AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2021
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupAGRICULTURAL SCIENCES PAPER 2
GRADE 12
NSC EXAMINATIONS
NOVEMBER 2021
MEMORANDUM
SECTION A
QUESTION 1
1.1
1.1.1 D
1.1.2 A
1.1.3 C
1.1.4 B
1.1.5 D
1.1.6 B
1.1.7 A
1.1.8 C
1.1.9 C
1.1.10 B
(10 x 2) (20)
1.2
1.2.1 E
1.2.2 H
1.2.3 D
1.2.4 A
1.2.5 B
(5 x 2) (10)
1.3
1.3.1 Green marketing
1.3.2 Capital
1.3.3 Pedigree
1.3.4 Species crossing
1.3.5 Breeding value
(5 x 2) (10)
1.4
1.4.1 Farm gate
1.4.2 Short term
1.4.3 Lipofection
1.4.4 Co-dominance
1.4.5 Polygenes
(5 x 1) (5)
TOTAL SECTION A: 45
SECTION B
QUESTION 2: AGRICULTURAL MANAGEMENT AND MARKETING
2.1 Marketing functions
2.1.1 The marketing functions
A - Transportation
D - Processing/value adding
2.1.2 TWO guidelines for packaging
- Product identification
- Recyclability/biodegradability
- Containment
- Protection
- Easy handling/convenience
- Health risks
- Improving shelf life of the product
- Must be appropriate to target market (Any 2) (2)
2.1.3 THREE factors hampering the marketing of agricultural products
- Poor infrastructure
- Lack of capital
- Perishability of agricultural products
- Risks/accidents/theft/spoilage
- Ineffective control of production
- Seasonal fluctuations in production
- Wide distribution of the product and distance to the market
- Low value in relation to volume
- Standardization of products
- High marketing/intermediaries/transport costs
- Legislation/strict marketing laws/export regulations (Any 3) (3)
2.2 Marketing type
2.2.1 The type of marketing system
Co-operative marketing (1)
2.2.2 TWO principles of co-operative marketing
- Voluntary and open membership
- Democratic member control
- Co-operation among members
- Members provided with education, training and information
- Autonomy and independence
- Each member has a single vote
- Members contribute money equally
- Members are paid dividends
- Products are standardized
- Take care/concern for the community
- Risk is shared by all members
- Only members may deliver products (Any 2) (2)
2.2.3 Explanation of the benefits of co-operative marketing
- Members of the co-operative save a lot of money by marketing as a group through a pool system OR
Members buy in bulk at cheaper prices (Any 1)(2) - The co-operative negotiates better prices on behalf of its members (2)
2.3 Supply and demand of oranges at different prices
2.3.1 Line graph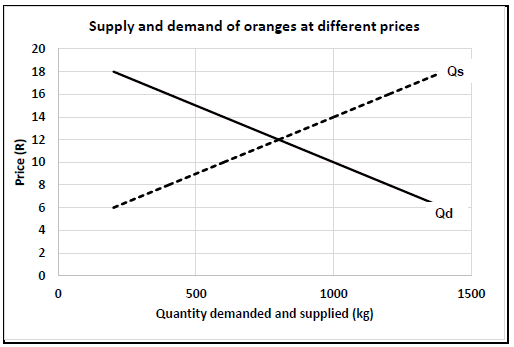
CRITERIA/RUBRIC/MARKING GUIDELINES
- Correct heading
- X-axis: Correctly calibrated and labelled (Quantity)
- Y-axis: Correctly calibrated and labelled (Price)
- Correct units (R and kg)
- Line graph
- Accuracy (6)
2.3.2 Identification of the price
- Highest shortage - R6
- Lowest surplus - R14
2.3.3 The equilibrium price
R12 (1)
2.4 Elasticity of demand and supply
2.4.1 Identification of
- Price elasticity of supply - Graph B
- Price inelasticity of demand - Graph A
2.4.2 Reason for the answer in
- A small change in price resulted in a huge change in the quantity supplied
- The huge change in price resulted in very little change in the quantity demanded
2.4.3 TWO factors that affect demand
- Availability of substitute products
- Price of complimentary and competing products
- Research
- Fashion
- Quality of the product
- Consumer preferences/tastes
- Festive seasons
- Usefulness of the product
- Number of consumers
- Legislation
- Advertising of the product
- Price of the product/price expectations
- Income/buying power/socio-economic circumstances of the consumers (Any 2) (2)
2.5 Scenario
2.5.1 Justification of the statement
The young farmer took an initiative to organise a farming business from the gift with its risks to make profit (1)
2.5.2 TWO entrepreneurial success factors
- Initiative/creative/innovative
- Confidence
- Perseverance
- Market driven
- Communication/interpersonal skills/relations
- Vision
- Hard-working/commitment
- Courage/motivation/positive attitude
- Risk taking
- Achievement
- Knowledge/skills (Any 2) (2)
2.5.3 Identification of
- TWO strengths for the farming business
- Possesses a lot of success factors
- Owns 1 790 hectares of land
- Achieved 98% calving rate
- Permanent workers
- The farmer is young and energetic (Any 2)
- ONE threat to the business
Farming in dry arid region (2)
[35]
QUESTION 3: PRODUCTION FACTORS
3.1 Land
3.1.1 Deduction of the
- Economic characteristic of land
Availability of land is limited - Function of land as a production factor
- Land provides space
- Land provides food (Any 1)
3.1.2 Reason
Arable land was 70 hectares in 1970 and decreased over years to only 10 hectares in 2020 (1)
3.1.3 TWO functions of land
- Land is a source of raw materials
- Land is a source of minerals
- Land is an asset/serves as collateral (Any 2) (2)
3.1.4 TWO methods to improve land productivity
- Improve soil fertility
- Improve water management/water supply
- Restoring land potential
- Changing cropping practices and farming systems
- Farming land more efficiently/precision farming
- Consolidating small uneconomical land units (Any 2) (2)
3.2 Labour
3.2.1 TWO main types of farm labourers
- Permanent/full-time
- Temporary/part-time (2)
3.2.2 Identification of tasks
- Casual labourers - Fencing
- Seasonal labourers - Harvesting
3.2.3 Labour problem
- Lack of skills/training
- Scarcity of labour
- Covid-19 (Any 1) (1)
3.2.4 Method to address lack of skills
- Training labourers/employment of skilled labour
- Employment of additional workers/improving working conditions
- Vaccination/enforcing all Covid-19 protocols (Any 1) (1)
3.3 Conditions of employment in FARM A and FARM B
3.3.1 Unfair conditions of employment
FARM A - Labourer (1)
3.3.2 TWO reasons to support the answer
- Low rate per day
- Longer working hours
- Fewer leave days/year
- Lower overtime payment in comparison with labourer B
(Any 2) (2)
3.3.3 Labour Legislation Act that the employer has violated
Basic Conditions of Employment Act/BCEA (Act No.75 of 1997) (1)
3.4 Value of capital items
3.4.1 The capital item
- Fixed capital - Capital item B
- Movable capital - Capital item A
3.4.2 Example of each capital
- Fixed capital - Land/farm/building/borehole/fence
- Movable capital - Tractor/truck/machinery/livestock
3.4.3 The problem of capital reflected by capital item A
Depreciation (1)
3.5 Financial records
3.5.1 Identification of the financial record
Cash flow statement (1)
3.5.2 Reason
It reflects:
- An opening balance
- A closing balance
- Receipts/income
- Payments/expenditure (Any 1) (1)
3.5.3 The total amount available to run the enterprise at the beginning of the second quarter
R 37 972 (1)
3.5.4 Calculation of the total costs over the first quarter
Total costs = Costs in Jan, Feb and March
= 9 450 + 8 400 + 4 300
= R 22 150 (2)
3.6 Management skills
- Problem solving/interpersonal skill
- Financial management skill
- Organisation and coordination skill
3.7 Risk factors
3.7.1 Risk management strategy
- Risk sharing
- Diversification
3.7.2 THREE forces beyond the direct control of the farmer
- Economic forces
- Political forces
- Ethical forces
- Legal forces
- Socio-cultural forces
- Competitive forces
- Technological forces
- Environmental forces (Any 3) (3)
[35]
QUESTION 4: BASIC AGRICULTURAL GENETICS
4.1 Mendelian study
4.1.1 The term
Genetics (1)
4.1.2 TWO Mendelian laws
- The law of dominance
- The law of segregation
- The law of independent assortment/recombination (Any 2) (2)
4.2 Feather colour in chickens
4.2.1 - White
4.2.2 - Black
4.2.3 - White
4.3. Parents and offspring where (Bb) represents horns and (bb) no horns
4.3.1 The phenotype visible in the offspring
Horned/polled (no horns) (1)
4.3.2 Calculation (in %) of the homozygous recessive phenotype
1 x 100
4
= 25% (2)
4.4 Punnet square method
4.4.1 Punnet square determining the ratio of the genotypes in the first crossing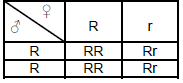
MARKING CRITERIA
- Correct male gametes
- Correct female gametes
- Correct offspring
- Punnet-square populated with gametes and offspring
- Genotypic ratio = 2 RR : 2 Rr OR 1 RR : 1 Rr (5)
4.4.2 The genotype of the unknown boar used in the F2 generation rr (1)
4.5 Breeding programme with green pepper cultivars
4.5.1 The genetic term for the following
- Heterosis/hybrid vigour
- Progeny selection
- Biometrics
4.5.2 Explanation why the two cultivars were used
Superior parents with the desired characteristics can produce the offspring required/with the desired/superior characteristics (2)
4.6 The values of heredity for sheep
4.6.1 Characteristic with the lowest improvement
Lean meat (1)
4.6.2 Characteristic with the most effective improvement
- Post-weaning gain
- Birth weight
- Fleece weight
4.6.3 ONE other factor to improve the post-weaning gain
Environmental/external factor (1)
4.7 Breeding systems and technologies
4.7.1 Identification of the breeding system in
- Upgrading
- Inbreeding
- Crossbreeding
4.7.2 TWO disadvantages of inbreeding
- Loss of genetic variation/diversity
- Leads to inbreeding depression/reduced production/fertility
- Increased expression of lethal genes
- Expensive system
- Reduced vitality
- Homozygosity of unwanted genes/deformities (Any 2) (2)
4.8 Technique used to genetically modify organisms
4.8.1 The technique used
Micro-injection (1)
4.8.2 Differentiation between
Conventional hybrid
DNA not altered/crossing of two lines/cultivars
GMO
Altered DNA/genes from another organism are inserted into a cell
4.8.3 TWO potential risks associated with genetically modified plants
- Health risks/allergies
- Environmental risks
- Economic/financial risks (Any 2) (2)
[35]
TOTAL SECTION B: 105
GRAND TOTAL:150