AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupAGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2018
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 A ✔✔
1.1.2 C ✔✔
1.1.3 D ✔✔
1.1.4 B ✔✔
1.1.5 D ✔✔
1.1.6 B ✔✔
1.1.7 A ✔✔
1.1.8 C ✔✔
1.1.9 D ✔✔
1.1.10 A ✔✔ (10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 G ✔✔
1.2.2 A ✔✔
1.2.3 C ✔✔
1.2.4 D ✔✔
1.2.5 H ✔✔ (5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 Innovation/creativity ✔✔
1.3.2 Budget ✔✔
1.3.3 Multiple alleles ✔✔
1.3.4 Family selection ✔✔
1.3.5 Genetic modification/engineering/manipulation✔✔ (5 x 2) (10)
1.4
1.4.1 Co-operative ✔
1.4.2 Occupational Health and Safety ✔
1.4.3 Species crossing ✔
1.4.4 Heterozygosity ✔
1.4.5 Gene ✔ (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
2.1 Table on marketing
2.1.1 Marketing system used
- Farmer A - Free marketing ✔ (1)
- Farmer B - Controlled marketing ✔ (1)
2.1.2 Reason for the system used by farmer B
- Price is determined/controlled by the government ✔ (1)
2.1.3 Justification for mass marketing
- Farmer B is reaching a wide range of consumers(larger markets) via the internet ✔ (1)
2.1.4 TWO ways to facilitate marketing in rural areas
- Improve roads/infrastructure ✔
- Improve market information through technology ✔
- Transportation of produce in vehicles with cooling facilities. ✔
- Cold storage depots ✔
- Market collectively by combining loads ✔ (Any 2) (2)
2.2 TWO roles of legislation in ensuring effective marketing
- Ensures increased market access to all participants ✔
- Makes provision for quality control over imports and exports of products ✔ (2)
2.3 Component of a business plan
2.3.1 Title/cover page ✔ (1)
2.3.2 Human resource plan ✔ (1)
2.3.3 Financial plan ✔ (1)
2.4 THREE common mistakes when drawing a business plan
- Provision of unrealistic assumptions/over-ambitious ✔
- Not being able to identify the potential risks/hiding risks ✔
- Provision of too much unnecessary information/leaving gaps/being too vague ✔
- Committing budget and cash flow errors/incomplete financials ✔
- No information on competitors/not highlighting competition ✔
- Use of incorrect format/poor writing/incomplete plan ✔
- Inadequate/poor research ✔
- Insufficient technical details ✔ (Any 3) (3)
2.5 Supply and demand of peaches
2.5.1 Line graph showing the supply and demand of peaches 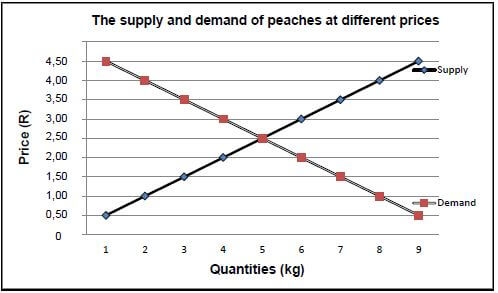
Criteria/rubric/marking guidelines
- Correct heading ✔
- X axis - correctly calibrated and labelled (Quantities) ✔
- Y axis - correctly calibrated and labelled (Price) ✔
- Correct unit (R and kg) ✔
- Line graph ✔
- Accuracy ✔ (6)
2.5.2 Determination of the equilibrium price
- R2,50 ✔ (1)
2.5.3 Situation when price is below the equilibrium price
- The quantity demanded is high ✔ and the quantity supplied is low ✔
OR - Quantity supplied is low ✔ and quantity demanded is high ✔ (2)
2.6 Linking statements to factors hampering marketing of products
2.6.1 Perishability ✔ (1)
2.6.2 Political situation ✔ (1)
2.6.3 Lack of control over production ✔ (1)
2.6.4 Bulkiness ✔ (1)
2.7 THREE requirements of a container for packaging
- It must be clean/dry/undamaged ✔
- Not import any foreign taste/odour to the product ✔
- It must be free from signs of fungal growth ✔
- It must be strong/rigid ✔ (Any 3) (3)
2.8 Type of consumers
2.8.1 Retailers ✔ (1)
2.8.2 Food processing companies/factories ✔ (1)
2.8.3 Exporters ✔ (1)
2.9 The law of demand
- The higher the price ✔ the less the people/consumers will demand the product ✔
OR - The lesser the price ✔ the more the people/consumers will buy the product ✔(2) [35]
QUESTION 3 : PRODUCTION FACTORS
3.1 Two groups of farmers
3.1.1 Factor of land addressed by the two scenarios
- Land availability/ area of production ✔ (1)
3.1.2 TWO benefits of the practices by Group B contributing to higher production
- Able to work on a large area faster✔
- Use of machinery is more effective ✔
- More cost effective to produce ✔
- Specialisation ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.1.3 TWO techniques for Group A that can improve production
- Use of scientific methods/technology ✔
- Consolidation of small units ✔ (2)
3.1.4 Economic characteristic negatively affected by monoculture and continuous cultivation
- Production potential of the land ✔ (1)
3.1.5 TWO functions of land as a production factor
- Provides food ✔
- Provides raw materials ✔
- Provides space ✔
- Source of raw minerals ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.2 Highly ethical and efficient work force
3.2.1 The type of permanent labour who operates an advanced tractor
- Skilled labour ✔ (1)
3.2.2 Indication of the expertise needed by the employee
- Technical/operational ✔ (1)
3.2.3 Act of misconduct
- Sleeping on duty ✔ (1)
3.2.4 Legislation that the employer would use to justify disciplinary steps
- Basic Conditions of Employment Act 75 of 1997 ✔ (1)
3.2.5 TWO problems related to farm labour
- Social/HIV and AIDS ✔
- Scarcity ✔
- Employers' concerns ✔
- Competition from industries/economic migrants ✔
- Lack of training/ education ✔
- Poor labour management ✔
- Safety ✔
- Poor working conditions ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.2.6 TWO actions an employer should take
- Provide incentives ✔
- Rewards for good work ✔
- Provide training/education ✔
- Improve working conditions ✔
- Improved living conditions ✔
- Mechanisation ✔
- Labour management ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.3 Management
3.3.1 Risk management strategy
- Diversification ✔ (1)
3.3.2 Reason for the management strategy
- There are a number of enterprises in one farm/agri-tourism ✔ (1)
3.3.3 TWO primary sources of risk in a farming business
- Technical ✔
- Market/price ✔
- Financial ✔
- Production ✔
- Legal ✔
- Human resources ✔ (Any 2) (2)
3.3.4 General business management skills applied by the manager
- Co-ordination/organisational ✔ (1)
- Analytic skills ✔ (1)
- Interpersonal/communication ✔ (1)
3.3.5 Definition of strategic management
- Management that allows the business to anticipate ✔ and adapt to changes in the future ✔
OR - The process of developing strategies that allow a business to achieve its vision, mission and objectives ✔ and adapt to changing conditions ✔ (2)
3.4 Capital
3.4.1 Fixed capital
- Land ✔ (1)
3.4.2 TWO sources of capital
- Grant ✔
- Loan ✔ (2)
3.4.3 Problem of capital
- Scarcity ✔ (1)
3.4.4 Term of repayment
- Medium term/5 years ✔ (1)
3.4.5 Calculation of the profit made by the community in 5 years
- Turnover: R12 000 000 x 5 = R60 000 000 ✔
- Expenses: R4 000 000 x 5 = R20 000 000 ✔
- Interest: R2 000 000 x 5% = R100 000 ✔
- R2 000 000 + R100 000 = R2 100 000 ✔
- Turnover – expenses:
R60 000 000 – R20 000 000 – R2 100 000 = - Profit: R37 900 000 ✔ (5) [35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
4.1 Heterozygous pea plant (G) and a pure breed pea plant (g)
4.1.1 Genotype of each parent in the first crossing
- Parent 1 - Gg ✔
- Parent 2 - gg ✔ (2)
4.1.2 Punnett square determining the possible genotype of the offspring in the first crossing
Gametes | G | g ✔ |
g | Gg | gg ✔ |
g | Gg | gg |
Punnett square with gametes and offspring ✔
Marking Guideline
- Complete Punnett square with gametes and offspring ✔
- Correct gametes ✔
- Correct offspring ✔ (3)
4.1.3 Type of dominance in the cross
- Complete dominance ✔ (1)
4.1.4 Reason for the type of dominance
- 50% of the seeds are yellow (G) ✔ and 50% of the seeds are green (g) ✔
OR - No intermediate/new colour ✔ as seeds resemble their parents ✔ (2)
4.1.5 Calculation of the percentage of heterozygous offspring
- 2 x 100 ✔
4
= 50% ✔ (2)
4.2 Identification of the breeding system
4.2.1 B ✔ (1)
4.2.2 A ✔ (1)
4.2.3 D ✔ (1)
4.2.4 C ✔ (1)
4.2.5 A ✔ (1)
4.3 Variation
4.3.1 TWO genetic processes causing variation
- Mutations ✔
- Meiosis/crossing over ✔
- Recombination of genes ✔
- Fertilisation ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.3.2 TWO importance of variation
- Animals/plants with superior characteristics can be selected for breeding purposes ✔
- Helps to improve the progeny/offspring ✔
- Generate new varieties/ breeds/cultivars ✔
- Maintains biodiversity ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.3.3 Distinction between
Continuous variation
- Displays a complete range of quantitative characteristics ✔ (1)
Discontinuous variation
- Qualitative characteristics have a few clear cut/distinct forms/with no intermediate forms in between ✔ (1)
4.4 Selection
4.4.1 Group of cattle to be selected
- Group with a mass of 250 kg ✔ (1)
4.4.2 Reason
- It has a higher average mass/average mass higher than the herd ✔ (1)
4.4.3 Identification of the type of selection method
- Mass selection ✔ (1)
4.4.4 Explanation of this selection method
- Selection based on the individuals with superior characteristics ✔ within the group ✔ (2)
4.4.5 TWO other selection methods
- Family selection ✔
- Pedigree selection ✔
- Progeny selection ✔
- Breeding values/EBV/biometrics ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.5 GM
4.5.1 Identification of the year
- 2012/2013 ✔ (1)
4.5.2 Reason
- An increase in yield/from10,6 – 12t/ha✔ (1)
4.5.3 TWO advantages that Farmer B got from using GM maize
- Yields increased ✔
- Increase started from 2012 ✔ (2)
4.5.4 TWO important characteristics of GM maize crops
- Resistant to herbicides ✔
- Not affected by insecticides ✔
- Crops have lower water requirements ✔
- Better adapted to the environment/region ✔ (Any 2) (2)
4.5.5 Reason for the resistance against the use of GM's
- Health risks ✔
- Environmental risks ✔
- Ethical/socio-economic concerns ✔ (Any 1) (1) [35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150