CIVIL TECHNOLOGY(WOODWORKING) GRADE 12 QUESTIONS - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2021
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupREQUIREMENTS:
- Drawing instruments
- A non-programmable calculator
- ANSWER BOOK
INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION
- This question paper consists of SIX questions.
- Answer ALL the questions.
- Read all questions carefully.
- Answer each question as a whole. Do NOT separate subsections of questions.
- Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this question paper.
- Start the answer to EACH question on a NEW page.
- Do NOT write in the margins of the ANSWER BOOK.
- You may use sketches to illustrate your answers.
- Write ALL calculations and answers in the ANSWER BOOK or on the attached ANSWER SHEETS.
- Use the mark allocation as a guide to the length of your answers.
- Make drawings and sketches in pencil, fully dimensioned and neatly finished off with descriptive titles and notes to conform to the SANS/SABS Code of Practice for Building Drawings.
- For the purpose of this question paper, the size of a brick should be taken as 220 mm x 110 mm x 75 mm
- Use your own discretion where dimensions and/or details have been omitted.
- Answer QUESTIONS 2, 3.2.1, 3.2.2, 3.3, 5.4, 6.2.2, 6.5 and 6.6 on the attached ANSWER SHEETS using drawing instruments, where necessary.
- Write your CENTRE NUMBER and EXAMINATION NUMBER on every ANSWER SHEET and hand them in with your ANSWER BOOK, whether you have used them or not.
- Drawings in the question paper are NOT to scale due to electronic transfer.
- Google Images was used as the source of all photographs and pictures.
- Write neatly and legibly
QUESTION 1: OHSA, SAFETY, MATERIALS, TOOLS, EQUIPMENT AND JOINING (GENERIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
1.1 Give ONE word/term for each of the following descriptions by choosing a word/term from the list below. Write down only the word/term next to the question numbers (1.1.1. to 1.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 1.1.6 casement.
1.1.1 To cover steel or iron with a layer of zinc (1)
1.1.2 Available in a water and oil base (1)
1.1.3 Improves mechanical and engineering properties of metals (1)
1.1.4 Process of keeping fresh concrete moist (1)
1.1.5 Applying as a finish to materials to resist extreme temperatures
1.2 FIGURE 1.2 below shows scaffolding that is used on a construction site to (1) reach the upper parts of a building.
1.2.1 Describe TWO aspects the scaffolding must adhere to before it is used. (2)
1.2.2 Name the omitted part in FIGURE 1.2 that should be fixed to the platform of the scaffold to prevent tools from falling off. (1)
1.2.3 Explain TWO safety precautions that have to be adhered to when working on scaffolding. (2)
1.3 State TWO methods that can be used to remove waste material safely from high places.
1.4 Describe TWO regulations regarding the safe use of trestle scaffolds.
1.5 Describe ONE precautionary measure you would apply when hoisting material and equipment in a builder’s hoist.
1.6 Explain in THREE chronological steps how you will join TWO solid 4 mm metal plates with a bolt and nut after the positions of the holes have been marked on the plates.
1.7 Complete in your ANSWER BOOK the information in the table below by indicating ONE use and ONE way to care for the tool.
| NAME OF TOOL | USE | WAY TO CARE |
| Multi-detector | To locate ... | Protect the multi-detector against ... |
QUESTION 2: GRAPHICS AS MEANS OF COMMUNICATION (GENERIC)
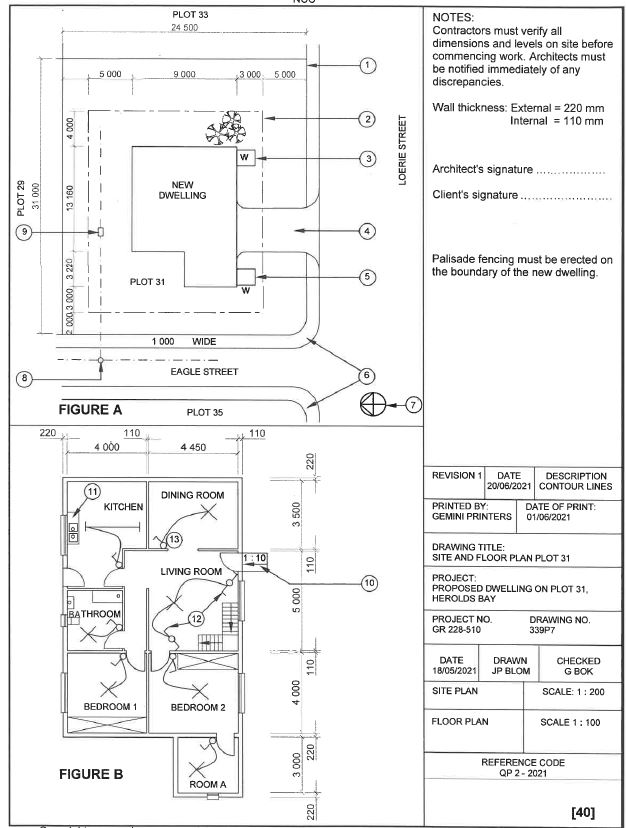
FIGURE A and B on the next page shows drawings that appear on a building plan. Analyse the drawings and complete the table on ANSWER SHEET 2.
QUESTION 3: CUPBOARDS, CASEMENTS, WALL-PANELLING AND QUANTITIES
(SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
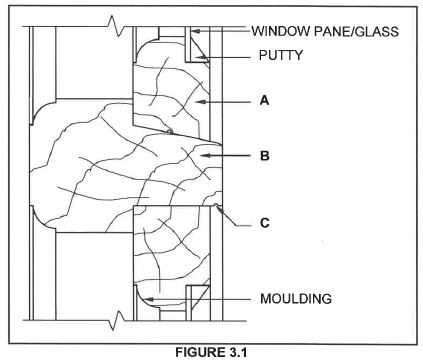
3.1 FIGURE 3.1 below shows the vertical sectional view through a part of a casement with a fanlight. Study the sketch and answer the questions that follow.
3.1.1 Identify part A.
3.1.2 Identify part B.
3.1.3 Recommend ONE other material, besides putty, that can be used to secure the glass in position.
3.1.4 Give ONE reason why the rail and stiles of the casement are moulded.
3.1.5 Explain the term fanlight.
3.1.6 Describe the function of C.
3.2 FIGURE 3.2 below shows the front view of a free-standing cupboard without doors.
3.2.1 Use ANSWER SHEET 3.2.1 and complete the cutting list for the timber needed, excluding the drawers.
Use the following specifications:
- The intermediate side is positioned in the middle of the cupboard.
- 16 mm melamine board is used to build the cupboard.
- The back is made of 16 mm melamine board.
- The depth of the cupboard is 550 mm. (7)
3.2.2 Use ANSWER SHEET 3.2.2, PROJECT and draw from the given front view a sectional view on cutting plane A-A. The depth of the base is indicated as the starting point and should be used for the depth of the cupboard.
Use the following specifications:
- 16 mm melamine board is used to build the cupboard.
- The back is made of 16 mm melamine board.
- The front rail is flush with the front of the cupboard.
- The depth of the base is equal to the depth of the cupboard.
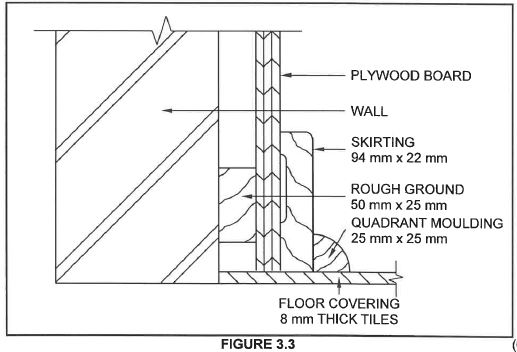
3.3 FIGURE 3.3 below shows the sectional left view at the bottom of the wall panelling.
Use ANSWER SHEET 3.3 and draw the front view of FIGURE 3.3 between the broken lines. Use scale 1 : 2 and show ALL the hidden detail.
(6)
[30]
QUESTION 4: ROOFS, CEILINGS, TOOLS, EQUIPMENT AND MATERIALS (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
4.1 Choose a description from COLUMN B that matches an item in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A—K) next to the question numbers (4.1.1.to 4.1.8) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 4.1.9 L.
| COLUMN A | COLUMN B |
| 4.1.1 Jack rafter 4.1.2 Closed eaves 4.1.3 Inverted box rib (IBR) 4.1.4 Truss hanger 4.1.5 Roof underlay 4.1.6 Purlin 4.1.7 Valley 4.1.8 Hipped roofs |
|
(8 x 1)(8)
4.2 Describe what an orbital sander and a belt sander have in common with regard to safe handling when starting and stopping the sanding process. (2)
4.3 Explain the safe handling of the mortising machine with regard to the square chisel with the drill bit (mortising attachment). (2)
4.4 What do a belt sander and a router have in common with regard to your hands when operating these machines? (2)
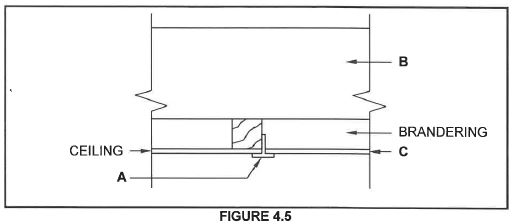
4.5 FIGURE 4.5 below shows a sectional view of a part of a trap door construction. Study the drawing and answer the questions that follow.
4.5.1 Identify part A. (1)
4.5.2 Identify part B. (1)
4.5.3 Name THREE materials that can be used to make C. (3)
4.5.4 Explain TWO reasons why aluminium is so popular for the manufacturing of A. (2)
4.6 Name TWO types of roof trusses that are constructed by using rafters only. (2)
4.7 Name the horizontal member of a king post and a collar-tie roof truss respectively. (2)
4.8 Name the beam that is placed at the top of a close-coupled roof truss. (1)
4.9 Describe the main purpose of the beam named in QUESTION 4.8. (1)
4.10 What will determine the number of queen posts to be used in a SA(Howe) roof truss? (1)
4.11 Name TWO members that can be used to change an open-eaves roof construction to a closed-eaves roof construction.(2)
4.12 The steps on how to install concrete roof tiles are given below in random order.
Analyse and rearrange the steps in the correct sequence. Write ONLY the numbers of the statements below in the CORRECT sequence in your ANSWER BOOK.
- Fix the flashing and barge boards as required.
- Lay the first tile at the bottom of the right-hand side of the roof.
- Attach the tiles to the eaves and gables of the roof.
- Lay the rest of the tiles from right to left.
- Install the ridge capping.
- Repeat the steps until all the tiles have been laid.
4.13 Name TWO types of varnish finishes. (6)
4.14 Distinguish between the equipment used to apply sanding sealer and wax. (2)
4.15 Explain what tends to happen to a wooden surface when water is spilled on it after the surface has been waxed. (2)
[40]
QUESTION 5: CENTERING, FORMWORK, SHORING AND GRAPHICS AS MEANS OF COMMUNICATION (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
5.1 Various options are given as possible answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A-D) next to the question numbers (5.1.1 to 5.1.5) in the ANSWER BOOK, e.g. 5.1.6 D.
5.1.1 Double-flying shores provide temporary support
- to a wall where cracks are being repaired.
- where openings are cut into a wall.
- to two parallel walls where one or both need(s) maintenance due to cracking.
- All the above-mentioned (1)
5.1.2 Dead shores ...
- Consist of vertical posts and beams (needles) that support openings in buildings.
- can be used to support the foundation of a building.
- do not need any braces in its construction.
- can only be erected on concrete floors. (1)
5.1.3 Steel dogs are
- used to secure the wall against the dead shore.
- driven into the folding wedges to secure them from moving.
- used to secure the sole plate to the ground.
- used to secure the joint between the prop and the needle. (1)
5.1.4 Sole plates ...
- A spread the weight transferred by the props over a wider area.
- spread the weight on top of the needle to support the wall.
- are made out of aluminium to ensure a good spread of weight.
- must be placed above the prop to ensure a proper load-bearing surface. (1)
5.1.5 Folding wedges are placed between the ...
- needle and the dead shore.
- sole plate and the dead shore.
- needle and the wall plate.
- sole plate and the natural ground level. (1)
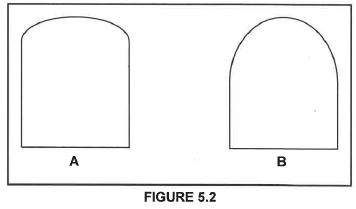
5.2 FIGURE 5.2 below shows the shapes of two arches for which centering must be made. Study the pictures and answer the questions that follow.
5.2.1 Identify the shape of the arch in A and B respectively. (2)
5.2.2 Name the lagging that must be used if the arch in B is built with specially made shaped bricks. (1)
5.2.3 Determine the rise of arch B if the span of the arch is 900 mm. (1)
5.2.4 Name ONE member that is used to secure the ribs in a centre for A. (1)
5.3 Draw in your ANSWER BOOK, in good proportion, a single-line diagram of an SA (Howe) roof truss. Label any ONE part of the truss. (1)
5.4 ANSWER SHEET 5.4 shows the incomplete sectional view for the formwork of a concrete beam with an attached floor on both sides of the prop. (9)
Use ANSWER SHEET 5.4 to complete the formwork around the beam and attached floor. Label any ONE of the parts of the formwork above the bearer. (11)
[30]
QUESTION 6: SUSPENDED FLOORS, STAIRCASES, IRONMONGERY, DOORS AND JOINING (SPECIFIC)
Start this question on a NEW page.
6.1 QUESTIONS 6.1.1 to 6.1.4 below describe some of the properties or advantages of different locks.
Name the lock that:
6.1.1 Has the advantage of automatically locking doors when it closes, making them efficient in securing external doors
6.1.2 Is mortised into one of the door stiles, while the back plate is screwed onto the door jamb
6.1.3 Is used as a temporary lock for doors, gates and sheds
6.1.4 Is screwed onto the internal surfaces of doors and drawers of cupboards
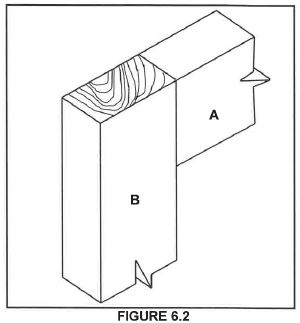
6.2 FIGURE 6.2 below shows the incomplete assembled view of an open haunched mortice and tenon joint. Study the picture and answer the questions that follow.
6.2.1 Name the TWO adjoining parts in the construction of a table where this joint will be used. (2)
6.2.2 Use ANSWER SHEET 6.2.2 and draw, in good proportion an ISOMETRIC view of the joint on part A. (8)
6.3 Explain, by means of a two-dimensional freehand sketch in your ANSWER BOOK, how you would fix the floor joists for an upper-level suspended timber floor, if the joists cannot be built into the wall. (3)
6.4 Explain, by means of two-dimensional freehand sketches, the difference between a straight flight of stairs with a landing and a stairwell with a half landing.
65 ANSWER SHEET (5)
6.5 shows an incomplete sectional view of a suspended timber floor with tongue and groove floor boards.
Draw a complete sectional view on the ANSWER SHEET. The following must be drawn:
- Closure of opening between wall and floor boards
- Members to support the floorboards
- One-brick pier with foundation
- Prevention of termites and moisture (10)
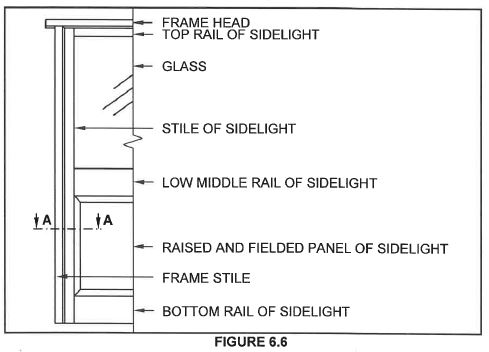
6.6 FIGURE 6.6 below shows a part of the front elevation of an entrance door with a fixed sidelight fitted in a door frame.
Use ANSWER SHEET 6.6 and draw, in a good proportion, a horizontal sectional view on section line A-A. (8)
[40]
TOTAL: 200