LIFE SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupLIFE SCIENCES
PAPER 1
GRADE 12
NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS
FEBRUARY/MARCH 2017
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
Read the following instructions carefully before answering the questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Write ALL the answers in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start the answers to EACH question at the top of a NEW page.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Present your answers according to the instructions of each question.
- Do ALL drawings in pencil and label them in blue or black ink.
- Draw diagrams, tables or flow charts only when asked to do so.
- The diagrams in this question paper are NOT necessarily drawn to scale.
- Do NOT use graph paper.
- You must use a non-programmable calculator, protractor and a compass, where necessary.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Write down the question number (1.1.1–1.1.10), choose the answer and make a cross (X) over the letter (A–D) of your choice in the ANSWER BOOK.
EXAMPLE:
1.1.11 ![]()
1.1.1 After sperm cells have been produced in humans, they are stored in the … until maturation.
- penis
- urethra
- epididymis
- seminal vesicles
1.1.2 Which ONE of the following parts in the diagram of a sperm cell contains a haploid number of chromosomes? 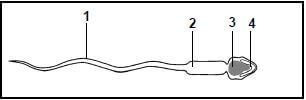
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
1.1.3 Which ONE of the following plant hormones is responsible for the germination of seeds?
- Growth hormone
- Abscisic acid
- Gibberellin
- Auxin
1.1.4 The phase in meiosis in which individual centromeres split is called …
- anaphase I.
- anaphase II.
- metaphase I.
- metaphase II.
1.1.5 When Jane plays in the snow, her body maintains a constant core temperature by …
- vasodilation and sweating.
- vasoconstriction and shivering.
- sweating and shivering.
- vasoconstriction and vasodilation.
1.1.6 Which ONE of the following hormones prepares the human body to react to emergency situations?
- Insulin
- Aldosterone
- Adrenalin
- Growth hormone
QUESTIONS 1.1.7 AND 1.1.8 REFER TO THE INVESTIGATION BELOW.
An investigation was carried out to determine the fertility levels of healthy males in different age groups.
The number of active sperm cells present in the semen was counted for each man in each age group and averages were calculated. |
1.1.7 Which ONE of the following is the dependent variable in the investigation?
- Fitness levels of the males
- Age groups of the males
- Number of active sperm cells
- Amount of semen
1.1.8 Which ONE of the following variables was kept constant during this investigation?
- Number of participants in each age group
- Fertility levels of males in each age group
- Number of active sperm cells
- Age groups of the males
QUESTIONS 1.1.9 AND 1.1.10 REFER TO THE GRAPH BELOW. THE GRAPH SHOWS THE CHANGES IN THE CONCENTRATION OF FEMALE HORMONES (LH AND FSH) IN TWO FEMALES DURING THE FIRST TWO WEEKS OF THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE. 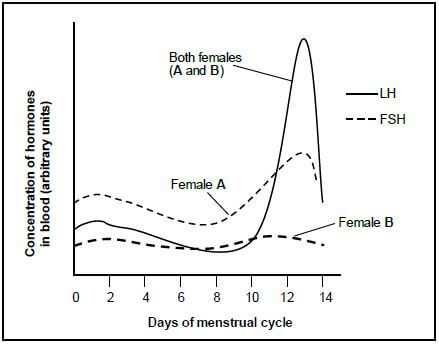
1.1.9 Which female will NOT ovulate on day 14?
- Female A, because the FSH levels are high
- Female A, because the LH levels are too high on day 13
- Female B, because LH inhibits the development of a follicle
- Female B, because a follicle did not develop in the ovary
1.1.10 Which ONE of the following statements is CORRECT regarding female A?
- FSH increases on day 14 because the Graafian follicle is secreting progesterone.
- FSH increases after day 9 as the pituitary gland/hypophysis is secreting progesterone.
- FSH decreases after day 4 to ensure that implantation occurs.
- FSH increases in the first two days to stimulate the development of a follicle.
(10 x 2) (20)
1.2 Give the correct biological term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question number (1.2.1 to 1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK.
1.2.1 The diploid cell formed by the process of fertilisation
1.2.2 A fluid that protects the human embryo against injuries and large-scale temperature changes
1.2.3 A disorder of the nervous system that is characterised by the breakdown of the myelin sheath of neurons
1.2.4 A hormone produced by the pituitary gland/hypophysis that stimulates milk production in human females
1.2.5 Having access to enough food on a daily basis to ensure healthy living
1.2.6 A blood vessel in the umbilical cord that transports nutrients to the foetus
1.2.7 A part of the neuron that conducts impulses towards the cell body
1.2.8 A disease that results from the body's inability to produce insulin
(8 x 1) (8)
1.3 Indicate whether each of the statements in COLUMN I applies to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A AND B or NONE of the items in COLUMN II. Write A only, B only, both A and B, or none next to the question number (1.3.1 to 1.3.3) in the ANSWER BOOK.
COLUMN I | COLUMN II |
1.3.1 The hormone that is in excess in a person that grows abnormally tall | A: ADH |
1.3.2 The part of the autonomic nervous system that controls involuntary actions | A: Sympathetic |
1.3.3 A hormone that controls the salt content in a human body | A: Adrenalin |
(3 x 2) (6)
1.4 The diagram below shows a phase of meiosis in an animal cell. 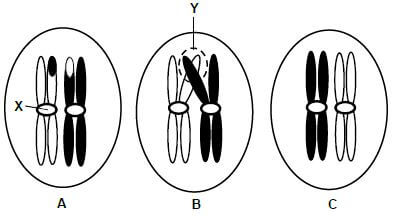
1.4.1 Identify:
- A (1)
- B (1)
- C (1)
1.4.2 Which phase of meiosis is illustrated in the diagram above? (1)
1.4.3 Name the phase that follows the one represented in the diagram above. (1)
1.4.4 How many chromosomes were there in the cell above before the process of meiosis began? (1)
1.4.5 What is the specific name given to meiosis when it takes place in a human female? (1)
(7)
1.5 The diagram below represents a section through a human eye. 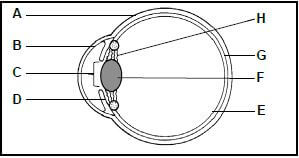
1.5.1 Identify:
- A (1)
- B (1)
- C (1)
1.5.2 Give the LETTER and NAME of the part that:
- Regulates the amount of light entering the eye (2)
- Contains a dark pigment that absorbs excess light in the eye (2)
- Contains receptors sensitive to light (2)
(9)
TOTAL SECTION A: 50
SECTION B
QUESTION 2
2.1 The diagram below represents the human female reproductive system. A 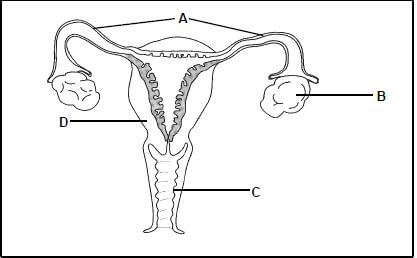
2.1.1 Identify part C. (1)
2.1.2 State ONE function of part D. (1)
2.1.3 Name the hormone secreted by part B during the first week of the menstrual cycle. (1)
2.1.4 State how the hormone named in QUESTION 2.1.3 influences part D. (1)
2.1.5 During tubal ligation, part A is surgically cut or tied.
Explain how this procedure prevents pregnancy. (3) (7)
2.2 An investigation was carried out to determine the effects of smoking during pregnancy on the baby's birth weight. Babies born weighing 2 499 g or less have a low birth weight.
The table below compares the percentage of babies with a low birth weight born to mothers who smoked with mothers who did not smoke in a certain city in 2009.
BIRTH WEIGHT (GRAMS) | PERCENTAGE OF TOTAL BIRTHS (%) IN 2009 | |
MOTHERS WHO SMOKED | MOTHERS WHO DID NOT SMOKE | |
<1 000 | 0,7 | 0,2 |
1 000–1 499 | 0,9 | 0,3 |
1 500–1 999 | 2,2 | 1,1 |
2 000–2 499 | 7,1 | 3,2 |
[Adapted from www.ainw.gov.au]
2.2.1 Draw a histogram to represent the percentage of births in each weight group born to mothers who smoked. (6)
2.2.2 Why were babies that weighed more than 2 500 g at birth not included in the investigation? (1)
2.2.3 State a general conclusion for the investigation based on the data in the table. (2)
2.2.4 Describe how chemicals from cigarette smoke are able to reach the baby's blood from the mother's blood. (2) (11)
2.3 Read the extract below.
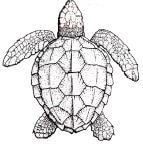
In a species of sea turtles (shown below), the females leave the water to lay their eggs in a nest on the beach. The female makes the nest by digging a hole with her hind legs. A female is known to lay about 100 or more eggs. After the eggs have been laid, the female covers the nest with sand to hide it from predators and leaves the eggs to incubate on their own. A sea turtle |
The graph below shows the percentage of survivors in a sea turtle population over a period of time. 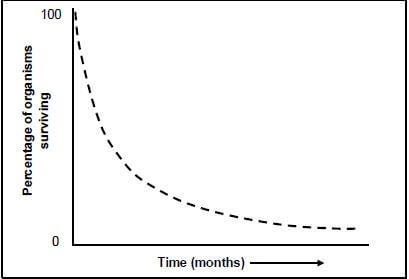
[Adapted from https://bioweb.uwlax.edu]
2.3.1 Write down whether the type of reproduction in sea turtles is oviparous, viviparous or ovoviviparous. (1)
2.3.2 Give a reason for your answer to QUESTION 2.3.1. (1)
2.3.3 The shape of the graph would differ if there were parental care.
- Describe how the shape of the graph would differ if there were parental care. (1)
- Explain your answer to QUESTION 2.3.3(a). (2) (5)
2.4 The diagram below represents parts of the human ear. 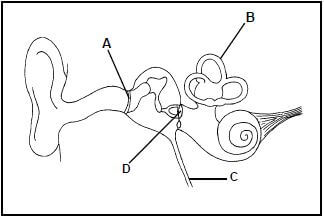
2.4.1 Identify parts:
- B (1)
- C (1)
- D (1)
2.4.2 Explain how parts A and D together are adapted to amplify sound. (3)
2.4.3 State ONE advantage of the middle ear being filled with air. (1) (7)
2.5 Read the extract below.
A LINK BETWEEN CONCUSSION AND BRAIN DAMAGE In 2002 a former American football player was found dead in his truck. The doctor who handled the autopsy discovered that the football player had severe brain damage and that his death was caused by repeated blows to the head or repeated concussions. He called this disorder chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE). [Adapted from www.wikipedia.org and www.theatlantic.com] |
2.5.1 The part of the brain affected by CTE is the cerebrum. State TWO possible symptoms of this disorder. (2)
2.5.2 State ONE way in which the brain is protected. (1)
2.5.3 Explain why CTE does not usually affect essential life processes such as breathing or heart rate. (2) (5)
2.6 TSH and thyroxin are both secretions of endocrine glands, namely the pituitary gland/hypophysis and the thyroid gland respectively.
2.6.1 Where will you look for evidence to detect the levels of TSH and thyroxin in the human body? (1)
2.6.2 A high level of TSH is detected in the human body. Explain TWO possible causes of high levels of TSH in the body. (4) (5)
[40]
QUESTION 3
3.1 An investigation was carried out to determine the effect of auxins on the growth of coleoptiles.
The procedure was as follows:
- The tip of one coleoptile (young shoot) was removed and placed on a block of agar jelly, as shown in diagram A.
- After two hours the agar jelly was placed on the cut surface of the original coleoptile, as shown in diagram B.
- The coleoptile was covered with a black box and allowed to grow for two days, as shown in diagram C.
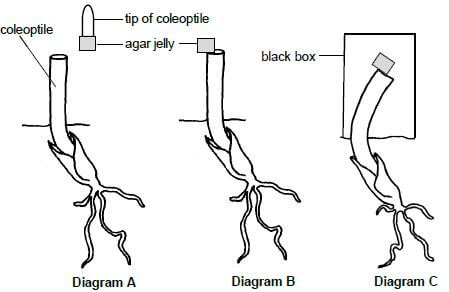
[Adapted from www.plantphys.info.com]
3.1.1 Explain why the tip of the coleoptile was placed on the agar jelly for two hours at the start of the investigation. (2)
3.1.2 Describe what occurred in diagram C to cause the coleoptile to bend even though no light was present. (4)
3.1.3 Describe a control for this investigation. (2) (8)
3.2 The diagram below represents a typical Snellen chart that is used to estimate visual acuity (ability to see clearly). The extract explains how a Snellen chart is used. 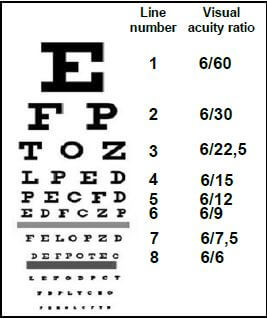
A person, whose visual acuity is being tested, stands 6 m away from the chart. One eye is covered and he/she reads the letters of each row out loud, beginning at the top. The smallest row that can be read accurately indicates the visual acuity in that specific eye. [Adapted from www.wikipedia.org] |
3.2.1 A person is only able to read accurately to the end of line 5 on the Snellen chart. What is his/her visual acuity ratio? (1)
3.2.2 Explain ONE reason why the special equipment, which can present different patterns, arrangements and sizes of letters, is used when testing eyesight for a driver's licence. (2)
3.2.3 Some clinics have half-size charts that must be read at a distance of 3 m instead of 6 m. Describe the process that occurs in the eye to ensure that the letters of the chart are in focus at 3 m. (4) (7)
3.3 Read the extract below.
TONS OF FOOD THROWN AWAY EACH YEAR In South Africa about 9 million tons of food per year is thrown away as waste, whilst around 13,8 million South Africans are food insecure. The drought that is currently affecting the country is expected to increase the number of food insecure South Africans. This food wastage costs the economy of South Africa about R60 billion each year.
The highest volume of waste occurs when the food is transported, especially over long distances. Packaging and processing accounts for the second highest volume of waste. [Adapted from The New Age, 1 February 2016] |
3.3.1 State TWO factors, according to the extract, that lead to the largest amount of food being wasted. (2)
3.3.2 Suggest TWO ways in which shopkeepers can reduce the amount of food going to waste. (2)
3.3.3 What percentage does seafood contribute to the total food wastage cost in South Africa? Show ALL your calculations. (2)
3.3.4 Explain TWO ways in which the drought is expected to increase the number of food-insecure South Africans. (4) (10)
3.4 The graph below shows the changes in the human population and the population of parrots (a type of bird) in a certain country over a period of 500 years. 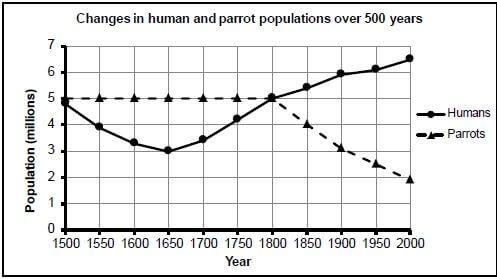
[Adapted from www.people.eku.edu]
3.4.1 When was the human population at 3 million? (1)
3.4.2 Describe the difference in the trends between the human population and the parrot population since 1800. (2)
3.4.3 Suggest TWO reasons for the trend described in QUESTION 3.4.2. (4)
3.4.4 If the current rate of decrease in the parrot population continues, explain how the organisms that feed mainly on the parrot population would be affected. (2) (9)
3.5 Describe how the excessive use of fertilisers by farmers impacts on the quality of water. (6)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
QUESTION 4
Nontobeko had been walking in the desert, without water, for two days, when she suddenly heard a sound behind her. She turned her head and saw a snake coming towards her. She became scared and turned around to run away. As she was running, she tripped and fell.
Describe how her body regulated water content during the two days and describe how her balance would have been restored after she fell down.
Content: (17)
Synthesis: (3)
(20)
NOTE: NO marks will be awarded for answers in the form of flow charts, tables or diagrams.
TOTAL SECTION C: 20
GRAND TOTAL: 150