GRADE 12 MATHEMATICS PAPER 1 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS SEPTEMBER 2017
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupGRADE 12 MATHEMATICS
PAPER 1
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
SEPTEMBER 2017
NOTE:
- If a candidate answered a question TWICE, mark the FIRST attempt ONLY.
- Consistent accuracy applies in ALL aspects of the memorandum.
- If a candidate crossed out an attempt of a question and did not redo the question, mark the crossed-out attempt.
- The mark for substitution is awarded for substitution into the correct formula.
MEMORANDUM
QUESTION 1
?
| 1.1 | 2?(? + 1) − 7(? + 1) = 0 (? + 1)(2? − 7) = 0 ? = −1 or ? = 72 | ? factors ? ?-value ? ?-value | (3) |
| 1.2 | ?2 − 5? − 1 = 0 ? = −? ± √?2 − 4?? 2? ? = −(−5) ± √(−5)2 − 4(1)(−1) 2(1) ? = 5,19 or ? = −0,19 | ? substitution into correct formula ?? x- values | (3) |
| 1.3 | 4?2 + 1 ≥ 5? 4?2 − 5? + 1 ≥ 0 (4? − 1)(? − 1) ≥ 0 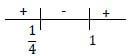 x ≤ 1/4 or ? ≤ 1 | ? standard form ? factors ?? ≤ ¼ ?? ≥ 1 | (4) |
| 1.4 | 54?+3. 100−2?+1 = 50 000 54?+3. (52. 22)−2?+1 = 50 000 54?+3. 5−4?+2. 2−4?+2 = 50 000 55. 2−4?. 22 = 50 000 2−4? = 22 −4? = 2 ? = − 1/2 | ?5−4?+2 ?2−4?+2 ?−4? = 2 ? answer | (4) |
| 1.5 | ? = 2? …………………..(1) ?2 + 2? − ? − ?2 = 36……….(2) ? = 2? sub into (2) (2?)2 + 2(2?) − ? − ?2 = 36 4?2 + 4? − ? − ?2 = 36 3?2 + 3? − 36 = 0 ?2 + ? − 12 = 0 (? − 3)(? + 4) = 0 ? = 3 or ? = −4 ? = 6 or ? = −8 | ?substitution ?standard form ? factors ? y − values ? x − values(5) | (5) |
| 1.6 | ?2 − ?? + ? − 1 = 0 ∆ = ?2 − 4?? ∆ = (−?)2 − 4(1)(? − 1) ∆ = ?2 − 4? + 4 ∆ = (? − 2)2 ∆ ≥ 0 roots are real and rational(perfect square) | ?substitution ? simplification ? (? − 2)2 ? conclusion(4) | (4) |
| [23] | |||
| QUESTION 2 | |||
| 2.1.1 | ?? = 4? − 1 483 = 4? − 1 484 = 4? ? = 121 121 terms in series | ? ?? = 4? − 1 ? equating 483 ? answer(3) | (3) |
| 2.1.2 | 121 ∑ (4? − 1) ?=1 | ? answer | (2) |
| 2.2.1 | (? − 3) − (2? − 4) = (8 − 2?) − (? − 3) −? + 1 = −3? + 11 2? = 10 ? = 5 | ? setting up equation ? simplification ? answer | (3) |
| 2.2.2 | … ; … ; … 6 ; 2 ; −2 ; … ; … ; … ?10 = 6 or ?? = −4? + 46 ? + 9? = 6 ?1 = −4(1) + 46 ? + 9(−4) = 6 ?1 = 42? = 42 | ? numerical values of?10; ?11; ?12 ? difference −4 ? a-value | (3) |
| 2.3 | ??2 + ??3 = −4 ? + ?(2) = −1 | ? setting of equations ? common factor ? ? = 2 ? value of a ? first three terms | (6) |
| [17 | |||
| QUESTION 3 | |||
| 3.1 | 41 ; 43 ; 47 ; 53 ; 61 ; 71 ; 83 ; 97 ; 113 ; 131 | ? 2nd difference ? ? = 1 ? ? = −1 ? ? = 41 ? ?? = ?2 − ? + 41 | (5) |
| 3.2 | ?41 = 412 − 41 + 41 Factors of 1681: 1 ; 41 and 1681 | ? ?41 = 1681 ? factors ? conclusion | (3) |
| 3.3 | Consider the unit digits only 1 ; 3 ; 7 ; 3 ; 1 ; 1 ; 3 ; 7 ; 3 ; 1 ; groups of 5 49999998 = 9999999,6 5 0,6 × 5 = 3 ?49999998 will end in 7 | ? unit digits ? groups of 5 ? conclusion | (3) |
| [11] | |||
| QUESTION 4 | |||
| 4.1.1 | ? = ?(1 + ?)? ? = 500 000 (1 + 7,2 )12? 1200 ? = 500 000(1.006)12? | ?sub into formula ? 12? | (2) |
| 4.1.2 | ? = 500 000(1.006)12? ? = 500 000(1.006)12×5 ? = ? 715894.21 | ? ? = 60 ? answer | (2) |
| 4.1.3 | ? = ?(1 + ?)? Will exceed R1 000 000 in 10 years. | ? setting up equation ? using logs ? conclusion | (3) |
| 4.2.1 | ?V = 10 000 [1 − (1 + 15/1200 ) −36] 15/1200 ?? = ?288 472,67 ???????/? = ?350 000 − ?288 472,67 ???????/? = ?61 527,33 | ? ? and ? ?sub into ?? formula ? ?? formuleü ?? = ?288 472,67 ? subtracting ? answer | (5) |
| 4.2.2 | 350 000 = ? [1 − (1 + 18,5/1200 ) −60] 18,5/1200 ? = ? 8 983,17 | ? ? = 18,51200 ?? = −60 ? substitution ? answer | (4) |
| [16] | |||
| QUESTION 5 | |||
| 5.1 | ?(−3; 0) | ? answer | (1) |
| 5.2 | ?(?) = ?2 + 3? ? = − ? 2? ? = − 3 2 ? (− 3) = (− 3)2 + 3 (− 3) 2 2 2 = − 9/4 ? (− 3 ; − 9) 2 4 | ?? = − 32 ?substitution ?answer | (3) |
| 5.3 | ?(−5) = 10 and ?(−3) = 0 ? = 10 − 0 −5 − (−3)? = −5 | ? calculating ?(−5) and ?(−3) ? substitution ? ?-value | (3) |
| 5.4 | ? < −3 or / of ? > 0 | ?answer | (2) |
| 5.5 | ? (− 3 ; − 9) or
| ? answer ? ?(? − 2) = ?2 − ? − 2 ? ? = − 12 | (2) |
| 5.6 | ?? = − 1/2 ? + 2 − (?2 + 3?) OR ?? = − 1/2 ? + 2 − (?2 + 3?) ? = − (− 7/4 ) 2 − 7/2 (− 7/4 ) + 2 OR ? = − ? | ? ?(?) − ?(?)
? ?(?) − ?(?)
??(?) − ?(?) | (4) |
| [15] | |||
| QUESTION 6 | |||
| 6.1 | 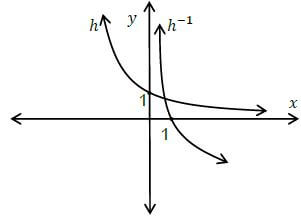 | ? shape ? y − intercept ? point on graph | (3) |
| 6.2 | ?(?) = 2? | ? answer | (1) |
| 6.3 | ℎ−1? = 2−? −? = log ? log 2 ? = − log ? / ? = − log2 ? /? = log½ ? log 2 | ? interchange ? and ? ? equation | (2) |
| 6.4 | ? ≥ 0 ; ? ∈ ? | (1) | |
| 6.5 | See 7.2.1 | ??shape and x-intercept | (2) |
| 6.6 | log1 ? = −321 −3( ) = ? 2? = 8∴ 0 < ? ≤ 8 | ?? = 8 ?0 < ? ≤ 8 | (2) |
| [11] | |||
| QUESTION 7 | |||
| 7.1 | ? = 5? = 2 | ?? = 5?? = 2 | (2) |
| 7.2 | ? = 5 − ? ? − 2 ? = −(? − 2) + 3 (? − 2) ? = 3 − 1 ? − 2 | ?? = 5−? ?−2 ?? = −(?−2)+3 (?−2) | (2) |
| 7.3 | ?(5; 0) ? = ? − 3 ? = ? + 3 ?′(0 + 3; 5 − 3) ?′(3; 2) | ?? = 3 ?? = 2 | (2) |
| [6] | |||
| QUESTION 8 | |||
| 8.1 | ?(?) = −2?2 + ?
| ? formula ? substitution of (? + ℎ) ? simplification to (−4?ℎ − 2ℎ2) ? common factor ? answer | (5) |
| 8.2 | 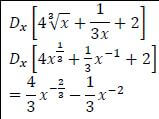 | (4) | |
| [9] | |||
| QUESTION 9 | |||
| 9.1 | ?(?) = (? − 1)2(? + 3) ?(?) = ?3 + ?2 − 5? + 3 ?′(?) = 3?2 + 2? − 5 3?2 + 2? − 5 = 0 (3? + 5)(? − 1) = 0 ? = − 5/3 or ? = 1 ?(1) = 0 ? (− 5/3 ) = 256 27 | ? ?(?) = ?3 + ?2 − 5? + 3 ? ?′(?) = 0 ? factors ? ?-values ? ?-values | (5) |
| 9.2 | 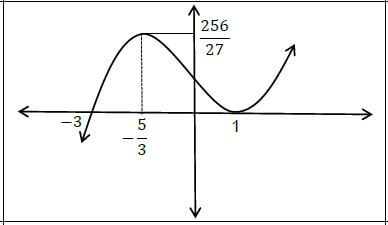 | ? shape ? ? − intercepts ? ? − intercept ? stationary points | (4) |
| 9.3 | ?′′(?) = 6? + 2 6? + 2 = 0 ? = − 1/3 ? = 128 / 27 / 4,74 / 4 20/27 | ? f′′(?) = 6? + 2 ?? = − 1/3 ? ? = 128 / 27 / 4,74 / 4 20/27 | (3) |
| 9.4 | 0 < ? < 25627 | ??answer | (2) |
| 9.5 | ?′(?) = 3?2 + 2? − 5 3?2 + 2? − 5 = −5 3?2 + 2? = 0 ?(3? + 2) = 0 ? = 0 or ? = − 2/3 ? (− 2) = 175 3 27 y = −5? + ? 175 = −5 (− 2/3 ) + ? 27 3? = 85 27 ? = −5? + 85 27 | ? f′(?) = −5 ? factors ? ? = − 2/3 ? f (− 2/3) = 175 27 ? substitution ? answer | (6) |
| [20] | |||
| QUESTION 10 | |||
| 10.1 | 243 = 2(? × 2?) + 2(2? × ℎ) + 2(? × ℎ) 243 = 4?2 + 4?ℎ + 2?ℎ 243 = 4?2 + 6?ℎ ℎ = 243 − 4?2 6? ℎ = 81 − 2? 2? 3 | ? TSA equation and sub ? simplification | (2) |
| 10.2 | ? = 2? × ? × (81 − 2?) (2? 3) ? = 81? − 4 ?3 3 | ?sub into volume formula | (1) |
| 10.3 | ?? = 81 − 4?2 ?? 81 − 4?2 = 0 ?2 = 81 4 ? = 9 = 4.5 2 | ? 81 − 4?2 ? 81 − 4?2 = 0 ? ?2 = 81 4 ? answer | (4) |
| [7] | |||
| QUESTION 11 | |||
| 11.1 | 9 × 9 × 9 × 5 × 4 = 14580 | ?9 × 9 × 9 ?5 × 4 ? 14580 | (3) |
| 11.2.1 | 12! = 119750400 2! .2! | ? 12! ?2!.2! ? 119750400 | (3) |
| 11.2.2 | 10! 2! = 1 = 0,015 119750400 66 | ?10!2! ? 119750400 ? answer | (3) |
| [9] | |||
| 11.3.1 | 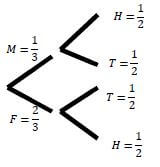 | ? first branch with values ? top part of second branch with values ? bottom part of second branch with values | (3) |
| 11.3.2 | ?(?) = 2 3 | ? ?(?) = 2/3 | (1) |
| 11.3.3 | ?(?/?) = 1 × 1 3 2 ?(?/?) = 1 6 | ? ?(?/?) = 1/6 | (2) |
| [15] | |||
| TOTAL: 150 | |||