TECHNICAL SCIENCES PAPER 1 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2021
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupTECHNICAL SCIENCES P1
NOVEMBER 2021
NATIONAL
SENIOR CERTIFICATE
GRADE 12
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of TEN questions. Answer ALL the questions in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page in the ANSWER BOOK.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Leave ONE line between two subquestions, e.g. between QUESTION 2.1 and QUESTION 2.2.
- You may use a non-programmable calculator.
- You may use appropriate mathematical instruments.
- You are advised to use the attached DATA SHEETS.
- Show ALL formulae and substitutions in ALL calculations.
- Round off your FINAL numerical answers to a minimum of TWO decimal places.
- Give brief motivations, discussions, etc. where required.
- Write neatly and legibly.
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1 to 1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.11 D.
1.1 An object's direction of motion is always the same as …
- the applied force acting on the object.
- a non-zero force acting on the object.
- the equilibrant of the forces.
- the resultant force acting on the object. (2)
1.2 The law of conservation of momentum implies that … after the collision.
- the kinetic energy before the collision is equal to the kinetic energy
- in an isolated system the kinetic energy before collision is equal to the kinetic energy
- in an isolated system the total linear momentum before the collision is equal to the total linear momentum
- both objects will be at rest (2)
1.3 Which ONE of the following statements is NOT correct?
- The work done on an object depends on the displacement of the object.
- The work done on an object depends on the nature of the substance.
- The work done on an object depends on the applied force.
- The work done on an object depends on the angle between the displacement and the applied force.
(2)
1.4 The property of the body by virtue of which the body regains its original shape and size when the deforming force is removed is known as ...
- elasticity.
- stress.
- deforming force.
- restoring force. (2)
1.5 The property of a liquid to oppose relative motion between its adjacent layers is called …
- surface tension.
- viscosity.
- coefficient of viscosity.
- internal load. (2)
1.6 The unit for pressure can be expressed as …
- kg.m2s-1
- kg.m2s-2
- kg.m-1s-2
- kg.m-2s2 (2)
1.7 Parallel rays of light strike a convex lens. Which ONE of the diagrams below shows what happens to the rays when they strike the lens?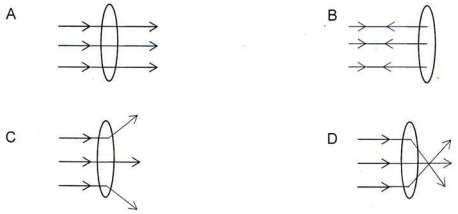
1.8 Which ONE of the diagrams below represents the magnetic field around a current-carrying conductor where the current flows OUT OF THE PAGE of the book?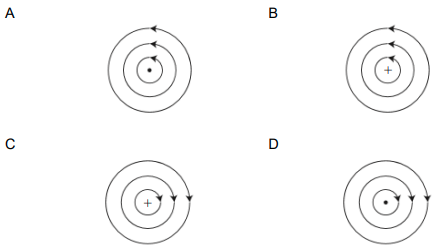
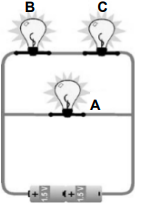
1.9 Three identical bulbs are connected in as in the circuit below. Which ONE of the following statements is TRUE about the circuit drawn below?
- Bulb A has the same brightness as bulbs B and C.
- Bulb A is dimmer than bulb B and bulb C.
- Bulb B has the same brightness as bulb C.
- Bulb C is brighter than bulb B. (2)
1.10 An electrical machine that uses a commutator (split-ring) and converts mechanical energy to electrical energy is called a/an …
- AC generator.
- AC motor.
- DC motor.
- DC generator. (2)
[20]
QUESTION 2 (Start on a new page.)
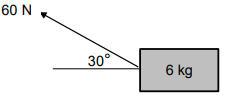
A 6 kg object is pulled with a force of 60 N at an angle of 30° across a rough surface, as shown in the diagram below.
2.1 State Newton's First Law of Motion in words. (2)
2.2 Calculate the magnitude of the:
2.2.1 Vertical component of the 60 N force (2)
2.2.2 Frictional force experienced by the object if the coefficient of kinetic friction (µk) between the surface and the object is 0,13 (4)
2.2.3 Horizontal component of the 60 N force (2)
2.3 Calculate the acceleration of the object. (4)
2.4 How will an increase in the angle between the applied force and the horizontal influence the friction?
Write only, INCREASE, DECREASE or STAYS THE SAME. Motivate your answer. (3)
2.5 A car is pulling a caravan on a rough horizontal surface as indicated in the diagram. (The system is NOT moving at constant velocity.)
2.5.1 State Newton's Third Law in words. (2)
2.5.2 Draw a labelled free-body diagram of ALL the forces acting on the caravan. (4)
[23]
QUESTION 3 (Start on a new page.)
3.1 On a railway shunting line a locomotive is coupling with a stationary carriage of a mass of 2 500 kg. The locomotive has a mass of 5 800 kg and it is moving due west at a velocity of 1,5 m·s-1. After coupling the locomotive-carriage combination moves due west.
3.1.1 Define the term momentum. (2)
3.1.2 Calculate the momentum of the locomotive before the collision. (3)
3.1.3 Calculate the velocity of the locomotive-carriage combination after the collision. (5)
3.1.4 Differentiate between elastic and inelastic collisions. (4)
3.2 The effective use of seat belts was demonstrated during a crash test at a motor manufacturing plant. The car hit the wall with a momentum of 24 300 kg.m.s-1 and took 1,2 s to come to rest.
3.2.1 Use physics principles to explain how seatbelts can save lives during a collision. (2)
3.2.2 Calculate the impulse experienced by the car. (3)
3.2.3 The wall was built to withstand a force of 80 kN. Determine, by means of a calculation, if this wall will be able to withstand the impact
of this test. (4)
QUESTION 4 (Start on a new page.)
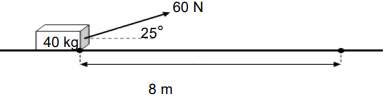
4.1 A toolbox of mass 40 kg is pulled with an applied force of 60 N over a distance of 8 m. The applied force makes an angle of 25° with the horizontal.
4.1.1 Define work done. (2)
4.1.2 Calculate the work done by the applied force over the 8 m. (3)
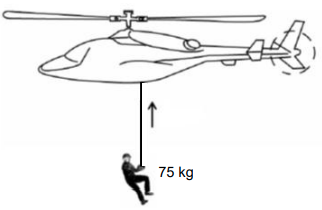
4.2 A construction worker of mass 75 kg is airlifted vertically upwards from a construction site, as shown in the diagram below. The worker is lifted, from the first floor of a building by a cable to a height of 12 m at a constant speed of 3 m·s-1
. (Ignore air friction and assume that there is NO sideways motion.)
4.2.1 State the principle of conservation of mechanical energy in words. (2)
4.2.2 Calculate the potential energy gained by the construction worker 12 metres above the first floor. (3)
4.2.3 Calculate his kinetic energy as he was lifted for 12 m. (3)
4.3 The total mechanical energy of the construction worker at the highest point is 11 500 J. Determine the potential energy of the construction worker just before he was airlifted by the helicopter. (4)
[17]
QUESTION 5 (Start on a new page.)
5.1 A force of 16 N is applied to a 3 m long metal wire. The wire stretches by 0,5 mm. The diameter of the metal wire is 2,5 mm.
Calculate the:
5.1.1 Stress in the wire (4)
5.1.2 Strain in the wire (3)
5.1.3 Young's modulus of the wire (3)
5.2 A hydraulic jack is used to lift a car weighing 1 278 N. The force applied to the input piston is 26 N. The area of the input piston is 7,855 x 10-5 m2
5.2.1 Define pressure at a particular point. (2)
5.2.2 Calculate the fluid pressure in the hydraulic system. (3)
5.2.3 Calculate the area of the output piston. (3)
[18]
QUESTION 6 (Start on a new page.)
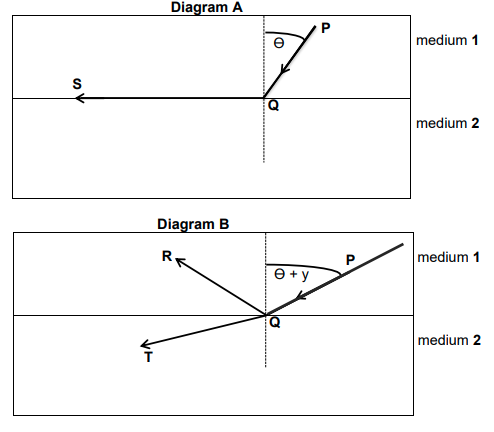
A light ray PQ is moving from medium 1 to medium 2 in diagrams A and B. Light rays QS, QR and QT are observed as the angle of incidence varies. Mediums 1 and 2 have different optical densities.
6.1 Define refraction. (2)
6.2 What is the name given to the angle of incidence (Ө) if light ray PQ follows the path of QS in diagram A? (1)
6.3 What is the magnitude (in degrees) of the angle of refraction for the angle of incidence in QUESTION 6.2? (1)
6.4 Which ONE of the two media is optically denser in diagram A? Write onlyn MEDIUM 1 or MEDIUM 2. Give a reason for your answer. (2)
6.5 Identify the light ray that undergoes total internal reflection in diagram B. (1)
6.6 State TWO conditions for total internal reflection to occur. (2)
[9]
QUESTION 7 (Start on a new page.)
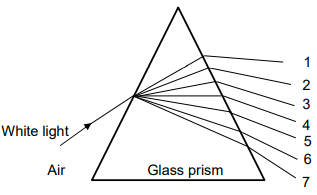
7.1 Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
7.1.1 Define the term dispersion of light. (2)
7.1.2 Identify the colours represented by numbers 3 and 6. Write down the correct colour next to the numbers in your ANSWER BOOK. (2)
7.1.3 Which wave property of light is responsible for the dispersion? (1)
7.1.4 State the relationship between the wavelength and the speed of a light wave. (2)
7.2
| Ultra-violet | Micro-waves | gamma rays | Visible light | Radio | X-rays | Infrared |
The table above represents the electromagnetic spectrum.
7.2.1 Define a wave. (2)
7.2.2 Name TWO characteristics of electromagnetic waves. (2)
7.2.3 Arrange the waves in the diagram above from the lowest to the
highest frequency. (2)
[13]
QUESTION 8 (Start on a new page.)
A potential difference of 120 V is applied across two parallel plates of a capacitor. The plates are 6 mm apart and have a 2 m2 area.
8.1 Define the term capacitance. (2)
8.2 Calculate the:
8.2.1 Capacitance of the capacitor (3)
8.2.2 Charge on each plate (3)
[8]
QUESTION 9 (Start on a new page.)
9.1 Define power in an electric circuit. (2)
9.2 A heater with a single element is marked 60 W, 220 V. Calculate the resistance of the heater element. (3)
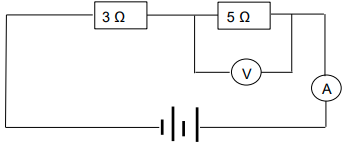
9.3 The diagram below shows a circuit that consists of two cells connected in series. Each cell has a potential difference of 1,5 V. Two resistors with a resistance of 3 Ω and 5 Ω are also connected in series.
Calculate the potential difference across the 5 Ω resistor. (5)
[10]
QUESTION 10 (Start on a new page.)
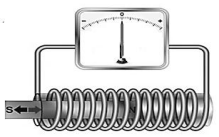
10.1 Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
10.1.1 What phenomenon is illustrated in the diagram above? (1)
10.1.2 If the speed at which the magnet is moved in and out of the coil is increased, a greater deflection of the needle is observed. Explain
this observation, in terms of rate of change in magnetic flux and induced emf. (2)
10.1.3 What type of current is induced in the above diagram? Write only ALTERNATING CURRENT or DIRECT CURRENT. (1)
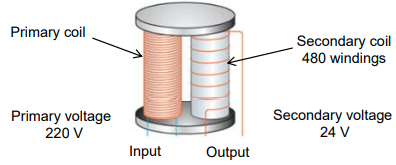
10.2 A step-down transformer is used to operate a 24 V radio player. The transformer has 480 windings in its secondary coil and the primary voltage is 220 V.
10.2.1 Give TWO reasons why this is a step-down transformer. (2)
10.2.2 Calculate the number of windings in the primary coil of the transformer. (3)
[9]
TOTAL: 150
DATA FOR TECHNICAL SCIENCES GRADE 12 PAPER 1
GEGEWENS VIR TEGNIESE WETENSKAPPE GRAAD 12 VRAESTEL 1
TABLE 1: PHYSICAL CONSTANTS/TABEL 1: FISIESE KONSTANTES
| NAME/NAAM | SYMBOL/SIMBOOL | VALUE/WAARDE |
| Acceleration due to gravity Swaartekragversnelling | g | 9,8 m·s-2 |
| Speed of light in a vacuum Spoed van lig in 'n vakuum | c | 3,0 x 108 m·s-1 |
| Planck's constant Planck se konstante | h | 6,63 x 10-34 J·s |
| Electron mass Elektronmass | me | 9,11 x 10-31 kg |
| Permittivity of free space Permittiwiteit van vry ruimte | ԑo | 8,85x10-12 F.m-1 |
TABLE 2: FORMULAE/TABEL 2: FORMULES
FORCE/KRAG
| Fnet = ma | p= mv |
| | fk = μkN |
| fnetΔt = Δp Δp = mvf - mvi | Fg = mg |
WORK, ENERGY AND POWER/ARBEID, ENERGIE EN DRYWING
| W = FΔx cosθ | U= mgh or/of EP = mgh |
| K=½mv2 or/of Ek = ½mv2 | Wnet = ΔK or/of Wnet = ΔEk ΔK = Kf − Ki or/of ΔEk = Ekf − Eki |
| Wnc = ΔK + ΔU or/of Wnc = ΔEk + ΔEp | P = W Δt |
| Pave = Fvvave / Pgemid = Fvgemid | ME = Ek + Ep |
ELASTICITY, VISCOSITY AND HYDRAULICS/ELASTISITEIT, VISKOSITEIT EN
HIDROULIKA
| σ = F A | ε = Δl L |
| σ = K ε | F1 = F2 A1 A2 |
| P = F A | P = pgh |
ELECTROSTATICS/ELEKTROSTATIKA
| C = Q V | C = εοA d |
CURRENT ELECTRICITY/STROOMELEKTRISITEIT
| R = V I | emf/emk (ε) I(R + r) |
| Rs = R1 + R2 + ... 1 = 1 + 1 + ... Rp R1 R2 | q = IΔt |
| W = VQ W = VIΔt W = I2RΔt W = V₂Δt R | P = W Δt P = VI P = I2R P = V2 R |
ELECTROMAGNETISM/ELEKTROMAGNETISME
| Φ = BA | ε = − N ΔΦ Δt |
| Vₛ = Nₛ Vp Np |
WAVES, SOUND AND LIGHT
| v = fλ | T = 1 f |
| E = hf or E = h c λ |