ECONOMICS GRADE 12 PAPER 2 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupECONOMICS
GRADE 12
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Answer FOUR questions as follows in the ANSWER BOOK:
- SECTION A: COMPULSORY
- SECTION B: Answer TWO of the three questions.
- SECTION C: Answer ONE of the two questions.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write the number of the question above each answer.
- Read the questions carefully and start each question on a NEW page.
- Leave 2–3 lines between subsections of questions.
- Answer the questions in full sentences and ensure that the format, content and context of your responses comply with the cognitive requirements of the questions.
- Answer only the required number of questions. Answers in excess of the required number will NOT be marked.
- Use only black or blue ink.
- A non-programmable pocket calculator may be used.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES
1.1 Various options are provided a possible answers to the following questions. Write down the question number (1.1.1–1.1.8), choose the correct answer and make a cross over the letter (A–D) of your choice in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.1.1 With cost-benefit analysis a project will be accepted when …
- social costs exceed social benefits.
- private benefit exceeds private cost.
- private costs exceed private benefit.
- social benefits exceed social costs.
1.1.2 Actual expenditure of a business on inputs required for production is called … costs.
- implicit
- explicit
- total
- average
1.1.3 Minimum returns required by the owners of a firm can be referred to as an/a … profit.
- pure
- economic
- supernormal
- normal
1.1.4 When average revenue is lower than average cost, the firm is …
- suffering an economic loss.
- making a normal loss.
- reaching break-even point.
- receiving excessive revenue.
1.1.5 Foreign tourists visiting South Africa are also called … tourists.
- domestic
- outbound
- inbound
- local
1.1.6 Headline inflation is also known as …inflation.
- adjusted core
- unadjusted CPI
- core
- PPI
1.1.7 Stagflation is associated with ...
- high unemployment, high growth and low inflation.
- low prices, high unemployment and high growth.
- low growth, high unemployment and high inflation.
- high growth, low unemployment and low inflation.
1.1.8 The market mechanism usually fails to … pollution.
- reduce
- control
- eradicate
- correct (8 × 2) (16)
1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
1.2.1 1.2.2 1.2.3 1.2.4 1.2.5 1.2.6 1.2.7 1.2.8 | Shutdown Privatisation Price ceilings Social cost Bracket creeping Transit tourism Preservation World Heritage Site |
(8 × 1) (8) | |
1.3 Give the correct concept for each of the following descriptions.
1.3.1 A legally established price floor on wages that is determined by the government
1.3.2 The variety of plant and animal life in a particular habitat
1.3.3 Carbon dioxide (CO2) gas that is released into the atmosphere due to different economic activities
1.3.4 An arrangement that occurs when sellers enter into an agreement to limit competition
1.3.5 Prices that are set by government or controlled by government through appointed authorities
1.3.6 Firms that have no influence on price (6 × 1) (6)
[30]
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer any TWO of the three questions from this section in your ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 2: MICRO ECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
2.1 Answer the following questions.
2.1.1 Name any TWO characteristics of oligopolistic markets. (2 × 1) (2)
2.1.2 Why is it only possible in the long run to vary all factors of production? (1 × 2) (2)
2.2 Study the graph below and answer questions that follow. 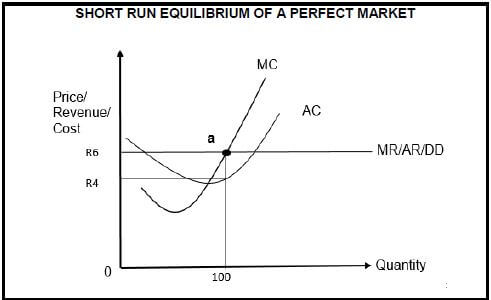
2.2.1 Which market structure is depicted in the graph above? (1)
2.2.2 Identify profit maximisation point in the above graph. (1)
2.2.3 Briefly describe the demand curve in the graph above. (2)
2.2.4 Briefly explain the output level of a perfect competitor. (2)
2.2.5 Calculate the profit/loss of the individual firm above. Show ALL calculations. (4)
2.3 Read the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
MARKET FAILURE Unemployment has been rising in South Africa for the past three decades, leading to an official unemployment rate of 27,7%. This implies a jobless total of 8,49 million, with more than 40% of the rural population unemployed and the development of a growing pool of workers who are excluded from the labour market. [Source: htp//www.opensadnu.uct.ac.za] |
2.3.1 What is the official unemployment rate in South Africa? (1)
2.3.2 Identify a reason for market failure mentioned in the extract above. (1)
2.3.3 Explain why more labourers are being excluded from the labour market. (2 × 2) (4)
2.3.4 How can the market failure mentioned in the extract above be resolved? (2 × 2) (4)
2.4 Explain free competition and nature of the product as characteristics of perfect markets. (2 × 4) (8)
2.5 With the aid of a diagram explain why oligopolists are reluctant to participate in price competition. (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
3.1 Answer the following questions.
3.1.1 Name TWO positive effects that tourism will have on our economy. (2 × 1) (2)
3.1.2 How does air pollution effect the environment? (1 × 2) (2)
3.2 Study the information below and answer questions that follow.
CULTURAL TOURISM AT ITS BEST The world tourism organisation claims that cultural tourism accounts for 37% of global tourism and continues to grow at 15% per year. Destinations should leverage what makes their societies unique and invest in developing cultural tourism, because it allows travellers to enjoy local rituals and taking home photos of shared memories and unique experiences. By embracing cultures, South Africa can boost economic growth. [www.solimarinternational.com June 2015] |
3.2.1 What type of tourism is portrayed in the picture above? (1)
3.2.2 At what rate is cultural tourism growing worldwide? (1)
3.2.3 Briefly describe the term Indigenous Knowledge Systems. (2)
3.2.4 Explain ONE reason for growth in the tourism industry. (2)
3.2.5 How can South Africa use its world heritage sites more effectively to promote tourism? (2 × 2) (4)
3.3 Study the information below and answer questions that follow.
ENEMY NUMBER ONE FOR OUR ECONOMY Rising prices for energy, food, commodities and other goods and services affect the entire economy. Inflation impacts the cost of living, cost of doing business, borrowing money and every other facet of the economy. When the economy is healthy, there is low unemployment and wage increases as business demand labour to meet the growing economy. [Adapted from: www.Cartoons] |
3.3.1 Who is the number one enemy for our economy depicted in the cartoon above? (1)
3.3.2 What happens to the economy according to the cartoon above? (1)
3.3.3 Briefly describe the term hyperinflation? (2)
3.3.4 How can taxation be used to reduce inflation? (2)
3.3.5 What is the relation between inflation and wage demands? (2 × 2) (4)
3.4 Discuss income and infrastructure as benefits of tourism to households. (2 × 4) (8)
3.5 What role does South Africa play in alleviating the negative effects of global warming? (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4 MICROECONOMICS AND CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
4.1 Answer the following questions.
4.1.1 Name TWO examples of renewable resources. (2 × 1) (2)
4.1.2 What is the purpose of inflation targeting? (1 × 2) (2)
4.2 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
WATER CRISIS IN THE EASTERN CAPE Large parts of the Eastern Cape have been gripped by drought and water shortage so severe that rivers, dams and boreholes are bone-dry. [Source: http//www.heraldlive.co.za] |
4.2.1 Which serious problem is currently experienced in the Eastern Cape? (1)
4.2.2 Why is food security threatened in the country? (1)
4.2.3 How can the public sector use education to ensure environmental sustainability? (2 × 2) (4)
4.2.4 What can the government do to solve the water crisis in the country? (2 × 2) (4)
4.3 Study the extract below and answer questions that follow.
MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION Monopolistic competition as a market structure was first identified in the 1930s by the economist Edward Chamberlin. [Adapted from: www.economicsonlinne.co.uk] |
4.3.1 Who was the first economist to identify monopolistic competition? (1)
4.3.2 Give an example of a business operating in a monopolistic market. (1)
4.3.3 Briefly describe the hybrid structure as a feature of monopolistic competition. (2 × 2) (4)
4.3.4 How can restaurants use differentiated strategies to attract more customers? (2 × 2) (4)
4.4 Explain externalities as a cause of market failures without a graph. (4 × 2) (8)
4.5 How has the implementation of minimum wages benefited workers in South Africa? (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer ONE of the two questions from this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
| STRUCTURE OF ESSAY | MARK ALLOCATION |
INTRODUCTION
| Max. 2 |
BODY:
| Max. 26 Max. 10 |
CONCLUSION
| Max. 2 |
| TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 5: MICROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
A monopoly is one of the extreme ends of our market structures and is an integral part of our economy.
- Examine the characteristics of a monopoly as a market structure. (26)
- Why, in your opinion, is a monopoly an undesirable type of market structure? (10)
QUESTION 6: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUE 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
In today’s declining economic climate, all the sectors of the economy are adversely affected by the negative effects of inflation.
- Analyse the causes of cost push inflation. (26)
- What impact does inflation have on the households? (10)
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150