GEOGRAPHY GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS JUNE 2022
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupQUESTION 1: CLIMATE AND WEATHER
1.1
1.1.1 B (1)
1.1.2 C (1)
1.1.3 C (1)
1.1.4 A (1)
1.1.5 A (1)
(5 x 1)(5)
1.2
1.2.1 B (1)
1.2.2 A (1)
1.2.3 B (1)
1.2.4 A (1)
1.2.5 A (1)
(5 x 1) (5)
1.3
1.3.1 15 (1) (1 x 1) (1)
1.3.2 Driven by the tropical easterlies/trade winds in a westerly direction (2)
Curve in an easterly direction due to cooler conditions over the ocean (2)
(1 x 2) (2)
1.3.3 The zone January – March next to Southern Africa justifies the summer months in which Eloise developed (2)
‘Eloise made landfall in South Africa’ – extract (2)
Weather disruptions in Limpopo/Mpumalanga/KwaZulu-Natal (2)
[ANY ONE] (1 x 2) (2)
1.3.4 Friction with land surface decreased the wind speeds (2)
Decrease in moisture levels caused less severe rainfall (2)
[ANY ONE] (1 x 2) (2)
1.3.5 Causes the deflection and rotation of air around the disturbance (2)
Keeps pressure low / sustains the low-pressure (2) (2 x 2) (4)
1.3.6 High rainfall will damage bridges, road, and rail infrastructure (2)
Power stations in Mpumalanga will be affected and can cause power outages and load shedding (2)
Avalanches/mudslides might bury buildings along the escarpment in KZN (2)
Harbours/ports in KZN might be damaged due to flooding and negatively impact service delivery (2)
Jamming of sluices of major dams due to silting (2)
[ANY TWO] (2 x 2) (4)
1.4
1.4.1 1020 hPa/mb (1) (1 x 1) (1)
1.4.2 The migration of the ITCZ caused it to be more northerly (2)
In winter cells B and C, lie north and closer to land since they migrate with the apparent movement of the sun (2)
[ANY ONE] (1 x 2) (2)
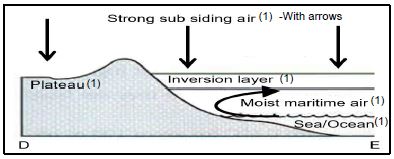
1.4.3
Mark allocation
1 mark for correct shape of cross profile
[ANY THREE LABELS] (1 + 3)
(4)
1.4.4 Berg wind conditions as air heat adiabatically down the escarpment causing evaporation at F/lowers humidity (2)
Coastal low causes clockwise circulation of air at F (2)
Off-shore flow of air due to clockwise circulation causes low moisture levels at F (2)
On-shore flow of air due to clockwise circulation occurs at G (2)
On-shore flow of air picks up moisture over the ocean and causes unstable and cloudy conditions at G (2)
[ANY FOUR] (4 x 2) (8)
[40]
QUESTION 2: GEOMORPHOLOGY
2.1
2.1.1 Y (1)
2.1.2 Y (1)
2.1.3 X (1)
2.1.4 Y (1)
2.1.5 X (1)
(5 x 1) (5)
2.2
2.2.1 River A (1)
2.2.2 headward (1)
2.2.3 watershed (1)
2.2.4 captured (1)
2.2.5 windgap (1)
(5 x 1) (5)
2.3
2.3.1 Dendritic (1) (1 x 1) (1)
2.3.2 Uniform in resistance (1)
Horizontally layered (1)
Sedimentary or igneous rocks (1)
[ANY TWO] (2 x 1)
(2)
2.3.3 2nd order (2) (1 x 2) (2)
2.3.4 Higher-order streams have more water in the river channel (2)
Lower-order streams have less water in the river channel (2)
[ANY ONE] (1 x 2)
(2)
2.3.5 Stream order
There will be more fingertip/1st order streams as run-off will
increase (2)
The total stream order will increase to possibly a 3rd order stream due to the increase in fingertip streams (2)
Water table
Stripping of vegetation will increase the run-off and decrease infiltration causing the water table to drop (2)
Cement/Tar constructions will decrease infiltration and lower the water table (2)
Less evapo-transpiration will decrease rainfall, with less infiltration, therefore causing the water table to drop (2)
[ANY FOUR] (4 x 2) (8)
2.4
2.4.1 Turbulent (1) (1 x 1) (1)
2.4.2 Upper course
Narrow (1) and shallow (1)
Middle course
Wider (1) and deeper (1)
[ANY TWO DIRECT DIFFERENCES] (2 x 1)
(2)
2.4.3
- Part of the river where there is a sharp change in the channel slope (2)
[CONCEPT] (1 x 2) (2) - The area is flat causing a balance between erosion and deposition (2) (1 x 2)
(2) - Increase in water volume causes headward erosion which removes knickpoints (temporary base level of erosion) (2)
(1 x 2) (2)
2.4.4 Saline conditions in the sea cause fine clay particles to flocculate (stick together) making particles larger and heavier which causes them to sink (2)
The gentle gradient causes the deposition of silt and clay near the river mouth (2)
Lack of sea currents decreases the removal of silt/clay increasing the building up of sediments around the river mouth (2)
The high/shallow seabed promotes the quick building up of sediments at the river mouth (2)
[ANY THREE] (3 x 2)
(6)
[40]
QUESTION 3: SETTLEMENTS
3.1
3.1.1 C (1)
3.1.2 B (1)
3.1.3 A (1)
3.1.4 B (1)
3.1.5 C (1)
(5 x 1) (5)
3.2
3.2.1 C (1)
3.2.2 C (1)
3.2.3 D (1)
3.2.4 B (1)
3.2.5 C (1)
(5 x 1) (5)
3.3
3.3.1 The ranking of urban settlements based on the number of functions found in the settlement (2)
[CONCEPT] (1 x 2) (2)
3.3.2 The land is above 300 m in height (1)
Steep areas (1)
Mountainous area (1)
[ANY ONE] (1 x 1) (1)
3.3.3 A (1) (1 x 1) (1)
3.3.4 A is linked to the main road, which increases its range (2)
Inhabitants of the Town prefer visiting/shopping at A rather than B, due to accessibility (2)
[ANY ONE] (1 x 2) (2)
3.3.5
- Regional shopping centre (1) (1 x 1) (1)
- Located outside the built-up areas, where land values are lower (2)
Ample space for future expansion (2)
Next to the highway for accessibility (2)
Roads link the shopping centre to all other settlements (2)
[ANY TWO] (2 x 2)
(4) - More people will pass through CITY A to reach the shopping centre (2)
People may relocate to CITY A to be nearer to the shopping centre (2)
The profits of the businesses of CITY A will increase due to the influx of people passing through (2)
[ANY TWO] (2 x 2)
(4)
3.4
3.4.1 Deterioration of parts of an urban area, especially where buildings are not maintained (2)
[CONCEPT] (1 x 2) (2)
3.4.2 Covid-19 (1) (1 x 1) (1)
3.4.3 Slum conditions (2)
Dilapidated building (2)
Illegal occupation of buildings (2)
Graffiti (2)
[ANY ONE] (1 x 2) (2)
3.4.4 Create job opportunities whilst upgrading and restoring (2)
More businesses will recover/re-open which increases job opportunities (2)
Better infrastructure and a healthier environment will attract investors and tourists (2)
[ANY ONE] (1 x 2)
(2)
3.4.5 Lack of continuity in the municipal leadership sphere (2)
Corrupt practices and a lack of attention/oversight by
municipalities (2)
Ineffective municipal by-laws (2)
Lack of legislation (no fines) for inhabitants and companies that dump refuse (2)
Inadequate municipal service delivery (2)
Shortage of skills, knowledge and expertise of administrators to deal with the issue of urban decay (2)
Street vendors/Informal businesses litter without any
repercussions (2)
Crime and social ills such as drug dealing makes the inner city unattractive and dangerous (2)
Poor monitoring and policing of the inner city (2)
[ANY FOUR] (4 x 2)
(8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: GEOGRAPHICAL SKILLS AND TECHNIQUES
4.1
4.1.1 D (ruin) (1) (1 x 1) (1)
4.1.2 C (1) (1 x 1) (1)
4.1.3 C (1) (1 x 1) (1)
4.1.4 TB = 22° (1) (Range – 21° – 23°)
MD = 19°24'W (1)
22° + 19°24'W
= 41°24' (1) (Range – 40°34' – 42°24') (3 x 1)
(3)
4.1.5
- 4,1 (1) cm x 100 = 410 m (1) (2 x 1) (2)
- 4/410 (substitution) (1)
1 : 102,5 (1) (2 x 1)(2)
4.2
4.2.1 C (1) (1 x 1) (1)
4.2.2 A (1) (1 x 1) (1)
4.2.3 A (1) (1 x 1) (1)
4.2.4
- Gorge (1) (1 x 1) (1)
- Steep slopes because the contour lines are near to one another (2) (1 x 2) (2)
- North westerly (1)
Reason:
Headward erosion is causing the waterfall to migrate
upstream (1) (1 + 1) (2)
4.2.5
- Nucleated (1) (1 x 1) (1)
- Cross road (1) (1 x 1) (1)
- Clustered near the water source (canals/furrows/river) (2)
Area is flat (2)
Nucleated around the crossing of the roads (2)
[ANY ONE] (1 x 2)
(2)
4.3
4.3.1 D (1) (1 x 1) (1)
4.3.2
- Data integration (1) (1 x 1) (1)
- Data of different themes/scales are being put together in one single theme (2) (1 x 2)
(2)
4.3.3 Vineyard and orchards (1) (1 x 1) (1)
4.3.4 Vector data (1) (1 x 1) (1)
4.3.5 Provide job opportunities (2)
Exporting of the raw materials (2)
Business potential from the sale of products (2)
[ANY ONE] (1 x 2) (2)
[30]
TOTAL: 150