MATHEMATICS PAPER 2 GRADE 12 MEMORANDUM - NSC PAST PAPERS AND MEMOS NOVEMBER 2021
Share via Whatsapp Join our WhatsApp Group Join our Telegram GroupMATHEMATICS PAPER 2
GRADE 12
MEMORANDUM
NOVEMBER 2021
QUESTION 1
| 10 | 11 | 13 | 14 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 18 | 18 |
| 19 | 19 | 20 | 2 | 35 | 35 | 37 | 40 | 41 |
1.1.1
x =396
18
x = 22
(2)
1.1.2
σ = 10,1707 ≈ 10,17 (1)
1.1.3
x + σ = 32,17
= 5 days (2)
1.2
22 x 18 = 396 ordered
20 x 18 = 360 sold/verkoop
Total not sold: 36
OR
22–20 = 2
2x18 = 36
(2)
1.3.1
Option B
Any one of the following reasons:
- Median= 18,5
- Q1 = 14
- IQR = 21
- Mean > Median, therefore the data is skewed to the right
(2)
1.3.2 Data is positively skewed/skewed to the right
[10]
QUESTION 2
| Price of milk in rands per 5-litre container (x) | 26 | 32 | 36 | 28 | 40 | 33 | 29 | 34 | 27 | 30 |
| Number of 5-litre containers of milk sold (y) | 48 | 30 | 26 | 44 | 23 | 32 | 39 | 29 | 42 | 33 |
SCATTER PLOT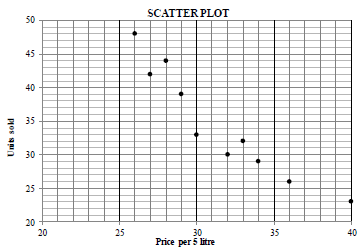
1 mark: 3 to 5 points plotted correctly
2 marks: 6 to 9 points plotted correctly
3 marks: all points plotted correctly
(3)
2.2
a = 90,478... ≈ 90,48
b = -1,773... ≈ -1,77
yˆ = 90,48 - 1,77x
(3)
2.3 y = 23,069… ≈23,07 units(calculator)
OR
y = 90,48 - 1,77(38)
y = 23,22 units
(2)
2.4 r = – 0,94
The value of r indicates a strong relationship between the cost per 5 litre and the number of units sold therefore there is a good chance of the prediction being accurate.(2)
[10]
QUESTION 3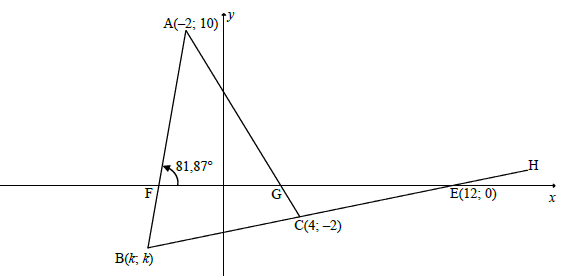
3.1.1
mBE = mCE = 0 -( - 2)
12 -4
= ¼
OR
mBE = mCE =-2 - 0
4 - 12
= ¼ (2)
3.1.2
mAB = tan81,87º
mAB = 7 (2)
3.2
y = mx + c
0 = ¼(12) + c
c = -3
y = ¼x - 3
or
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - 0 = ¼(x - 12)
y = ¼x - 3
OR
y = mx + c
-2 = ¼(4) + c
c = -3
y = ¼x - 3
or
y - y1 = m(x - x1)
y - (-2) = ¼(x - 4)
y = ¼x - 3
(2)
3.3.1
y = ¼x - 3
k = ¼k - 3
¾k = -3
k = -4
B = (-4; -4)
OR
mBE = ¼
0 - k = ¼
12 - k
-4k = 12 - k
k = -4
B = (-4; -4)
OR
mBE = ¼
k = ¼
k - 12
4k = k - 12
k = -4
OR
mAB = tan81,87º
mAB = 7
mAB = 10 - k
-2 - k
7(-2 - k) = 10 - k
-14 - 7k = 10 - k
-6k = 24
k = -4
B (-4; -4)
OR
EB: y = ¼x - 3 and AB: y = 7x + 24
¼x - 3 = 7x + 24
27/4x = -27
x = k = -4
B = (-4;-4)
(2)
3.3.2
In ΔAFG:
mAC = 10 - (-2) = -2
-2 -4
tanθ = mAC = -2
θ = 180 - 63.43...º
θ = 116,57º
Aˆ =116,57º - 81.87º[ext∠ of Δ]
Aˆ = 34.70º
OR
In ΔABC:
a = BC = 2√17; b = AC 6√5; c = AB 10√2
a2 = b2 + c2 -2bCosA
(2√17)2 = (6√5)2+(10√2)2- 2(6√5)(10√2).cosA
cos A = (6√5)2+(10√2)2-(2√17)2
2(6√5)(10√2)
= 0.8222...
A = 34.7º
(4)
3.3.3
M[12 + (-2) ; 10 + (0)]
2 2
Diagonals intersect at the point (5 ; 5)
3.4.1
BE = ET
4√17 = √(12 - p)2 + (0 - p)2
(4√17)2 = (√(12 - p)2 + (0 - p)2)
272 = 144 - 24p + p2 + p2
p2 = - 12p - 64 = 0
(p - 16)(p + 4) = 0
p = 16 or p = – 4 (n.a.)
∴T(16; 16)
(5)
3.4.2
- (x - 12)2 + y2 = (4√17)2 = 272(2)
- mradius = ¼
mtangent = -4
y = -4x + c
- 4 = -4(-4) + c
c = – 20
y = – 4x – 20
OR
y - y1 = -4(x - x1)
y - (-4) = -4(x - (-4))
y = -4x - 20 (3)
[24]
QUESTION 4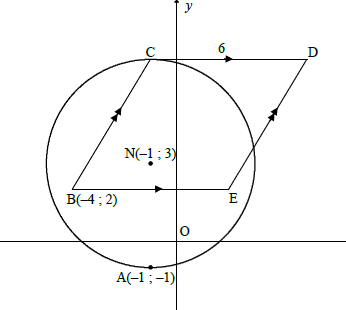
4.1 Radius = 4 units (1)
4.2.1
CD ⊥ CN
∴C( -1 ; 7) (2)
4.2.2
CD = 6 units
∴D(5 ; 7)
(2)
4.2.3
⊥h = 5units
DC = 6 units
Area ΔBCD = ½(6)(5)
=15units2
OR
⊥h = 5units
DC = 6 units
Area ΔBCD = ½[Area of ||m]
=½(5)(6)
=15units2
(3)
OR
Let andgle of inclionation of BC = a
tan a = 5/3
a = 59,036..º
BCD = 180º - a
BCD = 180º - 59,036º
BCD = 120,96º
Area ΔBCD = ½(√34)(6)sin120,96º
= 15 units2
(3)
4.3.1
M(3 ; –1) [reflection of N(–1 ; 3) about the line y = x]
MN = √(3 - (-1))2 + (-1 - 3)2
MN = √32 = 4√2 = 5,66units
(3)
4.3.2
M(3 ; –1)
mMN = 3 - (-1) = -1
-1 - 3
MN: -1 = -(3) + c
c = 2
y = -x + 2
or
y - 3 = -1(x + 1)
y - 3 = -x - 1
y = -x + 2
x = -x + 2
2x = 2
x = 1
y = 1
midpoint (1; 1)
OR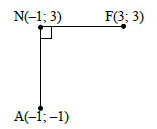
N(-1 ; 3)
yF = yN = 3
Reflected about y = x
F(3 ; 3)
midpoint (-1 + 3 ; -1 + 3) = (1 ; 1)
2 2
OR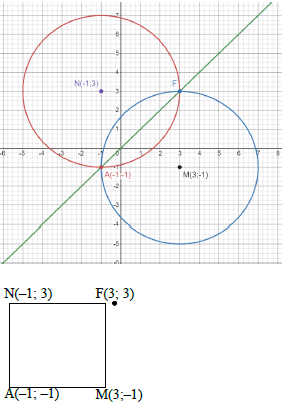
NAMF is a square (NA=NF=AM=MF and NA ⊥ AM)
Midpoint NM= (1 ; 1)
= Midpoint of AF
(4)
[15]
QUESTION 5
5.1
sin140.sin(360º - x)
cos 50.tan(-x)
= sin40º(- sin x)
sin40º(- tan x)
- sin x
- sin x
cos x
= cos x
(6)
5.2
LHS = -2sin2x + cos x + 1 RHS = 2cos x - 1
1 - cos(540º - x)
LHS = 2(1 - cos2x) + cos x + 1
1 - (- cos )
LHS = -2 + 2cos2x + cos x - 1
1 + cos x
LHS = (2cosx - 1)(cos x + 1)
1 + cos x
LHS = 2cos x - 1
LHS = RHS
(4)
5.3.1
sin 36º = √1 - p2
tan36º = √1 - p2
p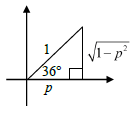
OR
cos236º = 1 sin236º
cos36º = √1 - (1 - p2)
= p
tan 36º = sin36º
cos 36º
= √1 - p2
p
(3)
5.3.2
cos108º
= -cos72º
= –cos (2×36°)
= -(2cos236º - 1)
= -2p2 + 1
OR
cos108º
= -cos72º
= –cos (2×36°)
= (1 - 2sin236º)
= 1 + 2(√1 - p2)2
= 1 + 2(1 - p2)
= -2p2 + 1
OR
cos108º
= -cos72º
= –cos (2×36°)
= -(cos236ºsin236º)
= - (p2 - (√1 - p2)2)
= - (p2 -(1 - p2))
= -2p2 + 1
OR
cos108º
= cos(2 x 54º)
= 2cos2 54º - 1
= 2(1 - p2) - 1
= 1 - 2p2
OR
cos108º = cos(72º + 36º)
= cos72º cos36º - sin 72º sin 36º
= (2cos236º 1) cos36º -(2sin 36º cos36º) sin 36º
= 2cos336º - cos36º - 2cos36ºsin236º
= 2p3 - p - 2p(√1 - p2)2
= 2p3 - p - 2p + 2p3
= 4p3 - 3p
(4)
[17]
QUESTION 6
6.1.1
cos(a + β)
= cos(a - (- β))
= cos a cos(- β) + sin a sin(- β)
= cos a cosβ +sin a(-sinβ)
= cos a cosβ - sin a sinβ
(3)
6.1.2
2 cos6 cos 4 - cos10x + 2sin2x
= 2 cos 6x cos 4x - cos(6x + 4x) + 2sin2x
= 2 cos 6x cos 4x - (cos 6x cos 4x - sin 6x sin 4x) + 2sin2x
= cos 6x cos 4x + sin 6x sin 4x + 2sin2x
= cos 2 + 2sin2x
= 1 - 2sin2x + 2sin2x
= 1
(5)
6.2
tan x = 2sin 2x
sin x = 2(2sin x cos x)
cos x
sin x = 4sin x cos2x
4sin x cos2x - sin x = 0
sin x (4cos2x - 1) = 0
sin x = 0
or
cos2x = ¼
cos x = - ½
x = 180° + k.360°; k∈Z
or
x = 120° + k.360°; k∈Z
x = 240° + k.360°; k∈Z
OR
tan x = 2sin 2x
sin x = 2(2sin x cos x)
cos x
sin x = 4sin x cos2x
4sin x cos2x - sin x = 0
4sin x(1 - sin2x) - sin x = 0
3sin - 4sin3 = 0
sin x (3 - 4sin2x) = 0
sin x = 0
or
sin2x = ¾
sin x = √3/2 or sin x = -√3/2
x = 180º + k.360º, k∈Z
or
x= 120º + k.360º,k∈Z
or
x = 240º + k.360º,k∈Z (7)
[15]
QUESTION 7
7.1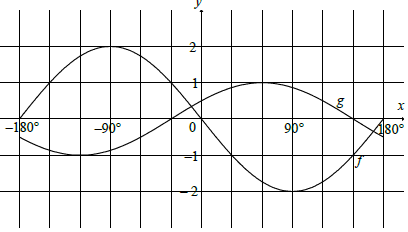
both turning points
both x intercepts (–30° & 150°)
shape (3)
7.2
Period = 120° (2)
7.3
x = -30º (1)
7.4
Range of g: y ∈ [-1;1]
Range of ½g: y ∈ [-½ ; ½]
Range of ½g + 1: y ∈ [-½ ; 3/2]
OR
Range of ½g + 1: ½ ≤ y ≤ 3/2 (2)
[8]
QUESTION 8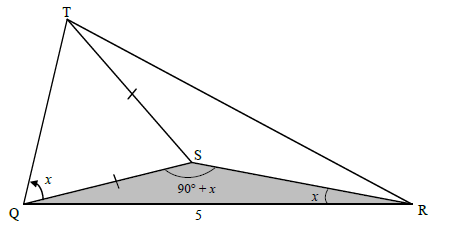
8.1
In ΔSQR:
QS = QR
sin x sin(90º + x)
QS = 5
sin x cos x
QS = 5sin x
cos x
QS = 5tan x
(3)
8.2
QT = TS
sin(180º - 2x) sin x
QT = 5tan x
sin 2x sin x
QT = 5tan x sin 2x
sin x
QT = 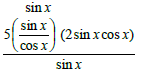
QT = 5sin x (2sin x)
sin x
QT = 10sin x (5)
OR
QT2 = QS2 TS2 - 2QS.TScosQST
QT2 = (5 tan )2 + (5tan )2 - 2(5 tan x).(5 tan x)cos(180º - 2x)
QT2 = 50 tan2 x - 50 tan2 x(cos2x)
QT2 = 50 tan2 x(1 + cos2x)
QT2 = 50 tan2 x(1 + 2cos2 x - 1)
QT2 = 50 tan2 x(2cos2x)
QT2 =100 sin2x (cos2x)
cos2x
QT2 = 100sin2x
QT2 = 10sin x
OR
TS2 =QS2 +TQ2 - 2QS.TQ.cos x
(5tan x)2 = (5tan x) + TQ2 - 2(5tan x).TQ.cos
0 = TQ - 2(5tan x).TQ.cos x
0 = TQ[TQ - 10 tan x .cos x]
TQ = 10 tan x.cos x(TQ ≠ 0)
= 10 sin x .cos
cos x
= 10sin x
(5)
8.3
Area of ΔTQR = ½.TQ.QRsinTQR
= ½(10sin 25º)(5)(sin70º)
= 9,93unit
(2)
[10]
QUESTION 9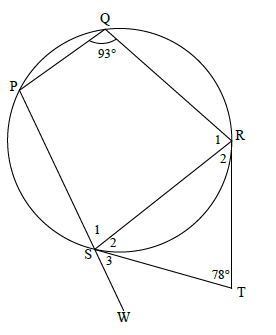
9.1
tangents from same(common) point (1)
9.2.1
Sˆ = SRT
S2 = 51º
[∠s opp equal sides]
[sum of ∠s in Δ]
(2)
9.2.2
S2 + S3 = 93º
S3 = 42º
S1 = 87º
S3 = 180º - (87º + 51º)
S3 = 42º
[∠s of cyclic quad]
[∠s on a str line]
[5]
QUESTION 10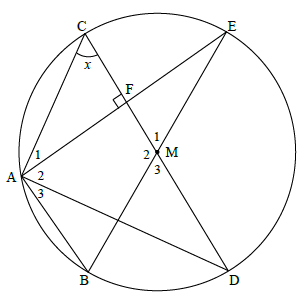
10.1
line from centre ⊥ to chord(1)
10.2
A1 = 90º[sum of ∠s in Δ]
M1 = 180º - 2x [∠ at centre=2× at circumf]
(3)
10.3
CAD = 90º
A2 = 90º - (90º - x)
A2 = C = x
AD is a tangent [converse tan-chord theorem]
OR
EMD = 2x [adj suppl ∠s]
A2 = x [∠ at centre= 2×∠ at circumf]
A2 = C = x
AD is a tangent [converse tan-chord theorem]
OR
M3 = 180º - 2x[vert. opp]
A3 = 90º - x [∠ at centre= 2×∠ at circumf= 2]
BAE = 90º [∠ in semi-circle]
A2 = C = x
AD is a tangent [converse tan-chord theorem]
OR
CD || AB [midpt. Thm]
BAE = 90º [∠ in semi-circle]
A3 = D = 90 - x [alt.∠s;CD||AB]
AD is a tangent [converse tan-chord theorem]
OR
CAD = 90º [∠ in semi circle]
AC = diameter [converse ∠ in semi circle]
AD is a tangent [converse radius ⊥ tangent]
(4)
10.4
AF = FE and BM = ME [given & radii]
FM = ½AB = 12 units [Midpt Theorem]
EM = MB = CM = 18 units [radii]
EB = 36 units [diameter = 2 radius]
AE2 = (36)2 – (24)2 [Pythagoras]
AE = 12√5 or 26,83 units
OR
AF = FE and BM = ME [given & radii]
FM = ½AB = 12units
AB = 12 units [Midpt Theorem]
EM = MB = CM = 18 units [radii]
FE2 = (18)2 – (12)2 [Pythagoras]
FE = 6√5
AE = 12 5 or 26,83 units (5)
[13]
QUESTION 11
11.1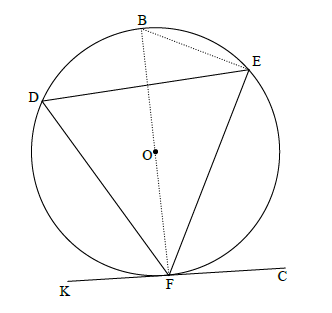
Construction: Draw diameter BF and draw BE
BFK = 90º or DFK = 90º - BFD [radius ⊥ tangent]
BEF = 90º[∠ in semi-circle]
DEF = 90º - BED
= 90° – BFD [∠s same segment]
DFK = DEF
(5)
OR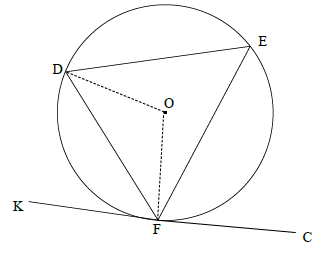
Construction: Draw radii DO and OF
OFK = 90º or DFK = 90º - OFD radius ⊥ tangent]
ODF = OFD [∠s opp = sides]
DOF = 180º - 2OFD [∠s of Δ]
DEF = 90º- OFD [∠ at centre = 2×∠ circumf]
DFK = DEF
(5)
OR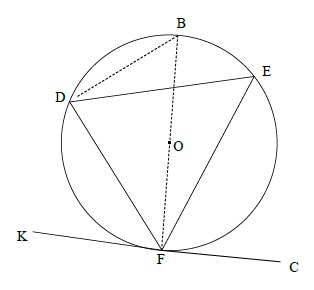
Construction: Draw diameter BF and join BD.
BFK = 90º or DFK = 90º - BFˆD [radius tangent]
FDB = 90º [∠ in half circle/semi-sirkel]
B = 90º -BFD
DFK = B
but B = E[∠s same segment]
DFK = E
(5)
11.2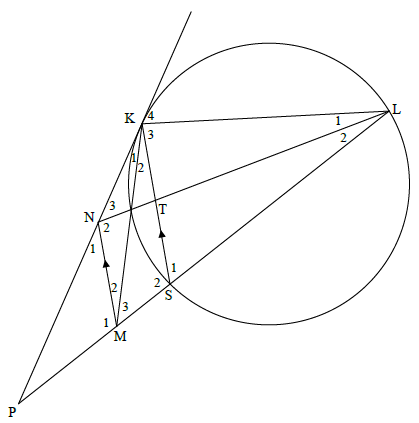
K4 = S1 [tan chord theorem]
M2 + M3 = S1 [corresp ∠s; MN || KS]
K4 = M2 + M3 = NML
(4)
K4 = M2 + M3 = NML
KLMN is a cyclic quad [ext∠ of quad = opp int ∠]
OR
N1 = K1 + K2 = NKS [corresp ∠s;MN || KS]
NKS = KLS [tan chord theorem]
N1 = KLS
KLMN is a cyclic quad [ext ∠ of quad = opp int ∠]
OR
NKL 180º - K4 [adj. suppl.]
NKL 180º - NML [proved]
KLMN is a cyclic quad [opp. s supplementary] (1)
11.2.2
In ΔLKN|||ΔKSM:
N3 = M3 [∠s in the same seg]
L1 = M2 [∠s in the same seg]
= K2 [alt ∠s; MN||KS]
NKL = MSK [∠s of Δ]
cLKN|||ΔKSM
OR
In ΔLKN|||ΔKSM:
N3 = M3 [∠s in the same seg]
NKL=M1 [ext ∠ of cyclic quad]
= S2 [corresp ∠s; KS || NM]
∠LKN|||ΔKSM [∠,∠,∠]
OR
In LKN|||ΔKSM:
N3 = M3 [∠s in the same seg]
K4 +NKL=S1 +S2 [∠s on straight line]
NKL=S2 [ K4 = S1]
∠LKN|||ΔKSM [∠,∠,∠]
(5)
11.2.3
LK/KS = KN/SM
=12/KS = 4/3
SM = 6
LT/NL = LS/ML
LT/16 = 13/19
LT = 208/19 = 10,95
[line || one side of Δ]
(4)
[23]
TOTAL: 150