Adele
PHYSICAL SCIENCE (PHYSICS) PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
PHYSICAL SCIENCE (PHYSICS)
PAPER ONE (P1)
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2016
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your NAME in the appropriate space on the ANSWER BOOK.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Non-programmable calculators may be used.
- Appropriate mathematical instruments may be used.
- Number the questions correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You are advised to use the attached DATA SHEETS.
- The formulae and substitutions must be shown in ALL calculations.
- Give brief motivations, discussions, etc. where required.
- Round off your final numerical answers to a minimum of TWO decimal places.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- All diagrams are not necessarily drawn according to scale.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Four possible options are provided as answers to the following questions. Each question has only ONE correct answer. Choose the best answer and write down A, B, C or D next to the question number (1.1–1.10) on your ANSWER BOOK.
1.1 A boy throws a tennis ball vertically upwards from the ground. At its maximum height above the ground, its acceleration is …
- upwards.
- equal to the velocity at that point.
- downwards.
- zero. (2)
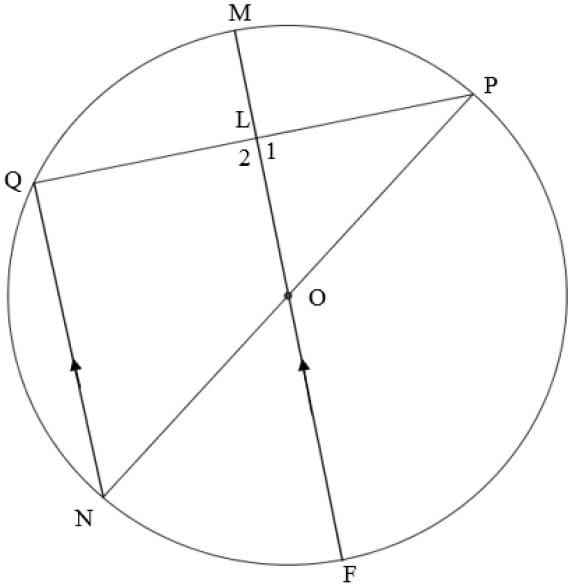
1.2 A CONSTANT FORCE F is applied to a box, causing the box to move at a CONSTANT VELOCITY over a rough horizontal surface. ![]()
The free-body diagram below shows all forces acting on the box. THE DIAGRAM IS NOT DRAWN TO SCALE. 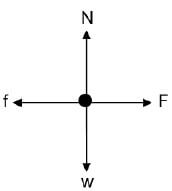
Which ONE of the following relationships is correct?
- F < f
- F > f
- F = w
- F = f (2)
1.3 An airbag can protect a driver from serious injury during a collision. Which ONE of the following best explains why this is possible? (2)
TIME OF IMPACT | NET FORCE | |
A | Increases | Increases |
B | Decreases | Decreases |
C | Increases | Decreases |
D | Remains the same | Decreases |
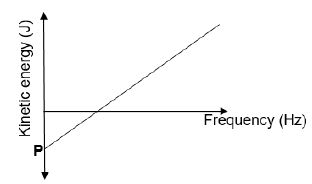
1.4 The graph below shows the relationship between maximum kinetic energy (Kmax) of the photoelectrons and frequency of incident photons during an experiment on the photoelectric effect.
The point labeled P on the graph represents the … of a photon.
- maximum velocity
- maximum frequency
- work function
- threshold frequency (2)
1.5 An observer runs towards a stationary sound source. As the observer approaches the source, its pitch appears to increase because the …
- loudness of the source appears to increase.
- frequency of the source appears to increase.
- frequency of the source appears to decrease.
- wavelength of the source appears to increase. (2)
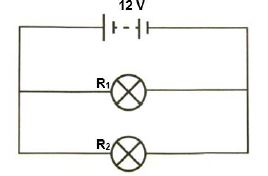
1.6 Two light bulbs are connected across a battery of emf ԑ and negligible internal resistance as shown in the diagram below.
The battery delivers maximum voltage. If the power of R1 is greater than the power of R2, which statement is CORRECT?
- The resistance of R1 is greater than the resistance of R2.
- The resistance of R2 is greater than the resistance of R1.
- The resistance of R1 is equal to the resistance of R2.
- The resistance of R1 is equal to 0 Ω. (2)
1.7 A line emission spectrum is produced when an electron in an excited atom makes a transition from …
- higher to lower energy levels and emit light energy.
- higher to lower energy levels and absorb light energy.
- lower to higher energy levels and emit light energy.
- lower to higher energy levels and absorb light energy. (2)
1.8 The sketch represents an alternating current (AC) generator that is rotated clockwise as shown below. 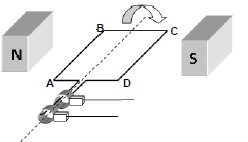
The direction of the induced current in the coil is from …
- B to A.
- C to B.
- A to B.
- D to C. (2)
1.9 Two small, identical positively charged spheres P and Q on insulated stands are placed a distance d apart as shown below. The magnitude of the force exerted by Q on P is F. 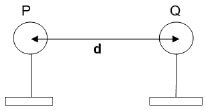
If the distance is now changed to ½ d, the new force between the spheres is …
- ¼ F.
- ½ F.
- 2 F.
- 4 F. (2)
1.10 The photoelectric effect is evidence of the fact that …
- metals contain electrons.
- light has a particle nature.
- light has a wave nature.
- metals have a positive charge. (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2 (Start on a NEW page.)
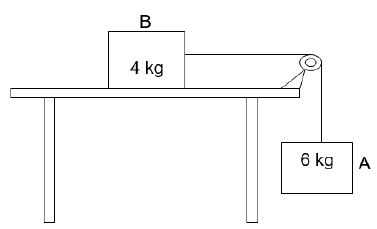
A 4 kg block B, resting on a flat, rough horizontal table, is connected by a light inextensible string to a 6 kg block A. The string is passed over a light frictionless pulley in such a way that block A hangs vertically downwards as shown in the diagram below.
2.1 Write down Newton’s Second Law of motion in words. (2)
2.2 Draw a free-body diagram of all forces acting on block B. (4)
2.3 The kinetic frictional force experienced by block B is 32,53 N to the left. Calculate the magnitude of the acceleration. (6)
2.4 Calculate the coefficient of kinetic friction between the surface of the table and block B. (3)
2.5 How will the frictional force on the block be affected if the 4 kg block is pulled at an angle of 30° to the horizontal?
Write down INCREASE; DECREASE or REMAIN THE SAME.
Explain your answer. (3)
[18]
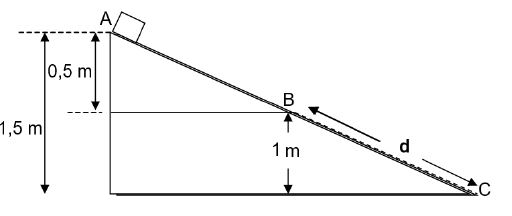
QUESTION 3 (Start on a NEW page.)
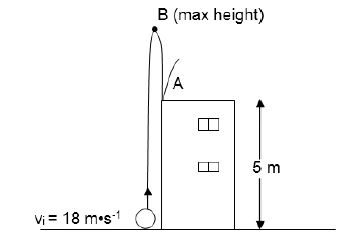
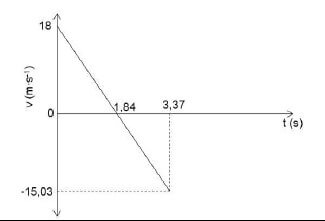
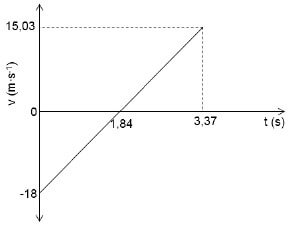
A ball is projected vertically upwards from the ground with a speed of 18 m•s-1. It passes the roof of a 5 m tall building on its way up and reaches its maximum height at B. On its way down, the ball strikes the roof of the building at point A as shown in the diagram below. Ignore the effects of air friction.
3.1 Write down the magnitude of the velocity of the ball at point B the maximum height above the ground. (1)
3.2 Write down the magnitude and direction of the acceleration of the ball at point B. (2)
3.3 Calculate the following regarding the ball:
3.3.1 The time it takes to reach point B above the ground (3)
3.3.2 The velocity at the instant it strikes the roof at point A (3)
3.3.3 The total time it takes, from the instant it is projected to the time it strikes the roof at point A (4)
3.4 Sketch the velocity-time graph for the motion of the ball from the ground up until it hits the roof of the building.
Indicate the following on your graph:
- initial velocity
- time at point B (the maximum height)
- final velocity (4)
[17]
QUESTION 4 (Start on a NEW page.)
A box is held stationary at point A, the top of a plane ABC, inclined at an angle to the horizontal. The portion AB of the plane is smooth while the portion BC is rough.
4.1 State the principle of conservation of mechanical energy in words. (2)
4.2 Calculate the speed of the box at position B. (4)
4.3 The box experiences a kinetic frictional force of 14,7 N as it moves with a constant velocity, from B to C, down the plane.
4.3.1 State the Work-Energy Theorem in words. (2)
4.3.2 Draw a free-body diagram showing ALL forces acting on the box at B. (3)
4.3.3 Use the work-energy principle to calculate the distance d, between B and C if the box has a mass of 3 kg. (5)
4.4 The angle between the incline and the horizontal is decreased.
How will this decrease affect the coefficient of kinetic friction acting on the box?
Write only INCREASE; DECREASE or REMAIN THE SAME. (1)
[17]
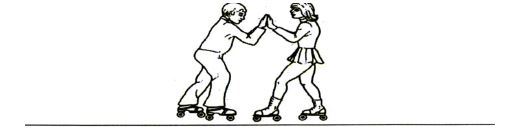
QUESTION 5 (Start on a NEW page.)
A man and a woman each wearing roller skates, stand facing each other on a flat frictionless horizontal surface. The man pushes the woman and the woman moves to the right at 4 m•s-1.
5.1 State the principle of conservation of linear momentum in words. (2)
5.2 The masses of the man and the woman are 80 kg and 50 kg respectively. How does the impulse on the woman compare to that on the man?
Write only GREATER THAN, SMALLER THAN or EQUAL TO. (1)
5.3 Calculate the man’s velocity immediately after pushing the woman away from him. (4)
5.4 Calculate the impulse on the woman. (3)
[10]
QUESTION 6 (Start on a NEW page.)
A police car is moving down along on a flat road at a constant speed and emits from its siren sound waves with a frequency 346 Hz. A woman sitting next to the road detects sound waves at a frequency that is 50 Hz more than the frequency of sound waves emitted by the siren as the police car is moving towards her.
6.1 State the Doppler effect in words. (2)
6.2 Explain, in terms of wave motion, why the frequency heard by the woman is higher than the frequency of the source. (2)
Assume that the speed of sound in air is 340 m•s-1.
6.3 Calculate the speed of the car. (5)
6.4 State ONE application of the Doppler effect in medicine. (1)
6.5 A line in a hydrogen spectrum has a frequency of 7,55 × 1014 Hz when measured in a laboratory. The same line in the spectrum of a distant star has a frequency of 17,23 × 1011 Hz.
State whether the distant star is moving TOWARDS or AWAY from the earth. Give a reason for the answer. (2)
[12]
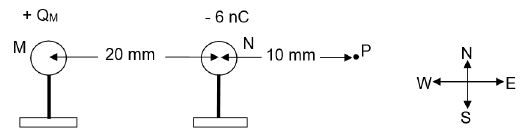
QUESTION 7 (Start on a NEW page.)
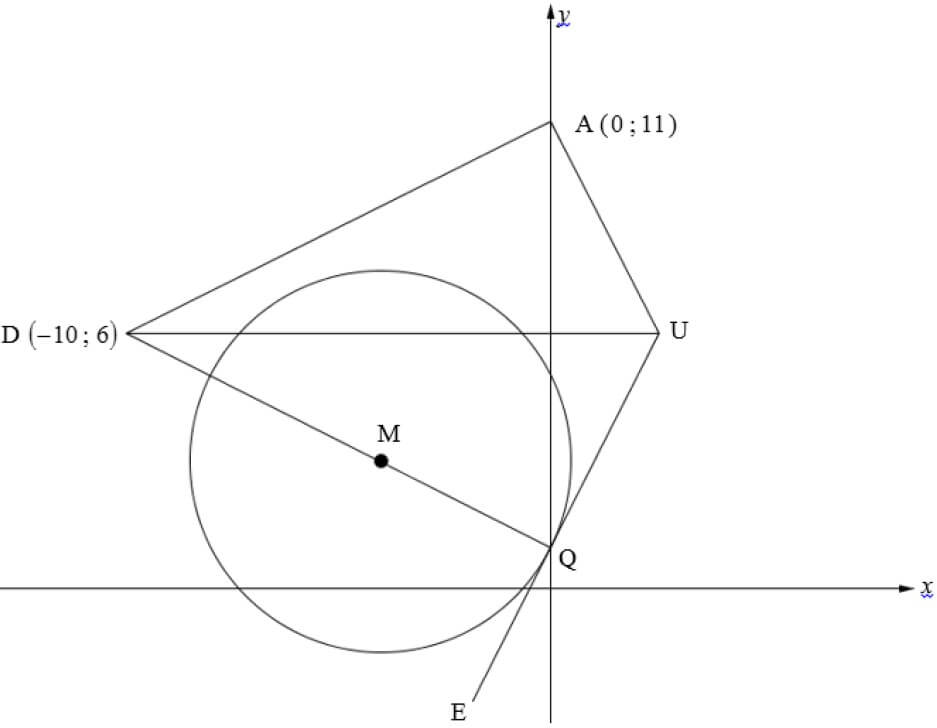
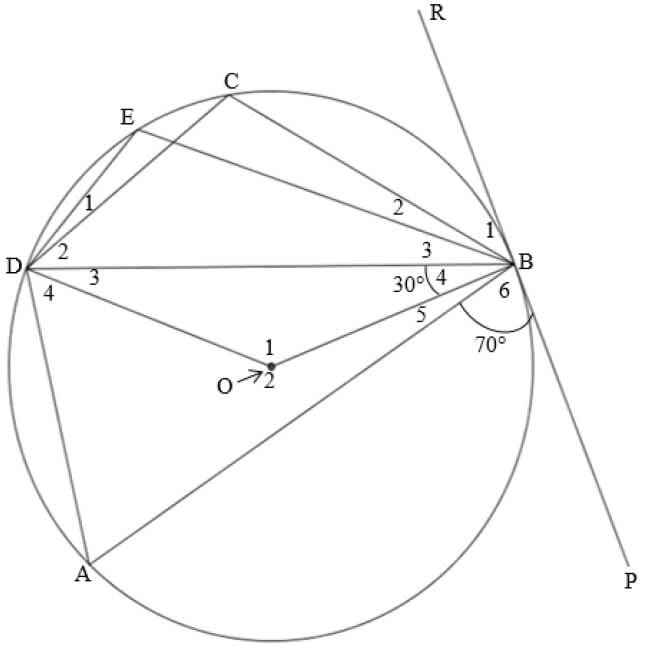
Two metal spheres, M and N, on insulated stands carry charges +QM and -6 nC respectively. The distance between the two charges is 20 mm and P is a point at 10 mm from sphere N as shown below. The NET ELECTRIC FIELD at point P due to presence of M and N is 5,2 × 105 N∙C-1 westwards.
7.1 Define the term ELECTRIC FIELD at a point. (2)
7.2 Calculate the magnitude of charge QM on sphere M. (7)
7.3 The two spheres were allowed to make contact and moved back to their original positions.
7.3.1 Draw the electric field pattern due to the two charges. (3)
7.3.2 Calculate the …
- number of electrons transferred from one sphere to another sphere after separation. (4)
- magnitude and the direction of the force that sphere M exerts on sphere N after contact. (3)
[19]
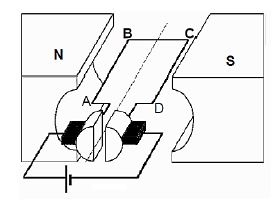
QUESTION 8 (Start on a NEW page.)
The simplified sketch below represents an electrical motor.
8.1 Name the type of electrical motor that is shown above. (1)
8.2 What energy conversion takes place in the above electrical motor? (2)
8.3 The turning effect of the electrical motor can be increased by increasing the number of turns of coil or by increasing the strength of the magnetic field.
8.3.1 Write down another way in which this turning effect can be increased. (1)
It is intended to produce a maximum potential difference in the electrical motor when a constant current is supplied.
8.3.2 In which position should the coil relative to the magnetic field be positioned in order to produce maximum potential difference?
Write only PARALLEL or PERPENDICULAR. (1)
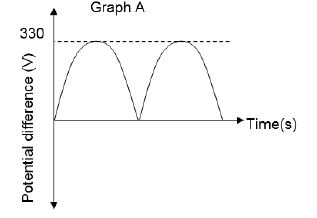
8.4 The graphs below shows the output of a generator.
8.4.1 Is the reading indicated as 330 V on the graph above a root mean square voltage (Vrms) or a maximum voltage (Vmax)? (1)
8.4.2 The generator produces the root mean square current (Irms) of 12 A. Determine the rate at which the generator will transfer energy. (4)
[10]
QUESTION 9 (Start on a NEW page.)
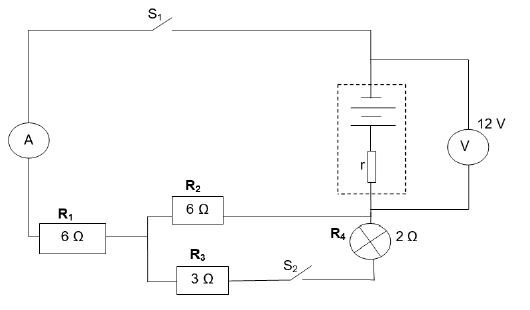
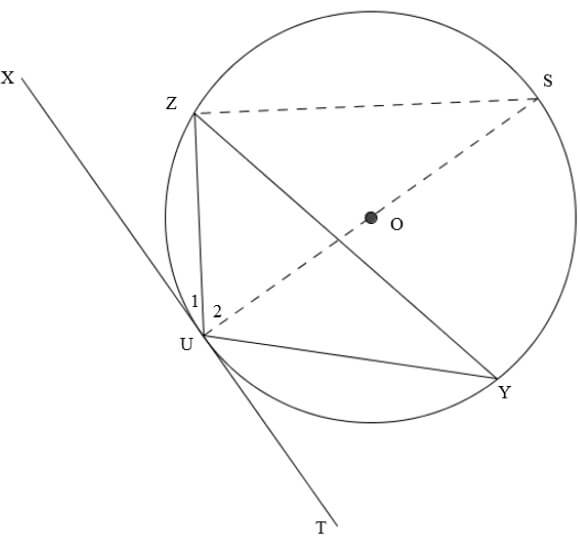
In the circuit below, the battery has an emf of 12 V and internal resistance r. The three resistors and the bulb are connected as shown in the diagram. The resistance of the bulb is 2 Ω. Initially both switches S1 and S2 are open. Assume that all the connecting wires and an ammeter A have negligible resistances.
9.1 With only switch S1 closed, the reading on the voltmeter drops to 10,8 V. Calculate the …
9.1.1 reading on ammeter A. (4)
9.1.2 internal resistance, r of the battery. (3)
9.2 With both switches, S1 and S2, closed, the ammeter reads 1,5 A.
9.2.1 Calculate the power dissipated by the bulb. (7)
9.2.2 What effect will the closing of both switches have on the “lost volts”? Write only INCREASE, REMAINS THE SAME OR DECREASE.
Fully explain your answer. (3)
[17]
QUESTION 10 (Start on a NEW page.)
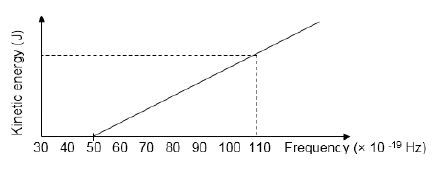
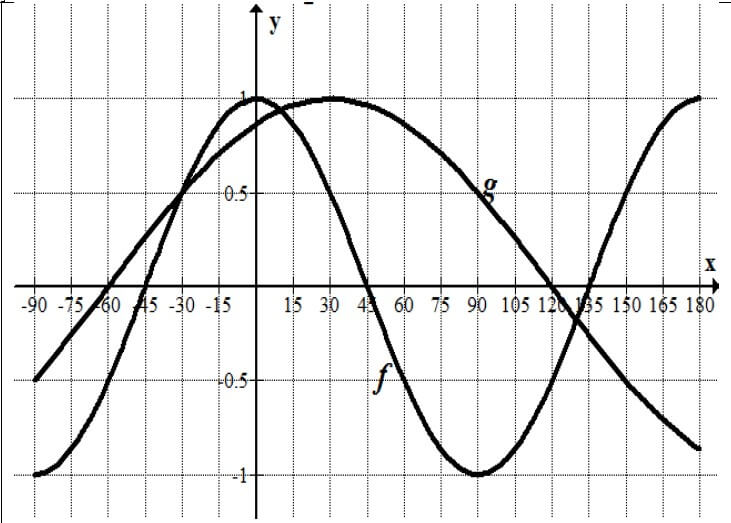
Different frequencies of light are shone onto the surface of a metal. The graph below shows the relationship between the kinetic energy of photo-electrons and frequency of the incident light.
10.1 Refer to the graph and write down the threshold frequency of the metal. (1)
10.2 Give a reason why no photo-electrons are released when light of frequency 45 × 10-19 Hz is used. (2)
10.3 Calculate the velocity of the ejected electrons when a light with a frequency of 110 × 10-19 Hz is shone onto the metal. (5)
10.4 What effect will an increase in the intensity of radiation have on the velocity of ejected electrons?
Write only INCREASE, DECREASE or STAYS THE SAME.
Explain your answer. (2)
[10]
TOTAL: 150
DATA FOR PHYSICAL SCIENCES GRADE 12
PAPER 1 (PHYSICS)
TABLE 1: PHYSICAL CONSTANTS
NAME | SYMBOL | VALUE |
Acceleration due to gravity | g | 9,8 m•s-2 |
Universal gravitational constant | G | 6,67 × 10-11 N•m2•kg-2 |
Speed of light in a vacuum | c | 3,0 × 108 m•s-1 |
Planck's constant | h | 6,63 × 10-34 J•s |
Coulomb's constant | k | 9,0 × 109 N•m2•C-2 |
Charge on electron | e | -1,6 × 10-19 C |
Electron mass | me | 9,11 × 10-31 kg |
Mass of earth | M | 5,98 × 1024 kg |
Radius of earth | RE | 6,38 × 103 km |
TABLE 2: FORMULAE
MOTION
| vf = vi + aΔt | Δx = ViΔt + ½aΔt2 or Δy = ViΔt2 + ½aΔt2 |
Vf2 = Vi2 + 2aΔx or Vf2 = vi2 + 2aΔy | Δx = [Vi + Vf]Δt or Δy = [Vi + Vf]Δt |
FORCE
Fnet = ma | p= mv |
fsmax = µsN | fk = µkN |
FnetΔt = Δp | w =mg |
F = Gm1m2 | g = G M |
WORK, ENERGY AND POWER
W =FΔxcosθ | U= mgh or EP = mgh |
K = ½mv2 or Ek = ½mv2 | Wnet = ΔK or Wnet = ΔEk ΔK = Kf −Ki or ΔEk =Ekf − Eki |
Wnc= ΔK + ΔU or Wnc= ΔEk + ΔEp | P = W Δt |
Pav = Fv |
WAVES, SOUND AND LIGHT
v = f λ | T =1/f |
fl = v ± vl fs fl = v ± vl fb | E = hf or E = h c |
E = W0 + Ek where | |
ELECTROSTATICS
| F = kQ1Q2 r2 | E = KQ |
E = V | E = F |
V = W | n = Q |
ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
R = V | emf (ε) = I(R + r) |
RS = R1 + R2 + ....... | q = I Δt |
W = Vq | P= W |
ALTERNATING CURRENT
I rms = Imax | Paverage = VrmsIrms |
PHYSICAL SCIENCE PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
PHYSICAL SCIENCE
PAPER ONE (P1)
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2016
GENERAL GUIDELINES
1 CALCULATIONS
1.1 Marks will be awarded for: correct formula, correct substitution, correct answer with unit.
1.2 No marks will be awarded if an incorrect or inappropriate formula is used, even though there are many relevant symbols and applicable substitutions.
1.3 When an error is made during substitution into a correct formula, a mark will be awarded for the correct formula and for the correct substitutions, but no further marks will be given.
1.4 If no formula is given, but all substitutions are correct, a candidate will forfeit one mark.
1.5 No penalisation if zero substitutions are omitted in calculations where correct formula/principle is correctly given.
1.6 Mathematical manipulations and change of subject of appropriate formulae carry no marks, but if a candidate starts off with the correct formula and then changes the subject of the formula incorrectly, marks will be awarded for the formula and correct substitutions. The mark for the incorrect numerical answer is forfeited.
1.7 Marks are only awarded for a formula if a calculation has been attempted, i.e. substitutions have been made or a numerical answer given.
1.8 Marks can only be allocated for substitutions when values are substituted into formulae and not when listed before a calculation starts.
1.9 All calculations, when not specified in the question, must be done to a minimum of two decimal places.
1.10 If a final answer to a calculation is correct, full marks will not automatically be awarded. Markers will always ensure that the correct/appropriate formula is used and that workings, including substitutions, are correct.
1.11 Questions where a series of calculations have to be made (e.g. a circuit diagram question) do not necessarily always have to follow the same order. FULL MARKS will be awarded provided it is a valid solution to the problem. However, any calculation that will not bring the candidate closer to the answer than the original data, will no count any marks.
2 UNITS
2.1 Candidates will only be penalised once for the repeated use of an incorrect unit within a question.
2.2 Units are only required in the final answer to a calculation.
2.3 Marks are only awarded for an answer, and not for a unit per se. Candidates will therefore forfeit the mark allocated for the answer in each of the following situations:
- Correct answer + wrong unit
- Wrong answer + correct unit
- Correct answer + no unit
2.4 SI units must be used except in certain cases, e.g. V.m-1instead of N.C-1, and cm∙s-1 or km.h-1instead of m∙s-1 where the question warrants this.
3 GENERAL
3.1 If one answer or calculation is required, but two are given by the candidate, only the first one will be marked, irrespective of which one is correct. If two answers are required, only the first two will be marked, etc.
3.2 For marking purposes, alternative symbols (s, u, t etc) will also be accepted.
3.3 Separate compound units with a multiplication dot, no a full stop, for example, m∙s-1. For marking purposes, m∙s-1 and m/s will also be accepted.
4 POSITIVE MARKING
Positive marking regarding calculations will be followed in the following cases:
4.1 Subquestion to subquestion: When a certain variable is calculated in one subquestion (e.g. 3.1) and needs to be substituted in another (3.2 of 3.3), e.g. if the answer for 3.1 is incorrect and is substituted correctly in 3.2 or 3.3, full marks are to be awarded for the subsequent subquestions.
4.2 A multistep question in a subquestion: If the candidate has to calculate, for example, current in die first step and gets it wrong due to a substitution error, the mark for the substitution and the final answer will be forfeited.
5 NEGATIVE MARKING
Normally an incorrect answer cannot be correctly motivated if based on a conceptual mistake. If the candidate is therefore required to motivate in QUESTION 3.2 the answer given in QUESTION 3.1, and 3.1 is incorrect, no marks can be awarded for QUESTION 3.2. However, if the answer for e.g. 3.1 is based on a calculation, the motivation for the incorrect answer could be considered.
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1 C ✓✓ (2)
1.2 D ✓✓ (2)
1.3 C ✓✓ (2)
1.4 C ✓✓ (2)
1.5 B ✓✓ (2)
1.6 B ✓✓ (2)
1.7 A ✓✓ (2)
1.8 C ✓✓ (2)
1.9 D ✓✓ (2)
1.10 B ✓✓(2)
[20]
QUESTION 2
2.1 When a resultant/net force acts on an object, the object will accelerate in the direction of the force at an acceleration that is directly proportional to the force✓and inversely proportional to the mass of the object.✓
OR
The net force acting on an object is equal to the rate of change of momentum✓✓ of the object (in direction of the force). (2 or 0)
2.2 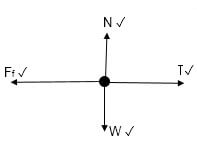 (4)
(4)
Accepted labels/Aanvaarde byskrifte | |
N | FN/ Fnormal/Normal |
T | FT/Tension |
w | Fg /Fw/weight/mg/gravitational force |
Ff | f/ friction |
Notes:
|
2.3 On 6 kg:
Fnet = ma ✓
Fg + (-T) = ma
(6 × 9,8) ✓ – T = 6 × a
58,8 – T= 6a
T = 58,8 – 6a (1)
On 4 kg:
Fnet = ma ✓
(-f) + T = ma
(-32,53) ✓ + T = 4 × a
T = 32,53 + 4a (2)
any one of the 2 above i.e (1) or (2)
(1) - (2): 0 = (58,8 – 6a) – (32,53 + 4a) ✓
a = 2,63 m∙s-2 ✓ (6)
2.4 Positive marking from QUESTION 2.3/
fk = μkN ✓ or fk = μkmg (any one)
32,53 = µk × 4 × 9,8 ✓
µk = 0,83 ✓ (3)
2.5 DECREASE ✓
At an angle of 30° the tension force will have a component in the vertical direction ✓and the block will be slightly lifted up. The normal will decrease and friction is directly proportional normal. ✓
[18]
QUESTION 3
3.1 0 m∙s-1 ✓ (1)
3.2 g = 9,8 m/s2 ✓ downwards ✓ (2)
3.3
3.3.1 (3)
OPTION 1 (downward positive) | OPTION 2 (upwards positive) |
3.3.2 (3)
OPTION 1 (Downwards is positive) | OPTION 2 (Upwards is positive) |
3.3.3
| Downwards is positive | Upwards is positive |
OPTION 1 | OPTION 2 |
OPTION 3 | OPTION 4 (4) |
OPTION 1 |
OPTION 2 |
Criteria to mark the graph | Marks |
Correct shape (straight line) | ✓ |
Graph starts at v = 18 m∙s-1/-18 m∙s-1 and t = 0 s | ✓ |
Graph cuts t-axis at 1,84 s at v = 0 m∙s-1 | ✓ |
Graph shows the ball bouncing with v = -15 m∙s-1/15,03 m∙s-1 at t = 3,37 s | ✓ |
(4)
[17]
QUESTION 4
4.1 The total mechanical energy in an isolated (closed) system ✓ remains constant (is conserved). ✓
NOTE
If total or isolated/closed is omitted (max:1/2) (2)
4.2 Emech at A = Emech at B/Emeg by A = Emeg by B ✓
(mgh + ½ mv2)A = (mgh + ½ mv2)B
m (9,8 × 0,5 + ½ × 02) ✓ = m (9,8 × 0 + ½ × v2) ✓
4,9 = ½ v2
v = 3,13 m∙s-1 ✓ (4)
4.3
4.3.1 The net/total work done on an object ✓ is equal to the change in the object’s kinetic energy. ✓
OR
The work done on an object by a resultant/net force is equal ✓ to the change in the object’s kinetic energy. ✓ (2)
4.3.2 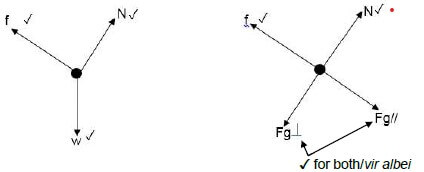 (3)
(3)
4.3.3
Wnet = ∆ EK ✓
Wnet = 0
Wf + Wg//= 0 ✓
f. ∆x ∙ cos θ+ mg. 1/∆x ∆x ∙cos θ= 0
14,7∙ d ∙cos 180°✓ + 3 × 9,8 (1/d cos 0° = 0
-14,7d + 29,4 = 0
d = 2 m ✓ (5)
4.4 REMAINS THE SAME ✓ (1)
[17]
QUESTION 5
5.1 The total( linear) momentum of an isolated (closed) system ✓ remains constant (is conserved) . ✓
OR
In a isolated (closed) system, the total(linear) momentum ✓ before collision is equal to the total linear momentum after colllision. ✓ (2)
5.2 EQUAL TO✓ (1)
5.3 Consider LEFT as positive
∑pi = ∑pf ✓ Any one
(mm + mw)vi = mvf m + mvf w
(80 + 50) × 0 ✓ = (80) vf + 50 × -4✓
vf = 2,5 m∙s-1 left ✓ (4)
5.4 (3)
OPTION 1 OR (either one) = m(vf – vi) | OPTION 2 Fnet. ∆t = ∆p ✓ OR (either one) = m(vf – vi) (3) |
[10]
QUESTION 6
6.1 The (apparent) change in frequency/ pitch of the sound ✓ detected by a listerner because the sound source and the listener have different velocities relative to the medium of sound propagation. ✓
OR
An (apparent) change in (observed/detected) frequency/pitch/wavelength ✓ as a result of the relative motion between a source and the observer /listener. ✓ (2)
6.2 As the police car is moving towards the woman, the wavelengths are compressed ✓ and become more shorter resulting in waves compressed and more waves will reach the listener per unit time, ✓ hence the frequency increases. (2)
6.3 
6.4
- Determine whether arteries are clogged/narrowed ✓
OR - Determine heartbeat of foetus ✓ (1)
6.5 AWAY ✓
Light from the distant star has a lower frequency compared to that of hydrogen. ✓ (Therefore the wavelength of the distant star is longer than the hydrogen which shows that it is shifted towards red.) (2)
[12]
QUESTION 7
7.1 The (electrostatic )force ✓ experienced per unit positive charge ✓( placed at a point) (2)
7.2
EM = kQ
r 2
= 9 × 109. QM✓ = 1 × 1013∙ QM (a)
(0,03)2
OR (either a or b)
EN = kQ
r2
= (9 × 109)(6 × 10-9 ) (b)
(0,03)2
= 540 000∙ N∙C-1
Enet = EM + (-EN ) ✓
5,2 × 105✔= 1x 10 13 ∙Qm – 540 000 ✓
5,2 × 105 + 540 000 = 1 × 1013∙QM
Qm = 2 × 10-9 C east ✓ (7)
7.3
7.3.1 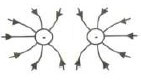 (3)
(3)
Criteria for sketch | Marks |
Correct shape | ✓ |
Correct direction | ✓ |
Field lines not crossing each other | ✓ |
7.3.2 (a) (4)
OPTION 1 |
OPTION 2 |
(b)
F = kQ1 Q2 |
(3)
[19]
QUESTION 8
8.1 Electric motor (DC motor) ✓ (1)
8.2 Electrical energy converted to mechanical energy ✓ (2)
8.3
8.3.1 Increase the strength of the current ✓ (1)
8.3.2 Parallel ✓ (1)
8.4
8.4.1 Maximum voltage✓
Accept: Vmax (1)
8.4.2
OPTION 1 Vrms = Vmax = 330 ✓ = 233,35 V | OPTION 2 Paverage = Vmax × I rms✓ |
For 8.4.2 accept range from Paverage from 2800,14 W to 2800,20 W | |
(4)
[10]
QUESTION 9
9.1
9.1.1 Rext = R1 + R2 = 6 + 6 = 12 Ω
Vext = I R ✓
10,8 ✓ = I × 12 ✓
I = 0,9 A ✓ (4)
9.1.2 POSITIVE MARKING FROM QUESTION 9.1.1 (3)
9.2
9.2.1 (7)
OPTION 1 | OPTION 2 |
OPTION 1 | OPTION 2 = 1 + 1 = 1 ✓ |
9.2.2 Increases. ✓ External resistance decreases ✓ and current increases ✓ (3)
[17]
QUESTION 10
10.1 50 × 10-19 Hz ✓ (1)
10.2 The 45 × 10-19 Hz is less than the threshold frequency of light that can eject/release electrons from the surface of the metal ✓✓ (2)
10.3
hf = W0 + ½ mv2
hf = Wo + EK ✓ ANY one
hf = hf0+ EK
(6,63 × 10-34)(110 × 10-19)✓=(6,63 × 10-34)(50 × 10-19) ✓+( × 9,11 × 10-31.v2)✓
v = 9,35 × 10-11 m∙s-1 ✓ (5)
10.4 STAYS THE SAME. ✓
Increase in the intensity increases the number of electrons emitted with the same kinetic energy. ✓ (2)
[10]
TOTAL 150
VISUAL ARTS PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
VISUAL ARTS
PAPER ONE (P1)
GRADE 12
EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2016
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
It is expected of you in this examination to demonstrate the following:
- The use of the correct art terminology.
- The use and implementation of visual analysing and critical thinking.
- Writing and research skills within a historical and cultural context.
- The placement of specific examples within a cultural, social and historical context.
- An understanding of characteristics/different creative styles.
Read the following instructions before deciding on which questions to answer:
- This question paper consists of EIGHT questions.
- Answer any FIVE questions for a total of 100 marks.
- Questions and sub-sections must be numbered clearly and correctly according to the numbering system used in the question paper.
- Questions appear on the left-hand pages, with visual sources on the right hand pages.
- Ensure that you refer to the visual sources reproduced in colour where required.
- Information already discussed in one question, will not earn marks if repeated in other answers. Cross reference of works of art is allowed.
- Name the artist and the title of each work of art which you discuss in your answers. Underline the title of the work of art or the name of a building.
- Write clearly and legibly.
- Write in a clear, creative and structured manner, in full sentences and paragraphs, according to the instructions for each question. Bullets are not acceptable, and act only as guidelines in your essay structuring.
- A list of facts/table will NOT be accepted. Use the following guidelines for the length of your answers.
Note the mark allocation:
6–8 marks: a minimum of ½–¾ page (paragraph)
10–14 marks: a minimum of 1–1½ pages (short essay)
20 marks: a minimum of 2 pages (essay)
GLOSSARY
Use the following vocabulary to ensure that you understand how to approach a specific question:
Aesthetics: Theory of beauty and art and the understanding of beautiful things.
Analyse: A detailed and logical discussion of the formal elements, such as line, shape, space, colour, tone, format and composition of the art work.
Compare: Point out differences and similarities in an ordered sequence within the same argument.
Contextualise: Relating to, or depending on the framework of information; relating to the situation, time (era) and location to which the information belongs.
Discuss: Present your point of view and give reasons for your statements.
Explain: Clarify and give reasons for your statements.
Interpret: Analyse and evaluate (give an informed opinion) an art work. Contextualise it historically, culturally, socially, etc. and substantiate your findings by referring to similar specific examples.
Evaluate: Showing insightful and analytical commentary, as to the comparative worth of an art work, in the broad world picture.
Justify: To support/motivate with proof or witness. Substantiate: To motivate with proof/supporting evidence.
State: Give exact facts and say directly what you think – give your opinion, as well as an explanation.
Visual sources: The visual images which are supplied in the question paper.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
THE VOICE OF EMERGING ARTISTS
| During the early and mid-twentieth century Black and White South African artists struggled to obtain formal art education but despite this, the then upcoming artists produced works of good quality, many of which are commenting on the daily lives of the communities within which they lived. |
1.1 Choose TWO artworks from FIGURE 1a, FIGURE 1b and FIGURE 1c and in separate paragraphs explain how the artists produced work that reflects a commentary on the daily lives of the communities within which they lived.
Refer to the following:
- Composition
- Application of art elements
- Medium and technique
- Evident influences on the styles
- Lifestyle atmosphere (10)
1.2 Choose TWO well-known Black South African artists you have studied whose work delivers social/economic commentary and in 1 to 1½ pages discuss ONE work of each artist.
Your discussion must include the following:
- Names of artists and works
- Inspiration and influences in their work
- Subject matter
- Composition, technique and style
- Evaluation of success of the work as a commentary (10)
[20]
QUESTION 2
SOUTH AFRICAN ARTISTS INFLUENCED BY AFRICAN AND/OR INDIGENOUS ART FORMS
| For centuries artists around the world have been influenced by African and other indigenous art forms, be it landscapes, deity figurines or primitive masks. This has led to emergence of new styles like Cubism and Urban art to name a few. |
2.1 With the above in mind, write a short essay of two paragraphs in which you anlyse and interpret FIGURE 2a and FIGURE 2b to show how each of the artists has succeeded in capturing the essence of Africa in a different context.
Refer to the following:
- Media and technique
- Composition
- Symbols
- Colour
- Subject matter (8)
2.2 Refer to FIGURE 2c. Discuss Andries Botha’s work with specific focus to the following:
- Application of formal elements of art
- Theme/message
- Mood as related to Africa (6)
2.3 Choose ONE work (other than works that appear in this question paper) by a South African artist that reflects African/Indigenous influence and in at least ½ a page analyse and evaluate the extent to which it reflects this influence by referring to the following:
- Name of artist and title of the work
- Application of formal elements of art
- Theme/message
- Mood as related to Africa (6)
[20]
QUESTION 3
SOCIO-POLITICAL ART – INCLUDING RESISTANCE ART
| There has always been a strong relationship between art and politics. During times of political unrest, artsists tend to use art either as a vehicle of promoting their propagandist views or as an expression of the oppression/repression of those views by those in authority. |
3.1 Write an essay of about one page in which you prove the above statement true by analysing FIGURE 3a, FIGURE 3b and FIGURE 3c with reference to the following:
- Hisorical context and subject matter
- Use of formal art elements and composition
- Materials and techniques
- Message or meaning. (10)
3.2 Choose TWO artworks which you have studied that deliver a socio-political message and (in two paragraphs of at least half a page each) write an essay on each in which you include the following:
- Name of artist(s) and title of the work
- Subject matter/issues adresssed by artist
- Media and technique
- Application of art elements
- An evaluation of the artist’s success in delivering his message. (10)
[20]
QUESTION 4
ART, CRAFT AND SPIRITUAL WORKS MAINLY FROM RURAL SOUTH AFRICA
Immediately, with the phrase ‘African craft’ one enters into the realm of what is art and what is craft? A never-ending discourse that will, one suspects, continue to be agitatedly discussed forever. |
4.1. With reference to the statement above, analyse and interpret the given FIGURE 4a and FIGURE 4b by writing an essay of 1½ to 2 pages. In addition also choose ONE artwork of your choice and ONE craft piece (from a rural area) of your choice, to explain when an object can be classified as art. Refer to the following in your essay:
- Elements of art
- Functionality
- Mediums
- Traditional use
- Religious and spiritual elements
- Titles
- Subject matter
Marks will be allocated as follows:
- 3 Marks for introduction which deals with your views on the question.
- 6 Marks for insightful commentary on the four artworks.
- 1 Mark for very short conclusion.
[20]
QUESTION 5
MULTI-MEDIA AND NEW MEDIA – ALTERNATIVE CONTEMPORARY AND POPULAR ART FORMS IN SOUTH AFRICA
Multimedia artists makes use of elements that “speak” to all five senses. Traditionally in classical art only the sense of sight was invoked. |
5.1 With reference to the above statement and visual source, FIGURE 5a. Write a paragraph (at least ½ page) in which you discuss the above statement by considering the following: (4)
- The medium used
- The message of the artwork
5.2 Also with reference to the above statement analyse and discuss FIGURE 5b in essay format (at least ½ page). Consider the following:
- Application of art elements and principles
- Mediums relevant to the concept
- Meaning or message (6)
5.3 For this question you may not use a work which appears in this question paper. However, you may use a different work by one of the artists used in this paper.
In essay format, of at least one page, recall, discuss and compare at least TWO works in multimedia which you have studied, substantiating each of the following:
- Name the work/s as well as the artist
- Media
- Messages and/or meanings
- Influenced by which style of art
- Presentation (10)
[20]
QUESTION 6
POST-1994 – DEMOCRATIC IDENTITIY IN SOUTH AFRICA
| Post-Apartheid visual art made definite contributions with regards to the integration and emancipation of different races in South Africa. This led to a believable, contemporary South Africa in which artists could once again focus on reviewing their own identities. |
6.1 Write an essay of about ¾ of a page in which you discuss how the individual artists of the visual sources of FIGURE 6a and FIGURE 6b relate to expression of identity.
Refer to the following:
- Mediums used
- Style and technique
- The commentary these artists make
- Which one makes the strongest impact, with reasons for your choice (8)
6.2 Write an essay of at least 1½ page, discussing the work of any TWO South African artists you have studied, who question and reflect on their post-1994 identity. Refer to specific works of art in you answer, which do not appear on this question paper. (12)
[20]
GLOSSARY |
 FIGURE 6a: Hasan and Husain Essop, Five Pillars, photograph, 2008. |
 FIGURE 6b: Wim Botha, Mieliepap Pieta, resin and mieliepap, 2004. |
QUESTION 7
GENDER ISSUES – MASCULINITY AND FEMININITY
| Since the Renaissance era the female body has been the prime subject matter for many artists, most of them male. In later centuries female artists use the female form, but not to portray the stereotypical idea of women. |
7.1 With reference to the above statement and referring to FIGURE 7a and FIGURE 7b write an essay of approximately ¾ page in which you explain and discuss how the female form is represented by the contemporary female artist.
Consider the following:
- Composition
- Style
- Formal elements of art
- How gender is questioned/affirmed (8)
7.2 Write an essay of approximately 1½ page, on any TWO artists you have studied, in whose works male and/or female identity is addressed. Name, describe and compare the works. Conclude your essay discussing the impact of each. (12)
[20]
GLOSSARY |
 FIGURE 7a: Jenny Saville, Propped, oil on canvas, 1992. |
 FIGURE 7b: Mary Sibande, Red dogs, Installation, 2014. |
QUESTION 8
ARCHITECTURE IN SOUTH AFRICA
| Magnificent examples of ground-breaking architecture have come out of the 20th and 21st centuries. Buildings that have been innovatively and environmentally designed are evident in many parts of the world. |
8.1 Considering the above-mentioned, study the images of the innovative structures each relevant in their own time FIGURE 8a and FIGURE 8b. Write an essay of one page, in which you evaluate the innovative accomplishments.
You may include thoughts on the following:
- Principles of design applied
- Influences and creative thought
- Peculiar characteristics
- Aims and effective functionality (8)
8.2 In an essay of approximately 1½ pages, clearly analyse TWO buildings by any popular contemporary South African architect/s. Discuss the shapes, materials and design which place them in a category of outstanding impact.
The following aspects may well be relevant:
- Names of architects/companies and buildings
- Special features
- Peculiar materials, technology and design
- Ecological considerations
- Environmental issues
- Functionality (12)
[20]
GLOSSARY |
 FIGURE 8a: Revel Fox and Partners, Cape Town Convention Centre, 2008. . |
 FIGURE 8b: House of Rhino, Crossways, self-sustainable eco-friendly house, 2011. |
TOTAL: 100
VISUAL ARTS PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
VISUAL ARTS
PAPER ONE (P1)
GRADE 12
EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2016
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before commencing marking:
- This memorandum consists of EIGHT answers. Candidates had to answer any FIVE questions for a total of 100 marks.
- It is MOST IMPORTANT that allowance is made for the candidates in many instances:
- Candidates must be given credit for providing their own opinions and ideas in answers.
- Credit must be given for lateral thinking.
- Arguments and statements must be well reasoned and qualified by reference to specific factors.
- Questions and subsections must be numbered clearly and correctly. Bullets usually act as guidelines to help structure candidates' answers.
- Information and artworks discussed in one answer must not be credited if repeated in other answers, but artworks may be cross-referenced.
- Where applicable, candidates must name the artist and title of each artwork mentioned.
- Where appropriate, candidates may discuss both two- and three-dimensional artworks in any answer.
- Remember that many candidates will be discussing these examples, never having seen them before. Markers therefore cannot expect factual, academic information. They should draw upon their own experiences, cultures and interpretations of the artworks, within the context of the question. Therefore, markers need to be open-minded and flexible in the marking process.
GENERAL INFORMATION FOR MARKERS
- This memorandum is to serve as both a guideline for markers as well as a teaching tool. Therefore, the memorandum for certain questions is in greater depth, as the information may be used as learning material. Other parts of the memorandum may merely be a suggested guideline.
NOTE: Markers are encouraged to reward candidates for what they know, rather than punish them for what they don't know. - Although the information for the questions is given in point form, candidates must use an essay/paragraph format discussing their information in a holistic manner.
- Candidates must answer all the questions in FULL SENTENCES or PARAGRAPHS, according to the requirements of each question. Answers in point form cannot receive full marks.
GUIDELINES:
It is expected of the CANDIDATE to demonstrate the following:
- To answer any FIVE questions for a total of 100 marks.
- Questions and sub-sections to be numbered clearly and correctly.
- Information already discussed in one question, not to be repeated. If repeated, marks are allocated the first time only. Cross reference to works of art is allowed.
- That answers will be in full sentences and paragraphs, according to the instructions for each question. POINT FORM WILL EARN ONLY MINIMAL MARKS.
- The use of correct art terminology.
- The use and implementation of visual analysing and critical thinking.
- Writing and research skills within a historical and cultural context.
- Placing of specific examples within a cultural, social and historical context.
- An understanding of characteristics/peculiar creative style.
- The identification of the professional practice of local artists.
It is expected of the MARKER to demonstrate the following: - Acceptance of substantiated reasoning within the context of the question.
- Keeping in mind information already supplied above in some of the questions.
- To mark according to guidelines supplied to the candidates above.
- To recognise that this memorandum is to serve as both a guideline for markers as well as a teaching tool. For this reason the information for some answers is in greater depth and information concerning other answers, may merely be suggested guidelines.
- To reward learners for what they know, rather than discrediting them for what they do not know.
- To refer to the Visual Arts SAG document rubric (p24) as guideline to assess levels of achievement. (See next page)
NOTE:
- Remember that many candidates will be discussing these examples never having seen them before. Markers therefore cannot expect factual academic information. They should draw upon their own experiences, cultures and interpretations of the artworks, within the context of the question. Therefore, markers need to be open minded and flexible in the marking process.
ACHIEVEMENT RATING CODE | TOPIC 4: VISUAL CULTURE STUDIES ? |
7 |
|
6 |
|
5 |
|
4 |
|
3 |
|
2 |
|
1 |
|
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
THE VOICE OF EMERGING ARTISTS
1.1
| During the early and mid-twentieth century Black and White South African artists struggled to obtain formal art education but despite this, the then upcoming artists produced works of good quality, many of which are commenting on the daily lives of the communities within which they lived. |
Choose TWO artworks from FIGURE 1a, FIGURE 1b and FIGURE 1c and in separate paragraphs explain how the artists produced work that reflects a commentary on the daily lives of the communities within which they lived.
Refer to the following:
- Composition
- Application of art elements
- Medium and technique
- Evident influences on the styles
- Lifestyle atmosphere
In FIGURE 1a:
Composition: The viewer’s eye catches the Zulu man’s portrait (head and shoulders) figure from an oblique view detaching the viewer’s eye contact from that of the old man who from his posture seems to be engrossed/engaged in a communicative dialogue with an unseen person on his right. The centrally placed figure is delicately painted in warm yellow red earthly browns which viewed against flat cool creamy browns renders him our focal point of study.
Art elements:
Colours: Warm earthly browns add to the feeling of Africaness of the portrait.
Line: Soft fine delicate lines define the forms while at the same time enriching the textural qualities of the regalia to enhance the naturalness of the figure and to suggest that the artist worked on a live model.
Forms: The fact the posture gives the figure three dimensionality also makes the represented features more natural and realistic.
Medium and Technique: Watercolour paint Brushstrokes are smooth. There is smooth tone integration that adds to the fine definition of the dress and facial features.
Influences on style: Western influence – Naturalism
Lifestyle atmosphere: Calming – Rural traditional calm atmosphere
Gerard Bhengu was an artist well known for his realistic representations of ethnic culture and life as a Zulu. He was encouraged to develop his natural skills but struggled to study art because of the lack of opportunities.as a result of Apartheid. The artwork in FIGURE 1a is a portrait of a Zulu man, done with watercolour paint. His use of colour was sepia as he could not afford to buy other colours. His technique is described as conservative naturalism but the uniqueness of his work can be found in the subject itself.
In FIGURE 1b: Dumile Feni, Father teach me how to pray, Conté crayon on paper.
Composition: The composition is a predominantly vertical structural thereby affirming the feeling of strength and power that the father in the upper part of the format has over his son below. The work comprises of two scenes that deny it a central area of focus. The scene at the top is broadly representative a disgruntled family with of an irresponsible (half dressed) who deprives and drinks away the baby’s milk. The mother is away leaving the cow to take her place only to be taken advantage of by the father. Below the son drawn in profile frustrated moans their situation seeking divine intervention but not knowing how; hence the title: ‘Father teach me how to pray’
Applying of art elements:
Strong tonal values are applied which emphasise certain aspects of the piece such as the figures and animals.
Strong expressive line is used to distort the forms adding to the mood of chaos.
Technique: Works primarily with graphic art in monochromatic hues, the artist had the ability and vision to transform the particular into the universal, with conté-crete on paper. Strong contrasts of dark shadows against the left out white areas illuminate the figures to give them a dream-like quality.
Evident influences on the style:
- Cecil Skotnes who introduced him to the medium of conté and helped him to develop his drawing techniques.
- Surrealism –They were executed spontaneously, according to the artist's subconscious thoughts and vision. They are, nevertheless, comprehensible, and for the viewer infused with poignant significance.
Lifestyle atmosphere: The content of these drawings were based on social realism, dealing chiefly with the social conditions and problems affecting the Black man’s identity in the urban South African setting. They carry an atmosphere of a dream-like narrative
Feni’s expressive abilities are unique and powerful. He was capable of surpassing his immediate circumstances by portraying what he experienced on a universally understandable level. Through this he was able to communicate his understanding of human suffering.
Western influence: Surrealism.
FIGURE 1c: George Pemba, New Brighton Port Elizabeth 1977, oil on canvas.
Composition: Pemba’s composition starts close to viewer and stretches into the distance. His position is in the middle of the street on what appears to be an island. Many people are painted in profile or their backs to the viewer as if they are going about their daily lives without being aware of the onlooker. Most of the composition is filled with street homes and people are closest to the viewer in the foreground. The band of light blue sky leads the eye towards the city in the distance.
Applying of art elements:
Use of bright colours:
- The contrast of warm and cold colours adds to the vibrant feeling of the community - The diagonals in the people suggest movement and activity
- Use of linear perspective with houses to create depth; Placement and size of figures also create depth
Technique: Pemba used visible brush marks that contribute to the three dimensionality of forms such as the trees, bushes and figures. He puts paint on with a constant texture and uses brush marks tot create roundness in his shapes.
Evident influences on the style:
- Professor Austin Winter Moore at Rhodes University
- Dorothy Kay with her naturalistic and realistic style
- Gerard Sekoto and Koenakeefe Mohl both encouraged him to become a full-time artist and to pay more attention to his immediate surroundings
- Impressionism – Pemba summarised his paintings according to what he saw and experienced
Lifestyle atmosphere: Everyday township street scene, bustling and energetic
Marks must be allocated for mentioning that the subject matter for all three figures is everyday life in South Africa.
1.2 The learner must choose TWO well-known Black artists who deliver social, economic or commentary in their art works and discuss in 1–1½ pages, ONE work of each which he/she has studied.
The following must be included:
- Names of artists and works
- Inspiration and influences on their work
- Specific subject matter
- Composition, technique and style
- Evaluation of success of the work as commentary
The discussion of the work by the artists is of importance and so is the learner’s substantiation of the success accomplished by each artist.
Award marks for each of the two works as from 5 + 5. (10)
[20]
QUESTION 2
SOUTH AFRICAN ARTISTS INFLUENCED BY AFRICAN AND/OR INDIGENOUS ART FORMS
| For centuries artists around the world have been influenced by African and other indigenous art forms, be it landscapes, deity figurines or primitive masks. This has led to emerging new styles like Cubism and Urban art to name a few. |
2.1 With the above in mind, write a short essay of two paragraphs in which you anlyse and intepret FIGURE 2a and FIGURE 2b to show how each of the artists has succeeded in capturing the essence of Africa in a different context. Refer to the following:
- Media and technique
- Composition
- Colour
- Subject matter
FIGURES 2a:
Media and technique: Black and white photography
Composition: Triangular composition. Fgures placed in centre which is the focal point.
Symbols: Graffiti on walls portryaing white Afrikaner poverty, Masks (Africa influence)
Colour: Black and white could be refferring to the forgotten and unseen or to the notion of contemporary Africaness which refers to Africaness as being a state of conscioussness thus accommodating both Black and White born and living in Africa.
Subject matter: The forgotten and unseen impoverished white Afrikaner in rural South Africa.
Die Antwoord Series. Roger Ballan uses black and white photography to communicate certain characteristics of the white Afrikaner’s life in poverty stricken rural South Africa. The figures in the photograph are wearing masks that resemble primitive African masks and the graffiti on the walls resemble native cave drawings. This highlights the primitiveness of rural life in South Africa.
FIGURE 2b: Irma Stern, Pondo Woman, 1929, oil on canvas.
Media and technique: Oil paint on canvas, use of loose brushstrokes, lively Composition: Triangular composistion; female figure placed in middle which is the focal point
Symbols: Traditional African dress and jewelry
Colour: Lots of browns and yellows (seen as harsh)
Subject matter: Pondo woman thinking (6)
The work Pondo Woman is an example of a figure study which simplified facial features, hair style, decorative beadwork and traditional clothing dominated the portrayal of the woman. This represents a type instead of the individual. The attitude of the woman is turned inwards. She is pensive, as if she is idle or busy daydreaming. The fact that the woman looked down, created a barrier between her and the viewer; her personality is hidden and therefore contributes to the stereotypical version of the woman. Like most of her portrait and figure studies, Stern placed the topic centrally in the composition. This is similar to Western portraits. The influence of German Expressionism is clearly evident, especially with the naked figure and the busy background.
2.2 Refer to FIGURE 2c. Discuss Andries Botha’s work with specific focus to the following:
- Formal elements of art
- Theme message
- Mood as related to Africa
The elephant herd installation at Panne beach in Belgium was created with 14 different types of wood collected from dead trees in Kwa-Zulu Natal or pieces of wood that had fallen from a tree. The wood has been carved and screwed in to place on a metal structure. This piece comments on the effects colonialism have had on Africa. How capitalism and commercialism has taken its toll on traditional culture, the natural environment and the animals that inhabit it. The elephant links to memory – they never forget – so they symbolise a memory. A memory of man’s domination of nature where animals have become trophies in Africa. (6)
2.3 Choose ONE work (other than works that appear in this question paper) by a South African artist that reflects African/Indigenous influence and in at least ½ a page analyse and evaluate the extent to which it reflects this influence by referring to the following:
The following must be included:
- Names of artists and their works
- Application of formal art elements
- Theme/message
- Mood as related to Africa
Award marks for each of the two works as from 3 + 3. (6)
[20]
QUESTION 3
SOCIO-POLITICAL ART – INCLUDING RESISTANCE ART
| There has always been a strong relationship between art and politics. During times of political unrest, artsists tend to use art either as a vehicle of promoting their propagandist views or as an expression of the oppression/repression of those views by those in authority. |
Write an essay of about one page in which you prove the above statement true by analysing FIGURE 3a, FIGURE 3b and FIGURE 3c with reference to the following:
- Hisorical context and subject matter
- Use of formal art elements and composition
- Materials and techniques
- Message or meaning.
3.1 FIGURE 3a – Hisorical context and subject matter
This painting celebrated the day, during the 1830 Revolution in France, that the people rose and fought for their liberty. Delacroix used the painting as a political poster for the revolution. Delacroix was a member of the National Gaurd, and he placed himself into the picture as the man on the left wearing a top-hat (close-up shown below). Liberty is portrayed as a majestic woman with the flag and gun leading the people against the king’s soldiers. The heroicism of the people of Paris is represented in scenes like the street boy with pistols, the worker with his sword and the intellectual with his top hat.
Max. 3
- Formal art elements and composition
In true romaticist style, Delacroix’s subject matter is informed by individual creativity as guided by passion to create emotional drama. The composition is based on dramatic diagonals as evinced in the charging womans body posture, her arm holding the flag as countered by the angle of the flag stick; the boys posture and arms holding the pistols;the posture of the legs of the stripped naked figure, the angle of the gun held by the man all intensfying the drama and movement in the work.The action is congested taking up the lower portion of the canvas where dead figures in the front form the basis of a triangular composition. The rich blue, Red and white in the clothes and the flag mixed with the yellows, browns and purples rendered in free brushstrokes all add to the intensity of emotion in the work. The background on the left is filled with hazy crowd of protesters while perspective on the right is halted by the clouds and smoke of the cannons adding to the explosive atmosphere.Max. 4 - Materials and techniques
Dalacroix used enriching quality of complementary colours banishing black from his pallete while using violets and greens for shadows. His loose brush strokes added vibrancy to the colours while at the same time increasing the intensity of the emotion of battle, life, agony, and death in the work. Max. 2 - Message and Meaning
People’s uprisings will always prevail over authoritariandictatorial regimes. (Accept any answer along the folowing lines.) Max. 1
FIGURE 3b:
Historical events: Commentary on American military actions presumably in Central America/Vietnam. In Interrogation III the complete vulnerability of the woman is evident as she is blindfolded and tied up. She is being interrogated and tortured by two policemen/soldiers.
ART ELEMENTS: Golub created his work on un-stretched canvas like banners hanging on walls.
Line: Line that alludes to Cezanne’s representation of structure is used to represent the interrogators gruesomeness of their torture.
Forms: The interrogating forms lack three-dimensionality creating a feeling of the inhumanness of their nature and their determination to dehumanise their victim
Texture: His painting technique itself depicts a kind of exposure as he layered the paint over the figures and strips parts away with solution and then scratches over it to create a hard rough textural mottled look of the skin that speaks of the hardness and brutality of the interrogators while at same time revealing the harsh bruise and scratches on the body of their victim.
Colour: Colours used are pale dark grey blues purples. The victim’s body is represented in pale purple to a feeling of gloom and bleak future for the victim.
Space: The background is painted in flat pale light purple echoed in a slightly dark hue of the victim creating flatness of a wall thereby giving the victim no chance of escape.
Materials: Acrylic on canvas stripped with solution and scratched not only reduces the chromatic effect of the paint but leaves a pale-harsh and bleak atmosphere.
Message and meaning:
The victim is a woman, mauled with seeming sexual intent by two clothed men as she sits nude, handcuffed, legs wide open on a mat. As she is the only female in the “Interrogation” cycle, she inevitably comes off as a general symbol of male oppression as well as a specific object of terrorism in a particular situation.
FIGURE 3c:
Hisorical context and subject matter: Graffiti done in 2005–2007 in Isreal and Palestine. Commenting on the ongoing war between these two contries.
Use of formal art elements and composition: The man and the flower wrapping are painted in black and white, the flowers and stems in colour.
Materials and techniques: Pre-made stencills, spraypainted on to walls/canvas – graffiti style.
Message or meaning: There is anger and frustration in the posture of the man, bombing the establishment with flowers. The flowers represent hope and a peaceful resolution of conflicts.
Banksy is the pseudonym of the famous British graffiti artist. His political and social commentary has showcased on streets, buildings and bridges worldwide. With regard to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict he created works on the Palestinian side of the wall in 2005 and again in 2007. According to Banksy his artwork transforms the Palestinian side of the wall into the world’s largest prison. He comments that this segregation is a travesty. In FIGURE 3c the petrol bomb is replaced by a bouquet of flowers. (10)
3.2 In two individual paragraphs of half a page each, the learner must evaluate TWO artworks which has been studied, portraying in an intelligible manner the following:
- Names of artist and work in each paragraph
- Description of composition
- The relevance of the art principles applied
- An analysis explaining the issues addressed by the artist
- An evaluation of the success of the approach of the artist (10)
[20]
QUESTION 4
ART, CRAFT AND SPIRITUAL WORKS MAINLY FROM RURAL SOUTH AFRICA
| Immediately, with the phrase 'African craft' one enters into the realm of what is art and what is craft? A never-ending discourse that will, one suspects, continue to be agitatedly discussed forever. Craft is essentially the production of an item that requires skill to produce it. This makes most 'art' craft. Does it make craft 'art'? A lot of the argument arises because, in the initial dialogue, Westerners decided that Africa had no 'art' as they knew it which was primarily based upon painting and representational art. Instead, African painting consisted of decorating surfaces like rock faces, hides, bark, pottery, mud huts, sculptures and human bodies. |
4.1 With reference to the statement above, analyse and interpret the given FIGURES 4a and 4b by writing an essay of 1 ½ to 2 pages, in addition to Figures 4a and 4b also choose ONE artwork of your choice and ONE craft piece (from a rural area) of your choice to explain when an object can be classified as art. Refer to the following in your essay:
- Elements of Art
- Functionality
- Mediums
- Traditional use
- Religious and Spiritual elements
- Titles
- Subject matter
Marks will be allocated as follows:
- 3 Marks for introduction which deals with your views on the question.
- 16 Marks for insightful commentary on the four artworks.
- 1 Mark for very short conclusion
FIGURE 4A:
Elements of Art:
Form: The bowl takes the spherical form of a traditional Xhosa/Zulu bowl which, though methods and techniques differ, went through similar, processes of extraction, processing, kneading, moulding and firing as used in the creation of any is spherical bowl made using modern ceramic making processes. Thus it can be ‘art’ or ‘craft’ depending on the perspective one views it from.
Colour: Most Zulu pots are blackened after the firing; this is largely for ritualistic purposes as the ancestors hide in dark, shady places. In time, through daily use, the pots develop a warm, brown, glossy patina characteristic of Zulu pots. This process alludes to the glazing process that adorns the modern ceramic pieces. The fact that the processes differ does not negate the classification of craft pieces. Art not defined by a specific process but by any process that results in the outcome being visually aesthetic.
Patterns: The patterns and decoration on the pots vary according to family and region. Usually one can distinguish two styles of decoration: incised decoration and raised decoration. The Nala family has incorporated both styles into their pots. Though the craft of the making and decorating the bowl is passed on from generation to generation to affirm its traditional identity, it these patterns that entrench it into the realm of art.
Functionality: Its function as a bowl is as good as any modern ceramic bowl that falls under the real of art, though it can be categorised as craft art
Mediums: Although art is about creativity, the aspect of reproduction that characterises the passing on the craft from generation to generation does not differ much from the reproductive process that characterises the reproduction of modern ceramic art pieces or prints.
Traditional use: Traditionally, three sizes were most common: the large Imbiza pot was used for brewing, the Ukhamba pot used for serving and the Umancishana pot size was used for cooking meat, storing water and grain and for drinking sour milk
Religious and spiritual elements: After meeting archaeologist, Len van Schalkwyk, and seeing pottery dating from the Iron age, Nala was influenced by the use of pattern by her ancestors. Nesta has passed the family’s pot making tradition to her daughters, Jabu, Thembi and Zanele. Although each daughter has her own particular style, they all sign their work; a feature unique to Zulu potters. Today, the tradition has passed on to their daughters, and thus continuing the Nala legacy.
Titles: Ukhamba Ceramic Piece – Ukhamba is Zulu for the pot that beer is served in.
Subject matter: The serving of beer is a very important part of Zulu culture. The artist wanted to preserve this tradition.
Accept any other logical and substantiated discussion and evaluation.
FIGURE 4B:
FIGURE 4b is sculpturing which falls under the realm of principles of sculpture that govern western sculptural art. Although made in wood which is traditionally used in the craft-making process of traditional African house-hold craft object and divine figures, the process, technique and final product all align it to be defined as pure art rather than ‘craft art.
Elements of Art:
Form: Composition is intertwined figures, flowing of form symbolising the flood, Composition is triangular suggesting victims of flood swimming upwards toward surface for air. The figures themselves are a bit flattened to express the magnitude of the force they are fighting.
Texture: Texture is relatively smooth to create a feeling of wavy atmosphere surrounding the victims.
Space: There is in and outward flow of space between the clinging inclined figure that create an illusion of a wild force of uncontrollable turbulence
Functionality: Decorative reminder of tragic event just as Picasso’s “Guernica’’
Mediums: Maroela wood. It was readily available just like the way marble was readily available to the Greeks or limestone was readily available to the Egyptians.
Traditional use:
Religious and Spiritual elements: Mabasa claims that she was told by an ancestor spirit to leave clay as a medium and pursue wood carving instead. – transgressing the boundaries of gender in her culture. From her dreams, Noria draws her power to create. From here she gets the physical strength that has allowed her to produce art for the past 25 years.
Titles: The Flood – reflecting on a devastating event that seemed to have been orchestrated by forces beyond nature.
Subject matter: Inspired by Television coverage of a flood in KZN which devastated parts of South Africa. The flood shows people and animals swirling around and reaching up, trying to escape flood waters. The people cling wildly to each other as they struggle to stay alive. A big battle between human beings and nature seems to be taking place.
Accept any other logical and substantiated discussion and evaluation.
[20]
QUESTION 5
MULTI-MEDIA AND NEW MEDIA – ALTERNATIVE CONTEMPORARY AND POPULAR ART FORMS IN SOUTH AFRICA
| Multimedia artists makes use of elements that “speak” to all five senses. Traditionally in classical art only the sense of sight was a focus. This lead to the concept having a greater significance in multimedia art. All thanks to Marchel Duchamp and his “Ready mades”. |
5.1 With reference to the above statement and visual source, FIGURE 5a. Write a paragraph (at least ½ page) in which you discuss the above statement by considering the following:
- The medium used
- The message of the artwork
FIGURE 5a (may use FIGURE 5b for reference only)
Kendall Geers The Terrorist’s Apprentice, 2002. Matchstick/found objects. The work consists of one matchstick displayed in a space on its own. Geers refers to a statement made by Winnie Mandela, Nelson Mandela’s ex-wife, in which she said: “We don’t have guns – we have rocks, boxes of matches and our “necklaces” with which we will free this country.” The statement is ironic as it displays a safety match which can cause endless destruction. The idea behind the work is more important than the object itself as the artwork is conceptual. (4)
5.2 Also with reference to the above statement analyse and discuss
FIGURE 5b in essay format (at least ½ page). Consider the following:
- Application of art elements and principles
- Mediums relevant to the concept
- Meaning or message
FIGURE 5c – Willem Boshoff. Blind Alphabet, 1990. Wood, steel, aluminium.
The artist set himself a task as he felt discriminated against because of his Afrikaans accent. Whilst teaching at an English school he composed a list of confusing English words. He used these words in conversations with native English speakers, to confuse them and expose their ignorance with regards to their own language. Thus he began to compile a dictionary of difficult words. Boshoff’s intention with creating Blind Alphabet was to create an experience for blind individuals wherein they could touch and thereby ‘see’ the artwork and learn something from it. Hereby putting the blind in the privileged position of having the power in relationship to the work. Whereas individuals with the ability to see were disadvantaged and left ‘illiterate”. The blind Alphabet ABC consists of 338 wooden statues placed in steel cases. The lid of each case has an aluminium plaque embossed with text in Braille. Braille is text which is read through the sense of touch, used specifically by the blind and sight impaired. The text consists of difficult English words, their meaning and origin. The statues inside represent the word on the plaque.
Accept any other interpretation as long as it substantiates a logical interpretation referenced from the work. (6)
5.3 In essay form of at least one page, the learner must recall and analyse at least one work in multimedia which has been studied, substantiating each of the following:
- Name the work/s as well as the artist
- Media
- Messages and/or meanings
- Influenced by which style of art
- Presentation
A work which appears in this question paper, may not be used, but a different work by one of the artists used in this paper is allowable. (10) [20]
QUESTION 6
POST-1994 – DEMOCRATIC IDENTITIY IN SOUTH AFRICA
| Post-Apartheid visual art made definite contributions with regards to the integration and emancipation of different races in South Africa this led to a believable contemporary South Africa in which artists could once again focus on their own identities |
6.1 In an essay of about ¾ page, the learner must discuss how the individual artists of the visual sources of FIGURES 6a and 6b relate to expression of identity, referring to the following:
- Formal art elements
- Style and technique
- The comments these artists make
- Which one makes the strongest impact, with reasons for his/her choice
In FIGURE 6a:
Formal art elements: Conceptual photography, Technique is less important than content and message
Style and technique: They use colour photographs as a medium to express their ideas, In Islam it is forbidden to depict the human form, and therefore the artists are also the subjects in their work.
The comments these artists make: The artists question their heritage as Muslim, Indian and South African. Searching for their place in a multicultural and multi-religious society. The Five Pillars depict the Five Pillars of Islam (Faith, prayer, fasting, charity, and pilgrimage). It seems that there is a bomber in the middle of the scene. He seems to be preparing for a deadly mission. This comments on the general Western view of Muslim people.
Which one makes the strongest impact, with reasons for his/her choice. (8)
In FIGURE 6b: Wim Botha. Mieliepap Pïeta, 2004, mieliepap, resin.
Formal art elements: Mirror representation of the Pïeta by Michelangelo. Dimensions correlate.
Style and technique: A classical naturalistic approach reminiscent of white marble used in the original Pieta is employed in this work. Maize-meal and resin is used to make the sculpture. Like the way flour is used to make unleavened bread. Maize- meal as part of African staple food is used to reiterate on the idea from an African context.
The comments these artists make: Botha’s Pïeta is about heartache and loss, communicating human tragedy. The youthful Madonna in contrast to the lifeless body of Christ draped across her. Her eyes fixed on his wounds. Mieliemeel is a staple food for South Africa’s lower economic classes. Botha links the idea of staple food to faith. She becomes an African Madonna.
Which one makes the strongest impact, with reasons for his/her choice
The learner must substantiate his/her choice for the highest impact of the two works.
6.2 In an essay of at least 1½ pages, the learner must discuss the work of any TWO South African artists which have been studied, who question and reflect on their post 1994 identity. Specific works, which do not appear in this paper, must be referred to in the answer. Note that “specific” indicates that works and artists must clearly be named. (12)
[20]
QUESTION 7
GENDER ISSUES – MASCULINITY AND FEMININITY
| Since the Renaissance era the female body has been the prime subject matter for many artists, most of them male. In later centuries female artists use the female form, but not to portray the stereotypical idea of women. |
7.1 With reference to the above statement and referring to FIGURE 7a and FIGURE 7b learners must explain how the female form was used by contemporary female artists in each artwork. Discuss in essay format with a substantial paragraph of approximately ¾ page, considering the following:
- Use of title
- Composition
- Style
- Formal elements of art
- How gender is questioned/affirmed
FIGURE 7a: Jenny Saville, Propped, 1992, oil on canvas.
Use of title: The title Propped literally refers to the figure propped on the chair, the chair holds the figure up, supports it, even though it is massive, fleshy and grotesque
Composition: Centre of canvas – focal point. The composition focuses on and emphasises the body and draws the viewer in with an exciting shortened frontal view of the female form. She depicts a small head and feet with overlarge thighs that remain disturbing to the viewer raising issues of beauty and seduction when it comes to feminine obesity.
Style: Figure painter, paintings based on herself. The application of paint recalls pain and bruises on an almost geographical portrayal of flesh.
Formal elements of art::
Line and Colour: There is a clear hard edged out-line to distinguish the massively obese propped Woman nude against the blue wall with partially erased inscriptions.
Form. Although directly facing the viewer, the tonal contrasts in the browns coupled with rendering of light on the features enhances the three dimensionality of the form to accentuate the figure’s obesity.
How gender is questioned/affirmed: Her work defies conventional female beauty where thin is synonymous with beautiful. The poses are often coquettish and seductive which makes them even more interesting. The beauty in the piece is found in its expressive nature, creating a Venus of Willendorf/Mother Earth feel. (8)
FIGURE 7b: Mary Sibande. Red Dogs, 2015, Installation.
Use of title: Five red dogs are in the foreground of the installation. The female figure looks to be setting them on someone/thing outside the frame or chasing them away like a person would chase away street scavenger dogs encroaching on his/her privacy.
Composition: Triangular composition. Female figure is in the middle – focal point – arm stretching forward, drawing the viewer in. Five dogs are on the attack of someone/thing outside the frame and seem to be running forward. It could mean she is scurrying them off to attack an unwanted intruder or caught them encroaching on her space and is chasing them off.
Style: The theatrical quality of her work places it in the realm of fantasy. Her work critiques stereotypical depictions of women, particularly black women in our society. Her interest in fashion and clothing has been channelled in her art to comment about different women’s status in society. In
Formal elements of art:
Form and Colour. The female figure used in the installation is a cast of the artist’s own body in fibreglass and silicone, like a mannequin.
Figure is purple, dogs are red (title) contrast of black and white in the background. The fact that Mary cast a forms representing a dangerous breed of dogs (Rot Wailers) and in Red emphasises their dangerousness and expression their viciousness.
How gender is questioned/affirmed: The artwork is not meant to create a feeling of anger, shame and humiliation but to transcend this reality where the an expecting mother (as represented in the arm protectively holding on to the lower part of her slightly extended tummy) is able to have full control of command on the blood thirsty (Red) scoundrels which by their numbers and appearance seem vicious and deadly to be surrounded with. Behind her denigration lies the power to control what men would fear.
7.2 In approximately 1½ pages, an essay must be written of any TWO artists which have been studied, in whose works male and/or female identity is addressed. The works must be named, described and compared. The essay must be ended with a conclusion regarding the impact of each. (12)
[20]
QUESTION 8
ARCHITECTURE IN SOUTH AFRICA
| Magnificent examples of ground-breaking architecture have come out of the 20th and 21st centuries. Buildings that have been innovatively and environmentally designed are evident in many parts of the world |
8.1 Considering the above-mentioned, study the images of the innovative structures each relevant in their own time FIGURE 8a and FIGURE 8b. Write an essay of one page, in which you elevate the innovative accomplishments. You may include thoughts on the following:
- Principles of design applied
- Influences and creative thought
- Peculiar characteristics
- Aims and effective functionality
FIGURE 8a – KIKS Building in Cape Town, South Africa
Big glass structures are placed in open modular steel structures. This creates a High Tech look and feel. This building has a three-story circulation “spine”. On the beachfront side heavy winds and high levels of noise had to be taken into account. Wind and Thermal studies concluded that hanging sunscreens and potplants were necessary to accommodate weather conditions and also create an element of eco-friendliness.
FIGURE 8b – House Rhino, 2011. Crossways, Eastern Cape, South Africa.
A pioneering green house, the first of its kind on the African continent. Recycled materials have been used extensively, including the decking – a natural rock feature and rock garden.
Due to its insulation properties there is a reduced need for heating and cooling in the house.
Hydromedic – all rainwater drains immediately and is collected underneath the house where it flows into the water recycling process.
The house is powered by roof-mounted solar photovoltaic panels. (8)
8.2 In an essay of approximately 1½ pages TWO buildings by any popular, contemporary South African architect/s must be clearly analysed. The shapes, materials and design which place them in a category of outstanding impact, must be discussed.
The following aspects may well be relevant:
- Names of architects/companies and buildings
- Special features
- Peculiar materials, technology and design
- Ecological considerations
- Environmental issues
- Functionality (12)
[20]
TOTAL: 100
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICS PAPER 1 MEMORANDUM - NSC EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
MATHEMATICS
PAPER ONE(P1)
GRADE 12
EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2016
NOTE:
- If a candidate answered a question TWICE, mark the FIRST attempt ONLY.
- Consistent accuracy applies in ALL aspects of the memorandum.
- If a candidate crossed out an attempt of a question and did not redo the question, mark the crossed-out attempt.
- The mark for substitution is awarded for substitution into the correct formula.
MEMORANDUM
| QUESTION 1 | ||||
1.1.1 | ?2 − 4?−12=0 | ✔ standard form (3) | ||
1.1.2 | 3?2+2?−6=0
| ✔ substitution ✔ x = −1,79 ✔ x = 1,12 (3) | ||
1.1.3 | 3?2 − 1 = 27-x OR 3?2 − 1 = 27 − ?3 | ✔ 3−3?−1
✔?2 −1 + 1 = 3−3? (4) | ||
| 1.2.1 | 1 +1/? = 0 ? + 1 = 0 ? ? =−1 or ?=0 | ✔ ? =−1 (2) | ||
| 1.2.2 | ?−1/? =1 1+1/? ? −1/?=1 +1/? ?2 − 1 = ? + 1 ?2 − ? − 2 = 0 (?+1)(?−2) = 0 ?=−1 or ?=2 ?=2 only | ✔ manipulation of equation (5) | ||
| QUESTION 2 | ||||
| 2.1 | ? − ? =3 ; ?? = 28 OR From (1) ? = ?−3 | ✔ ? = ? + 3
✔ ? = ? − 3✔ substitute in (2) (6) | ||
| 2.2 | ?2 ≤ 4 + 3? ; ? > 0 ?2 − 3? − 4 ≤ 0 (?+1)(?−4) ≤ 0 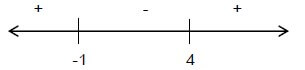 Solution −1 ≤ ? ≤4 But ? >0 0 < ? ≤ 4 | ✔ standard form/standaardvorm (4) | ||
| QUESTION 3 | ||||
| 3.1 |  ?? = ??2 + ?? + ? 2? = 2 ? =1 3? + ? = 2 3 + ? = 2 ? = −1 ? + ? + ? = 1 1 − 1 + ? =1 ? =1 ?? = ?2 − ? + 1 Row 80 Term 1 ?80 = 802 − 80 + 1 ?80 = 6321 | ✔ a = 1 (5) | ||
| 3.2 | Row 80 OR Row 80 Term 80 OR
?? = ?2 + ? − 1 | ✔ n= 80
✔ calculating term 80 of row
✔ ?? = ?2 + ? − 1 (4) | ||
| QUESTION 4 | ||||
| 4.1.1 | ?10 = ?10 − ?9 ?10 = 10(11)(12) − 9(10)(11) ?10 = 330 | ✔ setting up of equation ✔ substitution (3) | ||
| 4.1.2 | ? ;3? ;5? ;…………… OR
| ✔ first three terms
✔ ? = ? (4) | ||
| QUESTION 5 | ||||
| 5.1 | ? = ?+2
| ✔ ratio (2) | ||
| 5.2 | ?∞= ?
| ✔ substitution ✔ simplification ✔ ?2=16 ✔ both answers (4) | ||
| QUESTION 6 | ||||
| 6.1 | ? = ?(1−?)? ? = 635000(1−15/100)5 ? = 281 752,87 | ✔ ?=15/100 and ? =5 (3) | ||
| 6.2.1 | ?? = ?[1 − (1+?)−?] ? 50000 = ?[1− (1 + 16.75/1200)−48] 16.75/1200 ? = ? 1 436,29 | ✔ ?=16.75/1200 (4) | ||
| 6.2.2 | ?? = ?[1 − (1+?)−?] OR Outstanding balance (OB) | ✔ ?=−18 (5) ✔ ?=30 (5) | ||
| 6.3 | ? = ?(1+?)? ? = 2? and ? = ? 2? = ?(1+14.75/100)? ? = log2 log(1 +14.75/100) ? = 5.04 ????? | ✔ ? = 2? and ? = ? (4) | ||
| QUESTION 7 | ||||
| 7.1.1 | x = 0 | ✔answer (1) | ||
| 7.1.2 | x > -2 ; x # 0 | ✔x > -2 (2) | ||
| 7.1.3 | y = -4 | ✔answer (1) | ||
| 7.1.4 | ? = ?? − 4 5 = ?2 − 4 ?2 = 9 ? = ±3 ? = 3?−4 | ✔ sub of −4 (4) | ||
| 7.1.5 | x = -2 y = -1 | ✔x = -2 (2) | ||
| 7.1.6 | ? = ? −1 ?+2 −3 = ? − 1 0+2 ?=−4 ?= −4 − 1 ?+2 | ✔ sub of asymptotes (3) | ||
| 7.1.7 | ? = ? + 2 −1 ? = ? + ? ? = −(? + 2) −1 ? = −? − ? | ✔? = ? + ? (3) | ||
| 7.2.1 | ? = log½? ?−1 ∶ ?= log½? ? = (½)? OR ? = 2−? | ✔swopping of x and y (2) | ||
| 7.2.2 |  | ✔Shape (3) | ||
| 7.2.3 | g(x) = (½)-x OR g(x) = 2x | ✔✔Answer ✔✔Answer (2) | ||
| 7.2.4 | x > 1 | ✔✔x > 1 (2) | ||
| QUESTION 8 | ||||
| 8.1 | x = -3 | ✔x = -3 (1) | ||
| 8.2 | ? = ?(? + 3)2 − 5 4 = ?(9) − 5 9? = 9 ? = 1 ? = ?2 + 6? + 9 − 5 ?=?2 + 6? + 4 ? = 1 and ? = 6 | ✔ sub of turning point (3) | ||
| 8.3 | Δ = ?2 − 4?? Δ = 36 − 4(1)(4) Δ=20 ????? ??? ?????????? ??? ??????? | ✔ Δ=20 (3) | ||
| 8.4 | ?(?) = 2? Point (−2;−4) OR ?(?) = ?2 + 6? + 4 | ✔ ?(?) = 2?
✔ derivative (4) | ||
| QUESTION 9 | ||||
| 9.1 | ?(?) = 3?2 − 1
| ✔ formula (5) | ||
| 9.2.1 | ? = 5?2 + √? ? = 5?2 + ?½ ??/?? = 10? + ½?−½ | ✔?½ (3) | ||
| 9.2.2 | ?? [6?−4] 3? ??[6?/3?−4/3?] ??[2 − 4/3?−1] =−4/3?−2 or 4/3?2 | ✔ 2 (3) | ||
| 9.2.3 | ? = ?′(?) =3?2 ?2 ≥ 0 3?2 ≥ 0 ∴ no value of t will make ?′(?) negative. | ✔ derivative (2) | ||
| QUSTION 10 | ||||
| 10.1 | ?(?) = ?3 − ?2 − 8? + 12 OR ?+3 3?2 − 12? + 12 | ✔(?−2)
(4) | ||
| 10.2 | ?′(?) = 3?2 − 2? − 8 = 0 (3? + 4)(? − 2) = 0 ? = −4/3 or ? = 2 ?(−4/3) = (−4/3)3 −(−4/3)2 − 8(−4/3) +12 B(−4/3; 500/27 ) | ✔?′(?) (5) | ||
| 10.3 | ?′′(?) = 6? − 2 OR ?=−4/3+2 | ✔?′′(?) = 6? − 2 (2) | ||
| 10.4 | ? <−4/3 or ? > 2 | ✔? <−4/3 (2) | ||
| 10.5 | ?=? ;?<0 Only one Real Root | ✔answer (2) | ||
| QUESTION 11 | ||||
| 11.1 | ?(0) = 3 + ½(0)2 −14(0)3 ?(0)=3 ? | ✔?(0)=3 ? (1) | ||
| 11.2 | ?′(?) = ? − ¾?2 ?′(3) =3 −¾(3)2 =3 − 27/4 =−15/4 m/h / m/u | ✔?′(?) (3) | ||
| 11.3 | Decreasing | ✔Decreasing (1) | ||
| 11.4 | ?′(? )= 0 ?− ¾?2 = 0 4? − 3?2 = 0 ?(4 − 3?) = 0 ? = 0 or ? = 43 43 =1ℎ20??? Time: at 08h00 or 9h20 | ✔?′(? )= 0 (4) | ||
| QUESTION 12 | |||
12.1 | 12.1.1 | P(A′) = 1 − P(A) | ✔ P(A′) = 1 − P(A) (2) |
12.1.2 | P(AandB) = 0 | ✔ answer (1) | |
12.1.3 | P(A or B) = 0,35 + 0,52 | ✔ P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) (2) | |
12.2 | 12.2.1 | 6! = 720 | ✔ 6! or/of 720 (1) |
12.2.2 | 4! | ✔4! (2) | |
12.2.3 | 2!.5! = 240 = 1 OR 0,333 | ✔ 2! (4) | |
TOTAL: 150 | |||
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICS PAPER 2 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
MATHEMATICS
PAPER TWO (P2)
GRADE 12
EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2016
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1 | |||||||||||||||
Day | 0 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 17 | 19 | |||||||
Weight | 124 | 121 | 103 | 90 | 71 | 50 | 27 | 16 | |||||||
1.1 |
| ✔ 2-4 correct points | (3) | ||||||||||||
1.2 | a = 124,84
| ✔ A | (3) | ||||||||||||
1.3 | (x; y) = (8;5;75,25) | ✔(8;5;75,25)and y-int 124,84 | (2) | ||||||||||||
1.4 | 124,84 - 5,83x = 80 | ✔ substitution | (2) | ||||||||||||
1.5 | r = −0,998 | ✔ answer | (1) | ||||||||||||
1.6 | Very strong negative correlation. | ✔ answer | (1) | ||||||||||||
[12] | |||||||||||||||
QUESTION 2 | ||||
 | ||||
2.1 | 21 learners | ✔ answer | (1) | |
2.2 | 3 pages | ✔ answer | (1) | |
2.3 | x = 28,19 | ✔✔ answer | (2) | |
2.4 | σ =13,12 | ✔ answer | (1) | |
2.5 | ( 28,19 − 13,12; 28,19 +13,12) ∴ 8/21 × 100 = 38.10% | ✔ interval | (3) | |
[8] | ||||
QUESTION 3 | |||
| |||
3.1 | mPR= 5 - 1 | ✔ subst. P and R into correct formula
| (2) |
3.2 | mSQ = −2 SP⊥ PT | ✔mSQ = −2 | (3) |
3.3 | Equation of PR PR 1 y - 1 = ½(x + 4) OR y - 5 = ½(x + 4) | ✔ substituting m and P into equation of a str. line
✔ substituting m and R into equation of a straight line | |
3.4 | -2 = x + 1 2 = y - 4 | ✔ substituting into correct formula | (3) |
3.5 | SQ = √(-5 - 1)2 + (8 + 4)2 OR ∴area of ∆ PQS = ST ×PT 15unit2 | ✔ subt. into correct form
✔SQ = 6√5 | (5) |
[18] |
QUESTION 4 | |||
| |||
4.1 | x2 + 8x + 16 + y2 + 9 = 20 (x + 4)2 + (y - 3)2 = 20 ∴ M(-4; 3) | ✔ completing square | (4) |
4.2 | (0 + 4)2 + (y - 3)2 = 20 (y - 3)2 = 4 y = 3 ± 2 ∴y = 1 Q(0;10 | ✔ subst. x = 0 into circle equation | (3) |
4.3 | mradius = 3 - 1 = 1 | ✔mradius = ½ | (4) |
4.4 | y = 6 | ✔ answer | (1) |
4.5 | 6 = 2x + 1 x = 5/2 U(5/2 ;6) | ✔ 6 = 2x + 1 | (2) | |
4.6 | MAU = 11 - 6 | ✔mAU = −2 | (6) | |
[20] | ||||
QUESTION 5 | |||
| |||
5.1.1 | sin(-52º) = -sin 52º = √1 - t2 | ✔ − sin 52° | (3) |
5.1.2 | cos (2.19º) = cos38º | ✔cos(2.19°) = cos38° | (4) |
5.2 | 2cos(180º + x ).sin(180º - x ).sin 74º OR 2cos(180º + x ).sin(180º - x ).sin 74º | ✔ − cos x
✔ − cos x | (7) |
5.3.1 | 1 - cos 2x = 0 | ✔1− cos 2x = 0 | (4) |
5.3.2 | L.H.S/LK = 2sinx | ✔1− 2sin2 x | (3) |
[21] |
QUESTION 6 | |||||
6.1 | sin(x + 60º) = sin(90º - 2x) OR cos2x = cos(30º - x) | ✔co-ratio
✔co-ratio | (5) | ||
6.2 |
| g: ✔ x-intercept. f: ✔ x-intercept. | (6) | ||
6.3 | 240° | ✔ answer | (1) | ||
6.4 | h(x) = cos(2x −90°)−1= sin 2x −1 | ✔ substitution | (2) | ||
[14] | |||||
QUESTION 7 | |||
| |||
7.1 | NP2 = ON2 + OP2 | ✔ using Pyth theorem correctly | (2) |
7.2 | PQ2 = (103)2 + (103)2 - 2(103)(103) .cos(120º ) | ✔ subst. into cosine rule | (2) |
7.3 | cos N = (177,86)2 + (177,86)2 - (178.40)2 | ✔ substitution | (2) |
[6] | |||
QUESTION 8 | |||||
8.1 | Bisects the chord | ✔ answer | (1) | ||
8.2 |
| ||||
8.2.1 | Q = 90° [∠in semi circle.] | ✔ S ✔ R | (4) | ||
8.2.2 | MF= 8ML | ✔ | (1) | ||
8.2.3 | OP2 = OL2 + LP2 | ✔ using Pyth correctly | (3) | ||
[9] | |||||
QUESTION 9 | |||
| |||
9.1 | D3 = 30° [∠sopp equal sides] | ✔ S | (3) |
9.2 | A = 60º [∠at centre = 2∠at circumf.] | ✔ S | (2) |
9.3 | C =120° [opp. ∠sof cyclic quad.] | ✔ S | (2) |
9.4 | ADB = 70° Aˆ [tan chord theorem.] | ✔ S | (2) |
[9] | |||
QUESTION 10 | |||
10.1 |
| ✔constr. | |
| U2 = 90º - U1 [tan ⊥ radius] Z = 90º [∠in semi circle] S = 180º - (90º - U1) - 90º [sum of ∠s of a Δ] ∴S = U1 S = Y ∴U1 = Y | ✔ S/R | (5) | |
10.2 |
| |||
10.2.1 | A2 = x [∠sopp. = sides] | ✔ S/R | (5) | |
10.2.2 | S1 = T =x [proven in 10.2.1] | ✔ S | (2) | |
10.2.3 | AR = AT [line ║to one side of a ∆] | ✔ S/R | (4) | |
[16] | ||||
QUESTION 11 | ||||
| ||||
11.1 | A1 = C2 [tan chord theo.] | ✔ S | (4) | |
11.2 | Zˆ= Pˆ [∠sin same segment] | ✔ S/R | (3) | |
11.3 | B1 = D2 [ext. ∠of a cyclic quad.] | ✔ S | (5) | |
11.4 | ZA = RA [similar ∆s] | ✔ S/R ZA DC RA × ✔PC = ✔ S/R AZ AB RA × = ✔AC ✔ simplification | (5) | |
[17] | ||||
TOTAL: | 150 | |||
GRADE 12 MATHEMATICS PAPER 2 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
MATHEMATICS
PAPER TWO (P2)
GRADE 12
EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2016
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of 11 questions.
- Answer ALL the questions in the SPECIAL ANSWER BOOK provided.
- Clearly show ALL calculations, diagrams graphs, et cetera which you have used in determining the answers.
- Answers only will NOT necessarily be awarded full marks.
- If necessary round off your answers to TWO decimal places, unless stated otherwise.
- Diagrams are not necessarily drawn to scale.
- You may use an approved scientific calculator (non-programmable and non-graphical) unlessstated otherwise.
- An information sheet with formulae is included at the end of the question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
A Grade 12 learner recorded the daily weight of a bar of soap after he had taken his shower in themorning. The table below shows the data he recorded: “Day” shows the number of days since thebeginning of the experiment and “Weight” shows the weight of the bar of soap in grams.
| Day | 0 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 17 | 19 |
| Weight | 124 | 121 | 103 | 90 | 71 | 50 | 27 | 16 |
1.1 Represent the information above in a scatter plot on the grid provided in the ANSWER BOOK. (3)
1.2 Calculate an equation for the least squares regression line for the data. (3)
1.3 Draw the least squares regression line on the scatter plot drawn for QUESTION 1.1. (2)
1.4 Determine on which morning the mass of the bar of soap will be less than 80 grams. (2)
1.5 Calculate the value of the correlation coefficient. Round off your answer to THREE decimal places. (1)
1.6 Comment on the strength of the relationship between the variables. (1)
[12]
QUESTION 2
The stem-and-leaf plot shows how many pages of a textbook learners in a Mathematics class revised before writing their examination.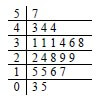
2.1 How many learners were in the class? (1)
2.2 What was the least number of pages of revision completed? (1)
2.3 Calculate the mean of the given data. (2)
2.4 Determine the standard deviation of the given data. (1)
2.5 Calculate the percentage of data that lies outside ONE standard deviation from the mean. Show ALL your calculations. (3)
[8]
QUESTION 3
In the diagram below P(-4 ; 1), Q(1 ; -4), R(4 ; 5) and S are the vertices of quadrilateral PQRS.
SQ ⊥ PR with T on PR. T is the midpoint of line SQ.
3.1 Determine the gradient of PR. (2)
3.2 Hence, determine the equation of line SQ. (3)
3.3 Show that the coordinates of T are (-2 ; 2). (5)
3.4 Hence, determine the coordinates of S. (3)
3.5 Calculate the area of ΔPQS. (5)
[18]
QUESTION 4
x2 + y2 + 8x - 6y = -5, is the equation of the circle with centre M. UE is a tangent to the circle at Q. QMD, DA, AU and UQE are straight lines. DU is parallel to the x-axis.
4.1 Determine the coordinates of M, the centre of the circle. (4)
4.2 Calculate the coordinates of Q, if y < 2. (3)
4.3 Calculate the equation of tangent UE. (4)
4.4 Write down the equation of DU. (1)
4.5 Calculate the coordinates of U. (2)
4.6 Prove that QUAD is a cyclic quadrilateral. (6)
[20]
QUESTION 5
5.1 If , determine, in its simplest form the following in terms of t, WITHOUT the use of a calculator.
5.1.1 sin (-52º) (3)
5.1.2 cos 19º (4)
5.2 Simplify WITHOUT the use of a calculator: (7)
2 cos(180º + x). sin(180º - x). sin74º
sin(x + 360º) . sin 37º. sin 53º. sin (x - 90º)
5.3 Given: 2sinx
2(1 - cosx)
5.3.1 Calculate all the values of x for which the expression above is undefined. (4)
5.3.2 Prove that 2sinx = 1 (3)
2(1 - cosx) sinx
[21]
QUESTION 6
Given: f(x) = cos2x and g(x) = sin(x + 60º) for x€(-90º;180º)
6.1 Solve for x if f(x) = g(x) and €(-90º;180º). (5)
6.2 Sketch the graph of f and g on the same set of axes for . Clearly show ALL intercepts with the axes, points of intersection as well as turning points. (6)
6.3 Write down the period of g(3/2x). (1)
6.4 Determine h if h(x) = f(x - 45º) - 1 (2)
[14]
QUESTION 7
The figure shows an open birthday card. The length of the card is145 mm and the breadth is 103 mm. The card is placed such that the angle formed between the two sides is 120º.
7.1 Calculate the length of NP. (2)
7.2 Calculate the length of PQ. (2)
7.3 Determine the size of PNQ . (2)
[6]
Give reasons for ALL statements in QUESTION 8, 9, 10 and 11.
QUESTION 8
8.1 Complete the following statement: A line drawn from the centre of the circle perpendicular to
a chord … (1)
8.2 In the diagram below O is the centre of circle PMQNF. PN and FM are diameters.
QN ║ FM
OL = 3ML
QP = 14 units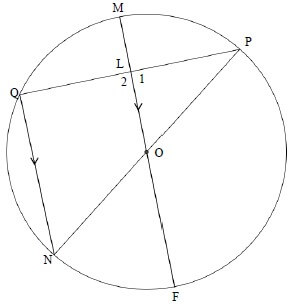
8.2.1 Prove that L is the midpoint of QP. (4)
8.2.2 Write down the length of MF in terms of ML. (1)
8.2.3 Determine the length of ML. Leave your answer in surd form. (3)
[9]
QUESTION 9
In the diagram below ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. RBP is a tangent to the circle with centre O.
B2 = 30º and B6 = 70º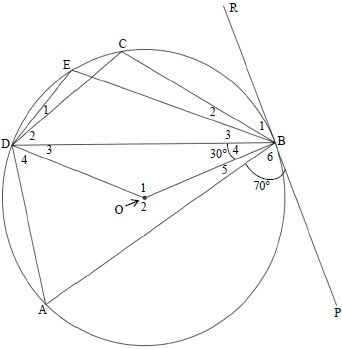
Determine the size of each of the following angles:
9.1 O1 (3)
9.2 A (2)
9.3 C (2)
9.4 AD (2)
[9]
QUESTION 10
10.1 In the diagram below O is the centre of circle UYZ.
XUT is a tangent to the circle at U.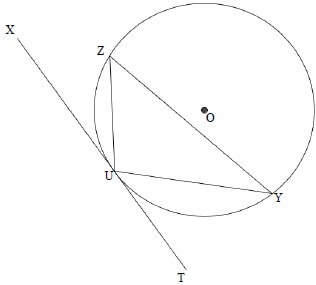
Prove that XUZ = Y (5)
10.2 CS and AS are two tangents of circle ABC. AB is produced to R. AC and SR are produced to T. AB = BC and TS║BC. Let C1 = X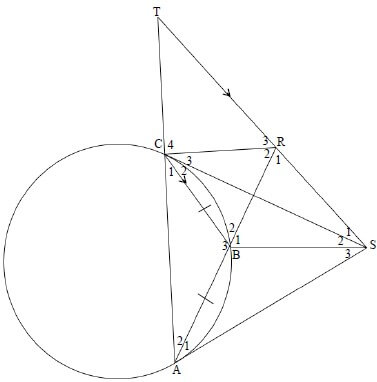
10.2.1 Name with reasons, 5 other angles each equal to x. (5)
10.2.2 Hence, show that ΔSCT is an isosceles triangle. (2)
10.2.3 If it is further given that, CS = 4 cm, AR/BR = 3/2 , calculate the length of AT. (4)
[16]
QUESTION 11
FAN is a common tangent to the smaller circle ABCD and the larger circle ARZP. FP is a tangent to the smaller circle at C. The straight line ABR meets the larger circle at R.
11.1 Prove that BC║RZ. (4)
11.2 Hence, prove that BC is a tangent to circle ACP. (3)
11.3 Prove that ΔRZA ||| ΔDPC. (5)
11.4 Hence, show that DC/CP × AC/AB = 1
(5)
[17]
TOTAL: 150

GRADE 12 MATHEMATICS PAPER 1 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
MATHEMATICS
PAPER ONE (P1)
GRADE 12
EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2016
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- This question paper consists of TWELVE questions. Answer ALL the questions.
- Clearly show ALL calculations, diagrams, graphs, et cetera that you have used in determining your answer.
- You may use an approved scientific calculator (non-programmable and non graphical), unless stated otherwise.
- Answers only will not necessarily be awarded full marks.
- If necessary, round off answers to TWO decimal places, unless stated otherwise.
- Diagrams are NOT necessarily drawn to scale.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
- An information sheet with formulae is included at the end of the question paper.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1 Solve for x:
1.1.1 x2 − 4x = 12 (3) 1
1.2 3x2 + 2x − 6 = 0 (correct to two decimal places) (3)
1.1.3 3x2−1 = 27−x
3 (4)
1.2Given the equation: x − 1/x = 1
1 + 1/x
1.2.1 For which value(s) of x is the equation undefined? (2)
1.2.2 Solve for x. (5)
[17]
QUESTION 2
2.1 Solve for x and y simultaneously in the following equations:
x − y = 3 and xy= 28 (6)
2.2 Solve for x.
x2 ≤ 4 + 3x and x > 0 (4)
[10]
QUESTION 3
Given the pattern below: 
3.1 Determine the value of the first term in Row 80. (5)
3.2 Calculate the sum of the terms in Row 80 only. (4)
[9]
QUESTION 4
4.1 The sum of the first p terms of a sequence of numbers is given by:
Sp = p (p + 1)(p + 2)
Calculate the value of T10
4.2 Calculate: 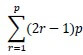 (4)
(4)
[7]
QUESTION 5
The following sequence represents a geometric progression:
x ; x+ 2 ; … … … … …
5.1 Write down the third term in terms of x. (2)
5.2 Calculate the value of x if it is given that S∞ = −8. (4)
[6]
QUESTION 6
6.1 The cost price of a car is R635 000. The value of the car depreciates according to the reducing balance method at a rate of 15% p.a. Calculate the value of the car exactly 5 years after it was bought. (3)
6.2 A loan of R50 000 is to be repaid in 48 equal monthly payments. Payments start one month after the loan has been granted. The interest rate on the loan is 16,75% p.a. compounded monthly.
6.2.1 Calculate the value of the equal monthly payments. (4)
6.2.2 Calculate the outstanding balance immediately after the 30th payment has been made. Give your answer to the nearest Rand. (5)
6.3 How many years will it take for an investment to double its value if the compound interest rate is 14,75% p.a? Leave your answer correct to one decimal digit. (4)
[16]
QUESTION 7
7.1 The sketch below shows the graph of ?(?) = ? + ? and ?(?) = ?? + ?.
? + ?
The ?-intercept of ? is at (−6; 0) and the ?-intercept of ? and ? is at (0; −3). The point (2; 5) lies on the graph of ?.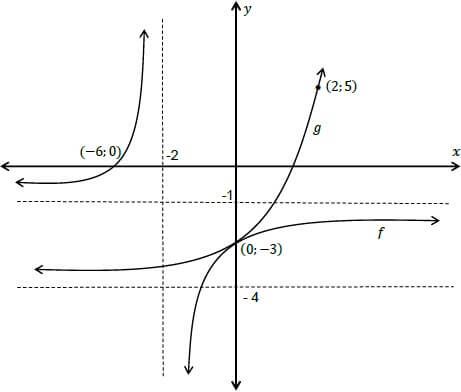
7.1.1 For which value(s) of x is ?(?) = ?(?)? (1)
7.1.2 For which values of x is ?(?) < ?(?)? (2)
7.1.3 Write down the equation of the asymptote of ? . (1)
7.1.4 Determine the equation of ? . (4)
7.1.5 Write down the equations of the asymptotes of ? . (2)
7.1.6 Determine the equation of ? . (3)
7.1.7 Determine the equations of the axes of symmetry of ? . (3)
7.2 Given ?(?) = log½? .
7.2.1 Write down the equation of ?−1, the inverse of ? , in the form ? = … (2)
7.2.2 Draw a neat sketch graph of ?−1. Clearly show all intercepts with the axes and any other point on the graph. (3)
7.2.3 Write down the equation of the function ? if ? is the mirror image of ?−1 in the y-axis. (2)
7.2.4 For which value(s) of x is: ?(?). ?−1(?) < 0? (2)
[25]
QUESTION 8
The sketch below, which is not drawn to scale, shows the graph of ?(?) = ??2 + ?? + ? and a straight line ?, passing through the origin. The y-intercept of ? is (0; 4). Point A (−3; −5) is the turning point of ?.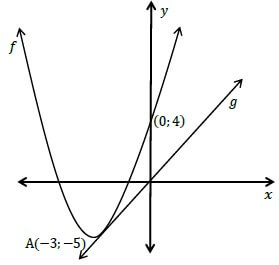
8.1 Write down the equation of the axis of symmetry of ?. (1)
8.2 Show by calculation that ? = 1 and ? = 6. (3)
8.3 Discuss the nature of the roots of ?. (3)
8.4 ? is a tangent to ? and the gradient of line ? is 2. Determine the coordinates ofthe point of contact. (4)
[11]
QUESTION 9
9.1 Given: ?(?) = 3?2 − 1
Determine ?′(?) from first principles. (5)
9.2 Determine:
9.2.1 ??/?? if ? = 5?2 + √? (3)
9.2.2 ?? [6? − 4] (3)
3?
9.3 Given ?(?) = ?3. Show that the gradient of any tangent to ? will never be negative. (2)
[13]
QUESTION 10
The sketch below shows the graph of the function ?(?) = ?3 − ?2 − 8? + 12
A is an x-intercept and B a turning point of the graph. The points C(0; 12) and D(2; 0), the other turning point, are given on the sketch.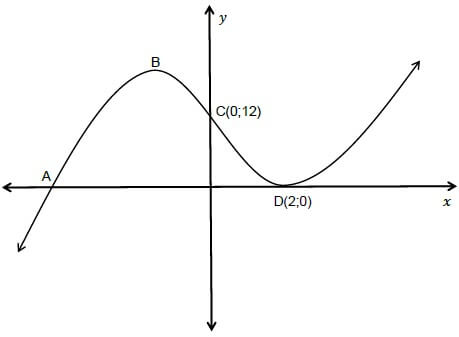
10.1 Determine the coordinates of A. (4)
10.2 Determine the coordinates of B. (5)
10.3 Calculate the x-coordinate of the point of inflection. (2)
10.4 Write down the value(s) of x for which ?′(?) > 0. (2)
10.5 How many real roots will the equation ?3 − ?2 − 8? + 12 = ? have if ? < 0? (2)
[15]
QUESTION 11
A water tank has both an inlet and an outlet which regulate the depth of water it contains. The depth D (in metres) is given by the function:
?(?) = 3 + ½ ?2 − ¼?3 where D is measured in metres and ? is measured in hours starting from 08h00.
11.1 Calculate the depth of the water at 08h00. (1)
11.2 Calculate the rate at which the depth is changing at 11h00. (3)
11.3 What happens to the depth of the water at 11h00? (1)
11.4 At what time will the inflow of water be the same as the outflow? (4)
[9]
QUESTION 12
12.1 A and B are mutually exclusive events. If it is given that the P(A) = 0,35 and P(B) = 0,52 determine:
12.1.1 P(A′) (2)
12.1.2 P(A and B) (1)
12.1.3 P(A or B) (2)
12.2 Three married couples – Mr and Mrs Brown, Mr and Mrs Green and Mr and Mrs White are to be seated on a bench.
12.2.1 How many different arrangements are possible? (1)
12.2.2 If Mr and Mrs Green must be seated in the middle, how many different arrangements are possible for the remaining persons? (2)
12.2.3 Determine the probability that Mr and Mrs Green will sit next to each other. (4)
[12]
TOTAL: 150

INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
PAPER TWO (P2)
GRADE 12
EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2016
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions:
SECTION A: Short questions (15)
SECTION B: System Technologies (24)
SECTION C: Communications and Network Technologies (26)
SECTION D: Data and Information Management (26)
SECTION E: Solution Development (22)
SECTION F: Integrated Scenario (37) - Answer ALL the questions.
- Read ALL the questions carefully.
- The mark allocation generally gives an indication of the number of facts/reasons required.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A: SHORT QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.1.1 A field that identifies each record with a unique value (1)
1.1.2 Performance of physical tasks, commonly repetitive or dangerous ones, by computer-controlled machines rather than by human beings (1)
1.1.3 A set of rules for encoding and decoding data for transmission across a network (1)
1.1.4 A device that makes it possible for networks to communicate over the Internet, by directing data to its correct destination (1)
1.1.5 A form of malware that tries to monitor and track the way you use your computer to discover confidential information,and then relay this to a third party (1)
1.1.6 Trend whereby separate technologies and functions from multiple devices are combined into a single multi-purpose device (1)
1.1.7 The ‘scrambling’ of text or data using a specified set of rules to ensures the privacy of data during communication, or for security purposes (1)
1.1.8 When the DBMS gets the instructions to reverse a transaction (or series of transactions) and restores the data back to its previous state (1)
1.1.9 A huge collection of data, often accumulated from a range of sources such as separate databases within a company (1)
1.1.10 A type of reasoning that works with probabilities in order to arrive at a decision (1)
1.2 Various options are given as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 Copyrighted software provide to a user at no cost is known as …
- shareware.
- wrap ware.
- freeware.
- adware. (1)
1.2.2 Which technique allows the processor of a computer system to run at a speed faster than the motherboard normally supports?
- Pipelining
- Cache
- Hyperthreading
- Clock multiplication (1)
1.2.3 Which one of the following software items is used for developing web pages?
- SQL
- HTTP
- HTML
- CSS (1)
1.2.4 The concept of hiding the details of an object is known as …
- abstraction.
- data mining.
- modular programming.
- encapsulation. (1)
1.2.5 A/An … directly executes, i.e. performs, instructions written in a programming or scripting language, without previously compiling them into a machine language program.
- interpreter
- computer
- compiler
- programmer (1)
TOTAL SECTION A: 15
SECTION B: SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGIES
QUESTION 2
One of your cousins is a manager at a local plant nursery, one of their computers has stopped working and after sending it for repairs he is told that the motherboard is faulty and needs to be replaced. Here are some of the specifications of the replacement motherboard.
CPU | VGA | ||
Memory | |||
Chipset | Front Side Bus | Expansion Slots | |
[Source: https://www.asus.com/za/Motherboards/P5GCMX1333/specifications/]
2.1 Explain the purpose of the motherboard, by giving THREE core functions. (3)
2.2 Refer to the System Clock and identify the highest system clock speed in the example. Answer the following questions.
2.2.1 What is the highest speed of the System Clock? (1)
2.2.2 State the relationship between System Clock and Front Side Bus. (1)
2.2.3 Which components are connected through the Front Side Bus? (2)
2.3 The CPU speed is given as being a 3.46 GHz processor, 512 MB L2 Cache and 2 MB L3 Cache.
2.3.1 Explain how the processor is able to work with the motherboard, since the motherboard speed is less than that of the processor. (2)
2.3.2 Briefly explain the purpose of cache in the processor. (1)
2.3.3 List AND explain TWO other places in the computer system where the cache is employed. (4)
2.4 You discuss with friends and one suggests that you use a tablet, and that it will do the same job, whilst the other one states that a tablets is not modular designed so it will not do the same job.
2.4.1 Are tablets modular designed? Justify your answer. (2)
2.4.2 Explain TWO advantages of modular design. (2)
2.5 One of your friends indicates that the operating system is very important for the computer system to work, and the best systems are open source.
2.5.1 State TWO functions of operating system software. (2)
2.5.2 List TWO advantage of open source software. (2)
2.5.3 List TWO disadvantage of open source software. (2)
TOTAL SECTION B: 24
SECTION C: COMMUNICATION AND NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES QUESTION 3
Computers, laptops, tablets and phones need to connect in order to share data, pictures, documents and databases amongst the three plant nursery branches, one in East London, another in Port Elizabeth and this one in Mthatha.
3.1 Advise on AND define the type of network that must be set up:
3.1.1 Between the branches (1)
3.1.2 At each branch (1)
3.2 Apart from cables, you want to know what hardware will be required to set up the network at each branch. Motivate why EACH of the following items are required by briefly explaining the function of each item in a network:
3.2.1 Network interface cards (NIC) (3)
3.2.2 Switch (2)
3.3 In order to communicate amongst each other one of the managers suggests that they must use twitter or Skype.
3.3.1 Which one of the two uses VOIP? (1)
3.3.2 Expand and explain the acronym VOIP. (2)
3.3.3 Which one of the two mediums of communication mentioned, refers to a microblog? (1)
3.3.4 Define a microblog by comparing it to a blog. (2)
3.4 While researching on a certain flower plan, you visit a website and you see the following message:
| 'This site uses cookies, by clicking and continuing browsing, it means you are in agreement …’ |
3.4.1 Explain what cookies are. (2)
3.4.2 State the main advantage of using cookies as the user. (1)
3.4.3 How can you ensure/verify that that the information found on the site is reliable? (2)
3.4.4 You also discover that the site uses digital certificates. What is the purpose of a digital certificate? (1)
3.5 Sharing files online using a popular cloud storage facility has been recommended for your team by the network administrator.
3.5.1 Provide at least TWO file sharing facilities/websites available online. (1)
3.5.2 The shared folders with information usually have different permissions, depending on the user. State AND explain TWO types of permissions that can be granted to a user of a shared folder. (4)
3.5.3 Are documents saved in these shared folders safe from viruses? Explain why. (2)
TOTAL SECTION C: 26
SECTION D: DATA AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
QUESTION 4
A database has been designed with information about the plants available in the nurseries.
4.1 The database needs to be accessible by the POS systems and other applications including the website, from all three centres but will be administered from one location.
4.1.1 Identify the appropriate type of database management system to use. (1)
4.1.2 Give an appropriate example of the database management system mentioned in QUESTION 4.1.1. (1)
4.1.3 Give TWO advantages of this type of database management system. (2)
4.1.4 Would you recommend this type of database management system for a worldwide corporation whose information changes every minute, from location to location? Substantiate your answer. (2)
4.2 Whilst discussing with the database administrator it is mentioned that the database must be data independent and data security needs to be implemented.
4.2.1 Give TWO functions of a database administrator. (2)
4.2.2 What does data independence mean? (1)
4.2.3 Give TWO advantages of data independence. (2)
4.2.4 Explain what is meant by data security. (1)
4.2.5 Suggest TWO ways of securing the data. (2)
4.3 Whilst designing the database, the following tables are proposed:
4.3.1 What does the term foreign key refers to? (1)
4.3.2 Identify the foreign key field in the Plant Details table. (1)
4.3.3 An attempt to normalise the database has been made. Explain what is meant by the term normalisation. (2)
4.3.4 Name THREE common types of anomalies associated with a poorly designed database. (3)
4.4 In order to create queries SQL is being used.
4.4.1 Write a statement to show all the information from the Plant Details table. (2)
4.4.2 Write a statement that will update the botanical name called ‘Merwilla pumbea’ to ‘Merwilla plumbea’. (3)
TOTAL SECTION D: 26
SECTION E: SOLUTION DEVELOPMENT
QUESTION 5
Programs to be used in the administrative office are being developed.
5.1 The following class diagram has been designed for the plant management program.
| Plant | |
Attributes | Methods |
-fplantID:String -fplantName:String; -fBotanicalName:String; -fPrice:Real -finStock:Boolean; | +getName:String; +getBotanicalName:String; -getStock:Real; +Constructor Create(cplantID, cplantName, cBotanicalName:String,cPrice:Real) +toString:String; |
5.1.1 Explain what the (-) and the (+) signs mean. (2)
5.1.2 Identify an accessor method in the Plant class. (1)
5.1.3 What is the purpose of the constructor method? (1)
5.1.4 Would it be possible to use the class Plant without the constructor method? Explain your answer. (2)
5.2 Analyse the following flowchart. 
5.2.1 Identify the type of loop indicated in the flowchart diagram above. (1)
5.2.2 Identify the statement(s) that are repeated. (2)
5.2.3 How many repetitions will take place? (1)
5.2.4 What is the condition for the loop to stop? (1)
5.2.5 Write the Pseudo code described by the flowchart. Display appropriate statements where needed. (6)
5.3 Arrays will be used to store and manipulate some of the data.
5.3.1 Define an array. (2)
5.3.2 Write an example of a one-dimensional constant array declaration. (3)
TOTAL SECTION E: 22
SECTION F: INTEGRATED SCENARIO
QUESTION 6
A website showcasing the company’s services and plants has been designed. Short videos, pictures and descriptions of plants including important information about the workers are all available on the site.
6.1 The website is hosted on website hosting company’s servers.
6.1.1 Name the type of software program that can be used to access the website. Give ONE example. (2)
6.1.2 Which protocol (give full name) will be used to transmit the website data when another computer on the internet requests information from the hosting company’s server? (1)
6.1.3 The monthly bandwidth allowed by the hosting company is 10 GB. Explain what is meant by the term bandwidth. (2)
6.1.4 Will it be possible for the company to host the website on their own to avoid paying the website hosting company? Substantiate your answer. (3)
6.2 The company has hired security consultants to advise them on many security aspects to help protect them from computer criminals and theft. The company plans to use e-mail, Twitter and Facebook extensively for their marketing activities online.
6.2.1 Name THREE items of personal information that should not be posted on a social networking site. (3)
6.2.2 Explain how hackers may use your e-mail to steal your personal information. (2)
6.2.3 Give ONE name used to describe this occurrence in QUESTION 6.2.2. (1)
6.2.4 One of the managers explains that he was trolled online. What is trolling? (1)
6.2.5 What measures can the manager take to avoid trolling? (1)
6.2.6 List THREE types of computer theft. (3)
6.2.7 List THREE types of computer criminals. (3)
6.3 An app has been designed by one of the programmers you hired which will enable buyers to select the plants that they may need to put in their gardens. One of the managers claims that appification has taken over the Internet.
6.3.1 What is an app? (1)
6.3.2 Suggest TWO devices that can be loaded with this app. (2)
6.3.3 What does the term appification mean? (2)
6.4 Each nursery has a Wi-Fi network to enable the managers and workers to share work.
6.4.1 What is Wi-Fi? (1)
6.4.2 One of the managers comes to you and complains that sometimes he is connected to the Wi-Fi but does not have Internet access.
Explain how this is possible. (2)
6.4.3 Which term is used to refer to the practice of intercepting data packets on a network? (1)
6.4.4 For EACH of the following technologies, state whether it is possible to protect the nursery’s data from being intercepted and used. Give a reason for your answer in EACH case.
- Firewall (2)
- Encryption (2)
- Virus Scan (2)
TOTAL SECTION F: 37
GRAND TOTAL: 150
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
PAPER TWO (P2)
GRADE 12
EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2016
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A: SHORT QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 Primary Key ✔ (1)
1.1.2 Robotics ✔ (1)
1.1.3 Protocol ✔ (1)
1.1.4 Router ✔ (1)
1.1.5 Spyware ✔ (1)
1.1.6 Convergence ✔ (1)
1.1.7 Encryption ✔ (1)
1.1.8 Rollback ✔ (1)
1.1.9 Data warehousing ✔ (1)
1.1.10 Fuzzy logic ✔ (1)
1.2
1.2.1 C ✔ freeware (1)
1.2.2 D ✔ Clock multiplication (1)
1.2.3 C ✔ HTML (1)
1.2.4 D ✔ encapsulation. (1)
1.2.5 A ✔ interpreter (1)
TOTAL SECTION A: 15
NOTE:
- Do not accept answers that use general terms: cheaper, faster
- Do not accept rephrasing of the question
- Do not accept rephrasing/duplication of the answers in a list
SECTION B: SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGIES
QUESTION 2
2.1
- Provides connectors to allow other circuits (CPU, RAM, etc.) to connect to it. ✔
- Ensures that all components of the computer can communicate with one another.✔
- Distributes power to the parts that connect to it. ✔ (3)
2.2
2.2.1 1 333 MHz ✔ (1)
2.2.2 The System clock measures the speed at which data is moved on the Front Side Bus. ✔ (1)
2.2.3 RAM✔ and CPU✔ (2)
2.3
2.3.1 Clock multiplication ✔+ definition (speed ratio between the FSB and the CPU , which allows the CPU to do more tasks as it waits for the FSB) ✔ (2)
2.3.2 High speed memory that stores frequently accessed instructions. ✔ (1)
2.3.3 Web/Internet Cache ✔ + description (temporary storage for visited web pages to reduce bandwidth usage). ✔
Hard Drive Cache ✔+ description (embedded memory on the hard drive that acts as buffer between the physical platter that stores data and the rest of the computer, keeping a record of frequently accessed data) ✔ (4)
2.4
2.4.1 No. ✔
ANY ONE of the following explanations: ✔
- No expansion slots
- Cannot change processor
- Add RAM etc. (2)
2.4.2 ANY TWO: ✔✔
- Easy to repair the computer by replacing a broken or faulty component.
- Easy to upgrade the computer by adding new parts or replacing existing ones with more powerful versions.
- Determine own system configuration by combining different components. (2)
2.5
2.5.1 Any TWO: ✔✔
- Manages hardware and software
- Manages memory space and tasks
- Provides a user interface (2)
2.5.2 Any TWO Advantages: ✔✔
- Often Free
- Can add to code
- Often available for multiple platforms. (2)
2.5.3 Any TWO Disadvantages: ✔✔
- Limited support
- Not always fully debugged
- Not always fully tested (2)
TOTAL SECTION B: 24
SECTION C: COMMUNICATION AND NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1 WAN ✔ (1)
3.1.2 LAN or WLAN ✔ (1)
3.2
3.2.1 Network Interface Cards:
Used to link the network cable to the PC – supplies the port ✔ and to convert the outgoing data to the format ✔that the cable will be able to carry ✔and vice versa to transform the incoming data into a format that the computer can work with. (3)
3.2.2 Switch: A device that connects computers in a network to a central location so that communication can occur. ✔ It directs traffic between devices connected to the network. ✔ (2)
3.3
3.3.1 Skype ✔ (1)
3.3.2 Voice Over Internet Protocol, ✔ is the protocol that allows telephone calls to be made over LAN, WAN and Internet. ✔ (2)
3.3.3 Twitter (1)
3.3.4 Microblogging is the posting of short text entries usually via a cellphone or smartphone on a platform like twitter ✔ whilst blogging is updating your website regularly with news and events like a journal. ✔ (2)
3.4
3.4.1 Cookies are small files which are stored on a user's computer. ✔ They are designed to hold a modest amount of data specific to a particular client and website, ✔and can be accessed either by the web server or the client computer. (2)
3.4.2 ∙ Not having to re-enter some of your information when you re-visit, ✔ as it remembers you. (1)
3.4.3 Any TWO ✔✔
- Must be from a reliable and well-known source (well-known author)
- Compare information from different websites
- Must be from authors who are frequently cited by other authors in the field.
Any other useful advice (2)
3.4.4 Used for security purposes to verify the authenticity of the owners of the site. ✔ (1)
3.5
3.5.1 Any TWO ✔✔
- Dropbox
- Google Docs
- Skydrive
any other valid online facility. (1)
3.5.2 Any TWO ✔✔ + Explanation ✔✔
- Read – The user is allowed to view the files only
- Write – The user can also delete, modify, and save new files.
- Execute – The user can run the directly programs from this location. (4)
3.5.3 Yes. ✔ Most of the services have strong online antiviruses installed on their servers. ✔ (2)
TOTAL SECTION C: 26
SECTION D: DATA AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
QUESTION 4
4.1
4.1.1 Server ✔ (1)
4.1.2 Any ONE ✔
- Blackfish
- Microsoft SQL Server
- MySQL
Any other valid server based DBMS (1)
4.1.3 Allows many concurrent connections ✔ / Can be accessed remotely ✔ (2)
4.1.4 No. ✔ A distributed database ✔ would be recommended so as to respond to local requirements. ✔ (2)
4.2
4.2.1 Any TWO ✔✔
- Management
- Maintenance
- Security access rights
- Backup
- Installing software
- Configuring software (2)
4.2.2 Data Independence – When the data is independent of storage media and application. ✔ (1)
4.2.3 Physical independence ✔ Logical independence ✔ (2)
4.2.4 Protection of data from unauthorised access by users. ✔ (1)
4.2.5 Any TWO ✔✔
- Passwords
- Access rights
- Data encryption (2)
4.3
4.3.1 A field that is used to link to a field in another table. ✔ (1)
4.3.2 InfoID ✔ (1)
4.3.3 The process of making a database optimal, ✔ by removing anomalies✔ like redundancy to enable easy reports. (2)
4.3.4 Update, ✔ Delete ✔ and Insert ✔ anomalies (3)
4.4
4.4.1 SELECT * ✔FROM PlantDetails ✔ (2)
4.4.2 UPDATE ✔PlantDetails SET BotanicalName= ‘Merwilla plumbea’✔
From PlantDetails WHERE BotanicalName=’Merwilla pumbea’✔ (3)
TOTAL SECTION D: 26
SECTION E: SOLUTION DEVELOPMENT
QUESTION 5
5.1
5.1.1 (-) private ✔
(+) public ✔ (2)
5.1.2 Any ONE ✔
- +getName:String;
- +getBotanicalName:String;
- +getStock (1)
5.1.3 The purpose of a constructor is to create an instance of the object/To instantiate the object. ✔ (1)
5.1.4 Yes, ✔ If a class does not contain a constructor, a default constructor will be called to instantiate the object. ✔✔ (2)
5.2
5.2.1 While Loop / Conditional Loop✔ (1)
5.2.2 Display iNumber ✔and Increase the value of iNumber by 13. ✔ (2)
5.2.3 7 ✔ (1)
5.2.4 As soon as iNumber >100✔? (1)
5.2.5
iNumber ? 13 ✔
Loop until iNumber>100 ✔
Dis? play iNumber ✔
iNu ? mber ? iNumber +13 ✔
End Loop ✔
Display Statement ✔ (6)
5.3
5.3.1 An Array is a data structure ✔ that contains elements of the same data type. ✔ (2)
5.3.2
ArrNames:Array[1..3] ✔of string✔ = (‘One’, ‘Two’,’Three’);✔ Alternative Solution:
Type
TarrNames=Array[1..3] of string = (‘One’, ‘Two’,’Three’);
Private
ArrNames:TarrNames; (3)
TOTAL SECTION E: 22
SECTION F: INTEGRATED SCENARIO
QUESTION 6
6.1
6.1.1 Web browser ✔
Any ONE ✔
- Internet Explorer
- Google Chrome
- Mozilla Firefox (2)
6.1.2 HyperText Transfer Protocol ✔ (1)
6.1.3 Bandwidth: The total volume of data that can be transmitted from one point to another during a given time. ✔✔ (2)
6.1.4 Yes. ✔ They need to setup their webserver ✔ and register their server address on the Internet. ✔ (3)
6.2
6.2.1 Any THREE ✔✔✔
- Phone numbers
- Address
- School
- E-mail address
Any other relevant answer. (3)
6.2.2 By sending e-mails purporting to be from reputable companies ✔ in order to induce individuals to reveal personal information, such as passwords and credit card numbers, online.✔ (2)
6.2.3 Phishing ✔ (1)
6.2.4 Trolling is sowing discord on the Internet by starting arguments or upsetting people, by posting inflammatory, extraneous, or off topic messages in an online community (such as a newsgroup, forum, chat room, or blog) with the deliberate intent of provoking the readers. ✔ (1)
6.2.4 Any ONE ✔
- If the person is a friend on social networks, unfriend him.
- Do not reply to their messages.
- Expose them online. (1)
6.2.5 Any THREE ✔✔✔
- Physical computer theft
- Theft of intellectual property
- Identity theft
- Money theft
- Data Theft/Espionage (3)
6.2.6 Any THREE ✔✔
- Hacker
- Cracker
- Virus Author
- Cybergang
- Spammer (3)
6.3
6.3.1 An app is a computer program designed to run on mobile devices such as smartphones and tablet computers. ✔ (1)
6.3.2 Any TWO Mobile devices ✔✔
- Cellphone
- Tablet
- iPad (2)
6.3.3 The trend for information that was previously accessed through conventional web pages and browsers, ✔ to be accessed by mobile apps on mobile devices.✔ (2)
6.4
6.4.1 Any ONE – Wi-Fi ✔
- Wireless network connectivity
- A standard that allows devices to communicate wirelessly with one another
- Wireless Fidelity (1)
6.4.2 Any suitable explanation ✔✔
- Some Wi-Fi networks are used for WLAN connectivity without Internet access.
- The business may require users to pay for Internet access. (2)
6.4.3 Any ONE ✔
- Packet-sniffing
- Eavesdropping (1)
6.4.4
- No. ✔ A firewall protect a computer from unwanted access but they do not secure outgoing data. ✔ (2)
- Yes. ✔ ∙ Any ONE ✔
- You can only decrypt the transmitted data if the encryption key is known.
- Without decrypting the data would not be useful. (2)
- No. ✔ Virus scan only scans local computers and does not affect outgoing data. ✔ (2)
TOTAL SECTION F: 37
GRAND TOTAL: 150