ECONOMICS PAPER 2 GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2021
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupINSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- Answer FOUR questions as follows in the ANSWER BOOK:
SECTION A: COMPULSORY
SECTION B: Answer TWO of the three questions.
SECTION C: Answer ONE of the two questions. - Answer only the required number of questions. Answers in excess of the required number will NOT be marked.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Write the question number above each answer.
- Read the questions carefully.
- Start EACH question on a NEW page.
- Leave 2–3 lines between subsections of questions.
- Answer the questions in full sentences and ensure that the format, content and context of your responses comply with the cognitive requirements of the questions.
- Use only black or blue ink.
- You may use a non-programmable pocket calculator.
- Write neatly and legibly.
SECTION A (COMPULSORY)
QUESTION 1 30 MARKS – 20 MINUTES
1.1 Various options are provided as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A–D) next to the question numbers (1.1.1 to 1.1.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.9 D.
1.1.1 The value of skills owned by the entrepreneur and used in the production process is called ... cost.
- explicit
- marginal
- implicit
- average
1.1.2 A situation where it is impossible to increase the welfare of one individual without making another worse off is called … efficiency.
- allocative
- technical
- Pareto
- market
1.1.3 The demand curve for an oligopolist is …
- positive sloping.
- kinked.
- horizontal.
- upward sloping.
1.1.4 Income enjoyed by producers of goods is known as … benefit.
- private
- external
- social
- public
1.1.5 An inflation rate that excludes items with highly volatile prices is called … inflation.
- administered
- headline
- inclusive
- core
1.1.6 Religious events are included under … tourism.
- paleo
- cultural
- local
- eco-
1.1.7 The process of converting waste material into economic goods is known as…
- recycling.
- re-using.
- restoring.
- inventing
1.1.8 Public sector intervention that allows businesses to sell their licences to other businesses is called …
- granting property rights.
- environmental subsidies.
- environmental taxes.
- marketable permits. (8 x 2) (16)
1.2 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches the item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A–I) next to the question number (1.2.1 to 1.2.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.2.9 J.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
| 1.2.1 Long run 1.2.2 Marginal revenue 1.2.3 Duopoly 1.2.4 Perfectly elastic demand curve 1.2.5 Consumer price index 1.2.6 Transit tourists 1.2.7 Kyoto Protocol 1.2.8 Biodegradable |
|
(8 x 1)(8)
1.3 Give ONE term for each of the following descriptions. Write only the term next to the question numbers (1.3.1 to 1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK. Abbreviations,acronyms and examples will NOT be accepted.
1.3.1 A situation where the market supplies goods that match the needs of the consumers
1.3.2 A market structure that consists of many businesses selling differentiated products
1.3.3 Goods that are seen to be socially harmful
1.3.4 Prices of goods and services that continuously decrease over a long period of time
1.3.5 Monetary policy approach used by the SARB to keep price changes within 3–6%
1.3.6 The variety of plant and animal life within an ecosystem (6 x 1) (6)
TOTAL SECTION A: 30
SECTION B
Answer any TWO of the three questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
QUESTION 2: MICROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
2.1 Answer the following questions.
2.1.1 State any TWO objectives of the competition policy. (2 x 1) (2)
2.1.2 Why is a monopolistic competitive market regarded as a hybrid market structure? (1 x 2) (2)
2.2 Study the cartoon below and answer the questions that follow.
2.2.1 In the above cartoon, identify a barrier to entry used by a monopolistic competitor to increase its market share. (1)
2.2.2 Name the type of monopoly that is characterised by the use of patents. (1)
2.2.3 Briefly describe the term economies of scale. (2)
2.2.4 How would barriers to entry influence profits in the market? (2)
2.2.5 Why is it a challenge for monopolies to charge excessively high prices? (2 x 2) (4)
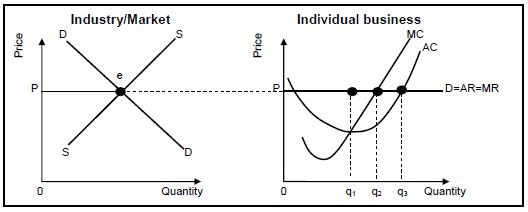
2.3 Study the graphs below and answer the questions that follow.
2.3.1 Identify the quantity where the individual business will maximise profit. (1)
2.3.2 Name the market structure illustrated above. (1)
2.3.3 Briefly describe the term economic profit. (2)
2.3.4 Why does the individual business take the price determined by the industry? (2)
2.3.5 How would the entry of new firms in the industry impact the individual business in the long run? (2 x 2) (4)
2.4 With the aid of a graph, explain the relationship between marginal revenue and the demand curve (AR) of a monopoly. (8)
2.5 Analyse measures that may be used by the government to promote competition in the economy. (8)
[40]
QUESTION 3: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES 40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
3.1 Answer the following questions.
3.1.1 State any TWO criteria for an activity to be regarded as tourism. (2 x 1) (2)
3.1.2 Why is it important to focus on preservation worldwide? (1 x 2) (2)
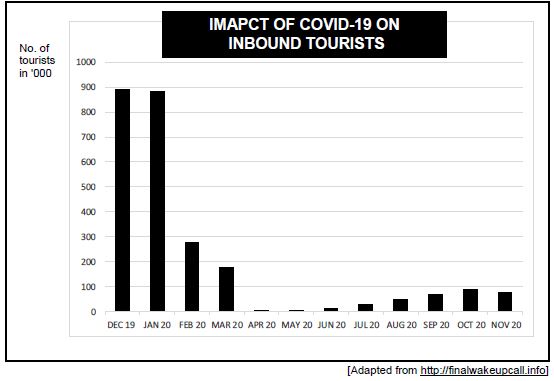
3.2 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.
[Adapted from http://finalwakeupcall.info]
3.2.1 Name the factor that caused a sharp decrease in tourism sales between January and April 2020. (1)
3.2.2 Give ONE reason why the government imposes tax on tourist activities. (1)
3.2.3 Briefly describe the term inbound tourist. (2)
3.2.4 E x plain the role played by tourism in infrastructure development in South Africa. (2)
3.2.5 How does a decline in tourism activities impact on rural communities? (2 x 2) (4)
3.3 Study the cartoon below and answer the questions that follow.
3.3.1 Name the type of pollution demonstrated in the above cartoon. (1)
3.3.2 Give the international measure that deals with the control of hazardous waste. (1)
3.3.3 Briefly describe the term conservation.(2)
3.3.4 Explain the effect of soil erosion on food security. (2)
3.3.5 How does human activity negatively affect environmental sustainability? (2 x 2) (4)
3.4 Briefly discuss the reasons why markets fail to ensure environmental sustainability. (4 x 2) (8)
3.5 Analyse marketing strategies used to promote tourism in South Africa. (8)
[40]
QUESTION 4: MICROECONOMICS AND CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES
40 MARKS – 30 MINUTES
4.1 Answer the following questions.
4.1.1 Name any TWO examples of fixed costs. (2 x 1) (2)
4.1.2 How does the Paris Agreement intend to reduce the impact of climate change? (1 x 2) (2)
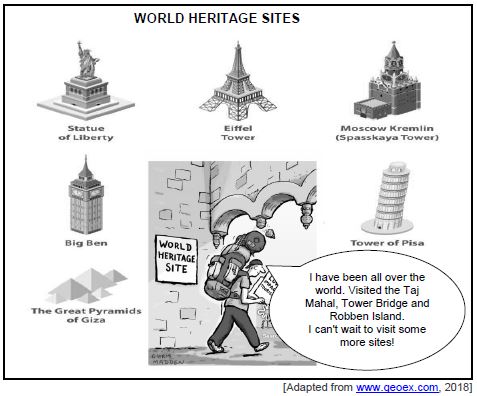
4.2 Study the information below and answer the questions that follow.
4.2.1 Identify ONE World Heritage Site in South Africa in the information above. (1)
4.2.2 Name ONE benefit of tourism for households. (1)
4.2.3 Briefly describe the term indigenous knowledge systems. (2)
4.2.4 How can the depreciation of the rand affect inbound tourism? (2)
4.2.5 Why do tourists visit South Africa as a tourist destination? (2 x 2) (4)
4.3 Study the extract below and answer the questions that follow.
OLIGOPOLY – COLLUSION IN THE BANKING SECTOR Three South African banks have been implicated in widespread collusion relating to price fixing of the rand. The investigation looked at cases of price fixing and market allocation in the trading of foreign exchange involving the rand. It has been alleged that the foreign exchange traders have been buying and selling US dollars in exchange for the rand at fixed prices. The competition policy has made provision for the establishment of the Competition Commission, Competition Tribunal and Competition Appeal Court to deal with issues of collusion in different sectors of the economy. [Adapted from BusinessTech] |
4.3.1 Identify the institution that is responsible for investigating anti-competitive behaviour. (1)
4.3.2 Name the type of collusion explained in the extract above. (1)
4.3.3 Briefly describe the term oligopoly. (2)
4.3.4 How does the existence of monopolies influence the supply of goods and services? (2)
4.3.5 What is the impact of price fixing on the market? (2 x 2) (4)
4.4 With the aid of a graph, explain shutdown-point in a perfect market. (2 x 4) (8)
4.5 Analyse the impact of an increase in the population on the environment. (8)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION B: 80
SECTION C
Answer any ONE of the two questions in this section in the ANSWER BOOK.
Your answer will be assessed as follows:
| STRUCTURE OF ESSAY | MARK ALLOCATION |
| Introduction The introduction is a lower-order response. A good starting point would be to define the main concept related to the question topic. Do NOT include any part of the question in the introduction. Do NOT repeat any part of the introduction in the body. Avoid mentioning in the introduction what you are going to discuss in the body. | Max. 2 |
| Body Main part: Discuss in detail/In-depth discussion/Examine/Critically discuss/Analyse/Compare/Evaluate/Distinguish/Differentiate/Explain/Draw a graph and explain/Use the graph given and explain/Complete the given graph/Assess/Debate A maximum of 8 marks may be allocated for headings/examples. Additional part: Critically discuss/Evaluate/Critically evaluate/Debate/ Deduce/Compare/Distinguish/Interpret/How?/Suggest A maximum of 2 marks may be allocated for mere listing of facts. |
Max. 10 |
| Conclusion Any higher-order conclusion should include: A brief summary of what has been discussed without repeating facts already mentioned Any opinion or valued judgement on the facts discussed Additional support information to strengthen the discussion/analysis A contradictory viewpoint with motivation, if required Recommendations | |
| TOTAL | 40 |
QUESTION 5: MICROECONOMICS 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
- Discuss, in detail, without drawing graphs, state intervention as a consequence of market failures. (26 marks)
- How can market inefficiency be reduced by global markets (globalisation)? (10 marks) [40]
QUESTION 6: CONTEMPORARY ECONOMIC ISSUES 40 MARKS – 40 MINUTES
- Discuss the consequences of inflation. (26 marks)
- How does foreign direct investment influence inflation in the economy? (10 marks)
[40]
TOTAL SECTION C: 40
GRAND TOTAL: 150