LIFE SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE2017
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupLIFE SCIENCES PAPER 1
GRADE 12
SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATIONS
MEMORANDUM
MAY/JUNE2017
PRINCIPLES RELATED TO MARKING LIFE SCIENCES
- If more information than marks allocated is given
Stop marking when maximum marks is reached and put a wavy line and 'max' in the right-hand margin. - If, for example, three reasons are required and five are given
Mark the first three irrespective of whether all or some are correct/incorrect. - If whole process is given when only a part of it is required
Read all and credit the relevant part. - If comparisons are asked for, but descriptions are given
Accept if the differences/similarities are clear. - If tabulation is required, but paragraphs are given
Candidates will lose marks for not tabulating. - If diagrams are given with annotations when descriptions are required
Candidates will lose marks. - If flow charts are given instead of descriptions
Candidates will lose marks. - If sequence is muddled and links do not make sense
Where sequence and links are correct, credit. Where sequence and links are incorrect, do not credit. If sequence and links become correct again, resume credit. - Non-recognised abbreviations
Accept if first defined in answer. If not defined, do not credit the unrecognised abbreviation, but credit the rest of the answer if correct. - Wrong numbering
If answer fits into the correct sequence of questions, but the wrong number is given, it is acceptable. - If language used changes the intended meaning
Do not accept. - Spelling errors
If recognisable, accept the answer, provided it does not mean something else in Life Sciences or if it is out of context. - If common names are given in terminology
Accept, provided it was accepted at the national memo discussion meeting. - If only the letter is asked for, but only the name is given (and vice versa)
Do not credit. - If units are not given in measurements
Candidates will lose marks. Memorandum will allocate marks for units separately. - Be sensitive to the sense of an answer, which may be stated in a different way.
- Caption
All illustrations (diagrams, graphs, tables, etc.) must have a caption. - Code-switching of official languages (terms and concepts)
A single word or two that appear(s) in any official language other than the learner's assessment language used to the greatest extent in his/her answers should be credited, if it is correct. A marker that is proficient in the relevant official language should be consulted. This is applicable to all official languages. - Changes to the memorandum
No changes must be made to the memoranda. The provincial internal moderator must be consulted, who in turn will consult with the national internal moderator (and the Umalusi moderators where necessary). - Official memoranda
Only memoranda bearing the signatures of the national internal moderator and the Umalusi moderators and distributed by the National Department of Basic Education via the provinces must be used.
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 C✓✓
1.1.2 D✓✓
1.1.3 B✓✓
1.1.4 D✓✓
1.1.5 C✓✓
1.1.6 B✓✓
1.1.7 A✓✓
1.1.8 B✓✓
1.1.9 B✓✓
1.1.10 D✓✓ (10 x 2)
(20)
1.2
1.2.1 Biodiversity✓
1.2.2 Carbon footprint✓
1.2.3 Thermal✓pollution
1.2.4 Eutrophicationddd✓
1.2.5 Testosterone✓
1.2.6 Vas deferens✓/sperm duct
1.2.7 Aldosterone✓
1.2.8 Prolactin✓
1.2.9 Cytokinesis✓ (9 x 1)
(9)
1.3
1.3.1 A only✓✓(2)
1.3.2 B only✓✓(2)
1.3.3 Both A and B✓✓(2)
(3 x 2)(6)
1.4
1.4.1
- D✓ Synapse✓(2)
- C✓ Interneuron✓/Connector neuron(2)
- A✓ Dendrite✓ (2)
1.4.2
- E✓(1)
- F✓ (1)
(8)
1.5
1.5.1
- Zygote✓(1)
- Morula✓(1)
- Placenta✓ (1)
1.5.2
- Fertilisation✓(1)
- Implantation✓(1)
1.5.3
- 46✓/23 pairs(1)
- 23✓(1)
(7)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1
2.1.1
- The hatchling's eyes are closed✓
- The hatchling can't move✓
- The hatchling can't feed on its own✓
- The hatchling has no feathers✓/wings are not developed
(Any 2) (MARK FIRST TWO ONLY)(2)
2.1.2
- Foetus develops inside the uterus✓ for greater protection✓
- Food is supplied by the mother✓ and is therefore supplied for a longer period✓
(Any 1 x 2)(2) (MARK FIRST ONE ONLY)
2.1.3
- More yolk allows for greater development✓ of the chick
- so that it can be more independent✓ after hatching(2)
(6)
2.2
2.2.1 Macular degeneration✓/Retina cells die(1)
2.2.2 14.1/142 ✓x 100✓ = 9.93✓%
(Accept 9.9 and 10%)(3)
2.2.3 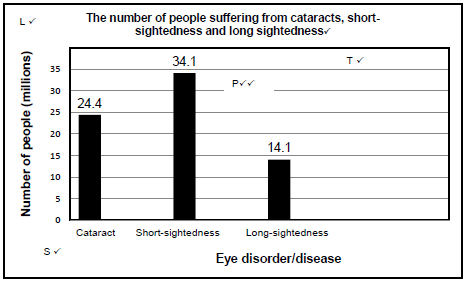
Mark allocation of the graph
| Criteria | Mark allocation |
| Bar graph drawn for 3 relevant diseases (T) | 1 |
| Title of graph | 1 |
| Correct scale for X-axis (equal width and spacing of the bars) and Y-axis (S) | 1 |
| Correct label and unit for X-axis and Y-axis (L) | 1 |
| Plotting of the bars (P) | 0: No bars plotted correctly 1: 1 to 2 bars plotted correctly 2: All 3 bars plotted correctly |
NOTE:
If a line graph is drawn – marks will be lost for the ‘type and scale'
If a histogram is drawn – marks will be lost for the 'type of graph and correct scale'(6)
2.2.4
- Cataract✓(1)
- Short-sightedness✓(1)
(12)
2.3
2.3.1
- Crop yields are dropping✓(1)
- Water supplies are decreasing✓(1)
2.3.2 395✓ parts per million✓/ppm (Accept 394 – 396 ppm)(2)
2.3.3
- Decreased photosynthesis✓
- Less CO2 ✓used from the atmosphere
- therefore more carbon dioxide accumulates in the atmosphere✓
- This leads to the enhanced greenhouse effect✓ causing more global warming (Any 3)
OR
- Burning of forests✓
- releasing CO2✓
- leading to the enhanced greenhouse effect✓ causing more global warming(3)
(7)
2.4
- An excessive growth of water hyacinths on the surface of the water will block out the light✓/deprive submerged plants of sunlight
- this limits photosynthesis✓/disrupts food chains/food webs
- Alien plants outcompete the indigenous species✓/Alien plants have no natural enemies
- this may lead to some of the indigenous species becoming eliminated✓/ disruption of the food chain/web
- The great demand of alien plants on natural resources,✓
- results in less resources being available for the indigenous species✓
(3 x 2) (MARK FIRST THREE ONLY) (6)
2.5
2.5.1 Centriole✓(1)
2.5.2 Metaphase II✓(1)
2.5.3
- Single chromosomes✓
- arranged at the equator✓ of the cell(2)
2.5.4
- There is a random arrangement of chromosomes at the equator✓/the chromosomes flip over
- Causing the chromosomes in the gametes to be different✓/Chromatids move in different combinations into each gamete(2)
2.5.5
- 6✓(1)
- 3✓(1)
2.5.6 Crossing over✓(1)
(9)
[40]
QUESTION 3
3.1
3.1.1 Does drinking coffee containing caffeine increase stamina? ✓✓(2)
3.1.2
- Amount of caffeine✓/Presence or absence of caffeine(1)
- Stamina✓
By measuring the average duration of cycling✓(2)
3.1.3 The average cycling time of the cyclists/stamina increased with the use of caffeine✓✓(2)
3.1.4
- Decaffeinated coffee serves as a control✓
- to eliminate any other factor✓ that may cause an increase in stamina/to confirm that caffeine causes the change(2)
3.1.5
- Knowing✓ whether caffeine is taken or not
- may subconsciously influence the performance✓of the participants.
OR
- The participants may think they have more stamina✓ if they know that they are taking caffeine and
- this may influence their performance✓(2)
3.1.6
- If too little time passes between the exercise tests, the participants may be tired✓
- which will influence their stamina for the second cycle test and therefore the validity✓ of the investigation
OR
- The participants must be equally rested✓ for both tests
- to ensure the validity✓ of the investigation
OR
- The cyclist may perform better in the second test because they are better warmed up✓ if the time between the tests is too short.
- This may influence the validity of the investigation✓
( Any 1 x 2)(2)
(13)
3.2
3.2.1
- Oestrogen✓(1)
- Progesterone✓ (1)
3.2.2
- It increases✓
- the thickness✓ of the endometrium/the blood vessels in the endometrium/the amount of glandular tissue in the endometrium (2)
3.2.3
- Release of an ovum✓ from the ovary✓/Graafian follicle(2)
- Day 14✓(1)
- LH✓/Luteinizing hormone(1)
3.2.4
- High levels of hormone B/progesterone will inhibit✓
- the secretion of FSH✓
OR
- No new ova/mature follicles✓
- are required during pregnancy✓ (2)
3.2.5
- The progesterone✓
- levels decreased✓
- because the corpus luteum degenerated✓ (3)
(13)
3.3
3.3.1 Geotropism✓/gravitropism(1)
3.3.2
- Auxins✓
- accumulate at the lower✓ part of the stem
- because of gravity✓
- The higher concentration of auxins at the lower part of the stem stimulates cell elongation✓/growth on the lower side of the stem
- The lower concentration of auxins at the upper part of the stem inhibits cell elongation✓/growth on the upper side of the stem
(Any 4)(4)
3.3.3
- The leaves and stem will be carried in such a way that they receive maximum sunlight✓
- for photosynthesis✓(2)
OR
- Exposes the flowers more favourably✓
- for pollination✓/seed dispersal
3.3.4 The roots will grow downwards✓/towards gravity(1)
(8)
3.4
3.4.1 Hypothalamus✓(1)
3.4.2
- As the level of ADH in the blood increases the tubular reabsorption of water increases✓✓
OR
- As the level of ADH in the blood decreases the tubular reabsorption of water decreases✓✓(2)
3.4.3
- On a cold day the body loses less water through sweating✓/ the blood has more water than normal
- The hypothalamus✓ sends impulses to the
- pituitary gland✓
- to secrete less ADH✓ (Any 3)(3)
(6)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
Thermoregulation✓
- Receptors✓ in the skin detect the stimulus
- Send the impulses to the hypothalamus✓ of the brain
- The hypothalamus sends impulses to the blood vessels✓ of the skin
- Blood vessels constrict✓ (become narrow)/vasoconstriction occurs
- Less blood flows to the skin✓
- Less heat is lost✓from the skin
- Less blood is sent to the sweat glands✓
- Sweat glands become less active✓/Less sweat is released
- There is less evaporation of sweat✓
- and less cooling of the skin✓
Max(8)
Hearing
- The pinna traps the sound waves✓
- and directs them into the auditory canal✓/meatus
- This causes the tympanic membrane to vibrate✓
- The vibration is transmitted to the auditory ossicles✓/(malleus, incus, stapes)
- The ossicles amplify the vibration✓
- and transmit it to the oval window✓
- The oval window vibrates✓
- creating pressure waves✓
- in the endolymph✓
- which stimulates the Organ of Corti✓
- The stimulus is converted to an impulse✓
- The impulse is transmitted via the auditory nerve✓
- to the cerebrum✓
- where sound is interpreted✓
Max(9)
Content:(17)
Synthesis:(3)
(20)
ASSESSING THE PRESENTATION OF THE ESSAY
| Relevance | Logical sequence | Comprehensive |
| All information provided is relevant to the question | Ideas arranged in a logical/ cause-effect sequence | Answered all aspects required by the essay in sufficient detail |
Only information regarding:
No irrelevant information. | The sequence of events in thermoregulation and hearing is in the correct order. | At least the following points should be included:
|
| 1 mark | 1 mark | 1 mark |
TOTAL SECTION C:20
GRAND TOTAL:150