Adele
BUSINESS STUDIES GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2018
BUSINESS STUDIES
GRADE 12
AMENDED SCE PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
MAY/JUNE 2018
NOTES TO MARKERS
PREAMBLE
|
- For marking and moderation purposes, the following colours are recommended:
Marker: Red
Senior Marker: Green
Deputy Chief Marker: Brown/Black/Blue
Chief Marker: Pink
Internal Moderator: Orange
DBE Moderator: Turquoise - Candidates' responses must be in full sentences for SECTIONS B and C. However, this would depend on the nature of the question.
- A comprehensive marking guidelines has been provided but this is by no means exhaustive. Due consideration should be given to an answer that is correct, but:
- Uses a different expression from that which appears in the marking guidelines
- Comes from another source
- Original
- A different approach is used
NOTE: There is only ONE correct answer in SECTION A.
- Take note of other relevant answers provided by candidates and allocate marks accordingly. (In cases where the answer is unclear or indicates some understanding, part-marks should be awarded, for example, one mark instead of the maximum of two marks.)
- The word 'Sub-max' is used to facilitate the allocation of marks within a question or sub-question.
- The purpose of circling marks (guided by 'max' in the breakdown of marks) on the right-hand side is to ensure consistency and accuracy in the marking of scripts as well as for calculation purposes.
- Subtotals to questions must be written in the right-hand margin. Circle the subtotals as indicated by the allocation of marks. This must be guided by 'max' in memo. Only the total for each question should appear in the left-hand margin next to the appropriate question number.
- In an indirect question, the theory as well as the response must be relevant and related to the question.
- Incorrect numbering of answers to questions or sub-questions in SECTION A and B will be severely penalised. Therefore, correct numbering is strongly recommended in all sections.
- No additional credit must be given for repetition of facts. Indicate with a 'R'.
- Note that no marks will be awarded for indicating Yes/No in evaluation type questions requiring substantiation or motivation. (Applicable to SECTIONS B and C)
- The differentiation between 'evaluate' and 'critically evaluate' can be explained as follows:
12.1 When 'evaluate' is used, candidates are expected to respond in either a positive/negative manner or take a neutral (positive and negative) stance, e.g. Positive: 'COIDA eliminates time and costs spent√ on lengthy civil court proceedings.'√
12.2 When 'critically evaluate' is used, candidates are expected to respond in either a positive/negative manner or take a neutral (positive and negative) stance. In this instance candidates are also expected to support their responses with more depth, e.g. 'COIDA eliminates time and costs spent√ on lengthy civil court proceedings√, because the employer will not be liable for compensation to the employee for injuries sustained during working hours as long as it can be proved that the business was not negligent.'√
NOTE: 1. The above could apply to 'analyse' as well.
2. Note the placing of the tick (√) in the allocation of marks. - The allocation of marks must be informed by the nature of the question, cognitive verb used, mark allocation in the marking guidelines and the context of each question.
Cognitive verbs, such as:
13.1 Advise, name, state, mention, outline, motivate, recommend, suggest, (list not exhaustive) do not usually require much depth in candidates' responses. Therefore, the mark allocation for each statement/answer appears at the end.
13.2 Describe, explain, discuss, elaborate, compare, distinguish, differentiate, justify, devise, analyse, evaluate, critically evaluate (list not exhaustive) require a greater depth of understanding, application and reasoning. Therefore, the marks must be allocated more objectively to ensure that assessing is conducted according to established norms so that uniformity, consistency and fairness are achieved. - Mark only the FIRST answer where candidates offer more than one answer for SECTION B and C questions that require one answer.
- SECTION B
15.1 If, for example, FIVE facts are required, mark the candidate's FIRST FIVE responses and ignore the rest of the responses. Indicate by drawing a line across the unmarked portion or use the word 'Cancel'.
NOTE: This applies only to questions where the number of facts is specified.
15.2 If two or more facts are written in one sentence, award the candidate FULL credit. Point 15.1 above still applies.
15.3 If candidates are required to provide their own examples/views, brainstorm this at the marking centre to finalise alternative answers.
15.4 Use of the cognitive verbs and allocation of marks:
15.4.1 If the number of facts are specified, questions that require candidates to 'describe/discuss/explain' may be marked as follows:- Fact 2 marks (or as indicated in the marking guidelines)
- Explanation 1 mark
The 'fact' and 'explanation' are given separately in the marking guidelines to facilitate mark allocation.
15.4.2 If the number of facts required is not specified, the allocation of marks must be informed by the nature of the question and the maximum mark allocated in the marking guidelines.
15.5 ONE mark may be awarded for answers that are easy to recall, requires one word answers or is quoted directly from a scenario/case study. This applies to SECTIONS B and C in particular (where applicable).
- SECTION C
16.1 The breakdown of the mark allocation for the essays is as follows:Introduction
Maximum:
32
Content
Conclusion
Insight
8
TOTAL
40
16.2 Insight consists of the following components:
Layout/Structure
Is there an introduction, a body and a conclusion?
2
Analysis and
interpretation
Is the candidate able to break down the question into headings/sub-headings/interpret it correctly to show understanding of what is being asked?
Marks to be allocated using this guide:
All headings addressed: 1 (One 'A') Interpretation (16 to 32 marks): 1 (One 'A')2
Synthesis
Are there relevant decisions/facts/responses made based on the questions?
Marks to be allocated using this guide:No relevant facts: 0 (Two '-S')
Some relevant facts: 1 (One '-S')
Only relevant facts: 2 (No '-S')Option 1: Where a candidate answers 50% or more of the question with only relevant facts: No'-S' appears in the relevant margin. Award a maximum of TWO (2) marks for synthesis.
Option 2: Where a candidate answers less than 50% of the question with only OR some relevant facts; ONE'-S' appears in the left margin.
Award a maximum of ONE (1) mark for synthesis.
Option 3: Where a candidate answers less than 50% of the question with no relevant facts; two'-S' appear in the left margin. Award a ZERO mark for synthesis.2
Originality
Is there evidence of examples, recent information, current trends and developments?
2
TOTAL FOR INSIGHT:
TOTAL MARKS FOR FACTS:
TOTAL MARKS FOR ESSAY (8 + 32):8
32
40NOTE:
1. No marks will be awarded for contents repeated from the introduction and conclusion.
2. The candidate forfeits marks for layout if the words INTRODUCTION and CONCLUSION are not stated.
3. No marks will be allocated for layout, if the headings INTRODUCTION and CONCLUSION are not supported by an explanation.
16.3 Indicate insight in the left-hand margin with a symbol e.g. ('L, A,-S and/or O').
16.4 The breakdown of marks is indicated at the end of the suggested answer/ marking guidelines to each question.
16.5 Mark all relevant facts until the SUB MAX/MAX mark in a subsection has been attained. Write SUB MAX/MAX after maximum marks have been obtained.
16.6 At the end of each essay indicate the allocation of marks for facts and marks for insight as follows:
L – Layout, A – Analysis, S – Synthesis, O – Originality as in the table below.CONTENT
MARKS
Facts
32(max.)
L
2
A
2
S
2
O
2
TOTAL
40
16.7 When awarding marks for facts, take note of the sub-maxima indicated, especially if candidates do not make use of the same subheadings. Remember, headings and subheadings are encouraged and contribute to insight (structuring/logical flow/sequencing) and indicate clarity of thought.
(See MARK BREAKDOWN at the end of each question.)
16.8 If the candidate identifies/interprets the question INCORRECTLY, then he/she may still obtain marks for layout.
16.9 If a different approach is used by candidates, ensure that the answers are assessed according to the mark allocation/subheadings as indicated in the marking guidelines.
16.10
16.10.1 Award TWO marks for complete sentences. Award ONE mark for phrases, incomplete sentences and vague answers.
16.10.2 Where candidates give complete sentences, the ticks (√) will be separated and indicated next to each fact, e.g. 'Product development is a growth strategy√, where businesses aim to introduce new products into existing markets.'√
This will be informed by the nature and context of the question, as well as the cognitive verb used.
16.11 With effect from November 2017, the maximum of TWO (2) marks for facts shown as headings in the memo, will not necessarily apply to each question. This would also depend on the nature of the question.
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 B√√
1.1.2 A√√
1.1.3 C√√
1.1.4 D√√
1.1.5 D√√
1.1.6 B√√
1.1.7 C√√
1.1.8 C√√
1.1.9 B√√
1.1.10 D√√ (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 specification√√
1.2.2 dividend√√
1.2.3 debenture holders√√
1.2.4 Jungian√√
1.2.5 administration√√ (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 H√√
1.3.2 J√√
1.3.3 G√√
1.3.4 A √√
1.3.5 F√√ (5 x 2) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 40
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS
QUESTION 1 | MARKS |
1.1 | 20 |
1.2 | 10 |
1.3 | 10 |
TOTAL | 40 |
SECTION B
Mark ONLY the FIRST THREE (3) questions in this section.
QUESTION 2: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS
2.1 Porter’s Five Forces model
- Threat of substitution/Substitutes√
- Bargaining power of buyers√
- Threat/Barriers to new entry to the market√
- Power of suppliers√
- Competitive rivalry√
NOTE: Mark the first FOUR (4) only. (4 x 1) (4)
2.2 Role of SETAs
- Develop skills plans in line with the National Skills Development Strategy. √√
- Draw up skills development plans for their specific economic sectors. √√
- Approve workplace skills plans and annual training reports. √√
- Allocate grants to employers, education and training providers. √√
- Pay out grants to companies that are complying with the requirements of the Skills Development Act. √√
- Monitor/Evaluate the actual training by service providers. √√
- Promote and establishes learnerships. √√
- Register learnership agreements/learning programmes. √√
- Provide training material/programmes for skills development facilitators. √√
- Provide accreditation for skills development facilitators. √√
- Oversee training in different sectors of the South African economy. √√
- Promote learnerships and learning programmes by identifying suitable workplaces for practical work experience. √√
- Collect levies and pay out grants as required. √√
- Report to the Director General. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to the role of SETAs in supporting the Skills Development Act.
Max (10)
2.3 BBBEE pillars
2.3.1 Supplier development/Enterprise and Supplier development/Preferential procurement√√
2.3.2 Social responsibility/Socio economic development√√
2.3.3 Skills development√√
2.3.4 Management/Employment Equity/Management control√√
2.3.5 Ownership√√ (10)
2.4 Distinction between product development and market development
PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT | MARKET DEVELOPMENT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sub max (4) | Sub max (4) |
NOTE:
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format.
- The distinction must be clear.
- Award a maximum of FOUR (4) marks if the distinction is not clear/Mark either product development or market development. Max (8)
2.5 Legislation
2.5.1 Compensation for Occupational Injuries and Disease Act, 1997 (Act 61 of 1997)/ COIDA. √√ (2)
2.5.2 Negative impact of COIDA on MGM/businesses
- Claiming processes/procedures√ can be time consuming for MGM. √
- Processes/Procedures required by this Act may be costly√ as paperwork places an extra administrative burden on MGM/businesses. √
- MGM/Employer has to register all their workers/make annual contributions to COIDA√, which may result in cash flow problems. √
- MGM/Employer may be forced to pay heavy penalties√ if they are found guilty of negligence/not enforcing safety measures. √
- Workers who are temporarily/permanently employed in foreign countries√ are not covered. √
- Domestic/Military workers√ are not covered. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact of COIDA on MGM/businesses.
NOTE: Accept relevant facts, if COIDA was incorrectly identified as an answer in QUESTION 2.5.1. Max (8)
2.6 Business environment
2.6.1 Secondary sector. √ (1)
2.6.2
CHALLENGE | BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT |
(a) SEE employees are regularly absent from work√ Sub max (1) | Micro√√ Sub max (2) |
(b) They buy their raw material from Early Bird Maize Farm which is out of stock sometimes. √ Sub max (1) | Market√√ Sub max (2) |
(c) The local government has instructed the management of SEE to register their products with the South African Bureau of Standards. √ Sub max (1) | Macro√√ Sub max (2) |
NOTE:
- Mark the first challenge for each environment only.
- If the business environment is not linked to the challenge, mark the challenge only.
- Allocate full marks for business environment even if the challenge is incomplete.
Max (9)
2.7 Impact of NCA on businesses
Positives/Advantages
- The whole credit process is transparent√ e.g. both businesses and customers know their responsibilities. √
- Lower bad debts√ resulting in better cash flow. √
- Protects businesses√ against non-paying consumers. √
- Increases cash sales√ because businesses only grant credit to qualifying customers/more customers are buying in cash. √
- Stamps out reckless lending√ and prevents businesses from bankruptcy. √
- Businesses do thorough credit checks√ and receive up-to-date documentation from the consumer as proof that they can afford the repayment. √
- Leads to more customers√ through credit sales as they are now protected from abuse. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the positive impact/advantages of the NCA on businesses.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- Business can no longer √ carry out credit marketing.√
- The paperwork and administrative process required by the Act√ are costly and time consuming.√
- The business needs to appoint additional staff√ to deal with the extra administration.√
- Should the credit agreement be declared reckless√ the business can forfeit the outstanding debt and the goods.√
- Businesses that are official credit providers√, must submit a compliance report every year.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact/disadvantages of the NCA on businesses.
Max (8)
[60]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS
QUESTION 2 | MARKS |
2.1 | 4 |
2.2 | 10 |
2.3 | 10 |
2.4 | 8 |
2.5.1 | 2 |
2.5.2 | 8 |
2.6.1 | 1 |
2.6.2 | 9 |
2.7 | 8 |
TOTAL | 60 |
QUESTION 3: BUSINESS VENTURES
3.1 Types of UIF benefits
- Unemployment√
- Maternity√
- Sick/Illness/Disability√
- Adoption√
- Dependants√
- Any other relevant answer related to types of UIF benefits.
NOTE: Mark the first FOUR (4) only. (4 x 1) (4)
3.2 Types of preference shares
3.2.1 Participating√√ (2)
3.2.2 Cumulative√√ (2)
3.3 Other types of preference shares
- Ordinary preference shares√√
- Non-cumulative√√
- Redeemable√√
- Non-redeemable√√
- Non-participating√√
- Convertible√√
- Non-convertible√√
NOTE: 1. Mark the first THREE (3) only.
2. Do not award marks for responses given in QUESTION 3.2. (3 x 2) (6)
3.4 Functions of the JSE
- Gives opportunities to financial institutions such as insurance companies√ to invest their funds in shares. √
- Serves as a barometer/indicator√ of economic conditions in South Africa. √
- Keeps investors informed on share prices√ by publishing the share prices daily. √
- Acts as a link√ between investors and public companies. √
- Shares are valued√ and assessed by experts. √
- Small investors are invited to take part in the economy of the country√ through the buying of shares. √
- Venture capital market√ is made possible. √
- Orderly market for securities√ serves as a disciplined market for securities. √
- Encourages√ new investments. √
- Mobilises the funds√ of insurance companies and other institutions. √
- Raises √ primary capital. √
- Regulates market√ for dealing with shares. √
- Plans, researches and advises√ on investment possibilities. √
- Ensures that the market√ operates in a transparent manner. √
- Provides protection√ for investors. √
- Encourages short-term√ investment. √
- Facilitates electronic trading√ of shares/STRATE. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the functions of the Johannesburg Securities Exchange (JSE.)
Max (8)
3.5 Forms of ownership
3.5.1 Partnership√√ (2)
Motivation
- Zama and Quinton are qualified lawyers who have started a business, called Z and Q Attorneys, which lacks continuity. √ (1)
NOTE: Do not award marks for the motivation, if the form of ownership was incorrectly identified. Max (3)
3.5.2 Success factors of a partnership and personal liability company
CRITERIA | PARTNERSHIP | PERSONAL LIABILITY COMPANY |
Management |
|
|
|
| |
| ||
Any other relevant answer related to management as a success factor. | ||
Sub max (2) | Sub max (2) | |
Taxation |
|
|
|
| |
| ||
Any other relevant answer related to taxation as a success factor. | ||
Sub max (2) | Sub max (2) | |
Division of profits |
|
|
|
| |
Any other relevant answer related to division of profits as a success factor. | ||
Sub max (2) | Sub max (2) | |
NOTE:
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format.
- Consider similarities if the partnership was incorrectly identified. Max (12)
3.6 Transformational leadership theory
- Suitable for a dynamic environment√, where change could be drastic. √
- The passion/vision/personality of leaders inspire followers√ to change their expectations/perceptions/motivation to work towards a common goal. √
- Strategic thinking leaders develop a long term vision for the organisation√ and sell it to subordinates/employees. √
- Leaders have the trust/respect/admiration√ of their followers/subordinates. √
- Promotes intellectual stimulation/creative thinking/problem solving√ which result in the growth/development/success of the business. √
- Followers are coached/led/mentored/emotionally supported through transformation/change√ so that they can share their ideas freely. √
- Encourages followers√ to explore/try new things/opportunities. √
- Leaders lead by example√ and make workers interested in their work. √
- Leaders have strong, charismatic personalities√ and are very good at motivating staff to achieve results. √
- Enable employees to take greater ownership for their work√ and to know their strengths and weaknesses. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the transformational leadership theory.
NOTE: Award marks if examples demonstrate understanding of the leadership theory which could be integrated in the answer.
Max (6)
3.7.1 Ways in which Ayisha responded to questions at the end of her presentation
- At the end of her presentation she ensured that no member of the audience dominated the discussion. √
- She apologised for making an error in her presentation. √
- She acknowledged good questions. √
NOTE:
- Mark the first THREE (3) only.
- Only allocate marks for responses that are quoted from the scenario. (3 x 1) (3)
3.7.2 Other ways to respond to questions after a presentation
- Ensure that you understand each question/what is being said. √√
- Comment/Rephrase questions if uncertain, before responding. √√
- Listen carefully to each question/Think carefully before responding. √√
- Address questions and not the person. √√
- Remain professional/polite/calm/open/non-aggressive. √√
- Do not get involved in a debate/argument. √√
- Avoid answering difficult questions when the answer is not known. √√
- Address the whole audience and not only the person asking the question. √√
- Promise to follow up on answers you do not know/unsure about. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to other ways to respond to questions after a presentation.
NOTE: Do not allocate marks for responses quoted in QUESTION 3.7.1. Max (8)
3.8 Investment factors
3.8.1 Inflation rate
- People are affected by a high inflation rate√, because their money/purchasing power decreases. √
- The return on investment√ should be higher than the inflation rate. √
- Inflation has a positive effect on some investments√ such as property/shares where the income will increase as inflation increases. √
- Any other relevant answer related to inflation rate as a factor that must be considered when making investment decisions. Max (2)
3.8.2 Investment period
- The investment period can be short, medium and/or long term√ depending on the investors’ needs. √
- Short term investments enable investors to access their money√ on a short period if needed. √
- The longer the investment period√ the higher the returns. √
- Any other relevant answer related to investment period as a factor that must be considered when making investment decisions. Max (2)
3.8.3 Return on investment
- There is a direct link√ between risk and return. √
- The return should be expressed as√ net after-tax gains on the investment. √
- Returns can be in the form of capital gains√ where the asset appreciates in value. √
- The net after-tax return should be higher√ than the inflation rate. √
- High risk investments√ yield higher returns. √
- Any other relevant answer related to return on investment as a factor that must be considered when making investment decisions. Max (2)
[60]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS
QUESTION 3 | MARKS |
3.1 | 4 |
3.2.1 | 2 |
3.2.2 | 2 |
3.3 | 6 |
3.4 | 8 |
3.5.1 | 3 |
3.5.2 | 12 |
3.6 | 6 |
3.7.1 | 3 |
3.7.2 | 8 |
3.8.1 | 2 |
3.8.2 | 2 |
3.8.3 | 2 |
TOTAL | 60 |
QUESTION 4: BUSINESS ROLES
4.1 King Code principles
- Transparency√
- Accountability√
- Responsibility√
NOTE: Mark the first THREE (3) only. (3 x 1) (3)
4.2 Causes of conflict in the workplace
- Differences in backgrounds/cultures/values/beliefs/language√
- Limited business resources√
- Different goals/objectives for group/individuals√
- Personality differences between group/individuals√
- Different opinions√
- Unfair workload√
- Ill-managed stress√
- Unrealistic expectations√
- Poor organisation/leadership/administrative procedures and systems√
- Confusion about scheduling/deadlines√
- Ignoring rules/procedures√
- Misconduct/Unacceptable behaviour√
- High/Intense competition/Competitiveness√
- Poor communication√
- Unclear responsibilities√
- Distracted by personal objectives√
- Constant changes in the workplace√
- Unfair treatment of workers/Favouritism by management/Discrimination√
- Lack of trust amongst workers√
- Any other relevant answer related to causes of conflict in the workplace.
NOTE: Mark the first THREE (3) only. (3 x 1) (3)
4.3 Diversity issues
4.3.1 Culture/Religion√√
4.3.2 Age√√
4.3.3 Disability√√
4.3.4 Language√√ Max (8)
4.4 Differences between CSR and CSI
CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY (CSR) | CORPORATE SOCIAL INVESTMENT (CSI) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sub max (2) |
Sub max (2) |
NOTE:
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format.
- The differences must be clear.
- Award a maximum of TWO (2) marks if the differences are not clear/Mark either CSR or CSI.
Max (4)
4.5 Stages of team development
4.5.1 Forming√√ (2)
Motivation`
- They were comfortable with each other during their first meeting. √ (1)
NOTE: Do not award mark for motivation if the stage of team development was incorrectly identified. Max (3)
4.5.2 Other stages of teamwork
Storming stage√√
- Teams go through a period of unease/conflict after formation. √
- Different ideas from team members will compete for consideration. √
- Team members open up to each other and confront each other's ideas/ perspectives. √
- Tension/Struggle/Arguments occur and upset team members/There may be power struggles for the position of the team leader. √
- In some instances, storming can be resolved quickly, in others, the team never leaves this stage. √
- Many teams fail during this stage as they are not focused on their task. √
- This phase can become destructive to the team/will lower motivation if allowed to get out of control. √
- This stage is necessary/important for the growth of the team. √
- Some team members tolerate each other to survive this stage. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the storming stage of team development.
Stage (2)
Explanation (1)
Sub max (3)
Norming stage/Settling/Reconciliation√√
- Team members form agreement and consensus. √
- Roles and responsibilities are clear and accepted. √
- Processes/Working style/Respect develops. √
- Team members have the ambition to work for the success of the team's goals. √
- Conflict may occur, but commitment and unity is strong. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the norming/settling/reconciliation stage of team development.
Stage (2)
Explanation (1)
Sub max (3)
Performing stage/Working as a team towards a goal√√
- Team members are aware of strategies and aims of the team. √
- They have direction without interference from the leader. √
- Processes and structures are set. √
- Leaders delegate and oversee the processes and procedures. √
- All members are now competent, autonomous and able to handle the decision making process without supervision. √
- Differences among members are appreciated and used to enhance the team's performance. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the performing stage/working as a team towards a goal of team development.
Stage (2)
Explanation (1)
Sub max (3)
Adjourning/Mourning stage√√
- The focus is on the completion of the task/ending the project. √
- Breaking up the team may be traumatic as team members may find it difficult to perform as individuals once again. √
- All tasks need to be completed before the team finally dissolves. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the adjourning/mourning stage of team development.
Stage (2)
Explanation (1)
Sub max (3)
NOTE: Mark the first THREE (3) only.
Max (9)
4.5.3 Implications of equality, respect and dignity on businesses
- Businesses/Team leaders should treat all their employees equally, regardless of their race/colour/age/gender/disability, √√ etc.
- All workers should have access to equal opportunities/positions/resources. √√
- Employers and employees need to comply with legislation with regard to equal opportunities/human rights in the workplace. √√
- Businesses should develop equity programmes/promote strategies to ensure that all employees are treated equally regardless of status/rank/power. √√
- Mission statement should include values of equality/respect. √√
- Training/Information/Business policies should include issues such as diversity/ discrimination/harassment. √√
- Employers/Team leaders should respond swiftly and fairly to reported incidents of discrimination in the workplace. √√
- Ensure that employees work in a work environment that is conducive to safety/ fairness/free from embarrassment. √√
- Orders/Tasks should be given respectfully and allow the recipient/employee to have a say in the manner in which the task should be performed. √√
- Treat workers with respect/dignity by recognising work well done/the value of human capital. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to the implication of equality, respect and dignity on businesses/team leaders.
Max (6)
4.6 Procedure for dealing with grievance in the workplace
- An aggrieved employee must verbally report the incident/grievance to his/her supervisor/manager√, who needs to resolve the issue within 3 to 5 working days.√
- Should the employee and supervisor not be able to resolve the grievance√, the employee may take it to the next level of management. √
- The employee may move to a more formal process√ where the grievance must be lodged in writing/completes a business grievance form. √
- He/She must receive a written reply√ in response to the written grievance. √
- A grievance hearing/meeting√ must be held with all relevant parties present. √
- Minutes of the meeting must be recorded√ and any resolution passed must be recorded on the formal grievance form. √
- Should the employee not be satisfied√, then he/she could refer the matter to the highest level of management. √
- Top management should organise a meeting with all relevant parties.
- Minutes of this meeting should be filed/recorded√ and the outcome/decision must be recorded on the formal grievance form. √
- Should the employee still not be satisfied, he/she may refer the matter to the CCMA√ who will make a final decision on the matter. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the correct procedure to deal with grievances in the workplace.
NOTE: The procedure may be in any order.
Max (8)
4.7 Ways of contributing to the wellbeing of employees
- Businesses should improve the general quality of life of employees, e.g. pay fair wages/skills development√√, etc.
- Start a nutritional programme so that employees may enjoy at least one meal per day to keep them healthy. √√
- Allow staff to use some working time to get involved/participate in projects of their choice. √√
- Provide transport to employees who work unusually long hours. √√
- Establish coaching/mentoring programmes for junior employees. √√
- Conduct team-building sessions to improve employees' morale. √√
- Encourage employees to attend capacity-building workshops/training/staff development/team-development programmes. √√
- Offer counselling sessions to employees with personal/emotional challenges. √√
- Working conditions should include safety/medical/canteen facilities/benefits like leave, retirement√√, etc.
- Pay fair bonuses based on the earnings/returns of the business. √√
- Allow for employees' participation in decision making. √√
- Provide recreational facilities for employees. √√
- Make annual assessment by a medical doctor/practitioner available. √√
- Offer financial support in the case of any hardship caused by unforeseen personal costs, e.g. medical costs. √√
- Allow for flexible working hours to enhance productivity. √√
- Offer support programmes to employees infected/affected by HIV/Aids. √√
- Any other relevant recommendation related to ways in which businesses can contribute to the wellbeing of their employees.
Max (8)
4.8 Strategies to deal with unethical business practices
4.8.1 Sexual harassment
- Implement internal complaints and disciplinary procedures. √√
- Educate employers on sexual harassment matters. √√
- Formulate a policy regarding sexual harassment. √√
- Create a good working environment where all employees' rights and dignity are respected. √√
- Internal investigation should be made in order to determine the seriousness of the harassment. √√
- Serious cases/matters on sexual harassment should be reported to the appropriate institutions such as the South African Police Services (SAPS). √√
- Ensure compliance with the law/business code of conduct. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to strategies to deal with sexual harassment as an unethical business practice.
NOTE: Mark the first TWO (2) only. (2 x 2) (4)
4.8.2 Pricing of goods in rural areas
- Businesses should be fair and apply reasonable pricing. √√
- Access to rural areas should be increased, so that more products and a bigger variety is available. √√
- Consumers in rural areas should insist on prices being fair and report any unfair pricing. √√
- Entrepreneurship should be encouraged in these areas. √√
- Cost effective ways of transporting the products can be investigated. √√
- Suppliers can work together when delivering products to remote rural areas. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to strategies to deal with pricing of goods in rural areas as an unethical business practice.
NOTE: Mark the first TWO (2) only. (2 x 2) (4)
[60]
BREAKDOWN OF THE MARKS
QUESTION 4 | MARKS |
4.1 | 3 |
4.2 | 3 |
4.3 | 8 |
4.4 | 4 |
4.5.1 | 3 |
4.5.2 | 9 |
4.5.3 | 6 |
4.6 | 8 |
4.7 | 8 |
4.8.1 | 4 |
4.8.2 | 4 |
TOTAL | 60 |
QUESTION 5: BUSINESS OPERATIONS
5.1 Aspects to be included in an induction program
- Safety regulations and rules. √
- Overview of the business. √
- Information about the business products/services. √
- Meeting with senior management who will explain the company’s vision/values/job descriptions/daily tasks. √
- Tour of the premises/Introduction to key people and close colleagues. √
- Conditions of employment, e.g. working hours/leave application process/ disciplinary procedures√, etc.
- Administration details on systems/processes/logistics. √
- Discussion of the employment contract and conditions of service. √
- Discussion of personnel policies, e.g. making private phone calls/using the internet√, etc.
- Discussion on employee benefits. √
- Corporate social responsibility programmes. √
- Any other relevant answer related to aspects that should be included in the induction program.
NOTE: Mark the first SIX (6) only. (6 x 1) (6)
5.2 Selection procedure
Option 1
- Determine fair assessment criteria on which selection will be based. √√
- Use the assessment criteria to assess all CV's/application forms received during recruitment/Preliminary screening is done by sorting the applications received according to the criteria for the job. √√
- Check that applicants are not submitting false documents such as forged certificates/degrees. √√
- Make a preliminary list of all applicants who qualify for the post. √√
- Screen and check references, e.g. check applicants' criminal records/credit history/social media. √√ etc.
- Conduct preliminary interviews to identify suitable applicants. √√
- Inform all applicants about the outcome of the application. √√
- Compile a shortlist of approximately five people. √√
- Invite the shortlisted applicants/candidates for an interview. √√
- Shortlisted candidates may be subjected to various types of selection tests, e.g. skills test. √√
- A written offer is made to the chosen candidates. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to the selection procedure/steps as an activity of the human resources function.
OR
Option 2
- Receive documentation, e.g. application forms and sort it according to the criteria of the job. √√
- Evaluate CV's and create a shortlist/screen the applicant. √√
- Check information in the CV's and contact references. √√
- Conduct preliminary sifting interviews to identify applicants who are not suitable for the job, although they meet the requirements. √√
- Assess/Test candidates who have applied for senior positions/to ensure the best candidate is chosen. √√
- Conduct interviews with shortlisted candidates. √√
- Offer employment in writing to the selected candidate (s). √√
- Any other relevant answer related to the selection procedure/steps as an activity of the human resources function.
NOTE: Procedure can be in any order.
Max (6)
5.3 Role of the interviewee/applicant during an interview
- Greet the interviewer by name√ with a solid handshake and a friendly smile. √
- Listen carefully to the questions√ before responding. √
- Make eye contact√ and have good posture/body language. √
- Show confidence√ and have a positive attitude/and be assertive. √
- Be inquisitive√ and show interest in the business. √
- Ask clarity seeking√ questions. √
- Show respect√ and treat the interview with its due importance. √
- Be honest about mistakes√ and explain how you dealt with it. √
- Know your strengths and weaknesses√ and be prepared to discuss them. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the role of the interviewee/applicant during an interview.
Max (8)
5.4 Salary determination method
5.4.1 Piece meal√√ (2)
Motivation
- Themba and Thoko are both paid according to the number of units sold. √ (1)
NOTE: Do not award mark for motivation if the salary determination method was incorrectly identified.
Max (3)
5.4.2 Impact of fringe benefits on businesses
Positives/Advantages
- Attractive fringe benefit packages√ may result in higher employee retention/reduces employee turnover. √
- Attracts qualified/skilled/experienced employees√ who may positively contribute towards the business goals/objectives. √
- It increases employee satisfaction/loyalty√ as they may be willing to go the extra mile. √
- Improves productivity√ resulting in higher profitability. √
- Businesses save money√ as benefits are tax deductible. √
- Fringe benefits can be used as leverage√ for salary negotiations. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the positive impact/advantages of fringe benefits on businesses.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- Fringe benefits are additional costs√ that may result in cash flow problems. √
- Administrative costs increase√ as benefits need to be correctly recorded for tax purposes. √
- Decreases business profits√, as incentive/package/remuneration costs are higher.√
- It can create conflict/lead to corruption√ if allocated unfairly. √
- Workers only stay with the business for fringe benefits√, and may not be committed/loyal to the tasks/business. √
- Businesses who offer employees different benefit plans may create resentment√ to those who receive less benefit resulting in lower productivity. √
- Businesses who cannot offer fringe benefits√ fail to attract skilled workers. √
- Businesses have to pay advisors/attorneys√ to help them create benefit plans that comply with legislation. √
- Errors in benefit plans√ may lead to costly lawsuits/regulatory fines. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact/disadvantages of fringe benefits on businesses.
Max (8)
5.5 Difference between quality performance and quality management
QUALITY PERFORMANCE | QUALITY MANAGEMENT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sub max (2) | Sub max (2) |
NOTE:
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format
- The difference must be clear.
- Award a maximum of TWO (2) marks if the difference is not clear/Mark either quality performance or quality management.
Max (4)
5.6 Total Quality Management (TQM)
5.6.1 Elements of TQM
Statement from the scenario | TQM element |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sub max (3) | Sub max (6) |
NOTE:
- Elements must be linked to the scenario.
- Award ONE (1) mark for each quote from the scenario without the correct identification of the TQM element.
- Allocate full marks for the TQM element even if the quote is incomplete.
Statements (3)
Elements (6)
Max (9)
5.6.2 Importance of quality circles in TQM
- Solve problems related to quality√ and implement improvements. √
- Investigate problems√ and suggest solutions to management. √
- Ensure that there is no duplication√ of activities/tasks in the workplace. √
- Make suggestions for improving systems√ and processes in the workplace. √
- Improve the quality of products/services/productivity√ through regular reviews of quality processes. √
- Monitor/Reinforce strategies√ to improve the smooth running of business operations. √
- Reduce costs√ of redundancy in the long run. √
- Increase employees' √ morale/motivation. √
- Quality circles discuss ways of improving√ the quality of work/workmanship. √
- Contribute towards the improvement √ and development of the organisation. √
- Reduce costs/wasteful efforts√ in the long run. √
- Increase the demand√ for products/services of the business. √
- Create harmony√ and high performance in the workplace. √
- Build a healthy workplace relationship√ between the employer and employee. √
- Improve employees’ loyalty√ and commitment to the business and its goals. √
- Improve employees’ communication√ at all levels of the business. √
- Develop a positive attitude/sense of involvement√ in decision making processes of the services offered. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the importance of quality circles in TQM.
Max (8)
5.7 Ways to improve quality of performance within the purchasing function
- Buy raw materials in bulk at lower prices. √√
- Select reliable suppliers that render the best quality raw materials/capital goods at reasonable prices. √√
- Place orders timeously and regular follow-ups to ensure that goods are delivered on time. √√
- Effective co-ordination between purchasing and production departments so that purchasing staff understand the requirements of the production process. √√
- Required quantities should be delivered at the right time and place. √√
- Implement and maintain stock control systems to ensure the security of stock. √√
- Maintain optimum stock levels to avoid overstocking/reduce out-dated stock. √√
- Monitor and report on minimum stock levels to avoid stock-outs. √√
- Effective use of storage space and maintain product quality while in storage. √√
- Involve suppliers in strategic planning/product design/material selection/quality control process. √√
- Ensure that there is no break in production due to stock shortages. √√
- Establish relationships with suppliers so that they are in alignment with the business's vision/mission/values. √√
- Have a thorough understanding of supply chain management. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to ways in which businesses can improve the quality of performance within the purchasing function.
Max (8)
[60]
QUESTION 6: MISCELLANEOUS TOPICS
BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS
6.1 Business strategies
6.1.1 Forward integration/Vertical integration/Integration√√
6.1.2 Market penetration/Intensive√√
6.1.3 Concentric diversification/Diversification√√
6.2 Impact of the LRA on businesses
Positives/Advantages
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS
QUESTION 5 | MARKS |
5.1 | 6 |
5.2 | 6 |
5.3 | 8 |
5.4.1 | 3 |
5.4.2 | 8 |
5.5 | 4 |
5.6.1 | 9 |
5.6.2 | 8 |
5.7 | 8 |
TOTAL | 60 |
Max (6)
- LRA provides for the principles of collective bargaining√ and puts structures in place with which disputes in the workplace can be settled. √
- Promotes a healthy relationship√ between the employer and employees. √
- Provides specific guidelines for employers√ on correct and fair disciplinary procedures. √
- Employers and employees have guidelines√ regarding correct and fair dismissal procedures. √
- Provides mechanisms√ such as statutory councils/collective bargaining/ CCMA.√
- Labour disputes are settled quicker√ and are less expensive. √
- Provides protection for employers√ who embark on lawful lock-outs. √
- Employers are entitled to compensation from the Labour Court√ if they suffered damages as a result of unprotected strikes. √
- Workplace forums can add value to businesses√ if it functions properly. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the positive impact/advantages of the LRA on businesses.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- Employers may have to disclose information about workplace issues to union representatives√ that could be the core of their competitive advantage. √
- Employers may not dismiss employees at will√, as procedures have to be followed. √
- Some businesses may feel that the LRA gives employees too much power√ as it creates lengthy procedures, e.g. consulting with workplace forums. √
- Employers may not get a court interdict√ to stop a strike. √
- Strike actions always result in loss of production√ for which employers may not claim. √
- Some trade unions may not promote the mandate of their members√ but embark on industrial action, which is harmful to labour relations between employers and employees. √
- Many employees and employers√ do not understand/respect the Labour Relations Act. √
- Labour disputes and bargaining council processes become disruptive/ time consuming√ and can lead to a decrease in productivity in businesses. √
- Many employees take advantage of the right to strike√ without acknowledging their responsibilities. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact/disadvantages of the LRA on businesses.
NOTE: Award a maximum of TWO (2) marks if the impact is on trade unions only.
Max (8)
BUSINESS VENTURES
6.3 Differences between limited and unlimited liability
LIMITED LIABILITY | UNLIMITED LIABILITY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sub max (2) | Sub max (2) |
NOTE:
- The answer does not have to be in tabular format
- The differences must be clear.
- Award a maximum of TWO (2) marks if the differences are not clear/Mark either limited liability or unlimited liability.
Max (4)
6.4 Investments
6.4.1 Unit trust√√ (2)
6.4.2 Advantages of unit trust
- The investor has a variety to choose from/a wider range of shares√ and a lower degree of risk. √
- Safe investments√, as it is managed according to rules and regulations. √
- A small amount√ can be invested per month. √
- Easy to invest in√, as investors simply fill in several forms or invest online. √
- Easy to cash in√ when an investor needs money. √
- Fluctuations in unit trust rates of return are often not so severe√ because of diversity of the investment fund. √
- Generally, beats inflation√ on the medium/long term. √
- Offer competitive returns√ in the form of capital growth and dividend distribution.√
- Fund managers are knowledgeable/experts/reliable/trustworthy√ as they are required to be accredited to sell unit trusts. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the advantages of unit trusts.
NOTE:
- Do not award marks for a diverse portfolio managed by a specialist.
- Accept relevant facts, if unit trust was incorrectly identified in QUESTION 6.4.1.
Max (6)
6.5 Compulsory insurance
6.5.1 Road Accident Fund/RAF/Road Accident Benefit Scheme/RABS. √√ (2)
6.5.2 Unemployment Insurance Fund/UIF. √√ (2)
BUSINESS ROLES
6.6 Types of problem solving techniques
- Delphi technique√
- Force-field analysis√
- Brainstorming√
- Mind mapping√
- Nominal group technique√
- SCAMPER√
- orced combinations√
- Empty chair√
NOTE: Mark the first FOUR (4) only. (4x1) (4)
6.7 Advantages of creative thinking in the workplace
- Better/Unique/Unconventional ideas/solutions√ is generated. √
- May give the business a competitive advantage√ if unusual/unique solutions/ ideas/strategies are implemented. √
- Complex business problems√ may be solved. √
- Productivity increases√ as management/employees may quickly generate multiple ideas which utilises time and money more effectively. √
- Managers/Employees have more confidence√ as they can live up to their full potential. √
- Managers will be better leaders√ as they will be able to handle/manage change(s) positively and creatively. √
- Managers/Employees can develop a completely new outlook√, which may be applied to any task(s) they may do. √
- Leads to more positive attitudes√ as managers/employees feel that they have contributed towards problem solving. √
- Improves motivation√ amongst staff members. √
- Managers/Employees have a feeling of great accomplishment√ and they will not resist/obstruct the process once they solved a problem/contributed towards the success of the business. √
- Management/employees may keep up√ with fast changing technology. √
- Stimulates initiative from employees/managers√, as they are continuously pushed out of their comfort zone. √
- Creativity may lead to new inventions√ which improves the general standard of living. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the advantages of creative thinking in the workplace.
Max (6)
6.8 Professional, responsible, ethical and effective business practices
- Businesses should treat all employees equally. √√
- Plan properly and put preventative measures in place. √√
- Pay fair wages/salaries which is in line with the minimum requirements of the BCEA/Remunerate employees for working overtime/during public holidays. √√
- Engage in environmental awareness programmes/Refrain from polluting the environment, e.g. by legally disposing of toxic waste. √√
- Refrain from starting a venture using other businesses' ideas that are protected by law. √√
- Business decisions and actions must be clear/transparent to all stakeholders. √√
- Businesses should be accountable /responsible for their decisions and actions/ patent rights. √√
- Hiring honest/trustworthy accountants/financial officers with good credentials. √√
- Regular/Timeous payment of taxes. √√
- Draw up a code of ethics/conduct. √√
- On-going development and training for all employees. √√
- Performance management systems/Appraisals should be in place. √√
- Adequate internal controls/monitoring/evaluation. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to ways in which professional, responsible, ethical and effective business practices should be conducted.
Max (6)
BUSINESS OPERATIONS
6.9 Quality of performance
6.9.1 Results of poor implementation of TQM from the scenario
- NGC received poor publicity due to the low quality of some products. √
- Their profits also declined resulting in investors withdrawing their money. √
NOTE:
- Mark the first TWO (2) only.
- Only allocate marks for responses that are quoted from the scenario. (2x1) (2)
6.9.2 Impact if TQM is poorly implemented by businesses
- Lack of training/skills development√ may lead to poor quality products. √
- Decline in sales√, as returns from unhappy customer's increase. √
- Decline in productivity√, because of stoppage. √
- High staff turnover√, because of poor skills development. √
- Unrealistic deadlines√ may not be achieved. √
- Businesses may not be able to make/afford the necessary changes√ that will satisfy customers' needs. √
- Loss of customers√ may lead to bankruptcy/closure. √
- Undocumented quality control systems/processes√ could result in error/deviations from pre-set quality standards. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the impact if TQM is poorly implemented by businesses.
NOTE: Do not allocate marks for responses that are quoted in QUESTION 6.9.1.
Max (6)
6.9.3 Benefits of a good quality management system
- Effective customer services are rendered, resulting in increased customer satisfaction.√√
- Time and resources are used efficiently.√√
- Productivity increases through proper time management/using high quality resources. √√
- Products/Services are constantly improved resulting in increased levels of customer satisfaction.√√
- Vision/Mission/Business goals may be achieved.√√
- Business has a competitive advantage over its competitors.√√
- Regular training will continuously improve√ the quality of employees’ skills/knowledge.√√
- Employers and employees will have a healthy working relationship resulting in happy/productive workers.√√
- Increased market share and profitability.√√
- Any other relevant answer related to the benefits of a good quality management system.
Max (6)
[60]
BREAKDOWN OF MARKS
QUESTION 6 | MARKS |
6.1 | 6 |
6.2 | 8 |
6.3 | 4 |
6.4.1 | 2 |
6.4.2 | 6 |
6.5.1 | 2 |
6.5.2 | 2 |
6.6 | 4 |
6.7 | 6 |
6.8 | 6 |
6.9.1 | 2 |
6.9.2 | 6 |
6.9.3 | 6 |
TOTAL | 60 |
TOTAL SECTION B: 180
SECTION C
Mark ONLY the FIRST TWO (2) questions in this section.
QUESTION 7: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTS (BUSINESS STRATEGIES)
7.1 Introduction
- A strategy is course of action that the business follows to achieve its purpose/ objectives. √
- The strategic management process is defined as the way an organisation defines its strategy. √
- The strategic management process enables managers to make choice of a set of strategies that will enable the business to achieve better performance. √
- PESTLE analysis is used to identify and evaluate the factors in the external environment that can influence the business. √
- PESTLE analysis enables to businesses to have a better understanding of the external environment and the industry in which it competes. √
- Defensive strategies enable business to solve challenges that are posed by the macro environment. √
- A business strategy must be evaluated in each stage of operation to measure performance. √
- Any other relevant introduction related to the initial stage of the strategic management process/PESTLE analysis/defensive strategies/strategy evaluation. (2x1) (2)
7.2 Initial stages of the strategic management process
OPTION 1
- Have a clear vision, a mission statement and measurable/realistic objectives in place. √√
- Identify opportunities/weaknesses/strengths/threats by conducting environmental scanning/situational analysis. √√
- Tools available for environmental scanning may include a SWOT and Porter's Five Forces model (industrial analysis tools). √√
OR
OPTION 2
- Review vision statement. √√
- Analyse/Re-examine mission statement. √√
- Conduct an analysis using models such as PORTER'S Five Forces model and SWOT. √√
NOTE:
- The initial process may be in any order.
- Mark the first TWO (2) only .
- Do not award marks for the PESTLE model and the remaining stages of the strategic management process.
Max (4)
7.3 Application of PESTLE model to deal with the challenges in the macro environment
FACTORS | APPLICATION |
Political√ |
|
Sub max (4) | |
Economic√ |
|
Sub max (4) | |
Social√ |
|
Sub max (4) | |
Technological√ |
|
Sub max (4) |
Legal√ |
|
| |
| |
Sub max (4) | |
Environmental √ |
|
Sub max (6) | Sub max (4) |
NOTE: Each PESTLE element must be linked to the application.
Factors: Max (6)
Application: Max (16)
Max: (22)
7.4 Types of defensive strategies
7.4.1 Divestiture/ Divestment√√
- The business disposes/sells some assets/divisions√ that are no longer profitable/ productive. √
- Businesses may sell off divisions/product lines√ with slow growth potential. √
- The business sells ownership√ by decreasing the number of shareholders. √
- Unproductive assets are sold√ to pay off debts. √
- Process used to withdraw its investment√ in another business (divesting). √
- Aims at acquiring additional capital. √
- Any other relevant answer related to divestiture/divestment as a defensive strategy.
NOTE: Accept unbundling as an alternative answer.
Strategy (2)
Description (2)
Sub max (4)
7.4.2 Liquidation√√
- All assets are sold to pay creditors√ due to a lack of capital. √
- Selling the entire business√ in order to pay shareholders a fair price for their shares. √
- Creditors may apply for forced liquidation√ in order to have their claims settled. √
- Companies in financial difficulty may apply for business rescue to avoid liquidation. √
- Any other relevant answer related to liquidation as a defensive strategy.
Strategy (2)
Description (2)
Sub max (4)
7.4.3 Retrenchment√√
- Terminating the employment contracts of employees√ for operational reasons. √
- Decreasing the number of product lines/Closing certain departments√ may result in some workers becoming redundant. √
- Any other relevant answer related to retrenchment as a defensive strategy.
Strategy (2)
Description (2)
Sub max (4)
NOTE: Mark the first THREE (3) only Max (12)
7.5 Steps in evaluating strategies
- Examine the underlying basis of a business strategy. √√
- Formulate strategies to meet objectives favourably. √√
- Implement strategies using action plans√√, etc.
- Look forward and backwards into the implementation process. √√
- Compare the expected results in order to determine the reasons for deviations and analyse these reasons. √√
- Take corrective action so that deviations may be corrected. √√
- Set specific dates for control and follow up. √√
- Draw up a table of the advantages and disadvantages of a strategy. √√
- Decide on the desired outcome. √√
- Consider the impact of the strategic implementation in the internal and external environments of the business. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to the steps in evaluating strategies. NOTE: Accept steps in any order.
Max (8)
7.6 Conclusion
- The strategic management process is an integral part of managerial accountability for senior managers. √√
- Businesses that apply the PESTLE analysis are able to respond quickly to the external pressures and adapt to them. √√
- Businesses must continuously evaluate strategies in order to change/adapt it according to current demands of the market/industry. √√
- Businesses that successfully monitor and respond to changes in the macro environment are able to differentiate from the competition and create a competitive advantage. √√
- Defensive strategies are used when a business wants to avoid problems that may arise in future. √√
- It is also a strategy to protect the business from suffering a loss of income/sales/ market share. √√
- Any other relevant conclusion related to the strategic management process/ PESTLE model/defensive strategies/evaluation of strategies.
Max (2)
[40]
QUESTION 7: BREAKDOWN OF MARK ALLOCATION
Details | Maximum | Total |
Introduction | 2 | Max 32 |
Initial stages of the strategic management process | 4 | |
PESTLE analysis: | ||
Factors | 6 | |
Application | 16 | |
Types of defensive strategies | 12 | |
Steps for strategy evaluation | 8 | |
Conclusion | 2 | |
INSIGHT | 8 | |
Layout | 2 | |
Analysis, interpretation | 2 | |
Synthesis | 2 | |
Originality/Examples | 2 | |
TOTAL MARKS | 40 |
*LASO - For each component:
- Allocate 2 marks if all requirements are met.
- Allocate 1 mark if some requirements are met.
- Allocate 0 marks where requirements are not met at all.
QUESTION 8: BUSINESS VENTURES (MANAGEMENT & LEADERSHIP)
8.1 Introduction
- Good leaders can also be good managers, as both can inspire/energise people and bring about change.√
- The attitude of a leader has an influence on the success and or failure of the business.√
- Leaders and managers can create opportunities and motivate people to be productive which lead to successful businesses.√
- Many managers are also good leaders with excellent management skills.√
- The democratic and laissez-faire leadership styles can be used in different situations to influence employees.√
- Any other relevant introduction related to management and leadership/role of personal attitudes/democratic and laissez-faire leadership styles/application of democratic and laissez faire leadership styles.
(2 x 1) (2)
8.2 Differences between management and leadership
MANAGEMENT | LEADERSHIP |
|
|
Sub max (6) | Sub max (6) |
NOTE:
- The answer does not have to be in tabular form but the differences must be clear.
- Mark the first THREE (3) only.
- Award a maximum of SIX (6) marks if the differences are not clear/ mark either management or leadership only.
Max (12)
8.3 Role of personal attitude in successful leadership
- Positive attitude releases√ leadership potential. √
- A leader's good/bad attitude√ can influence the success/failure of the business. √
- Leaders must know their strengths and weaknesses√ to apply their leadership styles effectively. √
- Great leaders understand that the right attitude√ will set the right atmosphere. √
- Leaders' attitude may influence√ employees'/teams' thoughts/behaviour. √
- Leaders should model the behaviour√ that they want to see in team members. √
- Successful leaders consider the abilities/skills of team members√ to allocate tasks/roles effectively. √
- Enthusiasm√ produces confidence in a leader. √
- A positive attitude is critical for good leadership√ because good leaders will stay with the task regardless of difficulties/challenges. √
- Successful employees and leaders have a constant desire to work√ and achieve personal/professional success. √
- Leaders with a positive attitude know√ that there is always more to learn/space to grow. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the role of personal attitude in successful leadership.
NOTE: Do not allocate marks for “promoting a good team spirit.”
Max (10)
8.4 Impact of democratic and laissez-faire/free reign leadership styles on businesses
8.4.1 Democratic
Positives/Advantages
- The leader allows the employees to participate in the decision making process√, so they feel empowered/positive. √
- Staff gives a variety of ideas/inputs/feedback/viewpoints√ that can lead to innovation/improved production methods/increased sales. √
- Clear/Two way communication√ ensures group commitment to final decision(s). √
- Authority is delegated√ which can motivate/inspire workers to be more productive. √
- Complex decisions can be made√ with inputs from specialists/skilled workers. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the positive impact/advantages of the democratic leadership style on businesses.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- Incorrect decisions may be made√ if staff is inexperienced/not fully informed. √
- Decision making may be time consuming√ because stakeholders have to be consulted. √
- Employees may feel discouraged√ if their opinions/inputs are not considered. √
- Leaders can rely too much on the input of the followers√ and fail to make a final decision. √
- Not effective in times of crisis√/when quick decisions need to be made. √
- Some employees only pretend to participate in decision making√ and their feedback may not always be accurate. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact/disadvantages of a democratic leadership style on businesses.
Sub max (8)
8.4.2 Laissez-faire/Free reign
Positives/Advantages
- Workers/Followers are allowed√ to make decisions on their own work/ methods.√
- Subordinates have maximum freedom√ and can work independently. √
- Leader motivates workers by trusting them√ to do things themselves/on their own. √
- Authority is delegated√, which can be motivating/empowering for competent workers’/increase productivity. √
- Subordinates are experts√ and know what they want/can take responsibility for their actions. √
- Suitable for coaching/mentoring√ to motivate employees to achieve more/better things. √
- It can be empowering for competent followers√ as they are completely trusted to do their job. √
- Individual team members may improve√/develop leadership skills. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the positive impact/advantages of a laissez faire leadership style on businesses.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- Lack of clear direction/leadership√ may be demotivating to employees. √
- Employees can be held responsible for their own work√ which may lead to underperformance. √
- Could lead to conflict√ when some team members act as leaders and dictate to other team members. √
- Workers are expected to solve their own√ conflict situations. √
- Productivity may be compromised√ with a lack of tight control over workers not meeting deadlines. √
- Productivity might be low√, if employees lack the necessary knowledge or skills.√
- Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact/disadvantages of laissez-faire leadership style on businesses.
Sub max (8)
Max (16)
8.5 Situations in which the democratic and laissez faire leadership styles can be applied in the workplace
8.5.1 Democratic leadership style
This leadership style can be used when:
- Group members are skilled and eager to share their ideas. √√
- The leader does not have all the information needed to make a decision and employees have valuable information to contribute. √√
- Cooperation is needed between a leader and a team. √√
- Decisions need to be looked at from several perspectives. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to situations in which the democratic leadership style may be applied in the workplace.
Sub max (4)
8.5.2 Laissez-faire/ Free reign
This leadership style can be used when:
- Subordinates are experts and know what they want/can take responsibility for their actions. √√
- The leader is very busy and delegation of tasks will increase productivity. √√
- Team members need to improve/develop leadership skills. √√
- Suitable when employees are highly experienced and know more about the task than the leader. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to a situation in which laissez-faire/free-reign leadership style may be applied in the workplace.
Sub max (4)
Max (8)
8.6 Conclusion
- Managers can also be successful leaders if they do not only focus on the task at hand, but also the people/workers who will execute the task. √√
- Leaders who understand various leadership styles may be able to lead effectively and handle any situation. √√
- A leader who is positive/enthusiastic/energetic will inspire his followers to improve/empower/uplift themselves to achieve their own personal goals. √√
- The democratic leadership style encourages innovative ideas and boosts the morale of workers. √√
- The laissez-faire leadership style provides experienced employees with the opportunity for persona/career growth. √√
- The style used depends on the personality of the leader and nature of the business.√√
- Any other relevant conclusion related to management and leadership/role of personal attitudes/democratic and laissez-faire leadership styles/application of democratic and laissez-faire leadership styles.
Max (2)
[40]
QUESTION 8: BREAKDOWN OF MARK ALLOCATION
Details | Maximum | Total |
Introduction | 2 | Max 32 |
Differences between leadership and management | 12 | |
Role of personal attitude in successful leadership | 10 | |
Impact of democratic and laissez-faire/free-reign styles | 16 | |
Application of democratic and laissez-faire leadership styles. | 8 | |
Conclusion | 2 | |
INSIGHT | 8 | |
Layout | 2 | |
Analysis, interpretation | 2 | |
Synthesis | 2 | |
Originality/Examples | 2 | |
TOTAL MARKS | 40 |
*LASO - For each component:
- Allocate 2 marks if all requirements are met.
- Allocate 1 mark if some requirements are met.
- Allocate 0 marks where requirements are not met at all.
QUESTION 9: BUSINESS ROLES (ECONOMIC RIGHTS, AND ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES)
9.1 Introduction
- Economic rights form part of human rights that must be observed in the workplace. √
- Business operations may have a negative impact on the environment if there are no preventative measures put in place. √
- Businesses who have more than twenty employees must appoint one/more health and safety representatives after consultation with employees. √
- Employers and employees have the responsibility of ensuring that workplace environment is free of hazardous material. √
- Any other relevant introduction related to economic rights/responsibilities of employers and employees in protecting the workplace environment/roles of health and safety representatives/ways to protect the environment and human health.
(2 x 1) (2)
9.2 Economic rights of employees in the workplace
- Free from forced labour. √√
- Free to accept or choose work. √√
- Fair wages/Equal pay/Equal pay for work of equal value. √√
- Reasonable limitation of working hours. √√
- Safe and healthy working conditions. √√
- Join/form trade unions. √√
- Right to participate in a legal strike. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to the economic rights of employees in the workplace.
Max (10)
9.3 Responsibilities of employers and employees in protecting the workplace environment
Responsibilities of employers
- Provide and maintain all the equipment√ that is necessary to perform the work. √
- Keep the systems to ensure that there will be no harmful impact√ on the health and safety of workers. √
- Reduce/Remove dangers to workers√ and provide personal protective clothing. √
- Ensure that that the workers’ health is not damaged√ by hazards resulting from production/processing/storage/transportation of materials or equipment. √
- Employers must know where potential dangers might be√ and take measures to eliminate or limit the harm. √
- Workers must be informed/instructed/trained/and supervised√ to limit potential dangers to them√/Emergency exit door signs√ should be visible to all employees.√
- Equipment must be used under the supervision√ of a designated trained worker.√
- Comply with safety laws which√ seek to promote healthy working environment. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the responsibilities of employers in protecting the workplace environment.
Sub max (6)
Responsibilities of employees
- Must take care of their own health√ and safety in the workplace. √
- Co-operate and comply with the rules and procedures√ e.g. wear prescribed safety clothing. √
- Report unsafe√ or unhealthy conditions. √
- Report accidents√ to the employer by the end of the shift. √
- Use prescribed√ safety equipment. √
- Take reasonable care√ of their own safety. √
- Inform the employer of any illness√ that may affect the ability to work. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the responsibilities of employees in protecting the workplace environment.
Sub max (6)
Max (12)
9.4 Roles of health and safety representatives in protecting the workplace environment
- Ensure that protective clothing√ is provided/available to all workers. √
- Identify√ potential dangers in the workplace. √
- Initiate/Promote/Maintain/Review measures√ to ensure the health and safety of workers. √
- Check/Monitor the effectiveness of health and safety measures√ with management. √
- Ensure that all equipment that is necessary to perform work√ are provided/ maintained regularly. √
- Promote safety training√ so that employees may avoid potential dangers/act pro actively. √
- Ensure that dangerous equipment is used√ under the supervision of trained/qualified workers. √
- Ensure that workers’ health and safety is not endangered√ by hazards resulting from production/processing/storage/transportation of material/equipment. √
- Work together with the employer, to investigate any accidents/complaints from the workers√ concerning health and safety in the workplace. √
- Ensure that employers comply√ with COIDA. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the roles of health and safety representatives in protecting the workplace environment.
Max (12)
9.5 Ways to protect the environment and human health
- Laws and regulations should be adhered to so that profits are not generated at the expense of the environment. √√
- Pollution and other environmental issues should always be considered in all business activities, e.g. safe disposal of waste/dumping of toxic waste√√, etc.
- Become involved in environmental awareness programs. √√
- The environment can be protected by altering production techniques in favour of cleaner and greener technologies. √√
- Water for human consumption should be tested before it is used. √√
- Promote nature conservation by looking after natural resources. √√
- Minimise pollution, by re-using, reducing and recycling. √√
- Reduce consumption of goods/services which are environmentally unfriendly. √√
- Register/Engage with recognised institutions/bodies that promote green peace. √√
- Physical working conditions should always be worker friendly, safe and promote occupational health. √√
- Physical working conditions, e.g. adequate lighting/ventilation should be available and functional.√√
- Machines must be serviced/maintained regularly.√√
- Educate people about hygiene issues.√√
- Encourage employees to do regular health checks.√√
- Any other relevant answer related to ways businesses can protect the environment and promote human health.
Max (12)
9.6 Conclusion
- Businesses should be cognisant of the economic rights of employees and strive to promote them. √√
- Businesses must ensure that the health and safety representatives have necessary facilities/assistance/ training in order to represent their members effectively. √√
- Businesses should assess/control/address all the physical,chemical and biological factors in the environment. √√
- Environmental and human health are closely linked as human health depends on environmental health. √√
- A polluted environment results in poor human health. √√
- Employees must take responsibility for their own safety and avoid unnecessary injuries. √√
- Any other relevant conclusion related to economic rights/responsibilities of employers and employees in protecting the workplace environment/roles of health and safety representatives/ways to protect environment and human health.
Max (2)
[40]
QUESTION 9: BREAKDOWN OF MARK ALLOCATION
Details | Maximum | Total |
Introduction | 2 | Max 32 |
Economic rights of employees | 10 | |
Responsibilities of employers and employees in protecting the workplace environment | 12 | |
Roles of health and safety representatives in protecting the workplace environment | 12 | |
Ways to protect the environment and human health | 12 | |
Conclusion | 2 | |
INSIGHT | 8 | |
Layout | 2 | |
Analysis, interpretation | 2 | |
Synthesis | 2 | |
Originality/Examples | 2 | |
TOTAL MARKS | 40 |
*LASO – For each component:
- Allocate 2 marks if all requirements are met.
- Allocate 1 mark if only some of the requirements are met.
- Allocate 0 marks where requirements are not met at all.
QUESTION 10: BUSINESS OPERATIONS (HUMAN RESOURCES)
10.1 Introduction
- The aim of internal recruitment is to find the right employee for a specific job. √
- The right employee will be the one with the right skills/qualifications/competency to fill vacancies in a business. √
- Employers and employees should adhere to the terms and conditions of the employment contract. √
- It is important that the business places the right person in the right job. √
- Training is a planned organised activity where employees gain knowledge and skills to improve their abilities/job performance. √
- The human resource function should ensure that all training programmes are conducted within the framework of the Skills Development Act to develop the skills of the employees. √
- Any other relevant introduction related to internal recruitment/legal requirements of the employment contract/placement procedure/implications of the Skills Development Act on the human resources function. (2 x 1) (2)
10.2 Impact of internal recruitment
Positives/Advantages
- The business recruits from existing employees√ through promotions/transfer from inside the business. √
- Opportunities for promotion reward good work√ and motivate current employees. √
- Staff morale and productivity increases√ if suitable staff members are promoted regularly. √
- Current employees understand√ how the business operates. √
- The business knows the candidate√, his/her personality, strengths and weaknesses. √
- Reliable/Key staff members are retained√ if they are promoted/ transferred within the business. √
- Detailed, reliable information on candidates√ can be obtained from super visors/employee records. √
- Recruitment process is faster/less expensive√ if the candidates are known. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the positive impact/advantages of internal recruitment.
AND/OR
Negatives/Disadvantages
- Current employees√ may not bring new ideas into the business. √
- Promoting a current employee may cause resentment√ amongst other employees. √
- The number of applicants is limited√ to current staff only. √
- Employees who do not really have the required skills for the new job√ may be promoted. √
- Current employees may need to be trained/developed before they can be promoted√, which can be expensive. √
- Staff that is not promoted may feel demotivated√ which may hamper productivity. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the negative impact/disadvantages of internal recruitment.
Max (16)
10.3 Legal requirements of the employment contract
- Employment contract is an agreement between the employer and the new employee√ and is legally binding. √
- Employer and employee must agree√ to any changes to the contract. √
- Aspects of the employment contract can be renegotiated√ during the course of employment. √
- No party may unilaterally√ change aspects of the employment contract. √
- TFS and the new employee must both√ sign the contract. √
- The employment contract should include a code of conduct√ and code of ethics. √
- TFS must explain the terms and conditions of the employment contract√ to the employee. √
- It may not contain any requirements that are in conflict√ with the BCEA. √
- Conditions of employment/duties/responsibilities of the employees√ must be stipulated clearly. √
- The remuneration package/including benefits√ must be clearly indicated. √
- All business policies, procedures and disciplinary codes/rules can form part√ of the employment contract. √
- The employer must allow the employee to thoroughly read through the contract√ before it is signed. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the legal requirements of the employment contract.
Max (14)
10.4 Placement procedure
- TFS should outline specific responsibilities/expectations of the new position. √√
- Determine the successful candidate’s strengths/weaknesses/skills/ interests by subjecting him to various psychometric tests. √√
- Determine the relationship between the position and the competencies of the new candidate. √√
- Any other relevant answer related to the placement procedure.
Max (6)
10.5 Implications of the Skills Development Act on the human resource function
- The human resources function should interpret the aims and requirements of the SDA√ and adapt workplace skills training programmes accordingly. √
- Identify the training needs of the employees√ and provide them with training opportunities so that they will perform their tasks efficiently. √
- Use the National Qualification Framework/NQF√ to assess the skills levels of employees. √
- Interpret/Implement the aims/requirements of the framework√ for the National Skills Development Strategy. √
- Assist managers in identifying skills/training needs√ to help them to introduce learnerships. √
- Contribute 1% of their salary bill√ to the Skills Development Levy/SDL. √
- Ensure training in the workplace√ is formalised/structured. √
- Appoint a full/part time consultant√ as a Skills Development Facilitator. √
- Any other relevant answer related to the implications of the Skills Development Act on the Human Resources function.
Max (10)
10.6 Conclusion
- Employees are one of the most important resources in any business, therefore businesses should check if the current staff has the potential to fulfill a new role. √√
- The relationship between the employer and employee should be guided by the employment contract √√
- The human resources manager must support the placement process by providing ongoing support throughout the probation period to employees who are newly placed in a position. √√
- A correct placement procedure will ensure that skilled/competent employees are retained. √√
- The human resources function has to co-ordinate/facilitate skills development in the workplace to ensure a competent staff. √√
- Any other relevant conclusion related to internal recruitment/legal requirements of the employment contract/placement procedure/implications of the Skills Development Act on the human resources function.
Max (2)
[40]
QUESTION 10: BREAKDOWN OF MARK ALLOCATION
Details | Maximum | Total |
Introduction | 2 | Max 32 |
Impact of internal recruitment | 16 | |
Legal requirements of the employment contract | 14 | |
Placement procedure | 6 | |
Implications of the SDA on the human resources function | 10 | |
Conclusion | 2 | |
INSIGHT | 8 | |
Layout | 2 | |
Analysis, interpretation | 2 | |
Synthesis | 2 | |
Originality/Examples | 2 | |
TOTAL MARKS | 40 |
*LASO - For each component:
- Allocate 2 marks if all requirements are met.
- Allocate 1 mark if some requirements are met.
- Allocate 0 marks where requirements are not met at all.
TOTAL SECTION C: 80
GRAND TOTAL: 300
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN P2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2018
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
AMENDED SCE PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
MAY/JUNE 2018
MEMORANDUM
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2018
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS AND DESIGN
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
AMENDED SCE PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
MAY/JUNE 2018
QUESTIONS
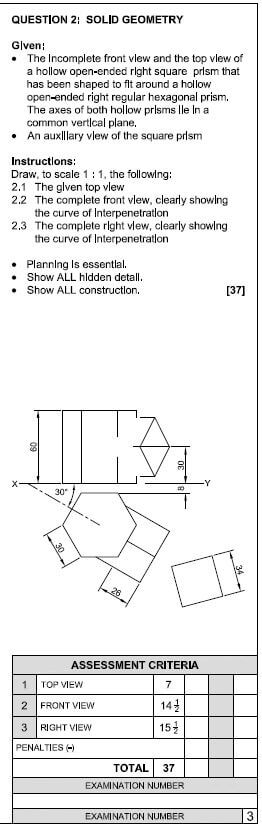
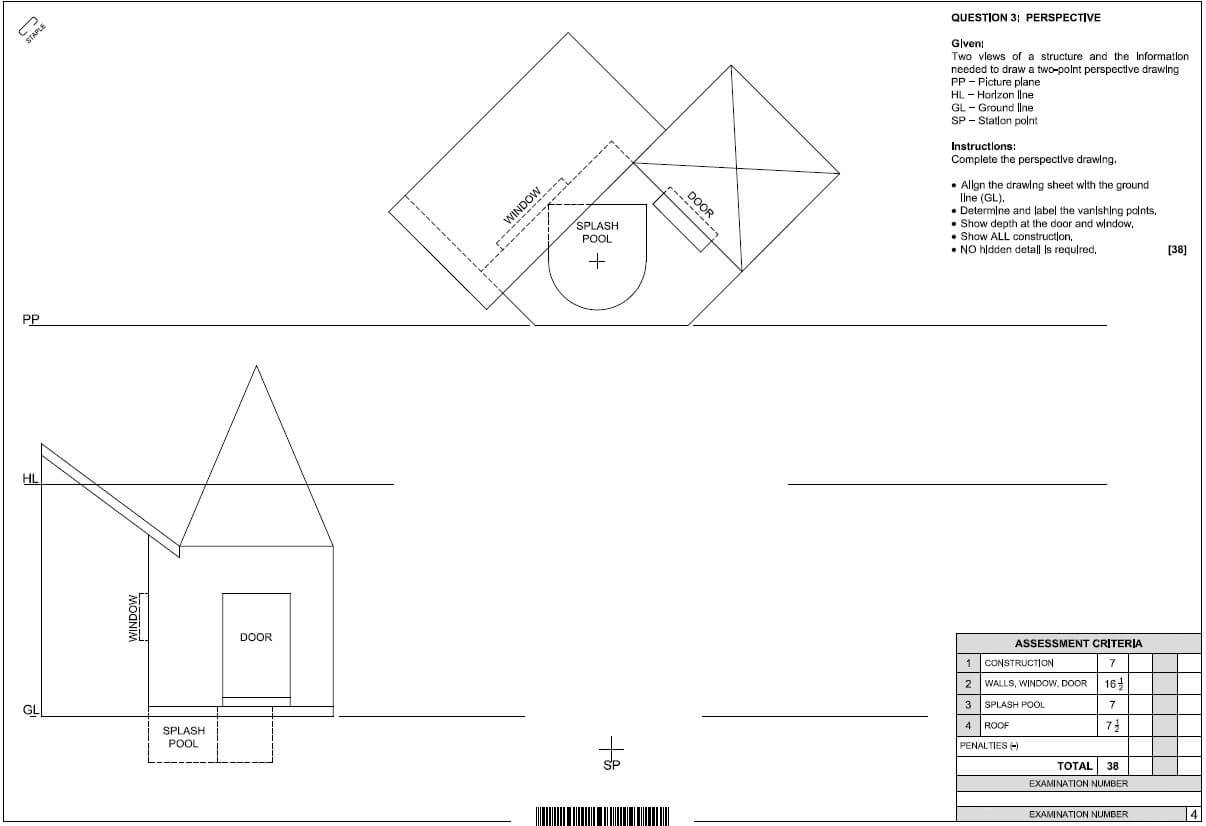
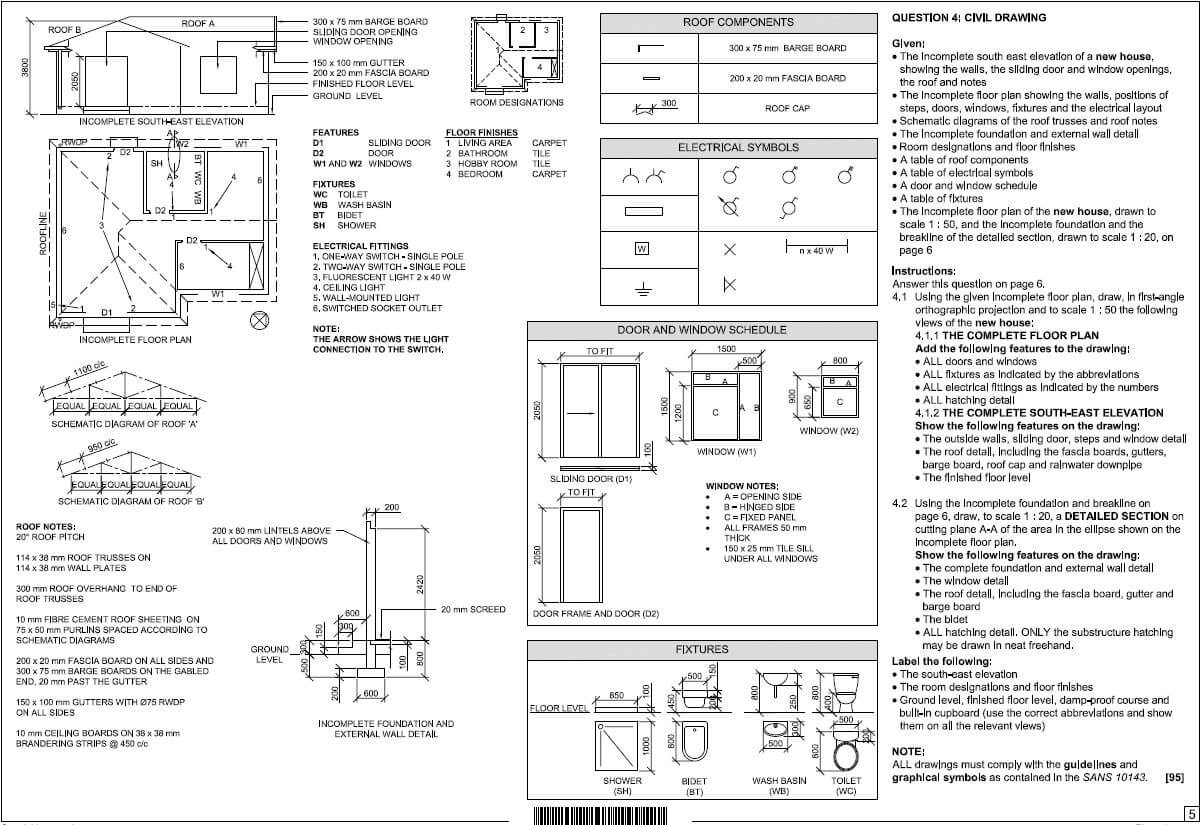
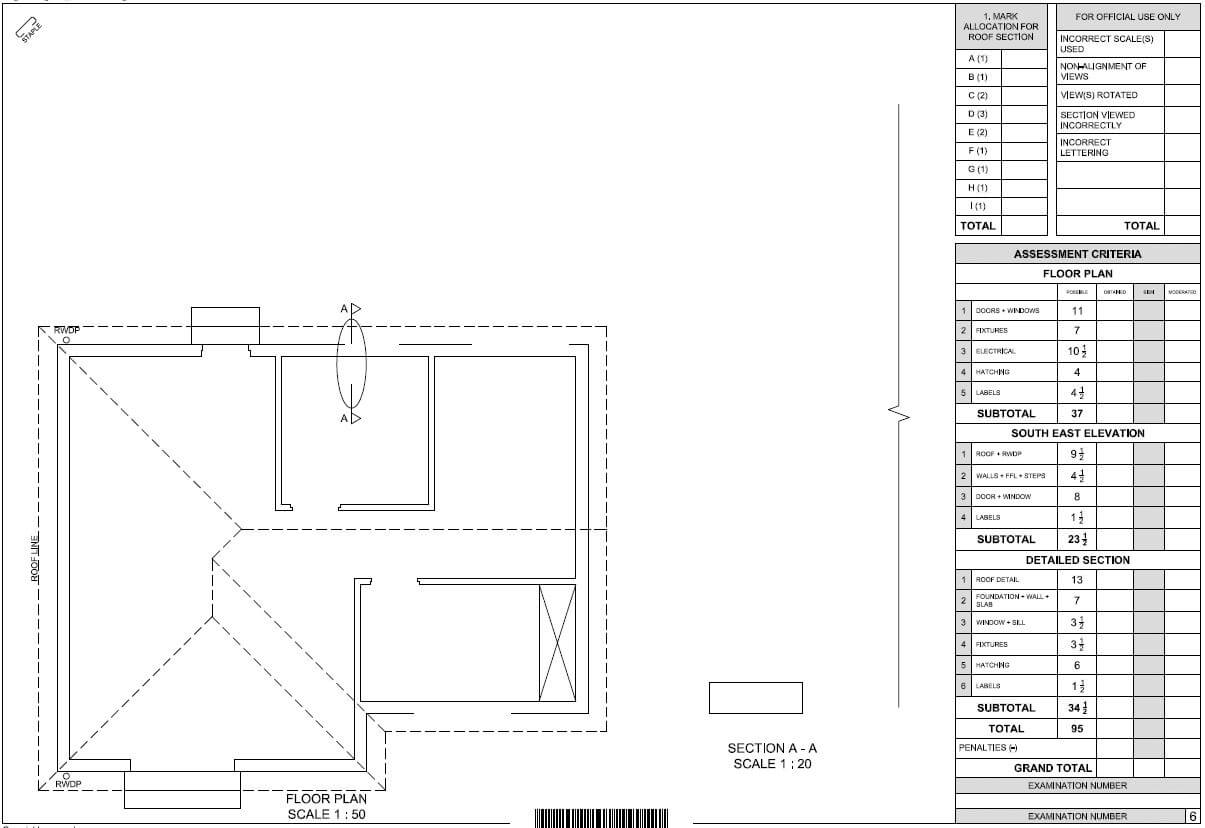
AGRICULTURAL TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2018
AGRICULTURAL TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
AMENDED SCE PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
MAY/JUNE 2018 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
1.1 This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
1.2 BOTH sections are COMPULSORY.
1.3 Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4 Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
1.5 You may use a non-programmable calculator.
1.6 Write neatly and legibly. - SECTION A: SHORT QUESTIONS
2.1 This section consists of THREE questions.
2.2 Follow the instructions when answering the questions. - SECTION B: STRUCTURED LONG QUESTIONS
3.1 This section consists of FIVE questions.
3.2 Start EACH question on a NEW page.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 The … is used to remove welding spatter from metal.
- prick punch
- rasp
- angle grinder
- hack saw
1.1.2 The … is used to remove a bearing from an alternator shaft without damaging the components.
- acetylene flame
- claw hammer
- bearing chisel
- bearing puller
1.1.3 The ideal number of teeth per 25 mm on a hacksaw blade used to cut 20 mm solid aluminium bar:
- 6 teeth per 25 mm
- 18 teeth per 25 mm
- 52 teeth per 25 mm
- 62 teeth per 25 mm
1.1.4 … is used for the manufacturing of O rings.
- Fibreglass
- Teflon
- Perspex
- Bakelite
1.1.5 This material should NOT be grinded with a bench grinder because the material clogs the grinding wheel pores causing the wheel to overheat:
- Cast iron
- Mild steel
- Copper
- Stainless steel
1.1.6 The use of compressed air in the farm workshop is associated with …
- soldering.
- MIG welding.
- TIG welding.
- plasma cutting.
1.1.7 Incorrect calibration of a diesel pump on a tractor can be identified by …
- black smoke exiting the exhaust.
- noisy valves.
- white smoke exiting the exhaust.
- the engine that back-fires.
1.1.8 Modern technological systems, such as …, are used to notify the operator when grain is blocking the system in a combine harvester.
- yield monitors
- flow sensors
- neutron probes
- tensiometers
1.1.9 The drain pipe connecting the toilet to the septic tank is made from …
- copper.
- latex.
- PVC.
- iron.
1.1.10 The most suitable all-purpose fire extinguisher for a welding workshop:
- Foam extinguisher
- Water hose
- Water extinguisher
- Dry powder extinguisher (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Change the UNDERLINED word(s) in each of the following statements to make the statements TRUE. Write only the word(s) next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.2.6 Tractor.
1.2.1 Safety signs attached to an electric fence must be made of plastic with a red background.
1.2.2 A newspaper is the most effective type of communication to inform farm neighbours about an immediate emergency.
1.2.3 A one-way valve is a device that is capable of adjusting the water delivering time in response to current environmental conditions.
1.2.4 Compressed air is used as a hydraulic fluid in a car's bottle jack.
1.2.5 Steel that has a copper coating produces poisonous gases when subjected to welding. (5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Choose a word/term from COLUMN B that matches the description in COLUMN A. Write down only the letter (A–H) next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.3.6 I.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.3.1 Alloy elements used in the manufacturing of stainless steel |
|
(5 x 2) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 40
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: MATERIALS AND STRUCTURES
(Start this question on a NEW page.)
2.1 Indicate the alloy metal that is specifically used to manufacture the following products and give TWO reasons why the metal is used:
2.1.1 Milk tanks (3)
2.1.2 Fittings for hot-water copper pipes (3)
2.1.3 Hammering tools that can be used in explosive atmospheres (3)
2.2 Name TWO hot-working processes that can be used to change the structural properties of brass. (2)
2.3 Concrete and fibreglass drinking troughs are used to provide water to farm animals.
2.3.1 Give TWO reasons why farmers would prefer fibreglass troughs instead of concrete troughs for cattle. (2)
2.3.2 Describe the resin that is used to manufacture fibreglass products. (2)
2.3.3 Name TWO methods that can be used to join fibreglass parts. (2)
2.4 Give FIVE reasons why Vesconite is the best material for the manufacturing of bushes. (5)
2.5 Describe how an adhesive should be applied to a surface to ensure sufficient cohesion. (4)
2.6 An earth return system, as shown in the illustration below, is needed for the electric fence to function effectively. 
2.6.1 Briefly discuss the procedure that must be followed when testing the earth system of an electric fence. (4)
2.6.2 Give TWO examples where electric fences are used on a farm. (2)
2.6.3 Name THREE alternative energy sources that can be used to supply energy to an electrical fence. (3) [35]
QUESTION 3: ENERGY
(Start this question on a NEW page.)
3.1 The sketch below shows parts of a wind turbine. Identify the TWO parts labelled A and B and describe the function of EACH.  (4)
(4)
3.2 The solar hot-water system shown below is used to heat water without using electricity. 
3.2.1 Explain the working of the solar hot-water system shown above. (4)
3.2.2 Name FOUR benefits of using solar energy to heat water. (4)
3.3 A geothermal energy plant is planned for construction in the Northern Cape.
3.3.1 State TWO geological aspects that should be considered to determine the location to construct a geothermal energy plant. (2)
3.3.2 Describe TWO advantages of a geothermal energy plant. (2)
3.4 Bio-energy is widely used as alternative fuel for agricultural machines.
3.4.1 Name TWO alternative fuels that can be manufactured from plant material. (2)
3.4.2 Name TWO crops that can be used to produce bio-fuel. (2) [20]
QUESTION 4: SKILLS AND CONSTRUCTION PROCESSES
(Start this question on a NEW page.)
4.1 The illustration below shows the nozzle of a MIG welding apparatus. 
4.1.1 Describe the origin and purpose of the shielding gas cloud that forms around the welding area. (3)
4.1.2 Explain the procedure that must be followed when the feed wire burns onto the copper welding tip. (4)
4.1.3 Name TWO circumstances that can cause the feed wire to melt onto the welding tip. (2)
4.1.4 Name THREE causes of cracks forming on the welding bead when performing MIG welding. (3)
4.2 Heat has an influence on the amount of shrinking that occurs in a metal during the welding process.
4.2.1 Describe shrinking as it occurs in a welding joint. (3)
4.2.2 Make a freehand drawing to illustrate longitudinal angular shrinking on a welded project. The dimensions of the two flat bar pieces that must be welded together is 50 mm x 10 mm x 100 mm.
The following must be included on the drawing:
- TWO pieces of metal (1)
- Welding bead (1)
- Longitudinal angular shrinking (1)
- Change in the shape of the metals (1)
4.2.3 State TWO measures that can be taken to prevent metal from distorting when welding is performed. (2)
4.3 The illustration below shows an oxy-acetylene set. 
4.3.1 Why is the use of sunglasses not recommended when cutting with the oxy-acetylene set? (2)
4.3.2 Describe the possible outcome for the gas cylinder if it accidentally topples over. (2)
4.3.3 Name TWO types of metal that can be cut with an oxy-acetylene welding set. (2)
4.4 Give technical advice to a farmer who wants to purchase a plasma cutting machine for general use on the farm. (2)
4.5 Name FOUR items of personal protective equipment (PPE) that must be worn when doing plasma cutting. (4)
4.6 State TWO factors that cause poor cutting performance when using the plasma cutting machine. (2) [35]
QUESTION 5: TOOLS, IMPLEMENTS AND EQUIPMENT
(Start this question on a NEW page.)
5.1 Specialisation plays a crucial role in the management of a farm to ensure success in the agricultural sector.
5.1.1 Name TWO disadvantages of farm mechanisation. (2)
5.1.2 Give TWO examples of fixed capital on a farm. (2)
5.2 State TWO functions of a shear bolt used in the drive system of a baling machine. (2)
5.3 Label the THREE parts of the clutch assembly, A, B and C, as shown in the photograph below.  (3)
(3)
5.4 Is it possible for a vehicle to turn around a bend if the differential is locked? Explain the answer. (3)
5.5 Give TWO advantages of using a bearing in a drive system.  (2)
(2)
5.6 Name TWO benefits of thermoplastic universal joints. (2)
5.7 Make a neat freehand drawing of a ratchet-type slip clutch and indicate the following components.
- Ratchet plate (1)
- Pressure spring (1)
- Driven gear with ratchet plate (1)
- Adjusting nut (1)
5.8 Explain to a tractor operator why it is better to move heavy loads with the rear fork lift rather than with the front fork lift, as shown in the picture below.  (2)
(2)
5.9 Describe what happens when the top link between a tractor and a plough is removed when ploughing. (2)
5.10 Name the connection points on the tractor where the quick coupling mechanism shown below should be connected.  (2)
(2)
5.11 Name THREE systems on a combine harvester that must be set or monitored to limit the loss of maize kernels during the harvesting process. (3)
5.12 Hammer mills that vibrate will not last long. Name THREE preventative measures that you must implement to keep a hammer mill from vibrating. (3)
5.13 Indicate TWO places on a tractor where an automatic depth control mechanism can be installed. (2)
5.14 State THREE advantages of using transmission oil in a tractor hydraulic system. (3)
5.15 A diesel tank with a surface area of 9 m² needs to be painted. Use a corrosion preventative paint with a covering capability of 3 m² per litre. TWO coats of paint are required on the tank.
Calculate the amount of paint required. (Show ALL calculations)  (3)
(3)
[40]
QUESTION 6: WATER MANAGEMENT
(Start this question on a NEW page.)
6.1 Complete the table below regarding different irrigation systems. Write only the answer next to the question numbers (6.1.1 to 6.1.4).
NAME | EXPLANATION/FUNCTION/WORKING | MATERIAL |
6.1.1(1) | Sprinkler irrigation consisting of several segments of pipe joined together and supported by trusses, mounted on wheeled towers with sprinklers positioned along its length. Permanently fixed to a middle point. | Aluminium and galvanised pipes |
Hydroponics | A system utilising sprinklers that are permanently installed | 6.1.2(1) |
Travelling gun sprinkler | 6.1.3 (1) | Polyethylene tubing and steel drum |
6.1.4(1) | A series of pipes, each with a wheel of about 1,5 m diameter. Sprinklers along its length with an engine installed at the middle of the pipe system for driving the system. | Coupled aluminium pipes on steel wheels |
6.2 State FOUR disadvantages of using a flood irrigation system. (4)
6.3 Name the function of EACH of the following parts of an irrigation system:
6.3.1 Sand filter (1)
6.3.2 Sprinkler (1)
6.3.3 Pump (1)
6.3.4 Solenoid valve (1)
6.3.5 One way valve (1)
6.4 The photographs below show devices used in irrigation scheduling. 
6.4.1 Name devices A and B above. (2)
6.4.2 What is the main purpose of the devices shown above? (1)
6.5 Name TWO devices that are used to control garden watering systems. (2)
6.6 Describe the operation of a septic tank drainage system. (3)
6.7 Name THREE points to consider when identifying a suitable location for the installation of a septic tank. (3)
6.8 Describe the operation of a pipe drainage system. (3)
6.9 Name THREE types of water purification systems that use a membrane to purify household water. (3) [30]
TOTAL SECTION B: 160
GRAND TOTAL: 200
AGRICULTURAL TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2018
AGRICULTURAL TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
AMENDED SCE PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
MAY/JUNE 2018 2018
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 C✔✔ (2)
1.1.2 D✔✔ (2)
1.1.3 B✔✔ (2)
1.1.4 B✔✔ (2)
1.1.5 C✔✔ (2)
1.1.6 D✔✔ (2)
1.1.7 A✔✔ (2)
1.1.8 B✔✔ (2)
1.1.9 C✔✔ (2)
1.1.10 D✔✔ (2) (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 yellow✔✔ (2)
1.2.2 cell phone/two way radio✔✔ (2)
1.2.3 smart controller✔✔ (2)
1.2.4 oil✔✔ (2)
1.2.5 zinc✔✔ (2) (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 D ✔✔ (2)
1.3.2 G✔✔ (2)
1.3.3 A✔✔ (2)
1.3.4 B✔✔ (2)
1.3.5 E✔✔ (2) (5 x 2) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 40
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: MATERIALS AND STRUCTURES
2.1 The alloy metal that is specifically used to manufacture the following products and TWO reasons why that metal is used.
2.1.1 Milk tanks
Stainless Steel✔ (1)
- Resistant to air, water and many chemical acids and alkali.✔
- Resistance against corrosion.✔
- Can be welded well.✔ (Any 2) (2)
2.1.2 Fittings for hot water copper pipes
Brass✔ (1)
- Strength✔
- Machinability✔
- Wear resistance✔
- Hardness✔
- Corrosion resistance✔ (Any 2) (2)
2.1.3 Hammering tools that can be used in explosive atmospheres.
Bronze(Beryllium Copper)✔ (1)
- Does not generate sparks✔
- Low friction✔
- Resist corrosion✔ (Any 2) (2)
2.2 TWO hot working processes that can be used to change the structural properties of brass.
- Annealing✔
- Stress relieving✔
- Tempering✔ (Any 2) (2)
2.3
2.3.1 TWO reasons for preferring fibre-glass troughs instead of concrete troughs for cattle.
- Easy to move around. (Light)✔
- Easy to fix/repair✔
- Rust resistance✔ (Any 2) (2)
2.3.2 Description of 'resin' as used in the manufacturing in fibreglass products.
- They are low viscosity fluids✔that can be transformed✔to tough flexible solids by adding✔a hardening agent. (Any 2) (2)
2.3.3 TWO methods used to join fibreglass parts.
- Pop rivet✔
- Bolt and nut✔
- Fibreglass✔
2.4 FIVE reasons why Vesconite is proven as the best material in the manufacture of bushes.
- It is ideal for many marine applications.✔
- It does not swell and seize.✔
- It remains hard.✔
- It does not delaminate.✔
- It has low friction.✔
- It does not corrode.✔
- Bushes can easy be removed.✔
- Does not contain any asbestos (healthy)✔/Safer to work with.
- Easy to machine.✔ (Any 2) (2) (Any 5) (5)
2.5 Description of how an adhesive should be applied to a surface to ensure sufficient cohesion.
- First clean the surface properly.✔
- If the surface is very slippery, the surface can be sanded to make it coarse.✔
- Apply a thin base coat if the surface is very porous.✔
- Apply only a thin layer of adhesive because a thick layer of adhesive will result in a weak joint.✔
- Apply adhesive to both surfaces.✔ (Any 4) (4)
2.6
2.6.1 The procedure that must be followed when testing the earth system of an electric fence.
- Firstly short out the live fence line to the ground.✔
- Switch the energizer ON.✔
- Measure the voltage between the GROUND and the Earth Spike with a meter.✔
- If this is above 200 volts the earth installation is inefficient.✔ (4)
2.6.2 TWO examples of the application of electric fences on the farm.
- Protection✔/Farm security purposes.
- Temporary fences.✔
- Fencing dangerous animals.✔ (Any 2) (2)
2.6.3 THREE alternative energy sources that can be used to provide energy for an electrical fence.
- Wind✔
- Solar✔
- Water✔ (3) [35]
QUESTION 3: ENERGY
3.1 The TWO parts labelled as A and B of the turbine, and the function of each.
A | Propeller-type blades✔ | Shaped to catch the wind, transfer wind energy into drive/kinetic/rotational energy.✔ (2) |
B | Generator✔ | Generates electricity and send it to the transformer and electric grid.✔ (2) |
3.2 3.2.1 The working of the solar hot water geyser.
- The sun heats the water in the glass tubes, the heated water rise to the highest point in the system.✔
- The heated water enters the geyser through a closed copper pipe network that runs through the geyser.✔
- The hot water inside the copper pipes heats up the cold water inside the geyser.✔
- The cooled water flows downwards back to the solar tubes where it is reheated.✔ (4)
3.2.2 FOUR benefits of using solar energy to heat water.
- Environmentally friendly energy source/No pollution.✔
- Installation is relative cheap and simple.✔
- Solar power is limitless.✔
- Transition losses are limited.✔
- Does not use a lot of space.✔ (Any 4) (4)
3.3
3.3.1 TWO geological aspects that should be investigated to determine the specific area to construct a geothermal energy plant.
- Rocks that is soft enough to drill✔/Type of rock
- Volcanic activities✔
- Accessibility✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.3.2 TWO advantages of a geothermal energy plant.
- A geothermal system does not create any pollution.✔
- The cost of the land to build a geothermal power plant on is usually less.✔
- Because geothermal energy is very clean, you may receive tax cuts, and/or no environmental bills.✔
- No fuel is used to generate the power.✔
- The running costs for the plants are very low.✔
- The overall financial impact of these plants is positive.✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.4
3.4.1 TWO alternative fuels that are obtained from plants.
- Ethanol✔
- Methanol✔
- Biodiesel✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.4.2 TWO crops that can be used to produce bio-fuel.
- Sugar cane✔
- Sunflower✔
- Maize✔
- Vegetables✔
- Sorghum✔ (Any 2) (2) [20]
QUESTION 4: SKILLS AND CONSTRUCTION PROCESSES
4.1
4.1.1 The origin and purpose of the cloud formed around a welding area.
- The inserted gas✔is fed through the pipe and nozzle and exit through the holes in the nozzle.
- The function is to shield the molten puddle✔from oxygen contamination.✔ (3)
4.1.2 The procedure that must be followed when the feed wire burns onto the copper welding tip.
- Release the trigger.✔
- Take a plier and cut the blob from the welding tip.✔
- Use a file and file the welding tip.✔
- Ensure that the feeding wire is separated from the tip and continue welding.✔ (4)
4.1.3 TWO circumstances that can cause the feed wire from melting onto the welding tip.
- Gap between the nozzle and work piece is too small.✔
- Wire feed is too slow.✔
- Welding too close to your material.✔
- Building up too much heat on the tip of the welding torch.✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.1.4 THREE causes of cracks forming on the welding bead when performing MIG welding.
- Root gap too small in restrained joint.✔
- Current too high.✔
- Deep narrow weld bead. ✔(with centre line cracking)
- Inadequate filling of crater.✔
- Inadequate pre-heat on high tensile and low alloys.✔
- Incorrect composition of electrode.✔ (Any 3) (3)
4.2
4.2.1 Description of 'shrinking' as it occurs in a welding joint.
- When metal is heated it expands and when cooling down it shrink.✔
- The shrinking of welded metal and weld runs cause distortion of metal when they cool down.✔
- Shrinking take place in all directions simultaneously and therefore cause various kinds of distortion.✔ (3)
4.2.2 A free hand drawing to illustrate angular shrinking longitudinally on a welded project. The dimensions of the two flat bar pieces that must be welded together is 50 mm x 10 mm x 100 mm. 
- Two pieces of metal✔ (1)
- Welding bead✔ (1)
- Shrinking✔ (1)
- Original shape of the metals✔ (1)
4.2.3 Prevention of metal distortion when welding on metal.
- Pre-setting✔
- Welding of patch work✔
- Clamping✔
- Spot welding✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.3 4.3.1 Reasons why sunglasses are not recommended when cutting with the oxy-acetylene set.
- They do not filter the ultraviolet light effectively.✔
- Sunglasses will not protect your eyes sufficiently from flying sparks.✔ (2)
4.3.2 The possible end results for the gas cylinder when it accidentally topples over.
- The main valve may break off.✔
- The cylinder will turn into a missile and cause extreme damage.✔ (explodes) (2)
4.3.3 TWO types of metals that can be cut with an oxy-acetylene welding set.
- Mild steel✔
- Carbon steel✔
- Cast iron✔
- Stainless steel✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.4 Technical advice to a farmer who wants to purchase a plasma cutting machine for general use on the farm.
- Buy a machine according to the thickness of the metal that must be cut.✔
- You need a compressor large enough for the required working pressure✔
- Buy a well-known brand/quality.✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.5 FOUR pieces of personal protective equipment (PPE) that must be used when doing plasma cutting.
- Fireproof gloves✔
- Face shield✔
- Flame resistant clothing✔
- Leather shoes✔ (4)
4.6 Factors that cause poor cutting performance when using the plasma cutting machine.
- The working pressure of the machine is too low.✔
- A too small compressor that provides insufficient air pressure.✔
- Water in the air system.✔
- Electrode and tip are worn.✔
- Use of a too thin air hose.✔
- Blocked air filters.✔ (Any 2) (2)
[35]
QUESTION 5: TOOLS, IMPLEMENTS AND EQUIPMENT
5.1
5.1.1 TWO disadvantages of mechanization on the farm.
- High initial input cost✔
- Higher salaries✔
- Skilled labourers are needed✔
- Labour regulations✔
- Loss of jobs✔ (Any 2) (2)
5.1.2 TWO examples of fixed capital on the farm.
- Land✔
- Buildings✔
- Kraals✔
- Boreholes✔
- Pumps✔ (Any 2) (2)
5.2 TWO functions of a shear bolt used in the drive system of a baling machine.
- Prevents heavy objects from being taken into the baler.✔
- Protects the pick-up if it is impeded by anything.✔
- Protects the auger if it becomes overloaded.✔ (Any 2) (2)
5.3 THREE parts of a clutch assembly A, B and C.
A = Pressure plate✔
B = Release bearing✔
C = Clutch plate✔ (3)
5.4 Is it possible that a vehicle can turn around a bend if the differential is locked? Explain your answer.
- No✔
- When the vehicle turn around a bend the wheels will momentarily turn around a common centre,✔
- but when the differential is locked this cannot happen because the half axle shaft of the outer wheel cannot revolve faster than that of the inner wheel.✔ (3)
5.5 TWO advantages of using a bearing in a drive system.
- Bearings increase efficiency.✔
- Bearings reduce friction and wear.✔
- Allows extended use at high speeds.✔
- Avoids overheating and premature failure of a drive system.✔ (Any 2) (2)
5.6 TWO advantages of thermoplastic universal joints.
- They are light weight✔
- They have negligible backlash✔
- Are corrosion resistant✔
- They have the capability for high-speed operation✔
- They are self-lubricating✔
- Does not delaminate or soften✔
- Easy removable✔
- Easy to machine✔
- Does not swell or seize✔ (Any 2) (2)
5.7 Freehand drawing of a ratchet type slip clutch and indicating of the following components.
- Ratchet plate (1)
- Pressure spring (1)
- Driven gear with ratchet plate (1)
- Adjusting nut (1)
 (4)
(4)
5.8 Reasons why it is better moving heavy loads with a rear attachments rather than with the front-end loader.
- Rear tyres are better suited/stronger to carry the extra weight.✔
- There is less chance of side overturns because the bale is not lifted high.✔
- More stress on the front wheels causes difficult steering.✔ (Any 2) (2)
5.9 The situation in case the top link between a tractor and plough are removed when ploughing.
- The back of the plough will tend to lift up out of the soil✔or the nose of the tractor will tend to lift up.✔ (2)
5.10 Parts where a quick coupling can be connected to a tractor.
- Two lifting arms✔
- Top link✔ (2)
5.11 THREE systems on a combine harvester that must be set to prevent the loss of cornels during harvesting.
- The pickup system must be set correctly.✔
- Set the drum speed correctly.✔
- Sieves must be set correctly.✔
- Gears/pulleys.✔ (Any 3) (3)
5.12 THREE aspects to consider in order to prevent a hammer mill from vibrating.
- Hammers should be checked to ensure that their mass is the same.✔
- When replacing hammers, the whole set of hammers should be replaced at the same time.✔
- Hammers that are reversed should be replaced in its original place.✔
- Nothing should be added or removed from the rotor.✔
- Run the hammer mill at the correct speed.✔
- The hammer mill must be properly anchored.✔ (Any 3) (3)
5.13 TWO places on a tractor where the automatic depth control mechanism can be installed.
- Where the top link is fitted.✔
- In the differential housing.✔
- At the base of the lifting arms.✔ (Any 2) (2)
5.14 THREE advantages of transmission oil in tractor hydraulic systems.
- Not compressible✔
- Good lubrication qualities✔
- Remains liquid over a large temperature range✔
- Not volatile✔
- Relatively cheap✔
- Easily conductible in pipes✔
- Flows through filters, pipes, oil pumps and cylinders with ease✔
- Contains detergents that keeps parts clean✔
- Contains anti-foam detergent✔
- Good cooling qualities✔ (Any 3) (3)
5.15 A diesel tank with a surface area of 9 m² needs to be painted. Use a corrosion resistant paint with a covering capability of 3 m² per litre.
Determine how much paint is required by showing all calculations, if TWO coats of paint are required on the tank.
- Paint required = 9 m² / 3 m² (covering capability per litre)✔
= 3 litres needed
= 2 coats X 3 litres per coat✔
= 6 litres of paint✔ (3)
[40]
QUESTION 6: WATER MANAGEMENT
6.1 Completion of the table regarding different irrigation systems.
6.1.1 Centre pivot irrigation✔ (1)
6.1.2 PVC pipes with plastic or brass sprinklers✔ (1)
6.1.3 Sprinklers can irrigate areas such as small farms, parks and pastures✔ (1)
6.1.4 Lateral wheel line irrigation✔ (1)
6.2 FOUR disadvantages of flood irrigation. (4)
- When water supply is weak flood irrigation is impossible.✔
- Surface gradient (steep) leads to erosion.✔
- Infiltration tempo not constant.✔
- Drainage problems.✔
- High costs of levelling of land.✔
- Increase salinity in soil.✔ (Any 4) (4)
6.3 The functions of the following irrigation system parts.
6.3.1 Sand filter Prevent blockage of sprinkler nozzles / filters the water.✔ (1)
6.3.2 Sprinkler Provide water to plants.✔ (1)
6.3.3 Pump Provide water to the system / sprinklers.✔ (1)
6.3.4 Solenoid valve Controlling the water flowing through the system.✔ (1)
6.3.5 One way valve Prevent water from flowing back to the pipe.✔ (1)
6.4
6.4.1 TWO devices, A and B.
A Tensio meter✔
B Evaporation pan/Class – A pan✔ (2)
6.4.2 The main purpose of the devices shown.
- To determine the water evaporation rate in a specific field.✔ (1)
6.5 TWO devices that are used to control garden watering systems.
- Electronic irrigation timer✔
- Mechanical timer✔ (2)
6.6 Operation of a septic tank system.
- Sewage is broken down by anaerobic bacteria in the first tank.✔
- Very little solids remain when the watery sewerage flows to the second tank.✔
- Only liquid sewage remains and drains away through the outlet pipe or stone trench.✔ (3)
6.7 THREE points to consider when choosing a suitable location for installing a septic tank.
- The tank should not be built near boreholes and drinking water installations.✔(water source)
- A suitable distance away from the house.✔
- Not near traffic.✔
- Not near where people eat, wash or work regularly.✔ (Any 3) (3)
6.8 The operation of a pipe drainage system.
- The water drains through the surface gravel✔and seeps into the pipe's perforations✔before traveling out the end of the pipe into an area that can accommodate extra water.✔ (3)
6.9 THREE types of water purification systems that make use of a membrane to purify household water.
- Reverse osmosis✔
- Faucet filters✔
- Jug or pitched filter✔
- Inline filter✔
- Whole house purification system✔ (Any 3) (3)
[30]
TOTAL SECTION B: 160
GRAND TOTAL: 200
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2018
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
AMENDED SCE PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
MAY/JUNE 2018
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1:
1.1
1.1.1 B ✔✔
1.1.2 B✔✔
1.1.3 C ✔✔
1.1.4 C ✔✔
1.1.5 A ✔✔
1.1.6 C ✔✔
1.1.7 D ✔✔
1.1.8 D ✔✔
1.1.9 A ✔✔
1.1.10 B ✔✔ (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 Both A and B ✔✔
1.2.2 None ✔✔
1.2.3 B only ✔✔
1.2.4 B only ✔✔
1.2.5 A only ✔✔ (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 Fodder/feed flow✔✔
1.3.2 Mastitis ✔✔
1.3.3 Cryptorchidism ✔✔
1.3.4 Mesoderm ✔✔
1.3.5 Corpus luteum ✔✔ (5 x 2) (10)
1.4
1.4.1 Ether/crude fat ✔
1.4.2 Foot and mouth disease/FMD ✔
1.4.3 Endometrium ✔
1.4.4 Dystocia ✔
1.4.5 Placenta/allanto-chorion/umbilical cord ✔ (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: ANIMAL NUTRITION
2.1 The alimentary canal of a farm animal
2.1.1 Identification of parts
- A Ventriculus/gizzard/muscular stomach ✔ (1)
- D Cloaca/vent ✔ (1)
- F Crop ✔ (1)
2.1.2 Importance of part
- B Stores/releases bile ✔(1)
- E Releases digestive juices/enzymes for digestion ✔ (1)
2.1.3 Definition of chemical digestion
- Process where complex food particles are broken down to simpler substances ✔
- through the series of chemicals/enzymes/juices ✔ (2)
2.2 Processes involved in the movement of food through the digestive tract
2.2.1 Identification of the processes labelled
- C Absorption ✔ (1)
- D Assimilation ✔ (1)
- E Excretion/egestion/defaecation ✔ (1)
2.2.2 Indication of the letter of process (1)
- C ✔ (1)
- B ✔
2.2.3 The enzyme responsible for the digestion of food in A
- Salivary amylase/ptyalin ✔ (1)
2.3 Mixture of TWO feeds (Pearson Square)
2.3.1 Indication of the parts
- Maize meal: 31 parts ✔ (1)
- Soya beans: 2 parts ✔ (1)
2.3.2 Justification of the answers
- Lesser DP/DP of 11%/more of it is needed to give the required protein/carbohydrate rich ✔ (1)
- Higher DP/DP of 44%/less of it is needed to give the required protein/protein rich ✔ (1)
2.3.3 Calculation of the quantity of maize meal (in kg) in a 285kg mix
- 31 x 285 ✔ = 267,72/268kg ✔
33
OR - 31 x 100 ✔ = 93,94 x 285 = 267,72/268kg ✔ (2)
33 100
2.4 Fodder flow
2.4.1 Calculation of the total feed supply (in ton) during the year
- 450 000 kg + 216 000 kg ✔
= 666 000 kg ÷ 1000 ✔
= 666 tons ✔ (3)
2.4.2 TWO problems of the feed flow programme
- Deficit/shortage/too little feed during the dry months ✔
- Calving period coincide with the dry period ✔
- Supplementary feeding is too costly/R756 000 ✔ (Any 2) (2)
2.4.3 ONE precautionary measure a farmer needs to take
- Make provision for the dry months from the excess feed during the rainy season/storage/making hay ✔
- Reduce the numbers of animals/culling/selling ✔
- Change calving to the rainy season ✔ (Any 1) (1)
2.5 Mineral/vitamin responsible for deficiency symptoms
2.5.1 Zinc/Zn ✔ (1)
2.5.2 Phosphorus/P ✔ (1)
2.5.3 Vitamin K ✔ (1)
2.5.4 Vitamin A/retinol ✔ (1)
2.6 Feed components of a ration
2.6.1 Indication of the type of the animal
- Ruminant/cattle/sheep/goat ✔ (1)
2.6.2 TWO reasons to support the answer
- Can consume feed high in crude fibre/roughage(Lucerne and oats hay) ✔
- Molasses is utilised to activate the rumen micro-organisms ✔
- Can utilize NPN/urea ✔ (Any 2) (2)
2.6.3 Identification of the concentrate in the ration
- Maize meal ✔ (1)
2.6.4 TWO reasons of including molasses in this ration
- Improves the palatability/digestibility of roughages ✔
- Molasses is utilised to activate the rumen micro-organisms/provide energy ✔
- Binds the ration together/reduce dust/wastage of a ration ✔ (Any 2) (2)
[35]
3.1 Production levels of a poultry farm on certain months of the year
3.1.1 Bar graph on egg and broiler production from February to July 
Criteria/rubric/marking guidelines
- Correct heading ✔
- X-axis: Correctly calibrated with label (Months of the year) ✔
- Y-axis: Correctly calibrated with label (Production levels) ✔
- Correct unit (‘000) ✔
- Bar graph ✔
- Accuracy ✔ (6)
3.1.2 The trend in broiler production from February to August
- Production from February increases/more/better until ✔
- June/July/August when production stabilised/constant ✔ (2)
3.2 Production systems
3.2.1 Identification of production systems
- A Extensive production system ✔ (1)
- B Intensive production/feedlotting system ✔ (1)
3.2.2 Comparison of the two systems on the basis of
- Capital investment
System A: Less capital investment ✔ (1)
System B: More capital investment ✔ (1) - Area of land in relation to production output
System A: More land occupied but relatively less production ✔ (1)
System B: Less land but very high production ✔ (1)
3.3 Naming of the structures
3.3.1 Battery cages/deep litter house ✔ (1)
3.3.2 Farrowing pen ✔ (1)
3.3.3 Holding pen ✔ (1)
3.4 Various stages of the life cycle of a parasite
3.4.1 Identification of the type of parasite
- External/ecto-parasite ✔ (1)
3.4.2 Classification of the type of parasite according to the life cycle
- Three-host parasite ✔ (1)
3.4.3 Letters representing the stages in the life cycle of the parasite (1)
- B ✔ (1)
- D ✔ (1)
- E ✔ (1)
3.4.4 TWO detrimental effects this parasite has on livestock
- Damage the skin/teats/genitals ✔
- Lowering the resistance/decreased immunity of the host ✔
- Anaemia as a result of blood sucked from the host ✔
- Transmission of diseases ✔
- Death ✔
- General deterioration/reduced production/reproduction/ weight loss/retarded growth ✔
- Irritation ✔
- Paralysis ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.5. Diseases in animals
A Virus ✔ (1)
B Anthrax ✔ (1)
C Cattle/sheep/goat ✔ (1)
D Heartwater ✔ (1)
E Fungus/fungal ✔ (1)
3.6 Salt poisoning in livestock
3.6.1 Identification of the poisoning
- Salt poisoning ✔ (1)
3.6.2 TWO preventative measures
- Enough/sufficient salt/not too much/avoid salt contaminated water ✔
- Supply enough/clean/fresh drinking water ✔ (2)
3.6.3 ONE symptom of salt poisoning in farm animals
- Excessive salivation ✔
- Staggering/dragging the hind legs/wobbling/circling/blindness/ seizures/partially paralysed ✔
- Red/dry mucus membranes of the mouth ✔
- Increased urination/defecation ✔
- Increases thirst ✔
- Vomiting ✔
- Constipation ✔
- Hypersensitivity to touch ✔
- Aggressiveness ✔
- Abdominal pain/diarrhoea ✔
- Inflammation of the stomach and small intestine ✔ (Any 1) (1)
3.6.4 TWO possible measures to treat salt poisoning
- Remove the source/salt ✔
- Provide smaller quantities of clean/fresh drinking water at shorter intervals ✔
- Treat animals with isotonic saline solution/ hypertonic dextrose ✔ (Any 2) (2)
[35]
QUESTION 4: ANIMAL REPRODUCTION
4.1 Reproductive system of a cow
4.1.1 A ✔ (1)
4.1.2 B ✔ (1)
4.1.3 D ✔ (1)
4.2 Hormones
4.2.1 Naming parts
- A Mature Graafian follicle ✔ (1)
- C Ovum/egg/female reproductive cell/gamete ✔ (1)
4.2.2 Indication of hormone
- Follicle stimulating hormone/FSH✔ (1)
- Progesterone ✔ (1)
4.2.3 The function of infundibulum
- It captures(picks up) the ova/channel ova into the fallopian tube ✔ (1)
4.3 Embryo transplantation
4.3.1 Identification of the process
- Embryo transplantation/transfer/ET ✔ (1)
4.3.2 TWO advantages of ET to farmers
- Fast/cost effective way to increase genetic improvement ✔
- Extend the reproductive life of older/unproductive cows ✔
- Offspring from superior animals are multiplied/higher calving percentage ✔
- Genetic material in the herd is conserved ✔
- Genetic material can be transported internationally ✔
- Can improve the medical properties of products ✔
- Produce animals with improved resistance towards diseases ✔
- Prevent the extinction of valuable and endangered animals ✔
- Profits from increased sales of quality genes/products ✔
- A planned breeding programme can be implemented ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.3.3 The term referring to the cow that is
- Donor cow ✔ (1)
- Recipient/surrogate cow ✔ (1)
4.4 Artificial Insemination (AI)
4.4.1 TWO characteristics of good quality semen
- Viability/mobility/motility/80% mobility/less than 15% dead sperm cells ✔
- Colour/opaque/milky white ✔
- Volume ✔
- Odour ✔
- pH between 6,4 - 6,9/slightly acidic pH ✔
- Percentage of sperm cells with defects/morphology/less than 20% deformation/fewer deformities ✔
- Concentration ✔
- No blood in semen ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.4.2 Functions of the dilutants of semen
- Provides energy for sperm cells ✔ (1)
- Protects sperm cells against temperature changes/damage from freezing ✔ (1)
- Protects sperm cells against bacterial growth/infections ✔ (1)
4.4.3 TWO disadvantages of AI
- Labour intensive procedure ✔
- Time consuming ✔
- Incompetent operator can harm/damage cows ✔
- Diseases can spread quickly/easily ✔
- Genetic abnormalities can spread quickly/easily ✔
- Heat detection is difficult under extensive farming conditions ✔
- Expensive in terms of storage/testing ✔
- Not always successful/improper handling can decrease conception rate ✔
- Inbreeding may occur ✔
- Genetic variability is reduced ✔
- High levels of management is needed ✔
- Expert knowledge is required ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.4.4 TWO congenital defects in bulls
- Cryptorchidism ✔
- Hermaphroditism ✔
- Hypoplasia ✔
- Sperm defects ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.5 The membrane layers around the embryo
4.5.1 Identification of the membranes
A Allantois ✔ (1)
D Chorion ✔ (1)
4.5.2 TWO functions of the fluid in B
- Protects the embryo against shock/injuries ✔
- Protects the embryo against temperature changes ✔
- Protection from the attachment to other tissues ✔
- Prevent dehydration/desiccation ✔
- Lubrication of the birth canal ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.5.3 The role of membrane D
- Connects the foetus to the uterine wall/attachment/forms placenta ✔ (1)
4.5.4 The last stage of pregnancy
- Foetal stage ✔ (1)
4.6 The milk production of a dairy cow
4.6.1 Identification of the process illustrated above
- Lactation ✔ (1)
4.6.2 Indication of the time (in weeks) when the following occurred
- Week 44 ✔ (1)
- Week 0 ✔ (1)
- Week 4 ✔ (1)
4.6.3 THREE factors influencing the quantity of milk produced during the peak production
- Nutrition ✔
- Climatic/environmental conditions/housing/shelter ✔
- Individuality ✔
- Breed ✔
- Age of the cow ✔
- Number of times a cow is milked during the day ✔
- Health status ✔ (Any 3) (3) [35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2018
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
AMENDED SCE PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
MAY/JUNE 2018
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1:
1.1
1.1.1 C ✔✔
1.1.2 A ✔✔
1.1.3 B ✔✔
1.1.4 D ✔✔
1.1.5 C ✔✔
1.1.6 D ✔✔
1.1.7 B ✔✔
1.1.8 B ✔✔
1.1.9 A ✔✔
1.1.10 C ✔✔ (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 C ✔✔
1.2.2 H ✔✔
1.2.3 F ✔✔
1.2.4 B ✔✔
1.2.5 A ✔✔(5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 Promotion ✔✔
1.3.2 Assets✔✔
1.3.3 Artificial selection ✔✔
1.3.4 Biometrics ✔✔
1.3.5 Epistasis ✔✔ (5 x 2) (10)
1.4
1.4.1 Cost ✔
1.4.2 Hedging ✔
1.4.3 Phenotype ✔
1.4.4 Gene ✔
1.4.5 Atavism/throw-back ✔ (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
2.1 Marketing channel used by farmers in a free marketing system
2.1.1 Identification of the marketing channel
- Fresh produce marketing channel ✔ (1)
2.1.2 TWO advantages of a fresh produce marketing channel
- Able to sell large quantities of farm produce/attracts more buyers ✔
- Producers can use an agent to market their produce ✔
- Producers take advantage of the higher prices in times of short supply ✔
- Cash on the spot/no delay in payment ✔ (Any 2) (2)
2.1.3 TWO disadvantages of a free marketing system for a producer
- Prices fluctuate ✔
- High market costs ✔
- Time-consuming/ producer responsible to market own products ✔
- Limited bargaining power ✔
- Great risk as production decisions may lead to financial losses/surplus production can lead to a price drop ✔
- Price fixing/competition ✔
- Producers can monopolize ✔
- Attracting consumers may not be so easy ✔ (Any 2) (2)
2.2 Cooperative marketing
2.2.1 Marketing system preferred for the producers
- Cooperative marketing ✔ (1)
2.2.2 Term describing the system where produce is brought together
- Pool system ✔ (1)
2.2.3 THREE benefits of the system
- More bargaining power ✔
- Lower marketing costs ✔
- Easy access to funding/support ✔
- Cheaper services ✔
- Higher average price/dividends ✔
- Risk sharing ✔
- Producers can secure larger contracts ✔
- Time saving/time for farming activities ✔ (Any 3) (3)
2.3 Products and their quantities demanded at different prices
2.3.1 TWO factors influencing the demand of PRODUCT 2
- Preference/taste of the consumer ✔
- Usefulness of the product ✔
- Income of consumers ✔
- Number of consumers ✔
- Price of competitive products ✔
- Season of the year/seasonal fluctuation ✔
- Consumer lifestyle ✔
- Advertising/promotion ✔
- Research/healthy tendencies/legislation ✔
- Substitute products ✔
- Quality of the product ✔ (Any 2) (2)
2.3.2 Trend of quantities demanded for PRODUCT 2
- Even when the price was going up ✔ the consumers continued to buy the product ✔
- No huge difference in quantities demanded ✔ even when there was an increase in price ✔
- Slight drop in quantities demanded ✔ even when there was an increase in price ✔ (Any 1) (2)
2.3.3 Line graph of the quantities demanded for PRODUCT 1 
CRITERIA/RUBRIC/MARKING GUIDELINES
- Correct heading ✔
- X axis: Correctly calibrated with label (Quantities demanded) ✔
- Y axis: Correctly calibrated with label (Price) ✔
- Correct units (R and kg) ✔
- Line graph ✔
- Accuracy ✔ (6)
2.3.4 The relationship between price and quantity demanded
- When the price is high ✔ the quantity demanded is low ✔
- When the price is low ✔ the quantity demanded is high ✔(Any 1) (2)
2.4 Business chain
2.4.1 Wholesaler ✔ (1)
2.4.2 Yoghurt plant ✔ (1)
2.4.3 Chain store ✔ (1)
2.4.4 Milk producer ✔ (1)
2.4.5 Warehouse ✔ (1)
2.5 The price trend of two agricultural products over a period of six months
2.5.1 The product mostly responsive to seasonal fluctuation
- Product 2 ✔ (1)
2.5.2 The effect of seasonal production on the price of product 2
- When the product is out of season ✔ the price is high ✔
- When the product is in season ✔ the price is low ✔ (Any 1) (2)
2.5.3 ONE reason related to production that lead to a constant price of product 1
- Production occurs throughout the year/consistent production/ available throughout the year/products not seasonal/storage ✔ (1)
2.6 FOUR phases of the entrepreneurial process
- Identification of the opportunity ✔
- Evaluate the opportunity ✔
- Determining resources required ✔
- Developing the business plan ✔
- Starting and managing the enterprise ✔
- Growing the business ✔ (Any 4) (4) [35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
3.1 Economic characteristics of land
3.1.1 TWO economic characteristics of land
- Production potential varies ✔
- Land is fixed/found in a specific environment/restrictedness ✔
- Land is subject to the law of diminishing return ✔
- Land is indestructible ✔
- Land is durable ✔
- Land is a passive factor ✔
- Land can be bought or sold ✔
- Value appreciates over time ✔
- Land is limited ✔
- Land is a primary production factor ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.1.2 TWO measure to improve productivity of land
- Use of technology/precision farming ✔
- Adapt to scientific methods/practices ✔
- Improve water management/provision ✔
- Changing cropping practices ✔
- Consolidating uneconomical units/farming more efficiently ✔
- Restore land potential/application of indigenous knowledge ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.1.3 TWO functions of land as a production factor
- For production/provision/supply of food ✔
- It provides physical space ✔
- It is a source of minerals ✔
- It is a source of raw materials ✔
- Can be used as collateral ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.2 Activities on the farm regulated by legislation
3.2.1 Indication of the labour legislation
- Occupational Health and Safety Act (85 of 1993) ✔ (1)
- Labour Relations Act (66 of 1995) ✔ (1)
- Compensation for Occupational Injuries and Diseases Act (130 of 1993) ✔ (1)
- Basic Conditions of Employment Act (75 of 1997) ✔ (1)
3.2.2 Classification of the farm worker
- Permanent/fulltime farm worker ✔ (1)
3.2.3 TWO labour issues that might have led to the protest action
- Poor working conditions ✔
- Failure to adhere to legislation ✔
- Farm evictions ✔
- Poor living conditions ✔
- Poor wages/salaries ✔
- Lack of training/education ✔
- Poor labour management ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.2.4 TWO measures by the farmer to address the labour issues
- Better working conditions ✔
- Better wages/bonuses/incentives ✔
- Better living conditions/housing ✔
- Improved relations/communications/recognition for work well done ✔
- Provision of training/education ✔
- Better labour management ✔
- Refrain from evictions ✔
- Adherence to legislation ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.3 Capital for running an enterprise
3.3.1 Examples of capital items
- Tractor ✔ (1)
- Pesticides/fertilizers/seeds ✔ (1)
- Land/borehole ✔ (1)
3.3.2 TWO sources of capital for the family farming enterprise
- Loan ✔
- Pension package pay-out ✔ (2)
3.3.3 The total value of the assets
- R1 189 000
+ R 280 000 ✔
R1 469 000 ✔ (2)
3.3.4 Deduction of two problems from the scenario
- Insufficient capital/scarcity/undercapitalisation ✔
- Credit that will attract interest/high interest rates ✔
- Capital is subject to high risk ✔
- Capital depreciates ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.4 The steps that forms part of the decision-making process
3.4.1 The correct sequence of steps
- B ✔ (1)
- D ✔ (1)
- A ✔ (1)
- C ✔ (1)
3.4.2 TWO factors influencing effective decision making
- Speed with which decisions are taken/timing of the decisions ✔
- The degree of accuracy with which decisions are taken ✔
- The acceptability of the decisions ✔
- Business sense ✔
- Social views/ethics ✔
- Economics ✔
- Profitability ✔
- Environmental sustainability ✔
- Politics ✔
- Outcome of the SWOT analysis ✔
- Past experience/available information/research ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.5 Farm with different operations that are managed with success
3.5.1 Identification of the risk management strategy
- Diversification ✔ (1)
3.5.2 Justification
- It is a means of managing risk/risk is spread amongst many farming enterprises/a means of spreading farm investment over several enterprises ✔ (1)
3.5.3 The management skill to decide in advance on a strategy
- Planning ✔ (1)
3.5.4 TWO examples of production risks
- Unpredictable weather and climatic conditions ✔
- Drought and flooding ✔
- Disease outbreak in crops and live stock ✔
- Insect infestation ✔
- Theft/predation ✔ (Any 2) (2) [35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
4.1 Animal breeding pairs
4.1.1 The percentage of red offspring
- PAIR 1: ¾ x 100 ✔ = 75% ✔ [[(2)
4.1.2 Punnet square of the genotype of the offspring in PAIR 2
✔ | D | d ✔ |
D | DD | Dd ✔ |
d | Dd | dd |
Marking guidelines/criteria
- Correct gametes ✔
- Correct offspring ✔
- Punnet square (with gametes and offspring) ✔ (3)
4.1.3 Phenotype ratio of the offspring
- 1 white:3 red ✔
OR - 3 red:1 white ✔
OR - white:red = 1:3/red:white = 3:1 ✔ (Any 1) (1)
4.1.4 Breeding pair with dominant alleles
- Pair 2 ✔ (1)
4.1.5 Reason
- D represents dominant alleles for red pigs/both parents are red ✔ (1)
4.2 Selection
4.2.1 Genetic term responsible for improved yield
- Hybrid vigour/heterosis ✔ (1)
4.2.2 Reason for using cultivars in a breeding programme
- Superior parents with the required characteristics ✔ can produce the offspring needed/with the required characteristics ✔ (2)
4.2.3 TWO factors influencing variation
- Genes/internal ✔
- Environment/external ✔ (2)
4.2.4 TWO importance of variation
- Helps to improve plant cultivars ✔
- Leads to development of new cultivars/cultivars become more evolved and cope with changing environment ✔
- Biodiversity ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.3 Dwarf-sized piglets
4.3.1 Identification of the breeding system
- Upgrading ✔ (1)
4.3.2 ONE disadvantage of the breeding system
- Male animals/boars of the first few generations cannot be sold as breeding stock ✔
- Improvement is relatively slow ✔
- Offspring cannot be bred 100% pure ✔
- Male animals/boars must always be bought ✔ (Any 1) (1)
4.3.3 The factor determining the success of the selection process The selection of superior males/boars/AA ✔ (1)
4.3.4 Explanation for selecting boars
- Boars have superior genetic characteristics ✔and sows have inferior genetic characteristics ✔ (2)
4.3.5 Term for an animal responsible for a recessive gene
- Carrier ✔ (1)
4.3.6 Genotype of a dwarf piglet
- aa ✔ (1)
4.4 Breeding systems
4.4.1Linking the breeding systems
- Outcrossing ✔ (1)
- Species crossing ✔ (1)
- Cross breeding ✔ (1)
- Inbreeding ✔ (1)
4.4.2 TWO types of mutagenic agents
- Physical ✔
- Chemical ✔
- Biological ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.5 Genetic modification versus conventional hybrids
4.5.1 Two techniques used to develop genetically modified plants
- Electroporation ✔
- Micro- injection ✔
- Bacterial carriers ✔
- Viral carriers ✔
- Biolistic/gene gun ✔
- Calcium phosphate precipitation ✔
- Gene splicing ✔
- Gene silencing ✔
- Lipofection ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.5.2 Differentiation between
Conventional hybrid seed (1)
- Produced through normal breeding practices ✔
Genetic modified seed (1)
- Produced by intentionally inserting desired genes ✔
4.5.3 THREE advantages of genetic engineering
- Process is fast ✔
- More precise ✔
- Not limited to the crossing of species that are related ✔ (3) [35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2018
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
AMENDED SCE PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
MAY/JUNE 2018 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show ALL calculations, including formulae, where applicable. 7. Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1 to 1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.11 B.
1.1.1 The process of designing and developing the product to suit the needs of consumers is …
- selling.
- trading.
- marketing.
- branding.
1.1.2 A measure of how much the demand for a product changes if there is a change in price is known as ...
- elasticity of demand.
- inelasticity of demand.
- elasticity of supply.
- inelasticity of product.
1.1.3 The law of demand states that …
- the greater the number of consumers, the lower the demand for a specific product.
- when the price of a product decreases, the demand for it increases.
- the higher the income, the less demand for a specific product.
- when the price of a product increases so does the demand.
1.1.4 The following are the reasons for drawing up an agribusiness plan:
- To determine whether it will be possible to implement the idea with success
- To pay back the loan obtained from Land Bank
- To guide daily operations
- To determine the money needed for the business
Choose the CORRECT combination:
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
1.1.5 The labour legislation that regulates farm workers' leave and working hours:
- Occupational Health and Safety Act, 1993 (Act 85 of 1993)
- Unemployment Insurance Act, 2001 (Act 63 of 2001)
- Basic Conditions of Employment Act, 1997 (Act 75 of 1997)
- Labour Relations Act, 1995 (Act 66 of 1995)
1.1.6 The net worth of a farming enterprise is defined as …
- the owner's equity.
- expenditure minus income.
- assets plus liabilities.
- the value of assets minus liabilities.
1.1.7 An example of a whole-farm budget with more than one enterprise:
- Expected income and expenses for cabbage seedlings, fertiliser and insecticides
- Estimated income and expenses for the production of maize, beef and fodder
- Estimated expenses for the production of wool sheep
- Expected expenses for the production and selling of lucerne
1.1.8 The ability to proactively deal with challenges that might occur in future:
- Integrated farm management
- Strategic farm management
- Organisational farm management
- Problem-solving farm management
1.1.9 A large increase in growth and productivity of the offspring compared to the parents:
- Heterosis
- Heritability
- Heterozygous
- Homozygous
1.1.10 Hereditary change in the genetic material of the offspring:
- Atavism
- Prepotency
- Mutation
- Variation (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Choose a term/phrase from COLUMN B that matches a description in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–J) next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.2.6 K.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.2.1 Profit driven |
|
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Give ONE word/term for EACH of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 The process of attracting consumers to buy a product by advertising on television and the radio
1.3.2 The items that have financial value and are owned by a farmer
1.3.3 Purposeful breeding of plants and animals which is done to get new varieties of species
1.3.4 The use of statistics to analyse the biological data of an individual to determine its breeding value
1.3.5 The expression of one gene that is controlled by another gene on a chromosome (5 x 2) (10)
1.4 Change the UNDERLINED WORD in EACH of the following statements to make it TRUE. Write only the answer next to the question numbers (1.4.1 to 1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 Market is calculated by adding a certain percentage to the production input in order to make a profit.
1.4.2 Flexibility is an approach used by a manager to reduce the impact of changes in a market by using future contracts.
1.4.3 Dominance is the visible characteristics produced from individual genotypes.
1.4.4 A chromosome is a section of the DNA that contains information for a particular genetic characteristic.
1.4.5 Prepotency is the reappearance of an ancestral characteristic in an organism after it has been absent for many generations. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 The picture below illustrates a marketing channel used by farmers in a free marketing system. 
2.1.1 Identify the marketing channel illustrated above. (1)
2.1.2 State TWO advantages of the marketing channel identified in QUESTION 2.1.1. (2)
2.1.3 Give TWO disadvantages of a free marketing system for a producer. (2)
Producers put their farm produce together and sell as a collective. This is done to eliminate the problem of producing and marketing their produce as individuals. |
2.2
2.2.1 Name the marketing system illustrated above. (1)
2.2.2 Name the system whereby farm produce from various farms is brought together and marketed as one mass. (1)
2.2.3 Indicate THREE ways in which producers can benefit from this system in QUESTION 2.2.2. (3)
2.3 The table below shows two competing agricultural products and the quantities demanded at different prices.
QUANTITY DEMANDED PRODUCT 1 (kg) | QUANTITY DEMANDED PRODUCT 2 (kg) | PRICE (Rand) |
90 | 150 | 10 |
80 | 140 | 20 |
70 | 140 | 30 |
60 | 130 | 40 |
50 | 130 | 50 |
40 | 120 | 60 |
30 | 110 | 70 |
20 | 100 | 80 |
10 | 100 | 90 |
2.3.1 Indicate TWO factors, other than price, that might have influenced the demand of PRODUCT 2. (2)
2.3.2 Indicate the trend of quantities demanded at different prices of PRODUCT 2. (2)
2.3.3 Draw a line graph showing the quantities demanded of PRODUCT 1 at different prices. (6)
2.3.4 Deduce the relationship between price and quantity demanded for PRODUCT 1. (2)
2.4 The illustration below indicates an agribusiness chain. 
From the agribusiness chain above, identify the component that relates to EACH of the following statements.
2.4.1 Yoghurt is sold to retailers in large quantities. (1)
2.4.2 A variety of heavy machines and equipment is used to make yoghurt. (1)
2.4.3 The yoghurt is displayed in smaller and more consumer-friendly units. (1)
2.4.4 The primary product is sold at the lowest price. (1)
2.4.5 The yoghurt is placed in boxes and staged in pallets. (1)
2.5 The graph below shows the price trend of two agricultural products over a six-months period. 
2.5.1 Identify the product which is responsive to seasonal changes. (1)
2.5.2 Explain the effect of seasonal production on the price of the product identified in QUESTION 2.5.1. (2)
2.5.3 Give ONE reason related to production, which has led to the constant price of Product 1. (1)
2.6 Name FOUR phases of the entrepreneurial process. (4) [35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 Land is the most important production factor.
3.1.1 Name TWO economic characteristics of land. (2)
3.1.2 Suggest TWO measures to improve the productivity of land. (2)
3.1.3 Indicate TWO functions of land as a production factor. (2)
3.2 The pictures below show activities on a farm that are regulated by legislation.
3.2.1 Name the labour legislation that regulates EACH of the following: 
- Ensures that the farm worker using the machinery in PICTURE A is safe (1)
- Allows for the protest action of the farm workers in PICTURE B (1)
- Protects the farm worker using the machinery in PICTURE A if he/she is injured while on duty (1)
- The farm worker using the machinery in PICTURE A is working within the stipulated time (1)
3.2.2 Identify the type of farm worker who has been operating the machinery in PICTURE A for 20 years. (1)
3.2.3 Suggest TWO labour issues that might have led to the protest actions of farm workers in PICTURE B. (2)
3.2.4 Indicate TWO measures the farmer can take to address the labour issues in QUESTION 3.2.3. (2)
3.3
A family received a pension package of R1 189 000 which was invested in a 15 ha piece of land. As they had no capital they applied for and received a loan of R280 000 from the bank. They used R50 000 for a borehole, R158 000 for a tractor and R15 000 for pesticides, seeds and fertilisers. |
3.3.1 Identify an example of a capital item in the scenario above which is categorised as follows:
- Movable capital (1)
- Working capital (1)
- Fixed capital (1)
3.3.2 Name TWO sources of capital used by the family in the scenario above. (2)
3.3.3 Calculate the total value of the assets of this farming enterprise. (2)
3.3.4 In the scenario above, deduce TWO problems associated with capital as a production factor. (2)
3.4 The steps below form part of the decision-making process.
A. Evaluate alternatives.
B. Identify the problem with regard to its importance.
C. Choose and follow the best solution.
D. Analyse possible alternatives.
3.4.1 Rearrange the steps above in the CORRECT sequence. Write down only the letters (A–D) next to the question number (3.4.1). (4)
3.4.2 Give TWO factors which influence the effectiveness of the decision-making process. (2)
3.5 The picture below shows a farm with different operations that are managed successfully. 
3.5.1 Identify the risk management strategy shown in the picture above. (1)
3.5.2 Justify the answer to QUESTION 3.5.1. (1)
3.5.3 Name the management skill that has enabled the manager to decide on the strategy in QUESTION 3.5.1 in advance. (1)
3.5.4 Give TWO examples of production risks that can directly affect the operations of the farming enterprise above. (2) [35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
Start this question on a NEW page.
A farmer received four pigs as a gift from a neighbour.
The farmer decided to divide them into two breeding pairs as parents of the F1-generation:
The letters D (red) and d (white) were used to represent the alleles for the colour of the pigs. |
4.1
4.1.1 Calculate the percentage of the offspring that are red in the F2-generation of BREEDING PAIR 1. (2)
4.1.2 Use the Punnet square to determine the genotype of the F1-generation offspring in BREEDING PAIR 2. (3)
4.1.3 Determine the phenotypic ratio of the offspring in QUESTION 4.1.2 above. (1)
4.1.4 Indicate the breeding pair (BREEDING PAIR 1 or BREEDING PAIR 2) that has parents with dominant alleles. (1)
4.1.5 Give a reason for the answer to QUESTION 4.1.4. (1)
4.2
Two cultivars, CULTIVAR A and CULTIVAR B, are crossed. CULTIVAR A has short stems and fleshy fruit that ripen quickly, while CULTIVAR B has long stems and the fruit takes long to ripen with less juice. |
4.2.1 A very large and drastic improvement in yield was achieved when CULTIVAR A was crossed with CULTIVAR B. Give the genetic term referring to the improved yield. (1)
4.2.2 Explain why the two cultivars above are used in this breeding programme. (2)
4.2.3 State TWO factors which influence the variation in the cultivars above. (2)
4.2.4 Give TWO reasons why variation in plant breeding is important. (2)
4.3
A farmer noticed dwarf-sized piglets (aa) being born from inferior sows. This farmer then decided to use boars (AA) from unrelated piggeries that appeared to be free of dwarfism for repeated mating with inferior sows. |
4.3.1 Identify the type of breeding system practised by the farmer. (1)
4.3.2 State ONE disadvantage of the breeding system identified in QUESTION 4.3.1. (1)
4.3.3 Indicate the most important factor that would determine the success of the breeding system by referring to the information above. (1)
4.3.4 Explain why the farmer selected boars and not sows for the breeding system. (2)
4.3.5 Give a term used to describe an animal that is responsible for a recessive genetic trait, such as dwarfism. (1)
4.3.6 Indicate the genotype of a dwarf piglet. (1)
4.4 Different breeding systems used by famers to improve the performance of their breeding stock are indicated below.
inbreeding; crossbreeding; species crossing; outcrossing; line breeding |
4.4.1 Match the breeding systems above with EACH of the following statements:
- Pure-bred Holstein bull x pure-bred Holstein cow who are not from the same line (1)
- Produce offspring that is sterile (1)
- The progeny produces better than the parents (1)
- Undesirable characteristics can be bred into the progeny (1)
4.4.2 Name TWO main types of mutagenic agents that can affect the breeding systems above. (2)
4.5
The yield obtained by farmers in a typical maize-growing area using conventional hybrid seed, is lower than the latest available genetically modified technology which uses genetically modified seeds. |
4.5.1 Name TWO techniques used to develop genetically modified plants. (2)
4.5.2 Differentiate between conventional hybrid seed and genetically modified seed. (2)
4.5.3 State THREE advantages of genetic engineering. (3) [35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2018
AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
AMENDED SCE PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
MAY/JUNE 2018 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show ALL calculations, including formulae, where applicable.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.11 B.
1.1.1 A feeding approach where farm animals have unlimited access to rations, roughage and licks:
- Vitamin provision
- Ad lib
- Natural grazing
- Supplementation
1.1.2 The end products of carbohydrate digestion by micro-organisms in the rumen:
- Amino acids
- Volatile fatty acids
- Ammonia
- Peptides
1.1.3 The term which describes the quantity of feed that is absorbed for maintenance and growth:
- Dry matter
- Nutritive ration
- Feed digestibility
- Feed palatability
1.1.4 The energy value of a feed that is calculated by subtracting energy lost through faeces, urine and gases from gross energy:
- Net energy
- Digestible energy
- Metabolic energy
- Kinetic energy
1.1.5 The following represent the life cycle of a bont tick:
- Larva, nymph and adult are found on separate hosts.
- Larva and nymph are found on one host.
- Larva is found on one host and nymph is found on another host.
- Larva and nymph are found on one host and the adult is found on another host.
1.1.6 Choose ONE description about the flight zone of an animal which is CORRECT:
- A point where a handler will initiate movement
- An area that an animal is not able to see without turning its head
- The space around the animal where it feels safe
- An area where the animal feels threatened
1.1.7 Pigs show the following behaviour when they are under stress:
- Eating hurriedly
- Lying calmly
- Wallow in water
- Biting their tails
1.1.8 Tail docking in sheep is done to …
- make animals ready for agricultural shows.
- improve wool and meat quality directly.
- improve their feed conversion rate.
- prevent blowfly infection.
1.1.9 During the process of spermatogenesis, the following occur:
- Spermatogonia divide during mitosis to form primary spermatocytes.
- Secondary spermatocytes divide during meiosis 1 to form spermatozoa.
- Primary spermatocytes divide through meiosis 1 to form two secondary spermatocytes.
- Spermatids undergo morphological changes to form spermatozoa.
Choose the CORRECT combination:
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
1.1.10 The oestrus stage in cows where there is rapid development of follicles:
- Met-oestrus
- Pro-oestrus
- Oestrus
- Di-oestrus (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Indicate whether each of the descriptions in COLUMN B applies to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A AND B or NONE of the items in COLUMN A. Write A only, B only, both A and B or none next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.2.6 B only.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
1.2.1 | A: | Abomasum | Secretion of gastric juice |
B: | Proventriculus | ||
1.2.2 | A: | NR of 1 : 7 | Feed suitable for producing ewes |
B: | NR of 1 : 10 | ||
1.2.3 | A: | Dosing | Appropriate method to control external parasites |
B: | Dipping | ||
1.2.4 | A: | Marbling | The stiffening of muscles in the body of an animal immediately after slaughtering |
B: | Rigor mortis | ||
1.2.5 | A: | Repeat-breeder syndrome | A cow that needs to mate three or more times before it can conceive |
B: | Freemartinism | ||
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Give ONE word/term for EACH of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 A plan for livestock farmers to ensure that there is enough feed on the farm on an on-going basis to meet animal requirements
1.3.2 A bacterial disease that affects mammary glands
1.3.3 The condition where the testes of male animals remain inside the abdominal cavity
1.3.4 The primary germ layer that surrounds the embryo from which the heart, skeleton and urogenital system develop
1.3.5 The yellow body that is formed in the empty follicle after ovulation, which secretes progesterone (5 x 2) (10)
1.4 Change the UNDERLINED WORD(S) in EACH of the following statements to make it/them TRUE. Write only the answer next to the question numbers (1.4.1 to 1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 The amount of fat and fat-soluble compounds in a feed is known as nitrogen extract.
1.4.2 Rift Valley Fever is a viral disease that causes blister-like lesions on the tongue and lips.
1.4.3 The inner layer of the uterus is called the myometrium.
1.4.4 Gestation is a prolonged and difficult parturition requiring frequent assistance.
1.4.5 The chorion transports oxygen and nutrients from the mother's blood to the foetus. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: ANIMAL NUTRITION
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 The diagram below represents the alimentary canal of a farm animal. 
2.1.1 Name parts A, D and F. (3)
2.1.2 Give the importance of parts B and E in the digestion of feed. (2)
2.1.3 Define the concept chemical digestion. (2)
2.2 The flow chart below shows different processes involved in the movement of food through the digestive tract of farm animals. 
2.2.1 Name processes C, D and E. (3)
2.2.2 Match the descriptions below with the processes in the flow chart above. Write only the letter (A–E) next to the question numbers (2.2.1(a) and 2.2.1(b)).
- Finger-like projections will increase the surface area for nutrient uptake (1)
- Enzyme digestion occurs (1)
2.2.3 Name the enzyme in non-ruminants that is responsible for the digestion of food in A. (1)
2.3 Two feeds are mixed according to the following proportions to obtain a balanced ration to meet the protein need of producing ewes: 
2.3.1 Indicate the parts that represent:
- Maize meal (1)
- Soya beans (1)
2.3.2 Justify the answers to QUESTIONS 2.3.1(a) and 2.3.1(b). (2)
2.3.3 Calculate the quantity of maize meal (in kg) needed to make 285 kg of the mixture. (2)
A dairy farmer keeps a 100 cows on a pasture that supplies a total of 450 000 kg during the rainy season and 216 000 kg during the dry season. The cows are due for calving during the dry months to prevent parasite infestation. The average animal's requirement is 360 000 kg during the rainy season and it increases to 390 000 kg during the dry months due to pregnancy and lactation. Supplementary feeding during the dry months costs a total of R756 000. |
2.4
2.4.1 Calculate the total feed supply (in tons) during the year. (3)
2.4.2 Identify TWO problems of this feed flow programme. (2)
2.4.3 Suggest ONE applicable precautionary measure a farmer needs to take to prevent the problem in QUESTION 2.4.2. (1)
2.5 Name the mineral or vitamin responsible for the following deficiency symptoms:
2.5.1 Parakeratosis in pigs (1)
2.5.2 Pica in cattle (1)
2.5.3 Poor blood clotting in chickens (1)
2.5.4 Night blindness in farm animals (1)
2.6 The graph below shows the feed components of a ration for a farm animal. 
2.6.1 Indicate the type of farm animal that can be fed with this ration. (1)
2.6.2 Support the answer to QUESTION 2.6.1 by giving TWO reasons based on the evidence in the graph. (2)
2.6.3 Identify a concentrate feed in the ration above. (1)
2.6.4 Give TWO reasons for including molasses in this ration. (2) [35]
QUESTION 3: ANIMAL PRODUCTION, PROTECTION AND CONTROL
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 The data below shows the production levels of a poultry farm on certain months of the year.
MONTH OF THE YEAR | PRODUCTION (EGGS) (thousand units) | PRODUCTION (BROILERS) (thousand units) |
January | 35 | 20 |
February | 25 | 20 |
March | 40 | 30 |
April | 30 | 40 |
May | 45 | 50 |
June | 50 | 60 |
July | 35 | 60 |
August | 40 | 60 |
3.1.1 Draw a combined bar graph of the egg and broiler production levels on a poultry farm from February to July. (6)
3.1.2 Indicate the trend in broiler production from February to August. (2)
3.2 The pictures below illustrate animal production systems. 
3.2.1 Identify the TWO animal production systems illustrated in the pictures above. (2)
3.3.2 Compare PRODUCTION SYSTEMS A and B on the basis of the following:
- Capital investment (2)
- Area of land in relation to production output (2)
3.3 Name the structure applicable in EACH of the situations below.
3.3.1 Birds are kept to lay eggs for the entire production cycle. (1)
3.3.2 Sows are housed during the late pregnancy period until after giving birth to prevent them from lying on piglets. (1)
3.3.3 Animals are kept at an auction site or just before loading for a short period of time. (1)
3.4 The diagram below indicates various stages of the life cycle of a parasite. 
3.4.1 Identify the type of parasite illustrated in the diagram above. (1)
3.4.2 Classify the parasite according to its life cycle as indicated in the diagram above. (1)
3.4.3 Write down the letter (A–F) that represents each of the following stages in the life cycle of the parasite in the diagram above:
- The larvae that hatch from the eggs (1)
- The nymph that will feed on the second host (1)
- The tick that will feed on the third host (1)
3.4.4 Name TWO detrimental effects this parasite could have on livestock. (2)
3.5 Complete the table below by writing the missing information next to the letters (A–E) in the ANSWER BOOK. (Do NOT copy the table.)
DISEASE | CAUSING ORGANISM | SYMPTOMS | TYPE OF ANIMAL |
Avian flu | A (1) | Swelling of the combs and nasal discharge | Poultry |
B (1) | Bacteria | Bloody discharge from the nose, mouth and rectum | C(1) |
D (1) | Protozoa | Froth around the mouth and heart | Cattle |
Lumpy wool | E (1) | Forms a crust on the skin | Wool sheep |
3.6 The picture below shows farm animals consuming a salt lick. Mortalities may occur when there is a high concentration of salt and a shortage of clean drinking water. 
3.6.1 Name the type of poisoning the farm animal above may contract. (1)
3.6.2 Name TWO preventative measures to take in case of the poisoning named in QUESTION 3.6.1. (2)
3.6.3 Indicate a symptom of this type of poisoning in farm animals. (1)
3.6.4 Briefly describe TWO possible measures to treat the poisoning named above. (2) [35]
QUESTION 4: ANIMAL REPRODUCTION
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 The diagram below illustrates the reproductive system of a cow. 
Write down only the letter (A–D) of the part where EACH of the following occurs:
4.1.1 Fertilisation (1)
4.1.2 Implantation of the fertilised ovum (1)
4.1.3 Deposition of semen by a male organ (1)
4.2 The diagram below illustrates the role of hormones in the development and functioning of organs in the female animal. 
4.2.1 Name parts A and C. (2)
4.2.2 Indicate the hormone that:
- Stimulates the growth and development of part A (1)
- Is produced by part B (1)
4.2.3 State the function of part D. (1)
4.3
A female animal is treated with hormones to make her super-ovulate. The eggs are fertilised and the embryos are removed and placed into another female animal. |
4.3.1 Identify the reproductive process above. (1)
4.3.2 State TWO advantages of the reproductive process identified in QUESTION 4.3.1 to farmers. (2)
4.3.3 Give the term for a cow that has undergone the following procedures:
- Treated with hormones to super-ovulate (1)
- Placement of an embryo (1)
4.4 Artificial insemination (AI) is a technique used by farmers to improve the quality of their livestock.
4.4.1 Indicate TWO characteristics of high quality semen for successful insemination. (2)
4.4.2 Give the function of EACH of the following dilutants of semen:
- Fructose (1)
- Glycerol (1)
- Antibiotics (1)
4.4.3 Name TWO disadvantages of AI. (2)
4.4.4 Name TWO congenital defects in bulls that can lead to unsuccessful fertilisation. (2)
4.5 The diagram below shows a developing embryo. 
4.5.1 Identify membranes A and D. (2)
4.5.2 State TWO functions of fluid B. (2)
4.5.3 What is the role of membrane D? (1)
4.5.4 Indicate the last stage of pregnancy. (1)
4.6 The graph below illustrates the milk production of a dairy cow. 
4.6.1 Identify the process illustrated above. (1)
4.6.2 Use the information in the graph and give the time (in weeks) when the following occurred:
- Drying off of the cow (1)
- Calving (1)
- Peak of milk production (1)
4.6.3 Name THREE factors that will influence the quantity of milk produced during the peak production period of the cow. (3) [35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150
AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT PRACTICES GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMS PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2018
AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT PRACTICES
GRADE 12
AMENDED SCE PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
MAY/JUNE 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This paper consists of TWO sections.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Read the question carefully and answer only what is asked.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 … is the most valuable natural resource that can be utilised as animal feed.
- Soil
- Climate
- Vegetation
- Water
1.1.2 The soil property that is changed with the addition of organic material to the soil:
- Texture
- Depth
- Slope
- Structure
1.1.3 A farming system where the produce is only for the needs of the family:
- Intensive farming
- Subsistence farming
- Extensive farming
- Commercial farming
1.1.4 A person who identifies a business opportunity, has the courage to take a risk and is able to manage the enterprise:
- A farm worker
- An entrepreneurship
- An entrepreneur
- A farm manager
1.1.5 A document that keeps track of all female animals that have given birth:
- Breeding record
- Budget
- Inventory
- Feed record
1.1.6 The farm management principle which is characterised by the comparison of performance and expected results:
- Planning
- Control
- Implementing
- Motivation
1.1.7 The process when farm products are advertised and transported from the farm to outlets for consumers to buy:
- Selling
- Buying
- Support
- Marketing
1.1.8 The price of the product that settles at the point where demand for a product is equal to the supply of the same product:
- Market equilibrium
- Demand price
- Supply price
- Equilibrium price
1.1.9 Actions that will improve the agribusiness chain include:
- Improving the roads
- Shortage of storage facilities
- Good market information
- Using cold storage to prevent loss
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
1.1.10 A method that a farmer can use to create capital from the farm:
- Grant
- Interest
- Selling produced products
- Collateral (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches a term in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–L) next to the question numbers (1.2.1 to 1.2.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.2.11 M. Use each description in COLUMN B only ONCE.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.2.1 Worker shortages |
|
(10 x 2) (20)
1.3 The following statements are INCORRECT. Change the UNDERLINED word(s) to make the statements correct. Write your answer next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.3.11 Fixed capital.
1.3.1 Soil quality is collected for description, analysing and measuring.
1.3.2 GIS is a technical tool in precision farming which is used to pin point the exact location of the driverless tractor.
1.3.3. The strength of a farming business is indicated when there is not enough funds to run the enterprise.
1.3.4 The financial activity of the farm manager is to keep records of labour and production.
1.3.5 Monitoring is a prerequisite for the implementation of policies and the achievement of aims and objectives.
1.3.6 The whole farm budget compares the budgets for two or more farming practices in a specific enterprise.
1.3.7 In the organogram of a commercial farm, the farm manager has direct jurisdiction over the supervisors of the general workers of that specific enterprise.
1.3.8 Daily planning is a way of increasing productivity by having more work completed per labour unit.
1.3.9 Breeding records is the indication of the productivity of young livestock animals from weaning age to two years old.
1.3.10 Marketable livestock is an example of a fixed asset.
(10 x 1) (10)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: PHYSICAL AND FINANCIAL PLANNING
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 Mechanisation implies the partial replacement of labour by making a capital investment.
2.1.1 Name FOUR factors farmers should consider when deciding to introduce machinery in their farming practices. (4)
2.1.2 Briefly discuss FOUR reasons why farmers would rather use machinery than manual labour. (4)
2.2
Land use differs from one area to another. There are factors, such as soil depth, pH, drainage and slope, which can affect the use of land negatively. Some of these limiting factors can be corrected, e.g. breaking impermeable layers, planting vegetation strips, increasing the organic matter content of the soil, opening waterways and the application of gypsum to brackish soils. |
Use the information in the passage above and make a direct deduction from the correction method and the soil characteristics influenced. Redraw and complete the table in your ANSWER BOOK.
CORRECTION METHOD | SOIL CHARACTERISTIC |
Breaking impermeable layers | |
Planting of vegetation strips | |
Opening waterways | |
Apply gypsum |
(4)
2.3 Name THREE factors which influence land use for livestock grazing. (3)
2.4 Classify the descriptions below according to the type of capital and the term of credit (short, medium or long term) as used in agriculture:
2.4.1 Monthly account at the veterinarian in town (2)
2.4.2 Production loan at the cooperative to buy seeds and fertiliser (2)
2.4.3 Mortgage at a commercial bank, payable over a period of 20 years, to obtain more land to expand the farm (2)
2.4.4 Loan at a commercial bank, payable over a period of 60 months, to buy new implements (2)
2.5 A budget is a detailed financial plan indicating the expected income and expenditure for the near future.
2.5.1 Give TWO important elements of a farm budget. (2)
2.5.2 Compile a budget for a farm enterprise of your choice.
(You have to indicate your enterprise to receive marks.)
The content of the budget should include the following:
(a) Heading and timeframe (period) (2)
(b) Content – at least FOUR entries
Use the following table to assist you.
ITEM | NUMBER | UNIT PRICE | TOTAL PRICE |
(4 x 2) (8)
2.6 A farmer does a soil analysis in a specific crop field. The following results were obtained:
- Type of soil – sandy loam
- Soil reaction – pH = 6,0
- Magnesium – less than 0,03 p.p.m. (Ideal magnesium level – 3 p.p.m.)
- Field water capacity – 15%
2.6.1 Name TWO methods this farmer can use to increase the field water capacity of the soil. (2)
2.6.2 Describe FOUR ways to improve the soil reaction. (4)
2.7 Discuss THREE negative effects associated with the excess use of herbicides. (6)
2.8 Name and discuss the negative aspects of a farming practice where a farmer plants the same crop on the same land consecutively. (3) [50]
QUESTION 3: ENTREPRENEURSHIP, RECORDING, MARKETING, BUSINESS PLANNING AND ORGANISED AGRICULTURE
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 Name the source document that is provided for the following transactions:
3.1.1 When goods are sold on credit (1)
3.1.2 Proof of a deposit made into the bank account (1)
3.1.3 To acknowledge that money has been received by the business (1)
3.1.4 Consumables bought for cash at an agricultural convenient store (1)
3.2 The Basic Conditions of Employment Act, 1997 (Act 75 of 1997) prescribes certain conditions which must be respected by the farmer.
3.2.1 Briefly explain the requirements of EACH of the following conditions:
- Working hours per week (2)
- Overtime (2)
3.2.2 State SIX items of information about each farm worker the farmer has to record daily. (6)
3.3 Briefly describe the term agricultural business plan. (4)
3.4 Categorise the following sources of information used during market research into primary research sources and secondary research sources. Each source can ONLY be used ONCE.
|
3.4.1 Primary research sources (4)
3.4.2 Secondary research sources (2)
3.5 The following is a Balance Sheet for a mixed livestock farmer for the period ended 30 October 2017.
Balance Sheet as at 30 October 2017
LIABILITIES | VALUE (R) | ASSETS | VALUE (R) |
Current liabilities | 50 000 | Current assets | 80 000 |
Medium-term liabilities | 120 000 | Medium-term assets | 100 000 |
Fixed liabilities | 500 000 | Fixed assets | 750 000 |
Net worth | |||
TOTAL LIABILITIES | TOTAL ASSETS |
3.5.1 Describe the aim of a Balance Sheet as one of the financial statements of a farm business. (2)
3.5.2 Use the correct formula and calculate the net worth of this farming enterprise. (4)
3.5.3 Briefly discuss the viability of this enterprise. (2)
3.6 The information below was extracted from a crop farmer's financial records. The crop was produced on 1 ha of land.
Labourer paid each month for the period from planting to harvesting. |
3.6.1 Compile an Income Statement for this farmer. Use the following table and headings:
EXPENDITURE | INCOME | ||||
DATE | ITEM | AMOUNT | DATE | ITEM | AMOUNT |
(8)
3.6.2 Use the information obtained in QUESTION 3.6.1. Determine whether the farmer made a profit or a loss. Show your answer using calculations. (3)
3.7 Differentiate between:
3.7.1 A Cash Flow Statement (2)
3.7.2 An Income Statement (3)
3.8 Briefly explain how climate records influence decision making in the farm planning process. (2) [50]
QUESTION 4: HARVESTING, PROCESSING, MANAGEMENT AND AGRITOURISM
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 Farmers use post-harvest storing facilities so that plant products are available during times when market prices are higher. The quality of the product must be maintained throughout the storage period.
4.1.1 State FOUR negative effects of moisture and high temperature on stored plant products. (4)
4.1.2 Name THREE methods that can be used to minimise damage to stored plant products in storage facilities. (3)
4.2 Use the descriptions below to identify the food preservation method used:
4.2.1 Preparation of vegetables before freezing by immersing them in boiling water for a short period (1)
4.2.2 Any process that eliminates all forms of life and other biological agents present in food (1)
4.2.3 The use of ultraviolet light (UV) (1)
4.2.4 Treating food and drinks, such as milk or juice, by heating it to a certain point to kill pathogenic organisms but not influencing the flavour of the food (1)
4.2.5 Separating solids from liquids, e.g. fruit juice (1)
4.3 Name FIVE requirements for workers in an agricultural processing factory with reference to the application of the Occupational Health and Safety Act, 1993 (Act 85 of 1993). (5)
4.4 State FIVE requirements of suitable wrapping material for perishable food products. (5)
4.5 Discuss FOUR motivation techniques that develop a sense of ownership and responsibility to increase the productivity of farm workers. (8)
4.6 Complete the table below by indicating whether the marketing channel is informal or formal. Each marketing channel can ONLY be used ONCE.
|
INFORMAL MARKETING | FORMAL MARKETING |
(6)
4.7 Farmers market their products at more than one place to reduce marketing risks. Explain how this marketing strategy can reduce the marketing risk. (4)
4.8 Farm managers make decisions for their farm enterprises in order to identify the actual problems and their solutions.
Draw a flow chart indicating the SIX steps of decision-making in sequence. (7)
4.9 Name THREE types of agritourism. (3) [50]
TOTAL SECTION B: 150
GRAND TOTAL: 200
 (4)
(4)