TECHNICAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2021
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupQUESTION 1
1.1 D ✓✓ (2)
1.2 C ✓✓ (2)
1.3 B ✓✓ (2)
1.4 A ✓✓ (2)
1.5 B ✓✓ (2)
1.6 C ✓✓ (2)
1.7 D ✓✓ (2)
1.8 A ✓✓ (2)
1.9 C ✓✓ (2)
1.10 D ✓✓ (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2
2.1 An object will remain at rest or continue moving at a constant velocity (or at constant speed in a straight line) ✓ unless acted upon by a non-zero external resultant force. ✓(2)
2.2.1
| OPTION 1 | OPTION 2 |
| Fy = 60.Sin30°✓ = 30 N✓ | Fy = 60.Cos60°✓ = 30 N✓ |
(2)
2.2.2
| OPTION 1 | OPTION 2 |
| Apply positive marking from 2.2.1 fk= µk N✓ = 0,13 [(6x9,8) – 60.Sin30°] ✓ = 3,74 N (to the right) ✓/na regs NOTE: Credit if 60.Sin30° is expressed as 30 | Apply positive marking from 2.2.1 N = mg - Fy N = (6x9,8) – 60.Sin30° ✓ = 58,8 - 30 = 28,8 N fk= µk N ✓ = 0,13 x 28,8 = 3,74 N (to the right) ✓/na regs NOTE: Credit if 28,8N is expressed as 58,8 - 30 |
(4)
2.2.3
| OPTION 1 | OPTION 2 |
| Fx = 60.Cos30° ✓ = 51,96 N✓ | Fx = 60.Sin60°✓ = 51,96 N✓ |
(2)
Positive marking from 2.2.2 and 2.2.3
2.3 Fnet = ma
Fx + fk = ma
60Cos30° + (-3,74)✓ = 6.a ✓
a = 8,04 m.s-2 to the left ✓/na links (4)
2.4 Decrease✓
The vertical component (Fy) will increase and thus the normal force will decrease. ✓✓
OR
The force will tend to lift the object from the surface and thus decrease the friction. (3)
2.5.1 When object A exerts a force on object B, object B simultaneously exerts an oppositely directed force of equal magnitude on object A. ✓✓
NOTE:Credit one mark if any of the key words is ommitted (1/2) (2)
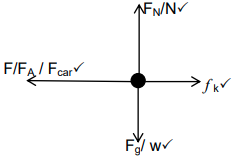
2.5.2
| ACCEPTABLE LABELS | NOTES: |
| N/FN: Normal/Normaal Fg/w: Force due to gravity/Weight/ F/FA/Fcar: Applied force/ f k/Ff/ f: frictional force/ | One mark for each force represented by an arrow with a correct label. Penalise (once) for each of the following volgende:
|
(4)
[23]
QUESTION 3
3.1.1 Product of the mass of an object and its velocity. ✓✓(2)
3.1.2 pL= mv✓
= 5800 x 1,5✓
= 8700 kg.m.s-1 west✓ (3)
3.1.3 Apply positive marking from 3.1.2
∑ p before = ∑ p after
mLvL + mWvW = mC vC
mLvL + mWvW = (mL +mw) vC
5800 x 1,5 + 2500 x 0 ✓ = 8300 x vC✓
∴ vC = 1,05 m.s-1✓ west✓/ (5)
3.1.4 During elastic collision, the total kinetic energy is conserved and the total linear momentum is conserved ✓✓and during inelastic collision, total kinetic energy is not conserved and the total linear momentum is conserved. ✓✓
Accept/Aanvaar : ∑ pbefore/voor = ∑ pafter/na and ∑ Ekbefore/voor = ∑ Ekafter/na
∑ pbefore/voor = ∑ pafter/na and ∑ Ekbefore/voor ∑ Ekafter/na
NOTE: Do not penalise if total linear momentum is ommitted
: Penalise one mark if the word ‘total’ is ommitted for elastic and inelastic collision (4)
3.2.1
- If the vehicle collides or come to a standstill, the driver and passengers would contiue moving at the initial velocity. ✓
- Safety belts will then prevent them from moving forward✓ and hurting themselves and others or even going through the windscreen.(2)
3.2.2
| OPTION | OPTION |
| Let the direction towards the wall be positive Fnet∆t = Impulse Impulse = ∆p Impulse = 0 – 24300 ✓ Impulse = - 24300 Impulse = 24300 kg.ms-1✓(away from the wall) | Let the direction towards the wall be negative Fnet∆t = Impulse Impulse = ∆p Impulse = 0 – (- 24300) ✓ Impulse = 24300 kg.ms-1 ✓ (away from the wall) |
(3)
Positive marking from 3.2.2
3.2.3
Fnet∆t = Impulse✓
Fnet x 1,2 = 24300✓
Fnet = 20 250 N
Force exerted by impulse/Krag deur impuls uitgeoefen = 20 250 N✓
The wall can withstand 80 000 N, so it will withstand the impact of the test. ✓/
NOTE: If Fnet is more than 80 000N then it will NOT withstand the impact of the test (resulting from positive marking). (4)
[23]
QUESTION 4
4.1.1 The product of the force applied on an object and the displacement in the direction of the force. ✓✓ (2)
4.1.2
W = FA ∆ x cosθ✓
W = 60 x 8 x cos 25°✓
W = 435,03 J✓ (3)
4.2.1 The total mechanical energy ✓of an isolated system is constant. ✓
OR
The sum of the gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy✓ in an isolated system remains constant. ✓(2)
4.2.2
Ep = mgh ✓
Ep = 75 x 9.8 x 12✓
Ep = 8 820 J ✓
(Accept : 8,820 kJ/8,82 x 103J) (3)
4.2.3
EK = ½ mv2
= 0.5 x 75 x 32 ✓
= 337,5 J✓ (3)
Positive marking from 4.2.3
4.3
MEtop = Ektop + Eptop ✓
11500 = 337,5 + Eptop ✓
Eptop = 11 162,5 J
Epbefore = Eptop − Epground
= 11 162,5 – 8820✓
= 2342,5 J✓ (4)
[17]
QUESTION 5
5.1.1
5.1.2
| OPTION 1 | OPTION 2 |
| ε = Δℓ L ε = 0.5 3 x 103 ε = 1,666 x 10-4 ✓ NOTE: Penalise if the unit is given. | ε = Δℓ L ε = 5 x 10-4 3 ε = 1,666 x 10-4 ✓ NOTE: Penalise if the unit is given. |
(3)
Positive marking from 5.1.1 and 5.1.2.
5.1.3
K = σ/ε
K = 3.26 x 106
1,666 x-4
K = 1,956 x 1010 Pa✓ (3)
5.2.1 Pressure at a particular point is the thrust acting on the unit area around that point. ✓✓
NOTE: Do not penalise if force is used instead of thrust (2)
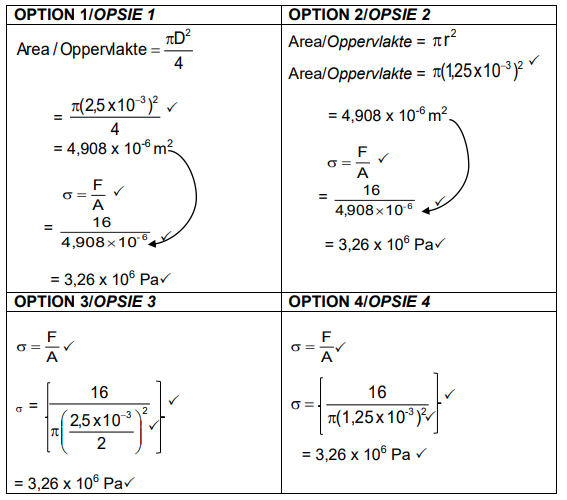
5.2.2
P=F/A
P = 26
7,855 x 10-5
P= 3,3099 x 105 Pa ✓ (3)
5.2.3
| OPTION 1 | OPTION 2 |
| F1/ A1 = F2/A2 26 = 1278 7855 x 10-5 A2 A2 = 3,861 x 10-3 m2 | A2 = 3,861 x 10-3 m P = F2/A2 33099 x 105 = 1278/A2 A2 = 3861 x 10-3m2 |
QUESTION 6
6.1 The bending of light when it passes from one medium to another (of different optical densities).✓✓ (2)
6.2 Critical angle✓/Kritieke hoek/Grenshoek (1)
6.3 90º✓ (1)
6.4 Medium 1✓/
Light ray QS bends away from the normal.✓(2)
6.5 QR✓ (1)
6.6 The light must travel from a more optically dense to a less optically dense medium.✓
The incident angle should be greater than the critical angle. ✓ (2)
[9]
QUESTION 7
7.1.1 The phenomenon whereby white light break up (spread out) into its component colours.✓✓ (2)
7.1.2
3. yellow✓/geel
6. Indigo✓ (2)
7.1.3 Refraction ✓/Refraksie/Breking (1)
7.1.4 When the wavelength increases the speed of the waves will also increase. ✓✓
Accept: Wavelength is directly proportional to the speed of the wave. (2)
7.2.1 A succession/repetition of pulses✓✓/
OR
A disturbance that transfers energy through matter or space./' (2)
7.2.2
- can propogate in a vacuum✓/kan in 'n vakuum voortplant
- move at the speed of light (3 x 108 m.s -1 ) ✓
(3 x 108 m.s -1 ) - transfer energy
- have a dual nature (particle and wave) nature
- can be polarized (any two) (2)
7.2.3
| Radio-wave | Micro-wave | Infrared | Visible light | Ultraviolet | X-rays | Gamma rays |
NOTE: 2 or zero(2)
[13]
QUESTION 8
8.1 Capacitance is the amount of charge a capacitor can store✓ per volt. ✓ (2)
8.2.1
C = εoA
d
(8,85 x 10‾ ¹²)(2)
6 x 10-3
= 2,95 x 10-9
F ✓ (3)
Positive marking from 8.2.1/Positiewe nasien vanaf 8.2.1.
8.2.2
C =Q/V
2,95 10-9 = Q/120
Q = 3,54 x 10-7 C ✓
(3)
[8]
QUESTION 9
9.1 It is the rate at which electrical energy is converted in an electric circuit. ✓✓ (2)
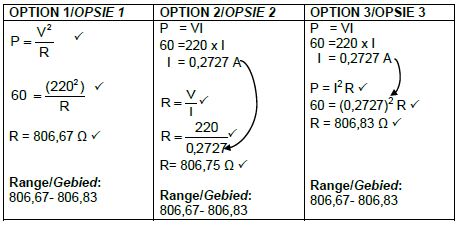
9.2
(3)
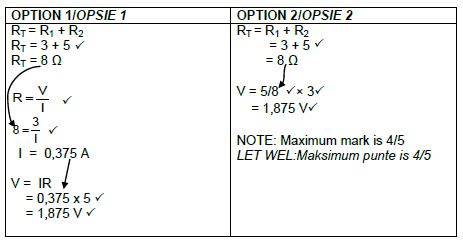
9.3
(5)
[10]
QUESTION 10
10.1.1 Electromagnetic induction✓(1)
10.1.2 When the speed at which the magnet is moved in and out of the coil is increased the rate of change in the magnetic flux increases/ The rate of
change of magnetic flux is directly proportional to the induced emf.✓
The induced emf/ the extent of deflection of the needle increase with the increase in change of the magnetic flux. ✓ 2)
10.1.3 Alternating current✓ (1)
10.2.1
- The primary voltage is higher (220 V) than the secondary voltage (24 V) ✓
- More windings on primary than on secondary coil✓
OR - The secondary voltage is lower (24 V) than the primary voltage (220 V)
- The windings on the secondary coil are fewer than that of the primary coil.
(2)
10.2.2
| OPTION 1 | OPTION 2 |
| Vs/Vp = Ns/ Np 24/220= 480/Np Np = 4400 windings✓ | Ratio: Vs : Vp 24 : 220✓ ∴Ns : Np 480 : 4400 windings✓ NOTE: Maximum mark is 2/3 (for OPTION 2) |
(3)
[9]
TOTAL/TOTAAL: 150