Adele
ECONOMICS PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2016
ECONOMICS
PAPER TWO (P2)
GRADE 12
NSC EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2016
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Answer FOUR questions as follows in the ANSWER BOOK:
SECTION A: COMPULSORY
SECTION B: Answer TWO of the three questions.
SECTION C: Answer ONE of the two questions. - Answer only the required number of questions. Answers in excess of the required number will NOT be marked.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write the question number above each answer.
- Read the questions carefully.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Leave 2–3 lines between subsections of questions.
- Answer the questions in full sentences and ensure that the format, content and context of your responses comply with the cognitive requirements of the questions.
- Use only black or blue ink.
- You may use a non-programmable pocket calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Write down the question number (1.1.1–1.1.8), choose the answer and make a cross (X) over the letter (A–C) of your choice in the ANSWER BOOK.
EXAMPLE: ![]()
1.1.1 An example of a variable-cost item:
- Electricity
- Rent
- Insurance
1.1.2 The slope of the demand curve of an individual firm under perfect market conditions …
- is vertical.
- is horizontal.
- slopes downwards from left to right.
1.1.3 The profitability of a monopolist depends on the cost of production and …
- savings.
- the number of competitors.
- demand.
1.1.4 The costs and benefits for third parties that are NOT included in the market price are called …
- social cost.
- externalities.
- cost of production.
1.1.5 The ratio of the GDP at current prices to the GDP at constant prices is called the … GDP deflator.
- implicit
- explicit
- constant
1.1.6 The variety of plant and animal life in a particular habitat is called …
- biodiversity.
- the carbon footprint.
- deforestation.
1.1.7 An economic situation where there is a high inflation rate together with a high unemployment rate is called ...
- deflation.
- stagflation.
- hyperinflation.
1.1.8 Tourism can help to reduce … in South Africa.
- job opportunities
- savings
- poverty (8 x 2)
(16)
1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches the item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.9 J.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.2.1 Private cost | A a general increase in prices caused by an increase in factor costs (8 x 1) (8) |
1.3 Give ONE term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 The profit that the producer receives over and above the normal profit
1.3.2 The duration (period) during which at least one factor of production is fixed
1.3.3 Where buyers and sellers of goods and services interact for trading purposes
1.3.4 The legal right whereby the holder obtains the exclusive right to manufacture a product
1.3.5 Gases that trap the heat within the Earth's atmosphere and contribute to global warming
1.3.6 The value of the alternative that is sacrificed when a choice is made in the production of two products (6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK. QUESTION 2: MICROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES 2.1 Answer the following questions.
2.1.1 Name any TWO institutions that regulate unfair competition in South Africa. (2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 How will producers benefit from minimum prices that are implemented by the government? (1 x 2) (2)
2.2 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow. 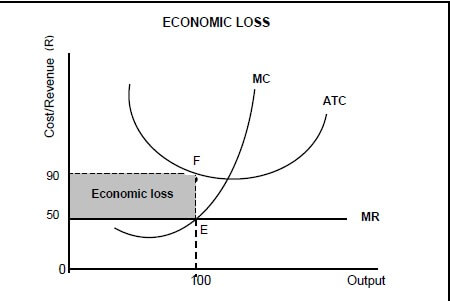
2.2.1 Identify the market structure in the graph above. (1)
2.2.2 Give the value of the market price depicted above. (1)
2.2.3 How will this equilibrium position change in the long run (long term)? (2)
2.2.4 What conditions must exist for this firm to shut down? (2)
2.2.5 Calculate the economic loss faced by this firm. (4)
2.3 Study the illustration below and answer the questions that follow. 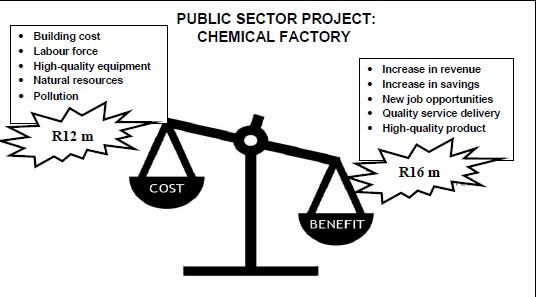
2.3.1 Identify ONE external cost in the project above. (1)
2.3.2 Identify a social benefit in the project above. (1)
2.3.3 What can the government do to reduce the external cost of the project above? (2)
2.3.4 How will the government benefit from the approval of the project above? (2)
2.3.5 Why should the government do a cost-benefit analysis before starting each new project? (2 x 2) (4)
2.4 Differentiate between productive inefficiency and allocative inefficiency. (2 x 4) (8)
2.5 How may differentiated products influence consumers and producers in a monopolistic competitive market? (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
3.1 Answer the following questions.
3.1.1 Name any TWO millennium development goals that form part of international agreements that ensure a sustainable environment. (2)
3.1.2 How may taxes be used to ensure environmental sustainability? (1 x 2) (2)
3.2 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
LABOUR MARKET – WAGE DEMANDS The National Union of Mineworkers (NUM) demanded an 84% rise in basic pay for entry-level gold-mining workers, a near 10 percentage point increase on previous demands. NUM, which represents 57% of the workers in the gold-mining industry, wants employers to pay entry-level workers R10 500 per month. [Source: www.publicnewshub.com, June 2015] |
3.2.1 Identify the percentage wage increase in the extract above that was demanded by workers in the transport industry. (1)
3.2.2 Which labour union represents the workers in the mining sector above? (1)
3.2.3 Why is the wage demand by the transport workers unrealistic? (2)
3.2.4 Briefly explain ONE reason for the excessive wage demand above. (2)
3.2.5 What will the impact be on the mining industry if the entry-level workers' wage demands of R10 500 per month are met? (2 x 2) (4)
3.3 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.
|
GLOBAL WARMING: THE DEBATE There is a 97 per cent consensus among climate experts and in climate science literature that humans are causing global warming. The scientific evidence of this question is overwhelming. [Adapted from Skeptical Science, September 2015] |
3.3.1 What, according to the information above, should be reduced to avoid global warming? (1)
3.3.2 Identify ONE negative effect of global warming. (1)
3.3.3 Briefly describe the term climate change. (2)
3.3.4 Why do businesses resist changing to more environmentally friendly production methods? (2)
3.3.5 What can be done to reduce the emissions caused by the burning of fossil fuels? (2 x 2) (4)
3.4 Differentiate between conservation and preservation. (2 x 4) (8)
3.5 How will you advise the Minister of Tourism to overcome the impact of negative externalities generated by tourism? (4 x 2) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: MICROECONOMICS AND CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
4.1 Answer the following questions.
4.1.1 Name any TWO types of tourism. (2 x 1) (2)
4.1.2 Why is a perfect competitor unable to influence the market price? (1 x 2) (2)
4.2 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow.
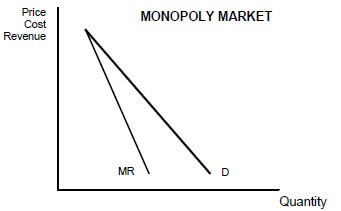
4.2.1 Which curve represents the average revenue (AR) curve? (1)
4.2.2 How many firms dominate this type of market? (1)
4.2.3 Why does the marginal revenue (MR) curve lie below the demand curve? (2)
4.2.4 Why will the monopolist not be able to charge excessively high prices for his/her product? (2)
4.2.5 Redraw the graph above into the ANSWER BOOK. Indicate economic profit on your graph by inserting the average cost (AC) curve and marginal cost (MC) curve on the same set of axes. (4)
4.3 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
TOURISM: A KEY GROWTH SECTOR Tourism is regarded as a modern-day engine of growth and is one of the largest industries globally. In 2014, G20 heads of state recognised tourism as a driver of growth and development, as well as a sector with the potential to spur global economic recovery. [Adapted from South Africa.info, May 2016] |
4.3.1 Give ONE reason in the extract above why South Africa is regarded as a very popular tourist destination. (1)
4.3.2 Identify in the extract above why the tourism industry has been earmarked as a key sector. (1)
4.3.3 Briefly describe the term tourism. (2)
4.3.4 Give ONE reason why the tourism industry is growing at such a high rate. (2)
4.3.5 In your opinion, how can the tourism industry benefit the poor, rural communities of South Africa? (2 x 2) (4)
4.4 Explain the goals of the South African competition policy. (8)
4.5 How do consumers as key market roleplayers fail to protect the environment? (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer any ONE of the two questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK. Your answer will be assessed as follows:
STRUCTURE OF ESSAY | MARK ALLOCATION |
Introduction | Max. 2 |
Body | Max. 26 Max. 10 |
Conclusion
| Max. 2 |
TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 5: MICROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
The oligopoly is a necessary market structure in a free-market system.
- Discuss in detail an oligopoly as a market structure. (26 marks)
- Explain, with the aid of a well-labelled graph, why the oligopolist will not compete on price to increase his/her market share. (10 marks)
[40]
QUESTION 6: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
Inflation originates from the demand side or supply side of the economy.
- Examine in detail the causes of demand-pull inflation. (26 marks)
- How successful have monetary policy measures been in combatting demand-pull inflation in South Africa? (10 marks)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
ECONOMICS PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2016
ECONOMICS
PAPER ONE (P1)
GRADE 12
NSC EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2016
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Answer FOUR questions as follows in the ANSWER BOOK:
SECTION A: COMPULSORY
SECTION B: Answer TWO of the three questions.
SECTION C: Answer ONE of the two questions. - Answer only the required number of questions. Answers in excess of the required number will NOT be marked.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write the question number above each answer.
- Read the questions carefully.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Leave 2–3 lines between subsections of questions.
- Answer the questions in full sentences and ensure that the format, content and context of your responses comply with the cognitive requirements of the questions.
- Use only black or blue ink.
- You may use a non-programmable pocket calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Write down the question number (1.1.1–1.1.8), choose the answer and make a cross (X) over the letter (A–C) of your choice in the ANSWER BOOK.
EXAMPLE: ![]()
1.1.1 Goods characterised by non-rivalry and non-excludability are known as … goods.
- public
- common
- private
1.1.2 The national aggregate that represents the value added in each phase of production is called the gross domestic …
- expenditure.
- product.
- income.
1.1.3 Large public corporations or business entities in the public sector are known as …
- corporates.
- enterprises.
- parastatals.
1.1.4 An exchange rate system where the forces of supply and demand entirely establish the value of a currency is called a … exchange rate system.
- fixed
- managed
- free-floating
1.1.5 The standard of living of a population is best described by the …
- balance of trade.
- per capita income.
- inflation rate.
1.1.6 Monetary policy focuses on … and the aggregate money supply.
- income
- interest rates
- taxation
1.1.7 The process whereby people move from rural areas to towns and cities is called …
- urbanisation.
- immigration.
- emigration.
1.1.8 A piece of land that forms a passageway that allows access from one area to another and is part of regional development is called a …
- custom.
- corridor.
- freeway. (8 x 2) (16)
1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches the item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.2.1 Globalisation | A the rate banks are paying for lending money from the central bank (8 x 1) (8) |
1.3 Give ONE term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 A fluctuation in economic activities over a period of time
1.3.2 The distance from the trend line to the peak and the trough
1.3.3 A tariff imposed as a percentage of the value of goods imported
1.3.4 The Act that promotes equal job opportunities for all
1.3.5 Compares a country's export prices to its import prices by means of indexes
1.3.6 People within the economically active population who are willing and able to work but cannot find a job (6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK. QUESTION 2: MACROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES 2.1 Answer the following questions.
2.1.1 Name TWO types of business cycles. (2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 How will foreign direct investment benefit the South African economy? (1 x 2) (2)
2.2 Study the cartoon below and answer the questions that follow. 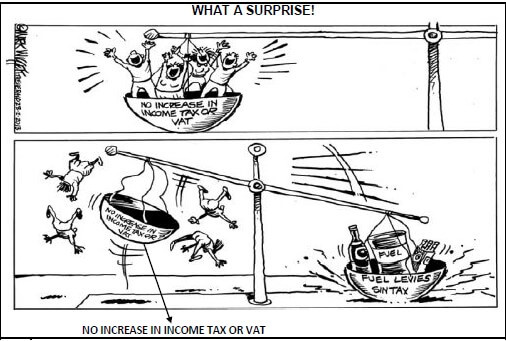
[Source: Business Times, February 2016]
2.2.1 Identify TWO indirect taxes in the cartoon above. (2 x 1) (2)
2.2.2 Name the fiscal instrument represented by the scale in the cartoon above. (2)
2.2.3 What is the 'surprise' depicted in the cartoon above? (2)
2.2.4 In your opinion, why did the Minister of Finance decide to keep income tax and VAT at the same levels? (2 x 2) (4)
2.3 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
SOUTH AFRICA OPENS DOORS FOR CHICKEN IMPORTS FROM THE UNITED STATES The Minister of Trade and Industry said South Africa will end punishing duties on US chicken and renew imports. [Adapted from Mail & Guardian, February 2016] |
2.3.1 Identify the reason in the extract why South Africa agreed to import chicken from the US. (1)
2.3.2 Name the trade initiative mentioned above. (1) 2.3.3 Briefly describe the term dumping. (2)
2.3.4 What will be the effect of population growth in South Africa on chicken imports from the US? (2)
2.3.5 What negative impact could this deal have on the local poultry industry? (2 x 2) (4)
2.4 Distinguish between exogenous approaches and endogenous approaches to business cycles. (2 x 4) (8)
2.5 How can imports be targeted to reduce the deficit on the balance of trade in South Africa? (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: ECONOMIC PURSUITS 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
3.1 Answer the following questions.
3.1.1 Name TWO social indicators related to income distribution. (2 x 1) (2)
3.1.2 How can deregulation benefit the business sector of South Africa? (1 x 2) (2)
3.2 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.
Though the NDP, which outlines a plan to address issues in SA, is not perfect, it provides a road map to where government would like us to be in 2030. The NDP provides an opportunity for South Africans to work together to confront our challenges and build a better future for ourselves and future generations. Let us not squander this opportunity. [Adapted from NDP and Mail & Guardian, February 2015] |
3.2.1 Identify any TWO previous strategies in the information above that were used to improve economic growth in South Africa. (2 x 1) (2)
3.2.2 State the main aim of the NDP. (2)
3.2.3 What negative impact will the NDP have on taxpayers? (2)
3.2.4 In your opinion, how successful will the implementation of the NDP be in the South African economy? (4)
3.3 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
LIVING STANDARDS – SOUTH AFRICA
The data shows the relative success of the government's service delivery efforts despite continuing backlogs and the fact that in many cases the quality of services delivered should have been higher. [Adapted from Institute of Race Relations, February 2016] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
3.3.1 What happened to the standard of living of South Africans between 1996 and 2015? (1)
3.3.2 Identify an element of the Human Development Index (HDI) in the information above. (1)
3.3.3 What can the government do to improve the quality of service delivery even further? (2)
3.3.4 How can the private sector get involved through public-private partnerships to strengthen the efforts of government? (2)
3.3.5 In your opinion, how can labour market access drive future improvement in living standards? (2 x 2) (4)
3.4 Briefly discuss growth and trade as globalisation challenges that face developing countries. (2 x 4) (8)
3.5 How does South Africa comply with various international bodies that require them to standardise their indicators? (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: MACROECONOMICS AND ECONOMIC PURSUITS
40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
4.1 Answer the following questions.
4.1.1 Give TWO reasons for public sector failure. (2 x 1) (2)
4.1.2 How will a decrease in export prices affect our country's terms of trade? (1 x 2) (2)
4.2 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow. 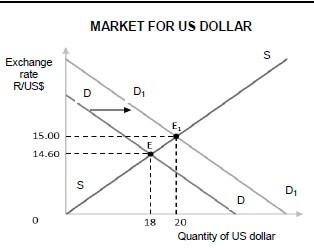
4.2.1 What market is depicted in the graph above? (1)
4.2.2 What effect does the shift in the demand curve have on the price of dollars? (1)
4.2.3 Briefly describe the term exchange rate. (2)
4.2.4 What will the effect of the new price for dollars be on export trade between South Africa and the United States? (2)
4.2.5 Explain how an increase in the number of US tourists to South Africa will influence the value of the rand. (2 x 2) (4)
4.3 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
SA ECONOMY CLOSING IN ON A RECESSION South Africa's economy is at risk of falling into a recession, the World Bank said, as it cut the nation's growth forecast for this year to 0,8%. [Adapted from Fin24, February 2016] |
4.3.1 Give TWO factors in the extract above that contributed to the poor performance of the South African economy. (2)
4.3.2 When is a country officially in a recession? (2)
4.3.3 What impact will a downgrading of South Africa's credit rating have on its economy? (2)
4.3.4 In your opinion, what can government do to stabilise the business cycle? (2 x 2) (4)
4.4 Briefly discuss any TWO arguments in favour of privatisation. (2 x 4) (8)
4.5 How will subsidies influence export-orientated businesses negatively? (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer any ONE of the two questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK. Your answer will be assessed as follows:
STRUCTURE OF ESSAY | MARK ALLOCATION |
Introduction | Max. 2 |
Body | Max. 26 Max. 10 |
Conclusion
| Max. 2 |
TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 5: MACROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
The circular-flow model shows how the economy works via the various markets.
- Discuss the role of the various markets in the circular flow without the use of a diagram. (26 marks)
- Explain the multiplier concept with the aid of a well-labelled graph. (10 marks)
[40]
QUESTION 6: ECONOMIC PURSUITS 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
Government actions encourage operations and new investments to boost industrial development.
- Discuss South Africa's Spatial Development Initiatives (SDIs), highlighting its initiatives, objectives and Industrial Development Zones (IDZs). (26 marks)
- What advice would you give government to promote industrial development in South Africa? (10 marks)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
CONSUMER STUDIES PAPER GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2016
CONSUMER STUDIES PAPER
GRADE 12
NSC EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2016
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions.
QUESTION | CONTENT | MARKS | TIME (minutes) |
1 | Short Questions (All topics) | 40 | 20 |
2 | The Consumer | 20 | 20 |
3 | Food and Nutrition | 40 | 40 |
4 | Clothing | 20 | 20 |
5 | Housing | 40 | 40 |
6 | Entrepreneurship | 40 | 40 |
TOTAL: | 200 | 180 | |
- ALL the questions are COMPULSORY and must be answered in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- You may use a calculator.
- Write in black or blue ink only.
- Pay attention to spelling and sentence construction.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTION 1: SHORT QUESTIONS
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Write down the question number (1.1.1–1.1.20), choose the answer and make a cross (X) over the letter (A–D) of your choice in the ANSWER BOOK.
EXAMPLE: ![]()
1.1.1 Municipalities are responsible for ...
- housing subsidies.
- refuse removal.
- security services.
- shopping centres. (1)
1.1.2 This body collects taxes on behalf of the government:
- National Consumer Forum
- Department of Finance
- South African Bureau of Standards
- South African Revenue Services (1)
1.1.3 This practice shows the most sustainable use of electricity:
- Boil water on a stove instead of using a kettle.
- Tumble dry clothes instead of ironing them.
- Reheat food in a microwave oven instead of using a conventional oven.
- Use an electric heater in winter instead of an electric blanket. (1)
1.1.4 Type 2 diabetes is controlled with …
- a normal diet.
- insulin injections.
- oral medication.
- vigorous exercise. (1)
1.1.5 A possible cause of hyperactivity in some children:
- Additives
- Anaemia
- Bulimia
- Diabetes (1)
1.1.6 When the nutrient content of a product is marked as 'low fat', it means the product contains … fat.
- no
- very little
- a moderate amount
- a high amount (1)
1.1.7 A possible advantage of genetically modified food:
- Healthier because no chemicals have been used
- No negative impact on the soil
- More people can be fed
- No antibiotics are used (1)
1.1.8 Study the signs below and indicate which ONE would be best to place in a takeaway restaurant to prevent the transmission of food-borne diseases.
[Source: Google Images]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4 (1)
1.1.9 The stage in the fashion cycle when clothing prices are marked down and sold at sales:
- Decline
- Innovation
- Peak
- Rise (1)
1.1.10 A characteristic that distinguishes a fashion fad from a classic style:
- Style appropriate for older people
- Timeless style
- Style with sudden popularity
- Style appropriate for most people (1)
1.1.11 Transfer duty:
- Charged to register the mortgage bond and title deed
- Government tax payable every time a property changes hands
- Payment to the estate agent who oversees the transfer process
- Payment to the attorney who draws up the bond document (1)
1.1.12 This insurance is the responsibility of a tenant:
- Bond protection insurance
- Homeowner's insurance
- Household insurance
- Lease agreement insurance (1)
1.1.13 The feature of a washing machine that shows a principle of universal design:
- Pictures and instructions appear in different languages in the manual
- The door at the front can open at an angle of 90°
- Touch-control buttons at the back of the washing machine
- Different cycles, for example economy cycle or rinse-only cycle (1)
1.1.14 The CORRECT statement regarding a government housing subsidy:
- South African citizens may receive it twice.
- An applicant must be married or have dependants.
- Any South African citizen may apply.
- It can be paid off over a period of 20 years. (1)
1.1.15 A disadvantage of building one's own house:
- Not cheap to start a new garden
- Not possible to customise the design to individual needs
- The building loan does not cover increases in municipal costs
- The house cannot be finished on a flexible schedule (1)
1.1.16 Procedure to ensure that the required standards of products are met:
- Product specifications
- Inventory management
- Quality control
- Financial control (1)
1.1.17 Maintaining equipment in a business is important, as it contributes to …
- efficient training of workers.
- improved storage procedures.
- selling products at a higher price.
- the efficient production of products. (1)
1.1.18 The key principle in designing an advertising pamphlet:
- To save printing costs, do not use pictures.
- Make the pamphlet small to save paper.
- Provide a lot of information to read.
- The headline must attract attention. (1)
1.1.19 The function of a cash flow projection for a business:
- To ensure sufficient cash to meet expenses
- To prevent poor stock control in the business
- To maintain quality control if there is adequate cash
- To ensure sustainable production of quality products (1)
1.1.20 The business that most likely shows sustainable profitability:
- Business A has many short-term goals.
- Business B uses social media to keep in touch with customers.
- Business C increases selling prices to have a competitive edge.
- Business D plans to take out a loan to pay the workers. (1)
1.2 Choose the symptoms from COLUMN B that match the food-borne disease in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–F) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.4) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.5 G.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.2.1 Dysentery | A cramps, diarrhoea that starts watery but may become bloody (4 x 1) (4) |
1.3 Give ONE word/term for each of the descriptions below. Write only the word/term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 A group of people who have joined together to pledge regular contributions to a common fund for specific purposes (1)
1.3.2 After declining a telephonic business offer, money was still deducted from the consumer's bank account (1)
1.3.3 Goods that have been imported into a country through unofficial or unauthorised distribution channels (1)
1.3.4 Members receive compensation for recruiting other members rather than from the sale of any goods or services (1)
1.3.5 According to the Consumer Protection Act, 2008 (Act 68 of 2008) a consumer has five days to cancel a transaction that resulted from direct marketing, without providing a reason or without financial implications (1)
1.3.6 Products are sold and salespeople receive a portion of the sales from a lower tier (1)
1.4 Select FOUR possible reasons why a business would reach its best sales scenario. Write only the letters (A–H) next to the question number (1.4) in the ANSWER BOOK.
A Customers had money available to buy the products.
B Expensive and luxurious packaging was used.
C Maintenance of equipment was done regularly.
D Products were good value for money.
E The business achieved its sales objective.
F The business grew due to good marketing.
G The business sold less than the break-even point.
H The staff was well trained and well paid. (4)
1.5 Choose the clothing item in each set of four options that would be the best choice to wear with the classic navy chino pants below to comply with the professional dress code of a corporate company. Write only the letter (A–X) next to the question number (1.5.1–1.5.6) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.5.7 Y.
Classic navy chino
Clothing items to choose from:





[Source: www.woolworths.co.za]
(6)
[40]
QUESTION 2: THE CONSUMER
2.1 Name TWO forms of renewable energy. (2)
2.2 Explain the term phishing. (3)
2.3 Read the extract below and answer the question that follows.
The Minister of Finance announced in his interim budget speech of October 2015 that an increase in VAT remains one of the options for 2016 to address shortfalls in revenue. [Adapted from The Star Business Report, 22 October 2015] |
Explain how an increase in VAT will affect food prices and the disposable income of South African consumers. (4)
2.4 Read the information below and answer the questions that follow.
Living in South Africa is not as cheap as it used to be because prices keep rising. The value of the rand keeps fluctuating. The country imports many products. The rise in the cost of petrol, diesel and consumer products over the last few years does not make the cost of living any cheaper. Clothing and consumer items, like computers, are marginally cheaper in South Africa. [Own text] |
2.4.1 Quote a sentence from the information above to describe the term inflation. (1)
2.4.2 Use the information above and identify TWO items that could be included in the 'consumer basket' when assessing the consumer price index. (2)
2.5 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.
Water flows into the shower head where it is mixed with air and compressed. The air-and-water mixture is forced out of the shower head, creating a strong shower stream at a very low flow rate. [Source: www.asparkleofgenius.com/bricor shower-head-review] | 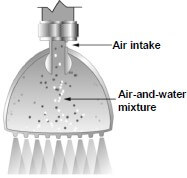 |
Discuss how installing this shower head may contribute to the sustainable consumption of:
2.5.1 Water (2)
2.5.2 Electricity (2)
2.6 Read the extract below and answer the question that follows.
ADVICE RETIRED PEOPLE WOULD GIVE TO THEMSELVES IF THEY WERE YOUNGER
[Adapted from Saturday Star, 7 November 2015] |
Choose any TWO of the statements above and analyse how retired consumers will benefit from EACH.
(4)
[20]
QUESTION 3: FOOD AND NUTRITION
3.1 Define the term obesity. (1)
3.2 Name FOUR points to keep in mind when treating gastroenteritis in adults. (4)
3.3 Study the information below that appeared on the label of a bottle of pasta sauce and answer the questions that follow.
SUNDRIED TOMATO AND PECORINO CHEESE PASTA SAUCE Ingredients [Source: 'Mrs Brown's Sundried Tomato and Pecorino Cheese Pasta Sauce'] |
3.3.1 Which ingredient is present in the largest quantity? (1)
3.3.2 Identify the ingredient that is most commonly irradiated. (1)
3.3.3 Identify THREE ingredients on the label that contain one or more of the most common allergens. (3)
3.3.4 Explain the function of sorbic acid as a chemical preservative in this product. (2)
3.3.5 Discuss why this product is NOT suitable for the prevention of osteoporosis. (2)
3.4 Study the menus for BREAKFAST A and BREAKFAST B below and answer the questions that follow.
BREAKFAST A Strawberry, mango, kiwifruit slices | BREAKFAST B Chocolate croissants with cream |
3.4.1 Identify TWO food items on the menus that must be avoided by a person with lactose intolerance. (2)
3.4.2 Explain why BREAKFAST B will contribute to arteriosclerosis. (6)
3.4.3 Give THREE reasons why BREAKFAST A will be the best choice to manage anaemia. (6)
3.5 Read the extract below and answer the question that follows.
A report from the Academy of Science of South Africa stated that most South Africans lack the following six micronutrients in their diet: Vitamin A, B vitamins, folic acid, selenium, iron and zinc. This has a serious influence on people living with HIV/Aids and tuberculosis. [Source: Die Burger, 15 August 2013] |
Explain why the nutrients in the extract above will have a positive influence on people with HIV/Aids. (4)
3.6 South Africa often experiences periods of drought. Analyse how droughts may affect food security and the South African economy negatively. (8) [40]
QUESTION 4: CLOTHING
4.1 Define the term dress code. (2)
4.2 Write a paragraph to explain what eco-friendly fabrics are. (6)
4.3 Explain how the changing role of women in the workplace has a positive influence on fashion changes by referring to the following factors:
4.3.1 Economic factors (2)
4.3.2 Social factors (2)
4.4 Study the picture below and answer the questions that follow.
 | The woman is wearing a cream-coloured jacket with a tied belt, black knee-high pants and black flat sandals. [Source: www.woolworths.co.za] |
4.4.1 Explain the optical illusions created by the use of colour in this outfit. (4)
4.4.2 Motivate why the jacket is a good choice as a basic item for a working wardrobe. (4)
[20]
QUESTION 5: HOUSING
5.1 Name TWO costs that are included in bond registration fees. (2)
5.2 State who is responsible for making the rules and regulations in a sectional title complex. (1)
5.3 Explain why monthly levies must be taken into account when buying sectional title property. (2)
5.4 Explain the following terms:
5.4.1 Mortgage bond (2)
5.4.2 Deed of sale agreement (2)
5.5 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.
GAS STOVE/HOB
[Own text with picture from Google Images] |
5.5.1 Compare a cash payment with a credit card payment when buying the gas stove. Tabulate your answer as follows:
CASH | CREDIT CARD |
(2) | (2) |
(4)
5.5.2 Explain the benefits of the following aspects of the gas stove:
- TWO universal safety design features (4)
- Human energy consumption (2)
- Non-human energy consumption (2)
5.5.3 Describe the positive impact of gas on the natural environment. (4)
5.6 Study the graph below and answer the questions that follow.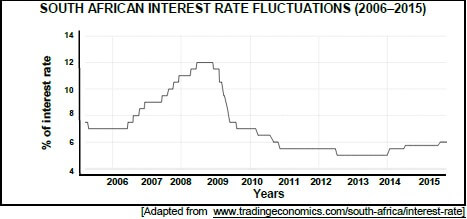
5.6.1 Identify the two-year period during which a fixed interest rate would have been more beneficial to a home owner with a mortgage bond. (1)
5.6.2 Give reasons for your answer to QUESTION 5.6.1. (2)
5.7 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
Mr Bones bought a house in an old residential area with a high crime rate. The price of the house was within his budget and he planned to rent out the house. [Own text] |
5.7.1 Discuss the disadvantages of renting out the house for Mr Bones. (4)
5.7.2 Mr Bones did not make a sound investment. Motivate the statement. (8)
[40]
QUESTION 6: ENTREPRENEURSHIP
6.1 State FOUR factors an entrepreneur must consider when choosing a suitable product for small-scale production. (4)
6.2 Give ONE example of EACH of the following types of media that could be used to advertise a product:
6.2.1 Print media (1)
6.2.2 Electronic media (1)
6.3 State the purpose of a financial feasibility study. (2)
6.4 Give reasons why it is important for a business to calculate the production cost and selling price of products accurately for sustainable profitability. (2)
6.5 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
Nelly, a Grade 11 Arts learner, sells beautiful, neatly crocheted and finished off hair bands at school and in the community. She does this to supplement her pocket money. [Own text] |
6.5.1 How does Nelly ensure that the design of the packaging for the hairbands is appealing to consumers? (6)
6.5.2
- Name the distribution method that Nelly uses to sell the hairbands. (1)
- Discuss TWO advantages of the distribution method that Nelly uses to sell her product. (2)
6.5.3 Discuss ways in which Nelly maintains sustainable production. (6)
6.5.4 Calculate the production cost and selling price of ONE hairband. Show ALL calculations and round off the final amount to the nearest rand. (7)
6.5.5 Analyse how Nelly ensures efficient production of quality products. (8)
[40]
TOTAL: 200
CONSUMER STUDIES PAPER GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2016
CONSUMER STUDIES PAPER
GRADE 12
NSC EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2016
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: SHORT QUESTIONS
1.1
1.1.1 B✔ Remembering, easy (Focus, p.182–184; Successful, p.202) (1)
1.1.2 D✔ Remembering, easy (Focus, p.163; Successful, p.180) (1)
1.1.3 C✓ Applying, moderate (Focus, p.173–4; Successful, p.192–4) (1)
1.1.4 C✔ Remembering, easy (Focus, p.72; Successful, p.81) (1)
1.1.5 A✔ Remembering, easy (Focus, p.95; Successful, p.111) (1)
1.1.6 B✔ Remembering, moderate (Focus, p.101; Successful, p.119) (1)
1.1.7 C✔ Remembering, easy (Focus, p.103; Successful, p.123–124) (1)
1.1.8 C/ D✔ Remembering, easy (Focus, p.89–91; Successful, p.103-109) (1)
1.1.9 A✔ Understanding, easy (Focus, p.49–50; Successful, p.50) (1)
1.1.10 C✔ Understanding, easy (Focus, p.49; Successful, p.51) (1)
1.1.11 B✔ Remembering, easy (Focus, p.128; Successful, p.146) (1)
1.1.12 C✔ Understanding, difficult (Focus,p.127–128;Successful, p.145) (1)
1.1.13 A/ D✔ Applying, difficult (Focus, p.137; Successful, p.157) (1)
1.1.14 B✔ Understanding, moderate (Focus, p.130; Successful, p.149) (1)
1.1.15 A✔ Understanding, easy (Focus, p.120; Successful, p.138) (1)
1.1.16 C✔ Remembering, moderate (Focus, p.16; Successful, p.22) (1)
1.1.17 D✔ Remembering, easy (Focus, p.25; Successful, p.25) (1)
1.1.18 D✔ Remembering, easy (Focus, p.31; Successful, p.30) (1)
1.1.19 A✓ Remembering, moderate (Focus, p.40; Successful, p.42) (1)
1.1.20 B✓ Applying, moderate (Focus, p.35; Successful, p.34) (1)
1.2
1.2.1 F✔ (Focus, p. 90; Successful, p. 107) (1)
1.2.2 A/ D✔ (Focus, p. 90; Successful, p. 106) (1)
1.2.3 C✔ (Focus, p. 89; Successful, p. 104) (1)
1.2.4 B✔ (Focus, p. 89; Successful, p. 103) (1)
Remembering, moderate
1.3
1.3.1 Stokvel/ savings club✓ (Foc, p. 161; Suc, p. 177) (1)
1.3.2 Unfair business practice/ scam/ fraud✓ (Foc, p. 157; Suc, p. 174) (1)
1.3.3 Grey goods/ parallel imports✓ (Foc, p. 158; Suc, p.176) (1)
1.3.4 (Illegal) Pyramid scheme✓ (Foc, p. 162; Suc, p.179) (1)
1.3.5 Cooling-off period✓ (Foc, p. 157; Suc, p. 173) (1)
1.3.6 Tiered-level scheme/ multilevel marketing scheme/ legal pyramid scheme✓ (Foc, p. 162; Suc, p. 179) (1)
Remembering, moderate
1.4
A✔ (in any sequence)
D✔
E✔
F✓ (4)
Understanding, moderate (Focus, pages 39–40; Successful, page 41)
1.5
1.5.1 D✔
1.5.2 F✔
1.5.3 I✔
1.5.4 O/ P✓
1.5.5 R✓
1.5.6 X✓ (6)
Analysing; applying, moderate (Focus, pages 56–60; Successful, pages 59–65) [40]
QUESTION 2: THE CONSUMER
2.1 Name TWO forms of renewable energy.
- Water energy/ hydroelectricity/ hydro power/ tidal energy✔1
- Wind (energy)✔2 (Not air energy)
- Solar/sun (energy)✔3
- Energy from wood/ dung/ fuel/ vegetable matter/ vegetable oil/ bio-energy/ bio-mass✔4
- Geothermal✔5 (Any 2) (2) Remembering, easy (Focus, pages 171–172; Successful, pages 191–192)
2.2 Explain the term phishing.
- Phishing e-mails are fake e-mails/ phone call/ website✔1
- usually pretending to be legitimate from banks/ other financial institutions,✔2
- asking the consumer to change his/ her personal details/ financial information/ tricks the consumer into giving his/ her credit card number, account user name and password to the phishers.✔3
OR - When an e-mail message/ website/ phone call✔4
- is designed to steal money from an unsuspecting consumer.✔5
- It is sometimes used for identity theft.✓6 (Any 3) Remembering, easy (Focus, pages 159–160; Successful, pages 176–177)
2.3 Explain how an increase in VAT will affect food prices and the disposable income of South African consumers.
- Some basic food items (brown bread/ maize meal/ lentils/ milk powder/ dried mealies/ mealie rice/ samp/ rice/ milk/ fruit/ vegetables/ eggs) are excluded/exempted from VAT/ zero-rated,✓1 these products will still be zero-rated after an increase in VAT.✓2
- If VAT increases, the production cost/ electricity/ transport/ water/ overheads of all food items (regardless if zero rated or not) will increase,✓3 and this will lead to higher food prices✓4, reducing the disposable income of consumers.✓5
- Consumers, especially lower income consumers, will suffer more/ consumers may not be able to meet their basic needs✓6 and consumers will purchase fewer products.✓7 (Any 4) (4)
Understanding, moderate (Focus, pages 164-165; Successful, page 181)
2.4
2.4.1 Quote a sentence from the information above to describe the term inflation.
- Living in South Africa is not as cheap as it used to be because prices keep climbing/rising✓1
- A rise in the costs of petrol, diesel and consumer products which have seen increases in the last few years✓2
- The value of the rand keeps fluctuating.✓3 Any 1) (1)
Remembering, easy (Focus, page 167; Successful, pages 184–85)
NOTE: Accept 'prices keep rising', it doesn’t have to be a full sentence.
2.4.2 Use the information above and identify TWO items that could be included in the 'consumer basket' when assessing the consumer price index.
- Petrol✓
- Diesel✓
- Clothing✓
- Computers✓
- Consumer products✓ (Any 2) (2)
Remembering, easy (Focus, pages 164–165; Successful, page 181)
2.5 Discuss how installing this shower head may contribute to the sustainable consumption of:
2.5.1 Water
This type of shower head uses 50%/ 60% less/ less water/saves water✓1 but still retains the pressure/ power/ force of water.✓2 (2)
2.5.2 Electricity
This saves electricity / less electricity is used✓1 as less heated water leaves the geyser.✓2 (2)
Understanding, moderate (Focus, p 180; Successful, page, 199)
2.6 Save more, save longer, delay your retirement:
- This will help to accumulate wealth/ have more money✔1as savings gain (compound) interest.✔2
- The longer one saves the more money is accumulated✔3 to help combat inflation/ increasing prices of goods and services.✔4
- Normally retirement income is less than income when working/ employed.✔5
- You will have more money for luxuries/ holidays/ helping your children✓6 (Any 2)
Have a good medical aid with a comprehensive cover:
- As one ages health deteriorates.✔1 Medical needs will become more.✔2 Therefore a comprehensive medical aid will ensure that medical needs are covered/ You will have to pay less out of your pocket✓3
- Inflation will cause an increase in the cost of medical expenses✓4 and will impact on the budget having less money available for daily living expenses.✔5
- Get good/ better health care/ do not have to go to the clinic.✓6 (Any 2)
Pay off your mortgage before retirement:
- The quicker a mortgage bond/ loan is paid off, less interest is paid.✔1
- When the bond is paid off, no monthly payments are due✓2 which increases the disposable income. ✔3
- A paid off property is an asset/ investment.✓4
- If the mortgage bond/ home loan is not paid off before retirement the instalments✔5 may not be affordable on pension/ retirement money/ income/ property may be repossessed.✓6
- May become dependent on other family members.✔7 (Any 2x2) (4)
Analysing, difficult (Focus, pages 166–169; Successful, pages 183–184)
NOTE: TWO marks can be awarded for any TWO of the three aspects.
[20]
QUESTION 3: FOOD AND NUTRITION
3.1 Define the term obesity.
- Obesity is a condition of excessive/ too much fatness/ body fat/ weight exceeds the standard based on height/ BMI is over 30/ when an individual is over 20% of normal weight.✓ (1)
Remembering, easy (Focus, page 83; Successful, page 96)
NOTE: Do not accept overweight
3.2 Name FOUR points to keep in mind when treating gastroenteritis in adults.
- Stop eating solid foods for a few hours so that your stomach can settle.✓1
- Avoid water of uncertain quality/ drink bottled water/ boiled water/ clear liquid/ fruit juices/ sports drinks/ drink at least 200 ml an hour for adults.✓2
- Prevent or treat dehydration/ prevent dehydration✓3 by sucking on ice or ice lollies/ take small, frequent sips of liquid
- Take electrolytes, e.g. sorol/ rehydrate solution/ mixture of boiled water, sugar and salt/ sports drink✓4
- Start eating again slowly/ gradually.✓5
- Eat foods that are usually well tolerated/ easily digested such as dry toast/ jelly/ bananas/ grated apple/ rice/ clear soup.✓6
- Avoid dairy products/ caffeine/ alcohol/ fatty food/ spicy food.✓7
- Consult a doctor/ clinic rather than attempt self-medication if the diarrhoea is severe/ it does not improve within several days/ there is blood and/ or mucus in the stool/ fever occurs with shaking chills/ or there is dehydration with persistent diarrhoea.✓8
- Rest✓9 (Any 4) (4) Remembering, easy (Focus, page 91; Successful, page 109)
3.3
3.3.1 Which ingredient is present in the largest quantity?
- Filtered water✓ (1)
Remembering, easy (Focus, page 97; Successful, page 118)
- Filtered water✓ (1)
3.3.2 Identify the ingredient which is most commonly irradiated.
- Spices✓ (1)
Understanding, moderate (Focus, page 105; Successful, page 128)
- Spices✓ (1)
3.3.3 Identify THREE ingredients which contain one or more of the most common allergens
- (Fresh) cream✓
- Butter✓
- (Cheese) Pecorino✓
- Parmesan✓
- Colourant✓
- Flavourant✓ (Any 3) (3)
Remembering, easy (Focus, page 79; Successful, page 92)
3.3.4 Explain the function of sorbic acid as a chemical preservative in this product.
- It was added to lengthen the shelf-life of the product/ protect the product✓1 against deterioration/ slow down enzyme activity✓2 which could lead to food spoilage/ decay.✓3
- Makes the food safer✓4 to eat as it inhibits/ retards spoilage caused by micro-organisms✓5 which could lead to food poisoning✓6 (Any 2) (2)
Understanding, moderate (Focus, page 94; Successful, page 113)
3.3.5 Discuss why this product is NOT suitable for the prevention of osteoporosis.
- Although the product contains calcium/ phosphorus✓1 it may not have an impact on the prevention of osteoporosis as it may not be consumed regularly/ daily.✓2/ The quantities present are inadequate,✓3 may not have an impact on the prevention of osteoporosis.
- There is very little/no vitamin D✓4 to assist with the absorption of calcium.✓5 (Any 2) (2)
Applying, easy (Focus, page 76, Successful, page 90)
3.4
3.4.1 Identify TWO food items on the menus that must be avoided by a person with lactose intolerance.
- Cream✓
- Milk✓
- Low fat milk✓ (Any 2) (2)
Remembering, easy (Focus, page 79; Successful, page 93)
3.4.2 Explain why Breakfast B will contribute to arteriosclerosis.
- Chocolate croissants/ cream/ full cream milk/ beef sausages/ fried egg/ butter/ non-dairy whitener✓1 contains animal/ (saturated) fat✔2 that forms plaque✓3 which will narrow/ clog the arteries/ blood vessels/ ✔4 and raise the blood cholesterol levels.✔5
- These foods are high in low-density lipoproteins/bad cholesterol,✔6 they will narrow the blood vessels/ arteries.
- Margarine spread on the bread/ chocolate in the croissants contains trans-fatty acids✔7 which will raise the low-density lipoproteins✔8 and contribute to atherosclerosis. This menu contains very little fibre✔9 which lowers cholesterol.✓10
- Excessive intake of refined carbohydrates like Corn flakes/ chocolate croissants✓11 contribute to atherosclerosis. (Any 6) (6 )
Applying, difficult (Focus, page 74; Successful, page 84)
3.4.3 Give THREE reasons why Breakfast A will be the best choice to manage anaemia.
- Strawberries/ mango/ kiwifruit is rich in vitamin C✔1 which will promote the absorption of -iron.✔2
- Muesli/ whole wheat bread/ liver contain iron✔3 to help in the formation of haemoglobin/ red blood cells.✔4 Iron from animal sources is better absorbed than iron from plant sources.✓5
- Muesli/ whole wheat bread/ liver contain folic acid✔6 which is needed for the production of red blood cells.✔7
- Liver/ egg contains vitamin B12✔8 which assists in the formation of red blood cells.✔9 (Any 3 x 2) (6)
Applying, moderate (Focus, page 77; Successful, pages 90–91)
3.5 Explain why the nutrients in the extract above will have a positive influence on people with HIV/Aids.
- All the listed nutrients/ Vitamin A, B vitamins, selenium, iron and zinc strengthen/protect/maintain the immune system.✓1
- A stronger immune system lowers the risk of infections in people with HIV/ Aids✓2
- Vitamin A keeps the linings of the lungs/ gut/ intestine healthy/intact✓3 to make it difficult for germs to enter the body and cause infections.✓4 During infections, there is an increased loss of vitamin A from the body✓5 and the vitamin A will not be replaced. Vitamin A is an anti oxidant✓6 which protects cells from damage.✓7* This helps to prevent infection✓*8 and may help to slow down the disease by keeping the immune system healthy.✓*9
- B vitamins are needed to maintain a healthy immune and nervous system.✓10
- Vitamin C/ Zinc/ Selenium protects the immune system by helping to activate available T cells.✓11 Selenium/ Vitamin C is an anti-oxidant✓12 which protects cells from damage.✓*13 This helps to prevent infection✓*14 and may help to slow down the disease by keeping the immune system healthy.✓*15
- Zinc improves the appetite.✓16
- As HIV/Aids weaken the immune system✓17, these nutrients are important to strengthen it.✓18
- For a person with HIV/Aids, these nutrients will help to fight infections✓19, improve well-being✓20, delay the development of full blown Aids✓21 and prolong life.✓22 (Any 4) (4)
NOTE: *The explanation of an anti-oxidant can only be awarded marks ONCE. The marks can be awarded for either the explanation of an anti-oxidant for vitamin A OR selenium.
Understanding, moderate (Focus, pages 84–85; Successful, pages 99–100,105)
3.6 South Africa often experiences periods of drought. Analyse how droughts may affect food security and the South African economy negatively.
- Families that plant their own vegetables/ have their own livestock/ self sufficient may not have sufficient food to eat.✔1Families may have to buy vegetables/ meat which will put extra strain on their disposable income.✔2
- A decline in food production may lead to increased food prices/ inflation.✔3 People/ the poor may not be able to afford enough food.✔4 If less fruits/ vegetables are eaten, consumers may not be able to meet their nutritional needs/ requirements,✓5 because their nutritional needs are not met they may become ill which causes more strain on the economy.✓6
- Grants may be given which will result in strain on the economy.✓7
- A decline in food production may lead to food being imported from other countries.✔8 This will lead to a further increase of food prices✓9 and more people going hungry✔10 because imported prices can be unaffordable.✔11
- South Africa may not have enough food/ preserved fruit/ wine/ avocados/ maize/ dairy products to export to other countries✔12 thus reducing the national income/ excise duty/ GDP (Gross domestic product).✔13There may be less funds/ money available to support hunger/ poverty stricken families.✔14
- If less food is produced farmers may earn less/ food factories may close down,✔15 people/ farm workers will lose their jobs✔16 resulting in less household income✔17 and less money to buy food. ✔18 With severe drought famers cull/slaughter livestock as they cannot afford to feed the animals/ stop farming.✔19 Workers become unemployed and move to urban areas which is one of the biggest strains on food security currently, as there are not enough job opportunities.✔20
- Food security statistics in South Africa reflects currently that food insecurity in urban areas is larger than in rural areas.✔21
- The inflation rate will increase.✓22
- There may be more unwanted fires,✓23 destroying farmland.
- All the above leads to more food insecurity/ less food security.✓24 (Any 8) (8)
Analysing, difficult (Focus, pages 106–107, 177–178; Successful, pages128–130)
[40]
QUESTION 4: CLOTHING
4.1 Define the term dress code.
- A dress code is a set of rules✓1 about the type of clothes the company expects employees to wear to work.✓2
- A document drawn up by a company to specify✓3 the type of dress that is acceptable for their employees.✓4
- A specific way a person should dress✓5 for a specific event at a specific time.✓6
- What you are expected to wear✓7 at a certain time, place or occasion.✓8
(Any 2) (2) Remembering, easy (Focus, page 54; Successful, page 57)
4.2 Write a paragraph to explain what eco-friendly fabrics are.
Eco-friendly fabrics are grown/ produced/ manufactured in an environmentally friendly way.✓1 Eco-friendly fabrics have a low carbon footprint.✓2 They are grown/produced from crops that require few/ do not require pesticides/
chemicals✓3 to be grown/ during processing. They use less water✓4 and energy✓5 to produce and process. They create less waste/ pollution.✓6 They are made from renewable resources (bamboo/ hemp)✓7 such as plants that yields good crops and requires less water.✓8 Organic textiles/ raw materials are used.✓9 Natural plant-based/ no harmful/ toxic dyes are used when manufacturing eco-friendly textiles.✓10 Some fibres are recycled✓11 reused✓12 to make new yarn thus reducing the need to manufacture new/ virgin fabrics/ fabric waste on landfills.✔13 Fabrics are manufactured in compliance with an ethical, social responsible code of manufacturing conduct/fair-trade.✔14 (Any 6) (6)
NOTE: Deduct ONE mark if the answer is not written in a paragraph.
Remembering, easy (Focus, page 61; Successful, page 67)
4.3
4.3.1 Explain how the changing role of women in the work place has a positive influence on fashion changes by referring to the following factors:
Economic factors
- When the economy grows it creates more job opportunities for women/ more women work✓1 and they have money/ more wealth/ they can afford✓2 to buy more clothes/ dress themselves as they please✓3 and this stimulates fashion change.✓4
- More women work✓5 and need professional/ formal clothes suitable for the workplace✓6 which leads to a positive change in fashion.✓7
- Because women are working, they become credit worthy,✓8 they buy more clothes✓9 and this stimulates fashion change.✓10 (Any 2) (2)
Applying, moderate (Focus, pages 49, 51; Successful, pages 53–54)
4.3.2 Social factors
- Women travel more/ have more mobility✓1 and this creates a need for comfortable clothes/ casual clothes✓2 which stimulates fashion change.✓3
- Women are more aware of their health/ body shape/ go to the gym/ exercise✓4 and this influences the development of sportswear.✓5
- Women copy celebrities/ women in leadership positions whom they admire✓6 and fashion designers continually develop new and innovative fashions to cater for the changing needs.✓7
- Women attend corporate functions ✓8 and need formal clothes,✓9 resulting in fashion change.✓10
- Cross cultural contact✓11 stimulates fashion change.✓12 (Any 2) (2)
Applying, moderate (Focus, page 49, 51; Successful, pages 53–54)
NOTE: 'Stimulates fashion change' cannot be awarded a mark if it stands on its own.
4.4
4.4.1 Explain the optical illusions created by the use of colour in this outfit.
- The two contrasting colours/ light colour used in the jacket✓1 visually cut the body in half/ two parts✓2 and create the illusion that the woman is shorter.✓3
- The cream colour creates a horizontal line✓4 over the hips. This creates the illusion that the hips are wider.✓5
- The light jacket/ colour✓6 creates the illusion that the upper body of the woman is bigger/ larger/ broader.✓7
- The dark pants/ colour✓8 creates the illusion that the lower body is smaller/ narrower and above the knee makes the lower body shorter.✓9 (Any 4) (4)
Applying, difficult (CAPS, Grade 11 work)
4.4.2 Motivate why the jacket is a good choice as a basic item for a working wardrobe.
- The jacket is suitable as it looks formal/ professional/ presentable/ sophisticated.✓1
- The style is classic✓2 and she will be able to wear it for a long time/ timeless.✓3
- It is versatile/ suitable for summer and winter/ can be mixed and-matched✓4 with skirts/ trousers/ dress
- The colour is neutral/ plain/ basic and can be mixed and matched with other colours.✓5
- It fits well/ compliments the figure/ not revealing.✓6
- The jacket is perceived to be good quality.✓7 (Any 4) (4)
Evaluating, moderate (Focus, pages 53–58; Successful, pages 62–64)
[20]
QUESTION 5: HOUSING
5.1 Name TWO costs that are included in bond registration fees. • Attorney's fee✓ for drawing up the bond documents/registering the bond
- Taxes/ stamp duty✓
- Postage✓
- Deeds office (bond registration) fees✓
- VAT✓ (Any 2) (2)
Remembering, easy (Focus, page 127; Successful, page 146)
5.2 State who is responsible for making the rules and regulations in a sectional title complex.
- Body corporate✓ (1)
Remembering, easy (Focus, page 123; Successful, page 141)
5.3 Explain why monthly levies must be taken into account when buying sectional title property.
- Levies must be paid every month/ compulsory.✓1
- Levies may possibly increase/ rise every year/ due to inflation.✓2
- The buyer must budget✓3 to ensure that he/ she can afford to pay the levies.✓4 (Any 2) (2)
Understanding, easy (Focus, pages 122–123; Successful, pages 140–141)
5.4 Explain the following terms
5.4.1 Mortgage bond
A mortgage bond is a loan/money✔1 that is secured on immovable property / house / gives the right over a property.✓2
OR
Borrowed money / a loan✔3 made to the property owner where the property is the security for the loan.✔4
OR
A document that the buyer signs to promise/agree that he / she will pay back the loan✔5 made for a property/house.✓6 (Any 2) (2)
Remembering, moderate (Focus, page 126; Successful, page 145)
5.4.2 Deed of sale agreement
- A formal written legal/ signed agreement/ terms and conditions✓1 between a buyer and seller/ both parties✓2 of property.
- The offer to purchase becomes the deed of sale✓3 after signed by the buyer and seller/ both parties✓4 of property. (Any 2) (2)
Remembering, easy (Focus, page 125; Successful, page 142)
5.5
5.5.1 Compare a cash payment with a credit card payment
CASH | CREDIT CARD |
|
(Any 2) |
5.5.2 Explain TWO benefits of the following aspects of the gas stove
- TWO Universal safety design features.
- Different sized burners✔1 because it is possible to match the cookware to the size of the burner✔2 to prevent accidents.
- Child safety lock✔3 makes the gas stove safe for children/reduces the risk of unsafe/ uncontrolled gas supply.✔4
- Safety feature that shuts down the flow of gas✓5 if the flame is not ignited.✔6
- Grid of the burner keeps cookware in place/ stable✔7 and prevents accidents.✓8
- Knobs/ buttons on the front✓9 are easy/ safe✓10 to use.
- Clear instruction manual✓11 makes it easy to understand and follow safety procedures.✓12 (2 x 2) (4)
Applying, moderate (Focus, page 136; Successful, page 159)
- Human energy consumption
- Clear instruction manual makes it easy to follow instructions✔1 and therefore easy to use the gas stove.✔2
- The grid can be lifted,✓3 so it is easy to clean underneath.✓4
- It is quicker/faster than electricity✓5 and saves time.✓6 (Any 2) (2)
Applying, moderate (Focus, pages 136–137; Successful, page 159)
- Non-human energy consumption
- Gas is cheaper than electricity, so it is cheaper to operate.✓1
- Different sized burners can be used which have a better distribution of heat, making it more effective as less gas is used.✓2
- The heat is instant/fast✓3, so less energy is required for cooking.✓4
- More environmentally friendly as less electricity is used – less water is used in the generating of electricity ✓4 and the pollution caused by generating electricity is reduced/ carbon footprint is smaller/less.✓5 (Any 2) (2)
Applying, moderate (Focus, page 139; Successful, page 159)
5.5.3 Describe the positive impact of gas on the natural environment.
- Gas is the cleanest fossil fuel,✔1 it does not give off smoke/ burns cleaner than coal/oil.✔2
- Produces very low carbon dioxide/ emissions✔3 therefore less (air) pollution.✔4 Gas is thus less harmful to the environment/ more eco/ environmentally friendly/ lower carbon footprint.✓5
- Very little contribution to global warming/ climate change/ less damage to the ozone layer.✔6 (Any 4) (4)
Understanding moderate (Focus pages 169–170; Successful pages 190,194–195)
5.6
5.6.1 Identify the two-year period during which a fixed interest rate would have been more beneficial to a home owner with a mortgage bond.
- 2007–2008/ 2009✓ (1)
Remembering, easy (Focus, page 127; Successful, page 145)
- 2007–2008/ 2009✓ (1)
5.6.2 Give reasons for your answer to QUESTION 5.6.1
- From 2007 – 2009, the interest rate increased/ rose significantly/ by about 5%.✓1
- Fixed interest rates mean that the home loan repayments remain constant/ did not change✓2 and the borrower is protected against upward fluctuations.✓3 (Any 2)
OR - If a homeowner had a fixed interest rate in 2007, interest rates would have remained the same/at about 7%✓4 and the monthly repayments would have stayed the same/would not have increased.✓5 (Any 2) (2)
Applying, moderate (Focus, page 127; Successful, page 145)
5.7
5.7.1 Discuss the disadvantages of renting out the house for Mr Bones.
- Mr Bones is responsible for paying rates/ taxes✓1 and maintenance/ repairs.✔2
- Tenants may not have the same pride✔3 as Mr Bones and damage the property which could result in more expenditure to fix damaged items/ untidy tenants✔4
- Mr Bones lost income in the long run✔5 because tenants did not pay a deposit/ tenants moved out without prior notice✔6 that he could have used for repairing damages✔7 to the property.
- Mr Bones struggled to get tenants willing to occupy the house for a long period.✓8 They did not follow the terms and conditions for renting (contract/ lease)✓9
- The house was in an old residential area/probably an old house/ area with a high crime rate.✔10 (Any 4) (4)
Applying moderate (Focus, page 122; Successful, page 137)
NOTE: The answer must relate to the scenario.
5.7.2 Mr Bones did not make a sound investment. Motivate the statement.
- Buying a house in an old residential area is a risk there is a high crime rate✔1 did not have a guarantee that he could resell it.✔2
- The old house requires more maintenance – is a risk.✓3
- Buying a house is a long-term commitment/more expensive,✔4 and he may not have been able to afford the bond/loan repayments every month✔5 as he did not have regular rental income.✓6
- He sold the house for a price slightly higher than the purchase price and that may not have been enough to purchase another house/low return on investment✔7 or to cover payment for capital gains tax.✓8
- The rent expected was too high for the area in which the house was located.✔9
- He may have made a loss.✔10 Allowing tenants to move in without paying the deposit was not a good investment.✔11
- He did not have a constant rental income.✓12
- He spent money on repairing✓13 the house and that money was never recovered when the house was sold for a small profit.✓14
- Mr Bones responsible for all costs incurred with the break in.✓15 (Any 8) (8)
Analysing, difficult (Focus, page 122; Successful, page 140)
[40]
QUESTION 6: ENTREPRENEURSHIP
6.1 State FOUR factors an entrepreneur must consider when choosing a suitable product for small-scale production.
- Availability of human skills✔
- Availability of financial resources/ start-up costs/ operational costs✔ • Available (work)space✔
- Available raw materials/ other resources✔
- Consumer appeal/ target market✔ (Any 4) (4) Remembering, easy (Focus, pages 10–13; Successful pages 16–20; CAPS document)
6.2 Give ONE example of each of the following types of media that could be used to advertise a product.
6.2.1 Print media
- Newspaper/ flyers/ pamphlets/ brochures/ posters/ business cards/ magazines/ price lists/ catalogues/ labels/ packaging✓ (Any 1) (1)
Remembering, easy (Focus, page 31; Successful, page 30)
- Newspaper/ flyers/ pamphlets/ brochures/ posters/ business cards/ magazines/ price lists/ catalogues/ labels/ packaging✓ (Any 1) (1)
6.2.2 Electronic media
- Internet/ Social media/ WhatsApp/ TV/ Radio/ Cinema/ Facebook/ Twitter/ Instagram/ Cell phone✓ (Any 1) (1)
Remembering, easy (Focus, page 31; Successful, page 30)
- Internet/ Social media/ WhatsApp/ TV/ Radio/ Cinema/ Facebook/ Twitter/ Instagram/ Cell phone✓ (Any 1) (1)
6.3 State the purpose of a financial feasibility study.
- To discover the strengths✓1 and weaknesses✓2 of an existing business/ a new business idea.
- To find out whether a business will be a success✓3 after taking into consideration its total costs and probable revenues.✓4
- Will help the entrepreneur to decide objectively whether to proceed with his/her idea of a business.✓5
- Will help to identify how the business idea could be changed/ adapted to ensure profitability. ✔6
- To calculate how much start-up capital is needed✓7 where it can be obtained✓8 the type of return/ profit on investment.✔9 (Any 2) (2) Remembering, moderate (Focus, page 35; Successful, page 35)
6.4 Give reasons why it is important for a business to calculate the production cost and selling price of products accurately for sustainable profitability.
- It will lead to realistic/ competitive pricing✓1 which will lead to stimulation of sales/ more sales,✓2 resulting in sustained profitability/sales. (2)
Understanding, moderate (Focus, page 18; Successful, page 22)
6.5
6.5.1 How does Nelly ensure that the design of the packaging for the hair bands is appealing to customers.
- The envelopes are attractive✓1 as she uses coloured✓2 paper and buttons✓3 to decorate the envelopes.
- The envelopes are handmade/ unique.✓4
- The envelopes can be re-used.✓5
- The packaging is cheap✓6 as she uses recycled/ cheap packaging materials.✓7
- The packaging is environmentally friendly/ eco-friendly as she uses recycled paper/ buttons/ raw materials.✓8
- The packaging is easy to open and close/ well designed.✓9
- The envelopes keep the hair bands clean.✓10 (Any 6) (6)
Understanding, moderate (Focus, page 30; Successful, page 29)
6.5.2
- Name the distribution method Nelly uses to sell the hair bands.
- Direct distribution/ selling✓ (1)
Remembering, easy (Focus, page 33; Successful, page 32)
- Direct distribution/ selling✓ (1)
- Discuss TWO advantages of the distribution method that Nelly uses to sell her product.
- There is no middle man that must be paid/ shares in the profits✓1
- Doesn't have to pay for a stall.✓2
- Additional transport costs not required as she goes to school every day.✓3
- She can interact directly with the customers/ talk to them/ build a relationship with them.✓4
- Hair bands can be customised according to the needs of the target market.✓5 (Any 2) (2)
Applying, moderate (Focus, page 33; Successful, page 32)
6.5.3 Discuss ways in which Nelly maintains sustainable production.
Target market needs:
- Nelly produces hair bands in a variety of patterns to satisfy a wider target market's needs.✔1
- She crochets every day thus sustains the production of hair bands.✔2
- She makes a profit that will sustain production.✔3
- She buys stock with the profit earned which will sustain production.✔4
- Good record keeping keeps her informed and enhances sustainable production.✔5
Environmentally friendly:
- She uses coloured, recycled paper✔6 and she re-uses buttons from old clothes✔7 for packaging, therefore reduces the use of natural resources/ new paper/ new buttons.✔8
- She uses patterns from magazines/ re-uses shoe boxes/ old buttons✓9, thus reducing waste✔10and pollution.✔11
- She reused her grandmother's crochet hooks.✔12
- Paper is biodegradable which enhances sustainability.✔13
- No toxic material/ no need for extra paint/ colouring/ chemicals/ new buttons.✔14 This reduces harm to the environment/ reduces the carbon footprint.✔15 (Any 6) (6)
Applying, difficult (Focus, page 26; Successful, page 2
6.5.4 Calculate the production cost and selling price of ONE hair band. Show ALL calculations and round off the final amount to the nearest rand.
Yarn for one hair band = R36,00/5 = R7,20✓
Glue for 1 envelope = R25,00/20 = R1,25✓
Labour for one hair band = R6,00
Total production cost for one hair band = R7,20 + R1,25 + R6,00
= R14,45✓
R14,45 x 65%✓ = R9,39✓
R14,45 + R9,39 = R23,84✓
= R24,00✓ (7)
NOTE: The Rand (R) value must be indicated at the selling price. No mark for only 24,00.
Applying, moderate (Focus, pages 35–40; Successful, pages 36–37)
6.5.5 Analyse how Nelly ensures efficient production of quality items.
- (Planning): Nelly plans her time/ production✔1 as she performs all her duties and still produces quality products/ hair bands.✔2
- (Adhering to specifications): She uses patterns from magazines to produce beautiful hair bands,✔3 according to specifications.✓4
- (Quality control): She applies quality control✓5 as the hair bands are beautiful/ neatly crocheted/ finished off/ makes her own envelopes/ packaging.✔6
- (Tidy workspace): Yarn/ crochet hooks/ packaging/ envelopes/ buttons are stored in shoe boxes/ patterns in flip file✔7 leaving her workspace tidy.✓8
- (Stock control): Nelly's storage methods✓9 helps her with stock control✓10 and makes it easy to determine how much yarn/ envelopes/ buttons/ glue/ raw materials she needs.✔11 (Careful control of finances): she records her income and expenses✓12 and she doesn’t spend much money on packaging.✓13 (Any 8) (8)
Analysing, difficult (Focus pages 15–19; Successful pages 21–23)
[40]
TOTAL: 200
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY PAPER GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2016
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY PAPER
GRADE 12
NSC EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2016
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: CONSTRUCTION, SAFETY AND MATERIAL
1.1.1 The worker should have ensured that:
- the grinder and grinding blade/disc were inspected for defects before use. √
- the angle grinder is used for the intended purpose only. √
- correct blade is correctly fitted for the purpose.
- he/she is trained to use the machine correctly.
- do not force the tool. (2)
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE OR ANY OTHER ACCEPTABLE ANSWER
1.1.2
- Hard hat/safety helmet √
- Safety goggles/goggles √
- Overall
- Safety gloves/gloves
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
1.1.3 The machine makes a loud noise √ that will damage your hearing. √ It is the rule or regulation on a building site to protect the hearing of workers. ANY OF THE ABOVE (2)
1.1.4
- dust mask
- face shield
- ear protection/ear plugs/ear muffs
- safety shoes √ (1)
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE
1.2
1.2.1
- Water √
- Patent sealer
- Wet sand
- Hessian
- Canvas or protective covering
- Plastic sheeting
- Straw
- Waterproof paper
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
1.2.2 7 to 28 days √ (1)
1.3 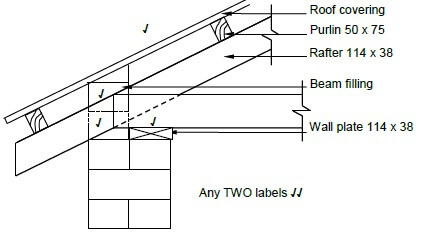 Any TWO labels √√
Any TWO labels √√
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Roof covering correctly drawn | 1 | |
Beam filling correctly drawn | 2 | |
Wall plate correctly drawn | 1 | |
Any TWO labels | 2 | |
TOTAL | 6 | (6) |
Single line for roof covering is acceptable.
Wall plate in good proportion acceptable.
1.4
- More battens are used √
- More roof trusses are used to carry weight of tiles √
- Clay/concrete tile more expensive than corrugated iron sheeting
- More labour intensive
- Needs roof underlay (2)
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE
1.5
- Tiles /cladding√
- Paint (1)
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE
1.6
- Tiles last longer/easy to clean/ water resistant √
- Paint does not last as long as tiles, easy to clean.
- Tiles/paint gives attractive/decorative appearance.
- Protect plaster.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
1.7
1.7.1 Channel-iron/U beam √ (1)
1.7.2 Exposed steel is prone to rust if not treated. √ (1)
1.7.3
- Paint the metal. √
- Can be galvanised.
- Powder coating/ epoxy coating.
- Can be covered with oil. (1)
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE
1.7.4
- Channel iron is used for bracing or as joists. √
- Frame of steel structures/struts/roof structures (1)
OR ANY OTHER ACCEBTABLE ANSWER
1.8
1.8.1
- Three quarter bat/brick
- 165 mm x 110 mm. √ (1)
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE
1.8.2 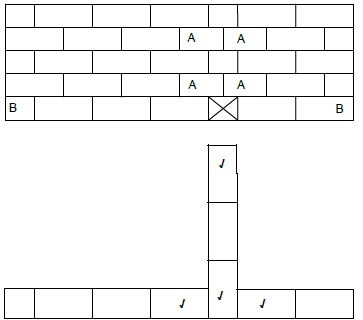 (4)
(4)
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Stretcher course | 2 | |
Header course | 1 | |
Correctness of T-junction | 1 | |
TOTAL | 4 |
1.9
- Cement fibre ceiling boards √
- Match board ceiling boards
- Steel ceilings
- Gypsum boards
- Knotty pine ceilings
- PVC/plastic/polystyrene ceilings(1)
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE
1.10
- To allow excess water or damp to escape √
- keeping the inner wall dry
- Ventilation(1)
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE
[30]
QUESTION 2: ADVANCED CONSTRUCTION AND EQUIPMENT
2.1
2.1.1 D √ (1)
2.1.2 L √ (1)
2.1.3 J √ (1)
2.1.4 H √ (1)
2.1.5 K √ (1)
2.1.6 A √ (1)
2.1.7 M √ (1)
2.1.8 I √ (1)
2.1.9 G √ (1)
2.1.10 B √ (1)
2.2
2.2.1 Chalk line √
USE
- To draw a straight line on a surface, by snapping the line. √
- Lay out walls on foundation.
- Some types can be used as a plumb bobs.
- Draw long lines on floors.(2)
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE
2.2.2 Try square √
USE
- Marking lines perpendicular to surfaces of materials. √
- Testing squareness, straightness.
- Calibrated blade can be used for measuring.
- As a straight edge to test whether small surfaces are flat and straight. (2)
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE
2.2.3 Mitre square √
USE
- The mitre can be used to check/end marks 45°angles. √
- Test squareness of corners.
- Test mitre angles/and mark them.
- Marking lines perpendicular to surfaces are flat and straight.
- Testing squareness, straightness of surfaces.
- Calibrated blade can be used for measuring.
- As a straight edge to test whether surfaces of materials. (2)
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE
2.2.4 Sliding bevel √
USE
- The blade is adjustable for setting out and testing of any angles. √
- Draw inclined or oblique lines as well as for the testing of angles.
- Draw angles other than 90˚
- Copying angles from one surface to another. (2)
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE
2.3
2.3.1
- The tensile strength of the concrete is compromised. √
- Weakens the structure/ structure will break easily/ collapse. √
- Will not be able to resist heavy loads. (2)
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE
2.3.2 To strengthen the concrete where it is the weakest against tensile strength. √ (1)
2.3.3
Stirrups strengthen concrete against shear forces. √
Shear forces are the greatest next to the support,
Stirrups resist shear stress. (1)
2.4
2.4.1 Slump test √ (1)
2.4.2 This test is used to test the workability of concrete/ consistency of the concrete √ (1)
2.4.3 For every new/fresh batch of concrete that is mixed √ (1)
2.5
- Cavity walls are to prevent the penetration of water into the wall as they have better water proofing qualities. √
- Cavity walls help to protect the inner wall of a house against moisture. √
- Cavity walls provide insulation against extreme temperatures and noise.
- Avoid expensive external rendering.
- Enable the use of cheaper or alternative materials for the inner construction.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
2.6
2.6.1
A – Compression force/pushing forces √
B – Tensile force/bending forces √
C – Lateral force √ (3)
2.7
2.7.1 Round/circular/cylindrical column formwork √ (1)
2.7.2 Hardboard/plywood/pvc/galvanised/metal sheets √ (1)
2.7.3 Bolt and nut/threaded rods with nuts/clamp √ (1)
2.7.4 Apply form oil/emulsion oil/releasing agents to formwork √ (1)
2.8
- A rib and block floor is very quick to install √ (1)
- quicker than in situ concrete floor
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE
2.9 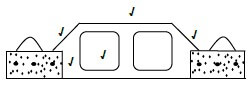
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Ribs | 2 | |
Block | 1 | |
Reinforcing on top of or inthe rib | ||
Hollow in block | 1 | |
TOTAL | 5 |
(5)
[40]
QUESTION 3: CIVIL SERVICES
3.1 
Labelling not required (2)
3.2 40/50 mm √ (1)
3.3
3.3.1
A Ventilation pipe/breather pipe/gas escape pipe √ (1)
B Inlet pipe/Inflow pipe/Influent √ (1)
C Settling chamber/Chamber 1 √ (1)
D Discharge chamber/Chamber 2 √ (1)
E Manhole cover/Manhole lid/Cover √ (1)
F Outlet pipe/Effluent √ (1)
3.3.2 The raw sewerage will be broken down by anaerobic/bacterial action. √ (1)
3.3.3
- G allows the liquids to flow from chamber C to chamber D. √
- Will also balance the liquid levels.(1)
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE
3.3.4 The liquids in D will flow out through F to a French drain. √ (1)
3.3.5 The level of the liquids will be the same. √ (1)
3.3.6
- The water coming from the bath or sink contains soap (chemicals) that is poisonous to the bacteria and will hinder the anaerobic/bacterial process. √ (1)
- It will fill up quicker if the frech drain gets saturated.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE
3.4 Storm water systems are used to carry storm water to rivers or low-lying dams. √ (1)
3.5 If you direct storm water into a sewerage system:
- the water will flood the reticulation plant. √
- raw sewerage will overflow into rivers and pollute water sources. √
- it is illegal to direct rain or storm water into a sewerage system.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
3.6 Pressure control valves (pressure-reducing valves) are used to ensure that:
- a constant pressure is maintained in the water installation√
- prevent pipes from bursting
- the pressure rating is in accordance with the pressure rating of the geyser.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
3.7
- An elbow will be used to change the direction of a pipe √
- A T-coupler will be used to split the water supply into two different flow directions/ to combine two different flow directions into one(shower).√ (2)
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE
3.8 Thermostat √ (1)
3.9 Gravity geyser/Low pressure geyser √ (1)
3.10 Black √ Absorbs the most heat √ (2)
3.11 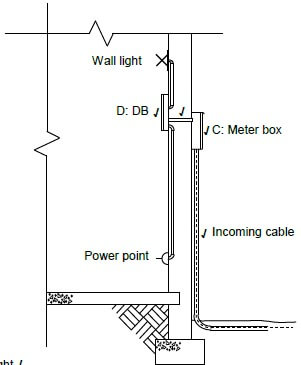
A: Wall light √
B: Power point/Socket outlet/Switch Socket outlet/Plug √(2)
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Incoming cable to meter box | 1 | |
Incoming cable to DB | 1 | |
Meter box | 1 | |
Distribution board | 1 | |
TOTAL | 4 | (4) |
ANY OTHER WAY OF INDICATING CONDUIT PIPES
[30]
QUESTION 4: QUANTITIES, MATERIALS AND JOINING
4.1
4.1.1 Door stile √ (1)
4.1.2 50 mm/50 √ (1)
4.1.3 600 √ (1)
4.1.4 3 √ (1)
4.1.5 693 mm/693 √ (1)
4.1.6 1 907 mm/1 907 OR 1 904 mm/1 904 √ (1)
4.1.7 20 mm/20 √ (1)
4.2
4.2.1 B √ (1)
4.2.2 A √ (1)
4.2.3 D √ (1)
4.2.4 D √ (1)
4.2.5 A √ (1)
4.2.6 D √ (1)
4.2.7 C √ (1)
4.3.1
A | B | C | D |
Area to be plastered: | |||
Length of ONE short wall: | |||
Length of ONE long wall | |||
Total length of one short and one long wall | |||
| (3) | |||
2/ | 11,12 | Area of internal walls before deductions: | |
2,7 √ | 60,05 m² √ | (2) | |
1/ | 1,2 | Area of window opening: | |
0,9 √ | 1,08 m² √ | (2) | |
1/ | 2,1 | Area of door opening: | |
0,9 √ | 1,89 m2 √ | (2) | |
Total wall area to be plastered | |||
√ √ √ 60,05 m² – 1,08 m² - 1,89 m² | |||
= 57,08 m² √ need to be plastered (4) |
4.3.2
Volume of plaster: | |||
1/ | √ 57,08 m2 | ||
√ 0,012 m | 0,68 m3 √ | (3) |
If candidates did not use the dimension paper/sheet 2 marks should be deducted
[30]
QUESTION 5: APPLIED MECHANICS
5.1
5.1.1 675 mm² √ (1)
5.1.2 4 800 mm² OR 4 400 mm² √ (1)
5.1.3 400 mm² √ (1)
5.1.4 5 075 mm² √ (1)
5.1.5 30 mm √ (1)
5.1.6 95 mm √ √ (2)
5.1.7 40 mm √ (1)
When the wrong unit were used the learner will be penalised with ONE mark.
Copyright reserved Please turn over
Civil Technology 15 DBE/November 2016 NSC – Memorandum
5.2 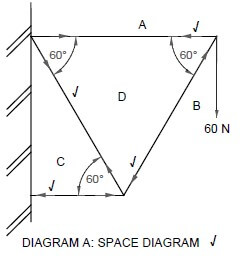
DIAGRAM A: SPACE DIAGRAM 
DIAGRAM B: VECTOR DIAGRAM/FORCE DIAGRAM
NOT ACCORDING TO SCALE
USE A MASK TO MARK THIS QUESTION
MEMBER | NATURE | MAGNITUDE |
BC | Strut √ OR --- | 65 N √ (Size to be determined as per vector diagram) OR 0 OR no force |
CD | Tie √ | -------------- |
DA | Tie √ | 32 N √ (Size to be determined as per vector diagram) |
BD | Strut √ | -------------- |
(6)
Tolerance of 1 N to either side
5.3.1 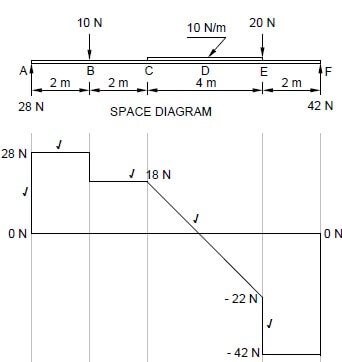
SHEAR FORCE DIAGRAM
USE A MASK TO MARK THIS QUESTION
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARKS | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Drawing correct | 5 | |
Indicate all values of shear forces on drawing | 1 | |
Correct application of scale | 1 | |
TOTAL | 7 |
5.3.2 Calculated from the left:
BMd: = (28 x 6) - (10 x 4) - (20 x 1) √
= 168 - 40 - 20 √
= 108 Nm √
OR
Calculated from the right:
BMd: = (42 x 4) - (20 x 2) - (20 x 1)
= 168 - 40 - 20
= 108 Nm (3)
[30]
ANSWER SHEET 6.1
NO. | QUESTIONS | ANSWERS | MARKS |
1 | Name the scale used for the site plan. | 1:200 √ | 1 |
2 | State the colour that you will use to indicate the proposed dwelling on the site plan. | Red √ | 1 |
3 | Identify number 1? | Rodding eye √ | 1 |
4 | Identify the line at number 2? | Building line √ | 1 |
5 | Identify number 3 | Sewer pipe/drainpipe √ | 1 |
6 | Determine the distance from the boundary line to the proposed dwelling on the right hand side of the building? | 5 000 mm/5 m √ | 1 |
7 | Identify number 4 | Manhole √ | 1 |
8 | Identify number 5 | Municipal connection √ | 1 |
9 | Draw the roofline of a hipped roof for the building indicated in the next column |
| 4 |
10 | Calculate the perimeter of the proposed dwelling. | 64 000 mm/64 m √ √ | 2 |
11 | What elevation will be closest to Long Street? | West elevation √ | 1 |
TOTAL | 15 |
QUESTION 6: GRAPHICS AND COMMUNICATION
ANSWER SHEET 6.2 
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARKS | LM |
External Walls | 4 | |
Internal Walls | 3 | |
Windows | 3 | |
Doors | 3 | |
Wash basin | 1 | |
Water closet | 1 | |
Double bowl sink | 1 | |
Dimensions | 4 | |
Floor coverings | 2 | |
Application of scale One or two incorrect = 3 | 3 | |
TOTAL | 25 |
NOT TO SCALE: USE A MASK TO MARK THIS QUESTION ONE MARK SHOULD BE DEDUCTED IF JUNCTIONS AT WALLS ARE CLOSED
ONE MARK SHOULD BE DEDUCTED IF INTERNAL DOORS HAVE A WALL BETWEEN THE OPENING
[40]
[200]
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY PAPER GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2016
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY PAPER
GRADE 12
NSC EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2016
REQUIREMENTS:
- Drawing instruments
- A non-programmable calculator
- ANSWER BOOK
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Answer each question as a whole. Do NOT separate subsections of questions.
- Start the answer to EACH question on a NEW page.
- Do NOT write in the margins of the ANSWER BOOK.
- You may use sketches to illustrate your answers.
- Write ALL calculations and answers in the ANSWER BOOK or on the attached ANSWER SHEETS.
- Use the mark allocation as a guide to the length of your answers.
- Make drawings and sketches in pencil, fully dimensioned and neatly finished off with descriptive titles and notes to conform to the SANS/SABS Code of Practice for Building Drawings.
- For the purpose of this question paper, the size of a brick should be taken as 220 mm x 110 mm x 75 mm.
- Use your own discretion where dimensions and/or details have been omitted.
- Answer QUESTIONS 1.3, 1.8.2, 3.11, 4.3, 5.2, 5.3, 6.1 and 6.2 on the attached ANSWER SHEETS using drawing instruments where necessary.
- Write your CENTRE NUMBER and EXAMINATION NUMBER on every ANSWER SHEET and hand them in with your ANSWER BOOK, whether you have used them or not.
- Due to electronic transfer, drawings in the question paper are NOT to scale.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: CONSTRUCTION, SAFETY AND MATERIAL
1.1 FIGURE 1.1 below shows a person working on a building site.
[Source: miryaglobalmedia]
FIGURE 1.1 (above)
1.1.1 Study FIGURE 1.1 and describe TWO aspects that the person should have considered to prevent this accident. (2)
1.1.2 Name TWO personal safety items that this person is wearing. (2)
1.1.3 Motivate why you think it is appropriate to wear ear protection when working with this power tool. (2)
1.1.4 Recommend ONE other important safety item that the person should have worn. (1)
1.2 Freshly cast concrete should be cured.
1.2.1 Describe what may be used to cure freshly cast concrete. (1)
1.2.2 State the duration of curing. (1)
1.3 FIGURE 1.3 below shows an incomplete sectional view of a wall and roof construction.
Use ANSWER SHEET 1.3 and complete the sketch by drawing the following:
- Beam filling
- The wall plate
- Corrugated iron sheeting
- Label any TWO parts of the drawing.
 (6)
(6)
1.4 Give TWO reasons why a roof covered with concrete tiles is more expensive than a roof covered with corrugated iron sheets. (2)
1.5 Recommend ONE material that you would use to finish a plastered wall in a bathroom. (1)
1.6 Give a reason for your answer to QUESTION 1.5. (1)
1.7 FIGURE 1.7 below shows a steel profile. 
1.7.1 Identify the steel profile. (1)
1.7.2 Describe ONE effect that the weather will have on exposed, untreated steel profiles. (1)
1.7.3 How would you prevent the effect that you have described in QUESTION 1.7.2? (1)
1.7.4 State ONE use of the steel profile. (1)
1.8 FIGURE 1.8 below shows the front elevation of a T-junction of a half-brick wall with dead ends. 
1.8.1 Identify bricks A. (1)
1.8.2 Use ANSWER SHEET 1.8.2 and project and draw, from the given front elevation, the plan course of a T-junction of course BB. The position of the T-junction is indicated with a cross (X) on the first course. (4)
1.9 Name ONE type of material that may be used for ceilings. (1)
1.10 Explain why cavity walls must have weep holes. (1)
[30]
QUESTION 2: ADVANCED CONSTRUCTION AND EQUIPMENT
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–M) next to the question number (2.1.1–2.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 2.1.11 N.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
2.1.1 Key brick | A adjustable support that may be used individually or combined with frames to support formwork (10) |
2.2 FIGURE 2.2 below shows hand tools that are used on a site and in a workshop. Write down the name and ONE use of each of the tools next to the question number (2.2.1–2.2.4) in the ANSWER BOOK. (8)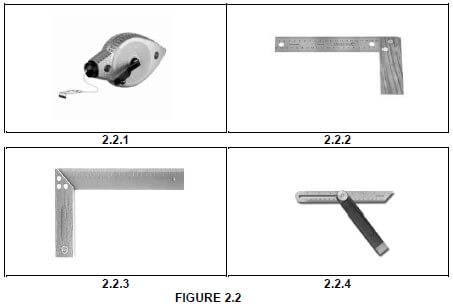
2.3 FIGURE 2.3 below shows an incomplete sectional view of a reinforced beam and column. 
2.3.1 Predict TWO negative consequences of not having reinforcement in concrete. (2)
2.3.2 Explain why the main bar is placed at the bottom of the beam. (1)
2.3.3 Explain why the stirrups in a beam are placed closer to each other near the support. (1)
2.4 The accessories below are used to test fresh concrete:
- Mould with a diameter of 100 mm at the top, 200 mm at the bottom and a height of 300 mm
- Baseplate 3 mm thick and 600 mm by 600 mm
- Steel rod 16 mm in diameter and 600 mm long
2.4.1 Name the test that may be performed with the above accessories. (1)
2.4.2 Explain why it is necessary to conduct this test. (1)
2.4.3 How often must this test be carried out? (1)
2.5 Explain TWO advantages of cavity walls. (2)
2.6 FIGURE 2.6 below shows two concrete columns with defects caused by forces acting on them. 
Name the type of forces responsible for the defects at A to C. (3)
2.7 FIGURE 2.7 below shows a type of formwork used in construction. 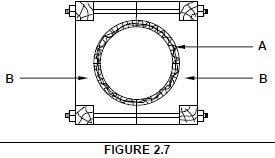
2.7.1 Identify the formwork in FIGURE 2.7. (1)
2.7.2 Recommend ONE material that may be placed on the inside around part A to give a smoother concrete finish. (1)
2.7.3 What is used to keep parts B together? (1)
2.7.4 Describe how you would prevent concrete from sticking to the inside of formwork. (1)
2.8 Distinguish between the installation of a rib and block floor and an in situ concrete floor regarding the duration of the installation. (1)
2.9 Make a neat, well-proportioned, two-dimensional sketch of a hollow block with a rib on either side of the block, as used in a rib and block floor construction. Show the reinforcement in the ribs. (5)
[40]
QUESTION 3: CIVIL SERVICES
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 Make neat freehand drawings to indicate the difference between a P-trap and an S-trap. (2)
3.2 Give the diameter of the PVC pipe that you would use for the wastewater at a sink. (1)
3.3 FIGURE 3.3 below shows a septic tank. Study the drawing and answer the questions that follow. 
3.3.1 Label parts A to F. (6)
3.3.2 Describe what happens to the raw sewerage in C. (1)
3.3.3 Explain the purpose of G. (1)
3.3.4 What is the purpose of F? (1)
3.3.5 Describe the liquid level in C and D when the septic tank is filled to capacity. (1)
3.3.6 Explain why you may NOT direct water coming from a bath or sink into a septic tank. (1)
3.4 Describe the main function of a storm water system. (1)
3.5 Explain why storm water should NOT be directed into a sewerage system. (2)
3.6 Explain the purpose of a pressure-reducing valve as used in cold and hot water installations. (1)
3.7 Distinguish between the purpose of an elbow and the purpose of a tee coupler/T-fitting, as used in water pipe installation. (2)
3.8 The temperature of the water in your geyser is too high due to a faulty part. Name the faulty part that will cause the water to overheat. (1)
3.9 What type of geyser would you use when the pressure of the incoming water from the municipality is low? (1)
3.10 The inside tray of a solar panel is painted a specific colour. Name the colour and give a reason for using this specific colour. (2)
3.11 FIGURE 3.11 on ANSWER SHEET 3.11 shows part of a vertical section through a building.
Use ANSWER SHEET 3.11.
3.11.1 Identify A and B. (2)
3.11.2 Complete the drawing by showing the following on the drawing:
- The incoming electricity cable in a kick pipe connected to a meter box at C
- Distribution board at D
- The conduit for the connection from the meter box to the distribution board at D (4)
[30]
QUESTION 4: QUANTITIES, MATERIALS AND JOINING
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 FIGURE 4.1 below shows the front view of a hollow-core flush panel door. Study the drawing and complete the incomplete cutting list. Write down the answer next to the question number (4.1.1 to 4.1.7) in the ANSWER BOOK. 
MEMBER | QUANTITY | UNIT | LENGTH | WIDTH | THICKNESS | MATERIAL |
4.1.1 | 2 | mm | 2 032 | 50 | 38 | SA pine |
Top rail | 1 | mm | 693 | 4.1.2 | 38 | SA pine |
Lock block | 2 | mm | 4.1.3 | 50 | 38 | SA pine |
Plywood panel | 1 | mm | 2 032 | 813 | 4.1.4 | Plywood |
Bottom rail | 1 | mm | 4.1.5 | 50 | 38 | SA pine |
Cardboard door filling | 1 | mm | 4.1.6 | 690 | 38 | Cardboard |
Edging | 1 | mm | 2 032 | 44 | 4.1.7 | Meranti |
(7)
4.2 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (4.2.1–4.2.7) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 4.2.8 C.
4.2.1 When joining copper pipes using the capillary method, you will ... the two pipes together.
- weld
- solder
- glue
- tape (1)
4.2.2 You can join ... pipes using the capillary method.
- copper
- copper and PVC
- copper and galvanised
- copper, PVC and galvanised (1)
4.2.3 When fixing a cornice to a wall, you will use ...
- panel pins.
- wire nails.
- steel cut nails.
- steel/masonry nail. (1)
4.2.4 A compression joint may be used to join ... pipes.
- copper
- PVC
- galvanised
- All of the above (1)
4.2.5 ... is used for joining roof trusses to brickwork.
- Hoop iron
- Building line
- Cement
- None of the above-mentioned (1)
4.2.6 ... may be used to join polyethylene pipes.
- Wood glue
- Insulation tape
- Contact glue
- PVC weld solvent (1)
4.2.7 Type of screw used when the head of the screw must be flush to the surface of the timber:
- Coach screw
- Round head screw
- Countersunk head screw
- Round head countersunk screw (1)
4.3 FIGURE 4.3 below shows the floor plan of a storeroom of which the walls need to be plastered. 
SPECIFICATIONS:
- Outside measurements of the storeroom: 8 000 mm x 4 000 mm
- Height of the walls: 2 700 mm
- Thickness of the walls: 220 mm
- Thickness of the plaster: 12 mm
- Size of the window: 1 200 mm x 900 mm
- Size of the door opening: 2 100 mm x 900 mm
Use ANSWER SHEET 4.3 and calculate the:
4.3.1 Total area of the inside of the building that must be plastered. Ignore the reveals. (13)
4.3.2 Volume of plaster needed for the internal walls (3)
[30]
QUESTION 5: APPLIED MECHANICS
Start this question on a NEW page.
5.1 FIGURE 5.1 below shows a shaped lamina with a square hole. All dimensions are in millimetres.
Study the lamina and answer the questions that follow by writing only the answer with the unit next to the question number (5.1.1–5.1.7) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 5.1.8 2 900 mm².
HINT: Use the formulae on the FORMULA SHEET.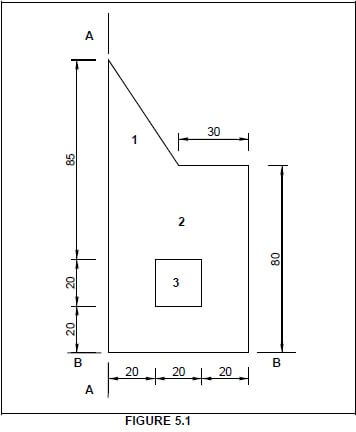
5.1.1 Calculate the area of part 1. (1)
5.1.2 Calculate the area of part 2 without the hole. (1)
5.1.3 Calculate the area of part 3. (1)
5.1.4 Calculate the total area of the lamina. (1)
5.1.5 Calculate the position of the centroid of part 2 from A–A. (1)
5.1.6 Calculate the position of the centroid of part 1 from B–B. (2)
5.1.7 Calculate the position of the centroid of part 2 from B–B. (1)
5.2 ANSWER SHEET 5.2 shows TWO diagrams of a cantilever frame. Use ANSWER SHEET 5.2 to answer the following questions.
5.2.1 Name DIAGRAMS A and B. (2)
5.2.2 On DIAGRAM A, indicate the nature of the forces in each member by means of arrows. (4)
5.2.3 Complete the table by indicating the nature and magnitude of the forces. (Deduce the information from the drawings given.) (6)
5.3 FIGURE 5.3 below shows the space diagram of a beam with a span of 10 metres with two point loads and a uniformly distributed load. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow. 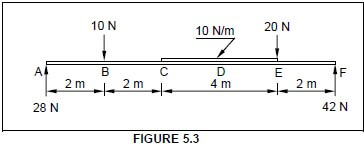
5.3.1 Deduce from FIGURE 5.3 the value of the shear forces at A, B, C, E and F and draw the shear force diagram on ANSWER SHEET 5.3. Indicate the value of the shear forces on the diagram.
Use scale 1 mm = 1 N. (7)
5.3.2 Calculate the bending moment at D. (3)
[30]
QUESTION 6: GRAPHICS AND COMMUNICATION
6.1 FIGURE 6.1 below shows the site plan of a proposed dwelling. Study the drawing and complete the table on ANSWER SHEET 6.1. 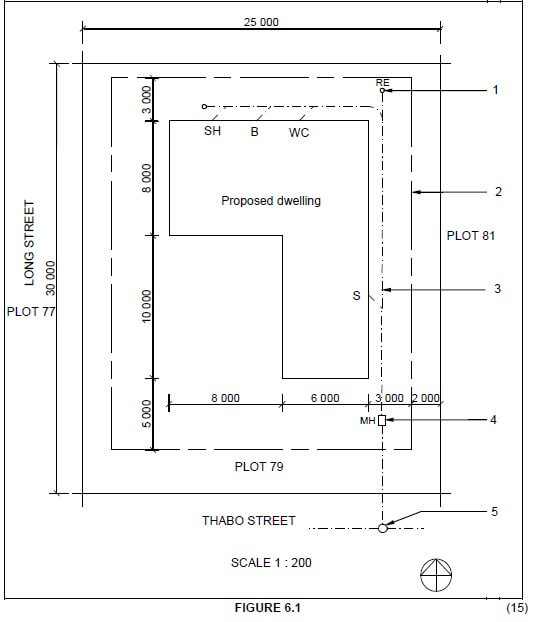 (15)
(15)
6.2 FIGURE 6.2 below shows a line diagram of the floor plan of an office with a storeroom. 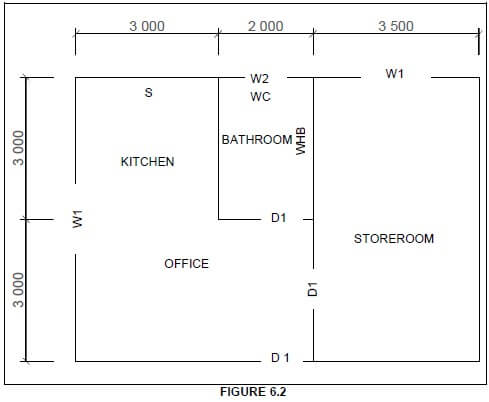
Study FIGURE 6.2 and develop and draw, on ANSWER SHEET 6.2, to scale 1 : 50, the FLOOR PLAN of the building. Use the specifications below and on the next page. (Use the assessment criteria on ANSWER SHEET 6.2 as a guideline for your drawing.)
SPECIFICATIONS:
- The measurements indicated on the drawing are the inside measurements of each room.
- Windows and doors:
WINDOWS AND DOORS | WIDTH | HEIGHT |
Window 1 (W1) | 1 500 | 1 200 |
Window 2 (W2) | 900 | 600 |
Door 1 (D1) | 900 | 2 100 |
- All windows are positioned in the middle of the external wall of each room.
- All doors are positioned 300 mm from the wall to the right of the door.
- The door of the storeroom is positioned in the middle of the wall shared by the office and the bathroom.
- All external walls of the house are 220 mm wide.
- All internal walls are 110 mm wide.
The following must also be shown on the floor plan: - The drawing symbols for a hand basin, water closet and double-bowl sink, as indicated by the abbreviations on the line diagram
- The total internal dimensions of the office on the western side of the building
- The dimensions of the thicknesses of the walls and sizes of rooms on the western side of the office
- Labels for the floor coverings for each room
- The windows and doors in the spaces, as indicated on the line diagram
THREE marks will be allocated for the application of the scale.
Start the drawing from corner A, as indicated in the bottom left-hand corner of ANSWER SHEET 6.2. (25)
[40]
TOTAL: 200
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 1.3 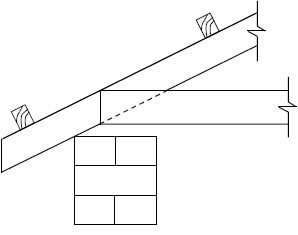
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Roof covering correctly drawn | 1 | |
Beam filling correctly drawn | 2 | |
Wall plate correctly drawn | 1 | |
Any two labels | 2 | |
TOTAL | 6 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 1.8.2
1.8.2
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Stretcher course | 2 | |
Header course | 1 | |
Correctness of T-junction | 1 | |
TOTAL | 4 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 3.11 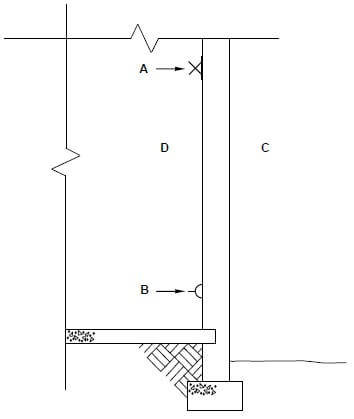
A: ________________________________ (1)
B: ________________________________ (1)
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Incoming cable | 2 | |
Meter box | 1 | |
Distribution board | 1 | |
TOTAL | 4 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 4.3
Complete your answers in the spaces indicated with _____________.
4.3.1
A | B | C | D |
Area to be plastered: | |||
Length of ONE short wall: | |||
= ______ – 2/________ = ______ | |||
Length of ONE long wall: | |||
= _____ – 2/________ = _______ | |||
Total length of one short and one long wall | |||
= _____________ + _____________ = _____________ (3) | |||
2/ | _______ | Area of internal walls before deductions: | |
_____ | _____ m2 | (2) | |
1/ | _______ | Area of window opening: | |
_______ | _____ m2 | (2) | |
1/ | _______ | Area of door opening: | |
_____ | _____ m2 | (2) | |
Total wall area to be plastered | |||
= _____________ - _____________ - ______________ | |||
=_______________ m2 (2) |
4.3.2 (3)
Volume of plaster needed: | |||
1/ | ______ | ||
______ | ________ |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 5.2 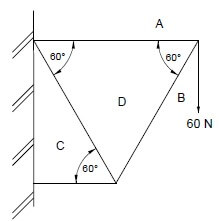
DIAGRAM A __________________________ (1) 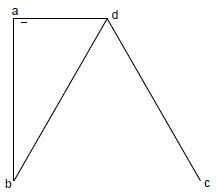
DIAGRAM B ________________________ (1)
SCALE: 1 mm = 1 N
MEMBER | NATURE | MAGNITUDE |
BC | ||
CD | --- | |
DA | ||
BD | --- |
(6)
Tolerance of 1 N to either side
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 5.3 
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARKS | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Drawing correct | 5 | |
Indicate all values of shear forces on drawing | 1 | |
Correct application of scale | 1 | |
TOTAL | 7 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 6.1
NO. | QUESTIONS | ANSWERS | MARKS |
1 | Name the scale used for the site plan. | 1 | |
2 | State the colour that you would use to indicate the proposed dwelling on the site plan. | 1 | |
3 | Identify number 1. | 1 | |
4 | Identify the line at number 2. | 1 | |
5 | Identify number 3. | 1 | |
6 | Determine the distance from the boundary line to the proposed dwelling to the right of the building. | 1 | |
7 | Identify number 4. | 1 | |
8 | Identify number 5. | 1 | |
9 | Draw the roof line of a hipped roof for the building. | 4 | |
10 | Calculate the perimeter of the proposed dwelling. | 2 | |
11 | Which elevation will be closest to Long Street? | 1 | |
TOTAL | 15 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 6.2
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARKS | LM |
External walls | 4 | |
Internal walls | 3 | |
Windows | 3 | |
Doors | 3 | |
Wash basin | 1 | |
Water closet | 1 | |
Double-bowl sink | 1 | |
Dimensions | 4 | |
Floor coverings | 2 | |
Application of scale One or two incorrect = 3 Three or four incorrect = 2 More than five incorrect = 1 No measurement correct = 0 | 3 | |
TOTAL | 25 |
FORMULA SHEET
IMPORTANT ABBREVIATIONS
SYMBOL | DESCRIPTION | SYMBOL | DESCRIPTION | SYMBOL | DESCRIPTION |
c | Centroid | b | Breadth/Width | r | Radius |
ℓ | Length | s | Side | A | Area |
FORMULAE
AREA OF | FORMULA (in words) | FORMULA (in symbols) | FORMULA FOR THE POSITION OF CENTROIDS | |
X-axis | Y-axis | |||
Square | side × side | s × s | s/2 | s/2 |
Rectangle | length × breadth | ℓ × b | ℓ /2 | b/2 |
Right-angled triangle | ½ x base × height | ½b × h | b/3 | h/3 |
Equilateral triangle/ Isosceles triangle | ½ x base × height | ½b × h | b/2 | h/3 |
Position of centroid = (A1×d) ± (A2 ×d)
Total area
OR
Y = ∑Ay
∑A
OR
X = ∑Ax
∑A
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2016
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER TWO (P2)
GRADE 12
NSC EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2016
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 A ✔✔
1.1.2 D ✔✔
1.1.3 B ✔✔
1.1.4 D ✔✔
1.1.5 B ✔✔
1.1.6 D ✔✔
1.1.7 B ✔✔
1.1.8 C ✔✔
1.1.9 A ✔✔
1.1.10 C ✔✔ (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 E ✔✔
1.2.2 G ✔✔
1.2.3 J ✔✔
1.2.4 B ✔✔
1.2.5 C ✔✔ (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 Elasticity ✔✔
1.3.2 Cash flow ✔✔
1.3.3 Breeding value ✔✔
1.3.4 Epistasis ✔✔
1.3.5 Inbreeding depression ✔✔ (5 x 2) (10)
1.4
1.4.1 Processing ✔
1.4.2 Productivity ✔
1.4.3 Lipofection ✔
1.4.4 Co-dominance ✔
1.4.5 Selection ✔ (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
2.1 Scenario on marketing
2.1.1 Identification of the marketing functions
- Transportation ✔ (1)
- Storage ✔ (1)
2.1.2 Economic term for each of the following statements
- Packaging ✔ (1)
- Cold storage/refrigeration ✔ (1)
- Processing/value adding ✔ (1)
2.1.3 TWO advantages of processing agricultural products
- Prevents spoilage/perishability/increases shelf-life of products ✔
- The product is available throughout the year ✔
- Improves food safety by heating to sufficient temperatures ✔
- Easy to transport ✔
- Easy storage ✔
- Adds value to farm products/increases the value of products/ higher income for the farmer ✔
- It provides job opportunities ✔
- Reduces wastage of excess produce ✔
- It is a way of overcoming over-supply of products ✔
- It allows for easier packing and handling of products/ simplification of products ✔ (Any 2) (2)
2.2 Case study on production of peppers
2.2.1 Farmer who marketed with success
Farmer B ✔ (1)
2.2.2 Reason
- Farmer B sold the produce for a higher price/R8/kg ✔
- The farmer identified/researched consumer needs and therefore sold the produce at a profit ✔
- Farmer worked the costs and is selling at a profit ✔
- Secured future contracts ✔
- No use of a middle man ✔
- Packaging according to consumer needs/preference ✔ (Any 1) (1)
2.2.3 TWO aspects to develop marketing strategy
- Product ✔
- Consumer preference/demand ✔
- Promotion ✔
- Pricing ✔
- Placement/distribution ✔ (Any 2) (2)
2.2.4 Marketing strategy used by Farmer B
- Research ✔
- Marketing mix ✔ (Any 1) (1)
2.2.5 TWO benefits of the marketing strategy to the farmer
- Sales/market/price are guaranteed ✔
- No middleman/intermediary ✔
- Secured a contract for the next season ✔
- Promotion of products ✔ (Any 2) (2)
2.3 Price experiment of oranges
2.3.1 Hypothesis
- The price of oranges will influence ✔ the demand thereof ✔
OR - A fall in the price of oranges ✔ will lead to a high demand/profit ✔
OR - An increase in the price of oranges ✔ will lead to a lower demand/profit/high loss ✔
OR - Sales of oranges will decrease ✔ with a price increase ✔
- Sales of oranges will increase ✔ with a price decrease ✔ (2)
- The price of oranges will influence ✔ the demand thereof ✔
2.3.2 Factor that influenced the demand
- Price ✔ (1)
2.3.3 Explanation of the factor influencing demand
- A fall in price of oranges ✔leads to an increase in demand ✔
OR - A rise in price of oranges ✔ leads to a decline/decrease in demand ✔ (2)
- A fall in price of oranges ✔leads to an increase in demand ✔
2.3.4 Impact of a higher price on profit margins
The increase in price ✔ leads to decrease in profit ✔ (2)
2.4 Analysing the advert
2.4.1 The type of labelling
Eco/green labelling ✔ (1)
2.4.2 TWO reasons for the labelling
- Packed in recyclable material/biodegradable ✔
- Organically produced ✔ (2)
2.4.3 Justification for environmental friendliness
- Packaging on recyclable bags/materials ✔
- Organically produced ✔ (Any 1) (1)
2.4.4 Marketing approach to promote the product
Sustainable agricultural marketing/green/eco friendly marketing ✔ (1)
2.5 SWOT Analysis
2.5.1 Linking statements with SWOT analysis
- A - Strength ✔ (1)
- B - Opportunity ✔ (1)
- C - Weakness ✔ (1)
- E - Threat ✔ (1)
2.5.2 How strengths/opportunities can improve the farming enterprise
- The farmer can take an advantage of a land with access to irrigation/assistance of extension officer/financial assistance from Land bank (strength) ✔
- Demand for baby carrot (opportunity) ✔ (2)
2.6 THREE personal characteristics of a successful entrepreneur
- Leadership ✔
- Motivation ✔
- Self confidence ✔
- Commitment ✔
- Hard working/energetic ✔
- Perseverance ✔
- Market driven ✔
- Innovative/creativity ✔
- Positive attitude ✔
- Risk taking ✔
- Dynamic/flexibility ✔
- Success driven ✔
- Responsibility ✔
- Communication ✔
- Visionary/goal orientated ✔ (Any 3) (3)
[35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
3.1 Land as a production factor
3.1.1 Bar graph on population size and area of land over time 
Criteria/rubric/marking guidelines
- Correct heading ✔
- Y-axis: Correctly calibrated and labelled (population size and available arable land) ✔
- X-axis: Correctly calibrated and labelled (years) ✔
- Correct units (millions and hectares) ✔
- Bar graph ✔
- All criteria presented correctly ✔ (6)
3.1.2 The economic characteristic of land
Land for agricultural purposes is limited/limitedness ✔ (1)
3.1.3 The impact of the limitedness of land on production
Increasing population is putting more pressure on the limited land ✔
resulting in a decrease in production ✔
OR
The higher the population size ✔
The lesser the arable land/production ✔
OR
The lower the population size ✔the more the arable land/production✔
OR
The more the arable land ✔ the more the production ✔
OR
The lower the arable land ✔ the less the production ✔ (2)
3.1.4 TWO measures to improve productivity of land
- Development of disease-resistant cultivars and breeds ✔
- Knowledge on the wise use of fertilisers/pesticides ✔
- Appropriate use of land/better care of agricultural land ✔
- Adapting to/use of scientific methods/use of technology to improve yields ✔
- Increased knowledge on agricultural education/precision farming ✔
- Consolidation of uneconomic units ✔
- Mechanisation ✔
- Diversification ✔
- Adapting to appropriate policies/legislation ✔
- Water provision/management ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.2 Labour contract
3.2.1 Employee with unfair conditions of service
Employee B ✔ (1)
3.2.2 Justification
- Long working hours/12 hours of work per day ✔
- Insufficient payment for work on Sunday/public holiday/R200 per day instead of R240 ✔
- Leave days not according to stipulation of legislation/10 days leave in 3 years ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.2.3 TWO labour legislation that could be used by employee
- Labour Relations Act ✔
- Basic Conditions of Employment Act ✔ (2)
3.3 Methods to increase labour productivity
3.3.1 Physical planning of infrastructure/physical farm planning ✔ (1)
3.3.2 Training/skills development ✔ (1)
3.3.3 Adequate living/environmental conditions ✔ (1)
3.3.4 Mechanisation ✔ (1)
3.4 Cash flow budget statement
3.4.1 Mini cash flow budget
Costs incurred | Amount |
Wages | R4 000 |
Chicken feed | R7 000 ✔ |
Electricity | R2 500 |
Other costs | R1 500 |
Total costs | R15 000 ✔ |
Income | |
Eggs/broilers sold/week | R10 000/R60 000 ✔ |
Net cash/week | – R5 000/R45 000 ✔ |
(4)
3.4.2 Net cash income for the month
- Egg income per week + broiler income per month – costs per month
- R10 000 x 4) ✔ + R50 000 = R90 000 – (R15 000 x 4) ✔
= R30 000 ✔ (3)
3.4.3 Business net worth based on the weekly cash flow
- Business cash flow per week is negative/positive (– R5000/R45 000) ✔
- Cash flow cannot be used to determine the net worth or income of a business/cash flow maybe restricted at a particular time even when business is profitable ✔ (2)
3.5 Problem associated with capital
3.5.1 Over- capitalisation ✔ (1)
3.5.2 Risk factor/uncertainty ✔ (1)
3.5.3 Scarcity of capital/interest rates ✔ (1)
3.5.4 Depreciation ✔ (1)
3.6 Management principle
3.6.1 Planning/decision making ✔ (1)
3.6.2 Control ✔ (1)
[35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
4.1 Crossing of a black-faced ram and white-faced ewe
4.1.1 Genotype of parent B
bb ✔ (1)
4.1.2 Indication whether parents are homozygous or heterozygous
Homozygous ✔ (1)
4.1.3 Reason
Parents have same alleles for a gene/pure bred ✔ (1)
4.1.4 Identification of the phenotype in the F2 generation
- F: black-faced ✔ (1)
- G: black-faced ✔ (1)
- H: white-faced ✔ (1)
4.1.5 Indication of the genotypic and phenotypic ratio in F2 generation
- Genotypic ratio 1:2:1 ✔ (1)
- Phenotypic ratio 3:1/3 black:1 white ✔ (1)
4.2 Estimated breeding values
4.2.1 Characteristic to select for in Bonsmara and Boer goat
Bonsmara - Meat tenderness ✔
Boer Goat - Post weaning weight ✔ (2)
4.2.2 Justification
The heritability of both characteristics is greater than 50%/ controlled more by genes ✔✔ (2)
4.2.3 TWO reasons for not selecting for birth, fleece and lean meat
- Heritability is less than 50% ✔
- Characteristics will be more influenced by the environment/ less controlled by genes ✔ (2)
4.3 Indication of the environmental factors causing variation
4.3.1 Light intensity/temperature/climate ✔ (1)
4.3.2 Feeding/nutrition ✔ (1)
4.3.3 Topography/relief/terrain ✔ (1)
4.3.4 Climate/low temperature ✔ (1)
4.4 Polygenic inheritance
4.4.1 Production of leghorn with BbGgkk genes
- B = 5 eggs ✔
- G = 5 eggs ✔
- 5 + 5 + 60 = 70 eggs ✔ (3)
4.4.2 Genotypes resulting in 90 eggs
BBGGKK ✔ (1)
4.4.3 Type of inheritance
Polygenic/quantitative ✔ (1)
4.5 Breeding heifers
4.5.1 Appropriate term for the phenomena represented by the data
Continuous variation/normal distribution/biometrics ✔ (1)
4.5.2 Number of heifers if 12% is selected
Total :10+15+20+30+40+60+75+65+45+35+15+10+5 = 425 ✔
12% (0,12) x 425 ✔
= 51 heifers ✔ (3)
4.5.3 Mass of the average animals
Average mass = 140 kg ✔ (1)
4.5.4 Farmer's intention
- Heifers with highest live mass
Selection for breeding purposes ✔ (1) - Heifers with lowest live mass
Cull/slaughter/sell ✔ (1)
- Heifers with highest live mass
4.6 Techniques to genetically modify tomatoes
4.6.1 Technique
Genetic modification/engineering/manipulation/micro-injection ✔ (1)
4.6.2 TWO advantages of GM/micro-injection to the farmer
- Better yield/harvesting ✔
- Increased shelf life/storage ✔
- Improved quality/increased nutritional value/value adding ✔
- Increased resistance to diseases/insects/pests ✔
- Resistance to harsh conditions/drought ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.6.3 TWO socio-economic effects of food from genetically modified plants to the farmer
- Small scale and poor farmers cannot afford GM crops/GM crops are expensive ✔
- A farmer is not allowed to re-use seeds from GM crops ✔
- The farmer may not use some seeds as they are sterile ✔
- Some consumers will not buy from the farmer due to ethical concerns ✔
- It encourages monopoly which does not allow small companies to develop/favours the producers and encourages exploitation of emerging farmers ✔ (Any 2) (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2016
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER TWO (P2)
GRADE 12
NSC EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2016
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show ALL calculations, including formulae, where applicable.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Write down the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10), choose the answer and make a cross (X) over the letter (A–D) of your choice in the ANSWER BOOK.
EXAMPLE:
1.1.11 ![]()
1.1.1 A measure by a farmer to reduce the risk on his/her income:
- Insurance
- Selling
- Pawning
- Bartering
1.1.2 The law of demand states that …
- the greater the number of consumers, the lower the demand for a specific product.
- the higher the income of consumers, the less demand there will be for a specific product.
- if the price of a product rises, the demand for it will increase too.
- if the price of a product falls, the demand for it will increase.
1.1.3 Which ONE of the following statements about an entrepreneur is INCORRECT?
An entrepreneur is a person who …
- takes risks
- only works for somebody else to earn a salary.
- works hard.
- has a desire to achieve success.
1.1.4 Peaches are summer fruits in South Africa. They are more expensive during winter and at the beginning of spring because the …
- supply of peaches is strictly controlled during this time.
- earlier peaches taste better.
- supply of peaches during winter and spring is still limited.
- price of peaches is affected by their availability.
Choose the correct combination:- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
1.1.5 Which ONE of the following is an internal factor that may influence a farming business?
- Legislation about labour practices
- The capability and competency of the management and farm workers
- Values and lifestyle choices of consumers
- Exchange rates and taxation
1.1.6 The following is NOT a problem associated with capital as a production factor:
- Subjected to risk
- Too little capital is invested
- Limited lifespan of goods
- Decreased competency of technicians
1.1.7 The Labour Relations Act, 1995 (Act 66 of 1995) deals with the following issues:
- The production status of animals
- Procedures for the resolution of labour disputes
- Ensures that some labourers receive financial training
- Ensures social justice and fair working conditions
Choose the correct combination:- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
1.1.8 An example of a factor of production with a value that appreciates over time:
- Equipment
- Machinery
- Farmland
- Money
1.1.9 A heterozygous Brahman bull is mated with a heterozygous cow. The expected phenotypic ratio will be ...
- 3 : 1
- 1 : 3 : 1
- 1 : 1
- 1 : 2 : 1
1.1.10 The image below represents …, which causes chromosome mutation. 
- deletion
- translocation
- inversion
- duplication (10 x 2)
(20)
1.2 Choose a term/phrase from COLUMN B that matches a description in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–J) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 K.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.2.1 A form of sustainable measure directed at consumers that takes environmental concerns into consideration | A Internetmarketing |
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 The way in which price changes a demand or supply curve
1.3.2 The movement of money in a business over a specific period of time
1.3.3 The total number of gene effects that are inherited by the progeny that will determine its performance for breeding purposes
1.3.4 The phenomenon where one gene affects the phenotypic expression of another gene
1.3.5 A gradual decrease in the performance from generation to generation due to the continual breeding of related animals (5 x 2) (10)
1.4 Change the UNDERLINED WORD(S) in each of the following statements to make them TRUE. Write only the answer next to the question number (1.4.1–1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 Value-adding is the alteration of the raw form of a product into a form that is easier for consumers to use.
1.4.2 Labour fatigue is the amount of work performed relative to the amount of money that is spent.
1.4.3 Electroporation involves using fats as carriers of the required DNA through the cell membrane into a nucleus.
1.4.4 Prepotency means that both alleles are equally dominant and visible in the phenotype of the offspring.
1.4.5 The purposeful method of deciding which individual plants and animals to choose for breeding to accomplish specific characteristics in the progeny, is called epistasis. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1
After harvesting, most products are taken to a facility where they are cleaned, graded, packed into boxes, stored and then transported to the market. |
2.1.1 Identify the functions of agricultural marketing above with regard to each of the following:
- Products are taken from the farm to the market. (1)
- Products are kept on the farm before they are transported to the market. (1)
2.1.2 Give an economic term used to describe each of the following statements:
(a) Products are packed into boxes. (1)
(b) Products are kept in a cool place to give them a long shelf life. (1)
(c) A product is altered from its raw form. (1)
2.1.3 State TWO advantages of processing agricultural products. (2)
2.2 The table below represents TWO farmers who produce peppers.
FARMER A | FARMER B |
|
|
2.2.1 Identify which farmer (A or B) marketed the produce successfully. (1)
2.2.2 Give a reason for the answer to QUESTION 2.2.1. (1)
2.2.3 State TWO aspects that the farmer in QUESTION 2.2.1 focused on when developing a marketing strategy. (2)
2.2.4 Name the marketing strategy used by FARMER B. (1)
2.2.5 State TWO ways in which the strategy in QUESTION 2.2.4 can benefit the farmer. (2)
2.3 The table below shows the results of a price experiment on bags of oranges that were sold at different prices per week.
PRICE (RAND PER BAG) | QUANTITY SOLD (BAGS OF ORANGES PER WEEK) | TOTAL REVENUE (R) | FIXED COST (R) | VARIABLE COST (R) | PROFIT (R) |
5 | 2 500 | 12 500 | 800 | 400 | 11 300 |
10 | 1 000 | 10 000 | 800 | 350 | 8 850 |
15 | 500 | 7 500 | 800 | 300 | 6 400 |
20 | 300 | 6 000 | 800 | 250 | 4 950 |
25 | 20 | 1 000 | 800 | 200 | 0 |
30 | 15 | 450 | 800 | 150 | –500 |
2.3.1 Formulate a hypothesis for the experiment above. (2)
2.3.2 Name ONE factor that influenced the demand for oranges, according to the data above. (1)
2.3.3 Explain the influence of the factor in QUESTION 2.3.2. (2)
2.3.4 Briefly explain the effect of a rising price on the profit margins, as shown in the data above. (2)
2.4 Read and analyse the advertisement below and answer the questions that follow. 
2.4.1 Identify the type of labelling in the advertisement above. (1)
2.4.2 Give TWO reasons in the advertisement to support the answer to QUESTION 2.4.1. (2)
2.4.3 The advertisement promotes environmental awareness. Motivate this statement by referring to the advertisement. (1)
2.4.4 Name the marketing approach used to promote the product. (1)
2.5 The schematic representation below shows the aspects of a SWOT analysis done by an emerging farmer. 
2.5.1 Link statement A, B, C and E in the schematic representation with the elements of a SWOT analysis. (4)
2.5.2 Explain how the farmer may use the strengths and opportunities in the schematic representation above to improve the farming enterprise. (2)
2.6 Name THREE personal characteristics of a successful entrepreneur. (3)
[35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 The table below shows the population size and available arable land in a certain region over a period of six decades.
YEARS | POPULATION SIZE (million) | ARABLE LAND AVAILABLE (million hectares) |
1961 | 24 | 15 |
1971 | 27 | 12 |
1981 | 30 | 10 |
1991 | 34 | 8 |
2001 | 39 | 6 |
2011 | 47 | 4 |
3.1.1 Draw a bar graph showing the population size and the arable land available over a period of six decades. (6)
3.1.2 State the economic characteristic of land illustrated in the graph in QUESTION 3.1.1. (1)
3.1.3 Describe how the characteristic stated in QUESTION 3.1.1 influences agricultural production. (2)
3.1.4 Suggest TWO measures a farmer can apply to improve the productivity of land. (2)
3.2 The table below shows conditions of employment in a farming business for two employees (A and B).
CONDITIONS OF EMPLOYMENT | EMPLOYEE A | EMPLOYEE B |
Daily rate | R120 | R120 |
Hours of work per day | 8 | 12 |
Payment for four Sundays/public holidays | R960 | R800 |
Leave credits per three-year cycle | 30 days | 10 days |
3.2.1 Identify the employee whose conditions of service are unfair. (1)
3.2.2 Give TWO reasons for the answer to QUESTION 3.2.1 by referring to the information in the table above. (2)
3.2.3 Give TWO examples of labour legislation that the employee in QUESTION 3.2.1 could use to challenge the employer. (2)
3.3 Name the method to increase labour productivity, which is represented by EACH of the following descriptions:
3.3.1 ![]() (1)
(1)
3.3.2 Sending tractor drivers for a basic course in mechanical engineering (1)
3.3.3 Providing workers with free transport between work and home (1)
3.3.4 Using a harvester to harvest a 100 ha field (1)
3.4
An emerging broiler and egg farmer wants to draw up a cash flow budget for a month, opening from a zero balance. Workers' wages cost R4 000 per week. Chicken feed costs R7 000 per week, electricity is R2 500 per week and some other costs amount to R1 500 per week. The farmer's income consists of the following:
|
3.4.1 Draw up a mini cash flow budget for ONE week. (4)
3.4.2 Determine the net cash income for ONE month. (3)
3.4.3 Explain whether the net income of this business can be guaranteed on the basis of its cash flow. (2)
3.5 Name the problem of capital associated with each of the following statements:
3.5.1 A farmer bought three tractors and two luxurious bakkies, which are underutilised. (1)
3.5.2 Drastic changes in the climate resulted in a drop in the expected yield. (1)
3.5.3 Short-term credit is used to pay labourers. (1)
3.5.4 A farmer sold a tractor bought five years ago at a lower price. (1)
3.6 Identify the effective management principle represented by EACH of the following statements:
3.6.1 Deciding on the size of the farming operation and the output it will give (1)
3.6.2 Monitoring all aspects of production (1)
[35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 A purebred black-faced ram is crossed with a purebred white-faced ewe. B represents the ram's face colour, which is dominant over the white face colour of the ewe. 
4.1.1 Write down the genotype of parent B. (1)
4.1.2 Indicate whether parents A and B are homozygous or heterozygous. (1)
4.1.3 Give a reason for the answer to QUESTION 4.1.2. (1)
4.1.4 Identify the phenotype in the F2 generation, as represented by F, G and H. (3)
4.1.5 Indicate the genotypic and phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation. (2)
4.2 The table below shows the estimated breeding value (EBV) for specified characteristics in Bonsmara cattle and boer goats.
SPECIES | CHARACTERISTIC | HERITABILITY |
Bonsmara | Birth weight | 38 |
Post-weaning weight | 30 | |
Meat tenderness | 65 | |
Lean meat | 38 | |
Boer goat | Birth weight | 35 |
Post-weaning weight | 60 | |
Lean meat | 35 | |
Fleece weight | 12 |
4.2.1 Identify ONE characteristic of EACH animal (Bonsmara cattle and boer goats) that farmers would select for breeding. (2)
4.2.2 Give a reason for the choice of characteristics in QUESTION 4.2.1. (2)
4.2.3 Give TWO reasons why boer goat farmers will probably not select birth weight, fleece weight and lean meat. (2)
4.3
Variation refers to the differences in characteristics between members of the same species. The differences may be caused by both external and internal factors. |
Name the environmental factor that has led to EACH of the following variations:
4.3.1 Animals at higher altitudes have darker pigmentation than those at lower altitudes. (1)
4.3.2 Animals are shorter than other animals with the same gene for tallness due to a nutrient deficiency. (1)
4.3.3 Goats kept on steeper slopes have longer and stronger legs than goats kept on flatter slopes. (1)
4.3.4 Herefords kept in colder regions have thicker hair than those found in warmer regions. (1)
4.4
Assume that egg laying in Leghorn laying hens is controlled by three pairs of genes. The net production of a laying hen with the genotype bbggkk is 60 eggs per week. Each additive allele contributes five eggs to the net production. |
4.4.1 Determine the net production of a laying hen with the genotype BbGgkk. (3)
4.4.2 Name the genotype that will result in 90 eggs. (1)
4.4.3 Indicate the type of inheritance that controls egg laying in Leghorn laying hens. (1)
4.5 In an animal production unit the following data of heifers has been collected for breeding purposes:
Live mass (kg) | 134 | 135 | 136 | 137 | 138 | 139 | 140 | 141 | 142 | 143 | 144 | 145 | 146 |
Number of animals | 10 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 60 | 75 | 65 | 45 | 35 | 15 | 10 | 5 |
4.5.1 Give the appropriate term for the phenomenon represented by the data above. (1)
4.5.2 Determine the number of heifers if 12% of the total number of heifers are selected. (3)
4.5.3 Use the data to find the mass of an average heifer. (1)
4.5.4 In a normal commercial production unit, what would a farmer do with:
(a) Heifers with the highest live mass (1)
(b) Heifers with the lowest live mass (1)
4.6 The illustration below shows a technique used by farmers to genetically modify tomatoes. 
4.6.2 State TWO advantages of the technique in QUESTION 4.6.1 for the farmer. (2)
4.6.3 Suggest TWO socio-economic implications that plants produced from the technique in QUESTION 4.6.1 and other related techniques have for the farmer. (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2016
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER ONE (P1)
GRADE 12
NSC EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2016
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 B ✔✔
1.1.2 A ✔✔
1.1.3 C ✔✔
1.1.4 C ✔✔
1.1.5 D ✔✔
1.1.6 D ✔✔
1.1.7 A ✔✔
1.1.8 D ✔✔
1.1.9 B ✔✔
1.1.10 C ✔✔ (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 A only ✔✔
1.2.2 None ✔✔
1.2.3 Both A and B ✔✔
1.2.4 B only ✔✔
1.2.5 A only ✔✔ (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 Polyneuritis ✔✔
1.3.2 Intermediary/intermediate host ✔✔
1.3.3 Anterior ✔✔
1.3.4 Enucleating ✔✔
1.3.5 Pedometer ✔✔ (5 x 2) (10)
1.4
1.4.1 Feed Conversion Ratio ✔
1.4.2 Infectious/contagious ✔
1.4.3 Donor/superior ✔
1.4.4 Dry ✔
1.4.5 Prolapsed vagina/prolapse✔ (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: ANIMAL NUTRITION
2.1 Alimentary canal of farm animals
2.1.1 Identification of a non-ruminant animal
- Animal 2 ✔ (1)
2.1.2 Reason
It does not have a complex stomach/has simple stomach ✔ (1)
2.1.3 Type of feed in ration of animal 1
Roughage ✔ (1)
2.1.4 ONE reason for the feeding a roughage
- Has a higher crude fibre/cellulose content needed for the activity of rumen micro flora ✔ (1)
2.1.5 Letter representing a part enabling the digestion of roughage
- A ✔ (1)
2.1.6 Explanation of the role of parts D and E in digestion
- Part D – Contains enzymes for digestion of grain feed ✔ (1)
- Part E – Helps to soften and moistens grain feed✔ (1)
2.2 Energy flow in an animal
2.2.1 Completion of representation
- A – Metabolic energy ✔ (1)
- B – Faeces ✔ (1)
- C – Body Heat ✔ (1)
2.2.2 Energy as final combustion heat released during oxidation
GE/Gross energy ✔ (1)
2.2.3 Formula to work out digestible energy
DE = gross energy – energy lost in faeces ✔ (1)
2.2.4 TWO reasons for the importance of net energy
- Needed for production ✔
- Needed for maintenance ✔ (2)
2.3 Biological values of feeds
2.3.1 Feeds and reasons
- Fishmeal ✔ (1)
Reason
It has the highest BV(90)/essential amino acids needed for growth✔ (1) - Maize ✔ (1)
Reason
It is has the highest energy value/energy value of 80 that is needed for fattening ✔ (1) - Barley ✔ (1)
Reason
They need feed with a low BV/BV of 50/energy value of 60% necessary for maintenance ✔ (1)
- Fishmeal ✔ (1)
2.3.2 Reason for high BV in lucerne over barley
- Lucerne is a legume crop that is rich in proteins ✔
- Barley is a non-legume which is poor in proteins/rich in carbohydrates ✔ (2)
2.4 Fodder flow programme
2.4.1 Total feed needed for the year:
Need for the dry season
Need per animal/day x number of animals x 30 days x 6 months
- 15 kg x 30 animals x 30 days x 6 months ✔
- = 81 000 kg ✔
Need for the whole year = Rainy season need + Dry season need
- 108 000 kg + 81 000 kg = 189 000 kg ✔ (3)
2.4.2 Total amount available for the dry season
- 0,15 x 1000 x 42 x 6 ✔
- = 37 800 kg ✔ (2)
2.4.3 Feed flow problem for the farmer during the dry season
Need of feed exceeds the available resources/shortage as 37 800 kg✔ available compared to 81 000 kg need for the animals ✔ (2)
2.4.4 Sustainable measure to correct the shortage
- Cutting fodder during rainy season✔
- Storage of fodder for dry season✔
- Culling/stock reduction ✔ (Any 1) (1)
2.5 Balanced ration
2.5.1 Amounts of maize and sunflower oilcake in 600kg
- Maize = 61.29 x 600 kg ✔
100
= 367.74 kg ✔ - Sunflower oilcake = 38.71 x 600 kg ✔
100
= 232.26 kg ✔ (4)
- Maize = 61.29 x 600 kg ✔
2.5.2 Feed constituting 19 parts
Maize meal ✔ (1)
[35]
QUESTION 3: ANIMAL PRODUCTION, PROTECTION AND CONTROL 3.1 Floor space required by pigs
3.1.1 Bar graph 
Criteria/rubric/marking guidelines
- Correct heading ✔
- X-axis – correct calibrations and labelled (Live mass) ✔
- Y-axis – correct calibrations and labelled (Floor space required) ✔
- Both units are correct unit (m2/kg) ✔
- Bar graph ✔
- Accuracy ✔ (6)
3.1.2 Trend between floor space required and live mass
- The increase in live mass✔ leads to
- Increase in floor space required✔ (2)
3.2 Apparatus used for procedures in animal production system
3.2.1 Identification of the apparatus
Illustrator/rubber ring ✔ (1)
3.2.2 TWO management practices for the use of the apparatus
- Tail docking ✔
- Castration ✔ (2)
3.2.3 ONE reason for the importance of each practice
Tail docking
- Hygienic purposes/prevention of blowfly attacks ✔
- Better reproduction ✔ (Any 1)
Castration
- For better breeding purposes
- All the inferior male animals are castrated ✔ (2)
3.3 Loading and transportation of farm animals
3.3.1 Facility to direct animal
Crush ✔ (1)
3.3.2 TWO measures to design a crush
- Should have high/strong/solid sides in order to prevent animals from seeing out ✔
- Should have single/narrow curves that are not sharp ✔
- Nothing that can harm/hurt/cause injury to animals should be included ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.3.3 Document needed to transport animals
Permit ✔ (1)
3.3.4 TWO precautionary measures to reduce stress in animals
- Keep animals to be transported together for 2 or 3 days ✔
- Group animals of the same size/sex/age together ✔ (2)
3.4 Life cycle of a blowfly
3.4.1 Name of the parasite
Blowfly ✔ (1)
3.4.2 Harmful stage in the life cycle
Larval stage ✔ (1)
3.4.3 Condition caused by larval stage
Blowfly strike/attacks ✔ (1)
3.4.4 Term used for removal of wool
Crutching ✔ (1)
3.4.5 THREE non-chemical management practices to control parasite infestation
- Correct timing of shearing and crutching ✔
- Clipping and cleaning of wool ✔
- Tail docking ✔
- Lambing time after shearing ✔
- Breeding and selection of resistant breeds ✔ (Any 3) (3)
3.5 Plant poisoning
3.5.1 Feed them before transporting ✔ (1)
3.5.2 Inspection of hay for fusarium/fungi ✔ (1)
3.5.3 Practise rotational grazing ✔ (1)
3.6 Animal diseases
3.6.1 Type of pathogen
Virus✔ (1)
3.6.2 Common characteristic
Both are contagious/deadly ✔
Both are enzootic ✔ (Any 1) (1)
3.6.3 TWO roles of state in controlling the spread of diseases
- Public awareness/notify public ✔
- Import/export bans ✔
- Supplying veterinary services ✔
- Setting of quarantine zones ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.6.4 TWO economic implications of diseases
- Export bans affect economy ✔
- Job loss ✔
- Financial implications/millions of rands lost ✔
- Cost/time/labour of medication ✔
- Suspension of production ✔ (Any 2) (2)
[35]
QUESTION 4: ANIMAL REPRODUCTION
4.1 Graph showing volume and concentration of semen in animals
4.1.1 Concentration of semen at volume of 6ml
- 1 billion/ml ✔ (1)
4.1.2 Correlation
Dairy cattle
- Dairy bulls produce a lot of semen✔that is less concentrated ✔ (2)
Sheep
- Sheep produce less semen✔ that is highly concentrated ✔ (2)
4.2 Semen colour and quality
4.2.1 Reason for the colour of semen
- Presence of fresh blood ✔ (1)
- Presence of old blood/infection ✔ (1)
4.2.2 TWO negative effects on quality of semen
- Poor nutrition ✔
- Severe environmental conditions/temperature✔
- Age✔
- Diseases ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.3 Techniques to increase number of offspring
4.3.1
- Cloning ✔(1)
- Embryo Transplantation ✔(1)
- Artificial insemination ✔(1)
- Cloning ✔ (1)
4.3.2 Correct stage of insemination
Oestrus ✔ (1)
4.3.3 Relationship between ovulation and insemination timing
- AI should be performed approximately 6–14 hours before ovulation ✔
- That gives time for semen to move to the fallopian tube ✔
- So that the ovum does not wait too long before fertilisation ✔ (3)
4.4 Multiple births
4.4.1 Types of twins in representation A and B
- A Dizygotic twin ✔
- B Monozygotic twin ✔ (2)
4.4.2 Justification
- A – two eggs fertilised to produce two different offspring ✔
- B – one egg cell fertilised to produce two similar offspring ✔ (2)
4.4.3 Process in representation B
Cleavage of the same zygote ✔ (1)
4.4.4 Reason for the gender of the twins in representation A
Fertilisation of two separate ova ✔ (1)
4.4.5 THREE factors for multiple births
- Fertility/genetics ✔
- Environmental factors ✔
- Breed type ✔
- Nutrition ✔ (Any 3) (3)
4.5 Foetal position
4.5.1 Identification of parturition stage
Preparatory ✔ (1)
4.5.2 Appropriate scientific name for calving difficulty
Dystocia ✔ (1)
4.5.3 TWO actions to save a calf and the cow
- Correcting the position before calving ✔
- Veterinary section if position cannot be corrected ✔ (2)
4.6 Milk ejection
4.6.1 TWO stimuli by the milker
- Washing of udder ✔
- Massage of the udder ✔
- Appearance and sound of the milker ✔
- Milking action ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.6.2 Hormone for milk ejection
Oxytocin ✔ (1)
4.6.3 Hormone inhibiting milk ejection
Adrenalin ✔ (1)
4.6.4 Bacterial disease affecting the udder
Mastitis ✔ (1)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2016
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER ONE (P1)
GRADE 12
NSC EXAM PAPERS AND MEMOS
NOVEMBER 2016
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show ALL calculations, including formulae, where applicable.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Write down the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10), choose the answer and make a cross (X) over the letter (A–D) of your choice in the ANSWER BOOK.
EXAMPLE:
1.1.11 ![]()
1.1.1 Farm animals that chew on foreign objects, like rags, show a symptom of a/an … deficiency.
- iron
- phosphorus
- copper
- sodium
1.1.2 To ensure an increased population of cellulolytic organisms in the rumen, the farmer should feed animals large quantities of ...
- roughage.
- starch.
- vitamins.
- Protein.
1.1.3 Young, growing animals require feed with a narrow nutritive ratio because ...
- it supplies more carbohydrates than protein.
- the level of protein is equivalent to that of carbohydrates.
- it has more protein than carbohydrates and minerals.
- protein is directly proportional to carbohydrates.
1.1.4 The non-nitrogen content in a feed with a TDN of 75% and DP of 12%:
- 87%
- 25%
- 63%
- 75%
1.1.5 The statements below apply to the management of chickens in an intensive production unit:
- Selection of high-quality chickens
- Inadequate floor space and feeding space
- Easy cleaning of broiler house
- Economy of construction of broiler house
Choose the CORRECT combination:- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
1.1.6 The following is NOT a measure to prevent absorption of a poison already ingested:
- Animals should be kept away from drinking water.
- Administer tannic acid.
- Dose animals with sugar or glucose.
- Provide supplementary feeding.
1.1.7 Examples of production systems applicable to pigs:
- Backyard and free range
- Backyard and deep litter
- House run and free range
- Free range and deep litter
1.1.8 Which ONE of the statements below about the seriousness of animal diseases is INCORRECT?
- Chronic diseases are long-lasting and recur in the same animals.
- Peracute diseases are sudden and animals die without previous signs.
- Acute diseases are sudden and may become chronic.
- Acute diseases cannot be cured.
1.1.9 A visible sign of a cow that is about to go into parturition:
- Rhythmic contraction of the muscles of the uterus
- Frequent urination and defecation
- Enlarged vagina and cervix to form one common canal
- Cow searching for a bull
1.1.10 A hormone in lucerne and clover pastures that may lead to pregnant animals coming into oestrus:
- Relaxin
- Oxytocin
- Oestrogen
- Prolactin (10 x 2)
(20)
1.2 Indicate whether each of the descriptions in COLUMN B applies to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A AND B or NONE of the items in COLUMN A. Write A only, B only, both A and B or none next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 B only.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
1.2.1 | A: | Biuret | A protein supplement in the ration of ruminant animals during dry winter months |
B: | Molasses | ||
1.2.2 | A: | Tranquillisers | Substances given to animals to regulate metabolism and growth rate |
B: | Antibiotics | ||
1.2.3 | A: | Modified environment | Intensive production system |
B: | Feeding closely monitored | ||
1.2.4 | A: | Dosing | Appropriate method of administering medicines for the treatment of external parasites |
B: | Spraying | ||
1.2.5 | A: | Embryo transplant | Removal and transfer of fertilised ova from genetically superior cows into the uterus of recipient cows |
B: | Artificial insemination | ||
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 A metabolic disorder resulting from a vitamin B1 deficiency that causes neuromuscular problems
1.3.2 The type of host represented by a snail in the life cycle of a fluke worm
1.3.3 The normal animal birth presentation where the head rests on the feet and the nose is stretched towards the pelvis
1.3.4 The process during which the nucleus of a female egg cell is removed for nuclear transfer
1.3.5 A device that is placed around the lower leg of a cow on heat to detect and record movement (5 x 2)
(10)
1.4 Change the UNDERLINED WORD(S) in each of the following statements to make them TRUE. Write only the answer next to the question number (1.4.1–1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 Fodder flow refers to the amount of feed consumed by an animal to gain a kilogram of body weight.
1.4.2 Foot-and-mouth disease is a non-contagious animal disease whereby the pathogen will multiply inside the host.
1.4.3 The recipient cow has superior genetic traits to produce the desired ova.
1.4.4 The lactation period is the time when the udder prepares for optimum milk production.
1.4.5 The condition where the vagina protrudes from the vulva resulting in sterility, is called abortion. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: ANIMAL NUTRITION
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 The diagrams below represent the alimentary canals of two farm animals. 
2.1.1 Which farm animal above (FARM ANIMAL 1 or FARM ANIMAL 2) is a non-ruminant? (1)
2.1.2 Give ONE reason for the answer to QUESTION 2.1.1. (1)
2.1.3 Indicate the type of feed which constitutes the greatest percentage of the ration for FARM ANIMAL 1. (1)
2.1.4 Give ONE reason for the answer to QUESTION 2.1.3. (1)
2.1.5 Write down the letter (A–E) of the part that enables FARM ANIMAL 1 to digest the type of feed in QUESTION 2.1.3. (1)
2.1.6 Explain how EACH of D and E in FARM ANIMAL 2 assist in the digestion of grain feed. (2)
2.2 The diagram below is a schematic representation of the energy flow in a farm animal. 
2.2.1 Refer to the schematic representation above and identify A, B and C. (3)
2.2.2 Identify the type of energy that serves as a potential energy value of a feed. (1)
2.2.3 Write down the formula used to work out digestible energy. (1)
2.2.4 Give TWO reasons why net energy is important to livestock. (2)
2.3 The table below shows feeds with different biological values (BV) and energy values.
TYPE OF FEED | BIOLOGICAL VALUE (BV) | ENERGY VALUE (%) |
Maize | 60 | 80 |
Fishmeal | 90 | 30 |
Lucerne | 75 | 45 |
Barley | 50 | 60 |
2.3.1 Identify, with a reason, a feed in the table above that will be suitable for:
- Growing calves (2)
- Cattle fattened for sale (2)
- Non-producing cows (2)
2.3.2 Give a reason for the high biological value of lucerne compared with the biological value of barley. (2)
2.4 Farm animals have certain fodder requirements at various stages of growth and production. The table below represents feed requirements and resources available over a twelve-month period.
ITEM | FIRST 6 MONTHS (RAINY SEASON) | LAST 6 MONTHS (DRY SEASON) | TOTAL |
Need per cow per day | 12 kg | 15 kg | |
Feed requirements in 6 months | 108 000 kg | … | … |
Resources available per month (kg) | 1,5 ton/ha | 0,15 ton/ha | 415 800 kg per year |
Total area for camps (ha) | 42 | 42 | 42 |
Number of animals | 50 | 30 |
2.4.1 Calculate the total feed required by the animals for a year. Show ALL calculations. (3)
2.4.2 Calculate, in kilogram (kg), the amount of available feed in the camps in the dry season. (2)
2.4.3 Refer to the values in QUESTION 2.4.2 and identify the feed flow problem that the farmer will encounter in the dry season. (2)
2.4.4 Give a sustainable action the farmer needs to take to reduce the impact of the problem in QUESTION 2.4.3. (1)
2.5
A balanced ration of maize meal with 14% DP and sunflower oilcake meal with 45% DP was prepared for a dairy herd. The feeds were mixed at a ratio of 12 : 19. The animals' digestible protein requirement is 26%. |
2.5.1 Determine the amount of EACH feed needed to prepare 600 kg of the ration if maize meal is 61,29% and sunflower oilcake meal is 38,71%. (4)
2.5.2 Indicate the feed that will constitute 19 parts. (1)
[35]
QUESTION 3: ANIMAL PRODUCTION, PROTECTION AND CONTROL
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 The table below represents information on the floor space required for pigs per live mass.
LIVE MASS (kg) | FLOOR SPACE REQUIRED FOR 10 PIGS (m2) |
20 | 14 |
40 | 22 |
60 | 30 |
80 | 37 |
100 | 42 |
120 | 47 |
140 | 53 |
3.1.1 Draw a bar graph to indicate the live mass of pigs and the floor space they require. (6)
3.1.2 Refer to the table above and indicate the trend in terms of floor space required in relation to the live mass of pigs. (2)
3.2 The photograph below shows an apparatus used to perform certain livestock management practices.
3.2.1 Identify the apparatus above. (1)
3.2.2 Name TWO management practices for this apparatus in sheep. (2)
3.2.3 Give ONE reason why EACH management practice in QUESTION 3.2.2 is important. (2)
The loading and transportation of farm animals may cause enormous stress and physical injuries. Proper facilities should be used when loading animals. A permit must be carried when transporting farm animals. |
3.3.1 Name the facility used to direct farm animals towards the loading ramp. (1)
3.3.2 Give TWO measures to consider when designing the facility in QUESTION 3.3.1. (2)
3.3.3 Identify the relevant document to be carried by the driver when transporting farm animals. (1)
3.3.4 State TWO precautionary measures a farmer has to take to reduce stress when transporting farm animals. (2)
3.4 The picture below represents the life cycle of a type of fly that attacks farm animals, especially wool sheep.
3.5 Identify the control measures a farmer may take to prevent plant poisoning in EACH of the following situations: 3.4.1 Identify the parasite in the life cycle above. (1)
3.4.2 Indicate the most harmful stage in the life cycle of this parasite. (1)
3.4.3 Identify the condition caused by the stage in QUESTION 3.4.2 that occurs in the wounds of wool sheep. (1)
3.4.4 Give the term used for the removal of wool around the tail and rear leg areas. (1)
3.4.5 Name THREE non-chemical management practices used to control infestation by this parasite. (3)
3.5.1 Animals graze after being transported over long distances (1)
3.5.2 Animals feed on hay kept in stables (1)
3.5.3 Overgrazed or overstocked camps (1)
3.6
H1N1 is a respiratory disease of fowls caused by the Type A influenza virus. This disease is very resistant and can remain infectious for many months. Swine fever is also a highly contagious, notifiable viral disease. The organism causing the disease can remain viable for several weeks in unprocessed pig meat. Both diseases are enzootic. |
3.6.1 Name the pathogen responsible for both H1N1 and swine fever. (1)
3.6.2 Identify a common characteristic of H1N1 and swine fever. (1)
3.6.3 Give TWO roles of the state in controlling the spreading of these diseases. (2)
3.6.4 State TWO economic implications of these diseases. (2)
[35]
QUESTION 4: ANIMAL REPRODUCTION
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 The graph below shows the volume and concentration of semen in different farm animals. 
4.1.1 Determine the concentration of semen at a volume of 6 mℓ in dairy cattle. (1)
4.1.2 Refer to the graph and give the correlation between semen volume and semen concentration of dairy cattle and sheep. (4)
4.2 The colour and quality of semen will determine the success of artificially inseminating livestock.
4.2.1 Give a reason why semen could have the following colour:
- Red (1)
- Grey (1)
4.2.2 State TWO ways in which the quality of semen may be negatively affected. (2)
4.3
Breeders are using new methods to increase the number of offspring and to improve the genetics of the progeny. Choosing the appropriate time to calve is also vital.
|
4.3.1 Choose a technique in the scenario above that matches EACH of the procedures that follow:
- The nucleus containing DNA is removed from the egg cell and the egg cell is enucleated. (1)
- A viable embryo is recovered from the donor using a Foley catheter. (1)
- Viable semen is harvested through electro-ejaculation. (1)
- Use somatic cells to produce a genetically identical organism. (1)
4.3.2 State the correct stage of the oestrus cycle to inseminate cows successfully. (1)
4.3.3 Why is the relationship between ovulation and the timing of insemination important? (3)
4.4 DIAGRAMS A and B below illustrate multiple births in farm animals.
4.4.1 Identify the TWO types of twins in DIAGRAMS A and B. (2)
4.4.2 Motivate the answer to QUESTION 4.4.1. (2)
4.4.3 Name the process that takes place in DIAGRAM B to produce this type of twins. (1)
4.4.4 Give ONE reason why the twins in DIAGRAM A will probably NOT be of the same gender. (1)
4.4.5 Name THREE factors that are responsible for the occurrence of multiple births. (3)
4.5 Calves that are incorrectly positioned before and during the time of parturition will cause difficult calving.
4.5.1 Refer to the pictures of foetal positions (A–C) above and identify the parturition stage. (1)
4.5.2 Give the correct scientific name for the calving difficulty that might be caused by foetal positions A, B and C. (1)
4.5.3 Suggest TWO actions that a farmer can take to save both the calf and the cow during calving difficulty. (2)
Milk ejection is initiated by the stimulation of the central nervous system, which is brought about by the milking action of the milker. The udder must be healthy and needs to be observed at all times to ensure optimal milk production. |
4.6.1 Give TWO stimuli initiated by the milker during the milking process. (2)
4.6.2 Name the hormone responsible for milk ejection. (1)
4.6.3 What hormone inhibits milk ejection? (1)
4.6.4 State the bacterial disease that affects the udder. (1)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150





 (6)
(6)