PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - AMENDED SENIOR CERTIFICATE PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS MAY/JUNE 2017
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupPHYSICAL SCIENCES: PHYSICS PAPER 1
GRADE 12
SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION
MEMORANDUM
MAY/JUNE 2017
QUESTION 1
1.1 D ✓✓ (2)
1.2 B ✓✓ (2)
1.3 D ✓✓ (2)
1.4 C✓✓(2)
1.5 D ✓✓ (2)
1.6 B ✓✓ (2)
1.7 C ✓✓(2)
1.8 C ✓✓ (2)
1.9 B ✓✓ (2)
1.10B ✓✓ (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2
2.1.1
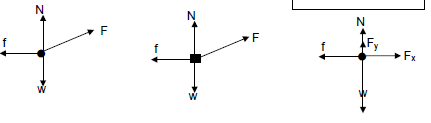
| Accepted labels | ||
| w | Fg/Fw/weight/mg/gravitational force | ✓ |
| f | Friction/Ff/fk/3 N/Fw | ✓ |
| N | Normal (force)/FnormaL/FN | ✓ |
| F | FA/Fapplied | ✓ |
Notes
- Mark awarded for label and arrow
- Deduct 1 mark if arrow(s) is (are) missing
- Do not penalise for length of arrows since drawing is not to scale.
- Any other additional force(s) Max :¾
- If force(s) do not make contact with body/Indien krag(te) nie met die voorwerp kontak maak nie: Max/Maks: ¾
(4)
2.1.2 fk = μkN ✓ (can use FN for N in equation)
3 = (0,2)N ✓
N = 15 N ✓
(3)
2.1.3 POSITIVE MARKING FROM QUESTION 2.1.2
Fnet = ma
N + Fvert - w = 0
N + Fvert = w
Any of the three
Fsin20o ✓= (2)(9,8) – 15 ✓
F = 13,45 N✓
(4)
2.1.4 POSITIVE MARKING FROM QUESTION 2.1.3
Fnet = ma
Fcos 20o – f = ma
Any two
13,45cos20o – 3 = 2a✓
a = 4,82 m.s-2 ✓
(3)
2.2
2.2.1 Any two particles (objects) in the universe will attract each other with a force which is directly proportional to the product of the masses ✓and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them (their centres). ✓ (2)
2.2.2 Increases✓
Gravitational force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the (centres of the) objects✓
OR
F=α 1
r2✓
(2)
[18]
QUESTION 3
3.1 The only force acting on the ball is the gravitational force. ✓✓
OR
The only force acting on the ball is its weight.
ACCEPT
The only force acting on the ball is gravity. (2)
3.2.1
| OPTION 1 UPWARDS AS POSITIVE Δy = viΔt + ½aΔt2✓ = (10)(3) + ½(-9,8)(32) ✓ = -14,10 Height of building = 14,10 m✓ | DOWNWARDS AS POSITIVE Δy = viΔt + ½ aΔt2✓ = (-10)(3) + ½ (9,8)(32) ✓ = 14,10 m ✓ Height of building = 14,10 m |
| OPTION 2 UPWARD AS POSITIVE For maximum height vf = vi + aΔt 0 = 10 + (-9,8)Δt Δt = 1,02 s Time taken from point A to ground = 3 - 2(1,02) = 0,96 s Δy = viΔt + ½ aΔt2✓ = (-10)(0,96) + ½ (- 9,8)(0,962)✓ = -14,1184 Height of building = 14,12 m✓ | UPWARD AS NEGATIVE For maximum height vf = vi + aΔt 0 = -10 + (9,8)Δt Δt = 1,02 s Time taken from point A to ground = 3 - 2(1,02) = 0,96 s Δy = viΔt + ½ aΔt2✓ = (10)(0,96) + ½ ( 9,8)(0,962) ✓ = 14,1184 m ✓ Height of building = 14,12 m |
| OPTION 3 UPWARD AS POSITIVE vf = vi + aΔt = 10 + (-9,8)(3) = -19,40 vf 2 = vi 2 + 2 aΔy✓ (-19,4)2 = (10)2 + 2(-9,8)Δy✓ Δy =-14,10 m Height of building = 14,10 m✓ | UPWARD AS NEGATIVE vf = vi + aΔt = -10 + (9,8)(3) = 19,40 vf 2 = vi 2 + 2 aΔy✓ (19,4)2 = (-10)2 + 2(9,8)Δy Δy = 14,10 m ✓ Height of building = 14,10 m |
| OPTION 4 UPWARD AS POSITIVE vf = vi + aΔt = (-10) + (-9,8)(0,96) = -19,408 vf 2 = vi 2 + 2 aΔy (-19,408)2 = (10)2 + 2(-9,8)Δy Δy =14,12 m Height of building = 14,12 m | UPWARD AS NEGATIVE vf = vi + aΔt = 10 + (9,8)(0,96) = 19,408 vf 2 = vi 2 + 2 aΔy (19,408)2 = (-10)2 + 2(9,8)Δy Δy = 14,12 m Height of building = 14,12 m |
| OPTION 5 Wnet = ΔEk = ΔK mgΔxcos0o = ½ m(vf2 – vi2) (9,8)Δx = ½ (19,4082 – 102) ✓ Δx = 14,12 m Height of building = 14,12 m✓ | vf = vi + aΔt = 10 + (9,8)(3) = 19,40 |
| OPTION 6 EmechA = EmechB (Ek + Ep)A = (Ek + Ep)B ½ mv2 + mgh = ½ mv2 + 0 ½(10)2 + (9,8)h = ½(19,40)2 ✓ Height of building = 14,12 m✓ | vf = vi + aΔt = 10 + (9,8)(3) = 19,40 |
| OPTION 7 Wnc = ΔEp + ΔEk✓ 0 = mg(hf – hi) + ½m(vf2 - vi2) 0 = m(9,8)(0 – hi) + ½m(19,4082 – 102) ✓ Height of building = 14,12 m✓ | vf = vi + aΔt = 10 + (9,8)(3) = 19,40 |
| OPTION 8 UPWARD AS POSITIVE vf = vi + aΔt = (10) + (-9,8)(3) = -19,40 m∙s-1 Δy=v1 + vf Δt ✓ 2 Δy = (10 -19,40) 3✓ 2 Height of building = 14,12 m✓ | UPWARD AS NEGATIVE vf = vi + aΔt = 10 + (9,8)(3) = 19,40 m∙s-1 Δy=v1 + vf Δt✓ 2 Δy = (10 -19,40) 3✓ 2 Δy = 14,12 m✓ Height of building = 14,12 m |
(3)
3.2.2
| OPTION 1 UPWARDS AS POSITIVE vf = vi + aΔt✓ = (10) + (-9,8)(3) ✓ = -19,40 m∙s-1 Speed = 19,40 m∙s-1✓ Spoed = 19,40 m∙s-1 | DOWNWARDS AS POSITIVE vf = vi + aΔt✓ = (-10) + (9,8)(3) ✓ = 19,40 m∙s-1 ✓ Speed = 19,40 m∙s-1 Spoed = 19,40 m∙s-1 |
| OPTION 2 UPWARDS AS POSITIVE vf2 = vi2 + 2aΔx ✓ = (-10)2 + 2(-9,8)(-14,1) vf = 19,4 m∙s-1 ✓ | DOWNWARDS AS POSITIVE vf2 = vi2 + 2aΔx ✓ = (10)2 + 2(9,8)(14,1) ✓ vf = 19,4 m∙s-1 ✓ |
POSITIVE MARKING FROM QUESTION 3.2.1
| OPTION 3 UPWARDS AS POSITIVE tΔ2v+v=yΔfi✓ Δy=v1 + vf Δt 2 -14.12 = (10 + vf) 3 2 Speed = 19,41 m∙s-1✓ Spoed = 19,41 m∙s-1 | DOWNWARDS AS POSITIVE Δy=v1 + vf Δt 2 -14.12 = (10 + vf) 3 2 vf = 19,41 m∙s-1 Speed = 19,41 m∙s-1 Spoed = 19,41 m∙s-1 |
(3)
3.2.3
| OPTION 1 UPWARDS AS POSITIVE vf2= vi2 + 2aΔy✓ 0 = vi2+ (2)(-9,8)(8) ✓ vi = 12,52 m∙s-1✓ Speed = 12,52 m∙s-1 | DOWNWARDS AS POSITIVE vf2= vi2 + 2aΔy✓ 0 = vi2+ (2)(9,8)(-8) vi = -12,52 m∙s-1✓ Speed = 12,52 m∙s-1 ✓ |
| OPTION 2 UPWARDS AS POSITIVE Δx = viΔt + ½aΔt2 -8 = 0 + ½ (-9,8)Δt2 Δt = 1,28 s vf = vi + aΔt ✓ 0 = vi + (-9,8)(1,28)✓ vi = 12,52 m∙s-1✓ Speed = 12,52 m∙s-1 | DOWNWARDS AS POSITIVE Δx = viΔt + ½aΔt2 8 = 0 + ½ (9,8)Δt2 Δt = 1,28 s vf = vi + aΔt ✓ 0 = vi + (9,8)(1,28)✓ vi = -12,52 m∙s-1 Speed = 12,52 m∙s-1 ✓ |
(3)
3.3 UPWARDS AS POSITIVE
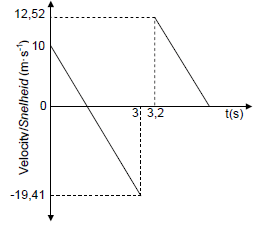
| CHECKLIST FOR MARKING | |
| Each line correctly drawn with calculated velocities. 1 x 2 | ✓✓ |
| Mark for lines being parallel | ✓ |
| Times 3 s and 3,2 s correctly shown | ✓ |
3.3 DOWNWARDS AS POSITIVE(4)
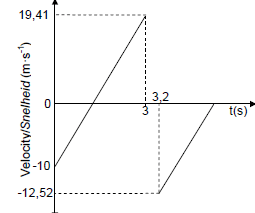
| CHECKLIST FOR MARKING | |
| Each line correctly drawn with calculated velocities. 1 x 2 | ✓✓ |
| Mark for lines being parallel | ✓ |
| Times 3 s and 3,2 s correctly shown | ✓ |
[15]
QUESTION 4
4.1
| OPTION 1 v=Δx Δt = 0,2 0,4 = 0,5 m∙s-1 | OPTION 2 v=Δx Δt = 0,4 0,8 = 0,5 m∙s-1 | OPTION 3 v=Δx Δt = 0,6 1,2 = 0,5 m∙s-1 |
Formula/Formule Correct substitution in all three equations Correct answer
|
OPTION 2
Trolley moves with equal displacements in equal time (intervals). (Full marks or zero)(3)
4.2 The total linear momentum of a closed (isolated) system remains constant (is conserved).
OR
In an isolated system, the total linear momentum before collision is equal to the total linear momentum after collision (2)
NOTE:
If the words “closed (isolated)” or “total” omitted, award 1/2.
4.3 POSITIVE MARKING FROM QUESTION 4.1
OPTION 1 Fnet = (vf - v1) = (6) (0.184-0) | |
| OPTION 2 Σpi = Σpf m1v1i + m2v2i = m1v1f + m2v2f (any one) (3,5)(0,5) ✓ = (3,5 + 6)vf ✓ vf = v6kg = 0,184 m∙s-1 | |
| For trolley B: FnetΔt = Δp = mΔv✓ Fnet(0,5) = 6(0,184 -0) ✓ Fnet = 2,21 N (2,24 N) ✓ | For trolley A: FnetΔt = Δp = mΔv✓ Fnet(0,5) = 3,5(0,184 -0,5) ✓ Fnet = - 2,21 N (2,24 N) ∴ Magnitude of the average net force experienced by trolley B = 2,21 N (2,24 N)✓ |
| (6) [11] | |
| OPTION 3 Σpi = Σpf m1v1i + m2v2i = m1v1f + m2v2f (any one) (3,5)(0,5) ✓ = (3,5 + 6)vf ✓ vf = v6kg = 0,184 m∙s-1 | |
| For trolley B: vf = vi + aΔt 0,184 = 0 +a(0,5) a = 0,368 ms-1 Fnet = ma✓ = (6)(0,368) = 2,21 N | For trolley A: vf = vi + aΔt 0,184 = 0,5 +a(0,5) a = - 0,632 ms-1 Fnet = ma✓ = (3,5)(-0,632) = - 2,21 N ∴ Magnitude of the average net force experienced by trolley B = 2,21 N (2,24 N)✓ |
| (6) [11] | |
QUESTION 5
5.1
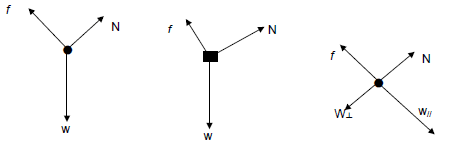
| Accepted labels | ||
| w | Fg/Fw/weight/mg/gravitational force | ✓ |
| f | Friction/Ff/50 N/wrywing/Fw | ✓ |
| N | Normal force/FNORMAL/FNOR/F NORMAAL | ✓ |
Notes
- Mark awarded for label and arrow
- Deduct 1 mark if arrow(s) is (are) missing
- Do not penalise for length of arrows since drawing is not to scale.Any other additional force(s)Max 2
- If force(s) do not make contact with body:Max: ¾
- Award 1 mark if both resolved components of w are correct.
5.2 The net/total work done on an object equals the change in the object's kinetic energy. ✓✓
OR
The work done by the net force equals the change in the object's kinetic energy. ✓✓(2)
5.3
| OPTION 1 Wnet = ΔEK fΔxcosθ + FgΔxcosθ = ½mvf2 – ½mvi2 (50)(25cos180o)✓ + (60)(9,8) (25cos70o) ✓ = ½(60)(152 – vi2) ✓ -1 250 + 5 027,696 = 6 750 – 30vi2 vi = 9,95(4) m.s-1✓ |
| OPTION 2 Wnet = ΔEK fΔxcosθ + Fg||Δxcosθ = ½mvf2 – ½mvi2 (50)(25cos180o ) ✓+ (60)(9,8sin20o)(25cos0o) ✓ = ½(60)(152 – vi2) ✓ -1 250 + 5 027,696 = 6 750 – 30vi2 vi = 9,95(4) m.s-1✓ |
| OPTION 3 Wnc = Δ EK + Δ EP fΔxcosθ = ½(mvf2 - mvi2) + (mghQ – mghP) EmechP + EmechQ + Wnc = 0 (50)(25cos180o) ✓= ½(60)(152 – vi2) ✓ + (60)(9,8)(-25sin 20o) ✓ -1 250 = 6 750 – 30 vi2 – 5 027,696 vi = 9,95 m.s-1✓ |
| OPTION 4 Fnet = 201,11 – 50 = 151,11 N Wnet = ΔEk ✓ FnetΔxcosθ = ½(mvf2 - mvi2) (151,11)(25)cos0o✓ = ½ (152 – vi2)✓ vi = 9,95 m∙s-1 ✓ |
(5)
5.4 POSITIVE MARKING FROM QUESTION 5.3
| OPTION 1 Pave = Fvave = 50✓(9.95 + 15) 2 = 623,75 W ✓ |
OPTION 2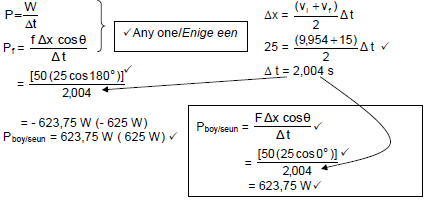 NOTE: Candidates can substitute -1 250 from QUESTION 5.3 directly into the equation |
(4)
[14]
QUESTION 6
6.1
6.1.1 It is the change in frequency (or pitch)✓ of the sound detected by a listener because the sound source and the listener have different velocities relative to the medium ✓of sound propagation.
OR
An apparent change in frequency (pitch), (wavelength) ✓as a result of the relative motion between a source and an observer ✓(listener). (2)
6.1.2 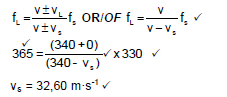 (5)
(5)
6.2 According to the Doppler Effect if the star moves away ✓from the observer a lower frequency/longer wavelength ✓is detected. This lower frequency/ longer wavelength corresponds to the red end of the spectrum✓ (3)
[10]
QUESTION 7
7.1 The magnitude of the electrostatic force exerted by one point charge (Q1) on another point charge (Q2) is directly proportional to the product of the (magnitudes of the) charges✓ and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (r) between them. ✓ (2)
7.2.1 Negative✓✓ (2)
7.2.2
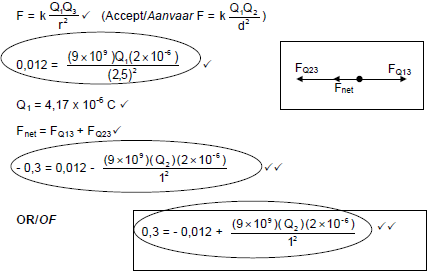
Q2 = 1,73 x10-5 C ✓
Do not penalise for the nature of the charges.
(7)
[11]
QUESTION 8
8.1 Electric field is a region of space in which an electric charge experiences a force. ✓✓ (2)
8.2
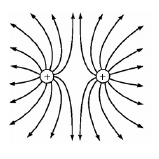
| Criteria for sketch | Marks |
| Correct shape as shown. | ✓ |
| Direction away from positive | ✓ |
| Field lines start on spheres and do not cross for correct diagram. | ✓ |
(3)
8.3 EPA = kQ
r2
= (9 x 109)(5 x 10-6)✓
(1.25)2
= 2,88 x 104 N∙C-1 to the right✓
EPB = = kQ
r2
= (9 x 109)(5 x 10-6)✓
(1.25)2
= 8,00 x 104 N∙C-1 to the left✓
Enet = EPA + EPB
= 2,88 x 104 + (-8,00 x 104)
= 5,12 x 104 N∙C-1 ✓ Vector addition
(5)
[10]
QUESTION 9
9.1.1 The potential difference across a conductor is directly proportional to the current in the conductor at constant temperature ✓✓
NOTE
If constant temperature is omitted -1 mark (2)
9.1.2
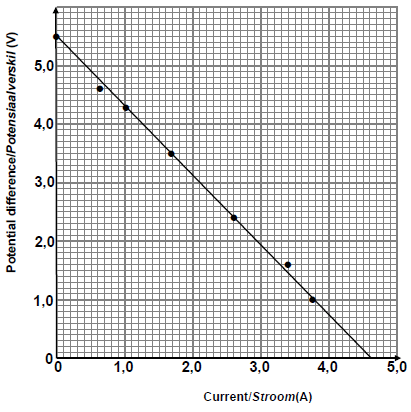
Straight line passing through 4 or five points✓
Straight line with intercepts on both axes✓. (2)
9.1.3 5,5 V (accept any value from 5,4 V to/tot 5,6 V based on graph drawn.)
NOTE :
The value must be the y-intercept.(1)
9.1.4
Slope = ΔV or y2 - y1 |
| NOTE: Any correct pair of coordinates chosen from the line drawn For the equation ε = I(R + r) or ε = Vext + Ir marks are awarded only if the correct I and V values are used from the graph |
(3)
9.2.1 R= V
I
I= V
R
V = IR
21,84 = Itot (8) ✓
Itot = 2,73 A✓
(3)
9.2.2
OPTION 1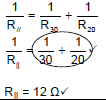 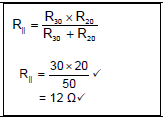 |
(2)
9.2.3 POSITIVE MARKING FROM QUESTION 9.2.1 AND 9.2.2
OPTION 1
Rtot = (8 + 12 + r) (for the addition)
= (20 + r)
ℇ = I(R + r) ✓
60 = (2,73)(20 + r) ✓
∴ r = 1,98 Ω✓
POSITIVE MARKING FROM QUESTION 9.2.1
OPTION 2
V|| = ItotR||
= (2,73)(12) ✓
= 32,76 V
∴Vterminal = (32,76 + 21,84) for addition
= 54,6 V
“Vlost” = 60 - 54,6 = 5,4 V
R= V
I
I= V
R
Any of these
V = IR
5,4 = 2,73 r
r = 1,98 Ω✓
ℇ = Vlost + V|| + V8
60 = (V”lost” + 32,76 + 21,84) ✓
V”lost” = 5,4 V
NOTE:
No penalisation for omitted subscripts (4)
9.2.4
| POSITIVE MARKING FROM 9.2 1 AND 9.2.2 (3) | ||
| OPTION 1 W = V2Δt R W = (54.6)2 (0.2) 20 = 29,81 J✓ | OPTION 2 W = I2RΔt✓ = (2,73)2 (20)(0,2) ✓ = 29,81 J✓ | OPTION 3 W = VIΔt✓ = (54,6)(2,73)(0,2) ✓ = 29,81 J ✓ |
(3)
[20]
QUESTION 10
10.1.1 R: armature/Coil(s)✓
T: (Carbon) brushes✓
X: Slip rings✓
NOTE:
Answers must be in that order if R, T and X are omitted. (3)
10.1.2 Faraday's Law ✓ (1)
10.2.1 15 V✓ (1)
10.2.2
| OPTION 1 Vrms = IrmsR Irms = 15 45 = 0,333 A Irms = Imax √2 Imax =(0,333)√2 = 0,47 A✓ |
| OPTION 2 Vrms = Vmax √2 Vmax = (15)√2 = 21,213V Vmax = Imax R Imax = 21.213 45 = 0,47 A✓ |
| OPTION 3 Imax= Irms√2 =√2 Vrms R =√2 Vrms R =√2 15 45 = 0,47 A ✓ |
OPTION 4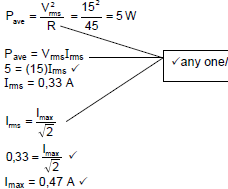 |
(4)
[9]
QUESTION 11
11.1 It is the process whereby electrons are ejected from a (metal) surface when light of suitable frequency is incident on that surface. ✓✓ (2)
11.2 INCREASE ✓
Increase in intensity means that (for the same frequency) the number of photons incident per unit time increase. ✓ Therefore the number of electrons ejected per unit time increases. ✓
Thus current increases.(3)
11.3
| OPTION 1 E = W0 + Ek(max) hf = hf0 + Ek(max) hf = hf0 + ½ mv2 E = W0 + ½ mv2 (6,63 x 10-34 x 5,9 x 1014) = (6.63 x 10-34)(3 x 108)+ 2,9 x 10-19 λ0 39.117 x 10-20 -2.9 x 1019) = 19.89 x 10-26 λ0 λo = 1,97 x 10-6 m✓ ✓Any one |
| OPTION 2 E = W0 + Ek(max) hf = hf0 + Ek(max) hf = hf0 + ½ mv2 E = W0 + ½ mv2 (6,63 x 10-34 x 5,9 x 1014) ✓ = (6,63 x 10-34)f0 + 2,9 x 10-19 fo = 1, 52 x 1014 Hz c = foλo 3 x 108 = (1,52 x 1014) λ0✓ λo = 1,97 x 10-6 m✓ |
| OPTION 3 E = W0 + Ek(max) hf = hf0 + Ek(max) hf = hf0 + ½ mv2 E = W0 + ½ mv2 (6,63 x 10-34 x 5,9 x 1014) ✓ =W0 + 2,9 x 10-19 Wo = 1,01 x 10-19 J Wo= hfo 1,01 x 10-19 = (6,63 x 10-34)fo fo= 1, 52 x 1014 Hz c = foλo 3 x 108 = (1,52 x 1014) λ0✓ λo = 1,97 x 10-6 m✓ |
(5)
11.4 From the photo-electric equation, for a constant work function, ✓ the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons is proportional to the energy of the photons.✓(2)
[12]