MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupMECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TEN questions.
- Read ALL the questions carefully.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Show ALL calculations and units. Round off ALL answers to TWO decimal places.
- Candidates may use non-programmable, scientific calculators and drawing instruments.
- Take the value of gravitational force as 10 m/s-2.
- All dimensions are in millimetres, unless stated otherwise in the question.
- A formula sheet for your use is attached to this question paper.
- Write neatly and legibly.
- Use the guidelines below to assist you in managing your time.
QUESTION | CONTENT | MARKS | TIME (minutes) |
1 | Multiple-choice questions | 20 | 15 |
2 | Safety | 10 | 10 |
3 | Tools and Equipment | 12 | 10 |
4 | Materials | 13 | 10 |
5 | Terminology | 30 | 20 |
6 | Joining Methods | 25 | 25 |
7 | Forces | 30 | 30 |
8 | Maintenance | 15 | 15 |
9 | Systems and Control | 25 | 25 |
10 | Turbines | 20 | 20 |
TOTAL | 200 | 180 | |
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1–1.20) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.21 D.
1.1 FIGURE 1.1 shows one of the steps to remove and replace bearings. Which safety procedure is indicated in FIGURE 1.1?
FIGURE 1.1
- Remove the dolly by tapping it with a hammer.
- Remove the burrs from the shaft to prevent damage to the dolly.
- Place the driving dolly against the inner ring of the bearing and tap the dolly with a hammer.
- Slacken the lock nut by tapping it lightly with a hammer. (1)
1.2 Which ONE of the following safety procedures applies to the maintenance of a hydraulic press?
- Do not apply a wrench to a revolving part.
- Guards could be removed when pressing soft material.
- Pressure gauges must be tested regularly and adjusted or replaced if any malfunction occurs.
- Use the machine table as an anvil. (1)
1.3 The function of a valve-spring tester is to test the valve spring for … and squareness before fitting.
- twisting
- tension
- shearing
- deflection (1)
1.4 What is the function of a depth micrometer?
- Measures the outside diameter of a workpiece accurately
- Measures the inside diameter of a hole in a work piece accurately
- Measures the pitch diameter of a screw thread accurately
- Measures the depth of a hole in a workpiece accurately (1)
1.5 Which structure of steel is characterised as intensely hard and brittle?
- Ferrite
- Pearlite
- Cementite
- Austenite (1)
1.6 Which ONE of the following mechanical properties of steel represents resistance to shock loads?
- Brittleness
- Toughness
- Hardness
- Elasticity (1)
1.7 What is the included angle of a metric V-screw thread?
- 60°
- 45°
- 55°
- 29° (1)
1.8 What is a disadvantage of down-cut milling?
- The cutter blunts rapidly when it is used to cut material with surface scale on it.
- It can cut through thin pipes and tubes.
- A better finish is produced.
- The coolant is carried down to the teeth where it is required. (1)
1.9 Which ONE of the following tests uses sound waves to penetrate a test piece?
- Ultrasonic test
- X-ray test
- Dye penetration test
- Nick-break test (1)
1.10 Which ONE of the following is the cause of undercutting during the welding process?
- Rapid chilling
- Current too high
- Slag not removed from the previous run weld
- Dirty or wet weld electrode (1)
1.11 Which ONE of the following statements defines strain in a material? Strain is the ratio between the …
- change in length and the original length.
- change in diameter and the original length.
- total length and the original length.
- change in stress and the original stress. (1)
1.12 Refer to FIGURE 1.12 below. What type of stress, caused by force F, will occur in the bolt of the joint? 
FIGURE 1.12
- Tensile stress
- Compressive stress
- Shearing stress
- Compression stress (1)
1.13 What is the unit measure for moments?
- N/m
- N.m
- N.m2
- N.m-2(1)
1.14 What is understood by the term viscosity regarding liquids? It is the resistance to …
- flow.
- boiling.
- cooling.
- foaming. (1)
1.15 Where will you use EP 90 oil?
- Engines
- Power steering
- Brakes
- Gearbox (1)
1.16 FIGURE 1.16 below represents a hydraulic system. What is the comparison between the fluid pressure at piston A and the fluid pressure at piston B? 
FIGURE 1.16
- The pressure at piston A is the same as the pressure at piston B.
- The pressure at piston A is more than the pressure at piston B.
- The pressure at piston A is less than the pressure at piston B.
- The pressure at piston A is double the pressure at piston B. (1)
1.17 Which ONE of the following statements defines Boyle's law?
- An ideal gas law where, at constant pressure, the volume of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to its absolute temperature.
- An ideal gas law where, at constant volume, the temperature of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to its absolute pressure.
- An ideal gas law where, at constant temperature, the volume of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to its absolute pressure.
- An ideal gas law where, at constant temperature, the volume of an ideal gas is proportional to its absolute pressure. (1)
1.18 What will the velocity ratio of a belt drive system be if the driven pulley rotates at 1 000 r/min and the driver pulley at 100 r/min?
- 1 : 10
- 10 : 1
- 1 : 100
- 100 : 1 (1)
1.19 A steam turbine is used to …
- increase the fuel consumption in relation to engine output.
- drive a generator to generate electricity.
- increase the volumetric efficiency of an engine.
- increase atmospheric pressure in an engine. (1)
1.20 The advantage of a turbocharger compared to a supercharger is that it uses … to drive it.
- exhaust gases
- power from the engine
- a belt
- a fuel/air mixture (1) [20]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY
2.1 When assembling a cylinder head of a motor vehicle's engine, the valve springs must be tested before installation. State TWO safety precautions you should observe when working with the spring tester. (2)
2.2 Why is it important to wear an arc welding helmet during arc welding? (1)
2.3 Why is it important to keep the copper electrodes of a spot welder cool during operation? (1)
2.4 Name ONE distinct safety precaution when using EACH of the following items of testing equipment:
2.4.1 Brinell hardness tester (1)
2.4.2 Tensile tester (1)
2.4.3 Torsion tester (1)
2.5 At what angle to the bearing should a bearing puller be used? (1)
2.6 The following safety measures apply when using a cylinder leakage tester. Name ONE reason why you have to adhere to the following safety measures:
2.6.1 Do not exceed the prescribed pressure in the cylinder. (1)
2.6.2 The tester should be fitted properly in the spark plug hole or injector hole. (1) [10]
QUESTION 3: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT
3.1 Tools and equipment are very important to complete different tasks in the workplace. Explain the function of EACH of the following testing equipment:
3.1.1 Cylinder compression tester (2)
3.1.2 Fuel pressure tester (2)
3.1.3 Torsion tester (2)
3.2 The gas analyser is used to determine the CO and CO2 readings of the exhaust gases of an internal combustion engine. Give TWO reasons for a high CO2 reading. (2)
3.3 Most welding companies use MIG/MAGS welding equipment for their welding.
3.3.1 Give TWO reasons for using inert gas during MIG/MAGS welding. (2)
3.3.2 State TWO advantages of the use of MIG/MAGS welding rather than arc welding. (2) [12]
QUESTION 4: MATERIALS
4.1 Temperature affects the structure of steel with regard to the iron-carbon content. State TWO characteristics of each of the following:
4.1.1 Austenite (2)
4.1.2 Ferrite (2)
4.2 Explain what happens at the following critical points in the iron-carbon equilibrium diagram:
4.2.1 Lower critical point (AC1) (2)
4.2.2 Higher critical point (AC3) (2)
4.3 Give TWO reasons for enhancing the properties of the material used for a crankshaft. (2)
4.4 Give TWO reasons for tempering a camshaft. (2)
4.5 Which heat treatment process is used on piston rings? (1) [13]
QUESTION 5: TERMINOLOGY
5.1 A parallel key must be machined to fit onto a 120 mm diameter shaft. Calculate the following:
5.1.1 The width of the key (2)
5.1.2 The thickness of the key (2)
5.1.3 The length of the key (2)
5.2 A spur gear with 124 teeth must be cut on a universal milling machine. Calculate the simple indexing to cut this gear with the help of a Cincinnati dividing head. (3)
5.3 The pitch of a metric V-screw thread is 3 mm. Calculate the height of the thread. (2)
5.4 A spur gear has 48 teeth and a module of 3. Calculate the following:
5.4.1 Addendum (1)
5.4.2 Dedendum (2)
5.4.3 Clearance (2)
5.4.4 Pitch circle diameter (2)
5.4.5 Outside diameter (2)
5.4.6 Cutting depth (2)
5.4.7 Circular pitch (2)
5.5 A metric V-screw thread needs to be cut on a centre lathe by setting the compound slide to half the included angle of the thread. The workpiece has been turned down to the required diameter and prepared to the necessary requirements. State the required settings to the lathe and cutting tool to enable you to cut the screw thread. (6) [30]
QUESTION 6: JOINING METHODS
6.1 Name TWO causes of EACH of the following welding defects:
6.1.1 Slag inclusion (2)
6.1.2 Incomplete penetration (2)
6.2 Name TWO causes of atmospheric contamination during MIG/MAGS welding. (2)
6.3 Explain the procedure to perform a nick-break test on a welded joint. (5)
6.4 Give ONE reason for performing the following destructive tests:
6.4.1 Bend test (2)
6.4.2 Machinability test (2)
6.5 Give ONE reason of conducting an X-ray test on a welding joint. (2)
6.6 Define the term weld crater. (2)
6.7 Study FIGURE 6.7 below.
FIGURE 6.7
6.7.1 Identify the welding process in FIGURE 6.7. (1)
6.7.2 Label parts A–E in FIGURE 6.7. (5) [25]
QUESTION 7: FORCES
7.1 Four forces are acting on the same point. Determine, by means of calculations, the magnitude and direction of the resultant force for the system of forces in FIGURE 7.1 below. (13)
FIGURE 7.1
7.2 A compressive force of 20 kN is applied to a mild steel bush. The outer diameter is 56 mm and the inner diameter is 38 mm. The original length of the bush was 50 mm. Calculate:
7.2.1 The resistance area of the bush (2)
7.2.2 The stress in the material (3)
7.2.3 The strain if the final length of the bush is 49,975 mm (3)
7.2.4 Young's modulus of elasticity for the material (3)
7.3 FIGURE 7.3 below shows a uniform beam, which is 6 m long, that is supported by two vertical supports, A and B. A uniformly distributed force of 100 N/m is exerted on the left-hand side of the beam between the two point loads of 600 N and 850 N. Determine, by means of calculations, the magnitudes of the reactions in supports A and B. 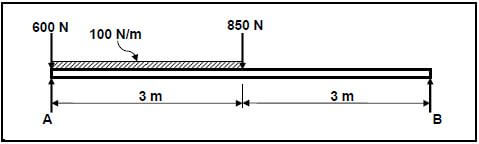
FIGURE 7.3 (6) [30]
QUESTION 8: MAINTENANCE
8.1 What is the reason for using SAE20W50 viscosity oil or other multigrade oil in an internal combustion engine? (2)
8.2 State TWO procedures to maintain V-belt drive systems. (2)
8.3 Define the term flashpoint of a lubricant. (3)
8.4 State TWO aspects to adhere to when taking care of cutting fluid used on a lathe. (2)
8.5 State TWO functions of the clutch plate. (2)
8.6 Give TWO reasons for skimming the flywheel before installing a new clutch plate. (2)
8.7 Give TWO properties of grease. (2) [15]
QUESTION 9: SYSTEMS AND CONTROL
9.1 FIGURE 9.1 below shows a gear-drive system. Driver gear A on the shaft of the electric motor has 20 teeth that mesh with gear B with 36 teeth on a counter shaft. On the counter shaft is another driver gear, C, with 18 teeth that mesh with gear D with 46 teeth. The second counter shaft has driver gear E with 42 teeth, which drives gear F with 80 teeth on the output shaft. 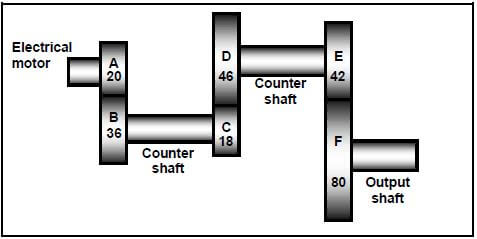
FIGURE 9.1
Calculate the:
9.1.1 Rotation frequency of the input shaft on the electric motor if the output shaft rotates at 160 r/min (3)
9.1.2 Velocity ratio between the input and output shaft (2)
9.2 FIGURE 9.2 below shows a belt drive system. The pulley, with a diameter of 0,24 m, drives the driven pulley with a diameter of 0,36 m. The driven pulley rotates at 733,33 r/min. T1 = 360 N and T2 = 90 N. 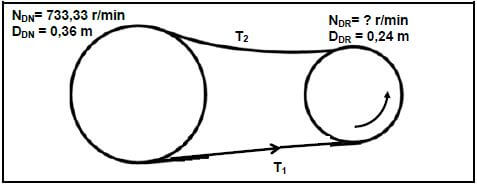
FIGURE 9.2
Calculate the:
9.2.1 Rotation frequency of the driver pulley in r/min (revolutions per minute) (3)
9.2.2 Power transmitted (2) 9.2.3 Belt speed of the system in m.s-1(metres per second) (2)
9.3 A hydraulic system is used to lift a machine. The specifications of the system are presented diagrammatically in FIGURE 9.3 below. 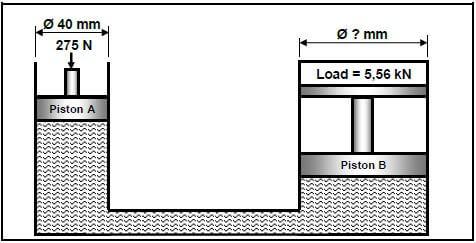
FIGURE 9.3
Calculate the:
9.3.1 Fluid pressure in the hydraulic system when in equilibrium (5)
9.3.2 Diameter of piston B to lift a load of 5,56 kN (4)
9.4 What is the purpose of the anti-lock brake system (ABS) in a vehicle? (2)
9.5 What does the abbreviation ECU stand for in terms of motor vehicles? (1)
9.6 State ONE advantage of a traction control system in a motor vehicle. (1) [25]
QUESTION 10: TURBINES
10.1 Name TWO types of reaction turbines. (2)
10.2 Explain the term boost in terms of superchargers. (2)
10.3 Name TWO types of blowers used as superchargers on a motor vehicle's engine. (2)
10.4 A gas turbine that is used as a jet engine is shown in FIGURE 10.4. Label A–F. 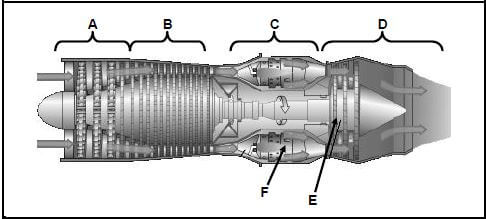
FIGURE 10.4 (6)
10.5 State TWO applications of a gas turbine. (2)
10.6 State TWO advantages of a gas turbine. (2)
10.7 What is the purpose of the waste gate in a turbocharger? (2)
10.8 Why is an engine with a turbocharger fitted with an oil cooler? (2) [20]
TOTAL: 200
FORMULA SHEET