorescent light ✔ and the light in the bathroom is a normal ceiling light ✔ | 2 |
26 | Recommend a suitable floor covering for the bathroom. | Tile/ Vinyl flooring(Novilon)/ Coloured screed/Polished or stained concrete flooring/Water proof laminated floor/carpet. ✔ | 1 |
27 | Recommend an appropriate scale to which FIGURE A should be drawn, according to SANS. | 1:50/100/200 ✔ | 1 |
28 | Recommend an alternative sanitary fitment to replace number 11 that will serve a similar purpose. | Shower ✔ | 1 |
29 | Calculate the internal area of the office in m² Show ALL calculations. | 4 m ✔ x 3 m ✔ = 12 m² ✔ OR 12 | 3 |
30 | Calculate the perimeter of the building. Show ALL calculations. | Positive marking | 7 |
TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 3: CONSTRUCTION ASSOCIATED WITH CIVIL SERVICES, OHS AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
3.1
3.1.1
- A manhole is a chamber that allows entrance to a drain. ✔ (1)
- Allow access to the sewage pipes of a sewage system.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE
3.1.2 Benching/Sloping/Haunching ✔ (1)
3.1.3 Pipe channel/Open channel/Channel ✔ (1)
3.1.4 Manholes are set in frames and have greased double seals for the following reasons:
- To make the manhole airtight. ✔
- To make the manhole watertight. ✔
- To ensure that gasses cannot escape.
- To ensure that liquids cannot escape.(2)
3.2 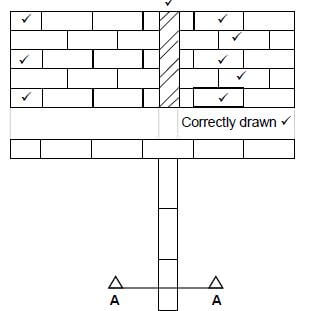 (10)
(10)
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | LEARNER MARK |
FIVE courses of bricks in stretcher bond correctly drawn | 5 | |
Alternate half bricks on left side | 3 | |
Section correctly drawn | 1 | |
Hatching lines | 1 | |
TOTAL: | 10 |
3.3
- If the sides are not properly supported, no person is allowed to work in the trench. ✔
- The supervisor ensures that no load, material or heavy machinery is placed near the edge of any excavation. ✔
- Excavations must be adequately protected by a fence. ✔
- Red warning lights and signs should be placed at regular intervals and be clearly visible.
- Orange warning signals must always be visible.
- Deep trenches should have shoring.
- Wear a harness.
- Any person entering an excavation trench must wear personal protective equipment.
ANY THREE OF THE ABOVE (3)
3.4
3.4.1 Shoring A ✔ (1)
3.4.2
- Vertical members/poling boards are closer together. This means loose or waterlogged soil cannot filter through the openings. ✔
- The loose or waterlogged soil will easily filter through the openings of B.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
3.5
3.5.1 Manhole ✔ (1)
3.5.2 Lifeline ✔ (1)
3.6
A | B | C | D | ||
| 3.6.1 | Volume of concrete for foundation: | ||||
Volume = l x b x h | |||||
1/ | 1,150 ✔ | ||||
1,0 ✔ | |||||
0,125 ✔ | 0,14 m³ ✔ | 0,14 m³ of concrete is needed | (4) | ||
| 3.6.2 | Number of bricks needed for the manhole: | ||||
1/ | 4,96 ✔ | Centre line of wall = 4,96 m | |||
1,0 ✔ | |||||
100 ✔ | 496 ✔ | 496 bricks are needed | (4) | ||
| [30] |
QUESTION 4: COLD AND HOT-WATER SUPPLY, TOOLS, EQUIPMENT AND MATERIALS (SPECIFIC)
4.1
4.1.1 High pressure geyser/Electrical geyser ✔ (1)
4.1.2 Element ✔ (1)
4.1.3 Gas geyser/Solar geyser/Coal/Biofuel/Wood geyser/Donkey/Solar panel ✔ (1)
4.2
4.2.1 A dripping geyser overflow may be an indication that the pressure control/relief valve/vacuum breaker is faulty/pipe joint leakage. ✔ (1)
4.2.2 If there is no hot water, one of the following may be the cause:
- No power to the geyser ✔
- Circuit breaker is faulty
- Electricity supply is interrupted
- Thermostat may be faulty
- Element may be faulty
- Blocked hot-water pipe
- No sun for solar geyser
- No gas for gas geyser
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
4.2.3 If water is leaking through the ceiling, one of the following may be the reason:
- Burst geyser or major leak. ✔
- Drip tray outlet pipe is blocked or overflowing.
- The drip tray may be cracked/no drip tray.
- Pipe joint leakage.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
4.3
4.3.1 F ✔ (1)
4.3.2 G ✔ (1)
4.3.3 E ✔ (1)
4.3.4 D ✔ (1)
4.3.5 B ✔ (1)
4.4 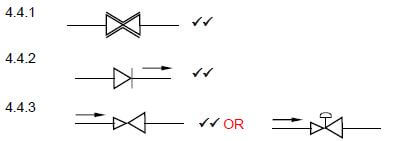 (@ 2)
(@ 2)
4.5
- Cut the damaged section from the pipe, using a pipe cutter/. ✔
- Move the pipe slightly sideways to allow the fixing of compression fittings. ✔
- Measure and cut the length of pipe to be replaced. ✔
- Slip the nuts over the pipes followed by the ferrules. Push the pipes into the fittings and tighten using the correct tools. ✔
OR - Dismantle the joint (4)
- Ensure sealing of joint (thread sealing tape)
- Replace compression joint
- Tighten all nuts properly
- Test for leaks
4.6
4.6.1 P-Trap/Water trap ✔ (1)
4.6.2 PVC/Plastic/Rubber✔ (1)
4.6.3 B ✔ (1)
4.6.4 The seal will ensure a watertight seal and prevent it from leaking. ✔ (1)
4.7
4.7.1 A Bibcock/Bib tap ✔ (1) B Stopcock/Stop tap ✔ (1)
4.7.2 A
- A bibcock can be used for sanitary fitments such as kitchen sinks, wash troughs, washbasins, dishwashers, washing machine, fridges, ice machines and baths. ✔ Outside of a house for hose pipes.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1) - A stopcock is used to close or shut off the water supply. ✔ (1)
4.7.3
- Plastic taps do not have the same resale value ✔as brass taps and is therefore not worth stealing/cheaper.
- Plastic taps are cheaper than brass taps. (1)
4.8
- To enable local authorities/consumer to calculate the amount of water consumed by a household. ✔
- To indicate if there is a leakage in water pipes.
- To enable the user to upload pre-paid water coupons. (1)
4.9
4.9.1 Description of dezincification:
- Dezincification is the selective leaching of zinc from copper alloys. ✔
- It is an electrochemical reaction between zinc and water. ✔ (2)
4.9.2 Problems caused:
- Zinc gradually dissolves from the surface of an alloy. ✔
- The material that remains is a weak, spongy copper layer. ✔
- It can progress through the part/fitting, causing leaks. ✔
- It can form blockages if it forms a deposit. (3)
ANY THREE OF THE ABOVE
4.10 Electrolytic cleaning/chemicals/scrubbing with wire brush/sand paper. ✔ (1)
4.11 Hydro-dynamic energy ✔ (1)
4.12 ∙ Drain cleaning rods ✔
- Jetting machine/drain cleaning machine/plunger
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
4.13 Compressed-air test apparatus ✔ (1) [40]
QUESTION 5: GRAPHICS AS MEANS OF COMMUNICATION, ROOF WORK AND STORM WATER (SPECIFIC)
5.1
5.1.1 Stop end ✔ (1)
5.1.2 Pitch of the roof ✔ (1)
5.1.3 Galvanised sheet metal ✔ (1)
5.1.4 Gutter ✔ (1)
5.1.5 Kerb ✔ (1)
5.2 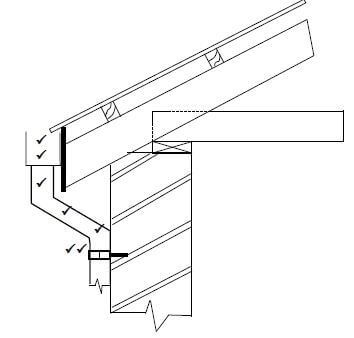 (7)
(7)
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | LEARNER MARK |
Square gutter | 2 | |
Downpipe with offset | 3 | |
Holder bat | 2 | |
TOTAL: | 7 |
5.3 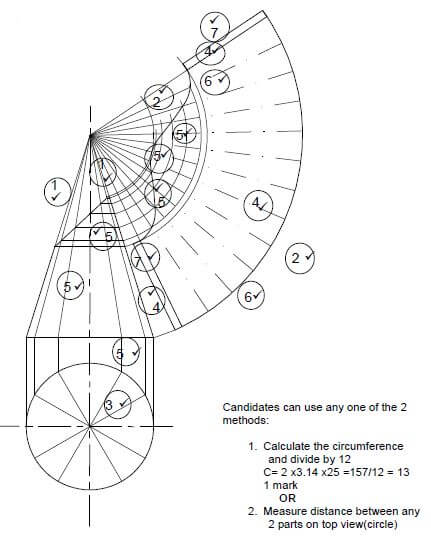
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CM | |
Construction lines to top of cone | 1 | 2 | |
Construction lines of outer circle | 2 | 2 | |
Divide outer circle in 12 parts | 3 | 1 | |
Construction lines from top of cone to outer circle | 4 | 3 | |
Cone measurement (marked/transferred) from front view to determine top part of development (ONE mark for every FOUR coordinates = 3) | 5 | 6 | |
Outside lines of development | 6 | 2 | |
3 mm seam on both sides | 7 | 2 | |
TOTAL: | 18 |
OR
5.3 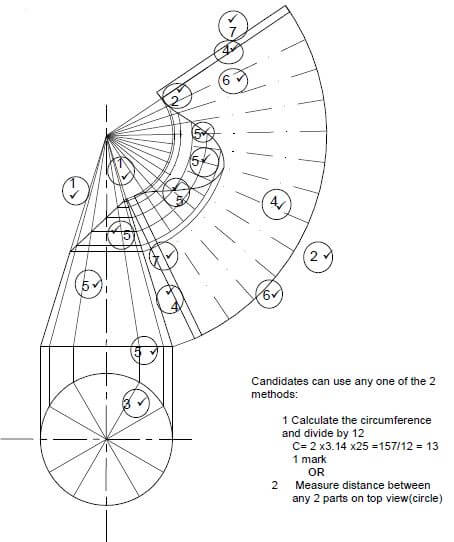
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CM | |
Construction lines to top of cone | 1 | 2 | |
Construction lines of outer circle | 2 | 2 | |
Divide outer circle in 12 parts | 3 | 1 | |
Construction lines from top of cone to outer circle | 4 | 3 | |
Cone measurement (marked/transferred) from front view to determine top part of development | 5 | 6 | |
Outside lines of development | 6 | 2 | |
3 mm seam on both sides | 7 | 2 | |
TOTAL: | 18 |
[30]
QUESTION 6: SEWERAGE, SANITARY FITTINGS AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
6.1
6.1.1 B ✔ (1)
6.1.2 A ✔ (1)
6.1.3 A ✔ (1)
6.1.4 C ✔ (1)
6.1.5 B ✔ (1)
6.2
6.2.1 C Waste junction135°/Y-junction 135°✔ (1)
6.2.2
- To allow access to the drainage system. ✔
- To remove blockages from the drainage system.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
6.2.3
- So that drain rods can be inserted easily into the pipe with the direction of flow. ✔
- A 90° junction at this point will make it impossible to use drain rods.
- A 90º junction will damage the main sewerage pipe if drain rods are forced into the pipe.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
6.3 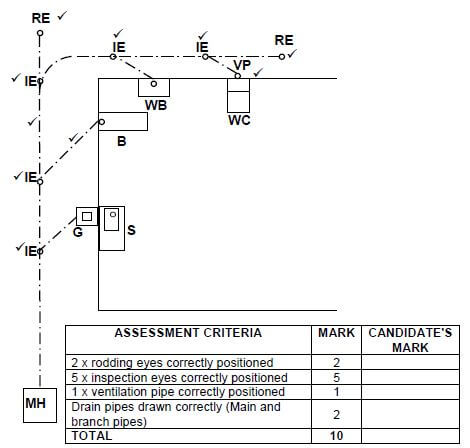 (10)
(10)
6.4.1 15 mm ✔ (1)
6.4.2 Shower rose/head ✔ (1)
6.4.3 To channel the water towards C. ✔ (1)
6.4.4
- The shower trap allows water to flow down the drainage pipes. ✔
- Keeps unwanted odours from entering the atmosphere.
- To ensure that water flows to the shower trap. (1)
6.4.5 Capillary joint/Soldered joint ✔ (1)
6.5 The function of an anti-siphonage pipe is:
- To supply air to the short branch pipe of the lower fixture at the time of suction to prevent loss of the water seal. ✔
- To act as a ventilation pipe for the lower fixtures.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
6.6 FIGURE A: Used above ground where soil pipe must bend. ✔ Where access to sewage pipes are needed/unblocking of pipes. To join sewage pipes at 90º.
FIGURE B: Used to connect soil pipes at an angle. ✔ To join three soil pipes at an angle of 135º (2)
6.7
- Water closet ✔
- Bidet
- Urinal
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
6.8
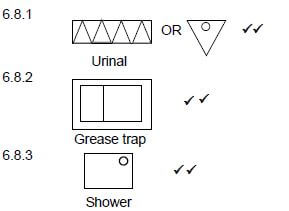 @ (2)
@ (2)
6.9 Materials that are commonly used for sanitary fittings are:
- Ceramics ✔
- Cast iron ✔
- Stainless steel
- Plastic/PVC
- Pressed steel
- Terrazzo
- Glass fibre/fibreglass (2)
- Copper/aluminium
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE
6.10
- 50/50 solder (plain/tinman's solder) ✔
- Wiping solder (plumber's solder) ✔
- 60/40 solder (fine solder)
- Lead-free solder
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
6.11 Chemical anchors can be used to:
- Mount air conditioners ✔
- Fit outdoor lights
- Fix brackets to walls
- Fix brackets to secure I-beams
- Fix balconies
- Fix railings
- Repair bathrooms
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
6.12
6.12.1 Rivet head ✔ (1)
6.12.2 Flange is created by the rivet gun to complete the bond between the two pieces of material/keep/secure the two parts together. ✔ (1) [40]
TOTAL: 200
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY: CONSTRUCTION GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY: CONSTRUCTION
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2018
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: OHSA, MATERIALS, TOOLS, EQUIPMENT AND JOINING (GENERIC)
1.1
1.1.1 F ✔ (1)
1.1.2 A ✔ (1)
1.1.3 G ✔ (1)
1.1.4 E ✔ (1)
1.1.5 B ✔ (1)
1.2
- Do not throw any tools or materials from a scaffold. ✔
- Never jump on to and off a scaffold. ✔
- Never overload a scaffold.
- Remove or cover sharp edges or corners.
- Always attach free-standing scaffoldings to a building.
- Use a ladder to get on and off a scaffold.
- Keep free of waste or any other obstruction.
- Never jump on a scaffold while working on it.
- Responsible/qualified person must ensure that scaffolding is safe, rigid, stable and firm or has no defects.
- Scaffold must be supplied with guard rails/toe boards.
- Scaffolds must be levelled on uneven ground.
- Do not work on a scaffold in bad weather.
- Wear a safety harness when working on scaffolding.
- Do not throw tools on/off a scaffold.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
1.3
- It prevents workers from falling off the scaffold. ✔
- It is used as a handrail. ✔
- It is used to strap on safety harnesses.
- To protect the worker working on the scaffold.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
1.4
- The primary purpose of painting is to protect metals, wood and other material against corrosion and decay. ✔
- Provides a decorative/aesthetic appearance/finishing. ✔
- Protects surfaces from moisture penetration.
- Protects surfaces from rust/uv rays.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
1.5 The curing of concrete:
- Increases the strength of concrete. ✔
- Decreases the permeability of hardened concrete.
- Improves durability of concrete by reducing cracks.
- Makes concrete more watertight.
- Minimises shrinkage cracks in concrete.
- Provides volume stability.
- Cured concrete can carry more weight without breaking/crumbling than uncured concrete.
- Prevents rapid drying of concrete.
- Curing ensures that the hydration process continues.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
1.6
1.6.1 Multi detector ✔ (1)
1.6.2 Tool A is used:
- to detect materials found in/behind walls, ceilings and underneath floors, including ferrous and non-ferrous metals, electrical wiring, wood and metal studs. ✔
- to locate steel bars and copper pipes. ✔
- in carpentry, plumbing, and construction.
- to measure the distance to/from covered objects.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
1.6.3 The batteries must be removed from the tool:
- to prevent the battery from running flat/battery can die. ✔
- to prevent acid leaks from batteries damaging the tool.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1) 1.7
1.7.1 A – Bolt and nut/Bolt ✔
B – Rawl bolt ✔ (2)
1.7.2 Bolt and nut
- Bolts and nuts are used to secure pipe supports to metal parts. ✔
- To join components together.
Rawl bolt
- A Rawl bolt is used to fix a truss hanger to a wall. ✔
- To fix brackets/structures/panels to a wall/concrete.
- For construction, renovation and industrial work
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2) [20]
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS AS METHOD OF COMMUNICATION (GENERIC)
ANSWER SHEET 2
NO. | QUESTIONS | ANSWERS | MARKS |
1 | Identify FIGURE A. | South Elevation/Elevation ✔ | 1 |
2 | Identify FIGURE B. | Ground floor plan/floorplan ✔ | 1 |
3 | Identify number 4. | First floor level/Second floor level/Suspended floor/Floor level/ dash line/ FFL/Expansion joint ✔ | 1 |
4 | Identify number 5. | Window Sill ✔ | 1 |
5 | Identify number 9. | Hand wash basin/Wash basin/Washing basin/HWB/basin ✔ | 1 |
6 | Identify number 10. | Water closet/WC/Toilet pan ✔ | 1 |
7 | Identify number 11. | Bath/B ✔ | 1 |
8 | On what date was the plan printed? | 2018/10/02 ✔ | 1 |
9 | Who drew the building plan? | JP Maloi ✔ | 1 |
10 | Name the feature in the column for the notes in FIGURE 2 that must be installed in front of the sliding door. | Ramp ✔ | 1 |
11 | Name the feature in the column for the notes in FIGURE 2 that must give access to the first floor. | Staircase/Stairs/Stairway✔ | 1 |
12 | Identify the type of roof that is used for the building in FIGURE A. | Gable roof ✔ | 1 |
13 | Explain the purpose of number 1. | To cover the opening/close the gap between the two slopes of the roof. ✔ | 1 |
| MARKS | |||
14 | Explain the purpose of number 2. |
| 1 |
15 | Explain the abbreviation FFL at number 6. | Finished floor level ✔ | 1 |
16 | Explain the purpose of number 7. | To channel the water from the gutter to the ground. ✔ | 1 |
17 | Explain the meaning of the arrow on the feature that must be installed in front of the sliding door. | It indicates the direction of the slope of the ramp/it indicates the slope. ✔ | 1 |
18 | Explain what is meant by 1:10 indicated on the symbol in the notes. | It indicates the slope or the gradient of the ramp/for every 10 metres horizontally rises 1 metre vertically.✔ | 1 |
19 | Which room will feature 15 serve? | The bathroom. ✔ | 1 |
20 | Explain the short dash lines on the windows. |
| 1 |
21 | Deduce the height of window 2 from the window schedule. | 1,2 m or 1 200 mm ✔(Ignore units) | 1 |
22 | Deduce the width of window 3 from the window schedule. | 2 m or 2 000 mm ✔(Ignore units) | 1 |
23 | On what elevation of the building is the bathroom window situated? | Western elevation/Western side ✔ | 1 |
24 | Differentiate between component number 3 and component number 8. | 3 – window/window frame/reveal frame stile/casement stile ✔ | 2 |
| MARKS | |||
25 | Differentiate between the light in the lounge and the light in the bathroom. | The light in the lounge is a fluorescent light/1 x 40W/2x40/3x40 fluorescent light ✔ and the light in the bathroom is a normal ceiling light ✔ | 2 |
26 | Recommend a suitable floor covering for the bathroom. | Tile/ Vinyl flooring (Novilon)/ Coloured screed/Polished or stained concrete flooring/Water proof laminated floor/carpet. ✔ | 1 |
27 | Recommend an appropriate scale to which FIGURE A should be drawn, according to SANS. | 1:50/100/200 ✔ | 1 |
28 | Recommend an alternative sanitary fitment to replace number 11 that will serve a similar purpose. | Shower ✔ | 1 |
29 | Calculate the internal area of the office in m² Show ALL calculations. | 4 m ✔ x 3 m ✔ = 12 m² ✔ OR 12 4 000✔ X 3 000✔ = 12 000 000mm2 | 3 |
30 | Calculate the perimeter of the building. Show ALL calculations. | Positive marking | 7 |
TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 3: ROOFS, STAIRCASES AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
3.1 5°/10/30° ✔ (1)
3.2 1 400 mm ✔ (1)
3.3 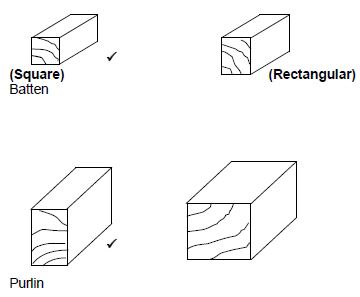
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE
3.4 50 mm x 76 mm/ 76 mm x 50 mm ✔ OR 76 mm x 76 mm (1)
3.5 (2)
Clay roof tiles | Fibre cement tiles |
650 mm/closer together ✔ | 760 mm/ further apart ✔ |
3.6
A - Ridge capping/Ridge plate/Roof capping ✔
B - Roof covering/Corrugated iron roof/IBR iron roof/roof sheeting ✔
C - Gang nail/Nail plate/Connector plate/Joining piece ✔
D - King post ✔ (4)
3.7 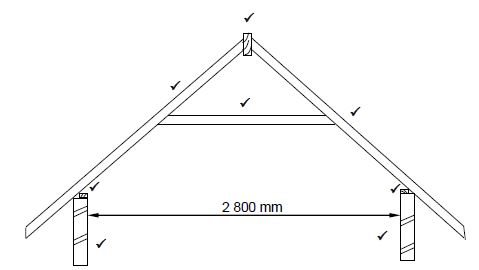
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Walls | 2 | |
Wall plates (Wrong position – 1 mark) | 2 | |
Rafters | 2 | |
Collar beam/Collar tie | 1 | |
Ridge beam correctly drawn | 1 | |
TOTAL: | 8 |
3.8.1 Riser ✔ (1)
3.8.2 Balusters ✔ (1)
3.8.3 Going/Tread ✔ (1)
3.8.4 Landing ✔ (1)
3.8.5 Run ✔ (1)
3.9 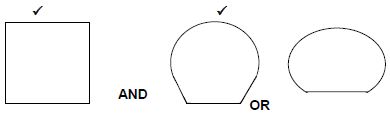
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE OR ANY OTHER SHAPE RESEMBLING A SQUARE OR ROUND SHAPE/ 2 AND 3 DIMENSIONAL DRAWINGS ACCEPTABLE
3.10
- Screwed on to the face of the wall. ✔
- By means of a bracket.
- Fixed to face of wall using Rawl bolts or sleeved anchors by means of a bracket.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
3.11
- Timber that is bolted to the top of the wall.✔
- Nailed or screwed to the wall. ✔
- A galvanised strap/hoop iron nailed or built into the wall.
- Tie with roof wire built into wall.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
3.12
- Supports the steel and withstands the loads. ✔
- The pin serves as a pivoting point to adjust the angle or to lower the steel section.
- The pin can be removed to separate the steel section from the base.
- To keep the steel section attached to the base plate/concrete base.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1) [30]
QUESTION 4: EXCAVATIONS, FORMWORK, TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT AND MATERIALS (SPECIFIC)
4.1
4.1.1 C ✔
4.1.2 D ✔
4.1.3 F ✔
4.1.4 E ✔
4.1.5 A ✔ (5)
4.2.1
- Keep excavated soil away from edge at least 600 mm. ✔
- Identify any equipment that will affect trench stability. ✔
- Trenches should be inspected at the start of each shift. ✔
- Trenches should be inspected after a rain storm.
- No worker will be allowed to work or move in trenches deeper then 1,5 metres if the sides are not protected by formwork or braced.
- Test for atmospheric hazards (low oxygen, hazardous fumes and toxic gases) when trenches are more than 1,3 metres deep.
- No load vehicle or plant equipment should be used, placed driven or used on or near the edge of any excavation where it is likely to cause a collapse and endanger workers lives.
- A warning system for mobile equipment should be provided.
- Always protect workers from loose rock or soil that could fall or roll from an excavation by installing protective barricades at appropriate intervals.
- Prohibit workers from working on faces of slopes or benched excavations at levels above other workers, unless workers at a lower level is protected against hazards of falling or sliding material or equipment.
- Members/parts of the support system (formwork or shuttering) should be securely connected to prevent sliding, falling material.
- Avoid overloading members of support systems.
- Formwork/shuttering should be removed in a manner that will protect workers from cave-ins.
- Before temporary removal of individual formwork members/parts, additional precautions should be in place, installing other structural members.
- Backfilling should always progress with the removal of the support system (formwork from the excavation).
- The area should be cordoned off and warning signs must be posted and must be clearly visible.
- Cover the entire work area after hours, especially if children might gain entry to the site.
- A suitable barrier(fence) must be provided where any excavation is more than 2 metres deep.
- Excavation sites should be well lit at night.
- Red warning lights should be placed strategically to warn the public.
- Workers should not work under suspended or raised loads of materials.
- Always start dismantling the formwork from the bottom of the formwork.
- Never work alone in deep excavations.
ANY THREE OF THE ABOVE (3)
4.2.2
- The site must be levelled. ✔
- The site must be cleared properly, and all loose soil must be removed.✔
- A baseline must be established. ✔ (3)
4.3 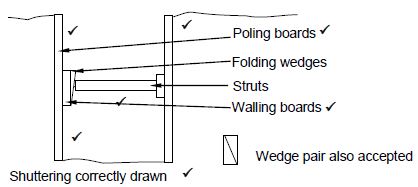
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Folding wedges | 1 | |
Walling boards | 1 | |
Poling boards | 2 | |
Struts | 1 | |
Shuttering correctly drawn | 1 | |
Any TWO labels | 2 | |
TOTAL: | 8 |
4.4 Good formwork should be:
- made accurately to the dimensions. ✔
- stable enough to bear the load of wet concrete.
- bear the mass of workers on it.
- able to withstand the vibrating and tamping of concrete.
- strong enough to provide enough support, without too much deflection, until the concrete has set and cured.
- easy to repair on site.
- secured with wire nails so that it can be easily dismantled.
- secured with bolts and nuts ranging from 13 mm to 19 mm in diameter.
- should be sealed properly.
- should be free of dirt such as saw dust.
- quick and simple to erect to ensure the correct cover depth for the reinforcing.
- removed only when concrete has cured.
- close-fittings along seams and joints.
- made of recyclable components.
- fitted with plywood laggings for a smooth finish.
- ensure the correct cover depth for the reinforcing in order to prevent structural failure.
- sealed properly so that the concrete does not leak and form a honeycomb effect.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
4.5
4.5.1 Beam formwork/Formwork for beams✔ (1)
4.5.2
A - Tie 50 mm x 25 mm at 600 mm centres ✔
B - Cleat 76 mm x 50 mm ✔
C - Fixing plate/Kicker plate 76 mm x 50 mm ✔
D - Brace/Strut 76 mm x 25 mm ✔ (4)
4.5.3
- The shape of folding wedges simplifies the erecting and dismantling of formwork. ✔
- Folding wedges can easily be removed by knocking one away from the other.
- Folding wedges help to keep formwork components sturdy/secured/stable.
- Folding wedges play an important role in the levelling of formwork for beams, floor slabs and columns.
- Folding wedges facilitate the raising or lowering of the formwork to the required height.
- Folding wedges are used as pins to strengthen adjoining concrete formwork (1)
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE
4.6
- Sturdy/Rigid enough to bear the mass of wet concrete without collapsing.✔
- Stronger than wood and timber board products. ✔
- Easily removed when the concrete has set.
- Not as adaptable as timber shuttering.
- More expensive than timber.
- Will last longer than timber.
- Can be used repeatedly.
- Tight along the seams and joints so that concrete does not leak.
- It’s prone to rust.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
4.7
4.7.1
- Operate with care and wear appropriate personal protective equipment. ✔
- Check the controls for proper response before use.✔
- Check the condition of the machine at the start and end of each shift.
- Never use a faulty machine.
- Never lay the machine on its side.
- Do not allow the vibrating pipe to make contact with any part of the body or formwork.
- Switch of the machine when it is left unattended.
- Long use of the machine exposes the operator to vibrations. Stop if you feel numbness.
- Switch off the machine and wait for all moving parts to stop before adjusting, repairing, inspecting or cleaning it.
- Must be operated by a qualified person. (2)
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE
4.7.2
- Maintain like all machinery. Lubricate and adjust according to the manufacturer’s instruction. ✔
- Clean after use and store in a safe dry place. ✔
- Service the concrete vibrator regularly.
- Repair or replace damaged electric cords.(2)
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE
4.8
- Service the tamping rammer/plate compactor regularly. ✔
- Remove loose dirt and soil after use. ✔
- Maintain like all machinery, lubricate and adjust according to the manufacturers instruction.
- Clean after use.
- Store in a safe dry place.
- Ensure that all parts are firmly attached to the machine.
- Repair or replace damaged electric cords. (2)
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE
4.9 Ready-mix concrete:
- is very expensive. ✔
- delivery and pouring delays may affect the quality of the concrete. ✔
- site batching in residential areas raises concerns about noise levels
- must be poured within a specified time.
- trucks may damage or soil house frontages and sidewalks.
- contaminations of storm-water drains.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
4.10 The purpose of the slump test:
- is to test the density of the concrete before it is placed by determining the percentage of water it contains. ✔
- Is to determine the workability and consistency of the batches that are mixed. ✔
- To determine the slump of the mixture.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
4.11
- Water – hosepipe or continuous spraying ✔
- Water- retaining substances, such as damp sand, damp sacking, straw, hessian and canvas. ✔
- Plastic membranes and plastic sheeting
- Chemical curing products
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2) [40]
QUESTION 5: PLASTER AND SCREED, BRICKWORK AND GRAPHICS AS MEANS OF COMMUNICATION (SPECIFIC)
5.1
5.1.1
A - Wet the wall thoroughly ✔
B - Apply plaster ✔
C - Scrape the plaster to obtain a flat surface/levelling ✔
D - Float to smooth the surface ✔ (4)
5.1.2 Straight edge ✔ (1)
5.2
LEFT VIEW INCORRECTLY DRAWN -1 (6)
CRITERIA ASSESSMENT | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Full bricks and ½ brick every alternate course on front view | 4 | |
Left view full brick every course | 1 | |
Left view ¼ brick every course | 1 | |
TOTAL: | 6 |
5.3
5.3.1
A- Herring bone paving pattern ✔
B- Basket-weave paving pattern ✔ (2)
5.3.2
- Dry-laid or sand-set ✔
- Bitumen-set
- Mortar-set
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
5.3.3
- River/Plaster sand is used to grout between paving bricks.
- Sand mixed with cement is used to grout between paving bricks ✔
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
5.4
SCALE: 1:10 ✔
NOT DRAWN TO SCALE
APPLICATION OF SCALE ✔ ✔✔
USE A MASK TO MARK THIS QUESTION ACCEPT ANY ANGLE BETWEEN 30° AND 45°.
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Wall: 220 mm wide face brick | 1 | |
Beam filling | 1 | |
Wall plate 114 mm x 38 mm | 1 | |
Tie beam 114 mm x 38 mm | 1 | |
Rafter 114 mm x 38 mm | 1 | |
Purlins 76 mm x 50 mm | 2 | |
Corrugated iron roof covering | 1 | |
Fascia board 230 mm x 38 mm | 1 | |
Any TWO labels | 2 | |
Print the scale below the drawing | 1 | |
Application of scale | 3 | |
TOTAL | 15 |
(15) [30]
QUESTION 6: REINFORCEMENT IN CONCRETE, FOUNDATIONS, CONCRETE FLOOR AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
6.1
6.1.1 B ✔ (1)
6.1.2 D ✔ (1)
6.1.3 D ✔ (1)
6.1.4 B ✔ (1)
6.1.5 A ✔ (1)
6.2 
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Column | 2 | |
8 Main bars | 2 | |
Binders/Stirrups | 2 | |
Min concrete cover | 1 | |
Any TWO Labels | 2 | |
Proportion | 1 | |
TOTAL | 10 |
6.3 Pile foundations:
- can be used in poor/unstable/soft/loose soil. ✔
- can be used anywhere even in water. ✔
- the larger base ensures stability. ✔
- is relatively quick to install if the equipment is available.
- where pre-fabricated piles are used, much time is saved.
- resists tensile stress well.
- is quick and less expensive to produce.
- can be manufactured and transported elsewhere.
- can be installed in poor weather conditions.
- the length can easily be adjusted.
- offers good resistance against moving soil.
ANY THREE OF THE ABOVE (3)
6.4
- Metal pipes that contain a dry concrete mix (gravel plug) are driven into a drilled hole in the ground. ✔
- The pipe is held firmly in position while a drop hammer is used to drive the pre-filled dry concrete mix (gravel plug) out of the pipe to form an extended base (toe) at the bottom of the hole. ✔
- Concrete is now poured into the pipe and compacted, using an internal drop hammer, until the pipe is filled to the top. ✔
- The steel pipe is slowly extracted as the concrete is poured into the pipe.
ANY THREE OF THE ABOVE (3)
6.5
6.5.1 Hollow-core concrete block/Concrete block/Block ✔ (1)
6.5.2
- Used for the placement of the conduit pipes. ✔
- Serves as insulation.
- Reduce the weight.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
6.5.3 Reinforced ribs/Ribs/Pre-stressed concrete ribs ✔ (1)
6.5.4
- Ribs (pre-stressed reinforced ribs) ✔
- Hollow-core blocks (polystyrene blocks can also be used) ✔
- Steel mat/Mesh/Steel/Reinforcement ✔
- In-situ cast concrete/Concrete
- Spacers
ANY THREE OF THE ABOVE (3)
6.5.5 After the installation of a rib-and-block floor:
- Ensure that the correct curing procedure is followed for 7 days to ensure a well-set slab. ✔
- allow 28 days for setting of the concrete slab.
- temporary props can be removed after the concrete slab has reached a crushing strength of 17 MPa.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
6.5.6
- Because the units are precast, mechanical handling is required on site. ✔
- The placing of the blocks between the ribs requires manual labour. ✔ (2)
6.6
ANSWER SHEET 6.6
A | B | C | D |
Skirting: Inside length of building | |||
= 8 000 mm – 440 mm ✓ OR – 2(220) | |||
= 7 560 mm ✓ (2) | |||
Skirting: Inside width of the building | |||
= 5 000 mm – 440 mm ✓ OR – 2(220) | |||
= 4 560 mm ✓ (2) | |||
Total length = 7 560 + 4 560 x 2 | |||
=12,12 x 2 | |||
= 24,24 ✓ meter skirting needed – 0,900 m for the door. | |||
= 23,34 m ✓ (2) | |||
1/ | 7,56 ✓ | Screed: Inside area of building | |
4,56 ✓ | |||
0,025 ✓ | 0,86 m³ ✓ | = 0,86 m³ screed is needed (4) |
(10) [40]
TOTAL: 200
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY: CONSTRUCTION GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY: CONSTRUCTION
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2018
REQUIREMENTS:
- Drawing instruments
- A non-programmable calculator
- ANSWER BOOK
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Answer each question as a whole. Do NOT separate subsections of questions.
- Start the answer to EACH question on a NEW page.
- Do NOT write in the margins of the ANSWER BOOK.
- You may use sketches to illustrate your answers.
- Write ALL calculations and answers in the ANSWER BOOK or on the attached ANSWER SHEETS.
- Use the mark allocation as a guide to the length of your answers.
- Make drawings and sketches in pencil, fully dimensioned and neatly finished off with descriptive titles and notes to conform to the SANS/SABS Code of Practice for Building Drawings.
- For the purpose of this question paper, the size of a brick should be taken as 220 mm x 110 mm x 75 mm.
- Use your own discretion where dimensions and/or details have been omitted.
- Answer QUESTIONS 2, 3.7, 4.3, 5.2, 5.4, 6.2 and 6.6 on the attached ANSWER SHEETS using drawing instruments, where necessary.
- Write your CENTRE NUMBER and EXAMINATION NUMBER on every ANSWER SHEET and hand them in with your ANSWER BOOK, whether you have used them or not.
- Drawings in the question paper are NOT to scale due to electronic transfer.
- Google Images was used as the source for all photographs and pictures.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: OHSA, MATERIALS, TOOLS, EQUIPMENT AND JOINING (GENERIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
1.1 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–G) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.6 H.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.1.1 Sole plate |
(5 x 1) (5) |
1.2 Describe TWO safety precautions that must be adhered to when working on a scaffold. (2)
1.3 What is the purpose of the guard rail of a scaffold in terms of safety? (2)
1.4 Explain the purpose of painting. (2)
1.5 Describe ONE advantage of the curing process of concrete. (1)
1.6 FIGURE 1.6 below shows a tool that is used in the building construction industry. 
FIGURE 1.6
1.6.1 Identify tool A. (1)
1.6.2 Explain TWO uses of tool A. (2)
1.6.3 Explain why the batteries should be removed from the tool if the tool is not going to be used for a long time. (1)
1.7 FIGURE 1.7 below shows joining fixtures that are used on building sites and in workshops. 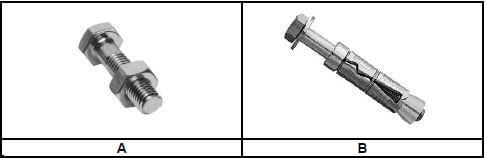
FIGURE 1.7
1.7.1 Identify fastener A and fastener B. (2)
1.7.2 Explain ONE use of fastener A and fastener B respectively. (2) [20]
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS AS METHOD OF COMMUNICATION (GENERIC)
FIGURE 2 on the next page shows different drawings that appear on a building plan. Analyse the drawings and complete the table on ANSWER SHEET 2.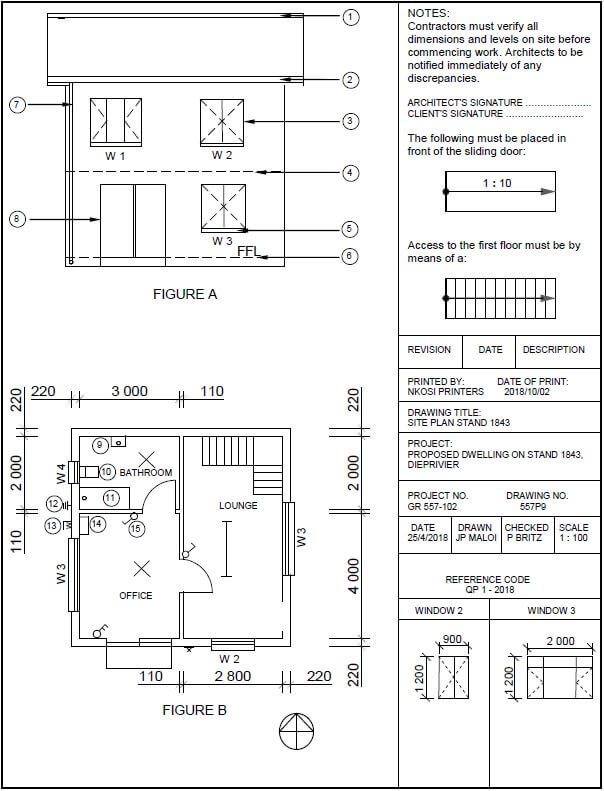
FIGURE 2 [40]
QUESTION 3: ROOFS, STAIRCASES AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 What is the minimum pitch of a roof when class A corrugated iron sheeting are used to cover a roof? (1)
3.2 State the maximum distance for the spacing between roof trusses for corrugated iron roof sheeting. (1)
3.3 Differentiate between the timber used to fix a roof tile and roof sheeting by means of neat freehand drawings of EACH in your ANSWER BOOK. Print the correct name under each drawing. (2)
3.4 What are the measurements of a purlin for corrugated iron roof sheeting? (1)
3.5 Differentiate between the spacing of roof trusses for clay tiles and roof trusses for fibre-cement tiles. Copy the table below in your ANSWER BOOK. (2)
CLAY ROOF TILES | FIBRE-CEMENT TILES |
3.6 FIGURE 3.6 below shows a vertical cross section of a part of the construction at the ridge of a roof truss. Identify parts A–D. 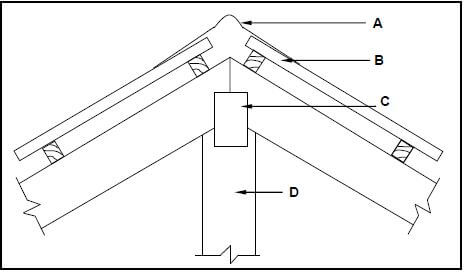
FIGURE 3.6 (4)
3.7 Use ANSWER SHEET 3.7 and draw, in good proportion, a neat sketch of a collar tie roof truss with a pitch of 45° resting on two supporting walls.
Show the following on your drawing:
- Walls
- Wall plates
- Rafters
- Collar beam/Collar tie
- Ridge beam (8)
3.8 Give ONE word/term for EACH of the following descriptions by choosing a word/term from the list below. Write only the word/term next to the question numbers (3.8.1 to 3.8.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 3.8.6 Riser.
run; landing; nosing; going/tread; apron; riser; pitch line; baluster; handrail; stairwell |
3.8.1 The vertical distance between two consecutive treads (1)
3.8.2 Vertical posts that hold up the handrail (1)
3.8.3 The flat, horizontal surface of a step on which one walks when descending or ascending a stair case (1)
3.8.4 The top horizontal area on top of a staircase (1)
3 8.5 The horizontal distance covered by the stairs (1)
3.9 Draw a neat sketch, in good proportion, of a square and round profile that can be used for handrails in your ANSWER BOOK. (2)
3.10 Explain ONE method of mounting handrails onto a wall. (1)
3.11 Describe TWO methods of securing a wall plate to a brick wall. (2)
3.12 Steel sections can be joined to a concrete base by means of a base plate and steel pin connection. Explain the purpose of the pin in this joining method. (1) [30]
QUESTION 4: EXCAVATIONS, FORMWORK, TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT AND MATERIALS (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–G) next to the question numbers (4.1.1 to 4.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 4.1.6 H.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
4.1.1 Excavations |
(5 x 1) (5) |
4.2 Excavation of loose soil is necessary on a building site to reach a firmer soil base.
4.2.1 Explain THREE safety factors that should be considered after excavations have been completed. (3)
4.2.2 Describe THREE tasks that must be performed after the site inspection in order to prepare the site. (3)
4.3 FIGURE 4.3 on ANSWER SHEET 4.3 shows a trench that has been excavated.
Use ANSWER SHEET 4.3 and draw a neat sectional drawing, in good proportion, of the shuttering for firm soil.
Show the following on your drawing:
- Folding wedges
- Walling boards
- Poling boards
- Struts
- Any TWO labels (8)
4.4 Describe ONE property of good formwork. (1)
4.5 FIGURE 4.5 below shows formwork in the construction process. Study the drawing and answer the questions that follow. 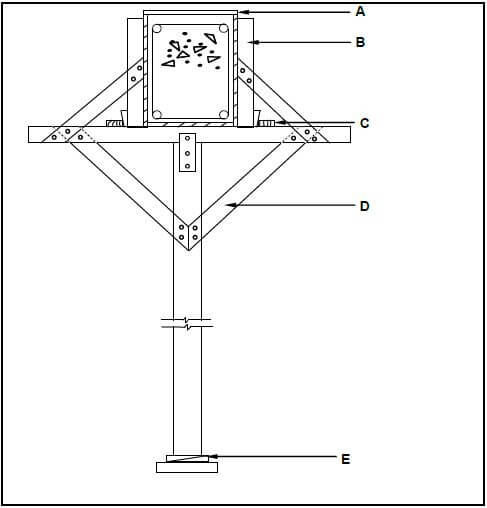
FIGURE 4.5
4.5.1 Identify the type of formwork in FIGURE 4.5. (1)
4.5.2 Name A to D. (4)
4.5.3 Justify the use of E. (1)
4.6 State TWO properties of steel shuttering. (2)
4.7 FIGURE 4.7 below shows a construction machine that is used on a building site.
Study FIGURE 4.7 and answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 4.7
4.7.1 Describe TWO safety precautions that must be adhered to when using the machine in FIGURE 4.7. (2)
4.7.2 Explain, in your own words, how you will take care of this construction machine. (2)
4.8 FIGURE 4.8 below shows a machine that is used on a building site. State TWO ways in which you will take care of this machine. 
FIGURE 4.8 (2)
4.9 Describe TWO disadvantages of ready-mixed concrete. (2)
4.10 Explain TWO purposes of the slump test. (2)
4.11 Name TWO different types of methods that can be used for the curing of concrete. (2) [40]
QUESTION 5: PLASTER AND SCREED, BRICKWORK AND GRAPHICS AS MEANS OF COMMUNICATION (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
5.1 FIGURE 5.1 below shows a worker plastering a wall. Study the drawing and answer the questions that follow. 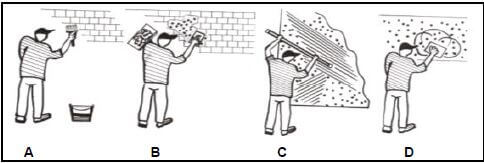
FIGURE 5.1
5.1.1 Describe the processes that take place from A to D. (4)
5.1.2 What type of tool is used in C? (1)
5.2 ANSWER SHEET 5.2 shows the outlines of the front and side views of a cavity wall. Use ANSWER SHEET 5.2 as a guide and draw FOUR courses of the external view of the cavity wall showing the front and left views. (6)
5.3 FIGURE 5.3 below shows TWO different paving patterns. Study the photographs and answer the questions that follow. 
FIGURE 5.3
5.3.1 Name paving patterns A and B. (2)
5.3.2 State ONE paving method that is commonly used. (1)
5.3.3 Describe the term jointing when laying paving bricks. (1)
5.4 Use ANSWER SHEET 5.4 and draw to a scale of 1 : 10 a detailed vertical section through the foot of a roof truss showing open eaves.
Show the following on your drawing:
- Wall: 220 mm wide, face brick
- Wall plate: 114 mm x 38 mm
- Tie beam: 114 mm x 38 mm
- Rafter: 114 mm x 38 mm
- Eaves overhang: 400 mm
- Purlins: 76 mm x 50 mm
- Corrugated iron roof covering
- Fascia board: 230 mm x 38 mm
Print the scale below the drawing.
Print any TWO labels on the drawing. (15) [30]
QUESTION 6: REINFORCEMENT IN CONCRETE, FOUNDATIONS, CONCRETE FLOORS AND QUANTITIES (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
6.1 Various options are given as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (6.1.1 to 6.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 6.1.6 C.
6.1.1 Reinforcement is indicated on a construction drawing according to a code. In the code 9 R 16 01 200, the 200 indicates the …
- diameter of the bar.
- centre-to-centre spacing.
- number of bars in the group.
- bar number. (1)
6.1.2 Which of the following is a force that can act on a structure?
- Tensile force
- Compression force
- Shear force
- All the above-mentioned (1)
6.1.3 During the planning of a rib and block floor, the following need to be considered:
- Straightness of units
- Water absorbing properties of units
- Nature of props
- Cross bracing for sturdiness (1)
6.1.4 Steel tube caisson piles make use of a …
- wet concrete plug.
- casing driven into the ground.
- steel tip.
- precast concrete pile. (1)
6.1.5 Type of soil where precast piling can be used:
- Soft soil
- Firm soil
- Stable soil
- All the above-mentioned (1)
6.2 Use ANSWER SHEET 6.2 and draw a neat sectional view of a square reinforced concrete column in good proportion.
Show the following on your drawing:
- Column
- 8 main bars
- Stirrups/Binders
- Minimum concrete cover
- TWO labels (10)
6.3 State THREE advantages of using pile foundations. (3) 6.4 Explain the method of installing in situ driven piles. (3)
6.5 FIGURE 6.5 below shows material for a floor component. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow. 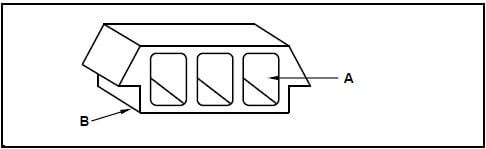
FIGURE 6.5
6.5.1 Identify the part in FIGURE 6.5. (1)
6.5.2 What is the purpose of the hole at A? (1)
6.5.3 Name the part that will fit in at B. (1)
6.5.4 Name THREE materials that are used for this type of floor construction. (3)
6.5.5 State ONE important safety factor that should be adhered to after the installation of this type of floor construction. (1)
6.5.6 Explain TWO disadvantages of this type of floor construction. (2)
6.6 FIGURE 6.6 below shows the floor plan of a storeroom with an opening for a door and a window. 
FIGURE 6.6
SPECIFICATIONS:
- Outside measurements of the storeroom: 8 000 mm x 5 000 mm
- The superstructure is a one-brick wall: 220 mm wide and 2 700 mm high
- Size of the opening for the window: 1 200 mm x 900 mm
- Size of the opening for the door: 2 100 mm x 900 mm
Use ANSWER SHEET 6.6 and calculate the following:
- Total length of the skirting for the store room (ignore the reveals) (6)
- Volume of screed for the floor if the screed is 25 mm thick (4)
Round off your answers to TWO decimal places. [40]
TOTAL: 200
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 2
NO. | QUESTIONS | ANSWERS | MARKS |
1 | Identify FIGURE A. | 1 | |
2 | Identify FIGURE B. | 1 | |
3 | Identify number 4. | 1 | |
4 | Identify number 5. | 1 | |
5 | Identify number 9. | 1 | |
6 | Identify number 10. | 1 | |
7 | Identify number 11. | 1 | |
8 | On what date was the plan printed? | 1 | |
9 | Who drew the building plan? | 1 | |
10 | Name the feature in the column for the notes in FIGURE 2 that must be installed in front of the sliding door. | 1 | |
11 | Name the feature in the column for the notes in FIGURE 2 that must give access to the first floor. | 1 | |
12 | Identify the type of roof that is used for the building in FIGURE A. | 1 | |
13 | Explain the purpose of number 1. | 1 | |
14 | Explain the purpose of number 2. | 1 |
| NO. | QUESTIONS | ANSWERS | MARKS |
15 | Explain the abbreviation FFL at number 6. | 1 | |
16 | Explain the purpose of number 7. | 1 | |
17 | Explain the meaning of the arrow on the feature that must be installed in front of the sliding door. | 1 | |
18 | Explain what is meant by 1 : 10 indicated on the symbol in the notes. | 1 | |
19 | Which room will feature 15 serve? | 1 | |
20 | Explain the short dashed lines on the windows. | 1 | |
21 | Deduce the height of window 2 from the window schedule. | 1 | |
22 | Deduce the width of window 3 from the window schedule. | 1 | |
23 | On what elevation of the building is the bathroom window situated? | 1 | |
24 | Differentiate between component number 3 and component number 8. | 2 | |
25 | Differentiate between the light in the lounge and the light in the bathroom. | 2 | |
26 | Recommend a suitable floor covering for the bathroom. | 1 | |
27 | Recommend an appropriate scale to which FIGURE A should be drawn, according to SANS. | 1 | |
28 | Recommend an alternative sanitary fitment to replace number 11 that will serve a similar purpose. | 1 |
29 | Calculate the internal area of the office in m². Show ALL calculations. | 3 | |
30 | Calculate the perimeter of the building. Show ALL calculations. | 7 | |
TOTAL | 40 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 3.7
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Walls | 2 | |
Wall plates | 2 | |
Rafters | 2 | |
Collar beam/Collar tie | 1 | |
Ridge beam correctly drawn | 1 | |
TOTAL: | 8 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 4.3 
FIGURE 4.3
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Folding wedges | 1 | |
Walling boards | 1 | |
Poling boards | 2 | |
Struts | 1 | |
Shuttering correctly drawn | 1 | |
Any TWO labels | 2 | |
TOTAL: | 8 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 5.2 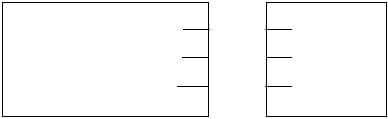
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Full bricks and ½ brick every alternate course on front view | 4 | |
Left view full brick every course | 1 | |
Left view ¼ brick every course | 1 | |
TOTAL: | 6 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 5.4
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Wall: 220 mm wide, face brick | 1 | |
Beam filling | 1 | |
Wall plate: 114 mm x 38 mm | 1 | |
Tie beam: 114 mm x 38 mm | 1 | |
Rafter: 114 mm x 38 mm | 1 | |
Purlins: 76 mm x 50 mm | 2 | |
Corrugated iron roof covering | 1 | |
Fascia board: 230 mm x 38 mm | 1 | |
Any TWO labels | 2 | |
Print the scale below the drawing | 1 | |
Application of scale: | 3 | |
TOTAL: | 15 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 6.2
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Column 500 mm x 500 mm | 2 | |
8 main bars | 2 | |
Binders/Stirrups | 2 | |
Minimum concrete cover | 1 | |
Any TWO labels | 2 | |
Proportion | 1 | |
TOTAL: | 10 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 6.6
A | B | C | D |
Skirting: Inside length of building | |||
__________ - __________ | |||
= (2) | |||
Skirting: Inside width of the building | |||
__________ – __________ | |||
= _________ (2) | |||
Total length = ________ + _________x 2 | |||
= __________ | |||
= __________ - __________ | |||
= __________ metres of skirting needed (2) | |||
Screed: Inside area of building: | |||
1/ | _______ | ||
_______ | |||
_______ | ______ m³ | = _________ (4) | |
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2018
QUESTIONS
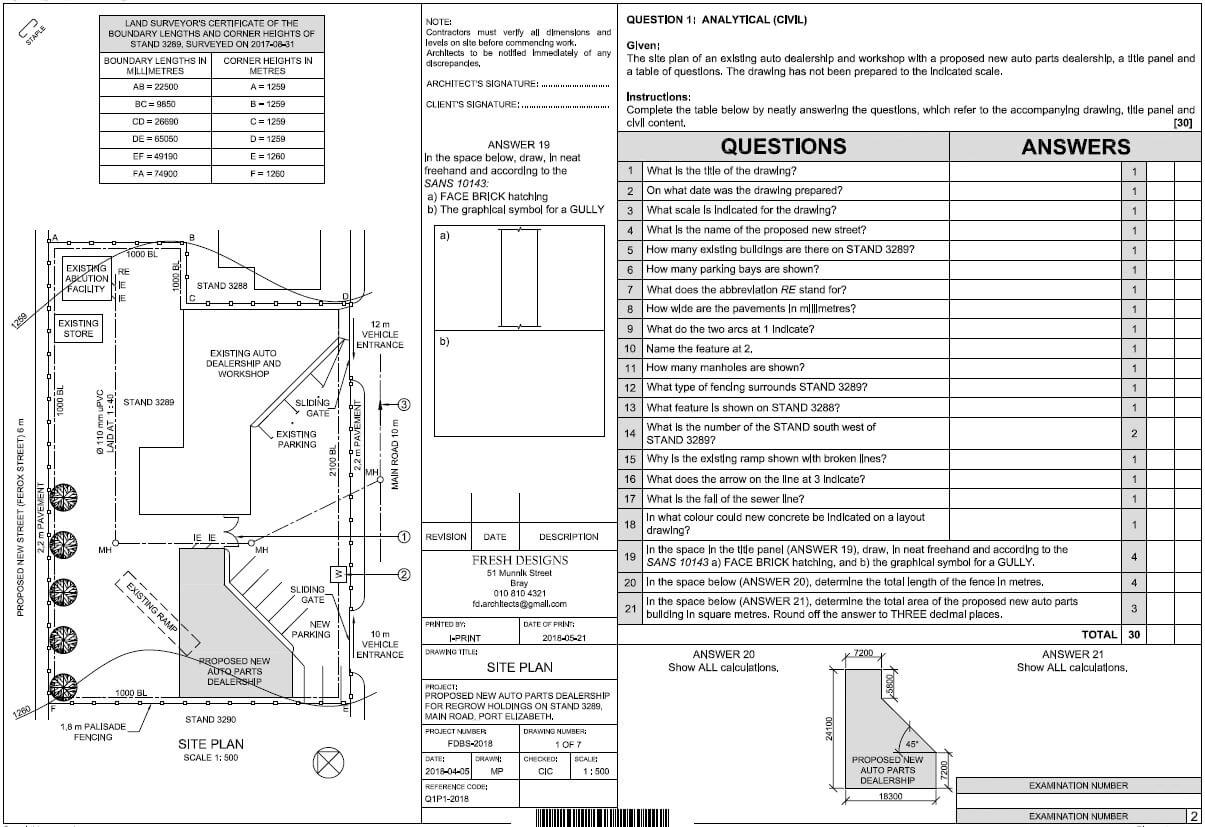
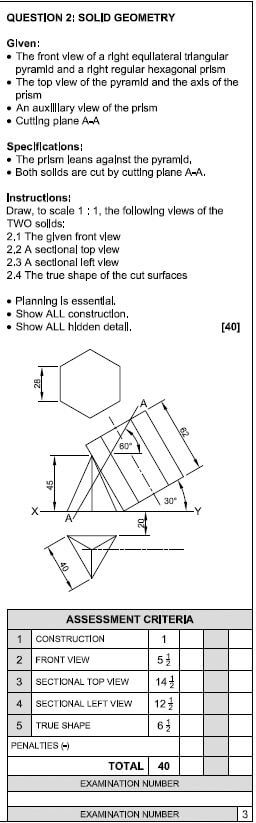
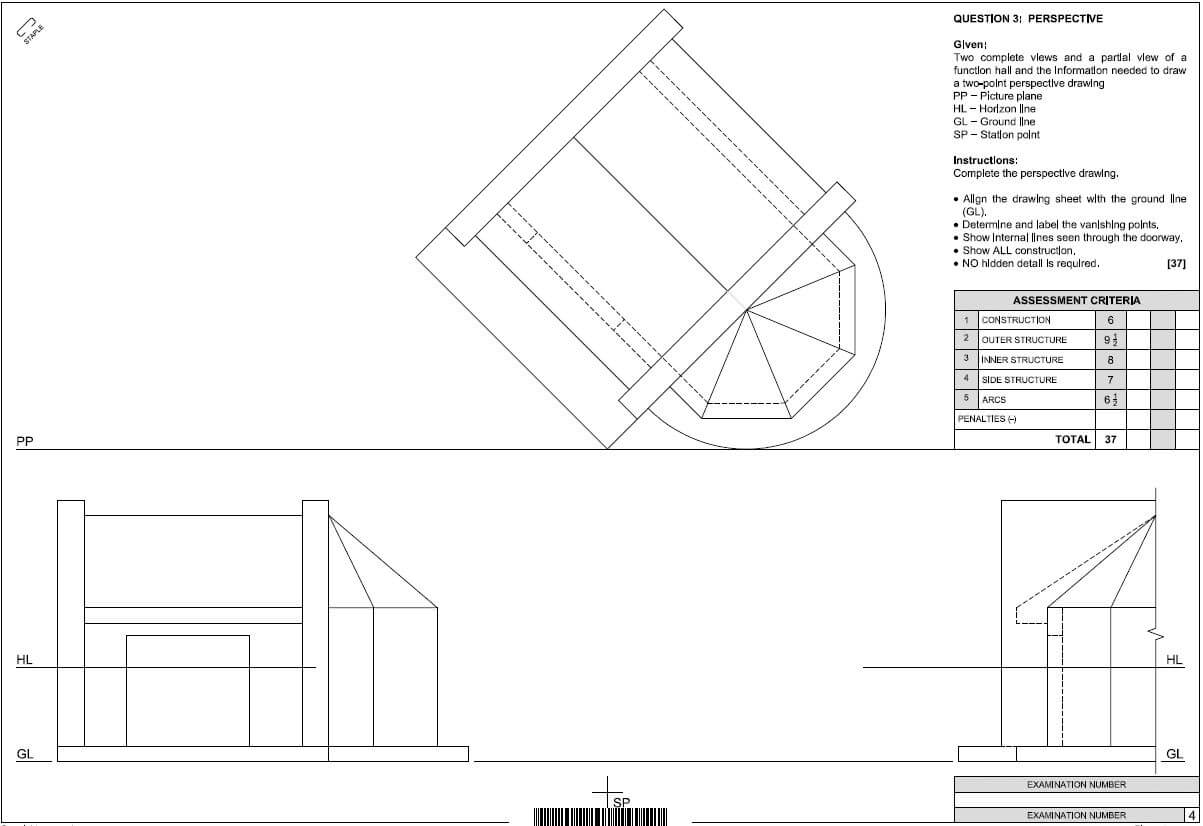
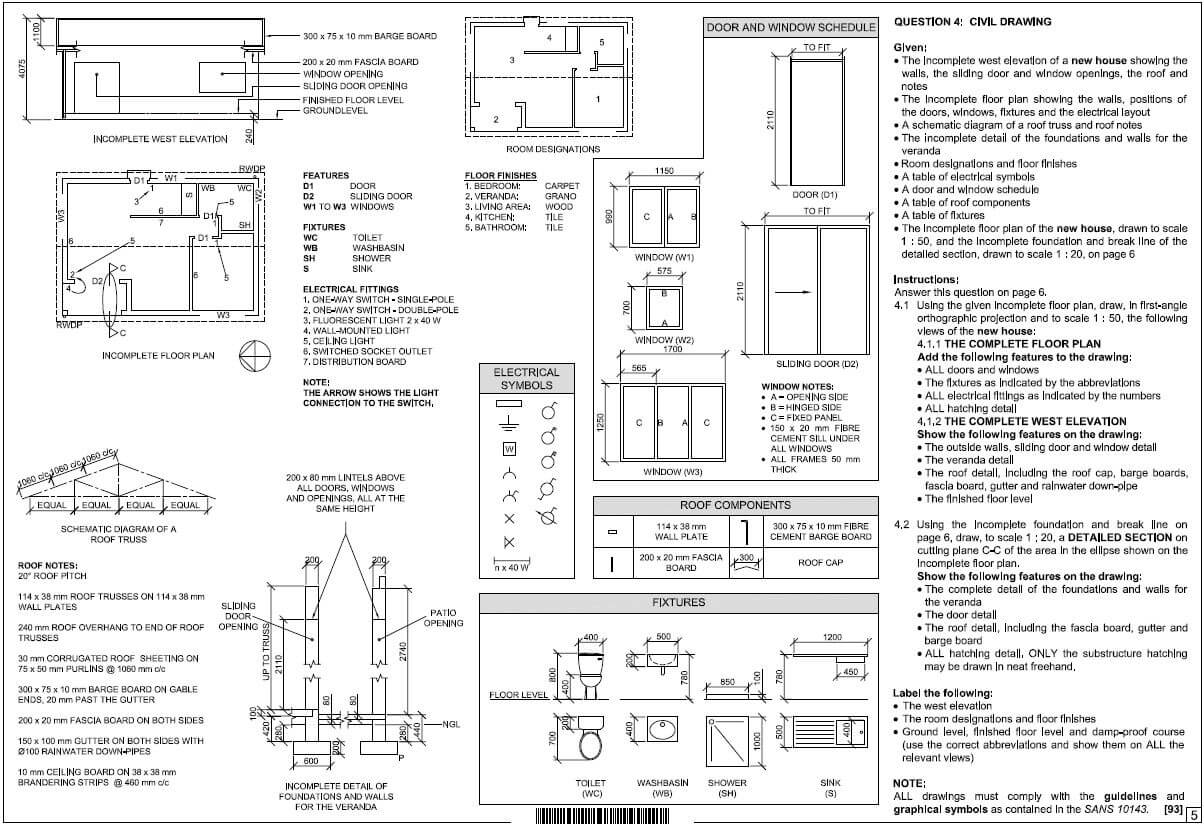
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2018
QUESTIONS





ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2018
MEMORANDUM






ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2018
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMS
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2018