AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupAGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TWO sections, namely SECTION A and SECTION B.
- Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- Show ALL calculations, including formulae, where applicable.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Write down the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10), choose the answer and make a cross (X) over the letter (A–D) of your choice in the ANSWER BOOK.
EXAMPLE: |
1.1.1 The factor that influences the supply and the demand of a product:
- An increase in the supply of the product
- Range of products available
- Price of the product
- Attitude and values of consumers
1.1.2 ONE of the following refers to the movement of products from the producer to consumers:
- Grading
- Processing
- Value adding
- Marketing
1.1.3 The factor that ensures a secure market and price for products:
- Demand
- Supply
- Contract
- Risk
1.1.4 The measure of how much the demand for a product changes with a change in price:
- Equilibrium
- Fluctuation
- Price elasticity of demand
- Price inelasticity of demand
1.1.5 An example of production capital in a dairy farming enterprise:
- Feed
- Breeding cows
- Fencing
- Milking machines
1.1.6 Net worth of a farming enterprise may be defined as …
- the value of assets minus the liabilities.
- the owner's equity.
- expenditure minus income.
- assets plus liabilities.
1.1.7 Capital that is invested in items of a more permanent nature, like a dam, is called … capital.
- floating
- movable
- working
- fixed
1.1.8 A worker who works on a farm only during the harvesting of oranges may be classified as a … labourer.
- seasonal
- casual
- permanent
- semi-permanent
1.1.9 Nguni cattle are preferred for breeding in South Africa due to the following traits:
- Very fertile
- Resistant to ticks and diseases
- Large frames
- High adaptability to harsh conditions
Choose the CORRECT combination:
- (i), (ii) and (iii)
- (i), (ii) and (iv)
- (i), (iii) and (iv)
- (ii), (iii) and (iv)
1.1.10 The structure that is changed by genetic modification:
- Cell
- Gene
- Nucleus
- Antigen (10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Choose a term/phrase from COLUMN B that matches a description in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–J) next to the question number (1.2.1–1.2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, for example 1.2.6 K.
COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
1.2.1 A challenge when marketing agricultural produce | A natural selection |
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the word/term next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.3.1 Telling people more about a product in order to convince them to buy it
1.3.2 The production output in relation to the financial input in a farming enterprise
1.3.3 An instrument used to transfer desirable genes into plant tissue
1.3.4 A form of biotechnology that involves the manipulation of genes to obtain desired characteristics
1.3.5 Characteristics that are determined by the outcome of only one gene (5 x 2) (10)
1.4 Change the UNDERLINED WORD(S) in each of the following statements to make them TRUE. Write only the answer next to the question number (1.4.1–1.4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.4.1 Grading is the provision of standard specifications which will give uniformity to a group of products.
1.4.2 An asset list is a record of capital goods on a farm.
1.4.3 A single hereditary factor is called dihybrid inheritance.
1.4.4 An allele represented by a capital letter is always recessive.
1.4.5 The law of independent assortment states that alleles separate into separate gametes so that each gamete contains only one gene for the characteristic. (5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
Start this question on a NEW page.
2.1 The graph below indicates the quantities offered and bought at different prices for a particular agricultural product. 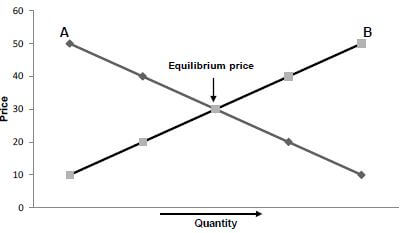
2.1.1 Identify curves A and B. (2)
2.1.2 Define the term equilibrium price. (2)
2.1.3 Explain the relationship between curves A and B in relation to price. (3)
2.2 The following are channels of a free marketing system.
Internet marketing; stock sales; fresh produce market; |
2.2.1 Match the channels of a free marketing system above to EACH of the following:
- The farmer sells spinach directly to consumers on the farm. (1)
- Goats, sheep and cattle are sold to the highest bidder. (1)
- An agreement or arrangement to sell directly to a wholesaler. (1)
- Mangoes and apples are delivered to markets immediately. (1)
- Goods are advertised and sold electronically. (1)
2.2.2 Name TWO disadvantages of a free marketing system for a farmer. (2)
2.3 The flow chart below illustrates the path of agricultural products from the producer to the consumer. 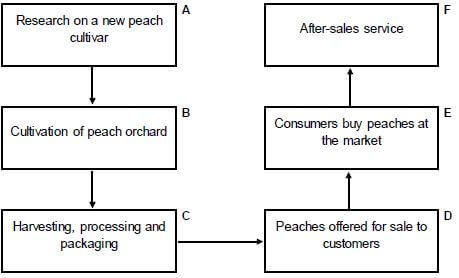
2.3.1 Indicate the letter (A–F) in the flow chart above, that represents EACH of the following:
- Demand (1)
- Supply (1)
2.3.2 Which factor may hamper marketing between stages C and D? (1)
2.3.3 Give TWO guidelines for packaging in stage C. (2)
2.3.4 State TWO factors determining the demand for peaches. (2)
2.4 The table below shows the number of bags of butternuts bought at different prices at a local market.
PRICE (RAND PER BAG) | NUMBER OF BAGS |
R5 | 200 |
R10 | 150 |
R15 | 140 |
R20 | 120 |
R25 | 100 |
R30 | 50 |
2.4.1 Use the data in the table above and draw a line graph to show the number of bags of butternuts bought at different prices. (6)
2.4.2 Refer to the line graph and identify the tendency in the price, as the number of bags of butternuts decline. (1)
2.5 Different phases in the process of entrepreneurship are shown below:
- Focus on carrying out the plan to produce and supply goods or services
- Determine available capital, labour and equipment
- Realisation of the absence of suitable products and services
- Plan the business to secure funding
2.5.1 Re-arrange the entrepreneurial phases (A–D) above in the correct order. (4)
2.5.2 State THREE problems that may be encountered during the planning phase. (3)
[35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
Start this question on a NEW page.
3.1
A farmer cannot afford to finance a farming enterprise. The only option is to request a loan at a financial institution. A loan of R190 000 is granted at an interest rate of 12,5%. After the harvest, the farmer sells the crop for R212 500. |
3.1.1 Calculate the interest this farmer will have to pay to the financial institution. (2)
3.1.2 Use a formula to calculate the profitability of this farming enterprise. (3)
3.1.3 Recommend whether the farmer should continue with this enterprise. Give a reason for the answer. (2)
3.2
Legislation, especially labour legislation such as the Occupational Health and Safety Act, 1993 (Act 85 of 1993), plays a very important role in any farming enterprise. |
3.2.1 Briefly explain the purpose of this Act. (2)
3.2.2 State THREE guidelines that the farmer has to comply with, as stipulated by the legislation above. (3)
3.3 The picture below shows the coordination of production factors for effective agricultural production. 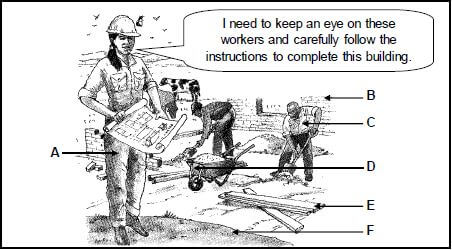
3.3.1 Identify the letter (A–F) representing EACH of the following:
- Farm manager (1)
- Farm labourer (1)
- Movable capital (1)
- Fixed capital (1)
3.3.2 Give the main management principle in the picture on the previous page. Give a reason for the answer. (2)
3.3.3 List THREE entrepreneurial skills in the picture. (3)
3.4
Different measures may be applied by a farmer to increase the production output and productivity of the farm per hectare. |
3.4.1 Indicate the measure to improve land productivity, as indicated by EACH of the following statements:
- Combining grain crops and leguminous crops (1)
- Using a larger field rather than individual smaller plots to cultivate (1)
- Burying water pipes to reduce damage and leaks (1)
- Determining the type and amount of fertiliser to use for a crop (1)
3.4.2 State THREE economic functions of land. (3)
3.5 The table below shows the records of a farming enterprise for a period of three months.
JANUARY | FEBRUARY | MARCH | |
Opening balance | R500 | R10 150 | R13 538 |
Receipts | |||
Bank loans | R3 500 | R3 500 | R2 000 |
Seed account | R4 300 | 0 | 0 |
Capital | R5 500 | R4 500 | R2 200 |
Receipt total | R13 300 | R8 000 | R4 200 |
Payments | |||
Accounts paid | R2 800 | R3 700 | R4 600 |
Wages | R500 | R500 | R3 500 |
Interest on amount owed | R350 | R412 | R674 |
Payments total | R3 650 | R4 612 | R8 774 |
Net cash | R9 650 | R3 388 | -R4 574 |
Closing balance | R10 150 | R13 538 | R8 964 |
3.5.1 Identify the farming record in the table above. (1)
3.5.2 Refer to TWO items in the record above to support the answer to QUESTION 3.5.1. (2)
3.5.3 Name a document that a farmer may use to determine the net worth of a farming business. (1)
3.5.4 Name TWO benefits for a farmer to have a record such as the one above. (2)
3.5.5 Indicate the implication of negative net cash in March. (1)
[35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 Nowadays farming demands the use of different methods and technologies for animal breeding.
4.1.1 Identify the breeding method indicated by EACH of the following scenarios:
- Commercial Holstein cow x stud Holstein bull using artificial insemination
- Sussex bull x Sussex cow (the bull's daughter)
- Afrikaner bull x Shorthorn cows (3)
4.1.2 Choose the breeding method in QUESTION 4.1.1 that will be the best option to change the enterprise from a commercial dairy herd to a dairy stud. (1)
4.1.3 Name the breeding method in QUESTION 4.1.1 that will ensure heterosis or hybrid vigour. (1)
4.1.4 State TWO disadvantages of crossbreeding. (2)
4.2
A recent development in the improvement of maize is the genetic modification that makes it resistant to the maize stalk borer. A soil bacterium, Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), naturally produces a toxin (poison) that kills the maize stalk borer. Genetic engineering techniques are used to transfer the Bt toxin gene from the bacterium to the DNA of maize plants. |
4.2.1 Identify TWO potential benefits of this genetically modified (GM) crop. (2)4.2.2 State TWO negative effects of GM crops on the environment. (2)
4.2.3 Explain the technique of using the bacterium in the scenario above to modify maize plants genetically. (2)
4.3 Variation is a phenomenon used for selection and breeding.
4.3.1 Give TWO benefits of variation in a breeding programme. (2)
4.3.2 Name TWO internal causes of variation. (2)
4.3.3 Differentiate between variation and selection. (4)
4.4 The gene for a brown coat in goats is dominant over that for a white coat. In the diagram below two brown-coated goats mated.
(Use the symbol B/b for coat colour.) 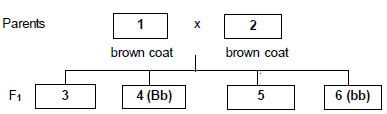
4.4.1 Determine the genotypes of individuals 1 and 2. (2)
4.4.2 Identify the phenotypes of offspring 3 and 5 in the F1 generation. (2)
4.4.3 Refer to the diagram and give the percentage of the F1 generation that is heterozygous for a brown coat. (1)
4.4.4 Predict the coat colour of the progeny, if individual 6 is crossed with another individual of similar genetic composition. Give a reason to substantiate the answer. (2)
4.5
The pattern of inheritance can lead to differences in the phenotype. If white flowers (W) are crossed with red flowers (R), the offspring in the F1 generation will all be pink. |
4.5.1 Use the Punnet square method to show the offspring of the F2 generation from the F1 parents above. (4)
4.5.2 Indicate the type of dominance in the offspring of the F1 generation that are all pink. (1)
4.5.3 Give a reason for the answer to QUESTION 4.5.2. (1)
4.5.4 Give the phenotypic ratio of the F2 generation. (1)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL: 150