ECONOMICS PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2022
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupSECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1.1.1 C ‒ Specialise ✓✓
1.1.2 D ‒ improving the efficiency of markets ✓✓
1.1.3 A ‒ central ✓✓
1.1.4 B ‒ double counting ✓✓
1.1.5 C ‒ gross capital formation ✓✓
1.1.6 A ‒ trend line ✓✓
1.1.7 B ‒ the average tax rate is the same for all taxpayers ✓✓
1.1.8 D ‒ depreciation ✓✓
(8 x 2) (16)
1.2 MATCHING ITEMS
1.2.1 G ‒ also known as the national product at constant prices ✓
1.2.2 I ‒ the minimum amount of money that the South African Reserve Bank requires banks to maintain in order to manipulate money creation activities ✓
1.2.3 A ‒ an incentive given to manufacturers to reduce the cost of production ✓
1.2.4 F ‒ an example of transfer payments ✓
1.2.5 B ‒ where resources cannot be reallocated to make one individual better off without making at least one individual worse off ✓
1.2.6 C ‒ shows the way that goods and services are produced and consumed in the economy ✓
1.2.7 H ‒ value of exports minus imports ✓
1.2.8 E ‒ a form of credit that the IMF can use for a consistent disequilibrium ✓
(8 x 1) (8)
1.3 GIVE THE TERM
1.3.1 Tertiary ✓
1.3.2 Autonomous ✓
1.3.3 Kuznets ✓
1.3.4 Phillips ✓
1.3.5 Composite indicator ✓
1.3.6 International trade ✓
(6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer TWO of the three questions in this section.
QUESTION 2: MACROECONOMICS
2.1
2.1.1 Name TWO kinds of securities that are found in the money market
- banker’s acceptance ✓
- treasury bills ✓
- reserve bank debentures ✓
- short-term government bonds ✓
- short-term company debentures ✓
(Any 2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 Why does the government give transfer payments to communities?
Transfer payments are given to communities by the government to:
- redistribute of income / (alleviate or reduce poverty) ✓✓
- correcting the imbalances of the past / promote equality ✓✓
- close the gap between the rich and the poor ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.)
(Any 1 x 2) (2)
2.2 DATA RESPONSE
2.2.1 Identify an example of an injection above.
Government spending ✓ (1)
2.2.2 Name a factor that influences the size of the multiplier.
Mpc/mps ✓ (1)
2.2.3 Briefly describe the term multiplier.
Shows how an increase in spending produces a more than proportional increase in national income. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) (2)
2.2.4 Explain the use of the multiplier by the government.
The government uses the multiplier to determine the total effects of investments, export income and government spending on the economy ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) (2)
2.2.5 What is the negative effect of low savings on economic growth?
- No interest is earned when others borrow from the banks ✓✓
- Low savings rate can lead to lower rate of economic growth ✓✓
- Less savings may decrease the distribution of income in the country ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.)
(Any 1 x 2) (2)
2.3 DATA RESPONSE
2.3.1 Identify the socio-economic challenge that increased when the economy went into a slump.
Unemployment/job losses ✓ (1)
2.3.2 Name the lower turning point of a business cycle.
Trough ✓ (1)
2.3.3 Briefly describe the term economic recession.
A negative economic growth rate for at least two consecutive quarters/a decline of economic output that lasts for 6 months or longer. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) (2)
2.3.4 Explain the relationship between GDP and business cycles.
- the business cycle model shows how a nations real GDP fluctuates overtime going through phases as aggregate output increases and decreases ✓✓
- over the long-term the business cycle shows a steady increase in the potential output in a fast-growing economy ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.)
(2 x 2) (4)
2.3.5 Why does inflation tend to fall during a recession?
Inflation falls during recession because:
- businesses have unsold goods and will try discounting their goods to get rid of their excess stock ✓✓
- reduced prices of goods lead to lower costs – pushing inflation down. ✓✓
- as unemployment rises, it becomes harder for workers to bargain for higher wages ✓✓
- low confidence in an economy usually reduces inflation expectation ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.)
(Any 2 x 2) (4)
2.4 Differentiate between the expenditure method and the income method to determine Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
EXPENDITURE METHOD
- GDP at market prices is determined by adding the spending of the four main sectors of the economy ‒ households, government, businesses and the foreign sector ✓✓
- Using this method to determine GDP yields GDP at market prices ✓✓
- Also known as GDP(E) ✓✓
- GDE =C+I+G while expenditure on GDP =C+I+G+X-M ✓✓
INCOME METHOD - GDP at factor prices by adding all the income earned by the owners of the factors of production (gross domestic income) ✓✓
- This method yields GDP at factor cost ✓✓
- Also known as GDP (I) ✓✓
(8)
2.5 How can monetary policy contribute to economic growth?
The monetary policy contributes to economic growth by:
- Increasing the money supply to advance credit to households and companies, affecting consumption and production positively ✓✓
- Implementation of open market transactions by buying back securities and bonds, will increase money available for loans ✓✓
- Adjusting interest rates downwards to allow consumers to borrow more money, which will stimulate demand for goods and services and influence production positively ✓✓
- Decreasing cash reserve requirements that will allow banks to loan out more money that will stimulate production ✓✓ (4 x 2)
(8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: MACROECONOMICS
3.1
3.1.1 Name TWO flows in an open circular flow economy
- Real flow ✓
- Money flow ✓
(2 x 1) (2)
3.1.2 Why is it not possible to exclude individuals from using public goods?
- It is impossible to prevent individuals from enjoying the benefits ✓✓
- It is not possible because once public goods have been provided, they can be used by everyone ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.)
(Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.2 DATA RESPONSE
3.2.1 Identify the participant that owns the factors of production.
Households/consumers ✓ (1)
3.2.2 Name ONE public good provided by the state.
- Education ✓
- Health ✓
- Welfare services ✓
- Housing ✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.)
(Any 1 x 1)(1)
3.2.3 Briefly describe the term factor market.
It is a market where factors of production are bought and sold. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.)
(1 x 2)(2)
3.2.4 What is the effect on national income if injections are less than withdrawals?
National income will decrease/fall/decline. ✓✓ (2)
3.2.5 Explain the impact of a decrease in taxes on the level of production
- disposable income will rise and expenditure on goods and services will increase ✓✓
- level of production will increase as the multiplier will increase ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.)
(2 x 2) (4)
3.3 DATA RESPONSE
3.3.1 Identify a macroeconomic objective of the public sector in the cartoon.
- Economic growth ✓
- Full employment ✓
(Any 1 x 1) (1)
3.3.2 Which fiscal policy instrument is the main source of government income?
Taxes/taxation ✓ (1)
3.3.3 Briefly describe the term economic growth.
Increase in the productive capacity of the economy/an increase the production of goods and service in a country. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.)
(2)
3.3.4 Explain how the public sector failure can lead to social instability
Public sector failure can lead to social instability when:
- There is poor service delivery of goods and services. ✓✓
- There is an increase in poverty due to a lack of skills as a result of poor education. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.)
(Any 1 x 2) (2)
3.3.5 Why is South Africa likely to fail in achieving its economic goals?
- Officials in management often lack knowledge, implement government policies wrongly, have hidden agendas ✓✓ e.g., self-enrichment ✓✓
- Government employees lack motivation in carrying out their duties ✓✓
- Lack of efficiency due to incompetence and corruption ✓✓
- Bureaucracy can cause delays in implementation of projects ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.)
(Any 2 x 2) (4)
3.4 Briefly discuss the role of firms in the circular flow.
- Firms purchase the factors of production from households in the factor market ✓✓
- They use the factors of production to produce goods and services ✓✓
- Businesses sell these goods and services to households, government and the foreign sector ✓✓
- They act as buyers in the factor market and sellers in the goods market, with profit as their aim ✓✓
- Businesses receive an income from the other three participants ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.)
(Any 4 x 2) (8)
3.5 Evaluate the impact of reducing the repurchase rate (repo rate) on the economy
POSITIVES
- Encouraging borrowing by economic participants as the prime interest rate charged by the commercial banks may also decrease ✓✓
- Reducing the financial burden on business and consumers with prime linked loans as repayments decrease ✓✓
- Increasing aggregate demand of goods and services as lower interest rate discourages savings ✓✓ (Any 2 x 2)
NEGATIVES - Reducing the country’s attractiveness as an investment destination as lower interest rate led to lower return on some investment portfolios ✓✓
- Leading to a depreciation of the currency against the major currencies therefore making imports expensive ✓✓
- Causing inflation if increase in total demand is not accompanied by increase in total supply ✓✓ (Any 2 x 2)
(Accept any other correct relevant response.)
(4 + 4) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: MACRO ECONOMICS AND ECONOMIC PURSUITS
4.1
4.1.1 Name TWO types of markets that form part of the financial system.
- Capital market ✓
- Money market ✓
(2 x 1)(2)
4.1.2 Why is it important to use moving averages to forecast business cycles?
- It removes fluctuations in economic data which makes it easier to predict business cycles. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.)
(1 x 2) (2)
4.2 DATA RESPONSE
4.2.1 Give an example of taxes on products.
- VAT ✓
- Sin tax / excise duty ✓
- Fuel levy ✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.)
(Any 1 x 1) (1)
4.2.2 Name the alternative term used for gross value added in national accounts.
- Gross Domestic Product/GDP ✓ (1)
4.2.3 Briefly describe the term secondary sector.
It refers to a sector where goods and services are produced. ✓✓
(Accept any correct relevant response.)
(1 x 2) (2)
4.2.4 How are basic prices converted to market prices?
- Taxes on products are added to and subsidies on products are subtracted from GDP at basic prices to get gross domestic product at market prices ✓✓/ GVA at basic prices PLUS taxes on products MINUS subsidies on products = GDP at market prices. ✓✓ (2)
4.2.5 Calculate the value of A. Show ALL calculations.
- 324 365 + 556 768 + 1 789 431 ✓✓
= 2 760 564 ✓✓
(Award 2 marks for answer only.)
(2 x 2) (4)
4.3 DATA RESPONSE
4.3.1 Identify the industry in the secondary sector which contributed the most towards economic growth in the diagram above.
- Manufacturing ✓ (1 x 1) (1)
4.3.2 Give ONE example of an industry in the primary sector.
- Mining / agriculture / forestry / fishing ✓ (Any 1 x 1) (1)
4.3.3 Briefly describe the term Gross Domestic Product.
- Refers to the total value of final goods and services produced within the borders / boundaries of the country during a specific period of time. ✓✓ (2 x 1) (2)
4.3.4 How does compensation of employees affect labour productivity?
- Lack of reward decreases employees’ productivity ✓✓
- Rewarded employees can lead to increased productivity ✓✓
(Any 1 x 2) (2)
4.3.5 Why is the multiplier effect on manufacturing important in the economy?
- Manufacturing has so many substantial links with so many other sectors throughout the economy, its output stimulates more economic activity across society than any other sector ✓✓
- Creates job and investment opportunities in all the other sectors that use its products, such as transportation, construction and retail. ✓✓
- It spurs growth and services such as finances and transportation. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.)
(Any 2 x 2) (4)
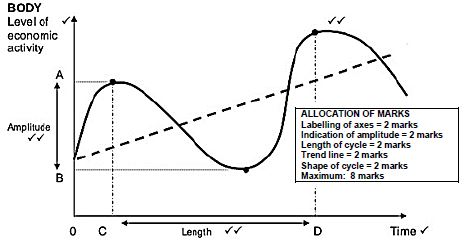
4.4 Draw a correctly labelled diagram of a business cycle, clearly indicating trend line, length, the amplitude and the trough.
(8)
4.5 With reference to the Phillips curve, analyse the relationship between inflation and unemployment.
- The Phillips curve shows that inflation will increase if there is less unemployment ✓✓
- A very high inflation can lead to stagflation ✓✓
- The demand for goods and services can be stimulated without increased employment ✓✓
- Capital intensive production processes would not necessarily contribute to further job creation ✓✓
- The worker might make use of extended credit facilities to enjoy the same standard of living when they experience price increases ✓✓
- Skills development and improved education that increases employment will create an increased demand for goods and services ✓✓
- Inflation targeting (3%–6%) will prevent stagflation ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.)
(Any 4 x 2) (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer ONE of the TWO questions in this section.
QUESTION 5: MACROECONOMICS
- Discuss in detail the reasons for international trade. (26 marks)
- How can a weaker rand impact on South Africa’s trade with other countries? (10 marks)
INTRODUCTION
International trade involves the exchange of goods or services across different countries in the world. ✓✓
(Accept another correct relevant introduction.)
(Max. 2) (2)
MAIN PART
The size of the population ✓
- If there is an increase in population growth, it causes an increase in demand, as more people’s needs must be satisfied. ✓✓
- Local suppliers may not be able to satisfy this demand. ✓✓
Income levels ✓
- Changes in income cause a change in the demand for goods and services ✓✓
- An increase in the per capita income of people results in more disposable income that can be spent on local goods and services, some of which may then have to be imported ✓✓
An increase in the wealth ✓
- An increase in the wealth of the population leads to greater demand for
goods. ✓✓ - People have access to loans and can spend more on luxury goods, many of which are produced in other countries. ✓✓
Preferences and tastes ✓
- Preferences and tastes can play a part in the determining of prices ✓✓ e.g., customers in South Africa have a preference for a specific product which is not produced locally and need to import, and this will make that product to have higher value than in other countries ✓✓
The difference in consumption patterns ✓
- The difference in consumption patterns is determined by the level of economic development in a country ✓✓
- For example, a poor country can have a high demand for basic goods and services but a lower demand for luxury goods ✓✓
Natural resources ✓
- Natural resources are not evenly distributed across all countries of the world ✓✓
- They vary from country to country and can only be exploited in places where these resources exist ✓✓
Climatic conditions ✓
- Climatic conditions make it possible for some countries to produce certain goods at a lower price than other countries ✓✓
- For example, Brazil is one of the biggest producers of coffee in the world ✓
Labour resources ✓
- Labour resources differ in quality, quantity and cost between countries. ✓✓
- Some countries have highly skilled, well-paid workers with high productivity levels, e.g., Switzerland ✓✓
Technological resources ✓
- Technological resources are available in some countries that enable them to produce certain goods and services at a low unit cost, ✓✓ e.g., Japan. ✓
Specialisation ✓
- Specialisation in the production of certain goods and services allows some countries to produce them at a lower cost than others ✓✓
- For example, Japan produces electronic goods and sells these at a lower price ✓✓
(Accept other correct relevant responses.) Max. (26)
ADDITIONAL PART
Positive impact by:
- increasing the quantity of exports as South African products can become affordable in countries with stronger currencies ✓✓
- attracting a lot of international tourists from rich countries as their currencies can give them more value for their money in South Africa ✓✓
- improving the Balance of Payment if the country earns more money from its exports than what it pays for its imports ✓✓
- discouraging imports of goods that are also produced by South African firms, therefore increasing consumption of local products ✓✓
Negative impact by:
- making imported inputs expensive thereby resulting in cost push inflation as producers may have to increase their prices ✓✓
- creating a deficit on the balance of payment if the amount of money paid on imports is more than the one received from exports ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant responses.)
(Allocate a maximum of 2 marks for mere listing of facts.)
(2)
Conclusion
- It is important for countries to clearly make assessment of which products give them absolute advantage and/or comparative advantage as this can help them to trade successfully with other countries ✓✓
(Accept any other correct higher order conclusion.) (Max. 2)
(2)
[40]
QUESTION 6: MACROECONOMICS
- Discuss in detail the main objectives of the public sector in the economy. (26 marks)
- How effective is the South African government in achieving full employment? (10 marks)
INTRODUCTION
The main objectives of the state are to serve the citizens of the country and bring about the systematic development for all of them. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant introduction.) Max. (2)
MAIN PART
Economic growth ✓
- Economic growth refers to an increase in the production of goods and services in the economy ✓✓
- The state must ensure that there is sustainable growth as it leads to an improvement in the standard of living ✓✓
- For economic development to take place, economic growth rate must be higher than the population rate ✓✓
Exchange rate stability ✓
- Depreciation and appreciation create uncertainty for producers and investors and should therefore be limited. ✓✓
- The state tries to protect the country’s currency from excess fluctuations ✓✓
- Monetary and fiscal policies are used to ensure that exchange rate remains relatively stable for longer periods ✓✓
Full employment ✓
- This means that all persons who would like to work and who are looking for work should be able to find work or be self-employed ✓✓
- High levels of employment is one of the crucial economic objectives for all governments ✓✓
Economic equity ✓
- In South Africa the government uses a progressive tax system to provide for free services to all its deserving people. ✓✓
- Free social services such as basic education, primary health care, basic economic services and paying cash grants to the poor and other vulnerable people ✓✓
- A redistribution of income and wealth is important in market economies ✓✓
Price stability ✓
- In South Africa the relative price stability means maintaining an inflation rate of between 3% and 6% ✓✓
- A market economy performs better when prices are stable ✓✓
- Any country strives for its prices not to fluctuate ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.)
(Mark subheadings and examples to a maximum of 8 marks.) Max.(26)
ADDITIONAL PART
- Simulating economic growth and performance of these enterprises by introducing innovative methods by private experts ✓✓
- Providing additional funds to the government through taxes which can make funds readily available for the provision of services ✓✓
- Promoting community economic participation rate while accelerating service delivery ✓✓
- Relieving the government from the financial burden placed by SOES like SAA thus leaving the state with more funds to invest on service delivery. ✓✓
(10)
(A maximum of 2 marks for mere listing of facts.)
CONCLUSION
- The state uses the national budget to try and achieve all its objectives using taxes a major source of income. ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response.) Max.
(2)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150