Adele
RELIGIOUS STUDIES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
RELIGIOUS STUDIES
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 EXAMPLE 1: CHRISTIANITY
- Catholic
- Protestant
- Eastern Orthodox/Charismatic churches
EXAMPLE 2: AFRICAN TRADITIONAL RELIGION
- AmaZulu (Southern Africa)
- Aka
- Yoruba
NOTE: Award TWO marks for naming each of the branches. The total of SIX marks is awarded for naming ALL branches of the selected religion. In the case of Islam, six marks must be awarded if Sunni and Shi'a are mentioned. (6)
1.1.2 EXAMPLE 1: CHRISTIANITY
Catholicism
- The Pope is seen as the successor of St Peter.
- As such, he is believed to represent all Christians.
- The Catholic Church sees itself as the original church.
- They believe that everyone is born in sin because of Adam and Eve's disobedience to God.
- God is made up of three persons: the Father, the Son and the Holy Spirit.
- The Holy Spirit comes from God the Father and the Son.
Eastern Orthodox
- The Holy Spirit comes only from God the Father.
- They believe that they are the rightly guided church.
Protestantism
- The Bible has more authority than the Pope.
- They teach that faith is the way to salvation.
- They teach that salvation is a gift given freely through the work of Jesus Christ.
EXAMPLE 2: AFRICAN TRADITIONAL RELIGION
AmaZulu
- They believe in the existence of a Supreme Being called uMvelinqangi.
- His status is so high, that one must communicate with Him via intermediaries.
- Communication is conducted through the intermediaries called ancestors, also known as the living dead.
- The AmaZulu recognise the existence of different gods and goddesses, e.g. uNomkhubulwane in the Zulu nation.
- The Supreme Being is regarded as the source of life and the ultimate cause of death.
Aka
- They also believe in a creator spirit called Bembe.
- They believe that Bembe retired after the act of creation.
- Today, the forest spirit, called Dzengi, receives most attention. This is because the Aka believe that they need Dzengi's protection during hunting.
- They believe in reincarnation, but this reincarnation occurs within a species.
- They also believe in sorcerers and witches, who can send misfortune to people.
Yoruba
- They believe that Olorun/Olodumare is the creator spirit.
- They also believe in deities called orishas.
- Ancestors are also important to the Yoruba.
- They venerate and sacrifice to the ancestors, much like the amaZulu.
NOTE: Any seven relevant facts must be credited. Relevant alternative answers must be credited. (14)
1.1.3
- They have a complete split/separation
- An example is the Sunni-Shia split in Islam.
- What began as a political difference has grown into major differences in both beliefs and practices.
- A split can even result in open warfare.
- An example of this is the Irish war, between the Catholics and Protestants.
- Some religions are more accepting of their internal differences.
- An example of this is Hinduism.
- From its beginnings, local customs and beliefs were incorporated into the main body of Hinduism.
- There is therefore tolerance of internal differences.
- Inter-denominational organisations are formed, to find common ground, and to unite the various subgroups of a religion.
- An example of this is the South African Council of Churches.
- Its aim is to unite the various branches of Christianity, after the divisions caused by apartheid.
- In addressing common social challenges (e.g. poverty), various denominations work together for the common good of humanity.
- A coordinated effort allows for a more efficient and economical use of resources.
- Examples of this are the Salvation Army and Gift of the Givers.
NOTE: Other relevant answers must be credited. (14)
1.2 EXAMPLE 1 :TAOISM
- Humans are a tiny, microscopic by-product of the Tao's creation.
- The Tao is infinitely more powerful than humans.
- Humans are not a special creation, and they are not in charge of the world.
- The universe will continue on its path, as determined by the Tao.
- Whatever humans do is exactly according to the whims of the Tao.
- Humans should look after the earth because polluting it is harmful for us.
- It is not done to appease the Tao.
- Humans can destroy only a small part of creation.
- In spite of this, the bountiful creative activity of the Tao will continue.
EXAMPLE 2: JUDAISM
- Humans are seen as God's most amazing creation.
- However, Judaism also teaches that humans are weak and insignificant.
- This is because of our temptation to sin.
- By following the Torah, man can achieve spiritual communion with God.
- As humans are created in the image of God, the goal of human existence is to try and be like God.
- Humans must not only believe in the teachings, but must express their faith through right actions.
- A major action that Jews must carry out is the act of charity.
- This is aimed at uplifting the Jewish community.
- It also includes outreach programmes for non-Jews, as their right action must benefit mankind as a whole. (16)
QUESTION 2
2.1
- In all religions, the original inspiration was first spread by oral tradition.
- This means that the original message was transmitted from generation to generation by word of mouth.
- Oral tradition was a normative source of primary importance throughout religious history.
- In African Traditional Religion, the family lineage is the primary sacred text.
- Sacred text is still spread through oral tradition, e.g. African Traditional Religion.
- The technology of writing entered religion about 4000 years ago.
- Oral traditions that were written down became more rigid.
- The sacred text for Christianity is the Bible.
- It contains the teachings of Jesus Christ. They were first transmitted from generation to generation through word of mouth.
- Eastern religions place less emphasis on sacred text than the Abrahamic faiths. The value of oral traditions is more significant in Eastern religions.
- Oral tradition is flexible as it reflects local dialects and cultures.
NOTE: Other relevant responses must be credited. (20)
2.2
2.2.1
- Prior to 1859, it was only religion that explained the existence of man and the universe.
- For example, the Book of Genesis in the Bible details how God created the universe, as well as man.
- Darwin's theory of evolution provided an alternative explanation of creation, which differs from the Abrahamic religious explanation of creation.
- This theory further provided an explanation that did not require the existence of a Supreme Being.
- Darwin's theory also relegated man to being just another animal that had evolved from apes.
- Most religions, however, give a special status to man.
- In the Abrahamic faiths, man is said to be created in the 'image of God'.
- The influence of this theory challenged the authenticity of the sacred texts as a message from God.
- Most people started to treat the Genesis account of creation as symbolic.
- Eastern religions, such as Hinduism and Taoism, were unaffected by Darwin' theory.
- This is because they lay less emphasis on right beliefs, and attach more importance to right action.
NOTE: Other relevant responses must be credited. (16)
2.2.2
- Religion is seen as divisive and exploitative.
- Many wars and other conflicts have been blamed on religion.
- With the development of printing, mass education and more recently, social media, the public have developed confidence to be independent thinkers.
- They have faith in their own powers of reasoning to question religious doctrine.
- Also, Darwin's theory of evolution is taught in schools as part of the curriculum.
- Recent scientific discoveries have contributed to the popularity of the theory, e.g. the humanoid fossils found at Marupeng (Cradle of human kind).
- It provides an alternative explanation to the religious point of view about how man came into existence.
- There is also a decline in religiosity (interest in religion)
- The increase in scientific research which provides solutions to human problems, results in people having more faith in science than in religion.
NOTE: Other relevant responses must be credited. (14) [50]
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1 EXAMPLES:
- A. Irish War of Independence.√√ Catholics√√ against Protestants. √√
- B. Israel-Palestine Conflict√√ Israelis/Jews√√ against Palestinians (Muslims and Christians.) √√
- C. Sri Lanka. √√Tamils (Hindu)√√ against Buddhists/Sinhalese√√ (6)
3.1.2 A.
- Northern Ireland is constitutionally part of the United Kingdom (UK).
- The population is made up of Catholics and Protestants.
- The conflict began in 1968 and ended in 1998.This period is referred to as 'The Troubles'.
- For many years, the Catholics of Northern Ireland waged a war of independence against the U.K, and wanted to unite with the Republic of Ireland (Eire).
- The militia were known as the Irish Republican Army (I.R.A.).
- The Protestants of Northern Ireland resisted, and supported the U.K.
- This conflict can be seen as religious nationalism, as Catholics wanted religious unity with Ireland.
- It can also be seen as fundamentalist, as Protestants were not allowed to join the IRA.
- The conflict led to a long and bloody civil war that has only recently been resolved.
B.
- The on-going conflict started with the establishment of Israel in 1946.
- Hard-line Israelis and Zionists claim that, according to their scriptures, Palestine rightfully belongs to the Jews.
- This claim is rejected by Palestinians, as well as many Jewish organisations, including some Orthodox Jews.
- Religion plays a minor role in the conflict.
- The land of Israel/ Palestine is sacred to Jews, Christians and Muslims.
- The al Aqsa mosque in Jerusalem is Islam's third holiest site.
- Jerusalem is also sacred to Christians, as it is where Christ was crucified.
- Jews regard Jerusalem as the location of the Temple Mount/Temple of Solomon.
- All these sites existed long before the creation of Israel, and were occupied by various tribes throughout history.
- Religion is used as an excuse for the conflict.
- There is no attempt by any side to convert people to their faith.
- The continuous occupation of Palestinian land by Jews (Jewish settlers) is a major factor in the conflict.
- The building of illegal settlements on this land is also a major factor.
C.
- In 1972, Ceylon changed its name to Sri Lanka and Buddhism was adopted as the country's religion. This antagonised the Tamil minority, who are Hindu.
- Tamil Hindus felt that the government favoured the Buddhist majority and discriminated against them.
- The Tamil Hindus accused the government of not promoting religious tolerance and human rights.
- E.g. Sinhalese was the only official language in Sri Lanka.
- This policy excluded Tamil Hindus from the economy.
- In addition, Tamils were prevented from tertiary education.
- In the 1980s, a militant group called the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) took up arms against the government. Their goal was to establish an independent Tamil state in the north of the country.
- In 2003, the government tried to make Buddhism the only state religion. This motion did not have the necessary political support, and was not made law.
- The conflict claimed some 60 000 lives.
- Religious and cultural discrimination was a major contributory factor in the conflict. (20)
3.1.3 A.
- At present, there is generally peace in the area.
- The majority of people support peaceful negotiation, instead of armed conflict.
- The IRA has dropped its demand for independence from the UK.
- There is currently political power sharing between the Protestants and the Catholics.
- Some political killings continue to occur, and the 'Real IRA' claims responsibility for it.
B.
- Numerous UN resolutions have been passed condemning this occupation.
- However, Israel continues to defy UN resolutions and is building more settlements on Palestinian land.
- There are sporadic attacks on Palestinians, as well as on Jews.
- The situation remains volatile.
- No solution to the situation has been found.
C.
- Today there is some power-sharing in the government.
- The economy is growing, and Sri Lanka is again a popular tourist destination.
- There are several calls for investigation into human rights abuses during the war.
- The country is moving towards becoming a fully demilitarised state.
- Conversion to the religion of one's choice is permitted i.e. freedom of religion is respected. (8)
3.2. YES
- In most parts of the world, religion is no longer a major influencing factor in politics.
- While conflicts occur world-wide, they are not caused by religion.
- Most countries today reflect considerable religious diversity.
- This is because there is global migration.
- Global migration occurs for several reasons, including natural disasters and wars.
- Immigrants introduce their own religions to their new countries.
- Examples of this are the Syrian refugees in Europe, who are mainly Muslim.
- This conflict is not about religion, but international politics.
- Another is the situation in South Sudan. Refugees are animist, Christian and Muslim. They take their religious beliefs to new countries.
- In addition, interreligious dialogue has become more common.
- Social media contributes to this, as it provides easy access to diverse religious information.
NO
- As countries are becoming multireligious, the possibility of religious conflict increases.
- This conflict is not open warfare, but involves oppression of minority religions.
- The oppression is compounded when it is exploited by governments for political gain.
- An example of this is the situation in the Central African Republic.
- Political differences quickly caused the country to split along Muslim Christian lines.
- The genocide of Rohingya Muslims by Buddhists in Myanmar is another example.
- Attacks on Coptic Christians in Egypt are an example of low-key conflict.
- In the Syrian conflict, there are strong undertones of Sunni-Shia tensions, as the Syrian government is supported by Shia Iran, while some of the militant groups are supported by the US, which is allied to Sunni Saudi Arabia.
- In Europe and the United States, religious intolerance often results in desecration of places of worship.
- It also results in religious discrimination, such as the recent US ban on visitors from some Muslim majority countries.
NOTE: Other relevant responses must be credited. (16) [50]
QUESTION 4
4.1
- A world view is the way we make sense of the world around us.
- There are two types of world views: the religious world view and the secular world view.
- A religious world view is the belief that the government and morality should be based on religion.
- A secular world view is the belief that government and morality should be based on human rights, and not necessarily on religion. (4)
4.2 EXAMPLE 1: ATHEISM
- Atheists reject the belief that divine or supernatural powers exist.
- Atheists often turn to science to explain the nature of the universe rather than relying on faith.
- There are different degrees of atheism.
- Soft or neutral atheists do not actively reject the existence of a supernatural being.
- Strong or positive atheists believe there is evidence to support their atheistic views.
- In some cases soft atheists reject both theism and strong atheism.
- This is because they feel both world views depend on proof to support their claims.
EXAMPLE 2: SECULAR HUMANISM
- Secular humanism believes that the divine does not exist.
- They reject religious belief and the existence of the supernatural.
- Like other forms of humanism, they hold a common belief that attaches prime importance to human thinking.
- In its teachings, the Council for Secular Humanism highlights the following:
- A need to test beliefs: A conviction that traditions, ideologies and dogma should be weighed and tested by each individual and not by faith.
- Reason, evidence, Scientific method: A commitment to the use of critical reason, factual evidence and scientific method of inquiry in seeking solutions to human problems.
- Fulfilment, growth and creativity: A primary concern with fulfilment, growth and creativity.
- Search for truth: A constant search for objective truth.
- Ethics: A search for viable individual, social and political principles of ethical conduct.
- Justice and fairness: An interest in securing justice and fairness in society.
- Building a better world: A conviction that reason, an open exchange of ideas, goodwill and tolerance can be used to build a better world. (10 x 2) (20)
4.3
- A secular world view leads to the development of democratic government.
- Secular laws become the highest laws of the world.
- Most religious people adapted to the secular view by accepting the separation of religion and the state.
- It promotes freedom of conscience and belief.
- It provides a framework of principles and ethical guidelines for life.
- Society has freedom to question the authority of religious teachings.
- Secular views led to the development of science and technology in society.
- It promotes freedom of speech where society can debate and question some of the traditional beliefs.
- Secular views led to the development of the Universal Declaration of Humans Rights.
- It prevents the domination of one religion. (14)
4.4 Historical context
- This means that the writings must be understood within the context of the time and circumstances in which the text was written.
Clearest meaning
- The meaning that is clearest to the readers should be considered.
Plan, purpose and context
- The writing plan or structure of the whole document must be taken onto account.
- The purpose of the writer should also be taken into account.
- The extract should be seen as the part of the whole.
Meanings of words
- For the correct interpretation, the original meaning must be used because the meaning of words often changes over time.
Figurative language
- Figurative language used in sacred texts must not be interpreted literally. Other sacred texts
- Sacred texts may be used to interpret other sacred texts on the same topic because there is consistency among teachings of a religion and its sacred texts.
NOTE: Any THREE of the above must be credited. (12) [50]
QUESTION 5
5.1
- Discrimination is the unjust or prejudicial treatment of people, especially on the ground of race, colour, gender, religion, age, etc.
- Discrimination also means excluding people of different social background from the economy of the country.
- It is a belief that people of a certain race are superior or inferior to other racial groups.
- Apartheid in South Africa.is a good example of racial discrimination.
- The holocaust in Burundi is also an example of racial discrimination in Africa.
- During the apartheid regime only Christianity was the religion of the state. Other religions were not recognised, and this is an example of religious discrimination.
- The killing of people with albinism is an example of discrimination based on superstition.
- Women in some occupations earn less than their male counterparts, and this is gender discrimination. (12)
5.2
- Victims of discrimination are often psychologically affected and lack self esteem.
- Discrimination causes violence in society when the victims demand equal treatment.
- Victims of discrimination become poor because they are excluded from the economy of the country.
- Discrimination causes a divided society where people live according to their racial groups. This builds up much animosity.
- It denies a country the opportunity of social cohesion.
- Discrimination is often the source of religious conflict in society. This happens when one religion is oppressed by another.
- Discrimination excluded the blacks from quality education in South Africa. This is still a challenge facing the democratic government.
- Violence against women occurs because of gender discrimination.
- Religious groups are often segregated according to their racial groups, e.g. black churches and white churches
- Religious discrimination led to syncretism and establishment of the African Independent Churches or African Initiated Churches. (10)
5.3 EXAMPLE 1: BUDDHISM
- Buddhism teaches that discrimination is an example of ignorance and superiority is an example of craving.
- Ignorance and craving cause people to suffer. This suffering is called dukkha.
- Buddhists believe in upekkha (equal respect for everyone).
- They believe that there is no fundamental difference between any human beings.
- Mahayana Buddhism believes that all people must be treated equally because we can all become enlightened beings.
- Everyone can become enlightened irrespective of culture, race or social background.
- They believe that reaching enlightenment is the solution to discrimination.
EXAMPLE 2: CHRISTIANITY
- Christians believe that all human beings were created in the image of God.
- We are all equal before the Creator, so we must treat each other with dignity and respect.
- Discrimination is against the creationism teachings of Christianity.
- Jesus Christ taught His followers to love one another as they love themselves.
- Discrimination is sin against the commandment of love
- One of the Ten Commandments is to love your neighbour as your love yourself.
- Love does not discriminate on the basis of race, colour, religion, gender and sexual orientation.
- In the parable of the righteous Samaritan, Jesus taught us that your neighbour is any living human being irrespective of race, colour or religion.
- Apostle Paul teaches that all nations were created in one blood and placed in different countries or places to seek God.
- There is no nation or race that is superior to another.
- One of the unique features of Christianity is the belief that Jesus died for all mankind and that means we have to treat each other as equals.
- 'For God so loved the world that He gave His only begotten Son', This shows that God did not discriminate on the grounds of religion or race, but sent 'His only begotten Son', for all mankind (18)
5.4
- Religious organisations must join hands with the government to have campaigns against discrimination.
- In their religious gatherings they must highlight teachings that encourage unity and reject any form of discrimination.
- They can print and distribute pamphlets against discrimination in their communities.
- International religious organisations must have branches that strategize and implement programmes against discrimination.
- Religious organisations must work with all sport organisations to fight discrimination even in sport.
- They must facilitate Youth interreligious and cultural camps where the youth can interact with people of various races and religions.
- Religious organisations must lead by example by ensuring that their organisations are inclusive of all races, gender, beliefs, colour and age groups. (10) [50]
TOTAL: 150
LIFE SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
LIFE SCIENCES
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Write ALL the answers in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start the answers to EACH question at the top of a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Present your answers according to the instructions of each question.
- Do ALL drawings in pencil and label them in blue or black ink.
- Draw diagrams, tables or flow charts only when asked to do so.
- The diagrams in this question paper are NOT necessarily drawn to scale.
- Do NOT use graph paper.
- You must use a non-programmable calculator, protractor and a compass, where necessary.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are given as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A to D) next to the question number (1.1.1 to 1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 The part of the female reproductive system where fertilisation takes place is called the …
- vagina.
- ovary.
- Fallopian tube.
- cervix.
1.1.2 The vibrations on the tympanic membrane are transferred to the …
- ossicles and then the oval window.
- oval window and then the ossicles.
- ossicles and then the round window.
- cochlea and then the ossicles.
1.1.3 The nerve impulse in the axon of a sensory neuron is transmitted …
- towards the dendrite of the sensory neuron.
- towards the cell body of the sensory neuron.
- away from the effector organ.
- away from the cell body.
1.1.4 Which part of the ear converts pressure waves into nerve impulses?
- Auditory nerve
- Organ of Corti
- Eustachian tube
- Auditory canal
1.1.5 During periods when the temperature is low, …
- the thyroxin levels are expected to be low.
- sweating increases.
- the blood vessels to the skin dilate.
- the ADH levels are expected to be low.
1.1.6 The level of aldosterone will most likely increase after …
- consuming food with a high salt content.
- sweating excessively.
- consuming food with a high glucose content.
- the constriction of blood vessels to the skin.
1.1.7 A person can feel pain in his legs but cannot move his legs. This is a result of damage to the …
- sensory neuron.
- sensory and motor neuron.
- motor neuron.
- sensory and interneuron.
1.1.8 Colour vision is difficult at night, because under dim light conditions ...
- rods are not stimulated.
- the pupil dilates.
- cones are not stimulated.
- the lens cannot change shape.
1.1.9 The table below indicates the effect of drinking different amounts of alcohol on the reaction times of a group of people.
The reaction time was determined by using the catch distance on a ruler that was dropped from a certain height.
The longer the catch distance on the ruler, the longer the reaction time.
Units of alcohol (5% per volume) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
Catch distance on the ruler (cm) | 14 | 12 | 10 | 18 | 22 | 25 | 29 |
The conclusion that can be drawn from the investigation is that drinking alcohol …
- increases the reaction time.
- initially increases the reaction time, after which further intake of alcohol decreases the reaction time.
- does not have any effect on the reaction time.
- initially decreases the reaction time, after which further intake of alcohol increases the reaction time.
1.1.10 The table below shows the speed at which impulses are transmitted through different types of nerve fibres, A, B, C and D.
NERVE FIBRE | DIAMETER (μm) | AVERAGE SPEED OF TRANSMISSION (m/s) |
A | 15 | 100 |
B | 7 | 19 |
C | 3 | 13 |
D | 1 | 1 |
Which ONE of the following is the best interpretation of the information in the table above?
- Nerve fibre A is found in patients suffering from multiple sclerosis.
- The speed of transmission of impulses is not important for the survival of an individual.
- The greater the diameter of the nerve fibre, the greater the speed of transmission.
- Nerve fibre D is found in patients suffering from Alzheimer's disease. (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Give the correct biological term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.2.1 to 1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 Growing the same species of crop on a farm year after year
1.2.2 The killing of pests by using their natural predators or parasites
1.2.3 A hollow ball of cells formed from the zygote
1.2.4 The hormone responsible for osmoregulation
1.2.5 The illegal killing or removal of organisms from their environments
1.2.6 The vesicle which contains enzymes found in the head of a sperm cell
1.2.7 The hormone that stimulates milk production for breastfeeding in humans
1.2.8 The part of the nervous system made up of cranial and spinal nerves (8 x 1) (8)
1.3 Indicate whether each of the descriptions in COLUMN I applies to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A AND B or NONE of the items in COLUMN II. Write A only, B only, both A and B or none next to the question number (1.3.1 to 1.3.3) in the ANSWER BOOK. (3 x 2) (6)
COLUMN I | COLUMN II |
1.3.1 Reduces biodiversity | A: Alien plant invasion |
1.3.2 Sustainable use of medicinal plants | A: Banning all sales of medicinal plants |
1.3.3 Result of non-disjunction of chromosome pair 21 in humans | A: Gamete with 22 chromosomes |
1.4 The diagram below represents a human brain. 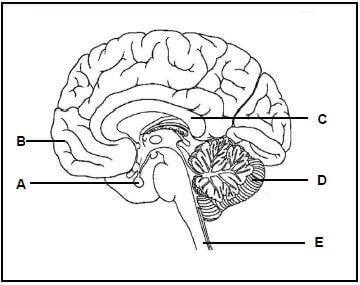
Give the LETTER and NAME of the part of the brain responsible for: 1.4.1 Memorising a cellular phone number (2) 1.4.2 Coordinating all voluntary movements (2) 1.4.3 Secreting hormones (2) 1.4.4 Connecting the two hemispheres of part B (2)
1.4.5 The reflex action that occurs when stepping barefooted on a sharp object (2) (10)
1.5 The diagrams below represent organisms with different reproductive strategies. 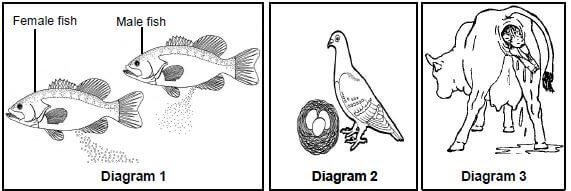
1.5.1 Which diagram(s) (1, 2 or 3) represent(s) organism(s):
- Where external fertilisation takes place (1)
- Where extra-embryonic membranes develop to assist with the protection and nutrition of the embryo (2)
- Which is/are oviparous (2)
1.5.2 Name the type of egg produced by the organism represented in Diagram 2. (1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1 The diagram below represents the sequence of events that takes place during the ovarian cycle of a female. 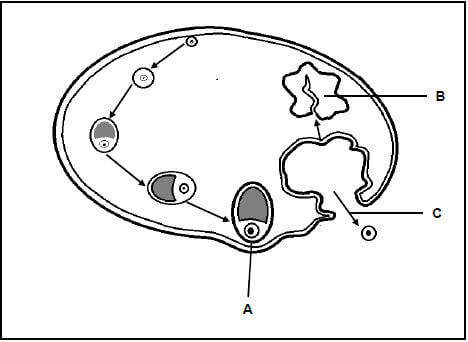
2.1.1 Give the name of the:
- Hormone that controls the development of structure A (1)
- Process taking place at C (1)
2.1.2 Describe the change that takes place in the uterus as the result of the hormone secreted by structure A. (2)
2.1.3 Structure B degenerates if fertilisation does not take place. Explain the implications of this for the:
- Ovarian cycle (3)
- Uterine cycle (3) (10)
2.2 Diagrams I and II below represent gametogenesis in human males and females (not in any particular sequence).
The diagrams are NOT drawn to scale. 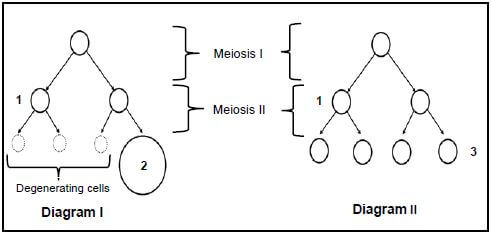
2.2.1 Identify the specific type of gametogenesis in Diagram I. (1)
2.2.2 Explain your answer to QUESTION 2.2.1 by referring to a visible difference between Diagram I and Diagram II. (2)
2.2.3 Where in the human body does the type of gametogenesis shown in Diagram II take place? (1)
2.2.4 Give the chromosome number of:
- The cells at 1 (1)
- Cell 2 (1)
2.2.5 Name TWO processes that take place during Meiosis I that lead to genetic variation in the four cells shown at 3 in Diagram II. (2)
2.2.6 Explain the implication for the human population size if the three cells referred to in Diagram I did not degenerate, but remained as gametes (2) (10)
2.3 The diagram below represents the structure of the human eye. 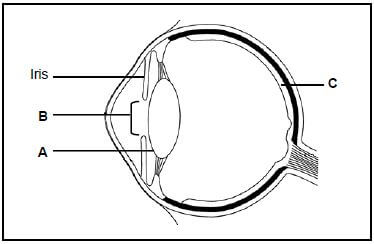
2.3.1 State ONE function of part:
- A (1)
- C (1)
2.3.2 Nocturnal animals sleep during the day and are active at night. Explain how part:
- B of nocturnal animals will differ from that found in animals that are active during the day (2)
- C of nocturnal animals will differ from that found in animals that are active during the day (2)
2.3.3 Describe how the iris controls the amount of light entering the eye when a person is exposed to bright light. (4) (10)
2.4 Describe how balance and equilibrium is maintained by the ear when a person changes his/her speed and direction. (5)
2.5 As the human population in South Africa increases, there is a proportional increase in the amount of solid waste that needs to be disposed of.
2.5.1 State TWO ways (apart from recycling) in which landfill sites can be managed to prevent further pollution. (2)
2.5.2 Explain how the recycling of paper can reduce global warming indirectly. (3) (5) [40]
QUESTION 3
3.1 Study the extract and the table below.
EMISSIONS FROM ELECTRICITY PRODUCTION Most of the electricity in South Africa is produced by burning coal. Coal burning is a very 'dirty' or inefficient way of producing energy because for every unit of electricity produced, more CO2 is released than with other fuels or methods. [Source: Climate change, Ethekweni Municipality Environmental Management Department, 2007, http://www.durban.gov.za/durban/municipality/environment] |
The table below shows the amount of CO2 emitted when producing energy from different sources.
ENERGY SOURCE | CO2 EMISSION (kg CO2/kW) |
Coal | 0,30 |
Petrol | 0,24 |
Diesel | 0,25 |
Paraffin | 0,20 |
Solar, wind, hydro power | 0,0 |
3.1.1 State why coal, petrol, diesel and paraffin are not renewable energy sources. (1)
3.1.2 State why the burning of coal to produce electricity is considered to be 'dirty' compared to using renewable sources or nuclear power. (1)
3.1.3 Name ONE greenhouse gas, other than CO2. (1)
3.1.4 Explain how increasing CO2 emissions could decrease food security. (4)
3.1.5 Draw a bar graph to represent the information in the table above. (6) (13)
3.2 A group of Grade 12 learners investigated the influence of different concentrations of auxins on plumule growth. A plumule is a young stem that grows from a seed.
The procedure was as follows:
- 35 bean seeds were germinated.
- The seedlings were then divided into five groups of seven seedlings each.
- In each group the seven seedlings were attached with Prestik to filter paper on which a 10 mm x 10 mm grid was drawn.
- The filter paper with seedlings was then glued to the inside of a petri dish.
- Each of these five petri dishes was placed in a beaker containing a different concentration of auxins.
The diagram below shows the set-up of a single beaker. 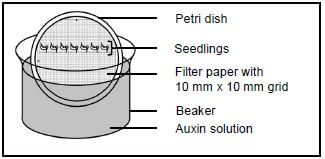
- All five beakers were placed inside a dark cupboard for three days.
- After three days the increase in the length of each plumule was measured.
- The average increase in length of the plumule in each beaker was calculated and recorded in the table below.
The table below shows the results of the investigation after three days.
BEAKER NUMBER | AUXIN CONCENTRATION IN PARTS PER MILLION (ppm) | AVERAGE INCREASE IN PLUMULE LENGTH (mm) |
1 | 0,1 | 1,5 |
2 | 1 | 3,2 |
3 | 10 | 4,8 |
4 | 50 | 2,3 |
5 | 100 | 0 |
3.2.1 For this investigation identify the:
- Independent variable (1)
- Dependent variable (1)
3.2.2 State the purpose of the grid that was placed inside each petri dish. (1)
3.2.3 Explain why the beakers were placed in a dark cupboard. (2)
3.2.4 State ONE way in which the learners ensured the reliability of this investigation. (1)
3.2.5 State THREE factors, not indicated in the procedure, that should be kept constant during this investigation. (3)
3.2.6 State the conclusion that can be made from the results in the table. (2) (11)
3.3 The diagram below represents one of the two cells that formed during Telophase I of meiosis in an organism. 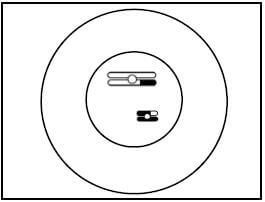
Draw a labelled diagram to show the cell during Anaphase II of meiosis. (5)
3.4 The diagram below represents the relationship between the blood system of the foetus and that of the mother. The arrows indicate the direction of blood flow in the blood vessels. 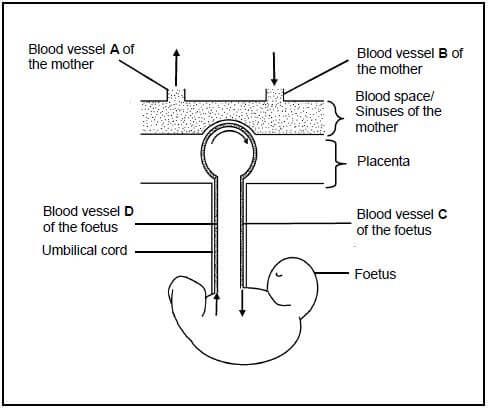
3.4.1 Apart from playing a role in the diffusion of substances from the mother's blood to the foetus' blood, and vice versa, state TWO other functions of the placenta. (2)
3.4.2 Blood vessel D is an artery. Tabulate TWO differences between the composition of blood found in blood vessel C and blood found in blood vessel D. (5)
3.4.3 Explain ONE consequence for the foetus if blood vessel D becomes blocked preventing blood flow. (2)
3.4.4 If the blood of the mother and the blood of the foetus come into contact with each another, it could lead to the death of the foetus. Describe why this would occur. (2) (11) [40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
An increase in the metabolic rate during strenuous exercise causes a decrease in the glucose level and an increase in the CO2 level in the blood.
Describe the mechanism that leads to an increase in the metabolic rate and the mechanisms involved in increasing the glucose level and decreasing the CO2 level back to normal.
Content: (17)
Synthesis: (3) (20)
NOTE: NO marks will be awarded for answers in the form of tables, flow charts or diagrams.
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150
LIFE SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
LIFE SCIENCES
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Write ALL the answers in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start the answers to EACH question at the top of a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Present your answers according to the instructions of each question.
- Do ALL drawings in pencil and label them in blue or black ink.
- Draw diagrams, tables or flow charts only when asked to do so.
- The diagrams in this question paper are NOT necessarily drawn to scale.
- Do NOT use graph paper.
- You must use a non-programmable calculator, protractor and a compass, where necessary.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A to D) next to the question number (1.1.1 to 1.1.9) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.10 D.
1.1.1 A molecule of RNA is copied from DNA by the process of …
- transcription.
- mitosis.
- mutation.
- translation.
1.1.2 Evidence supporting the evolution theory is obtained by studying the structure of vertebrate forelimbs.
This type of evidence for evolution is best described as …
- biogeography.
- modification by descent.
- DNA evidence.
- genetic evidence.
1.1.3 What is the percentage chance of a woman having a female child?
- 25%
- 100%
- 50%
- 75%
1.1.4 A small section of mRNA has the following sequence of bases that codes for different amino acids:
G C U C G U U A A
Which ONE of the following is the CORRECT representation of the anticodons and number of amino acids coded for by this section?
ANTICODONS | NUMBER OF AMINO ACIDS | |
| A | C G A G C A A U U | 9 |
| B | C G A G C A A U U | 3 |
| C | C G A G C A A T T | 9 |
| D | C G A G C A A T T | 3 |
1.1.5 If a recessive allele on the X-chromosome is passed on to the offspring it is an example of …
- sex-linked inheritance.
- incomplete dominance.
- multiple alleles.
- co-dominance.
1.1.6 The diagram below shows the DNA profiles of a child, her mother and four males. There is uncertainty about who the biological father is. To establish paternity, DNA profiling was conducted. 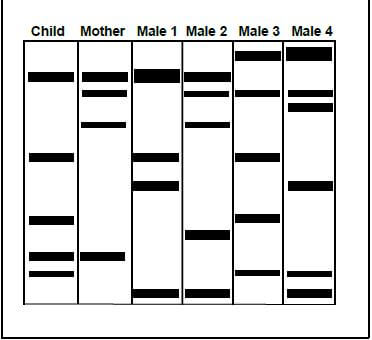
Which male is the biological father of this child?
- Male 1
- Male 2
- Male 3
- Male 4
1.1.7 Which ONE of the following is the correct genus and scientist for the discovery of the 'Taung Child' fossil?
- Ardipithecus; Raymond Dart
- Ardipithecus; Tim White
- Australopithecus; Raymond Dart
- Australopithecus; Tim White D
1.1.8 Different frogs, which all belong to the genus Lithobates, are found in the same forest. The graph below shows their mating activity. 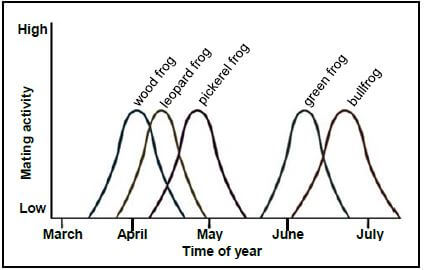
Based on the information, what kind of isolating mechanism is most likely keeping the bullfrogs and wood frogs as separate species?
- Geographic isolation through the presence of geographic barriers
- Reproductive isolation through species-specific courtship behaviour
- Reproductive isolation through breeding at different times of the year
- Reproductive isolation through the production of infertile offspring
1.1.9 Which ONE of the following statements is CORRECT for the 'Out of Africa' hypothesis?
- All modern humans originated in Africa and migrated to other parts of the world.
- All modern humans evolved from African apes and then migrated to other parts of the world.
- The most developed artefacts (tools; cutlery; art) were found in Africa.
- An analysis of mutations on the mitochondrial DNA shows that the oldest male ancestors were located in Africa. (9 x 2) (18)
1.2 Give the correct biological term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.2.1 to 1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 The type of RNA containing anticodons
1.2.2 The process during which genetically identical organisms are formed using biotechnology
1.2.3 Undifferentiated animal cells that can form any type of tissue
1.2.4 Type of inheritance where none of the two alleles is dominant over the other and an intermediate phenotype is produced
1.2.5 The breeding of organisms by humans to achieve a desirable phenotype
1.2.6 The point of crossing over between two adjacent chromosomes
1.2.7 The organelle in a cell where translation occurs
1.2.8 The variety of living organisms on Earth (8 x 1) (8)
1.3 Indicate whether each of the statements in COLUMN I applies to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A AND B or NONE of the items in COLUMN II. Write A only, B only, both A and B, or none next to the question number (1.3.1 to 1.3.3) in the ANSWER BOOK. (3 x 2) (6)
COLUMN I | COLUMN II |
1.3.1 Contains the sugar ribose | A: DNA B: RNA |
1.3.2 Chromosomes align at the equator | A: Metaphase I B: Metaphase II |
1.3.3 Produced the first X-ray image of the DNA molecule | A: Rosalind Franklin B: Watson and Crick |
1.4 The diagram represents a portion of a nucleic acid. 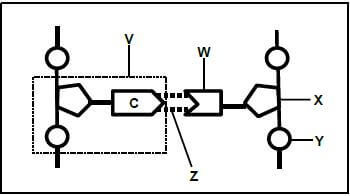
1.4.1 Name the nucleic acid. (1)
1.4.2 Name TWO places in animal cells where this nucleic acid may be found. (2)
1.4.3 Identify:
- Portion V (1)
- Nitrogenous base W (1)
- Molecule Y (1)
- Bond Z (1)
1.4.4 What is the natural shape of this molecule? (1)
1.4.5 Name the process during which this molecule makes a copy of itself. (1) (9)
1.5 The diagram below shows possible evolutionary relationships among some hominids. 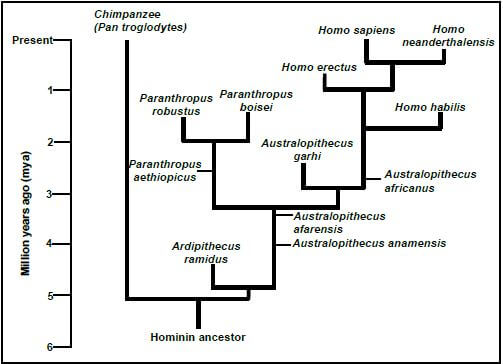
1.5.1 What is this type of diagram called? (1)
1.5.2 How many of EACH of the following are represented in the diagram:
- Genera (1)
- Homo species (1)
1.5.3 Name the species that have Paranthropus aethiopicus as a common ancestor. (2)
1.5.4 When did:
- Ardipithecus ramidus become extinct (1)
- Homo erectus first appear (1)
1.5.5 Name the:
- Hominid species that existed at the same time as Homo sapiens (1)
- First Homo species to use tools (1) (9)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1 The karyotype below shows the chromosomes of a person with Down syndrome. 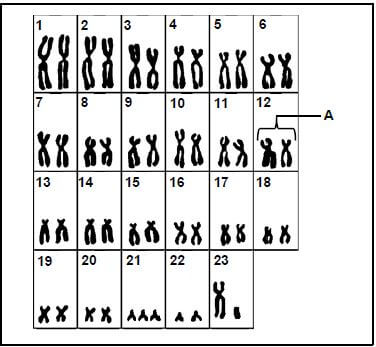
2.1.1 Give the label for A. (1)
2.1.2 How many autosomes are there in a nucleus of this cell? (1)
2.1.3 Name the type of chromosomes at position 23. (1)
2.1.4 What evidence suggests that this is a karyotype of a male? (1)
2.1.5 Name the type of mutation represented in the diagram. (1)
2.1.6 Describe the events that led to Down syndrome. (6) (11)
2.2 The diagram below shows the pattern of inheritance of deafness in a family. The letter H represents the allele for hearing and h represents the allele for deafness. 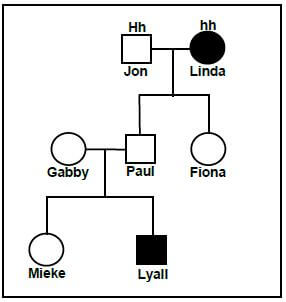
2.2.1 How many of EACH of the following are represented in this diagram?
- Males (1)
- Generations (1)
2.2.2 Give the:
- Phenotype of Jon (1)
- Genotype of Paul (1)
2.2.3 Both Lyall's parents can hear, yet he is deaf. Explain how he inherited deafness. (2)
2.2.4 Lyall marries a woman who is homozygous dominant for hearing. Use a genetic cross to show the percentage chance of them having a deaf child. (7) (13)
2.3 The extract below is about human evolution.
In 2004 scientists in Indonesia discovered the first fossil of the species Homo floresiensis along with stone tools and animal remains. The fossil was made up of a nearly complete skull and skeleton, including hand and foot bones and a pelvis. |
2.3.1 Name the TWO lines of evidence for human evolution that is referred to in the extract above. (2)
2.3.2 How long did Homo floresiensis exist on Earth? (1)
2.3.3 Name ONE Homo ancestor mentioned in the extract. (1)
2.3.4 State THREE features of the jaw of H. floresiensis that might have led scientists to believe that it resembled that of Australopithecus, rather than of a Homo species. (3)
2.3.5 Describe ONE feature of the skull that can be used as evidence for bipedalism. (2)
2.3.6 State TWO similarities between the hands of African apes and modern humans. (2)
2.3.7 Draw a table to show the brain volumes of the different Homo species, using information from the extract. (5) (16) [40]
QUESTION 3
3.1 The table below shows the percentage of the populations with different blood groups for two countries.
BLOOD GROUP | PERCENTAGE OF POPULATION | |
COUNTRY Q | COUNTRY R | |
O | 40 | 20 |
A | 10 | 35 |
B | 45 | 40 |
AB | 5 | 5 |
3.1.1 Which blood group shows the greatest percentage difference between the two countries? (1)
3.1.2 The population size of country Q is 5 million people. Calculate the number of people who have blood group O. Show ALL your working. (3)
3.1.3 Explain how the inheritance of blood group AB is an example of co-dominance. (2)
3.1.4 Explain why blood groups are considered an example of discontinuous variation. (2)
3.1.5 In the inheritance of blood groups, give the:
- Recessive allele (1)
- Phenotype of an individual who is homozygous recessive (1) (10)
3.2 Read the extract below.
The red-bellied black snake (Pseudechis porphyriacus) and the green tree snake (Denderelaphis punctulatus) are predators that sometimes feed on cane toads (Bufo marinus) that contain a toxin that may kill them. |
3.2.1 Define punctuated equilibrium. (3)
3.2.2 What characteristic of the toad species protects it from predation? (1)
3.2.3 Explain how the change in jaw size helped the snakes to survive. (3)
3.2.4 How would Lamarck have explained the development of a small jaw size in the snakes? (4) (11)
3.3 In a plant species two characteristics, flower colour and plant height, were studied. Each of these characteristics has two variations: flowers may be red or white in colour and the plants may be tall or short.
Plants that are heterozygous for flower colour have red flowers and plants that are homozygous recessive for plant height are short.
The alleles for each characteristic are shown in the table below.
CHARACTERISTIC | DOMINANT ALLELE | RECESSIVE ALLELE |
Flower colour | F | f |
Plant height | H | h |
3.3.1 What is the term given for a genetic cross involving two characteristics? (1)
3.3.2 Give the:
- Dominant phenotype for flower colour (1)
- Recessive phenotype for plant height (1)
- Phenotype of a plant that is heterozygous for flower colour and homozygous dominant for plant height (2)
- Genotype of a white flowering, short plant (2)
3.3.3 State Mendel's Law of Dominance. (3) (10)
3.4 Study the extract and the information provided.
An insecticide is used by farmers to control insect populations of Plodia interpunctella which feeds on stored grain. Farmers treat the grain with the insecticide to prevent an insect infestation. |
Scientists hypothesised that insect populations that had previously been exposed to the insecticide had a higher survival rate when the grain was treated again.
In an investigation to test this hypothesis, they:
- Identified storage bins that had previously been treated with the insecticide and bins that had never been treated with the insecticide
- Collected a sample of 300 insects from each bin
- Kept each sample in a separate container of equal size and the same conditions
- Sprayed the same concentration and volume of insecticide over both containers
- Allowed 24 hours for the insecticide to take effect
- Counted the number of insects that survived in each container
The results are given in the table below:
PREVIOUS EXPOSURE TO INSECTICIDE | NUMBER OF INSECTS THAT SURVIVED |
With previous exposure to insecticide | 182 |
No previous exposure to insecticide | 66 |
3.4.1 Give the:
- Independent variable (1)
- Dependent variable (1)
3.4.2 State THREE factors that were kept constant in this investigation. (3)
3.4.3 Give TWO reasons why the scientists' results may not be reliable. (2)
3.4.4 State a conclusion for this investigation. (2) (9) [40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
Describe how a gene mutation may influence the structure of a protein. Also use ONE example to describe the role of mutations in evolution in present times.
Content: (17)
Synthesis: (3)
NOTE: NO marks will be awarded for answers in the form of tables, flow charts or diagrams.
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150
LIFE SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
LIFE SCIENCES
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
PRINCIPLES RELATED TO MARKING LIFE SCIENCES
- If more information than marks allocated is given
Stop marking when maximum marks is reached and put a wavy line and 'max' in the right-hand margin. - If, for example, three reasons are required and five are given Mark the first three irrespective of whether all or some are correct/incorrect.
- If whole process is given when only a part of it is required Read all and credit the relevant part.
- If comparisons are asked for, but descriptions are given
Accept if the differences/similarities are clear. - If tabulation is required, but paragraphs are given
Candidates will lose marks for not tabulating. - If diagrams are given with annotations when descriptions are required Candidates will lose marks.
- If flow charts are given instead of descriptions
Candidates will lose marks. - If sequence is muddled and links do not make sense
Where sequence and links are correct, credit. Where sequence and links are incorrect, do not credit. If sequence and links become correct again, resume credit. - Non-recognised abbreviations
Accept if first defined in answer. If not defined, do not credit the unrecognised abbreviation, but credit the rest of the answer if correct. - Wrong numbering
If answer fits into the correct sequence of questions, but the wrong number is given, it is acceptable. - If language used changes the intended meaning
Do not accept. - Spelling errors
If recognisable, accept the answer, provided it does not mean something else in Life Sciences or if it is out of context. - If common names are given in terminology
Accept, provided it was accepted at the national memo discussion meeting. - If only the letter is asked for, but only the name is given (and vice versa) Do not credit.
- If units are not given in measurements
Candidates will lose marks. Memorandum will allocate marks for units separately. - Be sensitive to the sense of an answer, which may be stated in a different way.
- Caption
All illustrations (diagrams, graphs, tables, etc.) must have a caption. - Code-switching of official languages (terms and concepts) A single word or two that appear(s) in any official language other than the learner's assessment language used to the greatest extent in his/her answers should be credited, if it is correct. A marker that is proficient in the relevant official language should be consulted. This is applicable to all official languages.
- Changes to the memorandum
No changes must be made to the memoranda. The provincial internal moderator must be consulted, who in turn will consult with the national internal moderator (and the Umalusi moderators where necessary). - Official memoranda
Only memoranda bearing the signatures of the national internal moderator and the Umalusi moderators and distributed by the National Department of Basic Education via the provinces must be used.
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 A✔✔
1.1.2 B✔✔
1.1.3 C✔✔
1.1.4 B✔✔
1.1.5 A✔✔
1.1.6 C✔✔
1.1.7 C✔✔
1.1.8 C✔✔
1.1.9 A✔✔ ( 9 x 2) (18)
1.2
1.2.1 tRNA✔/transfer RNA
1.2.2 Cloning✔
1.2.3 Stem✔cells
1.2.4 Incomplete dominance✔
1.2.5 Artificial selection✔/selective breeding
1.2.6 Chiasma✔
1.2.7 Ribosome✔
1.2.8 Biodiversity✔ (8 x 1) (8)
1.3
1.3.1 B only✔✔
1.3.2 Both A and B✔✔
1.3.3 A only✔✔ (3 x 2) (6)
1.4
1.4.1 DNA✔/Deoxyribonucleic acid (1)
1.4.2
- Nucleus✔/chromosome
- Mitochondria✔
(Mark first TWO only) (2)
1.4.3
- Nucleotide✔ (1)
- Guanine✔ (1)
- Phosphate✔ (1)
- Hydrogen✔ bond (1)
1.4.4 Double helix✔ (1)
1.4.5 DNA replication✔ (1) (9)
1.5
1.5.1 Phylogenetic✔ (1)
1.5.2
- 5✔ (1)
- 4✔ (1)
1.5.3 (Paranthropus) robustus✔ and (Paranthropus) boisei✔(2)
1.5.4
- Accept any value in the range 4,3 to 4,5 million years ago✔/mya (1)
- 1 mya✔ (1)
1.5.5
- Homo neanderthalensis✔ (1)
- Homo habilis✔ (1) (9)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1 Homologous chromosomes✔ (1)
2.1.2 45✔(1)
2.1.3 Gonosomes✔(1)
2.1.4 The presence of a Y chromosome✔/XY chromosome (1)
2.1.5 Chromosome✔mutation (1)
2.1.6
- Non-disjunction occurred✔/A homologous pair of chromosomes failed to separate
- at position 21✔
- during Anaphase✔
- resulting in one gamete with 24 chromosomes✔/an extra chromosome/2 chromosomes at position 21
- The fertilisation of this gamete with a normal gamete✔/gamete with 23 chromosomes/1 chromosome at position 21
- results in a zygote with 47 chromosomes✔
- There are 3 chromosomes✔/an extra chromosome at position 21/ this is Trisomy 21 Any 6 (6) (11)
2.2
2.2.1
- 3✔
- 3✔
2.2.2
- Hearing✔/Normal
- Hh✔
2.2.3
- Lyall inherited one recessive allele✔
- from each parent✔
2.2.4 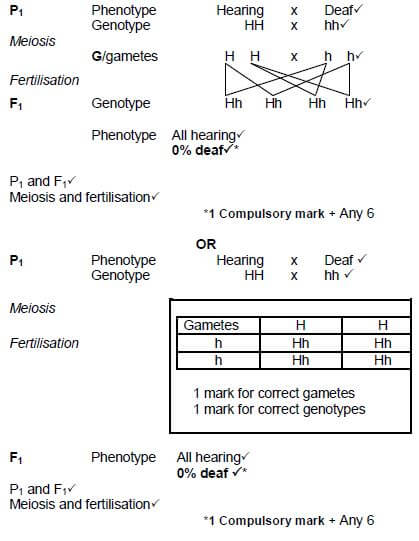 (7) (13)
(7) (13)
2.3
2.3.1
- Fossil✔/ ‘the first fossil’
- Cultural✔/ ‘stone tools’/’animal remains’ (2)
(Mark first TWO only)
2.3.2 83 000 years✔(1)
2.3.3 Australopithecus✔(1)
(Mark first ONE only)
2.3.4
- The jaw was more prognathous✔/protruding and
- larger✔than in humans
- The jaw was more rectangular✔
- The palate shape was less rounded✔/U-shaped/rectangular
- The canines were larger✔
- Large spaces✔/diastema between the teeth Any 3 (3)
(Mark first THREE only)
2.3.5
- A more forward✔position
- of the foramen magnum✔(2)
(Mark first ONE only)
2.3.6
- Opposable thumbs✔
- Bare fingertips✔
- Nails✔instead of claws
- Pentadactyl✔hand Any 2 (2)
(Mark first TWO only)
HOMO SPECIES✔ | BRAIN VOLUME✔(cm3) |
H. floresiensis | 426 |
H. habilis | 600 |
H. erectus | 860 |
H. sapiens/modern humans | 1300 |
Guideline for assessing the table
Correct table format | 1 |
Column headings | 2 |
Data entered | 1: 1 to 3 data sets correctly entered |
(5) (16) [40]
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1 Blood group A✔
3.1.2
- 40 ✔ x 5 000 000 ✔
100 1
= 2 000 000✔/2 million
3.1.3
- The alleles IAand IB✔
- are equally dominant✔
3.1.4
- When phenotypes fit into separate or distinct categories✔
- with no intermediate phenotypes✔
3.1.5
- i✔
- Blood group O✔
3.2
3.2.1
- It is characterised by long periods of little or no change✔
- alternating with short periods of rapid change✔
- during which new species may form✔
3.2.2 They contain toxins✔ which kill the snakes OR Too large✔ to be swallowed Any 1
3.2.3
- Having a smaller jaw✔
- means cane toads cannot be consumed✔
- thereby protecting the snakes from ingesting the toxins✔
3.2.4
- Since the snakes' jaws were used less ✔/not used
- the snakes developed smaller jaws✔
- This characteristic (of a smaller jaw) was inherited by the offspring✔
- Over many generations the jaw of the snake became smaller✔
3.3
3.3.1 Dihybrid✔ cross
3.3.2
- Red✔
- Short✔
- Red✔ and Tall✔
- ffhh✔✔
3.3.3
- When two organisms with pure breeding✔
- contrasting traits✔are crossed
- all the individuals of the F1 generation will display the dominant trait✔
OR - If an organism is heterozygous✔
- the dominant allele✔
- will determine the phenotype✔
3.4
3.4.1
- Exposure to insecticide✔
- Number of insects that survived✔/survival rate of insects
3.4.2
- Sample size✔/300 insects
- Size of containers✔
- Conditions✔
- Concentration of insecticide✔
- Volume of insecticide✔
- Time period✔/24 hours Any 3
(Mark first THREE only)
3.4.3
- They only conducted the investigation once✔/did not repeat
- They used a small sample/only 300 insects✔
- They used only two storage bins✔ Any 2
(Mark first TWO only)
3.4.4
- Insects that were previously exposed to the insecticide had a higher survival rate✔✔
OR - Insects that were not previously exposed to the insecticide had a lower survival rate✔✔ [40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
MUTATIONS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
- A mutation is a change in the nucleotide/nitrogenous base sequence✔
- of a DNA molecule✔/a gene
- since mRNA is copied from the DNA molecule✔
- during transcription✔
- This will result in a change in the codons✔
- As a result, different tRNA✔ molecules
- carrying different amino acids✔ will be required
- The sequence of amino acids changes✔
- resulting in the formation of a different protein✔
- If the same amino acid ✔is coded for
- there will be no change✔in the protein structure Any 9 (9)
MUTATIONS AND EVOLUTION IN PRESENT TIMES
- In a population of insects✔/bacteria/HI viruses/Galápagos' finches
- mutations are a source of variation✔
- which may make some organisms more resistant✔/better suited
- to insecticides✔/antibiotics/antiretroviral medication/ drought
- Those individuals that are not resistant/suited will die✔ whereas
- those that are resistant/ well suited, will survive✔
- to pass the resistant allele/resistance on to their offspring✔
- This is known as natural selection✔
- As a result, individuals of the future generations will be resistant to the insecticides✔/antibiotics/antiretroviral medication/adapted to drought Any 8 (8)
Content (17)
Synthesis (3) (20)
ASSESSING THE PRESENTATION OF THE ESSAY
Criterion | Relevance (R) | Logical sequence (L) | Comprehensive (C) |
Generally | All information provided is relevant to the question. | Ideas are arranged in a logical sequence. | All aspects of the essay have been sufficiently addressed. |
In this essay in Q4 | Only provided information relevant to:
There is no irrelevant information. | Information on:
| At least the following marks should be obtained:
|
Mark | 1 | 1 | 1 |
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150
LIFE SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
LIFE SCIENCES
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
PRINCIPLES RELATED TO MARKING LIFE SCIENCES
- If more information than marks allocated is given
Stop marking when maximum marks is reached and put a wavy line and 'max' in the right-hand margin. - If, for example, three reasons are required and five are given Mark the first three irrespective of whether all or some are correct/incorrect.
- If whole process is given when only a part of it is required Read all and credit the relevant part.
- If comparisons are asked for, but descriptions are given
Accept if the differences/similarities are clear. - If tabulation is required, but paragraphs are given
Candidates will lose marks for not tabulating. - If diagrams are given with annotations when descriptions are required
Candidates will lose marks. - If flow charts are given instead of descriptions
Candidates will lose marks. - If sequence is muddled and links do not make sense
Where sequence and links are correct, credit. Where sequence and links are incorrect, do not credit. If sequence and links become correct again, resume credit. - Non-recognised abbreviations
Accept if first defined in answer. If not defined, do not credit the unrecognised abbreviation, but credit the rest of the answer if correct. - Wrong numbering
If answer fits into the correct sequence of questions, but the wrong number is given, it is acceptable. - If language used changes the intended meaning
Do not accept. - Spelling errors
If recognisable, accept the answer, provided it does not mean something else in Life Sciences or if it is out of context. - If common names are given in terminology
Accept, provided it was accepted at the national memo discussion meeting. - If only the letter is asked for, but only the name is given (and vice versa) Do not credit.
- If units are not given in measurements
Candidates will lose marks. Memorandum will allocate marks for units separately. - Be sensitive to the sense of an answer, which may be stated in a different way.
- Caption
All illustrations (diagrams, graphs, tables, etc.) must have a caption. - Code-switching of official languages (terms and concepts) A single word or two that appear(s) in any official language other than the learner's assessment language used to the greatest extent in his/her answers should be credited, if it is correct. A marker that is proficient in the relevant official language should be consulted. This is applicable to all official languages.
- Changes to the memorandum
No changes must be made to the memoranda. The provincial internal moderator must be consulted, who in turn will consult with the national internal moderator (and the Umalusi moderators where necessary). - Official memoranda
Only memoranda bearing the signatures of the national internal moderator and the Umalusi moderators and distributed by the National Department of Basic Education via the provinces must be used.
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 C✔✔
1.1.2 A✔✔
1.1.3 D✔✔
1.1.4 B✔✔
1.1.5 D✔✔
1.1.6 B✔✔
1.1.7 C✔✔
1.1.8 C✔✔
1.1.9 D✔✔
1.1.10 C✔✔ (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 Monoculture✔
1.2.2 Biological control✔
1.2.3 Blastocyst✔/blastula
1.2.4 ADH✔
1.2.5 Poaching✔
1.2.6 Acrosome✔
1.2.7 Prolactin✔
1.2.8 Peripheral✔nervous system (8 x 1) (8)
1.3
1.3.1 .Both A and B✔✔ (2)
1.3.2 None✔✔ (2)
1.3.3 Both A and B✔✔ (2) (3 x 2) (6)
1.4
1.4.1 B✔ - Cerebrum✔ (2)
1.4.2 D✔ - Cerebellum✔ (2)
1.4.3 A✔ - Pituitary gland✔/Hypophysis (2)
1.4.4 C✔ - Corpus callosum✔ (2)
1.4.5 E✔ - Spinal cord✔ (2) (10)
1.5
1.5.1
- Diagram 1✔ (1)
- Diagram 2✔ and Diagram 3✔ (2)
- Diagram 1✔ and Diagram 2✔ (2)
1.5.2 Amniotic✔ egg (1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1
- FSH✔ /Follicle stimulating hormone
- Ovulation✔
2.1.2
- It causes the endometrium✔
- To become thicker✔ /more glandular/more vascular
2.1.3
-
- The levels of progesterone drop✔
- therefore FSH secretion is no longer inhibited✔ /FSH secretion is resumed
- and a new follicle starts to develop✔
-
- The levels of progesterone drop✔
- therefore the endometrium is no longer maintained ✔
- and menstruation takes place✔
2.2
2.2.1 Oogenesis✔
2.2.2
- At the end of the process in DIAGRAM I/oogenesis, one✔ gamete/ovum forms/three cells degenerate
- At the end of the process in Diagram II/spermatogenesis four✔ gametes/sperm form/none of the cells degenerate
2.2.3 Testes✔ /seminiferous tubules
2.2.4
- 23✔
- 23✔
2.2.5
- Crossing over✔
- Random arrangement✔ of chromosomes
(MARK FIRST TWO ANSWERS ONLY)
2.2.6
- This will result in multiple births✔ /There will be increased chances of fertilisation
- which will lead to an increase in human population✔
2.3
2.3.1
-
- A - Refraction of light✔
- Focus light rays on the retina✔ (Any 1) (1)
(MARK FIRST ANSWER ONLY)
-
- C - Converts light stimuli to impulses✔
- Forms images✔ (Any 1) (1)
(MARK FIRST ANSWER ONLY)
2.3.2
- The pupil/part B can dilate more✔ - to allow more light to enter the eye✔
- The retina/part C has more rods✔ - enabling them to see in dim light✔
2.3.3
- The radial muscles of the iris relax✔
- Circular muscle of the iris contract✔
- The pupil constricts✔
- and less light enters the eye✔
2.4
- The cristae✔
- are stimulated✔
- The stimuli are converted to impulses✔
- which are transported via the auditory nerve✔
- to the cerebellum✔
- Impulses are sent to the muscles to restore balance✔ (Any 5) (5)
2.5
2.5.1
- Cover the solid wastes brought in every day with soil✔
- The landfill site should be lined with clay✔ /plastic/rubber
- No hazardous waste should be dumped at landfill sites✔
- The leachate should be removed and detoxified✔
- Remove methane gas from the dumpsite✔
- Use plants to remove contamination from soil✔ (Any 2)
(MARK FIRST TWO ONLY)
2.5.2
- Fewer trees need to be cut down to make paper✔
- therefore more CO2 will be absorbed by these trees for photosynthesis✔
- reducing the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere✔
- This reduces the enhanced greenhouse effect✔ that causes global warming (Any 3)
OR - Less paper needs to be produced✔
- Less fossil fuels will be used for the production of paper✔
- therefore less greenhouse gases will be released✔
- This reduces the enhanced greenhouse effect✔ that causes global warming (Any 3)
OR - The amount of paper in the solid waste is reduced✔
- therefore less decomposition takes place✔
- Less greenhouse gases will be therefore released✔
- This reduces the enhanced greenhouse effect✔ that causes global warming (Any 3) [40]
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1 They are fuels that can be depleted/Millions of years required to replace (1)
3.1.2 CO2 is released✔ when coal is burned to generate electricity/ No CO2 is released when renewable energy or nuclear power is generated (1)
3.1.3
Methane✔/ CH4 | Carbon monoxide✔/CO | |
Sulphur dioxide✔/ SO2 | Water vapour✔/H2O(g) | |
Nitrous oxide✔/ N2O | Ozone✔/O3 |
(MARK FIRST ONE ONLY) (Any 1) (1)
3.1.4
- An increase in CO2 leads to global warming✔
- which causes climate change✔/changes in rainfall patterns
- that leads to more droughts✔/floods in certain areas
- resulting in crop losses✔
- and livestock deaths✔
- Therefore less food is produced✔ (Any 4) (4)
31.5 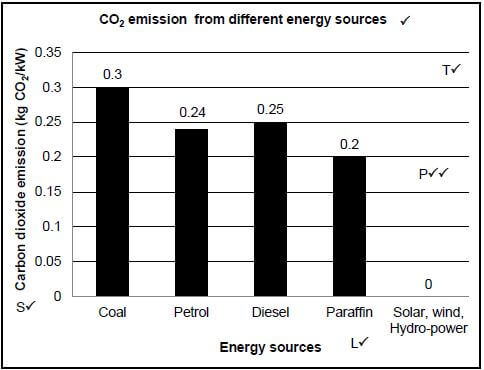
Mark allocation of the graph
Criteria | Marks |
Bar graph drawn (T) | 1 |
Title of graph (Including both variables) | 1 |
Correct scale for X-axis (equal width and spacing of the bars) and Y-axis (S) | 1 |
Correct label and unit for X-axis and Y axis (L) | 1 |
Plotting of the bars (P) | 0: No bars plotted correctly |
NOTE:
- If a line graph is drawn – marks will be lost for the 'type of graph' and for 'plotting' only.
- If a histogram is drawn – marks will be lost for the 'type of graph' and 'correct scale' only
3.2
3.2.1
- Auxin concentration✔
- Plumule growth✔
3.2.2 For measurement of the plumule length✔
3.2.3
- To simulate the same conditions✔ under which germination takes place for the normal growth✔ of the seedlings
- To expose the seedlings to uniform light✔
so that no other variable is introduced/to ensure validity/ to allow upward growth of the plumule for easy measuring✔
(MARK FIRST ONE ONLY) (Any 1 x 2)
3.2.4
- They used seven seedlings in each group/35 seeds in total/a large sample
- They calculated the average✔ increase in plumule length
(MARK FIRST ONE ONLY) (Any 1)
3.2.5
- Same species of beans✔
- Seedlings of the same age✔
- Seedlings of the same size✔
- Same temperature✔
- The same investigator✔
- Identical apparatus (beakers/petri-dishes/graph paper/grid/volume of solution) ✔ (Any 3)
(MARK FIRST THREE ONLY)
3.2.6 An increase in auxin concentration up to an optimum stimulates the growth rate of the plumule/stem. With further increase in auxin concentration there is an inhibition of plumule/stem growth ✔
✔
3.3 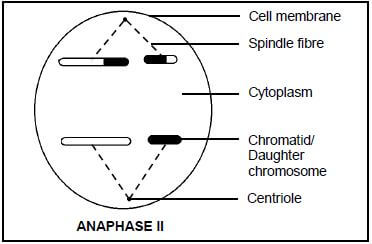
ANY ONE OF THE FOLLOWING ARRANGEMENTS INCLUDING CORRECT LABELS MARK ALLOCATION FOR DIAGRAM 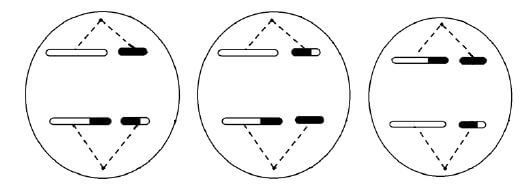
Correct phase drawn/chromatids separating (P) | 1 |
Correct shading of chromatids (S) | 1 |
Correct number and size of individual chromatids/daughter chromosomes (2 short and 2 long) (N) | 1 |
Any TWO correct labels | 2 |
TOTAL | 5 |
3.4
3.4.1
- It act as a micro-filter✔ /prevents harmful substances from reaching the foetus
- It secretes progesterone✔ /oestrogen during pregnancy
- Immunity is transferred from the mother to the foetus✔ (Any 2) (2)
(MARK FIRST TWO ONLY)
3.4.2
BLOOD VESSEL C | BLOOD VESSEL D |
High concentration of nutrients✔/example of nutrient | Low concentration of nutrients✔/example of nutrient |
Low concentration of waste products✔/example of waste product | High concentration of waste products✔/example of waste product |
High concentration of oxygen✔ | Low concentration of oxygen✔ |
Low concentration of carbon dioxide✔ | High concentration of carbon dioxide✔ |
(MARK FIRST TWO ONLY)
Table: (1) and (Any 2 x 2) (5)
3.4.3
- Waste products/nitrogenous waste/CO2 will accumulate✔ in the foetus' body causing the death of the foetus✔
(MARK FIRST ONE ONLY)
3.4.4
- Harmful substances✔ /bacteria
- may pass from the mother's blood to the blood of the foetus✔
OR - The blood types✔ /other proteins of the mother and baby
- may not be compatible✔
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
Increasing the metabolic rate
- To increase the metabolic rate the level of thyroxin must increase✔
- The pituitary gland is stimulated✔
- to secrete more TSH✔
- which stimulates the thyroid gland✔
- to secrete more thyroxin✔ (Any 4) (4)
Increasing the level of glucose
- As a result of the decrease in glucose level the pancreas is stimulated✔
- to secrete glucagon✔
- which stimulates the conversion of stored glycogen to glucose✔
- in the liver✔ /muscles
- The glucose is then released into the bloodstream✔
- The glucose level in the blood increases✔ and returns to normal (Any 5) (5)
Decreasing the level of CO2
- High CO2 levels stimulate the receptor cells in the carotid artery✔
- The stimulus is converted to an impulse✔
- and sent to the medulla oblongata✔
- which stimulates the heart✔
- to beat faster✔
- bringing blood with CO2 quickly to the lungs ✔
- It also stimulates the breathing muscles✔
- to increase the depth and rate of breathing✔
- CO2 is exhaled quickly from the lungs✔
- The CO2 level in the blood decreases✔and returns to normal (Any 8) (8)
Content: (17)
Synthesis: (3)
(20)
ASSESSING THE PRESENTATION OF THE ESSAY
Relevance | Logical sequence | Comprehensive |
All information provided is relevant to the question | Ideas arranged in a logical/ cause-effect sequence | Answered all aspects required by the essay in sufficient detail |
All the information provided is relevant to the:
| All the information regarding the:
| At least the following points should be included:
|
1 mark | 1 mark | 1 mark |
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX sections:
SECTION A: Short Questions (15)
SECTION B: Systems Technologies (24)
SECTION C: Communication and Network Technologies (24)
SECTION D: Data and Information Management (25)
SECTION E: Solution Development (23)
SECTION F: Integrated Scenario (39) - Answer ALL the questions carefully.
- Read ALL the questions.
- The mark allocation generally gives an indication of the number of facts/reasons required.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A: SHORT QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.6 D.
1.1.1 Rooting and jail breaking have the following effect on devices:
- Prevents malicious programs from being installed
- Freezes the software installed on the device
- Voids the manufacturer's warranty
- Causes a virus to be installed on the device (1)
1.1.2 What would be the effect on the network in the diagram below if one of the computers malfunctioned?
- The entire network will malfunction.
- The network will function as normal, excluding the faulty node.
- All the nodes will need to be replaced.
- The server will need to be replaced. (1)
1.1.3 Which ONE of the following will indicate that the motherboard battery has failed?
- Operating system passwords are lost.
- Files on the hard disk are lost or corrupted.
- Virtual memory on the hard disk is not accessible any longer.
- Hardware settings, including the current date and time, revert to default values. (1)
1.1.4 Which ONE of the following statements will NOT give the result of 10?
- 64 div 6
- Floor (64/6)
- Trunc (64/6)
- 64 mod 6 (1)
1.1.5 Which set of initial values assigned to variables L and N will result in the while-loop never being executed?
L ? ..
N ? ..
While (L < 2) OR (N < 5) do
…
end loop
- L = 1 and N = 5
- L = 2 and N = 4
- L = 2 and N = 5
- L = -2 and N = -5 (1)
1.2 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.10) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 Programs that are part of system software and do maintenance and administrative tasks (1)
1.2.2 The most common protocol used for downloading e-mail via the Internet (1)
1.2.3 A technology strategy used to obtain a high-ranking placement in the search results page of a search engine, such as Google (1)
1.2.4 A peer-to-peer protocol used to transfer and share large files across a network, such as the Internet (1)
1.2.5 A fixed physical address containing minimal office setup, which is used as shared space by people who work from a mobile office (1)
1.2.6 Specialised software and hardware designed to be used at a till point (1)
1.2.7 The combination of more than one field to identify a record in a database table uniquely (1)
1.2.8 A permanent digital connection to the Internet using a telephone line (1)
1.2.9 Compressing data by sacrificing some insignificant portions of the data (1)
1.2.10 A central registry that keeps track of all the URLs on the Internet (1)
TOTAL SECTION A: 15
SECTION B: SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGIES
QUESTION 2
In the first round of the Computer Olympiad, the participants are expected to have some knowledge of system technologies.
2.1 One of the functions of the motherboard is to provide connectors which allow components to be connected to the computer.
Name TWO other functions of a motherboard. (2)
2.2 Name ONE device that is connected to an expansion slot on the motherboard. (1)
2.3 EEPROM is a special type of PROM that can be electronically erased.
2.3.1 What is the software called that is saved on an EEPROM? (1)
2.3.2 What is the process called that involves the overwriting of existing data contained in EEPROM? (1)
2.4 Many laptop computers have an integrated video adaptor and a video card.
2.4.1 What does the term integrated refer to in this context? (1)
2.4.2 Explain why a laptop computer may have both an integrated video adaptor and a video card by referring to the different functions and its use of resources. (2)
2.5 'Cache' is a computer term that is often referred to when discussing the performance of a computer.
2.5.1 Explain the purpose of caching. (2)
2.5.2 When the Delphi text editor is closed and then opened again, it opens up much faster the second time. Give a detailed explanation of why the program opens up much faster the second time. (2)
2.6 Operating systems use different processing techniques to handle many tasks at the same time.
2.6.1 Identify each of the processing techniques illustrated below.
 (1)
(1) (1)
(1)
2.6.2 Explain how an operating system working with a multicore processor incorporates the processing techniques above for maximum performance. (2)
2.7 Choose a term/concept from COLUMN B that matches the description in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (2.7.1–2.7.4) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 2.7.5 E.
COLUMN A | COLOMN B |
2.7.1 Example of a programming language that uses a virtual machine to compile programming code |
(4 x 1) (4) |
2.8 123D Catch is an example of a consumer cloud application. Define the term cloud application. (2)
2.9 Dropbox is an example of an online storage service that allows for the synchronisation of files. What is the advantage of file synchronising services? (2)
TOTAL SECTION B: 24
SECTION C: COMMUNICATION AND NETWORK TECHNOLOGIES
QUESTION 3
The main office used to distribute the Olympiad data to regional offices countrywide will have cabled LAN access to the Internet.
The diagram below shows the layout of the network and some of the devices that will be used. 
3.1 Would you classify the network in the diagram above as a LAN, WAN, MAN or PAN? Motivate your answer. (2)
3.2 Many different users involved in the Olympiad need access to the network. This resulted in setting up the network as an intranet and extranet.
3.2.1 Distinguish between intranet, extranet and the Internet. (3)
3.2.2 Give an example of a possible user of the extranet in the Olympiad scenario. (1)
3.3 A client-server network is used in the main office.
3.3.1 Motivate the choice of using a client-server network rather than a peer-to-peer network. (1)
3.3.2 The desktop computers in the office are fat clients. State TWO differences between a thin client and a fat client. (2)
3.4 UTP cables are used for the LAN in the main office.
3.4.1 Signal attenuation is one of the weaknesses of UTP cables. State TWO other weaknesses of UTP cables. (2)
3.4.2 If UTP cables are to be used over a very long distance, suggest how the signal attenuation problem can be solved without replacing them with fibre-optic cables. (1)
3.5 The office network speed is very slow. Replacing the cables has been suggested. What else can be done in terms of hardware to improve the speed of the network? (1)
3.6 Is it possible that network cards for both wired and wireless network connections are installed in a computer? Motivate your answer. (1)
3.7 The administrator must decide whether to use cloud services or a VPN to access information regarding the Olympiad.
3.7.1 State TWO disadvantages of using cloud storage. (2)
3.7.2 If the administrator decides to use cloud services, choose a cloud storage service from the list below that would be the most suitable to store critical data, such as the question paper for the Olympiad. (1)
| Office 365; Google Docs; YouTube; Facebook; Gmail |
3.7.3 Suggest ONE technology that can be used to connect two devices to share files. (1)
3.7.4 Explain the benefit of using a VPN for sharing information. (2)
3.8 The Olympiad network could be subject to spyware and malware attacks.
3.8.1 Briefly explain the term spyware. (1)
3.8.2 State TWO ways in which to minimise the risk of a computer becoming infected with spyware. (2)
3.8.3 How will a firewall help protect the Olympiad data against malware attacks? (1)
TOTAL SECTION C: 24
SECTION D: DATA AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT
QUESTION 4
Visitors and participants attending the final round of the Olympiad will need accommodation in guesthouses. A database is required to facilitate bookings.
4.1 Data integrity is achieved by the correct use of primary and foreign keys in the design of a multitable database.
4.1.1 Explain in broad terms what data integrity refers to. (1)
4.1.2 What is the purpose of the foreign key in the design of a database table? (2)
4.1.3 Explain the term referential integrity. (2)
4.2 The database table below was designed by an apprentice programmer.
Fieldname | Data type | |
| GuesthouseID GuesthouseName TelephoneNum NumberOfRooms WiFiAvailable | Autonumber Text Text Text Text |
4.2.1 The GuesthouseID field has been identified as the primary key. What is the aim of the primary key in a database? (1)
4.2.2 The data types of some of the fields are not suitable. Identify ONE such field by writing down the fieldname and a more suitable data type. (2)
4.2.3 State TWO properties of quality data. (2)
4.3 The relational database, QuestHDB, below was designed to keep track of all the bookings at the various guesthouses. 
4.3.1 Write SQL statements for the following queries:
- Display ALL details of the guesthouses in alphabetical order of the guesthouse name where a spa is available. (4)
- Add a record for a new booking to tblBookings. A deposit was received for a booking at the guesthouse with HouseID 1212.
The booking is for two rooms from 8 June 2018 for three nights. (4)
4.3.2 An SQL statement has been compiled to display a list of guesthouses with a total monthly income of more than R50 000,00 for May. The cost per room per night is R400,00.
The total monthly income is a new calculated field. The calculation must be done as follows:
The number of rooms is multiplied by the number of nights and the cost per room per night.
Write down only the missing code at (a) to (e) to complete the SQL statement below correctly.  (7)
(7)
TOTAL SECTION D: 25
SECTION E: SOLUTION DEVELOPMENT
QUESTION 5
The Computer Olympiad organiser has received many questions that could be included in the Olympiad question paper. Each question needs to be evaluated for future use.
5.1 Write pseudocode to enter a word and then display the word with one less character each time, as shown in the example below.
If the word that is entered is COMPUTER, then the following should be displayed:
COMPUTER
COMPUTE
COMPUT
COMPU
COMP
COM
CO
C (4)
5.2 The results of participants have been saved incorrectly in an array called arrResults. The results of the first participant must be moved to the last index. The results for each of the other participants must be moved to the previous index.
For example, in the diagram below Brandon's results are actually Amy's results and must be moved to the first index. Claire's results are actually Brandon's results and must be moved to the second index, and so on for all the participants. Amy's results must be moved to the last index.
Write pseudocode to move the results to the correct positions in the arrResults array with an unknown number of results. (6)
5.3 An array called arrNumbers is populated with the following five values:
8 | 5 | 3 | 12 | 2 |
Another array called arrTemp is an empty array that can store five values.
The algorithm below extracts specific data from arrNumbers and stores the extracted data in arrTemp.
Loop x from 1 to length(arrNumbers)
If arrNumbers[x] modulus 4 = 0
arrTemp[x] = arrNumbers[x]
Redraw the trace table below in your ANSWER BOOK.
x | arrNumbers[x] | arrNumbers[x] modulus 4 = 0? | arrTemp[x] |
Complete the trace table above to show the contents of array arrTemp. (4)
5.4 The incomplete code given below is used to create a new file called Results.txt.
Line 1: Assignfile(TFile, 'Results.txt');
Line 2: ……………
Line 3: Writeln(TFile, 'Koos Jenkins: 78');
Line 4: Writeln(TFile, 'Amanda Smith: 78');
Line 5: ……………
Write down the statements to complete the following lines of code:
5.4.1 Line 2: Create an empty text file called Results.txt. (1)
5.4.2 Line 5: Ensure that the data will be saved to the text file. (1)
5.5 The class diagram below was designed for a school registration system.
TSchool |
- fSchoolCode - fRegDate (format dd/mm/yyyy) - fNumberOfEntries:integer - fPaid:boolean |
+ <<Constructor>> create(sCode:string;iNumEntries:integer;bPaid:boolean) + calcAmount(rFeePerEntry:real):real - determineRegDate:integer + getCode:string + getNumEntries:real + isPaid:boolean + toString:string |
5.5.1 What is the implication for the method determineRegDate being private (-) instead of public (+)? (1)
5.5.2 The number of entries was captured incorrectly.
The following method was created to change the number of entries
to the correct value received as a parameter:
Line
|
- Statement 3 is incorrect. Rewrite the statement so that the method will perform the task correctly. (1)
- What type of method is setEntries? Use a word in the list below. (1)
accessor; mutator; auxiliary
5.5.3 Analyse the declaration of the methods in the class diagram. Identify TWO possible mistakes and suggest ways in which to correct the mistakes. (2)
5.5.4 An object called objSchool of data type TSchool is used in the form class. The isPaid method is called in the OnClick event of a button.
Given:
var
bPaid: Boolean;
Explain why EACH of the following statements is INCORRECT:
- If TSchool.isPaid then … (1)
- bPaid := objSchool.isPaid := true; (1)
TOTAL SECTION E: 23
SECTION F: INTEGRATED SCENARIO
QUESTION 6
The Computer Olympiad will be managed from a main office and all communications will be sent from this office. On the day of the event the data will be distributed electronically to all institutions that have registered to participate in the Computer Olympiad.
6.1 The Olympiad website is a dynamic website which contains a link to a podcast and a video of the previous year's prize giving ceremony and links to the Olympiad's social networking tools. The instructions for the Olympiad are provided as a podcast.
6.1.1 What is a podcast? (2)
6.1.2 Name ONE file format that is used for podcasts. (1)
6.1.3 The video of the prize-giving ceremony can be streamed. Explain the concept of streaming. (2)
6.1.4 There was a request to develop an app for the Olympiad. Give TWO reasons why participants prefer to use an app instead of a web browser. (2)
6.1.5 Users want to receive automatic notifications of the latest results for the Olympiad. What technology is used to provide automatic notifications? (1)
6.1.6 Explain the difference between a dynamic website and a static website. (2)
6.1.7 Other than switching off their phones, describe TWO ways in which the office workers could manage the flood of social networking communication on their phones that can interfere with their work. (2)
6.2 Participants will need to access an encrypted file containing the Olympiad data. An 8-character password required to access the file will be sent to participants as an SMS.
6.2.1 Apart from the number of characters, state TWO other requirements for the password to be a strong password. (2)
6.2.2 Motivate the decision to send the password as an SMS rather than in an e-mail attachment if a receiver will access it on a phone. (1)
6.2.3 Explain the concept of public key encryption. (2)
6.3 Some participants may access the Olympiad questions using mobile devices.
6.3.1 State TWO disadvantages of using a mobile device for this purpose. (2)
6.3.2 How would location-based computing assist the organisers in gathering information about the participants using mobile devices? (1)
6.3.3 Suggest TWO ways in which to improve the battery life of mobile devices. (2)
6.4 A computer being used for the Olympiad displays a message indicating that the computer is low on virtual memory.
6.4.1 Define virtual memory. (2)
6.4.2 Explain why the use of virtual memory could affect the performance of a computer negatively. (2)
6.5 Cloud computing relies heavily on virtualisation technologies.
6.5.1 Name and discuss TWO ways in which virtualisation technologies can be used to benefit multiple users. (4)
6.5.2 State TWO benefits for the organisers of using SaaS (Software as a Service). (2)
6.6 One of the main reasons for the WannaCry ransomware attack was that the software on many networks and personal computers had not been updated.
6.6.1 What is ransomware? (2)
6.6.2 Why could updating the operating system software possibly prevent malicious software, such as ransomware, from accessing your computer? (1)
6.7 A DBMS for the Olympiad was designed, amongst other things, to enable the database administrator to create and edit the distributed database.
6.7.1 Name ONE other function that DBMSs allows the administrator to do. (1)
6.7.2 Explain what a distributed database system is. (2)
6.7.3 While saving data in the database, a power failure occurred. In order to protect the data integrity, a rollback of the transaction needed to be performed. Explain what a rollback of the transaction is. (1)
TOTAL SECTION F: 39
GRAND TOTAL: 150
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper is divided into THREE sections. Candidates must answer ALL the questions in ALL THREE sections.
- The duration of this examination is three hours. Because of the nature of this examination it is important to note that you will not be permitted to leave the examination room before the end of the examination session.
- This question paper is set with programming terms that are specific to Delphi programming language.
- Make sure that you answer the questions according to the specifications that are given in each question. Marks will be awarded according to the set requirements.
- Answer only what is asked in each question. For example, if the question does not ask for data validation, then no marks will be awarded for data validation.
- Your programs must be coded in such a way that they will work with any data and not just the sample data supplied or any data extracts that appear in the question paper.
- Routines, such as search, sort and selection, must be developed from first principles. You may NOT use the built-in features of Delphi for any of these routines.
- All data structures must be defined by you, the programmer, unless the data structures are supplied.
- You must save your work regularly on the disk/CD/DVD/flash disk you have been given, or on the disk space allocated to you for this examination session.
- Make sure that your examination number appears as a comment in every program that you code, as well as on every event indicated.
- If required, print the programming code of all the programs/classes that you completed. You will be given half an hour printing time after the examination session.
- At the end of this examination session you must hand in a disk/CD/DVD/ flash disk with all your work saved on it OR you must make sure that all your work has been saved on the disk space allocated to you for this examination session. Make sure that all files can be read.
- The files that you need to complete this question paper have been given to you on the disk/CD/DVD/flash disk or on the disk space allocated to you. The files are provided in the form of password-protected executable files.
NOTE:
Candidates must use the file DataENGMarch2018.exe.
Do the following:
- Double click on the password-protected executable file.
- Click on the extract button.
- Enter the following password: Sp@cE&18
Once extracted, the following list of files will be available in the folder DataENGMarch2018:
SUPPLIED FILES
Question 1:
- Image1.jpg
- Image2.jpg
- Question1_P.dpr
- Question1_P.dproj
- Question1_P.res
- Question1_U.dfm
- Question1_U.pas
Question 2:
- Centaurus.jpg
- Crux.jpg
- Orion.jpg
- Question2_P.dpr
- Question2_P.dproj
- Question2_P.res
- Question2_U.dfm
- Question2_U.pas
- Scorpio.jpg
- Star_U.pas
- StarData.txt
Question 3:
- Question3_P.dpr
- Question3_P.dproj
- Question3_P.res
- Question3_U.dfm
- Question3_U.pas
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1: GENERAL PROGRAMMING SKILLS
Do the following:
- Open the incomplete program in the Question 1 folder.
- Enter your examination number as a comment in the first line of the Question1_U.pas file.
- Compile and execute the program. The program has no functionality currently.
- The program contains FIVE tab sheets with different unrelated questions.
- Follow the instructions below to complete the code for EACH section of QUESTION 1, as described in QUESTION 1.1 to QUESTION 1.5.
1.1 Button [1.1 – Total area]
The user must use the edit boxes provided to enter the radius of the circle and the base and height of one of the triangles in the figure.
Write code to do the following:
- Extract the values entered by the user.
- Calculate the area of the circle, the area of the eight triangles in total and the total area of the figure using the following formulae:
Area of circle = pi x radius2 where the value of pi = 3.14159
Area of a triangle = ½ x base x height - Display the area of the circle, area of the eight triangles in total and the total area of the figure in the output component provided. The total area must be formatted to TWO decimal places.
Example of input:
Example of output:
| Area of circle = 233.433959996 Total area of triangles = 112.6912 Total area = 346.13 |
(12)
1.2 Button [1.2 – Next blue moon]
The first blue moon was seen in the year 1862. Thereafter, a blue moon was seen every three years.
Extract the year in which the first blue moon was seen from the lblInfo label. Use the year from the system date and the year extracted from the label to determine the year when the next blue moon will appear (excluding the current year). Display the output in the edit box provided. (9)
Example of output: ![]()
1.3 Button [1.3 – Highest common factor]
The user must enter two integer numbers. The highest common factor is the largest number that can divide into the two numbers without a remainder.
Write code to do the following:
- Extract the numbers entered by the user from the edit boxes provided.
- Determine the highest common factor of the two numbers.
- Display the highest common factor in the edit box provided.
Example of input and output:
(10)
1.4 Button [1.4 – Remove vowels]
The user must enter a sentence in the edit box provided.
Write code to do the following:
- Delete ALL the vowels from the sentence entered by the user, except where the vowel is the first letter of the word.
- Display the sentence after deleting the vowels in the edit box provided. Example of output:
(11)
1.5 Button [1.5 – Slide show]
A space exhibition centre presents a slide show to visitors in their conference centre which seats 100 people. Groups of people can attend the slide show as long as there are seats available for all the people in the group. Groups who can be accommodated will each be assigned a number, starting with the value 1 for the first group, 2 for the second group, and so on. If large groups are rejected, smaller groups can still be accommodated until all the seats are taken.
Write code to do the following:
- Use an input box to prompt the user to enter the number of people in the group. The user must be able to keep on entering the number of people for new groups until the total number of attendees reaches 100.
- For each group that is accepted, display the group number and the number of people in the group.
- If the number of people in the group exceeds the number of seats available, display a suitable message indicating that the group cannot be accommodated. The number of seats still available must be part of the message.
NOTE: Even though some of the groups will not be accepted to attend the slide show, the program must continue to allow the user to enter groups until a total of 100 people are accepted to attend the slide show.  (12)
(12)
|
TOTAL SECTION A: 54
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: OBJECT-ORIENTATED PROGRAMMING
A constellation is a group of related stars that covers the night sky. Some stars are considered to be navigational, while others are passive. A navigational star is used to assist with direction and movement. |
Do the following:
- Open the incomplete program in the Question 2 folder.
- Open the incomplete object class Star_U.pas.
- Enter your examination number as a comment in the first line of both the Question2_U.pas file and the Star_U.pas file.
- Compile and execute the program. Currently the program has no functionality. The following user interface is displayed:
- Complete the code for this program, as specified in QUESTION 2.1 and QUESTION 2.2.
2.1 An incomplete object class called TStar, which represents a celestial star, has been provided.
The declaration of the attributes and an accessor method for the fName attribute (getName) has been provided.
The attributes for the Star object have been declared as follows:
NAMES OF ATTRIBUTES | DESCRIPTIONS |
fName | Name of the star |
fMagnitude | The magnitude of a star is related to its brightness. The magnitude of the brightest star is -1. As the magnitude of a star increases, the star gets dimmer. Example: The magnitude of a dim star, such as Mimosa, is 1.25. |
fDistance | The distance of a star from Earth is an integer value measured in light years. Example: The distance of the star Mimosa from Earth is 279 light years. |
fConstellation | The name of the constellation the star belongs to |
fNavigationalStatus | A Boolean value which indicates whether the star is regarded as a navigational star or not |
2.1 Complete the code in the object class, as described in QUESTION 2.1.1 to QUESTION 2.1.5 below.
2.1.1 Write code for a constructor method that will receive the name of the star, its magnitude, its distance from Earth and the constellation it belongs to as parameters. Set the FOUR respective attributes to the received parameter values and initialise the fNavigationalStatus attribute to 'false'. (4)
2.1.2 Write code to create an accessor method for the constellation attribute fConstellation. (2)
2.1.3 Write code for a mutator method called setNavigationalStatus, which will receive a Boolean value as a parameter and set the navigational status attribute to the received value. (3)
2.1.4 Write code for a method called determineVisibility that will determine and return a description of the visibility of the star. The visibility of a star depends on its distance from Earth in light years and its magnitude.
Use the following criteria to determine the description of visibility that applies to a star: (11)
DISTANCE | MAGNITUDE | DESCRIPTION OF VISIBILITY |
Fewer than 80 light years | Any value | Clearly visible |
Between 80 and 900 light years (inclusive) | Up to 2 | Hardly visible to the naked eye |
Larger than 2 | Visible by means of standard optical aid | |
More than 900 light years | Any value | Only visible by means of specialised optical aid |
2.1.5 Write code to create a toString method which returns a string formatted as follows, depending on whether the star is a navigational star or not:
<name of star> belongs to the <constellation> constellation.
The star has a magnitude of <magnitude> and is <distance from Earth> light years away from Earth.
If the star is a navigational star, add the following line:
<name of star> is a navigational star.
If the star is NOT a navigational star, add the following line:
<name of star> is a passive star. (6)
2.2 An incomplete unit, Question2_U, has been provided which contains code for the following:
- The declaration of the object variable objStarX
- An array called arrNavigationStars which contains the names of stars that are navigational stars.
A text file called StarData.txt contains the data of an unknown number of stars (both passive and navigational). The details of each star appears in the following format in the file:
<common name of the star> |
Example of the details of the first two stars in the text file:
Acrux Mimosa |
Do the following to complete the code for the buttons in the main form unit, as described below:
2.2.1 Button [2.2.1 – Instantiate object]
The user is required to select the name of a star in the combo box. Write code to do the following:
- Extract the name of the selected star from the combo box.
- Use a conditional loop and search in the text file for the name of the selected star. The loop must stop when the name of the star has been found in the file.
If the name of the star has been found, do the following:- Instantiate a TStar object using the objStarX object variable that has been declared globally as part of the given code.
- Test whether the star is a navigational star using the arrNavigationStars array and set the value for the navigational status attribute accordingly.
- Enable the pnlButtons panel.
If the name of the star has NOT been found in the text file, do the following: - Display a message to indicate that the star was not found.
- Disable the pnlButtons panel. (24)
2.2.2 Button [2.2.2 – Display]
Display the details of the star in the rich edit component redQ2 using the toString method.
Load the image of the constellation that the star belongs to into the imgQ2 image component. The file name of the image to be displayed is the name of the constellation the star belongs to. The image files have the extension .jpg.
Example of output if the selected star is Mimosa: 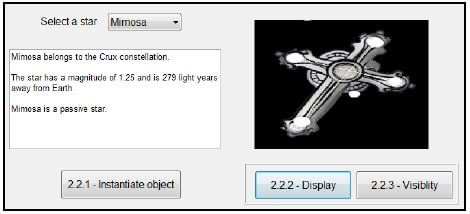 (3)
(3)
2.2.3 Button [2.2.3 – Visibility]
The brightness and visibility of a star is dependent on the magnitude and the distance of the star from Earth. Call the relevant methods to display the name and visibility of the star.  (3)
(3)
- Ensure that your examination number has been entered as a comment in the first line of the object class and the form class.
- Save your program.
- Print the code of both the object class and form class, if required.
TOTAL SECTION B: 56
SECTION C
QUESTION 3: PROBLEM-SOLVING PROGRAMMING
SCENARIO |
Do the following:
- Open the incomplete program in the Question 3 folder.
- Enter your examination number as a comment in the first line of the Question3_U.pas file.
- Compile and execute the program. Currently the program has no functionality.
Supplied GUI:
The GUI below represents the interface of the program. 
- Complete the code for each question, as described in QUESTION 3.1 to QUESTION 3.3.
NOTE:
- Good programming techniques and modular design must be applied in the design and coding of your solution.
- You may NOT change the code provided.
Supplied code:
The program contains the following code for the declaration of a two-dimensional array called arrGame:
arrGame: array [1..9, 1..9] of char;
The program must do the following:
- Populate the two-dimensional array when the game starts
- Allow the user to guess the positions of invisible planets placed randomly on the game board
- Determine whether the player has won or lost and terminate the game. The player wins when he/she identifies two planets on the game board within five guesses.
3.1 Button [3.1 – Start game]
A dash character (-) represents an open space in the two-dimensional array arrGame and a hash character (#) represents a planet.
The two-dimensional array must first be populated with open-space characters. Its content must be displayed in the game board area.
The level of difficulty selected from the radio group rgbQ3 determines the number of planets to be placed randomly in arrGame. The following applies:
Difficulty level 1: 50 positions in the array must be replaced by planets (#)
Difficulty level 2: 40 positions in the array must be replaced by planets (#)
Difficulty level 3: 30 positions in the array must be replaced by planets (#)
The value '0' must be displayed on panel pnlQ3NumberOfGuesses, which indicates the total number of guesses.
The 'Play' button must be enabled and the rich edit components cleared.
NOTE: The positions of the planets on the game board should NOT be visible (not displayed) to the player.
Example of output when the Start game button is clicked:  (22)
(22)
3.2 Button [3.2 – Play]
The player must guess the position of a planet by selecting a row number and a column number from the combo boxes provided. Then click the 'Play' button to see whether the position of a planet was guessed correctly.
If the position of a planet is guessed correctly:
- Update the display to show the position of the planet (#) that was guessed correctly.
- Update the number of correct guesses on the panel pnlQ3NumberOfGuesses.
HINT: Replace the planet character (#) that was guessed correctly with another character to show which planets were identified during the game play session. This information is required for Button 3.3 ('Reveal planets').
If the position guessed is NOT the position of a planet:
- Display the row and column values of the incorrect guess in the redQ3Incorrect output area.
The player must be able to guess the positions of planets repeatedly until he/she wins or loses the game.
NOTE: A game is won as soon as the positions of two planets are correctly guessed within the allowed five guesses.
Use a message box to display a suitable message based on the outcome of the game, either 'Game won' or 'Game lost'.
Disable the play button when the game is over.
Example of output if the positions of two planets were guessed correctly within two guesses:
Example of output if the player lost the game. The position of only one planet was guessed correctly within five guesses: 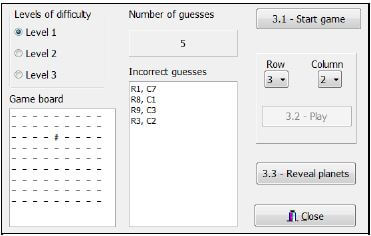 (13)
(13)
3.3 Button [3.3 – Reveal planets]
Write code to display the game board with all the randomly placed planets revealed.
Example of the output if the planets were randomly placed but the player has not played yet: 
Example of output if the player won by identifying the positions of two planets within two guesses: 
NOTE: The array in the sample output may be different because the indices for the planet symbols are randomly generated. (5)
|
TOTAL SECTION D: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
GENERAL INFORMATION
- These marking guidelines must be used as the basis for the marking session. They were prepared for use by markers. All markers are required to attend a rigorous standardisation meeting to ensure that the guidelines are consistently interpreted and applied in the marking of candidates' work.
- Note that learners who provide an alternate correct solution to that given as example of a solution in the marking guidelines will be given full credit for the relevant solution, unless the specific instructions in the question paper were not followed or the requirements of the question were not met.
- Annexures A, B and C (pages 3–8) include the marking grid for each question and a table for a summary of the learner’s marks.
- Annexures D, E, and F (pages 9–21) contain examples of a programming solution for QUESTION 1 to QUESTION 3 in programming code.
- Copies of Annexures A, B and C (pages 3–8) and the summary of learner’s marks (page 8) should be made for each learner and completed during the marking session.
MEMORANDUM
ANNEXURE A
SECTION A
QUESTION 1: MARKING GRID – GENERAL PROGRAMMING SKILLS
CENTRE NUMBER: | EXAMINATION NUMBER: | |||
QUESTION | DESCRIPTION | MAX. MARKS | LEARNER'S MARKS | |
A learner must be penalised only once if the same error is repeated. | ||||
1.1 | [Button 1.1 – Total area] | 12 | ||
1.2 | [Button 1.2 – Next blue moon] | 9 | ||
1.3 | [Button 1.3 – Highest common factor] | 10 | ||
1.4 | Button [1.4 – Remove vowels] | 11 | ||
1.5 | [Button 1.5 – Slide show] | 12 | |
TOTAL SECTION A: | 54 |
ANNEXURE B
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: MARKING GRID - OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING
CENTRE NUMBER: | EXAMINATION NUMBER: | |||
QUESTION | DESCRIPTION | MAX. MARKS | LEARNER'S MARKS | |
2.1.1 | Constructor: | 4 | ||
2.1.2 | accessor METHOD: | 2 | ||
2.1.3 | setNavigationalStatus PROCEDURE: | 3 | ||
2.1.4 | determineVisibility FUNCTION: | 11 | ||
2.1.5 | toString METHOD | 6 | ||
2.2.1 | Button – [2.2.1 - Search holder]: | 24 | |
2.2.2 | Button – [2.2.2 - Display]: | 3 | |
2.2.3 | Button – [2.2.3 - Visibility]: | 3 | |
TOTAL SECTION B: | 56 |
ANNEXURE C
SECTION C
QUESTION 3: MARKING GRID – PROBLEM SOLVING PROGRAMMING
CENTRE NUMBER: | EXAMINATION NUMBER: | |||
QUESTION | DESCRIPTION | MAX. MARKS | LEARNER'S MARKS | |
3.1 | Button [3.1 – Start game] | 22 | ||
3.2 | Button [3.2 - Play] | 13 | ||
| 3.3 | Button [3.3 – Reveal planets] Loop through rows ✔ Create output string✔ Loop through columns✔ Add array value to output string✔ Display output string✔ | 5 | ||
| TOTAL SECTION C: | 40 | |||
SUMMARY OF LEARNER'S MARKS:
CENTRE NUMBER: | EXAMINATION NUMBER: |
SECTION A | SECTION B | SECTION C | ||
QUESTION 1 | QUESTION 2 | QUESTION 3 | GRAND TOTAL | |
MAX. MARKS | 54 | 56 | 40 | 150 |
LEARNER'S MARKS |










HOSPITALITY STUDIES GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
HOSPITALITY STUDIES
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of FOUR sections.
SECTION A: Short questions (all topics) (40)
SECTION B: Kitchen and restaurant operations;
Hygiene, safety and security (20)
SECTION C: Nutrition and menu planning;
Food commodities (80)
SECTION D: Sectors and careers;
Food and beverage service (60) - Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A: SHORT QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
1.1 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
EXAMPLE:
1.1.11 A good source of vitamin C is …
- milk.
- oranges.
- meat.
- bread.
ANSWER: 1.1.11 B
1.1.1 The main function of a night auditor is to …
- perform petty cash payments.
- look after special guests at night.
- balance all front-office accounts.
- greet guests who arrive at night. (1)
1.1.2 Inedible yellow connective tissue in meat mainly consists of ...
- collagen.
- gelatin.
- elastin.
- sarcoplasm. (1)
1.1.3 A symptom of hepatitis A is ...
- continuous coughing.
- severe diarrhoea.
- night sweats.
- swollen glands. (1)
1.1.4 … is NOT suitable to serve at a cocktail function.
- Canapés and crudités
- Noisettes and tournedos
- Rissoles and kebabs
- Rösti and blini (1)
1.1.5 When gelatin is melted over hot water the process is known as …
- dispersion.
- gelation.
- hydration.
- setting. (1)
1.1.6 … is part of brand awareness and can also be used as a marketing tool.
- Packaging
- Promotion
- Advertising
- Presentation (1)
1.1.7 A drink that is made with two or more beverages is known as a/an …
- espresso.
- cordial.
- syrup.
- cocktail. (1)
1.1.8 The term that is used to describe the pricking of a pastry base with a fork before baking:
- Glazing
- Trapping
- Docking
- Lining (1)
1.1.9 Paula is a/an … vegetarian because she consumes fish and seafood.
- lacto
- ovo
- pollo
- pesco (1)
1.1.10 Pinotage is classified as a … wine.
- sparkling
- red
- fortified
- white (1)
1.2 The various cuts of beef are illustrated on the carcass below. Choose the number of the cut of beef in COLUMN A that matches the cut in COLUMN B and its specific use in COLUMN C. Write only the letter (A–G) from COLUMN B and the Roman numerals ((i)–(vii)) from COLUMN C next to the question number(1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 H (viii).
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | COLUMN C |
1.2.1 1 | A bolo | (i) club steak |
1.2.2 4 | B prime rib | (ii) tournedos |
1.2.3 8 | C wing rib | (iii) beef olives |
1.2.4 13 | D hump | (iv) Porterhouse steak |
1.2.5 12 | E fillet | (v) kebabs |
F rump | (vi) corned beef | |
G shin | (vii) stock |
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 ONE-WORD ITEMS
Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.10) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 The tool used by waiters to open wine bottles
1.3.2 A preservation process during which fruit is cooked repeatedly in highly concentrated syrup
1.3.3 Heating and cooling chocolate to make it more resistant to melting
1.3.4 The process used to fill joints of meat before cooking
1.3.5 A food-borne disease caused by contaminated water
1.3.6 A pastry used to make samoosas
1.3.7 A very small creamy nut that has an oval shape and which is used as an essential ingredient in Italian pesto sauce
1.3.8 The main nutrient in choux pastry
1.3.9 An enzyme that prevents the setting of gelatin because it breaks down the protein
1.3.10 A disease caused when the body is unable to produce sufficient insulin (10 x 1) (10)
1.4 SELECTION
Choose FIVE examples of baked desserts in the list below. Write only the letters (A–J) next to the question number (1.4) in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Crêpe Suzette
- Bread and butter pudding
- Malva pudding
- Banana fritters
- Trifle
- Apple strudel
- Crème caramel
- Chocolate soufflé
- Charlotte muscovite
- Churros (5 x 1) (5)
1.5 ONE-WORD ITEMS
Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions of serving equipment by choosing a word/term from the list below. Write only the word/term next to the question number (1.5.1–1.5.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
plunger; carving unit; service cloth; cloche; tongs; sauceboat; underliner; hot tray |
1.5.1 Used to protect the hands and wrists from burns (1)
1.5.2 Used to keep plates, serving dishes and food warm on the buffet table (1)
1.5.3 Equipment used to prepare coffee (1)
1.5.4 Used to cover food and prevent it from drying out (1)
1.5.5 Equipment used for serving all single portions of food (1)
TOTAL SECTION A: 40
SECTION B: KITCHEN AND RESTAURANT OPERATIONS;
HYGIENE, SAFETY AND SECURITY
QUESTION 2
2.1 Study the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
A newly appointed porter at the Gold Hotel is coughing up blood. |
2.1.1 Identify the disease that the porter is suffering from. (1)
2.1.2 Predict THREE other symptoms that the porter may have, other than the one identified in QUESTION 2.1.2. (3)
2.1.3 Do you think that the disease in QUESTION 2.1.1 will have a negative impact on the workforce? Motivate your answer. (3)
2.2 State TWO precautionary measures that should be taken by a food handler who is suffering from HIV/Aids. (2)
2.3 Study the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
Amanda was employed as a waiter at a local hotel recently. She told you that the hotel manager gave her just one look, appointed her and told her to start straight away, without interviewing her or introducing her to the point-of-sale (POS) system. |
2.3.1 Explain what impact the manager's action will have on service excellence. (3)
2.3.2 Amanda has decided to accept the job at the local hotel. Advise Amanda on 'professional work ethics' that she should display. (3)
2.4 One of the advantages of the POS (point of sale) system is to increase productivity. Evaluate the statement. (3)
2.5 Discuss TWO safety practices to follow when purchasing a product online. (2)
TOTAL SECTION B: 20
SECTION C: NUTRITION AND MENU PLANNING;
FOOD COMMODITIES
QUESTION 3
3.1 Study the dishes below and answer the questions that follow.
| Fruit kebabs | Filled eggs |
|
3.1.1 Identify the type of function where the dishes above will be served. (1)
3.1.2 Motivate why it is to the advantage of the caterer to host the type of function identified in QUESTION 3.1.1. (4)
3.1.3 Evaluate the suitability of the dishes above for guests with high cholesterol. (4)
3.1.4 Give reasons why the dishes above are suitable for people who are HIV positive. (4)
3.2 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
You have been advised by a dietician to become a vegetarian. You are told to exclude meat, poultry and fish and rather have a balanced intake of legumes, nuts, seeds, milk products and eggs. |
3.2.1 Identify the type of vegetarianism recommended by the dietician. (1)
3.2.2 Motivate why the dietician might have advised you to become a vegetarian. (2)
3.2.3 Name THREE types of seeds that you could include in your diet. (3)
3.2.4 List the nutrients found in nuts. (3)
3.3 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
The following costs were incurred at the Food and Wine Restaurant for a banquet prepared for 40 people.
|
3.3.1 Calculate the selling price. Show ALL calculations. (5)
3.3.2 Calculate the selling price per person for the banquet. Show ALL calculations. (3)
3.4 Study the label below and answer the questions that follow.
GOODFOOD A delicious blend of dried cranberries, golden raisins, cherries and blueberries |
3.4.1 Identify the preservation method above. (1)
3.4.2 Evaluate the information on the label above. (5)
3.4.3 State FOUR advantages of food preservation using the method identified in QUESTION 3.4.1. (4) [40]
QUESTION 4
4.1 Study the pictures below and answer the questions that follow. 
4.1.1 Distinguish between the three products. Redraw the table below in the ANSWER BOOK and complete the table. (6)
MILK TART | CREAM PUFFS | VOL-AU VENTS | |
Type of pastry | (1) | (1) | (1) |
Shaping technique | (1) | (1) | (1) |
4.1.2 Identify a product that should be baked blind. Motivate your answer. (3)
4.1.3 Comment on the appearance of the vol-au-vent. (3)
4.1.4 Name the pyramid-shaped product made by stacking cream puffs using caramel. (1)
4.1.5 Justify why the spun sugar used to decorate the product named in QUESTION 4.1.4, should be prepared on the same day it is used. (2)
4.1.6 Explain how spun sugar is made. (2)
4.1.7 The cream filling in the puffs can also be replaced by a chiffon filling. Explain how a chiffon filling is prepared. (3)
4.2 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
Grade 12 learners have prepared kiwi jelly and strawberry coulis for a practical lesson. |
4.2.1 Give suitable reasons for EACH of the following faults that occurred when preparing the jelly:
(a) There were ice crystals in the kiwi jelly. (1)
(b) The kiwi jelly did not set properly. (3)
4.2.2 Describe how the moulds should be prepared in order to ensure that the kiwi jelly unmoulds easily. (3)
4.2.3 Explain what a coulis is. (2)
4.3 Study the picture below and answer the questions that follow.
T-BONE |
4.3.1 Name the part of the beef carcass from which the T-bone was cut. (1)
4.3.2 Explain why T-bone steak is suitable for braaiing in South Africa. (3)
4.3.3 Give possible reasons why the T-bone above turned out to be extremely tough and dry when served at a restaurant. (4)
4.3.4 Name THREE factors to consider when purchasing the cut of meat above. (3) [40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 80
SECTION D: SECTORS AND CAREERS;
FOOD AND BEVERAGE SERVICE
QUESTION 5
5.1 Study the poster below and answer the questions that follow. 
5.1.1 Name THREE other visual marketing tools that can be used to market the product above. (3)
5.1.2 Predict the target market that the product above will appeal to. Motivate your answer. (2)
5.1.3 Explain how the sale of the product above will contribute to the South African economy. (4)
5.1.4 Evaluate the poster above. (5)
5.2 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
A young entrepreneur opened a ten-room guesthouse in the local community recently. He has appointed you as the accountant at his new business. |
5.2.1 Recommend THREE revenue-generating areas, other than the bedrooms, that could assist the guesthouse in generating income. (3)
5.2.2 Suggest FOUR responsibilities of an accountant in the guesthouse above. (4)
5.2.3 State FOUR characteristics that the young entrepreneur should have. (4)
5.2.4 A business plan is important when starting a business. State FIVE aspects that the young entrepreneur should include in his business description. (5) [30]
QUESTION 6
6.1 Read the extract, study the photographs with information below and then answer the questions that follow.
A group of guests is celebrating a 21st birthday party at a restaurant. The group orders a selection of popular South African sparkling wines, including Methóde Cap Classique and de-alcoholised sparkling wines. Mary, an 18-year-old waitress, has been assigned to serve the table. |
6.1.1 Define the term Methóde Cap Classique. (1)
6.1.2 Name TWO other methods used for making sparkling wines. (2)
6.1.3 Explain why the term 'Champagne' is incorrect when referring to the sparkling wines above. (1)
6.1.4 Suggest a suitable starter to pair with Champagne. (1)
6.1.5 Explain what a de-alcoholised wine is. (2)
6.1.6 Choose a suitable glass (A–D) and temperature for the sparkling wine above. (2)
6.1.7 Explain how the glasses above can be frosted. (2)
6.1.8 Discuss the legal requirements that restaurant owners have to comply with when serving wine. (3)
6.1.9 One of the guests becomes flirtatious with Mary and she feels uncomfortable. Discuss how Mary should handle the guest. (4)
6.2 Explain the steps to follow when presenting the bill to guests. (4)
6.3 Study the picture below and answer the questions that follow.
6.3.1 Evaluate the table layout in the picture above. (4)
6.3.2 Distinguish between a formal dinner and a cocktail function regarding the food-serving and clearing procedures a waiter should follow. Redraw the table below in the ANSWER BOOK and complete the table. (4) [30]
FORMAL DINNER | COCKTAIL FUNCTION | |
Food-serving procedure | (1) | (1) |
Clearing procedure | (1) | (1) |
TOTAL SECTION D: 60
GRAND TOTAL: 200
HOSPITALITY STUDIES GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
HOSPITALITY STUDIES
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (10)
1.1.1 | C√ |
1.1.2 | C√ |
1.1.3 | B√ |
1.1.4 | B√ |
1.1.5 | A√ |
1.1.6 | A√ |
1.1.7 | D√ |
1.1.8 | C√ |
1.1.9 | D√ |
1.1.10 | B√ |
1.2 MATCHING ITEMS (10)
1.2.1 | D√ | (vi) √ |
1.2.2 | A√ | (iii) √ |
1.2.3 | B√ | (i) √ |
1.2.4 | E√ | (ii) √ |
1.2.5 | F√ | (v) √ |
1.3 ONE-WORD ITEMS (10)
1.3.1 | Corkscrew / waiters friend√ |
1.3.2 | Crystallising√ |
1.3.3 | Tempering√ |
1.3.4 | Stuffing√ |
1.3.5 | Cholera/Hepatitis B√ |
1.3.6 | Phyllo/Purr √ |
1.3.7 | Pine nut√ |
1.3.8 | Carbohydrates/fats/protein√ |
1.3.9 | Proteolytic/Papain/Bromelin/Ficin√ |
1.3.10 | Diabetes√ |
1.4 SELECTION
B√
C√
F√
G√
H√ (5)
1.5 ONE-WORD ITEMS (5)
1.5.1 | Service cloth√ |
1.5.2 | Hot tray√ |
1.5.3 | Plunger√ |
1.5.4 | Cloche√ |
1.5.5 | Tongs√ |
TOTAL SECTION A: 40
SECTION B: KITCHEN AND RESTAURANT OPERATIONS. HYGIENE, SAFETY AND SECURITY
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1 Tuberculosis√ (1)
2.1.2
- Fever, chills√
- Night sweats√
- Chest pains√
- Loss of appetite√
- Weight loss√
- Constant tiredness√
- Dyspnoea/shortness of breath√ (Any 3) (3)
2.1.3 Yes √
- Workflow disruption√
- Reduction in productivity√
- Increases in indirect costs related to care and treatment of the employees√
- Inhibits economic growth because they have less money to invest in productive activities√ (Any 3) (3)
2.2
- Wear gloves√
- Follow good personal hygiene√ and sanitation√
- If coughing occurs a mouth cover can be used√ (Any 2) (2)
2.3
2.3.1 It can have both a negative and a positive impact;
Negative:
- She hasn’t been trained on the use of the POS system and might struggle√
- She hasn’t received training and might struggle with the service aspect and knowledge of the dishes served in the restaurant√
Positive:
- Amanda could have a good attitude and has displayed a good first impression resulting in her being hired without an interview√
- She could have portrayed a professional appearance√ (3)
2.3.2 For Amanda to show professional work ethics she needs to:
- Be honest√
- Be reliable√
- Be punctual√
- Be patient/tolerant√
- Keep confidential matters to herself√
- Work well with others and respect them√
- Get to know herself and others√
- Be creative√ (Any 3) (3)
2.4 A POS system:
- Reduces time spent on doing inventory√
- Reduces time on sales on paper work√
- Barcode scanners make checking out faster√
- Makes ordering processes streamlined√
- Service is more faster and accurate√
- Assists the staff not to omit items in the bill√/ charging incorrectly√ (Any 3) (3)
2.5
- Use a credit card with small limits√
- Use a secure connection√
- Do business with reputable organisation√
- Use the recommended website√
- Do not clink on any hyperlink contained within a 'spam' email√
- Always use a secure web browser√
- Look out for the closed padlock icon√
- Read the terms and conditions of the suppliers website√ (Any 2) (2)
TOTAL SECTION B: 20
SECTION C: NUTRITION, MENU PLANNING AND FOOD COMMODITIES
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1
- Cocktail√
- Finger lunch√ (Any 1) (1)
3.1.2
- A large number of people can be entertained at one time√
- A small space can be used√
- Little cutlery and crockery is required√/ or none√
- A diverse mix of guests can be accommodated√
- Duration of the function is usually short√
- Menus can be cheap√
- A variety of snacks is served√ (Any 4) (4)
3.1.3
- Fruit kebabs are suitable√
- Fruits need to be incorporated in the diet√
- The filled eggs are unsuitable√
- They need to avoid egg yolks√ and avoid mayonnaise which has been incorporated in the egg yolk. √ (Any 4) (4 )
3.1.4
- The important elements of a balanced diet are included√
- Fruit kebabs have vitamins and minerals√ which will help improve the immune system of the HIV sufferer√.
- The filled eggs have protein√ which will repair and build body tissue√ and help maintain muscle mass√ (Any 4) (4)
(Any other relevant answer)
3.2
3.2.1 Lacto-ovo vegetarian√ (1)
3.2.2
- Helps prevents diabetes, obesity and heart disease√
- Lower cholesterol and blood pressure√
- Less hormones in vegetables than meat√
- Healthy living lifestyle√ (Any 2) (2)
3.2.3
- Sunflower√
- Pumpkin√
- Flax√
- Lin√
- Poppy√
- Sesame√ (Any 3) (3)
3.2.4
- Protein√
- B Vitamins√
- Fat√
- Minerals (magnesium, phosphorous, potassium)√ (Any 3) (3)
3.3
3.3.1
- Selling price = Food cost + Overhead cost +Labour costs + Profit
= R4 450 + R650 + R1600
= R6 700√ X 40/100√
= R2 680√ - SP = R6 700 + R2 680√
= R9 380√ (5)
3.3.2
- Cost per person = Selling price/ number of guests
= R9380√/ 40√
= R234.50√ (3)
3.4
3.4.1 Drying √ (1)
3.4.2 The following information is available on the label:
- The name of the product√
- The brand name of the product√
- Picture/Image of the product√
- Net weight of the product√
The following information is unavailable on the label:
- Name and address of the manufacturer is not available√
- Sell-by-date / expiry date√
- Nutritional information√
- Ingredient list√
- Country of origin√ (Any 5) (5)
3.4.3
- Growth of micro-organisms is retarded due to lack of moisture√
- The shelf life of food is improved√
- Drying makes food lighter to transport√
- Food products are available of all year round√
- Easy to store√
- Saves time and labour√ (Any 4) (4) [40]
QUESTION 4
4.1
4.1.1 (6)
Milk tart | Cream puffs | Vol-au-vent | |
Type of pastry | Shortcrust √ (1) | Choux√ (1) | Puff√ (1) |
Technique in the shaping of pastry |
|
|
|
4.1.2
- Milk Tarts√
Because you add a cooked filling to the pastry√ - To keep the crust from blistering√
- To ensure that the pastry case is cooked thoroughly√
- To help the crust to become crisp√ (Any 3) (3)
4.1.3
- Light , flaky layers√
- Uneven surface√
- Good volume√
- Shape is round√
- Looks baked through√ (Any 3) (3)
4.1.4 Croquembouche√ (1)
4.1.5 Because the caramel will absorb moisture√ and become soft√ and not hold its shape√ (Any 2) (2)
4.1.6 Melt sugar (water optional) until golden brown.√ Flick caramel sugar√ over dowels or wooden spoons√ to create long, fine hairy thread of sugar√ (Any 2) (2)
4.1.7 Made from hot egg custard√ or fruit puree√ to which hydrated gelatine is added√. Whipped egg whites are folded in the base√ (Any 3) (3)
4.2
4.2.1
- It was set in the freezer instead of the fridge√ (1)
-
- Too little gelatine was used√
- Too much sugar was used√
- Large pieces of kiwi were used√
- It was set at room temperature instead of the fridge√
- Enzymes in the kiwi broke down the proteins in the gelatin √ thus destroyed the setting ability√ (Any 3) (3)
4.2.2
- Rinse moulds in cold water√
- Lightly spray moulds with non-cook spray√
- Lightly brush moulds with oil√ (3)
4.2.3 Pureed √fruit sauces√ cooked or uncooked√ with or without sugar (Any 2) (2)
4.3
4.3.1 Loin√/Sirloin√ (1)
4.3.2
- There is a good distribution of marbling on the T-bone√,
- it will add to the tenderness√ and flavour to the meat√
- It is a soft meat cut with little connective tissue√ (Any 3) (3)
4.3.3
- Meat may have been cooked too long√
- The meat may have been obtained from an old carcass/ involved in a lot of muscle activity√
- The wrong cooking method may have been used√
- Animal may have been stressed during slaughtering√
- Carcass was not matured sufficiently√ (Any 4) (4)
4.3.4
- Bright red colour√
- Well-marbled√
- Pleasant smell√
- Creamy coloured fat√
- Cut surface must be smooth/satin/velvety √
- Bones should be red and porous√
- Texture should be firm but not dry√ (Any 3) (3) [40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 80
SECTION D: FOOD AND BEVERAGE SERVICE
QUESTION 5
5.1
5.1.1
- Leaflets√
- Brochures√
- Flyers√
- Adverts√ (Any 3) (3)
5.1.2
- School going children√
- University students√
- Families√
- Teenagers√ (Any 1)
Reason: the reasonable price will make it affordable for people to buy√ (1) (2)
5.1.3
- It creates job opportunities.√
- Economic growth is stimulated and local income will increase.√
- It will contribute to the development√ and improvement of the infrastructure√
- Tourists will bring valuable currency.√
- The esteem and standard of the community improves√. (Any 4) (4)
5.1.4 Negative:
- Not easy to read√
- Pictures do not relate to the product being advertised√
- It is untidy and unattractive√
- There is no slogan on the poster√
- No contact details are provided√
- Spelling mistakes on the name Burgers (Burghers) and
- Reasonable (Reasonabl) √
Positive:
- Price is included√
- Discount is included, (Cheap Cheap) √
- Information is not cluttered√ (Any other relevant 5) (5)
5.2
5.2.1
- Guest and function rooms√
- Food and beverage√
- Bars√
- Laundry√ (Any 3) (3)
(Any other relevant answer)
5.2.2
- Paying staff salaries√
- Controlling banking procedures√
- Overseeing the auditing of hotel funds√
- Ensuring payments of VAT√
- Keeping track of the money coming in and out of the business√
- Safeguarding the business assets√
- Preparing financial reports√
- Drawing up budgets√ (Any 4) (4)
5.2.3 An entrepreneur must possess the following characteristics:
- Have an ability to identify business opportunities and take calculated risks to achieve success√
- Be committed and determined√
- Have a sense of responsibility and a love of achievement√
- Be creative, self-reliant and adaptable√
- Have a perspective that is future orientated√
- Be confident to achieve success√
- Possess good organising and management skills√
- Have high levels of energy and a sense of humour√ (Any 4) (4)
5.2.4
- Business address√
- Form of business√
- Branding√
- Short , medium and long term goals√
- Street map showing location of business√
- Site plan showing layout of the business√ (Any 5) (5) [30]
QUESTION 6
6.1
6.1.1
- The second fermentation occurs in the bottle√
- Similar to the Traditional Champagne Method √ (Any 1) (1)
6.1.2
- Carbonation Method√
- Tank Method/ Charmat Method√
- Transfer Method√ (Any 2) (2)
6.1.3 Champagne is only bottled in France√ in the Champagne district√ (Any 1) (1)
6.1.4
- Caviar√
- Oysters√ (Any relevant hors d’ oeuvres) (1)
6.1.5 Grape juice is fermented √ then the alcohol is removed√ before bottling√ (Any 2) (2)
6.1.6
- Glass B√
- 7-12˚C√ (2)
6.1.7
- Use sugar or salt to coat the rim of the glass√
- Place in the refrigerator/freezer to become frosted√
- Dip glasses in beaten egg white√ or lemon juice√ and then dip them in granulated sugar or powders√ (Any 2) (2)
6.1.8
- Liquor can only be served with a meal√
- Liquor cannot be sold to anyone under the age of 18√
- Liquor cannot be sold to guests who are already intoxicated√
- Adequate toilet facilities must be provided√
- Any liquor bought on the premises must be consumed on the premises√ (Any other relevant answer) (3)
6.1.9
- Mary must be polite without being familiar√
- She must be attentive , but not respond to the flirting√
- She must serve the meal as soon as possible√
- If the situation gets out of hand, Mary should report the guest to the Maître d’ hotel or manager√
- Mary can ask if another waiter of a different gender can take over the service of the table√ (Any 4) (4)
6.2
- Always present the bill to the host√/from the left√
- Place the bill folded in the billfold or side plate√
- Allow enough time for the customer to place the correct amount of money in the folder√
- Bring the card machine if the guest requests it√
- Collect the folder with the money and the bill, and take it to the cashiers√ (Any 4) (4)
6.3
6.3.1
- The tables are close together√, It will make moving around the tables very difficult√ for both the guests and the waiters√.
- The tables look cluttered√ however the space per cover seems sufficient for the guest to eat comfortably. √
- Tables and chairs aren’t aligned properly. √ (Any 4) (4)
6.3.2 (4)
Formal Dinner | Cocktail Function | |
Food serving procedure |
|
|
Clearing procedure |
|
|
TOTAL SECTION D: 60
GRAND TOTAL: 200
 (1)
(1) (1)
(1)