AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES GRADE 12 PAPER 1 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupAGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
GRADE 12
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Read ALL the questions correctly and answer only what is asked.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Non-programmable calculators may be used.
- Show ALL your calculations, including units and formula, where applicable.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.1.11 A.
1.1.1 The process whereby the waste matter is separated and expelled from the body through the anus is known as ...
- eructation.
- ingestion.
- regurgitation.
- excretion.
1.1.2 The gross energy value of a feed minus the energy lost through manure, urine and gases:
- Digestible
- Metabolic
- Net
- Gross
1.1.3 The ratio of maize meal to sunflower meal is 22 : 7. The percentage of maize meal in this mixture is ...
- 24,1.
- 67,8.
- 75,9.
- 7,59.
1.1.4
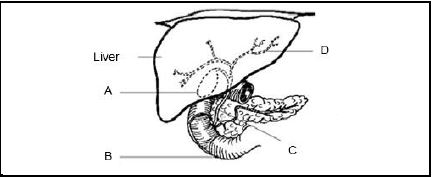 |
The fluid secreted from the part labelled A assist in digestion by …
- changing the pH from acidic to alkaline.
- promoting the absorption of fatty acids and glycerol.
- stimulating the conversion of glucose to glycogen.
- creating an alkaline medium for the functioning of enzymes.
Choose the correct combination:
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
1.1.5 A tool used in a bloodless method to castrate ONLY young animals:
- Burdizzo
- Tail docker
- Electric knife
- Elastrator
1.1.6 A supplementary feed given to young suckling animals for fast growth and high weaning weight:
- Creep
- Flush
- Finisher
- Weaner
1.1.7 Diseases that are contagious:
- Some are zoonotic
- Some are enzootic
- All virus diseases
- All are bacteria diseases
Choose the correct combination:
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
1.1.8 The membrane that grows out of the urinary system of the embryo and collects the urine from the unborn calf is the ...
- allantois.
- chorion.
- placenta.
- amnion.
1.1.9 The following statement is NOT a disadvantage of Embryo transplantation:
- It is more expensive than conventional breeding methods.
- Top genetics are introduced into a herd rapidly.
- Recipients could abort the eggs after being inseminated.
- Level of expertise is required in embryo handling procedures.
1.1.10 The spermatozoa receive nutrition from the secretion of ...
- seminal vesicles.
- Cowper's gland.
- prostate gland.
- bulbo-urethral gland. (10 × 2) (20)
1.2 Indicate whether each of the descriptions in COLUMN B applied to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A and B or NONE of the items in COLUMN A. Write A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A and B or NONE next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 B only.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
1.2.1 | A | Production ration | The feed given to an animal when it produces no product |
B | Maintenance ration | ||
1.2.2 | A | Pearson square | A method of balancing the ration to determine the required value of a particular nutrient in a feed mixture |
B | Punnet square | ||
1.2.3 | A | Marbling | The stiffness of the meat after slaughtering |
B | Rigor mortis | ||
1.2.4 | A | Thorn apple | Administer tannic acid to neutralise its effects |
B | Maize fungus | ||
1.2.5 | A | Maceration | Hardening and drying of the dead foetus after skeleton has been formed |
B | Absorption |
(5 × 2) (10)
1.3 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 A labour saving feeding approach where animals have unlimited access to feed
1.3.2 The application of an ointment to the open wound
1.3.3 A tendency by animals to come close to each other on hot days in an attempt to seek shade
1.3.4 The condition when the sexually ripe female animal shows no sign of oestrus
1.3.5 The mixture of the sperms and the fluids that are expelled during ejaculation (5 × 2) (10)
1.4 Change the underlined word(s) in each of the following statements to make it TRUE. Write only the correct word(s) next to the question number
(1.4.1–1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 Pepsin is an enzyme in the saliva of pigs that changes starch into maltose.
1.4.2 Lower critical temperature is the most suitable temperature for the animal to produce.
1.4.3 Sertoli cells are responsible for the production of testosterone in the male reproductive system.
1.4.4 Abortion is the termination of pregnancy without the visible loss of the foetus.
1.4.5 Fertilisation is the process when blastocyst attaches to the wall of the uterus. (5 × 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: ANIMAL NUTRITION
Start this question on a NEW page.
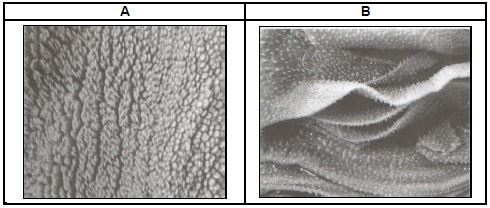
2.1 The pictures below show the stomach compartments in farm animal.
2.1.1 Indicate the example of an animal with the stomach compartments in the picture above. (1)
2.1.2 Identify the letter from the pictures representing the compartment where the following occurs:
- Microbial fermentation (1)
- Grinding of food (1)
- Heating rods keep the temperature constant (1)
2.1.3 Explain how the compartment labelled B is structurally suited to perform its function. (2)
2.1.4 The compartments above assist the animal to live mainly on feed with a high crude fibre content. Refer to the compartment labelled A to justify this statement. (3)
2.2 The graph below shows the feed components and their quantities that are included in a ration prepared for animals: 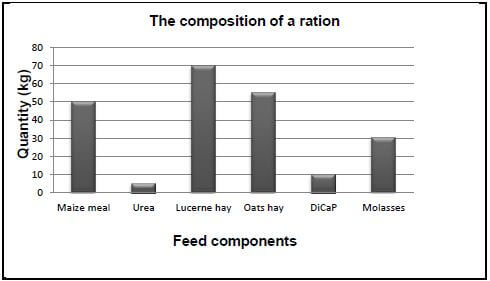
2.2.1 Indicate TWO types of roughages and give an example for each from the graph above. (4)
2.2.2 Provide the feed component that is an energy rich concentrate. (1)
2.2.3 Suggest whether the ration above can be fed to pigs. (1)
2.2.4 Give a reason for the suggestion in QUESTION 2.2.3. (2)
2.3 The table below shows the feed composition, feed intake and feed excreted by an animal in a feed trial. The animal consumed 7 kg of feed and excreted 4 kg.
FEED COMPOSITION | FEED INTAKE (%) | FEED EXCRETED (%) |
Crude protein | 5,0 | 3,0 |
Crude fiber | 78 | 73 |
2.3.1 Indicate whether the trial was done from the ruminant or non ruminant. (1)
2.3.2 Refer to the data in the table above to justify the answer in QUESTION 2.3.1. (2)
2.3.3 Calculate the amount of feed digested by an animal as a percentage. (2)
2.3.4 Explain the implication of the calculated figure in QUESTION 2.3.3. (2)
2.4 Compare roughages and concentrates with regard to the following: 2
.4.1 Crude fibre content (2)
2.4.2 Percentage of Total Digestible Nutrients (2)
2.5 The table below shows a fodder flow programme for a period of six months.
Criteria | Yield (t/ha) | Area (ha) | July (t) | Aug (t) | Sep (t) | Oct (t) | Nov (t) | Dec (t) | DM Total |
Veld supply | 5 | 26,2 | ---- | ---- | --- | 10 | 18 | 25 | |
Teff grass | 10 | 30 | 25 | 30 | |||||
Lucerne | 15 | 19,6 | 40 | 35 | 54 | 46 | 17 | 30 | |
Total feed | 40 | 35 | 54 | 56 | 60 | 85 | |||
Feed requirement | 63 | 65 | 66 | 60 | 72 | 84 |
2.5.1 Calculate the total quantity of Lucerne produced in tons. (2)
2.5.2 Identify the month with the most shortage of feed. (1)
2.5.3 Give a reason for the answer in QUESTION 2.5.2. (2)
2.5.4 Calculate the total dry matter (DM) available from October to December. (2)
[35]
QUESTION 3: ANIMAL PRODUCTION, PROTECTION AND CONTROL
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1 The pictures below illustrate animal production systems commonly used by farmers. 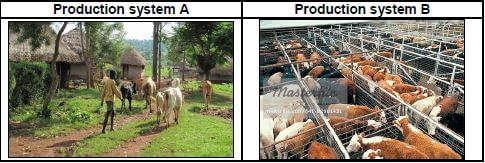
3.1.1 Identify the animal production systems labelled A and B. (2)
3.1.2 Give a reason visible in the pictures for identified production systems in QUESTION 3.1.1. (2)
3.1.3 Link each of the production system in QUESTION 3.1.1 with a farming system. (2)
3.1.4 Name TWO factors a farmer can put in place to ensure the increased production in picture B. (2)
3.2 The picture below shows the handling facility used to handle farm animals. 
3.2.1 Identify the facility in the picture above. (1)
3.2.2 Name TWO possible reasons for handling sheep in a facility illustrated in the picture above. (2)
3.2.3 State TWO features of the facility above to ensure that the animals are not injured. (2)
3.3 There are basic guidelines stipulated when transporting animals from farm to farm. Indicate the guideline stipulated when transporting animals under the following:
3.3.1 To alert motorists about animals on the road (1)
3.3.2 To avoid suspicion by police that the animals transported are stolen (1)
3.3.3 To ensure easy loading and offloading of animals in a truck (1)
3.4 The table below show diseases affecting farm animals, their symptoms and mode of transmission.
Disease | Pathogenic organism | Main symptom | Vector transmitting the disease |
Mastitis | A | Udder inflammation | Flies |
Foot-and-mouth disease | Virus | B | ---- |
Heartwater | C | Nervousness, frothy from the mouth and nose | D |
E | Fungus | Hair loss, itchy grey white scabs | Flies |
3.4.1 Complete the table by filling the missing information from A to E. (Do not redraw the table, just write the correct answer for A to E) (5)
3.4.2 Farmers are required to report to government authorities some diseases once they are detected. Give a term referring to those diseases. (1)
3.4.3 Identify the disease from the table above that needs to be reported once detected. (1)
3.4.4 Indicate TWO measures the State can take to control further spread of the disease in QUESTION 3.4.3 once it has been reported. (2)
3.5 The illustration below shows the lifecycle of a parasite affecting farm animals. 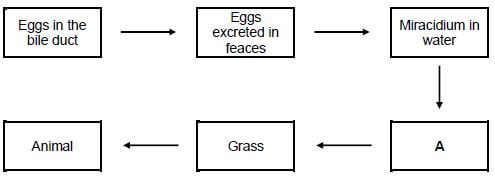
3.5.1 Classify the parasite illustrated above. (1)
3.5.2 Give the name of the parasite classified in QUESTION 3.5.1. (1)
3.5.3 The parasite illustrated above need an intermediate host to complete its life cycle. Name the intermediate host in label A. (1)
3.5.4 Indicate how the animal get infested by the parasite in QUESTION 3.5.2. (1)
3.5.5 Indicate the metabolic disease caused by the parasite on animal. (1)
3.5.6 Suggest TWO management practices that the farmer can put in place to control the parasite infestation on pasture. (2)
3.6 Salt is one of the essential minerals needed by animals but the consumption of large amount can be fatal to livestock.
3.6.1 Indicate ONE symptom of salt poisoning. (1)
3.6.2 Suggest TWO measures the farmer can take to treat animals with salt poisoning. (2)
[35]
QUESTION 4: ANIMAL REPRODUCTION
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 The diagram below illustrates the development of twins in a cow.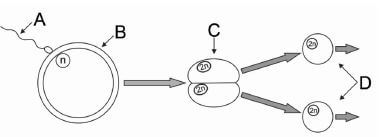
4.1.1 Identify the type of multiple birth illustrated in the diagram above. (1)
4.1.2 Give a reason for the answer in QUESTION 4.1.1. (1)
4.1.3 Indicate TWO characteristics of the twins illustrated in the diagram with regard to:
- Gender (1)
- Physical appearance (1)
4.1.4 Indicate an enzyme released by the sperm cell to facilitate its penetration in part B. (1)
4.1.5 Name the stage of gestation during which part C is formed. (1)
4.2 The graph below shows the number of cows in oestrus during different time periods.
4.2.1 Translate the data from the graph above to a table. (6)
4.2.2 Suggest the appropriate time to inseminate 10 cows. (1)
4.2.3 Give a reason for the answer in QUESTION 4.2.1. (2)
4.3 During the process of oogenesis and spermatogenesis, the cells undergo mitosis and meiosis, but these divisions give rise to different cells. Differentiate between oogenesis and spermatogenesis with regard to the following:
4.3.1 Cells formed during mitosis (2)
4.3.2 Cells formed during meiosis 2 (2)
4.3.3 Organs where they are formed (2)
4.4 After the process of spermatogenesis has been completed, sperms move through various primary and secondary organs until they reach the mating organ. Indicate the organ responsible for each of the following functions.
4.4.1 Transports sperms from the epididymis to the urethra (1)
4.4.2 Secretes a sticky alkaline mucus that gives semen a characteristic smell (1)
4.4.3 Secretes a buffer that protects sperms against pH changes (1)
4.5 Difficult birth is a challenge for farmers but can be corrected in some cases by proper management:
4.5.1 Give the term referring to the condition above. (1)
4.5.2 Indicate TWO reasons leading to the condition in QUESTION 4.5.1. (2)
4.6 The illustration below show processes occurring during a reproductive technique in female animals. 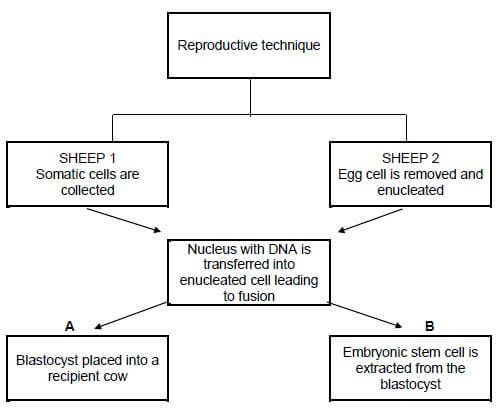
4.6.1 Identify the reproductive technique illustrated above. (1)
4.6.2 Indicate an appropriate name given to an animal represented by sheep 1 and sheep 2. (2)
4.6.3 There are TWO main types of the technique mentioned in QUESTION 4.6.1. Indicate these main types as labelled in A and B. (2)
4.6.4 Indicate the purpose for which the technique labelled B is done. (1)
4.6.5 The technique in A has an economic benefit for the farmer. Validate this statement by mentioning TWO economic benefits of this technique to the farmer. (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150