Adele
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY PAPER GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY PAPER
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2016
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: CONSTRUCTION PROCESSES
1.1
1.1.1 Raking shore √ (1)
1.1.2
1.1.A – Shoring planks / board / steel panel √
1.1.B – Raking shore √
1.1.C – Sole plate √ (3)
1.2 Name the following tools an name ONE use of each:
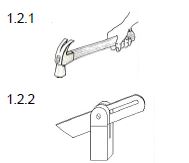
1.2.1 - Claw hammer
Any ONE use:
- Hammering in nails √√
- Claws are used to pull out nails √√ (Any 1 x 2) (2)
1.2.2 - Sliding bevel
Any ONE use:
- Marking lines at any angle √√
- Test angles √√ (Any 1 x 2) (2)
1.2.3 - Short jointer
Any ONE use:
- Finishing vertical mortar joints √√ (2)
1.2.4 - Bricklaying pins and lines
Any ONE use:
- Setting building lines √√ (2)
1.2.5 - Portable jig saw
Any ONE use:
- Cutting of curves √√
- Cutting straight cuts √√ (Any 1 x 2) (2)
1.3 (1) The turning blade can (2) cause damage / injuries to the subject it is placed on. (2)
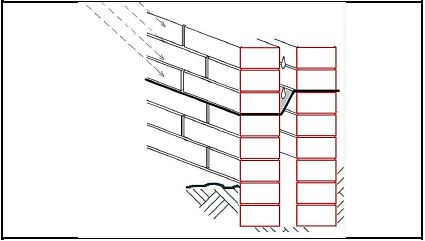
1.4 FIGURE 1.4 shows the brickwork for an outer wall.
1.4.1 Cavity wall (1)
1.4.2 Any THREE advantages of this type of wall construction.
- Prevent damp to penetrate to the inner wall. √
- Good thermal isolation √
- No rendering / plastering required for outer walls √
- Inner walls can be built with cheaper bricks √
- Good sound isolation √ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
1.4.3 (1) So that damp / water that penetrate the wall, (2) can be discharged. (2)
1.5 FIGURE 1.5 shows the uncompleted fixing of a roof truss on a wall. Answer the following questions with regard to the construction in FIGURE 1.5. 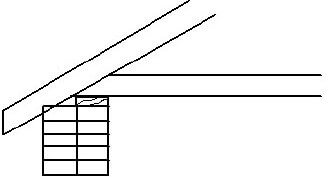
1.5.1
1.5.A – Rafter √
1.5.B – Tie beam √
1.5.C – Wall plate √ (3)
1.5.2 (1) Distribute the load (2) of the truss to the wall. (2)
1.5.4 Any similar answer:
(1) Wall plate
(2) pressure on the
(3) bending part of the tie beam.
OR
(2) Wall plate
(2) pressure on
(3) intersection / corner of rafter and tie beam.
OR 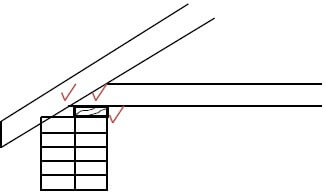 (3)
(3)
[30]
QUESTION 2: ADVANCED CONSTRUCTION PROCESSES
2.1 (1) Carry loads / brick work (2) over openings / windows / doors. (2)
2.2
- Soda √
- Silica √
- Chalk √ (3 x 1) (3)
2.3 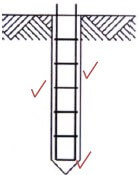 (3)
(3)
2.4 (Any similar description.)
- Soil below offers
- better stability / hardness / firmness. (2)
2.5 Any FOUR factors which will have an influence in the choice of the correct type of foundation:
- Load bearing ability of the ground √
- Depth at which load bearing ground can be found √
- Level of water table √
- Distance from trees and other structures √
- Weight of the building √ (Any 4 x 1) (4)
2.6 (1) Prevents the damp proofing (2) from being punctured by (3) the hardcore filling. (3)
2.7
2.7.1 THREE requirements to which steel reinforcement must comply.
- Resist tensile stress. √√
- Easily be bent into the required shape. √√
- The surface must bond with the concrete. √√ (3 x 1) (3)
2.7.1
- Gloves
- Overalls
- Safety shoes
- Hard hat
- Safety glasses (Any 3 x 1) (3)
2.8
2.8.1 FALSE (1)
2.8.2 FALSE (1)
2.8.3 FALSE (1)
2.8.4 FALSE (1)
2.8.5 TRUE (1)
2.8.6 TRUE (1)
2.8.7 TRUE (1)
2.8.8 TRUE (1)
2.9
2.8.1 Flat arch √ (1)
2.8.2 (Similar answer) (1) Prevents illusion (2) that the arch is bent downwards. (2)
2.8.3
2.8.A – Voussoirs √
2.8.B – Abutment √ (2)
2.9 (1) Bind different (2) steel parts together. (2)
2.10 2.10.1 300 mm √ (1) 2.10.2 600 mm √ (1)
[40]
QUESTION 3: CIVIL SERVICES
3.1
3.1.1 Water service point √ (1)
3.1.2
3.1.B – Stop cock √
3.1.C – Water meter √
3.1.D – Municipal water supply / Reticulating piping √
3.1.E – User / consumer pipe √ (4)
3.1.3 Ø20 mm √ (1)
3.1.4 Local authority / Municipality √ (1)
3.2 (1) Catch water when (2) geyser is leaking / serviced / water not damaging the ceiling. (2)
3.3 (Any similar answer.) (1) Receiving most sun rays (2) from northern side. (2) 3.4 3.4.1 Ball valve √ (1)
3.4.1 Any TWO positions
- Geyser √
- Water storage tank of water closet (toilet) √ (2 x 1) (2)
3.5
3.5.1 UNDERGROUND √ (1)
3.5.2 TWO √ (1)
3.5.3 SETTLE DOWN √ (1)
3.5.4 ANAEROBIC BACTERIA √ (1)
3.6 Test if drain pipe is clear of obstructions. √ (1)
3.7 600 mm √ (1)
3.8 Any THREE positions in a drain system where access openings must be installed.
- Drain change in direction √
- Junction with other drain pipes √
- Every 45 m in system √
- Beginning of drain √
- Drain gradient change √ (3 x 1) (3)
3.9 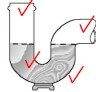 (4)
(4)
3.10 Cleaning rods √ (1)
3.11 Any TWO advantages of wind turbines for electricity supply.
- Clean fuel √
- No pollution √
- Renewable √ (2 x 1) (2)
[30]
QUESTION 4: MATERIALS AND QUANTITIES
4.1 Any THREE properties of coal tar creosote for wood preservation.
- Outdoor use √
- Use for wood that is in contact with the ground √
- Resistant to maceration √
- Dark colour √
- Discolours the timber √
- Cannot be painted √
- Does not affect the dimensions √
- Strong odour √ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
4.2
1.6.1 Natural / air seasoning √ (1)
1.6.2 (1) Ensure proper air circulation and (2) not absorb moisture from the ground. (2)
1.6.3 Any TWO requirement of the foundation for this seasoning method.
- Sturdy √
- Treated poles / Concrete / bricks √
- Even √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.3 Any FOUR advantages of PVC for the use drain pipes.
- Light in weight √
- Long lengths available √
- Less jointing √
- Tight joints √
- Handle / install easy √
- Good flow efficiency √
- Resistance to chemicals / sewer √ (Any 4 x 1) (4)
4.4 (1) Odd number of (2) layers of veneer (3) with the grain glued at right angles. (3)
4.5
4.5.1 FALSE (1)
4.5.2 FALSE (1)
4.5.3 TRUE (1)
4.5.4 FALSE (1)
4.5.5 TRUE (1)
4.6 FIGURE 4.6 shows the foundation strips for a building. The foundations are 700 mm wide and 200 mm thick and a concrete mix of 1 : 3 : 4 is used. The centre line measurement of the building is 31,6 m and the total volume concrete needed for the foundation is 4,424 m³. Determine the following quantities for the concrete mix:
4.6.1 Volume sand needed.
4,424 m³ x 3/8 = 1,659 m³ (3)√√√
4.6.2 Volume stone needed.
4,424 m³ x 4/8 = 2,212 m³ (3) √√√
4.6.3 Calculate the number bags of cement needed if the content of a bag cement is 0,033 m³.
4,424 m³ x 1/8 = 0,553m³/0,033 = 16,75 = 17 bags cement (4)√√√√
[30]
QUESTION 5: APPLIED MECHANICS
5.1 Calculate the centroid of the body in FIGURE 5.1 from point P.
X = b/3 = 3/3 = 1 √
= 3 – 1 + 1 = 3 √
Y = h/3 = 6/3 = 2 √
= 2 + 2 = 4 √(4)
5.2 FIGURE 5.2, on ANSWER SHEET A, shows the space diagram for a roof truss. Determine graphically, on ANSWER SHEET A by drawing the force diagram and completing the table, the size and nature of the forces in the parts of the truss. (18) 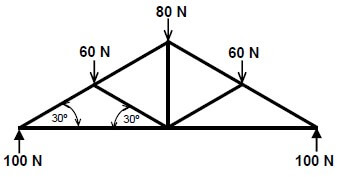
5.3 FIGURE 5.3 shows a beam with point loads. Calculate the reaction forces of the supports A and B. 
Around A Around B
M.L M.R
(B x 6)+(20 x 2) = (25 x 4)+(30 x 6) (A x 6) = (25 x 2) + (40 x 6) + (20 x 8)
B6 + 40 = 100 + 180 A6 = 50 + 240 + 160
B6 = 280 – 40 A6 = 450
B = 240/6 A = 450/6
= 40 N = 75 N (8)
[30]
QUESTION 6: GRAPHICS AND COMMUNICATION
6.1 FIGURE 6.1 on ANSWER SHEET B shows the outer lines of a structure which must be built on a site. Draw the site plan on scale 1 : 200 on ANSWER SHEET B so that the structure is in the middle of the site. The site plan must comply too the following requirements:
6.1.1 Site size is (1) 20 m wide from east to west and (2) 30 m long from south to north (2)
6.1.2 Pavement of (1) 2 m and the street of (2) 6 m at the (3) south side (4)
6.1.3 Building boundaries are (1) 2 m at the (2) east, north and west sides and (3) 4 m at the south side (4)
6.1.4 (1) 3 m Wide entrance to (2) the site (2)
6.1.5 (1) Datum level in the (2) north-western corner of the site (2)
Draw also the roof plan on the structure and indicate the following:
6.1.6 Overhang of 400 mm (2)
6.1.7 Hipped end at the north end (2)
6.1.8 American cable end at the south end (3)
6.1.9 Ridge (1)
Indicate the following measurements:
6.1.10 Length and width of the site (4)
6.1.11 Southern and western building boundaries (2)
6.2 Sketches to illustrate the following symbols on a floor plan:
6.2.1 Water meter (2)
6.2.2 Vent pipe ![]() (2)
(2)
6.2.3 Bath (2)
6.2.4 Water closet (2)
6.2.5 Sink (2)
6.2.6 Power point (2)
[40]
TOTAL: 200
ANSWER SHEETA | CIVIL TECHNOLOGY | NAME: |
QUESTION 5.2 (18) 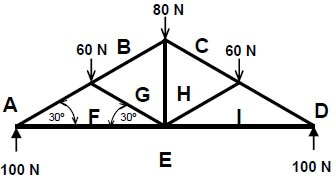
SPACE DIAGRAM:
SCALE: 2 mm = 1 N
| PART | STRUT ↔ | TIE |
| AF | 100N | |
| BG | 70N | |
| CH | 70N | |
| DI | 100N | |
| EI | 85N | |
| EF | 85N | |
| FG | 30N | |
| GH | 30N | |
| HI | 30N |
ANSWER SHEETB | CIVIL TECHNOLOGY | NAME: |
QUESTION 6.1 (28)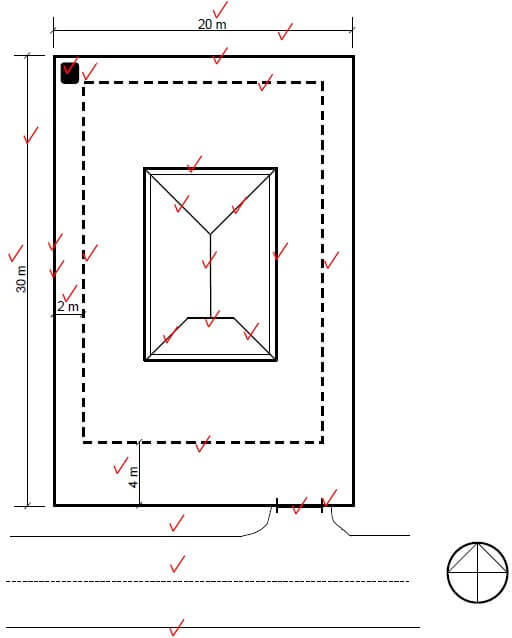
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY PAPER GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY PAPER
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2016
QUESTIONS
REQUIREMENTS:
- ANSWER BOOK
- Drawing instruments
- A non-programmable calculator
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions.
- ALL questions are COMPULSORY.
- . Answer each question as a whole. Do NOT separate sub-questions
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Sketches may be used to illustrate your answers.
- ALL calculations and written answers must be done in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Use the mark allocation as a guide for the length of your answer.
- Drawings and sketches must be fully-dimensioned and neatly finished off with titles and labels to conform to SANS (SABS) Recommended Practice for Building Drawings.
- For the purpose of this examination, the size of a brick should be taken as 220 mm x 110 mm x 75 mm.
- Use your discretion where dimensions and/or details have been omitted.
- Answer QUESTION 5.2 and QUESTION 6.1 on the ANSWER SHEETS that is provided.
QUESTION 1: CONSTRUCTION PROCESSES
1.1 FIGURE 1.1 shows a shoring that must support the ground in an excavation. Answer the following questions with regard to the shoring in FIGURE 1.1. 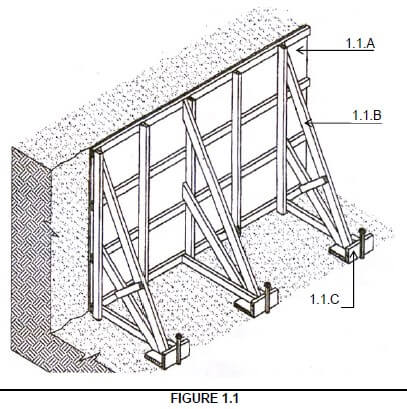
1.1.1 What is this type of shoring called? (1)
1.1.2 Name the parts 1.1.A to 1.1.C. (3)
1.2 Name the following tools and name ONE use of each: 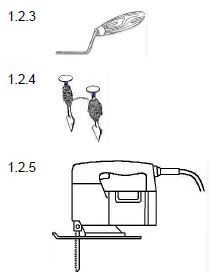
1.3 Briefly motivate why the blade of the portable power saw must come to a standstill, before it is put down. (2)
1.4 FIGURE 1.4 shows the brickwork for an outer wall. Answer the following questions with regard to the brickwork in FIGURE 1.4.
FIGURE 1.4
1.4.1 What is this type of wall construction called? (1)
1.4.2 Name THREE advantages of this type of wall construction. (3 x 1) (3)
1.4.3 Briefly motivate why each third vertical mortar joint above the damp-proof layer must be left open. (2)
1.5 FIGURE 1.5 shows the uncompleted fixing of a roof truss on a wall.
Answer the following questions with regard to the construction in FIGURE 1.5. 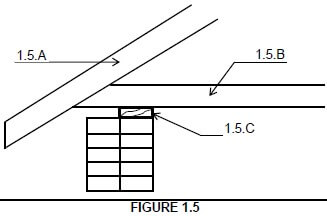
1.5.1 Name the parts 1.5.A to 1.5.C. (3)
1.5.2 Briefly describe the purpose of part 1.5.C. (2)
1.5.4 Identify the wrong installing process of the roof truss in FIGURE 1.5 and describe how the correct installing should be done.
Sketches can be used to illustrate the correct installing. (3)
[30]
QUESTION 2: ADVANCED CONSTRUCTION PROCESSES
2.1 Briefly describe the purpose of a lintel. (2)
2.2 Name the THREE main components used in the manufacturing of glass. (3 x 1) (3)
2.3 Make a neat sketch to illustrate the construction of a pile foundation. (3)
2.4 Briefly motivate why foundations must be cast below the ground surface. (2)
2.5 Name FOUR factors that will have an influence in the choice of the correct type of foundation. (4 x 1) (4)
2.6 Briefly describe the purpose of the wearing course under a concrete floor. (3)
2.7
2.7.1 Describe THREE requirements with which steel reinforcement for concrete must comply. (3 x 1) (3)
2.7.2 Name THREE types of safety wear you would buy for workers working with steel reinforcements. (3 x 1) (3)
2.8 Indicate whether the following statements with regard to formwork construction are TRUE or FALSE. Write only the word ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the number in the ANSWER BOOK.
2.8.1 The moisture content of the boards must be at least 30%. (1)
2.8.2 Joints must be left open to allow shrinking and expansion of the boards. (1)
2.8.3 G-clamps are used to keep together the formwork boards for large construction. (1)
2.8.4 The purpose of the yoke is to seal the formwork. (1)
2.8.5 Laminated formwork boards give a better finish to concrete. (1)
2.8.6 Mould oil is applied to the formwork boards to prevent the concrete from binding with the formwork. (1)
2.8.7 Old and new formwork material must not be used together. (1)
2.8.8 The spacing of the clamps and yokes is also determined by the type of concrete mix. (1)
2.9 Answer the following questions with regard to the arch construction in FIGURE 2.9. 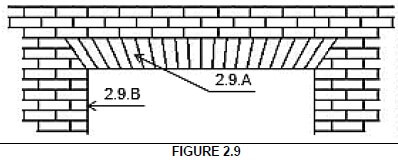
2.9.1 What is this type of arch called? (1)
2.9.2 Briefly motivate why the middle of the arch is made slightly higher. (2)
2.9.3 Name parts 2.9.A and 2.9.B. (2)
2.10 Briefly describe the purpose of the gusset plates in steel frame structures. (2)
2.11 What are the standard depths of the following kitchen cupboard parts?
2.11.1 Wall unit (1)
2.11.2 Floor unit (1)
[40]
QUESTION 3: CIVIL SERVICES
3.1 FIGURE 3.1 shows the municipal water supply to a site. Answer the following questions with regard to the system. 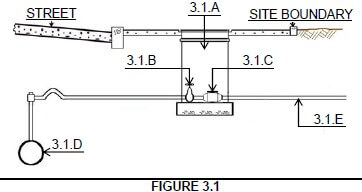
3.1.1 What is the structure 3.1.A called? (1)
3.1.2 Name parts 3.1.B to 3.1.E. (4)
3.1.3 What is the section size of part 3.1.E? (1)
3.1.4 Who is responsible for the system from point 3.1.D to 3.1.A? (1)
3.2 Briefly motivate why a drip tray must be installed underneath a geyser. (2)
3.3 Briefly motivate why the sun collectors in the southern hemisphere must be installed at true north. (2)
3.4 Answer the following questions with regard to the valve in FIGURE 3.4. 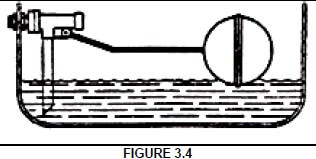
3.4.1 What is the valve in FIGURE 3.4 called? (1)
3.4.2 Name TWO positions in a house water supply system where this valve must be installed. (2 x 1) (2)
3.5 Identify the correct answer in each of the following descriptions of a septic tank. Write only the correct answer next to the question number in the ANSWER BOOK.
3.5.1 It is an impermeable UNDERGROUND / ABOVE-GROUND structure. (1)
3.5.2 It consist of TWO / FOUR rooms. (1)
3.5.3 The heavier parts of the inflow water FLOAT / SETTLE DOWN. (1)
3.5.4 The organic matter is decomposed by the action of CHEMICAL PROCESSES / ANAEROBIC BACTERIA action. (1)
3.6 What is the purpose of the ball test for drains? (1)
3.7 What is the minimum depth of drains underneath ground surface? (1)
3.8 Name THREE positions in a drain system where access openings must be installed. (3 x 1) (3)
3.9 Make a neat sketch to illustrate a P-type drain trap. Also indicate the water level inside the trap. (4)
3.10 Which tool is used to clear blocked drains? (1)
3.11 Name TWO advantages of wind turbines for supplying electricity. (2 x 1) (2)
[30]
QUESTION 4: MATERIALS AND QUANTITIES
4.1 Name THREE properties of coal tar creosote for wood preservation. (3 x 1) (3)
4.2 Wood must be seasoned to decrease the moisture content of it. Answer the following questions with regard to the seasoning method illustrated in FIGURE 4.2. 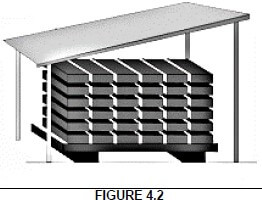
4.2.1 What is this seasoning method called? (1)
4.2.2 Briefly motivate why the bottom timber must be approximately 600 mm above ground. (2)
4.2.3 Name TWO requirements of the foundation for this seasoning method. (2)
4.3 Name FOUR advantages of using PVC as drain pipes. (4 x 1) (4)
4.4 Briefly describe what plywood is. (3)
4.5 Indicate whether the following statements with regard to materials are TRUE or FALSE. Write only ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the number in the ANSWER BOOK.
4.5.1 Fibre board is used in the manufacturing of table tops. (1)
4.5.2 The cube test is used to test the compressive stress of wood. (1)
4.5.3 A cornice is installed between the ceiling and the wall. (1)
4.5.4 The compacting of concrete is done 28 days after it has been cast. (1)
4.5.5 Aluminium is a light metal. (1)
4.6 FIGURE 4.6 shows the foundation strips for a building. The foundations are 700 mm wide and 200 mm thick and a concrete mix of 1 : 3 : 4 is used. The centre line measurement of the building is 31,6 m and the total volume concrete needed for the foundation is 4,424 m³.
Determine the following quantities for the concrete mix: 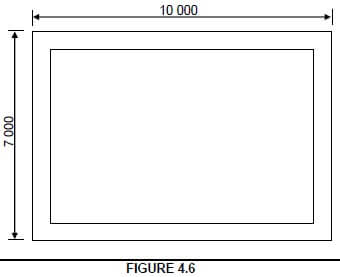
4.6.1 Calculate the volume of sand needed (3) 4.6.2 Calculate the volume of stone needed (3)
4.6.3 Calculate the number of bags of cement needed, if the content of a bag of cement is 0,033 m³ (4)
[30]
QUESTION 5: APPLIED MECHANICS
5.1 Calculate the centroid of the body in FIGURE 5.1 from point P. (4)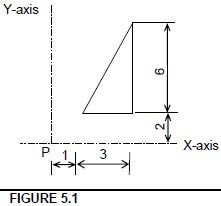
5.2 FIGURE 5.2, on ANSWER SHEET A, shows the space diagram for a roof truss. Determine graphically, on ANSWER SHEET A by drawing the force diagram and completing the table, the size and nature of the forces in the parts of the truss. (18) 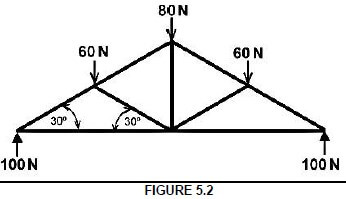
5.3 FIGURE 5.3 shows a beam with point loads. Calculate the reaction forces of the supports A and B. (8)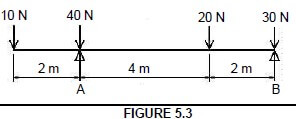
[30]
QUESTION 6: GRAPHICS AND COMMUNICATION
6.1 FIGURE 6.1 on ANSWER SHEET B shows the outer lines of a structure which must be built on a site. Draw the site plan on scale 1 : 200 on ANSWER SHEET B so that the structure is in the middle of the site. The site plan must comply with the following requirements:
6.1.1 Site size is 20 m wide from east to west and 30 m long from south to north (2)
6.1.2 Pavement of 2 m and the street of 6 m on the south side (4)
6.1.3 Building boundaries are 2 m on the east, north and west sides and 4 m on the south side (4)
6.1.4 3 m wide entrance to the site (2)
6.1.5 Datum level in the north-west corner of the site (2) Also draw the roof plan on the structure and indicate the following:
6.1.6 Overhang of 400 mm (2)
6.1.7 Hipped end at the north end (2)
6.1.8 American cable-end at the south end (3)
6.1.9 Ridge (1) Indicate the following measurements:
6.1.10 Length and width of the site (4)
6.1.11 South and west building boundaries (2)
6.2 Make neat sketches to illustrate the following symbols on a floor plan:
6.2.1 Water meter (2)
6.2.2 Vent pipe (2)
6.2.3 Bath (2)
6.2.4 Water closet (2)
6.2.5 Sink (2)
6.2.6 Power point (2)
[40]
TOTAL: 200
ANSWER SHEET A | CIVIL TECHNOLOGY | NAME: |
QUESTION 5.2 (18)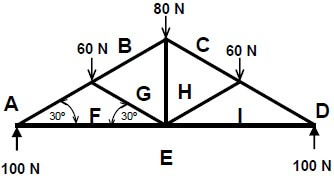
SPACE DIAGRAM:
SCALE: 2 mm = 1 N
| PART | STRUT ↔ | TIE
|
| AF | ||
| BG | ||
| CH | ||
| DI | ||
| EI | ||
| EF | ||
| FG | ||
| GH | ||
| HI |
ANSWER SHEET B | CIVIL TECHNOLOGY | NAME: |
QUESTION 6.1 (28)
|
FORMULA SHEET
IMPORTANT ABBREVIATIONS
SYMBOL | DESCRIPTION | SYMBOL | DESCRIPTION | SYMBOL | DESCRIPTION |
G | Centre of gravity | h | Height | d | Diameter |
C | Centroid | b | Breadth/Width | r | Radius |
L | Length | s | Side | A | Area |
| π | Pi = 22/7 = 3,142 | ∅ | Diameter | V | Volume |
FORMULAE
AREA OF | FORMULA (in words) | FORMULA (in symbols) | FORMULA FOR THE POSITION OF CENTROIDS | |
X-axis | Y-axis | |||
Square | Length x Breadth | l x b | b/2 | b/2 |
Rectangle | Length x Breadth | l x b | I/2 | b/2 |
Right-angled triangle | ½ x base x height | ½b x h | b/3 | h/3 |
Equilateral triangle/Pyramid | ½ x base x height | ½b x h | b/2 | h/3 |
Circle | π x radius x radius | πr2 | Centroid is in the centre | |
Circle | π x diameter x diameter divided by 4 | πd2 | ||
Semi-circle | π x radius r x radius divided by 2 | πr2 | Centroid is 0,424r on the centre line | |
Position of centroid = (A1 × d) ± (A2 × d)
Total area
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER 1 (P1)
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2016
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 C √√
1.1.2 B √√
1.1.3 A √√
1.1.4 A √√
1.1.5 D √√
1.1.6 A √√
1.1.7 C √√
1.1.8 B √√
1.1.9 A √√
1.1.10 D √√ (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 None √√
1.2.2 B only √√
1.2.3 A only √√
1.2.4 B only √√
1.2.5 Both A and B √√ (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 Pancreas √√
1.3.2 Stock density √√
1.3.3 Virus √√
1.3.4 Impotence √√
1.3.5 Concentration √√ (5 x 2) (10)
1.4
1.4.1 Urea √
1.4.2 Conduction √
1.4.3 Mesoderm √
1.4.4 Posture √
1.4.5 Bulbo-urethral/Cowpers gland √ (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: ANIMAL NUTRITION
2.1
2.1.1 Non-ruminant/monogastric √ (1)
2.1.2 Single/Simple stomach/Monogastric √ (1)
2.2
2.2.1 C √ (1)
2.2.2 D √ (1)
2.2.3 F √ (1)
2.2.4 I √ (1)
2.2.5 E √ (1)
2.3
2.3.1 It is highly soluble than biuret. √ (1)
2.3.2 Avoid keeping the lick in rain. √ (1)
2.3.3 ∙ A mixture of 2 kg urea and 20 kg molasses be sprayed on grazing √ ∙ Use of premixed fodders/mixtures/stock licks √ (2)
2.4
2.4.1
- Only abomasum is functioning √
- Rumen/reticulum/omasum still underdeveloped √
- Oesophogal groove transport milk to the abomasum √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.4.2 When the calf starts eating solid food/starts grazing √ (1)
2.4.3
- Enable to digest cellulose √
- Hydrolyse protein √
- Synthesis of vitamins √
- Synthesis of amino acids √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.5
2.5.1 DE of 5 kg DM intake = Gross Energy – energy lost in faeces
= 92,5 J – 42,5 J√
= 50 J √ (2)
2.5.2 Nett energy = Metabolic energy – Energy lost as heat
Metabolic energy = 50 J – 18,5 J = 31,5 J √
Nett energy = Metabolic energy – Energy lost as heat
= 31,5 J – 9 J √
= 22,5 J √
NB: Learners may use different ways/formula to arrive at 22,5 J, e.g. OR NE = DE – energy lost in urine + gases – heat loss |
(3)
2.6
Percentage of feed mixture
Ratio of Maize meal : peanut oilcake meal = 22 : 7,5
22 + 7,5 = 29,5 √
% of peanut oilcake meal = (7,5 / 29, 5) × 100 √
= 25, 42% √ (3)
2.7
2.7.1
Concentrate requirement = kg/day
= 42 kg/cow/day √
= 42 kg × 30 days × 100 cows √
= 126 000 kg (126 tons) √ (3)
2.7.2
Feed supply = 650 kg × 30 × 6 = 117 000 kg √
Feed required = 100 × 60 kg × 30 = 180 000 kg p/month × 6
= 1 080 000 kg √
= Feed supply – Feed required
= 117 000 kg –1 080 000 kg
= -963 000/1 000 √
= -963 tons √ (4)
2.7.3 Not enough √ - pasture has a shortage of 963 tons √ (2)
2.8
2.8.1 Tranquillisers √ (1)
2.8.2 Antibiotics √ (1)
[35]
QUESTION 3: ANIMAL PRODUCTION, PROTECTION AND CONTROL
3.1
3.1.1
A Feeding shed √
B Holding pen √ (2)
3.1.2
(a) Holding pen / B √ (1)
(b) Feeding shed / A √ (1)
3.1.3
- Give cows time to pick up their calves before moving √
- Cows and calved should be moved slowly √
- Avoid trying to work cows and calves with dogs √ (3)
3.2
3.2.1 To warn animals of your presence √ (1)
3.2.2 Makes them feel insecure √ (1)
3.2.3 Allow animals to establish social groups √ (1)
3.3
3.3.1 D √ (1)
3.3.2 C √ (1)
3.3.3 A √ (1)
3.3.4 B √ (1)
3.4
Subsistence | Commercial | |
| 3.4.1 Purpose (2) | Produce only enough to feed the family √ | Produce to sell for a profit √ |
| 3.4.2 Management (2) | Limited as only few animals and crops produced √ | Intensive to ensure increased production √ |
3.5
3.5.1
A Chronic √
B Very sudden/develops within an hour/weeks √
C Acute √
D Deadly √ (4)
3.5.2 Anthrax √ (1)
3.5.3
- Burn the carcass √
- Do not cut open the animal carcass √
- Burry carcass deep in the ground √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.6
3.6.1 Nasal worm √ (1)
3.6.2
(a) C √ (1)
(b) A/B √ (1)
3.6.3 Summer √ (1)
3.6.4
- Sneezing and nasal irritation √
- Yellow nasal discharge √
- Shaking of head to get rid of the parasite √ (3)
3.7
3.7.1 Proper hygiene standards in abattoirs √ (1)
3.7.2 Quarantine of imported animals at ports of entry √ (1)
3.7.3
- Reporting any suspicion of the disease √
- Eradication programs √
- Immunisation campaigns √ (Any 1) (1)
[35]
QUESTION 4: ANIMAL REPRODUCTION
4.1
4.1.1 Embryo transfer √ (1)
4.1.2
- Prostglandin injection √
- Gonadotropin - release hormone √ (2)
4.1.3 A Donor √ (1)
4.1.4 37 °C √ (1)
4.1.5
(a) Their reproductive cycle is extended to produce more progeny √ (1)
(b) More profit from selling superior animals √ (1)
4.2
4.2.1
A Oestrus √
B Di-oestrus √
C Met-oestrus √
D Pro-oestrus √ (4)
4.2.2
(a) A √ (1)
(b) C √ (1)
4.3
4.3.1
B vas deference √
D scrotum√
F seminal vesicle √ (3)
4.3.2
- Hypoplasia √
- Cryptochidism √
- Sperm defects √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.4
4.4.1 Exhaustion/Fatigue √ (1)
4.4.2 Malnutrition √ (1)
4.4.3 Lack of experience √ (1)
4.4.4 Temperament √ (1)
4.5
4.5.1 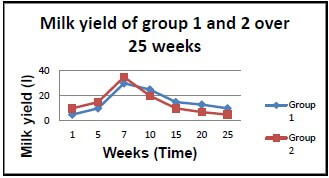
Marking graph with the following checklist:
Criteria | Yes: 1 mark | No: 0 mark |
1 Line graph | 1 | 0 |
2 Y-axis labelled | 1 | 0 |
3 X-axis labelled | 1 | 0 |
4 Points correctly labelled in group 1 and group 2 | 1 | 0 |
5 Correct heading | 1 | 0 |
6 Units (and time) | 1 | 0 |
(6)
4.5.2 Milk yield increases drastically in week 7 and drops from week 15 to week 20. √
OR
For both groups milk yield increases from week 1 to week 7 and then it decreases after week 7 until week 25. (1)
4.6
4.6.1 C √ allantois √ (2)
4.6.2 F √ placenta √ (2)
4.6.3 B √ chorion/embryonic sac √ (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER 2 (P2)
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2016
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1. 1 QUESTION 1.2
1.1.1 C √√ 1.2.1 D √√
1.1.2 A √√ 1.2.2 H √√
1.1.3 B √√ 1.2.3 A √√
1.1.4 D √√ 1.2.4 J √√
1.1.5 B √√ 1.2.5 G √√ (5 x 2) (10)
1.1.6 A √√
1.1.7 C √√
1.1.8 A √√
1.1.9 D √√
1.1.10 B √√ (10 x 2) (20)
QUESTION 1.3 QUESTION 1.4
1.3.1 Gene gun/Biolistics √√ 1.4.1 Genes √
1.3.2 Grant √√ 1.4.2 shortage/under production √
1.3.3 Liabilities √√ 1.4.3 Land/natural resources √
1.3.4 Seasonal worker √√ 1.4.4 marketing mix √
1.3.5 Species crossing √√ 1.4.5 Threats √
(5 x 2) (10) (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
2.1
2.1.1 Description marked XX
Surplus √ (1)
2.1.2 Explanation to QUESTION 2.1.1.
- The quantity supplied exceeds/is more than √ the quantity demanded. √
- The quantity demanded is lower/less than √ the quantity supplied.
- There is over supply of the product. √√ (Any 1 x 2) (2)
2.1.3 Identification of letter K and lines MM and BB
K = equilibrium price √
MM = Supply curve √
BB = Demand curve √ (3)
2.2
2.2.1 Difference between marketing and selling.
Marketing | Selling |
Emphasis is on customers’ wants √ | Emphasis is on the agricultural product √ |
The business determines customers’ wants and how to produce and deliver a product to satisfy those wants. √ | The business produces a product, and then decides how to sell it. √ |
Management is profit oriented. √ | Management is sales-volume oriented. √ |
Planning is long term, based on new products, tomorrows’ markets and future growth. √ | Planning is short-term, based on current products and market. √ |
Focuses on the wants of buyers. √ | Focus on the needs of sellers. √ |
(Any 2 x 1) | (Any 2 x 1) (4) |
2.2.2 Functions of agricultural marketing
- Transport √
- Storage √
- Packaging √
- Processing √
- Standardisation √
- Grading √
- Financing √
- Risk bearing √
- Market intelligence √
- Product design and promotion √
- Customer support √
OR
- Exchange functions √
- Physical functions √
- Facilitating functions √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.2.3 How eco-labelling influences consumers
- Eco-labels certify that the product was produced in an environmentally friendly way. √
- They enable consumers to compare green shops. √
- It shows consumers how resources were used and managed during the production of the product. √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.2.4 Reasons for processing meat
- It reduces wastage/decomposition √
- It provides job opportunities. √
- It increases the value of the meat √
- It is a way of overcoming over-supply of the product √
- It allows for easier packing and handling. √
- The products have a longer shelf life. √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.3
2.3.1 Definition of marketing chain
- The flow of products from production point (farm) √ to consumption point (consumer). √ (2)
2.3.2 Post-harvest management of the marketing chain
- Collection √
- Selection/grading/standardisation √
- Packaging √
- Transformation √
- Added value √
- Transport √
- Sale of product √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.3.3 Classification
(a) Value adding – supply chain √ (1)
(b) Packaging – supply chain √ (1)
(c) Cash flow and profitability – demand chain √ (1)
2.4
2.4.1 Explanation of co-operative society
Group(s) of farmers/people who unite voluntarily √ to meet their mutual needs, whether economic or social. √ (2)
2.4.2 Benefits of agricultural cooperative
- They have more bargaining power. √
- Potential for growth. √
- Economies of scale through pooling resources. √
- They have access to better infrastructure. √
- They have access to professional expertise. √
- Middleman is eliminated. √
- They make bulk purchases. √
- They have access to funding. √
- They develop branding for themselves √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.5
2.5.1 Characteristics of a buyer who is a traditionalist
- Will not buy new products and will try to convince other consumers not to either. √
- Will only buy products that they know and that are generally accepted as the preferred choice. √
- They make up only a small part of consumers. √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.5.2 Ways sellers could make profit from the scenario
- By promoting what they sell √
- By adopting different approaches to market their goods. √ (2)
2.5.3 Ways to promote sales
- Advertise through newspapers, television, radio, magazines etc. √
- In-store promotion √
- Direct mailing through mobile phones, posts. √
- Trade fairs and exhibitions. √
- Personal selling √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.6 Difference between niche marketing and stock sales
Niche marketing – The focus is on selling to a small segment of the market that is not served by mainstream produce suppliers. √
Stock sales – Livestock are sold on auction at a sale yard to the highest bidder. √ (2)
[35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
3.1
3.1.1 Very scarce farm labourer
- Tractor operator/the skilled labourer/A √ (1)
3.1.2 Reasons to QUESTION 3.1.1
- A skilled labourer √
- He/she requires specialised training √
- He/he offers special service √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.1.3 Methods to improve economic conditions for worker
- Provide incentives for workers √
- Paying higher salaries √
- Pay bonuses √
- Entering into partnership deals with workers √
- Providing medical insurance √
- Supplying farm products such as oranges or milk to workers at reduced prices. √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.1.4 Laws that could apply
- Occupational Health and Safety Act √ (1)
- Unemployment Insurance Fund (UIF) Act √ (1)
3.2
3.2.1 Calculations
Total amount invested
R15 000,00 + R28 000,00 + R20 000,00 √ = R63 000,00 √
Gross income R73 000,00
Profit/loss R73 000,00 – R63 000,00 = R10 000,00 √ profit √ (3)
3.2.2 Methods used to raise the capital
- Borrowed money from the bank
- Borrowed money from a friend
- Sold chickens (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.2.3 Methods the manager could use to create capital
- ∙Own savings √ (2)
3.2.4 Document that shows expected income and expenditure
- Budget √ (1)
3.3
3.3.1 Characteristic of land in photograph
- Agricultural land is limited. √ (1)
3.3.2 Justification
- The land/mountainous land is not suitable for commercial farming. √
- Agricultural land with high production potential is limited. √
- Agricultural land varies in production potential √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.3.3 Functions of land as a factor of production in agriculture
- It provides space for agricultural activities √
- It is a source of minerals √
- It provides food for plants and animals √
- It is an asset that can be used as a collateral √
- It is a source of raw materials √ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
3.3.4 Scientific way to improve productivity of land
- Improving soil fertility/application of fertilisers √
- Improving water management/irrigation √
- Changing cropping practices and farming systems √
- Restoring land potential/soil reclamation √
- Farming land more efficiently/consolidating small fields √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.4
3.4.1 Why managing a poultry farm is different from managing a shop.
- The kind and daily duties involved when managing a poultry farm. √
- The management of layers involved in farming √
- Specific skills needed for different farming operations √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.4.2 Specific management skills
- Financial management √
- Labour management √
- Crises management √ (3)
3.4.3 Production risks in crop production
- Weather hazards/drought/hail/storm √
- Pests/rodents √
- Fire √
- Equipment breakdown √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.5 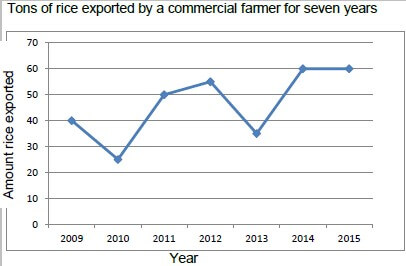
Criteria for marking
- Correct heading/title √
- Correct labelling of X-axis and Y-axis √
- Correct scaling, using ruler √
- Line graph √
- Correct plotting on line graph √ (5)
[35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
4.1
4.1.1 Calculation of EBV (Estimated Breeding Value)
Average weaning weight of the animals = 22,5 kg
Weaning weight of male animal = 24,6 kg
Weaning weight of female animal = 23,7
EBV of male = 24,6 kg − 22,5 kg √ = +2,1 kg √
EBV of female = 23,7 kg − 22,5 kg √ = +1,2 kg √ (4)
4.1.2 Expected genetic gain
(EBV of male + EBV of female) ÷ 2 x 50%
(2,1 kg + 1,2 kg) ÷ 2 x 50% √
3,3 ÷ 2 x 0,5
= 0,81 kg √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.2
4.2.1 Punnet square √
♂ ♀ | Q | Q √ |
q√ | ||
q | Qq √ |
(4)
4.2.2 Percentage of white-faced bull in F2 generation
F2 generation
White (QQ) will be 3
Black (qq)will be 1
Percentage of white (QQ) = ¾ x 100 √ = 75% √√ (3)
4.2.3 Appropriate genetic term
- Variation (1)
4.2.4 Difference between phenotype and genotype
Phenotype:
- The visible or observable characteristics of an individual. √
Genotype:
- The genetic composition of an individual. √ (2)
4.3
4.3.1 Chromosomes of the zygote
- 58 √ + XX chromosomes √ (2)
4.3.2 Gender of offspring in QUESTION 4.3.1
- Female (1)
4.4 Definitions of terms
- Mutation – a sudden random change √ in the genetic composition/ material (DNA) cell. √ (2)
- Out crossing – crossing of a line-bred breed √ with an unrelated breed. √ (2)
4.5
4.5.1 Aims of genetic modification in plants
- Indirectly improving crop yield by making it easier to manage pests, diseases and weeds that can interbreed. √
- Directly improving crop yield by improving tolerance to extreme environmental conditions. √
- Improving commercial properties, such as flavour and shelf life. √
- Increasing the nutritional value of crops (biofortification). √
- Producing pharmaceutical crops that produce proteins, drugs and vaccines for humans. √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.5.2 Advantages of GMO over traditional methods
- GMO is faster √
- It is precise √
- It is not limited to crossing species √
- Genes from a micro-organism can be transferred to the DNA of a plant and the other way round. √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.5.3 Disadvantages of inbreeding
- Expert knowledge needed as it can be a complicated method √
- No certainty that a superior inbred line with outstanding traits will be produced. √
- Bad characteristics may become so fixed that they cannot be bred out. √
- Reduced vigour and production √
- Deformed animals occur more frequently √
- Inbreeding depression may occur √
- Leads to decrease in variation √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.5.4 Pedigree selection
It is a selection based on the records of an individual’s ancestors on both the mother’s and father’s side. √√
Progeny selection
Selection of individuals based on the records of their offspring. √√ (2 + 2) (4)
4.6 Environmental causes of variation in plants
- Soil factors √
- Sunlight √
- Water √
- Temperature √
- Pest and diseases √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
Agricultural Sciences
Paper 2 (P2)
Grade 12
Nsc Past Papers And Memos
September 2016
QUESTIONS
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
1. This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
2. Answer ALL questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
3. Start EACH question on a NEW page.
4. Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
5. You may use a non-programmable calculator.
6. Show ALL your calculations, including formulae, where applicable. 7. Write neatly and legibly.
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 A breeder mated a good sire on a farm with a female of inferior quality to improve the quality of a poor herd. The breeding system used by the breeder is …
A species crossing.
B in-breeding.
C upgrading.
D out-crossing.
1.1.2 ... refers to a lack of response to price change. For example bread will be in demand even if the price rises.
A Price inelasticity
B Price elasticity
C Elasticity of supply
D Elasticity
1.1.3 To establish a successful business venture, you need to have the following:
(i) Commitment
(ii) Management skills
(iii) leadership
(iv) Academic degree
Choose the correct combination:
A (ii), (iii) and (iv)
B (i), (ii) and (iii)
C (i), (ii) and (iv)
D (i), (iii) and (iv)
1.1.4 One of the following descriptions constitutes a SWOT analysis of developing a business strategy:
A Strengths, wealth, opportunities and time
B Seriousness, weakness, opportunities and threats
C Strengths, weakness, opportunities and trust
D Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats
1.1.5 By the way of minimising or spreading risk, Grade 12 learners kept sheep, chicken and sheep and also cultivated vegetables on one farm. This is an example of …
A niche marketing.
B diversification.
C co-operative marketing.
D specialisation.
1.1.6 The type of credit required to purchase the illustration below is ... credit.
A medium term
B long term
C short term
D minimum term
1.1.7 The legislation which labour unions apply to fight against inappropriate working hours, leave, over time and how wages must be paid in the workplace.
A Employment Equity Act
B Labour Relations Act
C Basic Conditions of Employment Act
D Skills Development Act
1.1.8 The illustration below indicates one of the processes in which chromosomes may change. 
A Inversion
B Duplication
C Translocation
D Deletion
1.1.9 One of the following is NOT a reason for drawing up a business plan:
A Attracting investors or finding potential partners
B Obtaining financing
C Mapping out the direction of your business
D Employing a good entrepreneur
1.1.10 A … refers to a plant or grouping of plants selected for desirable characteristics.
A hybrid
B cultivar
C mutagen
D breed (10 x 2)
(20)
1.2 Choose a term/phrase from COLUMN B that matches a term in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–J) next to the question number (1.2.1−1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 K.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
| 1.2.1 Contract A two equivalent genes 1.2.2 Business plan B DNA 1.2.3 Alleles C budget | A two equivalent genes B DNA |
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Write the agricultural term/phrase for each of the following descriptions next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 An apparatus that fires bullets into a piece of plant tissue
1.3.2 A sum of money provided for a specific purpose by a government that does not have to be repaid
1.3.3 Financial obligations such as the debts and loans that a company owes
1.3.4 Workers who are employed during peak periods, often for a specific task such as harvesting
1.3.5 The breeding system in which the offspring is always sterile or cannot reproduce (5 x 2) (10)
1.4 Change the UNDERLINED WORD/S in the following statements to make them TRUE. Write only the appropriate word(s) next to the question number (1.4.1–1.4.5) on the attached ANSWER SHEET.
1.4.1 Cells are the units of inheritance.
1.4.2 There is a/an liquidity of products when the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied.
1.4.3 Capital is a production factor that does not depreciate, spoil, become old or get used up.
1.4.4 The approach that a company takes to marketing its products is called consumer index.
1.4.5 Negative external elements that could hamper the success of a business is creativity. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 Study the illustration below and answer QUESTIONS 2.1.1 to 2.1.3 based on the illustration.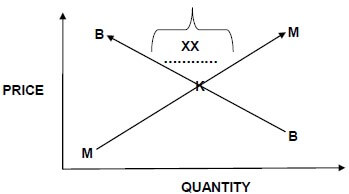
2.1.1 Identify the description marked XX in QUESTION 2.1. (1)
2.1.2 Explain your answer to QUESTION 2.1.1. (2)
2.1.3 Identify the letter K and the lines MM and BB in QUESTION 2.1. (3)
2.2
| You attended a seminar where one group of the participants were debating the difference between selling and marketing of processed goods. Another group was discussing eco-labelling and how it influences consumer behaviour. You were invited to draw TWO clear distinctions between marketing and selling. |
2.2.1 Tabulate the difference between marketing and selling. Provide TWO descriptions EACH for marketing and selling. (4)
2.2.2 State TWO main functions of agricultural marketing. (2)
2.2.3 Suggest TWO ways eco-labelling influence consumer behaviour. (2)
2.2.4 List TWO reasons why meat is processed. (2)
2.3 The illustration below is an example of a marketing chain showing the different components of supply chain and demand chain.
| MARKETING CHAIN | ||||||
SUPPLY CHAIN | DEMAND CHAIN | |||||
Purchasing | Manufacturing | Distribution | Marketing | Sales | Service | |
2.3.1 Define the underlined description in QUESTION 2.3. (2)
2.3.2 List TWO functions of post-harvest management in the marketing chain. (2)
2.3.3 Classify the following under either the supply chain or the demand chain.
(a) Value adding
(b) Packaging
(c) Cash flow and profitability (3)
2.4 You met a potential farmer standing next to the signboard below. The farmer asked you some questions about the signboard because the farmer wants to join the co-operative society.
2.4.1 Explain briefly what an agricultural co-operative society is to the farmer. (2)
2.4.2 State TWO benefits of agricultural co-operative societies for a farmer. (2)
2.5
| When marketing to consumers, it is important to know the different types of buyers and their characteristics. A buyer can be an innovator, adopter or a traditionalist. Consumers have different reasons why they purchase goods. Sellers should try to promote what they sell and adopt different approaches to marketing in order to make maximum profit on sales. |
2.5.1 Predict TWO characteristics of a buyer who is a traditionalist. (2)
2.5.2 Identify TWO ways sellers could make a profit from the scenario. (2)
2.5.3 State TWO ways sellers could promote sales. (2)
2.6 Differentiate between niche marketing and stock sales. (2)
[35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 Different types of farm labour are indicated in the illustration A, B, C and D below. 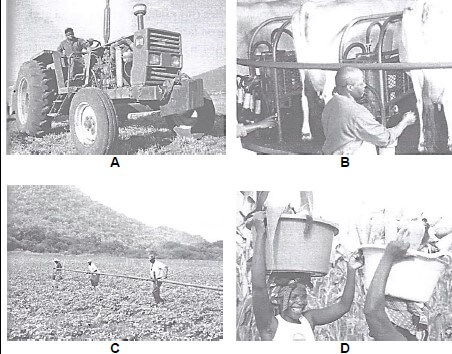
3.1.1 Indicate the type of farm labourer in illustrations A, B, C and D above that could be very scarce to commercial crop farmers. (1)
3.1.2 Justify your answer to QUESTION 3.1.1 with TWO reasons. (2)
3.1.3 Suggest TWO methods to improve the economic conditions of the workers in the illustrations (3.1). (2)
3.1.4 State a labour law that could apply in the following cases:
(a) The tractor operator could fall from the tractor which is in motion (1)
(b) The workers in D are no longer employed. (1)
3.2
| A farm manager is considering expanding a structure on the farm. The manager borrowed R15 000,00 from a friend. The manager took a bank loan of R28 000,00 and sold 5 000 birds to raise an additional R20 000,00. The gross income on the farm after two years was R73 000,00 |
3.2.1 Determine the net profit or loss of the farmer after two years. (3)
3.2.2 Identify TWO methods the manager used to raise capital from the scenario. (2)
3.2.3 Mention ONE other method the manager could use to create capital apart from the methods mentioned in QUESTION 3.2.2. (2)
3.2.4 Recommend the best record that could show all the expected income and expenditure over the period. (1)
3.3 A potential farmer wants to cultivate vegetables on commercial basis. A piece of land was sold to the farmer. When the farmer went to look at the land, the land looked like the picture below.
3.3.1 Suggest ONE economic characteristic of land as a production factor that can best describe the photograph in 3.3. (1)
3.3.2 Justify your answer in QUESTION 3.3.1 with TWO reasons. (2)
3.3.3 State THREE functions of land as a production factor in agriculture. (3)
3.3.4 Recommend TWO scientific methods to increase the productivity of land for agricultural purposes. (2)
3.4
| What sets farm management apart from other business management is the kind and number of daily duties involved, as well as the many management layers involved in farming. Even among farms, the process will vary depending on the type of farming business involved and the overall size of the business. Specific skills are therefore needed for different farming operations. |
3.4.1 Identify TWO reasons from the scenario to justify why managing poultry farm is different from managing a shop. (2)
3.4.2 Mention the specific management skills required in the following:
(a) Being able to keep the farm profitable and successful (1)
(b) Being able to deal with labour problems (1)
(c) Being able to deal with unforeseen issues or problems (1)
3.4.3 Outline TWO production risks that a farm manager may experience in crop production. (2)
3.5 The table below shows rice (in tons) exported by a commercial farmer for a period of seven years.
YEAR | QUANTITY EXPORTED |
2009 | 40 |
2010 | 25 |
2011 | 50 |
2012 | 55 |
2013 | 35 |
2014 | 60 |
2015 | 60 |
Translate the information into a line graph. (5)
[35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1
| A breeder wants to increase the weaning weight of some animals. The average weaning weight of the animals on the farm is 22,5. The breeder selects a male animal with a weaning weight of 24,6 and a female with a weaning weight of 23,7. The heritability of weaning weight in the animals is 50%. |
4.1.1 Calculate the EBVs of the parents. (4)
4.1.2 Calculate the expected genetic gain of the off-spring. (2)
4.2 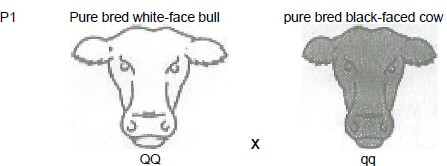
4.2.1 Draw a punnet square to complete the crosses illustrated in 4.2. (4)
4.2.2 State the possible percentage of white-faced offspring during the F2 generation. (3)
4.2.3 Give ONE appropriate genetic term to describe the differences in appearance of the two animals. (1)
4.2.4 Differentiate between phenotype and genotype. (2)
4.3
| For most organisms, sex is determined by chromosomal differences. During the formation of gametes by the process of meiosis and gametogenesis, two chromosomes of each homologous pair separate. Assume that a male gamete (29+X chromosomes) fuses with a female gamete (29+X chromosomes). |
4.3.1 Solve the chromosomes of the zygote. (2)
4.3.2 Predict the gender of the offspring. (1)
4.4 Define the following terminologies:
(a) Mutation (2)
(b) Out-crossing (2)
4.5
| Our ancestors had their traditional plant and animal improvement methods of selection and breeding such as mass selection and inbreeding respectively. A new method of plant and animal improvement has been developed, called genetic modification, which involves taking genes from one organism, the donor, and inserting them into another organism, the recipient. |
4.5.1 Deduce TWO aims of the genetic modification of plants. (2)
4.5.2 Provide TWO advantages of genetic modification over traditional methods. (2)
4.5.3 List TWO disadvantages of inbreeding. (2) 4.5.4 Distinguish between pedigree selection and progeny selection. (4)
4.6 State TWO environmental causes of variation in plants. (2) [35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
Agricultural Sciences
Paper 1 (P1)
Grade 12
Nsc Past Papers And Memos
September 2016
QUESTIONS
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
1. Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
2. Start EACH question on a NEW page.
3. Read ALL the questions correctly and answer only what is asked.
4. Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
5. Non-programmable calculators may be used.
6. Show ALL your calculations, including units and formula, where applicable.
7. Write neatly and legibly.
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A to D) next to the question number (1.1.1 to 1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK. for example 1.1.11 A.
1.1.1 The following region does NOT form part of the stomach of the pig:
A Cardiac
B Fundus
C Gastric
D Pylorus
1.1.2 Secretion of a digestive juice that contains an amylase deposited into the small intestines occurs in the ...
A liver.
B pancreas.
C salivary gland.
D intestinal gland.
1.1.3 A feed with a total digestible nutrients (TDN) of 85% and a DP of 10% has ...
A high fibre and low DP.
B low fibre and high DP.
C narrow NR and high DP.
D wide NR and low fibre.
1.1.4 The sketch below shows the process that assist in the digestion of a ruminant. 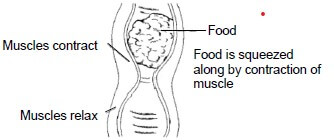
During the process above the following occurs:
Choose the correct combination:
(i) The muscle above the bolus contracts to push the feed downward.
(ii) The muscle below the bolus relaxes to move the feed upward.
(iii) If the rate of the process is reduced, the feed will move slowly leading to constipation.
(iv) The muscle below the bolus relaxes to move the feed downward.
A (i), (iii) and (iv)
B (ii), (iii) and (iv)
C (i), (ii) and (iv)
D (i), (ii) and (iii)
1.1.5 Farm animals are homeothermic because the body temperature is ...
A usually slightly lower than the environment.
B high when environmental temperature is high.
C fluctuating with the fluctuation of environmental temperature. D usually slightly higher than that of the environment.
1.1.6 The eggs of liver flukes are passed from the ... into the faeces.
A bile
B blood
C urine
D lymph
1.1.7 The following statements relates to extensive animal production system:
(i) Large area of land with low production output.
(ii) Low capital input with low production output.
(iii) Low management and control of the environment.
(iv) High production output with high inputs.
Choose the correct combination:
A (i), (iii) and (iv)
B (ii), (iii) and (iv)
C (i), (ii) and (iii)
D (i), (ii) and (iv)
1.1.8 The stage of courtship during mating is characterised by ...
A release of semen into the front part of vagina.
B fleshman response by male animal due to pheromones.
C cow allowing a bull to jump on her.
D pushing of male organ by sigmoidal muscle.
1.1.9 The following statement is NOT a disadvantage of artificial insemination:
A Semen of superior bulls is used.
B Undesirable traits are transferred to the offspring.
C Testing, storage of semen and insemination is expensive.
D Heat detection is difficult under extensive farming conditions.
1.1.10 The correct order in the development of the ovum after fertilisation is ...
A zygote ? blastocyte ? morula ? implantation.
B zygote ? implantation ? blastocyte ? morula.
C zygote ? morula ? implantation ? blastocyte.
D zygote ? morula ? blastocyte ? implantation. (10 x 2)
(20)
1.2 Indicate whether each of the descriptions in COLUMN B applied to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A and B or NONE of the items in COLUMN A. Write A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A and B or NONE next to the question number (1.2.1 to 1.2.5) in your ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 B ONLY.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
1.2.1 | A | Abomasum | Micro-organisms hydrolyse protein to form amino acids |
B | Duodenum | ||
1.2.2 | A | Pyridoxine | Pain and poor co-ordination of hind legs in pigs |
B | Cobalamine | ||
1.2.3 | A | Subsistence | Lower contributor to environmental pollution |
B | Commercial | ||
1.2.4 | A | Redwater | Transmitted by a three-host tick |
B | Heartwater | ||
1.2.5 | A | Copulation | The process replaced by artificial insemination |
B | Ejaculation | ||
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question number (1.3.1 to 1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 A digestive gland in the alimentary canal that secretes both digestive juices and hormones
1.3.2 The number of chicken per surface area in a broiler house
1.3.3 The type of micro-organism that causes foot-and-mouth disease in cattle
1.3.4 Inability of male animal to serve the cow though it shows an interest
1.3.5 The number of sperms in one millilitre of ejaculation (5 x 2) (10)
1.4 Change the underlined word(s) in each of the following statements. Write only the correct word(s) next to the question number (1.4.1 to 1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 Molasses is the compound used as a cheap non-protein source for ruminant animals.
1.4.2 The loss of heat when an animal's body is in contact with a colder surface is excretion.
1.4.3 Ectoderm is a layer that surrounds the embryo from which the heart, skeleton and uro-genital system develops.
1.4.4 Presentation refers to the position of the head and limbs in relation to the body.
1.4.5 Prostate is a pair of glands located along the urethra secreting fluid which cleans and lubricate the urethra before ejaculation. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: ANIMAL NUTRITION
2.1 The diagram below represent the alimentary canal of a farm animal.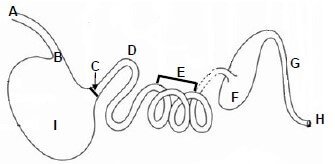
2.1.1 Classify the animal represented by the diagram above. (1)
2.1.2 Give a reason visible in the diagram for the answer in QUESTION 2.1.1 above. (1)
2.2 Identify the letter from the diagram above that represents the part where the following occurs:
2.2.1 It opens to move the pulp (1)
2.2.2 Brunner's gland secretes a liquid that protects the effects of the acids (1)
2.2.3 Fermentation of undigested food by micro-organisms (1)
2.2.4 Churning of bolus and gastric juice into chyme (1)
2.2.5 Food is mostly absorbed (1)
2.3 Urea and biuret are non-protein nitrogen substances which are given to ruminants only. Urea should be given with caution to ruminants.
2.3.1 Give a reason why urea is more poisonous than biuret. (1)
2.3.2 Indicate the precautionary measures a farmer can take to avoid urea poisoning in a lick. (1)
2.3.3 Name TWO ways in which the farmer can supplement urea to animals correctly. (2)
2.4 Young calves are not really ruminants when they are born. Functionally a calf is monogastric.
2.4.1 Suggest TWO reasons for the statement above. (2)
2.4.2 Indicate the period when the microbial population develops in the calf. (1)
2.4.3 State TWO ways in which the calf can benefit from the presence of microbial population. (2)
2.5 The table below shows the gross energy value as well as energy losses per kg in a 5 kg feed consumed by a cow.
ENERGY | VALUES (J/kg) | VALUES (J/5 kg) |
Gross energy | 18,5 | 92,5 |
Energy in faeces | 8,5 | 42,5 |
Energy in urine | 1,2 | 6 |
Energy lost as heat | 1,8 | 9 |
Energy in methane | 2,5 | 12,5 |
2.5.1 Calculate the digestible energy value in a 5 kg feed consumed by the cow. (2)
2.5.2 Determine the amount of energy that will be available to use for growth and production. (3)
2.6 A dairy farmer mixed maize meal and peanut oilcake meal at a ratio of 22 : 7,5 to prepare a meal with 18% DP.
Calculate the percentage of peanut oilcake meal in this mixture. (3)
2.7 A dairy farmer keeps 100 cows on a 500 ha pasture which supplies 1 200 kg DM per day for the first 6 months and 650 kg/day during the last 6 months.
The average daily animal's requirement to produce optimally is 60 kg with 70% concentrate and 30% roughage.
2.7.1 Calculate the monthly concentrate requirement of these cows. (3)
2.7.2 Work out the feed required against feed supplied during the last 6 months in tons. (4)
2.7.3 Comment on whether the quantity of the pasture available during the last 6 months is enough for dairy cows. (2)
2.8 Indicate the supplement which the farmer may consider to use in each of the following conditions:
2.8.1 To calm down cattle in a feedlot (1)
2.8.2 To improve growth of chicken by preventing harmful micro-organisms (1) [35]
QUESTION 3: ANIMAL PRODUCTION, PROTECTION AND CONTROL
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 The diagrams below illustrate facilities used in a production system. 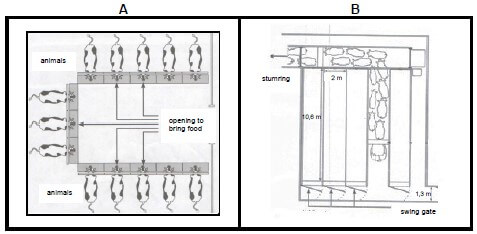
3.1.1 Identify the facility labelled A and B. (2)
3.1.2 Indicate the facility from the diagrams above that can be used when each of the following procedures is done:
(a) Sorting animals for auction sale (1)
(b) Feeding animals according to their specific needs (1)
3.1.3 The facility in B can be used to guide animals to a loading truck when they are going to be transported.
Name THREE guidelines when moving cows with calves. (3)
3.2 Farm animals have to be handled correctly when carrying out certain management practices.Give the reason for each of the following measures when handling animals:
3.2.1 Use of recognisable signal like touching the cow (1)
3.2.2 Not yelling when working with animals (1)
3.2.3 Grouping animals before transporting them (1)
3.3 The illustration below shows different spots one should consider when approaching farm animals. 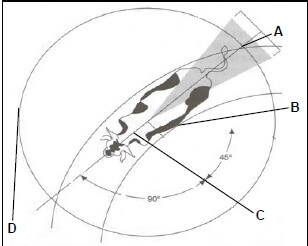
Indicate the letter that represents the following position:
3.3.1 The distance the animals like to keep between themselves and a threat to danger (1)
3.3.2 A point of balance (1)
3.3.3 An area in which an animal will kick when approached (1)
3.3.4 A handler initiates animal movement (1)
3.4 Compare in a table form subsistence and commercial production systems with regard to the following:
3.4.1 Purpose (2)
3.4.2 Management (2)
3.5 The seriousness of a disease depends on how the disease lasts and how quickly it develops. The table below shows the level of seriousness of the diseases.
Level of disease seriousness | Duration of the disease | Impact on animal |
A | Longer period | Mild |
Per-acute | B | Not deadly |
C | Short period | D |
3.5.1 Identify the labels A, B, C and D. (4)
3.5.2 Indicate a bacterial disease that is deadly within few hours of attack if not noticed immediately. (1)
3.5.3 Suggest TWO ways a farmer can prevent further spread of the disease in QUESTION 3.5.2 above from the dead animal. (2)
3.6 The picture below is a lifecycle of a parasite commonly found in sheep. 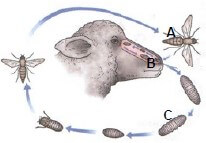
3.6.1 Give the name of a parasite above. (1)
3.6.2 Indicate the letter that represents the part where the following occurs:
(a) The larva pupate (1)
(b) The eggs are deposited into the nostrils (1)
3.6.3 Predict the season which favours infestation of the parasite. (1)
3.6.4 The parasite infestation can be visible from the host.
Name THREE signs that may be visible when an animal has been infested by the parasite above. (3)
3.7 Outline the role of the state to ensure the following:
3.7.1 Meat is not contaminated during the slaughtering process (1)
3.7.2 Prevention of introduction of disease from abroad (1)
3.7.3 Preventing an outbreak of a notifiable disease (1)
[35]
QUESTION 4: ANIMAL REPRODUCTION
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 The illustration below indicate the steps involved during a reproductive process. 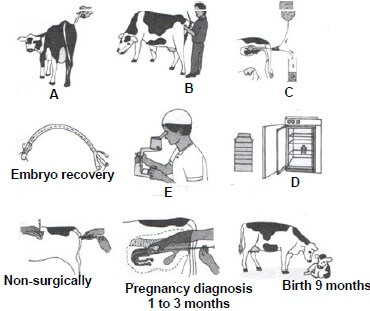
4.1.1 Identify the reproductive process illustrated above. (1)
4.1.2 Name TWO hormones that initiate the step labelled A. (2)
4.1.3 Provide the name given to animal labelled A. (1)
4.1.4 Indicate the temperature requirement in label D if the procedure is delayed up to 8 hours. (1)
4.1.5 Explain how the farmer can benefit from the process through the following:
(a) Non-producing and older cows (1)
(b) Economic benefit (1)
4.2 In female animals, hormonal and reproductive changes occur from one heat period to the next period. This occurs in phases which are marked by distinctive characteristics. Below are the characteristics applicable to each stage: 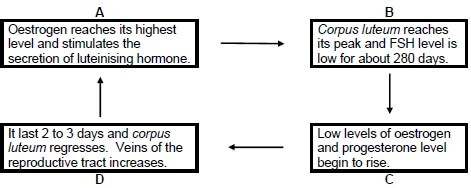
4.2.1 Match the characteristics labelled A, B, C and D with the phases of cycle. (4)
4.2.2 Indicate the letter that represent the stage where the following occurs:
(a) Graafian follicle ruptures to release the ovum (1)
(b) Ovum enters the fallopian tube for fertilisation and the ruptured follicle forms corpus luteum (1)
4.3 The diagram below is a reproductive system of a bull. 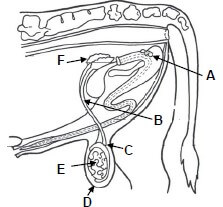
4.3.1 Indicate what is represented by part labelled B, D and F in the diagram above. (3)
4.3.2 Suggest TWO congenital defects in part labelled E that may lead to a complete loss of fertility in bulls. (2)
4.4 The bull may appear healthy and normal but shows no interest in cows due to several factors. Name the factor that is associated with each of the following statements:
4.4.1 Bull is used throughout the ploughing season (1)
4.4.2 Unbalanced ration to bull (1)
4.4.3 Young bull is raised in isolation (1)
4.4.4 Incorrect handling and care (1)
4.5 The table below shows the milk yield of two groups of lactating cows over 25 weeks.
MILK YIELD (litres) | ||
WEEKS | GROUP 1 | GROUP 2 |
1 | 5 | 10 |
5 | 10 | 15 |
7 | 30 | 35 |
10 | 25 | 20 |
15 | 15 | 10 |
20 | 13 | 7 |
25 | 10 | 5 |
4.5.1 Draw a line graph to show the milk yield of TWO groups of lactating cows over the 25 week period. (6)
4.5.2 Indicate the trend of milk yield in both groups over the lactation period. (1)
4.6 The diagram below shows the layers covering the foetus. Write down the letter and the name of the layer where the following occurs: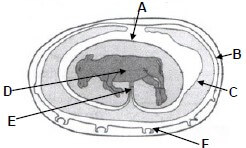
4.6.1 Collect the urine of the unborn calf (2)
4.6.2 Allows nutrient uptake, waste elimination through the mother (2)
4.6.3 Attaches the foetus to the caruncles (2) [35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
ENGLISH FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
English First Additional Language
Paper 2 (P2)
Grade 12
Nsc Past Papers And Memos
September 2016
MEMORANDUM
MARKING GUIDELINES
1. A candidate may not answer more than ONE question on the same genre.
2. If a candidate gives two answers where the first one is wrong and the next one is correct, mark the first answer and ignore the next.
3. If answers are incorrectly numbered, mark according to the memo.
4. If a spelling error affects the meaning, mark incorrect. If it does not affect the meaning, mark correct.
5. If the candidate does not use inverted commas when asked to quote, do not penalise.
6. For open-ended questions, no marks should be awarded for YES/NO or I AGREE/I DISAGREE. The reason/substantiation/motivation is what should be considered.
7. No marks should be awarded for TRUE/FALSE or FACT/OPINION. The reason/substantiation/motivation is what should be considered.
SECTION A: NOVELS
QUESTION 1: TO KILL A MOCKINGBIRD
1.1 1.1.1 Walter asked Scout to explain why he could not accept the quarter from Miss Caroline (the teacher). √ OR
Scout blamed Walter for starting off on the wrong foot with Miss Caroline. √ (1)
1.1.2 The obvious action is for brother and sister to protect each other. √
It is expected from Jem, as a brother to stand up for his younger sister. √ (2)
1.1.3 “fists were half cocked” √√
Do not penalise the candidates if the quotation marks have been omitted. (2)
1.1.4 False.
His eyes were red-rimmed and watery.
There was no colour in his face. √√
(NO MARK allocated for True or False. ONLY for reasons given.) (2) 1.1.5 A / Scout √ (1)
1.1.6 Cal is Calpurnia, the housekeeper. √ She is Jem and Scout’s mother figure who offers support and advice to everyone in the family. √ (2)
1.1.7 Frightened because:
- Of the stories about Boo being a homicidal-manic killer.
- They fear that he would kill them if they approach the house. √√
Fascinated because:
- Atticus told them not to be.
- Of the mysterious tenant of the house. √√ (4)
1.1.8 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows an understanding of the reason why Jem would feel more confident.
For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated.
A candidate can score 1 mark for a response which is not well substantiated. √√ (2)
1.1.9 Calpurnia wants to avoid any problems between the two worlds she lives in. She speaks the black dialect when she is amongst her family and friends, and she speaks “white” English when she is at the Finch’s. √√ (2)
1.2.1
- Atticus cannot do anything special.
- He is not young.
- He is too old for football.
- He has weak eyesight.
- He is not dashing or fashionable. √√√ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
1.2.2 My father is a dump-truck driver for the county/a sheriff/a farmer/works in a garage. √√ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
1.2.3 His family is jinxed by blindness or weak eyesight in the left eye. (Accept any other reasonable explanation.) √ (1)
1.2.4 C / Francis Hancock √ (1) 1.2.5 blue jays √ (1)
1.2.6 True. Atticus could beat everybody on both sides of the Landing where he grew up. √
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for ‘True’.
The reason is what should be considered. (1)
1.2.7 They make music for people to enjoy. √√ /
They sing their hearts out. √√ (2)
1.2.8 Accept a relevant response which shows an understanding of what caused the turn around.
For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated.
Possible answer:
- The Radley’s do not have a phone, so Calpurnia runs off to warn about ‘mad dong’s comin’!’ Heck Tate (the sheriff) is reluctant to take the shot, because if he misses the bullet will hit the Radley Place. He asked Atticus to take the shot. Atticus reluctantly takes the weapon, walk to the middle of the street, aims, fires and kills the dog. Jem is flabbergasted. √√√√ (4)
1.2.9 Open-ended.
DO NOT award a mark for Yes or No. Award full marks for a well substantiated answer.
Yes. He thought Atticus would not want her to, since he never mentioned it before. √√
OR
No. He has deprived her of the opportunity to convince her friends that her father is not only a good lawyer but a very good shot as well. √√ (2) [35]
OR
QUESTION 2: LORD OF THE FLIES
2.1 2.1.1 In the morning meeting, the boys decide they will have organised leadership on the island. √ There will be an order for who can speak and they will decide things in an orderly fashion. √ By the evening meeting, the fire has gone out, √ Piggy’s glasses are stolen, and the trees are on fire. It went from organised to disorganised in a hurry. √ (2 + 2) (4)
2.1.2 No. He passed a hand through his fair hair and spoke. √√
NO mark is awarded for Yes/No. 2 marks awarded for the quote. (2)
2.1.3
(a) B / A twelve-year-old English boy who is elected leader of the group of boys √ (1)
(b) D / A whiny, intellectual boy √ (1)
(c) A / He becomes the leader of the hunters but longs for total power √ (1)
(d) C / A shy, sensitive boy in the group √ (1)
2.1.4
(a) Food/Water for drinking and washing/the beach for swimming/mountain to climb/forests to hunt pigs. √√ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
(b) Medicine/education/shelter/civilisation √√
NOTE: Accept any TWO of the above. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.1.5 Ralph had not yet learned the role of a leader. √
He was still a child at heart who wanted to play with the other children. √ (2) 2.1.6 Personification √ (1) 2.1.7 They used Piggy’s eyeglasses. √ (1)
2.2
2.2.1 B / violence. √ (1)
2.2.2 (a) Open ended.
Suggestion: A mother always thinks her own children are the best and the most beautiful/handsome. √ (1)
(b) If Percival was not very attractive “even to his mother”, it means that he was pretty ugly. √ (1)
2.2.3
- The little boys aged six and younger.
- They do nothing but play.
- They do not take part in the growing struggle around them.
- ‘Littluns’ is a contraction for little ones and they have no purpose.
- They can be seen as a burden, because they had to be looked after. √√√ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
2.2.4 False. ‘they made no protest’ √√ (2)
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for ‘False’.
Only the quotation should be taken into consideration.
Do not penalise if the candidate has omitted quotation marks. (2)
2.2.5 It was evident that Percival suffered from mental torture of being abandoned on the island. √
The word “peaked” indicates that he was sickly-looking. √
He was red-eyed because he was crying a lot because he was doomed. √ (3)
2.2.6 Open-ended.
Accept a relevant response which shows an understanding of Roger’s ill-mannered and rough ways of dealing with the littluns, kicking down sand castles and throwing sand at others. √√√√
For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated.
Do not award a mark for YES/NO.
A candidate can score 1 mark for a response which is not well substantiated. (4) 2.2.7 Guilt/Remorse (1)
2.2.8 Johnny (1)
[35]
QUESTION 3: A GRAIN OF WHEAT
3.1
3.1.1 He would earn respect/higher status among the other African workers. √ (1)
3.1.2
(a) B / Anti-social and isolated from the community √
(b) D / He confessed to being a member of the Movement. √
(c) E / She cared for her family during the State of Emergency √
(d) C / While Gikonyo was imprisoned she slept with Karanja, who had been appointed village chief by the colonial power √ (4 x 1) (4)
3.1.3 It reveals her racism and prejudice towards the Africans. √
She generalises from her experience of only a few Africans. √ She wants him to feel that she is in authority. √ (3)
3.1.4
(a) He resents it because it lowers his status in the eyes of his co-workers. √ (1)
(b) He endures it because he wants to keep his good reputation amongst the white people. √ (1)
3.1.5 The Thompsons will be leaving Kenya after independence. √ (1)
3.1.6 False. John Thompson is sad and he thinks of the dreams he had since he was young. He is not hopeful that the Kenyans will be able to run the research station once the British have left. √√ (2)
3.1.7
(a) painful/sore/aching/excruciating√ (Accept any other suitable synonym.) √ (1)
(b) Karanja thought of Mumbi and it hurts. The relationship between Mumbi and Karanja is still a sore point. √√ (2) (c) Figuratively √ (1)
3.1.8 C / cringe. √ (1)
AND
3.2.1 Member of Parliament √ (1)
3.2.2
(a) Carpenter √ (1)
(b) Trader √ (1)
3.2.3 Gikonyo is honest and hardworking. √√ (2)
3.2.4
(a) He thought he was going to enquire about his decision for his speech on Independence Day. √ (1)
(b) To speak about his troubled heart. Mumbi has changed since he came back from detention. √√ (2)
3.2.5 Gikonyo wants to emphasise how deeply troubled he is. √ (1)
3.2.6 Barbed wire and flat, dry country √√ (2)
3.2.7 False. Mugo was confused about why he has been asked to give the speech at the Independence Day celebrations, therefore to avoid seeing anyone in Thabai, Mugo walks to Rung’ei. √√ (2)
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for ‘False’.
The reason is what should be considered.
3.2.8 Yes.
He thought that he had been called to lead the people.
No one needed to know the truth. √√ (2)
3.2.9 Safety/sanctuary/refuge/protection/shelter (Any reasonable word in this regard.) √ (1)
3.2.10 “suspicious” √ (1)
TOTAL SECTION A: 35
SECTION B: DRAMA
QUESTION 4: ROMEO AND JULIET
4.1
4.1.1 Romeo is their enemy because he is a Montague. √ (1)
4.1.2 A name is merely a title by which a person is addressed but the crucial nature of the person lies elsewhere and not only in a name. If Romeo were to have any other name other than Montague, he would be satisfactory to her family. √√ (2)
4.1.3 He has done so without her permission. It is a sign of his immaturity. √√
OR
It is a reminder of their intimacy. It is a sign of their affection and being less traditional. √√ (2) 4.1.4 (a) A / purity and virginity. √ (1)
4.1.5 Romeo, if you give up your Montague name, although it is an essential part of you, I will reward you by giving you all of myself. √√√
NOTE: Accept any reasonable paraphrasing of Juliet’s request. (3)
4.1.6
- She is used to obeying the Nurse's authority, and during the balcony scene, she disappears twice.
- She also defies authority twice in order to reappear and continue her conversation with Romeo.
- Her quick decision to marry Romeo and defy her parents. √√√ (3)
4.1.7 False. The moon is forever changing and therefore unreliable. √√ (2)
4.1.8 Romeo
Romeo became more confident.
Increasing maturity.
Romeo is no longer the melancholy lover.
Romeo has expressed his emotions in a traditional, colloquial style. (ANY TWO)
Juliet:
Increasing self-possession.
Confidence that leads to the idea of marrying Romeo.
She takes lead in making practical arrangements. √√√√ (ANY TWO)
ACCEPT any other reasonable and visible changes that occurred. (4)
AND
4.2
4.2.1
(a) B / Herald of the morning √
(b) C / Sings every night on a nearby pomegranate tree √
(c) D / Stars √
(d) A / They have changed their eyes √ (4)
4.2.2 They were in Juliet’s bedroom chambers where they spent their first night of marriage. √√ (2)
4.2.3 Romeo realises that if he leaves then he will live, but if he stays he will die because of the feud between the two families. √√ (2)
4.2.4 Juliet was crying because of Romeo’s departure.
Juliet’s mother thought she was mourning Tybalt death. √√ (2)
4.2.5
(a) A “dram” is a very small amount of liquid/medicine. √ (1)
(b) It will kill Romeo, rather than making him feel better. √ (1)
4.2.6
Lady Capulet thought the idea of poisoning Romeo would satisfy Juliet.
Juliet says that if Lady Capulet could find someone to take poison to Romeo, she "would temper it”,
To "temper" a liquid is to mix it with something else;
Lady Capulet is supposed to think that Juliet would make the poison more poisonous, but Juliet means the opposite.
Juliet says she hates to hear Romeo’s name when she "cannot come to him / To wreak [revenge] the love I bore my cousin / Upon his body that slaughter’d him!" Juliet would “wreak the love ... upon his body" with hugs and kisses instead. √√√ (3)
4.2.7 The use of light and dark signifies the blossoming of Romeo and Juliet’s romance. Romeo stands in the shadows and looks to the balcony and compares Juliet to the sun. √√ (2)
[35]
OR
QUESTION 5: NOTHING BUT THE TRUTH
5.1
5.1.1
(a) B / A funeral director √
(b) A / A librarian √
(c) D / The deceased √
(d) C / A history teacher √ (4)
5.1.2 Sipho feels anger towards Themba and he feels that his mother was biased. √ (2)
5.1.3 Sipho’s younger brother, Themba, has died in London. √
Themba has requested to be buried next to his parents in South Africa. √
Therefore Mr Khahla is needed to take him to the airport to collect the corpse. √ (3)
5.1.4 FALSE. Sipho is frustrated because he secretly wanted to make amends with his brother. √√
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for ‘True’.
The reason is what should be considered. (2)
5.1.5
(a) Sipho applied for the position of Chief Librarian. (1)
(b) He has been working at the library for a very long time. √
Mrs Potgieter has strongly recommended him. √ He is the one who knows the library the best. √ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
(c) Although he knew the library best, he was only in charge of the Xhosa section, which was barely used. √ His age. √ They would prefer to appoint someone who is not close to retirement. √ He is black person and the story takes place during the apartheid era. √ (3)
5.1.6 Sipho is spoiling her or over-protective because Thando is the only ‘posession’ that he has. He does not want anything to happen to her/he does not want to lose her as he lost his parents, brother, his son and his wife. √ (1)
AND
5.2
5.2.1 A / Themba’s daughter and brought his remains home. √ (1)
5.2.2 She should be angry … frowning. √
She should be very distressed … perhaps teary eyes. √
NOTE: Accept any reasonable explanation. (2)
5.2.3 False. Mandisa made the harsh discovery during the TRC hearings of what happened in South Africa during the apartheid era. √√
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for ‘True’. The reason is what should be considered. (2)
5.2.4 Sipho went to a tavern which was unusual. √ (1)
Reasons:
- He was not appointed as the Chief Librarian.
- They have appointed someone much younger than him.
- The memories of Themba came back to him.
- The ‘funeral’ of Themba had to be explained to the elders.
- He was upset because instead of a body, ashes of Themba arrived at the airport. √√√ (Any 3 x 1) (3)
5.2.5 Thando is traditional and her values are African. She is respectful and obedient to her elders. √√
Mandisa is a westernised girl who has a mind of her own and is quick to challenge her elders. √√ (4)
5.2.6
(a) He loved his country./He considered South Africa to be his home./He considered himself to be a South African. √√ (2)
(b) He taught her that her roots were in South Africa/that she was a South African in spite of being born in London/in spite of never having been to South Africa./He instilled in her a love for South Africa./He raised her to believe that her father’s family was more important/closer to her than her mother’s (family). √√ (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 35
SECTION C: SHORT STORIES
QUESTION 6
6.1 RELATIVES – CHRIS VAN WYK
6.1.1
(a) D / Cape Town √
(b) C / Simple breakfasts, lunches and suppers √
(c) A / Great Uncle √
(d) B / Train √ (4)
6.1.2 “prominently and truthfully” √√ (2)
6.1.3
(a) Metaphor √ (1)
(b) The train is compared to a snake sliding along the ground. √√ (2)
6.1.4 C / superior √ (1)
6.1.5 Before the young men left the tone was light-hearted. The tone of the three young men were friendly and happy. After they disembarked the mood was dark/sombre. The two brothers were swearing and they were telling details about how they will murder their brother’s murderer. √√√√ (4)
6.1.6 The writer was twenty-one (21). √ (1)
6.1.7 When the murderer (Georgie) disembarked the train at Cape Town station, he was met by his wife and children. He was publicly slapped in his face by his wife. √√ (2)
[17]
AND
6.2 MANHOOD
6.2.1
(a) Mr Wiilison wants his son to be fit, so that he could be chosen for the rugby team of the school. √√ (2)
(b) Mr Willison/Rob’s father. √ (1)
(c) It is clear from Rob’s attitude that he is not interested in getting fit / he is not interested in being chosen for the rugby team of the school. √
NOTE: Accept any ONE of the above. (1)
6.2.2 B / frustrated. √ (1)
6.2.3 No. He did not want to continue cycling. √
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for ‘No’. The reason is what should be considered. (1)
6.2.4 He insisted that Rob must sit/lie on his jacket to keep warm. He immediately suggested that Rob’s back must be strengthened. √√ (2)
6.2.5 False. Rob is exaggerating because his father is pressurising him. √
OR
False. Rob is exaggerating because he wants his father to know that he had enough. √ (1)
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for ‘False’. The reason is what should be considered.
6.2.6
(a) Mr Willison’s mistake:
- He is domineering/assertive/controlling. √
- He is prescriptive in that he decides what his sonshould or should not do./He never asks his son’s opinion. √
- He attempts to fulfil himself through his son. √
- He measures manliness and strength in terms of physique and excellence at sport. √
NOTE: Accept any THREE of the above. (3)
(b) Mrs Willison’s mistake:
- She is over-protective. √
- She does not consult with her son. √
- She is as inflexible as her husband. √
- Like her husband, she prevents/inhibits her son’s natural development. √
NOTE: Accept any THREE of the above. (3)
6.2.7 Yes / A parent would like to give opportunities to their children what they were deprived of.
No. / Every individual should live his/her life according to his/her own abilities/talents. √
NOTE: Accept any reasonable/mature answer.
Do NOT award a mark for ‘Yes’/‘No’
The reason is what should be considered. (1)
6.2.8 Open-ended.
Mrs Willison needs to give Rob space to find himself. Rob needs to be honest with his parents. √√ (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION C: 35
SECTION D: POETRY
QUESTION 7
7.1 Let me not to the marriage of true minds by William Shakespeare
7.1.1
(a) union √ (1)
(b) mentally √ (1)
(c) friendship √ (1)
7.1.2 ‘Love is not love, Which alters when alteration finds’ √ (1)
7.1.3 Love is the indestructible foundation to all relationships because no matter what the storms, love will hold a relationship together. In essence the poet compares it to a lighthouse, no matter what waves crash over it, it will stand immovable. √√ (2)
7.1.4 It is a ship (known in Shakespearian times as a barque). √ (1)
7.1.5 False. The captains of these sailing ships mapped their progress by taking reading from the stars at night. √
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for ‘False’. The reason is what should be considered. (1)
7.1.6
(a) Metaphor √ (1)
(b) Time is compared to a harvester, perhaps the well-known “grim reaper,” suggesting that true love escapes the effects of time. √√ (2)
7.1.7 ‘Within his bending sickle’s compass come; Love alters not with his brief hours and weeks,’ √√ (2)
7.1.8 Open-ended.
The lines pose a challenge to the readers that if they have any proof that he is wrong, and indeed if it is so, then he has never written anything and that nobody has ever been in love before. If love turns out to be less than eternal, the poem’s truth immediately becomes impossible to dispute. √√√√
(Accept a relevant response which shows an understanding of the poet’s character.)
For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated.
A candidate can score 1 mark for a response which is not well substantiated. (4)
AND
7.2 Elementary school classroom in the slum by Stephen Spencer
7.2.1
(a) The children look pale and they do not look healthy. √√ (2)
(b) The children in the slum have never seen the sea; or has never been on holiday to the sea, therefore they look untanned. √√ (2)
7.2.2
(a) B / shorter. √ (1)
(b) There is a tall girl whose head is weighed-down with sadness, disinterestedness or shame or a mixture of all the three. She is probably over-aged for the class. √√ (2)
7.2.3 The boy is supposed to be reciting his schoolwork, instead he is suffering from a disease passed on by his father. √√ (2)
7.2.4 “dim” √ (1)
7.2.5
(a) Yes. The classroom has cream-coloured walls, the poet twists the cream that it literally refers to sour cream; distaste – having an unpalatable/inedible/ taste. √ (1)
(b) The poet makes the walls sound ugly and distasteful/ disgusting/unpleasant. √√ (2)
7.2.6 C / limited to what they can see through the windows of the classroom. √ (1)
7.2.7 ‘slag heap’ √ (1) 7.2.8 Simile √ (1)
7.2.9 Open-ended.
The green leaves are those of the plants in the forests.
The white leaves are those pages in the book.
Green leaves open in spring, the season of sunshine and growth. The white leaves open to enable the children to read, to open their minds with beauty, enrichments and dreams. √√
Accept any relevant response which shows knowledge of the content of the poem and poet’s attitude.
For full marks, the response must be well-substantiated.
Do not award a mark for YES/NO.
A candidate can score 1 mark for a response which is not well substantiated. (2) [35]
TOTAL SECTION D: 35
GRAND TOTAL: 70
ENGLISH FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE PAPER 3 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
English First Additional Language
Paper 3 (P3)
Grade 12
Nsc Past Papers And Memos
September 2016
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
This memorandum must be used together with the attached English FAL Assessment Rubrics for SECTIONS A, B and C.
NOTE: All pieces of writing should be read at least TWICE during assessment, once for content and once for language respectively. Errors have to be indicated in your second reading.
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A: ESSAY
QUESTION 1
INSTRUCTIONS TO MARKERS:
- Candidates are required to write on ONE topic only.
- The ideas listed below the topics are only some ways in which the topics could be interpreted. Full credit must be given for the candidates’ own interpretation.
- Use the 50-mark assessment rubric to mark the essays. The texts produced by candidates must be assessed according to the following criteria as set out in the assessment rubric:
- Content and planning = 30 marks
- Language, style and editing = 15 marks
- Structure = 5 marks
NOTE: No additional penalties may be imposed as the rubric itself imposes penalties. If a candidate exceeds the word limit, read up to TEN words above the upper limit and ignore the rest.
1.1 The negative side of South African youth culture
Narrative/Descriptive/Reflective
The following must be considered:
- If narrative, a strong storyline must be evident in which a series of events leads to a positive outcome. There must be a logical sequence of tense.
- If descriptive, there must be a vivid description of an experience/incident.
- If reflective, there must be a personal account of thought processes and feelings/emotions. [50]
1.2 Living positively in challenging times
Narrative/Descriptive/Reflective
The following must be considered:
- If narrative, a strong storyline must be evident in which a series of events leads to a positive outcome. There must be a logical sequence of tense.
- If descriptive, there must be a vivid description of an experience/incident.
- If reflective, there must be a personal account of thought processes and feelings/emotions. [50]
1.3 We can escape the cycle of death and disease in South Africa. Do you agree?
Argumentative
The following must be considered:
- The essay must offer one distinct opinion, therefore the essay must be either FOR OR AGAINST the topic given.
- There should be a clear defence/motivation/argument for the position taken. [50]
1.4 What I imagine the world would be like in 30 years
Descriptive/Reflective
The following must be considered:
- If descriptive, there must be a vivid description of an experience/incident.
- If reflective, there must be a personal account of thought processes and feelings/emotions. [50]
1.5 Is the culture of human rights being abused by South Africans? Discuss your views.
Discursive/Reflective
The following must be considered:
- If discursive, a balanced view of both sides of the statement must be reflected. Opposing views must be presented impartially.
- If reflective, there must be a personal account of thought processes and feelings/emotions. [50]
1.6 Betrayal (being sold out to an enemy) at the hands of a trusted friend
Descriptive/Narrative/Reflective
The following must be considered:
- If descriptive, there must be a vivid description of an incident/experience to illustrate the statement.
- If narrative, a strong storyline illustrating the statement must be evident in which a series of events are shown. There must be a logical sequence of tense.
- If reflective, there must be a personal account of thought processes and feelings/emotions. [50]
1.7 Interpretation of pictures
- The writer may interpret the picture in any way.
- The writer may choose to write any type of essay.
- The interpretation must be linked to the picture.
- The writer should give the essay a suitable title.
- The writer may write in any appropriate tense.
1.7.1 Picture: old and torn shoes/boots
The writer may interpret the picture in the following ways, among others:
- Literal interpretation: poverty and deprivation, destitution, being desperate for things etc.
- Figurative interpretations: life experiences, challenges in life, culmination of one’s life struggles etc. [50]
1.7.2 Picture: A ‘No Entry’ road sign
The writer of the essay may interpret the pictures in the following ways, among others:
- Literal interpretations: ignoring road rules, accidents, how to reduce road fatalities in SA etc.
- Figurative interpretations: constraints, limitations in life, barriers to success, being deprived of opportunities etc. [50]
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B: LONGER TRANSACTIONAL TEXT
QUESTION 2
Instructions to Markers:
- Candidates are required to answer ONE question.
- Marking must be objective. Give credit for relevant ideas.
- Use the 30-mark assessment rubric to mark the responses in this section. The texts produced by candidates must be assessed according to the following criteria as set out in the assessment rubric.
- Content, planning and format (18 marks).
- Language, style and editing (12 marks)
NOTE: No additional penalties may be imposed as the rubric itself imposes penalties.
2.1 DIALOGUE
- The tone must be informal
- The following ideas may be explored, among others:
- A brief scenario (context) must be sketched before the speakers start speaking.
- The names of speakers must appear on the left-hand side of the page.
- A colon must appear after the name of each speaker.
- A new line must be used to indicate each speaker.
- Stage directions (tone of voice, actions etc.) must be written in brackets, if applicable.
- The following ideas may be explored, among others:
- The friend must show regret for his/her actions.
- He/she must be willing to change his/her behaviour. [30] ∙
2.2 AGENDA AND MINUTES OF MEETING
- The language and register should be appropriate to the audience of the meeting.
- The agenda and minutes should be arranged separately.
- The items in agenda should correlate with those in minutes.
- Minutes should be relevant to the occasion (should address the specific content of the meeting).
- A logical and appropriate arrangement of items should be evident.
- Full sentences are not necessary. [30]
2.3 OBITUARY
- The tone must be formal.
- The following aspects of format should be included:
- Full name of the deceased
- Date of birth
- Date of death
- The following information may also be included:
- Birth place
- Where the person was living at the time of death
- Key survivors
- Biographical information
- Content should include the following, among others:
- Contribution to community’s small businesses
- A tribute must also be paid to the deceased [30]
2.4 FORMAL LETTER
- The letter should be addressed to the bus company.
- The tone and register should be formal.
- The following aspects of format should be included:
- Address of sender
- Date
- Address of recipient
- Greeting
- Subject line
- Suitable ending
- Signature/name of sender
- The following information should be included, among others:
- Complaint about damaged luggage
- Asking for compensation for loss. [30] ∙
TOTAL SECTION B: 30
SECTION C: SHORTER TEXT TRANSACTIONAL/REFERENTIAL/ INFORMATIONAL
QUESTION 3
Instructions to Markers:
- Candidates are required to answer ONE question.
- Marking must be objective. Give credit for relevant ideas.
- Use the 20-mark assessment rubric to mark the responses in this section. The texts produced by the candidates should be assessed according to the following criteria as set out in the assessment rubric.
- Content, planning and format (12 marks)
- Language, style and editing (8 marks)
NOTE: No additional penalties may be imposed as the rubric itself imposes penalties.
3.1 ADVERTISEMENT
The following information must be included, among others:
- Persuasive language and catchy phrases should be used.
- Provide adequate information regarding the person to be voted for.
- Promises relating to service to be provided may be included.
- An appeal for support should be evident (to become RCL member)
- No marks are awarded for illustrations. [20]
3.2 POSTCARD
- The language (including salutation and ending/conclusion) can be informal and colloquial but should not include slang expression.
- Complete sentences are not required.
- The content must be brief but informative.
- The following details about content should be included, among others:
- Wonderful holiday experiences
- Do not award marks for illustrations [20]
3.3 INSTRUCTIONS
- Instructions may be in point or paragraph form.
- Numbers or bullets may be used to indicate each new instruction.
- The language should be clear and instructive.
- Candidates may also choose to write each instruction on a new line or leave lines between instructions.
- Complete sentences are not necessary.
- Details about content should include the following, among others:
- Tips on how to save water [20]
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL 100
SECTION A: RUBRIC FOR ASSESSING ESSAY FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE [50 marks]
- Always use the rubric when marking the creative essay (Paper 3, Section A).
- The marks from 0–50 have been divided into 5 major level descriptors.
- In the Content, Language and Style criteria, each of the five level descriptors is divided into an upper and a lower level sub-category with the applicable mark range and descriptors.
- Structure is not affected by the upper level and lower level division.
Criteria | Exceptional | Skilful | Moderate | Elementary | Inadequate | |
CONTENT AND PLANNING (Response and ideas)
30 MARKS | UPPER LEVEL | 28–30 | 22–24 | 16–18 | 10–12 | 4–6 |
|
|
|
|
| ||
LOWER LEVEL | 25–27 | 19–21 | 13–15 | 7–9 | 0–3 | |
|
|
|
|
| ||
LANGUAGE, STYLE AND EDITING
15 MARKS | UPPER LEVEL | 14–15 | 11–12 | 8–9 | 5–6 | 0–3 |
|
|
|
|
| ||
| LOWER LEVEL | 13 | 10 | 7 | 4 | ||
|
|
|
| |||
STRUCTURE
5 MARKS | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 0–1 | |
|
|
|
|
| ||
MARKS RANGE | 43–50 | 33–40 | 23–30 | 13–20 | 0–10 |
SECTION B: ASSESSMENT RUBRIC FOR LONGER TRANSACTIONAL TEXT FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE [30 MARKS]
Criteria | Exceptional | Skilful | Moderate | Elementary | Inadequate |
CONTENT PLANNING AND FORMAT
18 MARKS | 15–18 | 11–14 | 8–10 | 5–7 | 0–4 |
|
|
|
|
| |
LANGUAGE, STYLE AND EDITING
12 MARKS | 10–12 | 8–9 | 6–7 | 4–5 | 0–3 |
|
|
|
|
| |
MARKS RANGE | 25–30 | 19–23 | 14–17 | 9–12 | 0–7 |
SECTION C: ASSESSMENT RUBRIC FOR SHORTER TRANSACTIONAL FIRST TEXT ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE [20 MARKS]
Criteria | Exceptional | Skilful | Moderate | Elementary | Inadequate |
CONTENT PLANNING AND FORMAT
12 MARKS | 10–12 | 8–9 | 6–7 | 4–5 | 0–3 |
|
|
|
|
| |
LANGUAGE, STYLE AND EDITING
8 MARKS | 7–8 | 5–6 | 4 | 3 | 0–2 |
|
|
|
|
| |
MARKS RANGE | 17–20 | 13–15 | 10–11 | 7–8 | 0–5 |
ENGLISH FIRST ADDITIONAL LANGUAGE PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2016
English First Additional Language
Paper 1 (P1)
Grade 12
Nsc Past Papers And Memos
September 2016
MEMORANDUM
INSTRUCTIONS TO MARKERS
1. Candidates are expected to answer ALL the questions.
2. This memorandum serves as a guide to markers. Some responses may require a marker’s discretion.
3. Candidates’ responses should be assessed as objectively as possible.
SECTION A: COMPREHENSION
NOTE: Incorrect spelling and language errors should not be penalised, because the focus is on understanding.
QUESTION 1
1.1 ‘adornments’ (1)
1.2 Africa (1)
1.3 It is still early in the morning/the sun has just risen √ so people are not yet moving around/venturing out. √ (2)
1.4 Beads are being sold at these stalls. (1)
1.5 The markets in Ghana have a party atmosphere/have loud music playing/are noisy √ while the atmosphere in Koforudua is less noisy/more respectful. √ (2)
1.6 B is done in a lively manner. (1)
1.7 A diamond is a precious/valuable stone. √ The simile suggests that every bead is precious/valuable √ because it depicts the country’s history and heritage. √ (3)
1.8
At a baby’s naming ceremony.
When a baby’s growth is measured.
At the passage from adolescence to adulthood.
At the time of death.
NOTE: Accept any THREE answers. (Any 3 x 1) (3)
1.9 True
“In West Africa beads are worn decoratively; but are also highly symbolic ...”
NOTE: No marks should be awarded for TRUE/FALSE. The reason is what should be considered. (1)
1.10 The title is suitable because beads are threaded onto a string. √ The beads tell the story of the Ghanaian culture and heritage. √ (2)
1.11 It is believed that they have medicinal √ and magical powers. √ (2)
1.12 The parking lot can be regarded as the ‘most unlikely heritage site’ since it is not a place/an area where one would expect to find √ something depicting the culture or heritage of the country. √ (2)
1.13 Open-ended. Accept a suitable response, e.g. I would consider the exportation of beads to be an advantage because it contributes to the economy by providing employment/jobs. People in other countries are able to share in the history of Ghana and learn from it.
OR
I would consider the exportation of beads to be a disadvantage because by exporting these beads, the country loses its culture and heritage. The beads end up on foreign shores where people might not value and appreciate what the beads symbolise.
NOTE: The above are merely examples. A candidate can score 1 or 2 marks for an answer that is not well-substantiated. (3)
TEXT B
1.14
The atmosphere of vacation is depicted by the sea in the background. The family looking relaxed
The family having fun together.
The family enjoying themselves on the beach.
NOTE: Accept any TWO answers. (Any 2 x 1) (2)
1.15 The message that the advertisement is trying to convey is that by booking tickets in advance √ you can save money. √ (2)
1.16 R399/three hundred and ninety-nine rand (1) 1.17 SA Express is offering its clients cheap flights/fares over the holiday period. (1) TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B: SUMMARY
QUESTION 2
The following points form the answer to the question.
QUOTATIONS | FACTS (NOTE: Candidates may phrase the facts differently.) | |
1 | “Take regular stand up breaks throughout the day.” | Try to walk around often during the day. |
2 | “Make a weekly weighing date and stick to it.” | Make a decision to weigh yourself every week and adhere to it. |
3 | “Swivel, tap, wiggle whenever you can.” | Fidget whenever you can. / Move around whenever you can. |
4 | “Get in the habit of eating slowly.” | Make a concerted effort to eat slowly. |
5 | “Get up 30 minutes earlier to make time to eat a healthy breakfast.” | Ensure that you get up a half an hour earlier to eat a healthy breakfast.” |
6 | “Focus on your food and think about the tastes and textures as you chew.” | Concentrate on your food and focus on the tastes and textures as you chew. |
7 | “Try getting seven to eight hours sleep at night” | Try to sleep for seven or eight hours a night. |
Marking the summary
The summary should be marked as follows:
- Mark allocation:
- 7 marks for 7 points (1 mark per main point)
- 3 marks for language
Total marks: 10
- Distribution of language marks when a candidate has not quoted verbatim:
- 1–3 points correct: award 1 mark
- 4–5 points correct: award 2 marks
- 6–7 points correct: award 3 marks
- Distribution of language marks when a candidate has quoted verbatim:
- 6–7 quotes: award no language mark
- 1–5 quotes: award 1 language mark
NOTE:
- Word Count:
- Markers are required to verify the number of words used.
- Do not deduct any marks if the candidate fails to indicate the number of words used, or if the number of words used is indicated incorrectly.
- If the word limit is exceeded, read up to the last sentence above the stipulated upper limit and ignore the rest of the summary.
TOTAL SECTION B: 10
SECTION C: LANGUAGE
- Spelling
- One-word answers must be marked correct even if the spelling is incorrect, unless the error changes the meaning of the word.
- In full-sentence answers, incorrect spelling should be penalised if the error is in the language structure being tested.
- Where an abbreviation is tested, the answer must be punctuated correctly.
- Sentence structures must be grammatically correct and given in full sentences/as per instruction.
- For multiple-choice questions, accept BOTH the letter corresponding with the correct answer AND/OR the answer written out in full as correct.
QUESTION 3: ANALYSING AN ADVERTISEMENT
TEXT D
3.1 Men who are going bald. √ The advertisement shows pictures of men who have undergone this procedure/who are going bald. √ (2)
3.2 The pictures serve as proof/evidence that this procedure works. √
OR
The pictures are meant to attract attention to the product since these are famous men. √ (1)
AND
The signatures suggest that these well-known cricket legends endorse/approve of/ recommend this procedure. √ (1) (2)
3.3 It allows the reader to obtain more information about the clinic/procedure. (1)
3.4 A check your hair free of charge. (1)
3.5 One can visit the Advanced Hair Clinic to have this procedure done. (1)
3.6 It suggests that the hair will gradually start to grow/take some time to regrow/reappear over a period of time/slowly start to grow. (1)
3.7 Open-ended. Accept a suitable response which shows that the candidate has understood the message of the advertisement and is able to connect it to the picture.
NOTE:
- Do not award a mark for YES or NO only.
- Accept a well-substantiated response for full marks.
- The above are merely examples of possible responses. Allow for the candidate’s own but relevant interpretation. (2) [10]
QUESTION 4: ANALYSING A CARTOON
TEXT E
ZITS
4.1
4.1.1 His friend’s body is leaning forward suggesting he is running. He enters head first. (Any ONE of the above.) (Any 1 x 1) (1)
4.1.2
He is resting his head on his knees.
He is staring straight ahead of him.
He is quiet/silent.
(Any ONE of the above.) (Any 1 x 1) (1)
4.2 His friend puts his arm around Jeremy’s shoulder. (1)
4.3 ‘dude’ / ‘cooler’ (1)
4.4 D expresses how remarkable his phone is. (1)
4.5 In frame 1 Jeremy’s friend’s haste and the sympathy that he expresses,√ creates the impression that something serious has occurred√ just to discover in frame 3 that the mood that he is experiencing is because his dad has a better phone than him.√ (3)
4.6 Open-ended response.
Yes
Adults do not know how the latest phones operate so they have to constantly ask their children for assistance. This annoys the children. Jeremy’s emotions can be justified because with his knowledge he could put the phone to better use.
OR
No
Jeremy’s dad has the right to have the latest phone. He works so he is allowed to buy himself any phone that he wants.
NOTE: Do NOT award a mark for YES or NO ONLY.
The above are merely examples of possible responses. Allow for the candidate’s own but relevant interpretation. (2)
[10]
QUESTION 5: LANGUAGE AND EDITING SKILLS
NOTE: The spelling in this question must be correct.
TEXT F
5.1 5.1.1
(a) received (1)
(b) was (1)
(c) access (1)
(d) up (1)
5.1.2 This √ scene√ made a lasting impression on Chris. (2)
5.1.3 incompatible (1)
5.1.4 Chris is working in Malawi for two years. (1)
5.1.5 There was quite a commotion in the hospital, wasn’t there/was there not? (1)
5.1.6 A a definite article. (1) 5.1.7 A direct transfusion was arranged by the doctor. (1)
5.1.8 Chris said that for him it was about being healthy enough to donate blood.
NOTE: Award ONE mark for each of the underlined changes and ONE mark for removing the comma, removing the quotation marks and inserting the final full stop as well as the correct use of capital and small letters throughout. (3)
TEXT G
5.2 5.2.1
(a) effect (1)
(b) better (1)
5.2.2
(a) naturally (1)
(b) pretence (1)
(c) example (1)
5.2.3 People who are sincerely kind often choose to be doctors or nurses to make a difference in people’s lives. (1)
[20]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 80
PHYSICAL SCIENCES PHYSICS PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAM PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2016
Physical Sciences (Physics)
Paper One (P1)
Grade 12
Amended Senior Certificate Exam Past Papers And Memos
May/june 2016
Memorandum
QUESTION 1
1.1 A✓✓ (2)
1.2 B✓✓ (2)
1.3 D✓✓ (2)
1.4 C✓✓ (2)
1.5 B✓✓ (2)
1.6 B✓✓ (2)
1.7 A✓✓ (2)
1.8 D✓✓ (2)
1.9 C✓✓ (2)
1.10 D✓✓ (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2
2.1 A body will remain in its state of rest or motion at constant velocity ✔unless a resultant/net force✔ acts on it.
OR
Every body continues in its state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line ✔unless a resultant/net force ✔acts on it. (2)
2.2 0 (N)✔/zero/nul (newton)
NOTE: No penalisation if the unit is omitted (1)
2.3
Accepted labels | |
w | Fg / Fw / weight / mg / gravitational force |
T | FT / tension |
15 N | Fa / F15N / Fapplied / Ft / Ftoegepas / F |
Accept
OR (3)
(3)
Notes
|
2.4 (7)
2 kg block 10 kg block |
NOTE:L |
Massless string approximation/Systems approach (4/7) |
2.5 Smaller than ✔ (1)
2.6 Remains the same ✔ - The coefficient of kinetic friction is independent of the (apparent microscopic) surface areas in contact. ✔
OR
The coefficient of kinetic friction depends only on the type of materials used✔ (2)
[16]
QUESTION 3
3.1 An object upon which the only force✔ acting is the force of gravity.✔
ACCEPT
An object that falls freely ✔with an acceleration of (g) 9,8 m∙s-2 ✔
An object that is launched ✔(or synonyms) with an initial velocity under the influence of the force of gravity.✔ (2)
3.2.1 (4)
OPTION 1 | |
Upward positive vf = vi + aΔt ✔ | Downward positive vf = vi + aΔt ✔ |
OPTION 2 | |
Upward positive vf = vi + aΔt ✔ | Downward positive vf = vi + aΔt ✔ |
OPTION 3 | |
Upward positive Δy = viΔt + ½ aΔt2✔ | Downward positive Δy = viΔt + ½ aΔt2✔ |
OPTION 4 | |
Upward positive Fnet∆t = ∆p = (mvf – mvi)✔ | Downward positive Fnet∆t = ∆p = (mvf – mvi)✔ |
OPTION 5 | |
Upward positive From top to bottom | Downward positive From top to bottom |
3.2.2
POSITIVE MARKING FROM QUESTION 3.2.1 |
OPTION 1 Δy = viΔt + ½ aΔt2 ✔ OR POSITIVE MARKING FROM QUESTIONS 3.2.1 Δy = viΔt + ½ aΔt2 ✔ |
OPTION 2 vf = vi + aΔt Δy = viΔt + ½ aΔt2 ✔ OR Δy = vf + vi Δt✔ OR vf2 = vi2 + 2aΔx ✔ | Downward positive vf = vi + aΔt Δy = viΔt + ½ aΔt2✔ OR Δy = vf + vi Δt✔ OR/OF vf2 = vi2 + 2aΔx ✔ |
OPTION 3 vf = vi + aΔt Δy = vf + vi Δt✔ | vf = vi + aΔt Δy = vf + vi Δt✔ Distance = |Δy| = 25,12 m✔ |
OPTION 4 Δy = viΔt + ½ Δt2 ✔ | Downward positive Δy = viΔt + ½ Δt2✔ |
(4)
3.3 (4)
POSITIVE MARKING FROM QUESTION 3.2.1 | |
Upward positive Δy = viΔt + ½ aΔt2✔ | Downward positive Δy = viΔt + ½ aΔt2✔ 50✔= vi (4,12) + [½ (9,8)(4,12)2]✔ vi = - 8,05 m∙s-1 speed/spoed = 8,05 m∙s-1✔ |
3.4
POSITIVE MARKING FROM QUESTIONS 3.2.1 AND 3.2.2 |
Criteria | Marks |
Correct shape of A | ✔ |
Correct shape of Graph B parallel to A below A | ✔ |
Time at which both A and B reach the ground (6,12 s) | ✔ |
Time for A to reach the maximum height (3,06 s) shown | ✔ |
NOTE :
Do not penalise if velocities are not indicated
3.4
POSITIVE MARKING FROM QUESTIONS 3.2.1 AND 3.2.2 |
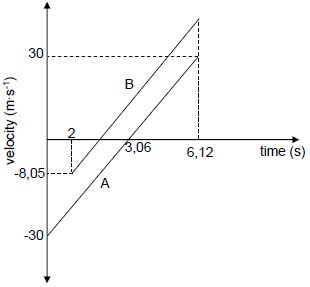
Criteria | Marks |
Correct shape of A | ✔ |
Correct shape of Graph B parallel to A above A | ✔ |
Time at which both A and B reach the ground (6,12 s) | ✔ |
Time for A to reach the maximum height (3,06 s) shown | ✔ |
(4)
[18]
QUESTION 4
4.1 The total (linear) momentum of an isolated (closed) system ✔is constant (is conserved) ✔
OR
In an isolated (closed) system, the total (linear) momentum ✔before collision is equal to the total linear momentum after collision. ✔ (2)
4.2.1 (4)
∑pi = ∑pf OR Δp5kg = -Δp3kg ✔ |
4.2.2 (4)
OPTION 1 Fnet∆t = ∆p = (pf – pi) = (mvf – mvi) ✔ | |
OPTION 2 = m (vf- vi)✔ = 8 (0 - 2,5) ✔= - 66,67 N | OPTION 3 |
OPTION 4 Wnet = ΔEk Fnet (Vf + Vi) Δt cos 180º = ½m(Vf2 - Vi2)✔ |
[10]
QUESTION 5
5.1 The total mechanical energy in an isolated (closed) system ✔remains constant (is conserved). ✔
NOTE
If total or isolated/closed is omitted (max: 1/2 ) (2)
5.2.1 (3)
W = F∆x cosθ✔ |
5.2.2 (5)
OPTION1 |
OPTION 2 Wnet = ΔEK |
5.3 (4)
F = w// + f Pave = Fvave ✔ |
[14]
QUESTION 6
6.1 X ✓ (1)
6.2 As ambulance approaches the hospital the waves are compressed✓or wavelengths are shorter. Since the speed of sound is constant✓ the observed frequency must increase✓. Therefore the hospital must be located on the side of X (from v = fλ)
OR
The number of wave fronts per second reaching the observer are more at X✓✓. For the same constant speed, this means that the observed frequency increases ✓therefore the hospital must be located on the side of X. (from v = fλ) (3)
6.3 (5)
| fL= V ± VL fS OR FL = V FS✔ V ± VS V - VS fL = 304 ✔ (400)✔ (340 -✔ 30) fL = 438,71 Hz✔ NOTE: |
6.4 (3)
v = fλ✔ |
[12]
QUESTION 7
7.1 (3)
n = Q / e ✓ | n = Q / e ✓ |

7.2 (3)
Accepted label | |
w | Fg/Fw/weight/mg/gravitational force |
T | FT/tension Fs/spanning |
FE | Felectrostatic/FQ1Q2 /Coulomb force/F |
7.3 (5)
Fnet = 0 ACCEPT FE = wQ2 ✔ |
[11]
QUESTION 8
8.1 The (electrostatic) force experienced by a unit positive charge (placed at that point).✔✔
NOTE:
If the words “unit positive” is omitted (max 1/2) (2)
8.2 (2) 
8.3 (3)
Guideline for allocating marks | ||
Lines must not cross / Lines must touch the spheres but not enter spheres | ✔ | |
Arrows point outwards | ✔ | |
Correct shape | ✔ | |
(5) ↓
E =kQ ✔ EQ1X = EQ2X ✔For equating equations 5,477 = 6,708 |
[10]
QUESTION 9
9.1.1 (3)
OPTION 1 P = V2 / R✔ R = 36 Ω✔ | OPTION 2 P = VI V = IR✔ | OPTION 3 P = V I P = I2 R ✔ |
9.1.2 Increase✔ (1)
9.1.3 No change✔ - Same potential difference✔ (and resistance) (2)
9.2.1 (4)
V = IR ✔ V”lost” = Ir OR ε= I(R + r) |
9.2.2 Work done ✔in moving a unit charge ✔ through a cell.
ACCEPT
Energy transferred per unit charge/ Work done in moving in 1 C of charge. (2)
9.2.3
OPTION 1 V|| = I6R6 Vx = IRx✔ OR V = IR |
OPTION 2 V”lost” = Ir V|| = IpRp
RX = 9 Ω✔ |
(5)
[17]
QUESTION 10
10.1.1 a to b ✔ (1)
10.1.2 Fleming's left hand rule /Left hand motor rule✔
ACCEPT
Right hand rule (1)
10.1.3 Split rings /commutator ✔ (1)
10.2.1 Mechanical/Kinetic energy to electrical energy. ✔✔ (2 or/of 0) (2)
10.2.2 (5)
OPTION 1 Vrms = Vmax✔ I = V/R✔ = 304,06/400 ✔ | OPTION 2 Vmax = ImaxR ✔ √2 = 1,075 ✔ √2 = 0,76 A✔ |
OPTION 3 Vrms = Vmax✔ | OPTION 4 Vrms = Vmax✔ Pave = I2rmsR✔ 231,13 = I2rms (400) ✔ Irms = 0,76 A✔ |
[10]
QUESTION 11
11.1.1 It tells us that light has a particle nature.✔ (1)
11.1.2 Remain the same. ✔ - For the same colour/ frequency/wavelength the energy of the photons will be the same✔. (The brightness causes more electrons to be released, but they will have the same maximum kinetic energy.)
OR
Intensity only affects the number of ejected photo-electrons and not the maximum kinetic energy or maximum speed of the ejected photo-electrons
OR
Maximum kinetic energy of ejected photo-electrons is independent of intensity of radiation (2)
11.1.3 (5)
E = W0 + Ek |
11.2 Q✓ and/en S ✓ - Emission spectra occur when excited atoms /electrons drop from higher energy levels to lower energy levels. ✓✓ (4)
[12]
TOTAL: 150