ECONOMICS PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupECONOMICS
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1.1.1 B the Johannesburg Securities Exchange ✔ ✔
1.1.2 C zero ✔ ✔
1.1.3 A/C differentiated/unique ✔ ✔
1.1.4 D decreases ✔ ✔
1.1.5 A/C stagflation/hyperinflation ✔ ✔
1.1.6 C day ✔ ✔
1.1.7 D objective ✔ ✔
1.1.8 B labour ✔ ✔ (8 x 2) (16)
1.2 MATCHING ITEMS
1.2.1 D – Total revenue is equal to total cost ✔
1.2.2 F – Large number of buyers and sellers ✔
1.2.3 H – An example of tacit collusion in an oligopoly market with regard to pricing ✔
1.2.4 E – Creates an excess supply of labour ✔
1.2.5 I – Visiting museums and art galleries ✔
1.2.6 C – Make decisions on repo (repurchase) rate ✔
1.2.7 G – Manage the environment in such a way that it remains intact ✔
1.2.8 A – Controlled by the government ✔ (8 x 1) (8)
1.3 GIVE ONE TERM
1.3.1 Subsidy ✔
1.3.2 Shut down point ✔
1.3.3 Duopoly ✔
1.3.4 Core inflation ✔
1.3.5 Non-renewable✔
1.3.6 Infrastructure ✔ (6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer TWO of the three questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 2: MICROECONOMICS
2.1 Answer the following questions.
2.1.1 Give any TWO examples of variable costs.
- Raw materials ✔
- Electricity / Water ✔
(Accept any other correct relevant responses) (2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 Why is it difficult for new firms to enter an oligopoly market?
- High start-up capital required/existing firms may use aggressive marketing which is expensive
- Difficult to compete with established existing brands due to high advertising costs ✔ ✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
2.2 DATA RESPONSE
2.2.1 What market structure is depicted above?
- Perfect competition ✔ (1)
2.2.2 What is the market price at which the business will sell his/her product?
- R50 ✔ (1)
2.2.3 Briefly describe the term opportunity cost?
- The value of next best alternative that is given up ✔ ✔ (2)
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
2.2.4 Why is it not possible for a single business to adjust its selling price?
- There are many sellers in the market and a single business is very small to influence the market price ✔ ✔
- They are price takers, if they increase prices they won’t sell anything / If they decrease prices they will make a loss ✔ ✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.2.5 Explain the effect on the market in the long run, if the businesses in a perfect market made an economic profit.
- This will attract new entrants into the market which will result in the market supply curve shifting to the right ✔ ✔
- Market equilibrium price will fall which will reduce profits ✔ ✔
- Normal profit will be achieved in the long run✔ ✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 2) (4)
2.3 DATA RESPONSE
2.3.1 Identify the type of a monopoly depicted in the cartoon.
- Artificial ✔ (1)
2.3.2 How many firms usually dominate this type of market?
- One ✔ (1)
2.3.3 Describe the nature of the product produced by a monopoly.
- The product is unique. There is no close substitute for the product ✔ ✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.3.4 How are natural monopolies created?
Natural monopolies are created by:
- associating with high development or input cost ✔ ✔
- being owned or regulated by the government ✔ ✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.3.5 Why will this monopolist always make economic profit in the long run?
The monopolist will always make economic profit in the long run because:
- entry of other firms into the market is limited due the barriers of entry. Entry is blocked ✔ ✔
- this monopolist has a patent which give him exclusive to manufacture a product ✔ ✔
- monopolies normally produce less than the market demand in order to sell their products at higher price ✔ ✔
- if the monopolist makes a loss in the short run he can always adjust prices so that he makes an economics profit in the long run ✔ ✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 2) (4)
2.4 Explain the aims of South Africa's anti-monopoly policy.
- To promote economic transformation of the economy by making sure that there is no restriction on entry in any industry ✔ ✔
- To curb the economic power of big businesses in South Africa in order to achieve a more equitable distribution of income and wealth ✔ ✔
- To help South African businesses to become more competitive / lower prices ✔ ✔
- To ensure that South African competition law is in line with international standards ✔ ✔
- To prevent monopolies and other powerful businesses from abusing their power. ✔ ✔
- To regulate the formation of mergers and acquisitions who wish to exercise market power. ✔ ✔
- To stop firms from using restrictive practices like fixing prices, dividing markets ✔ ✔
- Regulates transfer of ownership in keeping with public interest ✔ ✔
- All South Africans gets equal opportunity to participate fairly in net economy ✔ ✔
- Provides markets in which consumers have access to freely select quantity and variety ✔ ✔
- Provides environment to compete effectively in internal markets ✔ ✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(A maximum of 4 marks may be allocated for the mere listing of facts/examples) (4 x 2) (8)
2.5 Why do oligopolies often collude although it is illegal in South Africa?
Collusion between oligopolies occur because:
- it is an effort to reduce uncertainty ✔ ✔
- they can enjoy the advantage of higher profit and limit other businesses to enter the market (to control the market / to form a collective monopoly) ✔ ✔
- the cost of doing business in an oligopoly market is very high, that is why these firms use non-price competition such as advertising, and this can cost a very large amount of money ✔ ✔
- firms are mutually interdependent and large amounts of money is often required to monitor one another's actions ✔ ✔
- it increases the firms' total cost of doing business ✔ ✔
- this often makes firms to engage in cooperation with one another instead of competing even though it is illegal in South Africa ✔ ✔ (8)
(A maximum of 2 marks may be allocated for mere listing of facts/ examples) [40]
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
QUESTION 3: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
3.1 Answer the following questions.
3.1.1 State any TWO measures used by government to ensure environmental sustainability
- Environmental taxes / Green taxes ✔
- Environmental subsidies ✔
- Issuing environmental permits ✔
- Command and control ✔
- Voluntary agreements ✔
- Education ✔
- Granting property rights ✔
- Charging for the use of the environment ✔ ✔ ✔ (2 x 1)
(Accept any other relevant response) (2)
3.1.2 What do monetarists believe to be the main reason for inflation?
- The increase in the country's total money supply which results in an increase in demand for goods and services ✔ ✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
3.2 DATA RESPONSE
3.2.1 Identify ONE cause of demand pull inflation in the information above.
- Fewer savings ✔
- Easy access to credit ✔ (1)
3.2.2 Identify ONE cause of cost push inflation in the information above.
- Natural disasters ✔
- Higher wages ✔ (1)
3.2.3 Briefly describe the term inflation.
- Inflation is a sustained and significant increase in the general price level ✔ ✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.2.4 What is the main instrument used by the South African reserve bank to control inflation.
- Repo rate / Interest rates ✔ ✔ (2)
3.2.5 Why is the SARB concerned about the impact of inflation on the Balance of Payments?
The impact of inflation on the BoP concerns SARB because:
- trade between countries will be affected negatively ✔ ✔
- it would be difficult to export goods as it would be more expensive ✔ ✔
- exports will decrease which will create a deficit on the BOP ✔ ✔
- this would mean borrowing money which creates a further burden especially to the tax payer ✔ ✔
- The inflation impacts exchange rate stability, that might cause foreign investors to withdraw their investments ✔ ✔ Any (2 x 2)
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (4)
3.3 DATA RESPONSE
3.3.1 Identify the most polluted urban area in South Africa in the information above. Hartebeespoort ✔ (1)
3.3.2 Which organisation, in the information above, links health risks to air pollution?
- World Health Organisation (1)
3.3.3 Briefly describe the term air pollution. (2)
- The release of poisonous gases into the atmosphere ✔ ✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
3.3.4 Why is pollution resulting from production such a serious problem?
- Pollution resulting from production affects the whole environment – the land, sea and atmosphere, and includes acid rain, smoke, gases, toxic chemicals, pesticide contaminants, causes diseases, (health risks) cause global warming and damage to the ozone layer ✔ ✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.3.5 Why are the major cities in South Africa the most polluted?
- High traffic congestion which results in high carbon emissions ✔ ✔
- There are a number of factories which contribute to the release of poisonous gases into the atmosphere ✔ ✔
- These cities are more industrialised as such production in the factories can result in emission of greenhouse gases ✔ ✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Any 2 x 2) (4)
3.4 Briefly describe the negative effects of tourism on the environment.
- The construction of tourist facilities such as resorts often results in destruction of natural environment (fauna and flora) ✔ ✔
- Tourists are often willing to pay higher prices for goods and services, therefore this affect the cost of living of local residents near tour attractions ✔ ✔
- On natural areas such as mountains, tourists who engage in activities such as expeditions often throw their wastes such as camping equipment on the land ✔ ✔
- A large number of tourists may add pressure on a country's infrastructure ✔ ✔
- Spoiling the views and landscape by providing tourism infrastructure ✔ ✔
- Noise, air and water pollution through tourist activities ✔ ✔
- Development of tourist facilities on scarce land ✔ ✔
- Effects on population dynamics such as migration and increased urban densities accompanied by declining population in other rural areas ✔ ✔ (8)
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (4 x 2)
(A maximum of 4 marks may be allocated for the mere listing of facts / examples)
3.5 How does the government contribute to higher inflation?
The government contributes to higher inflation by:
- increasing government spending without an increasing the aggregate supply and causes prices to rise ✔ ✔
- spending on capital projects e.g. roads, housing etc. that are more than the economy's capacity, will cause prices to rise✔ ✔
- increasing spending on consumption such as education, health and safety ✔ ✔
- spending large amounts in the social sector because they feel the need to reduce unemployment and poverty ✔ ✔
- borrowing money to raise the levels of social grants at a higher rate than the inflation rate ✔ ✔
- decreasing personal income tax creates greater consumer demand ✔ ✔
- decreasing company tax / import duties will lead to increased production and imports ✔ ✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(A maximum of 2 marks may be allocated for the mere listing of facts/examples) (8) [40]
QUESTION 4: MICROECONOMICS AND CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
4.1 Answer the following questions.
4.1.1 Give any TWO reasons why governments levy tax on tourism.
- To recover external costs ✔
- To increase revenue ✔
- To maintain infrastructure ✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 1) (2)
4.1.2 Why does the government sometimes set minimum prices (price floors) for certain products? .
- To enable producer to make a profit and to encourage them to supply important essential goods
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
4.2 DATA RESPONSE
4.2.1 Identify ONE example of a monopolistic competitor from the above information.
- Pizza hut ✔
- McDonalds ✔
- Burger King✔
- KFC ✔
- Jollibee ✔
- Chowking ✔ (1)
4.2.2 Which word in the information above suggests that a monopolistic competitor is a combination of two market structures?
- Hybrid ✔ (1)
4.2.3 Briefly describe the term normal profit.
- It is a profit that is sufficient to ensure the entrepreneur continues production/minimum earnings required to prevent the entrepreneur from leaving and using his/her production factors elsewhere ✔ ✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
4.2.4 Why is the demand curve of a monopolistic competitor more elastic than that of a monopoly?
- The products of a monopolistic competitor are good substitutes✔ unlike a monopolist where the there are no close substitutes ✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
4.2.5 How does branding play a key role in a monopolistic competitive market structure?
Branding plays a key role in monopolistic competitive markets by:
- each business selling a slightly differentiated product. ✔ ✔
- it is based on the opinion of consumers ✔ ✔
- building customer loyalty where a consumer will choose one producer over another ✔ ✔ e.g. Checkers no-name brand ✔ (2 x 2)
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (4)
4.3 DATA RESPONSE
4.3.1 Give the name of ONE city in the extract where climate change conferences were held.
- Kyoto ✔
- Berlin ✔
- Durban ✔ (1)
4.3.2 Identify the international organisation in the extract above that initiates climate change conferences.
- United nations / UN ✔ (1)
4.3.3 Describe how greenhouse gases contribute to global warming.
- Forms a blanket that traps the heat within the earth's atmosphere / A stronger greenhouse effect will warm oceans and partially melt glaciers and other ice, increasing sea level ✔ ✔ (2)
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
4.3.4 How can a green fund help to reduce global warming?
- It can enable the establishment and use of renewable (clean/eco friendly) energy ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
4.3.5 Why is global warming increasing despite the many international conferences on climate change?
Global warming is increasing due to:
- Governments, as parties to international agreements, being unable or less interested in implementing the agreements ✔✔
- rising conflict between the goal of reversing global warming and that of increasing economic development ✔✔
- industries who are more interested in increase in profits, which is possible only when increase in production takes place ✔✔
- increased production accompanied by emission of greenhouse gases, which leads to global warming ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant answers) Any (2 x 2) (4)
4.4 Describe the fiscal measures that can be used to combat demand-pull inflation.
- An increase in direct taxes e.g. PAYE to reduce excessive demand in the economy ✔✔
- An increase in indirect taxes e.g. VAT will reduce the demand for many goods ✔✔
- A loan levy can be introduced to discourage borrowing✔✔
- Reducing government spending by postponing certain projects ✔✔
- Imposing a surcharge on imported goods to reduce the demand ✔✔
- Financing the budget deficit from the non-banking sector instead of the banking sector where borrowing rates are higher ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (4 x 2) (8)
(A maximum of 4 marks may be allocated for the mere listing of facts/ examples)
(Monetary measures must not be accepted or allocated any marks)
4.5 Draw a well-labelled graph to illustrate economic profit in a monopoly market. 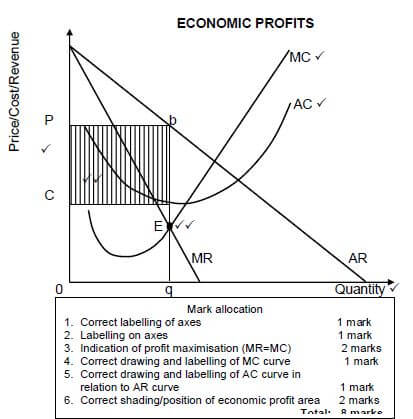
Total: 8 marks
NOTE: If candidates drew the long term economic profit, allocate marks. (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer any ONE of the two questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 5: MICROECONOMICS
- Discuss the following causes of market failure without using any graphs:
- Externalities (13)
- Missing markets (13) (26 marks)
- With the aid of a graph explain the effect of a negative externality on production levels. (10 marks) [40]
INTRODUCTION
Market failure means that the best available resources or optimal production outcome has not been achieved ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Max 2)
MAIN PART
EXTERNALITIES
- Sometimes ideal market conditions prevail and the mechanisms of the market work perfectly, however, the market does not produce optimally ✔✔
- With negative externalities, goods are over-produced (because the cost of production is not included in the market price) and with positive externalities goods are under-produced (because the benefit is not included in the market price) ✔✔
- Both result in a misallocation of resources ✔✔
- Side effects of production and consumption activities that impact on people who are not involved in the activity ✔✔
- In certain instances, people gain while other people losses out. This is because externalities prevail ✔✔
- Externalities are the cost and benefits (spill-over effects or third party effects) that convert private cost and benefits into social cost and benefits ✔✔
NOTE: THE CANDIDATE SHOULD ADDRESS THE ABOVE ISSUES TO EARN FULL MARKS
Private cost ✔
- Internal costs are also known as private costs ✔✔
- They are the usual costs that consumers incur when they buy goods and services ✔✔ E.g. a family buys a car ✔
Private benefits (internal benefits) ✔
- These benefits accrue to those who buy the goods and those who produce the goods ✔✔
- E.g. the family enjoy using the car and the producer sells it (profit) ✔
Social costs ✔
- This is the costs of goods or services to those who create them and to society at large ✔✔
- E.g. pollution caused by waste products, such as tyres, batteries, oil ✔
- No value is given for these extra or external costs because no market exists to price them ✔✔
- Private costs plus external costs is equal social cost ✔✔
Social benefits ✔
- Sometimes externalities are positive, e.g. municipalities provide clean water, for which consumers pay ✔✔
- Consumers pay for a private benefit, however, society at large has the benefit of fewer illnesses from contaminated water ✔✔
- A healthier workforce can work more productively and is often absent from work less ✔✔
- These are external benefits ✔✔
- Private benefits plus external benefits are equal to social benefits ✔✔ (13)
PUBLIC GOODS / MISSING MARKETS
- A significant market failure is the failure to produce some goods and services despite it being needed ✔✔
- It relates to public goods rather than private goods ✔✔
- Markets can only perform under certain conditions and when these conditions are absent, markets may struggle to exist ✔✔
Community goods ✔
- These are goods such as defence, police services, prison services, street lighting etc. ✔
- Free for everyone to use and often exploited and wasted by certain users to the detriment of other users ✔✔
Collective goods✔
- These are goods such as parks, beach facilities, streets, pavements, roads, bridges ✔
- They are privately owned and can be consumed by many people without causing a decrease in quantity ✔✔
- Goods that are specially characterised when it is possible to exclude free-riders by levying fees and tolls ✔✔
Public goods ✔
- Community and public goods are known as public goods ✔✔ They have two features:
- Non-rivalry ✔ the consumption by one person does not in any way reduce the consumption by another person ✔✔
- E.g. a lighthouse or street light ✔
- Non-excludability ✔ the consumption of a good cannot be confined to those who have paid for it, so there are free-riders ✔✔
- People enjoy the product without paying for, e.g. radio and television services ✔✔
- Public goods are in high demand but are not supplied by the market because of the low profit gained from them and the high cost of capital needed to supply them ✔✔
- Public goods are not provided by the price mechanism because producers cannot withhold the goods for non-payment and there is no way of measuring how much a person consumes, there is no basis for establishing a market price✔✔
Merit goods ✔
- Highly desirable for general welfare, but not highly rated by the market ✔✔
- E.g. health care, education and safety ✔
- If people had to pay the market price for them, very little would be consumed ✔✔
- The market fails because the market produces less than the desired quantity ✔✔
Demerit goods✔
- These are over-consumed goods e.g. cigarettes✔✔
- Thus more of the good is produced than is socially desirable ✔✔
- The government bans or reduces consumption of these products through taxation, and provides information to the population on their harmful effects ✔✔ (13)
(A maximum of 8 marks can be allocated for mere listing of facts/examples)
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Max 26)
ADDITIONAL PART
NEGATIVE EXTERNALITY 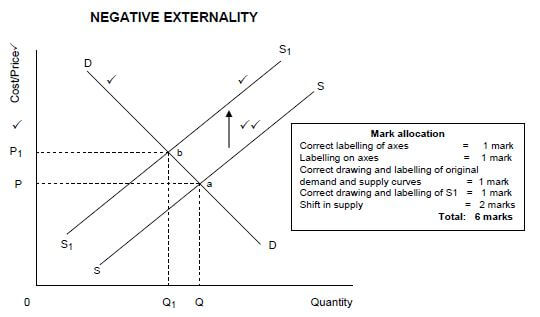
- At point a, the price charged for the good is P and Q is the quantity sold ✔✔
- This represents private costs ✔✔
- However, if it was possible to calculate the external costs, these could have been added to the private costs ✔✔
- If consumers were required to pay the full cost (social cost), a different equilibrium would prevail at b, giving a higher price of P1 and a reduced output of Q1 ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Max 6)
CONCLUSION
Market failure can have devastating effect unless government intervenes to reduce them ✔✔
(Max 2) (Accept any other correct relevant higher order response) [40]
QUESTION 6: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
Discuss the benefits of tourism for:
- Business (10)
- Infrastructure development (8)
- Households (8) (26 marks)
How can tourism attractions in less popular destinations be successfully marketed? (10 marks) [40]
INTRODUCTION
Tourism is the activities of people travelling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for no more than one consecutive year for leisure, business or other purposes ✔✔
(Max 2) (Accept any other correct relevant response)
MAIN PART
Business sector
- Tourism stimulates business in areas such as accommodation and entertainment ✔✔
- The construction industry, in private-public partnership with the government to provide the infrastructure, manufacturing sector and recreation sector all benefits from increased demand due to tourism ✔✔
- The previously disadvantaged communities get entrepreneurial opportunities through the black economic empowerment schemes ✔✔
- A large number of people get business opportunities in the informal sector ✔✔ e.g. selling of artefacts ✔
- Local retailers may have an increase in sales (and profits) because of increased demand from tourists ✔✔
- Private businesses and government work in partnership to provide the infrastructure needed for tourism ✔✔
- This increases the market share of and income of the these businesses ✔✔
- Allow existing businesses to improve the quality and variety of their products ✔✔
- Allow natural monopolies e.g. Table Mountain Cableway to achieve abnormal profits ✔✔
- The public sector also provides a range of financial incentives for private sector tourism investment (grants, subsidies, loans, tax rebates) ✔✔ (10)
Infrastructure development
- Adequate and well-maintained infrastructure is essential for tourist destinations ✔✔
- Locals share this infrastructure with tourists ✔✔
- Government often prioritises economic infrastructure such as ports and beaches ✔✔
- In addition to physical and basic infrastructure, social infrastructure is also important for the growth of tourism ✔✔
- Most of the SDIs and development corridors also have tourism as an important focus ✔✔✔✔✔✔ (8)
Households
- Members of households earn income from the tourism sector as tour operators, travel agents etc. ✔✔
- Many households are indirectly involved in tourism as employees ✔✔ e.g. in hotels, transport sector ✔
- Entrepreneurs from households that operate as curio producers or musicians can earn income from tourism ✔✔
- A large number of households acquire skills in the tourism industry ✔✔
- School curriculum and learnership offer opportunities to acquire these skills ✔✔
- Encourages rural development because many tourist attractions are located in rural areas ✔✔ (8)
(Accept any other correct relevant response)
(Allocate a maximum of 8 marks for mere listing of facts/examples) (Max. 26)
ADDITIONAL PART
Tourism can be successfully marketed in less popular destinations by:
- advertising the firms' attractions in a variety of media including social media and internet which may reach both local and international potential tourists ✔✔
- focusing on a clear message that concentrates on the strength of the attraction/ uniqueness of the destination ✔✔
- using the indigenous knowledge systems of that particular area where possible ✔✔
- describing the service offered in the best possible way to catch the interest of the likely tourist ✔✔ E.g. the use of slogans ✔
- charging a price that is competitive and money well spent for the service offered ✔✔
- helping the tourist to view the entire service as value for money – deliver a world class visitor experience ✔✔
- highlighting other places of interest in the vicinity of the attraction as part of a package ✔✔
- focusing on proudly South African products/services / Sho’t Left campaign ✔✔
- help disadvantaged South Africans to benefit from tourist attractions in the less popular destinations ✔✔
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Max. 10)
CONCLUSION
A weaker exchange rate has been a major contributing factor to South Africa's tourism industry growth over many years ✔✔
(Accept any correct relevant response) (Max 2) [40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150