ECONOMICS PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupECONOMICS
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1
1.1 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
1.1.1 C – cost equals marginal revenue ✓✓
1.1.2 A – monopoly ✓✓
1.1.3 B – negatively sloped ✓✓
1.1.4 B – rent ✓✓
1.1.5 B – interest rate ✓✓
1.1.6 C – inbound ✓✓
1.1.7 A – cultural ✓✓
1.1.8 C – volatile ✓✓ (8 x 2) (16)
1.2 MATCHING ITEMS
1.2.1 C ✓ the additional cost when producing an extra unit
1.2.2 E ✓ an arrangement between businesses with the aim of limiting competition amongst them
1.2.3 G ✓ intervention by government to recover external cost
1.2.4 A ✓ the minimum earnings required to prevent an entrepreneur from leaving the business
1.2.5 I ✓ an increase in the general price level in a particular year
1.2.6 B government sets regulations which enforce environmental standards
1.2.7 H ✓ shows the relative importance of an item in a basket of goods and services that are used to calculate inflation
1.2.8 D ✓ dumping waste on the earth's surface (8 x 1) (8)
1.3 IDENTIFY THE CONCEPT
1.3.1 Duopoly ✓
1.3.2 Homogeneous ✓
1.3.3 Natural ✓
1.3.4 Hyperinflation ✓
1.3.5 Preservation ✓
1.3.6 Infrastructure / public goods ✓ (6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 2: MICROECONOMICS
2.1
2.1.1 Name TWO kinds of inefficiencies that can exist in the imperfect market.
- Productive/technical inefficiencies ✓
- Allocative inefficiencies ✓ (2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 What would happen if firms in an oligopolistic market compete on prices?
- It can lead to a price war which will lower profits which might lead to certain firms leaving the market in the long run ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
2.1 Data response
2.2.1 What is the selling price for the monopolist?
- Selling price is R60 ✓ (1)
2.2.2 Does the equilibrium position above represent a short run or a long run?
- Short run ✓ (1)
2.2.3 Why will a monopolist always make economic profit in the long run?
- It is possible to manipulate prices to ensure a profit because there is no competitors ✓✓
- There is a deliberate decline in produce – less than the market demand, therefore higher prices are charged ✓✓
- Sell a unique product without any competition ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.2.4 What is the requirement for this monopoly be classified as an artificial monopoly?
- If entry is restricted by factors such as legal requirement e.g. licencing, patents and copyrights ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant answer) (2)
2.2.5 Calculate the total profit this monopolist is making. Show all calculations.
- Total Profit = Total revenue – Total Cost
= (60 x 50) – (30 x 50) ✓
= 3 000 – 1 500 ✓
= 1 500 ✓✓
OR - Total Profit = Unit profit x quantity
= (60-30) ✓ x 50 ✓
= R1 500 ✓✓- Max 2 marks if only the correct answer is given.
- If the formula is given, a mark can be awarded if the calculations are incorrect. (4)
2.3 Data Response
2.3.1 Which cause for market failure is illustrated above?
- Incomplete information/lack of information ✓✓ (2)
2.3.2 Briefly describe the concept market failure.
- The best available (optimal) production outcome has not been achieved / misallocation of resources ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.3.3 How can labour as a factor of production become more mobile?
- Training/attaining skills/increased wages/travelling facilities or infrastructure/technology ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
2.3.4 How does the South African government attempt to solve the problem of income inequality?
The government can attempt to solve the problem of income inequality by:
- implementing a progressive tax system which has reduced the income gap between income earners ✓✓
- levying indirect taxes on consumption (e.g. VAT), while certain basic items that the poor often consumes, were excluded ✓✓
- providing free primary health care in provincial hospitals and clinics ✓✓
- making provision for those who cannot afford to pay by offering a free basic education ✓✓
- making transfer payments and subsidies payable to the poor and previously disadvantaged ✓✓
- implementing minimum wages ✓✓
- implement job creation programmes ✓✓
- implementing BBBEE and labour laws ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Any 2 x 2) (4)
2.4 Compare monopolistic competition with perfect competition.
- Under monopolistic competition less will be produced at a higher price than the perfect competitor ✓✓
- The perfect competitor produces at the minimum point on the LAC curve, whereas this is not the case under monopolistic competition ✓✓
- Both the perfect competitor and monopolistic competitor will make a normal profit in the long run ✓✓
- It is easier for the perfect competitor to enter the market, compared to the monopolistic competition ✓✓
- (Accept any other correct relevant answer)
- (Accept tabular format)
- (Accept comparison in terms of other characteristics) (4 x 2)
- (Allocate a maximum of 4 marks for mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
2.5 Explain why governments sometimes proceed with a project even if the private costs exceed the private benefits in a Cost-Benefit Analysis?
Governments might proceed with a project when:
- the primary objective is to provide public goods and services. ✓✓
- social costs and social benefits are also taken into account when deciding on a project. ✓✓
- a service is vital to the existence of the community. ✓✓
- when a need for infrastructure is necessary but might not have any benefits in terms of profit, e.g. the building of a community centre or a bridge ✓✓
- funding of these projects are mainly financed through tax revenue and does not impoverish any individual as such. ✓✓
- this infrastructure adds to the welfare of the community at large and is non-excludable to anyone using it. ✓✓
(Allocate a maximum of 2 marks for mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
3.1
3.1.1 Name TWO causes of cost push inflation.
- Higher Wages ✓
- Increase in input costs ✓
- Increase in price of imports ✓
- Exchange rate depreciation ✓
- High profit margins ✓
- Low productivity ✓
- Limited natural resources ✓
- Increase in interest rates ✓
- Supply shock ✓
- Natural disasters ✓ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
3.1.2 What effect will green tax have on the production output of a business that generates a negative externality?
- The levying of taxes will reduce the output of those products ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
3.2 Data response
3.2
3.2.1 Identify TWO markets in the table that contributed the most to tourism in South Africa during 2015?
- Africa land ✓
- Europe ✓ (2 x 1) (2)
3.2.2 Suggest possible reasons that have led to a general decline in international tourism in 2015?
- Dampening of the world economy (Recession) ✓✓
- Legislation governing international traveling e.g. VISA regulation ✓✓
- Increase in crime in some areas (Safety issues) ✓✓
- Poor electricity supply / poor infrastructure ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Any 2 x 2) (4)
3.2.3 Calculate the percentage decline in total tourist arrivals in South Africa between 2014 and 2015.
Show all calculations.
- 143 172 ✓ x 100 ✓
2 435 341 1
= 5,8 / 5.9 / 6 % ✓✓
Allocate 2 marks for the correct answer. (4)
3.3 Data response
3.3.1 What is the effect of the emission of greenhouse gases on the environment?
- It can lead to increased temperatures/global warming/climate change ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.3.2 What is the message conveyed by the cartoon?
- Despite numerous summits on environmental issues, climate change is still a problem ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
3.3.3 Name the international agreement that was formed to deal with global warming and climate change.
- Kyoto Protocol ✓✓ (2)
3.3.4 How can the world stop the global warming trend?
- Reduce the emission of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere by using environmentally friendly technology such as solar energy ✓✓
- Planting of trees that produces oxygen which is important for cleaner air ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 2) (4)
3.4 Differentiate between Production Price Index and Consumer Price Index.
Production price index
| Consumer price index
|
(2 x 4)
(Allocate a maximum of 4 marks for mere listing of facts / examples)(8)
3.5 Why is South Africa regarded as a major air polluter in the world?
- Industries such as SASOL and ESKOM (Medupi) burn a larger quantity of coal and this produces CO2 into the atmosphere / The country has the world's largest single CO2 emitter which is at SASOL in Secunda ✓✓
- Mining activities such as extraction and refining creates a large amount of air pollution ✓✓
- South Africa is the biggest CO2 polluter in Africa (40%) and rated the world's 13th largest producer of greenhouse gases. Top 6 in the developing world for Greenhouse gasses ✓✓
- The use of non-environmentally friendly energy sources ✓✓
- (Accept reference to the candidate’s local environment)
- (Accept any other correct relevant response)
- (Allocate a maximum of 2 marks for mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: MICROECONOMICS AND CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
4.1
4.1.1 Name TWO methods of non-price competition.
- Advertising ✓
- Loyalty points ✓
- After sales services ✓
- Packaging ✓
- Branding ✓
- Door-to-door sales ✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 1) (2)
4.1.2 How can a decline in savings influence the economy negatively?
- When people save less, they often spend more ✓ which can lead to higher prices. ✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
4.2 Data response
4.2.1 Identify any TWO sectors in South Africa where minimum wages are applied in the extract above.
- Civil Engineering ✓
- Contract Cleaning services ✓
- Domestic Workers ✓
- Farm Workers ✓
- Forestry ✓
- Hospitality ✓
- Leadership Allowance ✓
- Private Security ✓
- Wholesale and Retail ✓
- Taxi ✓
- Bargaining Council Minimum Wages ✓ (Any 2 x 1) (2)
4.2.2 Briefly describe the term minimum wage.
- It is the minimum remuneration a worker should earn legally per hour, day or week for work done ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2)
4.2.3 What is the advantage of having a national minimum wage instead of a minimum wage per sector?
- Prevent discrimination among workers in the different sectors ✓✓
- That national minimum wage could be higher which will improve the standard of living ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (1 x 2) (2)
4.2.4 Refer to the above graph and explain the implication of the R3 500 minimum wage imposed by the government.
- The wage rate will be higher than the market rate of R2 500✓✓
- At this rate more people will avail themselves, therefore the supply of labour will increase from 200 to 300 ✓✓
- On the other side, the demand for labour will decrease from 200 to100 ✓✓
- This will create an oversupply of workers, supply exceeds demand / unemployment will increase ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 2) (4)
4.3 Data response
4.3.1 What, according to the extract, is the effect of inflation on money?
- It reduces the value of money ✓✓ (2)
4.3.2 Briefly describe the term stagflation.
- Stagflation can be described as low economic growth, high unemployment and high rates of inflation ✓✓ (2)
4.3.3 Explain the effect of an increase in interest rates on inflation.
- An increase in interest rates makes buying on credit more expensive. This often results in a decrease in aggregate demand which will lead to a lower inflation rate ✓✓
(Accept other correct relevant response) (2)
4.3.4 What are the negative effects of inflation on economic growth?
- High inflation creates uncertainty of the economic environment and reflects negatively on production ✓✓
- Uncertainty discourages investment which in turn leads to reduced economic growth ✓✓
- Reduced growth has a knock on effect on all sectors of the economy which can lead to a recession ✓✓
- May lead to unemployment ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Any 2 x 2) (4)
4.4 Explain the roles played by any TWO key institutions that monitor competition in South Africa.
- Competition Commission ✓
- Investigate restrictive business practices ✓✓
- Grant permission in cases of mergers and take-overs ✓✓
- Makes recommendations about penalties for businesses that it finds guilty of uncompetitive behaviour ✓✓
- Competition Tribunal ✓
- Accept or reject recommendations made by the Competition Commission ✓✓
- Has jurisdiction throughout the Republic ✓✓
- It is a tribunal of record and independent from the other competition institutions ✓✓
- Grant exemption, authorise or prohibit large mergers, adjudicate if misconduct takes place ✓✓
- Competition Appeal Court ✓
- Make final rulings on disputed matters/Considers appeals made against decisions made by the Competition Tribunal ✓✓
- Has a status similar to High Court ✓✓
- It has jurisdiction throughout the Republic and is a Court of Record ✓✓ (8)
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (2 x 4)
(Allocate a maximum of 4 marks for mere listing of facts / examples)
4.5 To what extent is inflation targeting beneficial to the economy?
- It helps to keep prices at a lower level ✓✓
- It increases people's expectation that prices will be stable in the medium term ✓✓
- It is useful in controlling demand pull inflation because the concept is simple and easy to understand ✓✓
- It enhances producers' confidence in the economy as it enable them to make investments knowing that inflation will be under control ✓✓
- It reduces uncertainty and promotes sound planning in public and private sectors ✓✓
- It provides a yardstick that serves to discipline monetary policy and improves the accountability of the central bank ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (4 x 2)
(Allocate a maximum of 2 marks for mere listing of facts / examples) (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer any ONE of the two questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK. Your answer will be assessed as follows:
STRUCTURE OF ESSAY | MARK ALLOCATION |
Introduction | Max. 2 |
Body | Max. 26 Max. 10 |
Conclusion
| Max. 2 |
TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 5: MICROECONOMICS
In a perfect market the industry influences the behaviour of an individual business to a certain extent.
- With the aid of graphs, explain the following about an individual business under conditions of perfect competition:
- The effect on price if the individual producer increases or decreases his output (supply)
- The derivation of the supply curve from cost curves for the individual producer (26)
- Without using a graph, explain why the price of a product under perfect competition will be equal to the lowest point on the long-run average cost curve. (10) [40]
INTRODUCTION
Perfect competition is a market structure where the market price is determined by the interaction between demand and supply. ✓✓ (Max 2)
MAIN PART
The effect on price if the individual producer increases or decreases his output (supply) 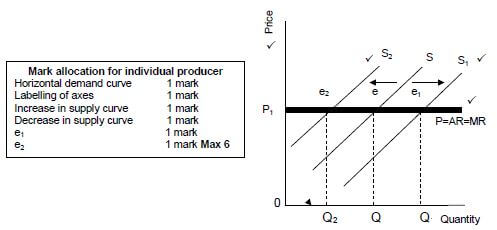
- The demand curve for the individual business is a horizontal line because he is a price taker ✓✓
- If the individual producer increases its supply, the supply curve will shift to the right from SS to S1S1 ✓✓
- At this point the equilibrium quantity has increased from Q to Q1, but the equilibrium price has remained at P1 ✓✓
- If the individual producer decreases its supply, the supply curve will shift from SS to S2S2 ✓✓
- The equilibrium quantity has decreased but the equilibrium price has remained constant at P1 ✓✓
- The individual producer is not able to influence the equilibrium or market price by manipulating its supply ✓✓
(Graphs max 6 marks and discussion max 8 marks)
(Max 14)
The derivation of the supply curve from cost curves for the individual producer 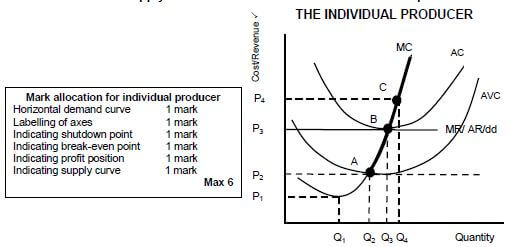
- The individual supply is derived by taking different market prices and determining how much the business should produce at each price ✓✓
- The individual firm maximizes profit where the marginal revenue (MR) is equal to marginal cost (MC) - Point B ✓✓
- Provided that the average income (AR) is enough to cover the average variable cost (AVC) ✓✓
- Average variable costs comprise costs like labour cost, material costs and fuel and electricity costs ✓✓
- Under perfect conditions, the producer will produce where P=MR=MC, if AR=P>AVC ✓✓
- Thus we derive that the supply curve of the firm is the section of the MC curve above the intersection with the AVC curve ✓✓
- The supply curve therefore is ABC on the graph ✓✓
- At P1, no production will take place ✓✓
- At P2, the AR=AVC, the firm will consider shutting down ✓✓
- At P3, the AR=AC, the breakeven point, where normal profits are made ✓✓
- At P4, where AR > AC - at this point abnormal (economic profits) are made ✓✓
(Graphs max 6 marks and discussion max 8 marks) (Max 14)
Max body (26)
ADDITIONAL PART
Without using a graph, explain why the price of a product under perfect competition will be equal to the lowest point on the long-run average cost curve. (10)
- If the firm is making economic profit, it could adapt its production capacity by building a bigger production plant ✓✓
- The industry can expand because new businesses could enter the market ✓✓
- The increased production will push the market supply curve to the right thus lowering the market price ✓✓
- Economic profits will eventually disappear due to falling average revenue ✓✓
- Long run equilibrium is achieved where the lowest point of the AC curve is tangent to the Demand/AR curve.(Which is the price) ✓✓
- If the business is making an economic loss then firms will leave the business or cut back on production ✓✓
- This will shift the market supply curve to the left thus increasing prices ✓✓
- Economic loss will eventually disappear due to increasing average revenue ✓✓
- This price will eventually be equal to the minimum point on the LAC curve i.e. Normal profit ✓✓
- Large scale production makes lower unit cost possible as a result of specialisation, and improved technology ✓✓
(Max 10)
CONCLUSION
The supply curve of the firm under perfect competition is the section of the MC curve above the intersection with the AVC curve ✓✓
(Accept any other correct relevant conclusion) (Max. 2)
[40]
QUESTION 6: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
Tourism plays an important role and can affect the economy negatively or positively.
- Examine the effects of tourism on the following:
- Poverty
- Employment
- Externalities (26)
- How can South Africa promote domestic tourism? (10) [40]
INTRODUCTION
Tourism is the activities of people travelling to places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year, for leisure, business and other purposes ✓✓ (Max. 2)
MAIN PART
Poverty
- Tourism is one of the fastest and most efficient redistribution mechanisms in development ✓✓
- Tourism stimulates economic growth and brings development to the poor in rural areas ✓✓
- Tourism offers opportunities to diversify sources of income for poor people ✓✓
- Allowing them a stake ✓ for example, to start and operate small-scale tourism businesses around community assets and to establish SMMEs to provide services ✓✓
- Empowerment ✓ for example, to exploit opportunities of on-the-job and other training ✓✓
- Creating partnerships ✓ linking up with mainstream tourism businesses supplying goods and services ✓✓ (Max 10)
Employment
- Tourism sector directly and indirectly employ people ✓✓
- The sector is the largest creator of jobs (employs 7% of the workforce in SA) ✓✓ for the following reasons:
- Tourism is labour intensive ✓ It has the lowest ratio of investment to employment creation ✓✓ This means that more jobs can be created with every unit of capital invested in tourism ✓✓ Many tourist activities are therefore within the reach of small tour operators ✓✓
- Tourism employ many skills ✓ Various skills are employed in the tourism sector ✓✓ for example, tour guides, hairdressers, accountant ✓ It also offers a huge potential for on-the-job training ✓✓
- Tourism provides immediate employment ✓ If it is properly organised and focused, the tourism sector can create many jobs within a short period of time ✓✓
- Tourism provides entrepreneurial opportunities ✓ The tourism industry accommodates informal sector enterprises ✓✓ from craft and fruit vendors to pavement vendors, chair rentals and others ✓ (Max 10)
Externalities
The rapidly expanding tourism industry could have both positive and negative impacts that extend well into the future:
- Attracts large amounts of revenue, but can cause undue environmental damage (uses resources and produces waste) ✓✓
- Rapid growth aimed at short-term benefits has more negative than positive effects: degeneration of traditions and cultural values, environmental damage to sites and natural settings – pollution and waste ✓✓
- Global tourism will grow due to increased population, improved living standards, increased free time and expansion of transportation systems, but put unnecessary pressure on tourist sites ✓✓
- Economic effect on individuals: new transport systems, recreation, shops and increase in property value compared to an increased inflation rate ✓✓
- Economic effect on government: more direct and indirect tax compared to conservation of infrastructure and tourist attractions ✓✓
- Social effect on individuals: improved health care and education compared to traffic congestion, crime ✓✓
- Social effect on government: an increased value put on culture, less migration compared to policing, sanitation, and health services ✓✓ (Max 10)
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Max 26)
(Allocate a maximum of 8 marks for mere listing of facts / examples)
ADDITIONAL PART
South Africa can promote domestic tourism by
- Improving its marketing and advertising ✓✓
- Domestic tourism is encouraged through increased advertising ✓✓
- TV magazine programmes like Shot'left inform people about local places of interest ✓✓
- Promoting special holiday packages ✓✓
- Special off-season rates make it possible to enjoy cheaper holidays ✓✓
- Enhancing efficiency of tourist information outlets✓
- Many towns have information outlets that supply pamphlets and information about a specific area. ✓✓
- Distributing information booklets (awareness) and offer transport to visit places of interest. This is mostly done by hotels and other accommodation resorts ✓✓
- Improving infrastructure ✓ a greater variety, using new technology to provide reliable infrastructure ✓✓
- Government effectively managing its tourist sites and other tourist attractions ✓✓ e.g. maintenance, upgrading, security etc. ✓
(Accept any other correct relevant response) (Max.10)
CONCLUSION
Tourist expenditure is as real as any other consumer expenditure and international tourism can in addition be seen as an invisible export product ✓✓ (Max. 2)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150