Adele
THE SECRET LIFE OF WALTER MITTY SHORT STORY QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS GRADE 12
THE SECRET LIFE OF WALTER MITTY SHORT STORY
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
GRADE 12
THE SECRET LIFE OF WALTER MITTY BY JAMES THURBER
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
Extract A
[Walter waits for his wife.]
He found a big leather chair in the lobby, facing a window, and he put the overshoes and the puppy biscuit on the floor beside it. He picked up an old copy of Liberty and sank down into the chair. ‘Can Germany Conquer the World Through the Air?’ Walter Mitty looked at the pictures of bombing planes and of ruined streets. 5 |
- Where is Walter Mitty and why is he there? (2)
- What is he doing? (1)
- Explain the meaning and significance of “Can Germany Conquer the World Through the Air?” (2)
- What grammatical signs do we have to show that he begins to fantasise? (2)
- What is the challenge or problem facing Mitty in this fantasy?
Give a reason for your answer. (2) - Which THREE words could be used to describe Mitty as he is in his secret world. Choose the correct words from the list below.
Sick, Heroic, Anxious, Brave, Respected, Fearful. (3) - Briefly explain why Mitty has this fantasy. (4) [16]
Answers
|
QUESTIONS 2
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
Extract B
[Walter and his wife drive in to town.]
“I don’t need overshoes,” said Mitty. She put her mirror back into her bag. “We’ve been all through that,” she said, getting out of the car. “You’re not a young man any longer.” He raced the engine a little. “Why don’t you wear your gloves? Have you lost your gloves?” Walter Mitty reached in a pocket and brought out the gloves. He 5 put them on, but after she had turned and gone into the building and he had driven on to a red light, he took them off again. “Pick it up, brother!” snapped a cop as the light changed, and Mitty hastily pulled on his gloves and lurched ahead. He drove around the streets aimlessly for a time, and then he drove past the hospital on his way to the parking lot. |
- What evidence does this passage give that Mrs Mitty is a nagging wife? (2)
- What evidence does this passage give to show that Mitty tries to do things his way. (2)
- What else does he usually do to escape his wife? (2)
- What does driving past the hospital make him think of? Describe his thoughts in detail. (4)
- What word in the passage tells us that he is bored? (1)
- Answer TRUE or FALSE and give a reason for your answer. Do you agree that Walter Mitty is a good driver? (2) [13]
Answers
|
THE SECRET LIFE OF WALTER MITTY SHORT STORY QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS GRADE 12
THE SECRET LIFE OF WALTER MITTY SHORT STORY
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
GRADE 12
THE SECRET LIFE OF WALTER MITTY BY JAMES THURBER
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
Extract A
[Walter waits for his wife.]
He found a big leather chair in the lobby, facing a window, and he put the overshoes and the puppy biscuit on the floor beside it. He picked up an old copy of Liberty and sank down into the chair. ‘Can Germany Conquer the World Through the Air?’ Walter Mitty looked at the pictures of bombing planes and of ruined streets. 5 |
- Where is Walter Mitty and why is he there? (2)
- What is he doing? (1)
- Explain the meaning and significance of “Can Germany Conquer the World Through the Air?” (2)
- What grammatical signs do we have to show that he begins to fantasise? (2)
- What is the challenge or problem facing Mitty in this fantasy?
Give a reason for your answer. (2) - Which THREE words could be used to describe Mitty as he is in his secret world. Choose the correct words from the list below.
Sick, Heroic, Anxious, Brave, Respected, Fearful. (3) - Briefly explain why Mitty has this fantasy. (4) [16]
Answers
|
QUESTIONS 2
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
Extract B
[Walter and his wife drive in to town.]
“I don’t need overshoes,” said Mitty. She put her mirror back into her bag. “We’ve been all through that,” she said, getting out of the car. “You’re not a young man any longer.” He raced the engine a little. “Why don’t you wear your gloves? Have you lost your gloves?” Walter Mitty reached in a pocket and brought out the gloves. He 5 put them on, but after she had turned and gone into the building and he had driven on to a red light, he took them off again. “Pick it up, brother!” snapped a cop as the light changed, and Mitty hastily pulled on his gloves and lurched ahead. He drove around the streets aimlessly for a time, and then he drove past the hospital on his way to the parking lot. |
- What evidence does this passage give that Mrs Mitty is a nagging wife? (2)
- What evidence does this passage give to show that Mitty tries to do things his way. (2)
- What else does he usually do to escape his wife? (2)
- What does driving past the hospital make him think of? Describe his thoughts in detail. (4)
- What word in the passage tells us that he is bored? (1)
- Answer TRUE or FALSE and give a reason for your answer. Do you agree that Walter Mitty is a good driver? (2) [13]
Answers
|
THE SISTERS SHORT STORY QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS GRADE 12
THE SISTERS SHORT STORY
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
GRADE 12
EXTACTS FROM THE SISTERS BY PAULINE SMITH
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
Extract A
[Marta agrees to marry Jan Redlinghuis.]
And she said again: “Sukey, my darling, listen now! If I marry old Jan Redlinghuis he will let the water into my father’s furrow, and the lands of Zeekoegatt will be saved. I am going to do it, and God will help me.” |
QUESTIONS
- Complete the following sentences by using the words provided in the list below. Write only the words next to the question numbers (1a) – 1d)).
This short story is set near the a) ... river in a place called b) ... The narrator of the story is c) ... and her father is d) ... (4)orange; Jan Redlinghuis; Sukey; Grootkops; Ghamka; Marta; Burgert de Jager; Platkops - Why does Marta’s father ask her to marry Jan Redlinghuis? State TWO points. (2)
- Using your own words, explain why Marta agrees to marry Jan Redlinghuis. (2)
- Choose the correct answer to complete the following sentence. Write only the answer (A–D).
Sukey’s father’s agreement with Jan Redlinghuis proves that he is ...- arrogant.
- careful.
- selfless.
- selfish. (1)
- Sukey thinks that Jan is “a sinful man” and often “a little mad” (line 5).
In your opinion, is he mad? Give a reason for your answer. (2) - Briefly describe the relationship between the two sisters, Marta and Sukey. Give an example to substantiate your answer. (2)
- Name TWO aspects of Marta’s character that are shown in this extract. (2)
- Sukey goes to see Jan Redlinghuis the next day.
- Explain why Sukey goes to see Jan Redlinghuis. (2)
- Identify the theme which is shown here. (1)
- Discuss your views on Marta’s decision to marry Jan Redlinghuis. (2) [20]
ANSWERS
|
Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
Extract B
[Marta has died.]
We buried Marta in my mother’s grave at Zeekoegatt ... And still they could not find Jan Redlinghuis. Six days they looked for him, and at last they found his body in the mountains. God knows what madness had driven old Jan Redlinghuis to the mountains when his wife lay dying, but there it was they found him, and at Bitterwater he was buried. |
QUESTIONS
- Which aspect of her personality caused Sukey’s mother to be severely saddened and upset by the feud between her husband and Jan Redlinghuis? (1)
- Is the following statement TRUE or FALSE? Write “true” or “false” and give a reason for your answer.
Mrs de Jager died of cancer. (2) - Give ONE reason why the people are looking for Jan Redlinghuis (lines 1–3). (1)
- Explain why Jan Redlinghuis goes to the mountain. (2)
- Refer to line 8 (“It is blood ... on my lands”).
- Identify the figure of speech used here. (1)
- Explain the meaning of this line in the context of the story. (2)
- Briefly explain how Burgert de Jager changes in this story. (2)
- Quote a sentence which proves that Sukey is submitting to her father. (1)
- In your opinion, who is to blame for Marta’s death? Explain your choice. (3) [15]
Answers
|
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
REQUIREMENTS:
- Drawing instruments
- A non-programmable pocket calculator
- ANSWER BOOK
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Answer each question as a whole. Do NOT separate subsections of questions.
- Start the answer to EACH question on a NEW page.
- Do NOT write in the margins of the ANSWER BOOK.
- You may use sketches to illustrate your answers.
- Write ALL calculations and answers in the ANSWER BOOK or on the attached ANSWER SHEETS.
- Use the mark allocation as a guide to the length of your answers.
- Make drawings and sketches in pencil, fully dimensioned and neatly finished off with descriptive titles and notes to conform to the SANS/SABS Code of Practice for Building Drawings.
- For the purpose of this question paper, the size of a brick should be taken as 220 mm x 110 mm x 75 mm.
- Use your own discretion where dimensions and/or details have been omitted.
- Answer QUESTIONS 1.12, 3.6, 3.7, 4.6, 5.2, 5.3, 6.1 and 6.2 on the attached ANSWER SHEETS using drawing instruments, where necessary.
- Write your CENTRE NUMBER and EXAMINATION NUMBER on every ANSWER SHEET and hand them in with your ANSWER BOOK, whether you have used them or not.
- Due to electronic transfer, drawings in the question paper are NOT to scale.
- Google Images was used as the source for all photographs and pictures.
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: CONSTRUCTION, SAFETY AND MATERIAL
1.1 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–L) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 M.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.1.1 Lintel |
|
(10 x 1) (10)
1.2 FIGURE 1.2 below shows two different safety signs for personal protection.
| A | B |
FIGURE 1.2
1.2.1 Explain when you would use safety boots A. (1)
1.2.2 Explain when you would use gum boots B. (1)
1.3 Give ONE reason why the rungs of a ladder should not be painted. (1)
1.4 Describe TWO safety precautions that must adhered to to ensure the safety of workers and the public during deep excavations. (2)
1.5 Name THREE accessories that you need to conduct a cube test. (3)
1.6 Name the purpose of water during the mixing process of concrete. (1)
1.7 Give ONE reason why you would use a damp-proof course in the following places:
1.7.1 In the walls of a basement (1)
1.7.2 Between a floor and a wall (1)
1.8 Name the preservative that you would use on timber if you want to see its natural colour. (1)
1.9 Name the type of roof covering that you would use if the roof covering is fixed on top of 38 mm x 38 mm battens. (1)
1.10 Name the roof component that you would use to close the gap where the roof coverings meet at the top of a roof. (1)
1.11 What will you use to join the roof truss members if the members have butt joints? (1)
1.12 FIGURE 1.12 on ANSWER SHEET 1.12 shows an incomplete drawing in stretcher bond of a plan course of a one-brick wall with a half-brick T-junction.
Complete the drawing by placing ALL the missing bricks, including the three quarter bricks, in the correct spaces. The bricks you draw must be of the same size as those on the given drawing. (5) [30]
QUESTION 2: ADVANCED CONSTRUCTION AND EQUIPMENT
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 Various options are given as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (2.1.1–2.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK,
for example 2.1.6 C.
2.1.1 The … is used to measure and set horizontal distances, vertical heights and angles.
- mortice
- mitre square
- dumpy level
- builder's square (1)
2.1.2 A transparent pipe can be used for …
- setting out foundations.
- marking perpendicular lines.
- testing the squareness of objects.
- transferring heights from one point to another. (1)
2.1.3 This hammer is mainly used to drive very small nails into wood:
- Cross-peen hammer
- Claw hammer
- Rubber mallet
- Wooden mallet (1)
2.1.4 A/An … is used to cut steel.
- portable circular saw
- angle grinder
- electric mitre saw
- sliding bevel (1)
2.1.5 A … is used for cutting along the length of wood.
- ripsaw
- crosscut saw
- portable electric planer
- panel saw (1)
2.2 FIGURE 2.2 below shows power tools and equipment that are used in the building industry. Write down the name and explain ONE use of each power tool next to the question number (2.2.1–2.2.2) in the ANSWER BOOK.
| 2.2.1 | 2.2.2 |
| | |
FIGURE 2.2 (4)
2.3 Name the hand tool that you will use to spring a straight line between two points. (1)
2.4 Name ONE hand tool that you would use during the building process to ensure that the corner of the walls of a house is square. (1)
2.5 Differentiate between a rough arch and a gauged arch in terms of the type of brick used to build the arch. (2)
2.6 FIGURE 2.6 below is a drawing of a pile. Study the drawing and answer the questions that follow. 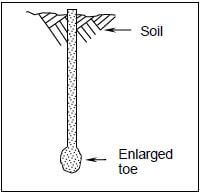
FIGURE 2.6
2.6.1 Name the type of pile in FIGURE 2.6. (1)
2.6.2 Describe TWO factors that will determine the use of this type of pile. (2)
2.6.3 Name the material that can be placed inside the pile to make the concrete in the pile stronger. (1)
2.7 FIGURE 2.7 below shows two types of reinforcing bars that can be used for reinforcing concrete. Study the figure and name EACH reinforcing bar. Write down the answer next to the number (2.7.1–2.7.2) in the ANSWER BOOK. 
FIGURE 2.7 (2)
2.8 FIGURE 2.8 below illustrates a flight of concrete stairs. Study the drawing and name parts A to C in the ANSWER BOOK. 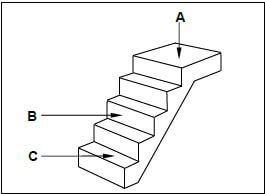
FIGURE 2.8 (3)
2.9 Name TWO defects that can occur in concrete due to shuttering. (2)
2.10 FIGURE 2.10 below shows a sectional view of an external wall. 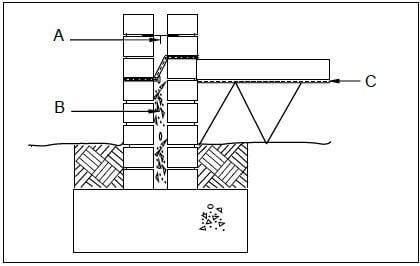
FIGURE 2.10
2.10.1 Identify the type of wall. (1)
2.10.2 Identify part A and explain the function of this part. (2)
2.10.3 Name the type of mixture that is used for B. (1)
2.10.4 Explain ONE reason for filling part B with this type of mixture. (1)
2.10.5 Identify part C. (1)
2.10.6 Give the minimum distance of the opening in the wall in FIGURE 2.10. (1)
2.11 FIGURE 2.11 below illustrates an incomplete vertical sectional view through a dry wall. Study the sketch and answer the questions that follow. 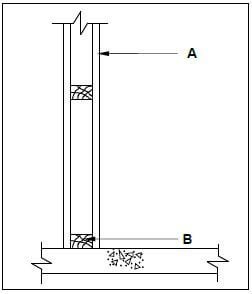
FIGURE 2.11
2.11.1 Identify parts A and B. (2)
2.11.2 Name any other material that B can be made of. (1)
2.11.3 Explain TWO advantages of dry walls. (2)
2.12 FIGURE 2.12 below is a sketch of components of a suspended floor. 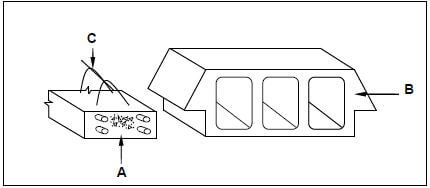
FIGURE 2.12
2.12.1 Name the type of suspended floor where these components will be used. (1)
2.12.2 Identify parts A to C. (3) [40]
QUESTION 3: CIVIL SERVICES
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 FIGURE 3.1 below shows a water trap that is used in civil services. 
FIGURE 3.1
3.1.1 Identify the water trap. (1)
3.1.2 Name ONE place where the trap can be used. (1)
3.2 FIGURE 3.2 below shows an electrical water-heating system. Study the sketch and answer the questions that follow. 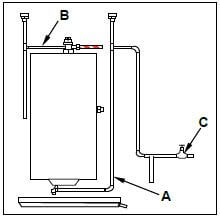
FIGURE 3.2
3.2.1 Explain the functions of pipes A and B as used in the geyser installation. (2)
3.2.2 Explain the purpose of C. (1)
3.2.3 Give ONE reason for using a drip tray in a geyser installation. (1)
3.3 FIGURE 3.3 below is a drawing of an open storm-water channel. Study the drawing and answer the questions that follow. 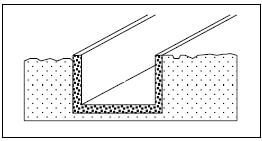
FIGURE 3.3
3.3.1 Explain the term storm water. (1)
3.3.2 Explain the function of storm-water channels. (1)
3.4 Describe ONE advantage of shallow water wells. (1)
3.5 Water from a borehole is extracted by using an electric pump, a hand operated pump or a solar-powered pump. Name ONE other method that can be used to extract water from a borehole. (1)
3.6 FIGURE 3.6 on ANSWER SHEET 3.6 shows an incomplete floor plan of a kitchen. Complete the drawing by drawing the symbols and wiring for the following electrical fittings:
3.6.1 Two-way switch at A (2)
3.6.2 Socket outlet at B (2)
3.6.3 Light at C (2)
3.6.4 Electrical wiring from A to C (2)
3.7 FIGURE 3.7 on ANSWER SHEET 3.7 shows the incomplete layout of a one-pipe sewerage system connected to a conservancy tank. Study the drawing and draw the layout of the sewerage system on ANSWER SHEET 3.7. All regulations and design principles of a good sewerage system must be adhered to.
The sewerage system must consist of the following and it should be indicated with the correct drawing symbols:
- 1 x rodding eye (1)
- 1 x gully at the kitchen sink (1)
- 1 x ventilation pipe (1)
- Main sewerage pipes (2)
- 4 x inspection eyes (4)
- 1 x manhole (1)
- Any TWO abbreviations for the sanitary fixtures (2) [30]
QUESTION 4: QUANTITIES, MATERIALS AND JOINING
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 Below are pictures of fasteners that are used on building sites and in workshops. Write down the name and ONE use of EACH fastener next to the question number (4.1.1–4.1.3) in the ANSWER BOOK. (6)
(6)
4.2 Name ONE fastener that you will use to fix a truss hanger to a wall. (1)
4.3 Name ONE method of joining copper pipes. (1)
4.4 Name TWO advantages of screws when compared to nails. (2)
4.5 FIGURE 4.5 on the next page shows the brandering layout of a ceiling construction and the four walls. Study the drawing and complete the incomplete cutting list. Write down the answer next to the question number (4.5.1 to 4.5.7) in the ANSWER BOOK.
Use the following specifications to answer the question.
- Ceiling board: 6,4 mm x 900 mm x 3 000 mm
- Brandering: 38 mm x 38 mm
- Brandering is placed 75 mm away from each wall.
- Cornice: 75 mm x 75 mm
- Metal cover strips: 7 mm x 20 mm x 3 000 mm
- The longest brander (brandering) touches the short walls.
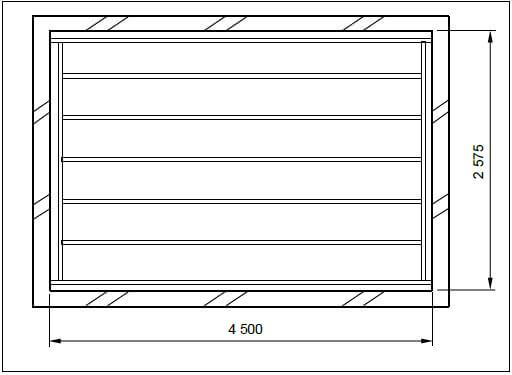 FIGURE 4.5
FIGURE 4.5
CUTTING LIST FOR CEILING | |||||||
MEMBER | QUANTITY | UNIT | LENGTH | WIDTH THICKNESS | TOTAL LENGTH | MATERIAL | |
Long-wall branders (brandering) | 2 | mm | 4 575 | 4.5.1 | 38 | 9 150 | SA pine |
Short-wall branders (brandering) | 2 | mm | 4.5.2 | 38 | 38 | 10 300 | SA pine |
Intermediate branders (brandering) | 4.5.3 | mm | 4 349 | 38 | 38 | 21 745 | SA pine |
Ceiling boards | 5 | mm | 4.5.4 | 900 | 6,4 | 11 780 | Gypsum board |
Cornices: Short wall | 2 | mm | 2 575 | 75 | 75 | 4.5.5 | Gypsum board |
Cornices: Long wall | 2 | mm | 4.5.6 | 75 | 75 | 9 150 | Gypsum board |
Metal cover strips | 4 | mm | 2 575 | 20 | 7 | 4.5.7 | Steel/ Aluminium |
(7)
4.6 FIGURE 4.6 below shows the floor plan of a room. You must install ceiling boards and skirtings in this room.
SPECIFICATIONS:
- External measurements of the room: 6 500 mm x 3 800 mm
- The external walls are one-brick walls (220 mm).
- Door opening: 2 100 mm x 900 mm
- Size of ceiling boards: 3 900 mm x 900 mm
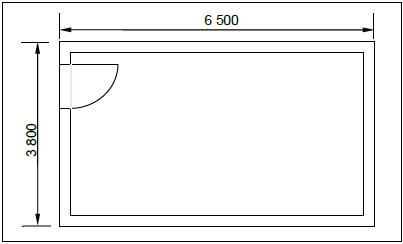 FIGURE 4.6
FIGURE 4.6
Use ANSWER SHEET 4.6 and answer the following questions.
4.6.1 Calculate the inside floor area of the room in square metres (m²). Round off your answer to TWO decimals. (6)
4.6.2 Calculate the area of ONE ceiling board in square metres (m²). (3)
4.6.3 Calculate the total length of the skirtings for the room in metres (m). (4) [30]
QUESTION 5: APPLIED MECHANICS
Start this question on a NEW page.
5.1 FIGURE 5.1 below shows a shaped lamina. All dimensions are in millimetres.
Study the lamina and calculate the centroid of the lamina from B–B. Round off your answer to TWO decimal places.
HINT: Use the formula on the FORMULA SHEET 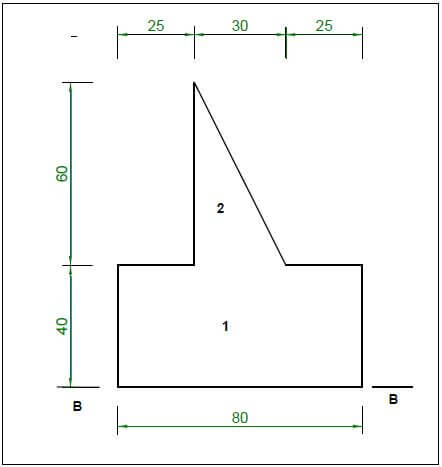
FIGURE 5.1 (10)
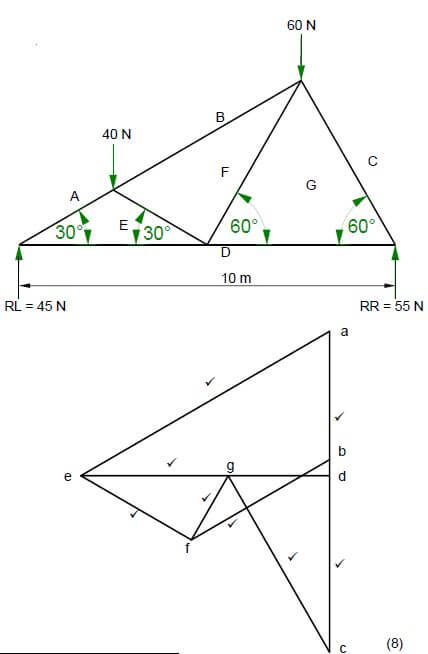
5.2 FIGURE 5.2 below shows the space diagram of a truss with two point loads and a span of 10 metres. 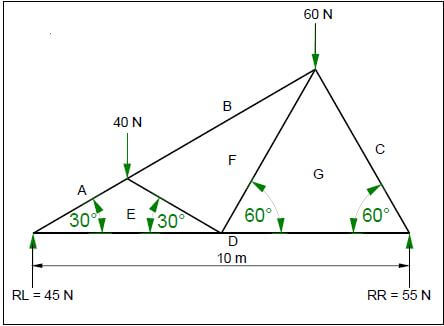
FIGURE 5.2
5.2.1 Use ANSWER SHEET 5.2 and develop and draw a vector diagram to determine the nature and magnitude of the forces in the members of the truss graphically.
Use scale 1 mm = 1 N. (8)
5.2.2 Use the information in the space diagram and vector diagram and complete the table on ANSWER SHEET 5.2. (4)
5.3 FIGURE 5.3 below shows the space diagram of a beam with a span of 10 metres, with three point loads and a uniformly distributed load. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.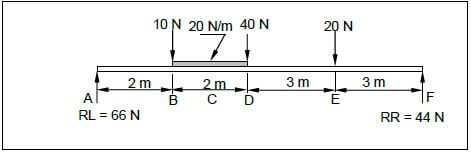
FIGURE 5.3
5.3.1 Convert the uniformly distributed load to a point load and write down the value of the converted point load. (1)
5.3.2 Determine the distance of the converted uniformly distributed load that now is a point load from RR. (1)
5.3.3 Determine the distance of the converted uniformly distributed load that now is a point load from RL. (1)
5.3.4 The value of the bending moments at A = 0 Nm, B = 132 Nm, C = 178 Nm, D = 204 Nm, E = 132 Nm and F = 0 Nm. Use ALL the available information and draw the bending moment diagram on ANSWER SHEET 5.3. Use scale 1 mm = 2 Nm. (5) [30]
QUESTION 6: GRAPHICS AND COMMUNICATION
6.1 FIGURE 6.1 below shows the west elevation of a proposed dwelling. Study the drawing and complete the table on ANSWER SHEET 6.1. 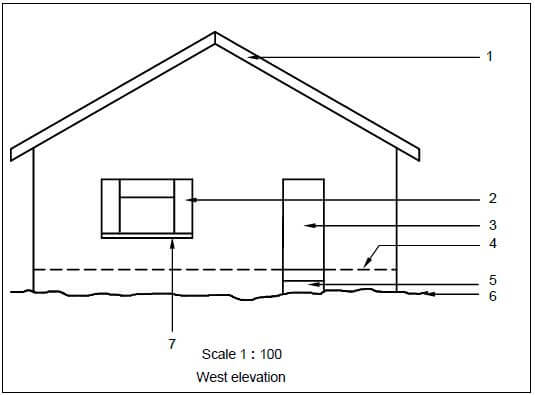
FIGURE 6.1 (15)
6.2 FIGURE 6.2 below shows the floor plan of a site office with a gable roof with open eaves. 
FIGURE 6.2
Draw on ANSWER SHEET 6.2, to scale 1 : 20, a sectional view on section line A–A. Show the top 600 mm of the wall and just more than half of the king post roof truss. Start your drawing from corner A on ANSWER SHEET 6.2.
Use the specifications on the next page.
SPECIFICATIONS:
- Wall: 220 mm wide, plastered on both sides
- Plaster: 20 mm thick
- Wall plate: 114 mm x 38 mm
- Span of roof: 4 110 mm
- A king post roof truss with an open eave is used.
- Slope of roof: 30°
- Tie beam: 114 mm x 38 mm
- Rafters: 114 mm x 38 mm
- King post: 114 mm x 38 mm
- Branders (Brandering): 38 mm x 38 mm on 450 mm centre to centre
- Gypsum ceiling board: 6 mm
- Cornice: 75 mm x 75 mm
- Eaves overhang: 500 mm
Print the title and scale below the drawing.
Print any FOUR labels on the drawing. (25) [40]
TOTAL: 200
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 1.12 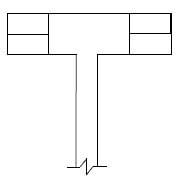
FIGURE 1.12
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
One-brick wall | 2 | |
Half-brick wall (T-junction) | 1 | |
Three-quarter bricks | 2 | |
TOTAL | 5 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 3.6 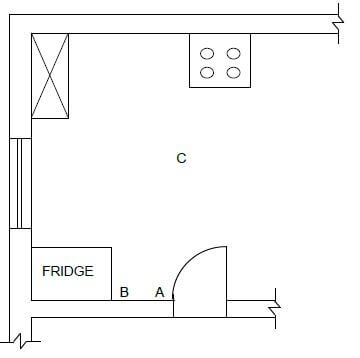
FIGURE 3.6
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
2-way light switch | 2 | |
Socket outlet | 2 | |
Light | 2 | |
Electrical wiring | 2 | |
TOTAL | 8 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 3.7 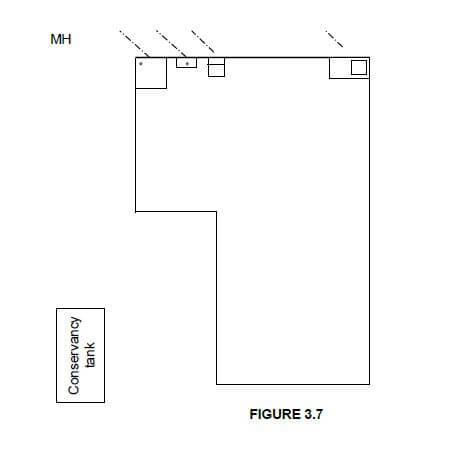
FIGURE 3.7
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Rodding eye | 1 | |
Gully | 1 | |
Ventilation pipe | 1 | |
Main sewerage pipes | 2 | |
Inspection eyes | 4 | |
Manhole | 1 | |
Any TWO abbreviations for the sanitary fixtures | 2 | |
TOTAL | 12 |
SDFS
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 4.6
Complete your answers in the spaces indicated with _____________.
A | C | D | |
Inside measurement of room: | |||
Long walls = mm – _____ mm | |||
= mm | |||
Short walls = mm – _____ mm | |||
= _____ mm | |||
(4) | |||
1/ | ______ | Inside floor area of room: | |
______ | _____ m² | (2) | |
Area of one ceiling board: | |||
1/ | One board is 3 900 mm x 900 mm. | ||
_______ | _____ m² | (3) | |
Length of skirtings: | |||
= | |||
= | |||
= | |||
(4) | |||
(13) |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 5.2
5.2.1 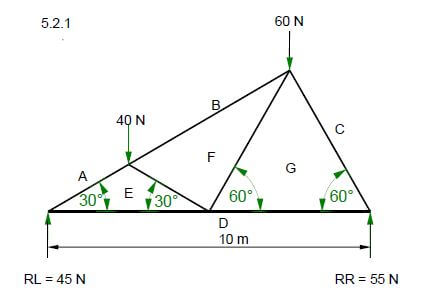
 (8)
(8)
5.2.2
MEMBER | NATURE | MAGNITUDE |
FG | ||
BF |
Tolerance of 1 N to either side (4)
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 5.3 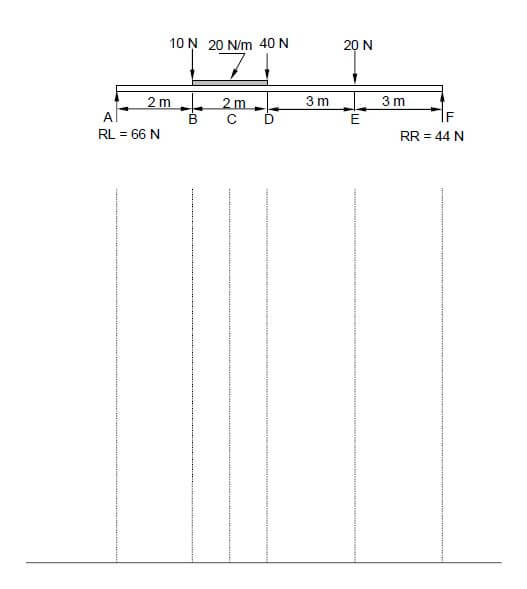
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ANSWER SHEET 6.1
NO. | QUESTIONS | ANSWERS | MARKS |
1 | Name the scale used for the west elevation. | 1 | |
2 | Identify number 1. | 1 | |
3 | Identify number 2. | 1 | |
4 | Identify number 3. | 1 | |
5 | Identify number 4. | 1 | |
6 | Identify number 5. | 1 | |
7 | Identify number 6. | 1 | |
8 | Identify number 7. | 1 | |
9 | Name the material that can be used for the soffit board at a closed eave. | 1 | |
10 | Recommend a suitable exterior finish for the wall. | 1 | |
11 | On which elevations will the gutters of this house be placed? | 2 | |
12 | Draw the roof lines for the roof of the building shown in FIGURE 6.1 in the column alongside. |  | 3 |
TOTAL | 15 |
CENTRE NUMBER: |
EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARKS | LM |
Correctness of drawing | 3 | |
External wall | 1 | |
Symbol for wall | 1 | |
Plaster | 2 | |
Wall plate | 1 | |
Tie beam | 1 | |
Rafters | 2 | |
King post | 1 | |
Branders (Brandering) | 1 | |
Ceiling board | 1 | |
Cornice | 1 | |
Fascia board | 1 | |
Print title and scale | 2 | |
Any FOUR labels | 4 | |
Application of scale:
| 3 | |
TOTAL | 25 |
ANSWER SHEET 6.2 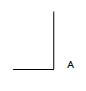
FORMULA SHEET
IMPORTANT ABBREVIATIONS
| SYMBOL | DESCRIPTION | SYMBOL | DESCRIPTION | SYMBOL | DESCRIPTION |
| c | Centroid | b | Breadth/Width | r | Radius |
| ℓ | Length | s | Side | A | Area |
FORMULAE
| AREA OF | FORMULA (in words) | FORMULA (in symbols) | FORMULA FOR THE POSITION OF CENTROIDS | |
| X-axis | Y-axis | |||
| Square | side x side | s x s | s 2 | s 2 |
| Rectangle | length x breadth | ℓ x b | ℓ 2 | b 2 |
| Right-angled triangle | ½ x base x height | ½b x h | b 3 | h 3 |
| Equilateral triangle/ Isosceles triangle | ½ x base x height | ½b x h | b 2 | h 3 |
Position of centroid = (A1 x d) ± (A2 x d)
Total area
OR
Y = ΣAy
ΣA
OR
X = ΣAx
ΣA
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
CIVIL TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1: CONSTRUCTION, SAFETY AND MATERIAL
1.1
1.1.1 B ✔ (1)
1.1.2 E ✔ (1)
1.1.3 A ✔ (1)
1.1.4 D ✔ (1)
1.1.5 F ✔ (1)
1.1.6 C ✔ (1)
1.1.7 H ✔ (1)
1.1.8 I ✔ (1)
1.1.9 G ✔ (1)
1.1.10 J ✔ (1)
1.2
1.2.1 A – To protect your feet against falling objects. ✔ (1)
1.2.2 B – To protect your feet when working with wet material. ✔ (1)
1.3 The paint conceals defects ✔ (1)
1.4
- Excavations must be fenced off. ✔
- Red warning lights should be placed at intervals to warn the public. ✔
- All excavations must take place under supervision.
- The contractor must test the stability of the terrain before commencement of excavations.
- Shoring should be cross braced.
- Bracing should be strong enough to support the shoring.
- No tools or materials other than those in use are allowed inside the trench when excavations are in progress.
- Access to the excavation should be safe e.g. ladders can be used.
- A responsible person must inspect and investigate underground electricity and water supply.
- The sides should be braced and protected if deeper than 1,5 meters.
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE OR ANY OTHER ACCEPTABLE ANSWER (2)
1.5
- Baseplate ✔
- Mould/Cube ✔
- Tamping rod ✔
- Plaster trowel/straight edge/shovel
ANY THREE OF THE ABOVE (3)
1.6
- Water makes the fresh concrete workable. ✔
- Water acts as a lubricant.
- Water is also needed for the hydration process.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
1.7
1.7.1To prevent moisture from getting into the building. ✔ (1)
1.7.1 To prevent moisture from moving up in the walls. ✔ (1)
1.8
- Preservatives with a base of water-soluble salts. ✔
- Varnish
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
1.9 Roof tiles/Clay tiles/Concrete tiles ✔ (1)
1.10 Ridge capping ✔ (1)
1.11 Gang nails/plate connectors ✔ (1)
1.12 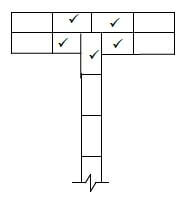 (5)
(5)
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATES MARK |
One brick wall | 2 | |
Half brick wall (T-junction) | 1 | |
Three-quarter bricks | 2 | |
TOTAL | 5 |
[30]
QUESTION 2: ADVANCED CONSTRUCTION AND EQUIPMENT
ANSWER THIS QUESTION ON A NEW PAGE.
2.1
2.1.1 C ✔ (1)
2.1.2 D ✔ (1)
2.1.3 A ✔ (1)
2.1.4 B ✔ (1)
2.1.5 A ✔ (1)
2.2
2.2.1 Portable electric generator ✔ – It is used to generate electricity ✔ (2)
2.2.2 Portable electric circular saw ✔ – It is used for cross cutting and ripping of timber. ✔ (2)
2.3 Chalk line ✔ (1)
2.4
- Flat steel square ✔
- Tape measure
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
2.5
- Rough arch will be built with common bricks ✔
- Gauge arch will be built with face bricks ✔ (2)
2.6
2.6.1 Driven in-situ pile ✔ (1)
2.6.2
- Low bearing capacity of soil ✔
- Subsoil – subjected to movement ✔
- Subsoil – subjected to high moisture content.
- Recently placed filling materials that is not sufficiently compacted
- Unstable soil structure
- High water table
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
2.6.3 Steel reinforcement ✔ (1)
2.7
2.7.1 Twisted square bar ✔ (1)
2.7.2 Round bar (mild steel) ✔ (1)
2.8
- – Landing ✔
- – Rise ✔
- – Tread ✔ (3)
2.9
- Blow holes ✔
- Uneven colour/discoloration ✔
- Honey comb effect/Leaking of grout
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
2.10
2.10.1 Cavity wall ✔ (1)
2.10.2
- A – Wall tie ✔
- Keeps the two skins of the wall securely together. ✔
- It strengthens the wall
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
2.10.3
- B – Weak concrete mixture ✔
- Concrete mixture
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
2.10.4
- To strengthen the wall below the DPC (damp proof course) ✔
- To close the cavity below the damp proof course
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
2.10.5 C – Damp-proof membrane ✔ (1)
2.10.6 50 mm ✔ (Unit must be part of the answer) (1)
2.11
2.11.1
- – Cladding (or any cladding material) ✔
- –
- Timber floor board ✔
- Base plate
- Base board
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE FOR B (2)
2.11.2
- Steel ✔
- Metal
- Aluminium
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
2.11.3
- There is no wet material ✔
- There is no heavy material to carry ✔
- Dry walls are light in weight.
- Dry walls are easier to install
- Dry walls are easy to remove if required
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
2.12
2.12.1 Rib and Block floor ✔ (1)
2.12.2
- – Rib ✔
- – Hollow block/Block ✔
- – Reinforcing steel/Steel rod/Reinforcement ✔ (3) [40]
QUESTION 3: CIVIL SERVICES
3.1
3.1.1 P-trap ✔ (1)
3.1.2 Washbasin/Urinal/Shower/Sink ✔ (1) ANY ONE
3.2
3.2.1
- -Is the inlet pipe for cold water ✔
- -Is the outlet pipe for warm water ✔ (2)
3.2.2 To shut down water supply during maintenance. ✔
ANY OTHER ACCEPTABLE ANSWER (1)
3.2.3
- To prevent water from leaking through the ceiling ✔
- It is compulsory to install a drip tray
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
3.3
3.3.1 Storm water is hail, snow, rain that falls to the earth in large quantities. ✔
ANY OTHER ACCEPTABLE ANSWER (1)
3.3.2 Storm water is guided into the channels where after the water is guided to storm water pipes and catchment areas. ✔
ANY OTHER ACCEPTABLE ANSWER (1)
3.4 Water in shallow wells is:
- Easily dug out ✔
- Cheap
- Relatively reliable
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
3.5 Wind pump ✔ (1)
3.6 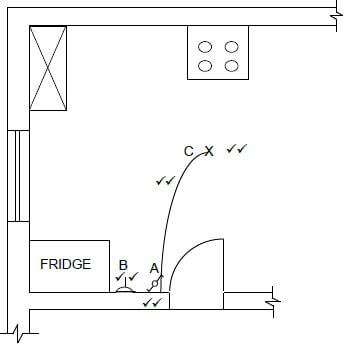 (8)
(8)
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
2 way light switch | 2 | |
Socket outlet | 2 | |
Light | 2 | |
Electrical wire | 2 | |
TOTAL | 8 |
3.7 ANSWER SHEET 3.7 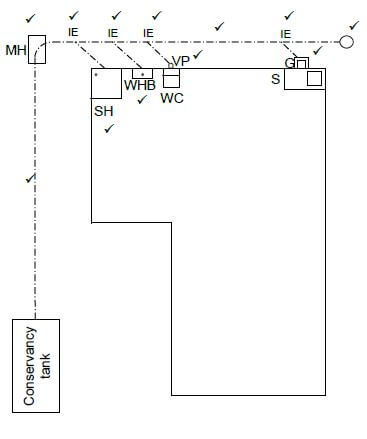 (12)
(12)
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARK | CANDIDATE'S MARK |
Rodding eye | 1 | |
Gully | 1 | |
Vent pipe | 1 | |
Main sewerage pipes | 2 | |
Inspection eyes | 4 | |
Manhole | 1 | |
Any TWO abbreviations for the sanitary fixtures | 2 | |
TOTAL | 12 |
[30]
QUESTION 4: QUANTITIES, MATERIALS AND JOINING
4.1
4.1.1
- Gang nail ✔ (1)
USE: - Gang nails are used to join the members of roof trusses. ✔
- Extend the length of a timber board/beam.
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE USES (1)
4.1.2
- Bolt and nut ✔ (1)
USE: - Bolts and nuts are used to join the members of roof trusses. ✔
- Join material to brackets
- To fix truss hangers to rafters
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE USES (1)
4.1.3
- Dry wall screw ✔ (1)
USE: - Drywall screws are used to fix dry wall materials. ✔
- Joining ceilings and battens to other members
- Joining timber to each other (1)
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE USES
4.2
- Rawl bolt/Expansion anchor ✔
- Sleeve anchor
- Dina bolt
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
4.3
- Compression joint ✔
- Capillary joint
ANY ONE OF THE ABOVE (1)
4.4
- Screws have greater holding power than nails ✔
- They can be fixed where vibration has to be avoided ✔
- Screws can easily be removed
- The appearance of screws is better in finishing than nails
ANY TWO OF THE ABOVE (2)
4.5
4.5.1 38 or 38 mm ✔ (1)
4.5.2 2 349 or 2 349 mm ✔ (1)
4.5.3 5 √ (1)
4.5.4 2 575 or 2 575 mm ✔ (1)
4.5.5 5 150 or 5 150 mm ✔ (1)
4.5.6 4 500 or 4 500 mm ✔ (1)
4.5.7 10 300 or 10 300 mm ✔ (1)
4.6
A | B | C | D |
Inside measurement of: | |||
Long walls = 6 500 – 2/220 ✔ | |||
= 6 060 mm ✔ | |||
Short walls = 3 800 – 2/220 ✔ | |||
= 3 360 mm ✔ | |||
(4) | |||
1/ | 6,06 | Inside floor area of the room is | |
3,36 ✔ | 20,36 m2 ✔ | (2) | |
Area of one ceiling board: | |||
1/ | 3,9 | One board is 3 900 mm x 900 mm | |
0,9 ✔ | 3,51 m2 ✔ | (3) | |
Length of skirting: | |||
= 2(6 060 ✔+ 3 360 ✔) – 900 mm ✔ | |||
= 17,94 m ✔ | |||
OR 12 120 + 6 720 - 900 | |||
=17,94 m | |||
OR 6 060 + 6 060 + 3 360 + 3 360 - 900 | |||
=17,94 m | |||
(4) | |||
(13) |
[30]
QUESTION 5: APPLIED MECHANICS
5.1
5.1.1
- (A1 x d) + (A2 x d)
Total area
= (3 200 x 20) + (900 x 60)
4 100 ✔
= 64 000 mm3 + 54 000 mm3
4 100
= 118 000 mm3 ✔
4 100 mm2
= 28,78 ✔ mm ✔
OR
Part | Area (A) | Y | AY |
1 | 3 200 mm² ✔ | 20 mm ✔ | 3 200 x 20 = 64 000 mm3 ✔ |
2 | 900 ✔ mm² | 60 mm ✔ | 900 mm x 60 mm = 54 000 mm3 ✔ |
∑ | 4 100 mm² ✔ | 118 000 mm3 |
- Y = ∑ Ay
∑ A
= 118 000 mm3 ✔
4 100 mm2
= 28,78 ✔ mm ✔ (10)
5.2.1
 (8)
(8)
MEMBER | NATURE | MAGNITUDE |
FG | Tie ✔ | 23 N ✔ |
BF | Strut ✔ | 50 N ✔ |
Tolerance of 1 N to either side (4)
NOT TO SCALE DUE TO ELECTRONIC TRANSFER USE A MASK TO MARK THIS QUESTION
5.3
5.3.1 40 Nm ✔ (1)
5.3.2 7 m ✔ (1)
5.3.3 3 m ✔ (1)
5.3.4 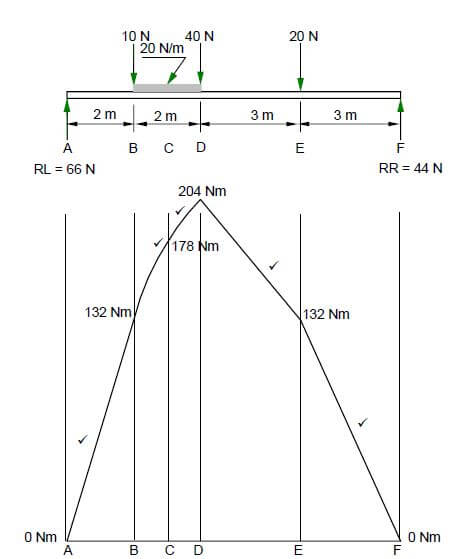 (5)
(5)
SCALE 1 mm = 2 Nm
NOT TO SCALE DUE TO ELECTRONIC TRANSFER
USE A MASK TO MARK THIS QUESTION
- If the bending moment diagram is not to scale, deduct 1 mark.
- Marks are allocated for each line between A to F.
- If the lines between B and D are straight lines no marks will be awarded for these lines. [30]
ANSWER SHEET 6.1
NO. | QUESTIONS | ANSWERS | MARKS |
1 | Name the scale used for the West elevation. | 1:100 ✔ | 1 |
2 | Identify number 1. | Barge board ✔ | 1 |
3 | Identify number 2. | Window/window pane/glass casement ✔ | 1 |
4 | Identify number 3. | Door/door opening ✔ | 1 |
5 | Identify number 4. | FFL/Finished floor level ✔ | 1 |
6 | Identify number 5. | Step ✔ | 1 |
7 | Identify number 6. | NGL/Natural ground level ✔ | 1 |
8 | Identify number 7. | Window sill ✔ | 1 |
9 | Name the material that can be used for the soffit board at a closed eave? | Fibre cement ✔ | 1 |
10 | Recommend a suitable exterior finish for the wall. | Paint/plaster/face brick/ cladding ✔ | 1 |
11 | Deduce on which elevations will the gutters be placed in this house? | North elevation ✔ and South elevation✔ | 2 |
12 | Draw the roof lines for the roof of the building shown in FIGURE 6.1 in the column alongside. |  | 3 |
TOTAL | 15 |
QUESTION 6: GRAPHICS AND COMMUNICATION
ANSWER SHEET 6.2 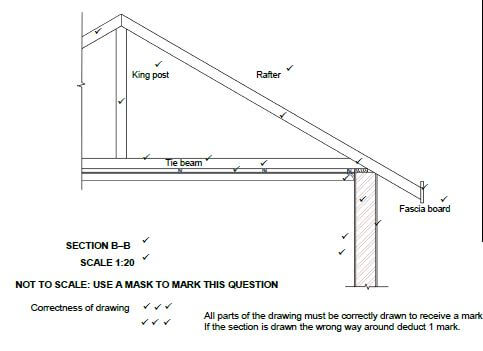
ASSESSMENT CRITERIA | MARKS | LM |
Correctness of drawing | 3 | |
External wall | 1 | |
Symbol for wall | 1 | |
Plaster | 2 | |
Wall plate | 1 | |
Tie beam | 1 | |
Rafters | 2 | |
King post | 1 | |
Brandering | 1 | |
Ceiling board | 1 | |
Cornice | 1 | |
Fascia board | 1 | |
Print title and scale | 2 | |
Any FOUR labels | 4 | |
Application of scale:
| 3 | |
TOTAL | 25 |
[40]
200
SONNET 116 POEM QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS GRADE 12
SONNET 116 POEM
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
GRADE 12
SONNET 116: LET ME NOT TO THE MARRIAGE OF TRUE MINDS
BY WILLIAM SHAKESPEARE
Let me not to the marriage of true minds
Admit impediments. Love is not love
Which alters when it alteration finds,
Or bends with the remover to remove.
O no! it is an ever-fixed mark
That looks on tempests and is never shaken;
It is the star to every wand'ring bark,
Whose worth's unknown, although his height be taken.
Love's not Time's fool, though rosy lips and cheeks
Within his bending sickle's compass come;
Love alters not with his brief hours and weeks,
But bears it out even to the edge of doom.
If this be error and upon me prov'd,
I never writ, nor no man ever lov'd.
QUESTIONS
Refer to the poem above and answer the questions below.
- Complete the following sentence by using the words provided in the list below.
This is a typical (1.1) ... sonnet because of the three (1.2) ... and the (1.3) ... that rhymes. (3)Petrarchan; sestet; Elizabethan; Couplet; quatrains; octave - Quote a word in the first line which has connotations of love and unity. (1)
- Refer to the following words in line 1 (“... the marriage of true minds”).
To what do these words refer? (2) - Refer to lines 2-4 (“Love is not love ... remover to remove”).
Using your own words, explain the meaning of these lines. (2) - Choose the correct answer to complete the following In line 5, the words “O, no ...” show that the speaker is ...
- uncertain.
- arrogant.
- doubtful.
- convinced. (1)
- Refer to line 7 (“It is the star to every wand’ring bark”).
Give the literal meaning of the underlined words. (1) - Is the following statement TRUE or FALSE? Quote THREE consecutive words to support your answer.
It is impossible to measure the value of love. (2) - Refer to the following words in line 9 (“Love’s not Time’s fool”). Identify the figure of speech used (1)
- Refer to lines 13 and 14 (“If this be ... man ever loved”).
How does the poet use the last two lines to make his argument on true love convincing? (2) - Do you agree with the speaker’s view of love? Explain your (2) [17]
Note:
- Connotations - words with meanings linked to a key word. For example, the connotations of "morning" are fresh,new,early.
- Consecutive words - words that directly follow after one another.
ANSWERS
|
Hint ; In question 7, one mark will be given if the first part of the answer (true) is correct. To get 2 marks, give the correct answer and quote the correct three words.
Note: When a question asks for your own view or opinion, you must say if you agree or not and then give a reason for your viewpoint to get 2 marks.
DEATH BE NOT PROUD POEM QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS GRADE 12
DEATH BE NOT PROUD POEM
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
GRADE 12
Death, be not proud (Holy Sonnet 10)
Death, be not proud, though some have called thee
Mighty and dreadful, for thou are not so;
For those whom thou think'st thou dost overthrow
Die not, poor Death, nor yet canst thou kill me.
From rest and sleep, which but thy pictures be,
Much pleasure; then from thee much more must flow,
And soonest our best men with thee do go,
Rest of their bones, and soul's delivery.
Thou'art slave to fate, chance, kings, and desperate men,
And dost with poison, war, and sickness dwell,
And poppy'or charms can make us sleep as well
And better than thy stroke; why swell'st thou then?
One short sleep past, we wake eternally,
And death shall be no more; Death, thou shalt die.
QUESTIONS
Refer to the poem above and answer the questions below.
- Refer to the following words in line 1 (“Death be not proud”):
Identify the figure of speech used (1) - Explain why the poet has used this figure of (2)
Hint: to explain this figure of speech, think of how and why the poet talks to Death as a person. - Which three words from the list below could be used to describe Death? (3)
arrogant; clever; proud; friendly; over-confident; loving - Is the following statement TRUE or FALSE?
Everyone fears Death.
Quote ONE word from the poem to support your answer. (2)
note: Write down either true or false and then your one word answer. Remember that this is a quote so make sure you spell the word exactly as it is in the poem. - Complete the following sentences by using the words provided in the list Write down only the words next to the question number.
The poet says that “rest and sleep” are “pictures” of Death, meaning they only (5.1) ... like death. However, people rest and sleep for (5.2) ... (2)entertainment; temporary; relaxation; end; look; final - Using your own words, write down THREE causes of death statedin the poem. (3)
- Refer to the following words in line 12 (“why swell’st thou then?”) Explain the meaning of these words as they are used in the (1)
- Refer to lines 10-14. Name two things which have the sameeffect as Death. (2)
- Write down the correct tone word in brackets for each of the lines below:
- “Death be not proud for, thou art not so” (lines 1- 2) (triumphant/critical/ mocking)
- “Thou art slave to Fate, Chance, kings, and desperate men” (line 9) (triumphant/critical/mocking)
- “And poppy, or charms can make us sleep as well, And better than thy stroke” (lines 11-12)
(triumphant / critical / mocking) - Death, thou shalt die.” (line 14) (triumphant/critical/mocking) (4)
- In the last two lines (13–14) the speaker’s tone is ...
- triumphant and victorious
- submissive and angry.
- sad and disappointed.
- thoughtful and fearful. (1)
- Discuss the message the poem has for its (2) [23]
To get 2 marks, you must give 2 points.
ANSWERS
- Personification OR apostrophe ✓ (1)
- Personification: The poet gives Death human qualities in order to mock/poke fun at/ridicule/laugh at Death/ to show that Death is like an ordinary human/mortal/ not powerful ✓✓
OR
Apostrophe: He addresses Death as if Death is present/ in front of him. ✓✓ (2) - arrogant ✓/proud ✓/over-confident ✓ (3)
- False. “some” ✓✓ (2)
- 5.1 look ✓ (1)
5.2 relaxation ✓ (1) -
- You are destined to die in a certain way (Fate). ✓
- You can die in an accident (Chance). ✓
- Your death can be ordered by kings/powerful people. ✓
- You can die in a war. ✓
- You can be murdered. ✓
- You can kill yourself/ suicide. ✓
- You can die by taking poison. ✓
- You can die from illness/disease. ✓ (3)
- The poet is questioning/asking why Death is filled with pride/proud/OR why Death is arrogant/pompous/haughty/ swollen with pride. ✓ (1)
- “poppy” ✓ and “charms” ✓ (2)
-
- critical ✓
- critical ✓
- mocking ✓
- triumphant ✓ (4)
- A / triumphant and victorious ✓ (1)
-
- You should not be afraid to die. ✓
- Death has no power. ✓
- Death is temporary/does not last forever. ✓
- There is life after death. ✓ (2) [23]
NOTE:
- In question 4, a mark is awarded only if both parts of the answer are correct: False and "some".
- Any three of the answers in question 6 are acceptable
- Any 2 of the answers n question11 are acceptable
AN ELEMENTARY SCHOOL CLASSROOM IN A SLUM POEM QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS GRADE 12
AN ELEMENTARY SCHOOL CLASSROOM IN A SLUM POEM
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
GRADE 12
An Elementary School Classroom in a Slum
QUESTIONS
- Complete the following sentences by using the words provided in the list Write down only the words next to the question number (1 - 3).
The setting (background) of the poem is a (1) ... school in a (2) ... area. There are very few (3) ... in the classroom. (3)good; primary; children; resources; high; poor - Using your own words, describe the children in the classroom
State THREE points. (3)
NOTE: in this question use your own words. Do not quote directly from the poem. For 3 marks, give 3 points. - Refer to lines 6-8.
In your OWN words, say how this child is different from the rest of the children in his class. (1) - Refer to stanza
How does the speaker feel about the “donations”? Give a reason for your answer. (2)
Note: When you are asked to give a reason, the reason must be based on the poem. - Refer to line 15 (“A narrow street sealed in with a lead sky”).
5.1 Identify the figure of speech used (1)
5.2 Explain why the poet has used this figure of (2) - Refer to stanza
Is the following statement TRUE or FALSE? Quote TWO consecutive words to support your answer.
The children’s homes are large and comfortable. (2) - Choose the correct answer to complete the following sentence: In stanza 4, the speaker’s tone shows that he is ...
- commenting critically.
- pleading passionately.
- complaining bitterly.
- demanding forcefully. (1)
- Refer to stanza
Name ONE experience the speaker wishes the children to have. (1) - In your view, how does the speaker (poet) feel about the children? Using your OWN words, give TWO reasons for your (3) [19]
Note: When asked for your view, the answer requires your emotional response and understanding of the poem. For 3 marks, make 1 point about the speaker,s feeling (1 mark) and then give 2 reasons (2 marks).
ANSWERS
|
AUTO WRECK POEM QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS GRADE 12
AUTO WRECK POEM
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
GRADE 12
"Auto Wreck" by Karl Shapiro
Its quick soft silver bell beating, beating,
And down the dark one ruby flare
Pulsing out red light like an artery,
The ambulance at top speed floating down
Past beacons and illuminated clocks
Wings in a heavy curve, dips down,
And brakes speed, entering the crowd.
The doors leap open, emptying light;
Stretchers are laid out, the mangled lifted
And stowed into the little hospital.
Then the bell, breaking the hush, tolls once.
And the ambulance with its terrible cargo
Rocking, slightly rocking, moves away,
As the doors, an afterthought, are closed.
We are deranged, walking among the cops
Who sweep glass and are large and composed.
One is still making notes under the light.
One with a bucket douches ponds of blood
Into the street and gutter.
One hangs lanterns on the wrecks that cling,
Empty husks of locusts, to iron poles.
Our throats were tight as tourniquets,
Our feet were bound with splints, but now,
Like convalescents intimate and gauche,
We speak through sickly smiles and warn
With the stubborn saw of common sense,
The grim joke and the banal resolution.
The traffic moves around with care,
But we remain, touching a wound
That opens to our richest horror.
Already old, the question Who shall die?
Becomes unspoken Who is innocent?
For death in war is done by hands;
Suicide has cause and stillbirth, logic;
And cancer, simple as a flower, blooms.
But this invites the occult mind,
Cancels our physics with a sneer,
And spatters all we knew of denouement
Across the expedient and wicked stones.
QUESTIONS
Refer to the poem on page 31 and answer the questions below.
- Complete the following sentences by using the words provided in the list Write only the words next to the question number (1.1–1.3)
This poem describes how the (1.1) … rushes to the scene of the (1.2) … The (1.3) … are picked up and taken to hospital. (3)police van; accident; dead; ambulance; break-down; injured - Refer to stanza
2.1 At what time of the day does this incident happen? (1)
2.2 In lines 4-6 (“The ambulance at ... and illuminated clocks”) the ambulance is compared to a bird. Quote TWO separate words that support this (1) (2) - Choose the correct answer to complete the following Write only the answer (A-D).
The word “mangled” in line 9 tells us that ...- The vehicles are badly damaged.
- Some of the bystanders are very upset.
- The policemen are emotionless.
- The accident victims are seriously injured. (1)
- Refer to lines 15 and 16 (“We are deranged … and composed”).
Quote TWO separate words that show the difference in the reactions of the speaker and the policemen. (2) - Refer to line 25 (“We speak through sickly smiles ...”).
Explain why the onlookers have “sickly smiles”. (2) - Refer to stanza
Using your own words, name TWO things that the onlookers are concerned about. (2) - Complete the following sentences by using the words provided in the list below.
In the last stanza, the speaker argues that there is always a (7.1) ... for Suicide, while stillbirth is (7.2) ... However, a car crash (7.3)... the minds of ordinary people. (3)solution; confuses; reason; unnatural; clarifies; logical - Explain why the poet mentions war, suicide, stillbirth and cancer in a poem about a road (2)
- The poem was first published in Do you think it is still relevant today?
Discuss your view. (2) - Has this poem changed your understanding of the causes of road deaths? Discuss your (2) [22]
ANSWERS
|
ON HIS BLINDNESS POEM QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS GRADE 12
ON HIS BLINDNESS POEM
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
GRADE 12
ON HIS BLINDNESS BY JOHN MILTON
When I consider how my light is spent
Ere half my days in this dark world and wide,
And that one talent which is death to hide
Lodg'd with me useless, though my soul more bent
To serve therewith my Maker, and present
My true account, lest he returning chide,
"Doth God exact day-labour, light denied?"
I fondly ask. But Patience, to prevent
That murmur, soon replies: "God doth not need
Either man's work or his own gifts: who best
Bear his mild yoke, they serve him best. His state
Is kingly; thousands at his bidding speed
And post o'er land and ocean without rest:
They also serve who only stand and wait."
QUESTIONS
Refer to the poem On His Blindness by John Milton and answer the questions below.
- Complete the following sentences by using the words provided in the list Write only the words next to the question number (1.1–1.3)
This poem is a Miltonic (1.1) … The octave gives the reader the (1.2) … and the sestet gives the reader the (1.3) … (3)ballad; sonnet; problem; solution; cause; result - Refer to lines 1 and 2 (“When I consider ... world and wide”)
Quote TWO contrasting words that best describe the poet’s concern. (2) - Refer to line
3.1 Quote a word from the first line which Milton uses in place of “eyesight”. (1)
3.2 Why do you think he uses this word? (2) - Refer to lines 3 and 4 (“And that one ... Soul more bent”).
Why does the poet consider his talent to be useless? (2) - Refer to lines 6 and 7 (“My true account ... labour, light denied?”).
5.1 What is the poet’s fear in these lines? (1)
5.2 Why does he have this fear? (1) - Refer to line 8 (“I fondly But Patience, to prevent”).
6.1 Identify the figure of speech used (1)
6.2 Explain why the poet uses this figure of (2) - How does the poet’s mood, or how do his feelings change in the course of the poem?
Choose two words from the box below to complete this sentence:
At the start of the poem the poet feels 7.1… but at the end of the poem the poet experiences 7.2… (2)joy; acceptance; frustration; blind - Refer to lines 10 and 11 “Who best/Bear his mild yoke, they serve him best”.
Choose the correct word in brackets:
8.1 “his/him” are pronouns referring to (God/ the poet). (1)
8.2 “they” is a pronoun referring to (blind people/ all people). (1)
8.3.1 What figure of speech has been used in these lines?- Simile
- Metaphor
- Personification. (1)
8.3.2 Explain the figure of speech by choosing the correct answer to complete the sentence below.
The speaker is comparing the “mild yoke” that God puts on us to:- A donkey pulling a cart
- A small burden or job
- A kind joke (1)
- Choose the correct answer to complete the following Write only the answer (A–D).
The word which best describes the poet’s feeling in lines 9-14 (“That murmur, soon … stand and wait”) is:- acceptance.
- anger.
- depression.
- joy. (1)
- Refer to the last 4 lines of the
Is the following statement TRUE or FALSE? Write “true” or “false” and quote TWO consecutive words to support your answer. (2)
The poet feels that our burdens are not heavy. - Consider the poem as a
11.1 Do you feel sorry for the poet? Discuss your (2)
11.2 Do you think a disabled person should be expected to perform at the same level as an able person? Discuss your (2) [28]
Answers
- 1.1 Sonnet ✓
1.2 Problem ✓
1.3 Solution ✓ (3) - “Light” ✓ and “dark” ✓ (2)
- 3.1 “Light” ✓ (1)
3.2 Joy/ hope/ clarity/ visibility/ warms/ shining/ inspiration ✓✓ (2) - The poet’s talent is that he can write and he will not be able to use this talent if he is blind. ✓✓
OR
He is unable to see. Therefore, he cannot write poetry/ use his gift. ✓✓ (2) - 5.1 He is afraid that God will punish him/ not be satisfied with what he has done. ✓ (1)
5.2 He has not used the talent that God gave him./ He did not use his talent well./ He did not do a full day’s work. ✓ (1) - 6.1 Personification ✓ (1)
6.2 Personification: It becomes the voice of reason/ his conscience. ✓✓
OR
Patience becomes a person who is answering his question. ✓✓
OR
He personifies his thoughts in order to accept his burden. ✓✓ (2) - 7.1 Frustration ✓ (2)
7.2 Acceptance ✓ (1) - 8.1 “His”/ “him” are pronouns referring to God. ✓ (1)
8.2 “They” is a pronoun referring to all people. ✓ (1)
8.3.1 Metaphor ✓ (1)
8.3.2 The speaker is comparing the “mild yoke” to a small burden or job. ✓ (1) - A/acceptance ✓ (1)
- True. “Mild yoke”. ✓✓ (2)
- 11.1 Yes. He has a talent and he cannot use it. ✓✓
OR
No. I admire him for accepting his blindness. ✓✓ (2)
11.2 Yes. Disabled people often perform better than those without disabilities and tend to feel insulted if you make allowances for them. ✓✓
OR
No. You have to make concessions to accommodate disabled people as they have barriers to overcome. ✓✓ (2) [28]