Adele
COMPUTER APPLICATION TECHNOLOGY PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
COMPUTER APPLICATION TECHNOLOGY
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Owing to the nature of this practical examination, it is important to note that, even if you complete the examination early, you will NOT be permitted to leave the examination room until all the administrative functions associated with the examination have been finalised. During the examination, normal rules regarding leaving the examination room apply.
- Enter your examination number in the header or footer of EVERY document that you create or save, where applicable.
- The invigilator will give you a CD/DVD/flash disk containing all the files needed for the examination OR you will be told where the files can be found on the network or computer. If a CD/DVD has been issued to you, you must write your examination number and centre number on the CD/DVD. If you are working on the network, you must follow the instructions provided by the invigilator/educator.
- A copy of the master files will be available from the invigilator. Should there be any problems with a file, you may request another copy from the invigilator.
- This question paper consists of SEVEN questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Ensure that you save each document using the file name given in the question paper. Save your work at regular intervals as a precaution against possible power failures.
- Read through each question before answering or solving the problem. Do NOT do more than is required by the question.
- At the end of the examination, you must hand in the CD/DVD/flash disk given to you by the invigilator with ALL your answer files saved onto it, OR you should make sure that ALL your answer files are saved on the network/computer as explained to you by the invigilator/educator. Make absolutely sure that all files can be read. Do NOT save unnecessary files/folders. Do NOT hand in duplicate answer files/folders.
- The information sheet that has been provided with the question paper MUST BE COMPLETED AFTER THE THREE-HOUR EXAMINATION SESSION. Hand it to the invigilator at the end of the examination.
- During the examination, you may consult the offline help functions of the programs that you are using. You may NOT use any other resource material.
- Unless instructed otherwise, use formulae and/or functions for ALL calculations in spreadsheet questions. Use absolute cell references only where necessary to ensure that formulae are correct when you copy them to other cells in a spreadsheet.
- NOTE: All formulae and/or functions should be inserted in such a manner that the correct results will still be obtained even if the data changes.
- If data is derived from a previous question that you could not answer, you should still proceed with the questions that follow.
- In all questions involving word processing, you should set the language to English (South Africa). The paper size is assumed to be A4 Portrait, unless instructed otherwise.
- Ensure that the regional settings are set to South Africa and date and time settings, number settings and currency settings are set correctly.
- The examination folder/CD/DVD/flash disk that you receive with this question paper contains the files listed below. Ensure that you have all the files before you begin with this examination.
- 1Luck Image file
- 1Pat Word processing file
- 1StPat Image file
- 2Place Word processing file
- 3Cost Spreadsheet file
- 4Dublin Spreadsheet file
- 5Data Database file
- 6Button Image file
- 6Eye Image file
- 6Flag Image file
- 6Lep Image file
- 6Quiz HTML file
- 6Rip Image file
- 6Three Image file
- 7New Database file
- 7Old Database file
- 7St Word processing file
- 7Top Word processing file
QUESTIONS
SCENARIO |
QUESTION 1: WORD PROCESSING
Open the 1Pat word processing document, which contains background information about St. Patrick's Day, and insert your examination number in the header or the footer.
1.1 Change the font size of the whole document to 12 pt AND fully justify the text. (2)
1.2 Make the following changes to the heading 'ST. PATRICK'S DAY HISTORY AND TRADITIONS' at the top of the first page:
- Change this heading to any WordArt.
- Fill the text with any green colour.
- Change the text outline to 3 pt. (3)
1.3 Certain words in the document contain the symbols '㜀', which is not English text.
Replace these symbols every time they occur with the letters 'fi' to make the words meaningful. (3)
1.4 Find the text 'insert citation' in the second paragraph. Replace this text with a citation as follows:
- The citation must refer to the existing website source 'Happy St. Patrick's Day'. Select 'Yes' if a warning message appears.
- Display only the title of the website. (3)
1.5 Find the text 'soda bread' in the second paragraph.
Insert a footnote at this text as follows:
- Use the '♣' symbol (Symbol, character code 167) as the footnote custom mark.
- Insert the text 'Bread without yeast' as the footnote text. (3)
1.6 Find the text on the first page that begins with 'Parades …' and ends with '… (prime pea-planting conditions).' and apply bullets to this text as follows:
- Insert the 1StPat image as a bullet.
- Align the bullet 0.5 cm from the margin.
- Set the text indent at 2 cm. (3)
1.7 Find the text that begins with 'Boston …' and ends with '… streets.' below the heading 'Worldwide St. Patrick's Day Parades and Celebrations' and do the following:
- Convert the selected text to a table with 2 columns.
- Change the width of the first column to 3 cm.
- Change the paragraph setting of the table to prevent the table from flowing over to the next page. (3)
1.8 Modify the 'Heading 1' style as follows:
- Change the font to small caps AND the font colour to any shade of green.
- Change the paragraph spacing to set the spacing 'after' to the same value as the spacing 'before'.
- Apply the changes automatically to all the cases where 'Heading 1' is used in the document. (4)
1.9 Use a word processing feature to replace the word 'celebrations' at the end of the document with a synonym from the word processor's list of suggestions. (1)
1.10 Insert a link to the 1Luck file in the examination folder so that it appears as an icon at the end of the document. (2)
1.11 Change the date format of the current date field in the footer to dd MMM yyyy. (1) Save and close the 1Pat document. [28]
QUESTION 2: WORD PROCESSING
Open the 2Place word processing document that contains tourist attractions that turn green for St. Patrick's Day and insert your examination number in the header or the footer.
2.1 Insert an automatic table of contents on the first page of the document as follows:
- Display only one level.
- Ensure that the heading '2. The Leaning Tower of Pisa, Italy' is included in the table of contents. (4)
2.2 Change the picture below the heading '1. The Empire State Building …' as follows:
- Edit the picture to display similar to the one shown above.
- Add any shadow effect of your choice to the picture. (2)
2.3 Find the picture below the heading '6. Selfridges Department Store, …' and do the following:
- Use the information in the comment as a caption for the picture.
- Delete the comment from the heading.
NOTE: The label of the caption should be 'Figure 4'. (3)
2.4 Find the text starting with the heading '7. Table Mountain, Cape …' and ending with '… Table Mountain National Park.' and do the following:
- Change only the selected text to landscape orientation AND let it appear on a separate page.
- Insert the text 'Table Mountain' in the footer of the landscape page only. (4)
2.5 Insert a hyperlink on the text 'Day' in the last paragraph of the document to link to the bookmark 'March'. (2)
2.6 Change the bibliography under the heading 'Bibliography' towards the end of the document as follows:
- Edit the source 'History of St. Patrick's Day' so that the month in which the website was accessed is July instead of August.
- Remove the source 'Tourism Ireland announces Global Greening line-up for St. Patrick's Day' from the document.
- Update the bibliography. (3)
2.7 Find the heading 'Table of figures' and do the following below the heading:
- Insert an automatically generated table of figures.
- Do not display the labels and figure numbers in the table of figures. (2)
2.8 Find the text 'Total number of words:' at the end of the document. Insert a field next to the text to display the number of words in the document. (2)
Save and close the 2Place document. [22]
QUESTION 3: SPREADSHEET
NOTE:
- Use formulae and/or functions for ALL calculations in the spreadsheet.
- Use absolute cell references ONLY where necessary to ensure that formulae are correct when you copy them to other cells in the same column (copy down).
- All formulae and/or functions should be inserted in such a manner that the correct results will still be obtained even if the existing data changes.
Open the 3Cost spreadsheet showing the spending habits of people celebrating St. Patrick's Day.
Work in the Spending worksheet.
3.1 Centre the data in cell A1 vertically. (1)
3.2 Change the page setup as follows:
- Change the left margin to 2 cm.
- Centre the worksheet horizontally on the page.
- Repeat row 2 at the top of each page. (3)
3.3 Column A contains an identification code for each participant, where the first participant's identification code will be 'STP 1', the second participant's identification code will be 'STP 2', et cetera.
Use a spreadsheet feature to continue the identification code numbering in column A so that every participant will have an identification code. (1)
3.4 The rand/dollar exchange rate (number of rands that buy 1 dollar) for December 2017 is indicated in cell I1. The value provided in column G is in dollars.
Insert a formula in cell H3 to determine the rand value of the items purchased (cell G3).
- Ensure that the correct answers will be displayed if the formula is copied to the rest of the cells in column H.
- Display the amount in cell H3 in the South African currency. (5)
3.5 Insert a function in cell I4 to display the word 'Green' only if a participant celebrated the day by wearing green clothes (column D) AND spent money on accessories (column E), otherwise nothing should be displayed. (6)
3.6 Insert a function in cell M3 to calculate the average amount spent (column G) by the participants.
NOTE: The amount displays in dollars. (2)
3.7 Insert a function in cell M4 to determine the total amount spent (column G) by the participants on snacks (column E) during the St. Patrick's Day celebrations.
NOTE: The amount displays in dollars. (4)
3.8 A function was inserted in cell M5 in an attempt to calculate the number of participants who attended a party (a private party or a party in a bar/ restaurant) on St. Patrick's Day.
The function does not give the correct answer. Correct the function. (2)
3.9 Copy all the information of participants who bought products online (column F) to celebrate St. Patrick's Day to the Green worksheet.
NOTE: Do NOT delete any data from the Spending worksheet. (2) Save and close the 3Cost spreadsheet. [26]
QUESTION 4: SPREADSHEET
NOTE:
- Use formulae and/or functions for ALL calculations in the spreadsheet.
- Use absolute cell references ONLY where necessary to ensure that formulae are correct when you copy them to other cells in the same column (copy down).
- All formulae and/or functions should be inserted in such a manner that the correct results will still be obtained even if the existing data changes.
Open the 4Dublin spreadsheet that shows a group of St. Patrick's Day visitors who attended the 2017 Dublin celebrations.
Work in the List worksheet.
4.1 Insert a formula in cell E3 to calculate the number of days Miriam Paterno spent in Dublin for the St. Patrick's Day celebrations. (2)
4.2 The two letters in an e-mail address, which indicate the country from which the e-mail originated, commonly known as the domain extension, appear in the Codes worksheet.
Use the country in column G and insert an appropriate LOOKUP function in cell H4 to determine the domain extension for Korea. (4)
4.3 Modify the formula in cell I5 to create a lower case e-mail address for Lucian Bradford by combining the following:
- The first letter of her name in column B
- Followed by the last four letters of her surname in column A
- Followed by the text This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it..' (this has already been placed in the formula in cell I5)
- Followed by the domain in column H
EXAMPLE: Miriam Paterno will be This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.. (6) Work in the Summary worksheet.
4.4 The function to determine the total number of visitors from all the cities appears in cell C1.
Change the function in cell C1 to display 'True' if the total number of visitors to all the cities in cells A2:B21 is the same as the total number of all the visitors in the List worksheet, otherwise display 'False'. (5)
4.5 The total number of visitors for each country is displayed in cells A23:E43. Some of the countries and their totals are repeated.
Use a spreadsheet feature to remove all the extra entries. (1)
4.6 Change the 'USA Cities Represented' chart/graph to appear as shown below. 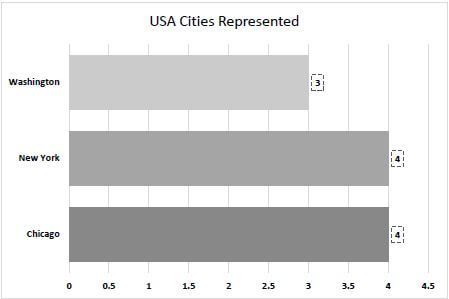
- Change the chart/graph type to the one shown in the example above.
- Display only the USA cities (Chicago, New York and Washington).
- Change the gap width between the data sets to 40%.
- Use a chart feature to vary the colours by city.
- Display the data labels with any dashed line border. (6)
Save and close the 4Dublin spreadsheet. [24]
QUESTION 5: DATABASE
Open the 5Data database which stores music and artists for St. Patrick's Day.
5.1 Information about artists available for bookings for the St. Patrick's Day celebrations is stored in the tbGroups table.
Open the tbGroups table.
5.1.1 Rename the ID field to GroupID. (1)
5.1.2 Change the field properties of the Artist field to display a drop-down list with the following options:
- Soloist
- Group
- Band (2)
5.1.3 Set the field properties of the Manager field so that it always displays in upper case. (1)
5.1.4 Change the field properties of the CellNo field to accept data in the following format only:
- '+27'
- Followed by TWO numbers and a space
- Followed by SEVEN numbers (3)
5.1.5 Change the Available field to a more suitable data type. (1)
5.1.6 Set the field properties of the DateBooked field so that:
- The user may only enter dates from 14 March 2018 to 17 March 2018
- The user is forced to enter data for this field (4)
Save and close the tbGroups table.
5.2 Open the frm5_2 form. Modify the form as follows:
- Format the Artist field to display in bold.
- Insert a label next to the ReleaseDate field to guide the user to enter data for the ReleaseDate field in the format MMM-yy.
- Remove the NoOfCDsInShop field AND its label.
Save and close the frm5_2 form. (4)
5.3 Open the qry5_3 query.
- Sort the data in alphabetical order according to the title.
- isplay only those records that do NOT have a release date OR display all the records where no copies of the CD are available in the shop.
Save and close the qry5_3 query. (5)
5.4 Open the qry5_4 query.
Change the query to display as the example below.
- Display artists who released more than one title.
- Display the artist, the number of titles released and the LAST release date on which an artist released a title.
NOTE:
- The CountOfTitle field uses the Title field and the LastOfReleaseDate field uses the ReleaseDate field. These fields will be calculated by using functions.
- The names of the fields CountOfTitle and LastOfReleaseDate may differ.
Artist | CountOfTitle | LastOfReleaseDate |
Abbey Ceili Band | 3 | 2011-02-01 |
Brian Boru Ceili Band | 2 | 2012-02-01 |
Ceili Time | 2 | |
Heather Breeze | 4 | |
Matt Cunningham Ceili Band | 22 | 2016-01-01 |
Michael Sexton Ceili Band | 2 | 2004-01-01 |
Michéal Sexton and Pat Walsh | 2 | 2005-01-01 |
PJ Hernon | 2 | 2006-01-01 |
Rise The Dust | 2 | 2015-07-01 |
Shaskeen | 4 | 2004-01-01 |
Swallow's Tail | 2 | 2011-09-01 |
Temple House Ceili Band | 2 | 2003-01-01 |
Tommy McCarthy | 5 | 1998-01-01 |
Various Artists | 4 | 2002-01-01 |
Save and close the qry5_4 query. (5)
5.5 Open the qry5_5 query.
- Modify the query to show all titles that are in 'Tape' or 'DVD' format.
- Display only the Title, Format and Price fields.
- Use a function in datasheet view to display the total of the prices as shown below.
Title | Format | Price |
Irish Set Dancing Made Easy Volume 1 DVD | € 9.00 | |
Buail Cois A | Tape | € 4.00 |
Buail Cois Eile Air | Tape | € 5.00 |
House At Home | Tape | € 12.00 |
Set Dances of Ireland Vol 1 | Tape | € 8.00 |
Set Dances of Ireland Vol 2 | Tape | € 7.00 |
Set Dances of Ireland Vol 3 | Tape | € 6.00 |
Set Dances of Ireland Vol 4 | Tape | € 6.00 |
Total | € 57.00 |
Save and close the qry5_5 query. (6)
5.6 Open the rpt5_6 report and modify the report as follows:
- Change the data source of the report from the tbCD table to the qry5_6 query.
- Insert the ZARPrice field in the detail section of the report.
- Display the label 'ZARPrice' at the top of every page.
- Group the report by artist.
- Insert a function to determine the total number of titles per group.
Save and close the rpt5_6 report. (8)
Save and close the 5Data database. [40]
QUESTION 6: WEB DESIGN (HTML)
A website was created for a quiz about St. Patrick's Day.
Open the incomplete 6Quiz web page in a web browser and also in a text/HTML editor (NOT a word processing program such as Word).
NOTE:
- Question numbers are inserted as comments in the coding as guidelines to show approximately where the answer(s) should be inserted.
- An HTML tag sheet has been attached for reference.
Your final web page should look like the example below.
NOTE: Use the example on the previous page to help you with this question.
6.1 Change the font of the heading 'St. Patrick's Day' to 'Forte' AND the font size to 10 pt. (3)
6.2 Change the top row of the table which contains the text 'Quiz for St. Patrick's Day' as follows:
- Merge the cells over the four columns.
- Vertically align the data to the top of the cell. (2)
6.3 Change the shading of the column headings in the second row to white. (2)
6.4 Change the bullets of the answers to the first question, '1. St. Patrick's Day is celebrated …', to numbering in the format A, B and C. (2)
6.5 The tag <input type="text"> is used to provide a space to enter data. A space to enter answers is provided for every question, except the first question.
Enter the tags to provide a space to enter the answer to the first question. (2)
6.6 Insert a hyperlink on the word 'Look' in the third row and fourth column to link to the 6Rip image in the examination folder. (1)
6.7 Modify the HTML code for the second question, '2. Where was St. Patrick born?', to appear in the same format as all the other questions. (2)
6.8 Correct the tags for the image in the fourth column of the fourth question, '4. What does leprechaun mean?', to display correctly. (2)
6.9 Even though all the elements for the sixth question have been added to the HTML file, they do not display in the browser. Add the necessary tags to display the sixth question correctly. (2)
6.10 Find the 6Button image at the bottom of the web page. Set the height and width of the image to 30. (2)
Save and close the 6Quiz web page. [20]
QUESTION 7: GENERAL
7.1 Open the 7St word processing document, which contains many interesting St. Patrick's Day traditions, and do the following:
7.1.1 Reject ALL track changes in the document. (1)
7.1.2 Insert a comment on the word 'Biography'. The comment must read 'See Source'. (2)
7.1.3 Find the picture on the third page, which is made up of seven images, and do the following:
- Edit the picture so that only six images appear as a single picture, as shown below.
- Save the remaining seventh image as a file called Saint in your examination folder and remove this image from the document.
 (4)
(4)
7.1.4 Find the 'Entry form' on the last page of the document and edit it as follows:
- Find the text form field next to the text 'Name and Surname' and set the maximum length to 30.
- Find the drop-down form field next to the text 'Category'. Add the option 'Dance' and display the list in alphabetical order.
- Change the default value of the check box form field next to the text 'Male' to be unchecked.
- Insert a text form field next to the text 'Date of Birth' so that it accepts a date of birth in any date format. (6)
Save and close the 7St document.
7.2 Open the 7New and 7Old databases.
Import the data from the tbDanceArticles table in the 7Old database to the 7New database.
Save and close the 7New and 7Old databases. (2)
7.3 The 7Top document contains a table with information about St. Patrick's Day organisers who collect money for charity.
Open the 7Top document and do the following:
- Determine the TOP TEN FEMALE charity collectors younger than 30 who collected the largest amount.
- Display ONLY the records of the top ten female charity collectors, ranked from the largest amount to the smallest amount.
NOTES:
- You may use any method/application to obtain the information.
- The information of the top ten female charity collectors must be saved in the 7Top document.
Save and close the 7Top document. (5)
[20]
TOTAL: 180
HTML TAG SHEET
Basic Tags | |
Tag | Description |
<body></body> | Defines the body of the web page |
<body bgcolor="pink"> | Sets the background colour of the web page |
<body text="black"> | Sets the colour of the body text |
<head></head> | Contains information about the web page |
<html></html> | Creates an HTML document – starts and ends a web page |
<title></title> | Defines a title for the web page |
<br/> | Inserts a line break |
<!-- --> | Comment |
Text Tags | |
Tag | Description |
<hl></hl> | Creates the largest heading |
<h6></h6> | Creates the smallest heading |
<b></b> | Creates bold text |
<i></i> | Creates italic text |
<font size="3"></font> | Sets size of font, from "1" to "7" |
<font color="green"> </font> | Sets font colour |
<font face="Times New Roman"></font> | Sets font type |
Links Tags | |
Tag | Description |
<a href="/URL"></a> | Creates a hyperlink |
<a href="/URL"><img src="name"></a> | Creates an image link |
<a name="NAME"></a> | Creates a target location in the document |
<a href="#NAME"></a> | Links to a target location created somewhere else in the document |
Formatting Tags | |
Tag | Description |
<p></p> | Creates a new paragraph |
<p align="left"> | Aligns a paragraph to the "left" (default), can also be "right", or "center" |
<br/> | Inserts a line break |
<ol></ol> | Creates a numbered list |
<ol type="A","a", "I","i","1"></ol> | Defines the type of numbering used |
<ul></ul> | Creates a bulleted list |
<ul type="disc", "square","circle"> </ul> | Defines the type of bullets used |
Formatting Tags continued | |
Tag | Description |
<li></li> | Inserted before each list item, and adds a number or symbol depending upon the type of list selected |
<img src="/name"> | Adds an image |
<img src="/name" align="left"> | Aligns an image: can be "left", "right"; "bottom", "top", "middle" |
<p align= "center"><img src="/name"></p> | Aligns an image to the "center" |
<img src="/name" border="1"> | Sets size of the border around an image |
<img src="/name" width="200" height ="200"> | Sets the height and width of an image |
<img src="/name" alt= "alternative text"> | Displays alternative text when the mouse hovers over the image or when the image is not found |
<hr/> | Inserts a horizontal line |
<hr size="3"/> | Sets size (height) of a line |
<hr width="80%"/> | Sets width of a line, in percentage or absolute value |
<hr color="ff0000"/> | Sets the colour of the line |
Table Tags | |
Tag | Description |
<table></table> | Creates a table |
<tr></tr> | Creates a row in a table |
<td></td> | Creates a cell in a table |
<th></th> | Creates a table header (a cell with bold, centred text) |
<table width="50"> | Sets the width of the table |
<table border="1"> | Sets the width of the border around the table cells |
<table cellspacing="1"> | Sets the space between the table cells |
<table cellpadding="1"> | Sets the space between a cell border and its contents |
<tr align="left"> | Sets the alignment for cell(s) ("left", can also be "center" or "right") |
<tr valign="top"> | Sets the vertical alignment for cell(s) ("top", can also be "middle" or "bottom") |
<td colspan="2"> | Sets the number of columns a cell should span |
<td rowspan="4"> | Sets the number of rows a cell should span |
INPUT MASK CHARACTER SHEET
CHARACTER | DESCRIPTION |
0 | Digit (0 to 9, entry required; plus [+] and minus [–] signs not allowed) |
9 | Digit or space (entry not required; plus and minus signs not allowed) |
# | Digit or space (entry not required; spaces are displayed as blanks while in Edit mode, but blanks are removed when data is saved; plus and minus signs allowed) |
L | Letter (A to Z, entry required) |
? | Letter (A to Z, entry optional) |
A | Letter or digit (entry required) |
a | Letter or digit (entry optional) |
& | Any character or a space (entry required) |
C | Any character or a space (entry optional) |
. , : ; - / | Decimal placeholder and thousand, date, and time separators (The actual character used depends on the settings in the Regional Settings Properties dialog box in Windows Control Panel.) |
< | Causes all characters to be converted to lower case |
> | Causes all characters to be converted to upper case |
! | Causes the input mask to display from right to left, rather than from left to right. Characters typed into the mask always fill it from left to right. You can include the exclamation point anywhere in the input mask. |
\ | Causes the character that follows to be displayed as the literal character (for example, \A is displayed as just A) |
CENTRE NUMBER ___________________________________________________________
EXAMINATION NUMBER _______________________________________________________
WORK STATION NUMBER______________________________________________________
SUITE USED
(Mark appropriate box with a cross (X)) WEB BROWSER USED (QUESTION 6)
(Mark appropriate box with a cross (X))
Microsoft Office 2010 | Microsoft Office 2013 | Microsoft Office 2016 | Office 365 |
Mozilla Firefox | Google Chrome | Internet Explorer | Other (Specify) |
FOLDER NAME_______________________________________________________________ Tick if saved and/or attempted.
Question Number | File name | Saved (✔) | Attempted (✔) | Maximum mark | Mark achieved | Marker | SM | CM | IM/EM |
1 | 1Pat | 28 | |||||||
2 | 2Place | 22 | |||||||
3 | 3Cost | 26 | |||||||
4 | 4Dublin | 24 | |||||||
5 | 5Data | 40 | |||||||
6 | 6Quiz | 20 | |||||||
7 | 7St | 20 | |||||||
7New | |||||||||
7Top | |||||||||
TOTAL | 180 | ||||||||
Comment (for office/marker use only)
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
BUSINESS STUDIES GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
BUSINESS STUDIES
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- This question paper consists of THREE sections and covers all FOUR main topics.
SECTION A: COMPULSORY
SECTION B: Consists of FIVE questions
Answer any THREE of the five questions in this section.
SECTION C: Consists of FOUR questions
Answer any TWO of the four questions in this section. - Read the instructions for each question carefully and take particular note of what is required.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper. NO marks will be awarded for answers that are numbered incorrectly.
- Except where other instructions are given, answers must be in full sentences.
- Use the mark allocation and nature of each question to determine the length and depth of an answer.
- Use the table below as a guide for mark and time allocation when answering each question.
SECTION
QUESTION
MARKS
TIME
(minutes)
A: Objective-type questions
COMPULSORY1
40
30
B: FIVE direct/indirect-type questions
CHOICE:
Answer any THREE.2
60
30
3
60
30
4
60
30
5
60
30
6
60
30
C: FOUR essay-type questions
CHOICE:
Answer any TWO.7
40
30
8
40
30
9
40
30
10
40
30
TOTAL
300
180
- Begin the answer to EACH question on a NEW page, for example QUESTION 1 – new page, QUESTION 2 – new page, et cetera.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 The … makes provision for the establishment of the CCMA and bargaining councils.
- National Credit Act, 2005 (Act 34 of 2005)
- Consumer Protection Act, 2008 (Act 68 of 2008)
- Employment Equity Act, 1998 (Act 55 of 1998)
- Labour Relations Act, 1995 (Act 66 of 1995)
1.1.2 Comfort Furniture specialises in the distribution of office furniture. It operates in the … sector.
- primary
- secondary
- tertiary
- public
1.1.3 Clinton invested R2 000 in a savings account at ABC Bank at 8% simple interest per year. He will earn … interest after two years.
- R160
- R320
- R2 160
- R2 320
1.1.4 The government holds the majority of shares in this form of ownership:
- Sakhisizwe SOC Ltd
- Neil (Pty) Ltd
- Johns Ltd
- Zamani and Son
1.1.5 Team members gather information and impressions about each other in this stage of team development:
- Mourning/Adjourning
- Storming
- Norming
- Forming
1.1.6 The right to choose and practise a religion is an example of ... rights.
- economic
- social
- consumer
- cultural
1.1.7 Creative thinking in the workplace means … to solve business problems.
- using old ways
- generating innovative ideas
- using routine thinking
- allowing one employee
1.1.8 The process of matching a new employee's skills and abilities with the requirements of a job:
- Selection
- Job analysis
- Placement
- Recruitment
1.1.9 The … function ensures that accurate information is available to management for decision-making.
- financial
- administration
- public relations
- marketing
1.1.10 The role of the interviewer is to …
- know the job specification and job description.
- explain how he/she has dealt with past mistakes.
- know his/her strengths and weaknesses and be prepared to discuss it.
- ask the same candidates different questions. (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Complete the following statements by using the word(s) in the list below. Write only the word(s) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
| dispute; National Skills; manager; fixed deposits; grievance; leader; RSA Retail Savings Bonds; forced combinations; quality management; public relations |
1.2.1 The … Development Strategy guides the responsibilities of education and training stakeholders in South Africa.
1.2.2 Gert inspires his workers to do their best. He is therefore a good …
1.2.3 An employee lodges a … through a formal, written complaint to senior management.
1.2.4 The National Treasury of South Africa offers … as a secure investment option.
1.2.5 Business operations meet the required standards through ... (5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches a term in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–J) next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.3.6 K.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
| 1.3.1 SETA 1.3.2 Fronting 1.3.3 Security 1.3.4 Force-field analysis 1.3.5 Involvement of all employees/People-based management |
|
(5 x 2) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 40
SECTION B
Answer ANY THREE questions in this section.
NOTE: Clearly indicate the QUESTION NUMBER of each question that you choose. The answer to EACH question must start on a NEW page, for example QUESTION 2 on a NEW page, QUESTION 3 on a NEW page, et cetera.
QUESTION 2: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS
2.1 List the THREE types of integration strategies. (3)
2.2 Name THREE types of business environments and state the extent of control businesses have over EACH environment.
Redraw the table below in the ANSWER BOOK to answer this question. (9)
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS | EXTENT OF CONTROL |
(a) | |
(b) | |
(c) |
2.3 Explain the provisions of the Basic Conditions of Employment Act (BCEA), 1997 (Act 75 of 1997) in terms of:
2.3.1 Sick leave
2.3.2 Annual leave
2.3.3 Maternity leave (3 x 2) (6)
2.4 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
BARKER INCORPORATED (BI) An employee of Barker Incorporated lost his hand due to an injury sustained while performing his duties. The management of the company is refusing to submit the claim to the Compensation Fund as they did not register the employee with the commissioner of the Compensation Fund. |
2.4.1 Identify the Act that allows employees to claim for workplace injuries. Motivate your answer by quoting from the scenario above. (3)
2.4.2 Discuss the penalties that Barker Incorporated may face for not complying with the Act identified in QUESTION 2.4.1. (6)
2.5 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
ROYAL STAR HOTEL (RSH) The management of Royal Star Hotel want to improve their strategic management process. They conducted an environmental scan and identified the following challenges:
|
2.5.1 List the THREE industrial analysis tools that could be applied during the environmental scan. For EACH tool, quote ONE challenge from the scenario above. (9)
2.5.2 Advise RSH on how to conduct their strategic management process. (6)
2.6 Recommend ways in which the business may comply with the Employment Equity Act (EEA), 1998 (Act 55 of 1998). (8)
2.7 Evaluate the impact of the Skills Development Act (SDA), 1998 (Act 97 of 1998) on businesses. (10) [60]
QUESTION 3: BUSINESS VENTURES
3.1 Identify the type of visual aid presented in EACH case below:
3.1.1 The financial manager is using slides to present financial reports to stakeholders.
3.1.2 The sales manager listed figures for November, December and January in columns to indicate sales turnover.
3.1.3 PSP Auditors are using web cameras on laptops and tablets to conduct meetings with stakeholders at distant locations. (3 x 2) (6)
3.2 Name FOUR factors that the presenter should consider during a presentation. (8)
3.3 Explain the differences between the democratic leadership style and the autocratic leadership style. (8)
3.4 Elaborate on the meaning of compound interest. (4)
3.5 Read the statement below and answer the questions that follow.
| Insuring assets against theft, damage, fire and burglary is essential for every business. Businesses should also plan carefully for risks which are not insurable. |
3.5.1 Quote THREE examples of insurable risks from the scenario above. (3)
3.5.2 Explain the term non-insurable risks and give ONE example of such a risk. (3)
3.5.3 Advise businesses on the importance of insurance. (8)
3.6 Discuss THREE types of benefits covered by the Unemployment Insurance Fund (UIF). (9)
3.7 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
MAPULE HAIRDRESSING SALON (MHS) Mapule Hairdressing Salon specialises in the latest unisex hair styles. Mapule is the only owner of the business and is also responsible for all business risks. |
3.7.1 Identify the form of ownership of MHS. Motivate your answer by quoting from the scenario above. (3)
3.7.2 Explain how division of profits and legislation may influence the success and/or failure of the form of ownership identified in QUESTION 3.7.1. (8) [60]
QUESTION 4: BUSINESS ROLES
4.1 Name FOUR human rights in the workplace. (4)
4.2 Indicate in EACH case below whether it represents an unethical or unprofessional business practice.
4.2.1 JJ Motors advertised a second-hand vehicle as new.
4.2.2 The receptionist of Mano's Consulting is using the office telephone for personal calls.
4.2.3 The owner of Timmy Shuttles did not keep his promise to deal with the complaints of the clients.
4.2.4 Getz Manufactures used some of the ideas of Fanon Manufactures in the design of their new products.
4.2.5 Lessing Engineers did not declare all their income to SARS. (5 x 2) (10)
4.3 Discuss the disadvantages of corporate social investment (CSI) for communities. (8)
4.4 Explain the implications of equality, respect and dignity for businesses. (6)
4.5 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
DORFS FINANCIAL SERVICES LTD (DFS) Dorfs Financial Services Ltd is failing to attract potential investors due to the company's poor performance. The shareholders discovered from whistle-blowers that the company's poor performance is the result of a lack of competency in the board of directors. The directors of DFS are denying this allegation. |
Redraw the table below in the ANSWER BOOK and then answer the questions that follow.
POOR CORPORATE GOVERNANCE (4.5.1) | KING CODE PRINCIPLE (4.5.2) | APPLICATION (4.5.3) |
(a) | ||
(b) |
4.5.1 Quote TWO examples of poor corporate governance from the scenario above. (2)
4.5.2 Identify the TWO King Code principles for good corporate governance that DFS did not apply. (4)
4.5.3 Advise DFS on how to apply each King Code principle identified in QUESTION 4.5.2 to improve their corporate governance. (8)
4.6 Evaluate the impact of the Delphi technique in solving business problems. (8)
4.7 Suggest ways in which businesses could protect the environment and promote human health in the workplace. (10) [60]
QUESTION 5: BUSINESS OPERATIONS
5.1 State FIVE aspects that should be included in an induction programme. (5)
5.2 Discuss the purpose of an interview as an activity of the human resources function. (6)
5.3 Explain screening as part of the selection procedure. (4)
5.4 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
SMART CONSTRUCTION (SC) Gail and Chris are employees of Smart Construction. Gail is remunerated according to the number of hours spent at work and Chris according to the number of houses built. Gail's employment contract has recently been terminated due to regular absence from work. |
5.4.1 Name the methods of remuneration applicable to Gail and Chris. Motivate your answer by quoting from the scenario above.
Redraw the table below in the ANSWER BOOK and then answer this question. (6)
METHODS OF REMUNERATION | MOTIVATION |
Gail: | |
Chris: |
5.4.2 Quote the reason for the termination of Gail's employment contract from the scenario above. (1)
5.4.3 Give TWO other reasons for terminating an employment contract. (4)
5.5 Distinguish between job description and job specification. (8)
5.6 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
HUGO SHOE FACTORY (HSF) Hugo Shoe Factory bought raw materials from Simba Suppliers who did not deliver on time. This resulted in delays in the manufacturing process. HSF is concerned about their productivity levels. |
BUSINESS FUNCTIONS (5.6.1) | QUALITY INDICATORS (5.6.2) |
(a) | |
(b) |
5.6.1 Identify TWO business functions that are directly affected by the challenges in the scenario above. (4)
5.6.2 Advise HFL on the quality indicators for EACH business function identified in QUESTION 5.6.1. (8)
5.7 Explain the differences between quality control and quality assurance. (8)
5.8 Advise businesses on the role of quality circles in improving the quality of their products and services. (6) [60]
QUESTION 6: MISCELLANEOUS TOPICS
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS
6.1 Identify the relevant pillar of the Broad-Based Black Economic Empowerment Act (BBBEE), 2003 (Act 53 of 2003) that Abil Bricks & Tiling Ltd complied with in EACH case below.
6.1.1 Thandi and Tsego were promoted to senior positions.
6.1.2 Previously disadvantaged employees were invited to buy shares in the company.
6.1.3 Employees are encouraged to attend training sessions regularly.
6.1.4 The human resources manager ensures that everyone is given an equal opportunity to apply for a vacancy. (4 x 2) (8)
6.2 Explain the differences between market development and product development. (8)
BUSINESS VENTURES
6.3 Discuss situational leadership as a management and leadership theory. (8)
6.4 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
KAY BED & BREAKFAST (KBB) Kay Bed & Breakfast insured their property for R600 000, but the property is valued at R800 000. Fire destroyed part of the property and damages amounted to R500 000. |
6.4.1 Identify the insurance clause that will be applied to KBB's claim for damages. (2)
6.4.2 Calculate the amount that the insurer will pay KBB for damages incurred. (4)
BUSINESS ROLES
6.5 Name FOUR components of corporate social responsibility (CSR). (4)
6.6 Explain the responsibilities of workers in promoting human health and safety in the workplace. (4)
6.7 Recommend ways in which businesses can contribute to the well-being of their employees. (6)
BUSINESS OPERATIONS
6.8 Give FOUR examples of fringe benefits in the workplace. (4)
6.9 Read the scenario below and answer the questions that follow.
JULIA CLOTHING MANUFACTURERS (JCM) Tudo has started working at JCM as a forklift operator recently. He was requested to read and sign the employment contract, which included his remuneration and details on the termination of the contract. |
6.9.1 Quote TWO aspects from the scenario above, included in Tudo's employment contract. (2)
6.9.2 Advise JCM on any other TWO aspects that must be included in the employment contract. (4)
6.10 Explain how total quality management (TQM) may impact on the reduction of the cost of quality. (6) [60]
TOTAL SECTION B: 180
SECTION C
Answer ANY TWO questions in this section.
NOTE: Clearly indicate the QUESTION NUMBER of each question chosen. The answer to EACH question must start on a NEW page, for example QUESTION 7 on a NEW page, QUESTION 8 on a NEW page, et cetera.
QUESTION 7: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS (LEGISLATION)
| The Consumer Protection Act (CPA), 2008 (Act 68 of 2008) promotes consumer rights. The National Credit Act (NCA), 2005 (Act 34 of 2005) was introduced to ensure that businesses address the needs of the consumer credit market. These Acts are beneficial to both businesses and consumers. |
You are an expert in consumer legislation. Write an essay on the following aspects:
- Discuss FOUR consumer rights according to the Consumer Protection Act (CPA).
- Explain the purpose of the National Credit Act (NCA).
- Evaluate the impact of the NCA on businesses.
- Recommend ways in which businesses can comply with the NCA. [40]
QUESTION 8: BUSINESS VENTURES (INVESTMENT: SECURITIES)
MPHO CAR WASH Recently Mpho Car Wash made large profits due to excellent services rendered. Mpho, the owner, wants to invest his surplus funds in unit trusts and buy shares which are listed on the Johannesburg Security Exchange Ltd (JSE). |
Write an essay to guide Mpho on the following investment aspects:
- Discuss the functions of the JSE.
- Explain the following factors that must be considered when making investment decisions:
- Return on investment
- Investment period
- Liquidity
- Describe FOUR types of shares.
- Advise Mpho on the effectiveness of unit trusts as a good investment. [40]
QUESTION 9: BUSINESS ROLES (DIVERSITY AND CONFLICT MANAGEMENT)
| Businesses employ people who have different ways of doing things, which may lead to conflict. It is important that businesses identify diversity issues and find ways to deal with them. Businesses should be well informed about handling conflict in the workplace. |
Write an essay on the following aspects:
- Discuss the benefits of a diverse work force.
- Suggest ways in which businesses may deal with language and age as diversity issues in the workplace.
- Explain the causes of conflict in the workplace.
- Advise businesses on how they should handle conflict in the workplace. [40]
QUESTION 10: BUSINESS OPERATIONS (QUALITY MANAGEMENT)
ZAMALEK LTD (ZL) Zamalek Ltd (ZL) lost customers due to the poor quality of their products. Their management does not know how to implement total quality management (TQM) to ensure the continuous provision of quality products and services to their customers. |
Consider the statement above and provide a detailed account on the following aspects:
- Explain the negative impact on ZL if TQM is poorly implemented.
- Discuss the benefits of a good quality management system.
- Evaluate the impact of the following TQM elements on ZL:
- Total client/customer satisfaction
- Continuous skills development/Education and training
- Advise ZL on how they should apply the PDCA model/cycle in order to improve the quality of their products. [40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 80
GRAND TOTAL: 300
BUSINESS STUDIES GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
BUSINESS STUDIES
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
NOTES TO MARKERS
PREAMBLE |
- For marking and moderation purposes, the following colours are recommended:
Marker: Red
Senior Marker: Green
Deputy Chief Marker: Brown/Black/Blue
Chief Marker: Pink
Internal moderator: Orange
DBE Moderator: Turquoise - Candidates' responses must be in full sentences for SECTIONS B and C. However, this would depend on the nature of the question.
- Comprehensive marking guidelines have been provided but this is by no means exhaustive. Due consideration should be given to an answer that is correct, but:
- Uses a different expression from that which appears in the marking guidelines
- Comes from another source
- Original
- A different approach is used
NOTE: There is only ONE correct answer in SECTION A.
- Take note of other relevant answers provided by candidates and allocate marks accordingly. (In cases where the answer is unclear or indicates some understanding, part-marks should be awarded, for example, one mark instead of the maximum of two marks.)
- The word 'Sub-max' is used to facilitate the allocation of marks within a question or sub-question.
- The purpose of circling marks (guided by 'max' in the breakdown of marks) on the right-hand side is to ensure consistency and accuracy in the marking of scripts as well as for calculation purposes.
- Subtotals to questions must be written in the right-hand margin. Circle the subtotals as indicated by the allocation of marks. This must be guided by 'max' in the marking guidelines. Only the total for each question should appear in the left-hand margin next to the appropriate question number.
- In an indirect question, the theory as well as the response must be relevant and related to the question.
- Incorrect numbering of answers to questions or sub questions in SECTIONS A and B will be severely penalised. Therefore, correct numbering is strongly recommended in all sections.
- No additional credit must be given for repetition of facts. Indicate with an 'R'.
- Note that no marks will be awarded for indicating Yes/No in evaluation type questions requiring substantiation or motivation. (Applicable to SECTIONS B and C)
- The differentiation between 'evaluate' and 'critically evaluate' can be explained as follows:
12.1 When 'evaluate' is used, candidates are expected to respond in either a positive/negative manner or take a neutral (positive and negative) stance, e.g. Positive: 'COIDA eliminates time and costs spent√ on lengthy civil court proceedings.'√
12.2 When 'critically evaluate' is used, candidates are expected to respond in either a positive/negative manner or take a neutral (positive and negative) stance. In this instance candidates are also expected to support their responses with more depth, e.g. 'COIDA eliminates time and costs spent√ on lengthy civil court proceedings√, because the employer will not be liable for compensation to the employee for injuries sustained during working hours as long as it can be proved that the business was not negligent.'√
NOTE:- The above could apply to 'analyse' as well.
- Note the placing of the tick (√) in the allocation of marks.
- The allocation of marks must be informed by the nature of the question, cognitive verb used, mark allocation in the marking guidelines and the context of each question.
Cognitive verbs, such as:
13.1 Advise, name, state, mention, outline, motivate, recommend, suggest, (list not exhaustive) do not usually require much depth in candidates' responses. Therefore, the mark allocation for each statement/answer appears at the end.
13.2 Describe, explain, discuss, elaborate, compare, distinguish, differentiate, justify, devise, analyse, evaluate, critically evaluate (list not exhaustive) require a greater depth of understanding, application and reasoning. Therefore, the marks must be allocated more objectively to ensure that assessing is conducted according to established norms so that uniformity, consistency and fairness are achieved. - Mark only the FIRST answer where candidates offer more than one answer for SECTION B and C questions that require one answer.
- SECTION B
15.1 If, for example, FIVE facts are required, mark the candidate's FIRST FIVE responses and ignore the rest of the responses. Indicate by drawing a line across the unmarked portion or use the word 'Cancel'.
NOTE: This applies only to questions where the number of facts is specified.
15.2 If two facts are written in one sentence, award the candidate FULL credit. Point 15.1 above still applies.
15.3 If candidates are required to provide their own examples/views, brainstorm this at the marking centre to finalise alternative answers.
15.4 Use of the cognitive verbs and allocation of marks: \
15.4.1 If the number of facts are specified, questions that require candidates to 'describe/discuss/explain' may be marked as follows:- Fact 2 marks (or as indicated in the marking guidelines)
- Explanation 1 mark
The 'fact' and 'explanation' are given separately in the marking guidelines to facilitate mark allocation.
15.4.2 If the number of facts required is not specified, the allocation of marks must be informed by the nature of the question and the maximum mark allocated in the marking guidelines.
15.5 ONE mark may be awarded for answers that are easy to recall, requires one word answers or is quoted directly from a scenario/case study. This applies to SECTIONS B and C in particular (where applicable).
- SECTION C
16.1 The breakdown of the mark allocation for the essays is as follows:
Introduction | Maximum: 32 |
Content | |
Conclusion | |
Insight | 8 |
TOTAL | 40 |
16.2 Insight consists of the following components:
Layout/Structure | Is there an introduction, a body and a conclusion? | 2 |
Analysis and interpretation | Is the candidate able to break down the question into headings/sub-headings/interpret it correctly to show understanding of what is being asked?
| 2 |
Synthesis | Are there relevant decisions/facts/responses made based on the questions?
Option 1: Where a candidate answers 50% or more of the question with only relevant facts; no '-S' appears in the left margin. Award the maximum of TWO (2) marks for synthesis. | 2 |
Originality | Is there evidence of examples, recent information, current trends and developments? | 2 |
TOTAL FOR INSIGHT: TOTAL MARKS FOR FACTS: TOTAL MARKS FOR ESSAY (8 + 32) | 8 32 40 | |
NOTE:
- No marks will be allocated for contents repeated from the introduction and conclusion.
- The candidate forfeits marks for layout if the words INTRODUCTION and CONCLUSION are not stated.
- No marks will be allocated for layout, if the headings INTRODUCTION and CONCLUSION are not supported by an explanation.
16.3 Indicate insight in the left-hand margin with a symbol e.g. ('L, A, S and/or O').
16.4 The breakdown of marks is indicated at the end of the suggested answer/ marking guidelines to each question.
16.5 Mark all relevant facts until the SUB MAX/MAX mark in a subsection has been attained. Write SUB MAX/MAX after maximum marks have been obtained.
16.6 At the end of each essay indicate the allocation of marks for facts and marks for insight as follows: (L – Layout, A – Analysis, S – Synthesis, O – Originality) as in the table below.
CONTENT | MARKS |
Facts | 32 (max.) |
L | 2 |
A | 2 |
S | 2 |
O | 2 |
TOTAL | 40 |
16.7 When awarding marks for facts, take note of the sub-maxima indicated, especially if candidates do not make use of the same subheadings. Remember, headings and subheadings are encouraged and contribute to insight (structuring/logical flow/sequencing) and indicate clarity of thought. (See MARK BREAKDOWN at the end of each question.)
16.8 If the candidate identifies/interprets the question INCORRECTLY, then he/she may still obtain marks for layout.
16.9 If a different approach is used by candidates, ensure that the answers are assessed according to the mark allocation/subheadings as indicated in the marking guidelines.
16.10
16.10.1 Award TWO marks for complete sentences. Award ONE mark for phrases, incomplete sentences and vague answers.
16.10.2 With effect from November 2015, the TWO marks will not necessarily appear at the end of each completed sentence. The ticks (√) will be separated and indicated next to each fact, e.g. 'Product development is a growth strategy√, where businesses aim to introduce new products into existing markets.'√
This will be informed by the nature and context of the question, as well as the cognitive verb used.
16.11 With effect from November 2017, the maximum of TWO (2) marks for facts shown as headings in the marking guidelines, will not necessarily apply to each question. This would also depend on the nature of the question.
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 D√√
1.1.2 C√√
1.1.3 B√√
1.1.4 A√√
1.1.5 D√√
1.1.6 D√√
1.1.7 B√√
1.1.8 C√√
1.1.9 B√√
1.1.10 A√√ (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 National Skills √√
1.2.2 leader√√
1.2.3 grievance√√
1.2.4 RSA Retail Savings Bonds√√
1.2.5 quality management√√ (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 I √√
1.3.2 H√√
1.3.3 A√√
1.3.4 G√√
1.3.5 B√√ (5 x 2) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 40
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS
QUESTION 1 | MARKS |
1.1 | 20 |
1.2 | 10 |
1.3 | 10 |
TOTAL | 40 |
SECTION B
Mark the FIRST THREE questions in this section ONLY.
QUESTION 2: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS
2.1 Types of integration strategies
- Forward vertical integration√
- Backward vertical integration√
- Horizontal integration√
NOTE:- Mark the first THREE (3) only.
- Award a maximum of ONE (1) mark for 'vertical integration'. (3 x 1) (3)
2.2 Types of business environments and control
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT | EXTENT OF CONTROL |
(a) Micro√ | Full control√√ |
(b) Market√ | Little control/No control, but can influence√√ |
(c) Macro√ (3 x 1) (3) | No control√√ Sub max (6) |
NOTE:
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format.
- Mark the first THREE (3) business environments only.
- The extent of control must be linked to the business environment.
- Do not award marks for the extent of control if the business environment is not mentioned. Max (9)
2.3 BCEA provisions for leave
2.3.1 Sick leave
- Workers are entitled to 30 days/6 weeks paid leave√ in a 3 year/36 months cycle.√
- During the first six months of employment√, workers are entitled to 1 day of paid sick leave for every 26 days worked.√
- A medical aid certificate should be submitted√ for absence from work for more than 2 consecutive days.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the BCEA provisions for sick leave.
Sub max (2)
2.3.2 Annual leave
- An employee is entitled to a minimum of 1 day√ for every 17 days worked.√
- An employee is entitled to 21√ consecutive days of annual leave.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the BCEA provisions for annual leave.
Sub max (2)
2.3.3 Maternity leave
- Pregnant employees are entitled to at least 4√ consecutive months of leave.√
- A pregnant employee may not be allowed to perform work√ that is hazardous to her or her child.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the BCEA provisions for maternity leave.
Sub max (2)
Max (6)
2.4 COIDA
2.4.1
- Compensation for Occupational Injuries and Diseases Act, 1997 (Act 61 of 1997)/
- Compensation for Occupational Injuries and Diseases Act, 1993 (Act 130 of 1993)/
- Compensation for Occupational Injuries and Diseases Act/COIDA.√√ (2)
Motivation:
- An employee of Barker Incorporated lost his hand due to an injury sustained while performing his duties/Management is refusing to submit the claim to the Compensation fund/They did not register the employee with the Commissioner of the Compensation Fund.√ (1) NOTE: Do not award marks for the motivation if the Act was identified incorrectly.
Max (3)
2.4.2 Penalties for non-compliance
- Barker Incorporated can be fined√ for refusing to lodge the claim/contravening the Act.√
- BI can be forced to make large payments√ if it did not take the necessary precautions according to the Act.√
- BI can be forced to pay any recovery costs√ required by the Compensation Fund.√
- The employee may take BI to court√ for not registering him/her with the Commissioner of the Compensation Fund.√
- If BI is found guilty of any misconduct√, they will have to pay large penalties/face imprisonment.√
- Any other relevant answer related to penalties for non-compliance with COIDA. Max (6)
2.5 Strategic management process
2.5.1 Industrial analysis tools
INDUSTRIAL ANALYSIS TOOLS | QUOTE |
SWOT analysis√√ | Many workers arrive late for work.√ |
Porter's Five Forces√√ | The new Dawn Hotel charges lower prices for similar services.√ |
PESTLE analysis√√ | RSH is located in an area where the unemployment rate is high.√ |
(3 x 2) (6) | Sub max (3) |
NOTE:
- Mark the first THREE (3) industrial analysis tools only.
- Award a maximum of TWO marks if the industrial analysis tool is repeated.
- The quoted challenge must be linked to each correct industrial analysis tool.
- Do not award marks for quotes if the industrial analysis tools were not mentioned.
Max (9)
2.5.2 Conduct of the strategic management process
OPTION 1
- RSH should have a clear vision, a mission statement and measurable/realistic objectives in place.√√
- Formulate alternative strategies to respond to the challenges.√√
- Develop (an) action plan(s), including the tasks to be done/deadlines to be met/ resources to be procured√√, etc.
- Implement selected strategies by communicating it to all stakeholders/organising business resources/motivating staff.√√
- RSH should continuously evaluate, monitor, measure strategies in order to take corrective action.√√
- Any other relevant answer related to the conduct of the strategic management process.
OR
OPTION 2
- RSH should review their vision statement.√√
- Analyse/Re-examine mission statement.√√
- Formulate a strategy, such as a defensive/retrenchment strategy.√√
- Implement a strategy, using a template such as an action plan.√√
- Control/Evaluate/Monitor the implemented strategy to identify gaps/deviations in implementation.√√
- RSH should take corrective action√ to ensure goals/objectives are met.√√
- Any other relevant answer related to the conduct of the strategic management process.
NOTE:
- The steps may be in any order.
- Do not award marks for 'conducting an environmental scan'.
- Award a maximum of TWO (2) marks for the industrial analysis tools if they were not listed in QUESTION 2.5.1.
Max (6)
2.6 Recommendations for compliance with the Employment Equity Act (EEA)
- Guard against discriminatory appointments.√√
- Assess the racial composition of all employees, including senior management.√√
- Ensure that there is equal representation of all racial groups in every level of employment.√√
- Promote equal opportunities and fair treatment.√√
- Clearly define the appointment process, so that all parties are well informed.√√
- Use certified psychometric tests to assess applicants/employees to ensure that suitable candidates are appointed.√√
- Ensure that diversity/inclusivity in the workplace is achieved.√√
- Implement affirmative action measures to redress disadvantages experienced by designated groups.√√
- Prepare an employment equity plan in consultation with employees.√√
- Implement an employment equity plan.√√
- Submit the employment equity plan to the Department of Labour.√√
- Assign one or more senior managers to ensure implementation and monitoring of the employment equity plan.√√
- Eliminate barriers that have an adverse impact on designated groups.√√
- Accommodate people from different designated groups.√√
- Retain/Develop/Train designated groups, including skills development.√√
- Regularly report to the Department of Labour on progress in implementing the plan.√√
- Any other relevant answer related to ways in which businesses could comply with EEA.
Max (8)
2.7 Impact of the Skills Development Act (SDA) on businesses Positives/Advantages
- Increases the number of skilled employees√ in areas where these skills are scarce.√
- Improves productivity√ in the workplace.√
- Business could become globally√ more competitive.√
- Increases investment in education and training√ in the labour market.√
- Higher investment in education and training in the labour market√ increases profits/return on investment.√
- On-going skills development, learning and the acquisition of new skills are encouraged√ to sustain the improvement of skills development.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the positive impact of the SDA on businesses.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- The SDA process is prescriptive and requires a large amount of paperwork and administration√ which can cost time and money.√
- Skills Development Levy could be an extra burden√ to financially struggling businesses.√
- It may be monitored and controlled by government departments√ that do not have education and training as their key priorities.√
- The SETAs may not be well organised√ and many courses offered by companies may not have unit standards that relate to the course content.√
- Many service providers that offer training services√ are not SAQA accredited.√
- Many businesses may not support√ this government initiative.√
- Implementation of the SDA√ can be difficult to monitor and control.√
- Employees are expected to attend learnerships during work hours√ which could affect the production process/productivity.√
- Costly for businesses√ to employ a person to implement, manage and control learnerships.√
- The time and money spent on improving employee skills is wasted√ if they leave the business.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact of SDA on businesses.
Max (10)
[60]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS
QUESTION 2 | MARKS |
2.1 | 3 |
2.2 | 9 |
2.3. | 6 |
2.4.1 | 3 |
2.4.2 | 6 |
2.5.1 | 9 |
2.5.2 | 6 |
2.6 | 8 |
2.7 | 10 |
TOTAL | 60 |
QUESTION 3: BUSINESS VENTURES
3.1 Visual aids
3.1.1 PowerPoint/Data projector√√
3.1.2 Tables√√
3.1.3 Video-conferencing/Skype√√ (3 x 2) (6)
3.2 Factors to consider during a presentation
- Establish credibility by introducing yourself as the presenter at the start.√√
- Mention/Show most important information first.√√
- Make the purpose/main points of the presentation clear at the start of the presentation.√√
- Use suitable section titles/headings/sub-headings/bullets.√√
- Summarise the main points of the presentation to conclude the presentation.√√
- Stand in a good position/upright, where the audience can clearly see the presenter/presentation.√√
- Avoid hiding behind equipment.√√
- Do not ramble on at the start, to avoid losing the audience/their interest.√√
- Capture listeners' attention/Involve the audience with a variety of methods, e.g. short video clips/sound effects/humour√√, etc.
- Maintain eye contact with the audience.√√
- Be audible to all listeners/audience.√√
- Vary the tone of voice/tempo within certain sections to prevent monotony.√√
- Make the presentation interesting with visual aids/anecdotes/examples/Use visual aids effectively.√√
- Use appropriate gestures, e.g. use hands to emphasize points.√√
- Speak with energy and enthusiasm.√√
- Pace yourself/Do not rush or talk too slowly.√√
- Keep the presentation short and simple.√√
- Conclude/End with a strong/striking ending that will be remembered.√√
- Ensure that the audience will leave with/take away specific information/benefits.√√
- Include a statement/quote that will allow a professional/striking ending.√√
- Manage time effectively to allow time for questions.√√
- Any other relevant answer related to factors to be considered during a presentation.
NOTE:
- Only accept factors to be considered DURING the presentation.
- Mark the first FOUR (4) only. (4 x 2) (8)
3.3 Differences between the democratic and autocratic leadership styles
DEMOCRATIC | AUTOCRATIC |
|
|
NOTE:
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format, but the differences must be clear.
- Award a maximum of FOUR (4) marks if differences are not clear/ Mark either the democratic or autocratic style only.
Max (8)
3.4 Meaning of compound interest
- Interest is calculated in every period√ on original/principal amount plus interest.√
- Interest is added to the original/principal amount√ and interest is earned on interest for each defined period.√
- As interest is added to the investment√, the capital increases.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the meaning of compound interest.
Max (4)
3.5 Insurance
3.5.1 Examples of insurable risks quoted from the scenario
- Theft√
- Damage√
- Fire√
- Burglary√
NOTE: Mark the first THREE (3) only. (3 x 1) (3)
3.5.2 Non-insurable risk
- These risks are not insured by insurance companies√ as insurance cost/risks are too high/remains the responsibility of the business.√
Sub max (2)
Example
- Losses caused by war.√
- Most risks occurring between placing orders and receiving goods.√
- Changes in fashion.√
- Losses caused by marketing malpractices by the business.√
- Advancement in technology/new machinery invention.√
- Any other relevant answer related to examples of non-insurable risks.
NOTE: Mark the FIRST example only.
Sub max (1)
Max (3)
3.5.3 Importance of insurance for businesses
- Transfers the risk from the business/insured to an insurance company/insurer.√√
- Transfer of risk is subject to the terms and conditions of the insurance contract.√√
- Protects the business against theft/loss of stock and/or damages caused by natural disasters such as floods, storm damage, etc.√√
- The business will be compensated for insurable losses, e.g. destruction of property through fire.√√
- Business assets, e.g. vehicles/equipment/buildings need to be insured against damage and/or theft.√√
- Business is protected against the loss of earnings, e.g. strikes by employees which result in losses worth millions.√√
- Protects the business against dishonest employees.√√
- Life insurance can be taken on the life of partners in a partnership to prevent unexpected loss of capital.√√
- Should the services of key personnel be lost due to accidents/death, the proceeds of an insurance policy can be paid out to the business/beneficiaries.√√
- Replacement costs for damaged machinery/equipment are very high; therefore insurance can reduce/cover such costs.√√
- Protects a business from claims made by a member of the public for damages that the business is responsible for.√√
- Protects the business against losses due to death of a debtor.√√
- Any other relevant answer related to the importance of insurance to businesses.
Max (8)
3.6 Benefits of UIF
- Unemployment benefits√√
- Employees, who become unemployed/retrenched due to restructuring/an expired contract, may claim within six months after becoming unemployed.√
- Unemployed employees may only claim, if they contributed to UIF.√
- Unemployed employees enjoy these benefits until the allocated funds are exhausted.√
- If a worker voluntarily terminates his/her contract, he/she may not claim.√
- No tax is payable on unemployment benefits.√
- Any other relevant answer related to unemployment benefits of UIF.
Benefit (2)
Explanation (1)
Sub max (3)
- Illness benefits√√
- Employees may receive these benefits if they are unable to work for more than 14 days without receiving a salary/part of the salary.√
- Employees may not claim these benefits if they refuse medical treatment.√
- Any other relevant answer related to illness benefits of UIF.
Benefit (2)
Explanation (1)
Sub max (3)
- Maternity benefits√√
- Pregnant employees receive these benefits for up to 4 consecutive months.√
- If an employee had a miscarriage, she can claim for up to six weeks/42 days.√
- Any other relevant answer related to maternity benefits of UIF.
Benefit (2)
Explanation (1)
Sub max (3)
- Adoption benefits√√
- Employees may receive these benefits if they adopt a child younger than two years.√
- Employees who take unpaid leave/may receive part of their salary while caring for the child at home.√
- Only one parent/partner may claim.√
- Any other relevant answer related to adoption benefits of UIF.
Benefit (2)
Explanation (1)
Sub max (3)
- Dependants' benefits√√
- Dependants may apply for these benefits if the breadwinner, who has contributed to UIF dies.√
- The spouse of the deceased may claim, whether he/she is employed or not.√
- Any other relevant answer related to dependants' benefits of UIF. Benefit (2)
Explanation (1)
Sub max (3)
NOTE:
- Mark the first THREE (3) only.
- The benefit could be integrated into the explanation. (3 x 3) (9)
3.7 Forms of ownership
3.7.1 Sole trader/Sole proprietorship√√ Sub max (2)
- Motivation:
'Mapule is the only owner of the business/is (also) responsible for all business risks'.√
Sub max (1)
NOTE: Do not award marks for the motivation if the form of ownership was not correctly identified.
Max (3)
3.7.2 Success and/or failure factors of a sole trader
SUCCESS | FAILURE | |
Division of profits | Owner receives all profits√ from the business.√ | Profits may not be large enough√ for expansion.√ |
The owner may use profit√ to expand the business.√ | Profits may not cover√ all business debts√/Owner may decide√ not to expand.√ | |
Any other relevant answer related to the influence of the division of profits on the success of a sole trader. | Any other relevant answer related to the influence of the division of profits on the failure of a sole trader. |
Sub max (4)
SUCCESS | FAILURE | |
Legis lation | It is easy/inexpensive√ to start.√ | Business may only qualify for more loans√ if they are licenced√/Loans√ are not easily obtainable.√ |
There are limited regulatory requirements√ regarding the name of the business.√ | Business has no legal entity/unlimited liability√ and the owner can be sued/held responsible for the debts of the business.√ | |
It is not compulsory√ to have financial statements audited.√ | Business has no continuity√ as it depends on the life of the owner.√ | |
Any other relevant answer related to the influence of legislation on the success of a sole trader. | Any other relevant answer related to the influence of legislation on the failure of a sole trader. |
Sub max (4)
Max (8)
NOTE:
- The answers do not have to be in tabular format.
- The success and/or failure factors must relate to sole trader/sole proprietorship. [60]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS
QUESTION 3 | MARKS |
3.1 | 6 |
3.2 | 8 |
3.3 | 8 |
3.4 | 4 |
3.5.1 | 3 |
3.5.2 | 3 |
3.5.3 | 8 |
3.6 | 9 |
3.7.1 | 3 |
3.7.2 | 8 |
TOTAL | 60 |
QUESTION 4: BUSINESS ROLES
4.1 Human rights in the workplace
- Privacy√
- Respect/Dignity√
- Equity√
- Freedom of speech and expression√
- Information√
- Freedom of association√
- Free choice of a trade/occupation/profession√
- Labour rights/Freedom of assembly/Right to protest√
- Freedom of thought and religion√
- Health care/food/water and social assistance√
- Fair labour practices√
- Access to Labour Court/institutions√
- Education and training/universal right to basic education√
- Safety/Security and Protection/Life√
- Freedom of slavery, servitude or forced labour√
- Vote√
- Freedom of movement√
- Children's rights√
- Freedom to choose your own language/participate in own cultural life√
NOTE: Mark the first FOUR (4) only.
(4 x 1) (4)
4.2 Unethical or unprofessional business practice
4.2.1 Unethical√√
4.2.2 Unprofessional√√
4.2.3 Unprofessional√√
4.2.4 Unethical√√
4.2.5 Unethical√√
Max (10)
4.3 Disadvantages of CSI for communities
- Distribution of scarce CSI resources to selected beneficiaries in the community√ may cause problems such as discrimination.√
- The benefits of the programmes may not filter to the intended persons√ within the community.√
- Programmes that do not satisfy all the needs√ of the community may be rejected.√
- Hand-out programmes discourage locals from taking their own initiative√ by making them dependent on social investment programmes.√
- Sustaining projects after businesses withdraw their assistance√ are often difficult without the right expertise.√
- Spending money on CSI programmes could imply that the business has to recover costs by increasing its prices√ which may have a negative impact on the community/ economy.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the disadvantages of CSI for the community. Max (8)
4.4 Implications of equality, respect and dignity for businesses
- Businesses should treat all their employees equally√, regardless of their race/ colour/age/gender/disability√, etc.
- All workers should have access√ to equal opportunities/positions/ resources.√
- Employers and employees need to comply with legislation√ with regard to equal opportunities/human rights in the workplace.√
- Businesses should develop equity programmes/promote strategies√ to ensure that all employees are treated equally regardless of status/rank/power.√
- Mission statement should include√ values of equality/respect.√
- Training/Information/Business policies√ should include issues such as diversity/ discrimination/harassment.√
- Employers should respond swiftly and fairly√ to reported incidents of discrimination in the workplace.√
- Ensure that employees work in an environment√ that is conducive to safety/ fairness/free from embarrassment.√
- Orders/Tasks should be given respectfully√ and allow the recipient/employee to have a say in the manner in which the task should be performed.√
- Treat workers with respect/dignity√ by recognising work well done/the value of human capital.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the implications of equality, respect and dignity for businesses.
Max (6)
4.5 King Code principles
POOR CORPORATE GOVERNANCE 4.5.1 | KING CODE PRINCIPLE 4.5.2 | APPLICATION 4.5.3 |
Shareholders discovered from whistle blowers that the company's poor performance is a result of a lack of competency in the board of directors.√ | Transparency√√ |
Sub max (4) |
The directors of DFS are denying this allegation.√ | Accountability√√ |
|
(2 x 1) (2) | (2 x 2) (4) | Max (8) |
NOTE:
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format.
- Mark the first TWO (2) examples and principles in QUESTIONS 4.5.1 and 4.5.2 respectively.
- Award a maximum of TWO (2) marks if application is based on the examples of poor corporate governance quoted in QUESTION 4.5.1.
- Award TWO (2) marks for the King Code principle identified in QUESTION 4.5.2, if the example of poor corporate governance was not directly quoted, but based on the scenario.
- The application in QUESTION 4.5.3 must link to the correct King Code principle in QUESTION 4.5.2.
4.6 Impact of Delphi technique
Positives/Advantages
- Business may use a group of experts√ without bringing them together.√
- The experts will give the business clear ideas/solutions√ on how to improve on productivity/profitability.√
- Information received from experts√ can be used to solve complex business problems.√
- Experts may give honest/credible opinions√ as they do not have a direct/personal interest in the business.√
- Conflict may be avoided√ especially if all employees are knowledgeable and well qualified.√
- Dominating employees may not take over the process√ as they do not form part of the problem solving process.√
- It reduces noise levels in an office environment√ since there is no group discussion.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the positives/advantages of the Delphi technique.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- It is an expensive technique to use√ due to high administrative costs.√
- May be time consuming/complicated√ to analyse data received from experts.√
- Not all experts are willing/interested√ to give feedback/complete questionnaires.√
- Some experts might not have an in-depth knowledge√ of certain topics.√
- Experts' suggestions may not be considered by some employees√ so consensus may not be reached.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the negatives/disadvantages of the Delphi technique.
Max (8)
4.7 Ways in which businesses could protect the environment and promote human health in the workplace
- Laws and regulations should be adhered to so that profits are not generated at the expense of the environment.√√
- Pollution and other environmental issues should always be considered in all business activities, e.g. safe disposal of waste/dumping of toxic waste√√, etc.
- Become involved in environmental awareness programmes.√√
- The environment can be protected by altering production techniques in favour of cleaner and greener technologies.√√
- Water for human consumption should be tested before it is used.√√
- Promote nature conservation by looking after natural resources.√√
- Minimise pollution, by re-using, reducing and recycling.√√
- Reduce consumption of goods/services which are environmentally unfriendly.√√
- Register/Engage with recognised institutions/bodies that promote green peace.√√
- Physical working conditions should always be worker friendly, safe and promote occupational health.√√
- Physical working conditions, e.g. adequate lighting/ventilation should be available and functional.√√
- Machines must be serviced/maintained regularly.√√
- Educate people about hygiene issues.√√
- Encourage employees to do regular health checks.√√
- Any other relevant answer related to ways in which businesses could protect the environment and promote human health.
NOTE: No sub max for environment and human health.
Max (10)
[60]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS
QUESTION 4 | MARKS |
4.1 | 4 |
4.2 | 10 |
4.3 | 8 |
4.4 | 6 |
4.5.1 | 2 |
4.5.2 | 4 |
4.5.3 | 8 |
4.6 | 8 |
4.7 | 10 |
TOTAL | 60 |
QUESTION 5: BUSINESS OPERATIONS
5.1 Aspects to be included in an induction programme
- Safety regulations and rules.√
- Overview of the business.√
- Information about the business products/services.√
- Meeting with senior management who will explain the company's vision/values/job descriptions/daily tasks.√
- Tour of the premises.√
- Introduction to key people and immediate colleagues.√
- Conditions of employment, e.g. working hours/leave application process/disciplinary procedures√, etc.
- Administration details on systems/processes/logistics.√
- Discussion of the employment contract and conditions of service.√
- Discussion of personnel policies, e.g. making private phone calls/using the Internet√, etc.
- Discussion of employee benefits.√
- Corporate social responsibility programmes.√
- Any other relevant answer related to aspects that should be included in an induction programme.
NOTE: Mark the first FIVE (5) only. (5 x 1) (5)
5.2 Purpose of an interview
- Obtains information about the strengths and weaknesses√ of each candidate.√
- Helps the employer in choosing/making an informed decision√ about the most suitable candidate.√
- Matches information provided by the applicant√ to the job requirements.√
- Creates an opportunity where information√ about the business and applicant can be exchanged.√
- To determine a candidate's suitability√ for the job.√
- Evaluate the skills√ and personal characteristics of the applicant.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the purpose of an interview as an activity of the human resources function.
Max (6)
5.3 Screening as part of the selection procedure
- Check application documents√ against the requirements of the job.√
- Candidates who meet the minimum requirements√ are separated from others.√
- Do background/credit/reference checks of applicants√ who qualify for the job.√
- Prepare a shortlist√ of suitable candidates after screening.√
- Any other relevant answer related to screening as part of the selection procedure. Max (4)
5.4.1 Methods of remuneration
METHODS OF REMUNERATION | MOTIVATION QUOTED FROM THE SCENARIO |
Gail: Time-related√√ | Gail is remunerated according to the number of hours spent at work√ |
Chris:Piecemeal/Piece rate/ Piece work√√ | Chris according to the number of houses built√ |
Sub max (4) | Sub max (2) |
NOTE:
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format.
- Do not award marks for the motivation quoted, if the methods of remuneration were not mentioned.
Max (6)
5.4.2 Reason for termination of contract quoted from the scenario
- Gail's employment contract has recently been terminated due to regular absence from work.√ (1)
5.4.3 Other reasons for termination of an employment contract
- Employer may no longer have work for redundant employees/cannot fulfil the contract/is restructuring.√√
- Employer may retrench some employees due to insolvency/may not be able to pay the employees.√√
- Employees decided to leave and resign voluntarily.√√
- An employee may have reached the pre-determined age for retirement.√√
- Any other relevant answer related to the termination of an employment contract.
NOTE:
- Mark the first TWO (2) only.
- Do not accept dismissal or misconduct due to absenteeism. (2 x 2) (4)
5.5 Distinction between job description and job specification
Job description | Job specification |
Written description of the job√ and its requirements.√ | Written description of specific qualifi cations/skills/experience/characteris tics√ required to do the job.√ |
Describes duties/responsibilities√ of a specific job√/Summary√ of the nature/type of job.√ | Describes the minimum acceptable personal qualities/skills/qualifications√ needed for the job.√ |
Describes key performance areas/ tasks for a specific job√, e.g. job title/ duties/working conditions/location of the place of work/relationship of the job with other jobs in the business√, etc. | Describes key requirements of the person who will fill the position√, e.g. formal qualifications/willingness to travel/work unusual hours√, etc. |
Any other relevant answer related to job description. | Any other relevant answer related to job specification. |
Sub max (4) | Sub max (4) |
NOTE:
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format, but the distinction must be clear.
- Award a maximum of FOUR (4) marks if the distinction is not clear/ Mark job description or job specification only.
Max (8)
5.6 Business functions and quality indicators
BUSINESS FUNCTIONS 5.6.1 | QUALITY INDICATORS 5.6.2 |
Purchasing function√√ (2) |
|
Production function√√ (2) |
|
(2 x 2) (4) | Max (8) |
NOTE:
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format.
- Mark the first TWO (2) business functions only.
- Where the business functions were incorrectly/not identified, award a maximum of FOUR (4) marks [sub max 2 each] for the quality indicators in QUESTION 5.6.2 relevant to the scenario.
5.7 Differences between quality control and quality assurance
Quality control | Quality assurance |
Inspection of the final product√ to ensure that it meets the required standards.√ | Carried out during and after the production process√ to ensure that required standards have been met at every stage of the process.√ |
Includes setting targets/measuring performance√ and taking corrective measures.√ | Ensures that every process is aimed at getting the product right the first time√ and prevents mistakes from happening again.√ |
Checking raw materials/employees/ machinery/workmanship/products√ to ensure that high standards are maintained.√ | The 'building in' of quality√ as opposed to 'checking for' quality.√ |
Any other relevant answer related to quality control. | Any other relevant answer related to quality assurance. |
Sub max (4) | Sub max (4) |
NOTE:
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format, but the differences must be clear.
- Award a maximum of FOUR (4) marks if differences are not clear/ Mark quality control or quality assurance only.
Max (8)
5.8 Role of quality circles
- Quality circles solve problems related to quality and implement improvements.√√
- Investigate problems and suggest solutions to management.√√
- Ensure that there is no duplication of activities/tasks in the workplace.√√
- Make suggestions for improving systems and processes in the workplace.√√
- Improve the quality of products/services/productivity through regular reviews of quality processes.√√
- Monitor/Reinforce strategies to improve the smooth running of business operations.√√
- Reduce costs of redundancy in the long run.√√
- Increase employees' morale/motivation.√√
- Any other relevant answer related to the role of quality circles in improving the quality of products and services.
Max (6) [60]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS
QUESTION 5 | MARKS |
5.1 | 5 |
5.2 | 6 |
5.3 | 4 |
5.4.1 | 6 |
5.4.2 | 1 |
5.4.3 | 4 |
5.5 | 8 |
5.6.1 | 4 |
5.6.2 | 8 |
5.7 | 8 |
5.8 | 6 |
TOTAL | 60 |
QUESTION 6: MISCELLANEOUS TOPICS
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS
6.1 Pillars of BBBEE
6.1.1 Management and control/Management√√
6.1.2 Ownership√√
6.1.3 Skills development√√
6.1.4 Employment equity√√ (4 x 2) (8)
6.2 Differences between market development and product development
MARKET DEVELOPMENT | PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT |
It is a growth strategy where businesses aim to sell its existing products√ in new markets.√ | It is a growth strategy where businesses aim to introduce new products√ into existing markets.√ |
Business implements√ the idea of expanding/selling products/services in other areas.√ | Business improves the product line√ by adding different types of related products/services.√ |
Finds new ways√ of distributing products/services.√ | Conduct test marketing/market research√ to establish whether new products will be accepted by existing customers.√ |
Restructure pricing policies√ to cater for customers of all income levels.√ | Ensure that new products of a higher quality are more reasonably priced√ than those of competitors.√ |
Any other relevant answer related to market development. | Any other relevant answer related to product development. |
Sub max (4) | Sub max (4) |
NOTE:
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format, but the differences must be clear.
- Award a maximum of FOUR (4) marks if the differences are not clear/Mark product development or market development only.
Max (8)
BUSINESS VENTURES
6.3 Situational leadership theory
- Different leadership characteristics√ are needed for different situations.√
- The task/situation dictates the leadership style that should be applied√, so leaders are adaptable/flexible/self-assured.√
- Relationships between leaders and employees√ are based on mutual trust/ respect/loyalty/integrity/honesty.√
- Leaders have the ability to 'read' the situation√ and get the most suitable people in the right positions to complete tasks successfully.√
- It enables leaders to use different leadership styles√ to accomplish their goals.√
- Leaders analyse group members/objectives/time constraints√, then adopt a suitable/relevant leadership style.√
- May lead to conflict when leaders use different leadership styles√ when managing employees in different situations.√
- Its success depends on the kind of relationship√ that exist between the leader and followers/subordinates/employees.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the situational leadership theory. Max (8)
6.4.1 Average clause √√ (2)
6.4.2 Calculation of average clause
- Insured amount x Loss/Damage√ (for formula)
Market value
= R600 000√ x R500 000√
R800 000
= R375 000√
NOTE:
- Award full marks (4) if the answer is correct and no workings are shown.
- If workings were shown correctly, but the final answer is wrong, award a maximum of THREE (3) marks.
- If the answer is incorrect, award a maximum of ONE (1) mark for the understanding of concept and method.
- If there are no workings shown and the answer is incorrect, award a ZERO mark.
Max (4)
BUSINESS ROLES
6.5 Components of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
- Environment√
- Ethical corporate social investment√
- Health and safety√
- Corporate governance√
- Business ethics√
- Employment equity√
- Supply chain/Distribution channel√
- Customers√
- Community√
- Any other relevant answer related to the components of CSR.
NOTE: Mark the first FOUR (4) only.
(4 x 1) (4)
6.6 Responsibility of workers in promoting human health and safety in the workplace
- Workers should take care of their own health√ and safety in the workplace.√
- Co-operate and comply with the rules and procedures√, e.g. wear prescribed safety clothing.√
- Report unsafe/unhealthy working conditions√ to the relevant authorities/ management.√
- Report accidents√ to the employer as soon as possible.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the responsibilities of workers in promoting human health and safety in the workplace.
Max (4)
6.7 Ways in which businesses could contribute to the wellbeing of their employees
- Pay fair wages/salaries to the workers based on the nature of their work/the prevailing economic conditions in the market.√√
- Working conditions should include safety/medical/canteen facilities/benefits like housing/leave/retirement√√, etc.
- Pay fair bonuses, based on business earnings, as acknowledgement for hard work and commitment.√√
- Provide for employees' participation in decision making that affects them.√√
- Provide recreational facilities for employees.√√
- Offer annual physical/medical assessments to workers.√√
- Make trauma debriefing/counselling/assistance available to any employee who requires these services.√√
- Offer financial assistance in the case of any hardship caused by unexpected medical costs.√√
- Allow flexible working hours to enhance productivity.√√
- Offer support programmes for employees infected and affected by HIV/Aids.√√
- Make childcare facilities available on the premises for working mothers in the business.√√
- Start a nutritional programme so that employees can enjoy one meal per day to keep them in a healthy condition.√√
- Give time to staff to get involved in projects they choose/Allow staff to use some of the working hours to participate in the projects of their choice.√√
- Encourage employees to stay fit and healthy by getting them involved in health activities to minimize stress/substance abuse/obesity.√√
- Provide transport for employees who work unusually long hours.√√
- Establish coaching and mentoring programmes for junior employees.√√
- Conduct team-building sessions to improve employees' morale.√√
- Encourage employees to attend capacity-building workshops/training programmes/ staff-development programmes/team-development programmes.√√
- Any other relevant recommendations related to ways in which businesses could contribute to the wellbeing of their employees.
Max (6)
BUSINESS OPERATIONS
6.8 Examples of fringe benefits in the workplace
- Medical Aid Fund/Health Insurance Fund√
- Pension Fund√
- Provident Fund√
- Funeral benefits√
- Car/Travel/Housing/Cellphone/Clothing allowance√
- Performance based incentives√
- Issuing of bonus shares√
- Staff discount/Free or low cost meal/Canteen facilities√
- Any other relevant example related to fringe benefits in the workplace.
NOTE: Mark the first FOUR (4) only. (4 x 1) (4)
6.9.1 Aspects of employment contract quoted from the scenario
- Remuneration√
- Details on the termination of his contract√
- Sign the employment contract√
NOTE: Mark the first two (2) only. (2 x 1) (2)
6.9.2 Other aspects to be included in the employment contract
- Job title√√
- Job description√√
- Working hours√√
- Overtime√√
- Normal place of work√√
- Leave√√
- Date of commencement of employment/Starting date√√
- Probation period√√
- Code of conduct and/or Code of ethics√√
- Disciplinary policy√√
- Signature of the employer√√
- Any other relevant answer related to aspects that should be included in the employment contract.
NOTE:
- Mark the first TWO (2) only.
- Do not award marks for responses quoted in QUESTION 6.9.1. (2 x 2) (4)
6.10 Impact of TQM on the reduction of the cost of quality
- Introduce quality circles√ to discuss ways of improving the quality of work/workman-ship.√
- Schedule activities√ to eliminate duplication of tasks.√
- Share responsibility for quality output√ amongst management and workers.√
- Train employees at all levels√, so that everyone understands their role in quality management.√
- Develop work systems that empower employees√ to find new ways of improving quality.√
- Work closely with suppliers√ to improve the quality of raw materials/inputs.√
- Improve communication about quality challenges/deviations√, so that everyone can learn from experience.√
- Reduce investment on expensive√, but ineffective inspection procedures in the production process.√
- Implement pro-active maintenance programmes for equipment/machinery√ to reduce/eliminate breakdowns.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the impact of TQM on the reduction of the cost of quality.
Max (6)
[60]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS
QUESTION 6 | MARKS |
6.1 | 8 |
6.2 | 8 |
6.3 | 8 |
6.4.1 | 2 |
6.4.2 | 4 |
6.5 | 4 |
6.6 | 4 |
6.7 | 6 |
6.8 | 4 |
6.9.1 | 2 |
6.9.2 | 4 |
6.10 | 6 |
TOTAL | 60 |
TOTAL SECTION B: 180
SECTION C
Mark the first TWO (2) questions in this section ONLY.
QUESTION 7 BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS (LEGISLATION)
7.1 Introduction
- The Consumer Protection Act (CPA) was introduced to redress the economic inequalities of the past.√
- CPA promotes and advances the social and economic welfare of consumers in South Africa.√
- The CPA applies to the promotion/sales of all goods and services.√
- The National Credit Act (NCA) deals mainly with regulating consumer credit.√
- The reason for the establishment of the NCA was to curb the high levels of consumer debt.√
- The NCA allows consumers to make informed decisions before buying on credit.√
- Any other relevant introduction related to the CPA/NCA.
(2 x 1) (2)
7.2 Consumer rights according to the CPA
7.2.1 Right to choose√√
- Consumers have the right to:
- choose suppliers√ and goods.√
- shop around√ for the best prices.√
- return goods√ that are unsafe/defective for a full refund.√
- reject goods√ that are not the same as the sample marketed.√
- cancel/renew√ fixed term agreements.√
- request written quotations√ and cost estimates.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the consumers' right to choose according to the CPA.
Right (2)
Discussion (2)
Sub max (4)
7.2.2 Right to privacy and confidentiality√√
- Consumers have the right to stop/restrict√ unwanted direct marketing.√
- They can object√ to unwanted promotional e-mails and telesales.√
- They have the right to stop/lodge complaints√ about the sharing of their personal details.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the consumers' right to privacy and confidentiality according to the CPA.
Right (2)
Discussion (2)
Sub max (4)
7.2.3 Right to fair and honest dealings√√
- Suppliers may not use physical force/harass customers√ to buy products.√
- Suppliers may not give misleading/false √ information.√
- Businesses may not promote pyramid schemes√ and chain-letter schemes.√
- Businesses may not overbook/oversell goods/services√ and then not honour the agreement.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the consumers' right to fair and honest dealings according to the CPA.
Right (2)
Discussion (2)
Sub max (4)
7.2.4 Right to information about products and agreements/Right to disclosure and information√√
- Contracts/Agreements should be in plain language√ and easy to understand.√
- Businesses should display prices√ which are fully inclusive/disclosing all costs.√
- Consumers may request the unit and bulk price√ of the same product.√
- If two prices for the same product are displayed√, consumers should pay the lower price.√
- Businesses should label products√ and trade descriptions correctly.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the consumers' right to information/ disclosure according to the CPA.
Right (2)
Discussion (2)
Sub max (4)
7.2.5 Right to fair/responsible marketing/promotion√√
- Businesses should not mislead consumers√ on pricing, benefits/uses of goods.√
- Consumers may cancel purchases made through direct marketing√ within five working days/cooling off-period.√
- All information related to the country of origin√, expiry dates/ingredients of the products should be disclosed.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the consumers' right to fair/responsible marketing/promotion according to the CPA.
Right (2)
Discussion (2)
Sub max (4)
7.2.6 Right to fair value/good quality and safety√√
- Consumers have the right to demand√ quality service or goods.√
- They have the right to return faulty items√ if the fault occurs within six months after purchasing the item.√
- Consumers may receive an implied/ a written√ warranty.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the consumers' right to fair value/good quality and safety according to the CPA.
Right (2)
Discussion (2)
Sub max (4)
7.2.7 Right to accountability from suppliers√√
- Consumers have the right to be protected√ in lay-bye agreements.√
- Businesses should honour credit vouchers√ and prepaid services.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the consumers' right to accountability from suppliers according to the CPA.
Right (2)
Discussion (2)
Sub max (4)
7.2.8 Right to fair/just/reasonable terms and conditions√√
- Businesses should provide consumers with written notices of clauses√ that may limit consumer rights.√
- Businesses may not market/sell goods√ at unfair prices.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the consumers' right to fair, just and reasonable terms and conditions according to the CPA.
Right (2)
Discussion (2)
Sub max (4)
7.2.9 Right to equality in the consumer market place√√
- Businesses should not limit access√ to goods and services.√
- Businesses may not vary the quality of their goods√ to different consumers.√
- Businesses may not charge different prices√ for the same goods/services.√
- Businesses should not discriminate√ when marketing their products and services in different areas/places.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the consumers' right to equality in the consumer market place according to the CPA.
Right (2)
Discussion (2)
Sub max (4)
NOTE: Mark the first FOUR (4) only. Max (16)
7.3 Purpose of the NCA
- Promotes the social√ and financial interests of South African consumers.√
- Promotes a fair/competitive√ credit market.√
- Promotes responsible granting of credit√ by credit providers.√
- Ensures that customers are well informed√ about what is included in their credit contracts.√
- Ensures that credit is equally available√ to all consumers.√
- Protects consumers from unfair business practices√ where credit is involved.√
- Protects lenders and borrowers from negligent lending practices√ that results in over-indebtedness for consumers.√
- Ensures that credit bureaux/credit providers/debt counsellors√ are registered to avoid consumer exploitation.√
- Creates national standards√ for the credit industry.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the purpose of the NCA.
Max (10)
7.4 Impact of the NCA on businesses
Positives/Advantages
- Lower bad debts√ resulting in better cash flow.√
- Protects businesses√ against non-paying customers.√
- Increases cash sales√ because businesses only grant credit to qualifying customers/more customers are buying in cash.√
- Stamps out reckless lending√ and prevents businesses from bankruptcy.√
- Businesses do thorough credit checks√ and receive up-to-date documentation from the consumer as proof that they can afford the repayment/credit.√
- Credit bureau information is made available to businesses√ so that they can check the credit worthiness of consumers before granting credit.√
- Authorised credit providers√ may attract more customers.√
- Leads to more customers through credit sales√ as they are now protected from abuse.√
- The whole credit process is transparent√, e.g. both businesses and customers know their responsibilities.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the positives/advantages of the NCA for businesses.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- A business must make sure that all attempts have been made to recover the debt√ before blacklisting the customer.√
- Debt collection procedures√ are more complex and expensive.√
- Credit providers cannot collect from consumers√ who are under debt reviews.√
- Credit which has been granted recklessly√ cannot be recovered.√
- Increases the administration burden√ on credit providers.√
- More working capital is needed√ as businesses cannot sell many goods on credit due to stricter credit application processes.√
- Fewer customers buy on credit√ as it is more difficult to obtain credit.√
- Businesses struggle to get credit√ such as bank loans/overdrafts.√
- Businesses that do not comply with the NCA√ may face legal action.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the negatives/disadvantages of the NCA for businesses.
Max (12)
7.5 Compliance to NCA
- Credit providers must be registered with the National Credit Regulator.√√
- Businesses must submit an annual compliance report to the National Credit Regulator.√√
- Conduct affordability assessment to ensure the consumer has the ability to meet his/her obligation.√√
- Conduct a credit check with a registered credit bureau and could also consult the National Credit Register.√√
- Credit providers must have procedures in place to comply with the provision of the Financial Intelligence Centre Act (FICA).√√
- Verify the identity of clients, report suspicious transactions/train staff on their obligations in terms of FICA.√√
- Any other relevant answer related to ways in which businesses can comply with the NCA.
Max (8)
7.6 Conclusion
- The National Credit Act and Consumer Protection Act enable businesses and consumers to be well conversant with the terms and conditions of sales.√√
- The Acts create awareness and protection of consumer rights.√√
- The NCA prevents unfair credit marketing practices and promotes responsible credit granting.√√
- The CPA protects consumers against unscrupulous businesses and against contracts that include unfair terms.√√
- Any other relevant conclusion related to the NCA/CPA.
Max (2) [40]
QUESTION 7: BREAKDOWN OF MARK ALLOCATION
Details | Maximum | Total |
Introduction | 2 | Max 32 |
Consumer rights | 16 | |
Purpose of NCA | 10 | |
Impact of NCA on businesses | 12 | |
Compliance to NCA | 8 | |
Conclusion | 2 | |
INSIGHT | 8 | |
Layout | 2 | |
Analysis/Interpretation | 2 | |
Synthesis | 2 | |
Originality/Examples | 2 | |
TOTAL MARKS | 40 |
- LASO - For each component:
- Allocate 2 marks if all requirements are met.
- Allocate 1 mark if some requirements are met.
- Allocate 0 marks where requirements are not met at all.
QUESTION 8: BUSINESS VENTURES (INVESTMENTS: SECURITIES)
8.1 Introduction
- Investors have a range of investment opportunities to choose from.√
- They measure these investment opportunities against criteria for good investment.√
- Investors set financial goals and consider different factors when making these decisions.√
- Entrepreneurs who started business ventures must show a return on their investment.√
- Unit trusts consist of a number of different shares and securities put together and managed by a fund manager.√
- The JSE is a formal market comprising of all the public companies that have been listed.√
- Shares represent the parts of the company that a person/group of people own.√
- Any other relevant introduction related to the JSE/shares/investment decisions/unit trusts. (2 x 1) (2)
8.2 Functions of the JSE
- Gives opportunities to financial institutions√, e.g. insurance companies invest their surplus funds in shares.√
- Serves as a barometer/indicator√ of economic conditions in South Africa.√
- Keeps investors informed√ by publishing share prices daily.√
- Acts as a link√ between investors and public companies.√
- Shares are valued√ and assessed by experts.√
- Small investors√ are invited to take part in the economy of the country through the buying/selling of shares.√
- Venture capital market√ is made possible on the open market.√
- Strict investment rules√ ensure a disciplined/orderly market for securities.√
- Raises primary capital√ by encouraging new investments in listed companies.√
- Mobilises the funds√ of insurance companies and other institutions.√
- Regulates the market√ for trading in shares.√
- Plans, researches and advises√ on investment possibilities.√
- Ensures that the market√ operates in a transparent manner.√
- Provides protection for investors√ through strict rules/legislation.
- Encourages short-term√ investment.√
- Facilitates electronic trading√ of shares/STRATE.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the functions of the JSE.
Max (10)
8.3 Factors to be considered when making investment decisions 8.3.1 Return on Investment (ROI)
- Refers to income from the investment√, namely interest/dividends/increased capital growth on the original amount invested.√
- Generally, there will be a direct link√ between risk and return.√
- The return should be expressed√ as net after-tax gains on the investment.√
- Returns can be in the form of capital gains√ where the asset appreciates in value over time.√
- The net after-tax return should be higher√ than the inflation rate.√
- Any other relevant answer related to ROI as a factor to be considered when making investment decisions.
Sub max (4)
8.3.2 Investment period
- This refers to the duration of the investment√ which may influence the return on investment.√
- It can be short, medium√ and/or long term.√
- The investment period will depend√ on an investor's personal needs.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the investment period as a factor to be considered when making investment decisions.
Sub max (4)
8.3.3 Liquidity
- An amount could be invested in a type of investment√ that can easily be converted to cash.√
- It is used to describe the ease and speed√ with which investors can convert an investment into cash.√
- Example: an investment in a savings account will be easier to convert into cash√ than an investment in a fixed deposit which is usually deposited for a fixed period of time.√
- Any other relevant answer related to liquidity as a factor to be considered when making investment decisions.
Sub max (4)
Max (12)
8.4 Types of shares
8.4.1 Ordinary/Equity shares√√
- Ordinary shares only receive dividends√ when profit is made.√
- Normally the higher the net profit√, the higher the dividend.√
- Shareholders are the last to be paid√, if the company is declared bankrupt liquidated.√
- Dividends vary from year to year according to profits made√ and are determined by the company/board of directors.√
- Shareholders have a right to vote√ at the Annual General Meeting/AGM.√ - Any other relevant answer related to ordinary shares.
Identification (2)
Description (2)
Sub max (4)
8.4.2 Founders' shares√√
- Issued to the founders√ and incorporators/promoters of the company.√
- They receive dividends√ after all other shareholders were paid.√
- Any other relevant answer related to founders' shares.
Identification (2)
Description (2)
Sub max (4)
8.4.3 Bonus shares√√
- Gifts/Payment in the form of shares√ to shareholders.√
- Issued as compensation√ for unpaid dividends.√
- Shareholders receive these shares√ without being required to pay for them.√
- Shareholders will own more shares√ and collect more dividends in the future.√
- Any other relevant answer related to bonus shares.
Identification (2)
Description (2)
Sub max (4)
8.4.4 Preference shares√√
- Some of these types of shares receive dividends√ regardless of whether a profit is made.√
- A fixed rate of return√ is paid on this type of shares.√
- Shareholders have a preferred claim on company assets√ in the event of bankruptcy/liquidation.√
- These shares enjoy preferential rights√ to dividends/repayment over ordinary shares.√
- Dividends are payable√ according to the type of preference share.√
- Voting rights are restricted√ to particular circumstances/resolutions.√
- Non-cumulative preference shareholders√ will not receive any outstanding dividends from previous years.√
- Cumulative preference shareholders√ will receive outstanding dividends from previous years.√
- Redeemable preference shares√ can be redeemed/bought back at the option of the issuing company on a pre-determined future date.√
- Non-redeemable preference shares√ are only bought back when the company closes down for reasons other than bankruptcy.√
- Convertible preference shares√ are converted to ordinary shares after a fixed period/on the date specified when the preference shares were issued.√
- Non-convertible preference shares√ will not be converted into ordinary shares.√
- Any other relevant answer related to preference shares.
Identification (2)
Description (6)
Sub max (8)
NOTE: Mark the first FOUR (4) only.
Max (16)
8.5 Effectiveness/Advantages of unit trusts as a good investment
- Managed by a fund manager who buys shares on the stock exchange/JSE.√√
- The investor has a variety to choose from/a wider range of shares from lower to higher degrees of risk.√√
- Safe investments, as it is managed according to rules and regulations.√√
- A small amount can be invested per month.√√
- Easy to invest in, as investors simply complete a few relevant forms or invest online.√√
- Easy to cash in when an investor needs money.√√
- Fluctuations in unit trust rates of return are often not so severe because of diversity of the investment fund.√√
- Generally beats inflation on the medium/long term.√√
- Offer competitive returns in the form of capital growth and dividend distribution.√√
- Fund managers are knowledgeable/experts/reliable/trustworthy as they are required to be accredited to sell unit trusts.√√
- Any other relevant answer related to the effectiveness/advantages of unit trusts as a good investment.
Max (8)
8.6 Conclusion
- A business that is managed successfully will make a number of investments over a period of time.√√
- Businesses should invest extra cash to generate more income rather than leaving it in the business's current account.√√
- Anyone can invest in unit trusts by investing a single lump sum/certain amount every month.√√
- After considering the various investment opportunities and risk factors, investors can make a calculated decision.√√
- Any other relevant conclusion related to the JSE/shares/investment decisions/unit trust.
Max (2)
[40]
QUESTION 8: BREAKDOWN OF MARK ALLOCATION
Details | Maximum | Total |
Introduction | 2 | Max 32 |
Functions of the JSE | 10 | |
Investment decisions | 12 | |
Types of shares | 16 | |
Effectiveness of unit trusts | 8 | |
Conclusion | 2 | |
INSIGHT | 8 | |
Layout | 2 | |
Analysis/Interpretation | 2 | |
Synthesis | 2 | |
Originality/Examples | 2 | |
TOTAL MARKS | 40 |
- LASO – For each component:
- Allocate 2 marks if all requirements are met.
- Allocate 1 mark if only some of the requirements are met.
- Allocate 0 marks where requirements are not met at all.
QUESTION 9: BUSINESS ROLES (DIVERSITY AND CONFLICT MANAGEMENT)
9.1 Introduction
- Diversity refers to the variety of people employed based on age/race/gender/ ethnic groups/disabilities/material wealth/personalities/how employees see themselves and others.√
- Businesses employ people from different cultural backgrounds.√
- Businesses should have systems in place to support diversity issues.√
- Diversity in teams may lead to better ideas/solutions, but may also cause conflict.√
- Conflict is a result of differences in values and attitudes.√
- Effective conflict management may have a positive influence on team performance.√
- Poor conflict management may lead to team failure or the dissolution of a team.√
- Any other relevant introduction related to diversity and conflict in the workplace. (2 x 1) (2)
9.2 Benefits of a diverse work force
- Work force diversity improves the ability of a business√ to solve problems/ innovate/cultivate diverse markets.√
- Employees value each other's diversity√ and learn to connect and communicate across lines of difference.√
- Diversity in the work force improves√ morale and motivation.√
- Employees demonstrate greater loyalty to the business√ because they feel respected/accepted/understood.√
- A diversified work force can give businesses a competitive advantage√ as they can render better services.√
- Being respectful of differences/demonstrating diversity√ makes good business sense/improves profitability.√
- A diverse workplace must ensure that its policies/practices√ empower every employee to perform at his/her full potential.√
- Customers/Stakeholders increasingly evaluate businesses√ on how they manage diversity in the workplace.√
- Employees from different backgrounds√ can bring different perspectives to the business.√
- A diversified work force stimulates debate√ on new and improved ways of getting things done.√
- Employees represent various groups√ and are therefore better able to recognise customer needs/satisfy consumers.√
- Businesses with a diverse work force are more likely to have a good public image√ and attract more customers.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the benefits of a diverse work force. Max (10)
9.3 Dealing with diversity issues in the workplace
9.3.1 Language
- Business may specify that all communications should be in one specific language only and would expect employees to have a certain level of fluency in that language.√√
- Provide training in the official language of the business.√√
- Employ an interpreter so that everyone can fully understand what is being said in a meeting.√√
- All business contracts should be in an easy-to-understand language and should be available in the language of choice for the relevant parties signing the contract.√√
- No worker should feel excluded in meetings conducted in one language only.√√
- Any other relevant answer related to how business could deal with language as a diversity issue in the workplace.
Sub max (6)
9.3.2 Age
- Promotions should not be linked to age, but rather to a specific set of skills.√√
- A business may not employ children aged 15 or younger.√√
- The ages of permanent workers should vary from 18 to 65 to include all age groups.√√
- A business may employ a person who is older than the normal retirement age,
- provided that person is the most suitable candidate.√√
- Businesses must encourage older employees to help young employees to develop their potential.√√
- Young employees must be advised to respect and learn from older employees.√√
- The business should encourage employees to be sensitive to different perspectives of various age groups.√√
- Any other relevant answer related to how businesses could deal with age as a diversity issue in the workplace.
Sub max (6)
Max (12)
9.4 Causes of conflict in the workplace
- Lack of proper communication√ between management and workers.√
- Ignoring rules/procedures√ may result in disagreements and conflict.√
- Management and/or workers√ may have different personalities/ backgrounds.√
- Different values/levels of knowledge/skills/experience√ of managers/workers.√
- Little/no co-operation√ between internal and/or external parties/stakeholders.√
- Lack of recognition for good work√, e.g. a manager may not show appreciation for extra hours worked to meet deadlines.√
- Lack of employee development√ may increase frustration levels as workers may repeat errors due to a lack of knowledge/skills.√
- Unfair disciplinary procedures√, e.g. favouritism/nepotism.√
- Little/no support from management√ with regard to supplying the necessary resources.√
- Leadership styles used√, e.g. autocratic managers may not consider worker inputs.√
- Unrealistic deadlines/Heavy workloads√ lead to stress resulting in conflict.√
- Lack of agreement on mutual matters√, e.g. remuneration/working hours.√
- Unhealthy competition/Inter-team rivalry√ may cause workers to lose focus on team targets.√
- Lack of commitment√ which may lead to an inability to meet pre-set targets.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the causes of conflict in the workplace.
Max (12)
9.5 Handling conflict in the workplace
- Acknowledge that there is conflict in the workplace.√√
- Identify the cause of the conflict.√√
- Pre-negotiations may be arranged where workers/complainants will be allowed to state their case/views separately.√√
- A time and place are arranged for negotiations where all employees involved are present.√√
- Arrange a meeting between conflicting employers/employees.√√
- Make intentions for intervention clear so that parties involved may feel at ease.√√
- Each party has the opportunity to express his/her own opinions/feelings/ Conflicting parties may recognise that their views are different.√√
- Analyse the cause(s) of conflict by breaking it down into different parts/Evaluate the situation objectively.√√
- Blame shifting should be avoided and a joint effort should be made.√√
- Direct conflicting parties towards finding/focusing on solutions.√√
- Devise/Brainstorm possible ways of resolving the conflict.√√
- Conflicting parties agree on criteria to evaluate the alternatives.√√
- The best possible solution(s) is/are selected and implemented.√√
- Parties must agree to on the best solution.√√
- Evaluate/Follow up on the implementation of the solution(s).√√
- Monitor progress to ensure that the conflict has been resolved.√√
- Expertise on handling conflict maybe sourced from outside the business.√√
- Any other relevant answer related to how businesses should handle conflict in the workplace.
NOTE: If problem solving steps do not demonstrate the handling of conflict (explanation), award a maximum of FOUR (4) marks.
Max (12)
9.6 Conclusion
- Businesses should effectively deal with diversity to avoid bias/racism/stereotypes in the workplace.√√
- Businesses must acknowledge employees' differences and develop strategies to deal with these differences.√√
- Businesses should be able to identify positive and negative conflict so that they can develop suitable strategies to handle conflict in the workplace.√√
- Any other relevant conclusion related to diversity and conflict in the workplace.
Max (2)
[40]
QUESTION 9: BREAKDOWN OF MARK ALLOCATION
Details | Maximum | Total |
Introduction | 2 | Max 32 |
Benefits of diversity | 10 | |
Dealing with diversity issues | 12 | |
Causes of conflict | 12 | |
Handling conflict | 12 | |
Conclusion | 2 | |
INSIGHT | 8 | |
Layout | 2 | |
Analysis/Interpretation | 2 | |
Synthesis | 2 | |
Originality/Examples | 2 | |
TOTAL MARKS | 40 |
- LASO – For each component:
- Allocate 2 marks if all requirements are met.
- Allocate 1 mark if only some of the requirements are met.
- Allocate 0 marks where requirements are not met at all.
QUESTION 10:BUSINESS OPERATIONS (QUALITY MANAGEMENT)
10.1 Introduction
- Quality management should not just be an inspection process, but become part of the culture of the business.√
- TQM is an integrated system and methodology applied throughout the business to design, produce and provide quality products/quality service to customers.√
- Total quality relates to products that totally satisfy customers' needs and expectations in every aspect on a continuous basis.√
- Everyone employed in a business has a role to play in ensuring that the needs of customers are satisfied.√
- Businesses should always provide employees with opportunities to increase their knowledge and skills by attending training programmes.√
- The main aim of the PDCA model is to ensure that businesses continuously improve their processes and systems so that they can get it right the first time.√
- Any other relevant introduction related to quality management. (2 x 1) (2)
10.2 Negative impact on businesses/ZL if TQM is poorly implemented
- Lack of training/skills development√ may lead to poor quality products.√
- Decline in sales√, as returns from unhappy customer's increase.√
- Decline in productivity√, because of stoppages.√
- Investors could withdraw investment√, if there is a decline in profits.√
- Bad publicity√ due to poor quality products supplied.√
- High staff turnover√, because of poor skills development.√
- Unrealistic deadlines√ may not be achieved.√
- Businesses may not be able to make/afford the necessary changes√ that will satisfy customers' needs.√
- Loss of customers√ may lead to bankruptcy/closure.√
- Undocumented quality control systems/processes√ could result in error/deviations from pre-set quality standards.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact on businesses/ZL if TQM is poorly implemented.
Max (8)
10.3 Benefits of a good quality management system
- Effective customer services are rendered√, resulting in increased customer satisfaction.√
- Time and resources√ are used efficiently.√
- Productivity increases√ through proper time management/using high quality resources.√
- Products/Services are constantly improved√ resulting in increased levels of customer satisfaction.√
- Vision/Mission/Business goals√ may be easily achieved.√
- Business has a competitive advantage√ over its competitors.√
- Regular training will continuously improve √ the quality of employees' skills/know ledge.√
- Employers and employees will have a healthy working relationship√ resulting in happy/productive workers.√
- Increased market share√ and profitability.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the benefits of a good quality management system.
Max (10)
10.4 Impact of TQM elements on Zamalek LTD (ZL)
10.4.1 Total client/customer satisfaction
Positives/Advantages
- ZL/A large business uses market research/customer surveys√ to measure/ monitor customer satisfaction/analyse customers' needs.√
- Continuously promote√ a positive business image.√
- May achieve a state of total customer satisfaction, if businesses follow sound business practices√ that incorporate all stakeholders.√
- Strive to understand and fulfil customer expectations√ by aligning cross-functional teams across critical processes.√
- Ensures that cross-functional teams understand its core competencies√ and develop/strengthen it.√
- May lead to higher customer retention/loyalty√ and businesses may be able to charge higher prices.√
- ZL/Businesses may be able to gain access√ to the global market.√
- May lead to increased√ competitiveness/profitability.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the positive impact of total client/customer satisfaction as a TQM element on ZL.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- Employees who seldom come into contact with customers√ often do not have a clear idea of what will satisfy their needs.√
- Monopolistic companies have an increased bargaining power√ so they do not necessarily have to please customers.√
- Not all employees√ may be involved/committed to total client/customer satisfaction.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact of total client/customer satisfaction as a TQM element on ZL.
Sub max (8)
10.4.2 Continuous skills development/Education and training
Positives/Advantages
- ZL has/Large businesses have a human resources department√ dedicated to skills training and development.√
- Human resources experts√ ensure that training programmes are relevant to increased customer satisfaction.√
- Ability to afford√ specialised/skilled employees.√
- ZL could conduct skills audits√ to establish the competency/education levels of staff performing work which could affect the quality of products/processes positively.√
- May be able to hire qualified trainers√ to train employees on a regular basis.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the positive impact of continuous skills development/education and training as a TQM element on ZL.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- Poor communication systems in ZL√ may prevent effective training from taking place.√
- Trained employees may leave for better jobs√ after they gained more skills.√
- De-motivates employees√, if they do not receive recognition for training.√
- Employees who specialise in narrowly defined jobs√ may become frustrated/ demotivated.√
- Employees may not be aware of the level of competency they should meet√ in order to achieve their targets.√
- It may be difficult to monitor/evaluate√ the effectiveness of training.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact of continuous skills development/education and training as a TQM element on ZL.
Sub max (8)
Max (14)
10.5 Application of PDCA model/cycle in improving the quality of products
Plan
- Zamalek Ltd/ZL should identify the problem and develop a plan for improvement to processes and systems.√√
- Answer questions√ such as 'What to do'/ 'How to do it'.√√
- Plan the new method and approach√ in order to improve the quality of their products.√√
Sub max (4)
Do
- ZL should implement the change on a small scale.√√
- Implement the processes and systems as planned.√√
Sub max (4)
Check/Analyse
- Use data to analyse the results of change.√√
- Determine whether it made a difference and what needs to be improved.√√
- Check whether the processes are working effectively.√√
- ZL should assess/test and establish if it is working/if things are going according to plan.√√
Sub max (4)
Act as needed
- Implement the improvement to meet the needs of the business.√√
- Devise strategies on how to continually improve.√√
- If the change was successful, implement it on a wider scale.√√
- ZL should continuously revise the process until they get it right the first time.√√
Sub max (4)
Any other relevant answer related to how ZL can apply the PDCA model/cycle to improve the quality of their products.
NOTE:
- The steps could be integrated in the application.
- Award a maximum of FOUR (4) marks for only mentioning the steps of the PDCA model.
Max (14)
10.6 Conclusion
- Businesses should put good quality management systems in place in order to remain sustainable and competitive in the market place.√√
- Total client satisfaction can be achieved through continuous and effective training programmes.√√
- Large businesses are more likely to have formal quality control/management systems that functions well.√√
- Businesses that implement the PDCA model have a competitive advantage as they keep abreast with the latest developments in the market.√√
- Any other relevant conclusion related to quality management.
Max (2)
[40]
QUESTION 10: BREAKDOWN OF MARK ALLOCATION
Details | Maximum | Total |
Introduction | 2 | Max 32 |
Impact of poorly implemented TQM | 8 | |
Benefits of a good quality management system | 10 | |
Impact of total client satisfaction and continuous skills development | 14 | |
Application of a PDCA model | 14 | |
Conclusion | 2 | |
INSIGHT | 8 | |
Layout | 2 | |
Analysis/Interpretation | 2 | |
Synthesis | 2 | |
Originality/Examples | 2 | |
TOTAL MARKS | 40 |
- LASO - For each component:
- Allocate 2 marks if all requirements are met.
- Allocate 1 mark if some requirements are met.
- Allocate 0 marks where requirements are not met at all.
TOTAL SECTION C: 80
GRAND TOTAL: 300
AGRICULTURAL TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
AGRICULTURAL TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
1.1 This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
1.2 BOTH sections are COMPULSORY.
1.3 Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4 Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
1.5 You may use a non-programmable calculator.
1.6 Write neatly and legibly. - SECTION A: SHORT QUESTIONS
2.1 This section consists of THREE questions.
2.2 Follow the instructions when answering the questions. - SECTION B: STRUCTURED LONG QUESTIONS
3.1 This section consists of FIVE questions.
3.2 Start EACH question on a NEW page.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 Steel, alloyed with chromium and … , is resistant to air, water and chemicals.
- manganese
- copper
- nickel
- zinc
1.1.2 The preferred plastic for the manufacturing of heat-resistant handles:
- Bakelite
- Perspex
- Fibreglass
- Polyvinyl chloride
1.1.3 ONE of the following is NOT an advantage of Vesconite:
- Corrosion resistant and non-conductive
- Will not wear shafts like traditional bearing materials
- Is easy to join
- Resistant to a wide range of chemicals
1.1.4 The best type of fire extinguisher to be kept in a welding workshop is a/an … extinguisher.
- oxygen(O2)
- foam
- carbon dioxide(CO2)
- water(H2O)
1.1.5 Which ONE of the following should NOT appear on an electricity safety sign?
- Electricity
- Height of fence
- Shock
- High voltage
1.1.6 The function of the … in a vehicle is to ensure that the gears can be changed while the vehicle is moving.
- differential
- drive shaft
- clutch
- final drive
1.1.7 … increases the heat of the flame when welding with the oxyacetylene set.
- Argon
- Oxygen
- Acetylene
- Helium
1.1.8 Pneumatic tools operate with ... pressure.
- air
- oil
- hydraulic
- water
1.1.9 The hub-lock mechanism of a 4x4 vehicle is located at the ….
- rear wheels.
- rear differential.
- front wheels.
- torque converter.
1.1.10 The function of the sensitivity element on a tractor is to automatically …
- control the depth of the implement according to immediate soil conditions.
- adjust the cross angle of the implement in relation to the tractor's movement.
- increase torque to the power take-off shaft when the baler is impeded.
- lower or raise the back of the implement in relation to the movement of the tractor. (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Change the UNDERLINED word(s) in each of the following statements to make the statements TRUE. Write only the word(s) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 Tractor.
1.2.1 Electronic devices, like radios, can be used to activate the centre-pivot irrigation system.
1.2.2 Stretching of the V-belt is a common problem when using this type of belt over long distances.
1.2.3 Pure ethanol is commonly used as racing fuel.
1.2.4 The side of the hydraulic cylinder which contains the shaft, is stronger than the other side, because of the smaller contact area that is subjected to the oil pressure in the cylinder.
1.2.5 An oil fire should be extinguished with a foam fire extinguisher. (5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Choose a word/term from COLUMN B that matches the description in COLUMN A. Write down only the letter (A–H) next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.3.6 I.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.3.1 Battery acid, pesticides and solvents can lead to health hazards |
|
(5 x 2) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 40
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: MATERIALS AND STRUCTURES
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 Name FOUR safety properties that insulation material used in the roofs of buildings must adhere to. (4)
2.2 Electric fencing protects what is kept inside and keeps certain unwanted elements out.
2.2.1 Recommend TWO measures to ensure that humans do NOT accidently come into contact with an electric fence. (2)
2.2.2 Explain the use of ceramic isolators between the wire and the post of an electric fence. (2)
2.2.3 Briefly discuss the function of the appliance in the photograph below.  (2)
(2)
2.2.4 Describe what will happen to a person when he/she touches an electric fence if the amperage is too high. (2)
2.2.5 A battery, similar to the one below, can be used as a power source for an electric fence energiser. Name TWO types of batteries that can be used.  (2)
(2)
2.2.6 Explain the factors that have an influence on the earth return system of an electric fence. (4)
2.2.7 Describe THREE ways of increasing the earth efficiency of an electric fence in particularly poor earth conditions, like very dry soil. (3)
2.3 Teflon is an invention of chemical engineering and innovation. Name FOUR uses of Teflon on a farm. (4)
2.4 Vesconite is a thermoplastic made from polymers. Name THREE applications of Vesconite on farm implements. (3)
2.5 Explain why bronze is preferred for the manufacturing of propellers of huge ships. (2)
2.6 Name FIVE influences that manganese has on stainless steel. (5) [35]
QUESTION 3: ENERGY
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 Alternative ways of generating electricity are high on the priority list of countries all over the world because of the depletion of coal reserves.
3.1.1 Name FIVE different types of renewable energy sources used by modern society. (5)
3.1.2 What should NOT be done when you extract steam and hot water from a geothermal source to protect it from cooling down too much? (1)
3.2 The photograph below shows solar energy cells that provides electricity.
3.2.1 Explain the factors that have a negative influence on the effectiveness of a solar energy cell. (4)
3.2.2 Name TWO types of energy that are directly generated from solar energy. (2)
3.2.3 Name a device used with solar panels that change direct current to alternating current. (1)
3.3 The structures in the photograph below can be up to 100 metres high with blades that are 60 metres in length, making the structures susceptible to serious wind damage.
3.3.1 Recommend TWO actions to prevent the blades of the structures above from being damaged when they turn too fast during a strong wind storm. (2)
3.3.2 State FIVE advantages of using a small wind energy system on a farm. (5) [20]
QUESTION 4: SKILLS AND CONSTRUCTION PROCESSES
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 The questions below refer to metal inert-gas (MIG) welding.
4.1.1 Name the THREE most possible causes of poor penetration during MIG welding. (3)
4.1.2 Why is it NOT necessary to use additional flux when doing MIG welding? (1)
4.1.3 Give TWO reasons why MIG welding is quicker than conventional arc welding. (2)
4.1.4 Name the type of material used for manufacturing suitable protective clothing for welding. (1)
4.1.5 Give a reason for your answer to QUESTION 4.1.4. (1)
4.1.6 Explain why a little metal ball, as seen in the photograph below, burns to the contact tip of the MIG welding torch when welding.  (2)
(2)
4.1.7 Describe TWO methods to remove the metal ball from the tip of the MIG welding torch. (2)
4.1.8 Name TWO different metals that can be welded successfully with a MIG welding machine. (2)
4.2 A welded joint on a planter has to be smoothed with the angle grinder, as shown below. Explain how you will achieve a neat final product.  (5)
(5)
4.3 Describe the overhead arc welding procedure in the diagram below.  (4)
(4)
4.4 Below is a diagram of an oxyacetylene cutting set.
4.4.1 Recommend a device that can be used to light the flame of an oxyacetylene torch. (1)
4.4.2 Explain why it is NOT advisable to use a cigarette lighter or matches when igniting the oxyacetylene torch. (1)
4.4.3 Discuss the procedure that must be followed to shut down the oxyacetylene equipment after welding is finished. (5)
4.5 Explain how you will deal with hazardous gases when using a plasma cutter. (5) [35]
QUESTION 5: TOOLS, IMPLEMENTS AND EQUIPMENT
Start this question on a NEW page.
5.1 Study the photograph of a ram baler below and answer the questions that follow. 
5.1.1 Identify component A. (1)
5.1.2 Explain the function of the ram. (2)
5.1.3 Name TWO functions of the slip clutch found in the drive mechanism of a baling machine. (2)
5.1.4 Describe FIVE procedures that must be followed before a baler is stored for a long period. (5)
5.2 Explain why it is necessary to use a four-wheel drive tractor with a front-end loader mechanism to move large round bales. (1)
5.3 A farmer wants to pump water from a river with an electrical motor and centrifugal pump. The diameter of pulley B on the electric motor is 200 mm and the speed is 3 750 r/min. The speed of pulley A on the centrifugal pump is 2 000 r/min. 
Na = speed of driving pulley
Da = diameter of driving pulley
Ng = speed of driven pulley
Dg = diameter of driven pulley
5.3.1 Calculate the diameter of pulley A on the pump. Show ALL calculations.
Use the formula: Na x Da = Ng x Dg (4)
5.3.2 The drive between the motor and the pump in the sketch above is brought about by V-belts. Name FOUR advantages of V-belts. (4)
5.4 The diagram below shows a plough hitched to a tractor. 
5.4.1 Analyse the diagram carefully and explain what arrow A illustrates. (3)
5.4.2 State THREE ways in which a farmer can change a tractor's mass displacement positively. (3)
5.4.3 Name THREE factors that have an influence on the forward movement of the tractor when ploughing. (3)
5.5 Explain the reason why a differential is installed in the rear axle of a tractor. (3)
5.6 Give FOUR causes why a tractor overturns. (4)
5.7 Name TWO places where the sensitivity element can be installed in a tractor. (2)
5.8 Name a medium that is used to drive EACH tool below.  (3) [40]
(3) [40]
QUESTION 6: WATER MANAGEMENT
Start this question on a NEW page.
6.1 Name FOUR types of filtering systems that are used to purify water for human consumption and describe the working of EACH. (8)
6.2 What does GIS stand for and discuss how you would use it in a modern farming enterprise? (5)
6.3 Explain why a farmer must determine the flow rate of water in an irrigation system. (2)
6.4 Answer the questions below regarding septic drains used on farms to treat raw household sewage.
6.4.1 Name the most important substance found in any septic drain that ensures that it will function properly. (1)
6.4.2 Describe the function of the distribution box of a septic drain. (3) 6.4.3 Name THREE places where a septic drain should NOT be build. (3) 6.5 Below is a photograph of an irrigation timer. 
6.5.1 Explain the use of the irrigation timer above. (2)
6.5.2 Name TWO basic types of irrigation timers that can be used on a farm. (2)
6.5.3 List FOUR different types of irrigation systems. (4) [30]
TOTAL SECTION B: 160
GRAND TOTAL: 200
AGRICULTURAL TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
AGRICULTURAL TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 C✔✔ (2)
1.1.2 A✔✔ (2)
1.1.3 C✔✔ (2)
1.1.4 C✔✔ (2)
1.1.5 B✔✔ (2)
1.1.6 C✔✔ (2)
1.1.7 B✔✔ (2)
1.1.8 A✔✔ (2)
1.1.9 C✔✔ (2)
1.1.10 A✔✔ (2) (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 cell phones✔✔ (2)
1.2.2 flat belt✔✔ (2)
1.2.3 methanol✔✔ (2)
1.2.4 weaker✔✔ (2)
1.2.5 Carbon-dioxide (CO2 )/dry powder✔✔ (2) (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 B✔✔ (2)
1.3.2 E✔✔ (2)
1.3.3 A✔✔ (2)
1.3.4 D✔✔ (2)
1.3.5 C✔✔ (2) (5 x 2) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 40
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: MATERIALS AND STRUCTURES
2.1 FOUR safety properties of insulation material
- Must not be harmful or dangerous to people when inhaled or touched.✔
- Should not burn easily.✔
- Rodents and insects must not be able to eat it or build their nests in it (treated with an anti pest agent).✔
- Should be light.✔ (4)
2.2 2.2.1 TWO measures of ensuring that humans do not accidently come into contact with an electric fence.
- Place safety signs on the fence and gates.✔
- Don’t erect near or across pathways.✔ (2)
2.2.2 Reasons for using ceramic insulators between the wire and the post of an electric fence.
- It is not a conductor of electricity.✔
- Weather resistance/Strong/Durable.✔ (2)
- 2.2.3 Function of the appliances shown in the picture.
- It applies tension on the wire of an electric fence.✔
- When the fence wire loses its tension it is not necessary to loosen the wire, it can be wind up with this appliance.✔ (2)
2.2.4 Description of what will happen to a person when he/she touches an electric fence if the amperage is too high.
- The result of too high amperage will be that a person will sustain a lethal shock that can cause tissue damage✔ or heart failure.✔ (2)
2.2.5 TWO types of batteries that can be used as a power source for an electric fence energizer.
- 12v dry disposable battery✔
- 12v wet rechargeable battery✔ (2)
2.2.6 Factors that have an influence on the earth return cycle of an electric fence.
- There must be a return path through the ground and an earth spike back to the energizer in order to complete the loop.✔
- The animal is the missing link that completes the loop.✔
- Vegetation will also complete the loop causing the output voltage of the energizer to drop.✔
- Therefore it is very important to keep any growth on the line to a minimum to ensure the animal receives the maximum shock from the energizer.✔ (4)
2.2.7 THREE ways of increasing the earth efficiency for particularly poor earth conditions like very dry soil.
- Increasing the number of earth spikes.✔
- Run an earth return wire in parallel to the fence line and connecting it to earth spikes at regular intervals.✔
- Using copper plates in the ground.✔ (3)
2.3 FOUR uses of Teflon on a farm.
- Automobile wiper blades✔
- Carpet or fabric protector✔
- All-weather clothing✔
- Coating for eyeglass lenses✔
- Magazines for guns✔
- Teflon coated cooking pans✔
- Teflon tape for sealing fittings✔
- Car wash products✔
- O-Rings✔
- Oil and water seals✔
- Teflon Taps and fitting✔
- Non-return valves✔
- Flanges✔
- Pipe saddles✔ (Any 4) (4)
2.4 THREE different applications of Vesconite on farm implements.
- Bushes✔
- Solid rods✔
- Wear plates✔ (3)
2.5 Bronze used to manufacture propellers of huge ships.
- Ships spend all their life in seawater that is highly corrodible.✔
- Bronze is the most cost effective metal because of its resistance against corrosion by seawater.✔ (2)
2.6 FIVE influences that manganese have on stainless steel.
- It combats corrosion.✔
- Gives steel a coarser structure.✔
- Changes the band structure, at the same time causing a reduction in striking strength.✔
- Increases tensile strength.✔
- Reduces the critical cooling tempo and by doing so improves hardening.✔
- Increases resistance against wear.✔
- Reduces magnetism.✔ (Any 5) (5) [35]
QUESTION 3: ENERGY
3.1
3.1.1 FIVE different types of renewable energy sources used by modern society.
- Solar energy✔
- Wind energy✔
- Hydro energy✔
- Geothermal energy✔
- Bio energy✔
- Tidal energy✔ (Any 5) (5)
3.1.2 The geothermal source protection from cooling down too much.
- Do not pump too much cold water into the hole✔ (1)
3.2
3.2.1 Factors that have a negative influence on the effectiveness of a solar energy cell.
- Climate, weather patterns✔
- High levels of pollution✔
- Sun energy is not available during the night time✔
- A cloudy day makes this energy source ineffective✔ (4)
3.2.2 TWO types of energy that are directly generated from solar energy.
- Heat✔
- Electricity✔ (2)
3.2.3 A device used with solar panels that change direct current to alternating current.
- Inverter✔/transformer✔ (1) (Any 1)
3.3
3.3.1 TWO actions to prevent the blades from being damaged when they turns too fast during a strong wind storm.
- Change the pitch of the blades✔
- Apply the brakes✔ (2)
3.3.2 FIVE advantages of a small wind energy system to the farmer.
- Decades of free electricity after initial-cost recovery.✔
- Increased property values.✔
- Reliable electricity.✔
- Relief from high and volatile prices of other forms of electricity.✔
- Personal energy independence.✔
- Ability to support clean energy and reduce global warming.✔ (Any 5) (5) [20]
QUESTION 4: SKILLS AND CONSTRUCTION PROCESSES
4.1
4.1.1 THREE of the most possible causes of poor penetration during MIG welding.
- Current too low✔
- Preparation too narrow✔
- Root face too large✔
- Root gap too small✔
- Worn contact tip causing irregular arc✔
- Incorrect alignment of plates✔ (Any 3) (3)
4.1.2 Reason why it is not necessary to use additional flux when MIG welding.
- The shielding gas (CO2) replaces the flux✔ (1)
4.1.3 TWO reasons why MIG welding is quicker than conventional arc welding.
- Rod is not changed regularly✔
- Flux does not have to be removed✔ (2)
4.1.4 Type of material used for manufacturing suitable protective clothing for welding.
- Cotton✔ (1)
4.1.5 A reason for your answer in QUESTION 4.1.4
- Other synthetic materials melt when exposed to heat/cotton does not melt when exposed to heat✔ (1)
4.1.6 Explanation of why a little metal ball occurs on the tip of your MIG welding torch.
- The gap between the welding tip and the work piece is too small.✔
- You are building up too much heat because the current setting is too high.✔ (2)
4.1.7 TWO ways of clearing the metal ball from the tip of the MIG welding torch.
- Use pliers to remove the blob of welding from the nozzle.✔
- Use a file or small grinder to remove the blob.✔
- In severe cases, replace the nozzle.✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.1.8 TWO different metals that can successfully be welded with a MIG welding machine.
- High alloy steel (stainless alloys)✔
- Aluminium✔
- Mild steel✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.2 Explanation on how you will achieve a neat final welded joint with the angle grinder.
- Use a grinding wheel on the angle grinder.✔
- Be careful as you approach the surface of the original stock. You don't want to grind through your nice new weld.✔
- Move the angle grinder around like you would a sander so as not to heat up, or grind away any one spot of the metal too much.✔
- If you see the metal get a blue colour to it you are either pushing too hard with the grinder or not moving the grinding wheel around enough.✔
- Wear a full face mask when grinding, a mask or respirator, and ear protection.✔ (5)
4.3 The overhead arc welding procedure.
- Use an arc as short as possible.✔
- Weld a number of runs without any lateral movement.✔
- When molten metal starts dripping, the amperage should be reduced slightly.✔
- Move electrode slightly faster.✔
- Hold electrode in same position as in relation to base metal.✔ (Any 4) (4)
4.4
4.4.1 A device that can be used to light the flame of an oxy-acetylene torch.
- Always light the oxyacetylene torch with the striker.✔ (1)
4.4.2 Explanation of why it is NOT advisable to use a cigarette lighter or matches when igniting the oxyacetylene torch.
- A cigarette lighter or match would put your hand too close to the ignition tip.✔ (1)
4.4.3 The procedure that must be followed to shut down the oxy-acetylene equipment after welding is finished.
- Turn off the acetylene valve on the torch handle.✔
- Turn off the oxygen valve on the torch handle.✔
- Turn the main cylinder valve clockwise on the top of both gas cylinders.✔
- Now open the two valves on the torch handle to 'bleed' the system.✔
- Turn both the oxygen and acetylene regulator handles counter clockwise until they are loose.✔
- Close both valves on the torch handle. (Any 5) (5)
4.5 Explanation of how to deal with hazardous gasses when using a plasma cutting torch.
- Under no circumstances inhale these gases.✔
- If you must inspect a piece as you cut it, view the piece from the side, not from above. This will minimize your exposure to hazardous gas.✔
- Make sure the work area is well-ventilated as well.✔
- An exhaust hood or a space open to the outside is recommended when using a plasma torch.✔
- Respirators or other breathing apparatus may be required.✔(5) [35]
QUESTION 5: TOOLS, IMPLEMENTS AND EQUIPMENT
5.1 5.1.1 Identify component A.
- Auger✔ (1)
5.1.2 The function of the ram.
- The hay is compressed in the baling chamber by the ram✔ with a forward backward movement.✔ (2)
5.1.3 TWO functions of the slip clutch found in the drive mechanism of a baling machine.
- To prevent heavy objects from being taken into the baler.✔
- To protect the pick-up if it is impeded by anything.✔
- To protect the auger if it becomes overloaded.✔ (Any 2) (2)
5.1.4 FIVE procedures that must be followed before the baler is stored for a long period.
- Remove all bales from baling chamber.✔
- Clean the baler properly.✔
- Drain and replace all oil.✔
- Releases the tension on all drive belts.✔
- Remove all chains, clean and oil them, and replace them.✔
- Dismantle all slip clutches, clean them and reassemble them but do not put the springs under tension.✔
- Totally reduce bale chamber tension.✔
- Cover all unpainted areas with a thin layer of grease.✔
- Grease all grease nipples.✔
- Store baler in a dry place under cover.✔ (Any 5) (5)
5.2 Reason why it is necessary to make use of a four-wheel drive tractor with a front-end loader mechanism, to move large round bales.
- The front suspension and wheels are stronger to carry the weight of the bales.✔ (1)
5.3
5.3.1 Calculation of the diameter of pulley A on the pump.
- Na x Da = Ng x Dg
Diameter of Driven pulley Dg = 3 750 x 200✔
2 000✔
Dg = 375✔ mm✔ (4)
5.3.2 FOUR advantages of V-belts.
- V-belts do not easily slip off pulleys.✔
- V-belts draw tighter round pulleys when tension increases.✔
- Lubrication is never necessary.✔
- V-belts are relatively strong, and under normal circumstances do not easily break.✔
- Cold, moist conditions, age or use do not cause V-belts to stretch or shrink.✔
- V-belts last longer than flat belts.✔ (Any 4) (4)
5.4
5.4.1 Meaning of illustration of arrow A.
- The illustration shows how the plough✔tends to push down the front wheels✔when a top link✔ is fitted between the plough and tractor. (3)
5.4.2 THREE ways a farmer could make use of to change a tractor`s mass displacement positively.
- Decrease the tow bar pulling force✔
- Lower the tow bar✔
- Increase the wheelbase✔ (3)
5.4.3 THREE factors that have an influence on the forward movement of the tractor when ploughing.
- Ploughing depth✔
- Soil resistance✔
- Forward speed of the tractor✔ (3)
5.5 The reason why a differential is installed in the rear axle of a tractor.
- Changing direction of rotation✔
- Speed reduction✔
- Dividing rotation equal between the rear wheels✔
- Increase torque✔ (Any 3) (3)
5.6 FOUR causes of tractor that overturns.
- Cornering at high speed.✔
- Driving off the shoulder of roads.✔
- Working on a steep ditch, hill or washout.✔
- Carrying loads too high in the front-end loader.✔
- Hitching too high when pulling heavy loads.✔
- Towing loads downhill too fast and/or without sufficient brakes.✔
- Sliding off loading ramps.✔
- The load on the trailer more than 75% of the tractors weight.✔ (Any 4) (4)
5.7 TWO places where the sensitivity element can be installed on a tractor.
- Where the top link is fitted✔
- In the differential housing✔
- At the base of the lifting arms✔ (Any 2) (2)
5.8 The medium that is used to drive each tool.
- Air ✔
- Oil✔
- Electricity✔ (3) [40]
QUESTION 6: WATER MANAGEMENT
6.1 FOUR types of filtering systems used to purify water for human consumption and describe the working of each.
- Distillers’ purification system✔
- They work with a boiling water/evaporation system.✔
- Reverse Osmoses purification system✔
- It works through a liquid system and through a membrane very slowly in molecule level.✔
- Whole house purification system✔
- Use cartridges to filter water.✔
- Faucet water filters✔
- Installed in the kitchen and cleaned water as needed.✔
- Jug /Pitcher filters
- The water will go in at the top and slowly filter down and finally captured at the bottom in a reservoir. (Any 4 x 2) (8)
6.2 Meaning of abbreviation 'GIS' and the use of it in a modern farming enterprise.
- GIS : Geographical Information System✔
- Remote sensing image data from the soil and crops is processed and then added to the GIS database.✔
- This data is analysed and interpreted.✔
- Problem areas or areas of under production in fields are identified.✔
- The problem areas can then be rectified by adding extra water or fertilizers.✔ (5)
6.3 Reasons for determining the flow rate of water in an irrigation system.
- To ensure the correct calibration of the sprayers.✔
- Effective scheduling of irrigation.✔
- To prevent the over utilization of the water source.✔
- To use water economically.✔ (2) (Any 2)
6.4
6.4.1 The most important substance that is found in any septic drain that ensures that it will function properly.
- Bacteria✔ (1)
6.4.2 The function of the distribution box of a septic drain.
- Serves to distribute the flow from the septic tank overflow evenly to the absorption field or seepage pits.✔
- It is important that each trench or pit receive an equal amount of flow.✔
- This prevents overloading of one part of the system.✔(3)
6.4.3 THREE places where a septic drain should not be build.
- Near boreholes or drinking water installations.✔
- Near the farmhouse.✔
- Near traffic.✔
- Where people usually eat, wash or work regularly.✔ (Any 3) (3)
6.5
6.5.1 The use of the irrigation timer.
- This device controls the watering through different irrigation lines.✔
- This device can start and stop the irrigation system.✔ (2)
6.5.2 TWO basic types of irrigation timers that can be used on a farm.
- Mechanical timers✔
- Electronic timers✔ (2)
6.5.3 FOUR different types of irrigation systems.
- Overhead irrigation systems✔
- Centre pivot irrigation systems✔
- Sprinkler irrigation✔
- Travel irrigation system✔
- Wheel line irrigation system✔ (Any 4) (4)
[30]
TOTAL SECTION B: 160
GRAND TOTAL: 200
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show ALL the calculations, including formulae, where applicable.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 … is necessary for the healing of damaged tissue and assists in the healing of wounds in pigs.
- Selenium
- Iodine
- Iron
- Zinc
1.1.2 The structure in the stomach of a young calf that is responsible for the transportation of milk directly into the abomasum:
- Trachea
- Crop
- Omasum
- Oesophageal groove
1.1.3 Digestible energy can be defined as the …
- energy that is released when a feed is completely burnt to its final oxidation product.
- total amount of energy released as heat.
- difference between the gross energy value and the energy lost in manure.
- energy that is available for maintenance and production.
1.1.4 One of the following is NOT correct with regard to factors influencing the digestibility of feeds:
- Composition of the feed
- Mineral content of the feed
- Crude fibre content of the feed
- Type of animal
1.1.5 The production system where animals are kept in high densities and fed highly specialised formulated feeds:
- Semi-intensive
- Extensive
- Battery
- Backyard
1.1.6 The following should be considered to avoid stress and aggressive conflicts in male sheep:
- Group and house all male sheep in one pen.
- Place animals of the same sex together regardless of body weight and size.
- Group animals that are familiar with one another and of the same age and sex.
- Place a number of male sheep with female sheep during the breeding season.
1.1.7 The following is applicable to feed provision in a well-designed feed flow plan:
- Buying feeds in small quantities is uneconomical.
- Make provision for storage facilities for feeds because not all feeds required are readily available on farms.
- Feed requirements of animals may be fulfilled by buying the feed at any time when needed.
- Feeds must be protected against rain, spoilage, insects and rodents.
Choose the CORRECT combination:
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
1.1.8 A method to administer medicine to the skin or directly to the wound:
- Topical
- Oral
- Injection
- Dosing
1.1.9 The hormone responsible for the ripening of the follicles:
- Progesterone
- Luteinising hormone
- Follicle stimulating hormone
- Prolactin
1.1.10 The common excretory canal for urine and semen in fowl:
- Urethra
- Cloaca
- Vagina
- Vas deferens (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Indicate whether each of the descriptions in COLUMN B applies to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A AND B or NONE of the items in COLUMN A. Write A only, B only, both A and B or none next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 B only.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
1.2.1 | A: | Duodenum | the structure where maximum absorption of nutrients occurs mainly |
B: | Jejunum | ||
1.2.2 | A: | Calcium and phosphorus | nutrients responsible for the formation of bones |
B: | Vitamin D and magnesium | ||
1.2.3 | A: | Optimal production | the level of animal production that would earn the farmer the largest income on the long run |
B: | Maximum production | ||
1.2.4 | A: | Testis degradation | the phenomenon where the testes remain in the abdominal cavity |
B: | Lack of libido | ||
1.2.5 | A: | Corpus luteum | the structure that develops on the ovary after ovulation |
B: | Placenta | ||
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Give ONE term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 The enzyme in the saliva of pigs responsible for the breaking down of starch to simple sugars
1.3.2 An organism that spends most or part of its life on the host animal
1.3.3 Materials, such as sawdust and straw, which are placed on the floors of pigsties to insulate cold cement floors and absorb moisture
1.3.4 The phenomenon where a superior cow is treated with hormones to produce many ova
1.3.5 The organelle in the mid-piece of the sperm cell that supplies energy for movement (5 x 2) (10)
1.4 Change the UNDERLINED WORD(S) in EACH of the following statements to make it TRUE. Write only the answer next to the question number (1.4.1–1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 Urea is a white water-soluble substance used to supplement carbohydrates in the rations and licks of ruminants.
1.4.2 The driving licence is a document carried by the driver with a clear identification of the animals transported on a public road.
1.4.3 The method used to increase the number of identical offspring from a single embryo, is embryo flushing.
1.4.4 The endoderm is the layer from which the heart, skeleton, muscles, urogenital and vascular systems develop.
1.4.5 Adrenalin is the hormone in bulls that enhances sexual desire. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: ANIMAL NUTRITION
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 The diagram below illustrates the alimentary canal of a farm animal. 
2.1.1 Write down the letter (A–D) of the part where cellulose digestion occurs. (1)
2.1.2 Name the cellulose-digesting enzyme secreted by the organisms in part A. (1)
2.1.3 State TWO requirements of the organisms found in part A. (2)
2.1.4 Indicate the type of digestion that occurs in part D. (1)
2.1.5 Give a reason for your answer to QUESTION 2.1.4. (1)
2.2 The pictures below show different animal feeds available. 
2.2.1 Classify the type of feed shown in FEED A and FEED C. (2)
2.2.2 Write down the letter (A–D) of the feed in the pictures above that can be recommended for farm animals under EACH of the following conditions:
- Finishing off of cattle for the abattoir (1)
- To correct mineral deficiency (1)
- To improve fertility in rams (1)
- To supply bulkiness in rations of ruminant animals (1)
2.2.3 Non-ruminants digest FEED B better when it is ground. Justify this statement. (2)
2.3 In a feed trial, an animal was fed 24 kg of dry hay and it excreted 12,5 kg of dry manure. Of this hay 11,5 kg was digested and absorbed.
2.3.1 Calculate the digestibility coefficient of this hay. (3)
2.3.2 Suggest at which stage the hay fed to the animals above was cut. (1)
2.3.3 Give a reason for your answer to QUESTION 2.3.2, based on the calculated value above. (2)
2.3.4 Name TWO supplementary substances that could be used to improve digestibility of this hay. (2)
2.4 The table below shows a fodder flow plan for 50 beef cattle over a period of 6 months.
JAN. | FEB. | MAR. | APR. | MAY | JUN. | |
Natural pasture (ton) | 160 | 160 | 140 | 120 | 80 | 60 |
Supplementary feed (kg/animal/day) | 1 | 2 | 4 | |||
Cost of supplementary feed (R/kg) | 30 | 38 | 50 | |||
Feed required (ton) | 140 | 140 | 140 | 140 | 140 | 140 |
Price of beef (R/kg) | 40 | 35 | 30 | 30 | 35 | 60 |
2.4.1 Identify any TWO months in the table above when the feed was insufficient. (2)
2.4.2 From the data above, give TWO reasons for your answer to QUESTION 2.4.1. (2)
2.4.3 Calculate the total quantity of supplementary feed (in tons) for ALL the animals during May. (3)
2.5 The table below shows the crude protein and crude fibre content of the different feeds.
FEED | CRUDE PROTEIN (CP) (%) | CRUDE FIBRE (CF) (%) |
Natural lucerne pastures | 23 | 26 |
Lucerne hay | 14 | 30 |
Oil-cake meal | 37 | 16 |
Maize meal | 9 | 2 |
Sorghum stover | 4 | 40 |
Use the data in the table above to draw a bar graph of the crude protein and crude fibre content of the different feeds. (6) [35]
QUESTION 3: ANIMAL PRODUCTION, PROTECTION AND CONTROL
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 The pictures below indicate TWO different pig production systems.
|
| PICTURE A |
| PICTURE B |
3.1.1 Identify the TWO production systems shown in PICTURES A and B. (2)
3.1.2 Compare the TWO production systems based on the following:
- Method of feeding (2)
- Space per production output (2)
3.2 The table below shows the feeding and temperature requirements for broilers at different stages of growth.
AGE | FEED | NUTRITIONAL VALUE | TEMPERATURE REQUIREMENTS |
0–1 | Starter mash | 23% protein fortified with vitamins and mineral salts | 32,2 °C to 35 °C |
1–2 | Starter mash | 23% protein fortified with vitamins and mineral salts | 29,4 °C to 32,2 °C |
3–4 | Grower mash | 20% protein fortified with vitamins and mineral salts | 26,7 °C to 29,4 °C |
5–slaughter | Finisher mash | 18% protein fortified with carbohydrates | Normal room temperature (25 °C) |
3.2.1 Identify the main nutrient for broilers of ALL age groups. (1)
3.2.2 Indicate the importance of the nutrient in QUESTION 3.2.1 for broilers. (1)
3.2.3 Give the main reason for the inclusion of carbohydrates in a finisher mash. (1)
3.2.4 Deduce the relationship between the protein level of the feed, temperature requirements and the age of the broilers. (3)
3.3 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions of tools used for farm animal identification purposes by choosing a word/term from the list below. Write only the word/term next to the question number (3.3.1–3.3.4) in the ANSWER BOOK.
ear tag; branding iron; smart neck band; tattoo pliers |
3.3.1 Used to leave a particular permanent mark on the animal, especially cattle (1)
3.3.2 Used to identify animals with specific coded information on family lines and generation (1)
3.3.3 Equipped with an advanced electronic device to locate an animal and send feedback on the actions performed by the animal (1)
3.3.4 Used for the identification of animals, especially stud horses (1)
3.4 The facility below is used in an animal production enterprise.
3.4.1 Identify the facility above. (1)
3.4.2 What is the facility, identified in QUESTION 3.4.1, used for? (1)
3.4.3 State TWO design features of this facility that will make it suitable for its use. (2)
3.4.4 Suggest TWO forms of harm to animals when the facility above is used. (2)
3.5 The diagrams below represent two parasites in farm animals. 
3.5.1 Classify the TWO types of parasites illustrated in A and B. (2)
3.5.2 Use the diagrams to motivate EACH answer to QUESTION 3.5.1. (2)
3.5.3 State ONE preventative measure against the parasite illustrated in B. (1)
3.6
Animal diseases are caused by pathogens. Some diseases can be transmitted on contact; others need a disease-carrying organism. All diseases have a negative impact on farmers, labourers and the economy of the country. |
3.6.1 Give a scientific term used in animal health to describe EACH of the following conditions:
- Diseases that can be transmitted from animal to animal (1)
- Disease-carrying organism (1)
3.6.2 Name ONE bacterial disease that can be transmitted from one animal to the other. (1)
3.6.3 State ONE role of the farmer to control the occurrence of the diseases in QUESTION 3.6.2. (1)
3.6.4 Suggest TWO ways in which farm workers can be exposed to animal diseases. (2)
3.6.5 Indicate TWO roles of the state in controlling the spread of infectious diseases. (2) [35]
QUESTION 4: ANIMAL REPRODUCTION
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 The diagram below represents a sperm cell. 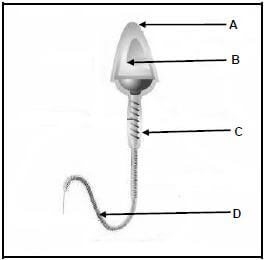
4.1.1 Identify part A. (1)
4.1.2 Give a function of the parts labelled:
- A (1)
- B (1)
- D (1)
4.1.3 Distinguish between a sperm cell and semen. (2)
4.1.4 Name the female reproductive cell. (1)
4.2 The diagram below illustrates foetus development in cattle. 
4.2.1 Identify parts B and F. (2) 4.2.2 State the function of part D. (1)
4.2.3 Name the condition described by EACH of the following statements:
- The foetus dies and all the fluids are reabsorbed with the hard and dry parts remaining in the uterus. (1)
- The foetus dies and the soft tissue decays and everything remains in the uterus. (1)
- Pregnancy is terminated before the normal time of parturition and the dead foetus is expelled. (1)
- The placenta remains in the uterus after parturition for seven days. (1)
4.3
A commercial dairy farmer has 100 fertile cows and one bull. All the animals are well fed, a disease control system is in place and the enterprise is well managed. However, the calving percentage was only 55% over the last three years. |
4.3.1 In the scenario above, identify the major problem in the enterprise. (1)
4.3.2 Advise the farmer on ONE scientific technique to use in cows that will result in a much higher conception rate. (1)
4.3.3 If the farmer does not use the technique in QUESTION 4.3.2, how can the conception rate of the cows be improved? (1)
4.3.4 Explain the impact of nutrition on the fertility of bulls. (2)
4.3.5 Give TWO other reasons why the bull in the scenario above performs poorly. (2)
4.4 The graph below illustrates the milk production of a dairy cow over a period of one year. 
4.4.1 Give the term describing the graph above. (1)
4.4.2 Write down the letter (A–H) on the graph that indicates where EACH of the following occurs:
- Drying off of the cow (1)
- Calving (1)
- Peak milk production (1)
- Time of conception if the cow needs to calf again eight weeks after she has dried off (1)
4.4.3 Give TWO reasons to explain the abnormal drop in the milk production between point F and point G. (2)
4.5 The picture below shows dairy cows in oestrus. 
4.5.1 Define the concept oestrus in dairy cows. (2)
4.5.2 State TWO visible signs of oestrus in dairy cows, except the one in the picture above. (2)
4.5.3 Name the cow (A or B) that is definitely in oestrus. (1)
4.5.4 Name the:
- Hormone responsible for the signs of oestrus (1)
- Duration of the oestrus cycle (in days) (1)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show ALL calculations, including formulae, where applicable.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 The marketing system that stimulates the entrepreneur to show initiative and drive because of direct contact with consumers is called … marketing.
- free
- co-operative
- controlled
- pool system
1.1.2 ONE of the following factors influences the supply of a product:
- Increase in the number of consumers
- Taste and preference of the consumers in the short term
- Government subsidies and taxation policies
- The range of a product
1.1.3 The main reason for packaging agricultural products is to …
- ensure food security.
- increase the storage period of products.
- ensure a constant flow of products to the consumer.
- protect products against physical damage.
1.1.4 The following statements are TRUE with regard to price elasticity:
- Staple foods are generally price inelastic.
- Price elasticity of the supply of agricultural products in the short term is inelastic.
- The elasticity of the supply of agricultural products is usually positive in the long term.
- The elasticity of the demand of all agricultural products is always negative in the short term.
Choose the correct combination:
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
1.1.5 The following is NOT a function of land as a production factor:
- It provides space for the production process.
- It stores raw material.
- It provides food for animals.
- It cannot be used up.
1.1.6 The farmer can apply the following measures to increase labour productivity on the farm:
- The farmer must have the correct type and number of labourers.
- Set clear unattainable goals for labourers.
- Give labourers an opportunity to be involved in decision making.
- Ensure the wellbeing of labourers.
Choose the correct combination:
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
1.1.7 Flexibility as a risk management strategy involves …
- decreasing the number of livestock as a result of drought.
- growing crops as well as keeping livestock.
- distribution of the cost of risk among several stakeholders.
- concentrating only on a livestock enterprise.
1.1.8 ONE of the following is a method to acquire short-term credit:
- Bank loan paid over 36 months
- Using fixed assets as security
- Use personal loans for 6 to 12 months
- Use a grant from the Land Bank
1.1.9 A heterozygous individual has the following genotype for a qualitative genetic characteristic:
- Two dominant alleles
- Two recessive alleles
- One dominant allele and two recessive alleles
- One dominant allele and one recessive allele
1.1.10 Cattle have 30 pairs of chromosomes in the nucleus. The male gametes will have … chromosomes.
- 30
- 15
- 45
- 60
1.2 Choose a term/phrase from COLUMN B that matches a description in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–J) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 K.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.2.1 Indicates the condition when the quantity supplied is more than the quantity demanded |
|
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 The entrepreneurial success factor of generating a new business idea
1.3.2 The prediction of expected income and expenditure for a particular year
1.3.3 An inheritance mechanism which involves more than two alleles
1.3.4 A selection method based on the qualities of the relatives
1.3.5 The modification of the DNA resulting in a change in the sequence of the genes (5 x 2) (10)
1.4 Change the UNDERLINED WORD(S) in each of the following statements to make it TRUE. Write only the correct word(s) next to the question number (1.4.1–1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 Controlled marketing is a system of marketing where two or more farmers work together to reach a common goal.
1.4.2 The Labour Relations, 1993 (Act 85 of 1993) regulates health and safety of all employees in the workplace.
1.4.3 The crossing of a line-bred farm animal with an animal from a different species is called inbreeding.
1.4.4 Hybrid vigour is attained through homozygosity.
1.4.5 The internal hereditary factor that will influence the performance of an individual to be used for selection and breeding is a chromosome. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 The table below shows different marketing systems used by FARMER A and FARMER B.
FARMER A | FARMER B | |
Access to market | Local retailers and wholesalers | Larger markets via the Internet |
Price determination | Determined by local supply and demand | Determined by government |
Competition | Local producers | Competition is international |
2.1.1 Name the marketing systems used by FARMER A and FARMER B. (2)
2.1.2 Give a reason for the marketing system used by FARMER B. (1)
2.1.3 FARMER B uses mass marketing for marketing the produce. Justify this statement by referring to the table above. (1)
2.1.4 Name TWO ways in which the agribusiness chain can be streamlined for FARMER A to access markets in rural areas. (2)
2.2 Indicate TWO roles of legislation to ensure effective marketing of agricultural products. (2)
2.3 Name the component of a business plan that will reflect EACH of the following types of information:
2.3.1 Business name and the details of the person (1)
2.3.2 The number and types of employees (1)
2.3.3 Amount of money needed and future projections (1)
2.4 Name THREE common mistakes that farmers make when drawing up a business plan. (3)
2.5 The table below shows the supply and demand of peaches at different prices.
PRICE PER kg (R) | QUANTITIES SUPPLIED (kg) | QUANTITIES DEMANDED (kg) |
0,50 | 1 | 9 |
1,00 | 2 | 8 |
1,50 | 3 | 7 |
2,00 | 4 | 6 |
2,50 | 5 | 5 |
3,00 | 6 | 4 |
3,50 | 7 | 3 |
4,00 | 8 | 2 |
4,50 | 9 | 1 |
2.5.1 Use the data above and draw a line graph of the supply and demand of peaches at different prices. (6)
2.5.2 Identify the equilibrium price of peaches per kg. (1)
2.5.3 Refer to the table to explain what happens when the price per kg is below the equilibrium price. (2)
2.6 Match the factors that hamper the marketing of agricultural products below with EACH of the statements. Write down only factor next to the question number (2.6.1–2.6.4).
standardisation; perishability; bulkiness; lack of control over production; political situation |
2.6.1 Agricultural products have a limited lifespan, which shortens their time on the market. (1)
2.6.2 Unrest in the country can impact negatively on the marketing of agricultural products. (1)
2.6.3 Agricultural products are produced by a large number of producers which can lead to a surplus and a drop in price. (1)
2.6.4 Agricultural products have large volumes with relative low value. (1)
2.7 Indicate THREE requirements of a container for the packaging of fresh produce to prevent damage and spoilage. (3)
2.8 Identify the types of consumer described by EACH of the statements below.
2.8.1 Buyers divide the large shipment of products and sell it to consumers in small units (1)
2.8.2 Buy a carcass to make canned beef and biltong (1)
2.8.3 Buy products to sell to foreign markets (1)
2.9 Explain the law of demand in a market situation. (2) [35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 The table below represents two groups of farmers with different ways of farming.
GROUP A | GROUP B |
|
|
3.1.1 Indicate the land factor described in EACH of the two scenarios. (1)
3.1.2 State TWO benefits of the practices by the farmers in GROUP B that may have contributed to the higher production per hectare. (2)
3.1.3 Suggest TWO techniques applicable to the farmers in GROUP A that can improve their production per hectare. (2)
3.1.4 Identify an economic characteristic of land that will be negatively affected by monoculture and continuous cultivation. (1)
3.1.5 State TWO functions of land as a production factor. (2)
3.2
It is important to have an ethical and highly efficient work force with an understanding that the business is not about the employer only, but for their benefit too. Sleeping on duty is misconduct if committed deliberately, as it does not only affect productivity, but could endanger lives especially where dangerous equipment is being used. The necessary steps need to be taken to caution, and even charge, the employee who commits such an act. |
3.2.1 Name the type of permanent labourer who operates an advanced tractor equipped with an advanced computer and pilot steering. (1)
3.2.2 Indicate the expertise needed by the employee in QUESTION 3.2.1. (1)
3.2.3 Identify a type of misconduct by employees that would warrant the employer to take disciplinary steps. (1)
3.2.4 Name the specific legislation that the employer would use to justify the disciplinary steps. (1)
3.2.5 State TWO problems related to labour on farms. (2)
3.2.6 Recommend TWO actions an employer should consider to encourage workers to improve their productivity. (2)
3.3
A family fruit tree business was started on 34 hectares (ha). It was later scaled down to 12 hectares and is now very successful. This success can be attributed to the introduction of pigs, chickens and sheep to the farm. The waste from these animals is used to make compost. The business also buys surplus fruit from neighbouring farms to make dried fruit and jam. Five guest cottages have been built on the farm. The kitchen waste from the guest cottages is used for the compost-from-worms project on the farm. |
3.3.1 Identify the risk management strategy employed by this family business. (1)
3.3.2 Give ONE reason for the answer to QUESTION 3.3.1. (1)
3.3.3 Suggest TWO primary sources of risk in a farming business. (2)
3.3.4 State the general business management skills applied by the manager of the family business in the following situations:
- The smooth functioning of the different enterprises of the family business with the same work force (1)
- Processing and analysing the market information and realising there was a greater demand for organic products in the global markets (1)
- Developing positive relations with workers, suppliers and the markets (1)
3.3.5 Define the concept strategic management of a farm. (2)
3.4
Initially a rural community with 900 ha of communal land had no source of capital. They fought poverty through innovation by planting commercial plantations, on the communal land. Now they not only source profits from the plantations, but also from adventure tourism. At first they operated using a government grant of R11 million and a loan of R2 million from the Land Bank, payable at a rate of 5% over the period of 5 years. Currently they have a turnover of R12 million and expenses of R4 million yearly. |
3.4.1 Identify the fixed capital item in the scenario above. (1)
3.4.2 Name any TWO sources of capital used by the community to start the commercial plantations. (2)
3.4.3 Identify the problem of capital experienced by the community when they started the business. (1)
3.4.4 Indicate the term of repayment of the loan from the Land Bank. (1)
3.4.5 Calculate the profits made by the community during the 5 years. Show ALL the calculations. (5) [35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 A farmer cross-pollinated a heterozygous pea plant with yellow seed (G) and a pure-bred pea plant with green seed (g).
4.1.1 Indicate the genotype of EACH parent in the first crossing. (2)
4.1.2 Use the Punnet square method to determine the possible genotype of the offspring in the first crossing. (3)
4.1.3 Name the type of dominance shown by the crossing in QUESTION 4.1.2. (1)
4.1.4 Explain a reason for the type of dominance in QUESTION 4.1.3. (2)
4.1.5 Calculate the percentage of heterozygous offspring in the F1-generation. (2)
4.2 The illustration below shows the breeding systems commonly used by farmers. 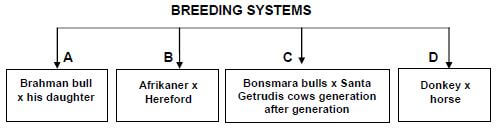
Identify the breeding system (A–D) that corresponds with EACH of the statements below. Write down only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (4.2.1–4.2.5).
4.2.1 It produces hybrid vigour. (1) 4.2.2 Its negative effects can be reduced by outcrossing. (1)
4.2.3 The offspring are hardy and can work under unfavourable conditions. (1)
4.2.4 A new breed is gradually imported into a new environment. (1)
4.2.5 Continual use leads to a gradual decrease in the performance of animals. (1)
4.3
Variation is a phenomenon that refers to differences in the characteristics of individuals which cause individual offspring to be slightly different from their parents. This phenomenon is a natural occurrence and is very important for farmers as it forms the foundation of selection and breeding programmes. |
4.3.1 Name TWO genetic processes that cause variation. (2)
4.3.2 Why is variation in a breeding programme important? Give TWO reasons. (2)
4.3.3 Distinguish between continuous variation and discontinuous variation. (2)
4.4
The farmer is breeding cattle for a weaning weight. The average weaning weight for the herd is 230 kg. One group of cattle has a mass of 220 kg and the other group has a mass of 250 kg. |
4.4.1 Indicate the group of cattle from which the farmer would select the animal to improve the weaning weight of the herd. (1)
4.4.2 Give a reason for the selection in QUESTION 4.4.1. (1)
4.4.3 Identify the selection method the farmer uses in QUESTION 4.4.1. (1)
4.4.4 Briefly explain the selection method in QUESTION 4.4.3. (2)
4.4.5 Name any TWO other selection methods the farmer can use to improve the weaning mass of the herd. (2)
4.5
The yields obtained by two maize farmers in a typical maize growing area are shown in the table below. FARMER A used conventional hybrid seed and FARMER B changed and used the latest available genetically modified (GM) seed. |
YEAR | YIELD (t/ha) (FARMER A) | YIELD (t/ha) (FARMER B) |
2011 | 10,0 | 10,2 |
2012 | 10,8 | 10,6 |
2013 | 9,6 | 12,0 |
2014 | 11,0 | 13,0 |
2015 | 10,4 | 15,0 |
2016 | 10,8 | 16,5 |
4.5.1 From the data in the table above, identify the year in which FARMER B changed to GM crops. (1)
4.5.2 Give a reason for the answer to QUESTION 4.5.1. (1)
4.5.3 Use the data above and name TWO advantages of the continued use of GM maize for FARMER B. (2)
4.5.4 Name TWO important characteristics of GM maize crops that could be responsible for the advantages that FARMER B experienced. (2)
4.5.5 Give ONE reason why there is public resistance against the use of GM cultivars or breeds. (1) [35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 A ✔✔
1.1.2 C ✔✔
1.1.3 D ✔✔
1.1.4 B ✔✔
1.1.5 D ✔✔
1.1.6 B ✔✔
1.1.7 A ✔✔
1.1.8 C ✔✔
1.1.9 D ✔✔
1.1.10 A ✔✔ (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 G ✔✔
1.2.2 A ✔✔
1.2.3 C ✔✔
1.2.4 D ✔✔
1.2.5 H ✔✔ (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 Innovation/creativity ✔✔
1.3.2 Budget ✔✔
1.3.3 Multiple alleles ✔✔
1.3.4 Family selection ✔✔
1.3.5 Genetic modification/engineering/manipulation✔✔ (5 x 2) (10)
1.4
1.4.1 Co-operative ✔
1.4.2 Occupational Health and Safety ✔
1.4.3 Species crossing ✔
1.4.4 Heterozygosity ✔
1.4.5 Gene ✔ (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
2.1 Table on marketing
2.1.1 Marketing system used
- Farmer A - Free marketing ✔ (1)
- Farmer B - Controlled marketing ✔ (1)
2.1.2 Reason for the system used by farmer B
- Price is determined/controlled by the government ✔ (1)
2.1.3 Justification for mass marketing
- Farmer B is reaching a wide range of consumers(larger markets) via the internet ✔ (1)
2.1.4 TWO ways to facilitate marketing in rural areas
- Improve roads/infrastructure ✔
- Improve market information through technology ✔
- Transportation of produce in vehicles with cooling facilities. ✔
- Cold storage depots ✔
- Market collectively by combining loads ✔ (Any 2) (2)
2.2 TWO roles of legislation in ensuring effective marketing
- Ensures increased market access to all participants ✔
- Makes provision for quality control over imports and exports of products ✔ (2)
2.3 Component of a business plan
2.3.1 Title/cover page ✔ (1)
2.3.2 Human resource plan ✔ (1)
2.3.3 Financial plan ✔ (1)
2.4 THREE common mistakes when drawing a business plan
- Provision of unrealistic assumptions/over-ambitious ✔
- Not being able to identify the potential risks/hiding risks ✔
- Provision of too much unnecessary information/leaving gaps/being too vague ✔
- Committing budget and cash flow errors/incomplete financials ✔
- No information on competitors/not highlighting competition ✔
- Use of incorrect format/poor writing/incomplete plan ✔
- Inadequate/poor research ✔
- Insufficient technical details ✔ (Any 3) (3)
2.5 Supply and demand of peaches
2.5.1 Line graph showing the supply and demand of peaches 
Criteria/rubric/marking guidelines
- Correct heading ✔
- X axis - correctly calibrated and labelled (Quantities) ✔
- Y axis - correctly calibrated and labelled (Price) ✔
- Correct unit (R and kg) ✔
- Line graph ✔
- Accuracy ✔ (6)
2.5.2 Determination of the equilibrium price
- R2,50 ✔ (1)
2.5.3 Situation when price is below the equilibrium price
- The quantity demanded is high ✔ and the quantity supplied is low ✔
OR - Quantity supplied is low ✔ and quantity demanded is high ✔ (2)
2.6 Linking statements to factors hampering marketing of products
2.6.1 Perishability ✔ (1)
2.6.2 Political situation ✔ (1)
2.6.3 Lack of control over production ✔ (1)
2.6.4 Bulkiness ✔ (1)
2.7 THREE requirements of a container for packaging
- It must be clean/dry/undamaged ✔
- Not import any foreign taste/odour to the product ✔
- It must be free from signs of fungal growth ✔
- It must be strong/rigid ✔ (Any 3) (3)
2.8 Type of consumers
2.8.1 Retailers ✔ (1)
2.8.2 Food processing companies/factories ✔ (1)
2.8.3 Exporters ✔ (1)
2.9 The law of demand
- The higher the price ✔ the less the people/consumers will demand the product ✔
OR - The lesser the price ✔ the more the people/consumers will buy the product ✔(2) [35]
QUESTION 3 : PRODUCTION FACTORS
3.1 Two groups of farmers
3.1.1 Factor of land addressed by the two scenarios
- Land availability/ area of production ✔ (1)
3.1.2 TWO benefits of the practices by Group B contributing to higher production
- Able to work on a large area faster✔
- Use of machinery is more effective ✔
- More cost effective to produce ✔
- Specialisation ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.1.3 TWO techniques for Group A that can improve production
- Use of scientific methods/technology ✔
- Consolidation of small units ✔ (2)
3.1.4 Economic characteristic negatively affected by monoculture and continuous cultivation
- Production potential of the land ✔ (1)
3.1.5 TWO functions of land as a production factor
- Provides food ✔
- Provides raw materials ✔
- Provides space ✔
- Source of raw minerals ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.2 Highly ethical and efficient work force
3.2.1 The type of permanent labour who operates an advanced tractor
- Skilled labour ✔ (1)
3.2.2 Indication of the expertise needed by the employee
- Technical/operational ✔ (1)
3.2.3 Act of misconduct
- Sleeping on duty ✔ (1)
3.2.4 Legislation that the employer would use to justify disciplinary steps
- Basic Conditions of Employment Act 75 of 1997 ✔ (1)
3.2.5 TWO problems related to farm labour
- Social/HIV and AIDS ✔
- Scarcity ✔
- Employers' concerns ✔
- Competition from industries/economic migrants ✔
- Lack of training/ education ✔
- Poor labour management ✔
- Safety ✔
- Poor working conditions ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.2.6 TWO actions an employer should take
- Provide incentives ✔
- Rewards for good work ✔
- Provide training/education ✔
- Improve working conditions ✔
- Improved living conditions ✔
- Mechanisation ✔
- Labour management ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.3 Management
3.3.1 Risk management strategy
- Diversification ✔ (1)
3.3.2 Reason for the management strategy
- There are a number of enterprises in one farm/agri-tourism ✔ (1)
3.3.3 TWO primary sources of risk in a farming business
- Technical ✔
- Market/price ✔
- Financial ✔
- Production ✔
- Legal ✔
- Human resources ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.3.4 General business management skills applied by the manager
- Co-ordination/organisational ✔ (1)
- Analytic skills ✔ (1)
- Interpersonal/communication ✔ (1)
3.3.5 Definition of strategic management
- Management that allows the business to anticipate ✔ and adapt to changes in the future ✔
OR - The process of developing strategies that allow a business to achieve its vision, mission and objectives ✔ and adapt to changing conditions ✔ (2)
3.4 Capital
3.4.1 Fixed capital
- Land ✔ (1)
3.4.2 TWO sources of capital
- Grant ✔
- Loan ✔ (2)
3.4.3 Problem of capital
- Scarcity ✔ (1)
3.4.4 Term of repayment
- Medium term/5 years ✔ (1)
3.4.5 Calculation of the profit made by the community in 5 years
- Turnover: R12 000 000 x 5 = R60 000 000 ✔
- Expenses: R4 000 000 x 5 = R20 000 000 ✔
- Interest: R2 000 000 x 5% = R100 000 ✔
- R2 000 000 + R100 000 = R2 100 000 ✔
- Turnover – expenses:
R60 000 000 – R20 000 000 – R2 100 000 = - Profit: R37 900 000 ✔ (5) [35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
4.1 Heterozygous pea plant (G) and a pure breed pea plant (g)
4.1.1 Genotype of each parent in the first crossing
- Parent 1 - Gg ✔
- Parent 2 - gg ✔ (2)
4.1.2 Punnett square determining the possible genotype of the offspring in the first crossing
Gametes | G | g ✔ |
g | Gg | gg ✔ |
g | Gg | gg |
Punnett square with gametes and offspring ✔
Marking Guideline
- Complete Punnett square with gametes and offspring ✔
- Correct gametes ✔
- Correct offspring ✔ (3)
4.1.3 Type of dominance in the cross
- Complete dominance ✔ (1)
4.1.4 Reason for the type of dominance
- 50% of the seeds are yellow (G) ✔ and 50% of the seeds are green (g) ✔
OR - No intermediate/new colour ✔ as seeds resemble their parents ✔ (2)
4.1.5 Calculation of the percentage of heterozygous offspring
- 2 x 100 ✔
4
= 50% ✔ (2)
4.2 Identification of the breeding system
4.2.1 B ✔ (1)
4.2.2 A ✔ (1)
4.2.3 D ✔ (1)
4.2.4 C ✔ (1)
4.2.5 A ✔ (1)
4.3 Variation
4.3.1 TWO genetic processes causing variation
- Mutations ✔
- Meiosis/crossing over ✔
- Recombination of genes ✔
- Fertilisation ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.3.2 TWO importance of variation
- Animals/plants with superior characteristics can be selected for breeding purposes ✔
- Helps to improve the progeny/offspring ✔
- Generate new varieties/ breeds/cultivars ✔
- Maintains biodiversity ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.3.3 Distinction between
Continuous variation
- Displays a complete range of quantitative characteristics ✔ (1)
Discontinuous variation
- Qualitative characteristics have a few clear cut/distinct forms/with no intermediate forms in between ✔ (1)
4.4 Selection
4.4.1 Group of cattle to be selected
- Group with a mass of 250 kg ✔ (1)
4.4.2 Reason
- It has a higher average mass/average mass higher than the herd ✔ (1)
4.4.3 Identification of the type of selection method
- Mass selection ✔ (1)
4.4.4 Explanation of this selection method
- Selection based on the individuals with superior characteristics ✔ within the group ✔ (2)
4.4.5 TWO other selection methods
- Family selection ✔
- Pedigree selection ✔
- Progeny selection ✔
- Breeding values/EBV/biometrics ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.5 GM
4.5.1 Identification of the year
- 2012/2013 ✔ (1)
4.5.2 Reason
- An increase in yield/from10,6 – 12t/ha✔ (1)
4.5.3 TWO advantages that Farmer B got from using GM maize
- Yields increased ✔
- Increase started from 2012 ✔ (2)
4.5.4 TWO important characteristics of GM maize crops
- Resistant to herbicides ✔
- Not affected by insecticides ✔
- Crops have lower water requirements ✔
- Better adapted to the environment/region ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.5.5 Reason for the resistance against the use of GM's
- Health risks ✔
- Environmental risks ✔
- Ethical/socio-economic concerns ✔ (Any 1) (1) [35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 D ✔✔
1.1.2 D ✔✔
1.1.3 C ✔✔
1.1.4 B ✔✔
1.1.5 C ✔✔
1.1.6 C ✔✔
1.1.7 A ✔✔
1.1.8 A ✔✔
1.1.9 B ✔✔
1.1.10 A/B ✔✔ (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 B only ✔✔
1.2.2 Both A and B ✔✔
1.2.3 A only ✔✔
1.2.4 None ✔✔
1.2.5 A only ✔✔ (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 Ptyalin/amylase ✔✔
1.3.2 External/ecto- parasites ✔✔
1.3.3 Bedding/litter ✔✔
1.3.4 Superovulation ✔✔
1.3.5 Mitochondria ✔✔ (5 x 2) (10)
1.4
1.4.1 Nitrogen/Protein ✔
1.4.2 Removal Certificate/Permit ✔
1.4.3 Splitting ✔
1.4.4 Mesoderm ✔
1.4.5 Testosterone ✔ (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: ANIMAL NUTRITION
2.1 Alimentary canal of a farm animal
2.1.1 Letter of the structure of cellulose digestion
- A ✔ (1)
2.1.2 Cellulose digesting enzyme
- Cellulase ✔ (1)
2.1.3 TWO requirements of the organisms in the part A
- Easily digestible carbohydrates
- Regular intake of food for fermentation ✔
- Sufficient mineral nutrients(Na/Cu/Co/P) ✔
- Anaerobic/oxygen free environment ✔
- Presence of CO2 ✔
- Sufficient nitrogen ✔
- Suitable pH/slightly acidic pH/pH of 5,5 to 6,5 ✔
- Warm environment/temperature of 38-420c ✔
- Continual elimination of end products ✔
- Osmotic condition/moist environment ✔ (Any 2) (2)
2.1.4 The type of digestion in part D
- Chemical/enzymatic digestion ✔ (1)
2.1.5 Reason for the answer
- Part D secrets digestive juices/enzymes ✔ (1)
2.2 Available animal feeds
2.2.1 Classification of FEED A and FEED C
- Feed A - Concentrate ✔ (1)
- Feed C - Roughage ✔ (1)
2.2.2 Letters recommended for each situation
(a) B ✔ (1)
(b) D ✔ (1)
(c) A ✔ (1)
(d) C ✔ (1)
2.2.3 Justification of better digestion of feed B when ground
- Ground feed/maize has smaller particles with an increased surface area ✔
- for more exposure to enzymes and better digestion ✔ (2)
2.3 Feed trial
2.3.1 Calculation of the digestibility co-efficient of hay
- = 11,5kg x 100 ✔
24kg
= 47,9 ✔ % ✔ (3)
2.3.2 Stage the hay was cut
- It was cut later in the season when it was old/matured ✔ (1)
2.3.3 Reason based on the calculated value
- Only 47,9% of the hay was digested and absorbed ✔
- The hay was hard/lignified/with a high crude fibre content/less/poorly/difficult to digest ✔ (2)
2.3.4 TWO supplementary substances to improve digestibility of hay ∙
- Non-protein nitrogen/NPN/urea/biuret ✔
- Molasses ✔
- Caustic soda ✔ (Any 2) (2)
2.4 Fodder flow plan
2.4.1 TWO months when feed was insufficient
- April ✔
- May ✔
- June ✔ (Any 2) (2)
2.4.2 TWO reasons
- The need is higher than the supply/there is a shortage ✔
- Supplementary feeding is provided ✔ (2)
2.4.3 Total quantity of the supplementary feed in May
- Supplementary feed(kg/animal) x number of days in May x number of animals
= 2 kg x 31 x 50 ✔
= 3 100 kg ✔
1 000
= 3,1 tons ✔ (3)
2.5 Bar graph showing the crude fibre and crude protein of the different feeds 
Criteria/rubric/marking guidelines
- Correct heading ✔
- Y axis - correctly calibrated and labelled (Quantities) ✔
- X axis - correctly calibrated and labelled (Feed) ✔
- Correct unit (%) ✔
- Bar graph ✔
- Accuracy ✔(6) [35]
QUESTION 3 ANIMAL PRODUCTION, PROTECTION AND CONTROL
3.1 Production systems
3.1.1 Identification of the TWO production systems represented by A and B
- A - Intensive production system ✔ (1)
- B - Extensive production system ✔ (1)
3.1.2 Comparison of the TWO production systems
(a) Method of feeding
- Intensive production system - feed is provided to animals ✔
- Extensive production system - animals graze/look for food ✔ (2)
(b) Space per production output
- Intensive production system - more production per area ✔
- Extensive production system - less production per area ✔ (2)
3.2 The feeding and temperature requirements at different stages
3.2.1 Main nutrient for broilers
- Proteins ✔ (1)
3.2.2 Importance of the nutrient element
- Need protein for muscle and tissue growth ✔
- Act as antibodies that provide immunity ✔
- Collagens support tendons, ligaments and a beak ✔
- Controls body fluid balance and muscle contraction ✔
- Repair worn out tissues ✔ (Any 1) (1)
3.2.3 Reason for the inclusion of carbohydrates in a finisher mash
- Need carbohydrates for fattening/rounding off ✔ (1)
3.2.4 The relationship between protein level, temperature requirements and the age
- The younger the broilers ✔ the higher the protein level of the feed ✔ and the higher the temperature requirement ✔
OR - The older the broilers ✔ the lower the protein level of the feed ✔ and the lower the temperature requirement ✔ (3)
3.3 Tools used for animal identification purposes
3.3.1 Branding iron ✔ (1)
3.3.2 Ear tag ✔ (1)
3.3.3 Smart neck band ✔ (1)
3.3.4 Tattoo pliers ✔ (1)
3.4 Handling facilities for specified operations
3.4.1 Identification of the facility
- Loading/off- loading ramp ✔ (1)
3.4.2 Use of the facility
- For loading/off-loading animals ✔ (1)
3.4.3 TWO design features of the facility
- High and strong walls ✔
- Width according to the type of animal ✔
- Angle not too steep ✔
- Not slippery ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.4.4 TWO forms of harm to an animal during the handling process ∙
- Physical/injuries ✔
- Stress/emotional ✔ (2)
3.5 Parasites in farm animals
3.5.1 The TWO parasites
- A - External parasite/ecto-parasite ✔ (1)
- B - Internal/endo-parasite ✔ (1)
3.5.2 Motivation from the diagram
- A - Larvae attaches itself onto the skin ✔ (1)
- B - Worms are swallowed and bore through the intestines into the liver ✔ (1)
3.5.3 Preventative measure against parasite B
- Avoid grazing in swampy areas/fencing off affected areas/removal of dung ✔
- Drinking spots should be kept dry ✔
- Rotational grazing ✔
- Breeding genetically resistant animals ✔
- Treat affected areas ✔
- Veld burning ✔
- Use of feeders ✔
- Provision of clean drinking water ✔
- Provision of good nutrition ✔
- Proper management of the breeding season/calving ✔ (Any 1) (1)
3.6 Animal diseases
3.6.1 Scientific term for animal health conditions
(a) Contagious/infectious diseases ✔ (1)
(b) Vector ✔ (1)
3.6.2 ONE bacterial disease that can be transmitted to the next animal
- Tuberculosis ✔
- Anthrax ✔ (Any 1) (1)
3.6.3 Role of the farmer
- Quarantine/isolation of sick animals ✔
- Regular inspections/monitoring for the presence of disease
- Vaccination/inoculation ✔
- Treatment of sick animals ✔
- Burning/burying carcass of infected animals ✔
- Report to the authorities ✔ (Any 1) (1)
3.6.4 TWO measures how farm workers can be exposed to animal diseases
- Exposure to/contact with infected animals ✔
- Use of unsterilized equipment ✔ (2)
3.6.5 TWO roles of the state in controlling the spread of infectious diseases
- Production of vaccines ✔
- Setting up quarantine areas/zones ✔
- Research ✔
- Publications ✔
- Import/export bans/control measures/movement permits ✔
- Veterinary services ✔ (Any 2) (2) [35]
QUESTION 4: ANIMAL REPRODUCTION
4.1 The diagram of a sperm cell
4.1.1 Identification of part A
- Acrosome ✔ (1)
4.1.2 The function of the part
(a) A - Facilitate penetration of the sperm cell into the ovum/protects the head of the sperm cell ✔ (1)
(b) B - Transmission of DNA/genetic material/information ✔ (1)
(c) D - Mobility/movement of the sperm cell ✔ (1)
4.1.3 Distinction between sperm cell and semen
- Sperm cell - Male gamete/reproductive cell for fertilisation ✔ (1)
- Semen - Mixture of sperm cells and the fluids from the accessory glands ✔ (1)
4.1.4 The female reproductive cell
- Ovum/egg cell/female gamete ✔ (1)
4.2 Foetus development in cattle
4.2.1 Identification of parts B and F
- B - Allantois ✔ (1)
- F - Umbilical cord ✔ (1)
4.2.2 The function of part D
- Protection for the foetus/shock absorber ✔
- Lubricates the birth canal ✔
- Regulates temperature around foetus✔
- Prevents dehydration✔ (Any 1) (1)
4.2.3 Conditions associated with pregnancy
- (a) Mummification ✔ (1)
- (b) Maceration ✔ (1)
- (c) Abortion ✔ (1)
- (d) Placenta retention ✔ (1)
4.3 Dairy farmer with 100 cows and one bull
4.3.1 Identification of the problem in this enterprise
- Bull: cow ratio not proportional/1 bull to 100 cows ✔
- The calving percentage is too low/conception rate problems ✔ (Any 1) (1)
4.3.2 Scientific technique that will result in a higher calving percentage Artificial insemination/AI ✔ (1)
4.3.3 Other method to improve the calving percentage
- Make use of more bulls/3–5 bulls ✔ (1)
4.3.4 Impact of nutrition on the fertility of bulls
- Underfeeding impacts negatively on spermatogenesis/sperm formation/volume/quality of semen ✔
- Overfeeding causes bulls to become fat/heavy/lazy reducing the ability to service cows(libido) ✔ (2)
4.3.5 TWO other reasons for this bull performing poorly
- Over exertion/exhaustion ✔
- Old age ✔
- Lack of libido ✔
- Conformational abnormalities ✔
- Inability to fertilise/low sperm count ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.4 Milk production of a dairy cow for one year
4.4.1 Term for the graph illustrated
- Lactation curve ✔ (1) .
4.4.2 Indication of the letter
- (a) H ✔ (1)
- (b) A ✔ (1)
- (c) B ✔ (1)
- (d) D ✔ (1)
4.4.3 Reasons for the drop in the milk production between point F and point G
- Illness/the cow was sick/disease ✔
- Injury ✔
- Adverse/bad environmental conditions ✔
- Malnutrition/over/under feeding ✔
- The cow is about to dry off ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.5 Oestrus in dairy cows
4.5.1 Definition of oestrus in dairy cows
- Period when non-pregnant cows show visible signs of oestrus ✔
- and will allow mating to take place ✔ (2)
4.5.2 Visible signs of oestrus in dairy cattle
- Mucus discharge from the vulva ✔
- Vulva is red/moist/swollen ✔
- Restless/bellows/excited ✔
- Feed/saliva on the back/hair is fluffed up ✔
- Feed intake decreases/loss of appetite ✔
- Milk production decreases ✔
- Sniffs the genitalia of other cows ✔
- Raises her head and curls her lips ✔
- Cows goes to the bull and allows mating✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.5.3 Cow in oestrus
- Cow A/B ✔ (1)
4.5.4 Oestrus
- (a) Oestrogen ✔(1)
- (b) 21 days ✔ (1)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT PRACTICES GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT PRACTICES
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
INSTRUCTION AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Read the questions carefully and answer only what is asked.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 A written plan that shows the future actions with regard to possible income and expenditures of a farming enterprise:
- Budget
- Trial balance
- Balance sheet
- Cash flow statement
1.1.2 The farm management component that involves the grouping of actions that will improve the productivity of a farming enterprise:
- Decision-making
- Coordination
- Organisation
- Control
1.1.3 The type of capital that a farmer uses to buy livestock and farming implements:
- Fixed capital
- Floating capital
- Movable capital
- Working capital
1.1.4 The return received by a farming enterprise after all operating expenses have been paid:
- Net farm income
- Farm profit
- Gross margin
- Variable cost
1.1.5 A written plan recording the production and financial decisions in a production enterprise:
- Business plan
- Budget
- Business advertisement
- Business image
1.1.6 The relative change in quantity demanded associated with a relative change in price.
- Inelastic demand
- Inelastic supply
- Demand elasticity
- Supply elasticity
1.1.7 The following does NOT affect an increase in local marketing costs:
- Packaging of food
- Export tax
- Processing of food
- Marketing service
1.1.8 The person who buys products from producers, processors and other marketing intermediaries for resale:
- Retailer
- Stockbroker
- Agent
- Wholesaler
1.1.9 The following marketing approach is used by cooperatives:
- Buy in bulk and sell in small scale
- Buy in small scale and sell in small scale
- Buy in small scale, combine produce with other cooperatives and sell in bulk
- Buy in bulk and sell in bulk
1.1.10 … is used for easier handling of agricultural products.
- Packaging
- Processing
- Standardisation
- Grading (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches a term in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–L) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.11 M.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.2.1 Employee |
|
(10 x 2) (20)
1.3 Give the CORRECT agricultural term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.3.11 Recording.
1.3.1 Credit required for the acquisition of movable capital, such as vehicles, equipment, breeding stock and machinery
1.3.2 The cost of labour or material which increases with every item produced or every service rendered
1.3.3 The process where the farmer ensures that the actual activities correspond with the production plan
1.3.4 An activity by farmers and processors to ensure that produce reaches every part of the country
1.3.5 The drive for behaviour that is caused by human characteristics, such as the quest for power, the need for the feeling of belonging or the desire for profit
1.3.6 The system where all the products produced are placed together and handled in bulk by the cooperative to sell the product
1.3.7 The costs that farm producers must incur from preparation of soils up to harvesting of the products
1.3.8 The function where a producer exchanges produce for capital
1.3.9 Starting a new business by innovative individuals who respond to opportunities in the industry
1.3.10 The entrepreneurial skills involving leadership, networking and teamwork (10 x 1) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: PHYSICAL AND FINANCIAL PLANNING
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 The diagram below represents soil depth in crop production.
2.1.1 Redraw the table below in the ANSWER BOOK to compare soil A and soil E with reference to the given criteria: (8)
CRITERIA | SOIL A | SOIL E |
Depth | ||
Water infiltration | ||
Drainage | ||
Water-holding capacity |
2.1.2 Choose between legumes and cereal crops and indicate which ONE will grow the best in:
- Soil A (1)
- Soil B (1)
2.2 Give FOUR reasons why livestock farmers prefer sweet veld over sour veld for grazing. (4)
2.3 Describe THREE disadvantages of an intensive farming system on soil as a result of the overuse of water and agrochemicals. (3)
2.4 Redraw the table below in the ANSWER BOOK to classify different types of pastures into artificial (planted) and natural pastures.
Types of pastures:
- Clover
- Grassland
- Legumes
- Perennial grasses
- Scrub
- Savannah (6)
ARTIFICIAL (PLANTED) PASTURE | NATURAL PASTURE |
2.5 Farmers lose farm workers because of ill health. The result is that the farmer has to employ and train new workers which means cost have to be incurred.
2.5.1 Explain THREE methods that a farmer can use to reduce the risk of losing income due to the ill health of farm workers. (3)
2.5.2 Name THREE items that must be included in the ill-health policy and programme of a farm business. (3)
2.6 Study the cartoon below and answer the following questions. 
2.6.1 Categorise the different types of capital mentioned in the cartoon above. (6)
2.6.2 Advise the farmer on how he/she can obtain extra money to purchase items needed on the farm. (1)
2.6.3 State THREE important requirements for a farm business to qualify for long-term credit. (3)
2.6.4 Briefly explain the difference between the following sources of capital:
- External sources (2)
- Internal sources (2)
2.7 Farmers should keep accurate farm records to enable them to manage the finances of the farm.
2.7.1 List FOUR prerequisites that enable the farm manager to compile the next Cash Flow Budget. (4)
2.7.2 Describe THREE valuable comparisons a farmer can make from the budget and the financial statement for the same period. (3) [50]
QUESTION 3: ENTREPRENEURSHIP, RECORDING, MARKETING, BUSINESS PLANNING AND ORGANISED AGRICULTURE
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1
A new small-scale farmer's labour force consists of seven permanent staff members. From time to time the farmer employs 20 seasonal workers. The farm manager must help with recordkeeping, especially for the labour force. |
Name FIVE labour-related records that need to be kept. (5)
3.2 List FOUR data items that are reflected in source documents required to complete the farm's financial accounts. (4)
3.3 Use the information on a vegetable enterprise below to complete the Income Statement for the year ending 31 December 2017.
Soil preparation R10 000, harvesting R6 000, casual labour R8 000, seeds R6 500, fertiliser R10 000, disease, pest and weed control R10 000, repairs and maintenance R15 500, packaging and marketing R4 000, sale of carrots R11 500, sale of onions R28 000, sale of tomatoes R20 000, sale of cabbages R9 400 |
3.3.1 Draw up an Income Statement using the headings in the table below. Write the information given above in the appropriate columns and calculate the totals.
INCOME STATEMENT FOR YEAR ENDING 31 DECEMBER 2017 (4)
INCOME | VALUE (Rand) | EXPENDITURES | VALUE (Rand) |
TOTAL | TOTAL |
3.3.2 Calculate the profit or loss for the year ending 31 December 2017. Indicate whether it was a profit or loss. (2)
3.4 Define the following agricultural terms as they are used in financial management:
3.4.1 Break-even point (1)
3.4.2 Debtor (1)
3.5 The Balance Sheet is a measure of what a business is worth and where the total assets are equal to the total liabilities.
A crop farmer had the following balances in his/her books on 31 August 2017:
ITEMS | AMOUNTS |
Cash | R2 000 |
Capital | R115 000 |
Land | R100 000 |
Bank overdraft | R15 000 |
Stocks | R20 000 |
Debtors | R13 000 |
Mortgage loan | R120 000 |
Implements | R25 000 |
Second-hand tractor | R50 000 |
Buildings | R50 000 |
Creditors | R10 000 |
Use the data in the financial records above to fill in the missing information in the balance sheet below. Write down the information next to the question number (3.5.1–3.5.6) in the ANSWER BOOK. (6)
ASSETS | VALUE | LIABILITIES | VALUE |
Fixed assets | Capital | R115 000 | |
3.5.1 | |||
Buildings | R50 000 | Mortgage loan | R120 000 |
3.5.2 | |||
Implements | R25 000 | ||
Current assets | Current liabilities | ||
R20 000 | 3.5.5 | ||
3.5.3 | Bank overdraft | R15 000 | |
3.5.4 | |||
Total | R260 000 | Total | 3.5.6 |
3.6 A strategic marketing plan is part of a business plan for an agricultural enterprise. It integrates all business activities and resources logically to meet customer needs and to generate profit. To eliminate mistakes during the marketing process it is important to acquire the correct information.
3.6.1 Give reasons why it is important to compile a strategic marketing plan for an agricultural enterprise. (2)
3.6.2 Compile a list of questions that you would use to collect information for a strategic marketing plan. (5)
3.7 A business plan is important to direct a new business.
3.7.1 Describe FOUR basic features of a business plan in relation to the product. (4)
3.7.2 Name FOUR aspects that a farmer will consider with regard to the place to sell his/her agricultural products. (4)
3.8 The table below represents the supply and demand of a crop.
PRICE (R/kg) | QUANTITY DEMANDED PER WEEK (kg) | QUANTITY SUPPLIED PER WEEK (kg) |
4 | 600 | - |
8 | 500 | 100 |
12 | 400 | 200 |
16 | 300 | 300 |
20 | 200 | 400 |
3.8.1 Draw a line graph of the data in the table above that represents the supply and demand for this crop. (5)
3.8.2 Indicate the price of the product at the point of market equilibrium. (1)
3.8.3 Briefly discuss TWO possible reasons for the shortage of the product in the market at specific times. (2)
3.8.4 Briefly explain the TWO strategies the farmer could use to deal with product shortages at certain times as mentioned in QUESTION 3.8.3. (4) [50]
QUESTION 4: HARVESTING, PROCESSING, MANAGEMENT AND AGRITOURISM
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 The planning stage is critical for the success of the harvest.
4.1.1 List FOUR factors that a farmer should take into consideration during the harvesting of a crop. (4)
4.1.2 Describe TWO basic principles of post-harvest handling of a crop. (2)
4.2
There is a variety of storage methods for different agricultural crops. |
4.2.1 Identify the storage facility shown in the picture above. (1)
4.2.2 State THREE environmental factors that can be controlled in the storage facility mentioned in QUESTION 4.2.1. (3)
4.3 Redraw the table below in the ANSWER BOOK. To demonstrate your understanding of the concepts of sorting and grading, place the statements listed below under the correct headings in the table.
- Removal of undesirable additional materials, for example leaves or stones, at first sight
- The assessment of a number of characteristics of a product to obtain an indication of its overall quality
- An expensive process due to the long procedure of setting standards
- Separation of raw materials into categories on the basis of shape, size, weight, image and colour
- Segregating grains, fruit or vegetables into marketable and unmarketable products
- Requires skilled personnel (6)
SORTING | GRADING |
4.4 The demand for processed agricultural products is higher than for raw agricultural products.
4.4.1 State THREE fermentation processes that can be used to preserve products. (3)
4.4.2 Cooling is one of the processes to preserve agricultural products. Explain the effect of moisture in the cooling process. (2)
4.5 A schematic presentation of an agribusiness chain can be drawn from the primary agricultural sector to the secondary agricultural sector and to the consumer.
4.5.1 Classify the following into the correct agricultural sector:
meat processing; crop farming; animal production; butchery; supermarket; fresh produce market |
Use only ONE enterprise as an example to draw the schematic presentation in your ANSWER BOOK using the following format:  (3)
(3)
4.5.2 State THREE tertiary-sector inputs that assist the primary and secondary sector in handling and marketing produce to the consumer. (3)
4.6 State THREE main functions of packaging materials in the handling of perishable products. (3)
4.7 Name TWO factors that will indicate the viability of value-adding of products on a farm. (2)
Modern tourists do not want to lounge around and read books when they are on holiday; they want experiences. The Rooibos Route was launched by two creative sisters, a team of hardworking people, a website and the tourism industry. [Adapted from Rooibosroete/Rooibos Route] |
4.8
4.8.1 Define the term product route as it is used in agritourism. (2)
4.8.2 Identify TWO activities in the scenario that are of interest to tourists. (2)
4.8.3 Give THREE aspects that illustrate the educational potential of the agritourism venture above. (3)
4.8.4 Identify THREE entrepreneurial characteristics displayed in the scenario above. (3)
4.9 In modern farming ventures, the management of a farm has become the main determinant for a successful and economically viable enterprise.
4.9.1 Briefly discuss FOUR roles of the farm manager in maintaining the financial viability of an agricultural enterprise to achieve financial sustainability. (4)
4.9.2 Name the FOUR basic types of coordination. (4) [50]
TOTAL SECTION B: 150
GRAND TOTAL: 200
 (4)
(4)