AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupAGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show ALL calculations, including formulae, where applicable.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Write down the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10), choose the answer and make a cross (X) over the letter (A–D) of your choice in the ANSWER BOOK.
EXAMPLE: |
1.1.1 The compartment of the ruminant stomach that corresponds to the simple stomach of the pig:
- Abomasum
- Omasum
- Rumen
- Reticulum
1.1.2 Mechanical digestion of food in a fowl takes place in the …
- crop.
- proventriculus.
- ventriculus.
- cloaca.
1.1.3 … secrete(s) an alkaline secretion rich in mucus in the duodenum that protects it from the acidic chyme.
- Duodenal glands
- Brunner's gland
- The parotid gland
- The gland of Lieberkühn
1.1.4 Bile is produced in the ... and then stored in the gall bladder.
- bile ducts
- liver
- pancreas
- small intestine
1.1.5 The best description of external parasites on cattle:
- Live on the skin of cattle
- Can damage the skin
- Can produce toxins
- Found in the liver
Choose the CORRECT combination:
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
1.1.6 The body temperature of farm animals is usually ... the environmental temperature.
- the same as
- in the same ratio as
- higher than
- lower than
1.1.7 Which of the statements below with regard to a feedlot production enterprise are TRUE?
- Shade and shelter are provided to animals.
- All pastures and feeds are harvested and then fed to the animals.
- Rotational grazing is practised.
- This enterprise is labour and capital intensive.
Choose the CORRECT combination:
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
1.1.8 The purpose of vaccination is mainly to … diseases in farm animals.
- control
- treat
- prolong
- prevent
1.1.9 A bacterial venereal infection causing the worst cases of abortion which results in infertility in cows:
- Anthrax
- Trichomoniasis
- Brucellosis
- Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis
1.1.10 The congenital defect where the testes are underdeveloped:
- Hypoplasia
- Impotence
- Cryptorchidism
- Hermaphroditism (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Indicate whether each of the descriptions in COLUMN B applies to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A AND B or NONE of the items in COLUMN A. Write A only, B only, both A and B or none next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 B only.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B | ||
1.2.1 | A: | High DP content | Concentrate feed suitable for growth, milk production and reproduction |
B: | Low fibre content | ||
1.2.2 | A: | NR of 1 : 6 | Feed ratio suitable for the fattening of farm animals |
B: | NR of 1 : 10 | ||
1.2.3 | A: | Liver fluke and chicken lice | Examples of external parasites in broilers |
B: | Blue ticks and wireworm | ||
1.2.4 | A: | Subcutaneous | Injecting animals between the layers of the skin |
B: | Intradermal | ||
1.2.5 | A: | Sodium citrate and penicillin | Dilutants mixed with semen |
B: | Egg yolk and water | ||
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 The enzyme in the saliva of pigs responsible for the chemical change from starch to simple sugars
1.3.2 A farmer who produces on a large scale and is profit-orientated
1.3.3 The phenomenon where a superior cow is treated with hormones to produce many ova
1.3.4 A powerful contraction of the urethra that deposits semen into the vagina of the cow
1.3.5 The stage of mating where male and female animals are attracted to one another (5 x 2) (10)
1.4 Change the UNDERLINED WORD(S) in each of the following statements to make them TRUE. Write only the answer next to the question number (1.4.1–1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 Fundic muscles prevent food from the oesophagus from entering the stomach of a pig.
1.4.2 Free-range is a system where chickens are kept on the floor of a house until they stop laying eggs.
1.4.3 The gestation period in dairy cattle refers to the period between two lactations.
1.4.4 Dolly, the famous sheep, produced seven identical lambs through the process of genetic modification.
1.4.5 A spermatozoon is the end product of the process of oogenesis. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: ANIMAL NUTRITION
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 The diagram below represents the alimentary canal of a farm animal. 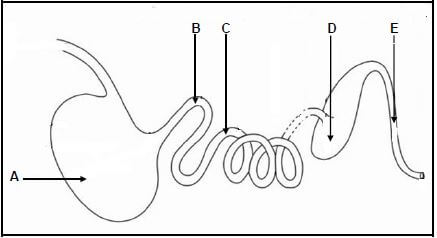
2.1.1 Name the farm animal represented by the alimentary canal in the diagram above. (1)
2.1.2 Indicate the importance of parts A and C in the digestion of feed of the farm animal identified in QUESTION 2.1.1. (2)
2.1.3 Explain mechanical digestion as it occurs in the alimentary canal of the farm animal identified above. (2)
2.2 The diagram below shows the absorption of nutrients from the small intestines into the blood circulatory system. 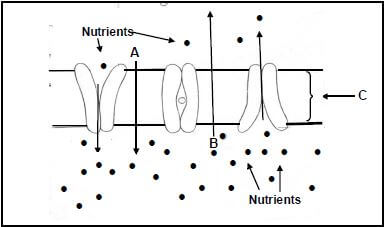
2.2.1 Identify the types of nutrient transport in A and B. (2)
2.2.2 Give a reason for the answer to QUESTION 2.2.1. (2)
2.2.3 Identify structure C. (1)
2.2.4 Name the nutrient that is absorbed through each of the following:
- Blood capillaries (1)
- Lacteal (1)
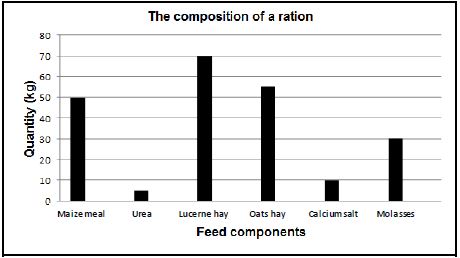
2.3 The graph below shows the feed components of a ration.
2.3.1 Identify ONE example of an energy-rich concentrate in the graph above. (1)
2.3.2 Identify the feed supplement that is mainly added to licks as a source of energy in the graph above. (1)
2.3.3 Comment, with a reason, on the suitability of urea as a supplement for pigs. (2)
2.3.4 Tabulate, using the rations in the graph above:
- A source of natural protein
- A source of NPN protein (3)
2.4 The table below is a farm fodder flow programme for a period of 120 days during winter.
TYPES OF ANIMALS | QUANTITY | LIVE MASS (kg) | INTAKE PER ANIMAL (kg) | REQUIREMENT PER DAY (kg) | REQUIREMENT FOR 120 DAYS (tons) | COST R1 127 (per ton) |
Cows | 60 | 500 | 10 | 600 | A | R81 144,00 |
Bulls | 3 | 750 | 15 | 45 | 5,4 | R6 085,80 |
Calves | 50 | 200 | 4 | 200 | B | R27 048,00 |
TOTAL | 113 | R114 277,80 |
2.4.1 Use the data above to calculate A and B. (4)
2.4.2 Use the data above and determine the average cost of feeding ONE animal for ONE day. (3)
2.5 The table below shows the composition of two animal feeds.
FEED A | FEED B |
80% TDN | 70% TDN |
10% DP | 12% DP |
NR = 1 : 7 | … |
2.5.1 Use a formula to calculate the nutritive ratio (NR) of FEED B. (3)
2.5.2 FEED A cannot be recommended for milk-producing cows. Refer to the nutritive ratio above to justify this statement. (2)
2.6 The table below shows information regarding animal feeds.
PRODUCT | CRUDE PROTEIN PERCENTAGE (%) |
Oats meal | 9 |
Sunflower oil cake meal | 38 |
Final ration | 14 |
Use the Pearson square method to calculate the ratio of the two feeds mentioned above. (4)
[35]
QUESTION 3: ANIMAL PRODUCTION, PROTECTION AND CONTROL
Start this question on a NEW page.
Animal production enterprises should make optimal use of all the natural resources available to maximise production. |
3.1 Explain how EACH of the following impacts on an extensive production system:
3.1.1 Natural resources (2)
3.1.2 Feeding (2)
3.1.3 Exploitative practices (2)
3.2 The pictures below indicate management practices applied to piglets. 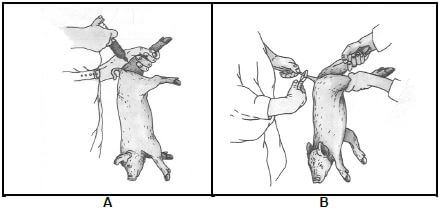
3.2.1 Identify management practices A and B in the pictures above. (2)
3.2.2 Give a reason for management practice A and B. (2)
3.2.3 Refer to A and name the mineral that is usually given to piglets. (1)
3.2.4 Give TWO reasons to motivate the answer to QUESTION 3.2.3. (2)
3.3
Shelter is important for animal production because it reduces the effect of extreme environmental conditions. It prevents the body temperature from dropping below the lowest critical temperature. |
The table below shows the lowest critical temperatures of different farm animals.
FARM ANIMAL | LOWEST CRITICAL |
Dairy cows | 5 |
Piglets | 30 |
Sows | 10 |
Day-old chicks | 20 |
Layers | 10 |
Baconers | 15 |
3.3.1 Use the data in the table above and draw a bar graph to indicate the lowest critical temperature of the different farm animals. (6)
3.3.2 Which farm animal in the table above will NOT utilise the feed efficiently if the environmental temperature is at 24 °C? (1)
3.3.3 Dairy cows can produce milk even when environmental temperatures are at 6 °C. Substantiate this statement. (1)
3.4 The illustration below represents the life cycle of a parasite that affects farm animals. 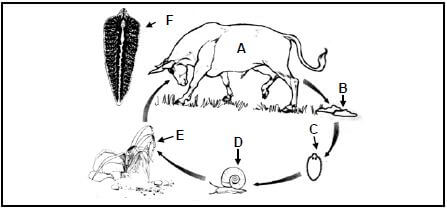
3.4.1 Classify and name the parasite represented above. (2)
3.4.2 Identify the letter (A–F) representing EACH of the following:
- Intermediate host (1)
- Eggs hatch into larva (1)
3.4.3 Suggest ONE precautionary measure a farmer can take to ensure that animals are not infected by this parasite. (1)
3.4.4 State THREE economic implications of this parasite for the farmer. (3)
3.5
The chicken house is mainly used to protect chicken from predators and to create an environment for growth and development. Aspects such as orientation, the types of walls and roofing, should be considered. Equipment and tools are also important. |
3.5.1 Identify TWO purposes of chicken housing in the extract above. (2) 3.5.2 State TWO factors to consider when building a chicken house. (2)
3.5.3 Name TWO examples of equipment in a poultry house. (2)
[35]
QUESTION 4: ANIMAL REPRODUCTION
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 The diagram below shows the embryo and foetus development in farm animals. 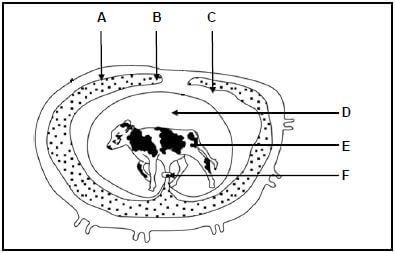
4.1.1 Identify structures B, E and F. (3)
4.1.2 State the following about structure D:
- ONE function (1)
- ONE constituent (1)
- Place where it is found (1)
4.1.3 Indicate the time (in months) during which dairy farmers should be able to detect the presence of a foetus with a rectal pregnancy diagnosis test. (1)
4.2 Hormones play an important role in the reproduction cycle of farm animals.
4.2.1 Explain the term hormone. (2)
4.2.2 Give the main function of EACH of the following hormones:
- Testosterone (1)
- Luteinising hormone (LH) (1)
- Oestrogen (1)
4.2.3 Name the hormone responsible for:
- Maintaining the corpus luteum (1)
- Growth and development of the Graafian follicle (1)
4.3 The graph below shows information on the oestrus cycle of dairy cattle. 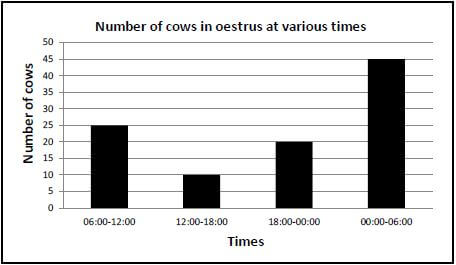
4.3.1 Determine the number of cows in oestrus from 12:00 to 18:00. (1)
4.3.2 Indicate the time during which 20 cows will be in oestrus. (1)
4.3.3 Refer to the graph and predict the trend of the number of cows in oestrus from 12:00 to 06:00. (1)
4.3.4 Calculate the number of cows in oestrus from 18:00 to 06:00. (2)
4.3.5 Refer to the graph above and suggest the best time to inseminate the cows. (1)
4.3.6 Give ONE reason for the answer to QUESTION 4.3.5. (1)
4.4 The diagram below represents the udder of a dairy cow. 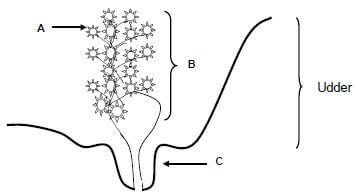
4.4.1 Identify parts A, B and C. (3)
4.4.2 Define the term lactation in dairy cows. (2)
4.4.3 Compare the change in milk production and butterfat production during ONE lactation period. (2)
4.5
Difficult births require more labour and attention. It may result in placenta retention and the death of both the cow and the calf. It is a heritable characteristic, occurring more frequently in heifers and bull calves. It can be corrected by means of proper management. |
4.5.1 Give an appropriate term commonly used for difficult births. (1)4.5.2 Explain the reason for difficult births in heifers. (2)
4.5.3 Indicate TWO managerial measures to reduce the probability of difficult births. (2)
4.5.4 Define the term placenta retention. (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150