Adele
ENGLISH FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE PAPER 3 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
English First Additional Language
Paper 3 (P3)
Grade 12 (questions)
Nsc Past Papers And Memos
September 2016
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of THREE sections:
SECTION A: Essay (50 marks)
SECTION B: Longer Transactional Text (30 marks)
SECTION C: Shorter Transactional Text (20 marks) - Answer ONE question from EACH section.
- Write in the language in which you are being assessed.
- Start EACH section on a NEW page.
- You must plan (e.g. using a mind map / diagram / flow chart / key words, etc.), edit and proofread your work. The plan must appear BEFORE each text.
- All planning must be clearly indicated as such and handed in. It is advisable to draw a line through all planning.
- You are strongly advised to spend approximately:
- 80 minutes on SECTION A
- 40 minutes on SECTION B
- 30 minutes on SECTION C
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write down the title/heading of your response in each section. 10. The title/heading must NOT be considered when doing a word count. 11. Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A: ESSAY
QUESTION 1
- Write an essay of between 250 and 300 words in length (1 to 1½ pages) on ONE of the following topics.
- Write down the number and title of your essay correctly, for example
1.1 The negative side of South African youth culture - Give your own title if your choice is QUESTION 1.7.1 OR 1.7.2.
- Spend approximately 80 minutes on this section.
1.1 The negative side of South African youth culture [50]
OR
1.2 Living positively in challenging times [50]
OR
1.3 We can escape the cycle of death and disease in South Africa. Do you agree? [50]
OR
1.4 What I imagine the world would be like in 30 years. [50]
OR
1.5 Is the culture of human rights being abused by South Africans? Discuss your views. [50]
OR
1.6 Betrayal (being sold out to an enemy) at the hands of a trusted friend [50]
OR
1.7 Choose ONE of the following pictures and write an essay on a topic that comes to mind. Write the question number (1.7.1 OR 1.7.2) and give your essay a suitable title.
NOTE: There must be a clear link between your essay and the picture you have chosen.
1.7.1  [50]
[50]
[Source: wakanow.files.wordpress.com]
OR
1.7.2  [50]
[50]
[Source: conservationmagazine.org]
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B: LONGER TRANSACTIONAL TEXT
QUESTION 2
- Respond to ONE of the following transactional writing tasks.
- The body of your response should be between 120 and 150 words in length.
- Write down the number and the title of the text you have chosen, for example 2.1 Dialogue
- Pay particular attention to format, language, register and audience. ∙ Spend approximately 40 minutes on this section.
2.1 DIALOGUE
One of your friends is facing disciplinary action for an act of gross disrespect to a teacher and a few other learners.
Write out the dialogue between yourself and your friend in which he/she shows regret for his/her action and is willing to change his/her behaviour.
NOTE: Use the dialogue format. [30] OR
2.2 AGENDA AND MINUTES OF MEETING
An RCL meeting (Representative Council of Learners) was held at your school to discuss the problem of the destruction of property and acts of vandalism to your school buildings and grounds.
Write out the agenda and minutes of the meeting in which the problems were discussed and solutions given. [30]
OR
2.3 OBITUARY
A well-known businessman/woman from your community has passed away after a long illness.
Write an obituary in which you point out how he/she contributed towards your community starting small businesses. You should also pay tribute to him/her. [30]
OR
2.4 FORMAL LETTER
Recently you boarded a bus from Pretoria to your destination. Some of your luggage was damaged and a few items got lost.
Write a letter to the bus company in which you complain about the damage to your luggage and ask for compensation for the loss you have suffered. [30]
TOTAL SECTION B: 30
SECTION C: SHORTER TRANSACTIONAL TEXT
QUESTION 3
- Choose ONE of the following topics and write a short text.
- The body of your response should be between 80 and 100 words in length.
- Write down the number and the title of the text you have chosen, for example: 3.1 Poster
- Spend approximately 30 minutes on this section.
3.1 ADVERTISEMENT
You have the ambition to serve in a leadership role at your school. And with RCL elections (Representative Council of Learners) about to take place you feel your time has come.
Design an advertisement in which you appeal to other learners to vote for you so that you get a chance to show your leadership skills. [20]
OR
3.2 POSTCARD
Recently you went on a short holiday to a coastal city. The holiday was sponsored by a local company that takes keen interest in youth empowerment programmes.
Write out a postcard in which you reflect on your wonderful experiences while on holiday. [20]
OR
3.3 INSTRUCTIONS
South Africa is experiencing severe water shortages at the moment. In about 30 years, disruptions to the water supply we have now could become more serious.
Taking this into consideration, write down seven tips or more on how to save water. [20]
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 100
ENGLISH FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
English First Additional Language
Paper 2 (P2)
Grade 12
Nsc Past Papers And Memos
September 2016
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read these instructions carefully before you begin to answer questions.
- Do NOT attempt to read the entire question paper. Consult the Table of Contents on the next page and mark the numbers of the questions set on texts you have studied this year. Thereafter, read these questions and choose the ones you wish to answer.
- This question paper consists of FOUR sections:
SECTION A: Novel (35)
SECTION B: Drama (35)
SECTION C: Short Stories (35)
SECTION D: Poetry (35) - Answer TWO QUESTIONS in all, ONE question each from ANY TWO sections.
SECTION A: NOVEL
Answer the question on the novel you have studied.
SECTION B: DRAMA
Answer the question on the drama you have studied.
SECTION C: SHORT STORIES
Answer the questions set on BOTH short stories.
SECTION D: POETRY
Answer the questions set on BOTH poems. - Use the checklist on page 4 to assist you.
- Follow the instructions at the beginning of each section carefully.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH section on a NEW page.
- Suggested time management: Spend approximately 60 minutes on each section.
- Write neatly and legibly.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION A: NOVEL
Answer ANY ONE question if you choose from this section.
QUESTION | QUESTION | MARKS | PAGE | |
1. | To kill a Mockingbird | Contextual question | 35 | 5 |
OR | ||||
2. | Lord of the Flies | Contextual question | 35 | 9 |
OR | ||||
3. | A Grain of Wheat | Contextual question | 35 | 13 |
SECTION B: DRAMA
Answer ANY ONE question if you choose from this section.
4. | Romeo and Juliet | Contextual question | 35 | 17 |
OR | ||||
5. | Nothing but the Truth | Contextual question | 35 | 21 |
SECTION C: SHORT STORIES
Answer BOTH questions if you choose from this section.
6.1 | ‘Relatives’ | Contextual question | 17 | 24 |
AND | ||||
6.2 | ‘Manhood’ | Contextual question | 18 | 26 |
SECTION D: POETRY
Answer BOTH questions if you choose from this section.
7.1 | ‘Let me not to the marriage of true minds.’ | Contextual question | 18 | 28 |
AND | ||||
7.2 | ‘Elementary school classroom in the slum’ | Contextual question | 17 | 30 |
CHECKLIST
Use the checklist provided below to assist you to see whether you have answered the required number of questions.
NOTE:
- Answer questions from ANY TWO sections.
- Tick the sections you have answered.
SECTION | QUESTION NUMBERS | NO. OF QUESTIONS TO ANSWER | TICK (✔) |
A: Novel | 1–3 | 1 | |
B: Drama | 4–5 | 1 | |
C: Short Stories | 6 | 1 | |
D: Poetry | 7 | 1 |
NOTE: Ensure that you have answered questions on TWO sections only.
SECTION A: NOVEL
In this section, there are contextual questions on the following novels:
- TO KILL A MOCKINGBIRD by Harper Lee
- LORD OF THE FLIES by William Golding
- A GRAIN OF WHEAT by Ngũgĩ wa Thiong’o
Answer ONE question from this section on the novel you have studied.
QUESTION 1: TO KILL A MOCKINGBIRD
Read BOTH extracts from the novel and answer the questions set on each. The number of marks allocated to each question serves as a guide to the expected length of your answer.
NOTE: Answer questions in your own words unless you are asked to quote. Answer the questions set on BOTH extracts, i.e. QUESTION 1.1 and QUESTION 1.2.
1.1 [The narrator looks back on events.]
| Walter had picked himself up and was standing quietly listening to Jem and me. His fists were half cocked, as if expecting an onslaught from both of us. I stomped at him to chase him away, but Jem put out his hand and stopped me. He examined Walter with an air of speculation. “Your daddy Mr Walter Cunningham from Old Sarum?” he asked, and Walter nodded. Walter looked as if he had been raised on fish food: his eyes, as blue as Dill Harris’s, were red-rimmed and watery. There was no colour in his face except at the tip of his nose, which was moistly pink. He fingered the straps of his overalls, nervously picking at the metal hooks. [Chapter 3] |
1.1.1 What event led to the confrontation between Scout and Walter? (1)
1.1.2 Refer to lines 2–3: ‘… if expecting an onslaught from both of us.’
Why do you think was Walter expecting Jem and Scout to attack him? (2)
1.1.3 Quote FOUR CONSECUTIVE words from lines 2–3 to prove that Walter was expecting them to attack him. (2)
1.1.4 State whether the following statement is TRUE or FALSE. Walter Cunningham’s image speaks of one who has been well nourished.
Write down TWO things from the extract to prove your answer. (2)
1.1.5 Choose the correct answer to complete the following sentence. Write only the answer (A–D).
“Walter’s face brightened, then darkened” because he feared …
- Scout.
- Miss Caroline.
- that he would not fit in.
- Boo Radley. (1)
1.1.6 Who is “Cal” and why would Scout refer her to her as “Our Cal”? (2)
1.1.7 Why are the children both fascinated and terrified of Boo Radley? (4)
1.1.8 Later in the chapter it states that Jem had little fear of Boo Radley when Scout and Walter walked beside him. Why do you think is this? (2)
1.1.9 Explain why Calpurnia speaks differently when at home and when she is working. (2)
AND
1.2
Atticus was feeble: he was nearly fifty. When Jem and I asked him why he was so old, he said he got started late, which we felt reflected upon his abilities and manliness. He was much older than the parents of our school contemporaries, and there was nothing Jem or I could say about him when our classmates said, “My father …” Jem was football crazy. Atticus was never too tired to play keep-away, but when Jem wanted to tackle him Atticus wold say, “I’m too old for that, son.” Our father didn’t do anything. He worked in an office, not in a drugstore. Atticus did not drive a dump-truck for the county, he was not the sheriff, and he did not farm, work in a garage, or do anything that could possibly arouse the admiration of anyone. [Chapter 10] |
1.2.1 Jem and Scout, like many other children, are embarrassed by their father. Write down THREE things about their father that led to their embarrassment. (3)
1.2.2 What, according to the text, can the children use to complete the sentence, “My father …”? Use any two. (2)
1.2.3 Refer to line 14: ‘… left eyes were the tribal curse of the Finches.’ Explain using you OWN WORDS what Atticus meant. (1)
1.2.4 From your knowledge of the rest of the chapter … gave Jem and Scout air-rifles.
Choose the correct option.
- Dill Harris
- Miss Maudie
- Francis Hancock
- Atticus Finch (1)
1.2.5 Complete the following sentence by filling in the missing word. Write down ONLY the number and the word of your choice.
Although Atticus preferred the children to shoot at tin cans, he gave them permission to shoot … (1)
1.2.6 Is the following statement TRUE or FALSE?
Write ‘True’ or ‘False’ and give a reason for your answer.
Atticus is the best checker-player in his town. (1)
1.2.7 Give the two reasons why Miss Maudie agrees with Atticus that it is a sin to kill a mockingbird. (2)
1.2.8 Just after this incident in the extract, something happened that changed the children’s attitude from being embarrassed to being very proud of their father.
Briefly relate what happened. (4)
1.2.9 Do you think Jem was right in not allowing Scout to tell everyone at school about Atticus? (2)
[35]
OR
QUESTION 2: LORD OF THE FLIES
Read the following extracts from the novel and answer the questions set on each. The number of marks allocated to each question serves as a guide to the expected length of your answer.
NOTE: Answer questions in your own words unless you are asked to quote. Answer the questions set on BOTH extracts, i.e. QUESTION 2.1 and QUESTION 2.2.
2.1 [The Lord of the Flies taunts Simon.]
By the time Ralph finished blowing the conch the platform was crowded. There were differences between this meeting and the one held in the morning. The afternoon sun slanted in from the other side of the platform and most of the children, feeling too late the smart of sunburn, had put their clothes on. The choir, less of a 5 group, had discarded their cloaks. Ralph sat on a fallen trunk, his left side to the sun. On his right were most of the choir; on his left the larger boys who had not known each other before the evacuation; before him small children squatted in the grass. 10 Silence now. Ralph lifted the cream and pink shell to his knees and a sudden breeze scattered light over the platform. He was uncertain whether to stand up or remain sitting. He looked sideways to his left, toward the bathing pool. Piggy was sitting 15 near but giving no help. Ralph cleared his throat. “Well then.” All at once he found he could talk fluently and explain what he had to say .He passed a hand through his fair hair and spoke. “We’re on an island. We’ve been on the mountain top and seen water all 20 round. We saw no houses, no smoke, no footprints, no boats, no people. We’re on an uninhabited island with no other people on it.” [Chapter 2] |
2.1.1 Refer to lines 2–3: ‘There were differences between this meeting and the one held in the morning.’
What were these differences? (2 + 2) (4)
2.1.2 Do you think Ralph was confident to speak to the boys? Quote a line from the text to prove your answer. (2)
2.1.3 Each of the characters in the novel play a vital role to create the success of the mood of the story. Choose the portrayal from COLUMN B to match the characteristic in COLUMN A. Write down only the letter (A–E) next to the question number (2.1.3(a)–2.1.3(d)).
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
(a) Ralph | A He becomes the leader of the hunters but longs for total power (4) |
2.1.4 Refer to lines 20–21: ‘We’ve been on the mountain top and seen water all round.’
- Later in the story Ralph commented that they had everything that they could want. Name TWO of these important elements. (2)
- What important things were not on the list? Name any TWO. (2)
2.1.5 At the announcement about making the fire, Ralph charged off with the rest of the boys. What does this action reveal about him? (2)
2.1.6 Refer to lines 3–4: ‘The afternoon sun slanted in from the other side of the platform’.
Identify the figure of speech in this line. (1)
2.1.7 What did the boys use to start the fire on the mountaintop? (1)
AND
2.2 [There is confrontation between Ralph and Jack.]
“Henry was a bit of a leader this afternoon, because the other two were Percival and Johnny, the smallest boys on the island. Percival was mouse-coloured and had not been very attractive even to his mother; Johnny was well built, with fair hair and a natural belligerence. Just now he was being obedient because he 5 was interested; and the three children, kneeling in the sand, were at peace. Roger and Maurice came out of the forest. They were relieved from duty at the fire and had come down for a swim. Roger led the way straight through the castles, kicking them over, burying the flowers, scattering the chosen stones. Maurice 10 followed, laughing, and added to the destruction. The three littluns paused in their game and looked up. As it happened, the particular marks in which they were interested had not been touched, so they made no protest. Only Percival began to whimper with an eyeful of sand and Maurice hurried away. In his 15 other life Maurice had received chastisement for filling a younger eye with sand. Now, though there was no parent to let fall a heavy hand, Maurice still felt the unease of wrongdoing. At the back of his mind formed the uncertain outlines of an excuse. He muttered something about a swim and broke into a trot. Roger remained, 20 watching the littluns. |
2.2.1 Refer to lines 4–5: ‘Johnny was well built, with fair hair and a natural belligerence.’
Choose the correct synonym to replace the underlined word in the above sentence. Write only the answer (A–D).
- happiness.
- violence
- hunger
- fatigue. (1)
2.2.2 Refer to lines 3–4: ‘Percival was mouse-coloured and had not been very attractive even to his mother; …’.
- Explain why you think this would be the most insulting thing to say to someone. (1)
- What does the above sentence disclose about Percival? (1)
2.2.3 In lines 11 and 21 they are referred to as ‘littluns’.
Briefly describe who they are and why the name is used for them. (3)
2.2.4 Is the following statement TRUE or FALSE? Write ‘True’ or ‘False’ and give a reason for your answer.
The little boys protested when Roger and Maurice destroyed the castles. Quote FOUR CONSECUTIVE words to substantiate your answer. (2)
2.2.5 Why do you think was the reason for Percival to be “peaked, re-eyed and miserable” as it is stated further in the story? State THREE points. (3)
2.2.6 If you were in Roger’s position, what would you have done differently? Discuss your view. (4)
2.2.7 Replace ‘the unease of wrongdoing’ with a single suitable word. (1)
2.2.8 From your knowledge of the rest of the extract, who was referred to as the person with ‘china-blue eyes’? (1)
[35]
OR
QUESTION 3: A GRAIN OF WHEAT
Read the following extracts from the novel and answer the questions set on each. The number of marks allocated to each question serves as a guide to the expected length of your answer.
NOTE: Answer questions in your own words unless you are asked to quote. Answer the questions set on BOTH extracts, i.e. QUESTION 3.1 and QUESTION 3.2.
3.1 [Karanja’s visit to the Thompson’s house.]
| Margery came back with two cups of coffee. “Do you take sugar in your coffee?” “No,” he said automatically, and knew, at the same time, he lacked the courage to ask her about the rumours. Karanja loathed tea or coffee without lots of sugar. Margery sat opposite Karanja and crossed her legs. She put 5 her cup on the arm of the chair. Karanja held his in both hands afraid of spilling a drop on the carpet. He winced every time he brought the cup near his lips and nostrils. “How many wives have you?” she asked. This was her favourite question to Africans; it began the day she discovered her latest cook had 10 three wives. Karanja started as if Margery had tickled a wound that had only healed at the surface. Mumbi. [Chapter 4] |
3.1.1 From your knowledge of the novel, why would Karanja wish others would see him having coffee with Margery? (1)
3.1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches a name in COLUMN A. Write down only the letter (A–E) next to the question number (3.1.2(a) – 3.1.2(d)) in the ANSWER BOOK.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
(a) Mugo | A John Thompson’s wife (4 x 1) (4) |
3.1.3 Refer to lines 13–14: ‘I thought you people – Are you going to buy a wife?’
Briefly account for the words “you people” as it is used by Margery in the extract. (3)
3.1.4 Karanja is appointed as the personal messenger to John Thompson and Mrs Dickens.
- In your opinion, why do you think he resents his job? (1)
- Why do you think he endures it? (1)
3.1.5 Refer to line 3: What rumour is this that Karanja would like to ask Margery about? (1)
3.1.6 Using your knowledge of the chapter, read the following statement and then decide if it is TRUE or FALSE. Give reasons for your response.
John Thompson is confident that the Kenyans will be able to run the research station after independence. (2)
3.1.7 Refer to lines 11–12: ‘Karanja started as if Margery had tickled a wound that had only healed at the surface.’
- How does it feel if a wound is tickled at the surface? (1)
- Why did Karanja start speaking as if Margery, ‘had tickled a wound that had only healed at the surface’? (2)
- Is the statement meant literally or figuratively? (1)
3.1.8 Refer to lines 7–8: ‘He winced every time he brought the cup near his lips and nostrils.’
Choose the correct answer to complete the sentence.
To ‘wince’ means to …
- fear.
- smile.
- cringe.
- frown. (1)
AND
3.2 [Gikonyo visits Mugo.]
“No. It is not that which brought me here tonight.” He told Mugo about his visit to Nairobi and his meeting with the MP Mugo, who sat on the bed opposite Gikonyo, waited for him to continue. The fire contained in the hearth place by three stones glowed between 5 them. [Chapter 6] |
3.2.1 Refer to line 2: What does the abbreviation MP stand for? (1)
3.2.2 Complete the following sentence by filling in the correct words. Gikonyo became a successful businessman both as a (a) … and (b) a … . (2)
3.2.3 How does Gikonyo’s personality contrast to that of the MP? (2)
3.2.4 Refer to line 1: ‘No. It is not that which brought me here tonight.’
- What did Mugo think was the reason for Gikonyo’s visit? (1)
- What was the factual reason for his visit? (2)
3.2.5 Refer to lines 6–7: ‘It is my troubles, troubles of the heart.’
Account for the repetition of the word ‘troubles’ in the sentence. (1)
3.2.6 Name TWO things, mentioned in the text, that are tantamount to concentration (detention) camps. (2)
3.2.7 Is the following statement TRUE or FALSE? Write ‘True’ or ‘False’ and give a reason for your answer.
Mugo was excited about his speech on Independence Day, therefore, to avoid seeing anyone in Thabai, Mugo walks to Nairobi. (2)
3.2.8 Did Mugo eventually speak at the Independence Day celebrations? Why/Why not?
Give TWO reasons for your answer. (2)
3.2.9 From your knowledge of the novel, what does the forest symbolise to the freedom fighters? (1)
3.2.10 Quote ONE word from the text that tells us that although Mugo was somewhat reassured, he was still unconvinced.(1) [35]
TOTAL SECTION A: 35
SECTION B: DRAMA
In this section, there are contextual questions on the following plays:
- ROMEO AND JULIET by William Shakespeare
- NOTHING BUT THE TRUTH by John Kani
Answer ONE question from this section on the play you have studied. QUESTION 4
ROMEO AND JULIET
Read the following extracts from the play and answer the questions set on each. The number of marks allocated to each question serves as a guide to the expected length of your answer.
NOTE: Answer questions in your own words unless you are asked to quote. Answer the questions set on BOTH extracts, i.e. QUESTION 4.1 and QUESTION 4.2.
4.1 [(Act 2, Scene 2) The balcony scene allows Juliet and Romeo to come to grips with the essential problem with which they are faced.]
JULIET ROMEO JULIET ROMEO JULIET ROMEO [Act 2, Scene 2] |
4.1.1 Refer to line 1:
'Tis but thy name that is my enemy’
What does Juliet mean by saying this? (1)
4.1.2 Refer to line 3:
‘What’s Montague? What’s in a name?’
Explain in your own words Juliet’s reasoning in these quotes. (2)
4.1.3 Was the invasion of Romeo in Juliet’s soliloquy impolite? Give a reason for your answer. (2)
4.1.4 Refer to the setting of Juliet’s speech.
Choose the correct answer to complete the following sentence. Write only the answer (A–D).
The garden setting invokes the images of the garden of Eden which symbolises …
- purity and virginity.
- evil and dishonesty.
- disobedience.
- a soliloquy. (1)
4.1.5 Refer to lines 10–12:
‘Romeo, doff thy name,
And for that name which is no part of thee
Take all myself’
Rewrite her words in modern English. (3)
4.1.6 Juliet was always a pure example of obedience before she fell in love with Romeo. How did her behaviour change? Name THREE incidents from this scene. (3)
4.1.7 Is the following statement TRUE or FALSE?
Write ‘True’ or ‘False’ and give a reason for your answer.
Juliet asked Romeo to NOT swear at the moon regarding his love for her because she would prefer he wait until dawn and swear on the sun. (2)
4.1.8 After what happened in this scene, some dramatic changes have taken place in both characters. Write down TWO changes that took place in both Romeo and Juliet respectively. (2 + 2) (4)
AND
4.2
LADY CAPULET JULIET LADY CAPULET 5 JULIET [Aside.] LADY CAPULET JULIET LADY CAPULET JULIET LADY CAPULET JULIET [Act 3, Scene 5] |
4.2.1 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches the symbol as used in the extract in COLUMN A. Write down only the letter (A–E) next to the question number (4.2.1(a)–4.2.1(d)).
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
(a) The lark | A They have changed their eyes (4 x 1) (4) |
4.2.2 Where did Romeo and Juliet find themselves before Lady Capulet entered? What was the reason for them being there? (2)
4.2.3 Earlier Juliet denies that day has dawned. State TWO reasons that Romeo gives why he had to leave. (2)
4.2.4 Refer to line 2: ‘Well, girl, thou weep’st not so much for his death’. Give the reason why Juliet was crying and what her mother thought the reason was for Juliet’s weeping. (2)
4.2.5 Refer to lines 20–21: ‘Shall give him such an unaccustom’d dram, That he shall soon keep Tybalt company:’
- What is a ‘dram’? (1)
- How would the villain keep Tybalt company? (1)
4.2.6 Explain briefly how Lady Capulet is ‘fooled’ by Juliet. (3)
4.2.7 Briefly discuss the significance of the use of light and dark imagery in this scene. (2)
[35]
OR
QUESTION 5: NOTHING BUT THE TRUTH
Read the following extracts from the play and answer the questions set on each. The number of marks allocated to each question serves as a guide to the expected length of your answer.
NOTE: Answer questions in your own words unless you are asked to quote. Answer the questions set on BOTH extracts, i.e. QUESTION 5.1 and
QUESTION 5.2.
5.1 [Sipho is preparing to go to the airport. He boils water on the stove, saving some for Thando.]
SIPHO: Typical. Just like him. Always not there to take responsibility. Even when we were kids. It was never his fault. Even when he lost my blazer, it wasn’t his fault. So said my mother. Damn you Themba. All I wanted was a little time. Just for the two of us. There are things that I wanted to talk to you about. There are questions I needed to 5 ask. But no. Themba doesn’t arrive. He is not available. As usual. I am the eldest. I must understand. [Checks the time.] Oh my God. Where is Thando? It’s getting late. [Goes to the telephone and dials.] Hello is that Mr Khahla – it’s me, yes Sipho. No, not yet. I was just reminding you. 10 [THANDO rushes in carrying her briefcase, handbag and books.] THANDO: I am home. I am sorry I’m late. [Act 1,Scene 1] |
5.1.1 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches a name in COLUMN A. Write down only the letter (A–E) next to the question number (5.1.1(a)–5.1.1(d)).
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
(a) Mr Khahla | A A librarian (4 x 1) (4) |
5.1.2 Refer to line 3: ‘… it wasn’t his fault. So said my mother.’
Describe Sipho’s feeling towards Themba and his mother. (2)
5.1.3 Why did Sipho need to remind Mr Khahla to pick him up at home? State THREE points. (3)
5.1.4 Refer to lines 3–4: ‘Damn you Themba.’
Do the above words prove Sipho’s bitterness towards Themba?
Write TRUE or FALSE and substantiate your answer. (2)
5.1.5 Refer to lines 17–18: ‘Hey, any news about the job?’
- What job is Thando referring to? (1)
- Explain in detail why Sipho feels that he deserves to get the job. (2)
- Write down THREE things that might count against him for not being successful in getting the job. (3)
5.1.6 Refer to line 17: ‘Oh Daddy you really spoil me,’ From your knowledge of the rest of the story, why would you say Sipho is spoiling Thando? (1)
5.2 [Thando and Mandisa return to Sipho’s house.]
THANDO: Hello Tata. No sign of him. Anybody home? [Looking into Sipho’s room.] That’s strange he’s always here by now. |
5.2.1 Choose the correct answer to complete the following sentence. Write only the answer (A–D).
Who is Mandisa and what is she doing in South Africa?
Mandisa is …
- Themba’s daughter and brought his remains home.
- Sipho’s daughter who came to claim her inheritance.
- Thando’s assistant at the TRC hearings.
- attending Luvuyo’s funeral. (1)
5.2.2 Refer to lines 14–16: ‘Then make me understand. Pretend I am an idiot. Explain it to me. A man sends a parcel bomb to two women and a child. It blows their guts out and he is not guilty of any crime.’
If you were the director of this play, what would you want Mandisa’s face to express when saying these lines? (2)
5.2.3 Is the following statement TRUE or FALSE? Write ‘True’ or ‘False’ and give a reason for your answer.
Mandisa, being a very outspoken person, was quiet in the car because Sipho was missing. (2)
5.2.4 In line 1 Thando says, “no sign of him”. Where did Thando and Mandisa find him?
In your answer give THREE reasons why Sipho went to this specific place. (1 + 3 x 1) (4)
5.2.5 Discuss TWO differences between Thando and Mandisa. (4)
5.2.6 From your knowledge of the play, discuss:
- Themba’s feelings about South Africa (2)
- The way in which Themba raised Mandisa (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 35
SECTION C: SHORT STORIES
In this section, questions have been set on the following stories:
- RELATIVES by Chris van Wyk
- MANHOOD by John Wain
QUESTION 6
Read the following extracts from the short stories and answer the questions set on each. The number of marks allocated to each question serves as a guide to the expected length of your answer.
NOTE: Answer questions in your own words unless you are asked to quote. Answer the questions set on BOTH extracts, i.e. ‘QUESTION 6.1 and QUESTION 6.2.
6.1 [In the train from Cape Town to Johannesburg.]
| The train from Cape Town – the very same one that had brought me there two weeks before – slid into the station. I bade Uncle Henkie goodbye with a promise that I would feature him prominently and truthfully in my novel. When the train slithered out, I turned to the passengers in the 5 compartment with whom I was going to spend the next sixteen hours or so on the way to Johannesburg. There were three young men, two bearded, two chubby." (If you think I can't count, remember the riddle of the two fathers and two sons who each shot a duck. Only three ducks were shot. Why? Be 10 cause one was a grandfather, the other a father, and the last a son. The man in the middle was both a father and a son, got it?) All youthful and exuberant,” they were drinking beer, straight from the can, and their conversation was full of the hammers and nails of their profession and punctuated with laughter and inane!” arguments. None 15 of them swore and they all flashed smiles at me, accepting me into their midst" with an easy friendliness. |
6.1.1 Match the vocabulary from the story in COLUMN A with the definition in COLUMN B. Write down only the letter (A–E) next to the question number (6.1.1(a)–6.1.4(d)).
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
(a) Mother City | A Great Uncle (4 x 1) (4) |
6.1.2 Refer to paragraph 1. Quote THREE CONSECUTIVE WORDS to prove that Uncle Henkie wants be a main character in the writer’s novel. (2)
6.1.3 Refer to line 5: ‘When the train slithered out …’
- Identify the figure of speech. (1)
- Explain what two things are compared. (2)
6.1.4 Refer to line 23: ‘I gave them a supercilious nod …’
In the context of the story supercilious nod means …
- stupid.
- quiet.
- superior.
- amusing. (1)
6.1.5 Refer to the last line of the text. ‘There were two other passengers in the compartment.’
With your knowledge of the story, compare the tone of the story before the three companions left the train and after they disembarked the train. (4)
6.1.6 How old was the writer at the time? (1)
6.1.7 Briefly explain IN YOUR OWN WORDS the comic ending and anti climax of Georgie’s story. (2)
AND
6.2 MANHOOD – John Wain
[Rob takes a rest.]
| Don’t lie there,’ said his father. You’ll catch cold.’ ‘I’m all right. I’m warm’ ‘Come and sit on this’. When you’re overheated, that’s just when you’re likely to catch-‘ ‘I’m all RIGHT, Dad. I want to lie here. My back aches.’ ‘Your back needs strengthening. That’s why it aches. It’s a pity we don’t live near 5 a river where you could do some rowing.’ The boy did not answer, and Mr Willison, aware that he was beginning to sound like a nagging, over anxious parent, allowed himself to be defeated. He stopped suggesting that Rob should come and sit on his jacket. Instead, he waited a moment, then glanced at his watch. 10 ‘Twenty to twelve. We must get going in a minute.’ ‘WHAT? I thought we were going to have a rest.’ ‘Well, we’re having one, aren’t we?’ said Mr Willison reasonably. I’ve got my breath back, so surely you must have.’ My back still aches. I want to lie here a bit.’ ‘Sorry,’ said Mr Willison, getting up and moving over to his bicycle. 15 We’ve got at least twelve miles to do, and lunch is at one.’ ‘Dad why did we have to come so far, if we’ve got to get back for one o’ clock? I know, let’s find a telephone box and ring up Mum and tell her we … ‘Nonsense! There is no reason why two fit men shouldn’t cycle twelve 20 miles in an hour and ten minutes.’ |
6.2.1
- What is the purpose of the father and son cycling? (2)
- Who do you think is more interested in the outcome of this exercise? (1)
- Give a reason for your answer. (1)
6.2.2 Refer to line 4: ‘I’m all RIGHT, Dad.’
Rob’s tone in this line reveal that he is …
- embarrassed.
- frustrated.
- sarcastic.
- bitter. (1)
6.2.3 Refer to line 4: ‘My back aches.’
Does Rob really have a weak back? Give a reason for your answer. (1)
6.2.4 Refer to lines 7–8: ‘… Mr Willison, aware that he was beginning to sound like a nagging, over-anxious parent …’
Write down TWO incidents from the extract that made Mr Willison ‘sound like a nagging, over-anxious parent’. (2)
6.2.5 Is the following statement TRUE or FALSE? Write ’True’ or ‘False’ and give a reason for your answer.
Rob is tired because they have done a million miles.
Give a reason for your answer. (1)
6.2.6 From your knowledge of the story, Rob’s parents did not agree in the upbringing of their son. What blunders did both of them make?
- Mr Willison’s weaknesses. (3)
- Mrs Willison’s weaknesses (3)
6.2.7 From your knowledge of the story, we have come to learn that Mr Willison tried to live his life through his son.
Do you think this is fair? Give a reason for your answer. (1)
6.2.8 If you were a close family member of the Willison’s, what advice would you give Rob and his mother in order to support them? (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION C: 35
SECTION D: POETRY
In this section, questions have been set on the following poems:
- 'Let me not to the marriage of true minds by William Shakespeare.
- ‘Elementary school classroom in the slum by Stephen Spencer.
Answer the questions on BOTH of the prescribed poems set. Read each poem carefully and then answer the questions which follow. The number of marks allocated to each question serves as a guide to the expected length of your answer.
QUESTION 7
7.1 Read the following poem and then answer the questions set on it.
Let me not to the marriage of true minds by William Shakespeare, 1 |
7.1.1 Complete the following sentences by using the words provided in the box below. Write down only the words next to the question numbers (7.1.1 (a) – (c)).
| union; hatred; mentally; friendship; minds; argument |
A marriage means a (a) … and in this sense of true minds. If two people are (b) … united, then nothing should come between their (c) … . (3)
7.1.2 The poet speaks about the stability of true love. Quote from the poem to prove this. (1)
7.1.3 Refer to lines 5–6: ‘It is an ever-fixed mark … shaken’.
The speaker implies that love should be solid. Explain in your own words how this can, in the context of the poem, be possible. (2)
7.1.4 What is a ‘wondering bark’? (1)
7.1.5 Is the following statement TRUE or FALSE? Write ‘True’ or ‘False’ and give a reason for your answer.
The stars were impractical to the captains of these sailing ships. (1)
7.1.6 Refer to lines 9: ‘Love’s not Time’s fool, though rosy lips and cheeks.
- Identify the figure of speech used in this line. (1)
- Explain what the figure of speech conveys to the reader. (2)
7.1.7 Quote TWO LINES from the poem that prove that love indeed will have nothing to do with the aging process. (2)
7.1.8 Summarise the couplet in your own words. (4)
AND
7.2 Read the following poem and then answer them questions set on it.
Elementary school classroom in the slum by Stephen Spencer Far far from gusty waves these children’s faces. On sour cream walls, donations. Shakespeare’s head, Surely, Shakespeare is wicked, and the map a bad example Unless, governor, teacher, inspector, visitor, 25 |
7.2.1 Refer to line 1: ‘Far far from gusty waves these children’s faces’.
- Explain the link between the ‘children’s faces’ and the ‘gusty waves’. (2)
- What is implied by the words, ‘Far far from gusty waves …’? (2)
7.2.2 Choose the correct answer to complete the following sentence. Write only the answer (A–D).
- Refer to line 3: ‘The tall girl with her weighed-down head.’
Tall girls often stoop in attempt to appear …
- friendly.
- shorter.
- difficult.
- sociable. (1)
- How in your choice in QUESTION 7.2.2(a) relevant to this poem? (2)
7.2.3 Refer to line 5: ‘… reciting a father’s gnarled disease’ Comment on the irony in the above line. (2)
7.2.4 Quote a word from stanza 1 to prove that the classroom is badly lit.
Quote only ONE word. (1)
7.2.5 Refer to line 9: ‘On sour cream walls …’
- Would you say that the above is used as a pun? Explain your answer. (1)
- What did the poet achieve by using this pun? (2)
7.2.6 Choose the correct answer to complete the following sentence. Write only the answer (A–D).
- Refer to lines 11–12: ‘Open-handed map / Awarding the world its world’
The world of the slum children is …
- beyond the slums.
- what the map offers.
- limited to what they can see through the windows of the classroom. (1)
- limitless.
7.2.7 Refer to line 20: Quote TWO CONSECUTIVE words that tell us that the poet does not have the slums of London in mind. (1)
7.2.8 Refer to lines 26–27: ‘This map becomes their window and these windows that shut upon their lives like catacombs’.
Identify the figure of speech in this line. (1)
7.2.9 Refer to line 31: ‘the white and green leaves open.’
Explain the contrast between the ‘white and green leaves and why each is ‘opening’. (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION D: 35
GRAND TOTAL: 70
ENGLISH FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
English First Additional Language
Paper 1 (P1)
Grade 12
Nsc Past Papers And Memos
September 2016
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of THREE sections.
SECTION A: Comprehension (30)
SECTION B: Summary (10)
SECTION C: Language (40) - Answer ALL the questions.
- Read ALL the instructions carefully.
- Start EACH section on a NEW page.
- Leave a line between answers.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- For multiple-choice questions, write only the question number and the letter (A–D) of the correct answer.
- Pay special attention to spelling and sentence construction.
- Use the following time frames as a guide:
SECTION A: 50 minutes
SECTION B: 30 minutes
SECTION C: 40 minutes - Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A: COMPREHENSION
QUESTION 1
Read both TEXT A and TEXT B and answer the set questions.
TEXT A
THREADING HISTORY In Ghana, beads are more than adornments. They are symbolic cultural objects that have become custodians of the country’s history and heritage.
[Adapted from Sawubona, June 2014] |
Glossary:* bauxite clay-like substance from which aluminium is obtained
NOTE:
- Answer ALL the questions in your OWN WORDS.
- For one-word answers, write only the question number and the word.
- For multiple-choice questions, write only the question number and the letter (A–D) of the correct answer.
1.1 Quote a SINGLE word from the subheading that has a similar meaning to ‘decorations’. (1)
1.2 What continent is being referred to in paragraph 1? (1)
1.3 Refer to paragraph 2: Why is the parking lot empty? (2)
1.4 What is being sold at these stalls? (1)
1.5 In your OWN words explain how the atmosphere at the markets in Ghana differs from that in Koforudua. (2)
1.6 The phrase ‘bargaining becomes spirited’ (line 11) means bargaining ...
- takes place reverently.
- is done in a lively manner.
- is done in a sombre manner.
- takes place spiritually. (1)
1.7 Discuss the effectiveness of the writer’s use of the simile, ‘even the tiniest one is treated like a diamond’ (line 12–13). (3)
1.8 Mention THREE instances in the Ghanaian culture where beads play an important role. (3)
1.9 Indicate whether the following statement is TRUE or FALSE. Give a reason for your answer.
In West Africa beads serve a dual purpose. (1)
1.10 Why is the title ‘Threading history’ suitable for the passage? (2)
1.11 Why are Bodom beads valued even today? (2)
1.12 Refer to paragraph 9.
Explain why the parking lot can be regarded as one of Africa’s ‘most unlikely heritage sites’. (2)
1.13 After reading the passage, would you consider the exportation of beads to be an advantage or a disadvantage to the people of Ghana? Give a reason for your answer. (3)
TEXT B

1.14 How does the picture depict a vacation atmosphere? State TWO points. (2)
1.15 What message is this advertisement trying to convey? (2)
1.16 Refer to the table:
How much will the cheapest flight cost you? (1)
1.17 What gift is SA Express offering its clients? (1)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B: SUMMARY
QUESTION 2
You have been asked to deliver a speech on how to lose weight.
Read the passage below (TEXT C) and list SEVEN points that you will include in the text of your speech on how to lose weight.
INSTRUCTIONS
- Your summary must be written in point form.
- List SEVEN points in full sentences, using not more than 70 words.
- Number your sentences from 1 to 7.
- Write only ONE point per sentence.
- Use your OWN words as far as possible.
- Indicate the total number of words you have used in brackets at the end of your summary.
TEXT C
HOW TO LOSE WEIGHT Losing weight does not have to mean a complete life overhaul. The difference between being fat and slim is as little as 419 kJ a day. [Adapted from: Discovery, Summer 2012] |
TOTAL SECTION B: 10
SECTION C: LANGUAGE
QUESTION 3: ANALYSING AN ADVERTISEMENT
Study the advertisement (TEXT D) and answer the set questions.
TEXT D
3.1 Who is the target audience? Give a reason for your answer. (2)
3.2 Why do you think the advertiser has included the pictures and signatures of these two cricket legends? Your answer must refer to the pictures and the signatures. (2)
3.3 What is the purpose of including the website address:
www.advancedhair.co.za? (1)
3.4 Choose the correct answer to complete the following sentence. Write down ONLY the question number (3.4) and the letter (A–D) of the correct answer.
‘A complimentary Hair Check’ means that the clinic will ...
- check your hair free of charge.
- charge you to check your hair.
- praise the condition of your hair.
- check your hair for lice. (1)
3.5 Mention the institution where this procedure is done. (1)
3.6 What does the phrase ‘strand-by-strand’ suggest about the time it will take for the hair to regrow? (1)
3.7 In your view, do the pictures in the advertisement support the message of the advertisement? Explain fully. (2) [10]
QUESTION 4: ANALYSING A CARTOON
Read the cartoon (TEXT E) below and answer the set questions.
TEXT E
ZITS 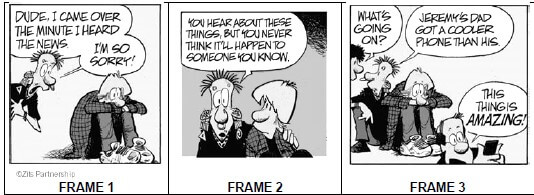
NOTE: In this cartoon, Jeremy’s friends are visiting him. Jeremy’s dad is the man with the cell phone in his hand. |
4.1 Refer to frame 1.
4.1.1 What visual clue does the cartoonist use to show that Jeremy’s friend arrived in a hurry? (1)
4.1.2 What visual technique does the cartoonist use to show that Jeremy is sulking? (1)
4.2 Refer to frame 2.
How do you know that Jeremy’s friend is trying to comfort him? (1)
4.3 Quote an informal word from the cartoon that is often used by teenagers. (1)
4.4 Refer to frame 3.
Jeremy’s dad’s behaviour can cause Jeremy to feel worse because his dad ...
- is silently enjoying his new phone.
- did not greet his friends.
- is aware of his mood.
- expresses how remarkable his phone is. (1)
4.5 Consider the cartoon as a whole. Explain why the statement by Jeremy’s friend in frame 3 can be considered to be an anti-climax. (3)
4.6 Consider the cartoon as a whole. Do you think Jeremy’s behaviour can be justified? Discuss your view. (2) [10]
QUESTION 5: LANGUAGE AND EDITING SKILLS
5.1 Read the passage (TEXT F) below, which has some deliberate errors, and answer the set questions.
TEXT F
CHRIS HONOURED FOR 275 BLOOD DONATIONS
[Adapted from PE Express, 11 November 2015] |
5.1.1 Correct the SINGLE error in each of the following sentences. Write down ONLY the question number (5.1.1(a)–(d)) and the words you have corrected.
- Chris Bester recieved his 275th blood donation milestone award during the Port Elizabeth donor award function. (1)
- The function were held on 4 November. (1)
- During his time at this hospital, he experienced horrific trauma scenes and the challenges of not having excess to sufficient blood. (1)
- A couple of years later, he finally signed in as a blood donor. (1)
5.1.2 Rewrite the following sentence in the singular form:
These scenes made a lasting impression on Chris. (2)
5.1.3 Refer to the following sentence:
As a blood donor, he knew that his blood group was O positive, compatible with all other rhesus positive blood groups.
Provide an antonym for the word compatible by using a prefix. (1)
5.1.4 Rewrite the following sentence in the present continuous tense:
Chris worked in Malawi for two years. (1)
5.1.5 Change the following sentence into a tag question:
There was quite a bit of commotion in the hospital. (1)
5.1.6 Choose the correct answer to complete the following sentence. Write down ONLY the question number (5.1.6) and the letter (A–D) of the correct answer.
He approached the Irish doctor.
The underlined word is an example of ...
- a definite article.
- an indefinite article.
- a preposition.
- an abstract noun. (1)
5.1.7 Rewrite the following sentence in the passive voice:
The doctor arranged a direct transfusion. (1)
5.1.8 Rewrite the following sentence in reported speech:
Chris said, “For me it is about being healthy enough to donate blood.” (3)
5.2 Study the following text (TEXT G) and answer the set questions.
TEXT G
[Adapted from You, 27 August 2015] |
5.2.1 Choose the correct word from those given in brackets. Write ONLY the question number (5.2.1(a)–(b)) and the words.
- Being kind has a positive (affect/effect) on people. (1)
- We should strive to make the world a (best/better) place. (1)
5.2.2 Rewrite each of the following sentences and give the correct form of each word within brackets.
- Some people are (natural) caring but all of us can choose to be compassionate. (1)
- Sometimes compassion can be a (pretend). (1)
- Many countries have produced compassionate people who have become an (exemplary) to humanity. (1)
5.2.3 Rewrite the following sentence, inserting the apostrophe in the correct place.
People who are sincerely kind often choose to be doctors or nurses to make a difference in peoples lives. (1) [20]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 80
PHYSICAL SCIENCES CHEMISTRY PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAM PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2016
Physical Sciences (chemistry)
Paper Two (P2)
Grade 12
Amended Senior Certificate Exam
Past Papers And Memos May/june 2016
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1 A ✓✓ (2)
1.2 B ✓✓ (2)
1.3 B ✓✓ (2)
1.4 C ✓✓ (2)
1.5 B ✓✓ (2)
1.6 D ✓✓ (2)
1.7 C ✓✓ (2)
1.8 B ✓✓ (2)
1.9 A ✓✓ (2)
1.10 C ✓✓ (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1 E ✓ (Accept: methyl propanoate) (1)
2.1.2 C ✓ (Accept: butan-1-ol) (1)
2.1.3 D ✓ (Accept: 2,2-dimethylpropane) (1)
2.2
2.2.1 Pent-2✓-yne✓ OR 2✓-pentyne✓ (2)
Marking criteria for 2.2.1
|
2.2.2 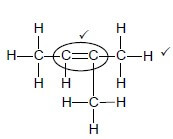 (2)
(2)
Marking criteria for 2.2.2:
|
2.2.3 2-methylbut-1-ene OR 3-methylbut-1-ene
Accept 2-methyl-1-butene (3)
Marking criteria:
|
2.3
2.3.1 Esters ✓ (1)
2.3.2 Sulphuric acid/H2SO4 ✓ (1)
2.3.3 Methyl✓ propanoate ✓ (2)
Marking criteria:
|
[14]
QUESTION 3
3.1 The temperature at which the vapour pressure equals the atmospheric pressure (external pressure). ✓✓ (2 marks or no marks)
3.2
Criteria for conclusion: | |
Dependent and independent variables correctly identified. | ✓ |
Relationship between the independent and dependent variables correctly stated. | ✓ |
Examples:
- Boiling point increases with increase in number of (C) atoms/chain length/ molecular size/molecular mass.
- Boiling point decreases with decrease in number of C atoms/chain length/ molecular size/molecular mass.
- Boiling point is proportional to number of C atoms/chain length/molecular size/molecular mass. (2)
IF:
|
3.3
3.3.1 P ✓ (1)
3.3.2 R ✓ (1)
3.4 ∙
- Between alkane molecules are London forces/dispersion forces/induced dipole forces. ✓
- In addition to London forces and dipole-dipole forces each alcohol molecule has (one site) for hydrogen bonding. ✓
- In addition to London forces and dipole-dipole forces each carboxylic acid molecule has two sites for hydrogen bonding. ✓ (Accept: more sites)
- Intermolecular forces in carboxylic acids are stronger than intermolecular forces in alkanes and alcohols./Intermolecular forces between alkane and alcohol molecules are weaker than intermolecular forces between carboxylic acid molecules.✓
- More energy is needed to overcome/break intermolecular forces in carboxylic acids than in the other two compounds. ✓ (5)
[11]
QUESTION 4
4.1
4.1.1 Addition/Hydrogenation ✓ (1)
4.1.2 Elimination/Dehydrohalogenation/Dehydrobromination ✓ (1)
4.1.3 Substitution/Halogenation/Bromination ✓ (1)
4.2
4.2.1 Pt/Ni/Pd/platinum/nickel/palladium ✓ (1)
4.2.2 H2SO4/H3PO4/sulphuric acid/phosphoric acid ✓ (1)
4.2.3 Hydration ✓ (1)
4.2.4 2✓-bromopropane ✓ (2)
Marking criteria:
|
4.3 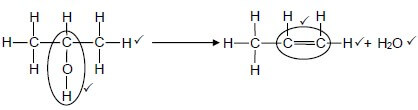 (5)
(5)
| Notes: Whole structure of alkene correct: ✓✓ Only functional group correc: ✓ |
Notes:
|
4.4 ∙
- Higher temperature ✓
- Concentrated base/Base dissolved in ethanol ✓ (2)
[15]
QUESTION 5
5.1 ANY TWO:
- Temperature (of reaction mixture)✓
- (Addition of a) catalyst ✓
- Concentration (of reactants) (2)
5.2 Sulphur/S ✓ (1)
5.3 Water is used to dilute/change the concentration (of the Na2S2O3(aq)) ✓ (1)
5.4
Criteria for investigative question: | |
The dependent and independent variables are stated correctly. | ✓ |
Asks a question about the relationship between dependent and independent variables.. | ✓ |
Dependent variable: rate (of reaction)/(reaction rate)
Independent variable: concentration
Examples:
- What is the relationship between concentration and reaction rate?
- How does the reaction rate change with change in concentration? (2)
5.5 A ✓ (1)
5.6 Experiment B:
- The concentration of Na2S2O3(aq) is higher./More Na2S2O3 particles per unit volume. ✓Accept: higher volume of Na2S2O3(aq) is used
- More particles with correct orientation ✓
- More effective collisions per unit time / Higher frequency of effective collisions. ✓
OR
Experiment D:
- The concentration of Na2S2O3(aq) is lower./Less Na2S2O3 particles per unit volume. ✓
- Less particles with correct orientation.✓
- Less effective collisions per unit time./Lower frequency of effective collisions. ✓ (3)
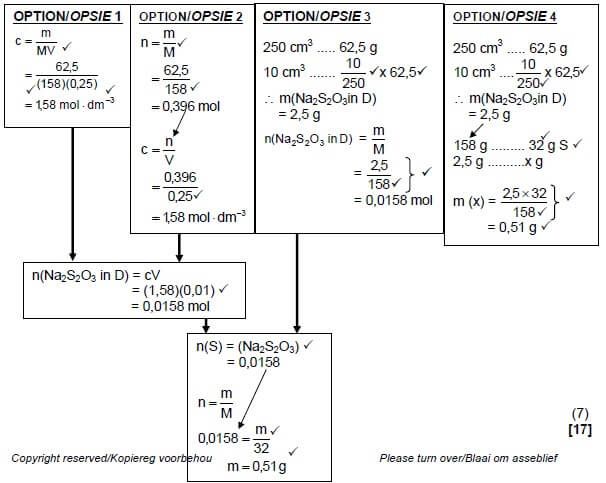
5.7
Marking guidelines for Option 1 and 2:
|
Marking guidelines for Option 3 and 4:
|
QUESTION 6
6.1 Reversible reaction ✓ (1)
6.2 Endothermic ✓ → ∆H is positive./∆H > 0/(Net) energy is absorbed./More energy is absorbed than released/Energy of product > energy of reactant. ✓ (2)
6.3 Larger than ✓ → Kc > 1 ✓ (2)
6.4 (9)
CALCULATIONS USING NUMBER OF MOLES
|
OPTION 1
n = m/M
= 168/28
= 6 mol
CO2 | CO | REMARKS | |
Initial quantity (mol) | x | 0 | |
Change (mol) | 3 | 6 ✓ | ratio ✓ |
Quantity at equilibrium (mol)/ | x – 3 ✓ | 6 | |
Equilibrium concentration (mol·dm-3) | x − 3 | 3 | Divide by 2 ✓ |
Kc = [CO]2
[CO2]✓
14 ✓ = (3)2
x − 3
2
∴x = 4,29 mol ✓
| No KC expression, correct substitution: Max 8/9 |
| Wrong KC expression: 6/9 |
OPTION 2
n = m/M c = n/v
= 168/28 = 6/2 (divide by 2)
= 6 mol = 3 mol.dm-3
CO2 | CO | ||
Initial concentration (mol·dm-3) | x | 0 | |
Change (mol·dm-3) | 1,5 | 3 ✓ | ratio✓ |
Equilibrium concentration (mol·dm-3) | x −1,5 ✓ | 3 |
Kc = [CO]2
[CO2]✓
14 ✓ = (3)2
x −1,5
∴x = 2,14 mol·dm-3
n(CO2) = cV
= (2,14)(2)
= 4,29 mol ✓
| No KC expression, correct substitution: Max 8/9 |
| Wrong KC expression: 6/9 |
OPTION 3
n = m/M
= 168/28
= 6 mol
CO2 | CO | ||
Initial quantity (mol) | 4,28✓ | 0 | |
Change (mol) | 3 | 6 | ratio ✔ |
Quantity at equilibrium (mol)/ | 1,28 ✓ | 6✔ | |
Equilibrium concentration (mol·dm-3) | 0,64 | 3 | multiply by 2 ✔ |
Kc = [CO]2
[CO2]✓
14 ✓ = (3)2
[CO2]✓
∴ [CO2] = 0,64 mol·dm-3
| No KC expression, correct substitution: Max 8/9 |
| Wrong KC expression: 6/9 |
6.5
6.5.1 Remains the same ✓ (1)
6.5.2 Decreases✓ (1)
6.5.3 Increases✓ (1)
[17]
QUESTION 7
7.1
7.1.1 An acid is a proton/ H+ donor. ✓✓ NOTE: not H3O+ (2 or/of 0) (2)
7.1.2 H2O ✓
H2CO3 ✓ (2)
7.1.3 H2O ✓ OR/OF HCO-3 (1)
7.2
7.2.1
 (8)
(8)
Marking guidelines:
|
7.2.2 POSITIVE MARKING FROM QUESTION 7.2.1 (4)
OPTION 1 | OPTION 2 pH + pOH = 14 |
[17]
QUESTION 8
8.1 Electrons are transferred. ✓ OR/OF The oxidation number of Mg/H changes. OR/OF Mg is oxidised / H+ is reduced. (1)
8.2 H+ ions/HCℓ/H+(aq)/HCℓ(aq) ✓ (1)
8.3 Ag is a weaker reducing agent ✓(than H2) and will not be oxidised ✓to Ag+ ✓ OR/OF H2 is a stronger reducing agent ✓ (than Ag) and will be oxidised ✓ to H+.✓ (3)
8.4 Electrode/Conductor of electrons (in hydrogen half-cell) ✓ (1)
8.5
8.5.1 Chemical energy to electrical energy ✓ (1)
8.5.2 Provides path for movement of ions./Completes the circuit./Ensures electrical neutrality in cell. ✓ (1)
8.5.3 2H+ + 2e- → H2 ✓✓ (2)
Notes H2 ← 2H+ + 2e- (0/2 ) 2H+ + 2e ← H2 (0/2 ) |
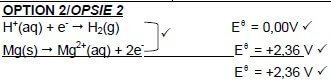
8.5.4 Mg(s) | Mg2+(aq) || H+(aq) | H2(g) | Pt ✓ ✓ ✓ OR/OF Mg(s) | Mg2+(1 mol·dm-3) || H+(1 mol·dm-3) | H2(g) | Pt
Accept
Mg | Mg2+ || H+ | H2 | Pt (3)
8.6 (4)
OPTION 1 | Notes
|
OPTION 2
| |
8.7 Increases✓ (1)
[18]
QUESTION 9
9.1
9.1.1 Electrolyte✓ (1)
9.1.2 Electrolytic (cell) ✓
Electrolysis 0/1 (1)
9.2 A to/na B ✓ (1)
9.3
9.3.1 B ✓(1)
9.3.2 A ✓(1)
9.4 Decreases ✓ Copper (Cu) is oxidised to Cu2+/Oxidation takes place at A/Electrons are lost. ✓
[7]
QUESTION 10
10.1
10.1.1 Air ✓ (1)
10.1.2 Natural gas/methane/oil/coal ✓ (1)
10.1.3 Sulphur/iron pyrite/Iron sulphide ✓ (1)
10.2
10.2.1 Haber ✓ (1)
10.2.2 Ammonia✓ (1)
10.2.3 H2SO4 ✓ (1)
10.2.4 SO3+ H2SO4 ✓→ H2S2O7 ✓ Bal. ✓ (3)
Notes:
|
10.3
10.3.1 %N[NH4NO3] = 28/80 ✓ x 100 = 35%
%N[(NH4)2SO4] = 28/132 ✓ x 100 = 21,21%
Ammonium nitrate (has the highest percentage of nitrogen) ✓ (4)
10.3.2 Ostwald (process) ✓ (1)
[14]
TOTAL: 150
PHYSICAL SCIENCES CHEMISTRY PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAM PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2016
Physical Sciences (Chemistry)
Paper Two (P2)
Grade 12
Amended Senior Certificate Exam
Past Papers And Memos 2016
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your centre number and examination number in the appropriate spaces on the ANSWER BOOK.
- This question paper consists of TEN questions. Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Leave ONE line between two subquestions, for example between QUESTION 2.1 and QUESTION 2.2.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- You may use appropriate mathematical instruments.
- You are advised to use the attached DATA SHEETS.
- Show ALL formulae and substitutions in ALL calculations.
- Round off your final numerical answers to a minimum of TWO decimal places. 11. Give brief motivations, discussions, et cetera where required.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Four options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Each question has only ONE correct answer. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1–1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.11 E.
1.1 A compound with the general formula CnH2n+2 is an ...
- alkane.
- alkene.
- alkyne.
- alcohol. (2)
1.2 Which ONE of the following is a product in ALL neutralisation reactions?
- H+
- H2O
- OH−
- NaCℓ (2)
1.3 Which ONE of the following pairs of products is formed during the catalytic oxidation of ammonia?
- NO2 and H2O
- NO and H2O
- NO and NO2
- H2O and HNO3 (2)
1.4 Consider the following potential energy diagram for a chemical reaction: 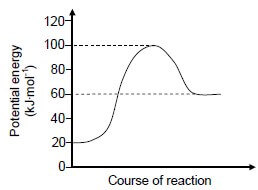
Which ONE of the following shows the values of the total energy change and the activation energy for this reaction? (2)
Energy change (kJ∙mol-1) | Activation energy (kJ∙mol-1) | |
A | 80 | 40 |
B | 60 | 100 |
C | 40 | 80 |
D | – 40 | 80 |
1.5 Which ONE of the following is a functional isomer of butanoic acid? (2) 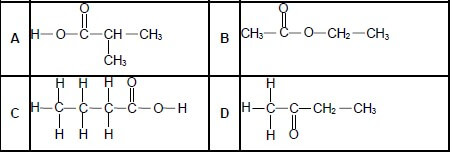
1.6 In the flow diagram below P and Q represent two organic compounds. ![]()
Compound Q is:
- CH2CH2
- CH3CH3
- CH3CH2Br
- CH3CH2OH (2)
1.7 Chromate ions and dichromate ions are in equilibrium with each other in an aqueous solution according to the following balanced equation:
2CrO2-4 (aq) + 2H+ (aq) + ⇌ Cr2O2-7 (aq) + H2O (ℓ)
yellow orange
Which ONE of the following reagents should be added to change the colour of the solution to yellow?
- HNO3
- HCℓ
- NaOH
- CH3COOH (2)
1.8 Which ONE of the following is a NON-SPONTANEOUS redox reaction? Refer to the Table of Standard Reduction Potentials (Table 4A or 4B).
- Zn(s) + 2HCℓ(aq) → ZnCℓ2(aq) + H2(g)
- Cu(s) + FeCℓ2(aq) → CuCℓ2(aq) + Fe(s)
- 2AgNO3(aq) + Cu(s) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
- 2Aℓ(s) + 3Ni(NO3)2(aq) → 2Aℓ(NO3)3(aq) + 3Ni(s) (2)
1.9 In the electrochemical cell below the letters X and Y represent two metal electrodes. 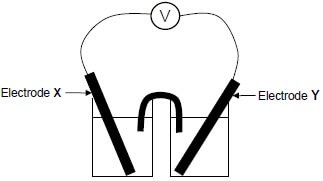
When the cell is functioning, ELECTRODE X GAINS MASS.
Which ONE of the following is the CORRECT cell notation for this cell?
- Y(s) | Y2+(aq) || X+(aq) | X(s)
- X(s) | X+(aq) || Y2+(aq) | Y(s)
- X+(aq) | X(s) || Y(s) | Y2+(aq)
- Y2+(aq) | Y(s) || X(s) | X+(aq) (2)
1.10 Graph Q (the solid line) below was obtained for the reaction of 100 cm3 of a 0,1 mol∙dm-3 HCℓ solution with excess magnesium powder.
Which graph (A, B, C or D) most probably represents the reaction of 100 cm3 of a 0,1 mol∙dm-3 CH3COOH solution with excess magnesium powder? (2)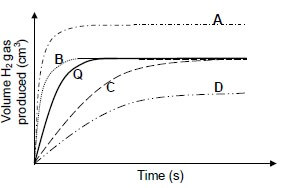
[20]
QUESTION 2 (Start on a new page.)
Consider the organic compounds A to F below. 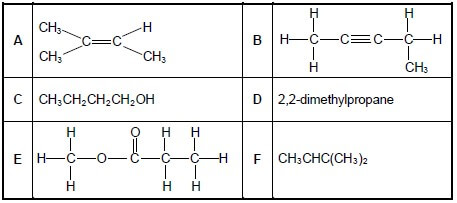
2.1 Write down the LETTER that represents a compound that:
2.1.1 Has a carbonyl group (1)
2.1.2 Is an alcohol (1)
2.1.3 Is a CHAIN ISOMER of CH3(CH2)3CH3 (1)
2.2 Write down the:
2.2.1 IUPAC name of compound B (2)
2.2.2 Structural formula of compound F (2)
2.2.3 IUPAC name of a POSITIONAL isomer of compound A (3)
2.3 Compound E is formed when a carboxylic acid reacts with another organic compound.
Write down the:
2.3.1 Homologous series to which compound E belongs (1)
2.3.2 NAME or FORMULA of the catalyst used for the preparation of compound E (1)
2.3.3 IUPAC name of compound E (2)
[14]
QUESTION 3 (Start on a new page.)
The relationship between boiling point and the number of carbon atoms in straight chain molecules of alkanes, carboxylic acids and alcohols is investigated. Curves P, Q and R are obtained.
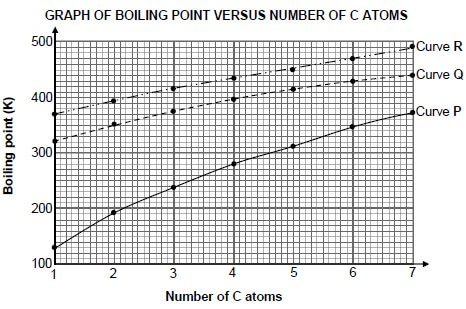 3.1 Define the term boiling point. (2)
3.1 Define the term boiling point. (2)
3.2 For curve P, write down a conclusion that can be drawn from the above results. (2)
3.3 Identify the curve (P, Q or R) that represents each of the following:
3.3.1 Alkanes (1)
3.3.2 Carboxylic acids (1)
3.4 Explain the answer to QUESTION 3.3.2 by referring to the:
- Types of intermolecular forces present in alkanes, carboxylic acids and alcohols
- Relative strengths of these intermolecular forces
- Energy needed (5)
[11]
QUESTION 4 (Start on a new page.)
The flow diagram below shows how prop-1-ene can be used to prepare other organic compounds.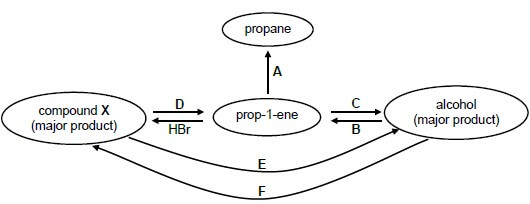 4.1 Write down the type of reaction represented by:
4.1 Write down the type of reaction represented by:
4.1.1 A (1)
4.1.2 D (1)
4.1.3 F (1)
4.2 Write down the:
4.2.1 NAME or FORMULA of the catalyst needed for reaction A (1)
4.2.2 NAME or FORMULA of the inorganic reagent needed for reaction B (1)
4.2.3 Type of addition reaction represented by reaction C (1)
4.2.4 IUPAC name of compound X (2)
4.3 Use structural formulae to write down a balanced equation for reaction B. (5)
4.4 Both reactions D and E take place in the presence of a strong base. State TWO conditions that will favour reaction D over reaction E. (2)
[15]
QUESTION 5 (Start on a new page.)
The reaction between dilute hydrochloric acid and sodium thiosulphate (Na2S2O3) is used to investigate one of the factors that influences reaction rate. The balanced equation for the reaction is:
Na2S2O3(aq) + 2HCℓ(aq) → 2NaCℓ(aq) + S(s) + H2O(ℓ) + SO2(g)
The hydrochloric acid solution is added to the sodium thiosulphate solution in a flask. The flask is placed over a cross drawn on a sheet of white paper, as shown in the diagram below. The time that it takes for the cross to become invisible is measured to determine the reaction rate. 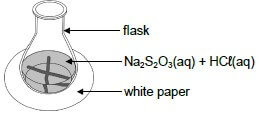 Four experiments, A to D, are conducted during this investigation. The volumes of reactants used in each of the four experiments and the times of the reactions are summarised in the table below.
Four experiments, A to D, are conducted during this investigation. The volumes of reactants used in each of the four experiments and the times of the reactions are summarised in the table below.
Experiment | Volume of Na2S2O3(aq) (cm3) | Volume of H2O(ℓ) (cm3) | Volume of HCℓ(aq) (cm3) | Time (s) |
A | 25 | 0 | 5 | 50,0 |
B | 20 | 5 | 5 | 62,5 |
C | 15 | 10 | 5 | 83,3 |
D | 10 | 15 | 5 | 125,0 |
5.1 State TWO factors that can influence the rate of the reaction above. (2)
5.2 Write down the NAME or FORMULA of the product that causes the cross to become invisible. (1)
5.3 Give a reason why water is added to the reaction mixture in experiments B to D. (1)
5.4 Write down an investigative question for this investigation. (2)
5.5 In which experiment (A, B, C or D) is the reaction rate the highest? (1)
5.6 Use the collision theory to explain the difference in reaction rate between experiments B and D. (3)
5.7 The original Na2S2O3 solution was prepared by dissolving 62,50 g Na2S2O3 crystals in distilled water in a 250 cm3 volumetric flask.
Calculate the mass of sulphur, S, that will form in experiment D if Na2S2O3 is the limiting reactant. (7)
[17]
QUESTION 6 (Start on a new page.)
Carbon dioxide reacts with carbon in a closed system to produce carbon monoxide, CO(g), according to the following balanced equation:
CO2(g) + C(s) ⇌ 2CO(g) ΔH > 0
6.1 What does the double arrow indicate in the equation above? (1)
6.2 Is the above reaction an EXOTHERMIC reaction or an ENDOTHERMIC reaction? Give a reason for the answer. (2)
Initially an unknown amount of carbon dioxide is exposed to hot carbon at 800 °C in a sealed 2 dm3 container. The equilibrium constant, Kc, for the reaction at this temperature is 14.
At equilibrium it is found that 168,00 g carbon monoxide is present.
6.3 How will the equilibrium concentration of the product compare to that of the reactants? Choose from LARGER THAN, SMALLER THAN or EQUAL TO.
Give a reason for the answer. (No calculation is required.) (2)
6.4 Calculate the initial amount (in moles) of CO2(g) present. (9)
6.5 State how EACH of the following will affect the yield of CO(g) at equilibrium. Choose from INCREASES, DECREASES or REMAINS THE SAME.
6.5.1 More carbon is added at constant temperature. (1)
6.5.2 The pressure is increased. (1)
6.5.3 The temperature is increased. (1)
[17]
QUESTION 7 (Start on a new page.)
7.1 Hydrogen carbonate ions react with water according to the following balanced equation:
HCO-3 (aq) + H2O(ℓ) ⇌ H2CO3(aq) + OH −(aq)
7.1.1 Define an acid according to the Lowry-Brønsted theory. (2)
7.1.2 Write down the FORMULAE of the two acids in the equation above. (2)
7.1.3 Write down the formula of a substance in the reaction above that can act as an ampholyte. (1)
7.2 During an experiment 0,50 dm3 of a 0,10 mol∙dm-3 HCℓ solution is added to 0,80 dm3 of a NaHCO3 solution of concentration 0,25 mol∙dm-3. The balanced equation for the reaction is:
NaHCO3(aq) + HCℓ(aq) → NaCℓ(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(ℓ)
Calculate the:
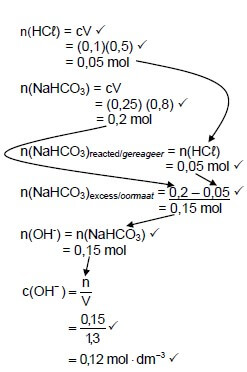
7.2.1 Concentration of the hydroxide ions in the solution on completion of the reaction (8)
7.2.2 pH of the solution on completion of the reaction (4)
[17]
QUESTION 8 (Start on a new page.)
Magnesium (Mg) reacts with a dilute hydrochloric acid solution, HCℓ(aq), according to the following balanced equation:
Mg(s) + 2HCℓ(aq) → MgCℓ2(aq) + H2(g)
8.1 Give a reason why the reaction above is a redox reaction. (1)
8.2 Write down the FORMULA of the oxidising agent in the reaction above. (1)
It is found that silver does not react with the hydrochloric acid solution.
8.3 Refer to the relative strengths of reducing agents to explain this observation. (3)
The reaction of magnesium with hydrochloric acid is used in an electrochemical cell, as shown in the diagram below. The cell functions under standard conditions. 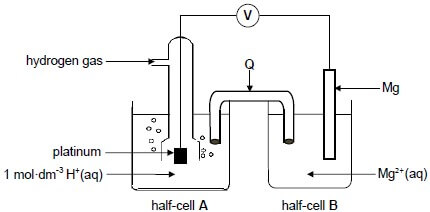
8.4 What is the function of platinum in the cell above? (1)
8.5 Write down the:
8.5.1 Energy conversion that takes place in this cell (1)
8.5.2 Function of Q (1)
8.5.3 Half-reaction that takes place at the cathode (2)
8.5.4 Cell notation of this cell (3)
8.6 Calculate the initial emf of this cell. (4)
8.7 How will the addition of concentrated acid to half-cell A influence the answer to QUESTION 8.6? Choose from INCREASES, DECREASES or REMAINS THE SAME. (1)
[18]
QUESTION 9 (Start on a new page.)
The diagram below shows an electrochemical cell used to purify copper. A solution that conducts electricity is used in the cell. 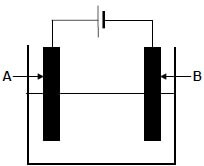
9.1 Write down:
9.1.1 ONE word for the underlined phrase above the diagram (1)
9.1.2 The type of electrochemical cell illustrated above (1)
9.2 In which direction (from A to B or from B to A) will electrons flow in the external circuit? (1)
9.3 Which electrode (A or B) is the:
9.3.1 Cathode (1)
9.3.2 Impure copper (1)
9.4 How will the mass of electrode A change as the reaction proceeds? Choose from INCREASES, DECREASES or REMAINS THE SAME.
Give a reason for the answer. (2)
[7]
QUESTION 10 (Start on a new page.)
A chemical company produces ammonium sulphate, (NH4)2SO4, starting from the raw materials P, Q and R, as shown in the flow diagram below. 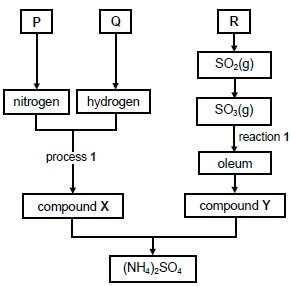
10.1 Write down the NAME of raw material:
10.1.1 P (1)
10.1.2 Q (1)
10.1.3 R (1)
10.2 Write down the:
10.2.1 NAME of process 1 (1)
10.2.2 NAME of compound X (1)
10.2.3 FORMULA of compound Y (1)
10.2.4 Balanced equation for reaction 1 (3)
10.3 The company compares the nitrogen content of ammonium sulphate with that of ammonium nitrate, NH4NO3.
10.3.1 Determine, by performing the necessary calculations, which ONE of the two fertilisers has the higher percentage of nitrogen per mass. (4)
10.3.2 Write down the name of the process that should be included in the flow diagram above if the company wants to prepare ammonium nitrate instead of ammonium sulphate. (1)
[14]
TOTAL: 150
DATA FOR PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 12
PAPER 2 (CHEMISTRY)
TABLE 1: PHYSICAL CONSTANTS
NAME | SYMBOL | VALUE |
Standard pressure | pθ | 1,013 x 105 Pa |
Molar gas volume at STP | Vm | 22,4 dm3∙mol-1 |
Standard temperature | Tθ | 273 K |
Charge on electron | e | -1,6 x 10-19 C |
Avogadro's constant | NA | 6,02 x 1023 mol-1 |
TABLE 2: FORMULAE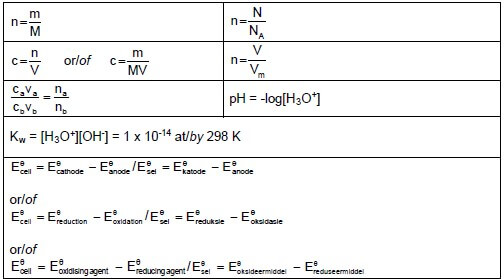
TABLE 3: THE PERIODIC TABLE OF ELEMENTS 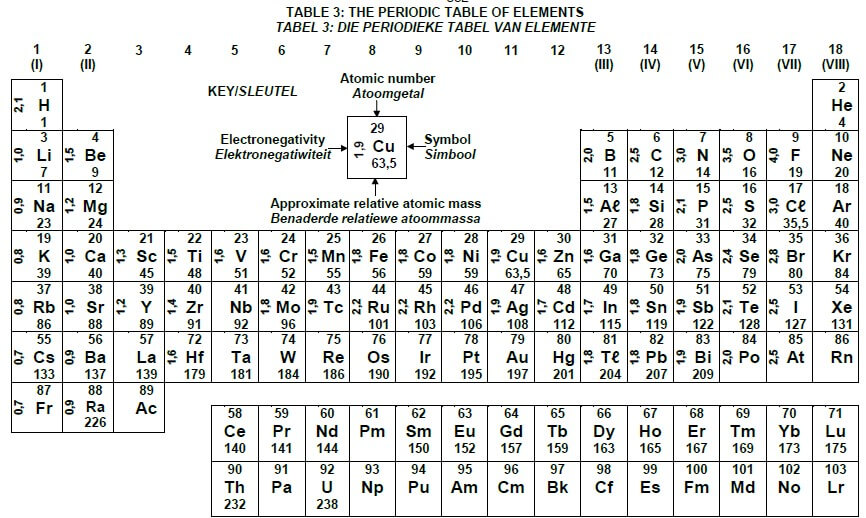
TABLE 4A: STANDARD REDUCTION POTENTIALS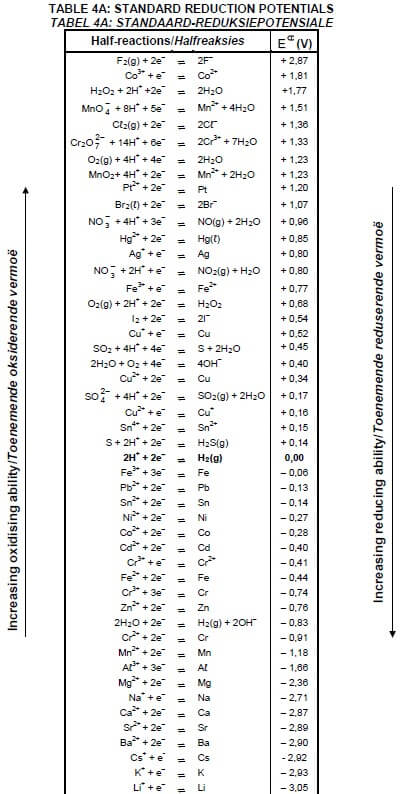
TABLE 4B: STANDARD REDUCTION POTENTIALS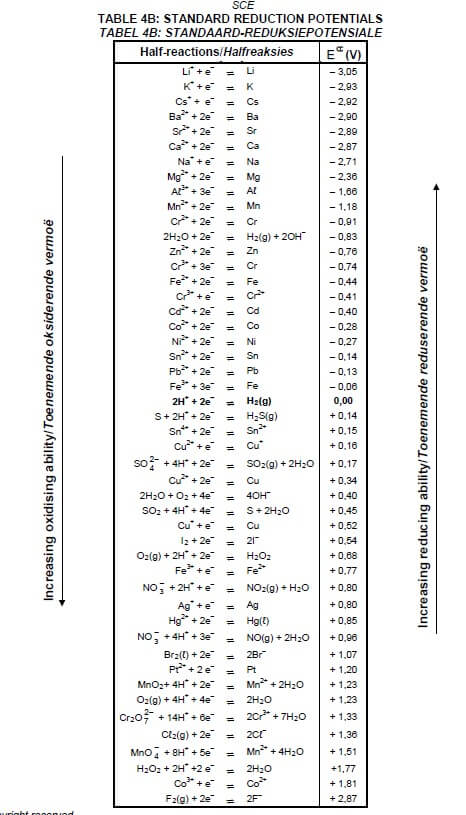
PHYSICAL SCIENCES PHYSICS PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAM PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2016
PHYSICAL SCIENCES (PHYSICS)
PAPER ONE (P1)
GRADE 12
AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAM
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2016
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of 11 questions. Answer ALL the questions
- Start EACH question on a NEW page in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Leave ONE line between two subquestions, for example between QUESTION 2.1 and QUESTION 2.2.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- You may use appropriate mathematical instruments.
- You are advised to use the attached DATA SHEETS.
- Show ALL formulae and substitutions in ALL calculations.
- Round off your final numerical answers to a minimum of TWO decimal places.
- Give brief motivations, discussions, et cetera where required.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Four options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Each question has only ONE correct answer. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1–1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.11 E.
1.1 An object, of mass m, hangs at the end of a string from the ceiling of a lift cage. The lift is moving upward at CONSTANT SPEED. The acceleration due to gravity is g. 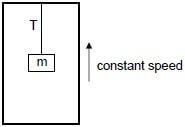
Which ONE of the following statements regarding the tension (T) in the string is CORRECT?
The tension T …
- will be equal to mg.
- will be less than mg.
- will be greater than mg.
- cannot be determined without knowing the speed of the lift cage. (2)
1.2 Two hypothetical planets, X and Y, have the same mass. The diameter of planet Y is twice that of planet X.
If the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of planet X is g, then the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of planet Y will be …
- g/16
- g/4
- g/2
- 2g (2)
1.3 A ball is projected vertically upwards from a height X above the ground. After some time, the ball falls to the ground and bounces back to the same height from which it was projected. Ignore friction and assume that there is a negligible time lapse during the collision of the ball with the ground.
Which ONE of the following is the CORRECT position-time graph for the motion of the ball as described above? 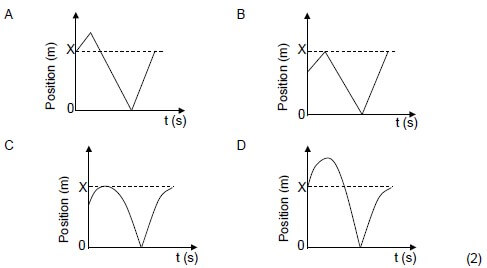
1.4 Which ONE of the following statements is always TRUE for inelastic collisions in an isolated system?
- Both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved.
- Both momentum and kinetic energy are not conserved.
- Momentum is conserved, but kinetic energy not.
- Kinetic energy is conserved, but momentum not. (2)
1.5 When the net work done on an object is positive (greater than zero), the …
- kinetic energy of the object is zero.
- kinetic energy of the object is increasing.
- kinetic energy of the object is decreasing.
- kinetic energy of the object remains unchanged. (2)
1.6 A police car with its siren wailing is moving away from a stationary observer at constant speed. The siren emits a sound of constant frequency.
Which of the following characteristics associated with the sound of the siren, as perceived by the observer, is/are CORRECT?
- The speed remains the same.
- The frequency increases.
- The wavelength increases.
- The pitch decreases.
- (iii) only
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (i) and (iii) only
- (i) and (ii) only (2)
1.7 The magnitude of the electric field at a point P from a positive point charge q is x N∙C-1.
Which ONE of the statements below regarding this electric field is CORRECT?
- A + 1 C charge placed at P will experience a force of magnitude x N directed away from q.
- The force on a + 2 C charge placed at P will have a magnitude ¼ x N directed away from q.
- A + 1 C charge placed at P will experience a force of magnitude x N directed towards q.
- The force on a + 2 C charge placed at P will have a magnitude ¼ x N directed towards q. (2)
1.8 Circuit I shows two identical lamps X and Y connected to a cell of negligible internal resistance. Switch S is closed. 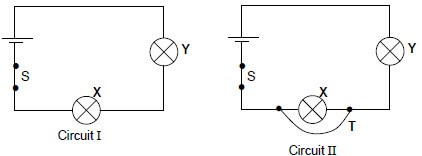
A wire T, of negligible resistance, is now connected across X as shown in Circuit II.
Which ONE of the statements below best describes how the brightness of the lamps have changed after T had been connected?
X | Y | |
A | Does not light up | Dimmer |
B | Brighter | Dimmer |
C | Brighter | Brighter |
D | Does not light up | Brighter |
(2)
1.9 Some learners decided to build a small electrical generator in the laboratory. They then used this generator to investigate how the magnitude of the induced emf would change as the magnetic field strength changed.
Which ONE of the following is CORRECT regarding the variables for the investigation?
DEPENDENT VARIABLE | INDEPENDENT VARIABLE | CONTROL VARIABLE | |
A | Magnitude of induced emf | Number of turns of coil of generator | Magnetic field strength |
B | Number of turns of coil of generator | Magnitude of induced emf | Magnetic field strength |
C | Magnitude of induced emf | Magnetic field strength | Number of turns of coil of generator |
D | Magnetic field strength | Number of turns of coil of generator | Magnitude of induced emf |
(2)
1.10 In an experiment on the photoelectric effect, a scientist shines red light on a metal surface and observes that electrons are ejected from the metal surface. Later the scientist shines blue light, with the same intensity as the red light, on the same metal surface.
Which ONE of the statements below will be the CORRECT observation as a result of this change?
- The number of ejected electrons per second will increase.
- The number of ejected electrons per second will decrease.
- The speed of the ejected electrons will decrease.
- The maximum kinetic energy of the ejected electrons will increase. (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2 (Start on a new page.)
The diagram below shows a 10 kg block lying on a flat, rough, horizontal surface of a table. The block is connected by a light, inextensible string to a 2 kg block hanging over the side of the table. The string runs over a light, frictionless pulley.
The blocks are stationary.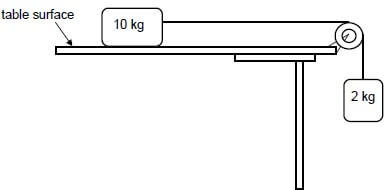
2.1 State Newton's FIRST law in words. (2)
2.2 Write down the magnitude of the NET force acting on the 10 kg block. (1)
When a 15 N force is applied vertically downwards on the 2 kg block, the 10 kg block accelerates to the right at 1,2 m∙s-2.
2.3 Draw a free-body diagram for the 2 kg block when the 15 N force is applied to it. (3)
2.4 Calculate the coefficient of kinetic friction between the 10 kg block and the surface of the table. (7)
2.5 How does the value, calculated in QUESTION 2.4, compare with the value of the coefficient of STATIC friction for the 10 kg block and the table? Write down only LARGER THAN, SMALLER THAN or EQUAL TO. (1)
2.6 If the 10 kg block had a larger surface area in contact with the surface of the table, how would this affect the coefficient of kinetic friction calculated in QUESTION 2.4? Assume that the rest of the system remains unchanged. Write down only INCREASES, DECREASES or REMAINS THE SAME. Give a reason for the answer. (2) [16]
QUESTION 3 (Start on a new page.)
Ball A is projected vertically upwards from the ground, near a tall building, with a speed of 30 m∙s-1. Ignore the effects of air friction.
3.1 Explain what is meant by a projectile. (2)
3.2 Calculate:
3.2.1 The total time that ball A will be in the air (4)
3.2.2 The distance travelled by ball A during the last second of its fall (4)
3.3 TWO SECONDS after ball A is projected upwards, ball B is projected vertically upwards from the roof of the same building. The roof the building is 50 m above the ground. Both balls A and B reach the ground at the same time. Refer to the diagram below. Ignore the effects of air friction.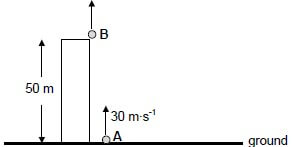
Calculate the speed with which ball B was projected upwards from the roof. (4)
3.4 Sketch velocity-time graphs for the motion of both balls A and B on the same set of axes. Clearly label the graphs for balls A and B respectively.
Indicate the following on the graphs:
- Time taken by both balls A and B to reach the ground
- Time taken by ball A to reach its maximum height (4)
[18]
QUESTION 4 (Start on a new page.)
The diagram below shows two sections, XY and YZ, of a horizontal, flat surface. Section XY is smooth, while section YZ is rough.
A 5 kg block, moving with a velocity of 4 m∙s-1 to the right, collides head-on with a stationary 3 kg block. After the collision, the two blocks stick together and move to the right, past point Y.
The combined blocks travel for 0,3 s from point Y before coming to a stop at point Z. 4 m∙s-1 0 m∙s-1 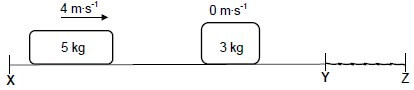
4.1 State the principle of conservation of linear momentum in words. (2)
4.2 Calculate the magnitude of the:
4.2.1 Velocity of the combined blocks at point Y (4)
4.2.2 Net force acting on the combined blocks when they move through section YZ (4) [10]
QUESTION 5 (Start on a new page.)
A 20 kg block is released from rest from the top of a ramp at point A at a construction site as shown in the diagram below.
The ramp is inclined at an angle of 30o to the horizontal and its top is at a height of 5 m above the ground. 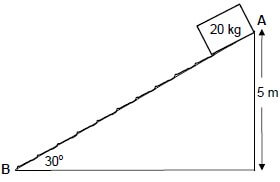
5.1 State the principle of conservation of mechanical energy in words. (2)
5.2 The kinetic frictional force between the 20 kg block and the surface of the ramp is 30 N.
Use energy principles to calculate the:
5.2.1 Work done by the kinetic frictional force on the block (3)
5.2.2 Speed of the block at point B at the bottom of the ramp (5)
5.3 A 100 kg object is pulled up the SAME RAMP at a constant speed of 2 m∙s-1 by a small motor. The kinetic frictional force between the 100 kg object and the surface of the ramp is 25 N.
Calculate the average power delivered by the small motor in the pulling of the object up the incline. (4) [14]
QUESTION 6 (Start on a new page.)
An ambulance is travelling towards a hospital at a constant velocity of 30 m∙s-1. The siren of the ambulance produces sound of frequency 400 Hz. Take the speed of sound in air as 340 m∙s-1.
The diagram below shows the wave fronts of the sound produced from the siren as a result of this motion. 
6.1 At which side of the diagram, X or Y, is the hospital situated? (1)
6.2 Explain the answer to QUESTION 6.1. (3)
6.3 Calculate the frequency of the sound of the siren heard by a person standing at the hospital. (5)
6.4 A nurse is sitting next to the driver in the passenger seat of the ambulance as it approaches the hospital. Calculate the wavelength of the sound heard by the nurse. (3)
[12]
QUESTION 7 (Start on a new page.)
A small sphere, Q1, with a charge of + 32 x 10-9 C, is suspended from a light string secured to a support. A second, identical sphere, Q2, with a charge of – 55 x 10-9 C, is placed in a narrow, cylindrical glass tube vertically below Q1. Each sphere has a mass of 7 g. Both spheres come to equilibrium when Q2 is 2,5 cm from Q1, as shown in the diagram. Ignore the effects of air friction. 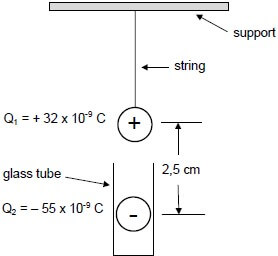
7.1 Calculate the number of electrons that were removed from Q1 to give it a charge of + 32 x 10-9 C. Assume that the sphere was neutral before being charged. (3)
7.2 Draw a labelled free-body diagram showing all the forces acting on sphere Q1. (3)
7.3 Calculate the magnitude of the tension in the string. (5)
[11]
QUESTION 8 (Start on a new page.)
8.1 Define electric field at a point in words. (2)
8.2 Draw the electric field pattern for two identical positively charged spheres placed close to each other. (3)
8.3 A – 30 μC point charge, Q1, is placed at a distance of 0,15 m from a + 45 μC point charge, Q2, in space, as shown in the diagram below. The net electric field at point P, which is on the same line as the two charges, is zero. ![]()
Calculate x, the distance of point P from charge Q1. (5)
[10]
QUESTION 9 (Start on a new page.)
9.1 In the diagram below, three light bulbs, A, B and C, are connected in parallel to a 12 V source of negligible internal resistance. The bulbs are rated at 4 W, 6 W and 10 W respectively and are all at their maximum brightness. 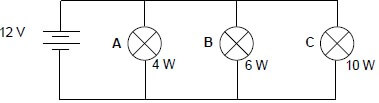
9.1.1 Calculate the resistance of the 4 W bulb. (3)
9.1.2 How will the equivalent resistance of the circuit change if the 6 W bulb burns out? Write down only INCREASES, DECREASES or NO CHANGE. (1)
9.1.3 How will the power dissipated by the 10 W bulb change if the 6 W bulb burns out? Write down only INCREASES, DECREASES or NO CHANGE. Give a reason for the answer. (2)
9.2 A learner connects a high-resistance voltmeter across a battery. The voltmeter reads 6 V. She then connects a 6 Ω resistor across the battery. The voltmeter now reads 4, 5 V.
9.2.1 Calculate the internal resistance of the battery. (4)
The learner now builds the circuit below, using the same 6 V battery and the 6 Ω resistor. She connects an unknown resistor X in parallel with the 6 Ω resistor. The voltmeter now reads 4,5 V.
9.2.2 Define the term emf of a cell. (2) 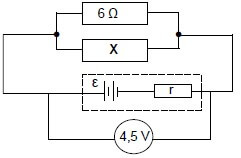
9.2.3 Calculate the resistance of X when the voltmeter reads 4,5 V. (5)
[17]
QUESTION 10 (Start on a new page.)
10.1 A part of a simplified DC motor is shown in the sketch below. 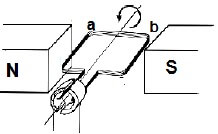
10.1.1 In which direction (a to b, OR b to a) is the current flowing through the coil if the coil rotates anticlockwise as indicated in the diagram? (1)
10.1.2 Name the rule you used to answer QUESTION 10.1.1. (1)
10.1.3 Which component in the diagram must be replaced in order for the device to operate as an AC generator? (1)
10.2 An electrical device of resistance 400 Ω is connected across an AC generator that produces a maximum emf of 430 V. The resistance of the coils of the generator can be ignored.
10.2.1 State the energy conversion that takes place when the AC generator is in operation. (2)
10.2.2 Calculate the root mean square value of the current passing through the resistor. (5)
[10]
QUESTION 11 (Start on a new page.)
11.1 In an experiment on the photoelectric effect, light is incident on the surface of a metal and electrons are ejected.
11.1.1 What does the photoelectric effect indicate about the nature of light? (1)
11.1.2 The intensity of the light is increased. Will the maximum speed of the ejected electrons INCREASE, DECREASE or REMAIN THE SAME? Give a reason for the answer. (2)
The wavelength corresponding with the threshold frequency is referred to as threshold wavelength.
The table below gives the values of threshold wavelengths for three different metals.
METAL | THRESHOLD WAVELENGTH (λ0) IN METRES |
Silver | 2,88 x 10-7 |
Calcium | 4,32 x 10-7 |
Sodium | 5,37 x 10-7 |
In the experiment using one of the metals above, the maximum speed of the ejected electrons was recorded as 4,76 x 105 m·s-1 for light of wavelength 420 nm.
11.1.3 Identify the metal used in the experiment by means of suitable calculations. (5)
11.2 The simplified energy diagrams showing the possible electron transitions in an atom are shown below. 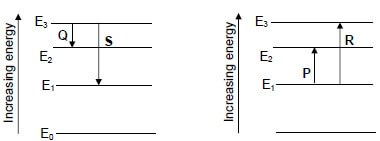
Using the letters P, Q, R and S, identify the lines that CORRECTLY show transitions that will result in the atom giving off an EMISSION SPECTRUM. Give a reason for the answer. (4)
[12]
TOTAL: 150
DATA FOR PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 12
PAPER 1 (PHYSICS)
TABLE 1: PHYSICAL CONSTANTS
NAME | SYMBOL | VALUE |
Acceleration due to gravity | g | 9,8 m·s-2 |
Universal gravitational constant | G | 6,67 x 10-11 N·m2·kg-2 |
Radius of the Earth | RE | 6,38 x 106 m |
Mass of the Earth | ME | 5,98 x 1024 kg |
Speed of light in a vacuum | c | 3,0 x 108 m·s-1 |
Planck's constant | h | 6,63 x 10-34 J·s |
Coulomb's constant | k | 9,0 x 109 N·m2·C-2 |
Charge on electron | e | –1,6 x 10-19 C |
Electron mass | me | 9,11 x 10-31 kg |
TABLE 2: FORMULAE
MOTION
v f = v i + a ∆ t | ∆x = v1∆t + ½a∆t2 or ∆y = v1∆t + ½a∆t2 |
| vf2 = v i 2+ 2a ∆ x or vf2 = v i 2+ 2a ∆ y | ∆x = [v1 + vf] ∆t or ∆y = [v1 + vf] ∆t 2 2 |
FORCE
Fnet = ma | p= mv |
fsmax = μsN | fk =μkN |
Fnet∆t = ∆p | w =mg |
| F = G M1M2 or F = G M1M2 d2 r2 | g = GM/d2 or g = GM/r2 |
WORK, ENERGY AND POWER
W = F∆x cos θ | U= mgh or EP = mgh |
K = ½mv2 or Ek = ½mv2 | Wnet = ∆K or Wnet = ∆Ek |
Wnc = ∆K + ∆U or Wnc = ∆Ek + ∆Ep | P=W/∆t |
Pave = Fvave / Pgemid = Fvgemid |
WAVES, SOUND AND LIGHT
v = f λ | T = 1/f |
| fl = v ± vl fs or fl = v ± vl fb v ± vs v ± vb | E= hf or E = hc/λ |
| E = WO + Ek(max) or E= WO + Ek(max) where E = hf and WO = hfo and Ek(max) = ½mv2max or k(max) = ½mv2max | |
ELECTROSTATICS
| F = kQ1Q2 r2 | E = kQ r2 |
| V = W/q | E = F/Q |
| n = Q/e or n = Q/qe |
ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
R = V/I | emf ( ε ) = I(R + r) |
Rs = R1 + R2 + ... | q = I∆t |
W = Vq | P = W/∆t |
ALTERNATING CURRENT
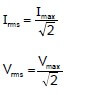 | 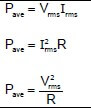 |
RELIGIOUS STUDIES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAM PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2016
Religious Studies Paper One (P1)
Grade 12
Amended Senior Certificate Exam
Past Papers And Memos 2016
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
In this section, each fact carries ONE mark, unless otherwise stated.
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 C✔ (1)
1.1.2 C✔ (1)
1.1.3 A✔ (1)
1.1.4 B✔ (1)
1.1.5 C✔ (1)
1.1.6 C✔ (1)
1.1.7 A✔ (1)
1.1.8 C✔ (1)
1.1.9 C✔ (1)
1.1.10 A✔ (1)
1.2
1.2.1
- The Kitáb-i-Aqdas is a Baha'i book
- It contains most of Bahá'u'lláh's doctrines in the Baha'i faith. ✔
- It is also referred to as the Book of Certitude. ✔ (2)
1.2.2
- Reincarnation is the belief in the rebirth of the soul. ✔
- It is the spirit in a new body.
- Reincarnation is a central belief in Hinduism. ✔ (2)
1.2.3
- A mantra is a verse, syllable or phrase that is believed to be of divine origin. ✔
- Its origin is in Hinduism.
- It is also used in ritual or meditation in different religions. ✔ (2)
1.2.4
- Yin and Yang refer to a belief in Taoism. ✔
- It teaches that everything in creation consists of two opposing forces. ✔
- The Yin is passive, dark, yielding and female. The Yang is active, light, forceful and male. ✔ (2)
1.2.5
- Comparability in a religious context refers to a comparison between different religions (interreligious comparison). ✔
- It is a comparison between different branches/movements within the same religion (intrareligious comparison). ✔ (2)
1.3
1.3.1 Moses ✔ He was a leader of the Jewish nation, while the others are names of the Supreme Being. ✔ (2)
1.3.2 St Luke ✔ He is not related to Taoism. ✔ (2)
1.3.3 Diviner ✔ The other words refer to normative sources/ sacred texts in different religions. ✔ (2)
1.3.4 Dharma ✔ The others are sects of Hinduism. ✔ Dharma is a term widely used in Eastern religions, meaning a way of higher truth, and has a variety of other meanings. ✔ (2)
1.3.5 Dar es Salaam. ✔ The other words refer to holy places. ✔ (2)
1.4 Interreligious conflict is conflict between different religions. ✔ 'Inter' means between two or more. ✔
Intrareligious conflict is conflict between the branches/movements or groups that belong to the same religion. ✔'Intra' means from within. ✔ (4)
1.5
1.5.1 E✔ (1)
1.5.2 D✔ (1)
1.5.3 F✔ (1)
1.5.4 B✔ (1)
1.5.5 A✔ (1)
1.5.6 H✔ (1)
1.6
1.6.1 False ✔ The Tripitaka is one of the sacred books of Buddhism./ The Torah is one of the sacred books of Judaism. ✔ (2)
1.6.2 False ✔ A person with conservative values displays deep religious commitment and holds on to traditional values. ✔ (2)
1.6.3 True✔✔ (2)
1.6.4 False ✔ The veneration of the ancestors is practised by African Traditional Religion. ✔ (2)
1.6.5 False ✔ A bodhisattva is someone who could enter nirvana but has decided to delay this entrance in order to help others, out of compassion for their suffering. ✔ (2)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
In this section, each fact carries two marks.
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1 Belief
- Belief is often used to mean the same as thinking deeply about religious teaching and accepting it as being true.
- Belief may mean acceptance of a fact, a thing, a statement or a teaching in a particular religion.
- It may also mean a firm opinion about religion.
- Belief may also be used as a synonym for religion.
- Belief may also refer to faith.
NOTE: Any other relevant responses must be credited. A maximum of TWO marks may be awarded for giving examples. (6)
2.1.2 Dogma
- The word 'dogma' comes from the Greek word 'dogma', which means appearance or opinion in religion.
- It is a principle or system laid down by a religious authority.
- It is a set of beliefs taken to be absolutely true and fixed in religion.
- The beliefs in dogma are not up for discussion.
- There is no absolute cut-off point between teaching and dogma in religion.
- In Islam, for example, there are dogmatic principles that are contained in the aqidah. (6)
2.1.3 Myth
- The word 'myth' comes from the word 'mythos', meaning a word or fable.
- It refers to those stories that reveal the deepest truths about creation and life.
- It teaches about life after death in religion.
- Myths form the basis of teaching and even dogma in some religions.
- A myth does not necessarily try to make a moral point in religion. (6)
2.1.4 Doctrine
- It is a set of beliefs or principles in religion.
- Doctrines are the beliefs that provide a central frame of reference for religion.
- It is also a statement of beliefs and its function is to safeguard what is important in a religion.
- Doctrines also refer to the entire set of beliefs in a religion. (6)
2.2
EXAMPLE 1: African Traditional Religion
- It is a clan-based religion.
- Elderly people are the major leaders in the ATR.
- It promotes the veneration of the ancestors.
- It focuses on moral practices and rituals.
- Punishment and reward are here and now, not after death.
- A communal way of life is central and individualism is discouraged.
- It has no founder.
- It also has no sacred book.
EXAMPLE 2: Christianity
- Christians believe that Jesus Christ is the Son of the Living God.
- They believe that God sent His Son to die for their sins.
- They believe that God took a human form in Jesus Christ.
- They believe in the Trinity – the Father; the Son and the Holy Spirit.
- They believe that Jesus Christ died and rose from the dead after three days.
- They believe that forgiveness is in the name of Jesus Christ.
- They believe that Jesus Christ is the only way to God.
- They celebrate the Holy Communion (Eucharist) as remembrance of the death of Christ. (10)
In 2.3, a maximum of TWELVE marks is awarded if only one religion is discussed.
2.3.1 Right to life
- According to various religions, human life is sacred.
- In some religions, e.g. in the Ten Commandments found in the Christian and Jewish scriptures, it is clearly stated that 'Thou shall not kill.'
- The protection of human life takes preference over all other religious activities in Islam.
- The Qur'an states that taking one human life unjustly is like killing the whole of humanity, and the saving of a human life is like saving all of humanity.
- In the Qur'an 4:29–30 the Muslims are expected to refrain from killing one another. They are also to bear in mind that Allah is merciful.
- In ATR, the birth of a child is a gift from the ancestors, hence the right to life is held in high regard.
- The Abrahamic Faiths teach that abortion is a major sin. (6)
2.3.2 Respect
- Respect is one of the basic teachings in all major religions.
- In the Baha'i faith, respect is of paramount importance and this religion teaches that women should be treated with respect and their dignity be protected.
- In the Abrahamic faiths the adherents are expected to teach respect for all God's creation at home.
- In the sacred Books, it is stated that husbands should love their wives and wives should honour their husbands.
- The children should be taught to obey the elderly and the elderly should not upset or treat the children with disrespect.
- The Buddhist religion teaches that the wife should be treated with honour and the wife should be faithful to her husband. (6)
2.3.3 Love
- The Christian Bible emphasises the value of love in John 3:16: 'For God so loved the world that He gave His only Son to die for us.'
- In the Qur'an, Allah is portrayed as love and merciful, therefore the Islamic followers are expected to reflect that love in their daily living.
- Ubuntu is a teaching in the African Traditional Religion that encourages people to display love among one another. (4)
[50]
QUESTION 3
3.1
- Jihad is an Arabic word meaning 'to strive, to apply oneself, to struggle, to persevere'.
- It is also the religious duty of Muslims to maintain their religion.
- It includes defensive military action to protect the religion and Muslim life.
- It is regarded as a Holy War.
[Source: islamicsupremecouncil.org] (4)
3.2 (12)
|
|
|
|
| |
|
3.3
- Religion plays a very small role in this conflict.
- This conflict started as a civil uprising in 2011.
- It was against the Syrian government of Bashar al-Assad.
- The United States and Europe promised to support the rebels (Free Syrian Army).
- However, Western support for the rebels stopped when the West realised that the rebels included groups that wanted to be independent of US influence/wanted to form a state based on Islamic values.
- The Syrian government gets Shi'a support from Hezbollah and Iran.
- The rebel movements are mainly Sunni.
- This is the extent of religious involvement in the conflict.
- IS (Islamic State) is also Sunni, but opposes both the rebels and the Syrian army.
- The Syrian army as well as the rebels both have outside support.
- This makes the conflict an international, political one between Russia and the West.
[Source: bbc.com/news/world-middle east] (14)
3.4
- The United States, France and Germany have been supporting the Syrian rebel movements from the start of the conflict.
- Iran has supported the Syrian government.
- Russia is Iran's ally, and has recently begun bombing campaigns against the enemies of the Syrian regime.
- IS, based in Iraq, has also taken sizeable parts of Syria (such as the Kweiris air base.)
- Millions of Syrian refugees have been forced to move to various parts of the world, including Lebanon, Jordan, Turkey and some European countries.
- The recent downing of a Russian passenger plane is alleged to be the work of IS.
- The attacks in Paris on 13 November 2015 are also linked to IS revenge on European attacks on its bases. (12)
3.5
3.5.1 Evangelical wars
- These are wars where a religious state decides that people of a neighbouring state must convert to the 'true' religion. (2)
3.5.2 Wars of self-defence
- These wars are waged in the interest of justice; evil must be opposed, and good upheld. (2)
3.5.3 Wars of retaliation.
- These are fought to avenge an offence committed against a specific religion. (2)
3.5.4 Wars of conquest
- These are fought for the glory of God. Military success is seen as a reflection of the glory of God. (2)
QUESTION 4
4.1 4.1.1
- Human rights, in a religious context, refers to the inherent dignity of a human being.
- It also means that the existence of a human being gives him or her high value on earth.
- This concept is centred upon the belief that all human beings are created in the image of God. (4)
4.1.2
- It had an office called 'The Holy Office of the Inquisition Against Heretical Depravity.'
- The purpose of the Holy Office was to try to keep Catholic beliefs and practices pure by prosecuting people who did not follow an orthodox version of Catholicism.
- It also worked to ensure that the converts from Islam and Jewish religions were genuinely converted.
- The Inquisition included trial by fire – 'true' Christians would not be consumed by the fire, while those burned at the stake were imposters. (6)
4.1.3
- The Spanish Inquisition violated many people's human rights since it did not consider the rights of the individual to freedom of choice/religion.
- The Holy Office disregarded the dignity of the person as an independent thinking being that could make sound decisions about his or her own spiritual life.
- The Spanish Inquisition deprived people of Islamic and Jewish religions of religious freedom.
- This body also subjected believers to cruel 'trials' which involved burning people at the stake.
- Accordingly, the Holy Office did not enable the people to practise their religions freely without intimidation.
- The Spanish Inquisition also interfered with people's right to privacy, since it always followed them around to ensure that they were not secretly practising their original religions.
- This Inquisition also put people on trial even if they were not guilty, but on the basis of suspicion. (12)
4.1.4 • Religious freedom is protected in South Africa by the Constitution.
- In South Africa, all religions are treated with equal respect by the government.
- At public gatherings, e.g. during Parliamentary sessions, a moment of silence is observed to allow for all religions to enjoy recognition.
- In public schools the curriculum has been designed to enable the learners to be exposed to a variety of religions through the introduction of Religion Studies as a subject.
- All religions have the right to observe their holy days and festivities without fear or intimidation.
- Different faith groups are encouraged to work together in order to tackle social ills.
- During the opening of Parliament, and the inauguration of the President of the country, various delegates from different religious formations participate in the prayer sessions.
- There is also a continuous interreligious dialogue to tackle issues of common interest.
NOTE: Other relevant facts must be credited. (12)
4.2
- They were able to organise exchange visits between landmine victims and survivors from Ethiopia, South Sudan and Uganda.
- They also sent women's delegations to Nordic countries.
- They formed the IFAPA Women's Network.
- They sent interfaith delegations to conflict risk areas.
- They also participated in the legislative elections in Togo.
- They participated in the World Social Forum held in Kenya.
- They also organised the Nakanyonyi Youth Peace Camp.
- They succeeded in holding the first continental/African interfaith youth consultation.
- They also established regional Youth Networks.
- Inaugurated the Rural Water Project in Rwanda. (16)
[50]
QUESTION 5
5.1
- There are four scripturally ordained goals in Hinduism e.g. Artha • They believe in reincarnation (rebirth of the soul).
- They believe in the Law of Karma -every action has future consequences. • Their social structure is based on a caste system.
- They believe in many manifestations of God.
- Each manifestation is depicted in the form of a god/goddess.
NOTE: Other relevant responses must be credited. (6)
5.2 There are many changes that took place with regard to interreligious relations. The following are only some of them:
- South Africa is now a secular state. It has no state religion.
- Multifaith services have been held in some of the local churches, where all faiths have been invited to celebrate an aspect of human rights and other activities.
- HIV/Aids patients are cared for and supported, often in prayer, by members representing all faith groups.
- There was a march by the representatives from South African religions and their followers to Parliament to deliver a scathing attack on pornography.
- In the opening of Parliament, various religious leaders from different faith groups commit themselves to a Greater Deity.
- Public holiday celebrations (e.g. a rally on Freedom Day) have on several occasions been conducted and addressed by an Imam, a guru and a priest.
- Religions come together whenever there is a problem.
- There is an appreciation of all spiritual endeavours, regardless of religion or sect.
- There is greater tolerance and respect of all faiths. This is evident in media coverage.
- Examples of this are 'Issues of Faith', Islam Channel, offering of prayers by different faiths on TV. (14)
5.3
5.3.1
- A 'bling pastor' is a flamboyant religious leader.
- She/he wears ostentatious clothing and jewellery.
- This person creates an image of being wealthy.
NOTE:Other relevant explanations must be credited. (4)
5.3.2
- The article displays a negative attitude towards religion.
- This article shows a clear antireligious bias.
- The miracles are described as 'tricks'.
- The churches are described as 'rogue' churches, even before the investigation is completed.
- It implies that churches hide their wealth.
- The SACC is described as 'toothless', meaning that it is ineffective.
- The pastors are referred to as 'bling' pastors, implying that they are all about ostentation and showmanship.
OR - The article treats religion in a fair and unbiased manner.
- It is reporting in the interest of the public good.
- It demands greater accountability to the public, in terms of funding, and in terms of “miracles”, which could be harmful to congregants.
- It encourages the regulation of churches. (12)
5.3.3 YES
- Religious organisations should be bona fide charity organisations.
- Some churches/organisations take advantage of gullible followers.
- They raise large sums of money from these gullible donors, and use it for themselves.
- Religious bodies should be regulated, so that their authenticity is checked.
- Congregants do not have the knowledge to distinguish between genuine and fake religious leaders.
- The credentials of the pastors are never checked.
NO
- Religion is about beliefs/faith.
- These beliefs cannot be proved or disproved by investigation. • Miracles cannot be explained by scientific inquiry, and yet they are accepted as fact by religious communities.
- Religions are self-regulated, as they answer to a supreme being.
- Religious leaders are often inspired. However, a non-believer will simply not accept the evidence of inspiration.
- The practices cannot be proven as authentic: they are held to be true in the minds of the congregants only.
- It is therefore not possible to regulate a religion from the point of view of a non-believer.
- Believers, on the other hand, see no need for regulation.
NOTE: Other relevant explanations must be credited. (6)
5.3.4
- The blessed/anointed pastors Penuel Mnguni and Daniel Mosoue have once again demonstrated their gifts/powers conferred upon them by the Lord/supreme being.
- Miraculously, the congregants drank petrol and ate poisonous snakes, without being harmed in any way.
- It is sheer jealousy of fake churches that they wish to investigate our organisation.
- If they were true churches, why can they not show us their miracles?
- Our loyal congregants are reminded that donations to the church are encouraged, but are completely voluntary.
NOTE: Other relevant responses must be credited. (8)
[50]
GRAND TOTAL: 150
RELIGIOUS STUDIES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAM PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2016
Religious Studies
Paper One (P1)
Grade 12
Amended Senior Certificate Exam
Past Papers And Memos 2016
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SECTION A and SECTION B.
- SECTION A: COMPULSORY
- SECTION B: Answer any TWO questions in this section.
- Read ALL the questions carefully.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 The Baha'i faith originated in ...
- Israel.
- India.
- Iran.
- Iraq. (1)
1.1.2 The headquarters of the Roman Catholic branch of Christianity is in …
- London.
- Jerusalem.
- Rome
- Mecca. (1)
1.1.3 Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels aimed at establishing a society based on …
- communism.
- socialism.
- capitalism.
- protestantism. (1)
1.1.4 Ubuntu is …
- a day used for communal worship in the African Traditional Religion.
- showing respect and empathy towards fellow human beings.
- a religious teaching with absolute authority.
- a word meaning 'people of African origin'. (1)
1.1.5 The following is a sacred text of Buddhism:
- The Book of Mormon
- Sigalovada Sutta
- Pali Canon
- Vedas (1)
1.1.6 A ceremony during which a believer is made a member of the Christian community through water:
- Cataclysm
- Appeasement
- Baptism
- Holy Communion (1)
1.1.7 A back and forth swinging from one side to the other in Taoism:
- Oscillation
- Waning
- Catechism
- Cosmology (1)
1.1.8 Conservative followers of the following religion do NOT object to the Big Bang theory:
- Christianity
- Judaism
- Buddhism
- Islam (1)
1.1.9 The first Parliament of the World's Religions was held in …
- The Hague.
- Rome.
- Chicago.
- Kyoto. (1)
1.1.10 A Muslim religious leader and teacher:
- Imam
- Cardinal
- Raja
- Apostle (1)
1.2 Explain each of the following terms in the context of religion. Write down TWO facts about each term using full sentences.
1.2.1 Kitáb-i-Aqdas (2)
1.2.2 Reincarnation (2)
1.2.3 Mantra (2)
1.2.4 Yin and Yang (2)
1.2.5 Comparability (2)
1.3 Choose the word in each list below that does NOT fit. Write the word and a reason next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 Moses; Modimo; Jehovah; Brahma (2)
1.3.2 Lao-tzu; Chuang-tzu; Taoists; St Luke (2)
1.3.3 Tao Te Ching; Bible; Book of Mormon; diviner (2)
1.3.4 Shaiva; Vaishnava; Shakteya; Dharma (2)
1.3.5 Mecca; Vatican City; Medina; Dar es Salaam (2)
1.4 Explain the difference between interreligious conflict and intrareligious conflict. (4)
1.5 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches the term in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–H) next to the question number (1.5.1–1.5.6) in the ANSWER BOOK.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.5.1 Torah | A spiritual leader of Tibetan Buddhism |
(6 x 1) (6)
1.6 Indicate whether the following statements are TRUE of FALSE. Give a reason if the statement is FALSE. Write TRUE or FALSE and the reason next to the question number (1.6.1–1.6.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.6.1 The Tripitaka is one of the sacred books of Judaism. (2)
1.6.2 A person with liberal values displays deep religious commitment and holds on to traditional values. (2)
1.6.3 Western secularism rejects conventional religion as a foundation for life and law. (2)
1.6.4 The veneration of ancestors is the most important moral order in Islam. (2)
1.6.5 The bodhisattva gains insight and makes the discovery of the unknown by using supernatural powers. (2)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
Answer any TWO questions in this section.
QUESTION 2
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
All religions have certain beliefs. Such beliefs are known as religious teachings. [Adapted from Shuters Religion Studies Grade 12, Hofmeyr et al.] |
2.1 Discuss the following terms in the context of religion:
2.1.1 Belief (6)
2.1.2 Dogma (6)
2.1.3 Myth (6)
2.1.4 Doctrine (6)
2.2 Choose ANY ONE religion, except Hinduism, and discuss FIVE of the religion's unique features. (10)
2.3 Discuss the teachings of various religions that promote the following values:
2.3.1 The right to life (6)
2.3.2 Respect (6)
2.3.3 Love (4) [50]
QUESTION 3
Study the article below and answer the questions that follow.
JIHAD REBELS DRIVEN OUT OF KEY TOWN IN SYRIA Syria's army, supported by Iranian forces, Lebanese Hezbollah militia and Russian air strikes, seized most of al-Hader, a key rebel-held town south of Aleppo yesterday. This was their second major advance in the province this week. State television announced the capture of the town of al-Hader, an opposition stronghold near the strategic Aleppo-Damascus highway. This victory came only 48 hours after Syria's forces broke the Islamic State terrorist group's siege of the Kweiris air base in the east of the Aleppo province … The town of al-Hader was largely controlled by al-Qaeda supporters, the al-Nusra Front, and other allied Islamic groups … [Source: The Times, 13 November 2015] |
3.1 What do you understand by jihad? (4)
3.2 Three warring groups are mentioned in this article. Name the THREE groups, together with any of their allies. (12)
3.3 To what extent is this a religious war? Give reasons for your answer. (14)
3.4 How has this war affected other parts of the world? (12)
3.5 Religious wars are permissible under certain conditions. Name FOUR such conditions. (8) [50]
QUESTION 4
4.1 Read the extract on human rights below and answer the questions that follow.
THE SPANISH INQUISITION The Spanish Inquisition was a law court established in Spain in 1478. It was linked to a branch of the Catholic Church called 'The Holy Office of the Inquisition Against Heretical Depravity'. The purpose of the Holy Office was to keep Catholic beliefs and practices pure by prosecuting people who did not follow an orthodox path. [Adapted from Shuters Religion Studies Grade 12, Hofmeyr et al.] |
4.1.1 Explain the term human rights in the context of religion, using TWO sentences. (4)
4.1.2 Explain how the Spanish Inquisition worked. (6)
4.1.3 Critically discuss how the Spanish Inquisition violated the rights of converts to freedom of religion. (12)
4.1.4 Discuss how religious freedom is protected in South Africa. (12)
4.2 The establishment of the Interfaith Action for Peace in Africa (IFAPA) was a significant effort to unite religions across Africa. List any EIGHT of this organisation's achievements. (16) [50]
QUESTION 5
5.1 State THREE unique features of Hinduism. (6)
5.2 Discuss some of the significant changes in interreligious relations after South Africa became a democratic state in 1994. (14)
5.3 Read the article below and answer the questions that follow.
RELIGION NEEDS REGULATION Penuel Mnguni, a preacher from Pretoria, fed his followers a live snake, saying it tasted like chocolate. Before that, his spiritual father, Daniel Mosuoe, gave his congregants petrol to drink, which turned into 'juice'. Both tricks were without consequence … [Adapted from The Star, 10 November 2015] |
5.3.1 What is a 'bling pastor'? (4)
5.3.2 What does this article show about the writer's attitude towards religion? Give supporting evidence from the article. (12)
5.3.3 Do you think religion should be regulated? Substantiate your answer. (6)
5.3.4 Suppose you are a journalist. Rewrite the article from the point of view of Penuel Mnguni and Daniel Mosuoe and defend their actions. (8) [50]
GRAND TOTAL: 150
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAM PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2016
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
PAPER TWO (P2)
GRADE 12
AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAM
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS 2016
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A: SHORT QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1.1 B ✔ (1)
1.1.2 A ✔ (1)
1.1.3 C ✔ (1)
1.1.4 D ✔ (1)
1.1.5 A ✔ (1)
1.2.1 Cookie ✔ (1)
1.2.2 Plug and Play ✔/PnP (1)
1.2.3 Spoofing ✔/Phishing (1)
1.2.4 SQL injection ✔ (1)
1.2.5 Streaming ✔ (1)
1.2.6 Artificial intelligence ✔(AI) (1)
1.2.7 Mediated search ✔ (1)
1.2.8 DBMS – Database Management Software ✔ (1)
1.2.9 Static website ✔ (1)
1.2.10 Peer-to-peer ✔ (1)
TOTAL SECTION A: 15
SECTION B: SYSTEM TECHNOLOGIES
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1
- Any ONE ✔✔
Cache is a small amount of high speed memory where data and instructions likely to be used next by the CPU, is stored eliminating the need to fetch it from the slower RAM.
Concepts:- Saving time in fetching of instructions
- High speed memory
- Cache memory is built in to/not removable ✔ from the processor (1)
- Any TWO ✔✔
- Faster at boot up time/faster access time
- No moving parts so less easily damaged/bigger life/lasts longer/more reliable
- Uses less power
- Generates less heat
- Smaller dimensions (2)
- Any ONE ✔✔
2.1.2
- Any TWO ✔✔
- Provides a user interface
- I/O management (Input/output management)
- Process management
- Manages system memory
- File management/Storage management
- Security
- Optimises efficiency/speed (2)
-
- Android: designed for mobile ✔ devices or example of mobile devices (1)
- Unix: designed to be used mostly in a network ✔ or server or desktop environment (not mobile) (1)
- Recently accessed web pages ✔ are stored locally on the hard drive ✔ and are retrieved faster from cache the next time they are accessed rather than from the web server.✔ (3)
- Any TWO ✔✔
2.2
2.2.1 Any ONE ✔
- Manage/Maintain/Control computer resources.
- Add more functionality for specific management tasks (1)
2.2.2 Any ONE ✔
- Internet filters
- Spam blockers
- Pop-up blockers
- Anti-spam programs
- Phishing filters
- Any other acceptable filtering mechanism (1)
2.2.3 Any ONE explained aspect ✔✔
- Programs often share files which are often spread over different folders, making it impossible to manually find all the files.
- If you delete one of these shared files, another program that was using the file might no longer function correctly
- The registry also has to be 'notified' that a program no longer exists, because that program was associated with certain files types, etc. (2)
2.2.4
-
- Backup: makes a copy ✔ of current files and are used for operational recoveries/to use if file is lost or damaged
- Archiving: moving ✔ less frequently used data/files to another area (2)
- Lossy compression – some insignificant/undetectable portion ✔ of data is sacrificed/lost ✔ when compression takes place. (2)
-
2.3
2.3.1 Virtual memory ✔
Also accept: sector (1)
2.3.2 When the RAM is full ✔, the operating system will move data ✔/ instructions that are not being used to the hard disk ✔ to free up space in RAM
Concepts:
- Reference to RAM being full/shortage
- Make use of hard drive space
- Memory allocations are split (3)
2.4 Any TWO✔✔
- OSS: Access to source code
- OSS: Freedom to adapt and change code to own needs
- OSS: Access to community of users/support (2)
TOTAL SECTION B: 26
SECTION C: COMMUNICATION AND NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES
QUESTION 3
3.1 Any TWO ✔✔
- High level of expertise needed to set it up
- Need a high level of security
- Malware can spread easily
- If network develops a problem, no one can work
- A central problem with server could lead to loss of connection to the network/network resources.
- Cost of hardware (2)
3.2
3.2.1
✔ switch/central connection point
✔ computers/nodes
✔ connected separately to the switch
2 Marks for a diagram without labels  (3)
(3)
3.2.2 Any TWO ✔✔
- Easy to troubleshoot
- Easy to add new nodes
- Can remove any computer that does not work without affecting network/Stability
- Easy to set up
- Faster transmission of data to correct computer through a switch (2)
3.3
3.3.1 Any ONE ✔
- Cheap to install
- Easy to install
- Flexibility of cables
- High bandwidth over short distances (1)
3.3.2 Any TWO ✔✔
Not sensible because:
- Expensive cabling
- Need expert to install these cables
- More suited to a backbone network
OR
Sensible because
- High bandwidth
- Many users (2)
3.4
3.4.1 HTTPS ✔ (1)
3.4.2 Making voice/audio/video calls over the Internet/network✔
OR
Provides a variety of methods for establishing two-way multimedia communication over the Internet. (1)
3.5
3.5.1 Video on Demand ✔ (1)
3.5.2 Hotspot ✔ (1)
3.5.3 To provide Internet access ✔
OR
Internet service provider (1)
3.5.4 Wi-Fi/Wireless connectivity ✔ (1)
3.5.5 Any ONE✔
- Short range
Speed of transfer is slow
Reduced battery life (1)
- Short range
3.6
3.6.1 GPS ✔ (1)
3.6.2 Any ONE ✔
- Marketing/Advertising when in close proximity to the venue
- Tracking system in the event devices are stolen (1)
3.7
3.7.1 The server will notify the device that a new message has arrived✔ and automatically download ✔ the message to the device
OR
E-mail is automatically downloaded to the device without the user having to check his e-mail
Concepts:
- Automatic download
- Notification/no user action (2)
3.7.2 Any TWO ✔✔
- Attachments can use up storage
- Attachments are not automatically downloaded
- Limited to the number of messages that can be stored on the device
- May not have app to open attachments
- Not easy to read certain documents because of size of screen (2)
TOTAL SECTION C: 23
SECTION D: DATA AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
QUESTION 4
4.1
4.1.1 Any TWO ✔✔
- Only 1 option can be selected at a time
- Only the valid/specific options are available
- Saves time – no need to type
- Do not have to check spelling, uppercase, etc. (2)
4.1.2 Any ONE ✔
- Use a mask edit (Delphi)
- Use 2 combo boxes – one for hours and one for minutes
- Give an example of time format in the text box (1)
4.1.3 (1 mark for valid with correct example) ✔(1 mark for correct with correct example) ✔
Valid – adhere to the specifications, e.g. hours must be in the range of 0 to 24
Correct – The data is within the specifications but incorrect based
on the specific information, e.g. instead of entering 10 which is the correct hour another incorrect but valid hour (e.g. 11) is entered.
Or any other correct explanation (2)
4.2
4.2.1 ComputerNumber is the primary key in the tblComputers table ✔ and must be placed in the tblUsers table as a foreign key. ✔ The ComputerNumber field in both tables can used to link the tables.
Concepts:
- Table set up: third table or add field to current table
Correct fields connected: primary and foreign keys (2)
NOTE: Ignore quote symbols in all SQL statements
- Table set up: third table or add field to current table
4.2.2
- SELECT LogoutTime FROM tblUsers WHERE PaymentMethod = 'Debit Card' ORDER BY LogoutTime
✔ SELECT LogoutTime
✔ FROM tblUsers
✔ WHERE PaymentMethod = 'Debit Card'/ LIKE ‘Debit%’
✔ ORDER BY LogoutTime (ASC optional)
Cannot be in descending order (DESC) (4) - UPDATE tblUsers SET PaymentMethod = 'Credit Card' WHERE UserIDNo = '7311017564076'
✔ UPDATE tblUsers
✔ SET PaymentMethod = 'Credit Card'
✔ WHERE UserIDNo = '7311017564076' (3) - SELECT Count(tblUsers.UserIDNo) AS CountCashIds
FROM tblUsers
WHERE PaymentMethod ='Cash';
✔ SELECT Count(UserIDNo)
✔ AS CountCashIds
✔ FROM tblUsers
✔ WHERE PaymentMethod='Cash'
NOTE: any field can be used to count the number of users (4) - SELECT * FROM tblUsers WHERE (LoginTime > '12:00') AND (LoginDate = #2016/02/25#)
✔ SELECT * FROM tblUsers
✔ WHERE (LoginTime >'12:00')
✔ AND
✔ (LoginDate = #2016/02/25#)
Also accept UserId as the field (4)
- SELECT LogoutTime FROM tblUsers WHERE PaymentMethod = 'Debit Card' ORDER BY LogoutTime
4.3 Audit trail – records who makes changes ✔ to the database and when the changes were made ✔ (2)
4.4
4.4.1 Any TWO ✔✔
- Using credit card or loyalty card when purchases are made
- With the completions forms for competitions, etc.
- Browsing the Internet/selecting webpages
- When using e-tags
Or any other correct answer (2)
4.4.2 Data mining (1)
TOTAL SECTION D: 27
SECTION E: SOLUTION DEVELOPMENT
QUESTION 5
5.1
5.1.1 Once ✔✔ (2)
5.1.2 Infinite/Endless loop/Continuously/Never-ending ✔✔ (2)
5.2
5.2.1 Space is created in memory✔ to keep the attributes of the specific object ✔
OR
The constructor is used to create an instance of the object class
OR
Instantiation is the creation of a real instance or particular
realisation of an abstraction or template (such as a class) of an object. (2)
5.2.2
- Accessor: to get access to private data/field/attribute values✔ (1)
- Mutator: allows field/attribute values to be changed ✔ or set (1)
5.2.3
✔ get log in minutes
✔ get log out minutes
✔ get log in hour
✔ get log out hour
✔ calculate the number of hours
✔ calculate the number of minutes
✔ convert hours to minutes and add minutes
✔ multiply with 3
Solution1:
loginMin? copy the login minutes
logoutMin ? copy the logout minutes
loginHr ? copy the login hour
logoutHr ? copy the logout hour
totalMinLogin ? loginHr*60 + loginMin
totalMinLogout ? logoutHr * 60 + logoutMin
numberofMinutes ? totalMinLogout – totalMinLogin
cost ? numberofMinutes x 3
Solution 2:
loginMin? copy the login minuteslogoutMin ? copy the logout minutes
loginHr ? copy the login hour
logoutHr ? copy the logout hour
numberof Minutes ? (logoutHr – loginHr) *60+logoutMin – loginMin
cost ? numberofMinutes x 3
Or any other correct solution (8)
5.3
Found | Is Found true? | randomNum | Is randomNum = number? | Counter | Display | |
False | No/False | |||||
5 | No | xxxx | ||||
40 | Yes | xxxxx |
1mark first 2 columns initial values
1 mark to indicate that counter and display will be undefined
Errors
1 mark initialise counter
1 mark increment regardless of if statement
Counter has not been initialised before the loop
If Counter is set to 0 :
Add 1 to Counter before it is displayed
OR
Change the If-statement as follows:
If number = randomNum then
Found = true
Increment Counter
OR
Also including the increment in the else part of the if
OR
Initialise counter to 1 (2 marks)
(4)
5.4 0 1 0 0 ✔
0 1 1 1 ✔ (2)
TOTAL SECTION E: 22
SECTION F: INTEGRATED SCENARIO
QUESTION 6
6.1
6.1.1 Radio waves ✔/explanation of how the technology works (1)
6.1.2 Any TWO ✔✔
- Item can be tracked
- Easy to do stock take/can scan tag
- Don't have to be very close to read the tag
- Can read more than 1 tag at a time
- Can read hidden tags
- Interact with data stored on the tag
- Use tag to broadcast information (e.g. temperature) about the environment
Any other valid example (2)
6.2
6.2.1 Specialised network software skills and knowledge are required to manage the network. ✔
Also accept an example of specialised duties
Do not accept: maintenance of the network (1)
6.2.2 Any TWO ✔✔
- Use a password with many characters
- Include special characters
- Do not use common words
- Do not use your personal details
- Uppercase and lowercase
- Avoid patterns/repetitions (2)
6.2.3 Remote desktop (or suitable example) ✔ uses software to view the screen of the server on the local computer and control the server remotely. ✔
VPN (or suitable example) ✔ is a secure connection to the server via the Internet ✔ (4)
6.2.4 Any ONE ✔
- Install a firewall
- Install anti-virus software
- Keep anti-virus software up to date
Any other correct answer (1)
6.2.5 Any TWO ✔✔
- Allocating user rights
- Adding and removing users
- Making backups
Any other correct answer
Do NOT accept: issuing passwords and avoiding virus attacks (2)
6.3
6.3.1 Unsolicited ✔ junk/adverts/email sent to many recipients ✔at once with the intention of trying to convince the receiver to purchase a product or visit a website. (2)
6.3.2 Any TWO ✔✔
- Do not give out personal information on web sites
- Check that the web site is secure
- Do not answer bogus e-mails
or any other valid example (2) 6.3.3 Encryption ✔ (1)
6.3.4 A digital certificate is used to authenticate the website/ person/organisation. ✔ (1)
6.3.5 Any TWO ✔✔
- Check whether the author is reputable.
- Check whether the site is reputable
- Compare information on the topic on different web sites.
- Check the creation date – should not be out dated information. (2)
6.3.6 Devices that connect to the Internet ✔ and interact with each other often without human interaction/remotely accessible ✔ (2)
6.3.7 Any TWO ✔✔
- Change the display setting to dim.
- Switch off GPS
- Switch off Bluetooth/Wi-Fi
- Do not play videos on the device
- Close unnecessary apps that are running in the background
Any other correct answer (2)
6.3.8 Collection of programs designed to gain administrator rights ✔ to take control of the computer at the most basic level✔ (2)
6.4
6.4.1 Peer-to-peer protocol/Internet ✔ (1)
6.4.2 Any ONE ✔
- IP address is open to other users/security of your computer is compromised
- Downloaded content may be pirated/illegal
- Up-bandwidth can be used up/Make Internet connection very slow due to use of bandwidth (1)
6.5
6.5.1 Any TWO ✔✔
- Attachments/files can sometimes be too large to e-mail
Also accept any advantage of file-sharing such as: - Collaboration
- Simultaneous editing of documents is possible
- Files are always the latest version
- Accessibility from anywhere (2)
- Attachments/files can sometimes be too large to e-mail
6.5.2 File syncing service:
- All changes to the files are copied to the cloud service automatically ✔
- Have access to all files even if offline ✔
- Have access anywhere, anytime to latest version ✔ (3)
6.6 Any THREE ✔ ✔
- Easy to navigate interface/smaller screen
- Managing Internet data use
- Less memory
- Less storage
- Less processing capability
- Dedicated purpose/specifically designed for an organisation
- Can make use of additional sensors (3)
TOTAL SECTION E: 37
GRAND TOTAL: 150
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAM PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2016
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
PAPER ONE (P1)
GRADE 12
AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAM
PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS 2016
GENERAL INFORMATION:
- These marking guidelines are to be used as the basis for the marking session. They were prepared for use by markers. All markers are required to attend a rigorous standardisation meeting to ensure that the guidelines are consistently interpreted and applied in the marking of candidates’ work..
- Note that learners who provide an alternate correct solution to that given as example of a solution in the marking guidelines will be given full credit for the relevant solution, unless the specific instructions in the paper was not followed or the requirements of the question was not met
- Annexures A, B and C (pages 3-7) include the marking grid for each question for using either one of the two programming languages.
- Annexures D, E and F (pages 6-17) contain examples of solutions for Java for Questions 1 to 3 in programming code.
- Annexures G, H and I (pages 18-30) contain examples of solutions for Delphi for Questions 1 to 3 in programming code.
- Copies of Annexures A, Band C (pages 3-7) should be made for each learner and completed during the marking session.
MEMORANDUM
ANNEXURE A:
SECTION A:
QUESTION 1: MARKING GRID- GENERAL PROGRAMMING SKILLS
CENTRE NUMBER: | EXAMINATION NUMBER: | |||
QUESTION | DESCRIPTION | MAX. MARKS | LEARNER'SMARKS | |
If a learner has a problem reading from a combobox, penalise only once for the error. | ||||
1.1 | Button - [Question 1.1] | 3 | ||
1.2 | Button - [Question 1.2] | 7 | ||
1.3 | Button - [Question 1.3] | 7 | ||
1.4 | Button - [Question 1.4] | 9 | ||
| 1.5 | Button - [Question 1.5] | 10 | ||
| 1.6 | Button - [Question 1.6] | 14 | ||
| TOTAL: | 50 | |||
ANNEXURE B:
SECTION B:
QUESTION 2: MARKING GRID - OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING
CENTRE NUMBER: | EXAMINATION NUMBER: | |||
QUESTION | DESCRIPTION | MAX. MARKS | LEARNER'S MARKS | |
2.1.1 | Declare attributes ✔ with the correct data types (String/Integer ✔; Boolean/double✔) | 3 | ||
2.1.2 | (a) Remove comment symbols from accessor methods✔ | 4 | ||
2.1.3 | Constructor: | 3 | ||
2.1.4 | calcAmount method: | 4 | ||
2.1.5 | calcDiscount method: | 5 | ||
2.1.6 | toString METHOD: | 4 | ||
| 2.2.1 | Button – [Quest2.2.1]: | 25 | ||
| 2.2.2 | Button – [Quest2.2.2]: | 10 | ||
| 2.2.3 | Button – [Quest2.2.3]: | 2 | ||
| TOTAL | 60 | |||
ANNEXURE C:
SECTION C:
QUESTION 3: MARKING GRID–PROBLEM SOLVING
CENTRE NUMBER: | EXAMINATION NUMBER: | ||||
SECTION | DESCRIPTION | MAX. MARKS | LEARNER'S MARKS | ||
User input validation | Validate the month: Check if user entered a month ✔ Convert to numeric value ✔ Check range✔✔ Validate user input for event to remove duplicates: Convert the string entered to uppercase/lowercase ✔ or use equalsIgnoreCase method (Java) | 8 | |||
Display of output | Heading contains event selected or All ✔ and month entered or All✔ | 9 | |||
Sorting of arrays | Declare temporary string variables for event and date ✔ | 8 | |||
Remove duplicates | Input event ✔, ignore/set the case of the characters✔ | 10 | |||
Program techniques | Modular design – at least two procedures/methods ✔✔ Descriptive variable names✔; Proper indentation ✔; Suitable comments ✔ | 5 | |||
TOTAL | 40 | ||||
SUMMARY OF LEARNER’S MARKS:
SECTION A | SECTION B | SECTION C | ||
QUESTION 1 | QUESTION 2 | QUESTION 3 | GRAND TOTAL | |
MAX. MARKS | 50 | 60 | 40 | 150 |
LEARNER'S MARKS |
ANNEXURE D: SOLUTION FOR QUESTION 1: JAVA
//A possible solution to Question 1
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class Question1_Solution extends javax.swing.JFrame {
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0.00");
String activityType = "Quiz";
int numParticipants = 50;
public Question1_Solution() {
initComponents();
this.setLocationRelativeTo(this);
txfEvent.setText(activityType);
}
=========================================================================
// Question 1.1
=========================================================================
private void btnQues1_1ActionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {
String category = (String)cmbCategory.getSelectedItem();
lblOutput.setText(activityType + ":" + category);
}
=========================================================================
// Question 1.2
=========================================================================
private void btnQues1_2ActionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {
numParticipants = Integer.parseInt(txfNumParticipants.getText());
int cost = 0;
if(numParticipants <= 20){
cost = numParticipants * 25;
}
else {
cost = (20 * 25) + ((numParticipants - 20) * 30);
}
txfIncome.setText("R" + df.format(cost));
}
=========================================================================
// Question 1.3
=========================================================================
private void btnQues1_3ActionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {
int base = Integer.parseInt(JOptionPane.showInputDialog("Enter the base"));
int exponent = Integer.parseInt(JOptionPane.showInputDialog("Enter the exponent"));
int power = (int)(Math.pow(base, exponent));
double squareRoot = Math.sqrt(power);
txfAns_1_3.setText("x = " + df.format(squareRoot));
}
=========================================================================
// Question 1.4
=========================================================================
private void btnQues1_4ActionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {
int numberOfPieces = numParticipants * 3;
double numberOfPizzas = numberOfPieces / 8.0;
txaOutput_1_4.setText("Exact value = " + String.format("%- 6.4f",numberOfPizzas));
txaOutput_1_4.append("\nNumber of pizzas to order = ");
if(numberOfPizzas == (int)numberOfPizzas){
txaOutput_1_4.append("" + (int)numberOfPizzas);
}
else
{
txaOutput_1_4.append("" + (((int)(numberOfPizzas)) + 1));
}
}
=========================================================================
// Question 1.5
=========================================================================
private void btnQues1_5ActionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {
//Question 1.5.1
// Code to determine the number of questions
txaOutput_1_5.setText("");
int numQuestions = 0;
if(rbtRound1.isSelected()){
numQuestions = 5;
}
else
{
if(rbtRound2.isSelected())
numQuestions = 8;
if(chbBonus.isSelected())
numQuestions += 2;
}
// Question 1.5.2
txaOutput_1_5.setText("");
txaOutput_1_5.append("Questions to answer\n");
String output = "";
for (int i = 1; i <= numQuestions; i++) {
for (int j = numQuestions; j >= i; j--) {
output = output + (j + " ");
}
output = output + "\n";
}
txaOutput_1_5.append(output + "\nQuiz completed");
}
=========================================================================
// Question 1.6
=========================================================================
private void btnQues1_6ActionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {
int numSeats = 30;
double ticketPrice = 50;
double totalIncome = 0;
txaOutput_1_6.append(String.format("%-10s%-10s%-16s%- 10s\n","Row","Seats","Ticket price","Income"));
for (int i = 1; i <=20 ; i++) {
double rowIncome = numSeats * ticketPrice;
totalIncome = totalIncome + rowIncome;
txaOutput_1_6.append(String.format("%-10s%-10sR%-15.2fR%- 10.2f\n",i,numSeats,ticketPrice,rowIncome));
numSeats = numSeats + 2;
ticketPrice = ticketPrice - 2;
}
txaOutput_1_6.append("\nTotal income is: R" + df.format(totalIncome));
}
}
ANNEXURE E: SOLUTION FOR QUESTION 2: JAVA
//A possible solution for the object class
OBJECT CLASS: DETAILS
package Question2Package;
=========================================================================
// Question 2.1.1
=========================================================================
public class Order
{
private String name;
private int numGroup;
private int numSingle;
private char paid;
=========================================================================
// Question 2.1.2
=========================================================================
// Question 2.1.2 (a)
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public int getNumGroup()
{
return numGroup;
}
public int getNumSingle()
{
return numSingle;
}
// Question 2.1.2 (b)
public String getPaid()
{
if (paid == 'Y')
return "Yes";
else
return "No";
}
=========================================================================
// Question 2.1.3
=========================================================================
public Order(String Name, int numGroup, int numSingle, char paid)
{
this.name = Name;
this.numGroup = numGroup;
this.numSingle = numSingle;
this.paid = paid;
}
=========================================================================
// Question 2.1.4
=========================================================================
public double calcAmount()
{
double total = (numGroup * 15.70) + (numSingle * 12.50); return total;
}
=========================================================================
// Question 2.1.5
=========================================================================
public double calcDiscount()
{
double discount = 0;
if ((numGroup >= 4 || numSingle >= 4) &&
getPaid().equalsIgnoreCase("Yes")){
discount = calcAmount() * 5 / 100.00;
}
return discount;
}
=========================================================================
// Question 2.1.6
=========================================================================
public String toString()
{
String data = "Name: " + name + "\nGroup: " + numGroup+"\nSingle: " + numSingle + "\nPaid: " + getPaid();
return data;
}
}
GUI CLASS: QUESTION2_SOLUTION
package Question2Package;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
import javax.swing.JTextArea;
public class Question2_Solution extends javax.swing.JFrame {
String nameOfSchool;
String name;
Details photoPackage;
public Question2_Solution() {
initComponents();
setLocationRelativeTo(this);
}
=========================================================================
// Question 2.2.1
=========================================================================
private void btnQues2_2_1ActionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {
boolean bFound;
txaOutput.setText("");
name = cmbNames.getSelectedItem().toString();
try
{
Scanner inFile = new Scanner(new FileReader("Photographs.txt")); nameOfSchool = inFile.nextLine();
lblSchoolName.setText(nameOfSchool);
bFound = false;
while (inFile.hasNext() && !bFound) {
String line = inFile.nextLine();
Scanner scLine = new Scanner(line).useDelimiter("#|;"); String newName = scLine.next();
if (newName.equalsIgnoreCase(name)) {
int group = scLine.nextInt();
int single = scLine.nextInt();
char paid = scLine.next().charAt(0);
photoPackage = new Order(name, group, single, paid); txaOutput.append(photoPackage.toString()); txaOutput.append(String.format("\n\nAmount: R%-5.2f",
photoPackage.calcAmount()));
bFound = true;
}
}
inFile.close();
if (bFound == false){
btnQues2_2_2.setEnabled(false);
btnQues2_2_3.setEnabled(false);
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, name + " was not found in text file");
} else {
btnQues2_2_2.setEnabled(true);
btnQues2_2_3.setEnabled(true);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException ex)
{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "File does not exist");
System.exit(0);
}
}
=========================================================================
// Question 2.2.2
=========================================================================
private void btnQues2_2_2ActionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {
PrintWriter outFile;
if (!photoPackage.getPaid().equals("Yes")) {
try
{
outFile = new PrintWriter(photoPackage.getName() + ".txt");
outFile.println("Group: " + photoPackage.getNumGroup());
outFile.println("Single: " + photoPackage.getNumSingle());
outFile.println("Total amount: " + photoPackage.calcAmount());
txaOutput.append("\nText file created ");
outFile.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException ex)
{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "File not found");
System.exit(0);
}
} else
{
txaOutput.append("\nAccount paid ");
}
}
=========================================================================
// Question 2.2.3
=========================================================================
private void btnQues2_2_3ActionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {
txaOutput.append(String.format("\nDiscount: R%-5.2f",
photoPackage.calcDiscount()) + "\n");
}
}
ANNEXURE F: SOLUTION FOR QUESTION 3: JAVA
// A possible solution to Question 3
package Question3Package;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class Question3_Solution extends javax.swing.JFrame {
DateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
String arrEvents[] = {
"Hockey", "Chess", "Rugby", "Chess", "Debating", "Hockey", "Soccer", "Rugby", "Debating", "Chess", "Rugby", "Debating", "Swimming", "Rugby", "Soccer", "Rugby", "Chess", "Choir", "Tennis", "Debating", "Debating", "Rugby", "Tennis", "Tennis", "Tennis", "Soccer", "Chess", "Swimming", "Hockey", "Rugby", "Chess", "Hockey", "Soccer", "Swimming", "Chess", "Choir", "Soccer", "Tennis", "Debating", "Rugby", "Choir", "Chess", "Choir", "Debating", "Rugby"};
String arrDates[] = {
"2015/10/04", "2015/03/20", "2015/09/17", "2015/03/20", "2015/05/24", "2015/10/04", "2015/06/03", "2015/07/19", "2015/09/16", "2015/07/01", "2015/03/17", "2015/11/19", "2015/07/29", "2015/09/18", "2015/10/23", "2015/07/15", "2015/03/07", "2015/06/08", "2015/04/01", "2015/03/07", "2015/09/12", "2015/11/12", "2015/10/03", "2015/05/11", "2015/10/03", "2015/05/28", "2015/09/28", "2015/05/10", "2015/09/24", "2015/10/14", "2015/04/23", "2015/03/23", "2015/06/03", "2015/07/29", "2015/09/18", "2015/08/29", "2015/11/10", "2015/04/01", "2015/04/10", "2015/03/23", "2015/10/04", "2015/10/07", "2015/05/03", "2015/07/30", "2015/11/25"};
int monthNumber;
int count = 45;
String eventName, sMonth;
public Question3_Solution() {
initComponents();
setLocationRelativeTo(this);
cmbEvents.setSelectedIndex(0);
}
private void btnCloseActionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {
System.exit(0);
}
//========================================================================
private void btnRemoveActionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {
sortArrays();
removeDuplicates();
display();
}
//========================================================================
private void btnDisplayActionPerformed(java.awt.event.ActionEvent evt) {
sortArrays();
display();
}
/∗∗
∗ @param args the command line arguments
∗/
public static void main(String args[]) {
/∗ Create and display the form ∗/
java.awt.EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
new Question3_Solution().setVisible(true);
}
});
}
//========================================================================
public void display(){
if (!txfMonthNumber.getText().equals("")) {
monthNumber = Integer.parseInt(txfMonthNumber.getText()); if (monthNumber < 1 || monthNumber > 12) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "Please enter a valid number in the range of 1 to 12");
txfMonthNumber.setText("");
}
}
if (txfMonthNumber.getText().equals("")) {
sMonth = "All";
}
else {
sMonth = "" + monthNumber;
}
//JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null,eventName.equals("All"));
eventName = (String) (cmbEvents.getSelectedItem());
txaOutput.setText("List of " + eventName.toLowerCase() + " events for month: " + sMonth + "\n\n");
txaOutput.append(String.format("%-15s%-10s\n", "EVENTS", "DATES"));
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
int testmonth = Integer.parseInt(arrDates[i].substring(5, 7)); if (((monthNumber == testmonth) || (sMonth.equals("All"))) && ((eventName.equalsIgnoreCase(arrEvents[i])) ||
(eventName.equals("All")))) {
txaOutput.append(String.format("%-15s%-10s\n", arrEvents[i], arrDates[i]));
}
}
}
}
//========================================================================
public void sortArrays()
{
String tempDate = "";
String tempEvent = "";
for (int i = 0; i < count - 1; i++)
for (int j = i + 1; j < count; j++) {
if (arrDates[i].compareTo(arrDates[j]) > 0) {
tempDate = arrDates[i];
arrDates[i] = arrDates[j];
arrDates[j] = tempDate;
tempEvent = arrEvents[i];
arrEvents[i] = arrEvents[j];
arrEvents[j] = tempEvent;
}
}
}
//========================================================================
public void removeDuplicates(){
String event = JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null, "Enter the event","");
int i = 0;
while (i < count) {
int j = i + 1;
while ((arrEvents[i].equalsIgnoreCase(event)) &&
(arrDates[i].equals(arrDates[j]) && j <= count)) {
for (int k = j; k < count - 1; k++){
arrDates[k] = arrDates[k + 1];
arrEvents[k] = arrEvents[k + 1];
}
count--;
}
i++;
}
}
ANNEXURE G: SOLUTION FOR QUESTION 1: DELPHI
unit Question1U_MEMO;
//A possible solution to Question 1
interface
uses
Windows, Messages, SysUtils, Variants, Classes, Graphics, Controls, Forms,
Dialogs, StdCtrls, Buttons, ExtCtrls, ComCtrls;
type
TfrmQuestion1 = class(TForm)
pnlButtons: TPanel;
bmbClose: TBitBtn;
grbQ1_1: TGroupBox;
lblOutput: TLabel;
lblCategory: TLabel;
lblEvent: TLabel;
edtEvent: TEdit;
cboCategory: TComboBox;
btnQuestion1_1: TButton;
grbQ1_2: TGroupBox;
lblNumParticipants: TLabel;
edtNumParticipants: TEdit;
btnQuestion1_2: TButton;
edtIncome: TEdit;
grbQ1_3: TGroupBox;
btnQuestion1_3: TButton;
edtAnswer: TEdit;
grbQ1_4: TGroupBox;
btnQuestion1_4: TButton;
grbQ1_5: TGroupBox;
btnQuestion1_5: TButton;
redQ14: TRichEdit;
redQ15: TRichEdit;
grbQ1_6: TGroupBox;
btnQuestion1_6: TButton;
redQ16: TRichEdit;
cbkBonus: TCheckBox;
rgpRound: TRadioGroup;
procedure FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
procedure btnQuestion1_1Click(Sender: TObject);
procedure btnQuestion1_2Click(Sender: TObject);
procedure btnQuestion1_3Click(Sender: TObject);
procedure btnQuestion1_4Click(Sender: TObject);
procedure btnQuestion1_6Click(Sender: TObject);
procedure btnQuestion1_5Click(Sender: TObject);
procedure rgpRoundClick(Sender: TObject);
private
{ Private declarations }
public
{ Public declarations }
end;
var
frmQuestion1: TfrmQuestion1;
implementation
{$R *.dfm}
{$R+}
uses Math, DateUtils;
var
sEvent : String = 'Quiz';
iNumParticipants : Integer = 50;
=========================================================================
// Question 1.1
=========================================================================
procedure TfrmQuestion1.btnQuestion1_1Click(Sender: TObject);
begin
lblOutput.Caption := edtEvent.Text + ':' +
cboCategory.Items[cboCategory.ItemIndex]; end;
=========================================================================
// Question 1.2
=========================================================================
procedure TfrmQuestion1.btnQuestion1_2Click(Sender: TObject);
var
rCost : real;
begin
rCost := 0;
iNumParticipants := StrToInt(edtNumParticipants.Text);
if iNumParticipants <= 20 then
begin
rCost := iNumParticipants * 25.00;
end
else
begin
rCost := (20 * 25.00) + ((iNumParticipants-20)* 30.00);
end;
edtIncome.Text := FloatToStrF(rCost, ffCurrency, 8, 2);
end;
=========================================================================
// Question 1.3
=========================================================================
procedure TfrmQuestion1.btnQuestion1_3Click(Sender: TObject);
var
iBase, iExp : integer;
rAnswer : real;
begin
iBase := StrToInt(InputBox('Base value', 'Enter the base', ' '));
iExp := StrToInt(InputBox('Exponent value',
'Enter the exponent', ' '));
rAnswer := Sqrt(Power(iBase, iExp));
edtAnswer.Text := 'x = ' + FloatToStrF(rAnswer, ffFixed, 8,2);
end;
=========================================================================
// Question 1.4
=========================================================================
procedure TfrmQuestion1.btnQuestion1_4Click(Sender: TObject);
var
rPizzas : real;
begin
rPizzas := (iNumParticipants * 3) / 8;
redQ14.Clear;
redQ14.Lines.Add('Exact value = ' + FloatToStrF(rPizzas, ffFixed, 8,4) +
13+ 'Number of pizzas to order = ' +
FloatToStrF(Round(rPizzas + 0.5), ffFixed, 8, 0));
end;
=========================================================================
// Question 1.5
=========================================================================
procedure TfrmQuestion1.btnQuestion1_5Click(Sender: TObject);
var
K,J,iNumQuestions : integer;
sOutput : String;
begin
//Question 1.5.1
// Code to determine the number of questions
if rgpRound.ItemIndex = 0 then
begin
iNumQuestions := 5;
cbkBonus.checked := false;
end
else
begin
if rgpRound.ItemIndex = 1 then
iNumQuestions := 8;
if cbkBonus.checked then
inc(iNumQuestions,2);
end;
//Question 1.5.2
//Correct incorrect code to display pattern
redQ15.Clear;
redQ15.Lines.Add('Questions to answer') ;
sOutput := '';
for I := 1 to iNumQuestions do
begin
for J:= iNumQuestions downto I do
sOutput := sOutput + IntToStr(J) + ' ';
sOutput := sOutput + #13;
end;
redQ15.Lines.Add(sOutput + #13 + 'Quiz completed');
end;
=========================================================================
// Question 1.6
=========================================================================
procedure TfrmQuestion1.btnQuestion1_6Click(Sender: TObject);
var
A, iRow, iNumSeats : integer;
rTotalIncome, rRowIncome, rTicketPrice : real;
begin
iNumSeats := 30;
rTotalIncome := 0.0;
rTicketPrice := 50.00;
redQ16.Clear;
redQ16.Paragraph.TabCount := 3;
redQ16.Paragraph.Tab[0] := 50;
redQ16.Paragraph.Tab[1] := 110;
redQ16.Paragraph.Tab[2] := 180;
redQ16.Lines.Add('Row' + #9 + 'Seats' + #9 + 'Ticket price' + #9 + 'Income');
for iRow := 1 to 20 do
begin
rRowIncome := (iNumSeats * rTicketPrice);
rTotalIncome := rTotalIncome + rRowIncome;
redQ16.Lines.Add(IntToStr(iRow) + #9 + IntToStr(iNumSeats) + #9 + FloatToStrF(rTicketPrice, ffCurrency, 8, 2) + #9 + FloatToStrF(rRowIncome, ffCurrency, 8, 2));
rTicketPrice := rTicketPrice - 2;
Inc(iNumSeats, 2);
end;
redQ16.Lines.Add(#13 + 'Total income: ' + FloatToStrF(rTotalIncome, ffCurrency, 8, 2));
end;
//====================================================================
procedure TfrmQuestion1.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
begin
edtEvent.Text := sEvent;
CurrencyString := 'R';
end;
procedure TfrmQuestion1.rgpRoundClick(Sender: TObject);
begin
cbkBonus.Enabled := rgpRound.ItemIndex = 1;
end;
end.
ANNEXURE H: SOLUTION FOR QUESTION 2: DELPHI
OBJECT CLASS: DETAILS
unit OrderU;
//A possible solution for the object class
interface
=========================================================================
// Question 2.1.1
=========================================================================
type
TOrder = class(TObject)
private
fName : String;
fNumGroup,
fNumSingle : integer;
fPaid : Char;
public
function getName : String;
function getNumGroup : integer;
function getNumSingle: integer;
function getPaid : String;
constructor Create(Name : String; Group, Single : integer; Paid : Char);
function calcAmount : real;
function calcDisount : real;
function toString : String;
end;
implementation
uses SysUtils, Math, DateUtils;
{ TDetails }
=========================================================================
// Question 2.1.2
=========================================================================
// Question 2.1.2 (a)
function TOrder.getName: String;
begin
Result := fName;
end;
function TOrder.getNumGroup: integer;
begin
Result := fNumGroup;
end;
function TOrder.getNumSingle: integer;
begin
Result := fNumSingle;
end;
//Question 2.1.2 (b)
function TOrder.getPaid: String;
begin
if (fPaid = 'Y') then
Result := 'Yes'
else
Result := 'No';
end;
=========================================================================
// Question 2.1.3
=========================================================================
constructor TOrder.Create(Name: String; Group, Single: integer; Paid: char);
begin
fName := Name;
fNumGroup := Group;
fNumSingle:= Single;
fPaid := Paid;
end;
=========================================================================
// Question 2.1.4
=========================================================================
function TOrder.calcAmount: real;
begin
Result := (fNumGroup * 15.70) + (fNumSingle * 12.50);
end;
=========================================================================
// Question 2.1.5
=========================================================================
function TOrder.calcDisount: real;
var
rDiscount : real;
begin
if ((fNumGroup >= 4) OR (fNumSingle >= 4)) AND (fPaid = 'Y') then
begin
rDiscount := calcAmount * 5 / 100.00;
end;
Result := rDiscount;
end;
=========================================================================
// Question 2.1.6
=========================================================================
function TOrder.toString: String;
begin
Result :=
'Name: ' + fName + #13 +
'Group: ' + IntToStr(fNumGroup) + #13 +
'Single: ' + IntToStr(fNumSingle)+ #13 +
'Paid: ' + getPaid;
end;
end.
MAIN FORM UNIT: QUESTION2_U.PAS
unit Question2U_MEMO;
//==============================
// A possible solution for Question 2
//==============================
interface
uses
Windows, Messages, SysUtils, Variants, Classes, Graphics, Controls, Forms, Dialogs, StdCtrls, Buttons, ExtCtrls, ComCtrls;
type
TfrmQuestionTwo = class(TForm)
pnlButtons: TPanel;
bmbClose: TBitBtn;
cboNames: TComboBox;
lblHeading: TLabel;
lblSelect: TLabel;
lblSchoolName: TLabel;
redQ2: TRichEdit;
btnQuestion2_2_1: TButton;
btnQuestion2_2_2: TButton;
btnQuestion2_2_3: TButton;
procedure btnQuestion2_2_1Click(Sender: TObject);
procedure btnQuestion2_2_2Click(Sender: TObject);
procedure btnQuestion2_2_3Click(Sender: TObject);
procedure FormClose(Sender: TObject; var Action: TCloseAction); procedure FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
private
{ Private declarations }
public
{ Public declarations }
end;
var
frmQuestionTwo: TfrmQuestionTwo;
implementation
uses DetailsU;
{$R *.dfm}
{$R+}
var
PhotoPackage: TOrder;
//======================================================================
procedure TfrmQuestionTwo.btnQuestion2_2_1Click(Sender: TObject);
var
tFile : TextFile;
sLine : String;
sSchool, sName: String;
bFound: boolean;
iGroup, iSingle: integer;
cPaid : Char;
begin
// =========================================================================
// Question 2.2.1
//=========================================================================
redQ2.Clear;
sName := cboNames.Items[cboNames.ItemIndex];
if NOT FileExists('Photographs.txt') then
begin
MessageDlg('File does not exists', mtError, [mbOk], 0);
Exit;
end;
AssignFile(tFile, 'Photographs.txt');
Reset(tFile);
readln(tFile, sSchool);
lblSchoolName.Caption := sSchool;
bFound := False;
while NOT EOF(tFile) AND NOT bFound do
begin
readln(tFile, sLine);
if pos(Uppercase(sName), Uppercase(sLine)) = 1 then
begin
Delete(sLine, 1, pos('#', sLine));
iGroup := StrToInt(Copy(sLine, 1, pos(';', sLine) - 1)); Delete(sLine, 1, pos(';', sLine));
iSingle := StrToInt(Copy(sLine, 1, pos(';', sLine) - 1)); Delete(sLine, 1, pos(';', sLine));
cPaid := sLine[1]; // true = Y / false = not Y
PhotoPackage := TOrder.Create(sName, iGroup, iSingle, cPaid);
redQ2.Lines.Add(PhotoPackage.toString + #13 + #13+ 'Amount: ' +
FloatToStrF(PhotoPackage.calcAmount, ffCurrency, 8, 2));
bFound := True;
end; // name found
end;
if NOT bFound then
begin
btnQuestion2_2_2.Enabled := False;
btnQuestion2_2_3.Enabled := False;
MessageDlg(sName + ' was not found in text file', mtError, [mbOk], 0); end
else
begin
btnQuestion2_2_2.Enabled := True;
btnQuestion2_2_3.Enabled := True;
end
end;
// ==========================================================================
procedure TfrmQuestionTwo.btnQuestion2_2_2Click(Sender: TObject);
var
tFile : TextFile;
sFileName : String;
begin
// =========================================================================
// Question 2.2.2
// ==========================================================================
if PhotoPackage.getPaid = 'Yes' then
begin
redQ2.Lines.Add('Account paid');
end
else
begin
sFileName := PhotoPackage.getName + '.txt';
AssignFile(tFile, sFileName);
Rewrite(tFile);
Writeln(tFile, 'Group: ' + IntToStr(PhotoPackage.getNumGroup));
Writeln(tFile, 'Single: ' + IntToStr(PhotoPackage.getNumSingle));
Writeln(tFile, 'Amount: ' + FloatToStrF(PhotoPackage.calcAmount,
ffCurrency, 8, 2));
CloseFile(tFile);
redQ2.Lines.Add('Text file created');
end;
end;
// ==========================================================================
procedure TfrmQuestionTwo.btnQuestion2_2_3Click(Sender: TObject);
begin
// =========================================================================
// Question 2.2.3
// ==========================================================================
redQ2.Lines.Add('Discount: ' + FloatToStrF(PhotoPackage.calcDisount, ffCurrency,8,2))
end;
// ==========================================================================
// Given Code
procedure TfrmQuestionTwo.FormClose(Sender: TObject; var Action: TCloseAction);
begin
if NOT(PhotoPackage = nil) then
begin
FreeAndNil(PhotoPackage);
end;
end;
procedure TfrmQuestionTwo.FormCreate(Sender: TObject);
begin
CurrencyString := 'R';
end;
// =========================================================================
end.
ANNEXURE I: SOLUTION FOR QUESTION 3: DELPHI
unit Question3U_Memo;
// A possible solution for Question 3
interface
uses
Windows, Messages, SysUtils, Variants, Classes, Graphics, Controls,
Forms,
Dialogs, StdCtrls, Buttons, ExtCtrls, ComCtrls;
type
TfrmQuestion3 = class(TForm)
pnlButtons: TPanel;
bmbClose: TBitBtn;
lblHead: TLabel;
btnDisplay: TButton;
grbInput: TGroupBox;
cboEvent: TComboBox;
lblEvent: TLabel;
edtMonth: TEdit;
lblMonth: TLabel;
redQ3: TRichEdit;
btnRemoveDuplicates: TButton;
procedure btnDisplayClick(Sender: TObject);
procedure btnRemoveDuplicatesClick(Sender: TObject);
procedure Display;
procedure SortArrays;
Procedure RemoveDuplicates;
procedure bmbCloseClick(Sender: TObject);
private
{ Private declarations }
public
{ Public declarations }
end;
Type
StringArray = Array [1 .. 45] of String;
var
frmQuestion3: TfrmQuestion3;
implementation
{$R *.dfm}
{$R+}
Uses DateUtils, Math;
var
arrEvents: array [1 .. 45] of String = (
'Hockey', 'Chess', 'Rugby', 'Chess', 'Debating', 'Hockey', 'Soccer', 'Rugby', 'Debating', 'Chess', 'Rugby', 'Debating', 'Swimming', 'Rugby', 'Soccer', 'Rugby', 'Chess', 'Choir', 'Tennis', 'Debating', 'Debating', 'Rugby', 'Tennis', 'Tennis', 'Tennis', 'Soccer', 'Chess', 'Swimming', 'Hockey', 'Rugby', 'Chess', 'Hockey', 'Soccer', 'Swimming', 'Chess', 'Choir', 'Soccer', 'Tennis', 'Debating', 'Rugby', 'Choir', 'Chess', 'Choir', 'Debating', 'Rugby');
arrDates: array [1 .. 45] of string = (
'2015/10/04', '2015/03/20', '2015/09/17', '2015/03/20', '2015/05/24', '2015/10/04', '2015/06/03', '2015/07/19', '2015/09/16', '2015/07/01', '2015/03/17', '2015/11/19', '2015/07/29', '2015/09/18', '2015/10/23', '2015/07/15', '2015/03/07', '2015/06/08', '2015/04/01', '2015/03/07', '2015/09/12', '2015/11/12', '2015/10/03', '2015/05/11', '2015/10/03', '2015/05/28', '2015/09/28', '2015/05/10', '2015/09/24', '2015/10/14', '2015/04/23', '2015/03/23', '2015/06/03', '2015/07/29', '2015/09/18', '2015/08/29', '2015/11/10', '2015/04/01', '2015/04/10', '2015/03/23', '2015/10/04', '2015/10/07', '2015/05/03', '2015/07/30', '2015/11/25');
iCount : Integer = 45;
// ==================================================================
procedure TfrmQuestion3.bmbCloseClick(Sender: TObject);
begin
Application.Terminate;
end;
procedure TfrmQuestion3.btnDisplayClick(Sender: TObject);
begin
SortArrays;
Display;
end;
//========================================================================
procedure TfrmQuestion3.btnRemoveDuplicatesClick(Sender: TObject);
begin
RemoveDuplicates;
SortArrays;
Display;
end;
//========================================================================
Procedure TfrmQuestion3.Display;
var
sEvent, sMonth: String;
iMonth,iTestMonth, A : Integer;
begin
redQ3.Clear;
redQ3.Paragraph.TabCount := 1;
redQ3.Paragraph.Tab[0] := 150;
sMonth := edtMonth.Text;
if sMonth <> '' then
begin
iMonth := StrToInt(sMonth);
if NOT(iMonth IN [1 .. 12]) then
begin
MessageDlg('Please enter a number in the range of 1 to 12', mtError, [mbOk], 0);
edtMonth.SetFocus;
Exit;
end;
end
else
sMonth := 'All';
// Display for selected event
sEvent := cboEvent.text;
redQ3.Lines.Add('List of ' + LowerCase(sEvent) + ' events for month: ' + sMonth + #13);
redQ3.Lines.Add('EVENTS ' + #9 + 'DATES');
for A := 1 to iCount do // or to high(arrEvents) do
begin
iTestMonth := StrToInt(copy(arrDates[A],6,2));
if ((iTestMonth = iMonth) OR (sMonth = 'All')) AND ((sEvent = arrEvents[A]) OR (sEvent = 'All')) then
redQ3.Lines.Add(arrEvents[A]+ #9 + arrDates[A]);
end;
end;
//========================================================================
Procedure TfrmQuestion3.SortArrays;
var
A, B : Integer;
sTempDate : String;
sTempEvent : String;
begin
// Sort arrays: arrDates & arrEvents
for A := 1 to iCount - 1 do
for B := A + 1 to iCount do
if arrDates[B] < arrDates[A] then
begin
sTempDate := arrDates[A];
arrDates[A] := arrDates[B];
arrDates[B] := sTempDate;
sTempEvent := arrEvents[A];
arrEvents[A] := arrEvents[B];
arrEvents[B] := sTempEvent;
end;
end;
//========================================================================
Procedure TfrmQuestion3.RemoveDuplicates;
var
i, j, indx : Integer;
sEvent : String;
begin
// Remove duplicates
indx := 0;
sEvent := Uppercase(InputBox('Event', 'Enter an event', '')); i := 1;
while i < iCount do
begin
j := i + 1;
While (Uppercase(arrEvents[i]) = sEvent) And (arrDates[j] = arrDates[i])
And (j <= iCount) do
begin
for indx := j to iCount-1 do
begin
arrdates[indx] := arrdates[indx+1];
arrEvents[indx] := arrevents[indx+1];
end;
Dec(iCount)
end;
inc(i);
end;
end;
end.