AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES GRADE 12 PAPER 2 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupAGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
GRADE 12
PAPER 2
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show ALL your calculations, including formulae, where applicable.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write ONLY the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 D.
1.1.1 In sex-linked characteristics, maleness or femaleness is considered a …
- genetic phenotype.
- genetic genotype.
- polygenic appearance.
- single base loss.
1.1.2 ... refers to the money from the profit of a business that is shared among the owners of the business.
- Savings
- Credits
- Dividends
- Cash flow
1.1.3 Labourers in a commercial farming enterprise can cause losses in production if they:
- Are not skilled to perform their jobs
- Are not supervised
- They are not motivated
- Are not transferred frequently to other farms
Choose the correct combination:
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
1.1.4 The agricultural legislation that ensures fair, transparent and efficient financial markets is the …
- Security Services Board Act No. 36 of 2004.
- Agricultural Produce Agents Act of 1952.
- Consumer Protection Act of 2008.
- Agricultural Produce Amendment Act of 2004.
1.1.5 Some of the attributes of selling farm produce are that:
- hey are product oriented
- They emphasise consumers’ needs and satisfaction
- Cost are reduced to achieve maximum sales and profits
- Technological innovation is important
Choose the correct combination:
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i) and (iii)
1.1.6 The relationship between a change in quantity demanded and the change in supply in the diagram below is an indication of ...
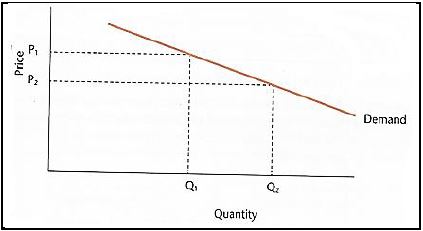 |
- elasticity of demand.
- inelastic demand.
- elasticity of supply.
- supply schedule.
1.1.7

The letter X represents …
- agricultural inputs.
- agricultural outputs.
- economies of business enterprises.
- input alternatives.
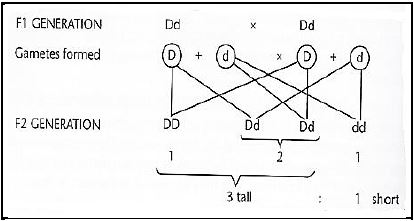
1.1.8 The percentage of the plants that are tall in the crossing below is …
- 1.1.9 An event where different buyers come together to bid on farm produce available. 25%.
- 50%.
- 75%.
- 100%.
- Cooperative farming
- Agricultural show
- Auction
- Liquidity
1.1.10 Cells that contain foreign genes that were deliberately transferred to its host are …
- somatic cells.
- transgenic cells.
- mutagenic cells.
- osteoclast cells. (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Choose a term/phrase from COLUMN B that matches a term in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–J) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 K.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.2.1 Motivation |
|
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Write the agricultural term/phrase for each of the following descriptions next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 Breeding of plants and animals that are chosen for certain desirable characteristics
1.3.2 When the price of a product settles at the point where demand is equal to supply
1.3.3 Entering into future contracts to ensure a secure market and price
1.3.4 A legally binding agreement between an employer and an employee
1.3.5 A type of mutation in which an individual has more than two whole sets of homologous chromosomes (5 x 2) (10)
1.4 Change the UNDERLINED WORD/S in the following statements to make them TRUE. Write only the appropriate word(s) next to the question number (1.4.1–1.4.5) on the ANSWER SHEET.
1.4.1 Variation is a mechanism of inheritance resulting from genes relating to sex chromosomes.
1.4.2 Capitalisation is when a business gives certain activities or functions to another business to perform on its behalf.
1.4.3 An entity’s income minus expenses for an accounting period is liabilities.
1.4.4 Items or products that are seen to not cause damage to the environment, are mass products.
1.4.5 The sequence of steps involved in transferring produce from the farm to the consumer is processing. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 The picture below shows the packaging of tomatoes on a commercial farm.
 |
2.1.1 State TWO reasons why the tomatoes are protected in boxes. (2)
2.1.2 Mention TWO important packaging information that could attract tomato buyers. (2)
2.1.3 Give ONE reason why materials used for packaging must not contain chemicals. (1)
2.2
| The connection between the price of goods and the quantity of goods supplied to the market, is known as the supply relationship. The price at which a product is eventually sold, is a reflection of both supply and demand. If prices are high, farmers and suppliers are likely to offer more goods for sale. |
2.2.1 Deduce the law of supply from the scenario in 2.2. (2)
2.2.2 State TWO factors that can affect the supply of meat in South Africa. (2)
2.2.3 State how the following factors can affect the demand of a product:
- Advertisement (2)
- Quality of a product (2)
2.3 The illustration below indicates the relationship between the demand and supply of oranges on a farm.
| Price in Rand | 5 | 10 | 15 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 45 | 50 |
| Quantity of oranges in bags | 60 | 50 | 45 | 40 | 30 | 25 | 25 | 20 |
2.3.1 Plot the information on a demand and supply curve graph. (5)
2.3.2 Determine the price at the market equilibrium. (1)
2.3.3 State ONE reason why the demand for oranges is lowest at R50. (1)
Related Items
2.4
| There are various marketing channels available to move a product from the producer to the consumer. Farmers operating in a free market system will usually adopt a free marketing system that best suit their situation. |
2.4.1 Explain the concept “free marketing” to your classmate. (2)
2.4.2 Recommend TWO channels/options of free marketing to a farmer. (2)
2.4.3 State TWO disadvantages of a free marketing system. (2)
2.5 The illustration below represents the distribution of milk from a dairy farm to the consumer. 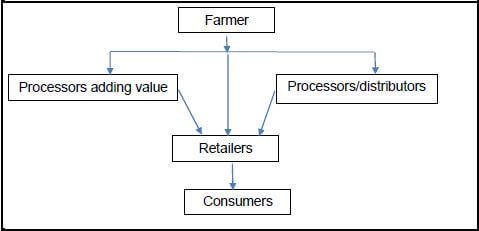
2.5.1 State THREE major marketing costs that could increase the price of the product to the consumer. (3)
2.5.2 Mention TWO major factors that can hamper the marketing of the milk by the distributer. (2)
2.5.3 Recommend TWO ways to improve and streamline the agric business chain. (2)
2.6 State TWO possible problems that may arise when compiling an agri business plan. (2)
[35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 For production of any product to take place, the following factors should be in place. Land is a permanent economic factor in agricultural science, however the availability of land for agricultural purposes is limited. 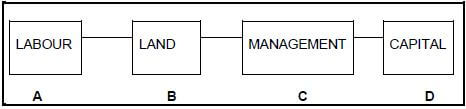
3.1.1 Indicate the production factor that could be used as collateral from 3.1 above. (1)
3.1.2 Justify your answer to QUESTION 3.1.1 with TWO reasons. (2)
3.1.3 Explain the underlined economic characteristic of land in the scenario in 3.1. (2)
3.1.4 Name TWO other economic characteristics of land apart from the underlined one in 3.1 to the entrepreneur. (2)
3.2
| Labour can be described as the sum total of human, physical and mental effort used to create goods and services. The labour market is a pool or group of people, skilled, semi-skilled and unskilled labourers who offer their labour to the highest bidder. |
3.2.1 Tabulate the following labourers into skilled, semi-skilled and unskilled labourers:
- Unqualified mechanic
- Veterinarian
- Apple picker (3)
3.2.2 Identify the labourer in QUESTION 3.2.1 who could be the highest in demand by a livestock farmer. (1)
3.2.3 Give ONE reason to justify your answer in QUESTION 3.2.2. (1)
3.2.4 Recommend TWO methods that could improve the economic conditions of the apple picker. (2)
3.2.5 State the labour legislation that could assist an unqualified mechanic to become qualified on a commercial farm. (1)
3.3 The document below was found by a worker in the drawer of the desk of a commercial farm manager. The worker approached you with some questions to find out what the document could be.
Income | R | C | Expenditure | R | C | ||
Sales | 15 000 | 85 | Tomato seedlings | 600 | 00 | ||
Interest on credits | 250 | 07 | Fertiliser | 750 | 00 | ||
Insecticides | 370 | 30 | |||||
Harvesting | 1 350 | 45 | |||||
Storage boxes | 650 | 80 | |||||
Transport by tractor | 800 | 00 | |||||
Total | Total |
3.3.1 Mention the type of document in QUESTION 3.3. (1)
3.3.2 Give TWO reasons for your answer in QUESTION 3.3.1. (2)
3.3.3 Identify TWO types of capital mentioned in the document in QUESTION 3.3, with examples of each. (2)
3.3.4 Calculate the profit or loss of the farmer according to the document in QUESTION 3.3. (3)
3.3.5 Mention TWO sources of capital to the farm worker. (2)
3.4
 |
3.4.1 Define the concept “farm management”. (2)
3.4.2 Indicate THREE components of strategic management. (3)
3.4.3 Explain conceptual skills as used in business management skills. (2)
3.4.4 State THREE socio-cultural forces that affect agricultural enterprises. (3)
[35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1
| The illustration below is a Punnett square diagram showing the F2 generation of the dihybrid cross between a pure-breed monkey with black short hair and a pure-breed monkey with white long hair. |
Key:
S = black s = white | Q = short q = long |
| SQ | Sq | sQ | sq |
SQ | SSQQ | SSQq | SqQQ | SsQq |
Sq | SSQq | SSqq | K | Ssqq |
sQ | L | SsQq | ssQQ | ssQq |
Sq | SsQq | Ssqq | ssQq | ssqq |
4.1.1 Name the genotype represented by K in the Punnet square above. (1)
4.1.2 State the phenotype that could appear in L in the Punnet square above. (1)
4.1.3 Determine the ratio of white and long hair to all the possible phenotypes. (2)
4.1.4 Calculate the percentage of black and short hair in the phenotypes. (4)
4.2
| Some genetic traits found in animals are characterised by segregation in the classical Mundelein ratios. Others can take on a whole series of values without clear boundary lines. These characteristics are classified as qualitative or quantitative. |
4.2.1 Distinguish between qualitative and quantitative genetic characteristics of organisms. (4)
4.2.2 Categorise the following into quantitative or qualitative characteristic of a bull:
- Gender of a bull (1)
- Body size of the bull (1)
4.3
| In traditional breeding, plants and animals from an existing stock that have the desired characteristics are selected and allowed to breed. The offspring will hopefully display the characteristics required. The best offspring are then allowed to breed, until all offspring display the desired characteristics. |
4.3.1 State TWO limitations of the breeding method mentioned in the scenario. (2)
4.3.2 Mention TWO current uses of genetically modified plants in South Africa. (2)
4.4 Define the following terminologies:
- Prepotency (2)
- Pedigree selection (2)
4.5 A farmer went to an agricultural show and bought two breeds of cattle. The photos of the cattle are shown in the picture below. The cow is a Scottish breed and the bull is a Sudan Abigcer. He intends breeding the cattle on his farm.
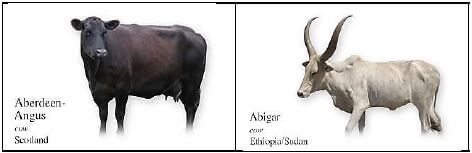 |
4.5.1 From the scenario, deduce the type of breeding that will take place on the farm. (1)
4.5.2 Give ONE reason for your answer to QUESTION 4.5.1. (2)
4.5.3 State THREE possible characteristics the farmer could expect from the offspring. (3)
4.5.4 Give ONE genetic terminology for the offspring. (1)
4.6
| Polygenic inheritance is mechanism of inheritance in which a genetic characteristic is controlled by many pairs of genes, instead of only a single pair of genes. The genotype aabbcc gives a milk yield of 3 000 litres. Imagine that each dominant gene adds a further 200 litres to the yield: |
4.6.1 Calculate the milk yield for the genotype aaBbcC, without using a calculator. (4)
4.7 The illustration below is one of the factors that cause mutation in genetics.
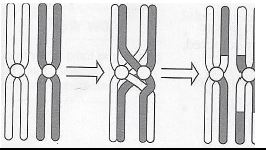 |
4.7.1 Make a prediction with regard to the process in the scenario in 4.7. (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150