AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupAGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show ALL calculations, including formulae, where applicable.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 The marketing system that stimulates the entrepreneur to show initiative and drive because of direct contact with consumers is called … marketing.
- free
- co-operative
- controlled
- pool system
1.1.2 ONE of the following factors influences the supply of a product:
- Increase in the number of consumers
- Taste and preference of the consumers in the short term
- Government subsidies and taxation policies
- The range of a product
1.1.3 The main reason for packaging agricultural products is to …
- ensure food security.
- increase the storage period of products.
- ensure a constant flow of products to the consumer.
- protect products against physical damage.
1.1.4 The following statements are TRUE with regard to price elasticity:
- Staple foods are generally price inelastic.
- Price elasticity of the supply of agricultural products in the short term is inelastic.
- The elasticity of the supply of agricultural products is usually positive in the long term.
- The elasticity of the demand of all agricultural products is always negative in the short term.
Choose the correct combination:
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
1.1.5 The following is NOT a function of land as a production factor:
- It provides space for the production process.
- It stores raw material.
- It provides food for animals.
- It cannot be used up.
1.1.6 The farmer can apply the following measures to increase labour productivity on the farm:
- The farmer must have the correct type and number of labourers.
- Set clear unattainable goals for labourers.
- Give labourers an opportunity to be involved in decision making.
- Ensure the wellbeing of labourers.
Choose the correct combination:
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
1.1.7 Flexibility as a risk management strategy involves …
- decreasing the number of livestock as a result of drought.
- growing crops as well as keeping livestock.
- distribution of the cost of risk among several stakeholders.
- concentrating only on a livestock enterprise.
1.1.8 ONE of the following is a method to acquire short-term credit:
- Bank loan paid over 36 months
- Using fixed assets as security
- Use personal loans for 6 to 12 months
- Use a grant from the Land Bank
1.1.9 A heterozygous individual has the following genotype for a qualitative genetic characteristic:
- Two dominant alleles
- Two recessive alleles
- One dominant allele and two recessive alleles
- One dominant allele and one recessive allele
1.1.10 Cattle have 30 pairs of chromosomes in the nucleus. The male gametes will have … chromosomes.
- 30
- 15
- 45
- 60
1.2 Choose a term/phrase from COLUMN B that matches a description in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–J) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 K.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.2.1 Indicates the condition when the quantity supplied is more than the quantity demanded |
|
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 The entrepreneurial success factor of generating a new business idea
1.3.2 The prediction of expected income and expenditure for a particular year
1.3.3 An inheritance mechanism which involves more than two alleles
1.3.4 A selection method based on the qualities of the relatives
1.3.5 The modification of the DNA resulting in a change in the sequence of the genes (5 x 2) (10)
1.4 Change the UNDERLINED WORD(S) in each of the following statements to make it TRUE. Write only the correct word(s) next to the question number (1.4.1–1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 Controlled marketing is a system of marketing where two or more farmers work together to reach a common goal.
1.4.2 The Labour Relations, 1993 (Act 85 of 1993) regulates health and safety of all employees in the workplace.
1.4.3 The crossing of a line-bred farm animal with an animal from a different species is called inbreeding.
1.4.4 Hybrid vigour is attained through homozygosity.
1.4.5 The internal hereditary factor that will influence the performance of an individual to be used for selection and breeding is a chromosome. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 The table below shows different marketing systems used by FARMER A and FARMER B.
FARMER A | FARMER B | |
Access to market | Local retailers and wholesalers | Larger markets via the Internet |
Price determination | Determined by local supply and demand | Determined by government |
Competition | Local producers | Competition is international |
2.1.1 Name the marketing systems used by FARMER A and FARMER B. (2)
2.1.2 Give a reason for the marketing system used by FARMER B. (1)
2.1.3 FARMER B uses mass marketing for marketing the produce. Justify this statement by referring to the table above. (1)
2.1.4 Name TWO ways in which the agribusiness chain can be streamlined for FARMER A to access markets in rural areas. (2)
2.2 Indicate TWO roles of legislation to ensure effective marketing of agricultural products. (2)
2.3 Name the component of a business plan that will reflect EACH of the following types of information:
2.3.1 Business name and the details of the person (1)
2.3.2 The number and types of employees (1)
2.3.3 Amount of money needed and future projections (1)
2.4 Name THREE common mistakes that farmers make when drawing up a business plan. (3)
2.5 The table below shows the supply and demand of peaches at different prices.
PRICE PER kg (R) | QUANTITIES SUPPLIED (kg) | QUANTITIES DEMANDED (kg) |
0,50 | 1 | 9 |
1,00 | 2 | 8 |
1,50 | 3 | 7 |
2,00 | 4 | 6 |
2,50 | 5 | 5 |
3,00 | 6 | 4 |
3,50 | 7 | 3 |
4,00 | 8 | 2 |
4,50 | 9 | 1 |
2.5.1 Use the data above and draw a line graph of the supply and demand of peaches at different prices. (6)
2.5.2 Identify the equilibrium price of peaches per kg. (1)
2.5.3 Refer to the table to explain what happens when the price per kg is below the equilibrium price. (2)
2.6 Match the factors that hamper the marketing of agricultural products below with EACH of the statements. Write down only factor next to the question number (2.6.1–2.6.4).
standardisation; perishability; bulkiness; lack of control over production; political situation |
2.6.1 Agricultural products have a limited lifespan, which shortens their time on the market. (1)
2.6.2 Unrest in the country can impact negatively on the marketing of agricultural products. (1)
2.6.3 Agricultural products are produced by a large number of producers which can lead to a surplus and a drop in price. (1)
2.6.4 Agricultural products have large volumes with relative low value. (1)
2.7 Indicate THREE requirements of a container for the packaging of fresh produce to prevent damage and spoilage. (3)
2.8 Identify the types of consumer described by EACH of the statements below.
2.8.1 Buyers divide the large shipment of products and sell it to consumers in small units (1)
2.8.2 Buy a carcass to make canned beef and biltong (1)
2.8.3 Buy products to sell to foreign markets (1)
2.9 Explain the law of demand in a market situation. (2) [35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 The table below represents two groups of farmers with different ways of farming.
GROUP A | GROUP B |
|
|
3.1.1 Indicate the land factor described in EACH of the two scenarios. (1)
3.1.2 State TWO benefits of the practices by the farmers in GROUP B that may have contributed to the higher production per hectare. (2)
3.1.3 Suggest TWO techniques applicable to the farmers in GROUP A that can improve their production per hectare. (2)
3.1.4 Identify an economic characteristic of land that will be negatively affected by monoculture and continuous cultivation. (1)
3.1.5 State TWO functions of land as a production factor. (2)
3.2
It is important to have an ethical and highly efficient work force with an understanding that the business is not about the employer only, but for their benefit too. Sleeping on duty is misconduct if committed deliberately, as it does not only affect productivity, but could endanger lives especially where dangerous equipment is being used. The necessary steps need to be taken to caution, and even charge, the employee who commits such an act. |
3.2.1 Name the type of permanent labourer who operates an advanced tractor equipped with an advanced computer and pilot steering. (1)
3.2.2 Indicate the expertise needed by the employee in QUESTION 3.2.1. (1)
3.2.3 Identify a type of misconduct by employees that would warrant the employer to take disciplinary steps. (1)
3.2.4 Name the specific legislation that the employer would use to justify the disciplinary steps. (1)
3.2.5 State TWO problems related to labour on farms. (2)
3.2.6 Recommend TWO actions an employer should consider to encourage workers to improve their productivity. (2)
3.3
A family fruit tree business was started on 34 hectares (ha). It was later scaled down to 12 hectares and is now very successful. This success can be attributed to the introduction of pigs, chickens and sheep to the farm. The waste from these animals is used to make compost. The business also buys surplus fruit from neighbouring farms to make dried fruit and jam. Five guest cottages have been built on the farm. The kitchen waste from the guest cottages is used for the compost-from-worms project on the farm. |
3.3.1 Identify the risk management strategy employed by this family business. (1)
3.3.2 Give ONE reason for the answer to QUESTION 3.3.1. (1)
3.3.3 Suggest TWO primary sources of risk in a farming business. (2)
3.3.4 State the general business management skills applied by the manager of the family business in the following situations:
- The smooth functioning of the different enterprises of the family business with the same work force (1)
- Processing and analysing the market information and realising there was a greater demand for organic products in the global markets (1)
- Developing positive relations with workers, suppliers and the markets (1)
3.3.5 Define the concept strategic management of a farm. (2)
3.4
Initially a rural community with 900 ha of communal land had no source of capital. They fought poverty through innovation by planting commercial plantations, on the communal land. Now they not only source profits from the plantations, but also from adventure tourism. At first they operated using a government grant of R11 million and a loan of R2 million from the Land Bank, payable at a rate of 5% over the period of 5 years. Currently they have a turnover of R12 million and expenses of R4 million yearly. |
3.4.1 Identify the fixed capital item in the scenario above. (1)
3.4.2 Name any TWO sources of capital used by the community to start the commercial plantations. (2)
3.4.3 Identify the problem of capital experienced by the community when they started the business. (1)
3.4.4 Indicate the term of repayment of the loan from the Land Bank. (1)
3.4.5 Calculate the profits made by the community during the 5 years. Show ALL the calculations. (5) [35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 A farmer cross-pollinated a heterozygous pea plant with yellow seed (G) and a pure-bred pea plant with green seed (g).
4.1.1 Indicate the genotype of EACH parent in the first crossing. (2)
4.1.2 Use the Punnet square method to determine the possible genotype of the offspring in the first crossing. (3)
4.1.3 Name the type of dominance shown by the crossing in QUESTION 4.1.2. (1)
4.1.4 Explain a reason for the type of dominance in QUESTION 4.1.3. (2)
4.1.5 Calculate the percentage of heterozygous offspring in the F1-generation. (2)
4.2 The illustration below shows the breeding systems commonly used by farmers. 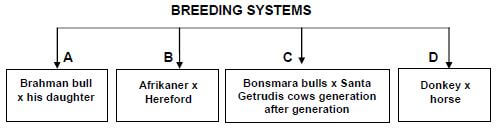
Identify the breeding system (A–D) that corresponds with EACH of the statements below. Write down only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (4.2.1–4.2.5).
4.2.1 It produces hybrid vigour. (1) 4.2.2 Its negative effects can be reduced by outcrossing. (1)
4.2.3 The offspring are hardy and can work under unfavourable conditions. (1)
4.2.4 A new breed is gradually imported into a new environment. (1)
4.2.5 Continual use leads to a gradual decrease in the performance of animals. (1)
4.3
Variation is a phenomenon that refers to differences in the characteristics of individuals which cause individual offspring to be slightly different from their parents. This phenomenon is a natural occurrence and is very important for farmers as it forms the foundation of selection and breeding programmes. |
4.3.1 Name TWO genetic processes that cause variation. (2)
4.3.2 Why is variation in a breeding programme important? Give TWO reasons. (2)
4.3.3 Distinguish between continuous variation and discontinuous variation. (2)
4.4
The farmer is breeding cattle for a weaning weight. The average weaning weight for the herd is 230 kg. One group of cattle has a mass of 220 kg and the other group has a mass of 250 kg. |
4.4.1 Indicate the group of cattle from which the farmer would select the animal to improve the weaning weight of the herd. (1)
4.4.2 Give a reason for the selection in QUESTION 4.4.1. (1)
4.4.3 Identify the selection method the farmer uses in QUESTION 4.4.1. (1)
4.4.4 Briefly explain the selection method in QUESTION 4.4.3. (2)
4.4.5 Name any TWO other selection methods the farmer can use to improve the weaning mass of the herd. (2)
4.5
The yields obtained by two maize farmers in a typical maize growing area are shown in the table below. FARMER A used conventional hybrid seed and FARMER B changed and used the latest available genetically modified (GM) seed. |
YEAR | YIELD (t/ha) (FARMER A) | YIELD (t/ha) (FARMER B) |
2011 | 10,0 | 10,2 |
2012 | 10,8 | 10,6 |
2013 | 9,6 | 12,0 |
2014 | 11,0 | 13,0 |
2015 | 10,4 | 15,0 |
2016 | 10,8 | 16,5 |
4.5.1 From the data in the table above, identify the year in which FARMER B changed to GM crops. (1)
4.5.2 Give a reason for the answer to QUESTION 4.5.1. (1)
4.5.3 Use the data above and name TWO advantages of the continued use of GM maize for FARMER B. (2)
4.5.4 Name TWO important characteristics of GM maize crops that could be responsible for the advantages that FARMER B experienced. (2)
4.5.5 Give ONE reason why there is public resistance against the use of GM cultivars or breeds. (1) [35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150