MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY(WELDING & METALWORK) GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2021
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupINSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Write your centre number and examination number in the spaces provided on the ANSWER BOOK.
- Read ALL the questions carefully.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Show ALL calculations and units. Round off final answers to TWO decimal places.
- Candidates may use non-programmable scientific calculators and drawing instruments.
- The value of gravitational acceleration should be taken as 10 m/s2.
- All dimensions are in millimetres, unless stated otherwise in the question.
- Write neatly and legibly.
- A formula sheet is attached at the end of the question paper.
- Use the criteria below to assist you in managing your time.
| QUESTION | CONTENT | MARKS | TIME IN MINUTES |
| GENERIC | |||
| 1 | Multiple-choice questions | 6 | 6 |
| 2 | Safety | 10 | 10 |
| 3 | Materials | 14 | 14 |
| SPECIFIC | |||
| 4 | Multiple-choice questions | 14 | 10 |
| 5 | Terminology (Templates) | 23 | 20 |
| 6 | Tools and Equipment | 18 | 15 |
| 7 | Forces | 45 | 40 |
| 8 | Joining Methods (Inspection of Welds) | 23 | 20 |
| 9 | Joining Methods (Stresses and Distortion) | 18 | 20 |
| 10 | Maintenance | 8 | 10 |
| 11 | Terminology (Development) | 21 | 15 |
| TOTAL | 200 | 180 | |
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (GENERIC)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1 to 1.6) in your ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.7 E.
1.1 What is the code of good practice for HIV/Aids and employment?
- Persons with HIV/Aids must use separate dining halls.
- The Act contains common guidelines on how employers and employees should respond to HIV/Aids in the workplace.
- The Act contains guidelines on how much work an employee is supposed to do.
- It contains the daily working hours of employees. (1)
1.2 Which ONE of the following types of personal protective equipment (PPE) is required when working in a workshop with Covid-19 regulations?
- Mask
- Sunglasses
- Welding helmet
- Clear goggles (1)
1.3 The … is responsible for the provision of safety gear in the workshop.
- employees
- cleaning staff
- foreman
- employer (1)
1.4 Which ONE of the following describes the reaction of mild steel when it is cut on a machine?
- Cuts easily; black crumbly chips
- Hard to cut; cuttings break in sharp chips
- Cuts easily; curly chips
- Hard to cut (1)
1.5 The purpose of hardening steel is to …
- resist wear.
- relieve strain.
- increase softness.
- quench the material. (1)
1.6 Which process follows on from hardening?
- Normalising
- Annealing
- Tempering
- Case hardening (1)
[6]
QUESTION 2: SAFETY (GENERIC)
2.1 Explain TWO first-aid measures to consider when treating an open wound. (2)
2.2 State TWO safety precautions that must be adhered to after the surface grinder has been switched on. (2)
2.3 Give ONE reason why the pressure gauge of a hydraulic press must be calibrated frequently. (1)
2.4 Which TWO hazards are prevented by the finger protectors fitted to power-driven guillotines? (2)
2.5 State TWO safety measures to be considered before gas welding or flame cutting operations can be performed. (2)
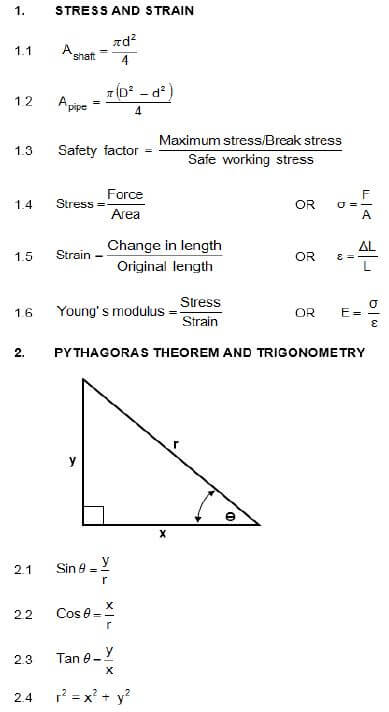
2.6 Which type of workshop layout is shown in FIGURE 2.6 below?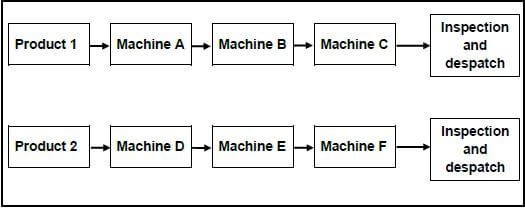
FIGURE 2.6 (1)
[10]
QUESTION 3: MATERIALS (GENERIC)
3.1 Describe the filing process as easy or difficult when conducting a file test for hardness on the following materials:
3.1.1 Cast steel (1)
3.1.2 Mild steel (1)
3.1.3 High-speed steel (1)
3.2 FIGURE 3.2 shows the annealing process during heat treatment. Label components A–C.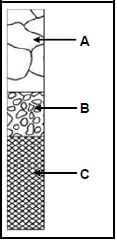
FIGURE 3.2 (3)
3.3 Describe how a bending test is conducted to determine the properties in a test metal. (3)
3.4 State the purpose of case hardening on steel. (2)
3.5 Name THREE types of quenching media that could be used to harden steel. (3)
[14]
QUESTION 4: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (SPECIFIC)
Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (4.1 to 4.14) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 4.15 E.
4.1 FIGURE 4.1 below shows a section of a roof truss. Identify part X.
FIGURE 4.1
- Top flange
- Purlin
- Ridging
- Internal bracing (1)
4.2 Which ONE of the following taps is used to cut a full thread in a blind hole?
- Taper tap
- Plug tap
- Intermediate tap
- Starting tap (1)
4.3 The type of deformation when a joint recovers after stress has been relieved is known as … deformation.
- longitudinal
- transverse
- shrinkage
- elastic (1)
4.4 What is the value of angle β as indicated in FIGURE 4.4 below?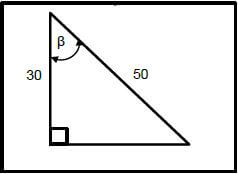
FIGURE 4.4
- 58,13º
- 62,56º
- 53,13º
- 38,87º (1)
4.5 The function of a tie in frameworks is to hold …
- tools together.
- pieces together when welding.
- roof covering together.
- parts of a structure together. (1)
4.6 Which ONE of the following components is part of a bench grinder?
- Tool rest
- Foot rest
- Interlock
- Grinding wheel dresser (1)
4.7 The web template is used for marking out holes on …
- channel irons and I-beams.
- pipes.
- longer sections of an angle iron.
- sheet metal. (1)
4.8 The off-set pinch roll is used for rolling …
- square bars.
- thin sheet metal.
- round bars.
- angle iron. (1)
4.9 The term strain in materials is the ratio between the …
- shearing load and stress.
- pushing load and original length.
- change in length and the original length.
- change in length and the compressive load. (1)
4.10 Which ONE of the following steps may be taken to prevent a transverse crack from forming?
- Quick cooling after welding
- Pre-heating the base metal
- Use a high welding current
- Prepare the root gap correctly (1)
4.11 Which ONE of the following tests is a non-destructive test?
- Nick-break test
- Guided bend test
- X-ray test
- Machinability test (1)
4.12 Which ONE of the following factors prevents slag inclusion during the welding process?
- Weld metal thickness
- Proper joint cleaning
- Type of welding machine
- Electrode thickness (1)
4.13 What is the cause of angular distortion during the welding process?
- Weld face thicker than the weld root resulting in more cooling of the face
- Cooled in water
- Round-step welding resulting in no cooling
- Incorrect electrode type (1)
4.14 The purpose of keeping service records of power machines is to monitor the … in the workshop.
- operations of machines
- lock-out clause of machines
- isolation switches
- condition of machines (1)
[14]
QUESTION 5: TERMINOLGY (TEMPLATES) (SPECIFIC)
5.1 A steel ring must be manufactured using a 60 x 60 mm square steel bar. The ring has an outside diameter of 960 mm.
5.1.1 Calculate the mean diameter of the ring. (2)
5.1.2 Calculate the mean circumference of the ring (round off answer to the nearest whole number). (3)
5.2 Draw the weld symbols for the following types of resistance welds:
5.2.1 Spot weld (2)
5.2.2 Projection weld (2)
5.2.3 Seam weld (2)
5.2.4 Foil seam weld (2)
5.2.5 Flash or resistance weld (2)
5.3 Identify the templates shown in FIGURES 5.3.1–5.3.3 below.
5.3.1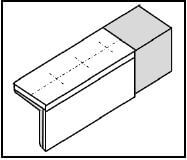
FIGURE 5.3.1 (1)
5.3.2 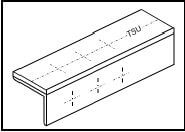
FIGURE 5.3.2 (1)
5.3.3 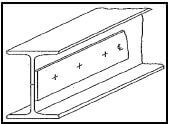
FIGURE 5.3.3 (1)
5.4 Name THREE hand tools that a template maker uses. (3)
5.5 Name TWO machines used in the template loft. (2)
[23]
QUESTION 6: TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT (SPECIFIC)
6.1 Explain the operating principles of a resistance welding machine. (5)
6.2 FIGURE 6.2 below shows arc welding equipment. Answer the questions that follow.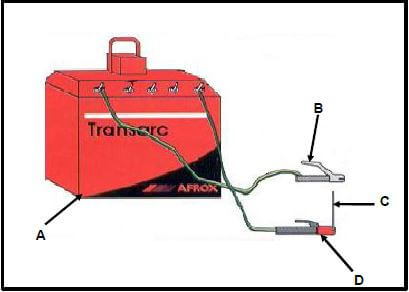
FIGURE 6.2
6.2.1 Label components A–D. (4)
6.2.2 What is the function of component D? (1)
6.3 Describe the process of cutting an external thread on a round shaft using circular split dies. (6)
6.4 State ONE advantage of using a punch machine over a pedestal drill. (1)
6.5 What are pyramid rollers used for? (1)
[18]
QUESTION 7: FORCES (SPECIFIC)
7.1 FIGURE 7.1 below shows a beam, supported at both ends by RL and RR. Three vertical point loads are exerted onto the beam. Answer the questions that follow.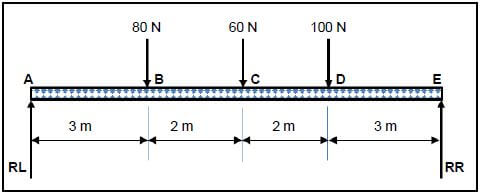
FIGURE 7.1
7.1.1 Calculate the reactions at RL and RR. (8)
7.1.2 Calculate the bending moments at points B, C and D. (3)
7.1.3 Construct the bending moment diagram for points B, C and D by using scale 1 m = 1 cm and 10 Nm = 1 cm. (7)
7.2 A load of 40 kN causes a tensile stress of 20 MPa in a round brass bar. The original length of the bar is 2 m and Young's module for brass is 90 GPa.
Calculate:
7.2.1 The diameter of the bar (6)
7.2.2 The strain (2)
7.2.3 The change in length in mm (3)
7.3 FIGURE 7.3 below shows a stress-and-strain diagram. Label parts A–E.
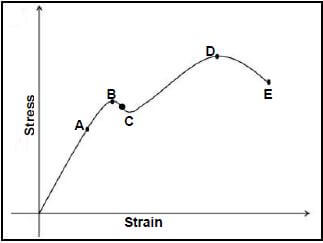
FIGURE 7.3 (5)
7.4 FIGURE 7.4 below shows a steel framework. Answer the questions that follow.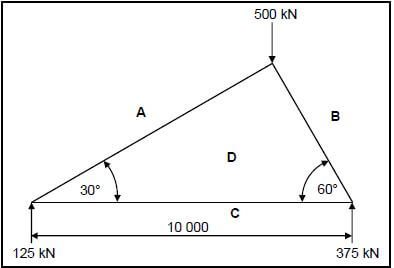
FIGURE 7.4
7.4.1 Construct the vector/force diagram using scale 1 mm = 1 kN. (5)
7.4.2 Determine graphically the magnitude and nature of the force in AD, BD and CD in the steel frame structure by using the space diagram in FIGURE 7.4. (6)
[45]
QUESTION 8: JOINING METHODS (WELD INSPECTION) (SPECIFIC)
8.1 State THREE welding aspects that must be focused on during the arc welding procedure. (3)
8.2 How can centre-line cracks in welding joints be reduced? (2)
8.3 State TWO causes of EACH of the following arc-welding defects:
8.3.1 Lack of fusion (2)
8.3.2 Porosity (2)
8.3.3 Incomplete penetration (2)
8.4 Describe the process of setting an oxy-acetylene torch flame to a neutral flame. (3)
8.5 Explain how to conduct a guided bend test on a welded joint. (3)
8.6 State TWO aspects that are tested when conducting a free-bend test on a welded joint. (2)
8.7 Name TWO different types of dye used to conduct a liquid dye penetration test. (2)
8.8 Explain why a nick-break test is conducted on a welded joint. (2)
[23]
QUESTION 9: JOINING METHODS (STRESSES AND DISTORTION) (SPECIFIC)
9.1 State TWO factors responsible for causing residual stress in welds. (2)
9.2 State THREE factors that affect the cooling rate in a welded joint. (3)
9.3 Describe FOUR effects of cold working on steel. (4)
9.4 State THREE effects of welding speed on distortion. (3)
9.5 State THREE quenching media used in the heat treatment of steel. (3)
9.6 State THREE methods used to reduce distortion. (3)
[18]
QUESTION 10: MAINTENANCE (SPECIFIC)
10.1 State TWO factors to be considered when conducting lockout and tagging of machines when maintenance is conducted. (2)
10.2 Why do tagging plates have multiple holes? (1)
10.3 Give the reason for conducting a minor service of a power-driven guillotine. (2)
10.4 Give TWO reasons for using cutting fluid on a power saw. (2)
10.5 State ONE effect of overloading on a rolling machine. (1)
[8]
QUESTION 11: TERMINOLOGY (DEVELOPMENT) (SPECIFIC)
11.1 Study FIGURE 11.1 below and calculate the true length of AC. Round off answer to the nearest whole number.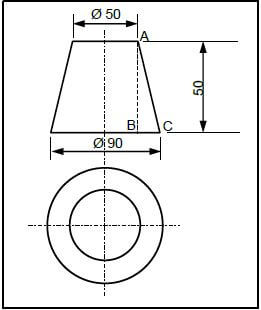
FIGURE 11.1 (6)
11.2 Identify the development shown in FIGURE 11.2 below.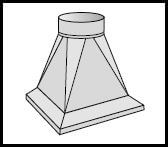
FIGURE 11.2 (3)
11.3 FIGURE 11.3 below shows a square-to-rectangle on-centre hopper with a vertical height (VH) of 500 mm.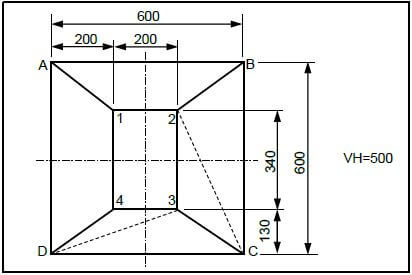
FIGURE 11.3
Calculate the following true lengths:
11.3.1 A–1 (4)
11.3.2 C–2 (4)
11.4 Identify the hoppers shown in FIGURES 11.4.1 and 11.4.2 below.
11.4.1 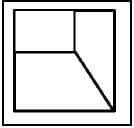
FIGURE 11.4.1 (2)
11.4.2 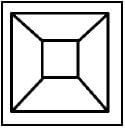
FIGURE 11.4.2 (2)
[21]
TOTAL: 200
FORMULA SHEET FOR MECHANICAL TECHNOLOGY: